

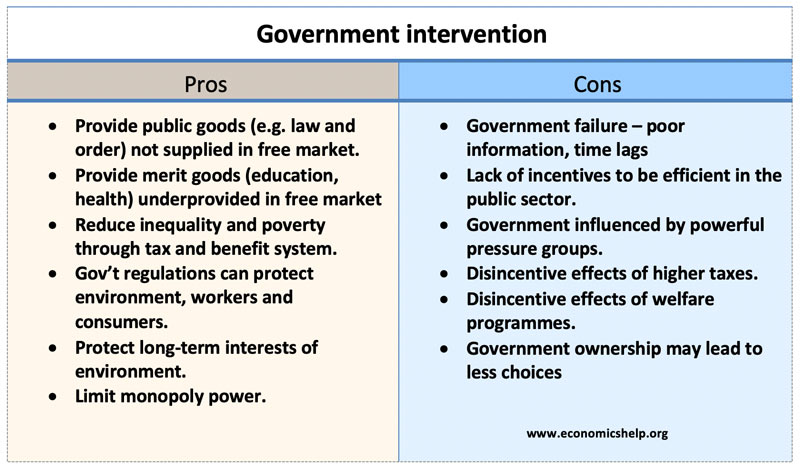
Pros and cons of government intervention
A key economic debate is the extent to which should governments intervene in the economy?
- At one extreme, free-market economists/libertarians, argue that government intervention should be limited to all but the most basic services, such as the protection of private property and the maintenance of law and order.
- At the other extreme, Marxist economists argue that the government should intervene in all areas of the economy to ensure the most efficient and equitable distribution of resources.
In between, most economists believe it is a question of balance, with the government intervening in areas where the market fails to provide a desirable outcome. Main areas of government intervention include:
- Provide public goods (e.g. national defense) from general taxation
- Provide basic health care and education standards.
- Environmental regulation and protection.
- Limit the power of monopolies.
- Regulation on worker rights.
Reasons for Government intervention
- Equality . In a free market, there is likely to be significant inequality and poverty. This is not due to a meritocracy, but it could be due to unfair advantages of circumstances (inherited wealth, superior education). Governments can intervene to provide a basic security net – unemployment benefit, minimum income for those who are sick and disabled. This increases net economic welfare and enables individuals to escape the worst poverty. This government intervention can also prevent social unrest from extremes of inequality.
- Public goods . Public goods tend not to be provided in a free market because there is no financial incentive for firms to provide goods that people can enjoy for free. Governments can provide national defence, law and order and pay for it out of general taxation. Looking after the environment is also a public good, there are an increasing number of areas, where a government is needed to deal with issues such as forest fires, rising sea levels and pressure on water supplies.
- Education . Merit goods are under-consumed in free-market because people underestimate the personal benefits and/or ignore the external benefits. This leads to an underprovision of health care and education. Government intervention to provide free education can lead to a significant improvement in the quality of life for people who are educated. There are also many positive externalities to the rest of society. A well-educated society can improve labour productivity and economic growth.
- Shift consumer behaviour . The consumption of demerit goods like alcohol, tobacco and opiates can cause personal costs and significant social costs (e.g. crime). If the government identifies damaging goods, they can slowly change consumer behaviour – such as using higher tax, advertising campaigns and behavioural economics , e.g. making cigarettes difficult to buy with unappealing packets. Long-term government campaigns to reduce smoking in the UK and US have been effective in reducing smoking rates – something that has helped to increase life-expectancy.
- Environment . The environment is an area with a significant need of government intervention. The free market ignores external costs of business on the environment. It also fails to consider long-term considerations. For example, market forces may lead to the burning of fossil fuels, which cause increasing environmental problems around the world – which will get worse in the future. Given the potential costs to future generations, there needs to be government action to shift behaviour to renewable energy which doesn’t cause these environmental costs. Also, the environment involves many issues where private ownership does not apply. If pollution causes a worsening air quality, then this affects everyone on the planet, but market mechanisms do not provide an opportunity to deal with the issue. (If someone pollutes your back-garden, you can sue them. But, if air quality deteriorates, who takes action?
- Monopoly power. In a free market, firms can gain monopoly power to charge high prices to consumers and monopsony power to pay lower wages to workers. This increases inequality and deadweight welfare loss . Government intervention to limit mergers and monopoly power can lead to increased economic welfare.
- Strategic planning on infrastructure . Another limitation of the free market is to underinvest in quasi-public goods like roads and railways. This can lead to transport bottlenecks. Governments can plan for future transport trends and invest in the roads and railways which are needed for the future.
Disadvantages of government intervention
- Government failure . Government failure is a term to describe how government intervention can cause its own problems. For example, the government may take decisions for short-term political consideration which lead to an inefficient outcome. For example, government tariffs to protect domestic industry spark off a trade war, where the economy contracts.
- Lack of incentives . In the free market, individuals have a profit incentive to innovate and cut costs, but in the public sector, this incentive is not there. Therefore, it can lead to inefficient production. For example, state-owned industries have frequently been inefficient, overstaffed and produce goods not demanded by consumers.
- Political pressure groups . Milton Friedman once quipped ‘There is nothing as permanent as a temporary government bailout.’ He was referring to farming subsidies. Introduced in the 1930s during the Great Depression to alleviate a farming recession. After the Second World War, no government dared to remove subsidies because farmers were a powerful pressure group who wanted to keep the subsidies.
- Less choice . Often government intervention in the economy (e.g. nationalisation of industries) has been associated with less choice. Government produced services have a monopoly. Command economies, often had very little choice as government decided what to produce. Choice is an important element of economic freedom and being able to maximise individual welfare. (Not all government intervention leads to less choice.
- Impact of personal freedom. An increasing aspect of government intervention is through efforts to shift consumer behaviour – e.g. reduce congestion, improve health through reducing smoking rates and a healthier lifestyle. This includes taxes, behavioural influences and regulations. Sometimes people can feel this is overbearing on their individual choice.

Example of government intervention in health care
Pros of intervention.
- The government can provide universal health care so no-one dies due to lack of affordability.
- Universal government health care is fair.
- Health care is considered a human right and intrinsic to good quality of life
- Better health care can improve long-term labour productivity as workers with better health can work for longer and take less time off due to sickness.
- Government health care can prevent the stress and costs of going bankrupt from medical bills. In the US where the private sector has large role, unexpected medical bills cause bankruptcy. (66% of bankruptcy-related to health costs – CNBC )
- Economies of scale in government provision. The government can bulk buy medicines, supplies and also offer specialised services.
- The government can provide medicines at cost rather than for the inflated prices of the private sector.
- The government can ration health care to where it is actually needed and helpful. Under a system of private insurance where someone else is paying, millions may be spent on treatments with only very marginal improvements on the quality of life. Government health care has to use resources where it is needed. The private sector may push treatments like plastic surgery which are of doubtful value.
- It is argued the private sector have a profit incentive to cut costs and be more efficient. However, in health care, this is not the case. Doctors and nurses are not motivated like profit as in other sectors. Cutting costs may involve cutting the quality of care.
- If firms don’t have to provide private health care costs, it will reduce the costs of employing workers.
Cons of intervention
- Government provision may reduce the choice of individuals who prefer to choose their private insurers and doctor.
- The private sector may have profit incentives to cut costs and offer innovative new treatments that would be desired.
- With government provision, services may be limited by tax revenue. It is more likely that services will be rationed leading to longer waiting lists and some treatments not available.
- Government health care will require higher tax. Higher income tax may lead to lower incentives to work (though whilst taxes will rise, health insurance costs will be lower.)
- Government Intervention in Markets
- Market Failure
11 thoughts on “Pros and cons of government intervention”
Can I get the possible effects of a government intervening in the labour Market by imposing a minimum wage
thank you very much🙏🏽🙏🏽
Thank you I appreciate🙏🙏🙏🙏
Really helpful with my Foundations economic studies. Recommend for my other colleague to use it too.
Thank you Gurame
Very helpful. Thank you for providing me with this useful information that I needed for my economics class. Much appreciated.
Thank you so much, this article was well put together, and I appreciate the step by step, easy to understand format. Have a good one.
“GOVERNMENT” Should not get invoked with the poor! Governments requires numerous hundred thousand dollar a year employees and pension and health benefits forever, for people working w/ an gov-Agency! Give it to the Salvation Army & charity groups!!
Comments are closed.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
This leads to an underprovision of health care and education. Government intervention to provide free education can lead to a significant improvement in the quality of life for people who are educated. There are also many positive externalities to the rest of society. A well-educated society can improve labour productivity and economic growth.
The grounds for government intervention are widely different in these two areas and justify very different types of action. General Education for Citizenship A stable and democratic society is impossible without widespread acceptance of some common set of values and without a minimum degree of literacy and knowledge on the part of most citizens.
The predicted probabilities in support of government intervention in health care across the life course of respondents with different party identifications in four different eras are depicted in Figure 2. 5 Model statistics with three-way interaction effects are included in Appendix III. Although the age curves of each party demonstrate ...