

How to Write a Nursing Reflective Essay (Guide for Nurse Students)

If you are a nursing or medicine student, you are aware that you will come across or have already come across assignments requiring you to write a nursing reflection essay. At first, such a task always appears challenging, but given the understanding of the steps, things flat out, and you can write reflective essays and get better grades.
Reflective practice is highly encouraged in nursing. Reflection entails making sense of situations, events, actions, and phenomena in the workplace.
As a nursing student, you will be asked to write a reflective essay on your clinical placement, practicum, shadowing experience, shadow health DCE activities, personal nursing philosophy, why you want to become a nurse, nursing program, ethical dilemma, knowledge, skills, and abilities, systems, and processes.
The easiest way to complete the reflective essay assignment is by first determining what reflective writing entails, its significance, its steps, and some of the best tips that form the core of this ultimate guide.
Basics of Reflective Writing in Nursing
Reflective writing is an analytical writing practice where the writer describes a real or imaginary event, scene, phenomenon, occurrence, or memory, including their takeaway. It entails the critical analysis of an experience, including recording how it has impacted you and what you intend to do with the new knowledge or how to act when such an occurrence recurs.
As you document the encounter, you can use first-person pronouns and write subjectively and objectively. This means that you can decide to either use personal experiences alone or support these experiences using citations from scholarly sources.
When writing a reflective essay in nursing, you must recount the events and give critical detail of how the events shaped your knowledge acquisition. Reflection helps nursing students develop skills in self-directed learning, which is directly associated with high motivation and improved quality of care .
In most cases, reflection occurs on what went well and what went wrong. It could be a successful operation, a thank you note from a patient, a patient who regained their health faster, or a new nursing care plan that worked. However, it can also be about adverse events such as death, postoperative complications, death of an infant at birth, dissatisfied patient, medical error, or a failed procedure.
As a nursing student, when you learn to reflect on situations, you grow to become a professional nurse who diligently does their noble duty.
When writing a reflective essay, you begin by setting the scene (explaining what, where, how, and who-the situation), detailing how you felt (emotional state), why it happened (making sense of the situation), critical review and development of insights, a note on what was learned, and strategies to address future recurrence.
Your professor may ask you to write a nursing reflective paper about various topics in your course or your experience working in a group, how you solved a problem, a healthcare issue, or clinical practice. Consider the following example of a reflective statement in nursing; in my clinical practices, I realized I focused more on the technical aspects but failed to explain what it was doing to improve their health. I would like to understand more about listening to patience and their concerns to better care for them.
As you will notice later, these reflective stages are structured into different reflective models and frameworks that we will explore in-depth. So, with the understanding of what comprises reflective writing and its importance in nursing, let's now get solid on the structure.
Related Reading:
- Philosophy of Nursing Example.
- Ideas and topics for nursing capstone or project papers
- How to write a SOAP note paper
- Top nursing debate topics
- Nursing Theories and Theorists.
Structure of a Reflective Essay in Nursing
A reflective essay is an analytical writing piece describing and evaluating encounters or experiences. When asked to write one, you should know that an excellent reflective essay consists of different parts, just like a typical academic essay. It comprises the cover or title page, introduction, body paragraphs, conclusions, and a references page.
The title page contains information about the assignment. If you are writing the reflective essay in APA, include these on the title page:
- Title of the reflective essay
- Course code and name
- Instructors name
- Name of your institution
- Date of submission
When writing in Harvard format, the title or the cover page will consist of the following:
- Title of the essay in title case and the page number (upper right margin),
- Title of the essay in CAPS,
- Name of class or course,
- Name of the instructor,
- Name of your school,
- City and state where your school is located and,
- The date of submission.
Introduction
The introduction begins with an attention grabber or a hook sentence to attract readers' attention. It should then explain the essay's purpose and signpost the ideas that will come later in the essay. The introduction also has a thesis statement at the end of the paragraph- the last sentence. The thesis is concise, clear, and relatable and should reflect your position.
Body Paragraphs
The body paragraphs of a reflective essay can be three or more, depending on the length of the essay. Essentially, the body comprises 80% of the total word count.
The first paragraph is where you describe the situation, including the events, why they occurred, how they occurred, and those involved.
The second paragraph entails your personal feelings or reaction to the situation and how it made you feel.
The third paragraph can include making sense of the situation. You have to think about why things happened the way they did. You should also critically review and develop insights based on the situation. Finally, think of the factors that could have influenced the situation.
The next paragraph should explain how the event or situation will change your practice, approach, decisions, perspective, or perception. This is where you evaluate the experience by detailing the knowledge and skills you took from the experience.
The last body paragraph should entail a critical reflection on the learning opportunities. First, describe the situation and what it made you learn. Next, elaborate on how you intend to make yourself better poised to address such situations.
Mostly, you should structure the body of your essay as per the preferred nursing reflective model.
After everything else falls into place, you need to summarize the information you presented in the essay. Then, finally, restate your thesis and have a call to action to bring a sense of closure to your readers.
Steps for Writing a Nursing Reflection Essay � The Guide
When assigned to write a reflective essay for your nursing class, here are the surefire steps to get you to success.
Read the instructions
The first step after receiving an assignment is to begin reading the instructions. as you read, note what your instructor or professor expects in the paper you will submit for marking.
Reading instructions helps you to get informed on the scope of the paper, word count, number of references and pages, and the formatting style to use.
Besides, you also get to plan your paper with the deadline highlighted in the instructions.
You need to get a conducive environment where you can start writing.
The first step of writing is to brainstorm about situations during your clinical hours when you were shadowing a Nurse Practitioner or one you have read about.
Assess whether the situation or scenario you have thought, encountered, or chosen can help you write a reflective essay that meets the requirements.
Research and Plan
After choosing a scenario, the next step is researching the best reflective model.
You can use your class text, the instructions, the college library, course readings, and online nursing journals to get articles and resources with information about specific reflective models.
Select the best reflective model and take notes on the steps it entails.
As you research, write down notes on how to address your paper based on your selected framework or model of reflection . Additionally, research nursing journal articles with information you can use when critically analyzing a situation.
Plan how you will handle the paper as well. For instance, as you research, develop a thesis statement that grounds your entire paper, then draft an outline on how to develop the thesis.
Write an Outline
Outlining is a crucial aspect of writing. It helps you envision how you will meet the objective of writing a reflective essay. As an essential part of the essay writing process, outlining helps create a good flow of ideas and can come in handy in helping you overcome writer's block. Your outline should comprise the following:
- The hook or attention grabber
- Thesis statement
- Main points of each body paragraph (topic sentence, evidence, examples, illustrations, etc.)
- Conclusion (restated thesis and call-to-action)
With the outline done, you should take a break and resume writing your first draft of the nursing reflection essay. Writing with an outline helps avoid mistakes and also helps you write faster.
Describe the Experience
Once you have identified the relevant experience, begin describing it chronologically.
Describe the experience that prompted you to consider nursing your ideal career goal. Think of this experience's key elements, such as the setting, patient demographics, and significant events that impacted you.
Show how these events changed your perspective on life. Ensure you are as descriptive as possible to paint a clear picture for readers.
Consider the following questions to come up with a good description:
- What happened?
- Was there someone involved? If yes, what part did they play?
- Where did the event take place?
- What actions did you take?
Set the context of this experience by giving relevant background information. Ensure you are objective and pay attention to the facts.
Provide a Reflection
Talk about your feelings and thoughts concerning the particular experience you went through. You have to be honest and open up about your initial expectations and challenges you faced at each stage of the experience. The following questions can help you come up with a good reflection:
- What was I trying to achieve?
- What prompted me to act the way I did?
- Are there any consequences for my actions? If yes, what are they?
- How did I feel about this event as it was happening?
- How did those around me react to it?
- How do I know how those around me felt about it?
Analyze the Experience
Description of an experience is essential, but so is analysis. You have to move beyond the surface and give a critical analysis of your experience.
State your actions, and your overall experience will give insights into your experience. Think of how the experience has impacted your actions, feelings, and thoughts.
Give an Evaluation
Evaluate the skills and knowledge you got from the experience. Show how you can apply these skills and knowledge in your nursing practice. Also, state the actions and interventions you took during the nursing experience.
State whether you achieved the desired outcome and if there are any specific areas that you need to improve on.
Talk about how you built or improved skills like communication, teamwork, and critical thinking.
As you evaluate the experience, identify what you believe to be your strengths and weaknesses in the nursing experience. What have you learned from the experience? State the areas where you excelled and what abilities contributed to your success.
Talk about how those you were with during the clinical experience complimented you. Similarly, acknowledge your weaknesses.
What kind of mistakes did you make, and how did you improve them? Talk about the tasks that drain you most during the experience.
Illustrate Learning
Demonstrate elements of deeper thought and reflection levels. This is a great point to include nursing theories in your reflection essay to support analysis of your experience.
Relate your experiences to the theoretical frameworks you were taught in class. This is effective learning and will demonstrate your ability to apply knowledge to real-life nursing situations.
Doing this will also show that you can effectively deduce different things from observations made during the reflection process.
Ensure you also demonstrate a change in perspective, as this will prove that you learned something from the experience.
Write Your Conclusion
Conclude by summarizing your points and highlighting the lessons learned.
The lessons you reached as part of your reflection should support your overall conclusion.
Also, restate your thesis statement.
Come Up with an Action Plan
Now that you have learned from your reflection develop an action plan for future nursing practice.
This part should contain all the details you have learned and actions needed to improve when faced with a similar situation. Consider the following questions:
- What would I change if faced with a similar situation?
- How can I develop the necessary skills needed to face this situation?
- How can I act differently in a similar situation?
Ensure you identify areas to improve and set realistic goals to enhance your nursing skills. Discuss how you intend to seek additional education, training, or mentorship to address your shortcomings.
Finally, end the essay with a happy note so readers know you learned something from the experiences.
Proofread, Edit, and Polish
After doing your first draft, take a break to relax and get out of the writing mood - it helps you to become objective.
You can then resume reading out loud to yourself, make necessary tweaks, and ensure that every part you include meets the rubric requirements.
Edit for grammar, punctuation, tenses, voice, spelling, and use of language. You should also proofread the essay to adhere to the style, organization, and presentation requirements.
Ensure that all the in-text citations are accounted for in the reference list and are up-to-date. You are good to go when you have an essay that meets all the instructions.
Finally, you can submit the paper for grading.
Writing is not everyone's cup of tea. For that reason, you can hire a nursing reflection essay writer from our website to assist you in crafting a top-grade paper. In addition, we have nursing writers whose forte is writing various nursing papers.
Choosing the suitable Reflective Model or Framework
As you can see above, many reflective models are used for your reflective essay. We have not exhaustively listed and expounded on all of them. Other reflective models and frameworks you can also consider when writing a reflective essay in nursing include:
- Bouds Reflective Model
- Brookfield Reflective Model
- Pender's Health Promotion Model
- Roper Logan and Tierney Model
- Driscoll Reflective Model
- The Johari window model
Note that most nursing instructors will often suggest the models they prefer for you to use in your essay.
For example, in most nursing reflective essays. Whichever the case, readily available information expands on each model to make it easier to write a reflection essay on a specific aspect of nursing education or practice.
Read the assignment rubric and instructions to understand the specific model. If it is unclear, ask for clarification from your instructor early enough.
Tips for Writing a Good Nursing Reflective Essay
As you try to figure out how to write a nursing reflective essay, keep the following tips in mind.
Choose the Right Topic
If the instructions from your professors involve choosing a topic for the reflective essay, you must select one that is meaningful to you.
This will ensure you can easily write and easily develop relevant elements about the topic. Therefore, take time to pick a topic that you find interesting.
As you write, ensure you stay on topic, whether sharing a one-off event or a recurrent story.
Use the Right Tone
A reflective essay is more personal, unlike other types of academic essays. This means you don't need a strict or formal tone.
Since this is about your experiences, use personal pronouns such as I and Me.
Be Vulnerable
You must be extremely vulnerable to learn how to write a reflective essay in nursing.
Be open about your thoughts, feelings, and beliefs about something you went through that sparked an interest in nursing.
It's okay to share mistakes or things you did wrong that eventually led you to this career path.
Choose the Right Focus
A reflection essay is all about narrating your experience during the nursing experience.
While including other people in your experience is okay, please let them not be the center of your reflection.
This is your essay, so you should be the focus of attention.
Keep it Brief
A good nursing reflection essay should be between 300 and 800 consciously written words. Because of this length, you must only write relevant information about your reflection. Refrain from lengthy reflections, as they make it difficult to pass your points across.
Convey Your Information Wisely
Even though a nursing reflection essay is about your personal experiences, it doesn't mean you should reveal everything about yourself. Ask yourself whether something is appropriate before including it in your paper.
Mistakes to Avoid When Writing a Reflection Essay in Nursing
A good reflection essay involves reflecting on your nursing studies and practices throughout school and career to demonstrate your competence. For this reason, there are certain mistakes you should be aware of when writing an essay.
Not including a Personal Story
Like food tastes bland without salt, so does a reflection essay without a personal story. At the center of a reflection essay is You. This means the essay should focus on your personal story that led you to want a nursing career. A lot of times, students miss out on this instead of talking about their story. You need more than just the personal qualities you think will be a great fit for the nursing program; you must also share a story that shows how well you contributed to nursing care.
Failing to Share Your Experience
You will lose points when you fail to include nursing-related experiences in your reflection essay. Mentioning that you want to be a nurse is great, but failing to show specific events that led to the desire will cost you a great point.
Plagiarizing Your Essay
Plagiarism is a serious academic offense because it is considered taking other people's ideas and using them as your own without crediting the author. So, provide relevant citations and references for any ideas that aren't your own. Also, an AI will not write your essay as a human writer would.
Related Readings:
- How to write a student nurse resume with no experience.
- PICOT examples and guides
Sample of a Nursing Reflective Essay
The following is a sample of a nursing Reflective essay using Gibb's Model of Reflection. Use this sample to guide you when writing your own.
Introduction Communication is an important element in healthcare practice as it determines patient satisfaction and treatment outcomes. This essay will focus on reflecting on an experience I went through with a 40-year-old diabetic patient who also had a foot infected with an ulcer. When I approached the patient to sign the consent form, I noticed that he wasn't happy because of the news given to him about his health. I concluded that there must be a communication dilemma. I will reflect on the experience using Gibb's Model of Reflection. Using this model, I will identify and discuss the actions taken to resolve the issue. Description This incident happened a few months ago when I was working as a wound nurse in a Methodist hospital in my hometown. I was part of a care team handling the case of a 40-year-old male patient with diabetes and an infected diabetic foot ulcer. After careful examination, a team comprising various specialists concluded that his leg needed amputation below the knee. After making this decision, the team left, and I was asked to give the patient a consent form to sign. When I came back from retrieving the form, I noticed the patient looked sorrowful because of the news given to him. Feelings As soon as I saw the patient, I knew what he was going through. He perceived the situation to be irreparable, but I wasn't sure whether to console the patient or not. I was powerless and couldn't imagine what he was going through. At the same time, I was startled that the team left without showing any compassion. They could have handled the situation more delicately. I, on the other hand, could have relayed the information better. I wasn't sure whether my approach would be acceptable or appropriate. Evaluation I always go back to that particular situation and wonder whether I could have acted better. The situation helped me better understand the importance of good communication in patient care, particularly in therapeutic care. Before the incident, I didn't acknowledge the role of nurses play in caring for patient's emotional needs. I realized nurses must show compassion and console patients in their low moments. Analysis Most healthcare professionals do not know how to deliver bad news to patients. They find the process extremely challenging and always feel psychologically unprepared. This has a negative impact on patients and could lead to bad health outcomes. Furthermore, how information is relayed could impact a patient's adherence to treatment. Because of these effects, multiple protocols and approaches were developed to help with communicating bad news to patients. One of the approaches that was proposed is emotion-centered. This proposes that a healthcare provider acknowledges how sad the patient is and builds a professional relationship based on empathy and sympathy. Action Plan I now understand the essence of communicating bad news with compassion. The experience allowed me to look closely at different aspects of my professional development that needed more improvement. Thus, I plan to be more empathetic and speak up in support of patient's emotional and psychological well-being, especially when presented with traumatic news about their health. Additionally, I now understand I am not powerless when dealing with a sorrowful patient. I believe I have learned from my experience, and I'm not able to communicate well with patients any more. Conclusion The experience allowed me to value good communication in nursing and the need to incorporate it into daily nurse-patient interaction. Nurses must learn how to deliver bad news and manage patient's sorrow. This has been and will continue to be my biggest priority in patient care. References Street Jr, R. L., Makoul, G., Arora, N. K., & Epstein, R. M. (2009). How does communication heal? Pathways linking clinician–patient communication to health outcomes. Patient education and counselling, 74(3), 295-301. Buckman, R. (1992). Breaking bad news: why is it still so difficult? BMJ: British Medical Journal, 304(6842), 886. Ptacek, J. T., & Eberhardt, T. L. (1996). Breaking bad news: a review of the literature. The Journal of the American Medical Association, 276(6), 496-502.
Writing is not everyone's cup of tea. For that reason, you can hire a nursing reflection essay writer from NurseMyGrade to assist you in crafting a top-grade paper. In addition, we have nursing writers whose forte is writing various nursing papers. Just place an order , and we will get back to you ASAP.
Struggling with
Related Articles

Nursing Topics for Research plus Ideas

Middle-Range Nursing Theories

The Importance of Psychology in Nursing
NurseMyGrades is being relied upon by thousands of students worldwide to ace their nursing studies. We offer high quality sample papers that help students in their revision as well as helping them remain abreast of what is expected of them.

AFS Programs
Reflective Nursing Essays: Tips and Examples for Effective Writing

Reflective nursing essays provide a platform for nurses to share their experiences, challenges, and insights gained from their interactions with patients. These essays play a crucial role in nursing education as they help to develop critical thinking skills, improve patient-centred care, and establish a strong belief in the value of reflection.
When faced with severe situations in healthcare settings, nurses must cope with the emotional and mental strain they can experience. Reflecting on these experiences and the outcomes of their actions helps nurses to better understand their own role and influence on patient care. In addition, it assists them in improving their skills and knowledge in order to fulfill their role as patient advocates and caregivers.
A prime example of a reflective nursing essay is Amanda’s narrative on her experience with a palliative care patient. She recalls a particular incident where she had to dress the patient’s wound. Before the incident, Amanda wasn’t fully informed about the patient’s condition and was feeling a bit apprehensive. However, by reflecting on this experience, she was able to identify her fears and address them to ensure the patient’s comfort and dignity were not compromised.
Reflective nursing essays also help to enhance the empathic and patient-centred approach in nursing practice. By reflecting on their interactions with patients, nurses can better understand the needs and emotions of the individuals they care for. This understanding enables them to provide more effective and holistic care, thereby improving patient outcomes.
Reflective writing is not just something that nurses do for themselves; it can also be a valuable tool for sharing knowledge and experiences with other healthcare professionals. By using a reflective writing module, nurses can communicate their insights, ideas, and lessons learned to their colleagues and the wider nursing community.
How to Write Effective Reflective Nursing Essays
Reflective nursing essays are a valuable tool for practitioners to reflect on their experiences in the field, gain a deeper understanding of their own practice, and improve patient care outcomes. Introduced in the 20th century, reflective essays have become an integral part of nursing education and professional development.
Understanding the Purpose
Reflective nursing essays provide practitioners with the opportunity to critically evaluate their experiences and identify areas for improvement. By reflecting on past experiences, nurses can develop a better understanding of their own strengths and weaknesses, allowing them to fulfill their roles more effectively.
The Writing Process
When writing a reflective nursing essay, it is important to carefully plan and structure your thoughts. Start by describing the incident or experience you wish to reflect upon, providing as much detail as possible. Consider the significance of the event and how it relates to your practice as a nurse.
Next, critically analyze the situation to identify any areas where your practice may have been compromised or could be improved. Discuss any negative outcomes or challenges you faced, and consider how you could have acted differently to achieve a better result.
Using relevant literature and references, support your reflections with academic evidence. Cite relevant nursing theories, patient-centered care approaches, and any other related resources that help to demonstrate a sound understanding of the topic. By integrating theory and practice, you can showcase your knowledge and understanding.
The Personal Perspective
Reflective nursing essays are also an opportunity to examine the personal emotions and thoughts that emerged during the incident. Consider how you felt at the time and how those feelings may have influenced your behavior or decision-making process.
Reflecting on your emotions and reactions can provide insight into your own personal growth as a nurse. It helps you understand how certain situations impact you and how you can cope with similar incidents in the future.
Learning from Others
Reflective nursing essays can also incorporate insights gained from working with other healthcare professionals, such as doctors, students, or other nurses. Discuss how these interactions influenced your practice and what you learned from them.
Sharing your thoughts and experiences helps build stronger relationships with colleagues and fosters a culture of learning and improvement within the healthcare team. Reflecting on the perspectives of others provides a broader understanding of the incident and allows for a more holistic approach to patient care.
Writing reflective nursing essays is an essential part of professional development in the nursing field. It allows practitioners to critically analyze their own practice, understand their strengths and weaknesses, and identify areas for improvement.
By incorporating personal experiences and insights gained from working with others, reflective nursing essays help nurses improve their patient-centered care and contribute to the overall quality of healthcare delivery.
Understanding Reflective Writing in Nursing
Reflective writing provides a platform for nurses to reflect on their interactions with patients, colleagues, and the healthcare system as a whole. It helps them identify areas where they can improve, learn from mistakes, and make informed decisions in the future.
As a nurse, I have undergone several reflective writing exercises that have helped me understand and improve my practice. For example, in a module on teamwork, I reflected on a situation where I had to work with a small team to care for a patient with a severe wound. Through reflecting on this experience, I gained a better understanding of the importance of teamwork and how it can improve patient outcomes.
Reflective writing has also introduced me to new knowledge and best practices in nursing. For instance, in a reflective essay about wound care, I learned about the latest wound care techniques and how they can be used to effectively treat and heal wounds.
Reflective writing in nursing is not just about documenting experiences; it is a process of critical analysis and self-reflection. It helps nurses examine their thoughts, feelings, and behaviors in order to identify areas for improvement and growth.
The Australian Nursing and Midwifery Council (ANMC) emphasizes the importance of reflecting on practice as an integral part of nursing. They believe that reflective writing helps nurses become more informed, competent, and reflective practitioners.
Through reflective writing, nurses can share their experiences, ideas, and learnings with others in the field. This sharing of knowledge and insights helps create a supportive and collaborative environment where all healthcare professionals can learn from one another.
Reflective writing also plays a vital role in promoting positive change and improvement in healthcare services. By reflecting on their experiences, nurses can identify areas that need improvement and suggest informed solutions to enhance patient care.
Tips for Writing Reflective Nursing Essays
Reflective nursing essays provide an opportunity for nurses to critically analyze their experiences and reflect on their practice. Here are some tips to help you write an effective reflective nursing essay:
1. Understand the Reflective Cycle
Before you start writing your essay, it is important to understand the reflective cycle. The reflective cycle consists of four stages: description, feelings, evaluation, and analysis. Make sure to address each stage in your essay to fully capture your experience.
2. Plan your Essay
3. be informed.
When writing a reflective nursing essay, make sure to support your reflections with relevant knowledge. Draw on your nursing education, experiences, and any research you have conducted to inform your analysis.
4. Use Examples
It is important to provide examples in your essay to illustrate your points. Use specific situations or experiences to support your reflections and show how your nursing practice has evolved.
5. Be Critical
Reflective nursing essays require you to critically analyze your experiences. Consider both the positive and negative aspects of your practice and reflect on how they have shaped your growth as a nurse.
6. Maintain a Holistic Approach
When reflecting on your nursing practice, consider the holistic needs of your patients. Reflect on how you have addressed their physical, emotional, and mental well-being in your practice.
7. Emphasize the Importance of Teamwork
Nursing is a team effort, and it is important to reflect on the significance of teamwork in your practice. Discuss how you have collaborated with other healthcare professionals to provide the best care for your patients.
8. Reflect on Ethical and Dignity Considerations
In your reflective nursing essay, reflect on how you have maintained the dignity of your patients and considered ethical considerations in your practice. Discuss any challenges you have faced and how you have overcome them.
Examples of Reflective Nursing Essays
Example 1: patient-centred care.
Reflecting on my experience working in a community healthcare clinic, I realized the importance of providing patient-centred care. During a consultation, I noticed that the patient seemed withdrawn and hesitant to share their concerns. I realized that my approach was not effectively establishing trust and comfort. To address this, I introduced myself and informed the patient about the purpose of the visit. By taking the time to listen and showing empathy towards their concerns, I was able to provide better care and fulfill the patient’s needs.
Example 2: Professionalism and Advocacy
During my clinical placement in a busy hospital, I encountered a situation where a patient’s care was compromised due to a lack of communication between healthcare professionals. The incident led to a negative outcome for the patient. Reflecting on this experience, I realized the importance of being an advocate for patients and speaking up when necessary. I learnt the importance of effective communication and collaboration in the healthcare team to ensure patient safety and well-being.
Exploring the Emotional Aspect of Reflective Writing in Nursing
Reflective writing plays a significant role in the nursing profession. It allows nurses to critically reflect on their experiences and gain insight into their practice. However, reflective writing also involves exploring the emotional aspect of nursing, which can be both challenging and rewarding.
When I first started my nursing career, I was excited to graduate and put my skills into practice. But having actual patients and being responsible for their care was a whole new world. I quickly learned that nursing goes beyond the technical duties and skills taught in school. It requires empathy, compassion, and the ability to connect with people on a deeper level.
Reflective writing helped me navigate through various emotional situations. For example, I remember a patient named Mary who was diagnosed with severe cystic fibrosis. While explaining her diagnosis and treatment plan, I closely listened to her concerns and fears. Reflective writing allowed me to process my own emotions and evaluate how I could best support her during this difficult time.
In addition, reflective writing helped me establish professionalism in situations where legal and ethical dilemmas arose. I often found myself in tough situations where I had to make critical decisions regarding patient care. Reflective writing became my tool to evaluate my actions, assess their significance, and ensure that I acted appropriately and in the best interest of my patients.
Reflective writing also helped me reflect on my relationships with other healthcare professionals. In one instance, I had a disagreement with a doctor regarding a patient’s medication dosage. Through reflective writing, I was able to objectively assess the situation, evaluate the doctor’s perspective, and find a way to communicate effectively and resolve the issue.
Reflective writing helped me acknowledge the emotional toll that nursing can have on a person. It allowed me to reflect on the difficult experiences and find ways to improve my practice. For example, I remember a particularly challenging shift in the acute care unit where multiple patients were experiencing severe pain. Reflective writing helped me critically reflect on my actions during this time and identify areas where I could have provided better pain management and support.
What is a reflective nursing essay?
A reflective nursing essay is a type of essay where nursing students reflect on their experiences in a clinical setting and analyze their thoughts, feelings, and actions.
Why is reflective writing important in nursing education?
Reflective writing is important in nursing education because it allows students to critically analyze their experiences and identify areas for improvement. It helps students develop self-awareness and enhances their ability to provide quality care to patients.
What is reflective nursing essay?
A reflective nursing essay is a piece of writing that explores and analyzes one’s own experiences and actions in a nursing context. It involves a thoughtful and critical analysis of the nursing practice, where the writer reflects on their beliefs, attitudes, and behaviors in order to promote personal growth and improve patient care.

By Alex Koliada, PhD
Alex Koliada, PhD, is a well-known doctor. He is famous for studying aging, genetics, and other medical conditions. He works at the Institute of Food Biotechnology and Genomics. His scientific research has been published in the most reputable international magazines. Alex holds a BA in English and Comparative Literature from the University of Southern California , and a TEFL certification from The Boston Language Institute.
Your web browser is outdated and may be insecure
The RCN recommends using an updated browser such as Microsoft Edge or Google Chrome

Reflective journal writing: how can it help?

Discover the benefits of writing down your thoughts and how to get started
Reflective journal writing is a way of documenting what you’re thinking and feeling in the moment, and can be a useful tool to help manage stress and anxiety.
Dr Christopher Westoby, author of The Fear Talking: The True Story of a Young Man and Anxiety, is a strong believer in the power of stories to educate, improve understanding and benefit the wellbeing of the storyteller.
We spoke to Chris about the benefits of writing for your mental wellbeing.
Can reflective writing help nursing staff?
Absolutely. Regardless of your background, and wherever you work, everyone has this universal need to reflect upon their own experiences and one of the best tools we have for that is writing. It is similar to the process of opening the windows to a room and letting some air in.
Everyone has this universal need to reflect upon their own experiences
We all have so many thoughts and memories whirling round our head at any given time – especially in the current climate. Sometimes the cloud of everything happening at once can be more overwhelming than any one event itself. Reflective journal writing can help with that.
How does it help?
We often struggle to come to terms with whatever it is we’ve been through unless we take a second and address these things head on. And while it may not always be an easy thing to do – or a quick fix – by writing what’s going on internally, what you’re doing is externalising something that has been haunting you or playing on your mind. Once it’s out there on the page, it’s like you can lay it to rest.
You also now have a choice on what you want to do with it. Are you going to delete it or keep it for yourself? Are you going to let someone else read it? As you make those decisions, you’re taking control of your emotions and the clouds may start to clear.

So, what are the benefits?
The sense of control over your own experiences can be empowering and help relieve any stress or anxiety you’re experiencing. You’ve let it be acknowledged that what you’re feeling is something, it’s being validated and now it’s written down, it may no longer feel quite so insurmountable.
Any tips to get started?
My first tip is to use whatever format works best for you – whatever it is that will help get you in the habit of doing it. Don’t use handwriting if you’d rather type, and vice versa.
I’ve worked with students before who have talked about using voice memos. They’ve just hit record and then they either deleted it or transcribed it depending on what they’ve found most beneficial.
My second tip is to think of prompts. Maybe ask yourself questions to help get you started – what am I grateful for? What have I found difficult? Perhaps focus on one part of the day – how did I feel after my shift? On the way to work? Going to bed?
Finally, think about setting yourself some restrictions. Try setting a timer on your phone and then keep writing until it goes off. The more restrictions you set, the less daunting writing can be. You might actually find yourself more inspired.
How often should I write?
It’s a good thing to try and do every day – even if it’s only a few sentences – for as long as you find it useful. I’d suggest giving it a go for two weeks and see how you’re finding it.
What if I find it hard writing about myself?
If it seems too difficult writing about yourself, try writing about someone else or something you observed today – perhaps something you noticed on your journey home or through your window. If you write about something else, you will inevitably find yourself beginning to include elements of yourself.
If you’re finding it too emotionally draining to revisit certain memories, remember this writing is your property – you can change what you need to, you can change the details and you can just talk about a small part of it. The key is to remember that you’re in control and it’s up to you how you document it.
The key is to remember you're in control
There are fewer ways to offload to one another at the moment, to distract ourselves and to blow off steam, so even if journal writing doesn’t work for you, it’s worth a try.
The benefits might surprise you.

About Chris
Chris is Programme Director of the Hull Creative Writing MA (Online). His book The Fear Talking: The True Story of a Young Man and Anxiety was published in December 2020. He led the RCN’s workshop “Time to Write for Yourself” last year.

The power of plants
Good for us, great for patients – here’s why houseplants benefit everyone

‘Patient attack forced me to leave nursing'
How the RCN helped one member get compensation after a shocking workplace incident

5 simple exercises for nursing staff
Tackle back and neck pain with these easy exercises
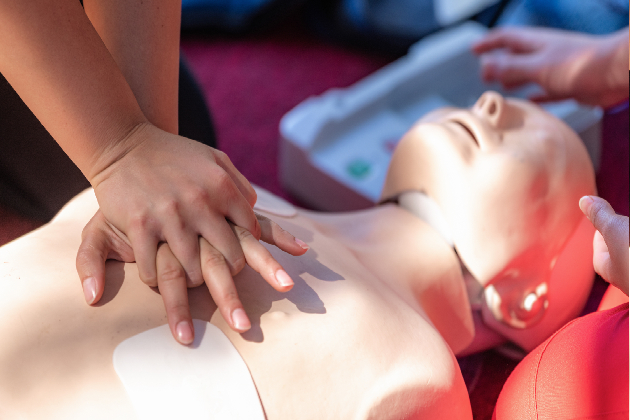
Tiring, distressing, emotional: the realities of giving CPR
And why debriefs are so important
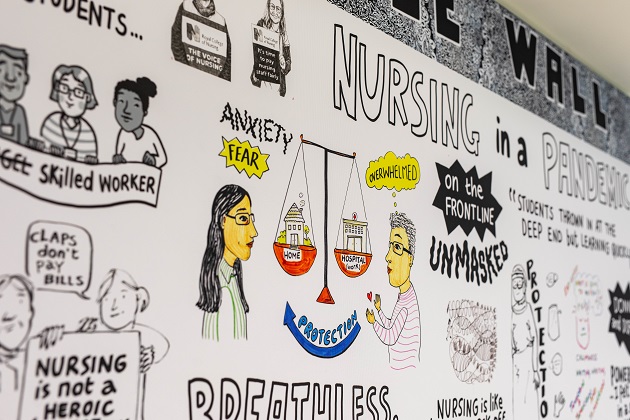

‘My doodles represent a silent scream’
How art helped this nurse with stress

A second chance at nursing
Hannah's story of hope after mental illness
{{ article.Title }}
{{ article.Summary }}
Reflection and mental health nursing. Part seven: reflection as a tool for teaching and learning
Reflection is an important skill in the armoury of the mental health nurse. Most nurses are familiar with its use in the review and development of their clinical client-centred practice; however, its use for the nurse's own development is less well appreciated. The author highlights how the elements of a reflective learning process can be used by the clinically based nurse to enhance the support of their students' learning. The principles of reflection before, during and after action are then explored as a tool in enhancing the clinician's own experiential learning, examining the dynamic relationship between experience and reflection.
- Related Documents
Mental Health Nurses as Psychotherapists: Missed opportunity or structural invisibility? Commentary on Hurley et al. (2020). The remarkable (Disappearing Act of the) mental health nurse psychotherapist. International Journal of Mental Health Nursing, doi: 10.1111/inm.12698
Mental health prescribing in scotland: time for change.
This article suggests that the time is right for the coherent strategic development of mental health nurse prescribing in Scotland. This conclusion comes from the synthesis of current theory and practice, i.e. there is no coherent theory opposing mental health nurse prescribing and the necessary supportive infrastructure is now known. In order to situate this discussion, the article begins with an overview of some of the broader issues mental health nurse prescribing faces. It then examines in detail one of the more enduring arguments which continues to oppose the introduction of prescribing in mental health nursing: nurses should not prescribe because they should be doing something else. A critical analysis of this position concludes that this perspective is misguided. More practical questions remain, however, but the article concludes that there is now enough evidence to support effective strategic leadership in mental health nurse prescribing, and reiterates the requisite infrastructure.
“But I’m not going to be a mental health nurse”: nursing students’ perceptions of the influence of experts by experience on their attitudes to mental health nursing
Objective structured clinical exam: a successful approach to pre-registration mental health nurse assessment.
Purpose Pre-registration mental health nursing courses are a mixture of clinical practice and university-based education completed over three years, culminating in a successful student entering the professional nursing register. During a student’s time at university they will encounter many different types of assessment, whether formative or summative. These are typically academic written assignments, academic exams, presentations, viva, assessed clinical practice by an approved mentor, and objective structured clinical exam (OSCE). The paper aims to discuss these issues. Design/methodology/approach An OSCE to assess second year mental health nursing students was determined to be a highly appropriate method of allowing students to demonstrate the skills associated with the nursing process, NMC standards and learning outcomes for the module. Findings It was recognised that preparation was essential in supporting the reduction of the student’s anxieties over the process, careful design and planning was needed to ensure reliability and validity of a logistically challenging assessment method. Originality/value OSCE have become a major contributor towards the assessment of student nurses and are regarded by some as the gold standard for assessment. However, this assessment has not been widely utilised within mental health nurse education and little research exists surrounding their use. This paper furthers the literature base on the use of OSCE by exploring the underpinning design rationale and the subjective experience of staff and students.
On becoming a qualifi ed mental health nurse
In this chapter we will consider the knowledge, skills, and attitudes expected of you as a newly qualified mental health nurse, before discussing how to apply for a job and develop your career. To help you consider this we have tried to include contributions from people who have a range of backgrounds and perspectives, who all contribute to mental health services, including a student about to qualify, a modern matron, a clinical manager, a director of nursing, a professor, and service users. To set the scene, our first personal contribution is from Julie Cresswell, a third year student nurse at the Birmingham City University and the Royal College of Nursing’s Student Nurse of the Year 2007. We asked Julie a series of questions that we hoped would help you in preparing to become a qualified nurse; these are her answers and thoughts about the future of mental health nursing and her career. In preparation for qualifying, I am now reflecting upon the experience, knowledge base, and skills that I have developed during my training, along with the transferable skills that I already had before I embarked upon this career. As mental health nursing students, we will all have followed a similar academic course equipping us with a certain level of theory and practical skills. However, what makes us individual is how we intend to use what we have learned throughout our lives and the philosophy that underpins our work. I began this course with the belief that psychiatric nursing was grounded in science. I now feel that while science can hypothesize about the causes of mental illness, understanding and accepting a client’s life experience is central to supporting them in times of mental distress. As I progress through my career, my approach may develop or change direction but for the moment, I feel that it will be vital to be able to communicate my own perspective to future employers. Developing your own approach to mental health nursing, along with an audit of what you can offer an employer in terms of practical skills, knowledge, and experience, establishes your own ‘unique selling point’ in a competitive jobs market.
Mental health law
This book has been written to reflect modern ideas about what constitutes good mental health nursing care, and you will see that values such as partnership working within the framework of a therapeutic relationship have been deliberately stressed. However, the role of the mental health nurse has always required some involvement in what is essentially custodial care. It is necessary for us as mental health nurses to try to balance the demands of these two seemingly paradoxical elements of the role of a mental health nurse. This chapter is intended to introduce you to some aspects of mental health law. We have partly based this upon the law as it currently applies in England and Wales but you will notice that we have also tried to include some material from an international perspective. The history of the profession of mental health nursing is inextricably bound up with the story of the rise and fall of the asylum and with institutionalized models of care. It was only following the Macmillan commission, which was set up to investigate allegations of abuse at Prestwich Hospital in 1924, that the term ‘psychiatric nurse’ (which later evolved to mental health nurse, Department of Health 1994) became a commonly used description (Coppock and Hopton 2000). Prior to this time, people working in institutions for the mentally disordered were more oft en referred to as ‘attendants’ or ‘keepers’ (Nolan 1998), and as these names imply, their roles were mostly custodial or supervisory in nature. Mental health nursing has moved away from this limited model of providing ‘care’ but is still unusual amongst other health care professions in that its members continue to be involved in compulsory detention (even though the main responsibility for this rests with the medical profession; Rogers and Pilgrim 2001). In England and Wales the 1983 Mental Health Act and its 2007 update is currently the legislation directing compulsory treatment of people with mental disorder. In common with legislation in most countries, this Mental Health Act aims to achieve a balance between the rights of the individual mental health patient to be treated and protected and the perceived need to protect others.
Resisting Technical Rationality in Mental Health Nurse Higher Education: A Duoethnography
This duoethnographic study has three aims: the first is to coherently situate our emerging duoethnographic dialogue in relation to an overview of both its parent methodology and related approaches within the narrative inquiry paradigm. Our second aim is to then enable readers to make contextual sense of our dialogue. We do so by prefacing it with a brief, focused overview of our theoretical, empirical and fiction work, and related literature, selected for the purpose of clarification. Following this, our final aim is to demonstrate in our dialogue the differences between our respective attempts as academics to work against the neoliberal ideology of technical rationality. We believe that this negatively impacts on contemporary mental health nurse higher education and thus necessitates our respective remedial contributions to this discipline. We conclude by considering the extent to which we feel we have met our aims and describing emerging implications for mental health nursing and other scholars, internationally.
Unpeeling the Onion: Deconstructing the Effectiveness of Two LTA Approaches to Reflective Learning
Selecting the most effective methods of integrating reflective practice into undergraduate nursing programmes remains a challenge for educators. This paper explores two pedagogical approaches of reflective learning in an undergraduate mental health nursing programme, with particular focus on developing the core attributes of self-awareness, empathy and compassion. The discussion is explored within the context of nursing in Scotland, which is undergoing transformative change including adapting to an all degree route to nurse regisration. Seismic changes such as these are occurring at a time when the nursing profession generally, and nurses individually, face regular criticism for poor care and lack of compassion. This discussion paper will focus on the necessity of reflective pedagogy in undergraduate nursing programmes in which the expectation is tocreate both critically aware and insightful individuals who are able to function in a health care culture that is predominately resource poor, time orientated and outcome focused. Although centred on mental health nursing, the paper also comments on the transferability and relevance of the teaching and learning approach to other professions in which human engagement is the key focus. The competing tensions of reflective practice and economically driven health care organisations alongside the significant professional challenges of emotional competency of nursing are discussed. This provides a background to the exploration of the examples of reflective pedagogy that may also be applied to other health and social care professions.
Mental health nursing and autism: I am a mental health nurse so why did it take me so long to realise I’m autistic?
Reflection and mental health nursing. part one: is reflection important.
In this new series, John Fowler, a noted nursing author, will explore the use of reflection in mental health nursing. Over the next eight issues, John will be examining some of the techniques that mental health nurses can use to aid their own reflection and how reflection can be applied to clinical practice and management. The series will cover portfolios, reflective learning, reflective evidence, the use of feedback and reflection in all aspects of life.
Export Citation Format
Share document.
Ask a question from expert
NURSING 3004 - Reflective Essay On Mental Health- Nursing
Oklahoma City University
Mental Health Nursing (NURSING 3004)
Added on 2020-02-24
About This Document
NURSING 3004 - Reflective Essay On Mental Health- nursing assignment, the Reflective process in nursing practice is essential in ensuring that the right skills are learned and into-operated into practice. In this reflective essay, I have highlighted my reflection on older persons' mental health nursing practice and knowledge of the pathophysiology of nursing health towards the provision of care. This reflective essay outlays my nursing skills in health care practice and supportive skills which are key in nursing practice towards elderly care with health diseases.
Added on 2020-02-24

End of preview
Want to access all the pages? Upload your documents or become a member.
Psychiatric Mental Health Nursing - PDF lg ...
Understanding the concepts of person, health, environment, and nursing lg ..., mental health nursing: holistic care, assessment, and interventions lg ..., schizophrenia among homeless elderly in australia: unique needs and nursing care plan interventions lg ..., leadership in public health lg ..., reflective essay in nursing practice lg ....
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- BMC Med Educ

Health professionals and students’ experiences of reflective writing in learning: A qualitative meta-synthesis
Giovanna artioli.
1 Azienda USL-IRCCS di Reggio Emilia, Viale Umberto I, 50, 42123 Reggio Emilia, Italy
Laura Deiana
2 Medical and Surgical Department, University of Parma, Parma, Italy
Francesco De Vincenzo
3 European University of Rome, Rome, Italy
Margherita Raucci
Giovanna amaducci, maria chiara bassi, silvia di leo, mark hayter.
4 Faculty of Health Sciences, University of Hull, Hull, UK
Luca Ghirotto
Associated data.
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Reflective writing provides an opportunity for health professionals and students to learn from their mistakes, successes, anxieties, and worries that otherwise would remain disjointed and worthless. This systematic review addresses the following question: “What are the experiences of health professionals and students in applying reflective writing during their education and training?”
We performed a systematic review and meta-synthesis of qualitative studies. Our search comprised six electronic databases: MedLine, Embase, Cinahl, PsycINFO, Eric, and Scopus. Our initial search produced 1237 titles, excluding duplicates that we removed. After title and abstract screening, 17 articles met the inclusion criteria. We identified descriptive themes and the conceptual elements explaining the health professionals’ and students’ experience using reflective writing during their academic and in-service training by performing a meta-synthesis.
We identified four main categories (and related sub-categories) through the meta-synthesis: reflection and reflexivity, accomplishing learning potential, building a philosophical and empathic approach, and identifying reflective writing feasibility. We placed the main categories into an interpretative model which explains the users’ experiences of reflective writing during their education and training. Reflective writing triggered reflection and reflexivity that allows, on the one hand, skills development, professional growth, and the ability to act on change; on the other hand, the acquisition of empathic attitudes and sensitivity towards one’s own and others’ emotions. Perceived barriers and impeding factors and facilitating ones, like timing and strategies for using reflective writing, were also identified.
Conclusions
The use of this learning methodology is crucial today because of the recognition of the increasing complexity of healthcare contexts requiring professionals to learn advanced skills beyond their clinical ones. Implementing reflective writing-based courses and training in university curricula and clinical contexts can benefit human and professional development.
Supplementary Information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1186/s12909-021-02831-4.
Education of healthcare professionals supportstheir transformation into becoming competent professionals [ 1 ] and improves their reasoning skills in clinical situations. In this context, reflective writing (RW) is encouraged by both universities, and healthcare training providersencourage reflective writing (RW) since its utility in helping health students and professionals nurture reflection [ 2 ], which is considered a core element of professionalism. Furthermore, the ability to reflect on one’s performance is now seen to be a crucial skill for personal and professional development [ 3 ]. Writing about experiences to develop learning and growth through reflection is called ‘reflective writing’ (RW). RW involves the process of reconsidering an experience, which is then analyzed in its various components [ 4 , 5 ]. The act of transforming thoughts into words may create new ideas: the recollection of the experience to allow a deeper understanding of it, modifying its original perception, and creating new insights [ 6 ]. RWis the focused and recurrent inspection of thoughts, feelings, and events emerging from practice as applied to healthcare practice [ 7 ].
Reflection may be intended as a form of mental processing or thinking used by learners to fulfill a purpose or achieve some anticipated outcome [ 2 ]. This definition recalls Boud and colleagues’ view of reflection as a purposive activity directed towards goals [ 8 ]. For those authors, reflection involves a three-stage process, including recollection of the experience, attending to own feelings, and re-evaluating the experience. This process can be facilitated by reflective practices, among which RW is one of the main tools [ 9 ].
Between reflection-on-action (leading to adjustments to future learning and actions) and reflection-in-action (where adjustments are made at the moment) [ 10 ], RW can be situated in the former. It involves theprofessional’s reflections and analysis of experiences in clinical practice [ 11 , 12 ]. Mainly,RWinvolves the recurrent introspection ofone’s thoughts, feelings, and events within a particular context [ 13 ]. Several studies highlight how RWinfluencespromoting critical thinking [ 14 ], self-consciousness [ 15 ], and favors the development of personal skills [ 16 ], communication and empathy skills [ 4 , 17 ], and self-knowledge [ 3 ]. Thanks to the writing process, individuals may analyze all the components of their experience and learn something new, giving new meanings [ 5 ]. Indeed, putting down thoughts into words enables the individual to reprocess the experience, build and empower new insights, new learnings, and new ways to conceive reality [ 6 , 18 – 20 ].
Furthermore, RW provides an opportunity to give concrete meaning to one’s inner processes, mistakes, successes, anxieties, and worries that otherwise would remain disjointed and worthless [ 21 , 22 ]. The reflective approach of RW allows oneself to enter the story, becoming aware of our professional path, with both an educational and therapeutic effect [ 23 ].
Reflection as practically sustained by RW commonly overlaps with the process of reflexivity. As noted elsewhere [ 24 ], reflection and reflexivity originate from different philosophical traditionsbut have shared similarities and meanings. In the context of this article, we adopt two different working definitions of reflection and reflexivity. Firstly, we draw from the work of Alexander [ 25 ]: who explains reflection as the deliberation, pondering, or rumination over ideas, circumstances, or experiences yet to be enacted, as well as those presently unfolding or already passed [ 25 ]. Reflexivity at a meta-cognitive level relates to finding strategies to challenge and questionpersonal attitudes, thought processes, values, assumptions, prejudices, and habitual actions to understand the relationships’ underpinning structure with experiences and events [ 26 ]. In other words, reflexivity can be defined as “the self-conscious co-ordination of the observed with existing cognitive structures of meaning” [ 27 ].
Given those definitions,a philosophical framework for helping health trainees and professionals conduct an exercise that can be helpful to them, their practice, and – ultimately – their patients can be identified. There is a growing body of qualitative literature on this topic – which is valuable – but the nature of qualitative research is that it creates transferrable and more generalizableknowledge cumulatively. As such, bodies of qualitative knowledge must besummarized and amalgamated to provide a sound understanding of the issues – to inform practice and generate the future qualitative research agenda. To date, this has not been done for the qualitative work on reflective writing: a gap in the knowledge base our synthesis study intends to address by highlighting what connects students and professionals while using RW.
This systematic review addresses the following question: “What are the experiences of health professionals and students in applyingRWduring their education and training?”
This systematic review and meta-synthesis followed the 4-step procedure outlined by Sandelowski and Barroso [ 28 , 29 ], foreseeing a comprehensive search, appraising reports of qualitative studies, classification of studies, synthesis of the findings. Systematic review and meta-synthesis referto the process of scientific inquiry aimed at systematically reviewing and formally integrating the findings in reports of completed qualitative studies [ 29 ].
The article selection processwas summarized as a PRISMA flowchart [ 30 ]; the search strategy was based on PICo (Population, phenomenon of Interest, and Context),and the study results are reported in agreement with Enhancing Transparency in Reporting the Synthesis of Qualitative Research (ENTREQ) guidelines [ 31 ].
Selection criteria
Inclusion criteria for the meta-synthesis were:
- Primary qualitative studies published in peer-reviewed English journals.
- With health professionals or health studentsas participants.
- UsingRW in learning contexts (both pre-and in-service training).
- Mixed methods where the qualitative part can be separated.
- Articles should report the voice of participants (direct quotations).
Given the meta-synthesis indications, we excluded quantitative studies, non-primary research articles, meta-synthesis of qualitative studies, literature and systematic reviews, abstracts, unpublished reports, grey literature. In addition, we also excluded studies where participants were using RW in association with other learning tools and where the personal experience was not about using RW exclusively.
Data sources and searches
An experienced information specialist (MCB) performed the literature search on Medline, Embase, Cinahl, PsycInfo, Eric, and Scopus for research articles published from Jan 1st, 2008 to September 30th, 2019,to make sure we incorporated studies reflecting contemporary professional health care experience. Additional searchinginvolved reviewing the references or, and citations to, our included studies.
We filled an Excel file with all the titles and authors’ names. A filter for qualitative and mixed methods study was applied. Table 1 shows the general search strategy for all the databases based on PICo.
Search strategy for databases based on PICo
* truncation
Four reviewers (GAr, MR, GAm, LD) independently screened titles and abstracts of all studies, then checked full-text articles based on the selection criteria. We also searched the reference lists of the full-text articles selected for additional potentially relevant studies. Any conflict was solved through discussion with three external reviewers (LG, MCB,SDL, and MH).
Quality appraisal
We used the Critical Appraisal Skills Programme (CASP): it provides ten simple guiding questions and examples to examine study validity, adequacy, and potential applicability of the results of qualitative studies. Guided by the work of Long and colleagues [ 32 ] and previously used in other meta-synthesis [ 33 ], we created 30 items from the 10 CASP questions on quality to ensure we could provide a detailed appraisal of the studies. FDV and LD independently assessed the quality of included studies with any conflicts solved by consulting a third reviewer (MCB and LG). Researchers scored primary studies weighingthe proposed items and ranking the quality of each included study [ 34 ] on high ( n > 20 items positively assessed), moderate (10 < n < 20), or low quality ( n < 10).
Analysis and synthesis
MCB created a data extraction table, GAr, GAm, and MRdescribed the included articles (Table 2 ). Quotations were extracted manually from the “results/findings” sections of the included studies by GAr, MCB, LDand inserted into adatabase. GAr, GAm, MR, and FDVperformed a thematic analysis of those sections, along with participants’ quotations. Then, they inductively derived sub-themes from the data, performing a first interpretative analysis of participants’ narratives (i.e., highlighting meanings participants interpreted about their experience). The sub-themes were compared and transferred across studies by adding the data into existing sub-themes or creating new sub-themes. Similar sub-themes were then grouped into themes, using taxonomic analysisto conceptually identify the sub-categories and the categories emerging from the participants’ narratives. This procedure allowed us to translate the themes identified from the original studies [ 28 ] into interpretative categories that could amalgamate and refine the experiences of health professionalsor health students on the use of RW [ 29 ]. The final categories are based on the consent of all the authors.
Summary of articles included in meta-synthesis (divided per groups: students and professionals)
Literature search and studies’ characteristics
A total of 1488 articles were retrieved. Duplicates ( n = 251) were removed. Then, articles ( n = 1237) were identified and reviewed by title and abstract. We excluded n = 1152 articles because they did not match the specified inclusion criteria, based on the title and abstract. Consequently, we assessed 85 full-text articles. Sixty-eight records did not meet the inclusion criteria. At the end of the selection process, 17 reportsof qualitative research were selected. Figure 1 illustrates the search process.

PRISMA flow diagram
Table Table2 2 shows the characteristics of the included studies. Eleven studies involved healthcare students (58%, including nurses, midwives, physiotherapists, doctors, dentists, and oral health students), and six (32%, including doctors, occupational and radiation therapists) were referred to health professionals. In thirteen studies, participants were trained on RW before using it: this information could not be retrieved from the remaining articles.
Five articles reported studies conducted in the US, three in Australia, two in Canada, and two in Israel. The other studies were carried out in Italy, UK, Korea, Taiwan, and Sweden.
Critical appraisal results
We critically evaluatedall 17 studies to highlight the methodological strengthsand weaknesses of the selected studies. No article was removed on a quality assessment basis. Results of the quality appraisal are reported in Table Table2 2 .
Meta-synthesis findings
Through the meta-synthesis, we identified four main categories (and related sub-categories): (i) reflection and reflexivity; (ii) accomplishing learning potential; (iii) building a philosophical and empathic approach; (iv) identifying reflective writing feasibility (for the complete dataset, please refer to supplemental material , where we have listed a selection of meaningful quotations of categories and sub-categories).
Given such categories, we developed an interpretative meta-synthesis model (Fig. 2 ) to illustrate the commonalities of the experience of using RW according to both students and professionals: RWas a vehicle for discovering reflection and allowing users to enter personal reflexivity to fulfillone’s learning potential, alongside the building of a philosophical and empathic approach. In their experience, reflection and reflexivity generate different skills and competencies: reflection matures skills such as professional skills and the ability to activate change and innovation. Reflexivity allows students and professionals to reach higher levels of competencyconcerning inner development and empathy reaching. Finally, from our analysis, participants, while recognizing the value of RW, also defined factors that could encourage or limit its use. Differences among participants’ groups are also outlined.

Meta-synthesis model: RW as experienced by health professionals and students
Reflection and reflexivity
Within this category, we collected the users’ narratives about the experience of applying RW and its disclosing capacity. By using RW, participants confronted themselves with both reflection and reflexivity. This category includes two sub-categories we named: discovering reflection and entering personal reflexivity.
Discovering reflection
The sub-category shows that experiencingRW deepened their reflection on experiences, practice, and profession. Thanks to RW, professionals, and students could explore previously unexplored topics and learn more about themselves.
“ Writing initiated me to think about my experiences … ” (professional) [ 46 ]. “ I think it’s good for physicians to reflect on what we’re doing ” (professional) [ 50 ]
“ Helped (me) reflect on positive aspects ” (student) [ 40 ]. “ I don’t usually think too much about what happens to me, but through critical reflective journaling, I was able to think carefully about things happening around me. This activity helped me to look into my mind ” (student) [ 44 ]
This sub-category explains transversal meanings coming from uniformly professionals and students.
Entering personal reflexivity
This sub-category includes data about RW enabling users’reflexivity. In this context, RW was considered training for reflexivity as it enabled participants to question themselves more often [ 48 ], reflect on their experiences [ 35 ], attitudes, actions [ 38 , 45 ], and also reconsider their actions and identify their strengths and weaknesses [ 40 , 44 ].
“ The questions in this study do make me stop and think about things – how I feel about what I’m doing in residency ”(professional) [ 46 ]. “ Helped me ID (identify) my strengths and weaknesses ” (student) [ 40 ] RW also helped eradicate the background noise that my mind does not yet know how to filter out [ 51 ] .
Interesting to note that this sub-category is more present in students’ narratives. While professionals referred to self-reflection practices (probably already acquired in other contexts), students often reported how RW helped them discover reflexivity.
Accomplishing learning potential
Our analysis showed how users RW used the technique to “Accomplish learning potential.”
According to the studies’ participants, RWcan enable a learning performancethat would be difficult to reach otherwise. In this context, participants addressed RW as a tool for“accomplishing learning potential.”Within this category, three sub-categories were highlighted: the improvement of skills, personal and professional growth, and assisting the change and development process.
Improvement of skills
Participants agreed that the development of skills and abilities through RWwas aimed at their clinical skills and –in relevant areas such as question asking – encouraged reflection and research [ 35 , 46 ]. Communication skills were also enhanced, as were their relationship with patients, family,colleagues, and friends [ 35 , 38 , 46 ].
Participants said:
“ Through reflective journal writing, my attitude towards learning has changed. I have been encouraged to be a proactive learner. (...) I have been able to identify necessary places for improvement and through research, question asking, goal-setting (...). I have improved my skills in relevant areas” (student) [ 35 ]. “I feel that it [participation in the study] has been a positive experience by motivating me to improve on my clinical, communication skills, and also my relationships with colleagues, patients, family, and friends ” (professional) [ 46 ]
Participants also reported that,in their experience, RWprovided an opportunity to assess and improve themselves and to enhance their self-confidence [ 38 , 40 ]. Cognitive skills, includinggaining more profoundknowledge and problem-solving, along withtime-management [ 35 , 40 , 46 , 49 ], were also enhanced: RW,therefore,represented a learning mode [ 45 ].
“ Without reflection, I absolutely believe these skills would be more unattainable for me ”(student) [ 35 ]
This sub-category applies more to students’ narratives. Health students mentioned the tools helping them most to develop their skills. Professionals focused principally on what RWcould improve (communication skills or organizational skills).
Personal and professional growth
Participantsidentifiedthat RWhad promoted personal [ 51 ] and professional growth [ 35 , 46 ]. RW meant for participants:an ameliorated attitude towards work [ 46 ]; a development path for one’s job potential [ 38 ]; an enhancement of their introspective knowledge [ 51 ]; an enrichment of their expressive capability [ 38 ];an improvement of their interpersonal relationships with patients and colleagues [ 50 ] and developed their use of critical and reflective thinking [ 38 ].
“ Reflecting introduces a new aspect to clinic that focuses on the individual’s learning experience ” (student) [ 35 ]. “I think that it does change the way that you think about the practice of medicine and your own personal tendencies and your interactions with your patients and colleagues. And I think it can be a really powerful driver of culture change ” (professional) [ 50 ]
This sub-category is more represented among students than professionals. Students are ‘surprised’ at how important RW was to their learning. Professionals still recognized how RW was an essential driver of change for their clinic activities.
Assisting the change and development process
We labeledthe third sub-category“assisting the change and development process.”The changeinvolvedintroducing modifications tothe way of working [ 48 ], assessing what needed to be changed to achieve a work-life balance [ 51 ], understanding elements that did not allow change, and how to act on them in the future, and also considering new and important issues [ 46 ], further information [ 51 ] and new ways of thinking. This sub-category equally explained the meaning given to RW by students and professionals.
“ I think writing answer to some of these questions has allowed me to reflect back on the year and think about specific important topics that I might not have thought about again.” (professional) [ 46 ]. (Reflective journaling encouraged) “Assessing and focusing on the changes that need to be done to achieve the balance in my life and being able to integrate that with my family and in my work as a nurse.” (Student 16/RJ2) [ 51 ]
However, thischange process could not be possible without witnessing change and becoming aware of it [ 38 , 46 ]. This allowedparticipants to ‘see one’slearning history and path of growth,‘have a picture of the problem, handle things differently, and broadening their vision of the problem [ 48 ].
Building a philosophical and empathic approach
The “Reflection and reflexivity” category is closely aligned with the “Building a philosophical and empathic approach” category. Participants defined RW as a means for nurturing an intimate and profound level of learning, i.e., a philosophical and empathic approach towards real-life professional issues. The third category consists of three sub-categories: the ability to find benefits in negativity/adversity, assuming an empathetic attitude, and the awareness of things, experiences,emotions.
Finding benefits in negativity/adversity
According to participants, RWexerted a therapeutic effect by encouraging professionals and students to focus on the present (43)strictly. It seemed that RWeventually reduced their emotional stress [ 44 , 51 ]. Likewise,in the contextofnegative experiences [ 49 ], its practice acted as a catharsis [ 46 ] that could even allow them tolook back at those experiencesafresh – enabling a change in perspective [ 39 ].
“While writing the journal entry, I felt like I was unloading something from inside myself and being set free. This process made me feel better ” (student) [ 44 ]. “It is always good to pause to reflect on my experiences. The most cathartic question was a few months back when I got to describe my really bad experience.” (professional) [ 46 ] “Very therapeutic. I wrote on a bad experience, but at the end, we were laughing at it.” (professional) [ 49 ]
This specific approach allowed the practitioner/trainee to improve their self-care and focus on work objectives [ 51 ]:
“Self-reflection and reflective journaling promote self-understanding and is another part of self-care.” (Student 5/RJ3) [ 51 ]
Even if more emerging from students’ voices, professionals appeared genuinely amazed at how learning can be generated out of negativity.
Assuming an empathetic attitude
Study participants stressed the fact that RWhelped them develop empathetic attitudes. It seems that RWemphasized the importance of sensitivity and empathy by trying ‘to be in someone else’sshoes,’ especially that of patients or colleagues [ 36 , 37 , 44 ].
“How reflecting on patient encounters through field notes allowed her to “take a walk in someone else’s shoes ” (student) [ 36 ]. “It helps you see the humanity... ” (professional) [ 50 ]
This approach also applied in contexts outside of work and helped the practitioner take off his/her‘white coat’ and understand that before being a professional,he/shewas a person and a human being [ 36 , 37 , 46 , 50 ].
“ Which has made me more open to other’s ideas and thoughts ” (professional) [ 46 ]
As previously mentioned, according to the participants’ statements, awareness was the cornerstone to effective personal and professional growth [ 40 , 51 ].
This sub-category is equivalently present among the participants’ groups. Nonetheless, different meaningscould also be highlighted. Students appreciated RWby stressing its value of allowing them to enter deeply ‘into the other’ inner world (mainly patients). Professionals claimed they could recognize the profession’s human and relational aspects, whichcould also be helpful for their extra-professional relationships (family members, friends).
Awareness of things, experiences, emotions
Impartially balanced among professionals and students, awareness was cited in terms of ‘how things have affected me rather than simply continuing to work in a robotic manner’ [ 46 ], the awareness of who one was and who one has become thanks to the process of change [ 51 ]. This professional and relational awareness made it possible to think clearly about one’s practice and the health resources present in the context of belonging [ 50 ].
“Just being aware of what I know now and what I’ll know by the end of the semester … is a great way to learn who I am and what I can change about me for the better.” (Student 9/RJ1) [ 51 ]
The process of awareness that was facilitated by how their RW allowedthem to transform shapeless and straightforward ideasinto words and givethem a specific value and emotional charge [ 36 , 47 , 51 ]: it wasan authentic opportunity to turn emotions and feelings into something tangible –a journey of discovery and personal acceptance [ 43 ].
“ After two years or so, when you look back, it’s like, oh,that’s how I was feeling at the time, and right now, I feel differently. There is also this level of satisfaction. Like you have matured out of this thinking ” (professional) [ 47 ]
Identifying RW feasibility
The fourth category consists of three sub-categories: perceived barriers/impeding factors, facilitating factors, and when and how to use RW. Students and healthcare professionals who had the experience of practicing the RW in their work identified both limitations and facilitating factors and indications about when and how to use RW.
Perceived barriers/impeding factors
Some study participants (almost entirely students) identified several barriers to their activity. Some students could not see the benefits and thought RW was a waste of time [ 35 , 38 , 51 ]. However, others, who did see the potential benefits still felt that they lacked the time needed to devote to RW [ 42 ] or, sufficient mental space to report and describe a work situation, an excessive similarity of this activity to the regular working practice and, consequently, a lack ofmotivation to write [ 47 , 51 ]. In addition, some described the strainthey felt in writing down personal/professional experiences [ 47 ]. A lack of privacy was another problem, both for the concern about sharing the reflection and for the respect of confidentialityin writing itself [ 51 ]. Taken together,it appeared that some study participants did not recognizeRW as an effective means of help [ 39 , 50 ]. Althoughrealizing the potential of RW,others felt that their tutors did not provide noticeably clearexplanations of the aim of RW– which they would have found useful and motivating [ 45 ].
“ To be honest, not a great deal ( … ) it wasn’t really some revelation ” (professional) [ 50 ]. “ I got a hard time referring it [my experience] to citations … I could have sat and cried yesterday when I did my essay … when I actually read it [my essay] I thought, oh I don’t know what it means, myself ” (Female 2 - student) [ 42 ]
Facilitating factors
This sub-category was exclusively interpreted from students’ narratives. They valued the perspectives to use RWin their practice seeing it as a valuable tool to be applied throughout their career [ 35 , 45 ],with many students reporting that they would continue with this technique [ 38 ]. Studentssaw RW as a valuable means of staying focused on their own goals and needs [ 40 , 51 ]. They remarked that it helped them reduce stress, gain clarity in one’s life and practice [ 41 ], and spiritually connect with themselves [ 45 , 51 ]. Furthermore, RW enabled studentsto discover more information about their health and well-being, ‘it also helped me tie in ideas and beliefs from different sources and relate it to my own’ [ 51 ]. RWhelped maintain awareness and recall the medical being/human being dichotomy [ 37 ]. It remindedstudentsof the difference between studying literature and refining manual skills and the ability to learn from experience and mistakes [ 35 ].
“ During the interview, I felt an element of being more like a ‘normal person’ having a ‘normal conversation’ with another human being. This was a strange realization because it reminded me of the dichotomy that physicians may experience, being doctor versus human ” (student) [ 37 ]
When and how to use RW
Health professionals (a few) and many students finally mentioned the time considered most appropriate to use RW, underlining its usefulness primarilywas during hardship rather than daily practice [ 47 ].Moreover,RWshould not be forced onto someone in any given moment but instead left to individual choice based on one’s spirit of the moment [ 40 , 46 ].
“. .. like if you had a patient die; that would be the only time you might write it down ” (professional) [ 47 ]
Otherparticipantsconsidered instructions on RW to be too forceful and notapplicable to their own experience of reflection [ 40 ]. ‘Reflection wasn’t just signing on the line.’ It allowed constructive feedback for the trainee or the professional. Constructive feedback could be positive or negative, but it was a powerful tool for thinking and examining things [ 45 ].
In this meta-synthesis of qualitative studies, we have interpreted the experiences of health professionals and students who used RWduring their education and training. Given the number of studies included, RW users’ experience was predominately investigated in students. This result, although not surprising, raises the question of whether RW in professional training is being used. RW is not used in professional training as often as it is in the academic training of healthcare students.
As to this review’s aim, we could highlight continuities and differences from study participants’ narratives. Our findings offer a conceptualization of usingRW in health care settings. According to the experience of both students (from different disciplines) and health professionals, RW allows its exponents to discover and practice reflectionas a form of cognitive processing [ 2 ] and enablethem to develop a better understanding of their lived situation. We also interpreted that RW allows users to make a ‘reflexive journey’ that involves them practicing meta-cognitive skills to challengetheir attitudes, pre-assumptions, prejudices, and habitual actions [ 24 , 26 ]. This was particularly true for students: “entering personal reflexivity” appears to be newer for them than for the professionals who are likely to acquire reflexivity during academic training. Students seemed more focused on tools than RW-related results. This consideration makes us affirm that reflective capacity is in progress for them.
Challenging pre-assumptions and entering reflexivityenabledRWusers to realize how RW may develop their learning potential to improve skills and personal/professional growth. Skills to be enhanced are quoted mainly by students. Conversely, professionals could comprehend the final purpose of learning, achievable through RW, in terms of communication or organizational abilities. Professionals interpreted skills from RW as abilities to apply in the clinical activities to find new solutions to problems.
The category “Accomplishing learning potential”confirms what many authors highlight: putting thoughts into words not only permits a deeper understanding of events [ 6 ], enhances professionalism [ 52 ] but also improves personal [ 16 ], communication, and empathy skills [ 4 , 17 ]. In this context, RW fulfills its mandate by letting human sciences [ 53 ] and evidence-based health disciplines affect clinical practice. As noted [ 54 ], students and health professionals’RW training allowed integrating scientific knowledge with behavioral and sociological sciences to supporttheir learning [ 55 ].
Users understood that RWcould be a powerful means of developing empathy and developing their philosophy of care: this consideration is in line with a recent study from Ng and colleagues [ 24 ]. Additionally, some authors [ 4 , 17 ] stressed these empathetic skills and “humanistic”competencies as essential to care for patients effectively [ 56 ]. Professionals were amazed how negativity could generate learning through RW. On the other hand, by recognizingand writing experienced negative situations, students could free themselves from feelings impeding empathy.
By employing RW, users reported factors that could encourage or limit its use. These findings further illustrate that RW is not always a tool that is easy to use without adequate training [ 57 ]. Almost exclusively, students reported hindering factors (limited time, difficulty in writing and understanding assignments, privacy issues, feeling bored or forced). As to professionals, few describedRW as a very stressful activity. Although students could identify impeding factors, they also recognized many positive ones. For professionals, RW was not to be used every day but in ‘extreme’ situations, requiring reflection and reflexivity to be applied. In general, enhancing motivation to write reflectively [ 58 ] should be the first goal of any training to make the process acceptable and profitable for trainees. If this first stage is not accomplished, it will reduce RW’sapparent professional and personal effectiveness among health professionals and students substantially.
Strengths, limitations, and research relaunches
This review may enrich our knowledge about providing RW as an educative tool for health students and professionals. However, the findings must be applied,taking into account some limitations. We focused our attention only on recent, primary, peer-reviewed studies within the time and publication limits. Qualitative studies often are available as grey literature: considering it may result in a different interpretation of students’ and professionals’ experience in using RW. Therefore, our conceptualization should be read bearing in mind a publication bias and the need to expand the literature search to other sources. Besides limiting the risk of missing published qualitative studies, we reviewed the reference listsof included studies for additional items. Our meta-synthesis is coherent to the interpretation of the included studies’ findings.
At least two reviewers have conducted each step of this systematic review. We purposely did not exclude studies based on a quality assessment to maintain a robust qualitative study sample size and valuable insights.
During analysis, all possible interpretations were screened by authors, and an agreement was reached. Nonetheless, we did not cover all the possible ways to interpret the voices of students and professionals.
Since RW is not used in professional training as often as it is in the academic training of healthcare students, a research relaunch could be investigatingwhether and to what extent RW is being used in in-service training programs. Moreover, the studies included in this review were conducted within Western countries. Students’ and professionals’ perspectives from Africa and Asia are underrepresented within the qualitative literature about experiences of using RW. Therefore, geographicalgeneralizations from the present meta-synthesis should be avoided, and our paper reveals the necessity for RW research in other cultures and settings. Nonetheless, authors of primary studies have paid little attention to cultural and regionaldiversity. Therefore, we recommend furtherinvestigations exploring the differences between cultural backgrounds and howRW is recognized within training programs in different countries. Finally, additional qualitative and quantitative research is required to deepen our understanding of RW’s clinical and psycho-social outcomes in high complexity health practice contexts.
Our analysis confirms the crucial role of RW in fostering reasoning skills [ 59 ] and awareness in clinical situations. While its utility in helping health students and professionals to nurture reflection [ 2 ] has been widely theorized, this meta-synthesis provide empirical evidence to support and illustrate this theoretical viewpoint. Finally, we argue that RWis even more critical given the increasing complexity of modern healthcare, requiringprofessionals to develop advanced skills beyond their clinical ones.
Practical implications
Two important implications can be highlighted:
- (i) students and professionals can recognize the potential of RW in learning advanced professional skills. ImplementingRW in academic training as well as continuing professional education is desirable.
- (ii) Despite recognizing the effectiveness of RW in healthcare learning, students and professionals may face difficulties in writing reflectively. Trainers should acknowledge and address this.
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Silvia Tanzi for her insightful feedback about this work and Manuella Walker for assisting in the final editing of the paper.
Abbreviations
Authors’ contributions.
GArwas responsible for the original concept. MCB performed the literature search on databases. MCB, GAr, GAm, LD, MR were responsible of data curation. GAr, MR, GAm, and LD screened titles and abstracts of all studies. LG, MCB, SDL, and MH served as external auditors. FDV and LD assessed the quality of included studies. MCB and LG gave a third opinion in case of disagreement. GAr, GAm, MR, and FDV derived sub-categories from the data. GAr, LG, MH drafted the first version of the manuscript. FDV, LD composed tables, and figures. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Not applicable.
Availability of data and materials
Declarations.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
- Covid-19 hub
- Latest hearings
- Written reflective accounts
Last Updated 26/05/2021
In this guide
Requirement, meeting the requirement, resources and templates.
You must have prepared five written reflective accounts in the three year period since your registration was last renewed or you joined the register.
Each reflective account must be recorded on the approved form and must refer to:
- an instance of your CPD, and/or
- a piece of practice-related feedback you have received, and/or
- an event or experience in your own professional practice
and how they relate to the Code .
We want to encourage nurses, midwives and nursing associates to reflect on their practice, so they can identify any improvements or changes to their practice as a result of what they have learnt.
Each of your five reflections can be about an instance of CPD, feedback or an event or experience from your work as a nurse, midwife or nursing associate – you can even write a reflection about a combination of these.
It's important to think about the Code when you write your reflections, and consider the role of the Code in your practice and professional development.
If you’re a midwife, you may find it helpful to use our reflective aid when thinking about your reflective accounts.
Recording your written reflective accounts
You must use the reflective accounts form to record your written reflective accounts.
These accounts don't need to be lengthy or academic-style pieces of writing. You can simply note down what you learnt, how it improved your practice, and how it relates to the Code.
You may choose to store the completed form either electronically or in paper format.
Be careful not to record any information which may identify another person. You may find the section on non-identifiable information in How to revalidate with the NMC useful.
Reflective accounts form (mandatory)
You must use this form to record your five written reflective accounts.
Examples of completed forms and templates
See pages 27-28 in our 'How to revalidate with the NMC' guidance for more details.
- Last Updated: 26/05/2021
We have lots of resources to help you get the best from revalidation. Download resources and templates
Did you find this information useful? Submit feedback
Related guides
Revalidation.
- What is revalidation?
- Revalidating as a nursing associate
- Practice hours
- Continuing professional development
- Practice-related feedback
- Reflective discussion
- Health and character
- Professional indemnity arrangement
- Confirmation
- Find out your revalidation date
- Submit your revalidation application
- Verification
- Information for confirmers
- Information for employers
- Guidance and information
- Forms and templates
- Training materials
- Introduction
- Amanda and Claire's revalidation story
- Amrit's revalidation story
- Caroline, Labour Ward Coordinator
- Carol, registered nurse and care home manager
- Catriona, interim lead midwife
- Gemma's revalidation story
- Hayley, community mental health nurse
- Heather, learning disabilities nurse
- John, Head of Undergraduate Studies
- Julie, GP practice nurse
- Lynne's revalidation story
- Marcela, GP practice nurse
- Miranda, self-employed aesthetic nurse
- Nina, midwife
- Sally, registered nurse
- Sarah, health visitor
- Susie, nursing associate
- Thulani, agency mental health nurse
- Victoria, senior consultant admiral nurse
- Anne, Head of Clinical Services
- Cate, clinical skills tutor
- Julie, social worker
- Hywel Dda University Health Board
- Western Health and Social Care Trust
- Central Manchester FT
Home — Essay Samples — Life — Nurse — Nurse Practitioner Admission Reflection
Nurse Practitioner Admission Reflection
- Categories: Advocacy Nurse
About this sample

Words: 486 |
Published: Mar 25, 2024
Words: 486 | Page: 1 | 3 min read

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Dr Jacklynne
Verified writer
- Expert in: Law, Crime & Punishment Life

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
3 pages / 1395 words
2 pages / 950 words
3 pages / 1445 words
2 pages / 790 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Nurse
The decision to pursue a career as a labor and delivery nurse is deeply rooted in my passion for healthcare and my unwavering commitment to providing support during one of life's most significant moments. In this essay, I will [...]
International Journal of Nursing Practice, Nursing Prioritization of the Patient Need for care: A tact knowledge embedded in the clinical decision-making literature October 2009Nurses storied experiences of direction and [...]
Gagnon, K., & Sabus, C. (2015). Professionalism in a Digital Age: Opportunities and Considerations for Using Social Media in Health Care. Physical Therapy, 95(3), 406–414.Nayak, S. G. (2018). Time Management in Nursing -- Hour [...]
Ball J. & Pike G. (2009). Shift length: A literature review. Nursing Management (Harrow), 16(4), 22-25.Bogossian, F., Winters-Chang, P., & Tuckett, A. (2014). Extended work shifts and the impact on patient safety, productivity, [...]
Sharma, R., Jain, A., Gupta, N., & Garg, S. (2014). Stressors in nursing and coping strategies. International Journal of Advance Research, 2(2), 400-405.Hofler, L. (2016). Challenges and stressors experienced by new graduate [...]
Have you ever stopped to think about how you would address the pain and what kind of words you would use to ask people who are from different cultures and have dissimilar thinking with you about their symptoms? In addition, how [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free

VIDEO
COMMENTS
The paper will show emphasise based on communication. This reflection has been chosen to highlight the need for nurses to have therapeutic communication skills in order to provide holistic care and encourage a good nurse-patient relationship. Gibbs (1988) reflective cycle has been chosen as a framework for this paper.
One of the most important ways that a mental health nurse develops their clinical expertise is by reflecting on their professional experiences. Previous articles in this series have examined some of the key elements of reflection and how these can be developed and incorporated into routine clinical practice for ongoing development. This formative approach to reflective practice helps build ...
1.1. Background. Based on Peplau's model of interpersonal relationships by (), which is the most widely held theory in the mental health nursing community, many authors have based their models on person‐centred mental health nursing (Barker & Buchanan‐Barker, 2010; O'Brien, 2001; Scanlon, 2006).All of them identify the therapeutic relationship as the foundation of nursing practice and the ...
examples of reflective writing from the perspectives of student nurse (Joe) and practice supervisor (Ross), then answer the questions in Activity 9.2. Scenario 9.1: Joe and Ross's confrontation Student reflection example (Joe) I'm a mental health student nurse and having difficulties with my practice supervisor, Ross.
The hook or attention grabber. Thesis statement. Main points of each body paragraph (topic sentence, evidence, examples, illustrations, etc.) Conclusion (restated thesis and call-to-action) With the outline done, you should take a break and resume writing your first draft of the nursing reflection essay.
Here are some tips to help you write an effective reflective nursing essay: 1. Understand the Reflective Cycle. Before you start writing your essay, it is important to understand the reflective cycle. The reflective cycle consists of four stages: description, feelings, evaluation, and analysis.
Discover the benefits of writing down your thoughts and how to get started. Reflective journal writing is a way of documenting what you're thinking and feeling in the moment, and can be a useful tool to help manage stress and anxiety. Dr Christopher Westoby, author of The Fear Talking: The True Story of a Young Man and Anxiety, is a strong ...
Abstract There is evidence that reflective practice, which focuses on the emotional aspects of nursing, can improve nurses' wellbeing and mental health, a need further highlighted by the Covid-19 pandemic. This article, the second in a series on reflective practice, looks at the main forms of reflection for wellbeing and mental health, and
This provides a background to the exploration of the examples of reflective pedagogy that may also be applied to other health and social care professions. ... In this new series, John Fowler, a noted nursing author, will explore the use of reflection in mental health nursing. Over the next eight issues, John will be examining some of the ...
Reflective practice 2: improving nurses' mental health and wellbeing | Nursing Times. Abstract There is evidence that reflective practice, which focuses on the emotional aspects of nursing, can improve nurses' wellbeing and mental health, a.
Students were directed to select and use a framework on which to formulate their reflective essays. The most commonly selected frameworks included those of . Research aim. The purpose of this research was to explore student mental health nurses' experiences of gaining skills and understanding in the critical appraisal of research papers.
Reflection on mental health nursing placement using Gibbs (1988) model of reflection. Better Essays. 1694 Words. 7 Pages. Open Document. This is a reflective essay based on my attendance at a multidisciplinary team (MDT) meeting whilst on my two-week placement at a local mental health day hospital. The aim of this essay is to discuss the ...
How I Feel About Mental Health Nursing." Beginning with thoughts about mental health nursing and personal course goals and concluding with their thoughts about mental illness, culture, and stigma, both personally and in society, this essay forms the basis of the clinical journal and serves as a point of reference for the final journal entry.
Illawarra Shoalhaven Local Health District, Mental Health Services, Australia ABSTRACT. Introduction: There exists a need for innovative thinking to identify new clinical placement opportunities for nursing students. Recovery-based clinical placements for mental health nurse students remain unique and require investigation. Aim:
reflection on psych rotation enjoyed my clinical experience in this psych rotation. it was unlike anything expected. when first set foot on the clinical floor, ... Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing for Accelerated BSN Students (NURS 360 ) 15 Documents. ... APA 7 Student Sample Paper; Related Studylists mental health Journals NURS 123.
This essay will illustrate how I developed from being a novice to an expert within my three year study of mental health nursing programme. The chosen topic from my log book to be discussed will be management. Dreyfus and Dreyfus student model (1986) and Benner's stages of skill acquisitions (1984) will be used to structure this essay.
A purposive sample was recruited from a cohort of second year mental health nursing students. The BSc Mental Health Nursing degree is a three-year long programme, and the second-year content is an important period on which to build understanding in EBP and critical appraisal, as the final year degree module involves a literature review ...
Download. Essay, Pages 5 (1183 words) Views. 13510. Within the realm of mental health care, the role of multidisciplinary teams (MDTs) cannot be overstated. This essay explores the significance of MDTs in the context of mental health care, shedding light on the various factors that can either bolster or hinder the effectiveness of such teams.
Reflective Essay On Mental Health- Nursing Introduction Reflective process in nursing practice is essential in ensuring that the right skills are learnt and inco-operated into practice. In this reflective essay, I have highlighted my reflection in older person's mental health nursing practice and knowledge in patho physiology of nursing health towards provision of care.
Reflective evaluation of care interventions and clinical decision making. Introduction This essay is a reflective examination of a care episode in the domain of mental health nursing, in relation to the processes of nursing decision making, clinical reasoning, and processes associated with patient care planning and management.
Background. Education of healthcare professionals supportstheir transformation into becoming competent professionals [] and improves their reasoning skills in clinical situations.In this context, reflective writing (RW) is encouraged by both universities, and healthcare training providersencourage reflective writing (RW) since its utility in helping health students and professionals nurture ...
You must use the reflective accounts form to record your written reflective accounts. These accounts don't need to be lengthy or academic-style pieces of writing. You can simply note down what you learnt, how it improved your practice, and how it relates to the Code. You may choose to store the completed form either electronically or in paper ...
Nurse Practitioner Admission Reflection. As I reflect on my journey towards becoming a nurse practitioner, I am reminded of the countless experiences that have shaped my passion for nursing and solidified my desire to advance my education in this field. From a young age, I have always been drawn to helping others and making a positive impact on ...