
- Copywriting
- Optimization
- Content Marketing
- Email Marketing
- Social Media
- Human Resources
- Entrepreneurship
- Customer Support
- Project Management

- Best Web Hosting Services
- Best Website Builders
- Best Domain Registrars
- Cheap Web Hosting
- VPS Hosting
- Free Web Hosting
- Dedicated Web Hosting
- cPanel Web Hosting
- Reseller Web Hosting
- Shared Web Hosting
- Cloud Web Hosting
- Best Blogging Platforms
- Best Ecommerce Website Builders
- Best HR Software
- Best Online Payroll Services
- Best PEO Service Providers
- Best Background Check Companies
- Best Conference Call Services
- Best Phone Services for Small Business
- Best Remote Access Software
- Best Accounting Software
- Best Business Checking Accounts
- Top 9 Best Time and Attendance Systems – In-Depth Review
- Best HR Outsourcing Services–Do You Really Need Them?
- Top 11 Best Business Formation Services – In-Depth Review
- Top 7 Best Business Card Printing Services – In-Depth Review
- Top 12 Best Business Loans
- The Best Online Legal Services (Don’t Get Scammed)
- Top 7 Best Billing and Invoicing Software
- Top 9 Best Invoice Factoring Companies
- How to Create a Website
- How to Build a Shopify Website
- How to Make Websites Mobile Friendly
- How to Start a Blog
- How to Make Money Blogging
- Types of Blogs
- How to Start an Online Store
- How to Create An Ecommerce Website
- How to Start a Business
- How to Write a Business Plan
- How To Ask For a Review
- How to Repair Your Online Reputation
- Link Building For SEO Starter Guide
- How to Learn SEO

A Step-by-Step Guide to Writing a Compelling Article Introduction
Wouldn’t it be great if every single person who clicked on one of your articles read it from start to finish, unable to pull their eyes away from the screen?
We think we both know the answer to that question.
To achieve this goal, however, you must master the art of writing intriguing introductions.
Wait a second , you’re thinking. Writing introductions? Isn’t that kind of a small detail of a 2,000-word article? Unfortunately, no. Your article intro is not a small detail.
The introduction to your article is often the difference between engaging readers and having a bounce rate high enough to make a click-baiter cringe .
Think about it. If you don’t grab your readers right away, you’ll lose them.
You went through all that work of writing a killer article, right? You worked hard at it. You spent a lot of time on it. You did a ton of research but if your introduction sucks, your efforts will be all for nothing. You’ll have lost before you even got started!
If you want to write great content , improve the success of your marketing campaigns, and increase the loyalty of your fans, you must master writing introductions.
Let us show you how.
5 Steps to Write an Article Introduction
Here’s how you write a blog introduction that doesn’t stink:
- Master the opening line
- Have something unique to say
- Keep it simple
- Speak directly to the reader
- Explain what the article is about
Step 1 – Master the Opening Line
To have a strong introduction, you need to open with a strong first sentence.
The millisecond your reader hits the page, they have an extremely high likelihood of leaving the page.

Data says so.
The first sentence has one single purpose: to entice the reader to read the next sentence. In doing so, it sets the tone for the rest of the article, hooking the reader in, one step at a time.
If you fail at this, you readers won’t scroll. That’s why its often best to have your first sentence act as a hook to engage a readers attention. The easiest way to do this is to cite a relevant fact or statistic that you know the reader will be interested in that relates to your article’s topic.

And if they don’t scroll, they won’t engage.
Check out this article by Dilbert author Scott Adams to see how the first sentence is done.

He writes this:
I went from being a bad writer to a good writer after taking a one-day course in “business writing.”
That’s a great opening line.
Why? Because it makes you want to know more!
- How did he become a good writer?
- What did he learn?
- Could I benefit from it too?
Adams nailed it. He drew us in by making us ask questions.
If you don’t know how to craft an intriguing first sentence, the remaining words of your article will be a complete waste.
Luckily for you, with a few simple tricks, writing a phenomenal first sentence can be quite easy.
The first thing to keep in mind is that you want to keep the first sentence short. This makes it easy for the reader to digest the first bits of information and prevents them from losing interest quickly.
But there is more to it than that.
You have to make sure that the first sentence grabs the reader’s attention and holds it for the rest of the article.
Here are a couple of tried-and-true tactics that make for super compelling first lines.
Ask the reader a question
This is an easy way to get the reader’s attention and get them engaged without a whole lot of effort on your part.
For example, if you are writing an article on quitting your job and starting your own company, you could open with the question: “Did you know that almost 70% of Americans report being actively disengaged from their careers?” Remember we mentioned using a statistic earlier?
Why does this work?
It has to do with the brain’s “ limbic reward system .”

When this system is activated, dopamine is released. And dopamine gives us a sense of reward and pleasure.
When we are intrigued by a question, i.e., experience a sense of curiosity, the limbic reward system lights up. And that’s why we want to keep reading—it’s rewarding to satisfy curiosity.
Here’s an example. Writer Olga Khazan asks a question that’s on everyone’s mind, causing the reader to be instantly interested:

We want to know the answer to that question, so we keep reading.
That’s why a question is a great opening line. You can even use the question as the article title.
Tell a story
The brain also lights up when it encounters a story.
According to the theory of neural coupling , certain portions of the brain are activated when a reader thinks about the same mental and physical activity that a character in a story is doing.

James Clear usually starts his blog articles with a story, often a true story.

The story makes his readers interested in the article and keeps them reading to the very end.
Use a shocking quote
Another great way to start your article is to use an attention-grabbing quote.
Let’s say you are writing an article on world travel. A great way to introduce the article would be with the quote from Helen Keller:
“Life is a daring adventure or nothing at all.”
Using a quote like this will grab the readers attention and make them want to learn more.
Tell the reader to imagine
Sparking the imagination is an instant way to draw the reader into the experience of the article.
Notice how this article begins:

The reader tries to obey the imperative by imagining. This effort compels the reader to read further, drawing them into the article.
Writers for The Atlantic are experts at their craft. This writer does the same thing—asking the reader to imagine.

Share an interesting fact
In a day and age when the Internet is so rife with untrustworthy information and fraudulent “gurus,” people are skeptical. They have every reason to be.
Opening your article with a relevant fact or statistic is a great way to establish trust and authority from the first sentence and let readers know you’ve done your research — like we said before.
Step 2 – Have Something Unique to Say
Okay, so you’ve crafted an excellent first sentence, and you have your reader’s interest.
Now, you have to hold that interest by having something interesting and uncommon to say.
Very few people take the time and energy to regularly produce new, thought-provoking content. If you do, you’ll set yourself apart from the herd in a big way.
Forget re-purposing of old articles or rewriting stuff from other people’s websites. If you want to have the reader’s respect and attention, you have to say something they’ve never heard before.
Unfortunately, a lot of the stuff you read today has been regurgitated 28 times before.
Let’s imagine you run a travel blog. Based on our advice, you write a number of 3,000-word comprehensive “How-To Guides.”
Whenever a reader opens your guide on financing their way around the world trip, they’ll expect to read all about airline rewards programs, frugality, and credit card points.
And that information is great, but it is also very generic.
A better introduction would be something like this:
How would you like to save up enough money in the next 6 months to spend all of 2017 traveling the world? That would be pretty epic, right? Well, this is entirely possible, and in today’s article, we’re going to show you how you can do this. It’s not by skipping your morning latte or spending thousands of dollars with your credit cards on a few hundred miles either. We’re going to show you how you can create a life of mobility and freedom by leveraging the skills you already have, tactically selecting your destinations, and using a little known tax secret that will save you thousands of dollars! Sound good? Let’s get to it.
It’s hard to be different. We realize that.
Sometimes, in order to create unique stuff, we simply have to work harder, think longer, and research more than our competition.
Here are some ways you can develop that unique voice in your article introduction:
- Share a personal story or fact. You’re the only you there is. You can share a story or experience no one else can. One way to tell such a story is to write, “If you know me…”
- Get your emotions in it. People have an emotional reaction to emotions. When we convey our emotions in our writing, people tend to respond. Besides, emotion is also a unique and personal thing. How do you communicate this in an introduction? Easy: “Want to know how I feel about it? I feel….”
- Share your goals or vision. If you have a guiding goal or vision for life, you can communicate this in your introduction. “That’s one of the reasons we wrote this post. Our goal in life is to…”
- Make a promise. A promise is a personal and attention-grabbing thing. Give your readers a promise, and it will secure their loyalty and their interest. “We promise that we’ll do our dead-level best to….”
Unique isn’t easy . But it’s worth it.
Step 3 – Keep it Simple
We live in a world where most people have an attention span of only a few seconds.
Apparently, our attention span is getting shorter!

After a few seconds, we get bored and move on to the next shiny object.
If you want your readers to make time in their days to read what you have to say, make sure you present things as simply as possible .
Longer articles, of course, deserve longer introductions. But it’s important to respect people’s time and attention. You can’t change what is (people’s short attention spans) by writing a long introduction based on what should be (longer attention spans).
Avoid rambling about how great your information is, and just share it already!
Step 4 – Speak Directly to the Reader
Whenever you are writing educational material for other people, you want to use the word “you” as much (and as naturally) as possible.
In this article, We’ve used some variation of the word you more than 100 times. Why? Because we’re talking to you! We want you to know this information. We want you to benefit from it.
By emphasizing the word “you” in your article, you show the reader you are directly addressing them and their situation and not just writing a generic article to the general populace.
But there’s another side to this. I should refer to myself as well. My goal is to convey a personal feel to this article. After all, it’s me talking to you, right? So it’s only natural that I would refer to myself too — although more sparingly.
Step 5 – Explain What the Article is About
The point of an introduction is exactly that: to introduce the content that will be presented in an article.
We cannot tell you the number of times online articles left us confused even after we had read a few of their paragraphs.
We couldn’t tell whether the authors were teaching us how to run successful Facebook ads , or telling us a weird story about their childhood.
That’s why its crucial to take a few sentences, and clearly explain what the article is going to cover without giving away too many details.
This will build suspense around the subject matter while still letting your audience know what they may be in for.
A great example of this comes from the Buffer blog. Notice how the introduction poses a question and then proposes to answer that question.

Your curiosity stays high, but the introduction sets the stage.
Explain the importance of the article
Once you’ve explained what the article is, now it’s time to explain why people should care.
Everyone on the Internet approaches every new piece of information with a simple question: “ What’s in it for me ?”

If you want to write introductions that hook the reader and help your content go viral , you have to master the art of explaining what the reader stands to gain from the information you are sharing.
How will it benefit your readers’ lives? How will it solve a problem they are facing? How will it cure a pain they are feeling?
If you understand how to quickly and efficiently answer these questions, you’ll keep your readers glued to your article till the last word.
Few things can make or break your article as easily as an introduction.
If you can master the art of the first few paragraphs, you’ll be able to increase reader engagement, improve sales, and earn a reputation as a phenomenal writer.
It’s not an easy skill to master, but like many things in Internet marketing, it’s fairly straightforward.
If you put in the work, you’ll get results.
Privacy Overview
Alexandra Cote 🚀
SaaS growth marketer
How to Start an Article – 100+ Examples of Article Introductions

While I love writing articles , I just dread putting together the perfect introduction. I don’t believe in a universal formula that you can apply to make it easier for you to write an effective blog post introduction. However, I assume there are certain things good introductions have in common.
So I’m having a closer look at 100+ article introductions to see if there are any similarities we can learn from:
Here’s a video version of the article:
Getting people to imagine
Oh, the power of imagination . Works like a charm every time for article introductions.

Introducing a common problem for a specific reader segment

Some authors prefer to target niche audiences and make assumptions regarding their interest and problems from the start:

Question in the article introduction

This technique does appear to be overly used because it’s a certain way of helping readers make the connection between the article they’re about to read and their own issues :

Often the question is there just so the article can answer it. So you’re essentially going to read one extra long answer after the article’s introduction:
Questions can also be used in article intros to take readers back to a past memory and create a sense of nostalgia :

The general statement as the article’s intro
Just that and used much too often as we’re already expecting a similar into for most articles. Frankly, this type of post introduction doesn’t add much value besides setting the context or introducing one main topic.

Closely related to the general statement, there’s also the “here’s why you should keep on reading this article” phrase/paragraph where the importance of the topic is highlighted first:

Here’s a mix of a quote and a question with the aim of making people relate to the quote :

Or perhaps you’d like to explain a quote or mantra by naturally inserting it into the first phrase:

Take advantage of seasons, holidays, news, or recent events

You can also take existing articles that are highly debatable, controversial, or just the ones that launch a new idea to discuss around:

Straight to the point
Skip the fluff and tell or show readers what they’re looking for :

Here are other similar example of article introductions:

The next blog post introduction takes advantage of various possible structures and text formatting you can use to create excitement around a launch or simply add some of your own brand’s personality:

I’ve always been an advocate of using CTAs to their best and consider all conclusions should have one call-to-action at least, but I must admit that adding them to your article’s introduction can also be the right way to go if it leads to your main goal for that specific piece of content:

Giving a definition

Never fail with studies

Statistics work just as fine:

Every time actually.

And you can use the article’s intro to tease the results and make people want to read more like here :

Another way of leveraging stats is by referencing past numbers and creating the expectation of improvement :

Putting the author first

Here’s another article introduction example from Coach the Life Coach :

In this sample, the author is using her past experience to present a problem the reader might have and suggest that further reading the article will provide a solution:

Of course, putting the author first often means bringing your brand or business to the front too :

You’ll also occasionally come across the “here’s what we’re doing” type of posts:

Or you can take the straight-forward way and boldly place what you’re promoting at the start of the article or directly create your blog post around that idea:

Sharing the experience of a brand or company is also highly valued:

Putting the reader first
In other words, repeated use of YOU or situations the reader might be familiar with .

Take a look at this example which puts emphasis on the reader while also getting him/her to imagine an existing or ideal reality :

Here’s a different way to appeal to the reader by making a typical assumption that you know what they’re thinking:

Another introductory paragraph on Newsweek where the transition is slowly being made from the author (first person) to the reader (second person) :

The third person
Or the go-to introduction for any interview and podcast .

Success stories are also favorably viewed loved by all kinds of audiences and it’s only natural to start the article by putting the person you’re going to talk about (or talk to) at the beginning:

You’ve seen this in use all too often:

Of course, this technique (although almost a standard so to say) is a bit outdated since we’re so used to seeing this structure, so here’s a different way of approaching the introduction of the person the article is centered around:

Storytelling starts within the introduction

Now this is a story anyone would want to hear:

Making a promise
This is an ever-common way of ensuring you’re getting visitors to keep reading the article and not just move on to another one after reading the first 3 sentences.

Everyone is following this trend:

A mix of promise and question to get brains moving:

Brian Dean takes advantage of this technique to make some pretty strong promises, but in his case, he manages to deliver them fairly accurately. Here are three of those statements as placed in introductions:

The last one also offers readers assurance on the credibility of the author as he writes about things he managed to achieve himself.
And such examples are endless:

Getting readers to think from the article’s intro
In this article introduction example from Scott H. Young , the author involves the reader by giving facts and asking a question that will get them to think and make their own assumptions before they read on:

Making structure work for you
Notice how articles on bigger outlets (particularly those that focus on news) tend to have an introductory phrase, similar to a subtitle , which resumes the article or creates the premise for the topic to be discussed:

Here’s another example, this time on Medium:

And another such “introduction” on The Guardian :

Slack also does this with their blog posts, proving it’s not just a technique for the news outlets:

Repeat the title

Simply rephrasing the headline in the post’s introduction is a more natural way of essentially emphasizing the main idea of the article:
Breaking the article introduction into several short paragraphs
Another trend related to the form of the introduction is separating each sentence in the intro into multiple paragraphs with plenty of white space between them:

Have any secrets to building a successful article introduction? Feel free to share them!
P.S.: I’m also doing a quick poll to see if people actually read and care about introductions or just skip them. If you have 3 seconds, cast in your vote:
By clicking submit, you agree to share your email address with the site owner and Mailchimp to receive marketing, updates, and other emails from the site owner.
Published by Alexandra Cote
Alexandra Cote is a SaaS content writer and strategist with a passion for workplace productivity, social media marketing wonders, conversion rate optimization, artificial intelligence, and keyword research (Hooray for SEO!). Reach out to her via LinkedIn or her blog. View more posts
One thought on “ How to Start an Article – 100+ Examples of Article Introductions ”
I love it so much
Leave a comment Cancel reply

- Already have a WordPress.com account? Log in now.
- Subscribe Subscribed
- Copy shortlink
- Report this content
- View post in Reader
- Manage subscriptions
- Collapse this bar
9 Simple Ways to Write a Good Introduction Sentence
Published: June 23, 2023

Compelling readers to read the article is an art form in itself. And if you don't do it well, you're missing out on potential subscribers, leads, and customers.
In this post, we'll share how to write powerful introductions that turn casual browsers into readers. Article introductions matter, and here’s how to make them count.
How to Write a Good Introduction Sentence
- Keep it short.
- Say something unexpected.
- Don’t repeat the title.
- Use the word “you” at least once.
- Tell readers what's coming next.
- Explain why the article is important.
- Refer to a concern or problem your readers might have.
- Be careful telling stories.
- Use a stat or a fact to convey urgency.
1. Keep it short.

I’m a big fan of short sentences. I love them because people can understand them easily. There's great value in short sentences that are readable, digestible, and punchy.
Writers often get caught up in the pressure of a good intro that they deliver long, run-on sentences. The problem with these sentences is that it makes readers work hard, which isn’t a great incentive to keep reading.
While the length of an introduction can vary, it’s best to aim for brevity with up to three short paragraphs. Using AI tools like our Paragraph Rewriter tool can help make your paragraphs more impactful and concise.
Readers are impatient to get to the meat of the article so don't bury the lede deep in your article – cut to the chase.
.png)
6 Free Blog Post Templates
Save time creating blog posts with these free templates.
- "How-to" Post
- "What is" Post
- Listicle Post
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
2. Say something unexpected.
You've probably heard advice like "Create a hook" and "Grab the reader's attention." But what kind of stuff actually grabs someone's attention?

Here are some great options:
- Personal stories
- Scene setting, e.g. “Imagine…”
Think about it – your reader has already clicked on the headline. So, they’re interested in your topic. But now, you have to reel them in a little further.
If your very first sentence is interesting enough to make people want to read the next one, then you've done a good job.
3. Don’t repeat the title.
You only have a few seconds to make a strong impression in your intro. It’s a wasted opportunity to repeat your headline.
Instead, take advantage of your chance to reinforce that title and to set the stage for the article and the value it will bring.
4. Use the word “you” at least once.

The word “you” is a powerful word.
It tells the reader that you, the author, are writing the article with them in mind. You empathize with them, you care about them, and you want your piece to resonate with them.
It's a simple trick that establishes a crucial connection with your reader.
5. Tell readers what's coming next.
What will you be covering? What will the reader learn? How will this help them? These are all questions you should answer in your intro.

This sets the reader's expectations and helps them navigate your article. They might just jump to the section they’re most interested in or read the whole thing. For example:
- “You’re about to find out why sea turtles always lay their eggs on the beach.”
- “And, if you’ve ever wondered why sea turtles lay their eggs on the beach, here's everything you need to know.”
- “This article explains the 17 reasons why these amazing creatures lay their eggs on beaches.”
- “Fascinating, funny, and shocking, these are the reasons why sea creatures lay their eggs on the beach.”
6. Explain why the article is important.
It may be obvious to you why your article is important to your readers, but it’s up to you to emphasize its value and put it in context.
For instance, say you’re writing an article about TikTok written for a marketing audience. You could lead with a surprising TikTok stat about its user base. Here’s an example:
“In the past two years, TikTok’s user base has grown by 15% while other platforms are seeing stagnant or declining engagement. This suggests that marketers may want to pay more attention to this short-form video platform.”
In two sentences, you’ve presented an interesting tidbit and explained why it matters.
Take the introduction to this article, you'll recall the following sentence: “ And if you don't do it well, you're missing out on potential subscribers, leads, and customers. ”
My goal here was to connect the topic of blog post introductions to a business’ bottom line.
7. Refer to a concern or problem your readers might have.
Everyone in every field has their set of problems. You should have some listed already from when you created your buyer personas . Communicate your awareness of those problems in your introduction and you're more likely to gain a sympathetic reader.

People want to solve their problems, and articles that explain how to do this will help you earn readership.
8. Be careful telling stories.
A lot of people will tell you that you need to write a story in the introduction. Stories can work , as in the example above, but there are good and bad ways to tell stories in your intro.
Do use storytelling to spark the reader's curiosity and empathize with her. But don't get carried away and write a long-winded story that loses readers along the way.
Remember the tip about keeping introductions short? That still applies when you're telling a story. Here's an example from one of my own QuickSprout blog posts:
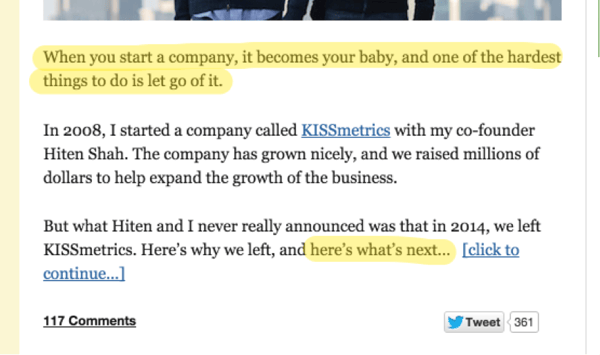
Notice that I highlighted the "empathy" section in the first sentence. Here, I helped form a connection with my readers. Then, I told a short story about my own experience. After that, I finished the introduction with what's next.
If you do begin your article with a story, here's a tip: Don't reveal the conclusion until the reader is deeper into the article, or even until the very end.
9. Use a stat or a fact to convey urgency.
When journalists begin a news story, they often give readers an eye-catching stat or fact about what's going on.

As a blogger or any type of writer, a really interesting stat or fact will draw your reader in and show them why your topic is really important.
For example, say you're a plumber writing a blog post on pipe replacement. You might pull in more readers if you start a post by explaining how frequently old pipes burst in the winter.
If readers see that this is a common issue that others face, they might keep reading to learn how they can avoid it.
Introduction Takeaways
The next time you write an article introduction, think about what kind of introduction would make you want to read the article.
To compel you to read past the introduction of an article, you want to read something unique, fresh, and engaging. You want to hear about yourself and your problems, making the article a must-read to help solve them.
Introductions are hard, and writing effective ones takes time and practice. But remember, it's all worth it if it means keeping the attention of a few more of your readers.
Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.
![introduction for article writing How to Write a Memo [Template & Examples]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/how-to-write-memo_0.webp)
How to Write a Memo [Template & Examples]

Comma Rules for Clear Writing (with Examples)

How to Write an Introduction: A Simplified Guide

How to Become a (Better) Editor: 13 Editorial Tips
![introduction for article writing How Long Should Blog Posts Be in 2021? [New Data]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/how-long-blog-posts.webp)
How Long Should Blog Posts Be in 2021? [New Data]

How to Improve Your Writing Skills and Escape Content Mediocrity (Infographic)

How The Flesch Reading Ease Test Can Help You Write Clear and Concise Copy

HubSpot's Guide to Becoming a Better Writer

What is a Metaphor? A 2-Minute Rundown
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform
- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources
How to Write a Journal Article Introduction Section
Our journal manuscript series has covered the various sections of a scientific article according to the order in which we recommend you write them ( Figures , Methods section , Results section , Discussion section , and Conclusion section ). In this second-to-last installment, we’ll talk about the Introduction and how to draft it in a way that intrigues your readers and makes them want to continue reading. After all, the journal publications industry is a business, so editors won’t accept your article unless they’re confident their readership will be interested.
What is an Introduction in a research paper?
After the Abstract (the final section of the paper you should draft) and the visual aids, like figures, a reader’s first true interaction with your work is the Introduction . Thus, like any other story, you must set a compelling stage that invites your readers into your research world. Essentially, your Introduction will establish the foundation upon which your readers will approach your work . You lay down the rules of interpretation, and if your manuscript follows the tips we’ve given in this series, your readers should be able to logically apply those rules throughout all parts of your paper, including the conclusion in your Discussion section.
Before we examine what specifically belongs in this critical context-defining section of your manuscript, let’s explore a practical point about writing the Introduction.
When should I write the Introduction section?
You may recall that we recommended a particular order for drafting your manuscript—an order that suggests the Introduction should be written second to last. You may also remember we talked about how the Discussion (or the Conclusion section for journals that separate the Discussion and Conclusion) should answer the questions raised in the Introduction. So which is it? Write the Introduction first or the Discussion? Honestly, the Introduction should come second to last because it is one of the harder sections of the manuscript to nail correctly. Therefore, we recommend writing the Introduction in two stages.
Start with a skeletal Introduction that clearly states the hypothesis (the question your research answers). Then proceed with fully drafting the remaining parts of your manuscript, including analyzing your results in the Discussion and drawing rough conclusions that you will later refine. Once you’ve finished the other parts, return to your Introduction and incorporate the information we outline further below under the heading “What should I include in the Introduction?” After, modify the Discussion’s conclusion accordingly and polish the entire piece once again.
What to Include in the Introduction Section
Your paper must read like a chronological story ; it will begin with point A (the Introduction) and advance in time toward point B (the Discussion/Conclusion). If you recall from our prior article, the Discussion should answer the questions “why this particular study was needed to fill the gap in scientific knowledge we currently have and why that gap needed filling in the first place.” The Introduction answers similar but distinct questions. The context you establish in the Introduction must first identify that there is a knowledge gap and then explain how you intend to fill that gap and why .
Imagine that your paper is an hourglass figure, as in the infographic below. Your Introduction holds the sand of knowledge that we currently have (the top bulb), and as the sand trickles through the neck (your research), it builds up a new base of knowledge (the bottom bulb). Thus your paper traces that journey from the top of the hourglass to the bottom, answering the questions in the infographic along the way. As a part of that journey, your Introduction is the starting point that answers the first three questions concisely.

As you can see from above, your Introduction should start broadly and narrow until it reaches your hypothesis. Now, let’s examine how we can achieve this flow of ideas more closely.
What is known about the current research topic?
- Start the Introduction with a strong statement that reflects your research subject area. Use keywords from your title to help you focus and avoid starting too broadly .
- Avoid stating too many obvious facts that your target readers would know . You should be precise about the area of focus so that readers can properly orient themselves before diving into your paper.
- As a trick to help you combat too broad a start, write down your hypothesis or purpose first .
- Then work backward to think about what background information your reader needs to appreciate the significance of your study.
- Stop going back when you reach the point where your readers would be comfortable understanding the statements you make but might not be fully confident to explain all the aspects of those facts.
- Cite relevant, up-to-date primary literature to support your explanation of our current base of knowledge . Make sure to include any significant works that might contradict your argument and address the flaws with that opposing line of thought. You want your readers to conclude that your approach is more plausible than alternative theories.
- Be sure to cite your sources . Plagiarism is a serious offense in the academic community that will hurt your credibility (not to mention it is a violation of many copyright laws). Direct copying or a closely matched language should be avoided. Instead, be sure to use your own words to rephrase what you read in the literature and include references.
- Remember that the Introduction is not meant to be a comprehensive literature review ! Don’t overwhelm your reader with a sea of citations. Instead, use key primary literature (i.e., journal articles) to quickly guide your reader from the general study area to more specific material covered by your hypothesis. In other words, the literature you cite should logically lead your reader to develop the same questions that prompted you to do your research project. Roughly a half page should suffice, but double-check with your target journal’s information for authors.
What is the gap in knowledge?
- As you describe our understanding of the relevant subject matter, highlight areas where too little information is available . However, don’t stop at saying “little is known about…” You must elaborate and tell your readers why we should care about unearthing additional information about this knowledge gap. See the subheading “How and why should we fill that gap?” for further details.
- Alternatively, your Introduction should identify what logical next steps can be developed based on existing research . After all, the purpose of sharing research is to prompt other researchers to develop new inquiries and improve our comprehension of a particular issue. By showing you have examined current data and devised a method to find new applications and make new inferences, you’re showing your peers that you are aware of the direction your field is moving in and confident in your decision to pursue the study contemplated by your paper.
How should we fill that knowledge gap?
- State your purpose/hypothesis clearly . Surprisingly, many people actually forget to do so! If all else fails, a simple “The purpose of this study was to examine/study X” will suffice.
- You are proposing a solution to a problem (the gap) you observed in our current knowledge base. As such, your Introduction must convince your readers that this problem needs solving .
- In particular, since we are writing with a particular journal’s readership in mind (or, at least, you should be!), make sure to address how pertinent your project would be to the reader’s interests.
- In other words, if we fill this gap, what useful information will the readers gain ? The answer to that question is the promise you are delivering to your readers, and in the conclusion part of your Discussion, you will give final confirmation of your findings and elaborate more on what your readers can now do with the information your project has contributed to the research community.
- DON’T draw any conclusions or include any data from your study . Those aspects belong in other parts of your paper.
- Similarly , DON’T talk about specific techniques in your Introduction because your readers ought to be familiar with most of them. If you employed a novel technique in your study, and the development of that process is central to your study, then, by all means, include a brief overview.
How to Write the Introduction Section
To round out our guide to drafting the Introduction of your journal article, we provide some general tips about the technical aspects of writing the Introduction section below.
- Use the active voice.
- Be concise.
- Avoid nominalizations (converting phrases, including adjectives and verbs, into nouns). Instead, use the verb form where practical. When you eliminate nominalizations, your sentences will shorten, you’ll maintain an active voice, and your sentences will flow more like natural speech.
- Do you see those uber long sentences in your draft? Revise them. Anything longer than three to four lines is absurd, and even sentences of that length should be rare. Shorter sentences are clearer, making it easier for your readers to follow your arguments. With that said, don’t condense every sentence. Incorporate a variety of sentence structures and lengths.
- Similarly, drop the extended sentences with semicolons and serial clauses connected by commas. Again, the purpose of your paper is to provide a CLEAR explanation of your findings.
- Avoid overusing first-person pronouns. Use them rarely at the beginning of the section and sprinkle them toward the end when you discuss your hypothesis and the rationale behind your study.
- Organize your thoughts from broad to specific (as described in the section “What should I include in the Introduction” above).
- BONUS TIP #1: Like any other type of writing, start your Introduction with an active hook . Writing a summary of your findings shouldn’t be boring. In fact, a dull start will make your readers stop long before they get to the good stuff—your results and discussion! So how do you make an exciting hook? Think about techniques in creative nonfiction like starting with a provoking anecdote, quote or striking piece of empirical data. You’re telling a story, after all, so make it enjoyable!
- BONUS TIP #2: As one author, reviewer, and editor once stated , your Introduction should avoid using phrases like “novel,” “first ever,” and “paradigm-changing.” Your project might not be paradigm-shifting (few studies truly are); however, if your idea isn’t novel in the first instance, then should you be writing the paper now? If you don’t feel like your research would make a meaningful contribution to current knowledge, then you might want to consider conducting further research before approaching the drafting table.
And keep in mind that receiving English proofreading and paper editing services for your manuscript before submission to journals greatly increases your chances of publication. Wordvice provides high-quality professional editing for all types of academic documents and includes a free certificate of editing .
You can also find these resources plus information about the journal submission process in our FREE downloadable e-book: Research Writing and Journal Publication E-Book .
Wordvice Resources
- How to Write a Research Paper Introduction
- Which Verb Tenses to Use in a Research Paper
- How to Write an Abstract for a Research Paper
- How to Write a Research Paper Title
- Useful Phrases for Academic Writing
- Common Transition Terms in Academic Papers
- Active and Passive Voice in Research Papers
- 100+ Verbs That Will Make Your Research Writing Amazing
- Tips for Paraphrasing in R esearch Papers
Additional Resources
- Guide for Authors. (Elsevier)
- How to Write the Results Section of a Research Paper. (Bates College)
- Structure of a Research Paper. (University of Minnesota Biomedical Library)
- How to Choose a Target Journal (Springer)
- How to Write Figures and Tables (UNC Writing Center)
Orsuamaeze Blessings, Adebayo Alaba Joseph and Oguntimehin Ilemobayo Ifedayo, 2018. Deleterious effects of cadmium solutions on onion (Allium cepa) growth and the plant’s potential as bioindicator of Cd exposure. Res. J. Environ. Sci., 12: 114-120. Online: http://docsdrive.com/pdfs/academicjournals/rjes/2018/114-120.pdf
- If you are writing in a new discipline, you should always make sure to ask about conventions and expectations for introductions, just as you would for any other aspect of the essay. For example, while it may be acceptable to write a two-paragraph (or longer) introduction for your papers in some courses, instructors in other disciplines, such as those in some Government courses, may expect a shorter introduction that includes a preview of the argument that will follow.
- In some disciplines (Government, Economics, and others), it’s common to offer an overview in the introduction of what points you will make in your essay. In other disciplines, you will not be expected to provide this overview in your introduction.
- Avoid writing a very general opening sentence. While it may be true that “Since the dawn of time, people have been telling love stories,” it won’t help you explain what’s interesting about your topic.
- Avoid writing a “funnel” introduction in which you begin with a very broad statement about a topic and move to a narrow statement about that topic. Broad generalizations about a topic will not add to your readers’ understanding of your specific essay topic.
- Avoid beginning with a dictionary definition of a term or concept you will be writing about. If the concept is complicated or unfamiliar to your readers, you will need to define it in detail later in your essay. If it’s not complicated, you can assume your readers already know the definition.
- Avoid offering too much detail in your introduction that a reader could better understand later in the paper.
- picture_as_pdf Introductions
9 Examples of Eye-Catching Introduction Paragraphs [2023]
![introduction for article writing 9 Examples of Eye-Catching Introduction Paragraphs [2023]](https://assets-global.website-files.com/5f7ece8a7da656e8a25402bc/65ad1331b40149fec3204d4b_9%20Examples%20of%20Eye-Catching%20Introduction%20Paragraphs.webp)
Table of contents

Christian Rigg
How well are you managing to hook your readers?
According to CNN , The average attention on a screen went down from 2.5 minutes (in 2004) to 47 seconds (in 2023). Studies show that for most cases, people don't even read past the headline.
As a writer, one of the best skills you can learn is to hook your readers with a compelling introduction. A good title gets people in the door, but it’s the introduction that decides if they stay or not.

The difference between a strong and a weak intro
A strong intro draws the reader in and evokes a sense of curiosity or interest, either by speaking to the reader’s pain points or by engaging them on an intellectual or emotional level.
A weak introduction paragraph, on the other hand, does the exact opposite. It fails to delight or intrigue, usually by being too generic. (This is one reason why introductions generated using text transformers like ChatGPT tend to “fall flat.”) Incidentally, failing to keep your readers on-page will result in higher bounce rates, which Google penalizes.
Have I convinced you to stick around? If so, great. In the rest of the article, we’ll go over the most important dos and don’ts of intros and look at some outstanding introduction paragraph examples for inspiration.
Write better introductions with this FREE AI writing tool > Free AI introduction generator >

The Dos and Don’ts of Strong Introductions
Here are some quick and simple tips for writing a compelling introduction .
✅ Do be human and relatable
Talk about a personal experience. Mention emotions like frustration or excitement. Utilize Use plain, conversational language.
✅ Do capture the reader's attention with an interesting or meaningful quote or statistic.
Just be sure to avoid clichés, keep it relevant to your topic, and don’t get too abstract.
✅ Do write concisely and clearly .
If you struggle with this like many people, try writing your introduction in the Wordtune editor. The suggestions on flow and clarity will help you stick to the point without being hard to understand.
✅ Do disarm, startle, or otherwise “shock” the reader into alertness.
This doesn’t mean being crass or crude, it means upending assumptions. What surprised you most when researching or writing your article? Start there.
✅ Do use descriptive , emotive, and sensory language, including vivid imagery and great storytelling .
Start in the middle of the story, then segue into how it all started. Or start at the end and work your way back.
✅ Do use humor and casual language.
It helps put the reader at ease and makes them feel like part of the conversation.
And here are some things to avoid, including some not-so-great introductory paragraph examples. Don’t worry, we’ll get to examples of how to do it right in the next section.
❌ Don’t rely on AI text generators like ChatGPT.
These tools “write” by adding the next most likely word, based on thousands of examples. As a result, the text lacks originality . It is, by definition, the most average way of saying something. If you want to make your content stand out from AI-generated content , start with an original introduction paragraph.
❌ Don’t give it all away.
Your introduction is not the place to plead your whole case. Introduce the reader to the topic, generate interest or empathy, and make a promise they want to see fulfilled.
❌ Don’t make it too long.
Readers get bored fast. They want to get to the good stuff.
❌ Don’t use gimmicks, clickbait, clichés, or obvious ploys.
“You won’t believe what…” “Here’s everything you need to know about…” “Are you ready to make your first million?” Unless the news really is shocking, you really do include everything the reader needs to know, or you have offer a long-term, validated strategy for earning a million, you’ll just come off looking like a hack.
❌ Don’t use generic statements.
“All businesses need to track their financial performance.” “Running a marathon is no easy task.” “It takes hard work to become the best.” Openers like these waste precious seconds on stating the obvious. If you’re lucky, your reader will be kind and keep scanning for something worthwhile. But they probably already hit the Back button.
Here are nine excellent introduction paragraph examples:
1. The statistical introduction example
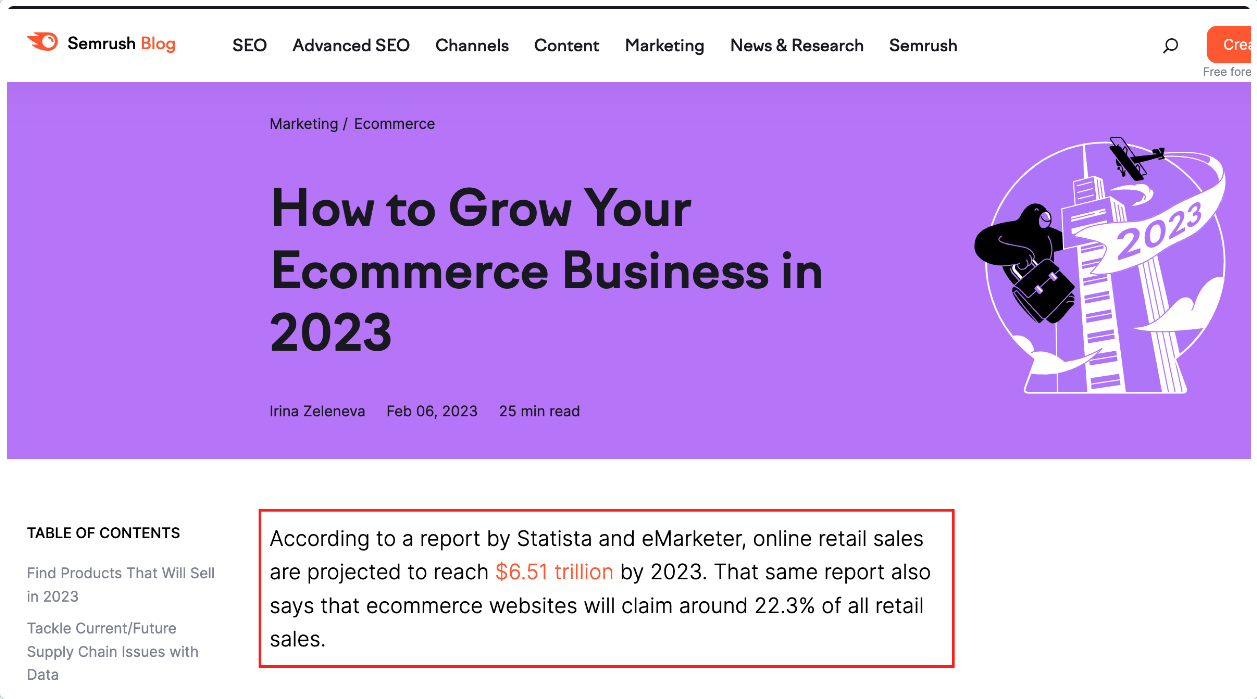
According to a report by Statista and eMarketer, online retail sales are projected to reach $6.51 trillion by 2023. That same report also says that ecommerce websites will claim around 22.3% of all retail sales.
So, if you weren’t planning on investing in your ecommerce strategy this year, you should.
The SEO experts at Semrush have included two interesting and impressive statistics here, sure to pique the reader’s interest. They make a bold statement, too: if you thought you could wait, you can’t .
To help you replicate this kind of introduction, try using Wordtune’s Spices features to find and add interesting statistics and facts.
2. The relatable introduction example

We’ve all seen that little white label that sits tucked away on the inside of our clothing: “Made in Australia”, “Made in Turkey”, “Made in Bangladesh”. But what do those labels really mean? In this article, we discuss whether locally made clothing is more ethical. Read on to find out before your next shop.
Nothing if not concise, this introduction catches the reader with a common human experience, asks an important question, and gives a quick bridge on what the article has to offer. It’s short and direct, and it speaks to readers who may well have just been looking at a “little white label” before popping the question into Google.
3. The dialogue introduction example

After a moonwalk in April 1972, the Apollo 16 astronauts Charles Duke and John Young returned to their capsule. In the process of putting their suits and other things away, Duke commented to Ground Control:
Duke: Houston, the lunar dust smells like gunpowder. [Pause]
England: We copy that, Charlie.
Duke: Really, really a strong odor to it.
First of all, how’s that for a title?
This introduction tells a fascinating story in just 57 words. Admittedly, the unique topic of cosmic moon dust makes it easier to capture readers’ interest. But the author’s choice to include this short exchange between Charles Duke and the Houston Space Center also pulls us right into the scene.
4. The personal story introduction example
Wordtune blog: Take Smart Notes From a Textbook (Using AI + Templates)
Call me crazy, but I’ve spent $11,750 on note-taking tools.
Physical stationery in the form of highlighters, post-its, colored pens, subject notebooks, roller scales—you name it. My beautifully-written, detailed, color-coded notes gave me the feeling of being a productive high-achiever.
But these notes rarely translated into results. I was consistently in the average tier of students, despite my organized study practices—till year two of highschool. It was then that I realized all I was doing was beautifying text and not understanding information.
From then on, I set out on a journey to understand which notetaking methods worked for my subjects. I translated this into a 9.2/10 CGPA in my 10th-grade examination and a 1900 score on my SATs. In addition, I was able to achieve these results while reducing my study time by half.
Today, I’m going to show you how to do the same with my step-by-step playbook. This article covers advanced tips for students wanting to upgrade their note-taking skills.
This introduction has a great hook that draws us in immediately: Hold on. $11,000 dollars on pens and post-its?? Then it tells an emotionally engaging story of failure to success. Finally, it clearly prepares us for what’s to come. All these are hallmarks of a strong introduction.
5. The common problem introduction example
Eleven Writing blog: 7 Reasons Your Business Should Invest In High-quality Blog Articles
Many businesses publish a new blog article, they wait, and then…
Nothing happens.
The anticipated flood of new traffic never materializes. The few visitors that arrive don’t click any links, sign up to your list, or share your article.
The marketing department starts to wonder if a blog is really worth the money and hassle compared to other available channels.
But what if better blog content could change all this?
This introduction was written by one of the SEO experts at Eleven Writing, the writing agency where I work as a writer, editor, and account manager. It features a short and punchy story with a relatable twist. “And then… Nothing happens.” Translation: 🤦
It finishes with an intriguing “What if?” scenario, which leads into an article of tips and practical takeaways. And it’s a reminder of another important point: make sure your article actually fulfills any promises you make in your introduction.
6. The alarming introduction example
European Commission: Consequences of climate change
Climate change affects all regions around the world. Polar ice shields are melting and the sea is rising. In some regions, extreme weather events and rainfall are becoming more common while others are experiencing more extreme heat waves and droughts. We need climate action now, or these impacts will only intensify.
Climate change is a very serious threat, and its consequences impact many different aspects of our lives. Below, you can find a list of climate change’s main consequences.
The above introduction comes from the European Commission and discusses the dangers of climate change. It starts with a bold and disarming statement: climate change affects everybody.
It discusses just a few of the consequences of climate change, priming the reader for what’s to follow, and then provides a simple bridge into the rest of the article.
It’s short and to the point, but uses descriptive, intense language to convey urgency and emotionally engage the reader.
7. The recap introduction example
Harvard Business Review: Rescuing ESG from the Culture Wars
In the past year, ESG investing has become caught up in America’s culture wars, as prominent GOP politicians claim that it is a mechanism investors are using to impose a “woke” ideology on companies. Former Vice President Mike Pence has railed against ESG in speeches and in an op-ed. A variety of Republican governors and red-state legislatures are considering executive action and legislation to boycott asset managers that use ESG as a screening tool for their investments. And in Washington, various Congressional committees have pledged to hold hearings in which the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and major asset managers will face public questioning about the legality of ESG investing.
This introductory paragraph from the Harvard Business Review dumps the reader into the throes of a heated political debate. Whether readers agree or disagree, powerful verbs like “railed against” and politically charged language like “culture wars” and “woke” are sure to grab the attention of those on both sides of the political spectrum.
8. The common problem intro example #2
KonMari blog: 5 Rituals to Build Self-Acceptance
Self-criticism is an all too common struggle. Even the most successful people in the world experience bouts of imposter syndrome and low self-esteem. But the person you’ll spend the most time with in your life is yourself. We owe it to ourselves to strengthen our self-compassion and embrace self-love.
One of the simplest ways to build self-acceptance is to make it a part of your self-care routine. The following rituals, sourced from mindfulness experts and one of our Master KonMari Consultants, can be completed in as little as five minutes daily. Try one for a month — you’ll be surprised how much better you treat yourself.
This intro comes from the queen of tidiness, Marie Kondo, and manages to both connect with the reader and gracefully plug an advertisement for KonMari’s consulting services. There’s a common idea in SEO that “linking away” in the introduction is bad practice, but in this case, it transforms an educational article into a commercial funnel.
There’s another neat trick in this intro: it extends a challenge to the reader. Try one of the methods below and see how much better you feel after a month. With a promise like that, who wouldn’t keep scrolling?
9. The 'new angle' introduction example
Crippled CEO Blog: Resistance and Leadership Capital
So much has been written on how important it is to have the right people in your company. All a business is, really, is a collection of people. That’s it. So, it follows that getting the people right is practically the only thing that truly matters.
And while I have seen this repeated ad nauseam, I don’t see a lot of people saying what those right (or wrong) people look like – what attributes they possess.
So, I wanted to talk about one of those attributes, and in particular one that I think isn’t just overlooked, but the very concept itself isn’t known, making it impossible to look out for at all.
This attribute is resistance.
Eric Lupton blogs about his experiences and perspective as a business leader with cerebral palsy. This introduction uses incisive language that will no doubt appeal to business readers and high-powered execs.
But it also comes from a very personal perspective, like much of Lupton’s writing, and so we feel like we’re about to sit down and speak one-on-one with someone who very clearly knows what they’re talking about.
It has a conversational tone (“So, I wanted to talk about…”) and promises to reveal to us something that “isn’t just overlooked, but the very concept itself is unknown.” Intrigued? I was.
Start writing!
A strong introduction paragraph bridges the gap between an intriguing title and an article’s real value. It pulls the reader in with boldness, intrigue, storytelling, or relatability.
It’s an art that takes practice, but these introduction paragraph examples show it can be done right. There are also some great tools out there to help you out. Wordtune’s Spices feature can offer ideas for analogies, examples, statistics, facts, and relevant quotes — all great sources of inspiration for a strong introduction paragraph.
After that, it’s your turn. Add personality, connect with your readers, and write more introductions, and you’ll be on your way to keeping your audience on the page.
Share This Article:

The Official Wordtune Guide

An Expert Guide to Writing Effective Compound Sentences (+ Examples)

A Step-by-Step Guide to Writing a Stellar Literature Review (with Help from AI)
Looking for fresh content, thank you your submission has been received.
We use cookies on this site to enhance your experience
By clicking any link on this page you are giving your consent for us to set cookies.
A link to reset your password has been sent to your email.
Back to login
We need additional information from you. Please complete your profile first before placing your order.
Thank you. payment completed., you will receive an email from us to confirm your registration, please click the link in the email to activate your account., there was error during payment, orcid profile found in public registry, download history, how to write an introduction to an academic article.
- Charlesworth Author Services
- 17 August, 2020
- Academic Writing Skills
How to write an Introduction to an academic article
The introduction to an academic article is the first section of the paper, immediately following the abstract. One of the most important functions of an introduction is to answer the question ‘why?’: why was the study performed, and why is it interesting and/or important? Given that the introduction is the beginning of the paper, it also serves to tell the reader why they should read the rest of the paper and prepares them to understand the importance and implications of the results.
To clearly establish the context for the study, the introduction contains four main components:
General background information
Specific background information.
- A description of the gap in our knowledge that the study was designed to fill
- A statement of study objective, and (optionally) a brief summary of study
This information should ideally be presented in a ‘funnel’ format, flowing from the most general information at the beginning of the section to more specific information as the text continues. Let’s take a closer look at each of these elements in turn.
The first paragraph of the introduction establishes the broad context for the study by providing a general introduction to the field. How broad this paragraph is depends on your target journal and audience. If you choose to submit to a general journal with a wide scientific readership, it is a good idea to start with some fairly general information, as not all readers will necessarily be familiar with your specific field. If you plan on submitting to a highly specialized journal, however, you can begin this section with a much more specific and focused description of the background, as most of your readers will already be familiar with the context of the study.
Let’s say, for example, that your study addresses MAPK signalling in triple negative breast cancer in a specific population. If you are submitting your paper to a journal with a broad focus, it could be useful to begin this section with a brief introduction to breast cancer in general. If, however, you choose to submit to a breast cancer–specific journal, it would be reasonable to start the introduction by discussing triple negative breast cancer, or even the role of MAPK signalling in triple negative breast cancer.
Once the general context of the study has been established, the next part of the introduction should go into more detail about the main topic of the study. This is the part of the introduction that provides a literature review, in which other studies that have addressed similar themes are discussed in detail, to provide readers with a clear picture of what is already known about the topic. The point of this section is to present a complete picture of the state of the field, as this will help explain how your study builds on previous work. Describing the current state of the field helps readers understand your thought process in designing the study, and the logical steps that led you to formulate the main question addressed by your study.
Continuing with the example outlined above, if submitting to a journal with a general readership, this would be the appropriate place to present more detail about triple negative breast cancer and the role of MAPK signalling. In the case of a more specialized journal, in our example this could be a good place to go into more detail about the specific population you studied.
Gap in knowledge
The description of closely related previous studies, as discussed above, should clearly outline a specific gap in our knowledge or understanding of a specific question or phenomenon in the field. Sometimes this is accomplished simply by describing the work that has recently been done to investigate related questions; for example, if risk factors for a disease have been investigated in African and European populations, but not in Asian populations, describing what is already known about this disease in those populations will help readers understand the logic behind exploring the same question in an underexplored population. In other cases, it may be appropriate to (respectfully) point out shortcomings or drawbacks of similar studies to highlight the way in which your study improves on this earlier work. For example, if previous studies have designed computational models that account for some, but not all, of the properties of a specific reaction, you could point out the importance of incorporating additional properties to explain the need for the new computational model described in your study.
While the part of the introduction that describes the specific context for your study should lead naturally to an understanding of the gap in our knowledge that the study addresses, it is often useful to state this explicitly, for the sake of clarity. It is common to do so by including a sentence just prior to the last paragraph of the introduction that begins: ‘However, it remains unclear…’ or ‘However, it is still unknown…’.
Statement of study aim
The final element of the introduction is a clear statement of the primary objective of the study. In some cases, this will be the main overarching question the study sought to answer; in other cases, this may be a formal hypothesis; and in yet other cases, this may be a goal. Regardless of the form it takes, it is important to state the study aim clearly, ideally in the final paragraph of the introduction, to help ensure that readers clearly understand the specific purpose of the study before going on to read about it in greater detail in the sections that follow. Keep in mind that this statement of the study aim should closely mirror the statement of the study aim in the abstract, to present a cohesive and consistent message about the purpose of the study.
In some cases, it is appropriate to conclude the introduction with a summary paragraph that provides a very concise overview of the key findings and overall conclusion. This brief paragraph can help remind readers of the key points of the study within the context of the background information provided in the rest of the introduction, and provide a structure for understanding the rest of the text.
What should be left out of the introduction?
As discussed above, the primary purpose of the introduction is to provide adequate background information for readers to understand the context and importance of the study. For this reason, we recommend leaving out any background information that is not related directly to the main topic of the study. For example, if mutations in the protein you investigated have been linked to both cardiovascular disease and cancer, but your study only looked at cancer, discussing mutations found in patients with cardiovascular disease could distract and confuse readers. For this reason, we suggest reviewing the text of the introduction carefully to ensure that all of the information it presents has a direct logical link to the main focus of your study.
In addition, the introduction is generally not the best place to discuss the methodology used in your study, as this section should primarily be dedicated to explaining why the study was performed, not how it was performed. An exception to this rule is if the main purpose of the study was to develop or test a novel methodology, in which case it would of course be appropriate to discuss other techniques and the rationale behind the design of the new technique developed in your study. Similarly, if the main novelty of your study is the method used to investigate the central question, then this would also be a case in which it would be appropriate to discuss the methodology in the introduction.
In summary, a well-written introduction sets the tone for your paper by providing readers with all of the information they need to understand why you performed your study, what makes it different from other similar studies, and why the findings are interesting and important.
If you are seeking additional support in writing an effective introduction, we are here to help. Charlesworth Author Services provide expert English language editing and publication support services. Why not get in touch with a member of our Charlesworth Author Services team for more information.
Our academic writing and publishing training courses, online materials, and blog articles contain numerous tips and tricks to help you navigate academic writing and publishing, and maximise your potential as a researcher. You can find out more about our Free author training webinar series by clicking here.
Maximise your publication success with Charlesworth Author Services.
Share with your colleagues
Related articles.

Getting the title of your research article right
Charlesworth Author Services 17/08/2020 00:00:00
Recommended webinars

Bitesize Webinar: How to write and structure your academic article for publication- Module 3: Understand the structure of an academic paper
Charlesworth Author Services 04/03/2021 00:00:00

Bitesize Webinar: How to write and structure your academic article for publication: Module 6: Choose great titles and write strong abstracts
Charlesworth Author Services 05/03/2021 00:00:00

Bitesize Webinar: How to write and structure your academic article for publication: Module 7: Write a strong theoretical framework section

Writing a strong Methods section
Charlesworth Author Services 12/03/2021 00:00:00

Bitesize Webinar: How to write and structure your academic article for publication: Module 8: Write a strong methods section

How to write a Methods section in your research paper
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Research paper
Writing a Research Paper Introduction | Step-by-Step Guide
Published on September 24, 2022 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on March 27, 2023.

The introduction to a research paper is where you set up your topic and approach for the reader. It has several key goals:
- Present your topic and get the reader interested
- Provide background or summarize existing research
- Position your own approach
- Detail your specific research problem and problem statement
- Give an overview of the paper’s structure
The introduction looks slightly different depending on whether your paper presents the results of original empirical research or constructs an argument by engaging with a variety of sources.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Step 1: introduce your topic, step 2: describe the background, step 3: establish your research problem, step 4: specify your objective(s), step 5: map out your paper, research paper introduction examples, frequently asked questions about the research paper introduction.
The first job of the introduction is to tell the reader what your topic is and why it’s interesting or important. This is generally accomplished with a strong opening hook.
The hook is a striking opening sentence that clearly conveys the relevance of your topic. Think of an interesting fact or statistic, a strong statement, a question, or a brief anecdote that will get the reader wondering about your topic.
For example, the following could be an effective hook for an argumentative paper about the environmental impact of cattle farming:
A more empirical paper investigating the relationship of Instagram use with body image issues in adolescent girls might use the following hook:
Don’t feel that your hook necessarily has to be deeply impressive or creative. Clarity and relevance are still more important than catchiness. The key thing is to guide the reader into your topic and situate your ideas.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing - try for free!
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Try for free
This part of the introduction differs depending on what approach your paper is taking.
In a more argumentative paper, you’ll explore some general background here. In a more empirical paper, this is the place to review previous research and establish how yours fits in.
Argumentative paper: Background information
After you’ve caught your reader’s attention, specify a bit more, providing context and narrowing down your topic.
Provide only the most relevant background information. The introduction isn’t the place to get too in-depth; if more background is essential to your paper, it can appear in the body .
Empirical paper: Describing previous research
For a paper describing original research, you’ll instead provide an overview of the most relevant research that has already been conducted. This is a sort of miniature literature review —a sketch of the current state of research into your topic, boiled down to a few sentences.
This should be informed by genuine engagement with the literature. Your search can be less extensive than in a full literature review, but a clear sense of the relevant research is crucial to inform your own work.
Begin by establishing the kinds of research that have been done, and end with limitations or gaps in the research that you intend to respond to.
The next step is to clarify how your own research fits in and what problem it addresses.
Argumentative paper: Emphasize importance
In an argumentative research paper, you can simply state the problem you intend to discuss, and what is original or important about your argument.

Empirical paper: Relate to the literature
In an empirical research paper, try to lead into the problem on the basis of your discussion of the literature. Think in terms of these questions:
- What research gap is your work intended to fill?
- What limitations in previous work does it address?
- What contribution to knowledge does it make?
You can make the connection between your problem and the existing research using phrases like the following.
Now you’ll get into the specifics of what you intend to find out or express in your research paper.
The way you frame your research objectives varies. An argumentative paper presents a thesis statement, while an empirical paper generally poses a research question (sometimes with a hypothesis as to the answer).
Argumentative paper: Thesis statement
The thesis statement expresses the position that the rest of the paper will present evidence and arguments for. It can be presented in one or two sentences, and should state your position clearly and directly, without providing specific arguments for it at this point.
Empirical paper: Research question and hypothesis
The research question is the question you want to answer in an empirical research paper.
Present your research question clearly and directly, with a minimum of discussion at this point. The rest of the paper will be taken up with discussing and investigating this question; here you just need to express it.
A research question can be framed either directly or indirectly.
- This study set out to answer the following question: What effects does daily use of Instagram have on the prevalence of body image issues among adolescent girls?
- We investigated the effects of daily Instagram use on the prevalence of body image issues among adolescent girls.
If your research involved testing hypotheses , these should be stated along with your research question. They are usually presented in the past tense, since the hypothesis will already have been tested by the time you are writing up your paper.
For example, the following hypothesis might respond to the research question above:
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
The final part of the introduction is often dedicated to a brief overview of the rest of the paper.
In a paper structured using the standard scientific “introduction, methods, results, discussion” format, this isn’t always necessary. But if your paper is structured in a less predictable way, it’s important to describe the shape of it for the reader.
If included, the overview should be concise, direct, and written in the present tense.
- This paper will first discuss several examples of survey-based research into adolescent social media use, then will go on to …
- This paper first discusses several examples of survey-based research into adolescent social media use, then goes on to …
Full examples of research paper introductions are shown in the tabs below: one for an argumentative paper, the other for an empirical paper.
- Argumentative paper
- Empirical paper
Are cows responsible for climate change? A recent study (RIVM, 2019) shows that cattle farmers account for two thirds of agricultural nitrogen emissions in the Netherlands. These emissions result from nitrogen in manure, which can degrade into ammonia and enter the atmosphere. The study’s calculations show that agriculture is the main source of nitrogen pollution, accounting for 46% of the country’s total emissions. By comparison, road traffic and households are responsible for 6.1% each, the industrial sector for 1%. While efforts are being made to mitigate these emissions, policymakers are reluctant to reckon with the scale of the problem. The approach presented here is a radical one, but commensurate with the issue. This paper argues that the Dutch government must stimulate and subsidize livestock farmers, especially cattle farmers, to transition to sustainable vegetable farming. It first establishes the inadequacy of current mitigation measures, then discusses the various advantages of the results proposed, and finally addresses potential objections to the plan on economic grounds.
The rise of social media has been accompanied by a sharp increase in the prevalence of body image issues among women and girls. This correlation has received significant academic attention: Various empirical studies have been conducted into Facebook usage among adolescent girls (Tiggermann & Slater, 2013; Meier & Gray, 2014). These studies have consistently found that the visual and interactive aspects of the platform have the greatest influence on body image issues. Despite this, highly visual social media (HVSM) such as Instagram have yet to be robustly researched. This paper sets out to address this research gap. We investigated the effects of daily Instagram use on the prevalence of body image issues among adolescent girls. It was hypothesized that daily Instagram use would be associated with an increase in body image concerns and a decrease in self-esteem ratings.
The introduction of a research paper includes several key elements:
- A hook to catch the reader’s interest
- Relevant background on the topic
- Details of your research problem
and your problem statement
- A thesis statement or research question
- Sometimes an overview of the paper
Don’t feel that you have to write the introduction first. The introduction is often one of the last parts of the research paper you’ll write, along with the conclusion.
This is because it can be easier to introduce your paper once you’ve already written the body ; you may not have the clearest idea of your arguments until you’ve written them, and things can change during the writing process .
The way you present your research problem in your introduction varies depending on the nature of your research paper . A research paper that presents a sustained argument will usually encapsulate this argument in a thesis statement .
A research paper designed to present the results of empirical research tends to present a research question that it seeks to answer. It may also include a hypothesis —a prediction that will be confirmed or disproved by your research.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, March 27). Writing a Research Paper Introduction | Step-by-Step Guide. Scribbr. Retrieved April 2, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/research-paper/research-paper-introduction/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, writing strong research questions | criteria & examples, writing a research paper conclusion | step-by-step guide, research paper format | apa, mla, & chicago templates, what is your plagiarism score.
How to Write an Article: A Proven Step-by-Step Guide
Are you dreaming of becoming a notable writer or looking to enhance your content writing skills? Whatever your reasons for stepping into the writing world, crafting compelling articles can open numerous opportunities. Writing, when viewed as a skill rather than an innate talent, is something anyone can master with persistence, practice, and the proper guidance.
That’s precisely why I’ve created this comprehensive guide on ‘how to write an article.’ Whether you’re pursuing writing as a hobby or eyeing it as a potential career path, understanding the basics will lead you to higher levels of expertise. This step-by-step guide has been painstakingly designed based on my content creation experience. Let’s embark on this captivating journey toward becoming an accomplished article writer!
What is an Article?

An article is more than words stitched together cohesively; it’s a carefully crafted medium expressing thoughts, presenting facts, sharing knowledge, or narrating stories. Essentially encapsulating any topic under the sun (or beyond!), an article is a versatile format meant to inform, entertain, or persuade readers.
Articles are ubiquitous; they grace your morning newspaper (or digital equivalents), illuminate blogs across various platforms, inhabit scholarly journals, and embellish magazines. Irrespective of their varying lengths and formats, which range from news reports and features to opinion pieces and how-to guides, all articles share some common objectives. Learning how to write this type of content involves mastering the ability to meet these underlying goals effectively.
Objectives of Article Writing

The primary goal behind learning how to write an article is not merely putting words on paper. Instead, you’re trying to communicate ideas effectively. Each piece of writing carries unique objectives intricately tailored according to the creator’s intent and the target audience’s interests. Generally speaking, when you immerse yourself in writing an article, you should aim to achieve several fundamental goals.
First, deliver value to your readers. An engaging and informative article provides insightful information or tackles a problem your audience faces. You’re not merely filling up pages; you must offer solutions, present new perspectives, or provide educational material.
Next comes advancing knowledge within a specific field or subject matter. Especially relevant for academic or industry-focused writings, articles are often used to spread original research findings and innovative concepts that strengthen our collective understanding and drive progress.
Another vital objective for those mastering how to write an article is persuasion. This can come in various forms: convincing people about a particular viewpoint or motivating them to make a specific choice. Articles don’t always have to be neutral; they can be powerful tools for shifting public opinion.
Finally, let’s not forget entertainment – because who said only fictional work can entertain? Articles can stir our emotions or pique our interest with captivating storytelling techniques. It bridges the gap between reader and writer using shared experiences or universal truths.
Remember that high-quality content remains common across all boundaries despite these distinct objectives. No matter what type of writer you aspire to become—informative, persuasive, educational, or entertaining—strive for clarity, accuracy, and stimulation in every sentence you craft.
What is the Format of an Article?

When considering how to write an article, understanding its foundation – in this case, the format – should be at the top of your list. A proper structure is like a blueprint, providing a direction for your creative construction.
First and foremost, let’s clarify one essential point: articles aren’t just homogenous chunks of text. A well-crafted article embodies different elements that merge to form an engaging, informative body of work. Here are those elements in order:
- The Intriguing Title
At the top sits the title or heading; it’s your first chance to engage with a reader. This element requires serious consideration since it can determine whether someone will continue reading your material.
- Engaging Introduction
Next comes the introduction, where you set expectations and hint at what’s to come. An artfully written introduction generates intrigue and gives readers a compelling reason to stick around.
- Informative Body
The main body entails a detailed exploration of your topic, often broken down into subtopics or points for more manageable consumption and better flow of information.
- Impactful Conclusion
Lastly, you have the conclusion, where you tie everything neatly together by revisiting key points and offering final thoughts.
While these components might appear straightforward on paper, mastering them requires practice, experimentation with writing styles, and a good understanding of your target audience.
By putting in the work to familiarize yourself with how to create articles and how they’re structured, you’ll soon discover new ways to develop engaging content each time you put pen to paper (or fingers to keyboard!). Translating complex concepts into digestible content doesn’t need to feel daunting anymore! Now that we’ve tackled the format, our focus can shift to what should be included in an article.
What Should Be in an Article?

Understanding that specific items should be featured in your writing is crucial. A well-crafted article resembles a neatly packed suitcase – everything has its place and purpose.
Key Information
First and foremost, you need essential information. Start by presenting the topic plainly so readers can grasp its relevance immediately. This sets the tone of why you are writing the article. The degree of depth at this point will depend on your audience; be mindful not to overwhelm beginners with too much jargon or over-simplify things for experts.
Introduction
Secondly, every article must have an engaging introduction—this acts as the hook that reels your audience. Think of it as a movie trailer—it offers a taste of what’s to come without giving away all the details.
Third is the body, wherein you get into the crux of your argument or discussion. This is the point at which you present your ideas sequentially, along with supporting evidence or examples. Depending on the nature of your topic and personal style, this may vary from storytelling forms to more analytical breakdowns.
Lastly, you’ll need a fitting conclusion that wraps up all previously discussed points, effectively tying together every loose thread at the end. This helps cement your main ideas within the reader’s mind even after they’ve finished reading.
To summarize:
- Critical Information: Provides context for understanding
- Introduction: Sheds further light on what will follow while piquing interest
- Body: Discusses topic intricacies using narratives or case studies
- Conclusion: Ties up loose ends and reemphasizes important takeaways
In my experience writing articles for beginners and experts alike, I found these elements indispensable when conveying complex topics articulately and professionally. Always keep them at hand when looking to produce written material.
How should you structure an article?

Crafting a well-structured article is akin to assembling a puzzle – every piece has its place and purpose. Let’s look at how to create the perfect skeleton for your content.
The introduction is your article’s welcome mat. It should be inviting and informative, briefly outlining what a reader can expect from your writing. Additionally, it must instantly grab the readers’ attention so they feel compelled to continue reading. To master the art of creating effective introductions, remember these key points:
- Keep it short and precise.
- Use compelling hooks like quotes or intriguing facts.
- State clearly what the article will cover without revealing everything upfront.
Moving on, you encounter the body of your piece. This segment expands on the ideas outlined in the introduction while presenting fresh subtopics related to your core story. If we compare article writing to crossing a bridge, each paragraph represents a step toward the other side (the conclusion). Here are some tips for maintaining orderliness within your body:
- Stick closely to one idea per paragraph as it enhances readability.
- Ensure paragraphs flow logically by utilizing transitional words or sentences.
- Offer evidence or examples supporting your claims and reinforce credibility.
As you approach the far side of our imaginary bridge, we reach an equally essential section of the article known as the conclusion. At this point, you should be looking to wrap your message up neatly while delivering on what was initially promised during the introduction. This section summarizes the main points, providing closure and ensuring readers feel satisfied.
Remember this golden rule when writing the conclusion: follow the “Describe what you’re going to tell them (Introduction), tell them (Body), and then summarize what you told them (Conclusion).” It’s a proven formula for delivering informative, engaging, and well-structured articles.
One final tip before moving on: maintaining an active voice significantly enhances clarity for your readers. It makes them feel like they’re participating actively in the story unfolding within your article. In addition, it helps ensure easy readability, which is vital for keeping your audience engaged.
Tips for Writing a Good Article

A persuasive, engaging, and insightful article requires careful thought and planning. Half the battle won is by knowing how to start writing and make content captivating. Below are vital tips that can enhance your article writing skills.
Heading or Title
An audience’s first impression hinges on the quality of your title. A good heading should be clear, attention-grabbing, and give an accurate snapshot of what’s contained in the piece’s body. Here are a few guidelines on how to create an impactful title:
- Make it Compelling: Your title needs to spark interest and motivate readers to delve further into your work.
- Keep it concise: You want to have a manageable heading. Aim for brevity yet inclusiveness.
- Optimize with keywords: To boost search engine visibility, sprinkle relevant keywords naturally throughout your title.
By applying these techniques, you can increase reader engagement right from the get-go.
Body of the Article
After winning over potential readers with your catchy title, it’s time to provide substantial content in the form of the body text. Here’s how articles are typically structured:
Introduction: Begin by providing an appealing overview that hooks your audience and baits them to read more. You can ask poignant questions or share interesting facts about your topic here.
Main Content: Build on the groundwork set by your introduction. Lay out detailed information in a logical sequence with clear articulation.
Conclusion: This reemphasizes the critical points discussed in the body while delivering a lasting impression of why those points matter.
Remember that clarity is critical when drafting each part because our objective here is to share information and communicate effectively. Properly understanding this approach ensures that the writing experience becomes creative and productive.
Step By Step Guide for Article Writing

How do you write an article that engages your readers from the first line until the last? That’s what most writers, whether beginners or seasoned pros are trying to achieve. I’ll describe a step-by-step process for crafting such gripping articles in this guide.
Step 1: Find Your Target Audience
First and foremost, identify your target readers. Speaking directly to a specific group improves engagement and helps you craft messages that resonate deeply. To pinpoint your audience:
- Take note of demographic attributes like age, gender, and profession.
- Consider their preferences and needs.
- Look into how much knowledge they are likely to possess concerning your topic.
Knowing this will help you decide what tone, language, and style best suits your readers. Remember, by understanding your audience better, you make it much easier to provide them with engaging content.
Step 2: Select a Topic and an Attractive Heading
Having understood your audience, select a relevant topic based on their interests and questions. Be sure it’s one you can competently discuss. When deciding how to start writing an article, ensure it begins with a captivating title.
A title should hint at what readers will gain from the article without revealing everything. Maintain some element of intrigue or provocation. For example, ‘6 Essentials You Probably Don’t Know About Gardening’ instead of just ‘Gardening Tips’.
Step 3: Research is Key
Good research is crucial to building credibility for beginners and experts alike. It prevents errors that could tarnish your piece immensely.
Thoroughly explore relevant books, scholarly articles, or reputable online resources. Find facts that build authenticity while debunking misconceptions that relate to your topic. Take notes on critical points discovered during this process—it’ll save you time when creating your first draft.
Step 4: Write a Comprehensive Brief
Having done your research, it’s time to write an outline or a brief—a roadmap for your article. This conveys how articles are written systematically without losing track of the main points.
Begin by starting the introduction with a punchy opener that draws readers in and a summary of what they’ll glean from reading. Section out specific points and ideas as separate headings and bullet points under each section to form the body. A conclusion rounds things up by restating key takeaways.
Step 5: Write and Proofread
Now comes the bulk of the work—writing. Respect the brief created earlier to ensure consistency and structure while drafting content. Use short, clear sentences while largely avoiding jargon unless absolutely necessary.
Post-writing, proofread ardently to check for typographical errors, inconsistent tenses, and poor sentence structures—and don’t forget factual correctness! It helps to read aloud, which can reveal awkward phrases that slipped through initial edits.
Step 6: Add Images and Infographics
To break text monotony and increase comprehension, introduce visuals such as images, infographics, or videos into your piece. They provide aesthetic relief while supporting the main ideas, increasing overall engagement.
Remember to source royalty-free images or get permission for copyrighted ones—you don’t want legal battles later!
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Article Writing

Regarding article writing, a few pitfalls can compromise the quality of your content. Knowing these and how to avoid them will enhance your work’s clarity, depth, and impact.
The first mistake often made is skimping on research. An article without solid underpinnings won’t merely be bland – it might mislead readers. Therefore, prioritize comprehensive investigation before penning down anything. Understanding common misconceptions or misinterpretations about your topic will strengthen your case.
Next, sidestep unnecessary jargon or excessively complex language. While showcasing an impressive vocabulary might seem appealing, remember that your primary objective is imparting information efficiently and effectively.
Moreover, failing to structure articles effectively represents another standard error. A structured piece aids in delivering complex ideas coherently. Maintaining a logical sequence facilitates reader comprehension, whether explaining a detailed concept or narrating an incident.
A piece lacking aesthetic allure can fail its purpose regardless of the value of its text. That’s where images come into play. Neglecting them is an all-too-common mistake among beginners. Relevant pictures inserted at appropriate junctures serve as visual breaks from texts and stimulate interest among readers.
Lastly, proofreading is vital in determining whether you can deliver a well-written article. Typos and grammatical errors can significantly undermine professional credibility while disrupting a smooth reading experience.
So, when pondering how articles are written, avoiding these mistakes goes a long way toward producing high-quality content that embodies both substance and style. Remember: practice is paramount when learning how to write excellent material!
How to Write an Article with SEOwind AI Writer?

Harnessing the power of artificial intelligence has been a major step in many industries. One such significant tool is SEOwind AI Writer , which is critical for those curious about how to write an article leveraging AI. In this section, I’ll cover how you can effectively use SEOwind AI writer to create compelling articles.
Step 1: Create a Brief and Outline
The first step in writing an article revolves around understanding your audience’s interests and then articulating them in a comprehensive brief that outlines the content’s framework.
- Decide on the topic: What ideas will you share via your article?
- Define your audience: Knowing who will read your text significantly influences your tone, style, and content depth.
- Establish main points: Highlight the key points or arguments you wish to exhibit in your drafted piece. This helps create a skeleton for your work and maintain a logical flow of information.
With SEOwind:
- you get all the content and keyword research for top-performing content in one place,
- you can generate a comprehensive AI outline with one click,
- users can quickly create a title, description, and keywords that match the topic you’re writing about.
As insightful as it might seem, having a roadmap doubles as a guide throughout the creative process. SEOwind offers a user-friendly interface that allows the easy input of essential elements like keywords, title suggestions, content length, etc. These provide an insightful outline, saving time with an indispensable tool that demonstrates the practicality of article writing.
Step 2: Write an AI Article using SEOwind
Once you have a brief ready, you can write an AI article with a single click. It will consider all the data you provided and much more, such as copywriting and SEO best practices , to deliver content that ranks.
Step 3: Give it a Human Touch
Finally, SEOwind’s intuitive platform delivers impeccably constructed content to dispel any confusion about writing an article. The result is inevitably exceptional, with well-structured sentences and logically sequenced sections that meet your demands.
However, artificial intelligence can sometimes miss the unique personal touch that enhances relatability in communication—making articles more compelling. Let’s master adding individualistic charm to personalize articles so that they resonate with audiences.
Tailoring the AI-generated piece with personal anecdotes or custom inputs helps to break the monotony and bolster engagement rates. Always remember to tweak essential SEO elements like meta descriptions and relevant backlinks.
So, whether it’s enhancing casual language flow or eliminating robotic consistency, the slightest modifications can breathe life into the text and transform your article into a harmonious man-machine effort. Remember – it’s not just about technology making life easy but also how effectively we utilize this emerging trend!
Common Questions on how to write an article
Delving into the writing world, especially regarding articles, can often lead to a swarm of questions. Let’s tackle some common queries that newbies and seasoned writers frequently stumble upon to make your journey more comfortable and rewarding.
What is the easiest way to write an article?
The easiest way to write an article begins with a clear structure. Here are five simple steps you can follow:
- Identify your audience: The first thing you should consider while planning your article is who will read it? Identifying your target audience helps shape the article’s content, style, and purpose.
- Decide on a topic and outline: Determining what to write about can sometimes be a formidable task. Try to ensure you cover a topic you can cover effectively or for which you feel great passion. Next, outline the main points you want to present throughout your piece.
- Do the research: Dig deep into resources for pertinent information regarding your topic and gather as much knowledge as possible. An informed writer paves the way for a knowledgeable reader.
- Drafting phase: Begin with an engaging introduction followed by systematically fleshing out each point from your outline in body paragraphs before ending with conclusive remarks tying together all the earlier arguments.
- Fine-tune through editing and proofreading: Errors happen no matter how qualified or experienced a writer may be! So make sure to edit and proofread before publishing.
Keep these keys in mind and remain patient and persistent. There’s no easier alternative for writing an article.
How can I write an article without knowing about the topic?
We sometimes need to write about less familiar subjects – but do not fret! Here’s my approach:
- First off, start by thoroughly researching subject-centric reliable sources. The more information you have, the better poised you are to write confidently about it.
- While researching, take notes and highlight the most essential points.
- Create an outline by organizing these points logically – this essentially becomes your article’s backbone.
- Start writing based on your research and outlined structure. If certain aspects remain unclear, keep investigating until clarity prevails.
Getting outside your comfort zone can be daunting, but is also a thrilling chance to expand your horizons.
What is your process for writing an article quickly?
In terms of speed versus quality in writing an article – strikingly enough, they aren’t mutually exclusive. To produce a high-quality piece swiftly, adhere to the following steps:
- Establish purpose and audience: Before cogs start turning on phrase-spinning, be clear on why you’re writing and who will likely read it.
- Brainstorm broadly, then refine: Cast a wide net initially regarding ideas around your topic. Then, narrow down those areas that amplify your core message or meet objectives.
- Create a robust outline: A detailed roadmap prevents meandering during actual writing and saves time!
- Ignore perfection in the first draft: Speed up initial drafting by prioritizing getting your thoughts on paper over perfect grammar or sentence compositions.
- Be disciplined with edits and revisions: Try adopting a cut, shorten, and replace mantra while trimming fluff without mercy!
Writing quickly requires practice and strategic planning – but rest assured, it’s entirely possible!
Seasoned SaaS and agency growth expert with deep expertise in AI, content marketing, and SEO. With SEOwind, he crafts AI-powered content that tops Google searches and magnetizes clicks. With a track record of rocketing startups to global reach and coaching teams to smash growth, Tom's all about sharing his rich arsenal of strategies through engaging podcasts and webinars. He's your go-to guy for transforming organic traffic, supercharging content creation, and driving sales through the roof.
Table of Contents
- 1 What is an Article?
- 2 Objectives of Article Writing
- 3 What is the Format of an Article?
- 4 What Should Be in an Article?
- 5 How should you structure an article?
- 6 Tips for Writing a Good Article
- 7 Step By Step Guide for Article Writing
- 8 Common Mistakes to Avoid in Article Writing
- 9 How to Write an Article with SEOwind AI Writer?
- 10 Common Questions on how to write an article
Related Posts

- How to Make ChatGPT Write Like a Human
- AI Writing Myths and Misconceptions: Separating Fact from Fiction

AI Ghostwriting: Craft Perfect Content Fast!
- #100Posts30DaysChallenge
- Affiliate program
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions
Latest Posts
- Boost Your SaaS Growth: Top SaaS Content Marketing Agency
- Content Intelligence and AI – Boost your strategy
- SEOwind vs MarketMuse vs Frase
- SEOwind vs Marketmuse vs Clearscope
- SEOwind vs Clearscope vs Frase
- SEOwind vs Surfer SEO vs Clearscope
- SEOwind vs Surfer SEO vs Frase
- SEOwind vs Jasper AI vs Frase
- SEOwind vs Rytr vs Jasper
- SEOwind vs Writesonic vs Rytr
- SEOwind vs Writesonic vs Copy.ai
© 2024 SEOwind.
- AI Article Writer
- Content Brief Generator
- Human vs AI Experiment
Privacy Overview
- How to Cite
- Language & Lit
- Rhyme & Rhythm
- The Rewrite
- Search Glass
How to Write a Good Introduction for an Article
Sometimes the hardest part of writing an article is getting started. Your introduction will pull in readers, so it needs to be the best paragraph of the entire article. Writing a good introduction is easy as easy as 1-2-3, if you know exactly how to go about doing it
Choose a topic for your article. This is will be what the article is mainly about.
Write a first sentence that draws in readers. Some great ideas include asking a question, using a quote or stating an amazing fact.
Write one or two sentences that answer the questions who, what, when, where, why and how. This is the typical outline for the first paragraph of a news article.
Consider a final sentence to sum up your article. This works in much of the same way as a thesis sentence in an essay.
Revise the paragraph. You may want to play with word choice and order to make it as readable as possible.
Check for spelling and grammar mistakes.
- You can move some of the information from the first paragraph to subsequent paragraphs if you think it will make the article more interesting. However, for articles in a newspaper, answering the questions in the first paragraph is usually a must.
- Try not to use words and language that is over-complicated. Simple words and sentence construction is best.
- If you're using a computer, save often in case your computer freezes or the power goes out.
This article was written by the CareerTrend team, copy edited and fact checked through a multi-point auditing system, in efforts to ensure our readers only receive the best information. To submit your questions or ideas, or to simply learn more about CareerTrend, contact us [here](http://careertrend.com/about-us).
How to Get Started with Article Writing: A Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners
So you've always had a way with words, and you've finally decided to dip your toes into the realm of article writing. Congratulations, my friend! Whether you're itching to express your thoughts and insights or aiming to make a career out of crafting captivating content, writing articles can unlock a world of creativity. But where do you begin? Fear not, for this step-by-step guide is here to help you embark on your journey as a budding wordsmith.
From finding your niche to perfecting your writing skills, let's dive in and uncover the secrets to kickstarting your article-writing adventure. Get ready to unleash your inner storyteller and captivate readers one word at a time!
What is Article Writing?
Article writing is the craft of creating written content for various purposes. It involves conveying information clearly and engagingly to a specific audience . Starting with a compelling introduction, an article provides valuable insights and knowledge on a given topic. It is essential to include relevant facts and examples to support your ideas. A well-structured article typically comprises of short paragraphs and uses headings and subheadings to guide readers.
Strong article writing requires good research skills, excellent grammar, and proper formatting. By mastering the art of article writing, beginners can effectively share their ideas and opinions with a broader audience.
Benefits of Article Writing for Beginners
Start for free
Article writing is an excellent starting point for beginners. It helps develop writing skills and boosts creativity. Writing articles enhances critical thinking by requiring research and analysis . It also enables the writer to share knowledge and ideas with others. The process of writing articles improves communication skills and helps build a writer's portfolio. Moreover, article writing allows beginners to explore different topics, positioning them as experts in a specific area.
Step 1: Choose a Topic
Finding a topic that interests you.
Finding a topic that interests you is crucial when starting your article writing journey. Think about subjects you enjoy or have knowledge about. Consider your hobbies, passions, or areas where you excel. It's important to choose a topic that you genuinely care about, as it will make the writing process more enjoyable and help you connect with your readers. Don't be afraid to explore different angles or niches within your chosen topic to make it more unique and engaging.
Remember, the more interested you are in your topic, the more likely it is that others will be interested too. So, choose wisely and have fun!
Researching Popular Topics
Researching popular topics is an essential step in article writing. It not only helps you stay updated with current trends but also enables you to create content that resonates with your target audience . Here are some tips to streamline your research process:
- Identify your target audience : Define the demographic and interests of your readers to understand what topics are most likely to engage them.
- Utilize online tools : Leverage search engines, social media platforms, and keyword research tools to identify popular topics in your niche.
- Analyze competition : Explore articles and blogs written by competitors to gain insights into what topics have performed well for them.
- Stay updated : Follow news websites, industry publications, and influencers in your field to keep up with the latest trends and topics that are gaining traction.
- Engage with your audience : Pay attention to comments, feedback, and questions from your readers to identify what they're interested in and shape your content accordingly.
By conducting thorough research, you can ensure that your articles are relevant, engaging, and resonate with your target audience.
Narrowing Down Your Topic
When choosing a topic for your article, it's important to narrow it down to something specific. Start by brainstorming all the potential ideas and then consider which ones interest you the most. Once you have a general idea, try to make it more focused by asking yourself questions like "Who is my target audience?" or "What aspect of this topic do I want to explore?" This will help you create a clear and concise angle for your article, making it easier to write and more engaging for your readers.
Remember, specificity is key!
Step 2: Understand Your Audience
Identifying your target audience.
Identifying your target audience is crucial when writing an article. Who are you trying to reach? Start by defining their demographics - age, gender, location. Dive deeper to understand their interests, needs, and pain points. Are they tech-savvy or more traditional? What challenges do they face? Consider their motivations and desires. By analyzing their behavior and preferences, you can tailor your content to resonate with them.
This will help you engage and connect with your readers on a morepersonal level. Remember, understanding your target audience is the key to creating impactful articles. So, take the time to do your research and get to know them well.
Understanding Audience's Needs and Preferences
In order to be an effective article writer , it is crucial to understand the needs and preferences of your audience. This means taking the time to research and analyze your target readers, their interests, and what they are searching for. By doing so, you can tailor your content to meet their expectations, making it more engaging and relevant.
Whether it’s providing informative guides or entertaining stories, remember to keep your writing concise, easy to understand, and free of unnecessary fluff. By doing this, you will attract and retain your audience's attention, building a loyal readership over time.
Step 3: Conduct Thorough Research
Gathering information from reliable sources.
When writing an article, it is crucial to gather information from reliable sources. This ensures that your content is accurate and trustworthy. Start by identifying reputable sources, such as reputable websites, academic journals, or expert interviews. Use multiple sources to get a well-rounded perspective on the topic. Check for citations and references in the sources you find, as this indicates the information has been substantiated by other experts.
Avoid using sources that lack credibility or have a biased agenda. By gathering information from reliable sources, you can provide valuable and accurate content to your readers.
Organizing Your Research Findings
When it comes to organizing your research findings, it's crucial to have a systematic approach. Here are some tips to help you make sense of all the information you've gathered:
- Create a clear and logical structure for your article, outlining the main points you want to cover.
- Determine the most relevant and valuable findings from your research and highlight key data or evidence to support your claims.
- Categorize your findings into different sections or subheadings, making it easier for readers to navigate through your article.
- Use bullet points or numbered lists to present concise information or important details.
- Consider creating an annotated bibliography or reference list to keep track of your sources and ensure correct citations.
By organizing your research findings effectively, you'll be able to present your ideas in a coherent and structured manner, enhancing the clarity and impact of your article.
Step 4: Create an Outline
Structuring your article.
Structuring your article is essential for effective communication. Start with a compelling title that grabs attention. Divide your article into clear sections using subheadings to guide the reader. In the introduction, present the main idea and provide context. Keep paragraphs short and focused, each discussing one key point. Use bullet points or numbered lists for easy comprehension. In the conclusion, summarize the main points and conclude with a thought-provoking statement.
Remember to edit and proofread for clarity and coherence. A well-structured article enhances readability and ensures your message is conveyed effectively.
Outlining Main Points and Subtopics
When starting an article, it is crucial to outline the main points and subtopics you want to cover. This helps you maintain focus and structure throughout your writing. Begin by identifying the main idea or argument you want to convey. Then, list the key points that support or elaborate on this idea. Make sure each point flows logically and sequentially.
Next, break down these key points into subtopics that provide further details or examples. This way, you can organize your thoughts in a clear and coherent manner, ensuring your readers will easily follow your train of thought.
Step 5: Start Writing
Developing a strong body.
Developing a Strong Body is essential for article writing beginners. Regular exercise is key. Start with simple activities like walking or jogging to improve stamina and overall fitness. Include strength training exercises to build muscle and boost metabolism. Focus on workouts that target different body areas such as squats for legs, push-ups for upper body, and planks for core. Consistency is crucial, so aim for at least 3-4 times a week.
Alongside exercise, eat a balanced diet rich in proteins, vegetables, and whole grains to fuel your body and aid in muscle recovery. Hydrate adequately to stay focused and energized during writing sessions. Prioritize self-care and get enough rest for optimal physical and mental performance. With a strong body, writing will become effortless.
Creating an Engaging Conclusion
In order to create an engaging conclusion for your article, consider leaving the reader with something to think about or a call to action. A thought-provoking question or a compelling statement can keep your readers engaged and encourage them to explore the topic further.
Additionally, you can summarize your main points briefly and end on a strong note. Remember, a good conclusion should leave a lasting impression and leave the reader wanting more.
Step 6: Edit and Revise
Checking for grammar and spelling errors.
When you finish writing your article, take a moment to check for grammar and spelling errors. Read it aloud or use a spell-check tool to catch any mistakes. Pay attention to punctuation, capitalization, and word choice. Double-check names, dates, and statistics to ensure accuracy. If possible, ask someone else to proofread your work. Give yourself time between writing and proofreading to identify errors more effectively.
Taking these simple steps can greatly improve the quality of your article and make it more professional.
Improving Sentence Structure and Clarity
To enhance your article writing, focus on sentence structure and clarity. Keep your sentences short and to the point. Avoid lengthy, convoluted sentences that confuse readers. Use active verbs to make your writing more engaging and dynamic. Break up long paragraphs into smaller chunks to improve readability. Use transition words to create smooth transitions between ideas. An automatic solution through which you can achieve all these things in your write-up is by utilizing a paraphrase tool . Lastly, always proofread your work to eliminate any grammatical errors and ensure clarity. By improving sentence structure and clarity, you can make your article more concise, engaging, and enjoyable for your readers.
Ensuring Coherence and Flow
Ensuring coherence and flow in your article is crucial for keeping the reader engaged. Start by using clear and concise language to express your ideas. Break your article into short paragraphs and vary their lengths to maintain a smooth flow. Use transition words and phrases to connect your ideas and guide the reader through the article.
Additionally, make sure each paragraph focuses on a single point to avoid confusion.
Finally, read your article aloud or ask someone to read it to ensure it flows naturally and is easy to understand. Remember, coherence and flow are keys to effective article writing.
Step 7: Proofread and Finalize
Reading and re-reading your article.
Once you finish writing your article, take a moment to step back and give it a read. Look for any typos, grammatical errors, or awkward phrasing. This initial read-through allows you to catch any obvious mistakes or areas that need improvement.
After this first pass, take a break. Give yourself some distance from the article before coming back to it for a second read. This time, focus on the overall flow and structure of your piece. Does it make sense? Is the information organized logically? Take note of any areas that feel disjointed or confusing.
When you're satisfied with the structure, read it through one final time, paying attention to the details. Check for consistency in verb tenses, formatting, and citation styles. Ensure that your article flows smoothly and that each sentence serves a purpose.
By actively reading and re-reading your article, you can catch errors, improve clarity, and deliver a polished final piece that engages and informs your readers.
Formatting and Styling
Formatting and styling is crucial when it comes to writing an article. A well-structured article enhances readability and grabs the reader's attention. Start with a catchy headline that summarizes your content. Use subheadings to break up the text and make it more scannable. Keep your paragraphs short and to the point. Bullet points and numbered lists are great for conveying information concisely. Incorporate relevant images to engage your readers visually.
Lastly, proofread your article for grammar and spelling errors. Taking the time to format and style your article properly will greatly improve its impact and readability.
Reflecting on Your Article Writing Journey
As you near the end of your article writing journey, take a moment to reflect on how far you've come. Think about the skills you've acquired, the topics you've delved into, and the challenges you've conquered. Remember the moments of frustration and the triumphs that followed. Embrace the growth you've experienced and the knowledge you've gained along the way. Appreciate the progress, no matter how small, and use it as fuel to continue honing your craft. Remember, every step counts and every article is an opportunity to improve. Keep writing, keep learning, and keep pushing yourself to new heights.
Taking Next Steps to Improve as a Writer
Now that you've taken your first steps into article writing, it's time to take the next ones in order to improve as a writer. One way to do this is by reading extensively. Pick up different genres and styles of writing to broaden your horizons. Another crucial step is to write consistently. Make a writing schedule and stick to it, even if it's just for a few minutes each day.
Additionally, seek feedback from others. Join writing groups or ask friends to read your work and provide constructive criticism. Remember, practice, exposure to different writing styles, and feedback are key to becoming a better writer.
Wrapping up
Writing articles can be a daunting task for beginners, but with this step-by-step guide, you'll be well on your way to becoming a proficient article writer.
First, choose a topic that interests you and conduct thorough research to gather all the necessary information. Then, create an outline to organize your thoughts and ensure a logical flow in your writing. When crafting the introduction, aim to grab your readers' attention with a compelling hook. In the body of the article, present your ideas clearly, providing evidence and examples to support your claims. Use subheadings and bullet points to enhance readability. Once the main points are covered, wrap up your article with a conclusion that summarizes your key takeaways and leaves a lasting impression on the reader. Remember to proofread and edit your work to eliminate any errors or inconsistencies. With practice and perseverance, you'll develop your own unique writing style and become an accomplished article writer.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Turk J Urol
- v.39(Suppl 1); 2013 Sep
How to write an introduction section of a scientific article?
An article primarily includes the following sections: introduction, materials and methods, results, discussion, and conclusion. Before writing the introduction, the main steps, the heading and the familiarity level of the readers should be considered. Writing should begin when the experimental system and the equipment are available. The introduction section comprises the first portion of the manuscript, and it should be written using the simple present tense. Additionally, abbreviations and explanations are included in this section. The main goal of the introduction is to convey basic information to the readers without obligating them to investigate previous publications and to provide clues as to the results of the present study. To do this, the subject of the article should be thoroughly reviewed, and the aim of the study should be clearly stated immediately after discussing the basic references. In this review, we aim to convey the principles of writing the introduction section of a manuscript to residents and young investigators who have just begun to write a manuscript.
Introduction
When entering a gate of a magnificent city we can make a prediction about the splendor, pomposity, history, and civilization we will encounter in the city. Occasionally, gates do not give even a glimpse of the city, and it can mislead the visitors about inner sections of the city. Introduction sections of the articles are like gates of a city. It is a presentation aiming at introducing itself to the readers, and attracting their attention. Attractiveness, clarity, piquancy, and analytical capacity of the presentation will urge the reader to read the subsequent sections of the article. On the other hand as is understood from the motto of antique Greek poet Euripides “a bad beginning makes a bad ending”, ‘Introduction’ section of a scientific article is important in that it can reveal the conclusion of the article. [ 1 ]
It is useful to analyze the issues to be considered in the ‘Introduction’ section under 3 headings. Firstly, information should be provided about the general topic of the article in the light of the current literature which paves the way for the disclosure of the objective of the manuscript. Then the specific subject matter, and the issue to be focused on should be dealt with, the problem should be brought forth, and fundamental references related to the topic should be discussed. Finally, our recommendations for solution should be described, in other words our aim should be communicated. When these steps are followed in that order, the reader can track the problem, and its solution from his/her own perspective under the light of current literature. Otherwise, even a perfect study presented in a non-systematized, confused design will lose the chance of reading. Indeed inadequate information, inability to clarify the problem, and sometimes concealing the solution will keep the reader who has a desire to attain new information away from reading the manuscript. [ 1 – 3 ]
First of all, explanation of the topic in the light of the current literature should be made in clear, and precise terms as if the reader is completely ignorant of the subject. In this section, establishment of a warm rapport between the reader, and the manuscript is aimed. Since frantic plunging into the problem or the solution will push the reader into the dilemma of either screening the literature about the subject matter or refraining from reading the article. Updated, and robust information should be presented in the ‘Introduction’ section.
Then main topic of our manuscript, and the encountered problem should be analyzed in the light of the current literature following a short instance of brain exercise. At this point the problems should be reduced to one issue as far as possible. Of course, there might be more than one problem, however this new issue, and its solution should be the subject matter of another article. Problems should be expressed clearly. If targets are more numerous, and complex, solutions will be more than one, and confusing.
Finally, the last paragraphs of the ‘Introduction’ section should include the solution in which we will describe the information we generated, and related data. Our sentences which arouse curiosity in the readers should not be left unanswered. The reader who thinks to obtain the most effective information in no time while reading a scientific article should not be smothered with mysterious sentences, and word plays, and the readers should not be left alone to arrive at a conclusion by themselves. If we have contrary expectations, then we might write an article which won’t have any reader. A clearly expressed or recommended solutions to an explicitly revealed problem is also very important for the integrity of the ‘Introduction’ section. [ 1 – 5 ]
We can summarize our arguments with the following example ( Figure 1 ). The introduction section of the exemplary article is written in simple present tense which includes abbreviations, acronyms, and their explanations. Based on our statements above we can divide the introduction section into 3 parts. In the first paragraph, miniaturization, and evolvement of pediatric endourological instruments, and competitions among PNL, ESWL, and URS in the treatment of urinary system stone disease are described, in other words the background is prepared. In the second paragraph, a newly defined system which facilitates intrarenal access in PNL procedure has been described. Besides basic references related to the subject matter have been given, and their outcomes have been indicated. In other words, fundamental references concerning main subject have been discussed. In the last paragraph the aim of the researchers to investigate the outcomes, and safety of the application of this new method in the light of current information has been indicated.

An exemplary introduction section of an article
Apart from the abovementioned information about the introduction section of a scientific article we will summarize a few major issues in brief headings
Important points which one should take heed of:
- Abbreviations should be given following their explanations in the ‘Introduction’ section (their explanations in the summary does not count)
- Simple present tense should be used.
- References should be selected from updated publication with a higher impact factor, and prestigous source books.
- Avoid mysterious, and confounding expressions, construct clear sentences aiming at problematic issues, and their solutions.
- The sentences should be attractive, tempting, and comjprehensible.
- Firstly general, then subject-specific information should be given. Finally our aim should be clearly explained.
The Bandzoogle Blog
How to write an effective musician bio (with examples).
Updated by Melanie Kealey on Dec 07, 2023 in: Website Tips
Posted on Oct 27, 2016

One of the most important pages on your music website is your bio page. Let's face it - although you may be great at composing melodies and lyrics, it’s hard to write about yourself. Writing a great musician bio is not an easy thing to do, but it’s a really important way to make your band appear professional.
A great musician bio will create the first impression of you to many of your website visitors, so make it a good one. It will help convert your visitors into fans, as well as give music reviewers and media a sense of who you are.
So how do you go about writing that perfect musician bio? These elements will help you write an effective bio that details your music and your background in a concise and inviting way.
1. An engaging introduction
The toughest part about writing your musician bio is getting started. Make a few notes on a piece of paper to begin. Jot down your name, and where you’re from. Add what your music sounds like, as objectively as you can, and then write down your influences.
This will help you shape a sentence or two as an introduction. You’ll want it to be engaging, but concise. It’s easy to go too long here, so think about how you might quickly introduce yourself to someone who has never met you or heard your music before.
Keep your tone in mind as you write your bio’s introduction. Depending on your style of music– and your personality–you may want to inject some humor into your bio. You may also want to write more formally.
2. Add background information
Include some relevant background information in your bio, including your musical history, but again: keep it short. You want to be sure to keep your visitors engaged - not lose them with lengthy paragraphs of text.
Write down your musical history and education, and choose just a few relevant parts to incorporate into your bio.
As a note, make sure to write your musician bio in the third person. This will make it quick to scan and understand, and will help with your website’s search engine optimization. It also allows media, bloggers, bookers, or venues to simply copy and paste your bio if they need it.
3. Describe your music
Although most of your fans will already be familiar with your music, a blogger or journalist may not yet have a sense of your sound. Add a quick description that talks about what your music is like.
It may be hard to fit your sound into a genre, but try to use a few familiar words so that people can place you. This will help someone reading your bio want to also listen to your music.
Talk a bit about what you’re currently up to with your music. Have you just gone into the studio? Released a single? Co-written a song with another artist?
Choose the most relevant and recent thing that you’ve done with your music, and add that to your musician bio.
If you’re in a band, you can write out the full band bio at the top of your page. Beneath it, you can add text talking about each band member. Include an image with each musician bio to create visual interest.
4. Career highlights and achievements
Think about everything you’ve accomplished with your music. Have you opened for a well-known band, or played a big festival? Have you had success on streaming music platforms, charted on college radio, or been nominated for an award?
Make a list of your achievements. Then pick two or three of the most impressive items, and include those in your musician bio. One of these items should be pretty recent, to show that you’re an active musician.
Don’t exaggerate or embellish in this part of your bio–stick to the facts, but present them in a positive way.
5. Add a media quote
A quote from a reviewer is a nice way to show that others are talking professionally about your music. Look for a quote that will enhance your musician bio–something that helps to describe your sound, or your latest album. It’ll lend some authority to your musician bio.
A quote can be a skillful way to emphasize your accomplishments, or your new music. It could be from a venue owner, a musician you’ve worked with, an album review, or someone in the media.
See where it fits in seamlessly–a quote about your new album will work when talking about your music to date, or a venue quote will help describe your live show with sold out numbers.
If you don’t have a quote, that’s ok–just keep it in mind for the future. You could reach out to someone you’ve connected with professionally to see if they can provide you with something you can use in your bio.
6. Up-to-date information
Your musician bio is an important part of your music website–it can let new visitors know who you are, and offers industry professionals something to use in their promotions. Add your bio to a couple of places on your website to make it easy to find.
You can place a short elevator pitch on your ‘Home’ page, and use your full, most in-depth musician bio on your ‘About’ page , including some downloadable press-quality images there as well.
You’ll also want to include a version of your bio in your electronic press kit (EPK) . You can use the short version, or add multiple versions for press and industry to choose from.
Make a note to update your bio in these places with any new projects, releases, collaborations, or upcoming tours. You’ll want to be sure to add new accomplishments as your career moves forward. A stale, outdated musician bio won’t serve you well, so make sure to refresh it regularly!
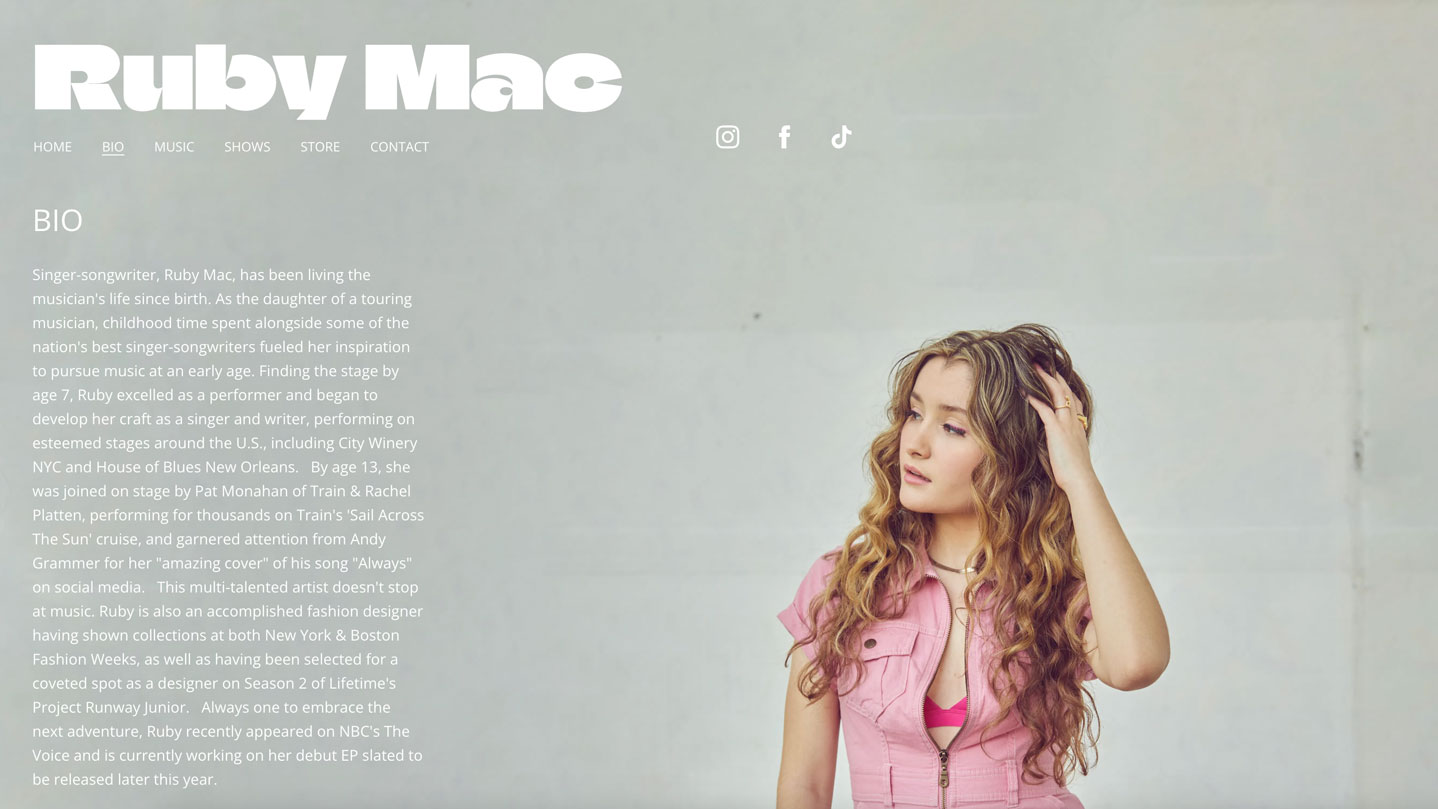
Artist: Ruby Mac
Sample musician bios
With all this in mind, it can still feel overwhelming to take every piece of advice and condense it into a readable musician bio. So, a sample musician bio might go a bit like this:
Quick introduction. Mention your name, your style of music, and your influences.
Next, move to your background. Mention how long you’ve been playing, the bands you’ve played with, and a notable accomplishment.
End with what you’re doing currently. This could be playing shows, recording, writing, or a mention of your latest album.
Below are a few examples of great musician bios to give you some inspiration.
Contemporary R&B / gospel artist Queen Makedah uses color and sections to give her musician bio a streamlined look. It’s got depth, with plenty of quotes and information, but is easy to scan, and enjoyable to read:

Singer/songwriter Ben Harold has created a bio that emphasizes his musical history and achievements, telling his story in a way that makes you want to read it. His bio text floats over the background imagery, lending his musician bio a balanced look:

Jazz guitarist Sam Wilson has created a musician bio that’s a great example of combining all of the important elements. From a description of her style, to her accomplishments, and a mention of her new, award-winning album, her bio covers all of the bases:
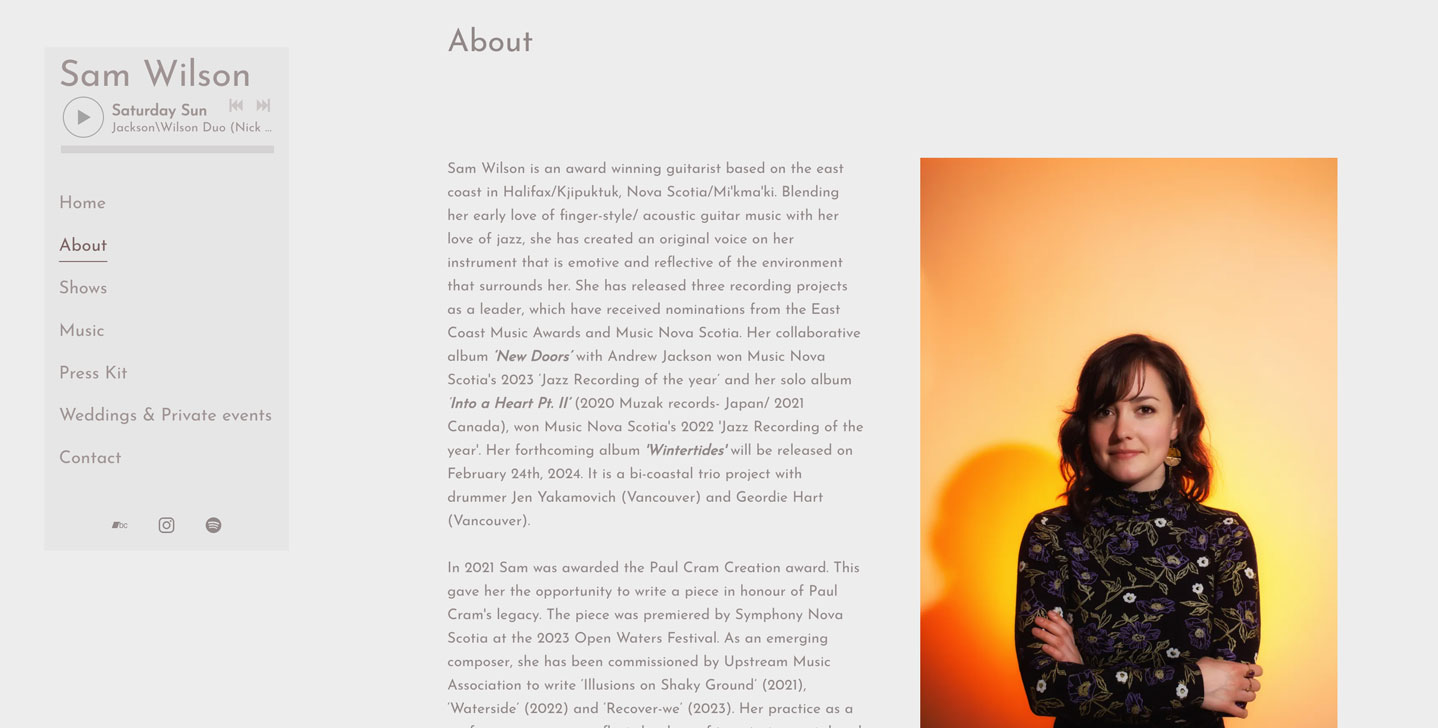
As a long-time musician, Eric Essix has written a bio that tells his story in detail. It’s interesting for fans to see where he has come from, and what he is doing now. Then he’s also included a succinct musician bio on his EPK page that sums up his latest project. It’s easy for industry to skim, with a button leading back to his full website for extra information:
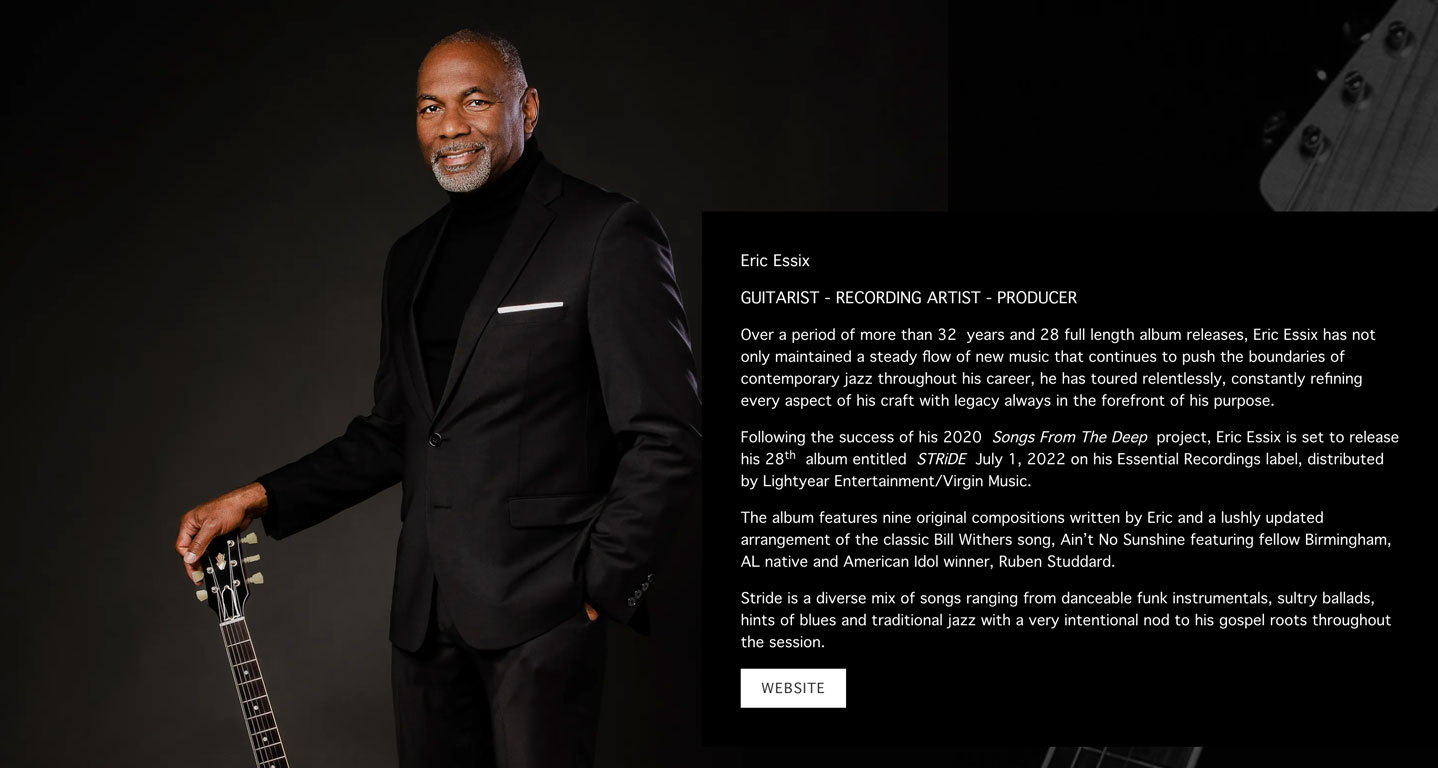
Once you’re done writing your musician bio, check your spelling. Then check it again. Be sure there are no errors or typos! It might even help to read it out loud a couple of times to be sure it flows well and makes sense. Consider passing it along to a few friends to get their eyes on it, too.
You can use these elements to create an effective musician bio. Use it in multiple places on your music website , and don’t forget to keep it up to date as your music career moves forward. It will serve you well if it’s up to date and compelling.
Why not share this with your friends? Twitter Facebook
Build a stunning band website and store in minutes.
- Promote your music on your own unique website.
- Sell music & merch directly to your fans. Keep 100%.
- Grow your fan base with built-in marketing tools.
Free 30 day trial, no credit card needed.
Share your thoughts
This website or its third-party tools process strictly necessary cookies to make our site work. In addition, if you consent, we will use optional functional, performance and targeting cookies to help us understand how people use our website, to improve your user experience and to provide you with targeted advertisements. To learn more, please refer to the cookie policy . You can accept all cookies or other identifiers by clicking accept all, or reject non-essential to continue to browse otherwise.
In 2017, the readers of New York times were calculated to be more than 9 million! The paper’s writers interact with their readers through articles. Keeping this in mind, we can say that articles are an integral part of the written communication world. They can be hidden right under our eyes and we may not know it. Evidently, you’re reading an article .
Suggested Videos
What is an article.
As you might’ve guessed, an article addresses its readers. In other words, we write an article to interact with our readers. Hence it should be tailored accordingly for an audience. Generally, articles are published in newspapers, magazines, journals, etc. Further, it should attract and retain the reader’s attention.
Learn more about the Paragraph Writing here in detail.
Often confused with reports , articles are less formal. Although, they can be both formal or informal , again depending on the target audience. Also, an article mostly contains the opinions and thoughts of the writer, backed by facts and evidence. Lastly, an article can describe events, occurrences, persons, places, experiences, etc.

Browse more Topics under Writing
- Descriptive Essay
- Diary Entry
- Formal Letters
- Informal Letters
- Letter Writing
- Non-Classified/Display Advertisements
- Story: Characters
- Story: Setting
The Format of Articles
There are many different formats for articles circulating around. Let’s have a look at the most general format of articles:
Topic of the Article
Contents of Articles
Similar to most of the written literary forms, articles contain an introduction , a body, and a conclusion. Again, we write an article for the target audience. Of course, if our article fails to appeal to the target audience, it would be of no use. Therefore, articles should have a title that grabs the eyeballs of their readers.
The introduction should talk more about the topic under concern in the article. If the introduction is lengthy and boring, the readers will bail out from reading and shift to another piece of writing.
The main body should contain 2 to 5 paragraphs, which further discuss the topic and explain the idea. Again, a lengthy and boring body would distract the reader’s attention and discourage them from further reading. Hence, articles should be tailored to suit the target audience’s taste. For example, if it is meant for 5th-grade students, then you should use simple terms. On the contrary, if it is meant for doctors, it should contain a language that makes your readers feel at home.
Read some Amazing Tips on Story Writing here in detail
A grand ending is as important as the article itself. Unlike an essay, where we conclude by summarizing all the ideas we’ve been discussing, articles follow a different approach. An article’s ending should be out of the box, something that leaves the readers thinking or calls for action. Ending with a question can be your best bet, right?
Solved Question for You
Q: Identify the best article heading for the following topic: UN has recognized the toy train of Darjeeling as a world heritage item.
- Darjeeling toy train new heritage item
- The UN recognizes toy train
- Heard this about the Darjeeling Toy Train?
- Darjeeling Toy Train
Ans: The correct option is C. It is a catchy title that draws the attention of the reader. It also uses correct punctuation and is the most appropriate among the options given.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Non-Classified or Display Advertisements
5 responses to “Story: Characters”
great article
very clean post.
awesome work
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Open access
- Published: 26 March 2024
Predicting and improving complex beer flavor through machine learning
- Michiel Schreurs ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-9449-5619 1 , 2 , 3 na1 ,
- Supinya Piampongsant 1 , 2 , 3 na1 ,
- Miguel Roncoroni ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-7461-1427 1 , 2 , 3 na1 ,
- Lloyd Cool ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-9936-3124 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 ,
- Beatriz Herrera-Malaver ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-5096-9974 1 , 2 , 3 ,
- Christophe Vanderaa ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-7443-5427 4 ,
- Florian A. Theßeling 1 , 2 , 3 ,
- Łukasz Kreft ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-7620-4657 5 ,
- Alexander Botzki ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-6691-4233 5 ,
- Philippe Malcorps 6 ,
- Luk Daenen 6 ,
- Tom Wenseleers ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-1434-861X 4 &
- Kevin J. Verstrepen ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-3077-6219 1 , 2 , 3
Nature Communications volume 15 , Article number: 2368 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
42k Accesses
786 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Chemical engineering
- Gas chromatography
- Machine learning
- Metabolomics
- Taste receptors
The perception and appreciation of food flavor depends on many interacting chemical compounds and external factors, and therefore proves challenging to understand and predict. Here, we combine extensive chemical and sensory analyses of 250 different beers to train machine learning models that allow predicting flavor and consumer appreciation. For each beer, we measure over 200 chemical properties, perform quantitative descriptive sensory analysis with a trained tasting panel and map data from over 180,000 consumer reviews to train 10 different machine learning models. The best-performing algorithm, Gradient Boosting, yields models that significantly outperform predictions based on conventional statistics and accurately predict complex food features and consumer appreciation from chemical profiles. Model dissection allows identifying specific and unexpected compounds as drivers of beer flavor and appreciation. Adding these compounds results in variants of commercial alcoholic and non-alcoholic beers with improved consumer appreciation. Together, our study reveals how big data and machine learning uncover complex links between food chemistry, flavor and consumer perception, and lays the foundation to develop novel, tailored foods with superior flavors.
Similar content being viewed by others
BitterSweet: Building machine learning models for predicting the bitter and sweet taste of small molecules
Rudraksh Tuwani, Somin Wadhwa & Ganesh Bagler
Sensory lexicon and aroma volatiles analysis of brewing malt
Xiaoxia Su, Miao Yu, … Tianyi Du
Predicting odor from molecular structure: a multi-label classification approach
Kushagra Saini & Venkatnarayan Ramanathan
Introduction
Predicting and understanding food perception and appreciation is one of the major challenges in food science. Accurate modeling of food flavor and appreciation could yield important opportunities for both producers and consumers, including quality control, product fingerprinting, counterfeit detection, spoilage detection, and the development of new products and product combinations (food pairing) 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 . Accurate models for flavor and consumer appreciation would contribute greatly to our scientific understanding of how humans perceive and appreciate flavor. Moreover, accurate predictive models would also facilitate and standardize existing food assessment methods and could supplement or replace assessments by trained and consumer tasting panels, which are variable, expensive and time-consuming 7 , 8 , 9 . Lastly, apart from providing objective, quantitative, accurate and contextual information that can help producers, models can also guide consumers in understanding their personal preferences 10 .
Despite the myriad of applications, predicting food flavor and appreciation from its chemical properties remains a largely elusive goal in sensory science, especially for complex food and beverages 11 , 12 . A key obstacle is the immense number of flavor-active chemicals underlying food flavor. Flavor compounds can vary widely in chemical structure and concentration, making them technically challenging and labor-intensive to quantify, even in the face of innovations in metabolomics, such as non-targeted metabolic fingerprinting 13 , 14 . Moreover, sensory analysis is perhaps even more complicated. Flavor perception is highly complex, resulting from hundreds of different molecules interacting at the physiochemical and sensorial level. Sensory perception is often non-linear, characterized by complex and concentration-dependent synergistic and antagonistic effects 15 , 16 , 17 , 18 , 19 , 20 , 21 that are further convoluted by the genetics, environment, culture and psychology of consumers 22 , 23 , 24 . Perceived flavor is therefore difficult to measure, with problems of sensitivity, accuracy, and reproducibility that can only be resolved by gathering sufficiently large datasets 25 . Trained tasting panels are considered the prime source of quality sensory data, but require meticulous training, are low throughput and high cost. Public databases containing consumer reviews of food products could provide a valuable alternative, especially for studying appreciation scores, which do not require formal training 25 . Public databases offer the advantage of amassing large amounts of data, increasing the statistical power to identify potential drivers of appreciation. However, public datasets suffer from biases, including a bias in the volunteers that contribute to the database, as well as confounding factors such as price, cult status and psychological conformity towards previous ratings of the product.
Classical multivariate statistics and machine learning methods have been used to predict flavor of specific compounds by, for example, linking structural properties of a compound to its potential biological activities or linking concentrations of specific compounds to sensory profiles 1 , 26 . Importantly, most previous studies focused on predicting organoleptic properties of single compounds (often based on their chemical structure) 27 , 28 , 29 , 30 , 31 , 32 , 33 , thus ignoring the fact that these compounds are present in a complex matrix in food or beverages and excluding complex interactions between compounds. Moreover, the classical statistics commonly used in sensory science 34 , 35 , 36 , 37 , 38 , 39 require a large sample size and sufficient variance amongst predictors to create accurate models. They are not fit for studying an extensive set of hundreds of interacting flavor compounds, since they are sensitive to outliers, have a high tendency to overfit and are less suited for non-linear and discontinuous relationships 40 .
In this study, we combine extensive chemical analyses and sensory data of a set of different commercial beers with machine learning approaches to develop models that predict taste, smell, mouthfeel and appreciation from compound concentrations. Beer is particularly suited to model the relationship between chemistry, flavor and appreciation. First, beer is a complex product, consisting of thousands of flavor compounds that partake in complex sensory interactions 41 , 42 , 43 . This chemical diversity arises from the raw materials (malt, yeast, hops, water and spices) and biochemical conversions during the brewing process (kilning, mashing, boiling, fermentation, maturation and aging) 44 , 45 . Second, the advent of the internet saw beer consumers embrace online review platforms, such as RateBeer (ZX Ventures, Anheuser-Busch InBev SA/NV) and BeerAdvocate (Next Glass, inc.). In this way, the beer community provides massive data sets of beer flavor and appreciation scores, creating extraordinarily large sensory databases to complement the analyses of our professional sensory panel. Specifically, we characterize over 200 chemical properties of 250 commercial beers, spread across 22 beer styles, and link these to the descriptive sensory profiling data of a 16-person in-house trained tasting panel and data acquired from over 180,000 public consumer reviews. These unique and extensive datasets enable us to train a suite of machine learning models to predict flavor and appreciation from a beer’s chemical profile. Dissection of the best-performing models allows us to pinpoint specific compounds as potential drivers of beer flavor and appreciation. Follow-up experiments confirm the importance of these compounds and ultimately allow us to significantly improve the flavor and appreciation of selected commercial beers. Together, our study represents a significant step towards understanding complex flavors and reinforces the value of machine learning to develop and refine complex foods. In this way, it represents a stepping stone for further computer-aided food engineering applications 46 .
To generate a comprehensive dataset on beer flavor, we selected 250 commercial Belgian beers across 22 different beer styles (Supplementary Fig. S1 ). Beers with ≤ 4.2% alcohol by volume (ABV) were classified as non-alcoholic and low-alcoholic. Blonds and Tripels constitute a significant portion of the dataset (12.4% and 11.2%, respectively) reflecting their presence on the Belgian beer market and the heterogeneity of beers within these styles. By contrast, lager beers are less diverse and dominated by a handful of brands. Rare styles such as Brut or Faro make up only a small fraction of the dataset (2% and 1%, respectively) because fewer of these beers are produced and because they are dominated by distinct characteristics in terms of flavor and chemical composition.
Extensive analysis identifies relationships between chemical compounds in beer
For each beer, we measured 226 different chemical properties, including common brewing parameters such as alcohol content, iso-alpha acids, pH, sugar concentration 47 , and over 200 flavor compounds (Methods, Supplementary Table S1 ). A large portion (37.2%) are terpenoids arising from hopping, responsible for herbal and fruity flavors 16 , 48 . A second major category are yeast metabolites, such as esters and alcohols, that result in fruity and solvent notes 48 , 49 , 50 . Other measured compounds are primarily derived from malt, or other microbes such as non- Saccharomyces yeasts and bacteria (‘wild flora’). Compounds that arise from spices or staling are labeled under ‘Others’. Five attributes (caloric value, total acids and total ester, hop aroma and sulfur compounds) are calculated from multiple individually measured compounds.
As a first step in identifying relationships between chemical properties, we determined correlations between the concentrations of the compounds (Fig. 1 , upper panel, Supplementary Data 1 and 2 , and Supplementary Fig. S2 . For the sake of clarity, only a subset of the measured compounds is shown in Fig. 1 ). Compounds of the same origin typically show a positive correlation, while absence of correlation hints at parameters varying independently. For example, the hop aroma compounds citronellol, and alpha-terpineol show moderate correlations with each other (Spearman’s rho=0.39 and 0.57), but not with the bittering hop component iso-alpha acids (Spearman’s rho=0.16 and −0.07). This illustrates how brewers can independently modify hop aroma and bitterness by selecting hop varieties and dosage time. If hops are added early in the boiling phase, chemical conversions increase bitterness while aromas evaporate, conversely, late addition of hops preserves aroma but limits bitterness 51 . Similarly, hop-derived iso-alpha acids show a strong anti-correlation with lactic acid and acetic acid, likely reflecting growth inhibition of lactic acid and acetic acid bacteria, or the consequent use of fewer hops in sour beer styles, such as West Flanders ales and Fruit beers, that rely on these bacteria for their distinct flavors 52 . Finally, yeast-derived esters (ethyl acetate, ethyl decanoate, ethyl hexanoate, ethyl octanoate) and alcohols (ethanol, isoamyl alcohol, isobutanol, and glycerol), correlate with Spearman coefficients above 0.5, suggesting that these secondary metabolites are correlated with the yeast genetic background and/or fermentation parameters and may be difficult to influence individually, although the choice of yeast strain may offer some control 53 .

Spearman rank correlations are shown. Descriptors are grouped according to their origin (malt (blue), hops (green), yeast (red), wild flora (yellow), Others (black)), and sensory aspect (aroma, taste, palate, and overall appreciation). Please note that for the chemical compounds, for the sake of clarity, only a subset of the total number of measured compounds is shown, with an emphasis on the key compounds for each source. For more details, see the main text and Methods section. Chemical data can be found in Supplementary Data 1 , correlations between all chemical compounds are depicted in Supplementary Fig. S2 and correlation values can be found in Supplementary Data 2 . See Supplementary Data 4 for sensory panel assessments and Supplementary Data 5 for correlation values between all sensory descriptors.
Interestingly, different beer styles show distinct patterns for some flavor compounds (Supplementary Fig. S3 ). These observations agree with expectations for key beer styles, and serve as a control for our measurements. For instance, Stouts generally show high values for color (darker), while hoppy beers contain elevated levels of iso-alpha acids, compounds associated with bitter hop taste. Acetic and lactic acid are not prevalent in most beers, with notable exceptions such as Kriek, Lambic, Faro, West Flanders ales and Flanders Old Brown, which use acid-producing bacteria ( Lactobacillus and Pediococcus ) or unconventional yeast ( Brettanomyces ) 54 , 55 . Glycerol, ethanol and esters show similar distributions across all beer styles, reflecting their common origin as products of yeast metabolism during fermentation 45 , 53 . Finally, low/no-alcohol beers contain low concentrations of glycerol and esters. This is in line with the production process for most of the low/no-alcohol beers in our dataset, which are produced through limiting fermentation or by stripping away alcohol via evaporation or dialysis, with both methods having the unintended side-effect of reducing the amount of flavor compounds in the final beer 56 , 57 .
Besides expected associations, our data also reveals less trivial associations between beer styles and specific parameters. For example, geraniol and citronellol, two monoterpenoids responsible for citrus, floral and rose flavors and characteristic of Citra hops, are found in relatively high amounts in Christmas, Saison, and Brett/co-fermented beers, where they may originate from terpenoid-rich spices such as coriander seeds instead of hops 58 .
Tasting panel assessments reveal sensorial relationships in beer
To assess the sensory profile of each beer, a trained tasting panel evaluated each of the 250 beers for 50 sensory attributes, including different hop, malt and yeast flavors, off-flavors and spices. Panelists used a tasting sheet (Supplementary Data 3 ) to score the different attributes. Panel consistency was evaluated by repeating 12 samples across different sessions and performing ANOVA. In 95% of cases no significant difference was found across sessions ( p > 0.05), indicating good panel consistency (Supplementary Table S2 ).
Aroma and taste perception reported by the trained panel are often linked (Fig. 1 , bottom left panel and Supplementary Data 4 and 5 ), with high correlations between hops aroma and taste (Spearman’s rho=0.83). Bitter taste was found to correlate with hop aroma and taste in general (Spearman’s rho=0.80 and 0.69), and particularly with “grassy” noble hops (Spearman’s rho=0.75). Barnyard flavor, most often associated with sour beers, is identified together with stale hops (Spearman’s rho=0.97) that are used in these beers. Lactic and acetic acid, which often co-occur, are correlated (Spearman’s rho=0.66). Interestingly, sweetness and bitterness are anti-correlated (Spearman’s rho = −0.48), confirming the hypothesis that they mask each other 59 , 60 . Beer body is highly correlated with alcohol (Spearman’s rho = 0.79), and overall appreciation is found to correlate with multiple aspects that describe beer mouthfeel (alcohol, carbonation; Spearman’s rho= 0.32, 0.39), as well as with hop and ester aroma intensity (Spearman’s rho=0.39 and 0.35).
Similar to the chemical analyses, sensorial analyses confirmed typical features of specific beer styles (Supplementary Fig. S4 ). For example, sour beers (Faro, Flanders Old Brown, Fruit beer, Kriek, Lambic, West Flanders ale) were rated acidic, with flavors of both acetic and lactic acid. Hoppy beers were found to be bitter and showed hop-associated aromas like citrus and tropical fruit. Malt taste is most detected among scotch, stout/porters, and strong ales, while low/no-alcohol beers, which often have a reputation for being ‘worty’ (reminiscent of unfermented, sweet malt extract) appear in the middle. Unsurprisingly, hop aromas are most strongly detected among hoppy beers. Like its chemical counterpart (Supplementary Fig. S3 ), acidity shows a right-skewed distribution, with the most acidic beers being Krieks, Lambics, and West Flanders ales.
Tasting panel assessments of specific flavors correlate with chemical composition
We find that the concentrations of several chemical compounds strongly correlate with specific aroma or taste, as evaluated by the tasting panel (Fig. 2 , Supplementary Fig. S5 , Supplementary Data 6 ). In some cases, these correlations confirm expectations and serve as a useful control for data quality. For example, iso-alpha acids, the bittering compounds in hops, strongly correlate with bitterness (Spearman’s rho=0.68), while ethanol and glycerol correlate with tasters’ perceptions of alcohol and body, the mouthfeel sensation of fullness (Spearman’s rho=0.82/0.62 and 0.72/0.57 respectively) and darker color from roasted malts is a good indication of malt perception (Spearman’s rho=0.54).

Heatmap colors indicate Spearman’s Rho. Axes are organized according to sensory categories (aroma, taste, mouthfeel, overall), chemical categories and chemical sources in beer (malt (blue), hops (green), yeast (red), wild flora (yellow), Others (black)). See Supplementary Data 6 for all correlation values.
Interestingly, for some relationships between chemical compounds and perceived flavor, correlations are weaker than expected. For example, the rose-smelling phenethyl acetate only weakly correlates with floral aroma. This hints at more complex relationships and interactions between compounds and suggests a need for a more complex model than simple correlations. Lastly, we uncovered unexpected correlations. For instance, the esters ethyl decanoate and ethyl octanoate appear to correlate slightly with hop perception and bitterness, possibly due to their fruity flavor. Iron is anti-correlated with hop aromas and bitterness, most likely because it is also anti-correlated with iso-alpha acids. This could be a sign of metal chelation of hop acids 61 , given that our analyses measure unbound hop acids and total iron content, or could result from the higher iron content in dark and Fruit beers, which typically have less hoppy and bitter flavors 62 .
Public consumer reviews complement expert panel data
To complement and expand the sensory data of our trained tasting panel, we collected 180,000 reviews of our 250 beers from the online consumer review platform RateBeer. This provided numerical scores for beer appearance, aroma, taste, palate, overall quality as well as the average overall score.
Public datasets are known to suffer from biases, such as price, cult status and psychological conformity towards previous ratings of a product. For example, prices correlate with appreciation scores for these online consumer reviews (rho=0.49, Supplementary Fig. S6 ), but not for our trained tasting panel (rho=0.19). This suggests that prices affect consumer appreciation, which has been reported in wine 63 , while blind tastings are unaffected. Moreover, we observe that some beer styles, like lagers and non-alcoholic beers, generally receive lower scores, reflecting that online reviewers are mostly beer aficionados with a preference for specialty beers over lager beers. In general, we find a modest correlation between our trained panel’s overall appreciation score and the online consumer appreciation scores (Fig. 3 , rho=0.29). Apart from the aforementioned biases in the online datasets, serving temperature, sample freshness and surroundings, which are all tightly controlled during the tasting panel sessions, can vary tremendously across online consumers and can further contribute to (among others, appreciation) differences between the two categories of tasters. Importantly, in contrast to the overall appreciation scores, for many sensory aspects the results from the professional panel correlated well with results obtained from RateBeer reviews. Correlations were highest for features that are relatively easy to recognize even for untrained tasters, like bitterness, sweetness, alcohol and malt aroma (Fig. 3 and below).
RateBeer text mining results can be found in Supplementary Data 7 . Rho values shown are Spearman correlation values, with asterisks indicating significant correlations ( p < 0.05, two-sided). All p values were smaller than 0.001, except for Esters aroma (0.0553), Esters taste (0.3275), Esters aroma—banana (0.0019), Coriander (0.0508) and Diacetyl (0.0134).
Besides collecting consumer appreciation from these online reviews, we developed automated text analysis tools to gather additional data from review texts (Supplementary Data 7 ). Processing review texts on the RateBeer database yielded comparable results to the scores given by the trained panel for many common sensory aspects, including acidity, bitterness, sweetness, alcohol, malt, and hop tastes (Fig. 3 ). This is in line with what would be expected, since these attributes require less training for accurate assessment and are less influenced by environmental factors such as temperature, serving glass and odors in the environment. Consumer reviews also correlate well with our trained panel for 4-vinyl guaiacol, a compound associated with a very characteristic aroma. By contrast, correlations for more specific aromas like ester, coriander or diacetyl are underrepresented in the online reviews, underscoring the importance of using a trained tasting panel and standardized tasting sheets with explicit factors to be scored for evaluating specific aspects of a beer. Taken together, our results suggest that public reviews are trustworthy for some, but not all, flavor features and can complement or substitute taste panel data for these sensory aspects.
Models can predict beer sensory profiles from chemical data
The rich datasets of chemical analyses, tasting panel assessments and public reviews gathered in the first part of this study provided us with a unique opportunity to develop predictive models that link chemical data to sensorial features. Given the complexity of beer flavor, basic statistical tools such as correlations or linear regression may not always be the most suitable for making accurate predictions. Instead, we applied different machine learning models that can model both simple linear and complex interactive relationships. Specifically, we constructed a set of regression models to predict (a) trained panel scores for beer flavor and quality and (b) public reviews’ appreciation scores from beer chemical profiles. We trained and tested 10 different models (Methods), 3 linear regression-based models (simple linear regression with first-order interactions (LR), lasso regression with first-order interactions (Lasso), partial least squares regressor (PLSR)), 5 decision tree models (AdaBoost regressor (ABR), extra trees (ET), gradient boosting regressor (GBR), random forest (RF) and XGBoost regressor (XGBR)), 1 support vector regression (SVR), and 1 artificial neural network (ANN) model.
To compare the performance of our machine learning models, the dataset was randomly split into a training and test set, stratified by beer style. After a model was trained on data in the training set, its performance was evaluated on its ability to predict the test dataset obtained from multi-output models (based on the coefficient of determination, see Methods). Additionally, individual-attribute models were ranked per descriptor and the average rank was calculated, as proposed by Korneva et al. 64 . Importantly, both ways of evaluating the models’ performance agreed in general. Performance of the different models varied (Table 1 ). It should be noted that all models perform better at predicting RateBeer results than results from our trained tasting panel. One reason could be that sensory data is inherently variable, and this variability is averaged out with the large number of public reviews from RateBeer. Additionally, all tree-based models perform better at predicting taste than aroma. Linear models (LR) performed particularly poorly, with negative R 2 values, due to severe overfitting (training set R 2 = 1). Overfitting is a common issue in linear models with many parameters and limited samples, especially with interaction terms further amplifying the number of parameters. L1 regularization (Lasso) successfully overcomes this overfitting, out-competing multiple tree-based models on the RateBeer dataset. Similarly, the dimensionality reduction of PLSR avoids overfitting and improves performance, to some extent. Still, tree-based models (ABR, ET, GBR, RF and XGBR) show the best performance, out-competing the linear models (LR, Lasso, PLSR) commonly used in sensory science 65 .
GBR models showed the best overall performance in predicting sensory responses from chemical information, with R 2 values up to 0.75 depending on the predicted sensory feature (Supplementary Table S4 ). The GBR models predict consumer appreciation (RateBeer) better than our trained panel’s appreciation (R 2 value of 0.67 compared to R 2 value of 0.09) (Supplementary Table S3 and Supplementary Table S4 ). ANN models showed intermediate performance, likely because neural networks typically perform best with larger datasets 66 . The SVR shows intermediate performance, mostly due to the weak predictions of specific attributes that lower the overall performance (Supplementary Table S4 ).
Model dissection identifies specific, unexpected compounds as drivers of consumer appreciation
Next, we leveraged our models to infer important contributors to sensory perception and consumer appreciation. Consumer preference is a crucial sensory aspects, because a product that shows low consumer appreciation scores often does not succeed commercially 25 . Additionally, the requirement for a large number of representative evaluators makes consumer trials one of the more costly and time-consuming aspects of product development. Hence, a model for predicting chemical drivers of overall appreciation would be a welcome addition to the available toolbox for food development and optimization.
Since GBR models on our RateBeer dataset showed the best overall performance, we focused on these models. Specifically, we used two approaches to identify important contributors. First, rankings of the most important predictors for each sensorial trait in the GBR models were obtained based on impurity-based feature importance (mean decrease in impurity). High-ranked parameters were hypothesized to be either the true causal chemical properties underlying the trait, to correlate with the actual causal properties, or to take part in sensory interactions affecting the trait 67 (Fig. 4A ). In a second approach, we used SHAP 68 to determine which parameters contributed most to the model for making predictions of consumer appreciation (Fig. 4B ). SHAP calculates parameter contributions to model predictions on a per-sample basis, which can be aggregated into an importance score.
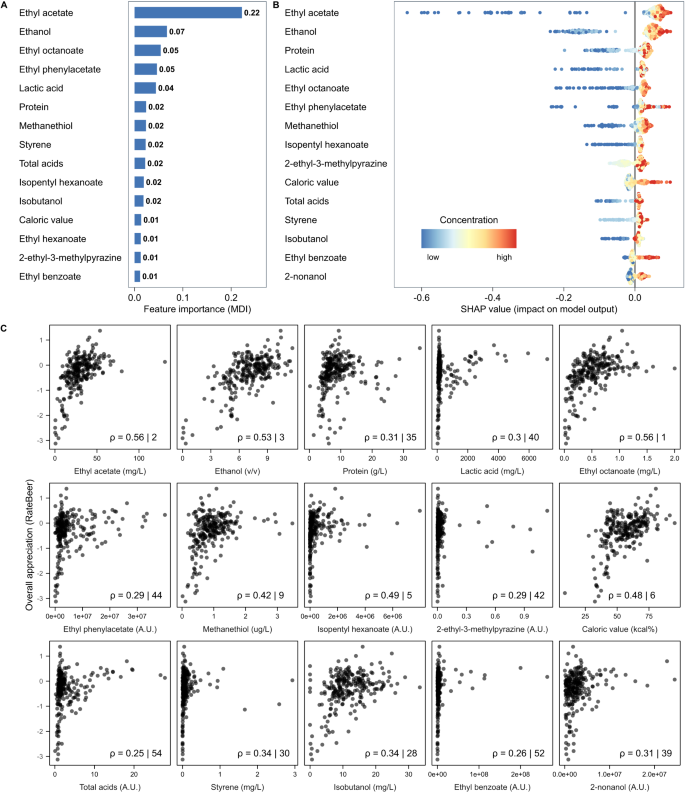
A The impurity-based feature importance (mean deviance in impurity, MDI) calculated from the Gradient Boosting Regression (GBR) model predicting RateBeer appreciation scores. The top 15 highest ranked chemical properties are shown. B SHAP summary plot for the top 15 parameters contributing to our GBR model. Each point on the graph represents a sample from our dataset. The color represents the concentration of that parameter, with bluer colors representing low values and redder colors representing higher values. Greater absolute values on the horizontal axis indicate a higher impact of the parameter on the prediction of the model. C Spearman correlations between the 15 most important chemical properties and consumer overall appreciation. Numbers indicate the Spearman Rho correlation coefficient, and the rank of this correlation compared to all other correlations. The top 15 important compounds were determined using SHAP (panel B).
Both approaches identified ethyl acetate as the most predictive parameter for beer appreciation (Fig. 4 ). Ethyl acetate is the most abundant ester in beer with a typical ‘fruity’, ‘solvent’ and ‘alcoholic’ flavor, but is often considered less important than other esters like isoamyl acetate. The second most important parameter identified by SHAP is ethanol, the most abundant beer compound after water. Apart from directly contributing to beer flavor and mouthfeel, ethanol drastically influences the physical properties of beer, dictating how easily volatile compounds escape the beer matrix to contribute to beer aroma 69 . Importantly, it should also be noted that the importance of ethanol for appreciation is likely inflated by the very low appreciation scores of non-alcoholic beers (Supplementary Fig. S4 ). Despite not often being considered a driver of beer appreciation, protein level also ranks highly in both approaches, possibly due to its effect on mouthfeel and body 70 . Lactic acid, which contributes to the tart taste of sour beers, is the fourth most important parameter identified by SHAP, possibly due to the generally high appreciation of sour beers in our dataset.
Interestingly, some of the most important predictive parameters for our model are not well-established as beer flavors or are even commonly regarded as being negative for beer quality. For example, our models identify methanethiol and ethyl phenyl acetate, an ester commonly linked to beer staling 71 , as a key factor contributing to beer appreciation. Although there is no doubt that high concentrations of these compounds are considered unpleasant, the positive effects of modest concentrations are not yet known 72 , 73 .
To compare our approach to conventional statistics, we evaluated how well the 15 most important SHAP-derived parameters correlate with consumer appreciation (Fig. 4C ). Interestingly, only 6 of the properties derived by SHAP rank amongst the top 15 most correlated parameters. For some chemical compounds, the correlations are so low that they would have likely been considered unimportant. For example, lactic acid, the fourth most important parameter, shows a bimodal distribution for appreciation, with sour beers forming a separate cluster, that is missed entirely by the Spearman correlation. Additionally, the correlation plots reveal outliers, emphasizing the need for robust analysis tools. Together, this highlights the need for alternative models, like the Gradient Boosting model, that better grasp the complexity of (beer) flavor.
Finally, to observe the relationships between these chemical properties and their predicted targets, partial dependence plots were constructed for the six most important predictors of consumer appreciation 74 , 75 , 76 (Supplementary Fig. S7 ). One-way partial dependence plots show how a change in concentration affects the predicted appreciation. These plots reveal an important limitation of our models: appreciation predictions remain constant at ever-increasing concentrations. This implies that once a threshold concentration is reached, further increasing the concentration does not affect appreciation. This is false, as it is well-documented that certain compounds become unpleasant at high concentrations, including ethyl acetate (‘nail polish’) 77 and methanethiol (‘sulfury’ and ‘rotten cabbage’) 78 . The inability of our models to grasp that flavor compounds have optimal levels, above which they become negative, is a consequence of working with commercial beer brands where (off-)flavors are rarely too high to negatively impact the product. The two-way partial dependence plots show how changing the concentration of two compounds influences predicted appreciation, visualizing their interactions (Supplementary Fig. S7 ). In our case, the top 5 parameters are dominated by additive or synergistic interactions, with high concentrations for both compounds resulting in the highest predicted appreciation.
To assess the robustness of our best-performing models and model predictions, we performed 100 iterations of the GBR, RF and ET models. In general, all iterations of the models yielded similar performance (Supplementary Fig. S8 ). Moreover, the main predictors (including the top predictors ethanol and ethyl acetate) remained virtually the same, especially for GBR and RF. For the iterations of the ET model, we did observe more variation in the top predictors, which is likely a consequence of the model’s inherent random architecture in combination with co-correlations between certain predictors. However, even in this case, several of the top predictors (ethanol and ethyl acetate) remain unchanged, although their rank in importance changes (Supplementary Fig. S8 ).
Next, we investigated if a combination of RateBeer and trained panel data into one consolidated dataset would lead to stronger models, under the hypothesis that such a model would suffer less from bias in the datasets. A GBR model was trained to predict appreciation on the combined dataset. This model underperformed compared to the RateBeer model, both in the native case and when including a dataset identifier (R 2 = 0.67, 0.26 and 0.42 respectively). For the latter, the dataset identifier is the most important feature (Supplementary Fig. S9 ), while most of the feature importance remains unchanged, with ethyl acetate and ethanol ranking highest, like in the original model trained only on RateBeer data. It seems that the large variation in the panel dataset introduces noise, weakening the models’ performances and reliability. In addition, it seems reasonable to assume that both datasets are fundamentally different, with the panel dataset obtained by blind tastings by a trained professional panel.
Lastly, we evaluated whether beer style identifiers would further enhance the model’s performance. A GBR model was trained with parameters that explicitly encoded the styles of the samples. This did not improve model performance (R2 = 0.66 with style information vs R2 = 0.67). The most important chemical features are consistent with the model trained without style information (eg. ethanol and ethyl acetate), and with the exception of the most preferred (strong ale) and least preferred (low/no-alcohol) styles, none of the styles were among the most important features (Supplementary Fig. S9 , Supplementary Table S5 and S6 ). This is likely due to a combination of style-specific chemical signatures, such as iso-alpha acids and lactic acid, that implicitly convey style information to the original models, as well as the low number of samples belonging to some styles, making it difficult for the model to learn style-specific patterns. Moreover, beer styles are not rigorously defined, with some styles overlapping in features and some beers being misattributed to a specific style, all of which leads to more noise in models that use style parameters.
Model validation
To test if our predictive models give insight into beer appreciation, we set up experiments aimed at improving existing commercial beers. We specifically selected overall appreciation as the trait to be examined because of its complexity and commercial relevance. Beer flavor comprises a complex bouquet rather than single aromas and tastes 53 . Hence, adding a single compound to the extent that a difference is noticeable may lead to an unbalanced, artificial flavor. Therefore, we evaluated the effect of combinations of compounds. Because Blond beers represent the most extensive style in our dataset, we selected a beer from this style as the starting material for these experiments (Beer 64 in Supplementary Data 1 ).
In the first set of experiments, we adjusted the concentrations of compounds that made up the most important predictors of overall appreciation (ethyl acetate, ethanol, lactic acid, ethyl phenyl acetate) together with correlated compounds (ethyl hexanoate, isoamyl acetate, glycerol), bringing them up to 95 th percentile ethanol-normalized concentrations (Methods) within the Blond group (‘Spiked’ concentration in Fig. 5A ). Compared to controls, the spiked beers were found to have significantly improved overall appreciation among trained panelists, with panelist noting increased intensity of ester flavors, sweetness, alcohol, and body fullness (Fig. 5B ). To disentangle the contribution of ethanol to these results, a second experiment was performed without the addition of ethanol. This resulted in a similar outcome, including increased perception of alcohol and overall appreciation.
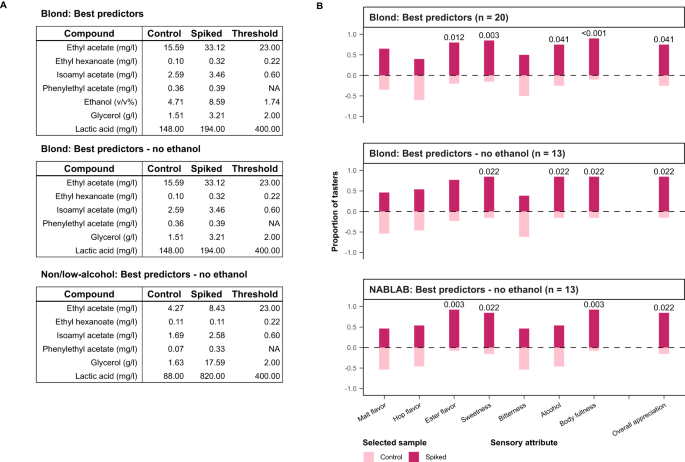
Adding the top chemical compounds, identified as best predictors of appreciation by our model, into poorly appreciated beers results in increased appreciation from our trained panel. Results of sensory tests between base beers and those spiked with compounds identified as the best predictors by the model. A Blond and Non/Low-alcohol (0.0% ABV) base beers were brought up to 95th-percentile ethanol-normalized concentrations within each style. B For each sensory attribute, tasters indicated the more intense sample and selected the sample they preferred. The numbers above the bars correspond to the p values that indicate significant changes in perceived flavor (two-sided binomial test: alpha 0.05, n = 20 or 13).
In a last experiment, we tested whether using the model’s predictions can boost the appreciation of a non-alcoholic beer (beer 223 in Supplementary Data 1 ). Again, the addition of a mixture of predicted compounds (omitting ethanol, in this case) resulted in a significant increase in appreciation, body, ester flavor and sweetness.
Predicting flavor and consumer appreciation from chemical composition is one of the ultimate goals of sensory science. A reliable, systematic and unbiased way to link chemical profiles to flavor and food appreciation would be a significant asset to the food and beverage industry. Such tools would substantially aid in quality control and recipe development, offer an efficient and cost-effective alternative to pilot studies and consumer trials and would ultimately allow food manufacturers to produce superior, tailor-made products that better meet the demands of specific consumer groups more efficiently.
A limited set of studies have previously tried, to varying degrees of success, to predict beer flavor and beer popularity based on (a limited set of) chemical compounds and flavors 79 , 80 . Current sensitive, high-throughput technologies allow measuring an unprecedented number of chemical compounds and properties in a large set of samples, yielding a dataset that can train models that help close the gaps between chemistry and flavor, even for a complex natural product like beer. To our knowledge, no previous research gathered data at this scale (250 samples, 226 chemical parameters, 50 sensory attributes and 5 consumer scores) to disentangle and validate the chemical aspects driving beer preference using various machine-learning techniques. We find that modern machine learning models outperform conventional statistical tools, such as correlations and linear models, and can successfully predict flavor appreciation from chemical composition. This could be attributed to the natural incorporation of interactions and non-linear or discontinuous effects in machine learning models, which are not easily grasped by the linear model architecture. While linear models and partial least squares regression represent the most widespread statistical approaches in sensory science, in part because they allow interpretation 65 , 81 , 82 , modern machine learning methods allow for building better predictive models while preserving the possibility to dissect and exploit the underlying patterns. Of the 10 different models we trained, tree-based models, such as our best performing GBR, showed the best overall performance in predicting sensory responses from chemical information, outcompeting artificial neural networks. This agrees with previous reports for models trained on tabular data 83 . Our results are in line with the findings of Colantonio et al. who also identified the gradient boosting architecture as performing best at predicting appreciation and flavor (of tomatoes and blueberries, in their specific study) 26 . Importantly, besides our larger experimental scale, we were able to directly confirm our models’ predictions in vivo.
Our study confirms that flavor compound concentration does not always correlate with perception, suggesting complex interactions that are often missed by more conventional statistics and simple models. Specifically, we find that tree-based algorithms may perform best in developing models that link complex food chemistry with aroma. Furthermore, we show that massive datasets of untrained consumer reviews provide a valuable source of data, that can complement or even replace trained tasting panels, especially for appreciation and basic flavors, such as sweetness and bitterness. This holds despite biases that are known to occur in such datasets, such as price or conformity bias. Moreover, GBR models predict taste better than aroma. This is likely because taste (e.g. bitterness) often directly relates to the corresponding chemical measurements (e.g., iso-alpha acids), whereas such a link is less clear for aromas, which often result from the interplay between multiple volatile compounds. We also find that our models are best at predicting acidity and alcohol, likely because there is a direct relation between the measured chemical compounds (acids and ethanol) and the corresponding perceived sensorial attribute (acidity and alcohol), and because even untrained consumers are generally able to recognize these flavors and aromas.
The predictions of our final models, trained on review data, hold even for blind tastings with small groups of trained tasters, as demonstrated by our ability to validate specific compounds as drivers of beer flavor and appreciation. Since adding a single compound to the extent of a noticeable difference may result in an unbalanced flavor profile, we specifically tested our identified key drivers as a combination of compounds. While this approach does not allow us to validate if a particular single compound would affect flavor and/or appreciation, our experiments do show that this combination of compounds increases consumer appreciation.
It is important to stress that, while it represents an important step forward, our approach still has several major limitations. A key weakness of the GBR model architecture is that amongst co-correlating variables, the largest main effect is consistently preferred for model building. As a result, co-correlating variables often have artificially low importance scores, both for impurity and SHAP-based methods, like we observed in the comparison to the more randomized Extra Trees models. This implies that chemicals identified as key drivers of a specific sensory feature by GBR might not be the true causative compounds, but rather co-correlate with the actual causative chemical. For example, the high importance of ethyl acetate could be (partially) attributed to the total ester content, ethanol or ethyl hexanoate (rho=0.77, rho=0.72 and rho=0.68), while ethyl phenylacetate could hide the importance of prenyl isobutyrate and ethyl benzoate (rho=0.77 and rho=0.76). Expanding our GBR model to include beer style as a parameter did not yield additional power or insight. This is likely due to style-specific chemical signatures, such as iso-alpha acids and lactic acid, that implicitly convey style information to the original model, as well as the smaller sample size per style, limiting the power to uncover style-specific patterns. This can be partly attributed to the curse of dimensionality, where the high number of parameters results in the models mainly incorporating single parameter effects, rather than complex interactions such as style-dependent effects 67 . A larger number of samples may overcome some of these limitations and offer more insight into style-specific effects. On the other hand, beer style is not a rigid scientific classification, and beers within one style often differ a lot, which further complicates the analysis of style as a model factor.
Our study is limited to beers from Belgian breweries. Although these beers cover a large portion of the beer styles available globally, some beer styles and consumer patterns may be missing, while other features might be overrepresented. For example, many Belgian ales exhibit yeast-driven flavor profiles, which is reflected in the chemical drivers of appreciation discovered by this study. In future work, expanding the scope to include diverse markets and beer styles could lead to the identification of even more drivers of appreciation and better models for special niche products that were not present in our beer set.
In addition to inherent limitations of GBR models, there are also some limitations associated with studying food aroma. Even if our chemical analyses measured most of the known aroma compounds, the total number of flavor compounds in complex foods like beer is still larger than the subset we were able to measure in this study. For example, hop-derived thiols, that influence flavor at very low concentrations, are notoriously difficult to measure in a high-throughput experiment. Moreover, consumer perception remains subjective and prone to biases that are difficult to avoid. It is also important to stress that the models are still immature and that more extensive datasets will be crucial for developing more complete models in the future. Besides more samples and parameters, our dataset does not include any demographic information about the tasters. Including such data could lead to better models that grasp external factors like age and culture. Another limitation is that our set of beers consists of high-quality end-products and lacks beers that are unfit for sale, which limits the current model in accurately predicting products that are appreciated very badly. Finally, while models could be readily applied in quality control, their use in sensory science and product development is restrained by their inability to discern causal relationships. Given that the models cannot distinguish compounds that genuinely drive consumer perception from those that merely correlate, validation experiments are essential to identify true causative compounds.
Despite the inherent limitations, dissection of our models enabled us to pinpoint specific molecules as potential drivers of beer aroma and consumer appreciation, including compounds that were unexpected and would not have been identified using standard approaches. Important drivers of beer appreciation uncovered by our models include protein levels, ethyl acetate, ethyl phenyl acetate and lactic acid. Currently, many brewers already use lactic acid to acidify their brewing water and ensure optimal pH for enzymatic activity during the mashing process. Our results suggest that adding lactic acid can also improve beer appreciation, although its individual effect remains to be tested. Interestingly, ethanol appears to be unnecessary to improve beer appreciation, both for blond beer and alcohol-free beer. Given the growing consumer interest in alcohol-free beer, with a predicted annual market growth of >7% 84 , it is relevant for brewers to know what compounds can further increase consumer appreciation of these beers. Hence, our model may readily provide avenues to further improve the flavor and consumer appreciation of both alcoholic and non-alcoholic beers, which is generally considered one of the key challenges for future beer production.
Whereas we see a direct implementation of our results for the development of superior alcohol-free beverages and other food products, our study can also serve as a stepping stone for the development of novel alcohol-containing beverages. We want to echo the growing body of scientific evidence for the negative effects of alcohol consumption, both on the individual level by the mutagenic, teratogenic and carcinogenic effects of ethanol 85 , 86 , as well as the burden on society caused by alcohol abuse and addiction. We encourage the use of our results for the production of healthier, tastier products, including novel and improved beverages with lower alcohol contents. Furthermore, we strongly discourage the use of these technologies to improve the appreciation or addictive properties of harmful substances.
The present work demonstrates that despite some important remaining hurdles, combining the latest developments in chemical analyses, sensory analysis and modern machine learning methods offers exciting avenues for food chemistry and engineering. Soon, these tools may provide solutions in quality control and recipe development, as well as new approaches to sensory science and flavor research.
Beer selection
250 commercial Belgian beers were selected to cover the broad diversity of beer styles and corresponding diversity in chemical composition and aroma. See Supplementary Fig. S1 .
Chemical dataset
Sample preparation.
Beers within their expiration date were purchased from commercial retailers. Samples were prepared in biological duplicates at room temperature, unless explicitly stated otherwise. Bottle pressure was measured with a manual pressure device (Steinfurth Mess-Systeme GmbH) and used to calculate CO 2 concentration. The beer was poured through two filter papers (Macherey-Nagel, 500713032 MN 713 ¼) to remove carbon dioxide and prevent spontaneous foaming. Samples were then prepared for measurements by targeted Headspace-Gas Chromatography-Flame Ionization Detector/Flame Photometric Detector (HS-GC-FID/FPD), Headspace-Solid Phase Microextraction-Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (HS-SPME-GC-MS), colorimetric analysis, enzymatic analysis, Near-Infrared (NIR) analysis, as described in the sections below. The mean values of biological duplicates are reported for each compound.
HS-GC-FID/FPD
HS-GC-FID/FPD (Shimadzu GC 2010 Plus) was used to measure higher alcohols, acetaldehyde, esters, 4-vinyl guaicol, and sulfur compounds. Each measurement comprised 5 ml of sample pipetted into a 20 ml glass vial containing 1.75 g NaCl (VWR, 27810.295). 100 µl of 2-heptanol (Sigma-Aldrich, H3003) (internal standard) solution in ethanol (Fisher Chemical, E/0650DF/C17) was added for a final concentration of 2.44 mg/L. Samples were flushed with nitrogen for 10 s, sealed with a silicone septum, stored at −80 °C and analyzed in batches of 20.
The GC was equipped with a DB-WAXetr column (length, 30 m; internal diameter, 0.32 mm; layer thickness, 0.50 µm; Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA) to the FID and an HP-5 column (length, 30 m; internal diameter, 0.25 mm; layer thickness, 0.25 µm; Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA) to the FPD. N 2 was used as the carrier gas. Samples were incubated for 20 min at 70 °C in the headspace autosampler (Flow rate, 35 cm/s; Injection volume, 1000 µL; Injection mode, split; Combi PAL autosampler, CTC analytics, Switzerland). The injector, FID and FPD temperatures were kept at 250 °C. The GC oven temperature was first held at 50 °C for 5 min and then allowed to rise to 80 °C at a rate of 5 °C/min, followed by a second ramp of 4 °C/min until 200 °C kept for 3 min and a final ramp of (4 °C/min) until 230 °C for 1 min. Results were analyzed with the GCSolution software version 2.4 (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan). The GC was calibrated with a 5% EtOH solution (VWR International) containing the volatiles under study (Supplementary Table S7 ).
HS-SPME-GC-MS
HS-SPME-GC-MS (Shimadzu GCMS-QP-2010 Ultra) was used to measure additional volatile compounds, mainly comprising terpenoids and esters. Samples were analyzed by HS-SPME using a triphase DVB/Carboxen/PDMS 50/30 μm SPME fiber (Supelco Co., Bellefonte, PA, USA) followed by gas chromatography (Thermo Fisher Scientific Trace 1300 series, USA) coupled to a mass spectrometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific ISQ series MS) equipped with a TriPlus RSH autosampler. 5 ml of degassed beer sample was placed in 20 ml vials containing 1.75 g NaCl (VWR, 27810.295). 5 µl internal standard mix was added, containing 2-heptanol (1 g/L) (Sigma-Aldrich, H3003), 4-fluorobenzaldehyde (1 g/L) (Sigma-Aldrich, 128376), 2,3-hexanedione (1 g/L) (Sigma-Aldrich, 144169) and guaiacol (1 g/L) (Sigma-Aldrich, W253200) in ethanol (Fisher Chemical, E/0650DF/C17). Each sample was incubated at 60 °C in the autosampler oven with constant agitation. After 5 min equilibration, the SPME fiber was exposed to the sample headspace for 30 min. The compounds trapped on the fiber were thermally desorbed in the injection port of the chromatograph by heating the fiber for 15 min at 270 °C.
The GC-MS was equipped with a low polarity RXi-5Sil MS column (length, 20 m; internal diameter, 0.18 mm; layer thickness, 0.18 µm; Restek, Bellefonte, PA, USA). Injection was performed in splitless mode at 320 °C, a split flow of 9 ml/min, a purge flow of 5 ml/min and an open valve time of 3 min. To obtain a pulsed injection, a programmed gas flow was used whereby the helium gas flow was set at 2.7 mL/min for 0.1 min, followed by a decrease in flow of 20 ml/min to the normal 0.9 mL/min. The temperature was first held at 30 °C for 3 min and then allowed to rise to 80 °C at a rate of 7 °C/min, followed by a second ramp of 2 °C/min till 125 °C and a final ramp of 8 °C/min with a final temperature of 270 °C.
Mass acquisition range was 33 to 550 amu at a scan rate of 5 scans/s. Electron impact ionization energy was 70 eV. The interface and ion source were kept at 275 °C and 250 °C, respectively. A mix of linear n-alkanes (from C7 to C40, Supelco Co.) was injected into the GC-MS under identical conditions to serve as external retention index markers. Identification and quantification of the compounds were performed using an in-house developed R script as described in Goelen et al. and Reher et al. 87 , 88 (for package information, see Supplementary Table S8 ). Briefly, chromatograms were analyzed using AMDIS (v2.71) 89 to separate overlapping peaks and obtain pure compound spectra. The NIST MS Search software (v2.0 g) in combination with the NIST2017, FFNSC3 and Adams4 libraries were used to manually identify the empirical spectra, taking into account the expected retention time. After background subtraction and correcting for retention time shifts between samples run on different days based on alkane ladders, compound elution profiles were extracted and integrated using a file with 284 target compounds of interest, which were either recovered in our identified AMDIS list of spectra or were known to occur in beer. Compound elution profiles were estimated for every peak in every chromatogram over a time-restricted window using weighted non-negative least square analysis after which peak areas were integrated 87 , 88 . Batch effect correction was performed by normalizing against the most stable internal standard compound, 4-fluorobenzaldehyde. Out of all 284 target compounds that were analyzed, 167 were visually judged to have reliable elution profiles and were used for final analysis.
Discrete photometric and enzymatic analysis
Discrete photometric and enzymatic analysis (Thermo Scientific TM Gallery TM Plus Beermaster Discrete Analyzer) was used to measure acetic acid, ammonia, beta-glucan, iso-alpha acids, color, sugars, glycerol, iron, pH, protein, and sulfite. 2 ml of sample volume was used for the analyses. Information regarding the reagents and standard solutions used for analyses and calibrations is included in Supplementary Table S7 and Supplementary Table S9 .
NIR analyses
NIR analysis (Anton Paar Alcolyzer Beer ME System) was used to measure ethanol. Measurements comprised 50 ml of sample, and a 10% EtOH solution was used for calibration.
Correlation calculations
Pairwise Spearman Rank correlations were calculated between all chemical properties.
Sensory dataset
Trained panel.
Our trained tasting panel consisted of volunteers who gave prior verbal informed consent. All compounds used for the validation experiment were of food-grade quality. The tasting sessions were approved by the Social and Societal Ethics Committee of the KU Leuven (G-2022-5677-R2(MAR)). All online reviewers agreed to the Terms and Conditions of the RateBeer website.
Sensory analysis was performed according to the American Society of Brewing Chemists (ASBC) Sensory Analysis Methods 90 . 30 volunteers were screened through a series of triangle tests. The sixteen most sensitive and consistent tasters were retained as taste panel members. The resulting panel was diverse in age [22–42, mean: 29], sex [56% male] and nationality [7 different countries]. The panel developed a consensus vocabulary to describe beer aroma, taste and mouthfeel. Panelists were trained to identify and score 50 different attributes, using a 7-point scale to rate attributes’ intensity. The scoring sheet is included as Supplementary Data 3 . Sensory assessments took place between 10–12 a.m. The beers were served in black-colored glasses. Per session, between 5 and 12 beers of the same style were tasted at 12 °C to 16 °C. Two reference beers were added to each set and indicated as ‘Reference 1 & 2’, allowing panel members to calibrate their ratings. Not all panelists were present at every tasting. Scores were scaled by standard deviation and mean-centered per taster. Values are represented as z-scores and clustered by Euclidean distance. Pairwise Spearman correlations were calculated between taste and aroma sensory attributes. Panel consistency was evaluated by repeating samples on different sessions and performing ANOVA to identify differences, using the ‘stats’ package (v4.2.2) in R (for package information, see Supplementary Table S8 ).
Online reviews from a public database
The ‘scrapy’ package in Python (v3.6) (for package information, see Supplementary Table S8 ). was used to collect 232,288 online reviews (mean=922, min=6, max=5343) from RateBeer, an online beer review database. Each review entry comprised 5 numerical scores (appearance, aroma, taste, palate and overall quality) and an optional review text. The total number of reviews per reviewer was collected separately. Numerical scores were scaled and centered per rater, and mean scores were calculated per beer.
For the review texts, the language was estimated using the packages ‘langdetect’ and ‘langid’ in Python. Reviews that were classified as English by both packages were kept. Reviewers with fewer than 100 entries overall were discarded. 181,025 reviews from >6000 reviewers from >40 countries remained. Text processing was done using the ‘nltk’ package in Python. Texts were corrected for slang and misspellings; proper nouns and rare words that are relevant to the beer context were specified and kept as-is (‘Chimay’,’Lambic’, etc.). A dictionary of semantically similar sensorial terms, for example ‘floral’ and ‘flower’, was created and collapsed together into one term. Words were stemmed and lemmatized to avoid identifying words such as ‘acid’ and ‘acidity’ as separate terms. Numbers and punctuation were removed.
Sentences from up to 50 randomly chosen reviews per beer were manually categorized according to the aspect of beer they describe (appearance, aroma, taste, palate, overall quality—not to be confused with the 5 numerical scores described above) or flagged as irrelevant if they contained no useful information. If a beer contained fewer than 50 reviews, all reviews were manually classified. This labeled data set was used to train a model that classified the rest of the sentences for all beers 91 . Sentences describing taste and aroma were extracted, and term frequency–inverse document frequency (TFIDF) was implemented to calculate enrichment scores for sensorial words per beer.
The sex of the tasting subject was not considered when building our sensory database. Instead, results from different panelists were averaged, both for our trained panel (56% male, 44% female) and the RateBeer reviews (70% male, 30% female for RateBeer as a whole).
Beer price collection and processing
Beer prices were collected from the following stores: Colruyt, Delhaize, Total Wine, BeerHawk, The Belgian Beer Shop, The Belgian Shop, and Beer of Belgium. Where applicable, prices were converted to Euros and normalized per liter. Spearman correlations were calculated between these prices and mean overall appreciation scores from RateBeer and the taste panel, respectively.
Pairwise Spearman Rank correlations were calculated between all sensory properties.
Machine learning models
Predictive modeling of sensory profiles from chemical data.
Regression models were constructed to predict (a) trained panel scores for beer flavors and quality from beer chemical profiles and (b) public reviews’ appreciation scores from beer chemical profiles. Z-scores were used to represent sensory attributes in both data sets. Chemical properties with log-normal distributions (Shapiro-Wilk test, p < 0.05 ) were log-transformed. Missing chemical measurements (0.1% of all data) were replaced with mean values per attribute. Observations from 250 beers were randomly separated into a training set (70%, 175 beers) and a test set (30%, 75 beers), stratified per beer style. Chemical measurements (p = 231) were normalized based on the training set average and standard deviation. In total, three linear regression-based models: linear regression with first-order interaction terms (LR), lasso regression with first-order interaction terms (Lasso) and partial least squares regression (PLSR); five decision tree models, Adaboost regressor (ABR), Extra Trees (ET), Gradient Boosting regressor (GBR), Random Forest (RF) and XGBoost regressor (XGBR); one support vector machine model (SVR) and one artificial neural network model (ANN) were trained. The models were implemented using the ‘scikit-learn’ package (v1.2.2) and ‘xgboost’ package (v1.7.3) in Python (v3.9.16). Models were trained, and hyperparameters optimized, using five-fold cross-validated grid search with the coefficient of determination (R 2 ) as the evaluation metric. The ANN (scikit-learn’s MLPRegressor) was optimized using Bayesian Tree-Structured Parzen Estimator optimization with the ‘Optuna’ Python package (v3.2.0). Individual models were trained per attribute, and a multi-output model was trained on all attributes simultaneously.
Model dissection
GBR was found to outperform other methods, resulting in models with the highest average R 2 values in both trained panel and public review data sets. Impurity-based rankings of the most important predictors for each predicted sensorial trait were obtained using the ‘scikit-learn’ package. To observe the relationships between these chemical properties and their predicted targets, partial dependence plots (PDP) were constructed for the six most important predictors of consumer appreciation 74 , 75 .
The ‘SHAP’ package in Python (v0.41.0) was implemented to provide an alternative ranking of predictor importance and to visualize the predictors’ effects as a function of their concentration 68 .
Validation of causal chemical properties
To validate the effects of the most important model features on predicted sensory attributes, beers were spiked with the chemical compounds identified by the models and descriptive sensory analyses were carried out according to the American Society of Brewing Chemists (ASBC) protocol 90 .
Compound spiking was done 30 min before tasting. Compounds were spiked into fresh beer bottles, that were immediately resealed and inverted three times. Fresh bottles of beer were opened for the same duration, resealed, and inverted thrice, to serve as controls. Pairs of spiked samples and controls were served simultaneously, chilled and in dark glasses as outlined in the Trained panel section above. Tasters were instructed to select the glass with the higher flavor intensity for each attribute (directional difference test 92 ) and to select the glass they prefer.
The final concentration after spiking was equal to the within-style average, after normalizing by ethanol concentration. This was done to ensure balanced flavor profiles in the final spiked beer. The same methods were applied to improve a non-alcoholic beer. Compounds were the following: ethyl acetate (Merck KGaA, W241415), ethyl hexanoate (Merck KGaA, W243906), isoamyl acetate (Merck KGaA, W205508), phenethyl acetate (Merck KGaA, W285706), ethanol (96%, Colruyt), glycerol (Merck KGaA, W252506), lactic acid (Merck KGaA, 261106).
Significant differences in preference or perceived intensity were determined by performing the two-sided binomial test on each attribute.
Reporting summary
Further information on research design is available in the Nature Portfolio Reporting Summary linked to this article.
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this work are available in the Supplementary Data files and have been deposited to Zenodo under accession code 10653704 93 . The RateBeer scores data are under restricted access, they are not publicly available as they are property of RateBeer (ZX Ventures, USA). Access can be obtained from the authors upon reasonable request and with permission of RateBeer (ZX Ventures, USA). Source data are provided with this paper.
Code availability
The code for training the machine learning models, analyzing the models, and generating the figures has been deposited to Zenodo under accession code 10653704 93 .
Tieman, D. et al. A chemical genetic roadmap to improved tomato flavor. Science 355 , 391–394 (2017).
Article ADS CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Plutowska, B. & Wardencki, W. Application of gas chromatography–olfactometry (GC–O) in analysis and quality assessment of alcoholic beverages – A review. Food Chem. 107 , 449–463 (2008).
Article CAS Google Scholar
Legin, A., Rudnitskaya, A., Seleznev, B. & Vlasov, Y. Electronic tongue for quality assessment of ethanol, vodka and eau-de-vie. Anal. Chim. Acta 534 , 129–135 (2005).
Loutfi, A., Coradeschi, S., Mani, G. K., Shankar, P. & Rayappan, J. B. B. Electronic noses for food quality: A review. J. Food Eng. 144 , 103–111 (2015).
Ahn, Y.-Y., Ahnert, S. E., Bagrow, J. P. & Barabási, A.-L. Flavor network and the principles of food pairing. Sci. Rep. 1 , 196 (2011).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Bartoshuk, L. M. & Klee, H. J. Better fruits and vegetables through sensory analysis. Curr. Biol. 23 , R374–R378 (2013).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Piggott, J. R. Design questions in sensory and consumer science. Food Qual. Prefer. 3293 , 217–220 (1995).
Article Google Scholar
Kermit, M. & Lengard, V. Assessing the performance of a sensory panel-panellist monitoring and tracking. J. Chemom. 19 , 154–161 (2005).
Cook, D. J., Hollowood, T. A., Linforth, R. S. T. & Taylor, A. J. Correlating instrumental measurements of texture and flavour release with human perception. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 40 , 631–641 (2005).
Chinchanachokchai, S., Thontirawong, P. & Chinchanachokchai, P. A tale of two recommender systems: The moderating role of consumer expertise on artificial intelligence based product recommendations. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 61 , 1–12 (2021).
Ross, C. F. Sensory science at the human-machine interface. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 20 , 63–72 (2009).
Chambers, E. IV & Koppel, K. Associations of volatile compounds with sensory aroma and flavor: The complex nature of flavor. Molecules 18 , 4887–4905 (2013).
Pinu, F. R. Metabolomics—The new frontier in food safety and quality research. Food Res. Int. 72 , 80–81 (2015).
Danezis, G. P., Tsagkaris, A. S., Brusic, V. & Georgiou, C. A. Food authentication: state of the art and prospects. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 10 , 22–31 (2016).
Shepherd, G. M. Smell images and the flavour system in the human brain. Nature 444 , 316–321 (2006).
Meilgaard, M. C. Prediction of flavor differences between beers from their chemical composition. J. Agric. Food Chem. 30 , 1009–1017 (1982).
Xu, L. et al. Widespread receptor-driven modulation in peripheral olfactory coding. Science 368 , eaaz5390 (2020).
Kupferschmidt, K. Following the flavor. Science 340 , 808–809 (2013).
Billesbølle, C. B. et al. Structural basis of odorant recognition by a human odorant receptor. Nature 615 , 742–749 (2023).
Article ADS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Smith, B. Perspective: Complexities of flavour. Nature 486 , S6–S6 (2012).
Pfister, P. et al. Odorant receptor inhibition is fundamental to odor encoding. Curr. Biol. 30 , 2574–2587 (2020).
Moskowitz, H. W., Kumaraiah, V., Sharma, K. N., Jacobs, H. L. & Sharma, S. D. Cross-cultural differences in simple taste preferences. Science 190 , 1217–1218 (1975).
Eriksson, N. et al. A genetic variant near olfactory receptor genes influences cilantro preference. Flavour 1 , 22 (2012).
Ferdenzi, C. et al. Variability of affective responses to odors: Culture, gender, and olfactory knowledge. Chem. Senses 38 , 175–186 (2013).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Lawless, H. T. & Heymann, H. Sensory evaluation of food: Principles and practices. (Springer, New York, NY). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-6488-5 (2010).
Colantonio, V. et al. Metabolomic selection for enhanced fruit flavor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 119 , e2115865119 (2022).
Fritz, F., Preissner, R. & Banerjee, P. VirtualTaste: a web server for the prediction of organoleptic properties of chemical compounds. Nucleic Acids Res 49 , W679–W684 (2021).
Tuwani, R., Wadhwa, S. & Bagler, G. BitterSweet: Building machine learning models for predicting the bitter and sweet taste of small molecules. Sci. Rep. 9 , 1–13 (2019).
Dagan-Wiener, A. et al. Bitter or not? BitterPredict, a tool for predicting taste from chemical structure. Sci. Rep. 7 , 1–13 (2017).
Pallante, L. et al. Toward a general and interpretable umami taste predictor using a multi-objective machine learning approach. Sci. Rep. 12 , 1–11 (2022).
Malavolta, M. et al. A survey on computational taste predictors. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 248 , 2215–2235 (2022).
Lee, B. K. et al. A principal odor map unifies diverse tasks in olfactory perception. Science 381 , 999–1006 (2023).
Mayhew, E. J. et al. Transport features predict if a molecule is odorous. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 119 , e2116576119 (2022).
Niu, Y. et al. Sensory evaluation of the synergism among ester odorants in light aroma-type liquor by odor threshold, aroma intensity and flash GC electronic nose. Food Res. Int. 113 , 102–114 (2018).
Yu, P., Low, M. Y. & Zhou, W. Design of experiments and regression modelling in food flavour and sensory analysis: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 71 , 202–215 (2018).
Oladokun, O. et al. The impact of hop bitter acid and polyphenol profiles on the perceived bitterness of beer. Food Chem. 205 , 212–220 (2016).
Linforth, R., Cabannes, M., Hewson, L., Yang, N. & Taylor, A. Effect of fat content on flavor delivery during consumption: An in vivo model. J. Agric. Food Chem. 58 , 6905–6911 (2010).
Guo, S., Na Jom, K. & Ge, Y. Influence of roasting condition on flavor profile of sunflower seeds: A flavoromics approach. Sci. Rep. 9 , 11295 (2019).
Ren, Q. et al. The changes of microbial community and flavor compound in the fermentation process of Chinese rice wine using Fagopyrum tataricum grain as feedstock. Sci. Rep. 9 , 3365 (2019).
Hastie, T., Friedman, J. & Tibshirani, R. The Elements of Statistical Learning. (Springer, New York, NY). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-21606-5 (2001).
Dietz, C., Cook, D., Huismann, M., Wilson, C. & Ford, R. The multisensory perception of hop essential oil: a review. J. Inst. Brew. 126 , 320–342 (2020).
CAS Google Scholar
Roncoroni, Miguel & Verstrepen, Kevin Joan. Belgian Beer: Tested and Tasted. (Lannoo, 2018).
Meilgaard, M. Flavor chemistry of beer: Part II: Flavor and threshold of 239 aroma volatiles. in (1975).
Bokulich, N. A. & Bamforth, C. W. The microbiology of malting and brewing. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. MMBR 77 , 157–172 (2013).
Dzialo, M. C., Park, R., Steensels, J., Lievens, B. & Verstrepen, K. J. Physiology, ecology and industrial applications of aroma formation in yeast. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 41 , S95–S128 (2017).
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Datta, A. et al. Computer-aided food engineering. Nat. Food 3 , 894–904 (2022).
American Society of Brewing Chemists. Beer Methods. (American Society of Brewing Chemists, St. Paul, MN, U.S.A.).
Olaniran, A. O., Hiralal, L., Mokoena, M. P. & Pillay, B. Flavour-active volatile compounds in beer: production, regulation and control. J. Inst. Brew. 123 , 13–23 (2017).
Verstrepen, K. J. et al. Flavor-active esters: Adding fruitiness to beer. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 96 , 110–118 (2003).
Meilgaard, M. C. Flavour chemistry of beer. part I: flavour interaction between principal volatiles. Master Brew. Assoc. Am. Tech. Q 12 , 107–117 (1975).
Briggs, D. E., Boulton, C. A., Brookes, P. A. & Stevens, R. Brewing 227–254. (Woodhead Publishing). https://doi.org/10.1533/9781855739062.227 (2004).
Bossaert, S., Crauwels, S., De Rouck, G. & Lievens, B. The power of sour - A review: Old traditions, new opportunities. BrewingScience 72 , 78–88 (2019).
Google Scholar
Verstrepen, K. J. et al. Flavor active esters: Adding fruitiness to beer. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 96 , 110–118 (2003).
Snauwaert, I. et al. Microbial diversity and metabolite composition of Belgian red-brown acidic ales. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 221 , 1–11 (2016).
Spitaels, F. et al. The microbial diversity of traditional spontaneously fermented lambic beer. PLoS ONE 9 , e95384 (2014).
Blanco, C. A., Andrés-Iglesias, C. & Montero, O. Low-alcohol Beers: Flavor Compounds, Defects, and Improvement Strategies. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 56 , 1379–1388 (2016).
Jackowski, M. & Trusek, A. Non-Alcohol. beer Prod. – Overv. 20 , 32–38 (2018).
Takoi, K. et al. The contribution of geraniol metabolism to the citrus flavour of beer: Synergy of geraniol and β-citronellol under coexistence with excess linalool. J. Inst. Brew. 116 , 251–260 (2010).
Kroeze, J. H. & Bartoshuk, L. M. Bitterness suppression as revealed by split-tongue taste stimulation in humans. Physiol. Behav. 35 , 779–783 (1985).
Mennella, J. A. et al. A spoonful of sugar helps the medicine go down”: Bitter masking bysucrose among children and adults. Chem. Senses 40 , 17–25 (2015).
Wietstock, P., Kunz, T., Perreira, F. & Methner, F.-J. Metal chelation behavior of hop acids in buffered model systems. BrewingScience 69 , 56–63 (2016).
Sancho, D., Blanco, C. A., Caballero, I. & Pascual, A. Free iron in pale, dark and alcohol-free commercial lager beers. J. Sci. Food Agric. 91 , 1142–1147 (2011).
Rodrigues, H. & Parr, W. V. Contribution of cross-cultural studies to understanding wine appreciation: A review. Food Res. Int. 115 , 251–258 (2019).
Korneva, E. & Blockeel, H. Towards better evaluation of multi-target regression models. in ECML PKDD 2020 Workshops (eds. Koprinska, I. et al.) 353–362 (Springer International Publishing, Cham, 2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-65965-3_23 .
Gastón Ares. Mathematical and Statistical Methods in Food Science and Technology. (Wiley, 2013).
Grinsztajn, L., Oyallon, E. & Varoquaux, G. Why do tree-based models still outperform deep learning on tabular data? Preprint at http://arxiv.org/abs/2207.08815 (2022).
Gries, S. T. Statistics for Linguistics with R: A Practical Introduction. in Statistics for Linguistics with R (De Gruyter Mouton, 2021). https://doi.org/10.1515/9783110718256 .
Lundberg, S. M. et al. From local explanations to global understanding with explainable AI for trees. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2 , 56–67 (2020).
Ickes, C. M. & Cadwallader, K. R. Effects of ethanol on flavor perception in alcoholic beverages. Chemosens. Percept. 10 , 119–134 (2017).
Kato, M. et al. Influence of high molecular weight polypeptides on the mouthfeel of commercial beer. J. Inst. Brew. 127 , 27–40 (2021).
Wauters, R. et al. Novel Saccharomyces cerevisiae variants slow down the accumulation of staling aldehydes and improve beer shelf-life. Food Chem. 398 , 1–11 (2023).
Li, H., Jia, S. & Zhang, W. Rapid determination of low-level sulfur compounds in beer by headspace gas chromatography with a pulsed flame photometric detector. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 66 , 188–191 (2008).
Dercksen, A., Laurens, J., Torline, P., Axcell, B. C. & Rohwer, E. Quantitative analysis of volatile sulfur compounds in beer using a membrane extraction interface. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 54 , 228–233 (1996).
Molnar, C. Interpretable Machine Learning: A Guide for Making Black-Box Models Interpretable. (2020).
Zhao, Q. & Hastie, T. Causal interpretations of black-box models. J. Bus. Econ. Stat. Publ. Am. Stat. Assoc. 39 , 272–281 (2019).
Article MathSciNet Google Scholar
Hastie, T., Tibshirani, R. & Friedman, J. The Elements of Statistical Learning. (Springer, 2019).
Labrado, D. et al. Identification by NMR of key compounds present in beer distillates and residual phases after dealcoholization by vacuum distillation. J. Sci. Food Agric. 100 , 3971–3978 (2020).
Lusk, L. T., Kay, S. B., Porubcan, A. & Ryder, D. S. Key olfactory cues for beer oxidation. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 70 , 257–261 (2012).
Gonzalez Viejo, C., Torrico, D. D., Dunshea, F. R. & Fuentes, S. Development of artificial neural network models to assess beer acceptability based on sensory properties using a robotic pourer: A comparative model approach to achieve an artificial intelligence system. Beverages 5 , 33 (2019).
Gonzalez Viejo, C., Fuentes, S., Torrico, D. D., Godbole, A. & Dunshea, F. R. Chemical characterization of aromas in beer and their effect on consumers liking. Food Chem. 293 , 479–485 (2019).
Gilbert, J. L. et al. Identifying breeding priorities for blueberry flavor using biochemical, sensory, and genotype by environment analyses. PLOS ONE 10 , 1–21 (2015).
Goulet, C. et al. Role of an esterase in flavor volatile variation within the tomato clade. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 109 , 19009–19014 (2012).
Article ADS CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Borisov, V. et al. Deep Neural Networks and Tabular Data: A Survey. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 1–21 https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2022.3229161 (2022).
Statista. Statista Consumer Market Outlook: Beer - Worldwide.
Seitz, H. K. & Stickel, F. Molecular mechanisms of alcoholmediated carcinogenesis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 7 , 599–612 (2007).
Voordeckers, K. et al. Ethanol exposure increases mutation rate through error-prone polymerases. Nat. Commun. 11 , 3664 (2020).
Goelen, T. et al. Bacterial phylogeny predicts volatile organic compound composition and olfactory response of an aphid parasitoid. Oikos 129 , 1415–1428 (2020).
Article ADS Google Scholar
Reher, T. et al. Evaluation of hop (Humulus lupulus) as a repellent for the management of Drosophila suzukii. Crop Prot. 124 , 104839 (2019).
Stein, S. E. An integrated method for spectrum extraction and compound identification from gas chromatography/mass spectrometry data. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 10 , 770–781 (1999).
American Society of Brewing Chemists. Sensory Analysis Methods. (American Society of Brewing Chemists, St. Paul, MN, U.S.A., 1992).
McAuley, J., Leskovec, J. & Jurafsky, D. Learning Attitudes and Attributes from Multi-Aspect Reviews. Preprint at https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1210.3926 (2012).
Meilgaard, M. C., Carr, B. T. & Carr, B. T. Sensory Evaluation Techniques. (CRC Press, Boca Raton). https://doi.org/10.1201/b16452 (2014).
Schreurs, M. et al. Data from: Predicting and improving complex beer flavor through machine learning. Zenodo https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10653704 (2024).
Download references
Acknowledgements
We thank all lab members for their discussions and thank all tasting panel members for their contributions. Special thanks go out to Dr. Karin Voordeckers for her tremendous help in proofreading and improving the manuscript. M.S. was supported by a Baillet-Latour fellowship, L.C. acknowledges financial support from KU Leuven (C16/17/006), F.A.T. was supported by a PhD fellowship from FWO (1S08821N). Research in the lab of K.J.V. is supported by KU Leuven, FWO, VIB, VLAIO and the Brewing Science Serves Health Fund. Research in the lab of T.W. is supported by FWO (G.0A51.15) and KU Leuven (C16/17/006).
Author information
These authors contributed equally: Michiel Schreurs, Supinya Piampongsant, Miguel Roncoroni.
Authors and Affiliations
VIB—KU Leuven Center for Microbiology, Gaston Geenslaan 1, B-3001, Leuven, Belgium
Michiel Schreurs, Supinya Piampongsant, Miguel Roncoroni, Lloyd Cool, Beatriz Herrera-Malaver, Florian A. Theßeling & Kevin J. Verstrepen
CMPG Laboratory of Genetics and Genomics, KU Leuven, Gaston Geenslaan 1, B-3001, Leuven, Belgium
Leuven Institute for Beer Research (LIBR), Gaston Geenslaan 1, B-3001, Leuven, Belgium
Laboratory of Socioecology and Social Evolution, KU Leuven, Naamsestraat 59, B-3000, Leuven, Belgium
Lloyd Cool, Christophe Vanderaa & Tom Wenseleers
VIB Bioinformatics Core, VIB, Rijvisschestraat 120, B-9052, Ghent, Belgium
Łukasz Kreft & Alexander Botzki
AB InBev SA/NV, Brouwerijplein 1, B-3000, Leuven, Belgium
Philippe Malcorps & Luk Daenen
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
S.P., M.S. and K.J.V. conceived the experiments. S.P., M.S. and K.J.V. designed the experiments. S.P., M.S., M.R., B.H. and F.A.T. performed the experiments. S.P., M.S., L.C., C.V., L.K., A.B., P.M., L.D., T.W. and K.J.V. contributed analysis ideas. S.P., M.S., L.C., C.V., T.W. and K.J.V. analyzed the data. All authors contributed to writing the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Kevin J. Verstrepen .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
K.J.V. is affiliated with bar.on. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information.
Nature Communications thanks Florian Bauer, Andrew John Macintosh and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work. A peer review file is available.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information, peer review file, description of additional supplementary files, supplementary data 1, supplementary data 2, supplementary data 3, supplementary data 4, supplementary data 5, supplementary data 6, supplementary data 7, reporting summary, source data, source data, rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Schreurs, M., Piampongsant, S., Roncoroni, M. et al. Predicting and improving complex beer flavor through machine learning. Nat Commun 15 , 2368 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-46346-0
Download citation
Received : 30 October 2023
Accepted : 21 February 2024
Published : 26 March 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-46346-0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines . If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing: Translational Research newsletter — top stories in biotechnology, drug discovery and pharma.

Tunisia: Authorities’ targeting of lawyers undermines access to justice
The Tunisian authorities’ growing judicial harassment and intimidation of lawyers solely for discharging their professional duties violates their rights and undermines access to justice and effective remedies for victims of human rights violations, said Amnesty International, a day ahead of the verdict in the case of lawyer Abdelaziz Essid who is being tried on spurious charges.
Authorities have targeted at least 20 lawyers representing members of political opposition groups, activists and victims of human rights violations with criminal investigations under bogus charges that range from “offending others”, “accusing public officials of illegal acts without proof or the discharge of their duties as lawyers,” “verbally assaulting a public officer” and “spreading fake news”. The charges fall under Tunisia’s Telecommunication Code, the Penal Code and Decree Law 54 respectively. If convicted, the lawyers could face up to 20 years in prison and hefty fines.
It is a travesty of justice to target lawyers solely for discharging their professional duties. Everyone, including lawyers, are entitled to their human rights. Fida Hammami, Amnesty International
“Undermining the independence of the legal profession and targeting lawyers who represent victims of human rights violations is yet another blow to the right to defence and fair trial rights more generally in Tunisia,” said Fida Hammami, Amnesty International’s Tunisia Research and Advocacy Advisor.
“The authorities must end their judicial harassment of the 20 lawyers who are being investigated solely for the peaceful exercise of their human rights. Lawyers should be able to perform their professional duties and freely express themselves without any intimidation, harassment or fear of reprisals.”
On 29 March, the Tunis Court of First Instance will issue its verdict in the case of Lawyer Abdelaziz Essid who is being tried for “offending others through telecommunications networks” and “accusing public officials of illegal acts without proof,” under article 86 of the Telecommunications Code and article 128 of the Criminal Code, respectively based on a complaint by the Minister of Justice
Essid is one of three members of the legal defence team of six detained political opposition members in the high profile “ conspiracy case ” who are themselves now being investigated or tried for the statements they made to the media about the case.
The charges against Essid are based on statements that he had made during a press conference claiming that there were discrepancies in the dates and facts in the “conspiracy case” casefile indicating the possibility that the file has been tampered with.
In one example the prosecution opened an investigation against 14 members of the legal defence team of Noureddine Bhiri, prominent member of the Ennahda opposition party, after a complaint against the group from a national guard officer following an argument between the lawyers and the national guard. An investigative judge banned the 14 lawyers from traveling under this investigation.
In four cases the investigations were opened soon after the lawyers had publicly criticized the Minister of Justice or made allegations of corruption against her.
“It is a travesty of justice to target lawyers solely for discharging their professional duties. Everyone, including lawyers, are entitled to their human rights,” said Fida Hammami.
These rights include the rights to liberty, security of person and freedom of expression, as guaranteed under articles 9 and 19 of the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights and articles 6 and 9 of the African Charter on Human and Peoples’ Rights to which Tunisia is a state party.
The UN Special Rapporteur on the Independence of Judges and Lawyers has urged public prosecutors “to closely monitor situations and cases in which lawyers might be criminalized for performing their duties. When such circumstances arise, appropriate orders should be issued to prevent public prosecutors from maliciously prosecuting members of the legal profession who criticize State officials and institutions in the exercise of their independence and freedom of expression.”

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Step 1 - Master the Opening Line. To have a strong introduction, you need to open with a strong first sentence. The millisecond your reader hits the page, they have an extremely high likelihood of leaving the page. Data says so. The first sentence has one single purpose: to entice the reader to read the next sentence.
Making structure work for you. Notice how articles on bigger outlets (particularly those that focus on news) tend to have an introductory phrase, similar to a subtitle, which resumes the article or creates the premise for the topic to be discussed: Here's another example, this time on Medium: And another such "introduction" on The Guardian:
A good introductory statement should be simple and clear, yet still, maintain interest. Generally speaking, not including enough information makes the article seem boring. Too much information, on the other hand, can make it confusing and unclear. Writing an introduction that is clear and concise shows knowledge of how to write a good ...
Use the word "you" at least once. Tell readers what's coming next. Explain why the article is important. Refer to a concern or problem your readers might have. Be careful telling stories. Use a stat or a fact to convey urgency. 1. Keep it short. I'm a big fan of short sentences.
To round out our guide to drafting the Introduction of your journal article, we provide some general tips about the technical aspects of writing the Introduction section below. Use the active voice. Be concise. Avoid nominalizations (converting phrases, including adjectives and verbs, into nouns).
Step 4: Leverage the intrigue into a hook for the rest of the article. " The Bermuda Triangle is an urban legend focused on the North Atlantic Ocean. Several aircraft and ships are said to have disappeared here under mysterious circumstances. But most reputable sources dismiss the idea that there is any mystery.
An introduction serves three main purposes: 1. To capture the reader's attention: The opening paragraph is the most crucial part of your paper because it's the reader's first impression and the best clue as to whether the paper will be worth the reader's time. The best introductions will not only be informative but also include a hook ...
In general, your introductions should contain the following elements: When you're writing an essay, it's helpful to think about what your reader needs to know in order to follow your argument. Your introduction should include enough information so that readers can understand the context for your thesis. For example, if you are analyzing ...
Here are nine excellent introduction paragraph examples: 1. The statistical introduction example. Semrush blog: How to Grow your eCommerce Business in 2023. According to a report by Statista and eMarketer, online retail sales are projected to reach $6.51 trillion by 2023.
Frankly, this type of post introduction doesn't add much value besides setting the context or introducing one main topic. 🔶Read the full article on my blog .🔶 Writing
To clearly establish the context for the study, the introduction contains four main components: General background information. Specific background information. A description of the gap in our knowledge that the study was designed to fill. A statement of study objective, and (optionally) a brief summary of study.
Step 1: Hook your reader. Step 2: Give background information. Step 3: Present your thesis statement. Step 4: Map your essay's structure. Step 5: Check and revise. More examples of essay introductions. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about the essay introduction.
Table of contents. Step 1: Introduce your topic. Step 2: Describe the background. Step 3: Establish your research problem. Step 4: Specify your objective (s) Step 5: Map out your paper. Research paper introduction examples. Frequently asked questions about the research paper introduction.
A typical article structure includes: Introduction: ... Writing articles is a craft that requires practice, dedication, and a commitment to continuous improvement. Whether you're writing for ...
Step 2: Select a Topic and an Attractive Heading. Having understood your audience, select a relevant topic based on their interests and questions. Be sure it's one you can competently discuss. When deciding how to start writing an article, ensure it begins with a captivating title.
Writing a good introduction is easy as easy as 1-2-3, if you know exactly how to go about doing it. Choose a topic for your article. This is will be what the article is mainly about. Write a first sentence that draws in readers. Some great ideas include asking a question, using a quote or stating an amazing fact.
Article writing is the craft of creating written content for various purposes. It involves conveying information clearly and engagingly to a specific audience . Starting with a compelling introduction, an article provides valuable insights and knowledge on a given topic.
Abstract. An article primarily includes the following sections: introduction, materials and methods, results, discussion, and conclusion. Before writing the introduction, the main steps, the heading and the familiarity level of the readers should be considered. Writing should begin when the experimental system and the equipment are available.
A well-balanced introduction is: Extension of the title — It provides more insights into the topic. The bearer of the message — It conveys the overall idea of the article. Problem summary — It describes the main pain points of the subject. Solution proposal — It is proof of your expertise on the subject.
Luckily, with the internet, it's easy to find articles on any topic of interest at the click of a mouse. 2. Choose Interesting Topics - It's hard to engage the reader when the writer is not themselves engaged. Be sure students choose article topics that pique their own interest (as far as possible!).
These elements will help you write an effective bio that details your music and your background in a concise and inviting way. 1. An engaging introduction. The toughest part about writing your musician bio is getting started. Make a few notes on a piece of paper to begin. Jot down your name, and where you're from.
Therefore, articles should have a title that grabs the eyeballs of their readers. The introduction should talk more about the topic under concern in the article. If the introduction is lengthy and boring, the readers will bail out from reading and shift to another piece of writing. The main body should contain 2 to 5 paragraphs, which further ...
Abstract. The perception and appreciation of food flavor depends on many interacting chemical compounds and external factors, and therefore proves challenging to understand and predict. Here, we ...
The Tunisian authorities' growing judicial harassment and intimidation of lawyers solely for discharging their professional duties violates their rights and undermines access to justice and effective remedies for victims of human rights violations, said Amnesty International, a day ahead of the verdict in the case of lawyer Abdelaziz Essid ...