Monday 1st May 2023, 12:00:00 PM
Analysis and Approaches Paper 1 (HL and SL)
Thursday 2nd May 2024, 8:00:00 AM
Analysis and Approaches Paper 2 (HL and SL)
Monday 6th May 2024, 12:00:00 PM
Analysis and Approaches Paper 3 (HL)
Wednesday 1st May 2024, 12:00:00 PM
Applications and Interpretation Paper 1 (HL and SL)
Applications and Interpretation Paper 2 (HL and SL)
Applications and Interpretation Paper 3 (HL)

Past Papers
All International Baccalaureate (IB) Maths Past Exam Papers for Analysis and Approaches (standard and higher level) and Applications and Interpretation (standard and higher level) can be found below. Analysis and Approaches is very similar to the old IB syllabus. Applications and Interpretation introduces many new topics and is quite a change from the old syllabus.
There are two maths courses offered (Analysis and Approaches and Applications and Interpretations). These are each offered at two difficulty levels - higher level (HL) and standard level (SL).
Difficulty Level
The higher level version of each of the two courses are harder than the standard level version of each two courses. In order of difficulty the courses are:
- Level 1: Applications and Interpretation Standard Level (AI SL)
- Level 2: Analysis and Approaches Standard Level (AA SL)
- Level 3: Applications and Interpretation Higher Level (AI HL)
- Level 4: Analysis and Approaches Higher Level (AA HL)
While difficulty is subjective, it is agreed upon that the new HL courses are much harder than the new SL courses. If maths is one of your strong subjects, higher level might be right for you. If you are not comfortable with higher level maths, then standard level maths will be the right option.
AA HL is considered one of the hardest classes the IB has (possibly other than Physics or Chemistry). However, some people are of the opinion that AI HL is slightly more difficult than AA HL just because a lot of the AI HL only topics are quite abstract. In my opiion, AA HL and AI HL are pretty similar in difficulty yet in different ways.
The gap between AI HL and SL is way bigger than the gap between AA HL and AA SL. AI HL is much, much more difficult than AA SL and schools will reward you for taking it. It is more important that you feel comfortable with everything up to Pre-Calculus, because otherwise, AA SL will be a struggle as well.
AA SL is calibrated for the average IB math student, but AI SL is more for those of those who struggle with maths so they can get the diploma.
Link to Older Syllabus (pre 2020)
Every 7 years the IB evaluates its subjects and course content and makes changes to keep relevant. The last syllabus and course change was in 2019 with first assessment in May 2021. The previous syllabus (pre 2020) had only one main maths course (maths) was offered at 3 different levels:
- Maths Studies
- Maths Standard Level
- Maths Higher Level
There was also a further maths option at both higher and standard level (like there is for A Level maths) for very able mathematicians. These courses went into degree level maths and only a handful of people took them each year.
A Level Further = IB Further SL > IB Maths HL > A Level Maths > IB Maths SL
The current syllabus has two maths course options at two different difficulty levels (HL and SL)
- Analysis and Approaches HL
- Analysis and Approaches SL
- Applications and Interpretatons HL
- Applications and Interpretatons SL
It is not wise to compare the new mathematics courses with their old counterparts, as there are significant differences between them. There is no official correspondence, but a gross over simplification of the relation can be described as follows:
AI SL is mostly maths Studies. AI HL is studies but with about 30-40% of Further Maths HL. AA SL is pretty much SL and AA HL is HL with only 20-30% of the Calculus option. Many will agree that AA HL is easier than the old maths higher level because ove r 80% of the Calculus option (then the most popular Option) was taken out and there are no longer Options. The Option took about 3 months to cover if having classes 5 times a week going at a moderate-fast pace.
Difference Between The Courses Offered/How to Decide Which Course To Take
The Analysis and Approaches (AA) course is suitable for future mathematicians, engineers, scientists and economists. This requires a more abstract and conceptual understanding and it is recommended to students who have a natural mathematical ability and enjoy solving complex mathematical problems. It focuses on developing analytical and problem solving skills. If you're the type of student who likes algebra (factorising, solving linear and quadratic equations and inequalities, algebraic fractions and indices), trigonometry , geometry and calculus (differentiation and integration) then this course is for you. It provides a strong foundation in mathematical reasoning and proof, making it a good choice for students who like theoretical maths as it focuses on theory and gives students the abilty to analyze abstract math theories that are the basis of all calculations. Students who like sitting down and solving equations and get satisfaction from solving complex equations should choose this course. In other words, this course has an emphasis on:
- algebraic methods
- developing strong skills in mathematical thinking
- real and abstract mathematical problem solving
The A pplications and Interpretation (AI) course is for students who are more passionate about humanities, social sciences, natural sciences, medicine, statistics, business, psychology and design. It is designed for students who have less of a natural mathematical ability and enjoy application type topics such as functions, modelling, statistics and probability . A pplications and Interpretation focuses mainly on the practical application and implementation of mathematics to real-world contexts. It is designed for students who prefer to apply mathematical concepts in practical scenarios and gives a student the 'know how' and the ability to apply maths to real world techniques and solve real world problems. If you are weaker mathematical student, but have a keen interest in the humanities or arts where applied mathematics and statistical analysis are more relevant then this course is for you. Students who take this course will be well equipped to analyse data, interpret mathematical models and solve problems using set mathematical techniques. In other words, t his course has an emphasis on:
- modelling and statistics
- developing strong skills in applying maths to real world and construct and communicate them mathematically and interpret conclusions or generalisations
- real mathematical problem solving using technology. AI expects you to become an expert in how to use your graphical calculator.
There are significant differences between the two courses in terms of teaching hours for each of the courses' components.
There are some common topics for AA and AI which are covered in the first 60 hours of the course. The SL demands 150 hour of teaching and HL requires 240 hours of teachinf.
In summary:
Applications and Interpetation covers a wider range of topics, however Analysis and Approaches covers a narrower range and in greater depth. In AI HL you still get exposed to the rigor of math/topics you would expect in a normal HL course, just not as much as in AA HL. Those wanting to enter maths orientated professions like engineering, machine learning, computer science, data science etc will find AA will give them the tools they need. Those looking at professions where the application of maths is more important than the theory like economics, management and so on will find that AI is right for them. Analysis and approaches focuses on developing analytical and deeper problem solving skills, whereas Applications and Interpetation focuses on the practical application of mathematical techniques. Analysis and Approaches is thought of as a pure course with lots of algebra whereas Applications and Interpetation is an applied course with lots of statistics and modelling. I f you enjoy maths (s olving equations and having to think deeper thus requiring further problem solving skills) and are naturally good at maths and fascinated by the "why" behind the theories take analysis and approaches, but if you prefer using the calculator and following set methods/techniques and want to learn "how" to use maths and are not interested in the theory behind it then take Applications and Interpetation. AI HL is for the fast learner and AA HL for the inquisitive learner. If you are not that strong at math, the recommendation is AA SL. AI SL is still quite a bit easier than AA SL and only choose it if you are fine with dealing with lots of data.
"Maths AA is like diving headfirst into the deep end of the mathematical ocean. It's for those who crave a challenge and want to explore the intricate depths of mathematics. On the other hand, Maths AI is like dipping your toes into the practical side of math, with a focus on real-world applications. It's perfect for students who want to see how mathematics can be used in fields like economics, business, or social sciences. It's all about finding the path that ignites your curiosity and aligns with your future goals"
Remember that you are going to spend two years studying this subject so make sure you like what you're doing and have confidence of doing well in the subject in your IB exams. Your performance and attitude in studying maths, and your individual strengths or weaknesses in individual components that may lead you to choose one course or another. If you are one of those all-rounders in maths, then perhaps you could choose based on university plans (see university recognition section further down). If you are not confident in maths skills but still want to pursue maths-related degrees, it is also an important factor to consider.
Consult your teachers and friends for further advice on subject selection. If you are uncertain about which module to choose, and if your school permits a module change consider opting for HL. Because initial stages of HL and SL are similar, dropping down to SL if HL is too much will not be a problem. Many schools will even let you start with SL and move to HL, however it is ALWAYS easier to go from HL to SL than it is from SL to HL. Some schools will also let you swap courses and start with AA and then switch down to AI before the end of the first term if you're finding AA too difficult.
Exam Paper Setup
The higher level courses each have 3 papers and the standard level courses each have 2 papers. There is no calculator allows for paper 1 for AA, but AI permits a calculator in all 3 papers. There is also a courswork based internal assessment (IA). The paper setup for both higher level subjects is the same and the setup for both standard level subjects is the same.
AA paper 1 and 2 (HL and SL) are both divided into 2 sections. Section A has short response questions and section B has extended response questions. AI (HL and SL) paper 1 is comprised of exclusively short questions and paper 2 is comprised of exclusively extended response quesitons. HL paper 3 for both AA and AI are both extended response questions and both of them share the same format, but have differing questions obviously due to their differing syllabi.
Analysis and Approaches SL setup:
Analysis and Approaches HL setup:
Applications and Interpretation SL setup:
Applications and Interpretation HL setup:
To calculate your grade:
HL Final Grade = (Paper 1 Score) x 30% + (Paper 2 Score) x 30 % + (Paper 3 Score) x 20 % + (IA) * 20 %
SL Final Grade = (Paper 1 Score) x 40% + (Paper 2 Score) x 40% + (IA) * 20%
Maths Higher Level Setup (old syllabus) :
In the past, teachers had choices in what to teach as their optional topic for HL to go into depth. The optional topic had 4 options to choose from
- calculus (formerly called series and differential equations)
- discrete mathematics
- statistics and probability
- sets, relations and groups
In the current syllabus, HL does not NOT have choices (out of the optional topics) of what the teacher can choose to teach, so everyone will learn the same materials in HL AA and all should be learning the same materials in HL AI.
Maths Standard Level Setup (old syllabus) :
Maths Studies Setup (old syllabus):
Grade Boundaries
Grades range from 7 to 1, with 7 being the highest. The grade boundaries change every year depending on what the scores are (how the students do and how difficult they found the papers overall) and they also change for every timezone. The following are a rough guide and what students should aim for in order should be 'safe'.
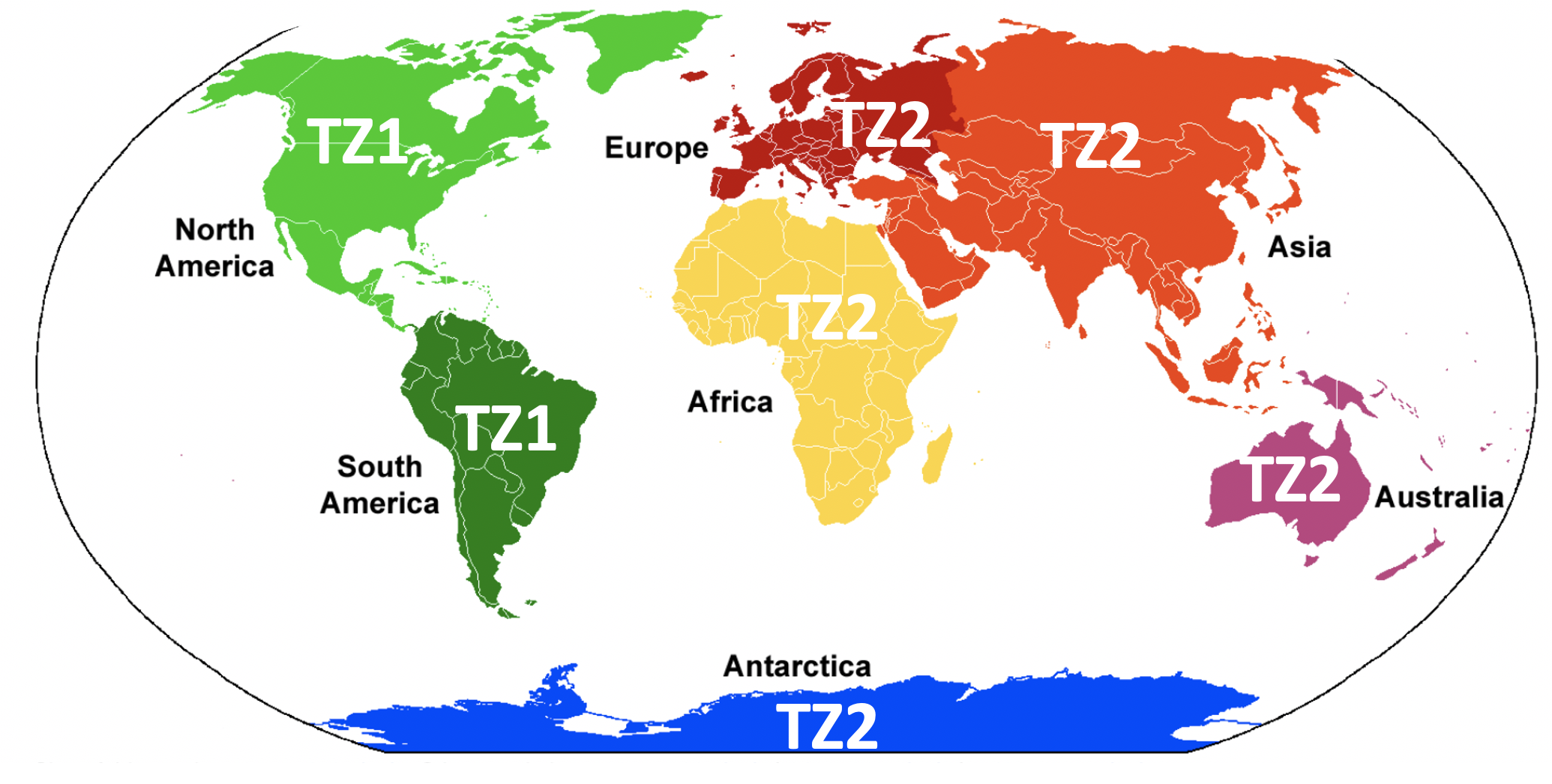
Old Time Zones (Time Zones 1 and 2) - Pre 2023
IB papers have different time zones to stop students from one time zone sharing the contents of their papers with the next time zone. There are two time zones for the May papers (time zone 1 and time zone 2) and one time zone for the November papers (time zone 0 only). Time zone 1 (TZ1) is the Americas, and time zone 2 (TZ2) is the rest of the world (Africa/Europe/Middle East/Asia). Time zone 0 (TZ0) is for when there isn't such a big demand and there aren't enough people taking the exam to warrant two separate exams November exams are mainly for re-take students (although some schools sit their exams in November rather than May) and hence only one time zone is necessary. There is a common misconception that November exams are more difficult. Although the exams may sometimes be harder, the grade boundaries reflect this.
New Time Zones (Time Zones A, B and C) - 2023 Onwards
There are now 3 times zones (A, B and C) for the first time since the May 2023 exam.
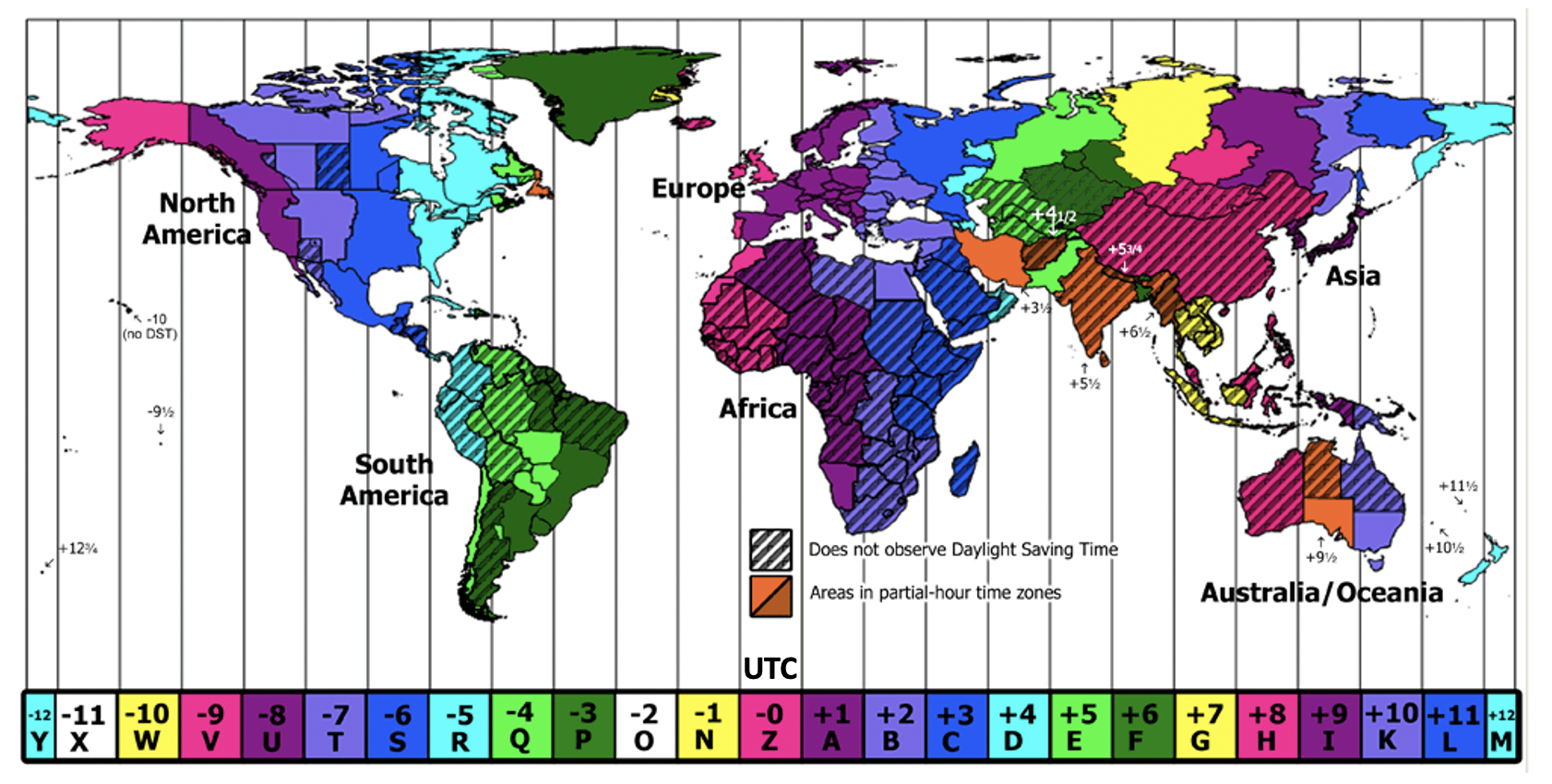
- Exam Zone A: UTC +12 to UTC +3.5
- Exam Zone B: UTC +3 to UTC +0
- Exam Zone C: UTC +1 to UTC +10
Exam Times:
Exams are either in the morning or afternoon. Morning exams must start after 7 AM and finish by 1 PM local time (the usual start time is 8:30 AM or 9:30 AM). Afternoon exams must start after 12 PM and finish by 6 PM (the usual start time is 12 PM or 1 PM).
Each "real world" has their own scheduled start times. For example UTC +3 to UTC +0 have the same exam in the same window (morning/afternnon) on the same day, but one might start at 8:30 and the other at 9:30.
University Recognition
Not only will you have to consider your own math background when deciding which course to choose, you'll need to also consider your fu ture academic and career path and the tier of unis you'll be applying to as well as the specific uni requirements. Neither HL or SL is inherently 'more' useful, as it is entirely dependent on your region and your ambition in college or university. For most univesities AA SL is sufficient. Any competitive top unis will require HL maths.
- Maths Degees: If there is a preference for AA or AI in terms of courses, it exists for engineering or maths-heavy courses such as physics, maths and data science degrees. In these cases, AA is preferred or even required, but it only applies to countries that differentiate between AA or AI. When you have two people with the same marks in AI or AA HL, unis tend to favor the one with AA HL.
- Economics Degrees: If planning studying economics at uni, AA HL is more focused on analytical thinking which is a central component in economics. You'll learn a wider range of maths in AI HL, but most of them won't show up in Economics. Either HL course is perfectly fine though.
- Medicine Degrees: As long as you take Biology Higher and Chemistry Higher it doesn't usually matter too which maths course or level you choose. Make sure to check with your university though.
- Computer Science Degrees: If you plan on studying computer scienceat university it is highly recommended to take HL maths, especially if you're planning on studying in the UK. Both AA HL and AI HL are suitable options, but AL HL is often preferred for computer science-related fields mostly because of all the discrete math stuff.
- Finance, Management and Business Degrees: It doesn't usually matter which maths course or level you choose, but most students applying for these course take AI.
The only reason that a lot of schools don't think highly of AI HL is due to one misleading document that says AI HL is Studies but more advanced. The truth of the matter is, AI HL has nearly half of Further Math HL curriculum. Neither course at HL is intended for students who are 'just ok' at maths, but taking AA SL will put you at a significant disadvantage when applying for computer engineering/science. As I have said above, AI HL is more suitable for CS because of all the discrete math, and it is more difficult than AA HL.
Below is a very brief summary for certain popular countries for further studies and their trends for preferring AA or AI. Be aware that there are so many exceptions, so be sure to research on your own as well - check which courses the unis that you are targeting require or prefer.
- United Kingdom: There are cases of differentiation in a considerable number of universities. Generally, AA HL is the course which opens the most doors, as nearly all engineering and math heavy degrees (and even medicine degrees) require AA HL. Many competitive economics programs even prefer or require AA HL. Of course, there are major exceptions, most notably being Oxbridge which has no preference between the two, as they already have their own entrance exams which include maths.
- United States: No AA/AI differentiation, but may require/prefer HL over SL for math heavy degrees. For US students who are planning a course load around their college major, I would highly highly recommend AA for like 90% of STEM Majors (esp any Engineering and Premed). If you are looking to apply to top unis where compeition is high, take HL Math. Most business and finance majors take AI.
- Canada: M any Canadian universities have a strong preference for AA. If you are planning to study business, science, engineering, math etc it is much better to take eith er level of AA. If not then Canadian schools are not generally strict about pre-requistes and either one at HL are ok.
- Australia: No AA/AI differentiation.
Featured documents:
Maths revision and resources for all maths courses.
What are you waiting for? It's time to get started!
Simple, easy to understand Maths


Sample exam papers
The following are examples of actual past examination papers, and a selection of specimen examination papers. They are provided for information only.
Join the IB's global alumni network
The IB is extremely proud of its graduates, and the alumni network connects them with one another and with the IB community.
Members of the alumni network receive opportunities to get involved in IB projects and to share their stories.
Students who will graduate in the next two years are encouraged to join.
- Join the network


We use cookies on this site. By continuing to use this website, you consent to our use of these cookies. Read more about cookies
Prediction Exams and November 2023 Past Paper Solutions available now!
The best resource for IB Mathematics just got better!
Now available: ib maths, physics, chemistry, biology, ess, business management, economics, psychology, and english, voted #1 ib mathematics resource by ib teachers & students, ib mathematics.
Pick a subject
IB Chemistry
Ib psychology, ib economics, ib business management, ib environmental systems and societies, practice ib exam style questions.
Thousands of exam style questions, filtered by topic, sub-topic & difficulty. Detailed and easy to understand mark-schemes and video solutions for all questions. Practice & master IB exam style questions.
no calculator
[Maximum mark: 6]
Consider an arithmetic sequence 2 , 6 , 10 , 14 , … 2,6,10,14,\dots 2 , 6 , 10 , 14 , …
Find the common difference, d d d . [ 2 ]
Find the 10 10 10 th term in the sequence. [ 2 ]
Find the sum of the first 10 10 10 terms in the sequence. [ 2 ]
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Check with RV Newton
The table shows the first four terms of three sequences: u n u_n u n , v n v_n v n , and w n w_n w n .
State which sequence is
arithmetic;
geometric. [ 2 ]
Find the sum of the first 50 50 50 terms of the arithmetic sequence. [ 2 ]
Find the exact value of the 13 13 13 th term of the geometric sequence. [ 2 ]
[Maximum mark: 7]
Write down the quadratic expression 3 x 2 + 5 x − 2 3x^2 + 5x - 2 3 x 2 + 5 x − 2 in the form ( a x − b ) ( x + c ) (ax-b)(x+c) ( a x − b ) ( x + c ) . [ 2 ]
Hence, or otherwise, find the coefficient of the term in x 9 x^9 x 9 in the expansion of ( 3 x 2 + 5 x − 2 ) 5 (3x^2+5x-2)^5 ( 3 x 2 + 5 x − 2 ) 5 . [ 5 ]
Over 80% of IB students globally are experiencing the power of Revision Village
#1 ib math resource.
Revision Village is ranked the #1 IB Math Resources by IB Students & Teachers.
34% Grade Increase
Revision Village students scored 34% greater than the IB Global Average in their exams (2021).
80% of IB Students
More and more IB students are using Revision Village to prepare for their IB Math Exams.
Students - Get started now
Teachers - Get started now
What makes Revision Village so effective?
Questionbank.
The #1 IB Mathematics Exam Questionbank for IB Students. Thousands of IB exam style questions (AA & AI), filtered by topic, sub-topic & difficulty. Video solutions & mark-schemes for all questions. Practice & master IB exam style questions.
Past Papers
Step-by-step video solutions to Past IB Math Exams. Short, easy to follow video tutorials taught by experienced IB Math teachers.
Practice Exams
Test yourself with a library of IB Math Practice Exams (AA & AI). Sub-topic Quizzes, Full Topic Exams, Mock Exam Papers, Difficulty Ladder Exams and more.
Key Concepts
Short summary videos that teach the key concepts tested in IB Math Exams. Perfect for learning from home.
More IB Math Resources
Analysis & approaches sl, analysis & approaches hl, applications & interpretation sl, applications & interpretation hl, join over 80% of the world's ib educators & students.
Try RV for free

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
All International Baccalaureate (IB) Maths Past Exam Papers for Analysis and Approaches (standard and higher level) and Applications and Interpretation (standard and higher level) can be found below. Analysis and Approaches is very similar to the old IB syllabus. Applications and Interpretation introduces many new topics and is quite a change ...
Papa Cambridge. This website has past IB math papers all the way to 2019, including Math HL and SL, Further Mathematics, Math Methods, and Math Studies. This site is a good one because in addition to the papers being official and recent, the website also includes notes and other resources to help you study.
Revising with IB Math Past Papers is a highly effective strategy to prepare for final exams. It provides students with guidance on the types of questions they will encounter, and the length and difficulty of the exam papers. If you are an IB student preparing for your upcoming IB mathematics exams, it’s recommended that one of your revision ...
DP IB Maths: AI SL. Revision Notes. Topic Questions. Practice Paper Questions. Our expert IB teachers & examiners have written revision notes, practice questions & tips for your IB exams, to help you get the best grades possible.
100,000 students, teachers, tutors and parents trust Save My Exams because it delivers real results. “ A brilliant platform! A brilliant platform for detailed and clear explanations for IB concepts in Maths, Physics and Chemistry. An amazing selection of past exam papers and concise solutions and explanations.
A common difficulty IB students encounter when revising with IB Math AA SL Past Papers is how to actually answer the exam questions. In addition, the official mark schemes accompanying the papers are often difficult to understand, or don’t show all the working steps on how to reach the final answer (the mark schemes are designed for the markers of exams, not the students).
Biology specimen papers and markschemes (first assessment 2025) [8.8MB] Chemistry specimen papers and markschemes (first exams 2025) [3.5MB] Physics specimen papers and markschemes (first assessment 2025) [3.6MB] Group 5: Mathematics. Mathematics: analysis and approaches [3MB] Mathematics: applications and interpretation [4.3MB]
The #1 IB Mathematics Resource. Analysis & Approaches (AA) and Applications & Interpretation (AI). Practice Exams, Questionbank, Past Papers, Videos
The markscheme will often explicitly include the subsequent values that come “from the use of 3 sf values”. Simplification of final answers: Candidates are advised to give final answers using good mathematical form. In general, for an A mark to be awarded, arithmetic should be completed, and. 25 5.
Mathematics: analysis and approaches Standard level Paper 2 Instructions to candidates y Write your session number in the boxes above. y Do not open this examination paper until instructed to do so. y A graphic display calculator is required for this paper. y Section A: answer all questions. Answers must be written within the answer boxes provided.