- Guide: Fishbone Diagram

Daniel Croft
Daniel Croft is an experienced continuous improvement manager with a Lean Six Sigma Black Belt and a Bachelor's degree in Business Management. With more than ten years of experience applying his skills across various industries, Daniel specializes in optimizing processes and improving efficiency. His approach combines practical experience with a deep understanding of business fundamentals to drive meaningful change.
- Last Updated: October 19, 2023
- Learn Lean Sigma
The Fishbone Diagram, also known by various other names such as Ishikawa Diagram, Cause and Effect Diagram or 6Ms, is a visual tool used in problem-solving and root cause analysis . Originating from the quality management sector, it is used as a systematic approach to identify, explore, and display possible causes of a specific problem.
Table of Contents
What is a fishbone diagram.
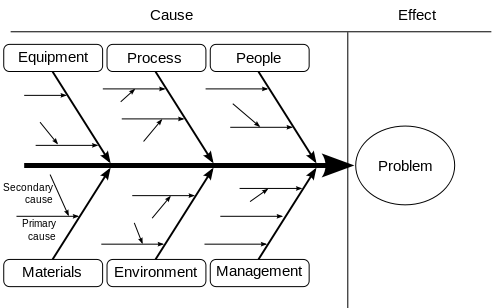
The Fishbone Diagram is a graphical tool used for identifying and organizing possible causes of a specific problem or outcome. The diagram resembles the skeletal structure of a fish, hence its name. At the “head” of the fish is the problem you’re trying to solve, and the “bones” branching off the spine are the multiple potential causes contributing to that problem.
The benefit of a Fishbone Diagram lies in its simplicity. It gives you a structured way to brainstorm and categorize the various factors affecting a specific issue. The diagram can get as detailed as you need it to be, allowing for sub-causes to branch off the main causes, offering even deeper insights.
The Components of a Fishbone Diagram
Head : The fish’s head represents the problem or effect you’re analyzing.
Spine : The long, horizontal line connecting to the head serves as the timeline or sequence of the problem.
Bones : These are the categories of potential causes. They branch off the spine, leading towards the head.
Sub-Bones : These are the more specific factors or sub-causes that stem from the main categories.
Why Use a Fishbone Diagram?
The Fishbone Diagram is a flexible tool that can be used for a range of applications. Here’s why it’s so useful:
1. Easy Visualization:
One of the primary advantages of using a Fishbone Diagram is its ability to simplify complex problems. With all potential causes visually represented in one place, it becomes easier to analyze and discuss the issues.
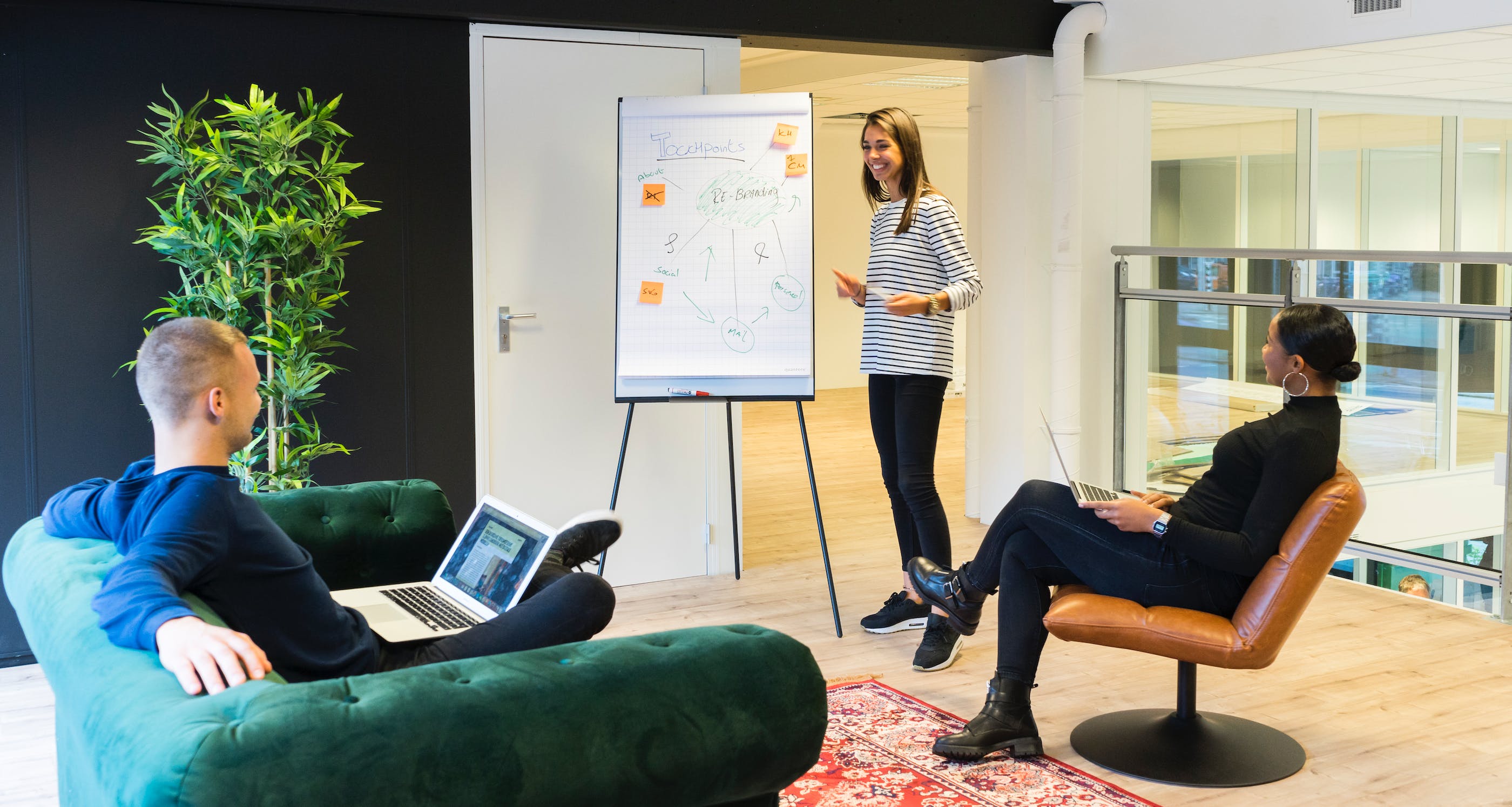
2. Team Collaboration:
The Fishbone Diagram is excellent for brainstorming sessions. It encourages team members to think critically and contributes to a shared understanding of the problem. It’s collaborative by design, allowing for the collective intelligence of the group to shine.
3. Root Cause Analysis:
Identifying symptoms of a problem is one thing; uncovering the root cause is another. The Fishbone Diagram excels at this by forcing you to dig deep into various contributing factors. By isolating these causes, you’re better positioned to find a lasting solution.
By using a Fishbone Diagram, you’re not just addressing a problem with a short-term fix; you’re conducting a thorough investigation to eliminate issues from the root up.
How to Create a Fishbone Diagram: A Detailed Guide
Creating a Fishbone Diagram might seem like a daunting task, but it’s actually a straightforward process. Here, we’ll break down each step in detail to ensure you can construct a Fishbone Diagram that serves its purpose effectively.
Materials You’ll Need:
- A whiteboard or large sheet of paper
- Markers or pens
- Sticky notes (optional)
- A team of people for brainstorming
Step 1: Identify the Problem
The first and most crucial step is to clearly identify the problem you’re trying to solve. This statement should be specific and concise. Write this problem statement at the far right side of your whiteboard or paper, as it will serve as the “head” of your fishbone diagram.
- Use data to define the problem whenever possible.
- Make sure the problem is mutually understood and agreed upon by all team members.
Step 2: Determine the Main Categories
Now, draw a horizontal line from the problem statement towards the left side of the board. This is the “spine” of your fish. Next, you’ll identify the major categories of causes that could be contributing to the problem. These categories will serve as the main “bones” branching off from the spine.
Common categories often include:
- Measurement
- Environment
- The categories can be industry-specific or general, depending on the problem you’re analyzing.
- Aim for 4-6 main categories for better manageability.
Step 3: Brainstorm Causes
Once you’ve determined the main categories, it’s time to brainstorm potential causes for each category. These causes will be the smaller “bones” that branch off from the main bones. If you’re working with a team, this is an excellent time for a brainstorming session.
- Use sticky notes to write down ideas so you can easily move them around.
- Encourage every team member to contribute; sometimes the most unexpected insights come from diverse perspectives.
The output of the root cause analysis at this point may look something like the below example. With the lack of preventative maintenance being explored with the 5Whys analysis.
Step 4: Dig Deeper with Sub-Causes
Sometimes, the primary causes can be broken down into smaller, more specific sub-causes. This is where the “ 5 Whys ” technique can be beneficial. For each primary cause, ask “Why?” up to five times to dig deeper into the root of the issue.
- Not all primary causes will need sub-causes; use your discretion.
- Keep the diagram organized to ensure readability.
Step 5: Analyze and Take Action
After all the causes and sub-causes have been identified, it’s time to analyze the Fishbone Diagram as a team. Highlight or circle the causes that seem most likely to be contributing to the problem. These are the areas that will need immediate attention and action.
- Use data or evidence to support your conclusions.
- Create an action plan assigning responsibility for each highlighted cause.
And there you have it! You’ve successfully created a Fishbone Diagram that will help you get to the root of your problem.
Examples and Case Studies: Understanding Fishbone Diagrams in Action
Case study: manufacturing unit with quality issues.
Imagine you run a manufacturing unit, and you’ve been receiving complaints about the quality of your products. You decide to use a Fishbone Diagram to get to the root of the issue.
Step 1: Identify the Problem Problem Statement: “High number of defective products in the last quarter.”
Step 2: main categories.
- People : Untrained staff, high employee turnover
- Process : Inconsistent quality checks, outdated SOPs (Standard Operating Procedures)
- Equipment : Aged machinery, lack of maintenance
- Environment : Poor lighting, extreme temperature fluctuations
Step 4: Dig Deeper (5 Whys)
- Untrained Staff : Why? No formal training program.
- Aged Machinery : Why? No budget allocated for equipment upgrades.
After analyzing the Fishbone Diagram, you realize that untrained staff and aged machinery are your primary culprits. Your next steps could involve investing in staff training programs and allocating budget for machinery upgrades.
By following these steps, you can develop targeted strategies to improve product quality significantly.
Common Mistakes and Tips: How to Make the Most of Your Fishbone Diagram
1. overlooking minor causes.
While it’s easy to focus on the most glaring issues, minor causes can accumulate and have a significant impact.
Tip : Don’t disregard a cause just because it seems minor. Sometimes, fixing smaller issues can lead to big improvements.
2. Ignoring Data
It’s tempting to rely solely on brainstorming and intuition, but data should be your guiding star.
Tip : Use metrics and KPIs to support or refute the causes you’ve identified. This adds credibility to your findings and helps you prioritize effectively.
3. Stopping at Symptoms
Identifying symptoms is just the first step; your ultimate goal should be to uncover the root causes.
Tip : Use techniques like the “5 Whys” to dig deeper into each cause and ensure you’re addressing the root of the issue, not just its manifestations.
Fishbone Diagrams are a fantastic asset in the toolbox of anyone interested in continuous improvement. Whether you’re a seasoned professional or just getting started, this simple yet powerful tool can help you dissect complex problems and develop targeted solutions.
They encourage you to look beyond the obvious and delve into the intricacies that contribute to each problem. So go ahead, grab that pen and paper (or a whiteboard, if you’re feeling fancy), and start your journey towards effective problem-solving.
- Ilie, G. and Ciocoiu, C.N., 2010. Application of fishbone diagram to determine the risk of an event with multiple causes. Management research and practice , 2 (1), pp.1-20.
- Coccia, M., 2018. The Fishbone diagram to identify, systematize and analyze the sources of general purpose Technologies. Journal of Social and Administrative Sciences , 4 (4), pp.291-303.
Q: What is the origin of the Fishbone Diagram?
A: The Fishbone Diagram was originally developed by Dr. Kaoru Ishikawa, a Japanese quality control statistician, in the 1960s. It’s also sometimes referred to as the Ishikawa Diagram in his honor.
Q: Can Fishbone Diagrams be used for non-manufacturing problems?
A: Absolutely! While Fishbone Diagrams are popular in manufacturing and quality management, their application is not limited to these areas. They can be used in healthcare, software development, event planning, and even for personal problem-solving.
Q: How many main categories should my Fishbone Diagram have?
A: The number of main categories can vary depending on the complexity of the problem. However, it’s generally advisable to have between 4-6 main categories for easier analysis and readability.
Q: Can I use software to create a Fishbone Diagram?
A: Yes, there are several software tools available for creating Fishbone Diagrams, such as Microsoft Visio, Lucidchart, and various other project management software options. However, a simple pen and paper or a whiteboard can be just as effective for smaller teams or simpler problems.
Q: How do I know which causes to prioritize after creating a Fishbone Diagram?
A: After creating your Fishbone Diagram, you should analyze it with your team to identify the most likely root causes of the problem. Using data to support your conclusions can be very helpful. You may also employ techniques like the Pareto Analysis to prioritize causes based on their impact.
Daniel Croft is a seasoned continuous improvement manager with a Black Belt in Lean Six Sigma. With over 10 years of real-world application experience across diverse sectors, Daniel has a passion for optimizing processes and fostering a culture of efficiency. He's not just a practitioner but also an avid learner, constantly seeking to expand his knowledge. Outside of his professional life, Daniel has a keen Investing, statistics and knowledge-sharing, which led him to create the website learnleansigma.com, a platform dedicated to Lean Six Sigma and process improvement insights.
Free Lean Six Sigma Templates
Improve your Lean Six Sigma projects with our free templates. They're designed to make implementation and management easier, helping you achieve better results.
Other Guides
Home Blog Business Fishbone Diagram: Cause and Effect Analysis (Examples & Templates Included)
Fishbone Diagram: Cause and Effect Analysis (Examples & Templates Included)
Identifying the relationship between events and things is required when solving a problem, where possible causes are inspected to know their effect in an effort to generate the possible causes of a problem and minimize them.
For this purpose, a visualization tool called the fishbone diagram is used to list all of the possible causes and effects of the problem at hand, sorting them into categories, identifying root causes, and finding their solutions.
In this article, we will explain what is a fishbone diagram for problem-solving, when to use it, the elements of a fishbone analysis, how to make a fishbone diagram, and a fishbone diagram examples.
Lastly, we will also discuss how a fishbone diagram, specifically a cause and effect fishbone diagram, can be presented, with bonus templates that can be used to construct a fishbone diagram to determine causes and effects and come up with a solution to the problem.
Table of Contents
What is a Fishbone Diagram?
When to use a fishbone diagram, elements of the fishbone diagram, how to construct a fishbone diagram for cause and effect analysis, alternative to fishbone diagram, examples of fishbone diagram, pros of fishbone diagrams, cons of fishbone diagrams, how to present a fishbone analysis, templates for presenting a fishbone diagram.
A fishbone diagram is a visualization tool, developed by Dr. Kaoru Ishikawa, a quality control specialist, for identifying the root causes of a problem, categorizing them, and generating solutions.
Also called the Ishikawa diagram, or cause and effect diagram, the fishbone analysis is often used in troubleshooting and product development processes where teams need to focus on a problem statement.
The fishbone diagram has categories with branches that detail the causes of the problem; it looks like the skeleton of a fish, hence the name “Fishbone.” Each bone of the fish branches out into smaller bones to address the root causes of a large problem.
A fishbone diagram is used to conduct a cause-and-effect analysis. It enables teams to identify potential and real causes that are further investigated to determine the root cause. It can be used when,
- Managers need to identify the root cause of a problem
- Supervisors try to understand the contributing factors of any system or process failure
- Collaborative team brainstorming is required for problem-solving
- Streamlining an existing workflow by uncovering bottlenecks
- Improve output quality and efficiency
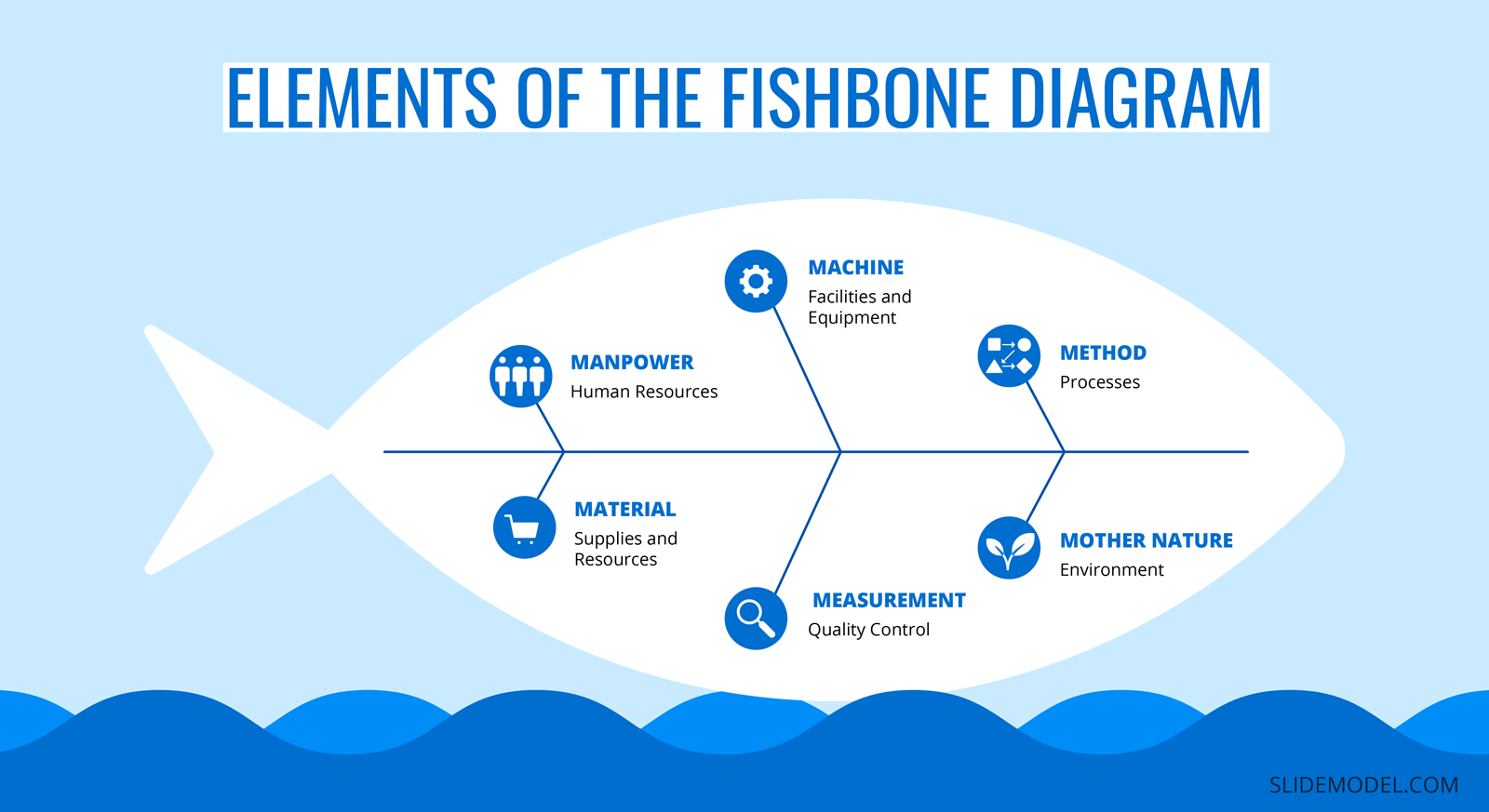
Manpower: Human Resources
Anything related to people that are involved with the process relevant to the problem statement. Manpower commonly includes operators, employees, maintenance teams, supervisors, and quality control specialists.
Machine: Facilities and Equipment
This includes machines used in the process, including all facilities and equipment that may be causing the problem. The causes can be associated with maintenance, usage, and assembly of equipment that could result in bottlenecks.
Method: Processes
Any standardized methods set by supervisors might not be followed by operators accurately. The instructions need to be evaluated to ensure all processes are clear to the team and all areas of operation are described in detail.
Material: Supplies and Resources
All supplies and resources used in the production or process are reviewed to determine their effect. Material defects, mishandling, low quality, and lack of proper inspection can result in problems further along the process.
Measurement: Quality Control
Techniques and tools used to measure quality standards are also a part of the fishbone analysis. Parts and processes need to be analyzed to determine whether they meet the quality control standards set in place, and all problems need to be reviewed to determine the root cause of the problem.
Mother Nature: Environment
When searching for a root cause, the environment plays a crucial role in production processes, whether it is the external factors of the production area or the environmental conditions such as temperature, humidity, pressure, etc. The production facilities must be able to handle the environment without having any negative impact on the production or process for a streamlined workflow.
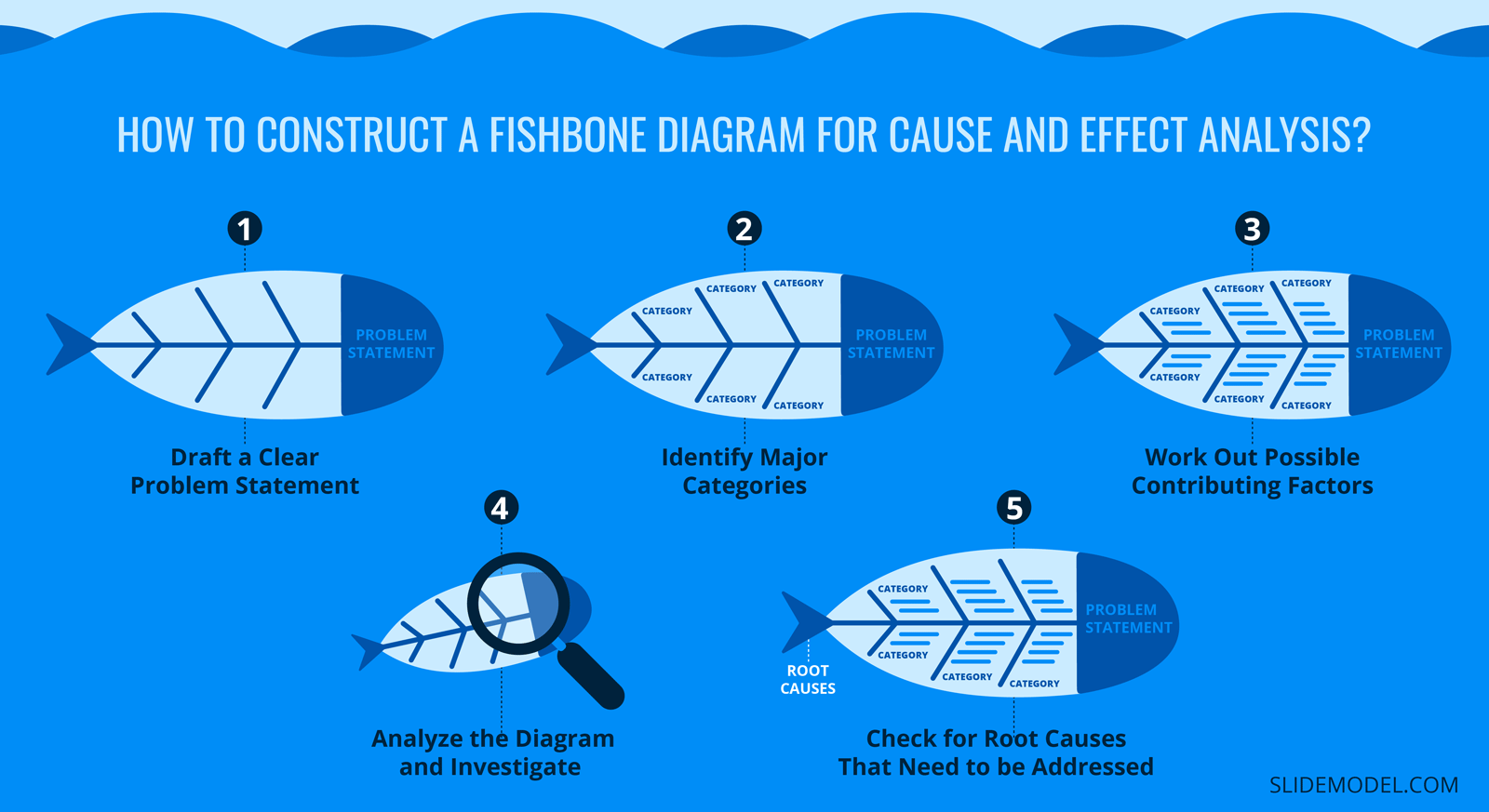
Draft a Clear Problem Statement
For constructing a fishbone diagram, a clear problem statement needs to be drafted to test causes in order to determine what’s causing the problem and present a solution.
During analysis, the problem statement is written at the right side of the fishbone, at the head of the fish. The problem is the effect, and the causes need to be categorized in the next step.
Identify Major Categories
Major categories that are involved in the process or procedure relevant to the problem need to be identified. The categories are connected to the backbone of the fish diagram.
Commonly, the 6M’s, as stated above, are used for the categorization of the causes, while the number of categories is not limited, and it can include different categories relevant to the problem.
Work Out Possible Contributing Factors
After categorization, possible contributing factors need to be brainstormed and attached to the appropriate category or the “rib.” Managers can create a list of causes and then attach them to the relevant rib, or some may find it easier to place ideas on the respective category as they are generated.
Some causes could also fit into multiple categories, which helps analyze the factor from different perspectives. Keep asking what’s causing the problem and evaluate each factor. The fishbone branches out into multiple ribs as more causes come to light.
Analyze the Diagram and Investigate
When the fishbone diagram is constructed with the problem, categories, and causes, the analysis of the diagram is required to understand why that factor is occurring. This can be done by asking the team why questions, typically known as the five whys and is usually represented in a root cause analysis presentation .
Asking five questions is usually enough to reach a root cause, while in some factors, more than five questions may be needed.
Check for Root Causes That Need to be Addressed
Lastly, as the root causes come to light after analyzing the fishbone diagram, they need to be addressed to minimize or eliminate the problem. What’s next is generating workable solutions that need to be implemented as a top priority.
A popular alternative to the fishbone diagram is the 5 whys method that is used for conducting a root cause analysis. The quality control tool can be used individually and even in combination with the fishbone diagram to determine the problem, its origin, why it happened, and most importantly, figure out how the chances of the problem recurring can be reduced.
The 5 whys fishbone analysis helps determine the causes of the problem and finds out the root causes. A set of 5 why questions lead the team to dig deeper into the problem, speed up the problem-solving process, and enable them to take action to prevent it from happening in the future.
Problem Statement:
In the first quarter of 2022, reported defects in production increased to 20%.
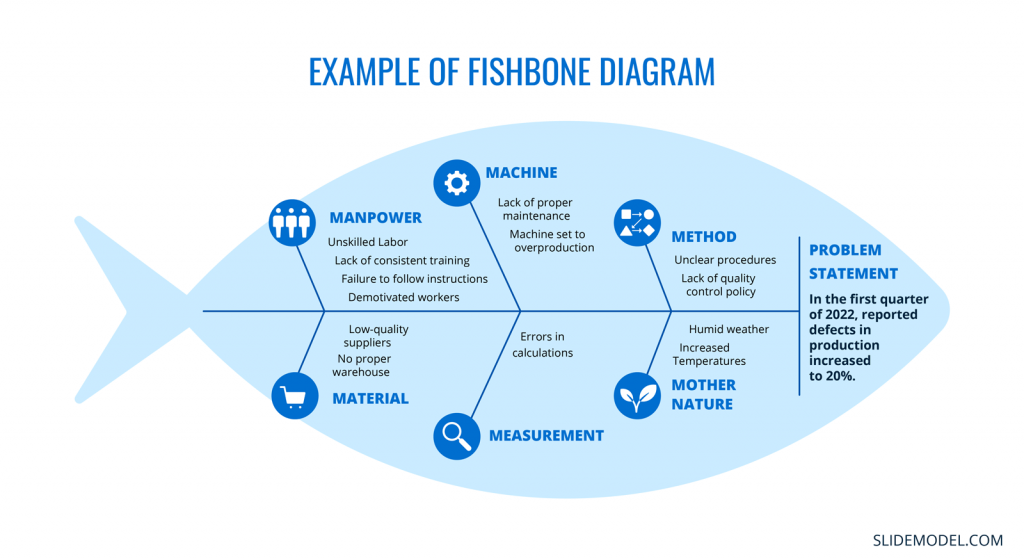
- Unskilled Labor
- Lack of consistent training
- Failure to follow instructions
- Demotivated workers
- Unclear procedures
- Lack of quality control policy
Measurement:
- Errors in calculations
- Lack of proper maintenance
- Machine set to overproduction
- Low-quality suppliers
- No proper warehouse
Mother Nature:
- Humid weather
- Increased Temperatures
Increase in customer complaints about product quality.
- Lack of training for employees
- Inadequate customer service skills
- Employee turnover affecting quality
- Inefficient quality control procedures
- Lack of clear product assembly guidelines
- Inadequate testing at different production stages
Product Design:
- Design flaws leading to defects
- Outdated machinery causing defects
- Lack of preventive maintenance leading to quality issues
Delays in project completion.
- Insufficient skilled project team
- Poor communication among team members
- Inadequate project management experience
- Unclear project scope and objectives
- Inadequate project planning and scheduling
- Lack of risk assessment and mitigation
- Inadequate budget allocation for project
- Limited availability of necessary resource
- Unreliable suppliers causing delays
External Factors:
- Regulatory changes impacting project
- Delays caused by adverse weather
Decrease in website traffic.
People/Skills:
- Lack of SEO knowledge among content creators and editors
- Inadequate social media marketing skills
Content Quality:
- Outdated and irrelevant website content
- Inadequate use of keywords for SEO
- Poorly written and unengaging content
Technical Issues:
- low website loading due to large images
- Broken links and frequent errors
- Ineffective mobile responsiveness
Marketing Strategies:
- Inconsistent promotion across platforms
- Lack of engagement with the target audience
- Ineffective use of online advertising
High employee turnover rate.
Work Environment:
- Poor workplace culture and lack of employee engagement
- Inadequate work-life balance
Management Practices:
- Ineffective leadership and communication
- Lack of recognition and rewards
- Inadequate opportunities for growth
Compensation:
- Below-market salaries and benefits
- Inadequate performance-based incentives
Recruitment and Hiring:
- Inaccurate job descriptions and expectations
- Insufficient screening of candidates
- Lengthy and inefficient hiring process
Pros and Cons of Fishbone Diagrams
Fishbone diagrams, also known as Ishikawa diagrams or cause-and-effect diagrams, are powerful tools for analyzing and solving complex problems. However, like any methodology, fishbone diagrams come with their own set of advantages and disadvantages. Let’s explore the pros and cons of using fishbone diagrams in problem-solving and decision-making processes.
- Visual Clarity: Fishbone diagrams provide a visual representation of the causes and effects of a problem, making it easier to understand the relationships between different factors.
- Holistic Analysis: They encourage comprehensive analysis by considering multiple categories of potential causes, ensuring a more thorough exploration of the problem.
- Structured Approach: Fishbone diagrams offer a structured framework for organizing thoughts and ideas, facilitating more organized problem-solving sessions.
- Collaborative Tool: They promote collaboration among team members by facilitating brainstorming sessions and encouraging diverse perspectives.
- Identification of Root Causes: Fishbone diagrams help in identifying the root causes of a problem, rather than just addressing its symptoms.
- Problem Prioritization: By categorizing causes and effects, teams can prioritize which issues to tackle first, leading to efficient problem-solving.
- Easy Communication: Fishbone diagrams provide a clear visual representation that can be easily shared with team members and stakeholders, enhancing communication.
- Data-Driven Analysis: They encourage data collection and analysis, enabling teams to make informed decisions based on evidence.
- Simplicity vs. Complexity: While fishbone diagrams work well for relatively simple problems, they might not be suitable for extremely complex issues with numerous interrelated causes.
- Subjective Interpretation: The process of categorizing causes and effects might involve subjective judgment, potentially leading to biased analysis.
- Overemphasis on Quantity: Focusing on listing numerous causes might divert attention from the most critical factors that require immediate attention.
- Time-Consuming: Constructing a fishbone diagram requires time, particularly when involving a large team. In time-sensitive situations, this can be a drawback.
- Limited to Known Causes: Fishbone diagrams rely on existing knowledge and may miss out on new or unexpected causes that were not previously considered.
- Complex Presentation: As the diagram becomes more intricate with more causes and categories, it might become difficult to interpret, defeating its purpose.
- Lack of Concrete Solutions: While fishbone diagrams identify causes, they don’t necessarily provide solutions. Further analysis is often required to determine the best course of action.
- Not a Standalone Solution: Fishbone diagrams are best used in conjunction with other problem-solving tools and methodologies for a well-rounded approach.
The purpose of a Fishbone Diagram Template is to inform the audience about the various problems affecting the company in a specific industry, and in turn, persuade them to present a plan of action to solve those problems.
A fishbone diagram can be visualized on paper, whiteboards, and even digitally with the help of digital whiteboards and presentations.
We recommend using Slide Model’s professionally designed 100% editable templates for PowerPoint and Google Slides to conduct a fishbone analysis.
From flat modern elements to a 3D perspective fishbone diagram, several different templates, including root cause analysis fishbone diagrams, can be used for conducting a root cause analysis, addressing problems, and presenting a solution to the team.
Here we have compiled a list of 100% editable fishbone diagram presentation templates that you can use for preparing presentations for cause & effect analysis.
1. Fishbone Infographic PowerPoint Diagram
A fishbone infographic PowerPoint template is a creative depiction of the Ishikawa diagram. The bone structure is made for presenting 4 categories, identifying causes, and analyzing their effects to get to the root of any problem.
Use This Template
2. Fishbone Diagram Template 3D Perspective
3D perspective fishbone template for PowerPoint and Google Slides is for conducting a cause and effect analysis in an appealing way and determining the root cause of the problem. Most likely factors can be presented with a proper analysis, while less impactful causes can be trimmed to reach the conclusion.
3. Animated 3D Fishbone PowerPoint Template
Another 3D template for the fishbone analysis that is fully compatible with PowerPoint and Google Slides can help managers present the root cause in any professional setting. The fishbone diagram is combined with 3D animations to create a realistic perspective making the RCA analysis interesting for the team.
4. Flat Fishbone Diagram for PowerPoint
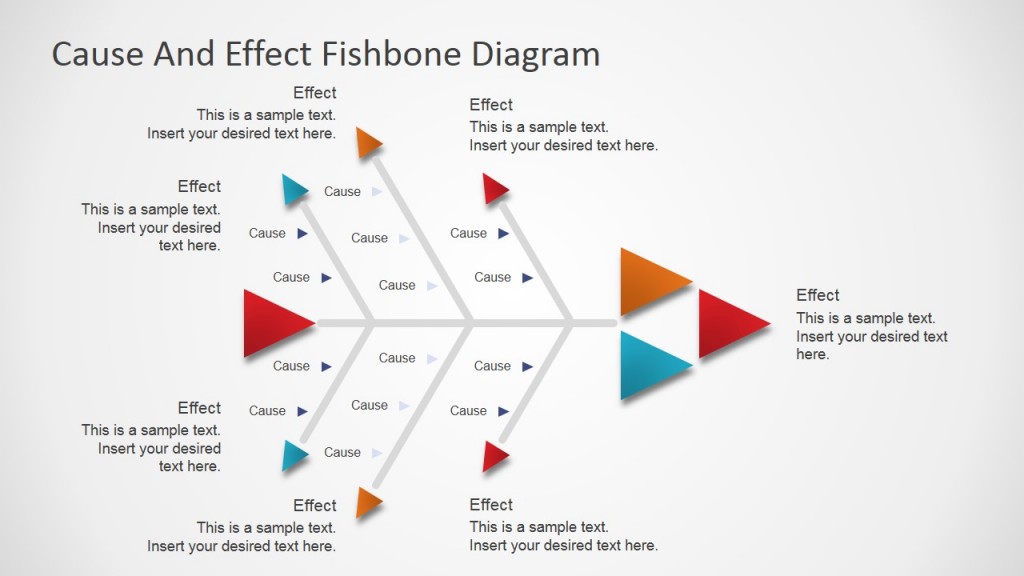
This flat fishbone template is a professional presentation diagram for determining factors that are contributing to the problem. The analysis can be presented and summarized easily, while the template can also be used during real-time brainstorming sessions to create the fishbone diagram.
5. Cause and Effects PowerPoint Infographic Template
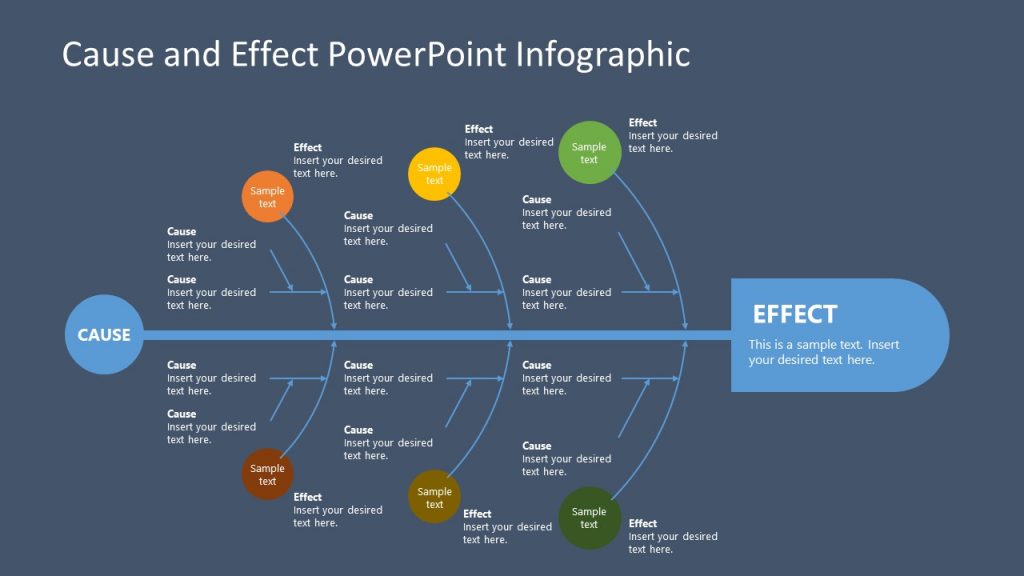
This cause and effect analysis template is for presenting a comprehensive look at the categories and their causes to determine the root cause of the problem. Fully customizable and compatible with PowerPoint and Google Slides, the template is a flat-vector-based Ishikawa diagram that enables teams to discuss project issues and drill down to the root cause of the problem.
6. Realistic Fishbone Diagram Template for PowerPoint
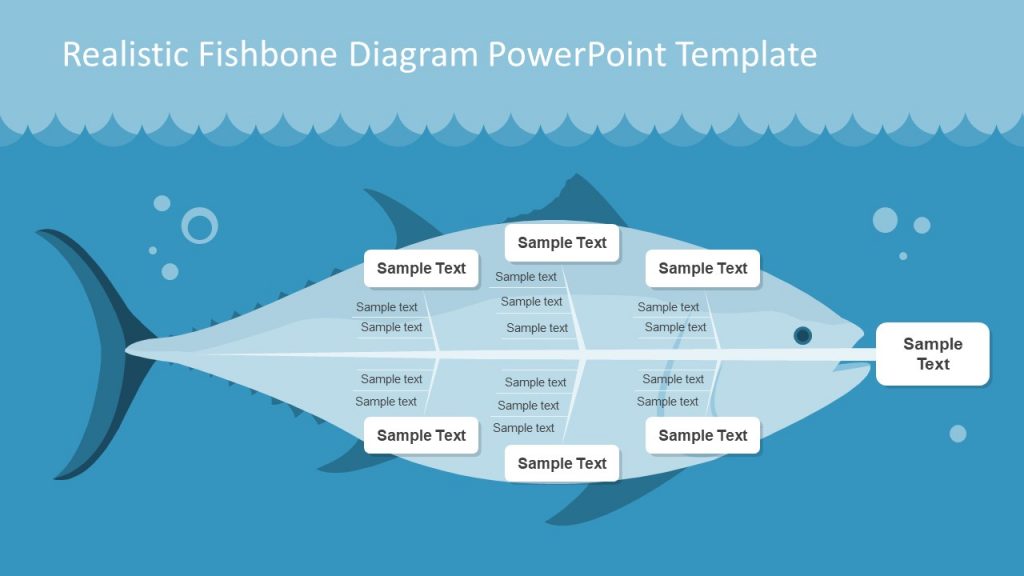
The realistic fish illustration in this fishbone template for PowerPoint and Google Slides can be used for analyzing problems, identifying root causes, and presenting solutions. Complex problems can be broken down to assist users in brainstorming and coming up with creative solutions for solving the problem.
7. Fishbone Template for PowerPoint
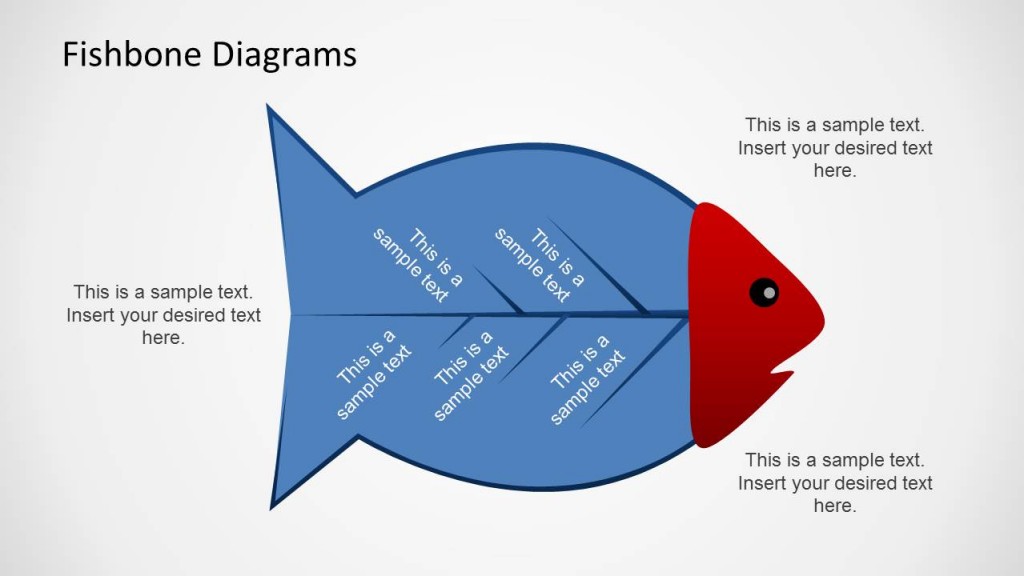
Another creative presentation template for the fishbone diagram that is helpful for conducting a root cause analysis (RCA) and presenting the cause and effect analysis results. The simple fish design makes the presentation engaging and memorable for the audience.
The fishbone analysis is a powerful tool for brainstorming potential causes of any problem and drilling down to the root cause for presenting a solution. It gives managers and teams a holistic look at the process categories and their issues and enables them to focus on areas that need to be fixed in order to minimize or eliminate the problem.
Our 100% editable fishbone diagram templates and root cause analysis templates made for PowerPoint and Google Slides are helpful for making professional presentations that can be used during brainstorming sessions, and also when presenting the solution after conducting the root cause analysis.
The simple-to-use, visual problem-solving tool is made to take corrective action with accurate analysis that can only be done while looking at the whole picture and improving processes by providing a framework for solving complex problems.
Like this article? Please share
Cause and Effect, Diagram Templates, Fishbone Analysis Filed under Business
Related Articles

Filed under Presentation Ideas • October 7th, 2023
Venn Diagram Ideas for PowerPoint Presentations
In this article, you will learn the basics of Venn diagrams, how they can be used in presentations and what type of information they are recommended for.

Filed under PowerPoint Tutorials • October 5th, 2023
How To Make Curved Arrows in PowerPoint
There are several methods by which you can make curved arrows for your presentations. In this article, we explain three different ways to draw arrows in PowerPoint.

• September 8th, 2023
Strategic Planning Process Templates For PowerPoint Presentations
Access a list of some very fine strategic planning process templates for PowerPoint that can be used for making business and academic presentations.
Leave a Reply
Advisory boards aren’t only for executives. Join the LogRocket Content Advisory Board today →

- Product Management
- Solve User-Reported Issues
- Find Issues Faster
- Optimize Conversion and Adoption
Cause and effect analysis with a fishbone (Ishikawa) diagram

Imagine you have been tasked with solving a problem: customers are experiencing lag while attempting to check out from their carts. Specifically, the app takes two minutes to transition from the cart page to the payment page once a customer clicks Continue .

What would you do? The first question that comes to mind is “why,” right? To answer this question, you’ll need to identify all the steps that customers take when checking out, and then assess how each step is performing. Together, these answers will enable you to determine the exact point in the checkout process where the problem is occurring.
This is called “root cause analysis” — you tried to list all the possibilities that could have created this problem. And out of all possibilities, you found which likely created the problem.
Let’s refer to the problem as the “effect,” and all the potential causes you identified during your analysis as the “causes.” Now, imagine trying to represent this cause-and-effect analysis visually. What types of diagrams could you create?
Maybe a tree whose roots are the effect and all the branches as the cause(s). Or maybe an Excel table listing all the causes and sub-causes in columns. Those are all good options, but in this article, we’ll discuss a cause-and-effect diagram (also called a fishbone diagram or Ishikawa diagram).
What is a fishbone diagram?
To start, a fishbone diagram (or Ishikawa diagram) is a tool to visually explore and represent the possible causes of an effect. The tool helps in identifying the potential causes that could have caused the problem.
A sample fishbone diagram looks like this:
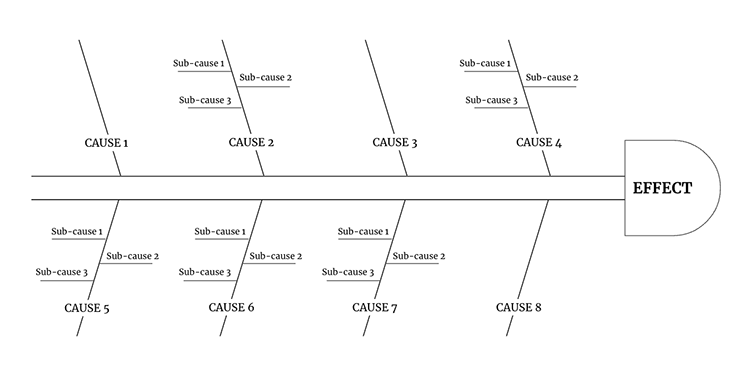
It is called a fishbone as it looks like the skeleton of a fish. The head of the fish explains the problem statement (or the effect) and the bones attached explain the possible cause and sub-causes.
The history behind fishbone diagrams
Although the early history of fishbone analysis is slightly unclear, fishbone diagrams are believed to have been in use since the 1920s. However, it was during the 1960s that the diagram gained widespread popularity, thanks to the work of Dr. Kaoru Ishikawa on quality management processes for Kawasaki Shipyards.
It’s believed that Ishikawa first presented the fishbone analysis method in 1945, as part of the development of a company-wide quality control process. The creation of quality improvement processes and tools, along with the introduction of quality circles, played a significant role in the evolution of the concept of total quality management. The Ishikawa diagram became recognized as one of the seven basic quality tools.
When to use a fishbone diagram
The purpose of the fishbone diagram is to identify all the root causes of a problem. You can use fishbone analysis in product development — let’s list a few cases where you should use fishbone analysis:
- When you have to identify the possible causes of a problem
- When you have to develop a feature or product to fix the cause of a problem. This is a reverse analysis where business analysts find the gap in market need and fill that gap with a product or feature
- When evaluating a business process to find loopholes or gaps that create problems
- When you’re defining a process for quality control. Evaluate and find the current gap in quality and build processes to fill it
You can apply the fishbone analysis tool to most applications that need an establishment of quality control and management.
Now, we’ll go over the fishbone diagram and how you can apply it to multiple industries. Most businesses fall into one of these operation areas: services, manufacturing, and marketing, each of which can use a different fishbone diagram. While manufacturing may not be directly relevant to digital products, the fishbone diagram can still be a useful tool for uncovering problems and identifying potential causes. You can modify them accordingly to fit the context of your product.
Let’s start with the 4 Ws: what, why, when, and where. Applying these will help you find the possible potential causes for any effect. This is a good way to brainstorm and all fishbone diagrams must start with these, regardless of the industry you’re in. The 4 Ws are:
- What? There will be materials, products, lines of code, and other resources involved in the problem creation. Ask “what?” to help to pinpoint the specific components or resources that may be contributing to the issue
- Why? There will be situations or conditions that lead to the problem. Asking “why?” may help to uncover factors such as network failure, temperature, weather conditions, or other external considerations that may be impacting the system
- When? There will be a moment when a particular problem occurs. Ask “when?” to find out the time the problem occurs and figure out if it’s a recurring or isolated incident
- Where? Asking this question can help to identify specific areas, such as during the checkout process, a different part of the application, or within a specific context where the issue is most prominent.
Many businesses in the service industry indeed share similarities when it comes to cause analysis in their operational areas. Specifically, the 5 S’s (systems, suppliers, surroundings, safety, and skills) can be applied to cause and effect analysis within the service business.

Over 200k developers and product managers use LogRocket to create better digital experiences
While all service businesses don’t need to conduct a complete cause analysis using the 5 S’s, many find that these principles can be applied at the initial levels and then gradually approached more thoroughly as they identify potential causes within their unique environment:
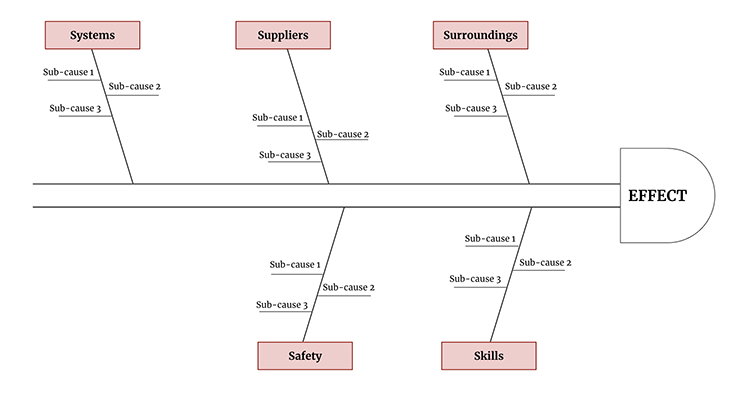
Systems are the methods, policies, processes, products, and tools used to build operational excellence and provide service without any failure.
Suppliers are any issues in delivering the service itself, like lower quality of service, failure to support customers, delay in refunding payments, agents or vendors delay, and more.
Surroundings are any external factors such as market, competition, public relations, brand value/image, etc. that may contribute to the issue.
Skills focus on finding issues in training, qualifications, skill set, and the experience of employees providing the service.
Safety focuses on finding issues in the system’s overall safety, products, operational procedures, and work environment.
Though the 6 Ms apply mainly to the manufacturing industry, you can transfer this framework into the software industry as well. Since digital products don’t have physical parts, not all of them will be relevant, but we’ll highlight them anyway:
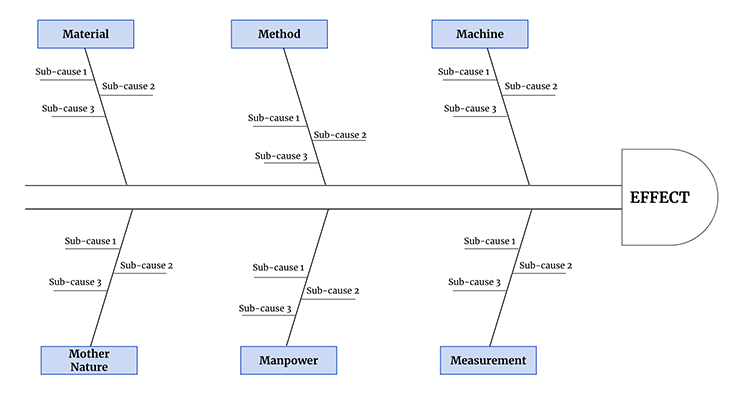
Material focuses on finding issues in any raw materials used for manufacturing. This includes issues with the quantity or quality of supplies, any issues with the timeline of procurement and supply, and more.
Method focuses on finding issues in processes, policies, regulations, training, and guidelines used by companies. Though this is relevant to manufacturing physical goods, these apply to digital products as well (in context).
Machine focuses on finding issues in machines that are used in manufacturing (production). This will help uncover any issues with the maintenance of machines, any failures in the machine or assembly line, etc.
Mother nature , aka the environment, focuses on finding issues in environmental conditions. For physical goods, this could mean issues with temperature, light conditions, etc. For digital products, this could mean issues with servers going down, weather causing latency problems, and more.
Manpower (aka people) focuses on finding issues in the workforce. This means any issues with the work itself, employee burnout, training and skill sets, and more.
Measurement focuses on finding issues in measuring the process and results. This is huge in any business, as metrics and measuring success are vital to the health of a company. Use this to find any issues in quality readings, calculations, and more.
There are 7 Ps that can be commonly applied in cause analysis. These are all related to marketing businesses, but nearly all physical and digital products have marketing functions that affect their product and that this can apply to:
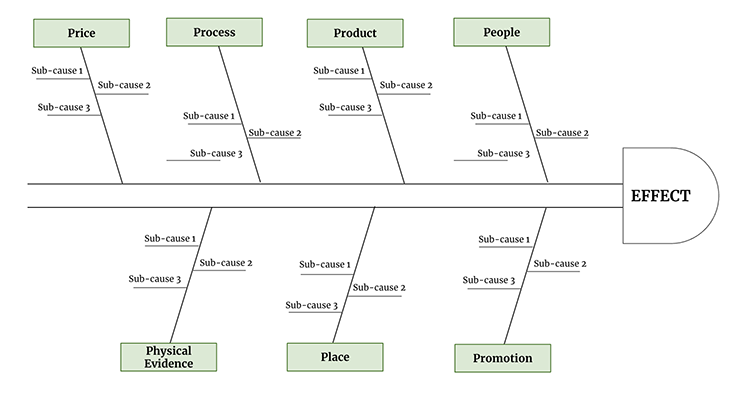
People focuses on finding issues in people involved in marketing a product or service to customers. This implies issues with not targeting the right audience or marketers not having a good understanding of the product.
Product is focused on finding issues in the product or service of an organization. This could be several things, including the perceived image of the product , issues with availability to reach customers, or failure to meet customer needs .
Process works on finding issues in procedures for promoting and marketing the product or service. Are there any gaps in cross-functional team collaboration ? Are they any issues with the escalation matrix?
Price is a big one. This is where to uncover issues in the pricing of the product or service. Is the price too low? Maybe it’s too high? Are there any issues with the price range not matching the competition or with accepting certain payment methods?
Promotion focuses on finding issues in promotion methods, mediums, and strategies. Are social media advertisements reaching the right audience? Is it generating enough clicks?
Place identifies problems with the location of your product. Are there any issues with the availability of your product on particular devices?
Physical evidence is the last of the Ps. It focuses on finding issues in the direct visibility of your product or service. If it has a physical component, is there a problem with the packaging? Physical evidence literally implies any physical issues with the product getting into the hands of customers.
Advantages and disadvantages of fishbone diagrams
There are many advantages you carry when you use a fishbone diagram as a tool for your cause analysis, including:
- Simplicity : the visual representation is simple and easy to understand. Anyone who understands the problem can easily go through all the possible causes of that problem
- Flexibility : you can dissect the cause into sub-causes and go deeper to find the cause
- Associativity : any cause becomes a potential candidate to generate the effect. The relationship with the problem is tightly defined, helping you conclude your analysis
- Ease of use : it’s easy to brainstorm with a team and explain how to use the diagram. Everyone can instantly adapt and be involved in a brainstorm
- Fast : it helps you analyze the root causes quickly by applying the 5 Why’s and drill down potential causes
- Prioritization : visual representation helps you to prioritize your causes and narrow down the most important ones
There are also a few limitations that can make fishbone diagrams difficult to use, including:
- Causes may not be as relevant as you once thought. This could lead to confusion on the path forward or create another problem by accident
- If oversimplified, the fishbone analysis may not uncover what you’re looking for
- There’s potential to prioritize smaller causes over critical ones. Since prioritization is so easy, the team may focus on small causes and waste time in fixing them
- The more dissection into sub-clauses you do leads to more complex diagrams. These may eventually become messy and difficult to understand
- The analysis is mostly based on understanding and brainstorming. It needs additional evaluation of the cause, which in case all possibilities have to be evaluated, can become inefficient and time-consuming

Fishbone diagram template
If you’d like a fishbone diagram template to work with, you can download this one I made on Google Sheets . Feel free to make a copy of it and customize it for your own use.
If you’d like to try to create a fishbone diagram yourself for your own team and organization, here are some common steps to make and analyze it:
- Identify and write the effect (problem statement) as the fish head
- Brainstorm and identify major causes. Write a major cause on each side bone. These major causes can be the Ms, Ps, or S’s with regard to the industry you’re in, or a combination of multiple
- Brainstorm and identify sub-causes. Write the sub-cause on each smaller bone
- Check for completeness. Evaluate or review for too few causes or narrow it down if you have too many
- Analyze each potential cause to narrow it down further. The goal is to end up with one or more that need to be fixed
- Prioritize the potential cause based on its severity on the effect
Let’s draw the fishbone diagram for a digital product. We’ll use the problem we listed at the beginning where customers are facing problems during the checkout process:
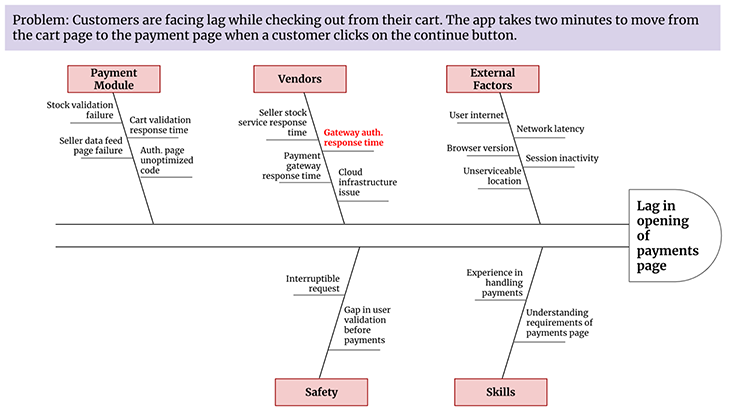
While this list may not be comprehensive, it does cover many potential causes that could lead to delays in opening the payments page. It’s important to note that during a brainstorming session, many potential causes can arise, but it’s important to focus on the most likely causes to address first. In this case, we’ve highlighted a sub-cause in red that represents the result of the analysis and the area that should be addressed.
How product managers can use fishbone diagrams
There are many cases where product managers have to analyze the cause of a problem, and a fishbone diagram is a powerful tool for product managers to benefit from. Its easy and quick creation helps quickly narrow down potential causes and act upon them.
A few examples where product managers can make use of fishbone diagram are:
- Finding the root cause for a reduction in feature usage
- Finding the root cause of churn
- Learn the effects of new features on the application upfront
- Analyze what the team should focus on while prioritizing enhancements for a feature
- Presenting the quality measures taken on certain features to senior management
The process type fishbone diagram
A not-so-popular and not-so-in-use flavor for creating fishbone diagrams is the process-type fishbone diagram. It’s very similar but has a small change in the drawing:
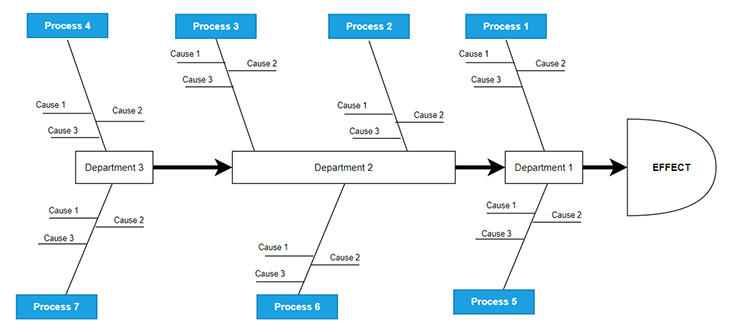
The main bone of the fish is divided into multiple cause areas. Team brainstorms potential causes that could have created the problem in each of these areas. It is called process type because each area in the main bone (mostly) represents a process, but each area in the main bone also represents a department. Causes are explored in the process of each department as a result.
These diagrams are not that popular but are an efficient way to involve multiple cross-functional teams from various departments.
Kaoru Ishikawa popularized the fishbone diagram to analyze the root cause of any problem. It is also called the Ishikawa diagram or cause and effect diagram.
One can use the 4 Ws — what, why, when, and where — to begin cause analysis. Based on industry type, there are common areas of cause analysis: the 5 S’ for services, 6 Ms for manufacturing, and 7 Ps for marketing. If your company or product has a combination of these, you can create multiple fishbone diagrams to get to the root cause of your issue.
Featured image source: IconScout
LogRocket generates product insights that lead to meaningful action
Get your teams on the same page — try LogRocket today.
Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- #product strategy

Stop guessing about your digital experience with LogRocket
Recent posts:.

Leader Spotlight: Growing the omnichannel market, with Christine Kuei
Christine Kuei, Director of Product Management at Forever 21, shares her experience growing and optimizing omnichannel experiences.

Decoding marketing jargon: A glossary of terms
The world of product marketing is always evolving. Even for experts, it can be hard to keep up with the latest concepts, terms, and jargon.
Leader Spotlight: Bettering learning velocity, with Jonas O. Klink
Jonas talks about his team’s initiatives to “better the learning velocity” — taking an initial idea through hypothesis-driven development to build customer-centric, scalable solutions.
Leader Spotlight: Energizing your leadership style, with Navya Rehani Gupta
Navya Rehani Gupta talks about her three main pointers for mastering the art of zooming in and zooming out.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply

Reading for Learning
Pedagogy, Curriculum and Assessment
Using A Fishbone Diagram for Writing Cause and Effect Texts
Morning – just a quick post on using a fishbone diagram to help students write more focused cause and effect texts – especially when there are multiple causes.

Each rib is for a separate cause contributing to the effect. Once the ribs have been completed with brief detail (which you can check as you go), the student can write a short introduction followed by a paragraph for each cause.

Advantages at the Fishbone Stage:
- Quick for the teacher to see where knowlegde gaps are (great for checking the whole class during the lesson).
- Great for supporting with vocabulary (e.g. “Instead of towns and cities , you could say urban areas .”)
- Students hate planning a text – this doesn’t feel like a plan.
- Good for revision later (they won’t re-read the text in 6 months time, but they might look at the fishbone).
- It’s quick –
Advantages at the Writing Stage:
- Students can concentrate on the quality of writing without having to hold all of the essay in their heads.
- The writing structure makes it easy to assess in class (Teach Like a Champion – Check for Understanding / Name the Lap – “This time I’m only going to look at your introduction sentence”).
- Reduces waffle.
I hope that’s useful. Let me know if you use a fishbone organiser to support writing during lockdown.
Share this:
Published by BenRogers
18 years secondary teacher: 4 years primary. MA in SciEd. Author of 'Big Ideas of Physics and How to Teach Them.' Director of Curriculum and Pedagogy for Paradigm Trust. View all posts by BenRogers
Leave a comment Cancel reply

- Already have a WordPress.com account? Log in now.
- Subscribe Subscribed
- Copy shortlink
- Report this content
- View post in Reader
- Manage subscriptions
- Collapse this bar
How to use a fishbone diagram for cause and effect analysis

Getting to the root of any problem is easier said than done.
This is especially true when you manage a large project and have multiple teams, systems, and processes to consider. With so many moving parts, you’ll inevitably run into problems. And their causes can be more complicated than you originally thought.
Though the problem-solving process is often an intricate one, there are tools and systems out there to help you navigate it. A fishbone diagram is a structured method that leads you to the true cause of a problem. You start by identifying the main issue and then work backward to pinpoint any contributing errors. By the time you map everything out, you’ll be left with a fish-shaped diagram that guides you directly to the root of the problem — and the first step to solving it.
What is a fishbone diagram?
The fishbone diagram, also known as the Ishikawa Diagram or cause-and-effect diagram, is a problem-solving method that uses a fish-shaped chart to model complications and their causes. The diagram was developed by Dr. Kaoru Ishikawa in the 1960s and frequently turns up in project management and education processes.
The fishbone diagram usually has a central “head” that describes the main problem. Each cause appears as a “bone” that branches out from the head. The bones may divide further into sub-causes, which branch off from the main bones.
By visually recording and breaking down the potential causes of a problem, you can better understand how different factors interact and identify areas for improvement. This helps you and your team develop a roadmap to solve the main problem and implement preventative measures so it doesn’t occur again.
What is a fishbone diagram used for?
Though the fishbone diagram was initially designed for troubleshooting in manufacturing settings, it has become useful across many different industries. Its barebones structure lets every type of team map out problems across various stages of project management, including planning and process improvement.
The beauty of the fishbone diagram lies in its simplicity. All you need to start constructing the diagram is a single problem, which provides an easy starting point. For that reason, you can use the fishbone diagram for root cause analysis in nearly any project.
Benefits of using a fishbone diagram
A fishbone diagram’s advantages extend beyond simply identifying a problem’s cause. Other benefits include:
- Systematic problem analysis: This diagram provides a structured approach to problem-solving. It’s a repeatable, universal arrangement that helps you break down significant problems into more manageable parts while staying organized.
- Facilitates team discussions: The visual nature of the fishbone diagram makes it easy to share during team discussions and brainstorming sessions. And when you collaborate with your team to develop one, you foster collaboration and transparency.
- Improves understanding of processes: By visually laying out a problem’s cause and effect, fishbone diagrams help you understand your processes better and pinpoint what needs improvement.
- Versatility: A fishbone diagram is a blank slate, and you can apply it across various industries and for many different types of problems. Whether it’s software development, healthcare, or manufacturing, the fishbone diagram works to identify issues and plan for resolution.
Challenges of using a fishbone diagram
While the fishbone diagram is a valuable tool for problem-solving and risk identification, it has its limitations. Challenges might include:
- Limited scope: This tool investigates cause-and-effect relationships for one main problem. Its usefulness wanes when your team wants to explore multidimensional issues where solutions could impact interconnected issues.
- Subjectivity: Constructing a diagram relies heavily on the team’s knowledge. You might end up with biased or incomplete results if the team lacks cognitive diversity or relevant expertise.
- Lack of prioritization: The fishbone diagram identifies several potential causes for a problem, but it lacks a mechanism to prioritize solutions. This means you might have to do additional work to decide which issues to address first.
- Time-consuming: Creating a comprehensive diagram, especially for complex problems, can take up precious time. Although it’s worth it to invest your team’s energy into problem-solving, there may be more efficient choices than this tool.
How to use a fishbone diagram
Creating a fishbone diagram may initially seem intimidating with so many lines and arrows. But the process is quite manageable when you break it down into steps. Here’s how to create a fishbone diagram in seven steps:
- Choose a platform: A simple word processor doc might not have the capabilities you need to create an in-depth diagram. Choose a whiteboard tool that lets you easily draw new lines, add text, and collaborate with your team.
- Identify the problem: Collaborate with your team to both identify the problem and whittle it down to a single statement. This is what you’ll write on the right side of the diagram, representing the head of the fish.
- Draw the backbone: Draw a horizontal line from the head to the left edge of your diagram. This line represents the backbone or spine.
- Identify cause categories: Now, identify the major causes of the problem and place them into categories. Common categories include people, measurements, and environment, but these can vary based on the specific situation and industry. Draw a diagonal line off the backbone for each one so the diagram resembles a fish’s bones.
- Identify causes: Now write the problem’s potential causes within each category. These will branch off from the fish’s body.
- Identify sub-causes: For each cause, think about what its underlying factors, or sub-causes, might be. A tight budget might be a cause, but there could be bigger decisions behind that, like stakeholder skepticism or a low revenue year. A common technique to identify sub-causes is known as the “5 Whys,” where you ask “why” five times in succession to dig deeper into the root of an issue.
- Review the diagram: Finally, review the diagram as a team. Look for areas where the same factor appears in multiple places because it could be a significant root cause. You should also try to find areas lacking in causes or sub-causes, as they may need further examination.
Fishbone diagram best practices
As you create the diagram, it’s easy to get carried away and forget to examine the big picture. Here are some tips for staying on track and implementing a productive process:
- Be specific: When identifying the problem and its potential sources, be as clear as possible. Vague descriptions can make pinpointing root causes and developing effective solutions difficult.
- Encourage team participation: The brainstorming process works best when you involve all team members. Different perspectives can bring light to nuanced issues and provide a more comprehensive understanding of the problem.
- Use data: Rely on data to understand the causes and sub-causes wherever possible. This helps validate the issues your team finds, and it offers a clearer direction for solutions.
- Update regularly: This tool should be a living document that you update and adjust as the problem evolves. That way, the diagram remains relevant and valuable, and you can use it to inform future issues that might fall into the same ballpark.
Analyze, strategize, and take action with Tempo
Fishbone diagrams are one of many valuable problem-solving options in your project management toolkit. And although they can help your team unpack a project’s obstacles, you’ll need more strategies to put you on the path to success.
Roadmunk by Tempo allows you to create audience-friendly roadmaps to align your team and foster transparent and productive collaboration. These roadmaps help you prioritize, manage, and track your projects in one intuitive platform. You’ll spend less time on administrative work and more on driving your projects to the top.
Latest Blog Posts

How to get your roadmaps ready for 2024

Shape your business’s future with financial forecasting

Impress stakeholders: Navigating how to measure profitability

Unlock the power of customer feedback for your business

How project management templates and roadmaps streamline workflows

Boost your productivity with innovative product management templates

How to engage stakeholders for optimal project outcomes

Unlock potential: Strategies to manage resource constraints efficiently

Understanding decision logs: Why they're crucial for your projects
Try roadmunk for free.
- Join Mind Tools

Cause and Effect Analysis
Identifying the likely causes of problems, (also known as cause and effect diagrams, fishbone diagrams, ishikawa diagrams, herringbone diagrams, and fishikawa diagrams.).
When you have a serious problem, it's important to explore all of the things that could cause it, before you start to think about a solution.
That way you can solve the problem completely, first time round, rather than just addressing part of it and having the problem run on and on.
Cause and Effect Analysis gives you a useful way of doing this. This diagram-based technique, which combines Brainstorming with a type of Mind Map , pushes you to consider all possible causes of a problem, rather than just the ones that are most obvious.
Click here to view a transcript of this video.
About the Tool
Cause and Effect Analysis was devised by professor Kaoru Ishikawa, a pioneer of quality management, in the 1960s. The technique was then published in his 1990 book, " Introduction to Quality Control ."
The diagrams that you create with are known as Ishikawa Diagrams or Fishbone Diagrams (because a completed diagram can look like the skeleton of a fish).
Although it was originally developed as a quality control tool, you can use the technique just as well in other ways. For instance, you can use it to:
- Discover the root cause of a problem.
- Uncover bottlenecks in your processes.
- Identify where and why a process isn't working.
How to Use the Tool
Follow these steps to solve a problem with Cause and Effect Analysis:
Step 1: Identify the Problem
First, write down the exact problem you face. Where appropriate , identify who is involved, what the problem is, and when and where it occurs.
Finding This Article Useful?
You can learn another 44 problem-solving skills, like this, by joining the Mind Tools Club.

Subscribe to Our Newsletter
Receive new career skills every week, plus get our latest offers and a free downloadable Personal Development Plan workbook.
Then, write the problem in a box on the left-hand side of a large sheet of paper, and draw a line across the paper horizontally from the box. This arrangement, looking like the head and spine of a fish, gives you space to develop ideas.
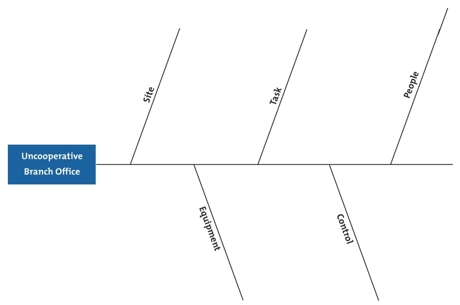
In this simple example, a manager is having problems with an uncooperative branch office.
Figure 1 – Cause and Effect Analysis Example Step 1

(Click image to view full size.)
Some people prefer to write the problem on the right-hand side of the piece of paper, and develop ideas in the space to the left. Use whichever approach you feel most comfortable with.
It's important to define your problem correctly. CATWOE can help you do this – this asks you to look at the problem from the perspective of Customers, Actors in the process, the Transformation process, the overall World view, the process Owner, and Environmental constraints.
By considering all of these, you can develop a comprehensive understanding of the problem.
Step 2: Work Out the Major Factors Involved
Next, identify the factors that may be part of the problem. These may be systems, equipment, materials, external forces, people involved with the problem, and so on.
Try to draw out as many of these as possible. As a starting point, you can use models such as the McKinsey 7S Framework (which offers you Strategy, Structure, Systems, Shared values, Skills, Style and Staff as factors that you can consider) or the 4Ps of Marketing (which offers Product, Place, Price, and Promotion as possible factors).
Brainstorm any other factors that may affect the situation.
Then draw a line off the "spine" of the diagram for each factor, and label each line.
The manager identifies the following factors, and adds these to his diagram:
Figure 2 – Cause and Effect Analysis Example Step 2
Step 3: Identify Possible Causes
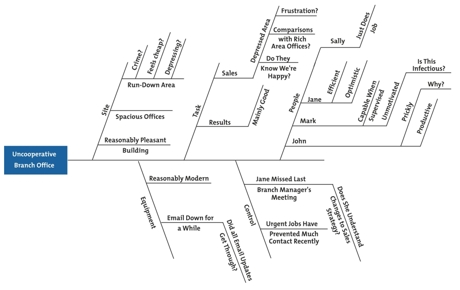
Now, for each of the factors you considered in step 2, brainstorm possible causes of the problem that may be related to the factor.
Show these possible causes as shorter lines coming off the "bones" of the diagram. Where a cause is large or complex, then it may be best to break it down into sub-causes. Show these as lines coming off each cause line.
For each of the factors he identified in step 2, the manager brainstorms possible causes of the problem, and adds these to his diagram, as shown in figure 3.
Figure 3 – Cause and Effect Analysis Example Step 3
Step 4: Analyze Your Diagram
By this stage you should have a diagram showing all of the possible causes of the problem that you can think of.
Depending on the complexity and importance of the problem, you can now investigate the most likely causes further. This may involve setting up investigations, carrying out surveys, and so on. These will be designed to test which of these possible causes is actually contributing to the problem.
The manager has now finished his analysis. If he hadn't looked at the problem this way, he might have dealt with it by assuming that people in the branch office were "being difficult."
Instead he thinks that the best approach is to arrange a meeting with the Branch Manager. This would allow him to brief the manager fully on the new strategy, and talk through any problems that she may be experiencing.
A useful way to use this technique with a team is to write all of the possible causes of the problem down on sticky notes. You can then group similar ones together on the diagram.
This approach is sometimes called CEDAC (Cause and Effect Diagram with Additional Cards) and was developed by Dr. Ryuji Fukuda, a Japanese expert on continuous improvement.
Professor Kaoru Ishikawa created Cause and Effect Analysis in the 1960s. The technique uses a diagram-based approach for thinking through all of the possible causes of a problem. This helps you to carry out a thorough analysis of the situation.
There are four steps to using the tool.
- Identify the problem.
- Work out the major factors involved.
- Identify possible causes.
- Analyze your diagram.
You'll find this method is particularly useful when you're trying to solve complicated problems.
This site teaches you the skills you need for a happy and successful career; and this is just one of many tools and resources that you'll find here at Mind Tools. Subscribe to our free newsletter , or join the Mind Tools Club and really supercharge your career!
Rate this resource
The Mind Tools Club gives you exclusive tips and tools to boost your career - plus a friendly community and support from our career coaches!

Comments (36)
- Over a month ago BillT wrote Hi AnotherFrancis, and Welcome to the Club! As with my response to Alex81, not everyone will find the example the most useful, as is the case with you. We appreciate your feedback. BillT Mind Tools Team
- Over a month ago AnotherFrancis wrote Nice article but, like Alex81, I didn't find the example to be very helpful.
- Over a month ago BillT wrote Hi Alex81, and Welcome to the Club! Thank you for your feedback on the Cause and Effect Analysis. I agree that not everyone may find the example the best way to demonstrate the resource. This diagram has also been known as the Ishikawa Diagram or Fishbone Diagram. You may find additional resources with better examples for you. Also, you may wish to post this in the Forums so that our members can provide their input into the topic. BillT Mind Tools Team
Please wait...
How to build a fishbone diagram and get the most out of it

No business operates without problems along the way. But to solve them in time, you’ll need to be able to determine the cause quickly. That’s where using a fishbone diagram comes in.
A fishbone diagram , also known as the Ishikawa diagram or cause-and-effect diagram, is a tool you can use to visualize all of a problem’s potential causes, allowing you to discover the root causes and identify the best possible solution.
We put this guide together to show you how to make a fishbone diagram based on a fictional problem we’ll be investigating: why a software company’s customer churn is so high.
Let’s get started.
Step 1 – Define the problem
The first step to solving any problem – and the key to learning how to make a fishbone diagram – is correctly defining it. A clearly defined problem makes it easier to identify causes. It also encourages us to determine whether there’s even a problem to begin with.
In this case, the problem we’ve identified is that 40% of users cancel their subscriptions after the first month — which keeps us from reaching our goal of keeping cancellations below 20%. Now that we’ve identified our main problem, we can go ahead and add that to the fishbone diagram.
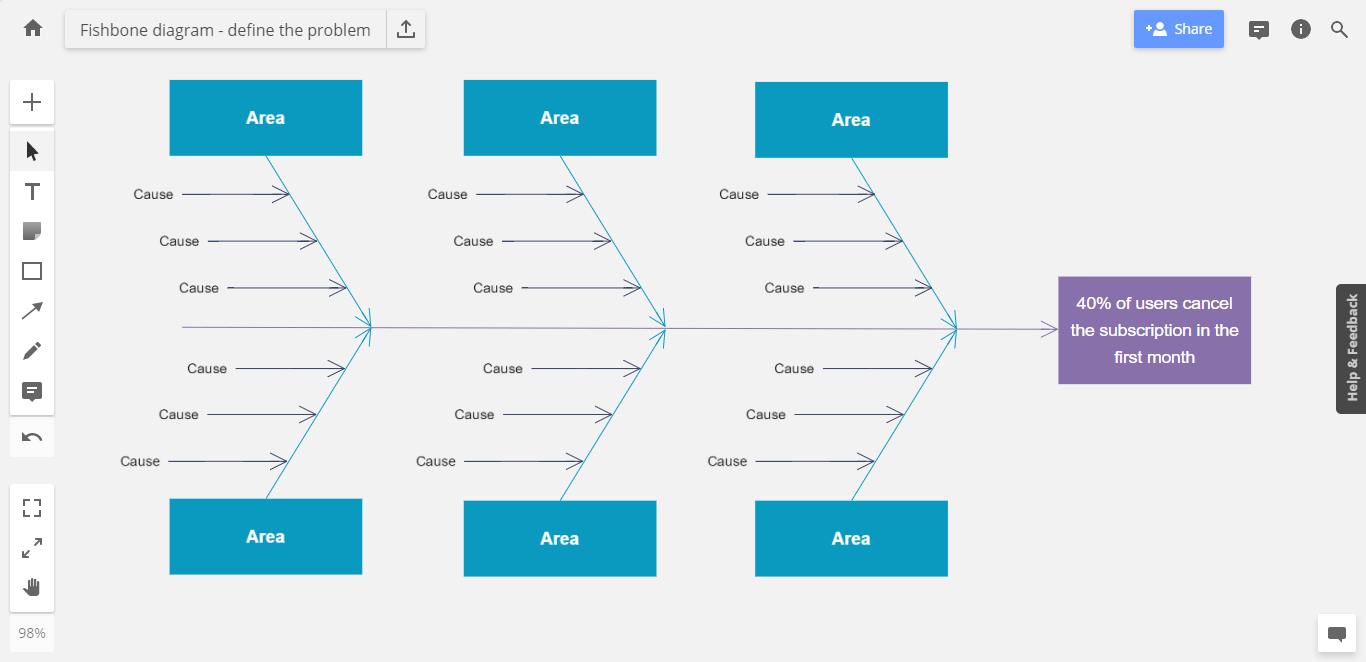
Problem definition tips:
- If you’re using the fishbone diagram to design a process or increase productivity, it’s just as important to correctly define your output. Your goals should be objective and achievable.
- Place the problem (the fish head) on one side of the diagram, and build the rest of the diagram (the fish bones) out to its left or right. The idea is that the “fish bones” indicate the impact of the causes.
- Place the causes with the biggest impact closer to the fish head and the causes with the smaller impact further away.
Step 2 – Decide on key categories of causes
Next, decide what areas of the problem are key to determining the actual cause. Going back to our example of investigating a high churn rate, here are three areas worth looking into:
- Subscription system
Once you start considering potential causes, you might find that most of them fall within one of these three categories. But you can always add more categories if needed. For example, If you think marketing impacted your retention figures, you could add that as a fourth area.
You can have as many areas as you need to. But to keep things simple, we recommend limiting yourself to no more than 10 — especially since we’re only learning how to make a fishbone diagram with this example.
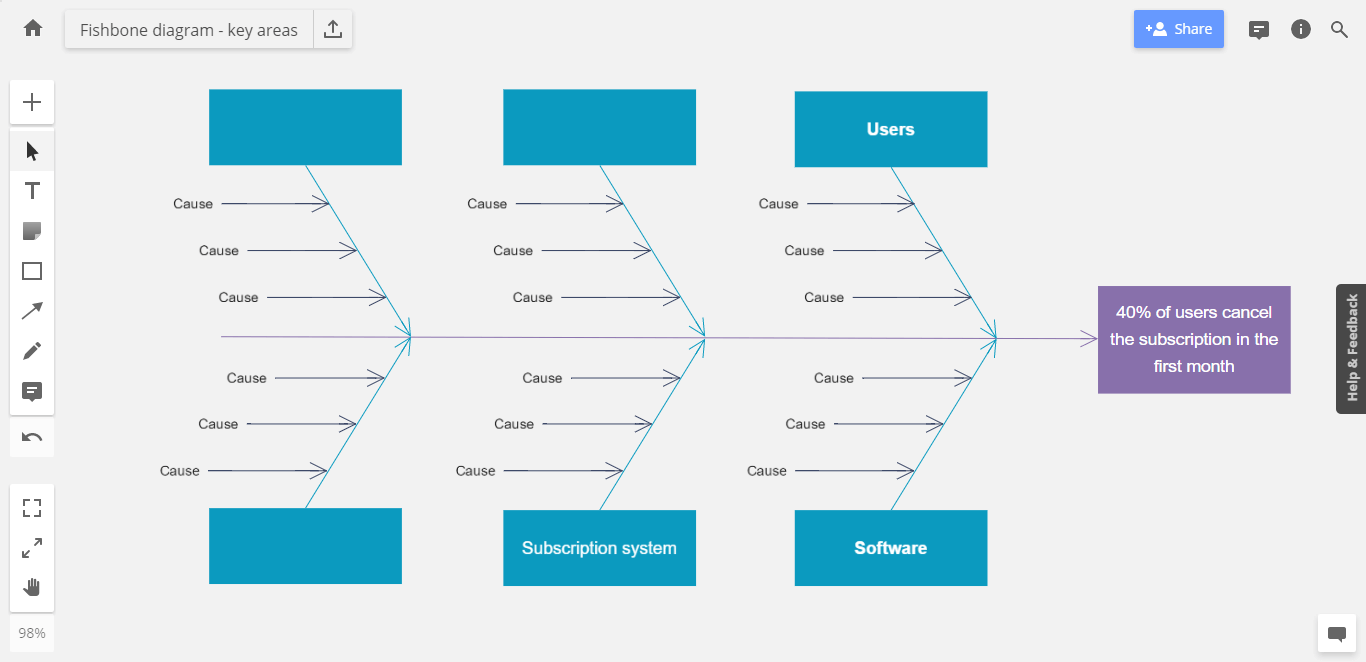
Step 3 – Determine the actual causes of the problem
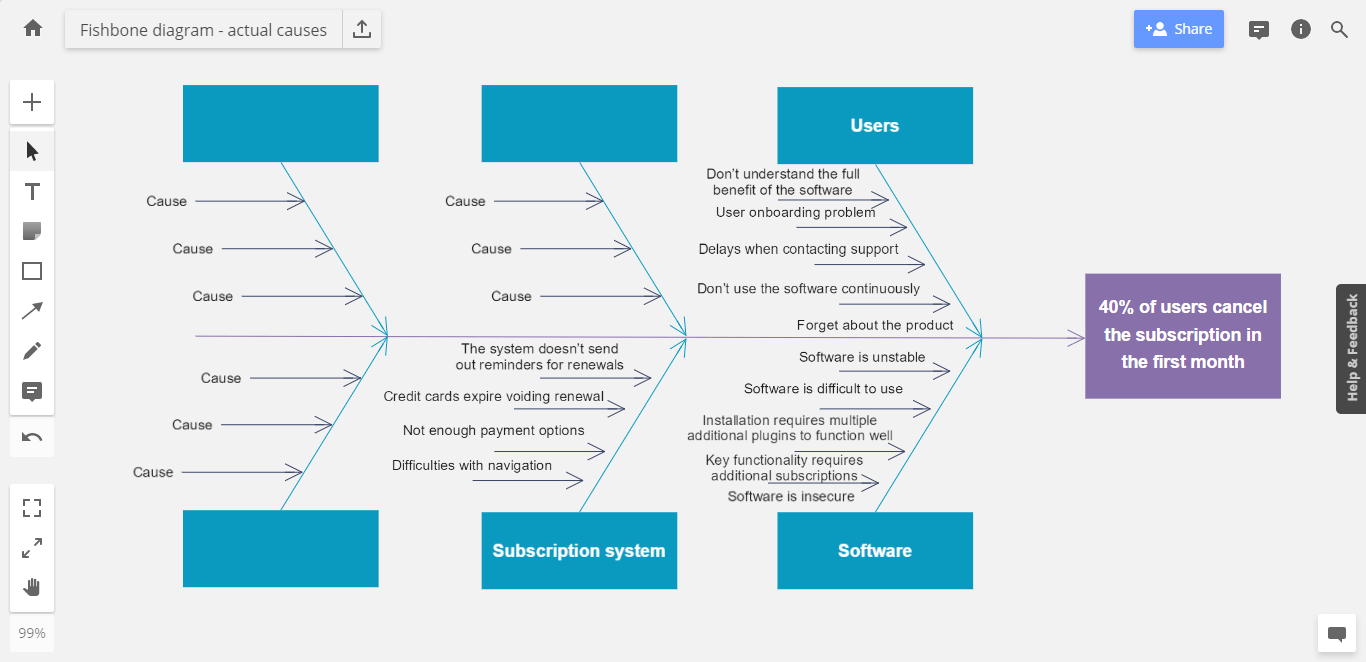
Now that you’ve defined the key areas to look into, let’s go through each one to determine all the individual influences that can affect our output. Look at each category and list every possible cause you can think of.
Looking at the subscription system, some possible causes include:
- We aren’t offering enough payment options
- The payment and registration systems are difficult to navigate
- Credit cards expire, voiding renewal
- The system doesn’t send out reminders for renewals.
When considering the user, potential causes include:
- Users don’t understand the full benefit of the software
- Users don’t know how to use all the functions
- Users experience delays when contacting support
- Users don’t use the software continuously, only requiring it for a few days at a time
- Users forget about the product.
When it comes to the software itself, potential causes may be:
- The software is unstable and crashes regularly
- The software is difficult to use
- Software installation requires multiple plugins to function well
- Key functionality requires additional subscriptions
- The software is insecure.
These are just a few potential causes. You should fill your fishbone diagram with as many different causes as you can come up with. Note that not every area of your diagram needs to have causes. Some might even have more causes than others.
Regardless, you now have a starting point to determine root causes. To keep going, investigate each cause to establish its actual effect on your output.
Tips to determine the actual cause:
- Run a brainstorming session or lay out a process map to generate better causes for your fishbone diagram
- Invite other team members in the process to make sure you’ve identified all the potential causes
- Some causes may have multiple sub-causes. Expand your fishbone diagram as needed to encompass all possible causes.
Step 4 – Using tools to plan the way forward
Remember, a fishbone diagram helps identify a problem’s causes. It doesn’t lead to solutions on its own. In fact, part of learning how to make a fishbone diagram is knowing what other tools you can use to identify causes more effectively.
Here are a few more tools to help you take your fishbone diagram to the next level:
Process Map
A process map is a flowchart of a specific system, showing all its inputs and outputs. It works best in areas like the manufacturing industry, where each product has a clearly defined process with multiple steps.
Process mapping involves looking at each step of the process one by one and listing all the potential influences. In an actual manufacturing environment, this may include being present on the production line and viewing the system, taking notes as you go through the process.
A process map is very effective at making sure you consider all the steps and influences involved in a system. In other words, it helps you clearly identify potential causes and add them to your fishbone diagram.
Brainstorming
Brainstorming is a fairly common tool in modern businesses. Instead of considering all the factors of a fishbone diagram by yourself, include others in the process. When working alone, it’s easy to overlook certain areas and completely miss others.
That’s why it’s worth making sure your brainstorming session takes the shape of a clearly-defined meeting. Have someone lead the session, taking note of any ideas team members offer up and leaving room for discussion. The goal is to end the brainstorming session with a list of causes to add to your fishbone diagram.
Once you’ve filled out your fishbone diagram, make sure everyone’s on the same page about how to follow up — whether it’s about delegating tasks or setting clear deadlines.
Tips for planning next steps:
- Not sure what causes to investigate? Collaborate with your team members on developing a cause-and-effect matrix. This way, you’ll get to rank causes by priority based on your team’s experience.
- Want to address a problem’s root cause and not just its symptom? Use our 5 Whys Template to take a closer look.
- How to make a fishbone diagram in a remote team
A fishbone diagram is more effective when multiple people get involved in creating it. But if your team works in remote and hybrid settings, you’ll need a tool designed to facilitate seamless collaboration.
Miro’s visual workspace is built for collaboration, making it easy to make a fishbone diagram together in real time — even if you aren’t in the same room. Seamlessly build diagrams using our intuitive, automated diagramming tools and our drag-and-drop, infinite canvas.
Not sure how to make a fishbone diagram from scratch? Save time using our free Fishbone Diagram Template . It’s fully customizable, allowing your team to add as much detail as you want and adjust its look and feel.
Tips for collaborating on a fishbone diagram in Miro:
- Invite your team to edit your board with you in real-time
- Invite stakeholders to view and comment on your Miro board for instant feedback
- Differentiate ideas by color-coding them
- Use frames to present your fishbone diagram and easily export it as a PDF or image
- Use sticky notes to add important context when building your fishbone diagram
Above all, avoid trying to build your fishbone diagram too quickly. Take the time to understand all the contributing factors, and make sure that anything you add to the fishbone diagram adds value.
- When to use a fishbone diagram?
Though fishbone diagrams were originally meant for problem-solving, they’re far more versatile — helping you break down any process or system into its contributing factors.
Here are a few use cases where knowing how to make a fishbone diagram comes in handy:
- To analyze a problem statement
- To brainstorm the causes of the problem (root cause analysis)
- To analyze a new design
- Process improvement
- Quality improvement
When in doubt, talk to your team to clarify the problem you’re investigating and how a fishbone diagram would help.
Miro is your team's visual platform to connect, collaborate, and create — together.
Join millions of users that collaborate from all over the planet using Miro.
- Step 1 – Define the problem
- Step 2 – Decide on key categories of causes
- Step 3 – Determine the actual causes of the problem
- Step 4 – Using tools to plan the way forward
Keep reading
Don’t let ideas die post-retro: 5 ways to make retrospectives more actionable.
Removing the hassle of brainstorm documentation with Miro + Naer
From ideas to execution: 5 ways to go beyond brainstorming to bring ideas to life
Fishbone Diagram Root Cause Analysis – Pros & Cons
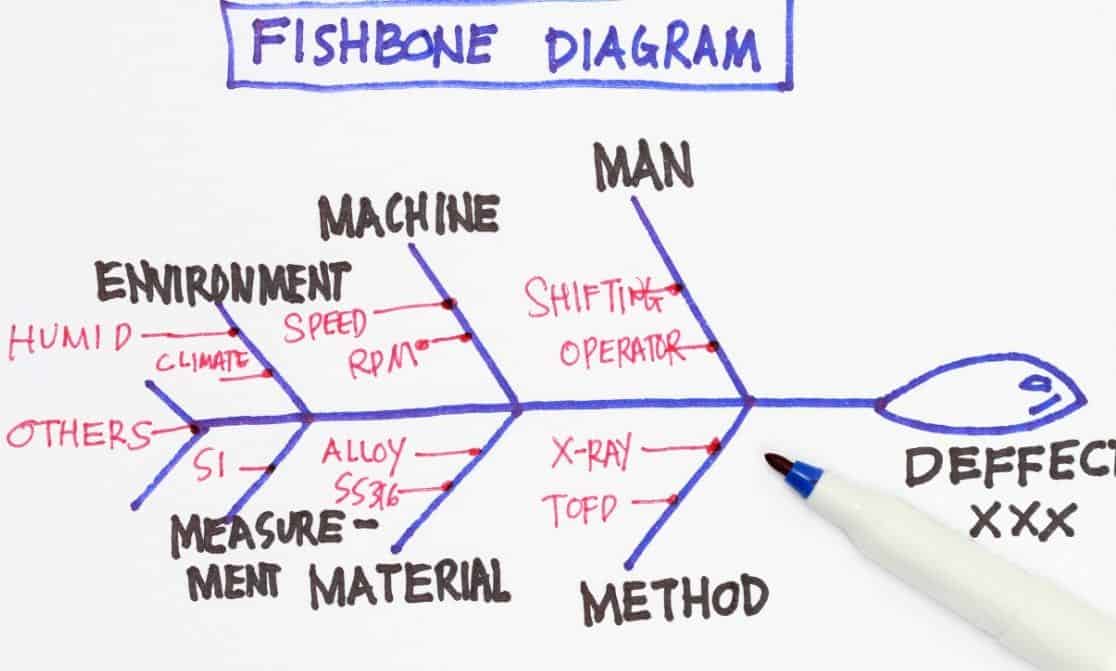
Pros & Cons of Fishbone Diagram Root Cause Analysis (Ishikawa Diagram)
Recently, I’ve seen several articles explaining Fishbone Diagram root cause analysis. They explain how they use the technique, but they usually leave out the disadvantages of using a Fishbone Diagram. Therefore, I thought I would outline the pros and cons of Fishbone Diagram root cause analysis.
How Fishbone Diagram Root Cause Analysis Works
The root cause analysis technique called a Fishbone Diagram (or an Ishikawa Diagram) was created by university professor Kaoru Ishikawa in the 1960s as a quality control tool. He published a description of the technique in 1990 in the book Introduction to Quality Control .

A Fishbone Diagram (a sample of which is shown below) shows the problem at the head of the fish-like looking diagram and a backbone with major factors that can bring success or failure to the process as the major bones attached to the backbone. In the example below, the major factors are:

Each of the major factors then has additional bones attached to that category that outline the cause-and-effect relationship that may be causing the problem.
You can use many techniques to develop a cause-and-effect relationship, but people often describe using a 5-Why type questioning process to create the cause-and-effect bone structure.
Another method that people use to develop the bone-like structure is brainstorming. The team brainstorms the major factors influencing performance (the main bones attached to the backbone). Then, they brainstorm potential root causes of the problem for each major performance factor. The team then reviews their potential causes and identifies the “most likely” root cause (or, in some cases, root causes).
The diagram above comes from this article ( LINK ), which also includes the video below that outlines the use of a Fishbone Diagram.
Another article used the example below to describe a Fishbone Diagram…

Now that you understand what a Fishbone Diagram looks like and how you might draw one – let’s review the pros and cons of the technique when it is used for root cause analysis.
Fishbone Diagram “Pros”
First, let’s review the pros of using Fishbone/Ishikawa Diagrams for root cause analysis.
Let’s start with the fact that a Fishbone Diagram is fairly easy to use. Like 5-Whys and Brainstorming (which can be used to develop the “bones”), the technique is simple to learn and apply.
Next, the technique is visual. It is easy to see what the investigator sees as the main problem (the head of the fish), the major factors influencing performance (the main bones attached to the spine), and the potential causes (the minor bones). the Fishbone Diagram provides a relatively easy-to-understand diagram of the cause-and-effect relationship that the investigator wants to communicate.
Also, Fishbone Diagrams have a long history of over 50 years of use. It certainly was one of the original techniques developed to help problem solvers understand the causes of a problem.
Finally, many claim that it is an effective root cause analysis tool.
Fishbone Diagram “Cons”
Now, let’s look at the cons (drawbacks) of using Fishbone/Ishikawa Diagrams for root cause analysis.
First, the technique is based on the root cause analysis technique of Cause and Effect. Cause and Effect has several drawbacks that we have documented in previous articles. For example, these three articles outline many of the drawbacks of Cause and Effect analysis…
“Fast” Root Cause Analysis: Brainstorming, 5-Whys and Fishbone Diagrams
Problems using 5-Whys? Read “Under Scrutiny” from Quality Progress to understand why!
Are You Dissatisfied with 5-Whys Root Cause Analysis?
Second, in all the examples I’ve seen, there is no guidance for building the bones of the fish. The building of the bone structure depends on the knowledge of the investigator or investigative team. And many (or should I say most?) investigators don’t have training in the causes of human errors (the science of human factors). Thus, the bones on their Fishbone Diagrams are their guesses at the causes of human errors, and they don’t have any human factors to guide them beyond their knowledge of human error.
Third, Fishbone Diagrams don’t have any guidance for what a “root cause” is
Many think they know the definition of a root cause but don’t have a standard definition for their team. For an article about defining a root cause, see THIS LINK .
Fourth, the other technique that can be used to develop the bones of a Fishbone Diagram – Brainstorming – has all the same drawbacks already mentioned.
Fifth, I’ve heard people use “voting” by the team as a way to determine the “root cause” of the many bones on the Fishbone Diagram. Brainstorming, followed by voting, is simply the team’s opinion. It doesn’t prove that the selected cause caused the incident (problem).
Sixth, Fishbone Diagrams don’t help the investigator determine what happened, which really should be explored before one starts trying to figure out why the incident/problem happened. You must understand “What Happened” BEFORE you start trying to find out “Why It Happened.” Without understanding what happened, people using Fishbone Diagrams often jump to conclusions without completing their fact-finding. Thus, they don’t have proof of why the bones on their Fishbone Diagram are root causes.
Seventh, Fishbone Diagrams provide no guidance to help investigators develop effective corrective actions. Therefore, the team often ends up picking one or more of the three standard corrective actions:
And these three standard answers certainly aren’t the whole list or an effective list of corrective actions.
The seven “cons” mentioned above are serious drawbacks to performing a thorough, fact-based root cause analysis and developing effective fixes. If these drawbacks concern you (and they should), you might consider another root cause analysis tool.
TapRooT® Root Cause Analysis
TapRooT® Root Cause Analysis is a systematic, guided process for investigating incidents (problems) and developing effective fixes to prevent repeat failures.
Here are three ways to learn more about how TapRooT® Root Cause Analysis can help you improve performance.
First, you can watch this video of Mark Paradies, one of the co-creators of the TapRooT® System, being interviewed on Worldwide Business by Kathy Ireland…
Second, click on the website’s picture below to discover the TapRooT® Advantages…

And finally, you can read a white paper that provides an example of how TapRooT® works. Just CLICK HERE to download the PDF.
TapRooT® Root Cause Analysis Training and Software
If you would like more information about TapRooT® Training, see THIS LINK .
If you would like more information about TapRooT® Software, see THIS LINK .
Thanks for reading this article about Fishbone Diagram root cause analysis. If you would like to talk about your root cause analysis needs, please call one of our experts at 865-539-2139 or contact us by using THIS LINK .

- Share To Twitter
- Share To Facebook
- Share To LinkedIn
- Share To Pinterest
2 Replies to “Fishbone Diagram Root Cause Analysis – Pros & Cons”
“Cause and Effect has several drawbacks…”
Is the issue more a matter of how certain “cause and effect” methodologies are applied, rather than the notion of “cause and effect” per se. Cause and effect is after all a pretty well-known construct of, well, everything really.
Cause and effect is a model of reality that we use to make sense of things.
The problems with cause and effect are problems of how we view things.
We jump to conclusions. We look for evidence that confirms our beliefs. We have limited knowledge and don’t know all the potential cause and effect combinations.
These limitations are inherent in humans and cause and effect.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
More Articles That Might Interest You...


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A fishbone diagram is a problem-solving approach that uses a fish-shaped diagram to model possible root causes of problems and troubleshoot possible solutions. It is also called an Ishikawa diagram, after its creator, Kaoru Ishikawa, as well as a herringbone diagram or cause-and-effect diagram. Fishbone diagrams are often used in root cause ...
Also called: cause-and-effect diagram, Ishikawa diagram. This cause analysis tool is considered one of the seven basic quality tools. The fishbone diagram identifies many possible causes for an effect or problem. It can be used to structure a brainstorming session. It immediately sorts ideas into useful categories.
The Fishbone Diagram is a graphical tool used for identifying and organizing possible causes of a specific problem or outcome. The diagram resembles the skeletal structure of a fish, hence its name. ... With all potential causes visually represented in one place, it becomes easier to analyze and discuss the issues. 2. Team Collaboration:
A fishbone diagram is a visualization tool, developed by Dr. Kaoru Ishikawa, a quality control specialist, for identifying the root causes of a problem, categorizing them, and generating solutions. Also called the Ishikawa diagram, or cause and effect diagram, the fishbone analysis is often used in troubleshooting and product development ...
The purpose of the fishbone diagram is to identify all the root causes of a problem. You can use fishbone analysis in product development — let's list a few cases where you should use fishbone analysis: When you have to identify the possible causes of a problem. When you have to develop a feature or product to fix the cause of a problem.
The Fishbone Diagram offers a visual way to organize the problem's multiple causal chains. Each primary bone represents a causal chain. The primary cause is written in the box at the end of the bone, and subcauses are written underneath the secondary bones jutting from the primary bone. Follow the steps below to use this template.
Morning - just a quick post on using a fishbone diagram to help students write more focused cause and effect texts - especially when there are multiple causes. Each rib is for a separate cause contributing to the effect. Once the ribs have been completed with brief detail (which you can check as you go), the student can write a short ...
A fishbone diagram, also referred to as a cause and effect diagram or an Ishikawa diagram, is a helpful tool for identifying the root cause of a problem.It allows you to list all the potential causes that may be contributing to the effect you are currently experiencing. This visual aid takes the shape of a fishbone, hence its name, and is commonly used during brainstorming sessions.
Consider trying out a fishbone diagram the next time you embark on an internal process improvement project for your company. This visual cause-and-effect analysis tool helps you identify the potential causes of a problem somewhere in your quality control chain so you can address and solve issues at their root.
The fishbone diagram, also known as the Ishikawa Diagram or cause-and-effect diagram, is a problem-solving method that uses a fish-shaped chart to model complications and their causes. The diagram was developed by Dr. Kaoru Ishikawa in the 1960s and frequently turns up in project management and education processes.
A fishbone diagram, also known as cause and effect diagrams, Ishikawa diagram and Herringbone diagram, is a visualization tool used to find the root cause of a problem. It helps you group all the potential causes of a problem in a structured way to find the ultimate cause of your problem. Kaoru Ishikawa invented this diagram in the 1960s to use ...
Download. A fishbone diagram, also known as a "cause and effect" diagram is a problem solving technique used in project management. It has also been referred to as an Ishikawa diagram after a Japanese professor; Kaoru Ishikawa. Problems arising in projects usually have many causes and in some cases, these problems may be interrelated and ...
Professor Kaoru Ishikawa created Cause and Effect Analysis in the 1960s. The technique uses a diagram-based approach for thinking through all of the possible causes of a problem. This helps you to carry out a thorough analysis of the situation. There are four steps to using the tool. Identify the problem. Work out the major factors involved.
The fishbone diagram has many names: the Ishikawa diagram, the Fishikawa diagram, the Herringbone diagram, and the cause-and-effect diagram. In Six Sigma, you use it in the "Analyze" phase of DMAIC ( define, measure, analyze, improve, and control). This diagram got the name Ishikawa because Professor Kaoru Ishikawa developed it in 1960.
In this video, we provide a fishbone diagram (aka Ishikawa diagram) tutorial.In the video we'll cover:- The key components of a fishbone.- A fishbone diagram...
Step 1 - Define the problem. The first step to solving any problem - and the key to learning how to make a fishbone diagram - is correctly defining it. A clearly defined problem makes it easier to identify causes. It also encourages us to determine whether there's even a problem to begin with. In this case, the problem we've ...
How to construct a fishbone diagram. 1. Problem Statement. Draft a clear problem statement, on which all team members agree. Be specific about how and when the problem occurs. Write the problem statement on the right side of your paper, at the head of the "fish." Your team will work out and away from this problem.
Fishbone diagrams have a few different names that are used interchangeably, including herringbone diagram, cause-and-effect diagram, and Ishikawa diagram. These are all ways to refer to the same thing- a problem-solving approach that uses a fish-shaped diagram to model possible root causes of problems and troubleshoot solutions.
Fishbone diagram (also called Ishikawa diagrams or cause-and-effect diagrams) is a graphical technique to show the several causes of a specific event or phenomenon. In particular, a fishbone ...
First, let's review the pros of using Fishbone/Ishikawa Diagrams for root cause analysis. Let's start with the fact that a Fishbone Diagram is fairly easy to use. Like 5-Whys and Brainstorming (which can be used to develop the "bones"), the technique is simple to learn and apply. Next, the technique is visual.
Fishbone Diagram Essay. Often when in teams using the fishbone diagram is a great solution for identifying and analyzing problems. The fishbone diagram is very helpful because it allows you to visually display multiple problems and effects that lie in a company for example materials,Assessment,People,method,Equipment, and environments.