
GCSE Physics Paper 2

Physics 101
Brainscape certified class.
AP® Physics
Separate Science - Physics Paper 1
By: revision monkey.
Physics Paper 1
By: deleted deleted.
Physics Paper 1 Trilogy 11A1
By: tom grice.
Separate Science - Physics Paper 2
Combined Science - Physics Paper 1 (Foundation)
Physics Paper 2 Trilogy
By: mr kent.
10AT Physics Paper 1 Separate
Physics Paper 1 Separate 10BT
Physics Paper 2 Separate
Physics Paper 1 Trilogy 111A
Combined Science - Physics Paper 1 (Higher)
Physics Paper 1 Trilogy 11B1
Combined Science - Physics Paper 2 (Higher)
GCSE PHYSICS AQA PAPER 1
By: molly gray.
Combined Science - Physics Paper 2 (Foundation)
Physics Paper 2 Trilogy 111A
Physics Paper 2 Trilogy 11A1
Physics Paper 1 Trilogy - 111B
Physics Paper 2 Trilogy 11B1
Physics Paper 2 Trilogy 11A2
Physics Paper 2 Trilogy 111B
By: miss a.m. jordan.
Physics Paper 2 Trilogy 11B2
Physics Paper 2 Trilogy B1
Physics Paper 1 Trilogy 11B2
10B1 Physics Paper 1 - Trilogy H
11A1 Physics Paper 2 Trilogy
By: dr towey.
Physics Paper 1 Trilogy
11B2 - Physics Paper 1 - Trilogy H
Physics Paper 2
AQA Physics [Paper 1]
By: kalos-trainer universe, knowledge genome.
- Corporate Training
- Teachers & Schools
- Android App
- Help Center
- Law Education
- All Subjects A-Z
- All Certified Classes
- Earn Money!
This website works best with JavaScript switched on. Please enable JavaScript
- Centre Services
- Associate Extranet
- All About Maths
GCSE Physics
- Specification
- Planning resources
- Teaching resources
Assessment resources
- Centre declaration sheets (4)
- Examiner reports (15)
- Grade descriptors (1)
- Mark schemes (22)
- Notes and guidance (4)
- Practice questions (2)
- Question papers (72)
- Paper 1 (46)
- Paper 2 (67)
- June 2018 (17)
- June 2019 (16)
- June 2022 (26)
- June 2024 (3)
- November 2020 (21)
- November 2021 (16)
- Sample set 1 (9)
- KS3 transition tests (1)
- Foundation (60)
- Higher (59)
Showing 120 results
Insert (Foundation; Higher): equations sheet - June 2024
Published 12 Jan 2024 | PDF | 349 KB
Insert (Modified A3 36pt) (Foundation; Higher): equations sheet - June 2024
Published 12 Jan 2024 | PDF | 609 KB
Insert (Modified A4 18pt) (Foundation; Higher): equations sheet - June 2024
Published 12 Jan 2024 | PDF | 622 KB
Exampro: Science Onscreen [exampro.co.uk]
Published 12 Dec 2023
Exampro: searchable past paper questions, marks and examiner comments [exampro.co.uk]
Centre declaration form: non-exam assessment, fieldwork and live performance: 2025
Published 10 Nov 2023 | PDF | 90 KB
Centre declaration form: non-exam assessment, fieldwork and live performance 2025
Published 10 Nov 2023 | DOCX | 293 KB
Insert (Foundation; Higher): equations sheet - June 2022
Published 14 Jul 2023 | PDF | 405 KB
Insert (Modified A3 36pt) (Foundation; Higher): equations sheet - June 2022
Published 14 Jul 2023 | PDF | 226 KB
Insert (Modified A4 18pt) (Foundation; Higher): equations sheet - June 2022
Published 14 Jul 2023 | PDF | 219 KB
Examiner report (Higher): Paper 2 - June 2022
Published 14 Jul 2023 | PDF | 150 KB
Examiner report (Foundation): Paper 2 - June 2022
Published 14 Jul 2023 | PDF | 181 KB
Examiner report (Foundation): Paper 1 - June 2022
Examiner report (Higher): Paper 1 - June 2022
Published 14 Jul 2023 | PDF | 202 KB
Question paper (Higher): Paper 2 - June 2022
Published 14 Jul 2023 | PDF | 1.4 MB
Question paper (Modified A4 18pt) (Higher): Paper 2 - June 2022
Published 14 Jul 2023 | PDF | 1.7 MB
Question paper (Modified A3 36pt) (Higher): Paper 2 - June 2022
Published 14 Jul 2023 | PDF | 3 MB
Question paper (Higher): Paper 1 - June 2022
Published 14 Jul 2023 | PDF | 603 KB
Question paper (Modified A4 18pt) (Higher): Paper 1 - June 2022
Published 14 Jul 2023 | PDF | 1.9 MB
Question paper (Modified A3 36pt) (Higher): Paper 1 - June 2022
Published 14 Jul 2023 | PDF | 2.9 MB
GCSE AQA Physics Revision
Exam-board-specific online course, featuring fast-paced tutorials taught by Mike, practice and test mode quizzing and checkpoint assessments preparing you for your Physics Paper 2 exam. We recommend that you study the Physics Paper 1 and The Roadmap courses along with this GCSE.

Enroll all your students for as little as
AQA GCSE Physics Past Papers
AQA GCSE (9-1) Physics (8463) past exam papers. If you are not sure what tier you are sitting foundation or higher check with your teacher. You can download the papers and marking schemes by clicking on the links below.
June 2022 AQA Physics GCSE (9-1) Past Papers (8463)
Paper 1 – Physics - Foundation (8463/1F) Download Paper - Download Marking Scheme
Paper 1 – Physics - Higher (8463/1H) Download Paper - Download Marking Scheme
Paper 2 – Physics - Foundation (8463/2F) Download Paper - Download Marking Scheme
Paper 2 – Physics - Higher (8463/2H) - Download Paper - Download Marking Scheme
Download Insert for all Papers
November 2021 AQA Physics GCSE (9-1) Past Papers (8463) (Labelled as June 2021)
November 2020 AQA Physics GCSE (9-1) Past Papers (8463) (Labelled as June 2020)
June 2019 AQA Physics GCSE (9-1) Past Papers (8463)
June 2018 AQA Physics GCSE (9-1) Past Papers (8463)
Paper 1 – Physics - Higher (8463/1H) Download Paper - Download Marking Scheme
Paper 2 – Physics - Higher (8463/2H) Download Paper - Download Marking Scheme
AQA Physics GCSE (9-1) Specimen Papers (8463)
Paper 1 – Physics - Foundation (8463/1F) Download Paper - Download Marking Scheme
Paper 1 – Physics - Higher (8463/1H) Download Paper - Download Marking Scheme
Paper 2 – Physics - Foundation (8463/2F) Download Paper - Download Marking Scheme
Paper 2 – Physics - Higher (8463/2H) Download Paper - Download Marking Scheme

June 2017 AQA Physics GCSE Past Exam Papers (4403)
June 2017 Science A – Unit 1 Physics P1 Foundation (PH1FP) - Download Paper - Download Marking Scheme June 2017 Science A – Unit 1 Physics P1 Higher (PH1HP) - Download Paper - Download Marking Scheme Download Inserts for both papers
June 2017 Additional Science – Unit 2 Physics P2 Foundation (PH2FP) - Download Paper - Download Marking Scheme June 2017 Additional Science – Unit 2 Physics P2 Higher (PH2HP) - Download Paper - Download Marking Scheme Download Inserts for both papers
June 2017 Physics – Unit 3 Physics P3 Foundation (PH3FP) - Download Paper - Download Marking Scheme June 2017 Physics – Unit 3 Physics P3 Higher (PH3HP) - Download Paper - Download Marking Scheme Download Inserts for both papers
June 2016 AQA Physics GCSE Past Exam Papers (4403)
June 2016 Science A – Unit 1 Physics P1 Foundation (PH1FP) - Download Paper - Download Marking Scheme June 2016 Science A – Unit 1 Physics P1 Higher (PH1HP) - Download Paper - Download Marking Scheme Download Inserts for both papers
June 2016 Additional Science – Unit 2 Physics P2 Foundation (PH2FP) - Download Paper - Download Marking Scheme June 2016 Additional Science – Unit 2 Physics P2 Higher (PH2HP) - Download Paper - Download Marking Scheme Download Inserts for both papers
June 2016 Physics – Unit 3 Physics P3 Foundation (PH3FP) - Download Paper - Download Marking Scheme June 2016 Physics – Unit 3 Physics P3 Higher (PH3HP) - Download Paper - Download Marking Scheme Download Inserts for both papers
June 2015 (4403)
Science A – Unit 1 Physics P1 Foundation (PH1FP) - Download Paper - Download Marking Scheme Science A – Unit 1 Physics P1 Higher (PH1HP) - Download Paper - Download Marking Scheme
Additional Science – Unit 2 Physics P2 Foundation (PH2FP) - Download Paper - Download Marking Scheme Additional Science – Unit 2 Physics P2 Higher (PH2HP) - Download Paper - Download Marking Scheme
Physics – Unit 3 Physics P3 Foundation (PH3FP) - Download Paper - Download Marking Scheme Physics – Unit 3 Physics P3 Higher (PH3HP) - Download Paper - Download Marking Scheme

Welcome, Login to your account.
Recover your password.
A password will be e-mailed to you.

PHYSICS TOPIC BY TOPIC QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
physics topic by topic questions and answers , you can download all the physics questions and answers for all topics for form 1, form 2, form 3 and form 4., the list includes all physics questions with their answers. use the links below. click on a link to a specific material., physics practicals instructions guide teacher.co.ke, physics p1 summarised notes teacher.co.ke, physics form one quick revision questions and answers teacher.co.ke, physics form 1-4 notes booklet teacher.co.ke, physics form 1 revision booklet teacher.co.ke, form 4_41. electronics q, form 4_41. electronics a, form 4_40. radioactivity q, form 4_40. radioactivity a, form 4_39. photo electric effect q, form 4_39. photo electric effect a, form 4_38. x rays q, form 4_38. x rays a, form 4_37. cathode rays a, form 4_37. cathode rays, form 4_36. mains electricity q, form 4_36. mains electricity a, form 4_35. electromagnetic induction 2q, form 4_35. electromagnetic induction 2a, form 4_34. electromagnetic spectrum q, form 4_34. electromagnetic spectrum a, form 4_33. floating and sinking q, form 4_33. floating and sinking a, form 4_32. circular motion q, form 4_32. circular motion a, form 4_31. thin lenses q, form 4_31. thin lenses a, form 4 - topic 41. electronics questions - teacher.co.ke, form 4 - topic 41. electronics a - teacher.co.ke, form 4 - topic 40. radioactivity questions - teacher.co.ke, form 4 - topic 40. radioactivity a - teacher.co.ke, form 4 - topic 39. photo electric effect questions - teacher.co.ke, form 4 - topic 39. photo electric effect a - teacher.co.ke, form 4 - topic 38. x-rays questions - teacher.co.ke, form 4 - topic 38. x-rays a - teacher.co.ke, form 4 - topic 37. cathode rays a - teacher.co.ke, form 4 - topic 37. cathode rays - teacher.co.ke, form 4 - topic 36. mains electricity questions - teacher.co.ke, form 4 - topic 36. mains electricity a - teacher.co.ke, form 4 - topic 35. electromagnetic induction 2questions - teacher.co.ke, form 4 - topic 35. electromagnetic induction 2a - teacher.co.ke, form 4 - topic 34. electromagnetic spectrum a - teacher.co.ke, form 4 - topic 34. electromagnetic spectrum questions - teacher.co.ke, form 4 - topic 33. floating and sinking questions - teacher.co.ke, form 4 - topic 33. floating and sinking a - teacher.co.ke, form 4 - topic 32. circular motion questions - teacher.co.ke, form 4 - topic 32. circular motion a - teacher.co.ke, form 4 - topic 31. thin lenses questions - teacher.co.ke, form 4 - topic 31. thin lenses a - teacher.co.ke, form 3_electrostatics ii, form 3_30. gas laws q, form 3_30. gas laws a, form 3_29. heat energy q, form 3_29. heat energy a, form 3_28. heating effect of electric current q, form 3_28. heating effect of electric current a, form 3_27. electrostatics ii q, form 3_27. electrostatics ii a, form 3_26. waves ii q, form 3_26. waves 11 a, form 3_25. current electricity q, form 3_25. current electricity a, form 3_24. work energy and power. a, form 3_24. work energy and power q, form 3_23. newtons laws of motion q, form 3_23. newtons laws of motion a, form 3_22. refraction of light q, form 3_22. refraction of light a, form 3_21. linear motion q, form 3_21. linear motion a, form 3 - topic 30. gas laws questions - teacher.co.ke, form 3 - topic 30. gas laws a - teacher.co.ke, form 3 - topic 29. heat energy questions - teacher.co.ke, form 3 - topic 29. heat energy a - teacher.co.ke, form 3 - topic 28. heating effect of electric current questions - teacher.co.ke, form 3 - topic 28. heating effect of electric current a - teacher.co.ke, form 3 - topic 27. electrostatics ii questions - teacher.co.ke, form 3 - topic 27. electrostatics ii a - teacher.co.ke, form 3 - topic 26. waves ii questions - teacher.co.ke, form 3 - topic 26. waves 11 a - teacher.co.ke, form 3 - topic 25. current electricity questions - teacher.co.ke, form 3 - topic 25. current electricity a - teacher.co.ke, form 3 - topic 24. work, energy and power. a - teacher.co.ke, form 3 - topic 24. work, energy and power questions - teacher.co.ke, form 3 - topic 23. newtons laws of motion questions - teacher.co.ke, form 3 - topic 23. newtons laws of motion a - teacher.co.ke, form 3 - topic 22. refraction of light questions - teacher.co.ke, form 3 - topic 22. refraction of light a - teacher.co.ke, form 3 - topic 21. linear motion questions - teacher.co.ke, form 3 - topic 21. linear motion a - teacher.co.ke, form 2_waves 1q, form 2_waves 1a, form 2_20. fluid flow a, form 2_20. fluid flow, form 2_19. sound q, form 2_19. sound a, form 2_17. hookes law q, form 2_17. hookes law a, form 2_16. electromagnetism 1q, form 2_16. electromagnetism 1a, form 2_15. reflection at curved surfaces q, form 2_15. reflection at curved surfaces a, form 2_14. equilibrium and c.o.g q, form 2_14. equilibrium and c.o.g a, form 2_13. turning effect of a force q, form 2_13. turning effect of a force a, form 2_12. measurements ii q, form 2_12. measurements ii a, form 2_11. magnetism q, form 2_11. magnetism a, form 2 - topic waves 1questions - teacher.co.ke, form 2 - topic waves 1a - teacher.co.ke, form 2 - topic 20. fluid flow a - teacher.co.ke, form 2 - topic 20. fluid flow - teacher.co.ke, form 2 - topic 19. sound questions - teacher.co.ke, form 2 - topic 19. sound a - teacher.co.ke, form 2 - topic 17. hooke's law questions - teacher.co.ke, form 2 - topic 17. hooke's law a - teacher.co.ke, form 2 - topic 16. electromagnetism 1questions - teacher.co.ke, form 2 - topic 16. electromagnetism 1a - teacher.co.ke, form 2 - topic 15. reflection at curved surfaces questions - teacher.co.ke, form 2 - topic 15. reflection at curved surfaces a - teacher.co.ke, form 2 - topic 14. equestionsuilibrium and c.o.g questions - teacher.co.ke, form 2 - topic 14. equestionsuilibrium and c.o.g a - teacher.co.ke, form 2 - topic 13. turning effect of a force questions - teacher.co.ke, form 2 - topic 13. turning effect of a force a - teacher.co.ke, form 2 - topic 12. measurements ii questions - teacher.co.ke, form 2 - topic 12. measurements ii a - teacher.co.ke, form 2 - topic 11. magnetism questions - teacher.co.ke, form 2 - topic 11. magnetism a - teacher.co.ke, form 1_9. electrostatics a, form 1_9. electrostatics 1q, form 1_8. rectilinear propagation of light q, form 1_8. rectilinear propagation a, form 1_7. modes of heat transfer q, form 1_7. modes of heat transfer a, form 1_6. thermal expansion q, form 1_6. thermal expansion a, form 1_5. particulate nature of matter q, form 1_5. particulate nature of matter a, form 1_4. pressure q, form 1_4. pressure a, form 1_3. force q, form 1_3. force a, form 1_2. measurements 1q, form 1_2. measurements 1a, form 1_10. cells and simple circuits q, form 1_10. cells and simple circuits a, form 1 - topic 9.electrostatics a- teacher.co.ke, form 1 - topic 9. electrostatics questions- teacher.co.ke, form 1 - topic 8. rectilinear propagation of light questions- teacher.co.ke, form 1 - topic 8. rectilinear propagation a- teacher.co.ke, form 1 - topic 7. modes of heat transfer questions- teacher.co.ke, form 1 - topic 7. modes of heat transfer a- teacher.co.ke, form 1 - topic 6. thermal expansion questions- teacher.co.ke, form 1 - topic 6. thermal expansion a- teacher.co.ke, form 1 - topic 5. particulate nature of matter questions- teacher.co.ke, form 1 - topic 5. particulate nature of matter a- teacher.co.ke, form 1 - topic 4. pressure questions- teacher.co.ke, form 1 - topic 4. pressure a- teacher.co.ke, form 1 - topic 3. force questions- teacher.co.ke, form 1 - topic 3. force a- teacher.co.ke, form 1 - topic 2. measurements 1questions- teacher.co.ke, form 1 - topic 2. measurements 1a- teacher.co.ke, form 1 - topic 10. cells and simple circuits questions- teacher.co.ke, form 1 - topic 10. cells and simple circuits a- teacher.co.ke.

Active English Grammar 1-Teacher.co.ke
Active english grammar 2-teacher.co.ke, active english grammar 3-teacher.co.ke, active english grammar 4-teacher.co.ke, active english grammar 5-teacher.co.ke, active english grammar 6-teacher.co.ke, basic english grammar-teacher.co.ke, class 6 cre notes complete-teacher.co.ke, class 7 cre notes complete-teacher.co.ke, class 8 cre notes complete-teacher.co.ke, english grammar notes complete-teacher.co.ke, grade 4 cre notes complete-teacher.co.ke, grade 4 cre notes-teacher.co.ke, guide to composition writing-teacher.co.ke, insha notes complete-teacher.co.ke, kiswahili std 5 notes-teacher.co.ke, kiswahili std 7 notes-teacher.co.ke, kiswahili 4 complete notes-teacher.co.ke, kiswahili 5 complete notes-teacher.co.ke, kiswahili 7 complete notes-teacher.co.ke, kiswahili 8 complete notes-teacher.co.ke, kiswahili grade 4 notes-teacher.co.ke, kiswahili insha-teacher.co.ke, kiswahili std 8 notes-teacher.co.ke, mathematics-revision-notes-std-7-8.
- Next Page »
You cannot print the contents of this website.
- LESSON NOTES
- LESSON PLANS
- 2021 SCHEMES
- POWERPOINT NOTES
- FORM 1 EXAMS
- FORM 2 EXAMS
- FORM 3 EXAMS
- FORM 4 EXAMS
- COMPREHENSIVE 1-4
- TOPICAL QUESTIONS
- K.C.S.E SYLLABUS
- REVISION MOCKS
- K.C.S.E REVISION
- 2018 K.C.S.E PAPERS
- 2017 K.C.S.E PAPERS
- 2016 K.C.S.E PAPERS
- 2015 K.C.S.E PAPERS
- 2014 K.C.S.E PAPERS
- 2013 K.C.S.E PAPERS
- 2012 K.C.S.E PAPERS
- 2011 K.C.S.E PAPERS
- 2010 K.C.S.E PAPERS
- 2008 K.C.S.E PAPERS
- 1996-2009 K.C.S.E PAPERS
- TOPICAL PAST PAPERS
- SECONDARY F1-4
- REVISION NOTES STD 4-8
- SCIENCE NOTES STD 4-8
- SOCIAL STUDIES NOTES STD 4-8
- COMPREHENSIVE NOTES STD 4-8
- SCIENCE POWERPOINT
- SOCIAL STUDIES POWERPOINT
- K.C.P.E TOPICAL REVISION
- BEST & WORST INSHAS
- 2018 K.C.P.E PAST PAPERS
- 2000-2017 K.C.P.E PAPERS
- SCHEMES STD 4-8
- GRADE 1 EXAMS
- GRADE 2 EXAMS
- GRADE 3 EXAMS
- GRADE 1 NOTES & CLASS READERS
- GRADE 2 NOTES & CLASS READERS
- GRADE 3 NOTES & CLASS READERS
- GRADE 1 SCHEMES OF WORK
- GRADE 2 SCHEMES OF WORK
- GRADE 3 SCHEMES OF WORK
- GRADE 1 CURRICULUM
- GRADE 2 CURRICULUM
- GRADE 3 CURRICULUM
- GRADE 1-3 SYLLABUS

Education News Hub
PHYSICS SYLLABUS COVERAGE AREAS (PAPER 1 TOPICS ARRANGED)
PHYSICS KNEC SYLLABUS AND THE CONTENTS
PAPER 1 TOPICS ARRANGED IN UNITS
Unit 1 (Measurement I and measurement II)
Measurement I
Specific objectives
By the end of the topic the learner should be able to:
- Define length, area,volume,mass,density,time interval and state the corresponding symbols and SI units
- Convert other metric units to SI units
- Estimate length, mass and time
- Use accurately various measuring instruments
- Determine experimentally the densities of substances
- Solve numerical problems on density
- Definition of length,area,volume,density and time
- Sin units and symbols
- Estimation of quantities
- Conversion of units
- Measuring instruments:metre rule, tape measure, beam balance, stop clock/watch, measuring cylinder, pipette and burette
- Experiments on density
Measurement II
By the end of the topic, the learner should be able to
- Measure length using vernier calipers and micrometer screw gauge
- Estimate the diameter of a molecule of oil
- Solve numerical problems in measurements
- Measurement of length using vernier calipers and micrometer screw gauge
- Decimal places ,significant figures and standard forms
- Estimation of the diameter of a molecule of oil(relate to the size of HIV virus ,mention the effects of oil spills on health and environment
- Problems in measurements
Unit 2 (Force, forces and moments, equilibrium and stability, Hooke’s law, particulate nature of matter)
By the end of the topic, the learner should be able to:
- Define force and state its SI unit
- Describe the types of forces
- Describe experiments to illustrate cohesion ,adhesion and cohesion
- State the effects of force
- State the difference between mass and weight, W=mg
- Define scalar and vector quantities
- Solve numerical problems involving W=mg
- Definition of force
- Types of forces (include cohesion, adhesion and surface tension
- Experiments to demonstrate cohesion, adhesion and surface tension(actual measurement of surface tension not required)
- Effects of force
- Mass, weight and their relationship
- Scalar and vector quantities
- Problems involving W=mg
Particulate nature of matter
- Give evidence that matter is made up of tiny particles
- Describe experiments to show that particles of matter are at constant random motion
- Explain the states of matter in terms of particle movement
- Explain diffusion
- Experiments to show that matter is made up of tiny particles (e.g cutting papers into small pieces ,dilution experiments etc)
- Brownian motion
- States of matter
- Diffusion (grahams law not require)
Turning effect of a force
By the end of the topic the learner should be able to;
- Define moment of a force about a point and state its SI unit
- State and verify the principle of moments
- Solve problems involving the principle of moments
Hot Downloads!!
Physics topic by topic questions and answers (all topics).
Free Physics notes, revision questions, KCSE past Papers, Exams, Marking Schemes,…
Free Secondary and Primary school notes, exams, schemes, lesson plans, revision…
Free updated schemes of work for all subjects (Secondary; Form 1-4)
KCSE Topical Revision Resources For All Subjects (Topic By Topic Questions…
Topic by Topic Revision Questions Free Downloads (All Form 1, 2,…
More Free Physics Resources.
Physics form one notes latest, free physics notes, revision questions, kcse past papers, exams, marking schemes, topical revision materials, syllabus and many more, physics free lesson plans for all topics (form one to four), physics simplified notes form 1 to 4 free, physics form 3 notes, revision questions and answers, physics form 2 notes, revision questions and answers.
- Moment of force ,SI unit of moment of a force
- Principle of moments
- Problems on principle of moments(consider single pivot only)
Equilibrium and centre of gravity
- Define center of gravity
- Determine experimentally the center of gravity of lamina objects
- Identify and explain the states of equilibrium
- State and explain factors affecting stability of an object
- Explain the applications of stability
- Solve numerical problems involving center of gravity and moments of a force
- Center of gravity (experimental treatment required)
- States of equilibrium
- Factors affecting stability
- Problems on center of gravity and moments of a force(consider single pivot only)
- Hooke’s law
- State and verify experimentally Hooke’s law
- Determine the spring constant
- Construct and calibrate a spring balance
- Solve numerical problems involving Hooke’s law
- Spring constant
- Spring balance
- Problems involving Hooke’s law
Unit 3 (Pressure, fluid flow, gas laws, floating and sinking)
Specific objective
- Define pressure and state its SI units
- Determine pressure exerted by solids
- Describe experiments to investigate factors affecting pressure in fluids
- Derive the formula p=ρgh
- State the principle of transmission of pressure in fluids (Pascal’s principle)
- Explain atmospheric pressure and its effects
- State and explain the applications of pressure
- Solve numerical problems involving pressure
- Definition of pressure
- Pressure in solids
- Factors affecting pressure in fluids(experimental treatment required0
- Derivation of p=ρgh
- Atmospheric pressure
- Simple mercury barometer, manometers
- Applications of pressure :drinking staw,syringe,siphon,hydraulic press, hydraulic brakes, bicycle pump, force pump, lift pump
- Problems on pressure
- Describe streamline flow and turbulent flow
- Derive the equation of continuity
- Describe experiments to illustrate Bernoulli’s effect
- Explain the Bernoulli’s effect
- Describe the applications of Bernoulli’s effect
- Solve numerical problems involving the equation of continuity
- Streamline flow and turbulent flow
- Equation of continuity
- Bernoulli’s effect(experimental treatment required)
- Applications of Bernoulli’s effect: Bunsen burner, spray gun,carburetor,aerofoil and spinning ball
- Problems involving the equation of continuity
- State the gas laws for ideal gas
- Verify experimentally the gas laws
- Explain how absolute zero temperature may be obtained from the pressure –temperature and volume –temperature graphs
- Convert Celsius scale to Kelvin scale of temperature
- State the basic assumptions of the kinetic theory of gases
- Explain the gas laws using the kinetic theory of gases
- Solve numerical problems involving gas laws
- Boyle’s law, Charles’ law, pressure law, absolute zero
- Kelvin scale of temperature
- Gas laws and kinetic theory of gases(p= 1 / 3 pc 2 not required)
- Problems involving gas laws (including PV / T =constant)
Floating and sinking
- State Archimedes’ principle
- Verify Archimedes’ principle
- State the law of floatation
- Define relative density
- Describe the applications of Archimedes’ principle and relative density
- Solve numerical problems involving Archimedes principles
- Archimedes’ principle ,law of floatation (experimental treatment required)
- Relative density
- Applications of Archimedes’ principle and relative density
- Problems of Archimedes’ principle
Unit 4 (Thermal expansion, heat transfer, quantity of heat)
Thermal expansion
- Define temperature
- Describe the functioning of the various thermometers
- Describe thermal expansion of solids, liquids and gases
- Explain expansion in terms of particle behavior
- Describe the unusual expansion of water and its effects
- Explain the effects and applications of thermal expansion
- Temperature
- Thermometer: liquid –in-glass, including clinical and six’s maximum and minimum thermometers
- Expansion of solids, liquids and gases
- Effects of expansion and contraction
- Unusual expansion of water(anomalous expansion0
- Applications of thermal expansion, include bimetallic strip
Heat transfer
- State the difference between temperature and heat
- State and explain the modes of heat transfer
- Describe experiments to illustrate factors affecting heat transfer
- Explain applications of heat transfer
- Heat and temperature
- Modes of heat transfer
- Factors affecting heat transfer (experimental treatment required)
- Applications of heat transfer on vacuum flask, domestic hot water system, solar concentrators
Quantity of heat
- Define heat capacity and specific heat capacity
- Determine experimentally specific heat capacity of solids and liquids
- Define specific latent heat of fusion and specific latent heat of vaporization of steam
- Determine experimentally the specific latent heat of fusion of ice and the specific latent heat of vaporization of steam
- State factors affecting melting point and boiling point
- Explain the functioning of a pressure cooker and a refrigerator
- Solve problems involving quantity of heat
- Heat capacity , specific heat capacity, units (experimental treatment required)
- Latent heat of fusion, latent heat of vaporization, units (experimental treatment required)
- Boiling and melting points
- Pressure cooker, refrigerator
- Problems involving quantity of heat ( Q=mc Δ T),Q=mL )
Unit 5 (Linear motion, Newton’s laws of motion, work, energy, uniform circular motion)
Linear motion
- Define distance,displacement,speed,velocity,and acceleration
- Describe experiments to determine velocity and acceleration
- Determine acceleration due to gravity
- Plot and explain motion time graphs
- Apply the equations of uniformly accelerated motion
- Solve numerical problems on uniformly accelerated motion
- Distance,displacement,speed,velocity,and acceleration(experimental treatment required)
- Acceleration due to gravity free-fall, simple pendulum
- Motion -time graphs-displacement time graphs, velocity time graphs
- Equations of uniformly accelerated motion
- Problems on uniformly accelerated motion
Newton’s laws of motion
- State the Newton’s laws of motion
- Describe simple experiments to illustrate inertia
- State the law of conservation of linear momentum
- Define elastic collision, inelastic collision and impulse
- Derive the equation F=ma
- Describe the application of frictional force
- Define viscosity
- Explain terminal velocity
- Solve numerical problems involving Newton’s laws and the law of conservation of linear momentum
- Newton’s laws of motion (experimental treatment of inertia required)
- Conservation of linear momentum ,elastic collisions, inelastic collisions, recoil velocity ,impulse (oblique collisions not required)
- The relation F=ma
- Frictional force
- Advantages and disadvantages
- Viscosity and terminal velocity (qualitative treatment only)
- Problems involving Newton’s laws and the law of conservation of linear momentum(exclude problems on elastic collisions)
Work energy power and machines
- Describe energy transformation
- State the law of conservation of energy
- Define work,energy,power,and state their SI units
- Define mechanical advantage ,velocity ratio and efficiency of machines
- Solve numerical problems involving work,energy,power and machines
- Forms of energy and energy transformations
- Sources of energy-renewable ,non-renewable
- Law of conservation of energy
- Work, energy and power (work done by resolved force not required)
- Kinetic energy and potential energy
- Simple machines
- Problems of work,energy,power and machines
Uniform circular motion
- Define angular displacement and angular velocity
- Describe simple experiments to illustrate centripetal force
- Explain the applications of uniform circular motion
- Solve numerical problems involving uniform circular motion
- The radian, angular displacement and angular velocity
- Centripetal force; the relations F=mv 2 / r ,F=mrω 2 (derivation of the formula not necessary experimental treatment required)
- Applications of uniform circular motion
- Centrifuge, vertical ,horizontal circles, banked tracks(calculation on banked tracks and conical pendulum not required)
- Problems solving (applications of relations F=mv 2 /r ,F=mrw 2 in numerical calculations)
PAPER 2 TOPICS ARRANGED IN UNITS
Unit 1 (Rectilinear propagation, reflection at curved surfaces, refraction of light and thin lenses)
Rectilinear propagation of light
- Perform and describe experiments to show that light travels in a straight line
- Describe the formation of shadows and eclipses
- Explain the functioning of a pin-hole camera
- State the laws of reflection
- Verify experimentally laws of reflection
- State the characteristics of images formed by plane mirrors
- Explain the applications of reflection at plane surfaces
- Solve numerical problems involving pinhole camera and mirrors inclined at an angle
- Rectilinear propagation of light(experimental treatment required)
- Formation of shadows and eclipses(umbra and penumbra)
- Pin-hole camera :image formation and magnification
- Laws of reflection
- Images formed by plane mirrors, ray diagrams, parallel and inclined mirrors
- Devices based on reflection:periscope,kaleidoscope
- Problems on pin-hole camera and mirrors inclined at an angle
Reflection at curved surfaces
- Describe concave,convex,and parabolic reflectors
- Describe using ray diagram the principal axis, principal focus, center of curvature and related terms
- Locate images formed by curved mirrors by construction of ray diagrams
- Determine experimentally the characteristics of images formed by a concave mirror
- Define magnification
- Explain the applications of curved reflecting surfaces
- Concave, convex and parabolic reflectors
- Principal axis, principal focus, center of curvature and related terms
- Location of images formed by curved mirrors by ray diagram method(experiments on concave mirrors required)
- Magnification formula
- Application of curved reflectors
Refraction of light
By the end topic the learner should be able to:
- Describe simple experiments to illustrate refraction of light
- State the laws refraction of light
- Verify Snell’s law
- Define refractive index
- Determine experimentally the refractive index
- Describe experiments to illustrate dispersion of white light
- Explain total internal reflection and its effect
- State the application of total internal reflection
- Solve numerical problems involving refractive index and critical angle
- Refraction of light-laws of refraction (experimental treatment required)
- Determination of refractive index-Snell’s law, real/apparent depth ,critical angle
- Dispersion of white light (experimental treatment required)
- Total internal reflection and its effect: critical angle
- Application of total internal reflection-prism periscope, optical fibres
- Problems involving refractive index and critical angle
Thin lenses
- Describe converging lenses and diverging lenses
- Describe using ray diagrams the principal focus, the optical centre and the focal length of a thin lens
- Determine experimentally the focal length of a converging lens
- Locate images formed by thin lenses using ray diagram construction method
- Describe the characteristics of images formed by thin lenses
- Explain image formation in the human eye
- describe the defects of vision in the human eye and how they can be corrected
- Describe the use of lenses in various optical devices
- Solve numerical problems involving the lens formula and the magnification formula
- Types of lenses
- Ray diagrams and terms used
- Images formed –ray diagrams,characteristics,magnification
- Determination of focal length:(experimental treatment required-estimation method, lens formula, lens-mirror method
- Human eye, defects (short sightedness and long sightedness)
- Optical devices –simple microscope ,compound microscope, the camera
- Problem involving the lens formula and the magnification
Unit 2 (Cells and simple circuits, current electricity, heating effect of electric current, mains electricity)
Cells and simple circuits
- Draw and set-up simple electric circuits
- Identify circuit symbols
- Define electric current
- Explain the working of primary and secondary cells
- Explain the care and maintenance of secondary cells
- Simple electric circuits:cell,ammeter,voltmeter,variable resistor, connecting wires bulbs and switches
- Circuit symbols
- Electric current and its SI unit
- Primary and secondary cells. (simple cell, dry Leclanche cell, lead acid cell)
Current electricity
- Define potential difference and state its SI unit
- Measure potential difference and electric current in a circuit
- Verify ohm’s law
- Define resistance and state its si unit
- Determine experimentally the voltage –current relationship[s for various conductors
- Define m.f and explain internal resistance of a cell
- Derive the formula for effective resistance of resistors in series and in parallel
- Solve numerical problems involving ohm’s law,resisitors in series and in parallel
- Scale reading :ammeter, voltmeter
- Electric circuits:current,potential difference
- Ohm’s law (experimental treatment required)
- Resistance: types of resistors, measurement of resistance, unit of resistance
- Electromotive force (e.m.f) and internal resistance of a cell. The relation (E=V+Ir)
- Resistors in series and parallel
- Problems involving ohm’s law resistors in series and parallel
Heating effect of electric current
- Perform and describe experiments to illustrate heating effect of an electric current
- State the factors affecting the heating e by an electric current
- Derive the equation for electrical energy and electrical power
- Identify devices in which heating effect of an electric current is applied
- Solve numerical; problems involving electrical energy and electrical power
- Simple experiments on heating effect
- Factors affecting electrical energy, the relation P=VIt and P=VI
- Heating devices :electric kettle, electric iron, bulb filament, electric heater
- Problems involving electrical energy and electrical power
Mains electricity
- State the source of mains electricity
- Describe the transmission of electric power from the generating station to the consumer
- Explain the domestic wiring system
- Define the kilowatt hour
- Determine the electrical energy consumption and cost
- Solve numerical problems involving mains electricity
- Sources of mains electricity eg. Geothermal ,hydro, nuclear e.t.c
- Power transmission (include dangers of high voltage transmission)
- Domestic wiring system
- Kwh,consumption and cost of electricity
- Problems involving mains electricity
Unit 3 (Electrostatic I and II)
Electrostatics I
- Describe electrostatic charging of objects by rubbing(experimental treatment required)
- Explain the sources of electrostatic charges
- State the two types of charges
- State the basic law of charges (electrostatics)
- State the unit of charge
- Construct a simple leaf electroscope
- Use a charged leaf electroscope to identify conductors , insulators and types of charge
- Electrostatic charging of objects by rubbing 9experimetal treatment required)
- Types of charges and law of charges
- The coulomb
- Leaf electroscope :features ,charging and discharging
- Charging by contact and induction
- Identification of charge
- Conductors and insulators
Electrostatic II
- Sketch electric field patterns around charged bodies
- Describe charge distribution on conductors of various shapes
- Define capacitance and state its SI unit
- Describe charging and discharging of a capacitor (calculation involving curves not required)
- State the factors affecting the capacitance of a parallel plate capacitors
- Sate the applications of capacitors
- Solve numerical problems involving capacitors.
- Electric field patterns
- Charge distribution on conductors :spherical and pear shaped conductors
- Action at points: lightning arrestors
- Capacitance: unit of capacitance(farad ,microfarad)factors affecting capacitance
- Applications of capacitors
- Problems involving capacitors (using Q=CV,C t =C 1 +C 2 1 / ct = 1 / c1 + 1 / c2 )
Unit 4 (Waves I and II,sound,electromagnetic spectrum)
- Describe the formation of pulse and waves
- Describe transverse and longitudinal waves
- Define amplitude (a), wavelength(λ),frequency (f) and periodic time(T) of a wave
- Derive the relation v=fλ
- Solve numerical problems involving v=fλ
- Pulse and waves
- Transverse and longitudinal waves
- Amplitude (a) ,wavelength(λ),frequency (f) and periodic time(t)
- Relation v=fλ
- Problems involving v=fλ
- Describe experiment to illustrate the properties of waves
- Sketch wave-fronts to illustrate the properties of waves
- Explain constructive interference and destructive interference
- Describe experiments to illustrate stationary waves
- Properties of waves including sound waves,reflection,refraction,diffraction and interfence (experimental treatment required)
- Constructive interference and destructive interference(qualitative treatment only)
- Stationary waves(qualitative and exp erimental treatment only)
- Perform and describe simple experiments to show that sound is produced by vibrating bodies
- Perform and describe an experiment to show that sound requires a material medium for propagation
- Explain the nature of sound waves
- Determine the speed of sound in air by echo method
- State the factors affecting the speed of sound
- Solve numerical problems involving speed of sound
- Sound :nature and source (experimental treatment
- Propagation of sound: compressions and rarefactions
- Speed of sound by echo method
- Factors affecting speed of sound
- Problems involving speed of sound
- Electromagnetic spectrum
- Describe the complete electromagnetic spectrum
- State the properties of electromagnetic waves
- Describe the methods of detecting electromagnetic radiations
- Describe the applications of electromagnetic radiations
- Solve numerical problems involving c=fλ
- Properties of electromagnetic waves
- Detection of electromagnetic radiations
- Applications of electromagnetic radiations (include green house effect)
- Problems involving c=fλ
Unit 5 (Magnetism,magnetic effect of electric current,electromagnetic induction)
- Describe the properties and use of magnets
- Identify magnetic and non-magnetic materials
- State the basic law of magnetism
- Describe patterns of magnetic field
- Describe methods of magnetization and demagnetization
- Explain magnetization and demagnetization using the domain theory
- Construct a simple compass
- Magnets: properties and uses
- Magnetic and non-magnetic materials
- Basic law of magnetism
- Magnetic field patterns
- Magnetization and demagnetization
- Domain theory of magnetism
- Care of magnets
- Construction of simple magnetic compass
Magnetic effect of electric current
- Perform and describe experiments to determine the direction of the magnetic field round a current carrying conductor
- Construct a simple electromagnet
- State the factors affecting the strength of an electromagnet
- Determine experimentally the direction of a force on a conductor carrying current in a magnetic field(motor effect)
- State the factors affecting force on a current carrying conductor in a magnetic field
- Explain the working of simple electric motor and electric bell
- Magnetic field due to a current
- Oersted’s experiment
- Magnetic field patterns on straight conductor and solenoid(right hand grip rule)
- Simple electromagnets
- Factors affecting the strength of an electromagnet
- Motor effect (Fleming’s left hand rule)
- Factors affecting force on a current carrying conductor in a magnetic field (qualitative treatment only)
- Applications-electric bell, simple electric motor
Electromagnetic induction
- Perform and describe simple experiments to illustrate electromagnetic induction
- State the factors affecting the magnitude and the direction of the induced e.m.f
- State the laws of electromagnetic induction
- Describe simple experiments to illustrate mutual induction
- Explain the working of an alternating current(a.c) generator and direct current (d.c) generator
- Explain the applications of electromagnetic induction
- Solve numerical problems involving transformers
- Simple experiments to illustrate electromagnetic induction
- Induced e.m.f –faradays law ,Lenz’s law
- Mutual induction
- Alternating current(a.c) generator and direct current (d.c) generator
- Fleming’s right hand –rule
- Transformers
- Applications of electromagnetic induction
- Problems involving transformers
(Photoelectric effect, X-rays, cathode rays, radioactivity and electronics)
Cathode rays and cathode ray tube
- Describe the production of cathode rays
- State the properties of cathode rays
- Explain the functioning of a cathode rays oscilloscope (C.R.O ) and a television tube (TV tube )
- Explain the use of a cathode ray oscilloscope
- Solve numerical problems involving cathode rays oscilloscope
- Production of cathode rays
- Properties of cathode rays
- R.O and TV tube
- Uses of CRO
- Problems involving CRO
- Explain the production of x-rays
- State the properties of x-rays
- State the dangers of x-rays
- Explain the uses of x-rays
- Production of X-ray, X-ray tube
- Energy changes in an x-ray tube
- Properties of X-rays
- Soft and hard X-rays
- Dangers of X-rays and precautions
- Uses of X-rays (Bragg’s law not required)
Photoelectric effect
- Perform and describe simple experiments to illustrate the photoelectric effect
- Explain the factors that affect photoelectric emission
- Apply the equation E =hf to calculate the energy of photons
- Define threshold frequency, work function and electron volt
- Explain photoelectric emission using Einstein equation(hf o + 1 / 2 mv 2 =hf)
- Explain the applications of photoelectric effect
- Solve numerical problems involving photoelectric emissions
- Photoelectric effect,photon,threshold frequency, work function, Planck’s constant and electron volt
- Factors affecting photoelectric emission
- Energy of photons
- Einstein equation(hf o + 1 / 2 mv 2 =hf)
- Applications of photoelectric effect-photo emissive cells, photo conductive cells, photovoltaic cells
Radioactivity
- Define radioactive decay and half life
- Describe the three types of radiation emitted in natural radioactivity
- Explain the detection of radioactive emissions
- Define nuclear fission and fusion
- Write balanced nuclear equations
- Explain the dangers of radioactive emissions
- State the applications of radioactivity
- Solve numerical problems involving half-life
- Radioactive decay
- Types of radiation, properties of radiations
- Detectors of radiations
- Nuclear fission and fusion
- Nuclear equations
- Hazards of radioactivity ,precautions
- Applications
- Problems of half-life(integration not required)
Electronics
- State the difference between conductors and insulators
- Define intrinsic and extrinsic semi-conductors
- Explain doping in semi-conductors
- Explain the working of a p-n junction diode
- Sketch current –voltage characteristic for a diode
- Explain the application of diodes in rectification
- Conductors,semi-conductors,insulators
- Intrinsic and extrinsic semi-conductors
- P-n junction diode
- Application of diodes: half wave rectification and full wave rectification
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
We are aware of some issues with pdfs on the website after last night's update. Some should now be fixed and others will be later today.

AQA A-Level Physics Revision
As papers 1 & 2, a-level paper 1, a-level paper 2, a-level paper 3, section b one of:.
- Revision Courses
- Past Papers
- Solution Banks
- University Admissions
- Numerical Reasoning
- Legal Notices
KNEC KCSE Physics Exam Topics Tested in Paper 1 and Paper 2

The beauty of KNEC KCSE physics exam papers is that the questions tested are normally organized according to topics. That is, topics are grouped in form of papers, paper 1 and paper 2.
There are 19 topics that are normally set in KNEC KCSE physics paper 1 and some 22 topics in paper 2.
These lists of topics will guide you as the student to know the areas that are usually set in each paper.
This will save you time so that during your study, you will only focus on specific areas set in paper 1 or paper 2 when studying for that paper.
Topics Set in the KNEC KCSE Physics Paper 1

KNEC KCSE Physics Paper 2 Topics
There you have it! I hope these KNEC KCSE physics exam topics will guide you to understand and know exactly the areas tested in each physics exam paper.
Areas that are mainly set in KCSE physics paper 3 include Mechanics, Optics and Electricity.
- Secondary KCSE Syllabus in PDF Format for all Subjects
- FREE KNEC PAST KCSE REVISION PAPERS
- Secondary School Notes
- Schemes of Work for Secondary Schools in Kenya
- Privacy Overview
- Strictly Necessary Cookies
- Cookie Policy
This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
Strictly Necessary Cookie should be enabled at all times so that we can save your preferences for cookie settings.
More information about our Cookie Policy
share this!
April 1, 2024
This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies . Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
The search for the perfect coronagraph to find Earth 2.0
by Mark Thompson, Universe Today
Studying exoplanets is made more difficult by the light from the host star. Coronagraphs are devices that block out the star light and both JWST and Nancy Grace Roman Telescope are equipped with them. Current coronagraphs are not quite capable of seeing other Earths but work is underway to push the limits of technology and even science for a new, more advanced device. A paper published on the arXiv pre-print server explores the quantum techniques that may one day allow us to make such observations.
Coronagraphs are devices that attach to telescopes and were originally designed to study the corona of the sun. The corona is the outermost layer of the sun's atmosphere but is usually hidden from view from the bright light emitted from the photosphere (the visible layer).
The device has also been modified to hide the light from stars to study faint objects in their vicinity. These stellar coronagraphs are often employed to hunt for extrasolar planets and the disks out of which they form.
There are a number of techniques to identify extrasolar planets but direct imaging is one of the chief ways to learn about their nature. The challenge, which is met by the stellar coronagraph , is the brightness of the star and the relative faintness of the planet and proximity to the star.
Coronagraphs can increase the ratio between noise (in this instance the light from the star) and the signal from the exoplanet by optically removing the light from the star. In the paper, authors Nico Deshler, Sebastian Haffert and Amit Ashok from the University of Arizona explore whether coronagraphs are the best method for hunting exoplanets.
Studying exoplanets is important to help us to learn about planetary formation, atmospheric sciences and even perhaps, the origins of life. The team approached their analysis of coronagraphic techniques by considering first the detection step and then the localization task in exoplanets research.
They first undertook a hypothesis test to see if it was likely an exoplanet existed. If the prediction played out and an exoplanet was found to exist then the team attempted to estimate its position. Turning to quantum limits for telescopic resolution, they used quantum mechanics to produced a limit of the position of the exoplanet.
The team then compared classical direct imaging coronagraphs to the quantum predictions above. It should be noted that this research was focusing on the capability of present coronagraphs to detect Earth-like exoplanets using quantum theory.
The research concludes that the complete rejection of a telescopes optical mode is key to achieving the best possible detection techniques. Host star and planet separations that are so close as to be below the diffraction limit of the telescopes are thought to be abundant across the universe. It is therefore necessary that quantum-optimal coronagraphs are developed and it is encouraging that this research finds they will yield some impressive results.
Journal information: arXiv
Provided by Universe Today
Explore further
Feedback to editors
Astronomers find 10 new millisecond pulsars in globular cluster Terzan 5
4 minutes ago
Spain's giant hail event worsened by marine heat waves, study finds

New research reveals that chickens were widely raised across southern Central Asia from 400 BCE
3 hours ago

AI improves monsoon rainfall predictions
16 hours ago

82% of EU farm subsidies bolster high emissions foods: Study

Leaves of three, let it be? Wide variability among poison ivy plants makes identification more challenging

Golfers' risk from pesticides used on turf grass is likely low, studies find

'Frankenstein design' enables 3D printed neutron collimator
New antibiotic class effective against multidrug-resistant bacteria discovered
17 hours ago
Computational tools fuel reconstruction of new and improved bird family tree
Relevant physicsforums posts, is there an equivalent "redshift" for cosmic rays due to expansion, tv series: 3 body problem - affects gravitational force.
9 hours ago
U.S. Solar Eclipses - Oct. 14, 2023 (Annular) & Apr. 08, 2024 (Total)
Mar 31, 2024
Our Beautiful Universe - Photos and Videos
Where are the black holes.
Mar 30, 2024
Terminology for motion in the solar system, ecliptic maybe?
More from Astronomy and Astrophysics
Related Stories

How Webb's coronagraphs reveal exoplanets in the infrared
Mar 27, 2023
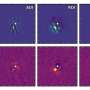
First exoplanet image from James Webb Space Telescope revealed
Sep 1, 2022

NASA puts next-gen exoplanet-imaging technology to the test
Jan 31, 2024

An ambitious new technology might be needed to see other Earths
Sep 19, 2023

In a research first, team uses precision astrometry to discover new exoplanet outside Earth's solar system
Apr 13, 2023

One exciting way to find planets: Detect the signals from their magnetospheres
Aug 17, 2022
Recommended for you

Curiosity rover searches for new clues about Mars' ancient water

Astronomers conduct first search for forming planets with James Webb Space Telescope
Mar 27, 2024

Climate change is messing with how we measure time: Study

'Cosmic cannibals' expel jets into space at 40% speed of light

Best geologic map created for a European rover on Mars
New nearby mini-Neptune exoplanet discovered
Mar 26, 2024
Let us know if there is a problem with our content
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form . For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines ).
Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request
Thank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.
E-mail the story
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Phys.org in any form.
Newsletter sign up
Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox. You can unsubscribe at any time and we'll never share your details to third parties.
More information Privacy policy
Donate and enjoy an ad-free experience
We keep our content available to everyone. Consider supporting Science X's mission by getting a premium account.
E-mail newsletter

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
What's assessed. Topics 5-8: Forces; Waves; Magnetism and electromagnetism; and Space physics. Questions in paper 2 may draw on an understanding of energy changes and transfers due to heating, mechanical and electrical work and the concept of energy conservation from Energy and Electricity. How it's assessed. Written exam: 1 hour 45 minutes.
Kick-start your revision with our 2-day online Physics GCSE Easter revision courses for AQA and Edexcel IGCSE. ... Paper 1. Topic 1: Energy. Topic 2: Electricity. Topic 3: Particle Model of Matter. Topic 4: Atomic Structure. Paper 2. Topic 5: Forces. Topic 6: Waves. Topic 7: Magnetism and Electromagnetism. Topic 8: Space Physics. Practical ...
You can find all of our AQA Physics resources right here, including the topics for AQA Physics Paper 1. We also have knowledge organisers for revision, lesson packs, practice exams and more! 5. Forces. Forces and their Interactions. Resultant Forces. Work Done and Energy Transfer. Forces and Elasticity.
2. Plane mirrors for seeing oneself 3. Telescopes 4. Kaleidoscope Two plane mirrors are inclined at an angle of 30o to each other. Determine the number of images observed Answer N = 360 - 1 θ = 360 - 1 30 -1 N = 11 Images Practice Question 1. At what angle must two plane mirrors be inclined for them to form 5 images?
AQA Physics 2 (8464/P/2) You can find all AQA Science GCSE (8464) Physics Paper 2 past papers and mark schemes, as well as selected model answers and video solutions, below: Physics Equations Sheet.
NEW & IMPROVED VERSION: https://youtu.be/31dJ57mEKssBuy me a coffee! https://bit.ly/scienceshortsdonate pdf: http://scienceshorts.net/resourcesSpace & Lenses...
GCSE Physics Paper 2. Forces. Waves. Magnetism. Space Physics (Triple Only) Required Practicals.
GCSE Physics: exam-style questions. Use our interactive tests to understand how the AQA foundation and higher physics GCSE exams work. Revise topics such as forces and learn equations and formulae.
Separate Science - Physics Paper 2. By: Revision Monkey. 239 Cards -. 4 Decks -. 458 Learners. Sample Decks: Separate Physics - P5 Forces, Separate Physics - P6 Waves, Separate Physics - P7 Magnetism and Electromagnetism. Show Class. Combined Science - Physics Paper 1 (Foundation)
The number of topics in your GCSE Physics course depends on the exam board you are sitting your exams with. That being said, most exam boards cover the same basic concepts of physics. These include motion and forces, energy, the particle model of matter, atomic structure and nuclear physics, electricity and circuits, magnetism, waves and ...
when an elastic object gets stretched too much and it become plastic. moment of a force. force x perpendicular distance from pivot to the line of action of the force. See more. AQA GCSE Physics Paper 2. 3.6 (8 reviews) vectors. Click the card to flip 👆. forces with magnitude and direction.
Question paper (Higher): Paper 2 - June 2022 Published 14 Jul 2023 | PDF | 1.4 MB Question paper (Modified A4 18pt) (Higher): Paper 2 - June 2022
AQA GCSE Physics Paper 2 Revision Topic 5: Forces Calculating pressure Pressure can be calculated using: P = F/A Where P is pressure (Pa), F is force (N) and A is surface area (m2). The force from the fluid acts at right angles (normal) to the surface. Note: A fluid is a liquid or a gas. The pressure in a liquid increases with
This playlist covers all of the Paper 2 topics (P5:Forces, P6:Waves and P7:Magnetism & Electromagnetism) for Combined Science. Hope you find this really help...
GCSE Physics questions by topic, past papers, videos and more for AQA. Home. ... Past Paper Questions by Topic. Notes. Videos. Past Papers. Specification. Flashcards by Collins. Bring Your Notes to Life with the AI Quiz Generator. Simply reading textbooks often isn't enough to solidify knowledge. Instead of just taking notes, transform your ...
GCSE. Level 2. 5 chapters. 48 Lessons. 10 Free lessons. Exam-board-specific online course, featuring fast-paced tutorials taught by Mike, practice and test mode quizzing and checkpoint assessments preparing you for your Physics Paper 2 exam. We recommend that you study the Physics Paper 1 and The Roadmap courses along with this GCSE.
Oxford AQA International AS Physics. Past Papers. Exam paper questions organised by topic and difficulty. Our worksheets cover all topics from GCSE, IGCSE and A Level courses. Give them a try and see how you do!
June 2016 AQA Physics GCSE Past Exam Papers (4403) June 2016 Science A - Unit 1 Physics P1 Foundation (PH1FP) - Download Paper - Download Marking Scheme. June 2016 Science A - Unit 1 Physics P1 Higher (PH1HP) - Download Paper - Download Marking Scheme. Download Inserts for both papers. June 2016 Additional Science - Unit 2 Physics P2 ...
Join Kenya's Largest Teachers Telegram Group with Over 80K Teachers FORM 1-4 CLASS 7-8 GRADE 1-6 PP1-PP2 KASNEB PTE. Physics Topic By Topic Questions and Answers for All Topics in Form 1, Form 2, Form 3 and Form 4 for Kenya Secondary Schools in preparation for KCSE .
PHYSICS KNEC SYLLABUS AND THE CONTENTS PAPER 1 TOPICS ARRANGED IN UNITS Unit 1(Measurement I and measurement II) Measurement I Specific objectives By the end of the topic the learner should be able to: Define length, area,volume,mass,density,time interval and state the corresponding symbols and SI units Convert other metric units to SI units Estimate length, The best site for education, TSC ...
AQA A-Level Physics Revision. Final exams on the horizon? Kick-start your revision with our 4-day online A Level Physics Easter revision courses for AQA, Edexcel and OCR (A). Check them out now! For each of the papers below, there are revision notes, summary sheets, questions from past exam papers separated by topic and other worksheets.
19. Radioactivity. F4. 20. Electronics. F4. There you have it! I hope these KNEC KCSE physics exam topics will guide you to understand and know exactly the areas tested in each physics exam paper. Areas that are mainly set in KCSE physics paper 3 include Mechanics, Optics and Electricity.
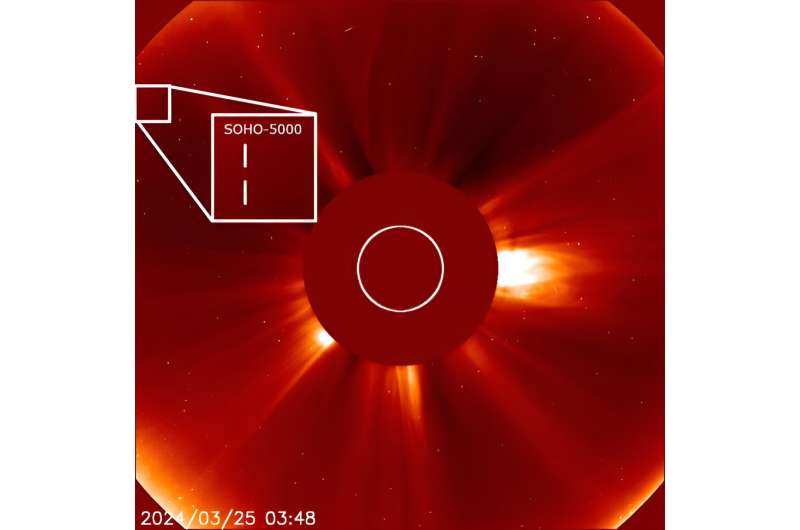
The search for the perfect coronagraph to find Earth 2.0. by Mark Thompson, Universe Today. The 5,000th comet discovered with the Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO) spacecraft is noted by a ...