
How to Critique an Article: Mastering the Article Evaluation Process

Did you know that approximately 4.6 billion pieces of content are produced every day? From news articles and blog posts to scholarly papers and social media updates, the digital landscape is flooded with information at an unprecedented rate. In this age of information overload, honing the skill of articles critique has never been more crucial. Whether you're seeking to bolster your academic prowess, stay well-informed, or improve your writing, mastering the art of article critique is a powerful tool to navigate the vast sea of information and discern the pearls of wisdom.
How to Critique an Article: Short Description
In this article, we will equip you with valuable tips and techniques to become an insightful evaluator of written content. We present a real-life article critique example to guide your learning process and help you develop your unique critique style. Additionally, we explore the key differences between critiquing scientific articles and journals. Whether you're a student, researcher, or avid reader, this guide will empower you to navigate the vast ocean of information with confidence and discernment. Still, have questions? Don't worry! We've got you covered with a helpful FAQ section to address any lingering doubts. Get ready to unleash your analytical prowess and uncover the true potential of every article that comes your way!
What Is an Article Critique: Understanding The Power of Evaluation
An article critique is a valuable skill that involves carefully analyzing and evaluating a written piece, such as a journal article, blog post, or news article. It goes beyond mere summarization and delves into the deeper layers of the content, examining its strengths, weaknesses, and overall effectiveness. Think of it as an engaging conversation with the author, where you provide constructive feedback and insights.
For instance, let's consider a scenario where you're critiquing a research paper on climate change. Instead of simply summarizing the findings, you would scrutinize the methodology, data interpretation, and potential biases, offering thoughtful observations to enrich the discussion. Through the process of writing an article critique, you develop a critical eye, honing your ability to appreciate well-crafted work while also identifying areas for improvement.
In the following sections, our ' write my paper ' experts will uncover valuable tips on and key points on how to write a stellar critique, so let's explore more!
Unveiling the Key Aims of Writing an Article Critique
Writing an article critique serves several essential purposes that go beyond a simple review or summary. When engaging in the art of critique, as when you learn how to write a review article , you embark on a journey of in-depth analysis, sharpening your critical thinking skills and contributing to the academic and intellectual discourse. Primarily, an article critique allows you to:
%20(3).webp)
- Evaluate the Content : By critiquing an article, you delve into its content, structure, and arguments, assessing its credibility and relevance.
- Strengthen Your Critical Thinking : This practice hones your ability to identify strengths and weaknesses in written works, fostering a deeper understanding of complex topics and critical evaluation skills.
- Engage in Scholarly Dialogue : Your critique contributes to the ongoing academic conversation, offering valuable insights and thoughtful observations to the existing body of knowledge.
- Enhance Writing Skills : By analyzing and providing feedback, you develop a keen eye for effective writing techniques, benefiting your own writing endeavors.
- Promote Continuous Learning : Through the writing process, you continually refine your analytical abilities, becoming an avid and astute learner in the pursuit of knowledge.
How to Critique an Article: Steps to Follow
The process of crafting an article critique may seem overwhelming, especially when dealing with intricate academic writing. However, fear not, for it is more straightforward than it appears! To excel in this art, all you require is a clear starting point and the skill to align your critique with the complexities of the content. To help you on your journey, follow these 3 simple steps and unlock the potential to provide insightful evaluations:
%20(4).webp)
Step 1: Read the Article
The first and most crucial step when wondering how to do an article critique is to thoroughly read and absorb its content. As you delve into the written piece, consider these valuable tips from our custom essay writer to make your reading process more effective:
- Take Notes : Keep a notebook or digital document handy while reading. Jot down key points, noteworthy arguments, and any questions or observations that arise.
- Annotate the Text : Underline or highlight significant passages, quotes, or sections that stand out to you. Use different colors to differentiate between positive aspects and areas that may need improvement.
- Consider the Author's Purpose : Reflect on the author's main critical point and the intended audience. Much like an explanatory essay , evaluate how effectively the article conveys its message to the target readership.
Now, let's say you are writing an article critique on climate change. While reading, you come across a compelling quote from a renowned environmental scientist highlighting the urgency of addressing global warming. By taking notes and underlining this impactful quote, you can later incorporate it into your critique as evidence of the article's effectiveness in conveying the severity of the issue.
Step 2: Take Notes/ Make sketches
Once you've thoroughly read the article, it's time to capture your thoughts and observations by taking comprehensive notes or creating sketches. This step plays a crucial role in organizing your critique and ensuring you don't miss any critical points. Here's how to make the most out of this process:
- Highlight Key Arguments : Identify the main arguments presented by the author and highlight them in your notes. This will help you focus on the core ideas that shape the article.
- Record Supporting Evidence : Take note of any evidence, examples, or data the author uses to support their arguments. Assess the credibility and effectiveness of this evidence in bolstering their claims.
- Examine Structure and Flow : Pay attention to the article's structure and how each section flows into the next. Analyze how well the author transitions between ideas and whether the organization enhances or hinders the reader's understanding.
- Create Visual Aids : If you're a visual learner, consider using sketches or diagrams to map out the article's key points and their relationships. Visual representations can aid in better grasping the content's structure and complexities.
Step 3: Format Your Paper
Once you've gathered your notes and insights, it's time to give structure to your article critique. Proper formatting ensures your critique is organized, coherent, and easy to follow. Here are essential tips for formatting an article critique effectively:
- Introduction : Begin with a clear and engaging introduction that provides context for the article you are critiquing. Include the article's title, author's name, publication details, and a brief overview of the main theme or thesis.
- Thesis Statement : Present a strong and concise thesis statement that conveys your overall assessment of the article. Your thesis should reflect whether you found the article compelling, convincing, or in need of improvement.
- Body Paragraphs : Organize your critique into well-structured body paragraphs. Each paragraph should address a specific point or aspect of the article, supported by evidence and examples from your notes.
- Use Evidence : Back up your critique with evidence from the article itself. Quote relevant passages, cite examples, and reference data to strengthen your analysis and demonstrate your understanding of the article's content.
- Conclusion : Conclude your critique by summarizing your main points and reiterating your overall evaluation. Avoid introducing new arguments in the conclusion and instead provide a concise and compelling closing statement.
- Citation Style : If required, adhere to the specific citation style guidelines (e.g., APA, MLA) for in-text citations and the reference list. Properly crediting the original article and any additional sources you use in your critique is essential.
How to Critique a Journal Article: Mastering the Steps
So, you've been assigned the task of critiquing a journal article, and not sure where to start? Worry not, as we've prepared a comprehensive guide with different steps to help you navigate this process with confidence. Journal articles are esteemed sources of scholarly knowledge, and effectively critiquing them requires a systematic approach. Let's dive into the steps to expertly evaluate and analyze a journal article:
Step 1: Understanding the Research Context
Begin by familiarizing yourself with the broader research context in which the journal article is situated. Learn about the field, the topic's significance, and any previous relevant research. This foundational knowledge will provide a valuable backdrop for your journal article critique example.
Step 2: Evaluating the Article's Structure
Assess the article's overall structure and organization. Examine how the introduction sets the stage for the research and how the discussion flows logically from the methodology and results. A well-structured article enhances readability and comprehension.
Step 3: Analyzing the Research Methodology
Dive into the research methodology section, which outlines the approach used to gather and analyze data. Scrutinize the study's design, data collection methods, sample size, and any potential biases or limitations. Understanding the research process will enable you to gauge the article's reliability.
Step 4: Assessing the Data and Results
Examine the presentation of data and results in the article. Are the findings clear and effectively communicated? Look for any discrepancies between the data presented and the interpretations made by the authors.
Step 5: Analyzing the Discussion and Conclusions
Evaluate the discussion section, where the authors interpret their findings and place them in the broader context. Assess the soundness of their conclusions, considering whether they are adequately supported by the data.
Step 6: Considering Ethical Considerations
Reflect on any ethical considerations raised by the research. Assess whether the study respects the rights and privacy of participants and adheres to ethical guidelines.
Step 7: Identifying Strengths and Weaknesses
Identify the article's strengths, such as well-designed experiments, comprehensive, relevant literature reviews, or innovative approaches. Also, pinpoint any weaknesses, like gaps in the research, unclear explanations, or insufficient evidence.
Step 8: Offering Constructive Feedback
Provide constructive feedback to the authors, highlighting both positive aspects and areas for improvement for future research. Suggest ways to enhance the research methods, data analysis, or discussion to bolster its overall quality.
Step 9: Presenting Your Critique
Organize your critique into a well-structured paper, starting with an introduction that outlines the article's context and purpose. Develop a clear and focused thesis statement that conveys your assessment. Support your points with evidence from the article and other credible sources.
By following these steps on how to critique a journal article, you'll be well-equipped to craft a thoughtful and insightful piece, contributing to the scholarly discourse in your field of study!
Got an Article that Needs Some Serious Critiquing?
Don't sweat it! Our critique maestros are armed with wit, wisdom, and a dash of magic to whip that piece into shape.
An Article Critique: Journal Vs. Research
In the realm of academic writing, the terms 'journal article' and 'research paper' are often used interchangeably, which can lead to confusion about their differences. Understanding the distinctions between critiquing a research article and a journal piece is essential. Let's delve into the key characteristics that set apart a journal article from a research paper and explore how the critique process may differ for each:
Publication Scope:
- Journal Article: Presents focused and concise research findings or new insights within a specific subject area.
- Research Paper: Explores a broader range of topics and can cover extensive research on a particular subject.
Format and Structure:
- Journal Article: Follows a standardized format with sections such as abstract, introduction, methodology, results, discussion, and conclusion.
- Research Paper: May not adhere to a specific format and allows flexibility in organizing content based on the research scope.
Depth of Analysis:
- Journal Article: Provides a more concise and targeted analysis of the research topic or findings.
- Research Paper: Offers a more comprehensive and in-depth analysis, often including extensive literature reviews and data analyses.
- Journal Article: Typically shorter in length, ranging from a few pages to around 10-15 pages.
- Research Paper: Tends to be longer, spanning from 20 to several hundred pages, depending on the research complexity.
Publication Type:
- Journal Article: Published in academic journals after undergoing rigorous peer review.
- Research Paper: May be published as a standalone work or as part of a thesis, dissertation, or academic report.
- Journal Article: Targeted at academics, researchers, and professionals within the specific field of study.
- Research Paper: Can cater to a broader audience, including students, researchers, policymakers, and the general public.
- Journal Article: Primarily aimed at sharing new research findings, contributing to academic discourse, and advancing knowledge in the field.
- Research Paper: Focuses on comprehensive exploration and analysis of a research topic, aiming to make a substantial contribution to the body of knowledge.
Appreciating these differences becomes paramount when engaging in the critique of these two forms of scholarly publications, as they each demand a unique approach and thoughtful consideration of their distinctive attributes. And if you find yourself desiring a flawlessly crafted research article critique example, entrusting the task to professional writers is always an excellent option – you can easily order essay that meets your needs.
Article Critique Example
Our collection of essay samples offers a comprehensive and practical illustration of the critique process, granting you access to valuable insights.
Tips on How to Critique an Article
Critiquing an article requires a keen eye, critical thinking, and a thoughtful approach to evaluating its content. To enhance your article critique skills and provide insightful analyses, consider incorporating these five original and practical tips into your process:
1. Analyze the Author's Bias : Be mindful of potential biases in the article, whether they are political, cultural, or personal. Consider how these biases may influence the author's perspective and the presentation of information. Evaluating the presence of bias enables you to discern the objectivity and credibility of the article's arguments.
2. Examine the Supporting Evidence : Scrutinize the quality and relevance of the evidence used to support the article's claims. Look for well-researched data, credible sources, and up-to-date statistics. Assess how effectively the author integrates evidence to build a compelling case for their arguments.
3. Consider the Audience's Perspective : Put yourself in the shoes of the intended audience and assess how well the article communicates its ideas. Consider whether the language, tone, and level of complexity are appropriate for the target readership. A well-tailored article is more likely to engage and resonate with its audience.
4. Investigate the Research Methodology : If the article involves research or empirical data, delve into the methodology used to gather and analyze the information. Evaluate the soundness of the study design, sample size, and data collection methods. Understanding the research process adds depth to your critique.
5. Discuss the Implications and Application : Consider the broader implications of the article's findings or arguments. Discuss how the insights presented in the article could impact the field of study or have practical applications in real-world scenarios. Identifying the potential consequences of the article's content strengthens your critique's depth and relevance.
Wrapping Up
In a nutshell, article critique is an essential skill that helps us grow as critical thinkers and active participants in academia. Embrace the opportunity to analyze and offer constructive feedback, contributing to a brighter future of knowledge and understanding. Remember, each critique is a chance to engage with new ideas and expand our horizons. So, keep honing your critique skills and enjoy the journey of discovery in the world of academic exploration!
Tired of Ordinary Critiques?
Brace yourself for an extraordinary experience! Our critique geniuses are on standby, ready to unleash their extraordinary skills on your article!
What Steps Need to Be Taken in Writing an Article Critique?
What is the recommended length for an article critique, related articles.
.webp)

IOE Writing Centre
- Writing a Critical Review

Writing a Critique

A critique (or critical review) is not to be mistaken for a literature review. A 'critical review', or 'critique', is a complete type of text (or genre), discussing one particular article or book in detail. In some instances, you may be asked to write a critique of two or three articles (e.g. a comparative critical review). In contrast, a 'literature review', which also needs to be 'critical', is a part of a larger type of text, such as a chapter of your dissertation.
Most importantly: Read your article / book as many times as possible, as this will make the critical review much easier.
1. Read and take notes 2. Organising your writing 3. Summary 4. Evaluation 5. Linguistic features of a critical review 6. Summary language 7. Evaluation language 8. Conclusion language 9. Example extracts from a critical review 10. Further resources
Read and Take Notes
To improve your reading confidence and efficiency, visit our pages on reading.
Further reading: Read Confidently
After you are familiar with the text, make notes on some of the following questions. Choose the questions which seem suitable:
- What kind of article is it (for example does it present data or does it present purely theoretical arguments)?
- What is the main area under discussion?
- What are the main findings?
- What are the stated limitations?
- Where does the author's data and evidence come from? Are they appropriate / sufficient?
- What are the main issues raised by the author?
- What questions are raised?
- How well are these questions addressed?
- What are the major points/interpretations made by the author in terms of the issues raised?
- Is the text balanced? Is it fair / biased?
- Does the author contradict herself?
- How does all this relate to other literature on this topic?
- How does all this relate to your own experience, ideas and views?
- What else has this author written? Do these build / complement this text?
- (Optional) Has anyone else reviewed this article? What did they say? Do I agree with them?
^ Back to top
Organising your writing
You first need to summarise the text that you have read. One reason to summarise the text is that the reader may not have read the text. In your summary, you will
- focus on points within the article that you think are interesting
- summarise the author(s) main ideas or argument
- explain how these ideas / argument have been constructed. (For example, is the author basing her arguments on data that they have collected? Are the main ideas / argument purely theoretical?)
In your summary you might answer the following questions: Why is this topic important? Where can this text be located? For example, does it address policy studies? What other prominent authors also write about this?
Evaluation is the most important part in a critical review.
Use the literature to support your views. You may also use your knowledge of conducting research, and your own experience. Evaluation can be explicit or implicit.
Explicit evaluation
Explicit evaluation involves stating directly (explicitly) how you intend to evaluate the text. e.g. "I will review this article by focusing on the following questions. First, I will examine the extent to which the authors contribute to current thought on Second Language Acquisition (SLA) pedagogy. After that, I will analyse whether the authors' propositions are feasible within overseas SLA classrooms."
Implicit evaluation
Implicit evaluation is less direct. The following section on Linguistic Features of Writing a Critical Review contains language that evaluates the text. A difficult part of evaluation of a published text (and a professional author) is how to do this as a student. There is nothing wrong with making your position as a student explicit and incorporating it into your evaluation. Examples of how you might do this can be found in the section on Linguistic Features of Writing a Critical Review. You need to remember to locate and analyse the author's argument when you are writing your critical review. For example, you need to locate the authors' view of classroom pedagogy as presented in the book / article and not present a critique of views of classroom pedagogy in general.
Linguistic features of a critical review
The following examples come from published critical reviews. Some of them have been adapted for student use.
Summary language
- This article / book is divided into two / three parts. First...
- While the title might suggest...
- The tone appears to be...
- Title is the first / second volume in the series Title, edited by...The books / articles in this series address...
- The second / third claim is based on...
- The author challenges the notion that...
- The author tries to find a more middle ground / make more modest claims...
- The article / book begins with a short historical overview of...
- Numerous authors have recently suggested that...(see Author, Year; Author, Year). Author would also be once such author. With his / her argument that...
- To refer to title as a...is not to say that it is...
- This book / article is aimed at... This intended readership...
- The author's book / article examines the...To do this, the author first...
- The author develops / suggests a theoretical / pedagogical model to…
- This book / article positions itself firmly within the field of...
- The author in a series of subtle arguments, indicates that he / she...
- The argument is therefore...
- The author asks "..."
- With a purely critical / postmodern take on...
- Topic, as the author points out, can be viewed as...
- In this recent contribution to the field of...this British author...
- As a leading author in the field of...
- This book / article nicely contributes to the field of...and complements other work by this author...
- The second / third part of...provides / questions / asks the reader...
- Title is intended to encourage students / researchers to...
- The approach taken by the author provides the opportunity to examine...in a qualitative / quantitative research framework that nicely complements...
- The author notes / claims that state support / a focus on pedagogy / the adoption of...remains vital if...
- According to Author (Year) teaching towards examinations is not as effective as it is in other areas of the curriculum. This is because, as Author (Year) claims that examinations have undue status within the curriculum.
- According to Author (Year)…is not as effective in some areas of the curriculum / syllabus as others. Therefore the author believes that this is a reason for some school's…
Evaluation language
- This argument is not entirely convincing, as...furthermore it commodifies / rationalises the...
- Over the last five / ten years the view of...has increasingly been viewed as 'complicated' (see Author, Year; Author, Year).
- However, through trying to integrate...with...the author...
- There are difficulties with such a position.
- Inevitably, several crucial questions are left unanswered / glossed over by this insightful / timely / interesting / stimulating book / article. Why should...
- It might have been more relevant for the author to have written this book / article as...
- This article / book is not without disappointment from those who would view...as...
- This chosen framework enlightens / clouds...
- This analysis intends to be...but falls a little short as...
- The authors rightly conclude that if...
- A detailed, well-written and rigorous account of...
- As a Korean student I feel that this article / book very clearly illustrates...
- The beginning of...provides an informative overview into...
- The tables / figures do little to help / greatly help the reader...
- The reaction by scholars who take a...approach might not be so favourable (e.g. Author, Year).
- This explanation has a few weaknesses that other researchers have pointed out (see Author, Year; Author, Year). The first is...
- On the other hand, the author wisely suggests / proposes that...By combining these two dimensions...
- The author's brief introduction to...may leave the intended reader confused as it fails to properly...
- Despite my inability to...I was greatly interested in...
- Even where this reader / I disagree(s), the author's effort to...
- The author thus combines...with...to argue...which seems quite improbable for a number of reasons. First...
- Perhaps this aversion to...would explain the author's reluctance to...
- As a second language student from ...I find it slightly ironic that such an anglo-centric view is...
- The reader is rewarded with...
- Less convincing is the broad-sweeping generalisation that...
- There is no denying the author's subject knowledge nor his / her...
- The author's prose is dense and littered with unnecessary jargon...
- The author's critique of...might seem harsh but is well supported within the literature (see Author, Year; Author, Year; Author, Year). Aligning herself with the author, Author (Year) states that...
- As it stands, the central focus of Title is well / poorly supported by its empirical findings...
- Given the hesitation to generalise to...the limitation of...does not seem problematic...
- For instance, the term...is never properly defined and the reader left to guess as to whether...
- Furthermore, to label...as...inadvertently misguides...
- In addition, this research proves to be timely / especially significant to... as recent government policy / proposals has / have been enacted to...
- On this well researched / documented basis the author emphasises / proposes that...
- Nonetheless, other research / scholarship / data tend to counter / contradict this possible trend / assumption...(see Author, Year; Author, Year).
- Without entering into detail of the..., it should be stated that Title should be read by...others will see little value in...
- As experimental conditions were not used in the study the word 'significant' misleads the reader.
- The article / book becomes repetitious in its assertion that...
- The thread of the author's argument becomes lost in an overuse of empirical data...
- Almost every argument presented in the final section is largely derivative, providing little to say about...
- She / he does not seem to take into consideration; however, that there are fundamental differences in the conditions of…
- As Author (Year) points out, however, it seems to be necessary to look at…
- This suggest that having low…does not necessarily indicate that…is ineffective.
- Therefore, the suggestion made by Author (Year)…is difficult to support.
- When considering all the data presented…it is not clear that the low scores of some students, indeed, reflects…
Conclusion language
- Overall this article / book is an analytical look at...which within the field of...is often overlooked.
- Despite its problems, Title offers valuable theoretical insights / interesting examples / a contribution to pedagogy and a starting point for students / researchers of...with an interest in...
- This detailed and rigorously argued...
- This first / second volume / book / article by...with an interest in...is highly informative...
Example extracts from a critical review
Writing critically.
If you have been told your writing is not critical enough, it probably means that your writing treats the knowledge claims as if they are true, well supported, and applicable in the context you are writing about. This may not always be the case.
In these two examples, the extracts refer to the same section of text. In each example, the section that refers to a source has been highlighted in bold. The note below the example then explains how the writer has used the source material.
There is a strong positive effect on students, both educationally and emotionally, when the instructors try to learn to say students' names without making pronunciation errors (Kiang, 2004).
Use of source material in example a:
This is a simple paraphrase with no critical comment. It looks like the writer agrees with Kiang. (This is not a good example for critical writing, as the writer has not made any critical comment).
Kiang (2004) gives various examples to support his claim that "the positive emotional and educational impact on students is clear" (p.210) when instructors try to pronounce students' names in the correct way. He quotes one student, Nguyet, as saying that he "felt surprised and happy" (p.211) when the tutor said his name clearly . The emotional effect claimed by Kiang is illustrated in quotes such as these, although the educational impact is supported more indirectly through the chapter. Overall, he provides more examples of students being negatively affected by incorrect pronunciation, and it is difficult to find examples within the text of a positive educational impact as such.
Use of source material in example b:
The writer describes Kiang's (2004) claim and the examples which he uses to try to support it. The writer then comments that the examples do not seem balanced and may not be enough to support the claims fully. This is a better example of writing which expresses criticality.
^Back to top
Further resources
You may also be interested in our page on criticality, which covers criticality in general, and includes more critical reading questions.
Further reading: Read and Write Critically
We recommend that you do not search for other university guidelines on critical reviews. This is because the expectations may be different at other institutions. Ask your tutor for more guidance or examples if you have further questions.
IOE Writing Centre Online
Self-access resources from the Academic Writing Centre at the UCL Institute of Education.
Anonymous Suggestions Box
Information for Staff
Academic Writing Centre
Academic Writing Centre, UCL Institute of Education [email protected] Twitter: @AWC_IOE Skype: awc.ioe
- Dissertation
- PowerPoint Presentation
- Book Report/Review
- Research Proposal
- Math Problems
- Proofreading
- Movie Review
- Cover Letter Writing
- Personal Statement
- Nursing Paper
- Argumentative Essay
- Research Paper
Critique Essay: Your Comprehensive Guide to Writing A+ Critique Essays

Table of Contents
Just like a concept essay , a critique essay is an essential assignment that examines another author’s work to analyze and interpret it. This task is common in college, and it’s also called an analytical essay .
But how do you handle this task and score excellent grades? This guide delves into all the details of composing an A+ critical paper. Read to learn more.
What Is a Critique Essay?
Let’s set the ball rolling by defining a critique essay . It is an academic assignment that summarizes a text and critically evaluates its validity. It aims to evaluate a given text’s impact in a specific discipline and shows whether the evaluated text achieved its intended goal or didn’t.
This assignment needs careful study of the texts before summarizing and critically analyzing them. Your main task is to understand the piece and present your critical assessment. Your final verdict can be negative or positive, depending on the work’s quality and analysis. We can summarize this paper in the following four terms.
- A description that gives readers a sense of the writer’s overall goal with their publications.
- An analysis that examines how the text’s structure and language convey its meaning.
- An interpretation that states each of the work’s parts’ significance.
- An assessment that judges the piece’s overall worth or value.
Types of Critique Essays
Critique essays come in three main forms, as discussed below.
- Descriptive
This essay examines a text or other works. It primarily focuses on a work’s specific features. Comparing and contrasting your analysis subject to a classic example of its genre is also possible.
- Evaluative
This analytical essay estimates a work’s value. It shows if it’s as good as you expected based on the recommendations or if you feel it wasted your time.
- Interpretive
Interpretive essays give your readers answers relating to a work’s meaning. To achieve this goal, you must choose a technique for establishing that meaning. For instance, you may read, watch, or observe your analysis subject before floating arguments.
Critique Essay Outline
Writing an excellent critique essay is difficult without an outline. An outline is the only way to save writing time and organize your ideas where they should fit. This step requires you to determine the evidence and arguments you will evaluate. These arguments support and validate your thesis statement.
Additionally, your paper’s outline shows you how your essay will look. After creating the wireframe, you may adjust it or add more details to make your writing more effective. Your skeleton takes the traditional five-paragraph essay format.
Introduction
Your work needs an introduction paragraph. This section opens with an introductory phrase about the work you are analyzing. It tells the reader what you will critique, who the author is, and provide its publication date. The intro specifies the work’s core argument. Its third sentence contains your thesis statement.
Your work requires a summary paragraph to show the reader what you discussed in the body paragraphs. This section follows your introduction and leads to a detailed discussion.
Your main body comprises three to five paragraphs or more if necessary. Each section addresses a given text dimension, like bias, tone, style, or organization. Moreover, every paragraph confirms your thesis statement regarding the piece’s effectiveness. Each body paragraph opens with a topic sentence summarizing the subsection. Next, you introduce your evidence and close the chapter by referring to the thesis.
Your conclusion gives your final verdict on a given piece’s effectiveness. This strong conclusion paragraph summarizes your main ideas and paraphrases your thesis statement to confirm that everything you discussed confirmed it.
How to Start a Critique Essay
Starting your critique essay is easy if you follow the correct process. This discussion explores how to commence this assignment.
Critical Reading
- Read the Literary Piece Carefully
Your journey starts by reading the piece you have to critique to understand it. Your careful reading should immerse you into the author’s world and imagine why they drafted their work. Also, take note and underscore essential facts. Your assignment must also highlight which literary tools succeeded in achieving the material’s goal. Lastly, determine what you dislike about the piece, such as incompleteness, gaps, or inconsistencies.
- Formulate the Author’s Thesis
Use the text you read to formulate the author’s thesis or primary arguments. You can find this argument in the paper’s introduction. If you are handling literary work, create one of the key themes because the thesis isn’t clear.
- Summarize the Analyzed Text
You need one paragraph to summarize your paper’s content and give the reader a gist of what you covered. It should come between the introduction and the three body paragraphs.
Analyze the Text
Analyze your text before composing your assignment. Your analysis should lead you to the following critical questions:
- How did your emotions respond to the text, and which methods, images, or ideas made you feel so?
- Based on the author’s background, which experiences made them formulate such a thesis?
- What other significant works has the author produced to demonstrate their general thought direction?
- Have you used the concepts correctly in the text?
- Are your references reliable, and do they adequately prove the author’s judgment?
Write Your Critical Essay
Lastly, draft your critique essay by writing a brief overview of the text you are examining. Next, formulate your thesis statement reflecting your stand on the work you are critiquing. Afterward, write a summary paragraph that captures the paper’s essence. Below are essential questions to ask and answer to ensure you did the correct thing:
- Who created the piece you are critiquing?
- Did you present your work objectively or subjectively?
- What is your work’s aim, and were they attained?
- What methods, styles, and media did the author use, and did they achieve their goal?
- What assumptions underlie the work, and how do they influence its validity?
- What forms of evidence or persuasion did you use, and is your evidence interpreted fairly?
- How is the material structured?
- Does the work favor a specific interpretation or viewpoint, and how effective is it?
- Does the work promote an understanding of vital ideas or theories?
- How does the piece resonate or fail to resonate with primary concepts or other works in its discipline?
Example of Critique Essay On Articles
An article-related critique essay is a paper that evaluates an article to determine its effectiveness in attaining a goal. An article could comprise opinions, personal experiences, and external research. This essay entertains, informs, persuades, or educates readers. An article critique differs from a summary because a summary doesn’t offer a critical analysis. A critique, in its turn, resembles a review because it evaluates the author’s ability to fulfill its stated purpose. Your article critique must back its claims regarding an issue through evidence in the text and other external sources.
A Sample Article Critique Paper
Nothing teaches better than an excellent model of what you are learning. Here’s a sample article critique paper.
The Education Sector Cannot Solve Problems It Doesn’t Acknowledge (David and Nelson, 2021). New York, a state in the United States of America, fully understands this problem and has formulated initiatives and policies to improve equity in public schools at all levels. Education policymakers have implemented an All-Inclusive Response Strategy(ARS) to achieve this noble goal. The practical goal of this strategy is to ensure that all New York children enjoy inclusive education. This approach seeks to eliminate biases, barriers, or power dynamics that discourage students’ learning potential. Acknowledging educational challenges and committing to developing solutions is the most critical step school administrators can take to support the education system. However, these principal players should formulate proper thought, research, and policy guidelines to ensure their policies and strategies include all the potential issues and leave enough room for improvement.
The procedures also proposed religious tolerance and accommodation, anti-discrimination, and all forms of harassment. This inclusive policy must have sound techniques for how other stakeholders will implement, review, and monitor it henceforth. Fortunately, New York has succeeded on this front. This article evaluates how well this equity program was executed in the state as it endeavors to promote equity and inclusivity in its public schools…
Do you still have questions regarding a critique essay ? This section answers some of the most frequently asked questions in this essay.
What are the five parts of a critique essay ?
A perfect critique paper comprises five sections, namely: the introduction, the summary paragraph, the first paragraph, the second paragraph, the third paragraph, and the conclusion.
What is an example of a critique?
A critique essay example should meet all assignment requirements. It also comprises all the essential components, as mentioned in question one.
What are the four rules of critique?
The four rules governing a good critique essay are as follows:
- An effective introduction that provides a quick background review, defines the necessary terminology, and ends with a thesis.
- A summary that gives a broad overview of what the source discusses.
- A critique that shows your personal opinion, supported by evidence.
A conclusion that summarizes your main ideas, reminds your readers of your thesis, and concludes the paper.

Abortion Research Paper: Facts To Know Before Writing

How to Create a Strong Conclusion Paragraph
How do you spell check the essay.
- All eBooks & Audiobooks
- Academic eBook Collection
- Home Grown eBook Collection
- Off-Campus Access
- Literature Resource Center
- Opposing Viewpoints
- ProQuest Central
- Course Guides
- Citing Sources
- Library Research
- Websites by Topic
- Book-a-Librarian
- Research Tutorials
- Use the Catalog
- Use Databases
- Use Films on Demand
- Use Home Grown eBooks
- Use NC LIVE
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary vs. Secondary
- Scholarly vs. Popular
- Make an Appointment
- Writing Tools
- Annotated Bibliographies
- Summaries, Reviews & Critiques
- Writing Center
Service Alert

Article Summaries, Reviews & Critiques
- Writing an article SUMMARY
- Writing an article REVIEW
Writing an article CRITIQUE
- Citing Sources This link opens in a new window
- About RCC Library
Text: 336-308-8801
Email: [email protected]
Call: 336-633-0204
Schedule: Book-a-Librarian
Like us on Facebook
Links on this guide may go to external web sites not connected with Randolph Community College. Their inclusion is not an endorsement by Randolph Community College and the College is not responsible for the accuracy of their content or the security of their site.
A critique asks you to evaluate an article and the author’s argument. You will need to look critically at what the author is claiming, evaluate the research methods, and look for possible problems with, or applications of, the researcher’s claims.
Introduction
Give an overview of the author’s main points and how the author supports those points. Explain what the author found and describe the process they used to arrive at this conclusion.
Body Paragraphs
Interpret the information from the article:
- Does the author review previous studies? Is current and relevant research used?
- What type of research was used – empirical studies, anecdotal material, or personal observations?
- Was the sample too small to generalize from?
- Was the participant group lacking in diversity (race, gender, age, education, socioeconomic status, etc.)
- For instance, volunteers gathered at a health food store might have different attitudes about nutrition than the population at large.
- How useful does this work seem to you? How does the author suggest the findings could be applied and how do you believe they could be applied?
- How could the study have been improved in your opinion?
- Does the author appear to have any biases (related to gender, race, class, or politics)?
- Is the writing clear and easy to follow? Does the author’s tone add to or detract from the article?
- How useful are the visuals (such as tables, charts, maps, photographs) included, if any? How do they help to illustrate the argument? Are they confusing or hard to read?
- What further research might be conducted on this subject?
Try to synthesize the pieces of your critique to emphasize your own main points about the author’s work, relating the researcher’s work to your own knowledge or to topics being discussed in your course.
From the Center for Academic Excellence (opens in a new window), University of Saint Joseph Connecticut
Additional Resources
All links open in a new window.
Writing an Article Critique (from The University of Arizona Global Campus Writing Center)
How to Critique an Article (from Essaypro.com)
How to Write an Article Critique (from EliteEditing.com.au)
- << Previous: Writing an article REVIEW
- Next: Citing Sources >>
- Last Updated: Mar 15, 2024 9:32 AM
- URL: https://libguides.randolph.edu/summaries

Writing Critiques
Writing a critique involves more than pointing out mistakes. It involves conducting a systematic analysis of a scholarly article or book and then writing a fair and reasonable description of its strengths and weaknesses. Several scholarly journals have published guides for critiquing other people’s work in their academic area. Search for a “manuscript reviewer guide” in your own discipline to guide your analysis of the content. Use this handout as an orientation to the audience and purpose of different types of critiques and to the linguistic strategies appropriate to all of them.
Types of critique
Article or book review assignment in an academic class.
Text: Article or book that has already been published Audience: Professors Purpose:
- to demonstrate your skills for close reading and analysis
- to show that you understand key concepts in your field
- to learn how to review a manuscript for your future professional work
Published book review
Text: Book that has already been published Audience: Disciplinary colleagues Purpose:
- to describe the book’s contents
- to summarize the book’s strengths and weaknesses
- to provide a reliable recommendation to read (or not read) the book
Manuscript review
Text: Manuscript that has been submitted but has not been published yet Audience: Journal editor and manuscript authors Purpose:
- to provide the editor with an evaluation of the manuscript
- to recommend to the editor that the article be published, revised, or rejected
- to provide the authors with constructive feedback and reasonable suggestions for revision
Language strategies for critiquing
For each type of critique, it’s important to state your praise, criticism, and suggestions politely, but with the appropriate level of strength. The following language structures should help you achieve this challenging task.
Offering Praise and Criticism
A strategy called “hedging” will help you express praise or criticism with varying levels of strength. It will also help you express varying levels of certainty in your own assertions. Grammatical structures used for hedging include:
Modal verbs Using modal verbs (could, can, may, might, etc.) allows you to soften an absolute statement. Compare:
This text is inappropriate for graduate students who are new to the field. This text may be inappropriate for graduate students who are new to the field.
Qualifying adjectives and adverbs Using qualifying adjectives and adverbs (possible, likely, possibly, somewhat, etc.) allows you to introduce a level of probability into your comments. Compare:
Readers will find the theoretical model difficult to understand. Some readers will find the theoretical model difficult to understand. Some readers will probably find the theoretical model somewhat difficult to understand completely.
Note: You can see from the last example that too many qualifiers makes the idea sound undesirably weak.
Tentative verbs Using tentative verbs (seems, indicates, suggests, etc.) also allows you to soften an absolute statement. Compare:
This omission shows that the authors are not aware of the current literature. This omission indicates that the authors are not aware of the current literature. This omission seems to suggest that the authors are not aware of the current literature.
Offering suggestions
Whether you are critiquing a published or unpublished text, you are expected to point out problems and suggest solutions. If you are critiquing an unpublished manuscript, the author can use your suggestions to revise. Your suggestions have the potential to become real actions. If you are critiquing a published text, the author cannot revise, so your suggestions are purely hypothetical. These two situations require slightly different grammar.
Unpublished manuscripts: “would be X if they did Y” Reviewers commonly point out weakness by pointing toward improvement. For instance, if the problem is “unclear methodology,” reviewers may write that “the methodology would be more clear if …” plus a suggestion. If the author can use the suggestions to revise, the grammar is “X would be better if the authors did Y” (would be + simple past suggestion).
The tables would be clearer if the authors highlighted the key results. The discussion would be more persuasive if the authors accounted for the discrepancies in the data.
Published manuscripts: “would have been X if they had done Y” If the authors cannot revise based on your suggestions, use the past unreal conditional form “X would have been better if the authors had done Y” (would have been + past perfect suggestion).
The tables would have been clearer if the authors had highlighted key results. The discussion would have been more persuasive if the authors had accounted for discrepancies in the data.
Note: For more information on conditional structures, see our Conditionals handout .

Make a Gift
- Undergraduate
- High School
- Architecture
- American History
- Asian History
- Antique Literature
- American Literature
- Asian Literature
- Classic English Literature
- World Literature
- Creative Writing
- Linguistics
- Criminal Justice
- Legal Issues
- Anthropology
- Archaeology
- Political Science
- World Affairs
- African-American Studies
- East European Studies
- Latin-American Studies
- Native-American Studies
- West European Studies
- Family and Consumer Science
- Social Issues
- Women and Gender Studies
- Social Work
- Natural Sciences
- Pharmacology
- Earth science
- Agriculture
- Agricultural Studies
- Computer Science
- IT Management
- Mathematics
- Investments
- Engineering and Technology
- Engineering
- Aeronautics
- Medicine and Health
- Alternative Medicine
- Communications and Media
- Advertising
- Communication Strategies
- Public Relations
- Educational Theories
- Teacher's Career
- Chicago/Turabian
- Company Analysis
- Education Theories
- Shakespeare
- Canadian Studies
- Food Safety
- Relation of Global Warming and Extreme Weather Condition
- Movie Review
- Admission Essay
- Annotated Bibliography
- Application Essay
Article Critique
- Article Review
- Article Writing
- Book Review
- Business Plan
- Business Proposal
- Capstone Project
- Cover Letter
- Creative Essay
- Dissertation
- Dissertation - Abstract
- Dissertation - Conclusion
- Dissertation - Discussion
- Dissertation - Hypothesis
- Dissertation - Introduction
- Dissertation - Literature
- Dissertation - Methodology
- Dissertation - Results
- GCSE Coursework
- Grant Proposal
- Marketing Plan
- Multiple Choice Quiz
- Personal Statement
- Power Point Presentation
- Power Point Presentation With Speaker Notes
- Questionnaire
- Reaction Paper
- Research Paper
- Research Proposal
- SWOT analysis
- Thesis Paper
- Online Quiz
- Literature Review
- Movie Analysis
- Statistics problem
- Math Problem
- All papers examples
- How It Works
- Money Back Policy
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- We Are Hiring
Article Critique Examples
Search by keywords
Paper Categories
568 Article Critique examples are found
Providing High Quality and Safe Nursing Care in Adult Nursing, Article Critique Example
According to the Department of Health (2008 np), high-quality care is seen as effective and safe nursing based on patient needs and building a positive patient. (Gaboyan and Pivkina, 2022, [...]
Pages: 8
Words: 2284
Critical Thinking Paper, Article Critique Example
Introduction From the YouTube video uploaded by Eidos84, Peter Singer explores the context of applied ethics by describing how the interests of human beings should be and will be determined [...]
Pages: 5
Words: 1241
Acquisition of Literacy in Bilingual Children, Article Critique Example
Summary This article discusses some of the reasons why students who speak English as a second language have difficulty with literacy. According to the article, there are three main reasons [...]
Words: 2282
Trouble in Paradise, Article Critique Example
To conduct a professional PhD level paper review, it is necessary to verify several aspects of the paper that is being examined (Question 1). First, it is necessary to detect [...]
Pages: 3
Words: 818
Penal Voluntary Services (PVS) Organizations and the Criminal Justice Domain, Article Critique Example
PVS organizations play a vital role in the criminal justice domain. They help provide education, training, spiritual, rehabilitation services, and other crucial services in the prison facilities (Abrams et al. [...]
Words: 1286
Impact of PVS Organizations on Criminalized Individuals and Their Communities, Article Critique Example
The increasing rates of incarceration and recidivism in the US confirm the need for public and private entities to run probation programs. The Penal Volunteer Sector (PVS) organizations are charitable [...]
Words: 1336
Time is precious
don’t waste it!
Plagiarism-free guarantee
Privacy guarantee
Secure checkout
Money back guarantee


How to Write an Article Critique
An article critique is a genre of academic writing that provides critical evaluation through intensive analysis of an article and involves giving a brief summary of the article. Reading an article critique helps an audience to understand the key points of the article, and the author’s ideas and intentions. It indicates the perceived success of an article and analyses its strengths and weaknesses.
As with other types of academic writing , an article critique has to be written in formal language and using a structured format. It should consist of an introduction, several body paragraphs and a conclusion. Though the general pattern is similar, some formatting styles have certain specific guidelines for writing an article critique. It is important to study how to write a critique properly and to be sure of what each formatting style requires. To be able to write an effective critique , writers must also have a full understanding of the topic they are analysing.
The main purposes of writing an article critique are to:
- describe the main ideas and what the author wants to express
- analyse each important and interesting point and develop an explanation of the article
- interpret the author’s intention
- summarise and evaluate the value of an article, stating whether you agree or disagree with the author, with supporting evidence.
Steps involved in writing an article critique:
- Read the article for the first time to understand its main ideas. If you are unsure whether you understand it clearly, reread it.
- Once you feel you understand what the article is talking about, read the article again and make notes as you go. If you find any interesting sentences or paragraphs that you think should be discussed, you should quote them as evidence to support your discussion.
- From your notes, analyse and discuss each important point. You can give your comments and opinions at this stage.
- Summarise and provide a conclusion regarding whether you like or dislike the article. Support your ideas with the evidence you found.
- Although called a ‘critique’, an article critique does not only give critical and negative feedback on an article. A good critique should include both positive praise and negative criticism for a particular work.
- Use direct quotations of the author’s work where appropriate to avoid accusations of plagiarism.
- Write the critique in the third person.

Dr Ellen McRae ,
Senior Managing Editor,
Elite Editing.
Request a quote
Please enter your details and we will email a quote to you.
- Enter the Word Count of your document *
- Phone This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
HELP: FORMATTING
- Choose 'leave formatting as it is' if you would like us to maintain the current formatting in your document. We will make sure it is neat and consistent.
- Choose 'I will upload the formatting guidelines' if you have specific instructions about formatting that need to be followed, for example, if you are submitting a thesis for editing and your university has specific thesis-formatting guidelines. Then, upload these guidelines when you upload your document for editing.
- Choose 'Elite Editing House Style' if you would like us to format your document according to our own guidelines, which have been specially designed to meet general university requirements.
- Choose 'APA 6th edition' if you want your document to be formatted according to the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association (APA) 6th edition. APA formatting is designed specifically for draft manuscripts of journal articles and certain aspects are not appropriate for a thesis that is divided into chapters and is in its final form. If you are submitting a thesis we will modify APA style according to the preferred thesis style of most universities.
Editing guidelines
Please paste a link to the journal editing guidelines if possible.
Copyright 2024, Elite Editing
Terms & Conditions | Privacy Policy
How to Write Critical Reviews
When you are asked to write a critical review of a book or article, you will need to identify, summarize, and evaluate the ideas and information the author has presented. In other words, you will be examining another person’s thoughts on a topic from your point of view.
Your stand must go beyond your “gut reaction” to the work and be based on your knowledge (readings, lecture, experience) of the topic as well as on factors such as criteria stated in your assignment or discussed by you and your instructor.
Make your stand clear at the beginning of your review, in your evaluations of specific parts, and in your concluding commentary.
Remember that your goal should be to make a few key points about the book or article, not to discuss everything the author writes.
Understanding the Assignment
To write a good critical review, you will have to engage in the mental processes of analyzing (taking apart) the work–deciding what its major components are and determining how these parts (i.e., paragraphs, sections, or chapters) contribute to the work as a whole.
Analyzing the work will help you focus on how and why the author makes certain points and prevent you from merely summarizing what the author says. Assuming the role of an analytical reader will also help you to determine whether or not the author fulfills the stated purpose of the book or article and enhances your understanding or knowledge of a particular topic.
Be sure to read your assignment thoroughly before you read the article or book. Your instructor may have included specific guidelines for you to follow. Keeping these guidelines in mind as you read the article or book can really help you write your paper!
Also, note where the work connects with what you’ve studied in the course. You can make the most efficient use of your reading and notetaking time if you are an active reader; that is, keep relevant questions in mind and jot down page numbers as well as your responses to ideas that appear to be significant as you read.
Please note: The length of your introduction and overview, the number of points you choose to review, and the length of your conclusion should be proportionate to the page limit stated in your assignment and should reflect the complexity of the material being reviewed as well as the expectations of your reader.
Write the introduction
Below are a few guidelines to help you write the introduction to your critical review.
Introduce your review appropriately
Begin your review with an introduction appropriate to your assignment.
If your assignment asks you to review only one book and not to use outside sources, your introduction will focus on identifying the author, the title, the main topic or issue presented in the book, and the author’s purpose in writing the book.
If your assignment asks you to review the book as it relates to issues or themes discussed in the course, or to review two or more books on the same topic, your introduction must also encompass those expectations.
Explain relationships
For example, before you can review two books on a topic, you must explain to your reader in your introduction how they are related to one another.
Within this shared context (or under this “umbrella”) you can then review comparable aspects of both books, pointing out where the authors agree and differ.
In other words, the more complicated your assignment is, the more your introduction must accomplish.
Finally, the introduction to a book review is always the place for you to establish your position as the reviewer (your thesis about the author’s thesis).
As you write, consider the following questions:
- Is the book a memoir, a treatise, a collection of facts, an extended argument, etc.? Is the article a documentary, a write-up of primary research, a position paper, etc.?
- Who is the author? What does the preface or foreword tell you about the author’s purpose, background, and credentials? What is the author’s approach to the topic (as a journalist? a historian? a researcher?)?
- What is the main topic or problem addressed? How does the work relate to a discipline, to a profession, to a particular audience, or to other works on the topic?
- What is your critical evaluation of the work (your thesis)? Why have you taken that position? What criteria are you basing your position on?
Provide an overview
In your introduction, you will also want to provide an overview. An overview supplies your reader with certain general information not appropriate for including in the introduction but necessary to understanding the body of the review.
Generally, an overview describes your book’s division into chapters, sections, or points of discussion. An overview may also include background information about the topic, about your stand, or about the criteria you will use for evaluation.
The overview and the introduction work together to provide a comprehensive beginning for (a “springboard” into) your review.
- What are the author’s basic premises? What issues are raised, or what themes emerge? What situation (i.e., racism on college campuses) provides a basis for the author’s assertions?
- How informed is my reader? What background information is relevant to the entire book and should be placed here rather than in a body paragraph?
Write the body
The body is the center of your paper, where you draw out your main arguments. Below are some guidelines to help you write it.
Organize using a logical plan
Organize the body of your review according to a logical plan. Here are two options:
- First, summarize, in a series of paragraphs, those major points from the book that you plan to discuss; incorporating each major point into a topic sentence for a paragraph is an effective organizational strategy. Second, discuss and evaluate these points in a following group of paragraphs. (There are two dangers lurking in this pattern–you may allot too many paragraphs to summary and too few to evaluation, or you may re-summarize too many points from the book in your evaluation section.)
- Alternatively, you can summarize and evaluate the major points you have chosen from the book in a point-by-point schema. That means you will discuss and evaluate point one within the same paragraph (or in several if the point is significant and warrants extended discussion) before you summarize and evaluate point two, point three, etc., moving in a logical sequence from point to point to point. Here again, it is effective to use the topic sentence of each paragraph to identify the point from the book that you plan to summarize or evaluate.
Questions to keep in mind as you write
With either organizational pattern, consider the following questions:
- What are the author’s most important points? How do these relate to one another? (Make relationships clear by using transitions: “In contrast,” an equally strong argument,” “moreover,” “a final conclusion,” etc.).
- What types of evidence or information does the author present to support his or her points? Is this evidence convincing, controversial, factual, one-sided, etc.? (Consider the use of primary historical material, case studies, narratives, recent scientific findings, statistics.)
- Where does the author do a good job of conveying factual material as well as personal perspective? Where does the author fail to do so? If solutions to a problem are offered, are they believable, misguided, or promising?
- Which parts of the work (particular arguments, descriptions, chapters, etc.) are most effective and which parts are least effective? Why?
- Where (if at all) does the author convey personal prejudice, support illogical relationships, or present evidence out of its appropriate context?
Keep your opinions distinct and cite your sources
Remember, as you discuss the author’s major points, be sure to distinguish consistently between the author’s opinions and your own.
Keep the summary portions of your discussion concise, remembering that your task as a reviewer is to re-see the author’s work, not to re-tell it.
And, importantly, if you refer to ideas from other books and articles or from lecture and course materials, always document your sources, or else you might wander into the realm of plagiarism.
Include only that material which has relevance for your review and use direct quotations sparingly. The Writing Center has other handouts to help you paraphrase text and introduce quotations.
Write the conclusion
You will want to use the conclusion to state your overall critical evaluation.
You have already discussed the major points the author makes, examined how the author supports arguments, and evaluated the quality or effectiveness of specific aspects of the book or article.
Now you must make an evaluation of the work as a whole, determining such things as whether or not the author achieves the stated or implied purpose and if the work makes a significant contribution to an existing body of knowledge.
Consider the following questions:
- Is the work appropriately subjective or objective according to the author’s purpose?
- How well does the work maintain its stated or implied focus? Does the author present extraneous material? Does the author exclude or ignore relevant information?
- How well has the author achieved the overall purpose of the book or article? What contribution does the work make to an existing body of knowledge or to a specific group of readers? Can you justify the use of this work in a particular course?
- What is the most important final comment you wish to make about the book or article? Do you have any suggestions for the direction of future research in the area? What has reading this work done for you or demonstrated to you?


Academic and Professional Writing
This is an accordion element with a series of buttons that open and close related content panels.
Analysis Papers
Reading Poetry
A Short Guide to Close Reading for Literary Analysis
Using Literary Quotations
Play Reviews
Writing a Rhetorical Précis to Analyze Nonfiction Texts
Incorporating Interview Data
Grant Proposals
Planning and Writing a Grant Proposal: The Basics
Additional Resources for Grants and Proposal Writing
Job Materials and Application Essays
Writing Personal Statements for Ph.D. Programs
- Before you begin: useful tips for writing your essay
- Guided brainstorming exercises
- Get more help with your essay
- Frequently Asked Questions
Resume Writing Tips
CV Writing Tips
Cover Letters
Business Letters
Proposals and Dissertations
Resources for Proposal Writers
Resources for Dissertators
Research Papers
Planning and Writing Research Papers
Quoting and Paraphrasing
Writing Annotated Bibliographies
Creating Poster Presentations
Writing an Abstract for Your Research Paper
Thank-You Notes
Advice for Students Writing Thank-You Notes to Donors
Reading for a Review
Critical Reviews
Writing a Review of Literature
Scientific Reports
Scientific Report Format
Sample Lab Assignment
Writing for the Web
Writing an Effective Blog Post
Writing for Social Media: A Guide for Academics
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2023 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
How to Write an Article Critique
Tips for Writing a Psychology Critique Paper
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Emily is a board-certified science editor who has worked with top digital publishing brands like Voices for Biodiversity, Study.com, GoodTherapy, Vox, and Verywell.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Emily-Swaim-1000-0f3197de18f74329aeffb690a177160c.jpg)
Cultura RM / Gu Cultura / Getty Images
- Steps for Writing a Critique
Evaluating the Article
- How to Write It
- Helpful Tips
An article critique involves critically analyzing a written work to assess its strengths and flaws. If you need to write an article critique, you will need to describe the article, analyze its contents, interpret its meaning, and make an overall assessment of the importance of the work.
Critique papers require students to conduct a critical analysis of another piece of writing, often a book, journal article, or essay . No matter your major, you will probably be expected to write a critique paper at some point.
For psychology students, critiquing a professional paper is a great way to learn more about psychology articles, writing, and the research process itself. Students will analyze how researchers conduct experiments, interpret results, and discuss the impact of the results.
At a Glance
An article critique involves making a critical assessment of a single work. This is often an article, but it might also be a book or other written source. It summarizes the contents of the article and then evaluates both the strengths and weaknesses of the piece. Knowing how to write an article critique can help you learn how to evaluate sources with a discerning eye.
Steps for Writing an Effective Article Critique
While these tips are designed to help students write a psychology critique paper, many of the same principles apply to writing article critiques in other subject areas.
Your first step should always be a thorough read-through of the material you will be analyzing and critiquing. It needs to be more than just a casual skim read. It should be in-depth with an eye toward key elements.
To write an article critique, you should:
- Read the article , noting your first impressions, questions, thoughts, and observations
- Describe the contents of the article in your own words, focusing on the main themes or ideas
- Interpret the meaning of the article and its overall importance
- Critically evaluate the contents of the article, including any strong points as well as potential weaknesses
The following guidelines can help you assess the article you are reading and make better sense of the material.
Read the Introduction Section of the Article
Start by reading the introduction . Think about how this part of the article sets up the main body and how it helps you get a background on the topic.
- Is the hypothesis clearly stated?
- Is the necessary background information and previous research described in the introduction?
In addition to answering these basic questions, note other information provided in the introduction and any questions you have.
Read the Methods Section of the Article
Is the study procedure clearly outlined in the methods section ? Can you determine which variables the researchers are measuring?
Remember to jot down questions and thoughts that come to mind as you are reading. Once you have finished reading the paper, you can then refer back to your initial questions and see which ones remain unanswered.
Read the Results Section of the Article
Are all tables and graphs clearly labeled in the results section ? Do researchers provide enough statistical information? Did the researchers collect all of the data needed to measure the variables in question?
Make a note of any questions or information that does not seem to make sense. You can refer back to these questions later as you are writing your final critique.
Read the Discussion Section of the Article
Experts suggest that it is helpful to take notes while reading through sections of the paper you are evaluating. Ask yourself key questions:
- How do the researchers interpret the results of the study?
- Did the results support their hypothesis?
- Do the conclusions drawn by the researchers seem reasonable?
The discussion section offers students an excellent opportunity to take a position. If you agree with the researcher's conclusions, explain why. If you feel the researchers are incorrect or off-base, point out problems with the conclusions and suggest alternative explanations.
Another alternative is to point out questions the researchers failed to answer in the discussion section.
Begin Writing Your Own Critique of the Paper
Once you have read the article, compile your notes and develop an outline that you can follow as you write your psychology critique paper. Here's a guide that will walk you through how to structure your critique paper.
Introduction
Begin your paper by describing the journal article and authors you are critiquing. Provide the main hypothesis (or thesis) of the paper. Explain why you think the information is relevant.
Thesis Statement
The final part of your introduction should include your thesis statement. Your thesis statement is the main idea of your critique. Your thesis should briefly sum up the main points of your critique.
Article Summary
Provide a brief summary of the article. Outline the main points, results, and discussion.
When describing the study or paper, experts suggest that you include a summary of the questions being addressed, study participants, interventions, comparisons, outcomes, and study design.
Don't get bogged down by your summary. This section should highlight the main points of the article you are critiquing. Don't feel obligated to summarize each little detail of the main paper. Focus on giving the reader an overall idea of the article's content.
Your Analysis
In this section, you will provide your critique of the article. Describe any problems you had with the author's premise, methods, or conclusions. You might focus your critique on problems with the author's argument, presentation, information, and alternatives that have been overlooked.
When evaluating a study, summarize the main findings—including the strength of evidence for each main outcome—and consider their relevance to key demographic groups.
Organize your paper carefully. Be careful not to jump around from one argument to the next. Arguing one point at a time ensures that your paper flows well and is easy to read.
Your critique paper should end with an overview of the article's argument, your conclusions, and your reactions.
More Tips When Writing an Article Critique
- As you are editing your paper, utilize a style guide published by the American Psychological Association, such as the official Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association .
- Reading scientific articles can be challenging at first. Remember that this is a skill that takes time to learn but that your skills will become stronger the more that you read.
- Take a rough draft of your paper to your school's writing lab for additional feedback and use your university library's resources.
What This Means For You
Being able to write a solid article critique is a useful academic skill. While it can be challenging, start by breaking down the sections of the paper, noting your initial thoughts and questions. Then structure your own critique so that you present a summary followed by your evaluation. In your critique, include the strengths and the weaknesses of the article.
Archibald D, Martimianakis MA. Writing, reading, and critiquing reviews . Can Med Educ J . 2021;12(3):1-7. doi:10.36834/cmej.72945
Pautasso M. Ten simple rules for writing a literature review . PLoS Comput Biol . 2013;9(7):e1003149. doi:10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003149
Gülpınar Ö, Güçlü AG. How to write a review article? Turk J Urol . 2013;39(Suppl 1):44–48. doi:10.5152/tud.2013.054
Erol A. Basics of writing review articles . Noro Psikiyatr Ars . 2022;59(1):1-2. doi:10.29399/npa.28093
American Psychological Association. Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association (7th ed.). Washington DC: The American Psychological Association; 2019.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."

Article Critique
In the realm of academia and intellectual discourse, the art of critiquing articles holds significant importance. It not only refines one’s skills but also contributes to the growth of knowledge. A well-executed article critique showcases your ability to analyze, evaluate, and engage with scholarly work. This article delves into the concept of article critiques, offering insights into their purpose and benefits, along with a step-by-step guide on how to craft one effectively.
1. Quantitative Article Critique

Size: 36 KB
2. Article Critique Guidelines
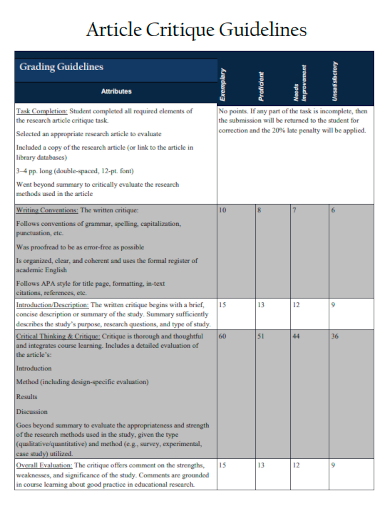
Size: 222 KB
3. Sample Article Critiques

Size: 321 KB
4. Critiquing Research Articles

Size: 123 KB
5. Basic Article Critique

Size: 402 KB
6. Article Review & Critiques

Size: 420 KB
7. Instructions for Article Critiques

Size: 282 KB
8. Article Critique or Annotated Bibliography

Size: 87 KB
9. Critique of an Academic Article
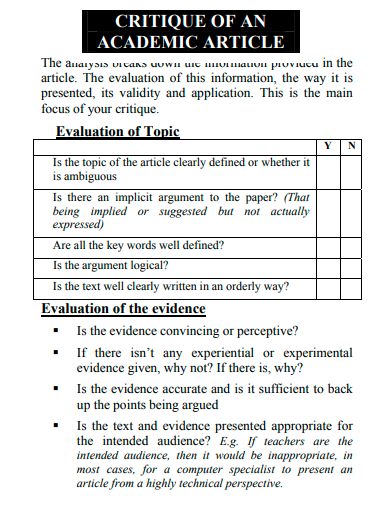
Size: 187 KB
10. Critique and Review of Research Articles

Size: 152 KB
11. Editable Article Critique

Size: 63 KB
12. Article Critique Assignment

Size: 10 KB
13. Qualitative Article Critique

Size: 99 KB
14. Article Critique Worksheet
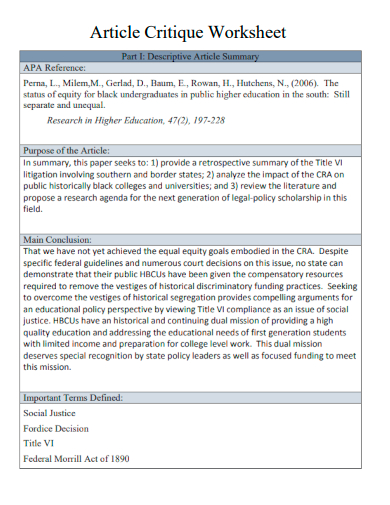
Size: 250 KB
15. Representative Article Critique

Size: 203 KB
16. Book Review or Article Critique

Size: 65 KB
17. Journal Article Critique

Size: 181 KB
18. Press Article Critique
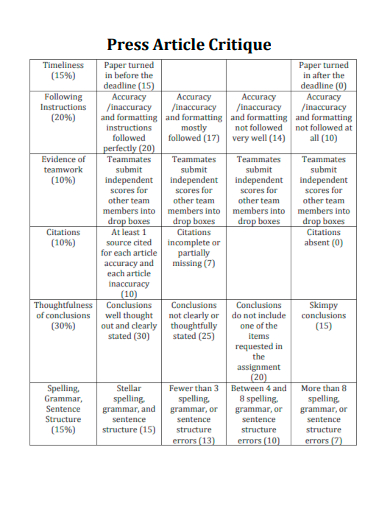
Size: 32 KB
19. Article Critique to a Literature Review
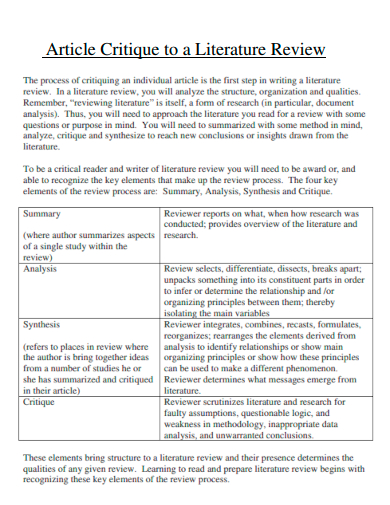
20. Formal Article Critique

Size: 395 KB
21. Assignment Outline Article Critique

Size: 255 KB
22. Modern Article Critique

Size: 140 KB
What is an Article Critique?
An article critique is a detailed evaluation and analysis of a scholarly article or research paper. It involves an objective assessment of the author’s arguments, evidence, methodology, and conclusions. An effective critique goes beyond summarizing the content; it delves into the strengths, weaknesses, and implications of the article. Developing this skill allows you to identify the characteristics that contribute to a compelling scholarly work, while also honing your ability to engage critically with academic literature.
How to Write an Article Critique
Mastering the art of crafting an effective article critique requires a systematic approach. Here is a step-by-step guide to help you navigate this process with finesse.
Step 1: Reading and Observation
Before diving into the critique, thoroughly read the article. Take notes on the main points, observation , objectives , and tone of the article. Identify the author’s goals and the case study , if applicable. This step is crucial for grasping the nuances of the work.
Step 2: Analyzing Structure and Content
Evaluate the structure of the article. Identify the introduction, main arguments, supporting evidence, and conclusion. Examine the use of verbs and analogies , as well as the cause-and-effect relationships presented. Analyze how effectively the author communicates their ideas.
Step 3: Assessing Methodology and Evidence
Scrutinize the methodology used by the author. Is it appropriate for the objectives of the article? Evaluate the quality and relevance of the evidence presented. Consider whether the evidence supports the author’s claims adequately.
Step 4: Critical Evaluation
Engage in a critical evaluation of the article. Identify its strengths and weaknesses. Does the author effectively address counterarguments? Are there any gaps in the logic? Assess the overall coherence and effectiveness of the article’s presentation.
What is the main objective of an article critique?
An article critique aims to assess the quality and validity of a scholarly work. It involves evaluating the author’s arguments, evidence, and methodology to determine the article’s overall contribution to the field.
How important is the tone in an article critique?
The tone of an article critique should be professional and objective. It’s essential to maintain a respectful tone while conveying your analytical insights and evaluations.
Can I use analogies in my article critique?
Yes, incorporating relevant analogies can enhance your critique’s clarity and impact. Analogies can help illustrate complex concepts and strengthen your points.
Mastering the art of article critique involves honing a set of skills that enable you to objectively evaluate scholarly works. By understanding the goals, analyzing the tone, assessing the evidence, and recognizing strengths and weaknesses, you contribute to the ongoing academic conversation in a meaningful way. Remember, an effective critique not only highlights areas of improvement but also acknowledges the valuable contributions made by the author. Through this process, you become an integral part of the scholarly exchange that drives intellectual growth and advancement.

AI Generator
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting

Writing a Critique
- About this Guide
- What Is a Critique?
- Getting Started
- Components of a Critique Essay
Examples of Critique
You can find critiques in DragonQuest by including the term "critique" in your search. Here are a few examples of articles that provide critiques:
Babb, A. M., Knudsen, D. C., & Robeson, S. M. (2019). A critique of the objective function utilized in calculating the Thrifty Food Plan. PLoS
ONE , 14 (7), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0219895
Greene-Woods, A. (2020). The Efficacy of Signing Standard English for Increasing Reading Achievement: An Article Critique. American Annals of
the Deaf , 165 (4), 456–460.
Pochron, R. Scott. (2008). Article Review: Advanced Change Theory Revisited: An Article Critique. Integral Review , 4 (2), 125–132.
Schmidt, N. (2020). Beyond the Personal: The Systemic Critique of German Graphic Medicine. Seminar: A Journal of Germanic Studies , 56 (3–4).
- << Previous: Components of a Critique Essay
- Next: Get Help >>
- Last Updated: May 22, 2023 10:46 AM
- URL: https://library.tiffin.edu/critique
How to Write an Article Review: Template & Examples
An article review is an academic assignment that invites you to study a piece of academic research closely. Then, you should present its summary and critically evaluate it using the knowledge you’ve gained in class and during your independent study. If you get such a task at college or university, you shouldn’t confuse it with a response paper, which is a distinct assignment with other purposes (we’ll talk about it in detail below).
Our specialists will write a custom essay specially for you!
In this article, prepared by Custom-Writing experts, you’ll find:
- the intricacies of article review writing;
- the difference between an article review and similar assignments;
- a step-by-step algorithm for review composition;
- a couple of samples to guide you throughout the writing process.
So, if you wish to study our article review example and discover helpful writing tips, keep reading.
❓ What Is an Article Review?
- ✍️ Writing Steps
📑 Article Review Format
🔗 references.
An article review is an academic paper that summarizes and critically evaluates the information presented in your selected article.

The first thing you should note when approaching the task of an article review is that not every article is suitable for this assignment. Let’s have a look at the variety of articles to understand what you can choose from.
Popular Vs. Scholarly Articles
In most cases, you’ll be required to review a scholarly, peer-reviewed article – one composed in compliance with rigorous academic standards. Yet, the Web is also full of popular articles that don’t present original scientific value and shouldn’t be selected for a review.
Just in 1 hour! We will write you a plagiarism-free paper in hardly more than 1 hour
Not sure how to distinguish these two types? Here is a comparative table to help you out.
Article Review vs. Response Paper
Now, let’s consider the difference between an article review and a response paper:
- If you’re assigned to critique a scholarly article , you will need to compose an article review .
- If your subject of analysis is a popular article , you can respond to it with a well-crafted response paper .
The reason for such distinctions is the quality and structure of these two article types. Peer-reviewed, scholarly articles have clear-cut quality criteria, allowing you to conduct and present a structured assessment of the assigned material. Popular magazines have loose or non-existent quality criteria and don’t offer an opportunity for structured evaluation. So, they are only fit for a subjective response, in which you can summarize your reactions and emotions related to the reading material.
All in all, you can structure your response assignments as outlined in the tips below.
✍️ How to Write an Article Review: Step by Step
Here is a tried and tested algorithm for article review writing from our experts. We’ll consider only the critical review variety of this academic assignment. So, let’s get down to the stages you need to cover to get a stellar review.
Receive a plagiarism-free paper tailored to your instructions. Cut 20% off your first order!
Read the Article
As with any reviews, reports, and critiques, you must first familiarize yourself with the assigned material. It’s impossible to review something you haven’t read, so set some time for close, careful reading of the article to identify:
- Its topic.
- Its type.
- The author’s main points and message.
- The arguments they use to prove their points.
- The methodology they use to approach the subject.
In terms of research type , your article will usually belong to one of three types explained below.
Summarize the Article
Now that you’ve read the text and have a general impression of the content, it’s time to summarize it for your readers. Look into the article’s text closely to determine:
- The thesis statement , or general message of the author.
- Research question, purpose, and context of research.
- Supporting points for the author’s assumptions and claims.
- Major findings and supporting evidence.
As you study the article thoroughly, make notes on the margins or write these elements out on a sheet of paper. You can also apply a different technique: read the text section by section and formulate its gist in one phrase or sentence. Once you’re done, you’ll have a summary skeleton in front of you.
Evaluate the Article
The next step of review is content evaluation. Keep in mind that various research types will require a different set of review questions. Here is a complete list of evaluation points you can include.
Get an originally-written paper according to your instructions!
Write the Text
After completing the critical review stage, it’s time to compose your article review.
The format of this assignment is standard – you will have an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. The introduction should present your article and summarize its content. The body will contain a structured review according to all four dimensions covered in the previous section. The concluding part will typically recap all the main points you’ve identified during your assessment.
It is essential to note that an article review is, first of all, an academic assignment. Therefore, it should follow all rules and conventions of academic composition, such as:
- No contractions . Don’t use short forms, such as “don’t,” “can’t,” “I’ll,” etc. in academic writing. You need to spell out all those words.
- Formal language and style . Avoid conversational phrasing and words that you would naturally use in blog posts or informal communication. For example, don’t use words like “pretty,” “kind of,” and “like.”
- Third-person narrative . Academic reviews should be written from the third-person point of view, avoiding statements like “I think,” “in my opinion,” and so on.
- No conversational forms . You shouldn’t turn to your readers directly in the text by addressing them with the pronoun “you.” It’s vital to keep the narrative neutral and impersonal.
- Proper abbreviation use . Consult the list of correct abbreviations , like “e.g.” or “i.e.,” for use in your academic writing. If you use informal abbreviations like “FYA” or “f.i.,” your professor will reduce the grade.
- Complete sentences . Make sure your sentences contain the subject and the predicate; avoid shortened or sketch-form phrases suitable for a draft only.
- No conjunctions at the beginning of a sentence . Remember the FANBOYS rule – don’t start a sentence with words like “and” or “but.” They often seem the right way to build a coherent narrative, but academic writing rules disfavor such usage.
- No abbreviations or figures at the beginning of a sentence . Never start a sentence with a number — spell it out if you need to use it anyway. Besides, sentences should never begin with abbreviations like “e.g.”
Finally, a vital rule for an article review is properly formatting the citations. We’ll discuss the correct use of citation styles in the following section.
When composing an article review, keep these points in mind:
- Start with a full reference to the reviewed article so the reader can locate it quickly.
- Ensure correct formatting of in-text references.
- Provide a complete list of used external sources on the last page of the review – your bibliographical entries .
You’ll need to understand the rules of your chosen citation style to meet all these requirements. Below, we’ll discuss the two most common referencing styles – APA and MLA.
Article Review in APA
When you need to compose an article review in the APA format , here is the general bibliographical entry format you should use for journal articles on your reference page:
- Author’s last name, First initial. Middle initial. (Year of Publication). Name of the article. Name of the Journal, volume (number), pp. #-#. https://doi.org/xx.xxx/yyyy
Horigian, V. E., Schmidt, R. D., & Feaster, D. J. (2021). Loneliness, mental health, and substance use among US young adults during COVID-19. Journal of Psychoactive Drugs, 53 (1), pp. 1-9. https://doi.org/10.1080/02791072.2020.1836435
Your in-text citations should follow the author-date format like this:
- If you paraphrase the source and mention the author in the text: According to Horigian et al. (2021), young adults experienced increased levels of loneliness, depression, and anxiety during the pandemic.
- If you paraphrase the source and don’t mention the author in the text: Young adults experienced increased levels of loneliness, depression, and anxiety during the pandemic (Horigian et al., 2021).
- If you quote the source: As Horigian et al. (2021) point out, there were “elevated levels of loneliness, depression, anxiety, alcohol use, and drug use among young adults during COVID-19” (p. 6).
Note that your in-text citations should include “et al.,” as in the examples above, if your article has 3 or more authors. If you have one or two authors, your in-text citations would look like this:
- One author: “According to Smith (2020), depression is…” or “Depression is … (Smith, 2020).”
- Two authors: “According to Smith and Brown (2020), anxiety means…” or “Anxiety means (Smith & Brown, 2020).”
Finally, in case you have to review a book or a website article, here are the general formats for citing these source types on your APA reference list.
Article Review in MLA
If your assignment requires MLA-format referencing, here’s the general format you should use for citing journal articles on your Works Cited page:
- Author’s last name, First name. “Title of an Article.” Title of the Journal , vol. #, no. #, year, pp. #-#.
Horigian, Viviana E., et al. “Loneliness, Mental Health, and Substance Use Among US Young Adults During COVID-19.” Journal of Psychoactive Drugs , vol. 53, no. 1, 2021, pp. 1-9.
In-text citations in the MLA format follow the author-page citation format and look like this:
- According to Horigian et al., young adults experienced increased levels of loneliness, depression, and anxiety during the pandemic (6).
- Young adults experienced increased levels of loneliness, depression, and anxiety during the pandemic (Horigian et al. 6).
Like in APA, the abbreviation “et al.” is only needed in MLA if your article has 3 or more authors.
If you need to cite a book or a website page, here are the general MLA formats for these types of sources.
✅ Article Review Template
Here is a handy, universal article review template to help you move on with any review assignment. We’ve tried to make it as generic as possible to guide you in the academic process.
📝 Article Review Examples
The theory is good, but practice is even better. Thus, we’ve created three brief examples to show you how to write an article review. You can study the full-text samples by following the links.
📃 Men, Women, & Money
This article review examines a famous piece, “Men, Women & Money – How the Sexes Differ with Their Finances,” published by Amy Livingston in 2020. The author of this article claims that men generally spend more money than women. She makes this conclusion from a close analysis of gender-specific expenditures across five main categories: food, clothing, cars, entertainment, and general spending patterns. Livingston also looks at men’s approach to saving to argue that counter to the common perception of women’s light-hearted attitude to money, men are those who spend more on average.
📃 When and Why Nationalism Beats Globalism
This is a review of Jonathan Heidt’s 2016 article titled “When and Why Nationalism Beats Globalism,” written as an advocacy of right-wing populism rising in many Western states. The author illustrates the case with the election of Donald Trump as the US President and the rise of right-wing rhetoric in many Western countries. These examples show how nationalist sentiment represents a reaction to global immigration and a failure of globalization.
📃 Sleep Deprivation
This is a review of the American Heart Association’s article titled “The Dangers of Sleep Deprivation.” It discusses how the national organization concerned with the American population’s cardiovascular health links the lack of high-quality sleep to far-reaching health consequences. The organization’s experts reveal how a consistent lack of sleep leads to Alzheimer’s disease development, obesity, type 2 diabetes, etc.
✏️ Article Review FAQ
A high-quality article review should summarize the assigned article’s content and offer data-backed reactions and evaluations of its quality in terms of the article’s purpose, methodology, and data used to argue the main points. It should be detailed, comprehensive, objective, and evidence-based.
The purpose of writing a review is to allow students to reflect on research quality and showcase their critical thinking and evaluation skills. Students should exhibit their mastery of close reading of research publications and their unbiased assessment.
The content of your article review will be the same in any format, with the only difference in the assignment’s formatting before submission. Ensure you have a separate title page made according to APA standards and cite sources using the parenthetical author-date referencing format.
You need to take a closer look at various dimensions of an assigned article to compose a valuable review. Study the author’s object of analysis, the purpose of their research, the chosen method, data, and findings. Evaluate all these dimensions critically to see whether the author has achieved the initial goals. Finally, offer improvement recommendations to add a critique aspect to your paper.
- Scientific Article Review: Duke University
- Book and Article Reviews: William & Mary, Writing Resources Center
- Sample Format for Reviewing a Journal Article: Boonshoft School of Medicine
- Research Paper Review – Structure and Format Guidelines: New Jersey Institute of Technology
- Article Review: University of Waterloo
- Article Review: University of South Australia
- How to Write a Journal Article Review: University of Newcastle Library Guides
- Writing Help: The Article Review: Central Michigan University Libraries
- Write a Critical Review of a Scientific Journal Article: McLaughlin Library
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to LinkedIn
- Share to email

Short essays answer a specific question on the subject. They usually are anywhere between 250 words and 750 words long. A paper with less than 250 words isn’t considered a finished text, so it doesn’t fall under the category of a short essay. Essays of such format are required for...

High school and college students often face challenges when crafting a compare-and-contrast essay. A well-written paper of this kind needs to be structured appropriately to earn you good grades. Knowing how to organize your ideas allows you to present your ideas in a coherent and logical manner This article by...

If you’re a student, you’ve heard about a formal essay: a factual, research-based paper written in 3rd person. Most students have to produce dozens of them during their educational career. Writing a formal essay may not be the easiest task. But fear not: our custom-writing team is here to guide...

Narrative essays are unlike anything you wrote throughout your academic career. Instead of writing a formal paper, you need to tell a story. Familiar elements such as evidence and arguments are replaced with exposition and character development. The importance of writing an outline for an essay like this is hard...

A précis is a brief synopsis of a written piece. It is used to summarize and analyze a text’s main points. If you need to write a précis for a research paper or the AP Lang exam, you’ve come to the right place. In this comprehensive guide by Custom-Writing.org, you’ll...

A synthesis essay requires you to work with multiple sources. You combine the information gathered from them to present a well-rounded argument on a topic. Are you looking for the ultimate guide on synthesis essay writing? You’ve come to the right place! In this guide by our custom writing team,...

Do you know how to make your essay stand out? One of the easiest ways is to start your introduction with a catchy hook. A hook is a phrase or a sentence that helps to grab the reader’s attention. After reading this article by Custom-Writing.org, you will be able to...

Critical thinking is the process of evaluating and analyzing information. People who use it in everyday life are open to different opinions. They rely on reason and logic when making conclusions about certain issues. A critical thinking essay shows how your thoughts change as you research your topic. This type...

Process analysis is an explanation of how something works or happens. Want to know more? Read the following article prepared by our custom writing specialists and learn about: process analysis and its typesa process analysis outline tipsfree examples and other tips that might be helpful for your college assignment So,...

A visual analysis essay is an academic paper type that history and art students often deal with. It consists of a detailed description of an image or object. It can also include an interpretation or an argument that is supported by visual evidence. In this article, our custom writing experts...

Want to know how to write a reflection paper for college or school? To do that, you need to connect your personal experiences with theoretical knowledge. Usually, students are asked to reflect on a documentary, a text, or their experience. Sometimes one needs to write a paper about a lesson...

A character analysis is an examination of the personalities and actions of protagonists and antagonists that make up a story. It discusses their role in the story, evaluates their traits, and looks at their conflicts and experiences. You might need to write this assignment in school or college. Like any...

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
After summarizing the article, critique the article by doing the following: Discuss the strengths and weaknesses of the article that you noted while critically reading the article. State your informed opinions about the clarity, relevancy, and accuracy of the article, using specific examples from the article to support your statements.
In simple terms, an article critique is a type of essay writing where an author should provide sufficient, unbiased, critical evaluation of the article in question. Of course, it will involve at least a brief summary of the contents and information about the author's background (if it is necessary). ... The Article Critique Example As an ...
Example of a critique To help you apply the concepts and steps described above, the following is a condensed example of a critique of an academic article: In the article "Anxiety Among Students: Higher Anxiety Levels Found in New Students," Hunter Allen examined the impact of anxiety across all levels of college students. He argued that students just entering college or who are in their first ...
Step 9: Presenting Your Critique. Organize your critique into a well-structured paper, starting with an introduction that outlines the article's context and purpose. Develop a clear and focused thesis statement that conveys your assessment. Support your points with evidence from the article and other credible sources.
It's your first essay in ENG 112, and, of course, you want to do well. This handout offers some helpful hints for writing the first essay—The Critique. Remember the author! The critique essay is not about concerned with the content of the article - but whether or not the AUTHOR of the article presented an effective (or ineffective) argument.
A 'critical review', or 'critique', is a complete type of text (or genre), discussing one particular article or book in detail. In some instances, you may be asked to write a critique of two or three articles (e.g. a comparative critical review). In contrast, a 'literature review', which also needs to be 'critical', is a part of a larger type ...
of the article and the supporting points that the article uses. o 3 Read the article again. To write a thorough article critique you must have thorough knowledge of the article. Reading it more than once helps to ensure that you haven't missed any important details. o 4 Consider the credentials of the author. Does the author of the article
The critique is your evaluation of the resource. A strong critique: Discusses the strengths of the resource. Discusses the weaknesses of the resource. Provides specific examples (direct quotes, with proper citation) as needed to support your evaluation. Discusses anything else pertinent to your evaluation, including.
so that your review will be clear to a reader who may not have read the study. 4. Aim for an objective, balanced, and well supported critique. Polit and Beck (2008) advise2: a. Balance your analysis to include both strengths and weakness b. Justify your criticism by giving examples of the study's weaknesses and strengths 5.
Example of Critique Essay On Articles. An article-related critique essay is a paper that evaluates an article to determine its effectiveness in attaining a goal. An article could comprise opinions, personal experiences, and external research. This essay entertains, informs, persuades, or educates readers. An article critique differs from a ...
A critique asks you to evaluate an article and the author's argument. You will need to look critically at what the author is claiming, evaluate the research methods, and look for possible problems with, or applications of, the researcher's claims. ... Was the sample too small to generalize from? Was the participant group lacking in ...
Writing Critiques. Writing a critique involves more than pointing out mistakes. It involves conducting a systematic analysis of a scholarly article or book and then writing a fair and reasonable description of its strengths and weaknesses. Several scholarly journals have published guides for critiquing other people's work in their academic area.
The increasing rates of incarceration and recidivism in the US confirm the need for public and private entities to run probation programs. The Penal Volunteer Sector (PVS) organizations are charitable [...] Essays.io is a stock of free Article Critique examples ️ from students accepted to Harvard, Stanford, and other elite schools.
Any article critique example APA opens up with a cover page that shows a paper title, student name, college or university name and date. Next goes the abstract. This is the specific feature of APA style so do not skip it. Abstract is about half a page long and it sums up what will be presented in the critique, that is, main points of analysis ...
interpret the author's intention. summarise and evaluate the value of an article, stating whether you agree or disagree with the author, with supporting evidence. Steps involved in writing an article critique: Read the article for the first time to understand its main ideas. If you are unsure whether you understand it clearly, reread it.
Step 3: Drafting the Essay. Finally, it is time to draft your essay. First of all, you'll need to write a brief overview of the text you're analyzing. Then, formulate a thesis statement - one sentence that will contain your opinion of the work under scrutiny. After that, make a one-paragraph summary of the text.
What is an Article Critique? An article critique is an evaluation of an article or essay to determine its effectiveness in achieving its goal. The terms "article" and "essay" are sometimes used ...
What is a Critique? An overview of the standard critique essay. Getting Started Tips to set yourself up for success when writing a critique Components of a Critique Essay The components of a critique essay and how to write them; Examples Example critique articles; Get Help Provides links to additional resources that were not otherwise mentioned.
To write a good critical review, you will have to engage in the mental processes of analyzing (taking apart) the work-deciding what its major components are and determining how these parts (i.e., paragraphs, sections, or chapters) contribute to the work as a whole. Analyzing the work will help you focus on how and why the author makes certain ...
To write an article critique, you should: Read the article, noting your first impressions, questions, thoughts, and observations. Describe the contents of the article in your own words, focusing on the main themes or ideas. Interpret the meaning of the article and its overall importance. Critically evaluate the contents of the article ...
An article critique is a detailed evaluation and analysis of a scholarly article or research paper. It involves an objective assessment of the author's arguments, evidence, methodology, and conclusions. An effective critique goes beyond summarizing the content; it delves into the strengths, weaknesses, and implications of the article.
Examples of Critique. You can find critiques in DragonQuest by including the term "critique" in your search. Here are a few examples of articles that provide critiques: Babb, A. M., Knudsen, D. C., & Robeson, S. M. (2019). A critique of the objective function utilized in calculating the Thrifty Food Plan. PLoS.
Article Review vs. Response Paper . Now, let's consider the difference between an article review and a response paper: If you're assigned to critique a scholarly article, you will need to compose an article review.; If your subject of analysis is a popular article, you can respond to it with a well-crafted response paper.; The reason for such distinctions is the quality and structure of ...