Frontiers for Young Minds

- Download PDF

The Impacts of Junk Food on Health
Energy-dense, nutrient-poor foods, otherwise known as junk foods, have never been more accessible and available. Young people are bombarded with unhealthy junk-food choices daily, and this can lead to life-long dietary habits that are difficult to undo. In this article, we explore the scientific evidence behind both the short-term and long-term impacts of junk food consumption on our health.
Introduction
The world is currently facing an obesity epidemic, which puts people at risk for chronic diseases like heart disease and diabetes. Junk food can contribute to obesity and yet it is becoming a part of our everyday lives because of our fast-paced lifestyles. Life can be jam-packed when you are juggling school, sport, and hanging with friends and family! Junk food companies make food convenient, tasty, and affordable, so it has largely replaced preparing and eating healthy homemade meals. Junk foods include foods like burgers, fried chicken, and pizza from fast-food restaurants, as well as packaged foods like chips, biscuits, and ice-cream, sugar-sweetened beverages like soda, fatty meats like bacon, sugary cereals, and frozen ready meals like lasagne. These are typically highly processed foods , meaning several steps were involved in making the food, with a focus on making them tasty and thus easy to overeat. Unfortunately, junk foods provide lots of calories and energy, but little of the vital nutrients our bodies need to grow and be healthy, like proteins, vitamins, minerals, and fiber. Australian teenagers aged 14–18 years get more than 40% of their daily energy from these types of foods, which is concerning [ 1 ]. Junk foods are also known as discretionary foods , which means they are “not needed to meet nutrient requirements and do not belong to the five food groups” [ 2 ]. According to the dietary guidelines of Australian and many other countries, these five food groups are grains and cereals, vegetables and legumes, fruits, dairy and dairy alternatives, and meat and meat alternatives.
Young people are often the targets of sneaky advertising tactics by junk food companies, which show our heroes and icons promoting junk foods. In Australia, cricket, one of our favorite sports, is sponsored by a big fast-food brand. Elite athletes like cricket players are not fuelling their bodies with fried chicken, burgers, and fries! A study showed that adolescents aged 12–17 years view over 14.4 million food advertisements in a single year on popular websites, with cakes, cookies, and ice cream being the most frequently advertised products [ 3 ]. Another study examining YouTube videos popular amongst children reported that 38% of all ads involved a food or beverage and 56% of those food ads were for junk foods [ 4 ].
What Happens to Our Bodies Shortly After We Eat Junk Foods?
Food is made up of three major nutrients: carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. There are also vitamins and minerals in food that support good health, growth, and development. Getting the proper nutrition is very important during our teenage years. However, when we eat junk foods, we are consuming high amounts of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, which are quickly absorbed by the body.
Let us take the example of eating a hamburger. A burger typically contains carbohydrates from the bun, proteins and fats from the beef patty, and fats from the cheese and sauce. On average, a burger from a fast-food chain contains 36–40% of your daily energy needs and this does not account for any chips or drinks consumed with it ( Figure 1 ). This is a large amount of food for the body to digest—not good if you are about to hit the cricket pitch!
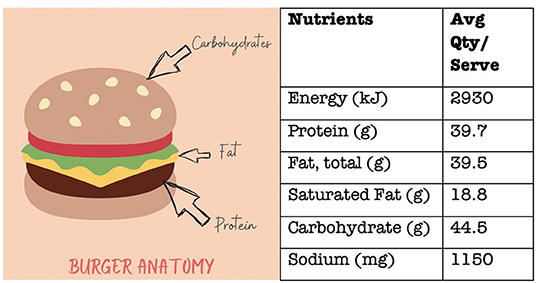
- Figure 1 - The nutritional composition of a popular burger from a famous fast-food restaurant, detailing the average quantity per serving and per 100 g.
- The carbohydrates of a burger are mainly from the bun, while the protein comes from the beef patty. Large amounts of fat come from the cheese and sauce. Based on the Australian dietary guidelines, just one burger can be 36% of the recommended daily energy intake for teenage boys aged 12–15 years and 40% of the recommendations for teenage girls 12–15 years.
A few hours to a few days after eating rich, heavy foods such as a burger, unpleasant symptoms like tiredness, poor sleep, and even hunger can result ( Figure 2 ). Rather than providing an energy boost, junk foods can lead to a lack of energy. For a short time, sugar (a type of carbohydrate) makes people feel energized, happy, and upbeat as it is used by the body for energy. However, refined sugar , which is the type of sugar commonly found in junk foods, leads to a quick drop in blood sugar levels because it is digested quickly by the body. This can lead tiredness and cravings [ 5 ].
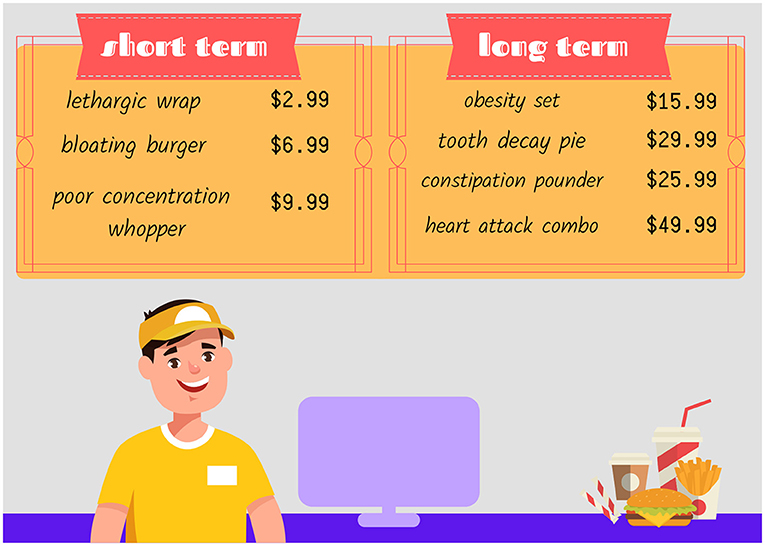
- Figure 2 - The short- and long-term impacts of junk food consumption.
- In the short-term, junk foods can make you feel tired, bloated, and unable to concentrate. Long-term, junk foods can lead to tooth decay and poor bowel habits. Junk foods can also lead to obesity and associated diseases such as heart disease. When junk foods are regularly consumed over long periods of time, the damages and complications to health are increasingly costly.
Fiber is a good carbohydrate commonly found in vegetables, fruits, barley, legumes, nuts, and seeds—foods from the five food groups. Fiber not only keeps the digestive system healthy, but also slows the stomach’s emptying process, keeping us feeling full for longer. Junk foods tend to lack fiber, so when we eat them, we notice decreasing energy and increasing hunger sooner.
Foods such as walnuts, berries, tuna, and green veggies can boost concentration levels. This is particularly important for young minds who are doing lots of schoolwork. These foods are what most elite athletes are eating! On the other hand, eating junk foods can lead to poor concentration. Eating junk foods can lead to swelling in the part of the brain that has a major role in memory. A study performed in humans showed that eating an unhealthy breakfast high in fat and sugar for 4 days in a row caused disruptions to the learning and memory parts of the brain [ 6 ].
Long-Term Impacts of Junk Foods
If we eat mostly junk foods over many weeks, months, or years, there can be several long-term impacts on health ( Figure 2 ). For example, high saturated fat intake is strongly linked with high levels of bad cholesterol in the blood, which can be a sign of heart disease. Respected research studies found that young people who eat only small amounts of saturated fat have lower total cholesterol levels [ 7 ].
Frequent consumption of junk foods can also increase the risk of diseases such as hypertension and stroke. Hypertension is also known as high blood pressure and a stroke is damage to the brain from reduced blood supply, which prevents the brain from receiving the oxygen and nutrients it needs to survive. Hypertension and stroke can occur because of the high amounts of cholesterol and salt in junk foods.
Furthermore, junk foods can trigger the “happy hormone,” dopamine , to be released in the brain, making us feel good when we eat these foods. This can lead us to wanting more junk food to get that same happy feeling again [ 8 ]. Other long-term effects of eating too much junk food include tooth decay and constipation. Soft drinks, for instance, can cause tooth decay due to high amounts of sugar and acid that can wear down the protective tooth enamel. Junk foods are typically low in fiber too, which has negative consequences for gut health in the long term. Fiber forms the bulk of our poop and without it, it can be hard to poop!
Tips for Being Healthy
One way to figure out whether a food is a junk food is to think about how processed it is. When we think of foods in their whole and original forms, like a fresh tomato, a grain of rice, or milk squeezed from a cow, we can then start to imagine how many steps are involved to transform that whole food into something that is ready-to-eat, tasty, convenient, and has a long shelf life.
For teenagers 13–14 years old, the recommended daily energy intake is 8,200–9,900 kJ/day or 1,960 kcal-2,370 kcal/day for boys and 7,400–8,200 kJ/day or 1,770–1,960 kcal for girls, according to the Australian dietary guidelines. Of course, the more physically active you are, the higher your energy needs. Remember that junk foods are okay to eat occasionally, but they should not make up more than 10% of your daily energy intake. In a day, this may be a simple treat such as a small muffin or a few squares of chocolate. On a weekly basis, this might mean no more than two fast-food meals per week. The remaining 90% of food eaten should be from the five food groups.
In conclusion, we know that junk foods are tasty, affordable, and convenient. This makes it hard to limit the amount of junk food we eat. However, if junk foods become a staple of our diets, there can be negative impacts on our health. We should aim for high-fiber foods such as whole grains, vegetables, and fruits; meals that have moderate amounts of sugar and salt; and calcium-rich and iron-rich foods. Healthy foods help to build strong bodies and brains. Limiting junk food intake can happen on an individual level, based on our food choices, or through government policies and health-promotion strategies. We need governments to stop junk food companies from advertising to young people, and we need their help to replace junk food restaurants with more healthy options. Researchers can focus on education and health promotion around healthy food options and can work with young people to develop solutions. If we all work together, we can help young people across the world to make food choices that will improve their short and long-term health.
Obesity : ↑ A disorder where too much body fat increases the risk of health problems.
Processed Food : ↑ A raw agricultural food that has undergone processes to be washed, ground, cleaned and/or cooked further.
Discretionary Food : ↑ Foods and drinks not necessary to provide the nutrients the body needs but that may add variety to a person’s diet (according to the Australian dietary guidelines).
Refined Sugar : ↑ Sugar that has been processed from raw sources such as sugar cane, sugar beets or corn.
Saturated Fat : ↑ A type of fat commonly eaten from animal sources such as beef, chicken and pork, which typically promotes the production of “bad” cholesterol in the body.
Dopamine : ↑ A hormone that is released when the brain is expecting a reward and is associated with activities that generate pleasure, such as eating or shopping.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
[1] ↑ Australian Bureau of Statistics. 2013. 4324.0.55.002 - Microdata: Australian Health Survey: Nutrition and Physical Activity, 2011-12 . Australian Bureau of Statistics. Available online at: http://bit.ly/2jkRRZO (accessed December 13, 2019).
[2] ↑ National Health and Medical Research Council. 2013. Australian Dietary Guidelines Summary . Canberra, ACT: National Health and Medical Research Council.
[3] ↑ Potvin Kent, M., and Pauzé, E. 2018. The frequency and healthfulness of food and beverages advertised on adolescents’ preferred web sites in Canada. J. Adolesc. Health. 63:102–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jadohealth.2018.01.007
[4] ↑ Tan, L., Ng, S. H., Omar, A., and Karupaiah, T. 2018. What’s on YouTube? A case study on food and beverage advertising in videos targeted at children on social media. Child Obes. 14:280–90. doi: 10.1089/chi.2018.0037
[5] ↑ Gómez-Pinilla, F. 2008. Brain foods: the effects of nutrients on brain function. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 9, 568–78. doi: 10.1038/nrn2421
[6] ↑ Attuquayefio, T., Stevenson, R. J., Oaten, M. J., and Francis, H. M. 2017. A four-day western-style dietary intervention causes reductions in hippocampal-dependent learning and memory and interoceptive sensitivity. PLoS ONE . 12:e0172645. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0172645
[7] ↑ Te Morenga, L., and Montez, J. 2017. Health effects of saturated and trans-fatty acid intake in children and adolescents: systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE. 12:e0186672. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0186672
[8] ↑ Reichelt, A. C. 2016. Adolescent maturational transitions in the prefrontal cortex and dopamine signaling as a risk factor for the development of obesity and high fat/high sugar diet induced cognitive deficits. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 10. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2016.00189
Payment is under Review
Dear Customer, your payment is being reviewed by payment system. Your writer will start work instantly as we get response. Just wait some moments...
Payment is Success
Dear Customer, thank you for payment. Your order is in progress now
Payment is Failed
Dear Customer, your payment has been refused. Try another card or payment method.
- Samples List
Causes and Effects of Eating Junk Food
Place new order. it's free, fast and safe, our customers say.
Jeff Curtis
"I'm fully satisfied with the essay I've just received. When I read it, I felt like it was exactly what I wanted to say, but couldn’t find the necessary words. Thank you!"
Ian McGregor
"I don’t know what I would do without your assistance! With your help, I met my deadline just in time and the work was very professional. I will be back in several days with another assignment!"
Shannon Williams
"It was the perfect experience! I enjoyed working with my writer, he delivered my work on time and followed all the guidelines about the referencing and contents."
- Essay Writing
- Essay Writer
- Essay Format
- Writing from Scratch
- Proofreading
- APA Essay Format
- Chicago Essay Format
- Harvard Essay Format
- Tubarian Essay Format
- 5-paragraph Essay
- Admission Essay
- Annotated Bibliography
- Argumentative Essay
- Article Review
- Book/Movie Review
- Business Plan
- Cause and Effect Essay
- Classification Essay
- Comparison Essay
- Creative Writing
- Critical Thinking/Review
- Deductive Essay
- Definition Essay
- Essay (Any Type)
- Exploratory Essay
- Expository Essay
- Informal Essay
- Literature Essay
- Multiple Choice Question
- Narrative Essay
- Personal Essay
- Persuasive Essay
- Powerpoint Presentation
- Reflective Writing
- Research Essay
- Response Essay
- Scholarship Essay
Already have an account? Log in .
Do not have one yet? Create an account .
Forgot Password
Please, enter your e-mail or login and push Send button. We send you new password on registration e-mail
Harmful Effects of Junk Food Essay for Students and Children
500+ words essay on harmful effects of junk food.
Junk Food is very harmful that is slowly eating away the health of the present generation. The term itself denotes how dangerous it is for our bodies. Most importantly, it tastes so good that people consume it on a daily basis. However, not much awareness is spread about the harmful effects of junk food.

The problem is more serious than you think. Various studies show that junk food impacts our health negatively. They contain higher levels of calories, fats, and sugar. On the contrary, they have very low amounts of healthy nutrients and lack dietary fibers. Parents must discourage their children from consuming junk food because of the ill effects it has on one’s health.
Impact of Junk Food
Junk food is the easiest way to gain unhealthy weight. The amount of fats and sugar in the food makes you gain weight rapidly. However, this is not a healthy weight. It is more of fats and cholesterol which will have a harmful impact on your health. Junk food is also one of the main reasons for the increase in obesity nowadays.
This food only looks and tastes good, other than that, it has no positive points. The amount of calorie your body requires to stay fit is not fulfilled by this food. For instance, foods like French fries, burgers, candy, and cookies, all have high amounts of sugar and fats. Therefore, this can result in long-term illnesses like diabetes and high blood pressure . This may also result in kidney failure .

Above all, you can get various nutritional deficiencies when you don’t consume the essential nutrients, vitamins, minerals and more. You become prone to cardiovascular diseases due to the consumption of bad cholesterol and fat plus sodium. In other words, all this interferes with the functioning of your heart.
Furthermore, junk food contains a higher level of carbohydrates. It will instantly spike your blood sugar levels. This will result in lethargy, inactiveness, and sleepiness. A person reflex becomes dull overtime and they lead an inactive life. To make things worse, junk food also clogs your arteries and increases the risk of a heart attack. Therefore, it must be avoided at the first instance to save your life from becoming ruined.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Ways to Avoid Junk Food
The main problem with junk food is that people don’t realize its ill effects now. When the time comes, it is too late. Most importantly, the issue is that it does not impact you instantly. It works on your overtime; you will face the consequences sooner or later. Thus, it is better to stop now.
You can avoid junk food by encouraging your children from an early age to eat green vegetables. Their taste buds must be developed as such that they find healthy food tasty. Moreover, try to mix things up. Do not serve the same green vegetable daily in the same style. Incorporate different types of healthy food in their diet following different recipes. This will help them to try foods at home rather than being attracted to junk food.
In short, do not deprive them completely of it as that will not help. Children will find one way or the other to have it. Make sure you give them junk food in limited quantities and at healthy periods of time.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

Healthdirect Free Australian health advice you can count on.
Medical problem? Call 1800 022 222. If you need urgent medical help, call triple zero immediately
healthdirect Australia is a free service where you can talk to a nurse or doctor who can help you know what to do.
Junk food and your health
11-minute read
Share via email
There is a total of 5 error s on this form, details are below.
- Please enter your name
- Please enter your email
- Your email is invalid. Please check and try again
- Please enter recipient's email
- Recipient's email is invalid. Please check and try again
- Agree to Terms required
Error: This is required
Error: Not a valid value
- 'Junk food' is food that contains high levels of fats, salt or sugar, and lacks nutrients such as fibre, vitamins and minerals.
- Reading nutritional information labels and following the Health Star Ratings system can help you make healthy food choices.
- Understanding the nutritional value of the food you eat and being aware of advertising 'tricks' can also help you reduce your junk food intake.
- Eating junk food, and having sweet drinks, can lead to short- and long-term health complications, including weight gain, diabetes and heart problems.
What is junk food?
'Junk foods' are foods that lack nutrients, vitamins and minerals , and are high in kilojoules (energy), salts , sugars , or fats . Junk food is so called because it doesn't play a role in healthy eating, especially if you eat too much of it. Junk food is also known as 'discretionary food' or 'optional food'.
Some examples of junk food include:
- cakes and biscuits
- fast foods (such as hot chips, burgers and pizzas)
- chocolate and sweets
- processed meat (such as bacon)
- snacks (such as chips)
- sugary drinks (such as sports, energy and soft drinks)
- alcoholic drinks
If your diet is high in fats, salt and sugar and you are not receiving essential nutrients , your risk of obesity and other chronic (long-term) diseases may increase.
These diseases include:
- cardiovascular disease
- type 2 diabetes
- non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
- some cancers
How do I know if a food product is 'junk food'?
While finding healthy alternatives to junk food can sometimes be difficult, the Health Star Rating system is a convenient tool to help you know how healthy a product is. It's a quick and easy way to compare similar packaged foods.
The Health Star Rating system rates packaged foods between half a star and 5 stars, based on how healthy they are. These ratings are found on the front of packaged items. However, it is important to note that this system is very general, and the nutritional value of some products may not be accurately expressed by the rating they receive.
Remember also that the Health Star Rating system is designed only for packaged products sold in shops, so it won't include some healthy foods — including fresh unpackaged food such as fruit and vegetables.
How do I make healthy food choices?
It's important to understand the nutritional value of the food you are buying. You can do this by reading the nutrition panel found on the back of all packaged items in Australia.
Food labels can tell you things like the amount of energy , protein , fat , carbohydrates , sugars, fibre and sodium (salt) in each product, as well as the recommended serving size.
Understanding health claims
When checking a product for its nutritional value, make sure you look at the health claims such as 'low in fat' or 'sugar free', as these can be misleading. When a product is advertised as 'light' or 'lite', this may refer only to the product's colour or flavour. This means that the product may still be 'full-fat' — be sure to read the nutrition information panel at the back of the package for the actual fat content.
Another common claim is that a product is 'sugar-free' or has 'no added sugar'. In truth, this means that a product has no added sucrose or table sugar, but it may still contain other types of sugar. The product may also contain salt or fat and may be high in kilojoules, so even sugar free products can be junk foods.
Note also that products known as 'health foods' such as some fruit juices and muesli bars can actually be junk food if they contain high levels of sugar, salt or fat. Check a product's Health Star Rating for a better guide to how healthy the product is. Keep in mind that this rating system is limited in accuracy, but may be a better guide than advertised claims.
Can I include a small amount of junk food in a healthy diet?
Yes, in line with the Australian Dietary Guidelines , a small amount of junk or discretionary food can be included in a healthy, balanced diet. This means you should only have junk food occasionally and in small amounts. In general, most Australians eat too much junk food and should work on eating less of it, less often.
It is important to balance your junk food intake with increased exercise to help burn off extra energy. This will help you avoid gaining excessive weight.
When thinking about how much junk food you eat, remember that everybody is different — if you are shorter or smaller than average, or you do less exercise than the average person, you will also need to eat less than the average person. If you are trying to lose weight, try and keep the amount of junk food you eat to a minimum.
Check the Australian Dietary Guidelines to help you decide if you need to improve your diet, and to guide your food and drink intake.
How can I reduce the amount of junk food I eat?
While it can be challenging to reduce the amount of junk food you eat, you don't have to give up on all your favourite foods.
Here are some tips on how to create healthy eating habits :
- Plan your meals and snacks ahead of time so you decide what you eat based on nutrition, not based on what is left in your pantry. Planning ahead also helps you keep to a budget and makes shopping easier.
- Choose wholefood options such as wholemeal and wholegrain carbohydrates like pasta, bread and flour.
- Choose fresh fruit for dessert instead of junk food to keep away from added salt, sugar and saturated fat.
- Check your food's nutritional value using the nutritional information panel on the back of the packet.
- Watch out for advertising 'tricks', including claims that a product has 'no added sugar', since it can still be high in kilojoules, salt or fat. A product can claim to be 'reduced in fat' as long as it has less fat than an earlier version of the product — but it may still be high in fat.
- Use the Health Star Rating system to compare similar packaged items and choose the healthiest one.
NEED TO LOSE WEIGHT? — Use the BMI Calculator to find out if your weight and waist size are in a healthy range.
Why is junk food so appealing?
While you may feel that you enjoy junk food just because it tastes so good, there is a scientific explanation for why you want to have more of it. The brain naturally encourages you to seek experiences that you find pleasurable, including eating tasty food. This encouragement from the brain is known as the 'reward' system.
When a person eats tasty food (including junk food) the reward circuit in the brain is switched on. This releases a brain chemical called dopamine . The chemical rush floods the brain with pleasure and so the brain creates more receptors for dopamine in response. In the same way that people with a drug or alcohol addiction require a bigger dose over time, you crave more junk food the more you eat it.
Does eating junk food cause health complications?
Eating too much junk food can have a negative effect on your general health and wellbeing and can also reduce your ability to be active.
Short-term effects of junk foods
As well as causing you to gain weight, the other short-term effects of eating junk food include:
- increased stress levels
- fatigue and decreased energy levels
- difficulty sleeping
- concentration difficulties
- feeling down
- tooth decay
Long-term effects of junk foods
In the long-term, eating junk food can lead to:
- heart-related problems (such as cardiovascular disease , high blood pressure and cholesterol )
- overweight and obesity
- osteoporosis
- certain cancers
- eating disorders
These complications are all associated with a diet high in sugar, salt, trans- and saturated fats and with a lack of essential nutrients like fibre, vitamins and minerals.
ARE YOU AT RISK? — Are you at risk of type 2 diabetes, heart disease or kidney disease? Use the Risk Checker to find out.
Is it more expensive to eat healthily?
Eating healthily doesn't have to be expensive, and can even save you money if you cut down on junk food purchases.
Here are some tips to help you eat healthily on a budget:
- Plan ahead and make a list you can stick to in the supermarket.
- Shop smart — buy what's in season and what's on special.
- Use the fresh fruit and vegetables you already have at home first, before buying more.
- Meal preparation means you can buy and cook in bulk, which will save you both time and money.
- Only buy what you need.
Resources and support
For more information and support, you can visit the following websites:
- Heart Foundation provides information on healthy eating to protect your heart
- Nutrition Australia aims to 'inspire healthy eating' through information, education and consultation services.
- Parents' Voice are parents interested in improving the food and physical activity of Australian children
- Rethink Sugary Drink highlight the amount of sugar in soft drinks
- Dietitians Australia teaches how diet and nutrition can improve your health and wellbeing — Call on 1800 812 942.
- The George Institute's FOODSWITCH website and app can help you find out what's in the packaged food you're looking to buy, as well as help you make healthier food choices.
Call healthdirect on 1800 022 222 at any time to speak to a registered nurse (known as NURSE-ON-CALL in Victoria) for more information and advice.
Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content .
Last reviewed: June 2023
Search our site for
- Healthy diet
- Dietary Sugars
- Soft Drinks
Need more information?
These trusted information partners have more on this topic.
Top results
Junk food is used to describe food and drinks low in nutrients (e.g. vitamins, minerals and fibre) and high in kilojoules, saturated fat, added sugar and/or added salt. They are also known as discretionary choices.
Read more on WA Health website

Kids may love junk food, but they should not form part of a regular, healthy diet.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website

LiveLighter - Junk Food Facts
Junk food used to be just an occasional “treat” but these days Australians are eating more, and more often. Find out how it all adds up.
Read more on LiveLighter website

Choosing nutritious foods | Eat For Health
The Australian Dietary Guidelines, recommend that we choose widely from the Five Food Groups and limit discretionary foods that are higher in saturated fat, added salt and added sugars.
Read more on NHMRC – National Health and Medical Research Council website

Discretionary food and drink choices | Eat For Health
What are discretionary food choices?
Healthy diet for children - MyDr.com.au
The average child's diet now gets over 40% of kilojoules from junk foods and drinks. Find out how to encourage better food choices.
Read more on myDr website

Low Gi Living | GI Foundation
CSIRO’s new tool to combat Australia’s #1 diet issue by sveas | Apr 7, 2021 | Gi Science, Latest news, Low Gi foods and lifestyleLow nutrient, high kilojoule food continues to be the top choice for Australians, with new research from CSIRO, Australia’s national science agency, showing that nearly 4 out of 5 Aussies overindulge in junk food every day! The new findings come from the recent
Read more on Glycemic Index Foundation website

Food cravings during pregnancy
Food cravings are sudden urges to eat a particular type of food. They are a real phenomenon and affect many females during pregnancy.
Healthy food groups: preschoolers | Raising Children Network
Preschoolers need foods from all five healthy food groups: vegetables, fruit, grain foods, dairy and protein. Try to limit salty, sugary and fatty foods.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website

9 food and heart health myths, busted | Heart Foundation
Let’s dive into nine common food and health myths and the facts behind them.
Read more on Heart Foundation website

Healthdirect Australia is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
Healthdirect 24hr 7 days a week hotline
24 hour health advice you can count on
1800 022 222
Government Accredited with over 140 information partners
We are a government-funded service, providing quality, approved health information and advice

Healthdirect Australia acknowledges the Traditional Owners of Country throughout Australia and their continuing connection to land, sea and community. We pay our respects to the Traditional Owners and to Elders both past and present.
© 2024 Healthdirect Australia Limited
Support for this browser is being discontinued
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- v.15(11); 2023 Nov
- PMC10734656

Unveiling the Gut Microbiome: How Junk Food Impacts the Gut
Sania s shah.
1 Microbiology, Datta Meghe Medical College, Datta Meghe Institute of Higher Education and Research (DU), Wardha, IND
Obaid Noman
2 Pathology, Datta Meghe Medical College, Datta Meghe Institute of Higher Education and Research (DU), Wardha, IND
Neha Jaiswal
The human gut microbiome, a complex community of microorganisms, profoundly influences human health and disease. Bacteroidetes and Firmicutes make up the majority of the normal human gut microbiota. These microorganisms wield considerable influence over our physiological functions, impacting both our well-being and our susceptibility to disease. The surge of interest in the gut microbiome over the past decade has been remarkable. Once overlooked, the gastrointestinal tract’s microbiota has gained recognition for its significance in maintaining optimal health. The food industry has capitalized on this, flooding the market with “probiotic” and “fermented” products. This article aims to provide a critical review of the current literature on the gut microbiome and its significance in human health, with a particular focus on the impact of dietary choices, especially junk food, on the composition and function of the gut microbiota. Microbes possess the remarkable ability to unlock nutrients from otherwise indigestible substances. The gut microbiome of individuals who consume healthy foods and those who prefer junk food varies significantly. Healthy diets promote a diverse and beneficial gut microbiome, while junk food consumption often leads to a less diverse microbiome with negative consequences for health.
Introduction and background
The human body hosts a diverse array of microorganisms, including bacteria, archaea, viruses, and eukaryotic microbes, collectively referred to as the human microbiome. Over 100 trillion microbial cells reside in our gut, where they form a complex ecosystem that affects human physiology, metabolism, nutrition, and immune function [ 1 ]. Bacteroidetes and Firmicutes make up the majority of the normal human gut microbiota. These microorganisms wield considerable influence over our physiological functions, impacting both our well-being and our susceptibility to disease [ 2 ]. They play pivotal roles in metabolism, protection against pathogens, and immune system education and, by extension, affect a wide range of bodily functions. Technological advancements have propelled the study of the human microbiome by enabling culture-independent analyses, a breakthrough in understanding these complex communities. Advancements in characterizing the microbiome’s structure have paved the way for investigating its functional interactions with the host. Understanding these functions is pivotal in comprehending the microbiome’s role in human health and disease [ 3 ].
The surge of interest in the gut microbiome over the past decade has been remarkable. Once overlooked, the gastrointestinal tract’s microbiota has gained recognition for its significance in maintaining optimal health. The food industry has capitalized on this, flooding the market with “probiotic” and “fermented” products. This newfound attention, however, has led to confusion due to the burgeoning data that leaves many questions unanswered [ 4 ]. The concept of influencing gut health through microorganisms isn’t new. Early in the 20th century, Élie Metchnikoff associated the longevity of rural Bulgarians with their consumption of fermented milk products [ 5 ]. He proposed that these products, rich in lactic acid bacteria, contributed to their extended lifespans. Metchnikoff’s work laid the foundation for understanding how healthy bacteria could replace harmful ones, a concept that earned him a Nobel Prize. However, the discovery of antibiotics shifted the focus away from bacterial therapies. As antibiotic resistance becomes a growing concern, researchers are revisiting bacterial interventions, especially with the advent of advanced molecular techniques [ 5 , 6 ]. In the realm of microbiome research, significant strides have been made in unraveling the mysteries of our body’s intricate microbial communities. Technological advancements have empowered the human race to explore the complex world of bacteria beyond traditional cultivation methods. Techniques such as 16S rRNA gene sequencing and metagenomic analysis have allowed us to delve into both the identity and potential functionality of these microorganisms [ 7 ]. This article aims to provide a critical review of the current literature on the gut microbiome and its significance in human health, with a particular focus on the impact of dietary choices, especially junk food, on the composition and function of the gut microbiota.
Methodology
To conduct a comprehensive literature search for a review article, we used the following databases: PubMed and Google Scholar. We searched for articles using the following search terms: (gut microbiome) OR (Gut microbiome) AND (Microbiota) OR (microbiota) AND (healthy food) OR ( healthy diet) OR (nutritional food) AND (chronic disease) OR (long-term disease) AND (immunity) AND (dysbiosis). We applied the following inclusion criteria for the final review: (1) review articles, (2) English language, (3) peer-reviewed, (4) relevant to the topic, and (5) full-text available (Figure 1 ) [ 8 ].

n, number of studies; PRISMA, preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses
Advancements in microbiome study
The advancement of technology has heralded a remarkable era in microbiome research, providing us with unprecedented tools to unravel the intricacies of microbial communities without the need to culture them in a lab. This scientific progress has been instrumental in exploring the world of microbes that inhabit the human body.
16S rRNA Gene Sequencing
Gene sequencing technique has been a linchpin in microbiome research. It enables scientists to zero in on specific bacterial populations by sequencing the variable regions of the 16S rRNA gene, a genetic marker that is present in all bacteria. It’s similar to identifying individual species by their unique DNA fingerprints but in the world of bacteria [ 7 ]. This approach has been instrumental in characterizing the composition and diversity of microbial communities residing in the human microbiome. It has provided a taxonomic roadmap, allowing researchers to identify and classify various microbial players, leading to a better understanding of who inhabits our microbiome [ 9 ].
Metagenomic Analysis
Metagenomic analysis takes the exploration to a more comprehensive level by scrutinizing the entirety of microbial DNA present in a given sample. This expansive approach goes beyond mere identification and uncovers the vast genetic potential encoded in the microbial genomes. It’s similar to reading the entire library of genetic information within the microbiome [ 10 ]. By doing so, researchers not only identify the microbial residents but also gain insights into their functional potential. This helps us understand what these microorganisms are capable of genetically and, importantly, how these capabilities may influence human health [ 11 ].
Meta-Transcriptomics
Meta-transcriptomics method delves into RNA, the dynamic molecule that reflects active gene expression within the microbiome. While genes provide a blueprint, RNA reveals the current construction project [ 12 ]. Meta-transcriptomics allows scientists to understand which genes are actively transcribed and which proteins are being produced by the microbial community. It provides a real-time snapshot of the activities within the microbiome, shedding light on how microorganisms engage with their environment, including their host [ 13 ].
Meta-Proteomics
Meta-proteomics goes even further by focusing on the proteins expressed by the microbiome. Proteins are the workhorses of biological processes, and by analyzing them, researchers gain insights into the functional aspects of the microbial community [ 14 ]. This method helps us understand how microorganisms interact with each other and with the human host. It unveils the active machinery within the microbiome and provides a window into the functions and activities of these tiny inhabitants [ 15 ].
Metabolomics
Metabolomics provides a glimpse of the small molecules (metabolites) produced by the microbiome. These metabolites include essential nutrients, signaling molecules, and byproducts of microbial metabolism [ 16 ]. Metabolites are critical players in host-microbe interactions, influencing various aspects of human health, from immune responses to metabolic processes. This approach reveals how the microbiome can impact the overall physiology of the host, offering insights into its far-reaching effects on health and disease (Table (Table1 1 ) [ 17 ].
Data accumulation on human microbiome
The MetaHIT study, in particular, stands out for its ambitious exploration of the genetic content of fecal microbial genes. This initiative delved deep into the microbiome’s genetic makeup, analyzing over 3 million fecal microbial genes [ 18 ]. Extensive genomic profiling has provided a detailed and intricate insight into the genetic diversity of these microorganisms. By pooling metagenomic data from various sources and samples, these projects have successfully compiled an extensive gene catalog comprising approximately 9.8 million microbial genes [ 19 ].
The sheer magnitude of this genetic data reflects the astonishing diversity and variability within these microbial communities. Each sample under scrutiny has, on average, been found to contain around 750,000 genes, highlighting the complexity of the microbiome and the vast genetic potential it holds [ 20 ]. This wealth of information has opened doors to exploring the functional aspects of these genes, shedding light on the metabolic capabilities and potential contributions of the microbiome to human health [ 21 ].
The thoroughness and scale of these data collection efforts represent a significant step forward in microbiome research. It provides a foundation for studying the microbiome’s role in various health conditions, including obesity, metabolic disorders, and gastrointestinal diseases [ 22 ]. It not only enhances our understanding of the microbiome’s genetic diversity but also underscores the intricate relationship between these microbial communities and the human host. The continued analysis of such extensive genetic data holds great promise for advancing personalized medicine, dietary interventions, and the development of novel therapies based on microbiome insights [ 23 ].
Microbiome and diseases
Microbes possess the remarkable ability to unlock nutrients from otherwise indigestible substances. For example, certain species of Bacteroides engage in the digestion of xyloglucans, which has significant implications for our dietary choices. Moreover, microbiota generates short-chain fatty acids (SCFA) from dietary fibers as an essential energy source [ 24 ]. The complex interplay that takes place between our bodies and the microorganisms that live within them is incredibly fascinating. The concept of dysbiosis, wherein the balance of our microbial companions shifts, has captured considerable attention [ 25 ]. Yet, navigating the labyrinthine relationship between these changes and diseases proves a challenging puzzle. The question of what causes what remains enigmatic, with microbiota changes often a response to diseases or interventions like antibiotics. This exploration gains further complexity as we delve into the roles of microbiota in specific conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis, cardiovascular disease, obesity, colorectal cancer, and diabetes, where the tendrils of microbial influence are still being untangled [ 26 ]. Gut microbiota plays a significant role in heart health, influencing cardiovascular disease through dietary phosphatidylcholine [ 27 ]. Treatments for irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) include dietary changes, probiotics, and antibiotics [ 28 ]. The microbiota-gut-brain axis connects gut changes with central nervous system symptoms [ 29 ]. Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) is rooted in gut microbiota, and microbiota-based therapies like fecal microbiota transplant (FMT) can prevent recurrent CDI [ 30 ]. Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a complex disease where environmental and genetic factors intersect, with microbial dysbiosis sometimes acting as both the cause and consequence of inflammation [ 31 ].
The alterations in brain-gut microbiota interactions are believed to be involved in the pathogenesis of brain disorders like IBS and functional gastrointestinal disorders. These alterations are also linked to brain disorders like autism spectrum disorders, Parkinson’s disease, mood and affect disorders, and chronic pain [ 32 ]. The gut microbiota and its metabolites modulate GI functions, behaviors, and brain processes, including stress responsiveness, emotional behavior, pain modulation, ingestive behavior, and brain biochemistry [ 33 ].
Gut microbiome composition in junk food consumers
The human gut is a dynamic community that interacts intimately with human physiology and has been implicated in a wide range of health outcomes, from metabolism and immunity to mental well-being [ 34 ]. Healthy food is rich in fiber, diverse, high in nutrients, low in added sugars, and balanced in carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids, promoting health and reducing the risk of metabolic diseases [ 35 ]. Junk food is high in saturated fats and sugars, with processed ingredients, additives, preservatives, and synthetic flavors. It lacks fiber, causes digestive problems, and lacks essential nutrients, leading to weight gain and metabolic disruption (Table 2 ) [ 36 ].
Diet and gut microbiome composition
The gut microbiome is highly responsive to dietary inputs, and research has consistently demonstrated that what we eat can significantly impact its composition (Table 3 ) [ 41 ].
IGF, insulin-like growth factor; IBD, inflammatory bowel disease; SCFA, short-chain fatty acids
The gut microbiome of individuals who consume healthy foods and those who prefer junk food varies significantly. Healthy eaters have a more diverse gut microbiome, with beneficial bacteria like Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus being more prevalent [ 42 ]. They also consume high-fiber foods, which provide prebiotics that support the growth of good bacteria in the stomach. In contrast, junk food eaters have a reduced diversity, leading to negative changes such as increased harmful bacteria growth and inflammation [ 43 ].
Healthy eaters and their gut microbiome
Individuals who adhere to a diet centered around nutritious, whole foods typically enhance a gut microbiome that reflects the positive impact of their dietary choices. Several key characteristics distinguish this group (Table 4 ).
SCFA, short-chain fatty acids
Junk food consumers and their gut microbiome
In complete contrast, individuals who favor diets predominantly composed of junk food exhibit a gut microbiome with distinct characteristics, often associated with negative consequences for health (Table 5 ).
Healthy eaters have a rich diversity of beneficial bacteria, such as bifidobacteria and lactobacilli, which are essential for digestion, production of SCFA, and gut wall reinforcement [ 49 ]. Junk food, on the other hand, encourages the expansion of harmful microorganisms like Firmicutes, linked to inflammation and obesity. SCFAs play a crucial role in maintaining gut health by acting as an energy source for gut bacteria, maintaining gut barrier function, promoting immune modulation, regulating gut pH, influencing appetite and metabolism, anti-inflammatory effects, increasing mucus formation, and protecting against pathogens [ 50 ].
A robust gut barrier and decreased systemic inflammation are linked to a diet high in nutritious foods, while diets high in junk food can result in chronic inflammation and weakened gut defenses, leading to systemic health problems [ 51 ]. The gut microbiome is also crucial in controlling metabolism, with healthy individuals having microbiomes that support improved cholesterol and glucose metabolism [ 51 ]. Understanding these differences in gut microbiome composition can lead to dietary interventions to promote gut health and reduce related health risks [ 52 , 53 ]. These include fiber-rich diets, prebiotics, probiotics, behavioral interventions like education and behavioral therapy, and personalized nutrition based on individual gut microbiota composition [ 54 ].
Conclusions
Microbiome research has made significant progress in understanding our body’s microbial communities, using techniques like 16S rRNA gene sequencing and metagenomic analysis. Large-scale initiatives like MetaHIT and HMP have provided a vast repository of data on the human microbiome’s diversity and genetic makeup. The gut microbiome is shaped by dietary choices, with healthy eaters having a diverse microbiome with beneficial bacteria, while junk food consumption leads to reduced diversity and an overabundance of pathogenic species. These dietary disparities impact inflammation, metabolic health, and overall well-being. Understanding the relationship between diet and gut microbiome can help promote gut health and prevent chronic diseases. Future research should continue to refine strategies for improving gut microbiome composition.
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.

Essay on Effects of Junk Food
Students are often asked to write an essay on Effects of Junk Food in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Effects of Junk Food
Introduction.
Junk food refers to food that has little nutritional value and often contains high levels of sugar, salt, and fat. Despite its popularity, consuming junk food can have serious health effects.
Effects on Health
Eating too much junk food can lead to obesity, heart disease, and diabetes. These foods are high in unhealthy fats and sugar, contributing to weight gain and high blood pressure.
Impact on Academic Performance
Junk food can affect a student’s academic performance. High sugar levels can cause energy spikes and crashes, making it hard to concentrate.
While junk food may be tempting, it’s important to understand the negative effects it can have on our health and performance.
250 Words Essay on Effects of Junk Food
Junk food, a term coined for food items with high caloric value and minimal nutritional content, has become a significant part of modern diets. Its ease of access, affordability, and enticing flavors have led to its widespread consumption. However, the adverse effects of junk food on human health are alarming and necessitate a closer examination.
Impact on Physical Health
A primary concern is the link between junk food and obesity. High in sugars and fats, junk food contributes to excessive caloric intake, leading to weight gain. This excess weight can trigger a cascade of health issues, including heart diseases, diabetes, and certain types of cancer. Furthermore, the lack of essential nutrients can lead to deficiencies, impacting overall bodily functions.
Effects on Mental Health
The effects of junk food extend beyond physical health, impacting mental well-being. Studies have shown a correlation between high junk food consumption and mental health disorders, including depression and anxiety. The high sugar content can lead to fluctuations in blood sugar levels, causing mood swings and fatigue.
Environmental Consequences
The environmental impact of junk food production is another area of concern. The mass production of these foods often involves intensive farming practices, contributing to deforestation, soil degradation, and water pollution.
The effects of junk food are far-reaching, impacting not only individual health but also our environment. As responsible consumers, it is imperative to understand these implications and make informed dietary choices. Encouragingly, a shift towards healthier alternatives can mitigate these adverse effects, promoting both personal health and environmental sustainability.
500 Words Essay on Effects of Junk Food
Junk food, a term popularized in the 20th century, refers to food items that are high in calories, sugar, salt, and fat, but low in nutritional value. Despite the well-documented health risks, the consumption of junk food has been on the rise, especially among young adults. This essay aims to explore the effects of junk food on various aspects of human life and society.
The Impact on Physical Health
The most immediate and visible effect of junk food is on physical health. The high-calorie content contributes to obesity, a significant public health issue affecting millions worldwide. Obesity, in turn, increases the risk of chronic diseases such as diabetes, heart disease, and certain types of cancer. Furthermore, the high sodium content in junk food can lead to hypertension, while excessive sugar can cause tooth decay and other oral health problems.
Recent research has shed light on the link between diet and mental health. Junk food, lacking in essential nutrients, can negatively impact brain function, leading to poor concentration, mood swings, and even depression. For instance, the excessive sugar in junk food can cause fluctuations in blood glucose levels, leading to mood instability and difficulty concentrating.
Socio-Economic Impact
The socio-economic effects of junk food consumption are far-reaching. The rising healthcare costs associated with treating chronic diseases caused by unhealthy diets strain economies, especially in developing countries. Moreover, the loss of productivity due to illness and the social stigma associated with obesity can lead to reduced quality of life and increased inequality.
Lastly, the production and consumption of junk food have significant environmental implications. Industrial farming practices used to produce junk food contribute to deforestation, water pollution, and climate change due to high greenhouse gas emissions. Moreover, the packaging of these foods often leads to excessive waste, contributing to the global plastic pollution problem.
Junk food, while convenient and appealing, has far-reaching effects on physical and mental health, socio-economic structures, and the environment. As society becomes more aware of these impacts, it is crucial to promote healthier dietary choices and sustainable food production practices. In the end, the responsibility lies not just with individuals, but also with governments, educators, and food producers to create an environment where making healthier choices becomes easier.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
- Essay on How to Avoid Junk Food
- Essay on Healthy Food vs Junk Food
- Essay on Disadvantages of Junk Food
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Harmful Effects Of Junk Food Essay
Harmful Effects of Junk Food Essay
500+ words essay on harmful effects of junk food.
The word ‘junk’ refers to fast food, which is easy to make and contains a low nutritional value. There are various types of junk food that are available in restaurants, such as cold drinks, pizza, burgers, sandwiches etc. Nowadays, fast-food restaurants and their chains are increasing because people around the world like to eat junk food. Junk food has become more popular because of its great taste, better shelf life and easy transportation. Junk food advertisement also plays a great role in making them popular, but these junk foods create a lot of health problems. So, with the help of this Junk Food Essay, we will make students aware of the harmful effects of junk food. Also, this Junk Food Essay will help you know how we can avoid these junk foods and follow a healthier diet regimen. Students can also get the list of CBSE Essay topics to practise essays on different topics.
Why Do People Prefer Junk Food?
Food is a basic need for human beings which provides energy to our body and protects us from diseases. Today, it’s common to have junk food in our diet. Junk foods are immensely popular among the younger generation. Junk meals contain a lot of fat and sugars, oils, salt, and excessive calories and have low nutritional value and quality. Many people like junk food as it has a delicious flavour. Junk food has unique tastes as it lets in a solid bunch of spices that make it tasty. Children like junk food the most and want to have them for breakfast and as snacks in the evening. Whether it’s any occasion, party or celebration, people prefer to eat junk food. We all must have seen that different varieties of fast food items are served during weddings or birthday parties.
Our life is becoming busy day by day, so we are going for easily made food like fast food and junk food. The junk food is smooth and fast to prepare. People can cook them instantly and consume them quickly. For example, making Maggi noodles does not take much time as compared to parathas. Also, it has become a fashion to eat junk food while watching a favourite show, match or movie on the television. Junk food can be easily transported. Now with shipping and delivery online, delivery of junk food is just a click away. The meal reaches the doorstep within 20 to 30 minutes.
Harmful Effects of Junk Food on Health
Junk food has high cholesterol and poor concentration. They are less nutritious and provide us with less energy. By eating junk food, fat accumulates in the body, and we become lazy. It gives rise to various health problems like obesity, diabetes, heart disease, blood pressure, etc. Mental disorders, loss of balance and lack of concentration can also occur due to excessive eating of junk food. Consumption of junk in early childhood can result in behaviour-associated problems like hyperactivity, aggressiveness, etc. Dental cavities can also be formed due to the excess consumption of junk food.
Ways to Avoid Junk Food
Eliminating the temptation for junk food and developing an awareness of fitness can help in avoiding junk food. We should not let our children get habituated to junk food. We must stop them from eating outside and make them eat home-cooked food. Keeping good food nearby and having meals right on time may help in this direction. The habit of eating junk food can be avoided by strong willpower and awareness of the side effects associated with them. People must be educated about the harmful effects of junk food on health. This will surely help in avoiding junk food and developing healthy eating habits.
Students must have found the Harmful Effects of Junk Food Essay useful for practising essay writing skills. They can get the study material and latest updates on CBSE/ICSE/State Board/Competitive Exams at BYJU’S.
Frequently Asked Questions on the Harmful Effects of Junk Food Essay
What are the impacts of junk food.
In the long run, junk food can cause stomach and colon upset, constipation, diarrhoea, skin rashes and infections.
Can junk food be addictive?
Yes, continuous consumption of junk food can lead to addiction in children and also adults. Certain additives in junk food can make us crave repetitive consumption of the same.
How to control the urge to have junk food?
Choose and select natural, home-cooked food which tastes similar to junk food.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

Counselling

It’s a wonderful world — and universe — out there.
Come explore with us!
Science News Explores
Warning junk foods can harm a teen’s brain.
Though hard to resist, these foods pose risks to learning and mental health

Adolescent brains have a hard time resisting junk food. Researchers now are showing that high-fat and high-sugar diets — such as burgers, fries and sweets — can lead to disturbing changes in mental health.
happy_lark/iStock/Getty Images Plus
Share this:
- Google Classroom
By Sharon Oosthoek
November 19, 2020 at 6:30 am
“You are what you eat.” When people say that, they mean a healthy diet can boost your health. But the opposite is also true. In fact, if you’re between the ages of 10 and 19, eating too much junk food can harm your body and your brain.
Junk food shapes adolescent brains in ways that impair their ability to think, learn and remember. It can also make it harder to control impulsive behaviors, says Amy Reichelt. It may even up a teen’s risk of depression and anxiety, she notes.
Reichelt is a brain and nutrition specialist at Canada’s Western University in London, Ontario. Adolescents are more sensitive than any other age group to foods with a lot of processed fat and sugar, she says. She is part of a group of scientists around the world who have been studying why.
Educators and Parents, Sign Up for The Cheat Sheet
Weekly updates to help you use Science News Explores in the learning environment
Thank you for signing up!
There was a problem signing you up.
She and two other researchers at Western recently reviewed more than 100 studies (including their own) about how poor food choices can impact adolescent brains. They described what they learned in the May issue of The Lancet Child and Adolescent Health .
One problem: Adolescent brains are not yet fully formed . And that actually leads to three problems in one, says Reichelt. First, adolescent brains are still developing the ability to assess risks and control actions. Second, teen brains get more pleasure than adult brains do from rewarding behaviors such as eating junk food. Third, adolescent brains can be more easily influenced by their environment. This can include any stress you’re feeling, any isolation or any drugs you may be taking. It can also be influenced by diet. Together, these all can combine to make junk food both hard to resist and extra bad for teen health.
Brains under construction
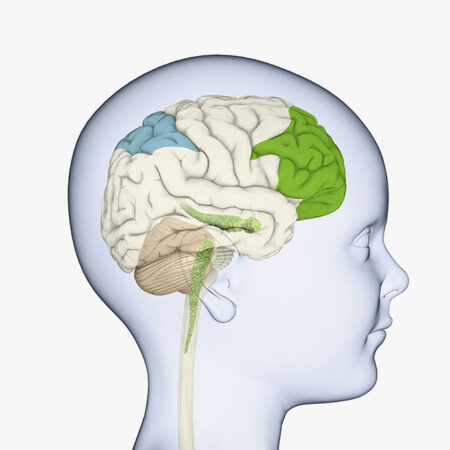
Let’s break that down, starting with preteen and teen behaviors. The brain region that tells us we shouldn’t eat chips all the time — and helps us resist that urge — is the last to mature. Called the prefrontal cortex, this region doesn’t fully develop until we are in our early 20s.
Brain imaging studies show that the prefrontal cortex turns on when we weigh risks and make decisions about how to act.
“Most of our complex brain functions happen in the prefrontal cortex,” says Reichelt. This includes complex math and reading. But she notes that it also includes “how to assess risky behavior.”
At the same time, teen brains get more buzz from rewards. Unlike the prefrontal cortex, the parts of the brain that make us feel good when we do something pleasurable — like eating tasty foods or being with friends — are fully developed by the teen years.
In fact, these regions are even more sensitive when we are young. That’s because of a natural chemical called dopamine (DOH-puh-meen). Dopamine is sometimes called the “feel good” chemical. It lifts our mood when we experience something rewarding. And it is especially active in adolescent brains.
As a neurotransmitter, it zips across the spaces between brain cells. Once it arrives at a new cell, dopamine binds to docking stations there. These molecules are known as receptors . When dopamine docks, those receptors relay the “feel good” signal from the last cell to this new one. That tells the brain that whatever it just experienced is worth getting more of. Adolescents have more dopamine receptors in the brain than do adults. So they get more good vibes from anything they find enjoyable.
The teen brain, thus, has two strikes against it when it comes to resisting junk food. “It has a heightened drive for rewards and reduced self-regulation,” says Reichelt.
That’s a big problem for adolescents because of the third issue: Growing brains can be more easily changed by eating high-fat, high-sugar foods. That’s what Reichelt and her team discovered in their studies of “teenage” mice.
Mouse brains on fat and sugar
Since mouse brains develop very much like our own, they can be used to understand how what we eat affects the human brain. In 2017, Reichelt was part of a team that fed adolescent mice high-fat foods to see how it affected their brains.
One group of mice ate a diet in which 63 percent of their calories came from fat. (That’s a lot of fat. It would be like eating bacon cheeseburgers and ice cream every day.) A second group ate a healthy diet.
As expected, mice eating high-fat food gained weight and put on body fat. But that was not all. These mice also performed worse on memory tests than did mice eating a normal diet.
The researchers tested the mice for what’s known as working memory. It’s the type that allows us to hold onto information long enough to use it. For example, working memory helps you remember which five things you need to buy at the store. Or what time you said you’d meet your friends. It’s also important for reasoning and decision-making. And it involves the prefrontal cortex — that’s the same brain area that helps make decisions.
Reichelt and her team used two different tests to gauge this working memory. In the first, they put the animals in a Y-shaped maze. Each mouse started in the center of the Y shape. From there they were free to explore two of the three arms of the maze. The third arm was blocked off.

Then the researchers opened up the maze’s third arm. Mice will naturally explore their environment and are drawn to new things. Given the chance, they should prefer to visit a new arm of the maze rather than one they’ve already explored. Or they would if they could remember which arms of the maze they had already visited.
Mice eating a healthy diet behaved as expected. They chose to explore the new arm of the maze. But those eating a high-fat diet did not prefer any one arm. The fact they explored all three at random seemed to show they could not remember which parts of the maze they had seen already.
The second test used a maze set up in a tank of murky water. The end of the maze is a platform just under the water’s surface. To get out of the water, a mouse must navigate to the platform by remembering landmarks. (The mice are scooped up to avoid drowning if they can’t find their way.)
Mice fed a healthy diet performed much better than did those eating high-fat chow. The fatter mice were just as good at swimming; they just did not find their way to the platform. This suggests they could not remember the landmarks.
Then the researchers looked at the animals’ brains. Here they found important differences in reelin, a chemical that helps brain cells chat with each other. Mice on high-fat chow had roughly 35 percent less reelin in their prefrontal cortex compared to mice on a healthy diet. The high-fat diet may have made the prefrontal cortex in these mice work less effectively.
People with brain diseases (such as schizophrenia and bipolar disorder) often have lower levels of reelin, too, says Reichelt. “We can’t blame that on junk food in adolescence,” she says. “But it may be a contributing factor [to risk of disease].”

Reichelt found similar behavioral effects in adolescent rats that got daily access to a sugary drink. They showed less desire to explore new things than did rats not fed sugar.
Each rat had been placed in an enclosed square area with different objects in each corner. The rats could explore all four objects. The researchers then removed the rats from the pen for five minutes and swapped the locations of two objects. Then each rat returned to the enclosure. Animals not fed sugar spent more time exploring objects that were now in a new place. This suggests they could tell the objects had been moved. But the sugar-fed rats spent just as much time with the unmoved objects as they did with the changed ones. It seems they couldn’t tell what had been moved.
Human brains on junk food
Other researchers have found links between brain health and what teenage kids eat. Felice Jacka is one of them. She is an expert in nutrition and psychiatry at Deakin University in Victoria, Australia.

In one 2013 study , she and her team recruited more than 2,000 11- to 14-year-olds living in London, England. Each answered questions about what they ate and how they felt, mentally. The kids were asked how many servings of fruits and vegetables they ate each day. They also were asked how often they ate chips, candy, cookies, fried foods and sugary soft drinks. Then they were sorted into five groups, depending on how healthy their diets were.
Next, the adolescents answered 13 questions designed to figure out if they suffered from depression. The questions asked about their emotions and behavior over the previous two weeks. They were phrased as statements. The kids described if those statements were true, not true or sometimes true. Questions ranged from “I feel miserable or unhappy” and “I didn’t enjoy anything at all” to “I felt so tired, I just sat around and did nothing.”
The researchers scored each kid’s answers for signs of depression. Adolescents who ate the most junk food were nearly 50 percent more likely to show signs of depression.
Why might eating junk food be linked to depression? The data are unclear. Some research suggests that processed foods, such as lunch meat, increases inflammation in the body and the brain. Inflammation is one of the body’s responses to cellular injury and involves swelling. Other research has linked inflammation with depression. In one study , researchers found that people with depression had 30 percent more brain inflammation than did people who were not depressed.
Good fat, bad fat
The good news is that you can make food choices that support a healthy brain.
“The brain is the most fat-rich organ we have,” notes Alexandra Richardson. She is an expert in how diet affects the brain and a researcher at the University of Oxford in England. “And where does it get its fats? From what we put in our bodies.”

But not all fats are the same. Our brains need a type known as omega-3 fats. These helpful fats are found in fish, flaxseed and some oils. These fats help build the membrane that surrounds brain cells. Brain cells need membranes to hold them together and to communicate well with each other.
In one 2005 study , Richardson and her team showed improved mental health in children who took omega-3 supplements. The 117 children who took part were between the ages of five and 12. All had problems with attention, hyperactivity and impulsivity. They also struggled with reading and spelling.
Over three months, about half the children took omega-3 pills. The others took look-alike pills with no fats. Such inactive “treatments” are known as placebos (Pluh-SEE-bohs). Compared to kids who got the placebo, those who took omega-3 pills showed improved attention and ability to control their hyperactive, impulsive behavior. Their reading and spelling scores also went up. This may have reflected being able to pay closer attention in class.
Junk food may trigger attention-related problems because it does not contain the good fats needed to build healthy brain cells, says Richardson. But downing foods with more good fats can support healthy brains.

Exercise for your brain
Research shows exercise can be a good way to fend off damage from junk food, notes Cassandra Lowe. She works at Western University, where together with Reichelt she has studied kids’ brain and nutrition.
Two important things happen in the brain when we exercise. The first is that the brain’s reward system — the one that feels good when we do something we like — becomes less sensitive to food cues. While scientists don’t quite know why, the outcome is a good thing. “We don’t find high-calorie foods as rewarding,” explains Lowe.
Exercise also triggers the body to make a protein called BDNF. That stands for brain-derived neurotrophic (Neur-oh-TROH-fik) factor. BDNF helps brain cells grow. It also strengthens links between them.
This means exercise can boost strong connections between the prefrontal cortex and other brain regions. When that happens, the prefrontal cortex “can exert control better,” says Lowe. In other words, better connections help us weigh risks, make informed decisions on how to act, and curb our impulses.
What is the take-home message for kids? Many already know that junk food can make people fat and physically unhealthy, says Richardson. Most don’t often understand that it also can lead to unhealthy brains.
Processed and fried foods, such as cold cuts, store-bought baked goods, candy and chips don’t have many of the nutrients our bodies and brains need, Richardson says. Kids need to understand that they tend to be rich both in calories and in “concoctions of chemicals that do not support human health — physical or mental.”
More Stories from Science News Explores on Health & Medicine

U.S. lawmakers look for ways to protect kids on social media

9 things to know about lead’s health risks — and how to curb them

Community action helps people cope with Flint’s water woes

Health problems persist in Flint 10 years after water poisoning

Family, friends and community inspired these high school scientists

The teen brain is especially vulnerable to the harms of cannabis
Synthetic biology aims to tackle disease and give cells superpowers

Being a teen has always been hard; now it’s especially so

What happens when you eat too much junk food?
Eating junk food on a regular basis can lead to an increased risk of obesity and chronic diseases like cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and some cancers.
Why do I overeat junk food?
Overeating certain foods doesn’t mean you’re a gluttonous or weak-willed person. It means your body has learned to crave junk food. Intensely addictive processed foods can spike your blood sugar, hijack your brain chemistry and drive you to seek out more.
What should I do if I ate too much junk?
Water. In addition to anything caffeinated, you’ll also want to sip some plain water throughout the day. Hydration is key, especially after a night of overconsumption. Water will help flush out toxins, aid digestion, and fight gas-induced bloating.
How much junk food is too much?
Remember that junk foods are okay to eat occasionally, but they should not make up more than 10% of your daily energy intake. In a day, this may be a simple treat such as a small muffin or a few squares of chocolate. On a weekly basis, this might mean no more than two fast-food meals per week.
What are the 10 harmful effects of junk food?
- It can cause memory and learning problems.
- It can cause type 2 diabetes.
- It can trigger digestive problems.
- It causes fatigue and weakness.
- Causes depression among teenagers.
- It causes fluctuations in blood sugar levels.
- It affects the brain function.
- It increases the risk of heart disease.
How eating junk food affects your body?
Long-term effects of eating junk food Eating a poor quality diet high in junk food is linked to a higher risk of obesity, depression, digestive issues, heart disease and stroke, type 2 diabetes, cancer, and early death. And as you might expect, frequency matters when it comes to the impact of junk food on your health.
How do you break a junk food addiction?
- Plan ahead. There’s no better way to handle cravings than planning your meals and snacks ahead of time.
- Shop the perimeter.
- Eat healthy fats.
- Eat enough protein.
- Taste the rainbow.
- Think about junk food differently.
- Focus on adding healthy foods.
What are the 10 most addictive foods?
- French fries.
- Cheeseburger.
- Soda (not diet)
How do you beat a junk food addiction?
- Decide that you want to change.
- Precisely articulate what triggers your cravings.
- Make a meal plan.
- Find yourself a distraction tactic.
- Write out and regularly re-read your goals.
- Don’t keep temping food in the house.
- Get you’re family & friends on board.
- Keep a food diary.
How long does junk food stay in your system?
Food typically takes 24-72 hours to digest, but the grease and trans fat inside a Big Mac means the digestion time for the McDonald’s signature burger can easily go beyond three days.
What should I drink after overeating?
Just sip on a cup of water (about 8 ounces) after a big meal. It can help your body get rid of excess salt you likely got from your meal. It can also keep you from getting constipated. Continue to drink water over the rest of the day to keep yourself hydrated.
Does drinking a lot of water flush out junk food?
It regulates your body temperature. It does all this and more, for zero calories. Yet drinking water alone won’t wipe out the effects of a bad diet.
How does junk food affect your energy?
Drain your energy A quick hit of refined carbohydrates and sugar causes a spike in your blood sugar, which prompts your body to produce a surge of insulin to quickly bring it down. This spike-and-crash cycle can leave you feeling tired and cranky.
What is the healthiest unhealthy food?
- 8 Popsicles.
- 7 Hamburgers.
- 6 Nachos and Salsa.
- 5 Pretzels.
- 4 Frozen Yogurt.
What are 5 negative effects of Eating junk food?
- Obesity. One of the most common and perceivable effects of junk food is a rise in obesity in an individual.
- Learning and memory problems.
- Loss of appetite and digestion.
- Mental impact leading to depression.
- Inadequate growth and development.
Why should we not eat junk food essay?
You become prone to cardiovascular diseases due to the consumption of bad cholesterol and fat plus sodium. In other words, all this interferes with the functioning of your heart. Furthermore, junk food contains a higher level of carbohydrates. It will instantly spike your blood sugar levels.
How does junk food affect your heart?
Consuming high-fat, high-salt, high-sugar, or processed foods can directly contribute to the build-up of plaque in the arteries. As this plaque blocks and constricts blood flow throughout your body, the result is a dramatically higher risk for heart disease, heart attack, and stroke.
How do I gain self control with food?
- Keep a food diary. Write down what you eat, how much you eat, when you eat, how you’re feeling when you eat and how hungry you are.
- Tame your stress.
- Have a hunger reality check.
- Get support.
- Fight boredom.
- Take away temptation.
- Don’t deprive yourself.
- Snack healthy.
Does not eating junk change your voice?
Passive Voice: Let not junk food be eaten.
What foods satisfy your cravings?
- Fresh Fruit. Fruit is naturally very sweet and a great choice when you get a sugar craving.
- Greek Yogurt. Greek yogurt tastes creamy and indulgent, but it’s also really healthy.
- A Hot Drink.
- Dark Chocolate.
- Fruit and Nut Butter.
- Cottage Cheese.
- Banana Ice Cream.
What food can cause addiction?
Consuming “highly palatable” foods, or foods that are high in carbohydrates, fat, salt, sugar, or artificial sweeteners, can trigger an addictive-like process in some individuals, activating reward-processing regions in the brain and releasing “feel-good” chemicals such as dopamine and serotonin.
Is food addiction a mental illness?
Food addiction is a mental health issue in which a person becomes addicted to food, especially processed junk foods. Numerous scientific studies confirm that food addiction involves the same brain areas as drug addiction ( 5 , 6 , 7 ).
What is the most craved food in the world?
Chocolate is the most widely and frequently craved food. People readily admit to being ‘addicted to chocolate’ or willingly label themselves as ‘chocoholics’. A popular explanation for this is that chocolate contains mood-enhancing (psychoactive) ingredients that give it special appeal.
Why do we binge eat at night?
You may be overeating at night because your body is compensating for something it needs. Perhaps you aren’t eating enough during the day, which leads to insatiable hunger in the evening. Or maybe you aren’t getting adequate sleep, which leaves your body feeling tired and craving carbohydrate-rich foods.
Will I lose weight if I stop eating junk food?
Most people experience weight loss when they cut out unnecessary sugar and fats from their diet. Eating healthier, nutrient-filled foods also improves muscle tone.
Privacy Overview
- Research Paper
- Book Report
- Book Review
- Movie Review
- Dissertation
- Thesis Proposal
- Research Proposal
- Dissertation - Abstract
- Dissertation Introduction
- Dissertation Review
- Dissertat. Methodology
- Dissertation - Results
- Admission Essay
- Scholarship Essay
- Personal Statement
- Proofreading
- Speech Presentation
- Math Problem
- Article Critique
- Annotated Bibliography
- Reaction Paper
- PowerPoint Presentation
- Statistics Project
- Multiple Choice Questions
- Resume Writing
- Other (Not Listed)
The Causes and Effects of Eating Junk Food (Essay Sample)
Customer order
Other Topics:
- Video Games and Juvenile Delinquency Description: With many expressing doubt on the credibility of video games towards mentoring of future lives among the youth, psychologists have argued that video games have a correlation with aggression... 2 pages/≈550 words | 5 Sources | APA | Literature & Language | Essay |
- Organizational Behavior in Healthcare and Management Thinking Description: In the field of healthcare management, medical errors are a real and alive threat to patient safety and, therefore, a grave threat to public health... 13 pages/≈3575 words | 10 Sources | APA | Literature & Language | Essay |
- Descriptive Summary Description: The author evaluates the various facets of paradigms and their relevance in the society. He makes various claims about the comparative features of paradigms.... 1 page/≈275 words | 1 Source | APA | Literature & Language | Essay |
- Exchange your samples for free Unlocks.
- 24/7 Support
Causes and Effects of Fast Food: Essay Example
Essay about fast food: introduction, causes of fast food: essay body paragraph, effects of fast food: essay body paragraph, fast food causes and effects: conclusion, reference list.
Food is an integral part of any culture and society around the globe. Until the last century, most people used to eat fresh, home-cooked food. Eating was a process that required specific preparations. However, now, we see that they prefer to eat fast food such as pizza, hamburgers, or fried chicken.
These fast-food restaurants have become common on our streets, and people of all ages visit them. The popularity of these restaurants has increased internationally. There are many reasons why fast food has become popular, and fast food also has some serious effects on humans and society.
The basic question is, what made fast food so popular this last century? One answer would be that the change in lifestyle compared to before is a cause for this. It pushes workers or people to eat fast food than cook food themselves.
For instance, two working parents are a good example of this. Due to their jobs, they do not have time to cook for their children or even themselves. As a consequence, they find it easier to order from these fast food restaurants rather than cook. That is why they favor fast food over their own cooked food.
Another cause of fast food usage is long working hours, which may also lead people to eat outside the home. There are many fast-food businesses in our cities. Some are McDonald’s, Burger King, Pizza Hut, etc. We can make a long list with hundreds of names from these restaurants.
During the last couple of years, we saw a lot of advertisements and promotions for those restaurants. Nevertheless, there still remains a question of why they spend to promote ineffective food. What are the reasons for this? The answer is that fast food is easy to cook. It does not take long to cook, and it is readily available. The shareholders of these businesses have their own goals, that of the profits they get from these restaurants.
Above, we have seen the causes that may have led to the flourishing of the fast-food industry. However, what is more important, is its effects on society and human beings. The primary effect that fast food has on human beings is that it can get your health in danger status. First, fast food can cause vitamin deficiencies that may, in turn, help to cause diseases.
Obesity is one of the consequences of fast food on the human body. Obesity comes because fast food is the factor that enriches the body with fats. So people will become less healthy, less effective, and less productive, and this is the conclusion of obesity (Adams, 2007, pp. 155).
Another serious effect of the popularity of fast food presences is the loss of the family tradition of eating together. The family used to eat together, and thus they had the opportunity to talk with each other about daily problems.
Fast food also affects the income of the family. The conclusion is that fast food is more expensive than the food you cook for yourself.
In conclusion, it can be said that fast food has been born out of the modern way of living in our societies. Unfortunately, its effects on the human body and health are unfavorable. It also has other adverse effects on the income of a family. It would be best to avoid eating fast foods as much as possible.
Adams, C., 2007. Reframing the obesity debate: McDonald’s role may surprise you. Journal of Law, Medicine, and Ethics, no. 35: pp. 154-157.
Cite this paper
- Chicago (N-B)
- Chicago (A-D)
StudyCorgi. (2020, January 12). Causes and Effects of Fast Food: Essay Example. https://studycorgi.com/fast-food-causes-and-effects/
"Causes and Effects of Fast Food: Essay Example." StudyCorgi , 12 Jan. 2020, studycorgi.com/fast-food-causes-and-effects/.
StudyCorgi . (2020) 'Causes and Effects of Fast Food: Essay Example'. 12 January.
1. StudyCorgi . "Causes and Effects of Fast Food: Essay Example." January 12, 2020. https://studycorgi.com/fast-food-causes-and-effects/.
Bibliography
StudyCorgi . "Causes and Effects of Fast Food: Essay Example." January 12, 2020. https://studycorgi.com/fast-food-causes-and-effects/.
StudyCorgi . 2020. "Causes and Effects of Fast Food: Essay Example." January 12, 2020. https://studycorgi.com/fast-food-causes-and-effects/.
This paper, “Causes and Effects of Fast Food: Essay Example”, was written and voluntary submitted to our free essay database by a straight-A student. Please ensure you properly reference the paper if you're using it to write your assignment.
Before publication, the StudyCorgi editorial team proofread and checked the paper to make sure it meets the highest standards in terms of grammar, punctuation, style, fact accuracy, copyright issues, and inclusive language. Last updated: November 8, 2023 .
If you are the author of this paper and no longer wish to have it published on StudyCorgi, request the removal . Please use the “ Donate your paper ” form to submit an essay.
Welcome Guest!
- IELTS Listening
- IELTS Reading
- IELTS Writing
- IELTS Writing Task 1
- IELTS Writing Task 2
- IELTS Speaking
- IELTS Speaking Part 1
- IELTS Speaking Part 2
- IELTS Speaking Part 3
- IELTS Practice Tests
- IELTS Listening Practice Tests
- IELTS Reading Practice Tests
- IELTS Writing Practice Tests
- IELTS Speaking Practice Tests
- All Courses
- IELTS Online Classes
- OET Online Classes
- PTE Online Classes
- CELPIP Online Classes
- Free Live Classes
- Australia PR
- Germany Job Seeker Visa
- Austria Job Seeker Visa
- Sweden Job Seeker Visa
- Study Abroad
- Student Testimonials
- Our Trainers
- IELTS Webinar
- Immigration Webinar
IELTS Writing Task 2 Discursive Essay of Band 8.0 – Topic : Health and Food
Updated On Oct 18, 2021

Share on Whatsapp
Share on Email
Share on Linkedin

Limited-Time Offer : Access a FREE 10-Day IELTS Study Plan!
Scientists agree that people are damaging their health by eating too much junk food. Some people think that the answer to this problem is to educate people. Others think education will not work. Discuss both views and give your opinion.
Get Evaluated for FREE:
Do you have an essay on this topic? Please post it in the comments section. One of our IELTS trainers will evaluate your essay from an examiner’s point of view and reply to the comment. This service is completely FREE of cost.
Discussion essay
Introduction
- Paraphrase the topic of the essay.
- Give an insight into what can be expected from the essay.
- Paragraph 1- On the one hand, education can stop people from further damaging their health by consuming fast food. From my perspective, although many eat fast food because of its affordability, the root cause of this lies in the fact that they are not adequately educated about the damaging consequences of junk food consumption, and the benefits of healthy eating.
- On the other hand, education alone will not work. The fact is that many people who are aware of the consequences of eating junk food are unduly pessimistic.
Conclude the topic of the essay by making an inference from it.
Sample Essay
Fast food has been proven to be the main culprit of obesity and other diet-related diseases, however, the habit of eating an excessive amount of fast food has never lost momentum. One school of thought holds that education can rectify this situation. However, there is still much scepticism about the effect of education. In this essay, both of these viewpoints will be analysed.
On the one hand, education can stop people from further damaging their health by consuming fast food. From my perspective, although many eat fast food because of its affordability, the root cause of this lies in the fact that they are not adequately educated about the damaging consequences of junk food consumption, and the benefits of healthy eating. According to recent studies conducted in the neighbourhoods where fast food stores are easily accessible, more than two-quarters of the residents know or care little about what they are consuming and how it can affect their health.
On the other hand, education alone will not work. The fact is that many people who are aware of the consequences of eating junk food are unduly pessimistic. In other words, they are often in denial and convince themselves that unhealthy habits are not as terrible as the media want them to believe. Secondly, it is very difficult for fast food eaters to reduce their dependency on fast food because it contains many addictive artificial flavours.
All things considered, education is one viable solution to put a stop to the obesity epidemic, but it does not suffice. I feel that more efforts should be made to combat obesity.
- To be the main culprit of: be the main reason for
- To lose momentum: become unpopular
- Accessible (adj. ) easily bought
- Because of its affordability: because it is cheap
- To be in denial: be unwilling to accept
- Reduce dependency: become less dependent
- Obesity epidemic: the problem of obesity
- It does not suffice: it is not enough.
- Combat (v.) fight against
Band 9 Sample Essay
Unlock Essay
Signup/login to unlock band 9 essay and ace the IELTS
In the wake of deteriorating and appalling health conditions of people today, scientists hold unhealthy food as the prime driving force behind it. Some people conjecture that this problem could be contained with proper education, while others don’t believe that could alleviate the issue alone. In this essay, we shall look upon both aspects and how the latter opinion is somehow correct.
The junk food on the platter has been considerably thriving owing to people’s convenience when it comes to having processed food just a doorstep away. A surge in the junk food market and its consumption, as some people say, is due to the oblivion of the generation and society, at large, today. People are ignorant when it comes to the causative, hazardous and catastrophic dynamics of such unhealthy, pernicious and st times, unhygienic food items that may render them frail, severely ill and deficient in the terms of nutrition. Hence, as is proposed by some, the government should take necessary steps in acknowledging and making people aware of such routine and dietary patterns that in the long run, could even be fatal.
However, education and information alone can’t wrap up the wound as people despite knowing the ill effects tend to drag such health sermons at the back seat and hence go by the sporadic sensation of taste. Technology and the modern digital era is most certainly the first and primary cause of it, as now the favourite food is just a “Click & Buy ” away. Not just that, with the upsurge of the digital epoch, the very idea and reflection of it of making the lives easier has indeed, made the lifestyle unhealthier than ever. Sedentary lifestyle, dormant state, frozen feet and barren body are just some of the deleterious physical effects of it, without even getting to the other aspects of it. With a wide plethora of options and alternatives which comes along with the new age, people choose the best ones. Now in order to keep up with the ever-growing demand and neck-jolting strife, the inculcation of the tastier and hazardous sweet poisons to the food material grows. The more people get away with the gustatory aspect of it, the worse they do with their physiologies. In such a case, education alone can’t tackle the demon of junk food, rather limiting and monitoring the advertisements or even precautions while advertising it should be acknowledged. Increasing the taxes on junk foods could yet again be a great alternative as money matters.
With this we can safely conclude that other than education alone there are some different prophylactic measures that could be taken to halt and digress the fast-moving junk food trend, thereby, saving people from the perils of derelict health.
More Writing Task 2 Essay Topics
- Students Today Can Access Information Online So Libraries Are Not Necessary
- In Some Countries Secondary Schools Aim To Provide a General Education Across a Range Of Subjects
- Some People Prefer To Directly Help Or Support People Who Need It In The Local Community
- Modern Technology Now Allows Rapid Uncontrolled Access
- Prevention Is Better Than Cure Out Of A Country Health Budget A Large Proportion
Also check:
- IELTS Essay Topics
- Tips to write introduction in IELTS Writing Task 2
- Tips to write great writing essay
- IELTS Sample essays
- IELTS Writing task 2 Preparation Tips
- IELTS Writing tips
- How to get band 8 in IELTS Writing Task 2
- IELTS Writing recent actual test
- Direct question essay
- IELTS Band 9 essays
- Advantage and Disadvantage Essays
- IELTS Writing Answer sheet
- IELTS map vocabulary
- IELTS Writing Task 1 Connectors
Practice IELTS Writing Task 2 based on Essay types

Start Preparing for IELTS: Get Your 10-Day Study Plan Today!
Janet had been an IELTS Trainer before she dived into the field of Content Writing. During her days of being a Trainer, Janet had written essays and sample answers which got her students an 8+ band in the IELTS Test. Her contributions to our articles have been engaging and simple to help the students understand and grasp the information with ease. Janet, born and brought up in California, had no idea about the IELTS until she moved to study in Canada. Her peers leaned to her for help as her first language was English.
Explore other Discussion Essays

Nehasri Ravishenbagam

Courtney Miller

Janice Thompson

Post your Comments
Recent articles.

Kasturika Samanta

Our Offices
Gurgaon city scape, gurgaon bptp.
Step 1 of 3
Great going .
Get a free session from trainer
Have you taken test before?
Please select any option
Get free eBook to excel in test
Please enter Email ID
Get support from an Band 9 trainer
Please enter phone number
Already Registered?
Select a date
Please select a date
Select a time (IST Time Zone)
Please select a time
Mark Your Calendar: Free Session with Expert on
Which exam are you preparing?
Great Going!

Kids Eating Too Much Junk Food: Causes, Effects, and Solutions

Childhood obesity has become a significant problem in many countries around the world. One of the main reasons for this is the increasing consumption of junk food by kids. While it’s okay to indulge in junk food occasionally, it’s essential to ensure that our children are eating a balanced diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and other healthy foods. In this article, we’ll explore the causes, effects, and solutions to the problem of kids eating too much junk food.
Causes of Kids Eating Too Much Junk Food:
Busy lifestyle:.
Many parents have busy lifestyles and often rely on fast food and convenience foods to feed their kids quickly. This can lead to a diet high in junk food, which lacks essential nutrients.
Advertising:
Junk food companies spend billions of dollars each year advertising their products to children, making it hard for parents to resist their children’s demands for these unhealthy foods.
Peer Pressure:
Kids are often influenced by their friends and peers. If their friends are eating junk food, they may feel the need to do the same.
Effects of Kids Eating Too Much Junk Food:
Consuming too much junk food can lead to weight gain and obesity in kids. This can put them at risk for numerous health problems, including diabetes, heart disease, and high blood pressure.
Poor Nutrition:
Junk food is typically high in calories, sugar, and unhealthy fats. Consuming too much of these foods can lead to a lack of essential nutrients, which are necessary for growth and development.
Behavioral Problems:
Some studies have linked a diet high in junk food to behavioral problems in children, including hyperactivity and attention deficits.
Solutions to Kids Eating Too Much Junk Food:
Educate your child:.
Teach your child about the importance of a balanced diet and why it’s essential to limit their consumption of junk food.
Encourage Healthy Eating:
Encourage your child to eat plenty of fruits, vegetables, and other healthy foods. Make healthy snacks readily available and limit the amount of junk food in your home.
Set an Example:
Children often model their behavior after their parents. Set an example by eating healthy foods yourself and avoiding junk food.
Get Active:
Encourage your child to get plenty of exercise each day. This can help them maintain a healthy weight and reduce their risk of health problems associated with a sedentary lifestyle.
In conclusion, while it’s okay for kids to indulge in junk food occasionally, it’s essential to ensure that they are eating a balanced diet that includes plenty of healthy foods. By educating your child, encouraging healthy eating, setting an example, and promoting physical activity, you can help your child develop healthy habits that will last a lifetime.
FOR MORE VALUABLE TIPS BUY OUR PARENTING COURSES AT https://www.kidzoot.com/courses/
CONSULT YOUR PERSONAL PARENTING SOLUTIONS VIA APPOINTINTMENT AT https://www.kidzoot.com/appointment-booking/
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Subscribe to Our Newsletter
Thank you for subscribing to our newsletter! You’ll now receive the latest news, tips, and resources to help you navigate the joys and challenges of parenting. We’re dedicated to supporting you on your journey, so keep an eye on your inbox for inspiring content and expert advice.
Insert/edit link
Enter the destination URL
Or link to existing content
- Free Samples
- Premium Essays
- Editing Services Editing Proofreading Rewriting
- Extra Tools Essay Topic Generator Thesis Generator Citation Generator GPA Calculator Study Guides Donate Paper
- Essay Writing Help
- About Us About Us Testimonials FAQ
- Studentshare
- Effects of eating too much junk food
Effects of eating too much junk food - Essay Example

- Subject: English
- Type: Essay
- Level: Undergraduate
- Pages: 2 (500 words)
- Downloads: 6
- Author: kesslerignacio
Extract of sample "Effects of eating too much junk food"
Effects of eating too much Junk Food Among the foods that are loved by most people in the world is junk food. In relation to this fact, the essay will mainly expound on the effect of junk food on the health of the consumers. Among the questions, the essay will address include: What is junk food? Why do people consume junk food? And What are the effects of consuming junk food? According to Jia (94), junk food constitute of French fries, potato chips, or soda. Many people love to consume the foods because they very tasty, cheap in terms of price, and easy to prepare.
Despite people having many reasons for consuming junk foods, it is evident that their negative implications on a consumer’s health are very many. Junk food affects children’s diet. This is evidenced by the fact that children who consume many snacks loose appetite for meals. In relation to this assertion, it is evident that improper diet results in nutritional imbalance for children, which has the potential to retard their growth and development. For instance, Jia (95) claims that imbalance of nutrition affects the development of a child’s brain and body.
Also, children who consume lots of junk food such as chips, candy and burgers become overweight. Majority of the heart diseases, unfortunately, are as a result of adding up extra weight. Unfortunately, overweight children tend not to like exercising. Such children not only become clumsy, but also lose confidence in themselves. Additionally, it is evident that obesity may result in shortness of breath as well as enhance the development of asthma in addition to sleep apnea. Consumption of high amounts of fast food also affects the formation of skin and bones.
This is evidenced by the fact that food rich in carbohydrates increase blood sugar levels triggering acne. Additionally, the consumptions of foods rich in carbs and sugar make the bacteria residing inside the mouth to produce acid that destroy tooth enamel, one of the contributing factors in dental cavities. Consumption of junk foods also hampers with the health of adults. According to Jia (94), the food rich in calories results in the accumulation of fat in the body, especially in elderly people.
Too much fat in the body can lead to the occurrence of diabetes, especially when the disease is genetic. Since junk food contains large amounts of calories, consuming junk food is one of the causes of serious diseases in adults (Jia 95). For instance, junk food clogs arteries, which means it affects the flow of blood around the body. Unfortunately, this complication can kill a person because of insufficient supply of deoxygenated blood to the needed sites. Consumption of high amounts of carbohydrates and calories (constituents of fast food), causes a spike in blood sugar level that, as a result, affects the normal insulin response.
Frequent rise in blood sugar is the key contributor factors for insulin resistance as well as type 2 diabetes. Too much sodium in the body also contributes to high blood pressure. Sorry to say, the combination of high blood pressure with high cholesterol is among the leading causation of heart diseases and stroke. In conclusion, fast food constitute of foods that are quick to serve and prepare. They are loved because they are sweet and easy to prepare. The effects of fast food in a person range from causing obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular disease to causation of death.
Work CitedJia, Peter Y. Simple Approaches to Writing Short Essays: (for Students of English As a Second Language). New York: iUniverse, Inc, 2006.
- effects of watching too much tv
- Cited: 0 times
- Copy Citation Citation is copied Copy Citation Citation is copied Copy Citation Citation is copied
CHECK THESE SAMPLES OF Effects of eating too much junk food
What is heathy eating, removal of junk foods from vending machines, the importance of healthy eating, considering cases regarding eating disorder and smoking in senior school students, consequences of eating fast food, causes and effects of fast foods, child development junk food, unhygienic food items and their effects.

- TERMS & CONDITIONS
- PRIVACY POLICY
- COOKIES POLICY

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Other long-term effects of eating too much junk food include tooth decay and constipation. Soft drinks, for instance, can cause tooth decay due to high amounts of sugar and acid that can wear down the protective tooth enamel. Junk foods are typically low in fiber too, which has negative consequences for gut health in the long term.
As for the effects of eating junk food, one of the common effects is that it will lead to heart diseases. It is said that most of the junk food contain lower nutrients but higher in calories, sugar, and salt. Such as potato chips, French fries, and some other kinds of fried and full of carbohydrates food contain large amount of salt and sugar ...
The key causes of fast food popularity include busy lifestyles, advertising, attractiveness as well as the convenience in accessing or preparing it. People, however, need to be wary of the effects of the junk food that include weight gain and such diseases as diabetes, asthma, and dementia among others.
CAUSES AND EFFECTS OF EATING JUNK FOOD 3. Junk food affects the consumers' health de trimentally sin ce it is primarily characterized. by saturated fat, sugar, and salt. Overc onsumption exposes individuals to the risk of obesity, diabetes, cancer, and heart diseases that have become common not only a mong the aging.
Impact of Junk Food. Junk food is the easiest way to gain unhealthy weight. The amount of fats and sugar in the food makes you gain weight rapidly. However, this is not a healthy weight. It is more of fats and cholesterol which will have a harmful impact on your health. Junk food is also one of the main reasons for the increase in obesity nowadays.
What is junk food? 'Junk foods' are foods that lack nutrients, vitamins and minerals, and are high in kilojoules (energy), salts, sugars, or fats. Junk food is so called because it doesn't play a role in healthy eating, especially if you eat too much of it. Junk food is also known as 'discretionary food' or 'optional food'.
Based on the reports, more than one-third of the adults eat junk food several times a week (Bauer et al., 2009). Studies have proven that Junk food tends to cause obesity (central adiposity), a primary concern of heart diseases and other non-communicable diseases (Rouhani et al., 2012; Musaiger, 2014). Poor nutrition could result in reduced ...
March 1, 2021. Hamburgers, fries, sugary sodas, and other less healthy foods may cause inflammation, a key player in the formation of artery-clogging plaque. Eating foods such as red meat and sugary treats may trigger inflammation, raising your risk of cardiovascular disease. But a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and other anti-inflammatory ...
1. Adverse Effects on Physical Health. Junk food is typically laden with excessive amounts of added sugars, unhealthy fats, and refined carbohydrates. The consumption of these components is linked to a host of negative health outcomes, including obesity, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases. Excessive intake of added sugars found in ...
Junk food diets are often associated with a reduction in the diversity of the gut microbiome. This means that there are fewer different types of microorganisms in the gut, which can have a negative impact on overall health. Shift toward harmful bacteria: Junk food consumption is linked to an increase in potentially harmful bacteria in the gut.
Effects on Mental Health. The effects of junk food extend beyond physical health, impacting mental well-being. Studies have shown a correlation between high junk food consumption and mental health disorders, including depression and anxiety. The high sugar content can lead to fluctuations in blood sugar levels, causing mood swings and fatigue.
By eating junk food, fat accumulates in the body, and we become lazy. It gives rise to various health problems like obesity, diabetes, heart disease, blood pressure, etc. Mental disorders, loss of balance and lack of concentration can also occur due to excessive eating of junk food. Consumption of junk in early childhood can result in behaviour ...
People who take junk food risk getting heart diseases. Junk food has high content of fat and cholesterol that leads to clogging of the heart arteries. Once the arteries are blocked a person can suffer from heart attacks that could lead to death or cause strokes. Therefore, overindulgence fast foods such as chips may pose death risks and ...
But the opposite is also true. In fact, if you're between the ages of 10 and 19, eating too much junk food can harm your body and your brain. Junk food shapes adolescent brains in ways that impair their ability to think, learn and remember. It can also make it harder to control impulsive behaviors, says Amy Reichelt.
Also, fast foods cause depression to children. One major cause of eating too much Fast food is that it causes obesity to children. Eating fast foods can be delectable , and children favor junk foods over eating cooking meals at homes. Because fast foods are tasty, children consume too much junk foods constantly.
Overeating causes the stomach to expand beyond its normal size to adjust to the large amount of food. The expanded stomach pushes against other organs, making you uncomfortable. This discomfort can take the form of feeling tired, sluggish or drowsy. Your clothes also may feel tight, too. Eating too much food requires your organs to work harder.
Long-term effects of eating junk food Eating a poor quality diet high in junk food is linked to a higher risk of obesity, depression, digestive issues, heart disease and stroke, type 2 diabetes, cancer, and early death. And as you might expect, frequency matters when it comes to the impact of junk food on your health.
Researchers found that eating an unhealthy diet high in processed food can affect people's deep sleep (also known as slow-wave sleep). During this sleep stage, the pituitary gland in the brain releases a burst of growth hormone, which helps build and repair muscles, bones, and other tissues. Deep sleep also boosts cognitive function and memory.
Taking junk food for only five days can deteriorate your memory. This stems from the fact that poor and toxic diet causes chemical reactions leading to inflammation of the hippocampus area of the brain usually associated with memory and recognition. Diets rich in sugar and fat suppress the ability of the brain to learn and form memory.
Obesity comes because fast food is the factor that enriches the body with fats. So people will become less healthy, less effective, and less productive, and this is the conclusion of obesity (Adams, 2007, pp. 155). Another serious effect of the popularity of fast food presences is the loss of the family tradition of eating together.
Sample Essay. Fast food has been proven to be the main culprit of obesity and other diet-related diseases, however, the habit of eating an excessive amount of fast food has never lost momentum. One school of thought holds that education can rectify this situation. However, there is still much scepticism about the effect of education.
Effects of Kids Eating Too Much Junk Food: Obesity: Consuming too much junk food can lead to weight gain and obesity in kids. This can put them at risk for numerous health problems, including diabetes, heart disease, and high blood pressure. Poor Nutrition: Junk food is typically high in calories, sugar, and unhealthy fats.
Too much fat in the body can lead to the occurrence of diabetes, especially when the disease is genetic. Since junk food contains large amounts of calories, consuming junk food is one of the causes of serious diseases in adults (Jia 95). For instance, junk food clogs arteries, which means it affects the flow of blood around the body.