An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- HHS Author Manuscripts


Immigration to the United States: Recent Trends and Future Prospects +
Charles hirschman.
University of Washington
Almost 13 per cent of the American population is foreign born, and if the children of the foreign born are included, about 1 in 4 Americans can be counted as part of the recent immigrant community. Although there is lingering prejudice and popular fears of immigrants, there is growing evidence that, on balance, immigrants make a positive contribution to the American economy and society. There is little evidence that immigrants have an adverse impact on the wages and employment of native born Americans. Moreover, immigrants and their children are disproportionately represented in a broad variety of scientific and cultural fields.
1. Introduction
The United States is, once again, in the midst of an age of immigration. In 2010, there were 40 million foreign-born persons living in the United States ( Grieco et al. 2012 ). Of the 220 million international migrants in the world in 2010—defined as persons living outside their country of birth—almost one in five were residents in the United States ( UN Population Division 2013 ). An even larger number, upwards of 75 million persons in the United States—almost one quarter of the current resident American population— is part of the immigrant community, defined as foreign born and the children of the foreign born ( U.S. Bureau of the Census 2010 ). 1
In spite of lingering prejudice and discrimination against immigrants, most Americans are beginning to acknowledge the positive contributions of immigrants. These beliefs are partially rooted in the historical image of the United States as a ‘nation of immigrants.’ The story that America was populated by peoples seeking economic opportunity, fleeing injustice or oppression in their homeland, and hoping for a better life for their children has a strong grip on the American immigration. Moreover, there is a growing body of research that shows that most immigrants do assimilate to American society and that immigration has net positive impacts on the American economy, society, and culture.
In this paper, I survey the trends in immigration to the United States with a focus on the most recent period—the Post 1965 Wave of Immigration, named for the reforms in immigration law that were enacted in the late 1960s as part of the Civil Rights revolution. I also review recent research on the demographic, economic, social, and cultural impact of immigration on American society.
2. Trends in Immigration to the United States
Figure 1 shows the history of the absolute and relative levels of the foreign born population in the United States. The histogram—the solid bars—shows the numbers (in millions) of foreign born persons in the country from 1850 to 2012. The foreign born includes everyone who is born outside the United States, including students and workers residing here temporarily. This category also includes many undocumented immigrants—those residing in the country illegally. The curved line shows the ratio of foreign born persons to the total US population in each decennial census from 1850 to 2000 and the comparable figures for recent years from the American Community Survey.

Source: US Bureau of Census, Census of Population, 1850–2000 (in Gibson and Jung, 2006 ), and American Community Survey, 2010.
The absolute number of the foreign born population rose rapidly from the mid-19th century through the early decades of the 20th century—popularly known as the ‘Age of Mass Migration.’ With the cessation of large-scale immigration after 1924, the absolute numbers of foreign born declined to below 10 million by 1970. With the renewal of immigration in recent decades, the number of foreign born persons has risen dramatically and is currently around 40 million.
The visibility of the foreign born—at work, in schools, and in neighbourhoods—is measured by the proportion of foreign born to the total population, that is, the curved line in Figure 1 . It is to be noted that the contemporary presence of immigrants is actually less than it was in the early 20 th century. For most of the 19 th and early 20 th centuries, the foreign born constituted around 14 to 15 per cent of the American population. Then, during the middle decades of the 20 th century, the figure dropped precipitously to below 5 per cent in 1970. With the renewal of mass immigration after 1965, the percent foreign born is currently 13 per cent of the total population. While this figure is high relative to the period from 1950 to 1970, it is slightly below the proportion of foreign born for much of American history.
The ‘Post-1965 Immigration Wave,’ was named for the 1965 immigration law that repealed the ‘national origins quotas’ enacted in the 1920s. These quotas were considered discriminatory by the children and grandchildren of Southern and Eastern European immigrants, and the 1965 immigration legislation was part of the reforms of the Civil Rights era. The advocates of reform in the 1960s were not pushing for a major new wave of immigration; they expected a small increase in the number of arrivals from Italy, Greece, and a few other European countries, as families that were divided by the immigration restrictions of the 1920s were allowed to be reunited ( Reimrs 1985 : Chap. 3).
Family reunification and scarce occupational skills were the primary criteria for admission under the 1965 Act ( Keely 1979 ). The new preference system allowed highly skilled professionals, primarily doctors, nurses, and engineers from Asian countries, to immigrate and eventually to sponsor their families. About the same time, and largely independently of the 1965 Act, immigration from Latin America began to rise. Legal and undocumented migration from Mexico surged after a temporary farm worker programme, known as the Bracero Programme, ended in 1964 ( Massey, Durand and Malone 2002 ). There have also been major waves of immigration to the United States with the fall of regimes supported by American political and military interventions abroad, including Cuba, Vietnam, and Central America. Each of these streams of immigrant and refugee inflows has spawned secondary waves of immigration as family members have followed.
3. Characteristics of the Post-1965 Wave of Immigrants
Most of the immigrants who arrived from 1880 to 1920 during the Age of Mass Migration were from Southern and Eastern Europe, including Italy, Germany, Poland, and Russia. Many of these ‘new’ immigrants in the early 20 th century were considered to be distinctly different from the older stock of white Americans in terms of language, religion, and in their potential for assimilation into American society. Popular opposition to immigration in the early 20 th century led to the laws of the 1920s that sharply restricted immigration from Southern and Eastern Europe. There were much smaller waves of immigration from China and Japan, but even stronger opposition ended Asian immigration in the late 19 th and early 20 th century.
When the doors to immigration were opened again in the years after 1965, only small numbers of Europeans arrived. The major regions of origin in the Post-1965 Wave of Immigration are Latin America and Asia. More than 11 million—about 30 per cent of all immigrants (foreign born)—are from Mexico, one of the nearest neighbours of the United States. Another 20 per cent of immigrants are from other countries in Latin America, with the largest numbers from Central America and the Caribbean. Migrants from Puerto Rico are domestic migrants, not immigrants, since Puerto Rico is an American territory and all Puerto Ricans are American citizens at birth.
About one quarter of the foreign-born are from Asia, and the relative share of Asian immigrants has risen in recent years. One of the hallmarks of contemporary Asian immigration is its diversity—almost every country in Asia is represented in the American immigrant population. The largest Asian immigrant communities in the U. S. are from China, India, and the Philippines, but there are also considerable numbers from Vietnam, Korea, Cambodia, Laos, and Thailand.
In the 1970s and 1980s, most ‘new immigrants’ settled in the West and East coast states, and a few other selected states, including Texas, Florida, and Illinois. About 40 per cent of all immigrants lived in California and New York. In the 1990s and 2000s, immigrants increasingly began settling in new destinations including smaller towns in the Midwest and Southeast. The majority of immigrants still live in California, New York, and other traditional destinations, but industries are attracting immigrant labour to many other regions. In addition to the high tech sectors and universities that attract highly skilled immigrants, less skilled immigrants are drawn to agriculture, food processing, and manufacturing industries that are often shunned by native born workers.
The distribution of education among recent immigrants to the United States is bimodal. The largest group of immigrants, particularly those from Mexico and Central America, has less education, on average, than the native-born American population. Less education, however, is not equivalent to unskilled labour. Many immigrants without a high school degree are able to work in the skilled construction industry, nursing homes caring for the elderly, and in the service sectors in restaurants, hotels, and gardening.
At the other end of the educational continuum are the highly educated immigrant streams from Taiwan, India, Iran, and many African countries. Almost half of Asian immigrants have a university degree compared to only a third of native born Americans. Many of these highly skilled immigrants fill key niches in the high tech sector, higher education, and many professional fields.
4. Popular Fears of Too Much Immigration
Existing alongside the pride of having immigrant grandparents (or great-grandparents) in the ‘nation of immigrants,’ many Americans fear that the United States has more immigrants than the country can absorb and assimilate. There are widespread popular beliefs that immigrants take jobs that would otherwise go to native born Americans and that the wages of native born workers are depressed by the presence of immigrant workers. Beyond the economic argument, many Americans also think that the presence of immigrants, especially large numbers of immigrants from ‘third world’ countries, are a threat to American values, culture, and institutions ( Bouvier 1992 ; Brimelow 1995 ; Huntington 2004 ). These sentiments have given rise to an anti-immigrant lobby that includes political leaders, TV and radio talk-show pundits, social movement organisations, including public interest organisations that publish reports and policy briefs, as well as unauthorised militia groups that patrol the U.S. Mexican border, such as the ‘Minutemen’.
Neither the presence of large numbers of immigrants nor the exaggerated claims about the negative impact of immigration are new phenomena. In 1751, Benjamin Franklin complained about the Germans in Pennsylvania and their reluctance to learn English ( Archdeacon 1983 : 20; Jones 1992 : 39–40). Based on a campaign of fear about the political dangers of unchecked immigration, primarily Irish Catholics, the ‘Know-Nothing’Party elected six governors, dominated several state legislatures, and sent a bloc of representatives to Congress in 1855. During World War I, Americans who wanted to retain their German-American identity were forced to be ‘100 percent Americans’ and to give up their language and culture ( Higham 1988 : Chap. 8).
In the late 19 th and early 20 th centuries, Chinese and Japanese migrants who worked as railroad and agricultural labourers were targeted by nativist groups who feared that Asian immigrants would harm the economic status of native workers and contaminate the ‘racial purity’ of the nation ( Hing 1993 : 22). The passage of the 1882 Chinese Exclusion Act was the first major step toward a closed society. After the Chinese Exclusion Act was passed, Japanese migrants became a new source of cheap labour on the West coast and Hawaii. Japanese immigration was targeted by the same groups that opposed Chinese immigrants.
Southern and Eastern European groups also faced an increasingly hostile context of reception as their numbers swelled at the turn of the twentieth century. A number of formal organisations sprang up among old line New England elites to campaign against the continued immigration of ‘undesirables’ from Europe ( Higham 1988 ; Jones 1992 : Chap. 9). After a long political struggle, Congress passed restrictive laws in the early 1920s that stopped almost all immigration except from Northwestern Europe.
5. Do Immigrants Assimilate into American Society?
In spite of the fears that immigrants are resistant to learning English and refuse to join the American mainstream, there is a large body of social science and historical research which concludes that immigrants have, by and large, assimilated to American society ( Alba 1990 , Alba and Nee 2003 ; Duncan and Duncan 1968 ; Lieberson 1980 ). This does not mean that assimilation was painless, automatic, or immediate. For the first generation of immigrants who arrived as adults, the processes of linguistic, cultural, and social change were painful and usually incomplete. Immigrants tend to settle in ethnic enclaves, prefer to speak their mother tongue, and gravitate to places of worship and social events that provide cultural continuity with their origins ( Handlin 1973 ; Portes and Rumbaut 2006 ). Many immigrants do learn English and find employment in the general economy, but few feel completely part of their new society. In the early decades of the 20 th century, evidence pointed to the slow and incomplete assimilation of the then ‘new’ immigrants ( Pagnini and Morgan 1990 ).
With the passage of time, and especially following the emergence of the second generation, there was unmistakable evidence of assimilation among the descendants of early 20 th century European immigrants. Acculturated through their attendance at American schools, the children of immigrants did not share the ambivalence of their immigrant parents. The second generation spoke fluent English and was eager to join the American mainstream. By all measures, including socio-economic status, residential mobility, and intermarriage, they left behind the ethnic world of their immigrant parents ( Alba and Nee 2003 ; Lieberson 1980 ). By the 1950s, patterns of suburbanisation broke down ethnic neighborhoods and intermarriage became more common ( Alba and Nee 2003 ; Lieberson and Waters 1988 ).
Although it is widely assumed that immigrants in the Post-1965 Immigration Wave are less likely to assimilate than those who arrived in the early 20 th century, there is growing evidence that the new immigrants, especially their children, are doing remarkably well ( Alba and Nee 2003 ; Kasinitz et al. 2008 ). On average, second generation immigrants are less likely to drop out of high school and more likely to attend college than the average native born American ( Hirschman 2001 ; White and Glick 2009 ). Intermarriage is also common: recent research estimates that one-third to one-half of second generation Hispanics and Asians marry outside of their community ( Duncan and Trejo 2007 ; Min and Kim 2009 ). The children of contemporary immigrants are on track for assimilation and upward mobility at about the same pace as the descendants of earlier waves of immigration from Europe.
6. The Impact of Immigration on America
There are widespread popular beliefs, including many influential voices within public policy circles, which argue that immigration is harmful to the economic welfare of the country, especially to native born Americans ( Borjas 1994 ; Bouvier 1992 ; Briggs 1984 ; Brimelow 1995 ). The central claim is that immigrants, because they are willing to work for lower wages, take jobs from native born American workers. Competition from immigrant workers is expected to depress wages, especially in the low-skilled labour market ( Borjas 1989 ). Finally, immigrants are thought to be an economic burden because they disproportionately receive public benefits, such as health care, schooling, and welfare without paying their fair share of taxes. These claims, however, are not supported by empirical evidence.
The definitive statement on the economic consequences of immigration was the 1997 report of the National Research Council (NRC) panel on the demographic and economic impacts of immigration, which drew on the theoretical and empirical research conducted by leading specialists in labour economics and public finance ( Smith and Edmonston 1997 ; 1998 , also see Card 1990 ; 2005 ). The major conclusion of the NRC report was that the net effects of immigration on the American economy were very modest. Immigration does expand labour supply and may increase competition for jobs and lower wages for native workers who are substitutes for immigrants, but immigration also expands total production (national income) and increases the incomes that accrue to native born workers who are complements to immigrants ( Smith and Edmondson 1997 : Chap. 4). Although some native born workers may compete for the same jobs as immigrants, many more may be complements to immigrants. This means that the arrival of unskilled immigrant labour may ‘push up’, rather than ‘push out’, many native born workers ( Haines 2000 : 202; Lieberson 1980 : Chap. 10). Moreover, many native born workers have direct or indirect income from capital through their savings, ownership of property, and as recipients of pension programmes.
The most likely reason for a lack of empirical support for the presumed negative impact of immigration is the questionable assumption that the only impact of additional workers (immigrants) on the labour market is through wage competition. The presence of immigrants has broader effects on economic growth, both locally and nationally, that leads to rising wage levels for native born workers. Among the potential mechanisms are increased national savings, entrepreneurship and small business development, a faster rate of inventive activity and technological innovation, and increasing economies of scale, both in the production and consumer markets ( Carter and Sutch 1999 ). There is a long-standing hypothesis in economic history that high levels of immigration stimulates economic growth by increasing demand for housing, urban development, and other amenities ( Easterlin 1968 ). A recent study found that immigration provided the necessary labour supply for the rapid growth of manufacturing during the American Industrial Revolution from 1880 to 1920 ( Hirschman and Mogford 2009 ).
Another major economic issue addressed by the 1997 NRC report was the impact of immigration on the governmental fiscal system—the balance between taxes paid and the value of government services received ( Clune 1998 ; Garvey and Espendshade 1998 ; Lee and Miller 1998 ; Smith and Edmonston 1997 : Chaps. 6 & 7). The NRC researchers report that the average native born household in New Jersey and California pays more in state and local taxes as a result of the presence of immigrants ( Smith and Edmonston 1997 : Chap. 6). These results are largely determined by the lower wages of immigrants and the demographic composition of immigrant households, which tend to be younger and have more children than the native born population. The largest component of local and state government budgets is schooling, and immigrant households, with more children per household than native born households, are disproportionately beneficiaries of state support for schooling.
Despite potential imbalances in the net transfer of revenues at the local and state level, an accounting of the federal fiscal system shows that immigrants (and their descendants) contribute more in taxes than they receive in benefits ( Smith and Edmonston 1997 : Chap. 7). Just as the age structure of immigrant households makes them disproportionately the beneficiaries of public education, the relative youth of immigrants also means they are less likely be beneficiaries of Social Security and Medicare (and Medicaid for many of the institutionalised elderly). Immigrants also help to relieve the per-capita fiscal burden of native born for the national debt, national security, and public goods, which are major federal expenditures that are only loosely tied to population size. An intergenerational accounting that counts the future taxes paid by the children of immigrants concludes that immigration helps, rather than hurts, the nation’s fiscal balance ( Lee and Miller 1998 ; Smith and Edmonston 1997 ; Chap. 7).
6.1 The Role of Immigration on the Advancement of Science, Technology and Higher Education
Scientific progress is a major source of modern economic growth, increasing longevity and other features of modern development that enhance the quality of life in the United States. It is frequently claimed that American economic development has been fostered by government investments in scientific and technological innovation in the industrial sector, as well as in universities and research institutes. How might immigration also affect scientific progress? Perhaps the most direct link is the migration of scientists from other countries and the high educational attainment of immigrants and their children.
Albert Einstein, perhaps the most eminent American scientist of the 20 th century, was a refugee from Nazi Germany. There are many other examples of distinguished scientists, researchers, academics, and entrepreneurs who arrived in the United States as students who pursued their talents in American universities and/or industry, including Enrico Fermi, Edward Teller, and Hans Bethe, the fathers of the atomic age, Elias Zerhouni, former director of the National Institutes of Health, and Andrew Grove, Jerry Yang, and Sergey Brin, the engineering entrepreneurs who led the American transition to the digital age. From 1990 to 2004, over one-third of US scientists who had received Nobel Prizes were foreign born ( Wulf 2006 ; also see Smith and Edmonston 1977 : 384–385).
The impact of immigration on the development of science in the United States is more than the story of a relatively open door for immigrants who are exceptionally talented scientists and engineers. Over the last four decades, American universities have played an important role in training immigrants and the children of immigrants to become scientists. Foreign students have become increasingly central to American higher education, particularly in graduate education in engineering and the sciences. After graduating with advanced degrees from American universities, many foreign students return to their home countries, but a significant share is attracted to employment opportunities in American universities, laboratories, and industries. Many of the foreign students who have become permanent residents or US citizens go on to make important contributions to the development of American science and engineering.
Several recent studies have found that foreign-born scientists and engineers are playing a critical role in in American universities, laboratories, and scientific industries ( Stephan and Levin 2007 ; Sana 2010 ). Foreign-born scientists and engineers are also over-represented among members of elected honorific societies such as the National Academy of Engineering and National Academy of Sciences, and among the authors of highly cited academic papers ( Stephan and Levin 2007 ). During the last decades of the twentieth century, immigrant entrepreneurs formed a significant contingent of all founders of US high-technology start-ups, particularly in Silicon Valley ( Saxenian 2001 ). One recent study estimates that one in four technology firms started in the United States between 1995 and 2005 was founded by at least one foreign-born entrepreneur ( Wadwha et al. 2007 ).
6.2 The Impact of Immigrants on the Evolution of American Institutions
All other things being equal, most societies, communities, organisations and cultures tend to resist change, especially from outside sources. The truism that ‘people prefer that which is familiar’ is reinforced by persons with authority, power, and status, who generally shape cultural expectations to revere conformity more than innovation. This pattern, an ‘ideal type’ to be sure, is especially common in traditional rural areas, among multi-generational families, and in religious and cultural organisations.
There are, of course, many exceptions to this pattern, especially during eras of rapid technological and social change, wartime, and other times of catastrophe. The simple proposition of cultural continuity helps to explain the generally conservative nature of intergenerational socialisation and the ubiquity of ethnocentrism—beliefs that value insiders and traditional culture more than outsiders. In traditional (and in many modern) societies, immigrants are feared because they might potentially challenge the existing social arrangements as well as familiar cultural patterns.
All things have not been equal during much of American history. The United States has received about 75 million immigrants since record-keeping began in 1820. This relatively open door was due to a confluence of interests, both external and internal. As modernisation spread throughout the Old World during the 18 th and 19 th centuries, the (relatively) open frontier beckoned the landless and others seeking economic betterment. These patterns culminated in the early 20 th century, when more than one million immigrants arrived annually—a level that is only being rivaled by contemporary levels of immigration. American economic and political institutions also gained from immigration. Immigrant settlement helped to secure the frontier as well as to provide labour for nation-building projects, including transportation networks of roads, canals, and railroads. During the era of industrialisation, immigrant labour provided a disproportionate share of workers for the dirty and dangerous jobs in mining and manufacturing ( Hirschman and Mogford 2009 ).
In spite of the national tradition of mass immigration, new arrivals have rarely received a welcome reception. The conservative backlash against immigrants has been a perennial theme of American history. During the Age of Mass Migration, the negative reaction against immigrants was not simply a response from the parochial masses, but also a project led by conservative intellectuals. Long before immigration restrictions were implemented in the 1920s, there was a particularly virulent campaign against the ‘new’ immigrants from Eastern and Southern Europe. Most of these immigrants were Catholics and Jews—religious and cultural traditions that were thought to be in conflict with the traditional ascendancy of white Protestants of English ancestry.
As most Northeastern and Midwestern cities became dominated by immigrants (both first and second generations) in the late 19 th century, many elite old-stock American families and communities created barriers to protect their ‘aristocratic’ status and privileges against newcomers ( Higham 1988 ). Residential areas became ‘restricted,’ college fraternities and sororities limited their membership, and many social clubs and societies only allowed those with the right pedigrees and connections to be admitted ( Baltzell 1964 ). Barriers to employment for minorities, especially Jews, were part of the culture of corporate law firms and elite professions ( Auerbach 1975 : Chap. 2). In the early 20 th century, many elite private universities were notorious for their quotas for Jewish students and their refusal to hire Jews and other minorities ( Baltzell 1964 : 336; Karabel 2006 ). In some cases, these quotas persisted until the 1960s.
Given this history, how were immigrants and their children able to make such impressive achievements to American science, arts, and culture? Part of the solution to this puzzle is that immigrants, and especially their children, were pulled into self-employment and new sectors of the economy where there was less discrimination. As noted above, prestigious organisations that celebrated tradition tended to be closed to outsiders. The early 20 th century was an era of rapid demographic, economic, and technological change. Rapid social change creates more flexibility and openness for outsiders to be absorbed into mainstream institutions.
The market for cultural and artistic performances was greatly expanded with the growth of cities in the early 20 th century. A significant share of the urban population, the potential consumers of art and culture, were of immigrant stock. The most important development of this era was the motion picture industry—a new form of the performing arts. In the 1920s, immigrant risk-takers, primarily Eastern European Jewish immigrants, transformed the fledgling motion picture industry with the development of large Hollywood studios. Although the new Hollywood moguls sought to create movies that appealed to mass audiences and ignored any hint of ethnicity or religion, their presence may have minimised traditional prejudices and discrimination among those who worked in Hollywood. Irving Howe characterised the openness of the performing arts (and sports) to talented outsiders:
… “the (entertainment industry) brushed aside claims of rank and looked only for the immediate promise of talent. Just as blacks would later turn to baseball and basketball knowing that here at least their skin color counted for less than their skills, so in the early 1900s, young Jews broke into vaudeville because here too, people asked not, who are you? but, what can you do?”
This openness is reinforced in fields and professions where talent and accomplishment are clearly recognised and visible, including professional sports and universities. Prior to World War II, competition was restricted in many institutions with barriers to admission and hiring. Professional baseball was closed to African Americans and elite universities restricted the admission of Jews and other minorities. In spite of these tendencies, many American institutions have become more open and meritocratic over the 20 th century. Baseball and other professional sports were integrated before most other institutions, including public school education. In recent decades, American professional sports have become more global, with a growing participation of talented international players. This trend is driven, in large part, by competition. Sports fans want winning teams, and large audiences increase revenues. The owners and management of sports teams respond to market pressures by recruitment of talented players from other countries. Similar processes are at work in universities and scientific organisations. More talented researchers generate more grants, more patents, and more commercial applications of scientific discoveries. The global search for talented graduate students and researchers by elite American universities and research organisations is driven by competitive pressures that have accelerated in recent decades. Other fields where merit is relatively easy to measure, such as in classical musical performance, have also become part of a global employment market.
There are similar competitive pressures in many American corporations and business for talented employees, but there are certainly wide variations depending on the pace of technological change, international market competition, and the ability to measure merit. Traditional manufacturing sectors of the economy, automobiles for example, may focus more on continuity, advertising, and efficiency than technological innovation. Other sectors, such as the electronic and computing industry are more at the forefront of technological innovation and international competition. It seems likely that these more competitive sectors, perhaps exemplified by Silicon Valley, would be the most meritocratic and willing to hire outsiders—immigrants and foreign students who have the necessary skills.
The same processes of competition certainly affected the development of Hollywood, Broadway, and many other American performing and cultural arts. Audience preferences may have tended toward familiar cultural content, but there was undoubtedly strong market pressure for ‘quality’, however defined. There was also considerable room for innovation in artistic and cultural performance in a pluralistic society with relatively few cultural touchstones. Immigrants and their children played important roles in the development of culture and art in 20 th century America, just as they have in science and academic institutions.
My contention is that the presence of immigrants and their offspring has helped to ‘push’ American institutions in the direction of increasing openness and meritocracy. This has not always been a smooth or conflict-free process. When Jewish students appeared in large numbers in leading American universities in the early 20 th century, they were deemed rate-busters who upset the traditional college student culture, which de-emphasised too much study or serious scholarly interests.
The growing number of talented Jewish students, mostly second generation immigrants, certainly raised the standards at universities that did not discriminate. As universities began to compete for faculty and graduate students during the post-World War II era, the quota restrictions eventually disappeared ( Karabel 2006 ). Elite colleges and universities still retain legacies of non-merit based admission systems, including programmes to privilege children of alumni. There is also evidence that Asian American students have not been admitted in numbers proportional to their test scores ( Espenshade and Chung 2005 ), but these current practices are only a shadow of those of earlier times. The point is not that universities are completely meritocratic, but that they have become more meritocratic with increasing competition and acceptance of talented ‘outsiders.’
Greater openness to hiring and promotion on the basis of merit has become an integral part of many American institutions in recent years. The reputation of the United States as a land of opportunity for those with ambition and ability—a theme in many Hollywood movies—made the country a beacon for prospective immigrants. In addition to raising the international stature of the United States, the participation of talented immigrants and their children has likely made American scientific and cultural institutions more successful.
7. Conclusions
Contemporary immigration to the United States, upwards of one million new arrivals per year, is not exceptional. In fact, the relative share of immigrants—about 13 per cent—is a bit lower than the 14 to 15 per cent that characterised much of American history prior to the 1920s. Absorbing large numbers of newcomers has costs as well as benefits. The costs are immediately apparent, but some of the benefits take longer to appear. Schools, hospitals, and social service agencies may have to arrange for translation services and other special programmes for immigrants. But most of the costs of these adjustments are paid by immigrants and their families. Immigrants have given up the familiarity of home in their quest for more rewarding careers and greater opportunities for their children. Immigrants must also contend with a receiving society that is ambivalent, and sometimes hostile, to their presence.
Contemporary immigrants do adapt and assimilate to American society—probably as fast as earlier waves of immigrants. Assimilation is not instantaneous, and, for adult immigrants, the process is never complete. But for their native born children, and for those who arrive in the United States as young children, assimilation is a natural process that reflects immersion in American schools and culture.
Immigrants and their children, however, are not the same as native born Americans. In addition to the many obvious characteristics, such as language, religion, and cuisine, they generally differ on social and educational characteristics. For the contemporary period, immigrants are over-represented both among college graduates and those with less than 12 years of schooling relative to native born Americans ( Portes and Rumbaut 2006 : Chap. 4). Immigrants are also not representative of the society from which they come ( Feliciano 2005a ; 2005b ; Model 2008 ). In contrast to popular images, immigrants are not drawn from the least successful ranks of their home societies, but are generally well above average in terms of their education and other skills.
Perhaps the most important contribution of immigrants is their children. Many immigrants have made enormous sacrifices for their children’s welfare, including the decision to settle in the United States. Immigrant parents often have to work in menial jobs, multiple jobs, and in occupations well below the status they would have earned if they had remained at home. These sacrifices have meaning because immigrant parents believe that their children will have better educational and occupational opportunities in the United States than in their homelands. Immigrant parents push their children to excel by reminding them of their own sacrifices.
These high expectations for the children of immigrants generally lead to high motivations for academic and worldly success ( Hao and Bonstead-Burns 1998 ). A large body of research shows that the children of immigrants do remarkably well in American schools. Holding constant their socio-economic status, the second generation obtains higher grades in school and above average results on standardised tests, is less likely to drop out of high school, and is more likely to go to college than the children of native born Americans ( Fuligni and Witknow 2004 ; Perreira, Harris and Lee 2006 ).
In addition to measures of socio-economic assimilation, immigrants and their children are over-represented in a broad range of rare achievements, including Nobel Prize winners, top scientists, American performing artists, and other contributors to the American creative arts. They have broadened our cultural outlook and sometimes, have even defined American culture through literature, music and art.
Compared with other societies, the United States is generally regarded as unusually competitive and places a high premium on progress and innovation. This dynamic characteristic may well arise from the presence of immigrants and on the evolution of American institutions and identity. The size and selectivity of the immigrant community means that immigrants (and/or their children) are competing for entry into colleges, jobs, and access to prestigious positions and institutions. Not all institutions have been open to outsiders on an equal footing with insiders. In particular, high status organisations often give preference to persons with the right connections and social pedigree. But institutions that opened their doors to talented outsiders—immigrants and their children—probably gained a competitive advantage. Over time, greater openness and meritocratic processes may have become a force that shaped the evolution of American institutions in the arts, sports, science, and some sectors of business. In turn, the participation of outsiders may have reinforced a distinctive American character and culture that values not ‘who are you?’ but, ‘what can you do?’
Because immigrants have to constantly work at learning the system, they are intensely curious about American culture. For the most talented, this leads to a level of creativity beyond the normal boundaries that has left its imprint on American music, theater, dance, film, and many other realms of artistic endeavour. Finally, American institutions – schools, universities, businesses, sports teams, and even symphony orchestras, are meritocratic and seek talent wherever they can find it. The United States is a competitive society that values progress and success. This dynamic characteristic has partly been created through the presence of immigrants, which has pushed the country to value skills and ability over social pedigree.
The fear of cultural conservatives is that immigrants will change American character and identity. Yet, the definition of American identity is elusive. Unlike many other societies, the United States does not have an identity tied to an ancient lineage. Given the two wars against the British in early American history (in 1776 and 1812), the founders of the new American republic did not make English origins the defining trait of American identity; rather it was acceptance of the Enlightenment ideas expressed in the founding documents of the Declaration of Independence, the Constitution, and the Bill of Rights ( Gleason 1980 ; Vecoli 1966). Even though these ideals were belied by the continuing stain of slavery, a civic identity rather than ancestry has been the distinctive feature of American ‘ peoplehood ’ from the very start. This trait combined with jus soli (birthright citizenship) 2 has slowed, if not stopped, efforts to define Americans solely on the basis of ancestral origins. Another reason for the broad definition of American identity is that the overwhelming majority of the American population, including white Americans, is descended from 19 th and 20 th century immigrants. Demographic estimates suggest that less than one-third of the American population in the late 20 th century were descended from the 18 th century American population ( Edmonston and Passel 1994 : 61, Gibson 1992 ).
Yet, there have been recurrent struggles to redefine American identity in terms of ancestry. The first naturalisation law passed by Congress in 1790 limited citizenship to whites. The broadening of American citizenship to include African Americans, American Indians, and Asian immigrants were epic battles. The short-lived, but remarkably successful ‘Know-Nothing’ political movement called itself the American Party to highlight the ancestral origins of its adherents. In the late 19 th century, as new immigrants from Southern and Eastern Europe were pouring in, some old stock Americans founded organisations such as the Sons of the American Revolution, Daughters of the American Revolution, and similar groups to celebrate their ancestral pedigrees and to distance themselves from recent immigrants. The national origin quotas of the 1920s were a clear victory for those who feared dilution of the white English Protestant composition of the American population. The current anti-immigrant sentiment also expresses a fear that American identity will be lost, yet it is unclear that a universal contemporary American identity exists. Although the English language is considered to be central, English Protestant ancestry is not emphasised. There is too much diversity, even within the white population, to focus on specific ancestral origins.
In an often quoted remark, Oscar Handlin, the famous historian, observed that after searching for the place of immigrants in American history, that immigrants are American history. The American experiment in nation building is, in large part, the story of how immigrants have been absorbed into American society and how immigrants have enlarged and transformed America. Immigrants settled the frontier; they participated in constructing canals, roads and railroads, and contributed significant manpower in many American wars. Immigrants provided much of the manufacturing labour for the American industrial revolution as well as a disproportionate share of the contemporary highly skilled scientists and engineers that are central to the modern electronic and biomedical economy. Most interestingly, immigrants and the children of immigrants have been among the most important creative artists who have shaped the development of the cultural arts, including movies, theatre, dance, and music.
Immigration is, perhaps, the most distinctive feature of American identity. Immigration has had a disproportionate effect on the demographic size, ethnic diversity, culture, and character of American society. Immigrants and their children have assimilated to America, but they have also shaped American institutions in ways that have allowed strangers to participate on a relatively open playing field.
Acknowledgments
The author thanks the Malaysian Population and Family Development Board for the invitation to participate in the conference, the Malaysian American Commission for Educational Exchange for a Fulbright Fellowship to Malaysia, the Faculty of Economics and Administration, University of Malaya for hosting me as a Visiting Fulbright Professor, and Associate Professor Tey Nai Peng for his advice on my conference paper.
+ An earlier version of this paper was presented at the International Conference on Migration, Urbanisation and Development at the University of Malaya, 8 July 2013.
1 The foreign-born refers to all persons who are born outside the United States or a United States territory. The Census Bureau defines the native born (the complement of the foreign born) as persons who are American citizens at birth. The terms foreign born and immigrants are used interchangeably here, but this is not technically true because many of the foreign born are in the United States as temporary workers or students.
2 The fourteenth amendment to the Constitution (adopted in 1868) defines citizenship as consisting of: “All persons born or naturalised in the United States, and subject to the jurisdiction thereof, are citizens of the United States and of the State wherein they reside.” Subsequent Supreme Court rulings have interpreted the citizenship clause to include the native born children of foreign nationals.
- Alba Richard. Ethnic Identity: The Transformation of White America. New Haven: Yale University Press; 1990. [ Google Scholar ]
- Alba Richard, Nee Victor. Remaking the American Mainstream: Assimilation and Contemporary Immigration. Cambridge: Harvard University Press; 2003. [ Google Scholar ]
- Archdeacon Thomas J. Becoming American: An Ethnic History. New York: The Free Press; 1983. [ Google Scholar ]
- Auerbach Jerald. Unequal Justice: Lawyers and Social Change in Modern America. New York: Oxford; 1975. [ Google Scholar ]
- Baltzell E Digby. The Protestant Establishment: Aristocracy and Caste in America. New York: Vintage Books; 1964. [ Google Scholar ]
- Borjas George J. Economic theory and international migration. International Migration Review. 1989; 23 (3):457–485. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Borjas George. The economics of immigration. Journal of Economic Literature. 1994; 32 :1667–1717. [ Google Scholar ]
- Briggs Vernon. Immigration Policy and the American Labor Force. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press; 1984. [ Google Scholar ]
- Brimelow Peter. Alien Nation: Common Sense About America’s Immigration Disaster. New York: Random House; 1995. [ Google Scholar ]
- Bouvier Leon F. Peaceful Invasions. Lanham, MD: University Press of America; 1992. [ Google Scholar ]
- Card David. The impact of the Muriel Boatlift on the Miami labor market. Industrial and Labor Relations Review. 1990; 43 :245–257. [ Google Scholar ]
- Card David. Is the new immigration really so bad? Economic Journal. 2005; 115 :F300–F323. [ Google Scholar ]
- Carter Susan, Sutch Richard. Historical background to current immigration issues. In: Smith James P, Edmonston Barry., editors. The Immigration Debate: Studies on the Economic, Demographic and Fiscal Effects of Immigration. Washington, DC: National Academy Press; 1999. pp. 289–366. [ Google Scholar ]
- Clune Michael S. The fiscal impacts of immigrants: A California case study. In: Smith James P, Edmonston Barry., editors. The Immigration Debate: Studies on the Economic, Demographic, and Fiscal Effects of Immigration. Washington, DC: National Research Council; 1998. pp. 120–182. [ Google Scholar ]
- Duncan Beverly, Duncan Otis Dudley. Minorities and the process of stratification. American Sociological Review. 1968; 33 :356–364. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Duncan Brian, Trejo Stephen J. Ethnic identification, intermarriage, and unmeasured progress by Mexican Americans. In: Borjas George., editor. Mexican Immigration to the United States. Chicago: University of Chicago Press; 2007. pp. 229–267. [ Google Scholar ]
- Edmonston Barry, Jeffrey Passel., editors. Immigration and Ethnicity: The Integration of America’s Newest Arrivals. Washington, DC: Urban Institute Press; 1994. [ Google Scholar ]
- Easterlin Richard. Population, Labor Force, and Long Swings in Economic Growth: The American Experience. New York: Columbia University Press; 1968. [ Google Scholar ]
- Espenshade Thomas J, Chung Chang Y. The opportunity cost of admission preferences at elite universities. Social Science Quarterly. 2005; 86 (2):293–305. [ Google Scholar ]
- Feliciano Cynthia. Does selective migration matter” explaining ethnic disparities in educational attainment among immigrant children. International Migration Review. 2005a; 39 :841–871. [ Google Scholar ]
- Feliciano Cynthia. How do immigrants compare to those left behind? Demography. 2005b; 42 :131–152. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Fuligni Andrew J, Witknow Melissa. The postsecondary educational progress of youth from immigrant families. Journal of Research on Adolescence. 2004; 14 :159–183. [ Google Scholar ]
- Garvey Deborah L, Espenshade Thomas J. Fiscal impacts of immigrant and native households: A New Jersey case study. In: Smith James P, Edmonston Barry., editors. The Immigration Debate: Studies on the Economic, Demographic, and Fiscal Effects of Immigration. Washington, DC: National Research Council; 1998. pp. 66–119. [ Google Scholar ]
- Gibson Campbell. The contribution of immigration to the growth and ethnic diversity of the American population. Proceedings of the American Philosophical Society. 1992; 136 :157–175. [ Google Scholar ]
- Gibson Campbell, Jung Kay. Historical Census Statistics on the Foreign Born Population of the United States: 1850 to 2000. Washington, DC: U.S. Bureau of the Census; 2006. (Population Division Working Paper No. 81). [ Google Scholar ]
- Gleason Philip. American identity and Americanization. In: Thernstrom Stephen., editor. Harvard Encyclopedia of American Ethnic Groups. Cambridge: Harvard University Press; 1980. pp. 31–58. [ Google Scholar ]
- Grieco Elizabeth M, Acosta Yesenia D, de la Cruz G Patricia, Gambino Christine, Gryn Thomas, Larsen Luke J, Trevelyan Edward N, Walters Nathan P. The Foreign Born Population of the United States. Washington, D.C: U.S. Bureau of the Census; 2012. (American Community Survey Reports, ACS-19). [ Google Scholar ]
- Handlin Oscar. The Uprooted: The Epic Story of the Great Migrations that Made the American People. 2. Boston: Little Brown and Company; 1973. (orig pub 1951) [ Google Scholar ]
- Hao Lingxin, Bonstead-Bruns Melissa. Parent-child differences in educational expecations and the academic achievement of immigrant and native students. Sociology of Education. 1998; 71 :175–198. [ Google Scholar ]
- Haines Michael R. The population of the United States 1790–1920. In: Engerman Stanley L, Gallman Robert E., editors. The Cambridge Economic History of the United States. Vol. 2. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 2000. pp. 143–205. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hing Bill Ong. Making and Remaking Asian America Through Immigration Policy 1850–1990. Stanford: Stanford University Press; 1993. [ Google Scholar ]
- Higham John. Strangers in the Land: Patterns of American Nativism 1860–1925. 2. New Brunswick: Rutgers University Press; 1988. (orig. pub. 1955) [ Google Scholar ]
- Hirschman Charles. The educational enrollment of immigrant youth: A test of the segmented-assimilation hypothesis. Demography. 2001; 38 :317–336. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hirschman Charles, Mogford Elizabeth. Immigration and the American industrial revolution from 180 to 1920. Social Science Research. 2009; 38 :897–920. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Howe Irving. World of Our Fathers: The Journey of Eastern European Jews to American and the Life They Founded and Made. New York: Simon and Schuster; 1976. [ Google Scholar ]
- Huntington Samuel L. Who are We? The Challenges to America’s National Identity. New York: Simon and Schuster; 2004. [ Google Scholar ]
- Jones Madwyn Allen. American Immigration. 2. Chicago: University of Chicago Press; 1992. (orig pub 1960) [ Google Scholar ]
- Karabel Jerome. The Chosen: The Hidden History of Admission and Exclusion at Harvard, Yale, and Princeton. New York: Houghton Mifflin; 2006. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kasinitz Philip, Mollenkopf John H, Waters Mary C, Holdaway Jennifer. Inheriting the City: The Children of Immigrants Come of Age. New York, NY: Russell Sage Foundation; Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press; 2008. [ Google Scholar ]
- Keely Charles. US Immigration: A Policy Analysis. New York: The Population Council; 1979. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lee Ronald D, Miller Timothy W. The current fiscal impact of immigrants and their descendents: beyond the immigrant household. In: Smith J, Edmonston B, editors. The Immigration Debate: Studies on the Economic, Demographic, and Fiscal Impacts of Immigration. Washington, DC: National Academy Press; 1998. pp. 183–205. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lieberson Stanley. A Piece of the Pie: Blacks and White Immigrants Since 1880. Berkeley: University of California Press; 1980. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lieberson Stanley, Waters Mary. From Many Strands: Ethnic and Racial Groups in Contemporary America. New York: Russell Sage Foundation; 1988. [ Google Scholar ]
- Massey Douglas S, Jorge Durand, Malone Noland J. Beyond Smoke and Mirrors: Mexican Immigration in an Era of Economic Integration. New York: Russell Sage Foundation; 2002. [ Google Scholar ]
- Min Pyong Gap, Kim Chigon. Patterns of intermarriages and cross-generation in-marriages among native born Asian Americans. International Migration Review. 2009; 43 :447–470. [ Google Scholar ]
- Model Suzanne. West Indian Immigrants: A Black Success Story. New York: Russell Sage Foundation; 2008. [ Google Scholar ]
- Most Andrea. Making Americans: Jews and the Broadway Musical. Cambridge: Harvard University Press; 2004. [ Google Scholar ]
- Pagnini Deanna L, Morgan S Philip. Intermarriage and social distance Among U.S. immigrants at the turn of the century. American Journal of Sociology. 1990; 96 :405–432. [ Google Scholar ]
- Perreira Krista, Harris Kathleen Mullan, Lee Dohoon. Making it in America: High School Completion by Immigrant and Native Youth. Demography. 2006; 43 (3):511–536. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Portes Alejandro, Rumbaut Rubén. Immigrant America: A Portrait. Third. Berkeley: University of California Press; 2006. [ Google Scholar ]
- Reimers David M. Still the Golden Door: The Third World Comes to America. New York: Columbia University Press; 1985. [ Google Scholar ]
- Sana Mariano. Immigrants and Natives in U.S. science and engineering occuaptions, 1994–2006. Demography. 2010; 47 :801–820. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Saxenian AnnaLee. Silicon Valley’s new immigrant entrepreneurs. In: Cornelius Wayne, Espenshade Thomas J, Salehyan Idean., editors. The International Migration of the Highly Skilled: Demand, Supply, and Development Consequences in Sending and Receiving Countries. San Diego: Center for U S Mexican Studies at the University of California, San Diego; 2001. pp. 197–234. [ Google Scholar ]
- Smith James P, Barry Edmonston., editors. The New Americans: Economic, Demographic, and Fiscal Effects of Immigration. Washington, DC: National Academy Press; 1997. [ Google Scholar ]
- Smith James P, Barry Edmonston., editors. The Immigration Debate: Studies on the Economic, Demographic, and Fiscal Impacts of Immigration. Washington, DC: National Academy Press; 1998. [ Google Scholar ]
- Stephan Paula E, Levin Sharon G. Foreign scholars in the US: Contributions and costs. In: Stephan Paula E, Ronald G., editors. Science and the University. Ehrenberg. Madison: University of Wisconsin; 2007. pp. 150–173. [ Google Scholar ]
- UN (United Nations) Population Division. Trends in International Migrant Stock, Table 1. 2013 Retrieved 7 October 2013 from: http://esa.un.org/unmigration/migrantstocks2013.htm?mtotals .
- U.S. Bureau of the Census. Foreign-Born Population of the United States Current Population Survey – March 2009 Detailed Tables (Table 4.1) 2010 Retrieved 26 August 2010 from http://www.census.gov/population/socdemo/foreign/cps2009/T4.1.xls .
- Vecoli Rudolph. The significance of immigration in the formation of an American identity. The History Teacher. 1996; 30 :9–27. [ Google Scholar ]
- Wadhwa Vivek, Saxenian AnnaLee, Rissing Ben, Gereffi Gary. America’s Immigrant Entrepreneurs: Part I. Master of Management Program, DukeUniversity School of Information; UC Berkeley: 2007. Retrieved 30 August 2009 from: ( http://people.ischool.berkeley.edu/~anno/Papers/Americas_new_immigrant_entrepreneurs_I.pdf ) [ Google Scholar ]
- White Michael, Glick Jennifer E. Achieving Anew: How New Immigrants Do in American Schools, Jobs, and Neighborhoods. New York: Russell Sage Foundation; 2009. [ Google Scholar ]
- Wulf William A. Foreign-born researchers are key to US prosperity and security. The National Academies in Focus. 2006 Winter-Spring; 6 Retrieved 30 August 2009 from http://www.infocusmagazine.org/6.1/president.html . [ Google Scholar ]
- Browse All Articles
- Newsletter Sign-Up
Immigration →

- 08 May 2023
- Research & Ideas
How Trump’s Anti-Immigrant Rhetoric Crushed Crowdfunding for Minority Entrepreneurs
When public anxiety about immigration surges, Black, Asian, and Hispanic inventors have a harder time raising funds for new ideas on Kickstarter, says research by William Kerr. What can platforms do to confront bias in entrepreneurial finance?

- 14 Feb 2023
Is Sweden Still 'Sweden'? A Liberal Utopia Grapples with an Identity Crisis
Changing political views and economic forces have threatened Sweden's image of liberal stability. Is it the end of the Scandinavian business-welfare model as we know it? In a case study, Debora Spar examines recent shifts in Sweden and what they mean for the country's future.

- 01 Nov 2022
- What Do You Think?
Why Aren’t Business Leaders More Vocal About Immigration Policy?
Immigration fuels the American economy, feeds the talent pool, and can directly affect company performance. And yet few executives and entrepreneurs have waded into the policy dialogue, says James Heskett. Open for comment; 0 Comments.

- 30 Mar 2021
- Working Paper Summaries
Whose Job Is It Anyway? Co-Ethnic Hiring in New US Ventures
The impact of immigration has been particularly sharp in entrepreneurship, yet there is remarkably little evidence about how immigration in the workplace connects to the creation and scaling of new firms. The economic consequences of greater workplace and entrepreneurial diversity deserve closer attention.
- 11 Jan 2021
The Political Effects of Immigration: Culture or Economics?
This paper reviews and explains the growing literature focused on the political effects of immigration, and highlights fruitful avenues for future research. When compared to potential labor market competition and other economic forces, broadly defined cultural factors have a stronger political and social impact.
- 03 Nov 2020
An Executive Order Worth $100 Billion: The Impact of an Immigration Ban’s Announcement on Fortune 500 Firms’ Valuation
President Trump’s executive order restricting entry of temporary foreign workers to the United States negatively affected the valuation of 471 publicly traded Fortune 500 firms by an estimated $100 billion. Closed for comment; 0 Comments.
- 15 Jun 2020
The Seeds of Ideology: Historical Immigration and Political Preferences in the United States
Researchers test the relationship between historical immigration to the United States and political ideology today.

- 11 May 2020
Immigration Policies Threaten American Competitiveness
At this time of crisis, America risks signaling to global innovators and entrepreneurs that they have no future here, says William R. Kerr. Open for comment; 0 Comments.
- 21 Apr 2020
Changing In-group Boundaries: The Role of New Immigrant Waves in the US
How do new immigrants affect natives’ views of other minority groups? This work studies the evolution of group boundaries in the United States and indicates that whites living in states receiving more Mexican immigrants recategorize blacks as in-group members, because of the inflow of a new, “affectively” more distant group.

- 06 Apr 2020
Where Do Workers Go When the Robots Arrive?
Marco Tabellini and colleagues investigate where workers go after losing their jobs to automation and Chinese imports. Open for comment; 0 Comments.
- 17 Feb 2020
The Impact of Technology and Trade on Migration: Evidence from the US
Labor mobility can re-equilibrate local labor markets after an economic shock. Both robot adoption and Chinese import competition between 1990 and 2015 caused large declines in manufacturing employment across US local labor markets (commuting zones, CZs). However, only robots were associated with a decline in CZ population, which resulted from reduced in-migration rather than by increased out-migration.
- 01 Jan 2020
Why Not Open America's Doors to All the World’s Talent?
SUMMING UP: The H-1B visa program is exploited by some employers to replace high-paid talent, but that doesn't mean foreign workers should be shut out of working in the United States, according to many of James Heskett's readers. Open for comment; 0 Comments.
- 19 Jun 2019
Migrant Inventors and the Technological Advantage of Nations
This study provides robust econometric evidence for how immigrant inventors shape the innovation dynamics of their receiving countries. Countries receiving inventors from other nations that specialize in patenting particular technologies are more likely to have a significant increase in patent applications of the same technology.
- 08 Jun 2019
The Gift of Global Talent: Innovation Policy and the Economy
High-skilled workers in today’s knowledge-based economy are arguably the most important resource to the success of businesses, regions, and industries. This chapter pulls from Kerr’s book The Gift of Global Talent to examine the migration dynamics of high-skilled individuals. He argues that improving our knowledge of high-skilled migration can lead to better policy decisions.
- 07 Feb 2019
Immigrant Networking and Collaboration: Survey Evidence from CIC
This study compares United States-born and immigrant entrepreneurs’ use of networking opportunities provided by CIC, the former Cambridge Innovation Center. Immigrants clearly take more advantage of networking opportunities at CIC, especially around the exchange of advice. It remains to be seen whether this generates long-term performance advantages for immigrants.
- 01 Nov 2018
Forecasting Airport Transfer Passenger Flow Using Real-Time Data and Machine Learning
Passengers arriving at international hubs often endure delays, especially at immigration and security. This study of London’s Heathrow Airport develops a system to provide real-time information about transfer passengers’ journeys through the airport to better serve passengers, airlines, and their employees. It shows how advanced machine learning could be accessible to managers.

- 01 Oct 2018
Is the US Losing its Ability to Attract Highly Skilled Migrant Workers?
As debates sharpen on the benefits and drawbacks of migrant labor, William R. Kerr's new book explores why global talent flows matter to national economic development and security. Book excerpt and author interview. Open for comment; 0 Comments.
- 19 Sep 2018
From Immigrants to Americans: Race and Assimilation During the Great Migration
The Great Migration of African Americans and the mass migration of Europeans both contributed to forming the modern American racial and ethnic landscape. This analysis finds that native whites more readily accepted European immigrants as African Americans arrived in the US North during the first Great Migration, facilitating the assimilation of European immigrants in northern urban centers.
- 07 Aug 2018
Gifts of the Immigrants, Woes of the Natives: Lessons from the Age of Mass Migration
Investigating the economic and political effects of immigration across US cities between 1910 and 1930, this paper finds that political opposition to immigration can arise even when immigrants bring widespread economic benefits. The paper provides evidence that cultural differences between immigrants and natives were responsible, at least in part, for natives’ anti-immigration reactions.

- 18 Jul 2018
No More General Tso's? A Threat to 'Knowledge Recombination'
Immigrants bring with them innovations from their homelands, knowledge that local inventors often build upon, says Prithwiraj Choudhury. Examples: turmeric medicine, double-entry bookkeeping, and American Chinese food. Open for comment; 0 Comments.

Immigration Research Library
Informing People Concerned About Immigration and Immigrants
Search form
Immigration research and information.
The Immigration Research Library is a free, online collection of contemporary, U.S. immigration reports, briefs, fact sheets, infographics, news and events. The Library hosts (with links to original sources) more than 1,500 U.S. immigration research reports with simple, straightforward abstracts drawn from respected universities and research institutes from across the country. This free Library is for anyone interested in U.S. immigration issues including students, researchers, journalists, educators, advocates, policymakers, direct-service providers, etc.

The Immigration Research Library is hosted by The Immigrant Learning Center’s Public Education Institute in Malden, MA, a not-for-profit organization that educates Americans on the contributions of immigrants. See “About Us” to learn more.
The Immigration Research Library was created with the assistance of three research institutes at the University of Massachusetts Boston: the Institute for Asian American Studies , the Mauricio Gastón Institute for Latino Community Development and Public Policy and the William Monroe Trotter Institute.
Please bookmark this page as new reports are uploaded every week.
Contact: [email protected]
How to Use the Library
The Immigration Research Library is divided into five sections: Research, Infographics, Resources, News and Events. In the Research section, you can easily filter reports by state, issues (e.g. rights and justice, demographics, economics), communities (e.g. refugees, children, Latinx immigrants, workers) and/or source organization for the report(s). Infographics are similarly tagged and may come up with your search results.
The Resources section contains links to large databases of immigration data and research from respected organizations such as Migration Policy Institute’s Immigration Data Hub.
The News section draws up-to-date immigration news articles from organizations such as the American Immigration Lawyers’ Association.
The Events section includes local and national webinars, conferences, festivals and other events related to immigration. Feel free to send us your event!
Suggestion for improvement? Know of a report that should be here? Something broken? Email Denzil Mohammed at [email protected] .
Read our research on: Gun Policy | International Conflict | Election 2024
Regions & Countries
Key facts about u.s. immigration policies and biden’s proposed changes.

Since President Joe Biden took office in January 2021, his administration has acted on a number of fronts to reverse Trump-era restrictions on immigration to the United States. The steps include plans to boost refugee admissions , preserving deportation relief for unauthorized immigrants who came to the U.S. as children and not enforcing the “ public charge ” rule that denies green cards to immigrants who might use public benefits like Medicaid.
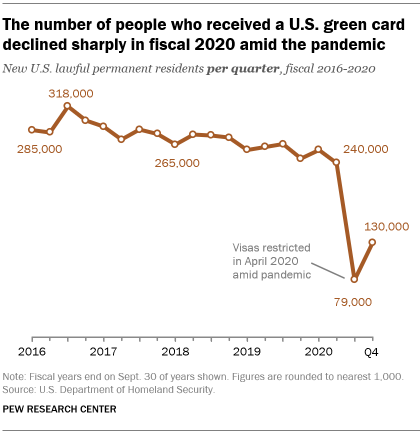
Biden has also lifted restrictions established early in the coronavirus pandemic that drastically reduced the number of visas issued to immigrants. The number of people who received a green card declined from about 240,000 in the second quarter of the 2020 fiscal year (January to March) to about 79,000 in the third quarter (April to June). By comparison, in the third quarter of fiscal 2019, nearly 266,000 people received a green card.
Biden’s biggest immigration proposal to date would allow more new immigrants into the U.S. while giving millions of unauthorized immigrants who are already in the country a pathway to legal status. The expansive legislation would create an eight-year path to citizenship for the nation’s estimated 10.5 million unauthorized immigrants , update the existing family-based immigration system, revise employment-based visa rules and increase the number of diversity visas . By contrast, President Donald Trump’s administration sought to restrict legal immigration in a variety of ways, including through legislation that would have overhauled the nation’s legal immigration system by sharply reducing family-based immigration.
The Biden administration has proposed legislation that would create new ways for immigrants to legally enter the United States. The bill would also create a path to citizenship for unauthorized immigrants living in the country.
To better understand the existing U.S. immigration system, we analyzed the most recent data available on federal immigration programs. This includes admission categories for green card recipients and the types of temporary employment visas available to immigrant workers. We also examined temporary permissions granted to some immigrants to live and work in the country through the Deferred Action for Childhood Arrivals and Temporary Protected Status programs.
This analysis relies on data from various sources within the U.S. government, including the Department of Homeland Security, Citizenship and Immigration Services, the Department of State, Federal Register announcements and public statements from the White House.
The Senate is considering several immigration provisions in a spending bill, the Build Back Better Act , that the House passed in November 2021. While passage of the bill is uncertain – as is the inclusion of immigration reforms in the bill’s final version – the legislation would make about 7 million unauthorized immigrants eligible to apply for protection from deportation, work permits and driver’s licenses.
Amid a record number of migrant encounters at the U.S.-Mexico border, Biden reinstated in December 2021 a Trump-era policy that requires those who arrive at the U.S.-Mexico border and seek asylum to wait in Mexico while their claims are processed. Biden had earlier ended the Migration Protection Protocols , or “Remain in Mexico” policy, and then restarted it after the U.S. Supreme Court upheld a lawsuit by Texas and Missouri that challenged the program’s closure. Asylum seekers do not receive a legal status that allows them to live and work in the U.S. until the claim is approved.
Overall, more than 35 million lawful immigrants live in the U.S.; most are American citizens. Many live and work in the country after being granted lawful permanent residence, while others receive temporary visas available to students and workers. In addition, roughly 1 million unauthorized immigrants have temporary permission to live and work in the U.S. through the Deferred Action for Childhood Arrivals and Temporary Protected Status programs.
Here are key details about existing U.S. immigration programs, as well as Biden’s proposed changes to them:
Family-based immigration
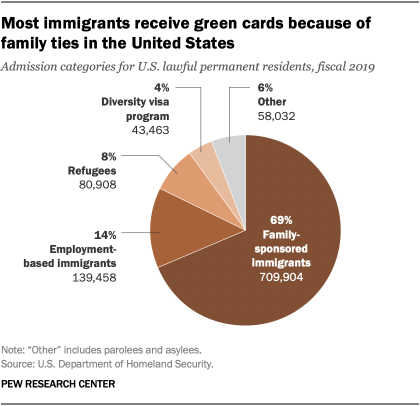
In fiscal 2019, nearly 710,000 people received lawful permanent residence in the U.S. through family sponsorship. The program allows someone to receive a green card if they already have a spouse, child, sibling or parent living in the country with U.S. citizenship or, in some cases, a green card. Immigrants from countries with large numbers of applicants often wait for years to receive a green card because a single country can account for no more than 7% of all green cards issued annually.
Biden’s proposal would expand access to family-based green cards in a variety of ways, such as by increasing per-country caps and clearing application backlogs. Today, family-based immigration – referred to by some as “ chain migration ” – is the most common way people gain green cards, in recent years accounting for about two-thirds of the more than 1 million people who receive green cards annually.
Refugee admissions
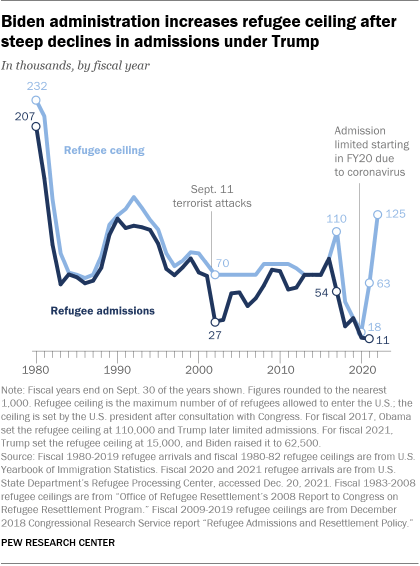
The U.S. admitted only 11,411 refugees in fiscal year 2021, the lowest number since Congress passed the 1980 Refugee Act for those fleeing persecution in their home countries. The low number of admissions came even after the Biden administration raised the maximum number of refugees the nation could admit to 62,500 in fiscal 2021 . Biden has increased the refugee cap to 125,000 for fiscal 2022, which started on Oct. 1, 2021.
The low number of admissions in recent years is due in part to the ongoing pandemic. The U.S. admitted only about 12,000 refugees in fiscal 2020 after the country suspended admissions during the coronavirus outbreak . This was down from nearly 54,000 in fiscal 2017 and far below the nearly 85,000 refugees admitted in fiscal 2016, the last full fiscal year of the Obama administration.
The recent decline in refugee admissions also reflects policy decisions made by the Trump administration before the pandemic. Trump capped refugee admissions in fiscal 2020 at 18,000 , the lowest total since Congress created the modern refugee program in 1980.
Employment-based green cards
In fiscal 2019, the U.S. government awarded more than 139,000 employment-based green cards to foreign workers and their families. The Biden administration’s proposed legislation could boost the number of employment-based green cards, which are capped at about 140,000 per year . The proposal would allow the use of unused visa slots from previous years and allow spouses and children of employment-based visa holders to receive green cards without counting them against the annual cap. These measures could help clear the large backlog of applicants. The proposed legislation also would eliminate the per-country cap that prevents immigrants from any single country to account for more than 7% of green cards issued each year.
Diversity visas
Each year, about 50,000 people receive green cards through the U.S. diversity visa program , also known as the visa lottery. Since the program began in 1995, more than 1 million immigrants have received green cards through the lottery, which seeks to diversify the U.S. immigrant population by granting visas to underrepresented nations. Citizens of countries with the most legal immigrant arrivals in recent years – such as Mexico, Canada, China and India – are not eligible to apply.
The Biden administration has proposed legislation to increase the annual total to 80,000 diversity visas. Trump had sought to eliminate the program .
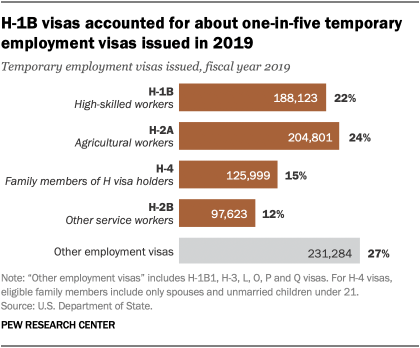
In fiscal 2019, more than 188,000 high-skilled foreign workers received H-1B visas . H-1B visas accounted for 22% of all temporary visas for employment issued in 2019. This trailed only the H-2A visa for agricultural workers, which accounted for nearly a quarter (24%) of temporary visas. In all, nearly 2 million H-1B visas were issued from fiscal years 2007 to 2019.
The Biden administration is expected to review policies that led to increased denial rate s of H-1B visa applications under the Trump administration. In addition, Biden has delayed implementing a rule put in place by Trump that sought to prioritize the H-1B visa selection process based on wages, which would have raised the wages of H-1B recipients overall. Biden also proposed legislation to provide permanent work permits to spouses of H-1B visa holders. By contrast, the Trump administration had sought to restrict these permits. The Trump administration also created an electronic registration system that led to a record number of applicants for fiscal 2021.
Temporary permissions
A relatively small number of unauthorized immigrants who came to the U.S. under unusual circumstances have received temporary legal permission to stay in the country. One key distinction for this group of immigrants is that, despite having received permission to live in the U.S., most don’t have a path to gain lawful permanent residence. The following two programs are examples of this:
Deferred Action for Childhood Arrivals
About 636,000 unauthorized immigrants had temporary work permits and protection from deportation through the Deferred Action for Childhood Arrivals program, or DACA, as of Dec. 31, 2020. One of Biden’s first actions as president was to direct the federal government to take steps to preserve the program , which Trump had tried to end before the Supreme Court allowed it to remain in place . DACA recipients, sometimes called “Dreamers,” would be among the undocumented immigrants to have a path to U.S. citizenship under Biden’s immigration bill. Senators have also proposed separate legislation that would do the same.
Temporary Protected Status
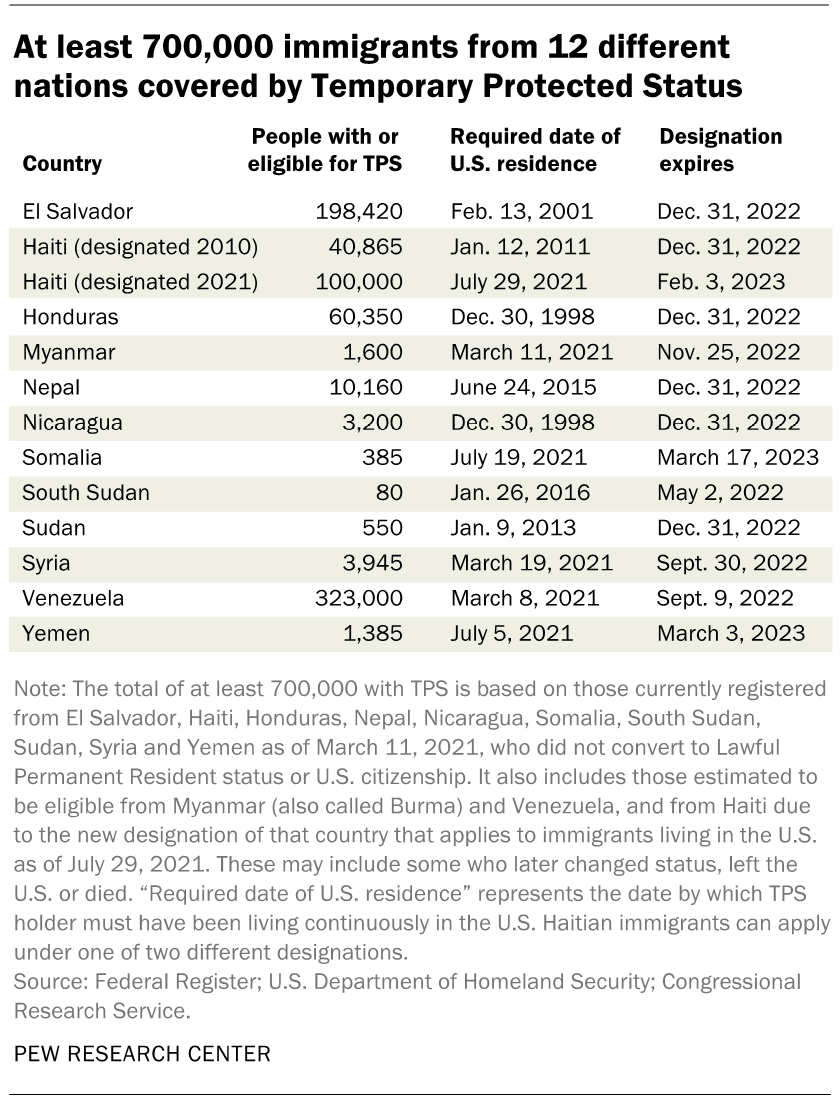
Overall, it is estimated that more than 700,000 immigrants from 12 countries currently have or are eligible for a reprieve from deportation under Temporary Protected Status, or TPS , a federal program that gives time-limited permission for some immigrants from certain countries to work and live in the U.S. The program covers those who fled designated nations because of war, hurricanes, earthquakes or other extraordinary conditions that could make it dangerous for them to live there.
The estimated total number of immigrants is based on those currently registered, in addition to those estimated to be eligible from Myanmar – also called Burma – and Venezuela.
Immigrants from Venezuela and Myanmar are newly eligible for TPS under changes made after Biden took office in January 2021 by the Department of Homeland Security, which oversees the program. The government must periodically renew TPS benefits or they will expire. The department extended benefits into 2022 and beyond for eligible immigrants from nine nations: El Salvador, Haiti, Honduras, Nepal, Nicaragua, Somalia, Sudan, Syria and Yemen. In addition, the Biden administration expanded eligibility for immigrants from Haiti based on recent turmoil.
Biden and congressional Democrats have proposed granting citizenship to certain immigrants who receive TPS benefits. Under Biden’s large immigration bill, TPS recipients who meet certain conditions could apply immediately for green cards that let them become lawful permanent residents. The proposal would allow TPS holders who meet certain conditions to apply for citizenship three years after receiving a green card, which is two years earlier than usual for green-card holders. By contrast, the Trump administration had sought to end TPS for nearly all beneficiaries, but was blocked from doing so by a series of lawsuits.
Note: This is an update of a post originally published March 22, 2021.

Sign up for our weekly newsletter
Fresh data delivered Saturday mornings
Most Latinos say U.S. immigration system needs big changes
Key findings about u.s. immigrants, facts on u.s. immigrants, 2018, most popular.
About Pew Research Center Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .

- MJC Library & Learning Center
- Research Guides
Immigration in America
- Research Immigration
Start Learning About Your Topic
Create research questions to focus your topic, find books @ the mjc library, featured books, find articles in library databases, find current news articles on immigration, videos on immigration, find web resources, cite your sources, key search words.
Use the words below to search for useful information in books and articles .
- immigration
- illegal aliens
- illegal immigration
- legal immigration
- undocumented workers
- birthright citizenship
Background Reading:
It's important to begin your research learning something about your subject; in fact, you won't be able to create a focused, manageable thesis unless you already know something about your topic.
This step is important so that you will:
- Begin building your core knowledge about your topic
- Be able to put your topic in context
- Create research questions that drive your search for information
- Create a list of search terms that will help you find relevant information
- Know if the information you’re finding is relevant and useful.
All of these resources are free for MJC students, faculty, & staff.
- Issues and Controversies: Immigration Recent pro/con articles on immigration issues
- CQ Researcher: Immigrantion Overhaul See also sidebar on the right of the Immigration Overhaul article for additional related articles on the immigration issue.
- Immigration and Migration: In Context A two volume encyclopedia that provides readers with key data to understand the roots of the issues that make contemporary migration and immigration so contentious around the globe.
- Encyclopedia of American Immigration A three volume eEncyclopedia that covers the full depth and breadth of American immigration history—from the arrival of the early ancestors of Native Americans to a broad range of twenty-first century immigration issues.
Immigration is a complex issue that involves the law, the economy, and politics. You could concentrate on one issue and do in-depth research on that, or use several of the questions below to focus more generally on the topic of immigration.
- What is the history of immigration in America?
- Is immigration a serious problem in America?
- What are the laws regulating immigration in America?
- What are the issues involved in the enforcement of immigration laws?
- Why do immigrants come to America illegally?
- What are the economic affects of illegal immigration?
- What are the pros and cons of passing the Dream Act for undocumented students?
- Should Congress make it easier for people who immigrated illegally to become citizens?
Why Use Books:
Use books to read broad overviews and detailed discussions of your topic. You can also use books to find primary sources , which are often published together in collections.
Where Do I Find Books?
You'll use the library catalog to search for books, ebooks, articles, and more.
What if MJC Doesn't Have What I Need?
If you need materials (books, articles, recordings, videos, etc.) that you cannot find in the library catalog , use our interlibrary loan service .
All of these resources are free for MJC students, faculty, & staff.
Search using the Key Search Words in this guide, or use words more specific to your topic.
- Gale Databases This link opens in a new window Search over 35 databases simultaneously that cover almost any topic you need to research at MJC. Gale databases include articles previously published in journals, magazines, newspapers, books, and other media outlets.
- EBSCOhost Databases This link opens in a new window Search 22 databases simultaneously that cover almost any topic you need to research at MJC. EBSCO databases include articles previously published in journals, magazines, newspapers, books, and other media outlets.
- Access World News This link opens in a new window Search the full-text of editions of record for local, regional, and national U.S. newspapers as well as full-text content of key international sources. This is your source for The Modesto Bee from January 1989 to the present. Also includes in-depth special reports and hot topics from around the country. To access The Modesto Bee , limit your search to that publication. more... less... Watch this short video to learn how to find The Modesto Bee .
Find videos and documentaries about immigration in Films on Demand . These film resources are free for MJC students, faculty, & staff.
Type immigration in the search box to access videos on this topic.
- Films on Demand This link opens in a new window Use Films on Demand when you want educational video content. This streaming video collection contains unlimited, 24/7 access to thousands of videos. Teachers can embed videos in Canvas. In addition, there are mobile options for iPad and Android. more... less... Instructions for embedding Films on Demand into Canvas .
- Kanopy This link opens in a new window Kanopy is a video streaming database with a broad selection of over 26,000 documentaries, feature films and training videos from thousands of producers. Instructions for embedding Kanopy into Canvas .
Use Google Scholar to find scholarly literature on the Web:

Browse Featured Web Sites:
- Migration Policy Institute "The Migration Policy Institute is an independent, nonpartisan, nonprofit think tank in Washington, DC dedicated to analysis of the movement of people worldwide."
- Pew Hispanic Center "The Pew Hispanic Center is a nonpartisan research organization that seeks to improve understanding of the U.S. Hispanic population and to chronicle Latinos’ growing impact on the nation. The Center does not take positions on policy issues."
- U. S. Citizenship and Immigration Services "U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS) is the government agency that oversees lawful immigration to the United States."
- U. S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement "ICE's primary mission is to promote homeland security and public safety through the criminal and civil enforcement of federal laws governing border control, customs, trade, and immigration."
- U. S. Customs and Border Protection "CBP has a responsibility for securing the border and facilitating lawful international trade and travel while enforcing hundreds of U.S. laws and regulations, including immigration and drug laws."
- MALDEF The Mexican American Legal Defense and Educational Fund, the nation's leading Latino civil rights organization, has many resources on immigration issues.
- Immigrant Resource Law Center The ILRC trains attorneys, paralegals, and community-based advocates who work with immigrants around the country. They inform the media, elected officials, and public to shape immigration policy and law.
Your instructor should tell you which citation style they want you to use. Click on the appropriate link below to learn how to format your paper and cite your sources according to a particular style.
- Chicago Style
- ASA & Other Citation Styles
- Last Updated: Feb 26, 2024 3:20 PM
- URL: https://libguides.mjc.edu/immigration
Except where otherwise noted, this work is licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0 and CC BY-NC 4.0 Licenses .

- Langson Library
- Science Library
- Grunigen Medical Library
- Law Library
- Connect From Off-Campus
- Accessibility
- Gateway Study Center

Email this link
Immigrants and refugees.
- How to Use this Guide
- What is an Immigrant or Refugee?
- Encyclopedias and Handbooks
Key Databases
Recommended starting points to find articles, important information for remote users.
- U.S. Immigration Law
- Troubles @ the US/Mexico Border
- Mixed Media
- Policy Papers
- International Law
- Interest Groups
- International Organizations
- Statistics and Data
Library Search

If UCI doesn't own a journal article, you can (freely!) get it with InterLibary Loan .
Got a Citation?
Learn more about Citations or how to Save and Manage them.
- InterLibrary Loans - How To Document Visual how-to to request interlibrary loans, from the catalog page or manually when needed.
- Social Science Research Network [SSRN] Downloadable full text documents. SSRN is "devoted to the rapid worldwide dissemination of social science research and composed of a number of specialized research networks in each of the social sciences..."
- AARN: Migration (Topic) Anthropology & Archaeology Research Network Research Paper Series - Migration focused journal articles
Sample SSRN Articles:
Lynch, Timothy E., The ICCPR, Non-Self-Execution, and DACA Recipients' Right to Remain in the United States (June 16, 2020). Georgetown Immigration Law Review, Vol. 34, 2020, Available at SSRN: https://ssrn.com/abstract=3628600
Campbell, Kristina Michelle, Dreamers Deferred: The Broken Promise of Immigration Reform in the Obama Years (December 1, 2019). 40 Immigr. & Nat'lity L. Rev. 265 (2019), Available at SSRN: https://ssrn.com/abstract=4261492
Ryo, Emily, Representing Immigrants: The Role of Lawyers in Immigration Bond Hearings (July 19, 2018). Law & Society Review, Vol. 52: 503-531 (2018); USC CLASS Research Paper No. CLASS18-11; USC Law Legal Studies Paper No. 18-11.
Gilman , Denise L., To Loose the Bonds: The Deceptive Promise of Freedom from Pre-Trial Immigration Detention (February 24, 2016). U of Texas Law, Public Law Research Paper No. 644.
The changing culture, discussion and challenges of migrants and refugees issues covers many disciplines; see these interdisciplinary databases to search many disciplines and resource types, like newspapers, trade journals or scholarly journals, at once.
- Migration & Diaspora Journals Group of journals in these subject areas from BrowZine
- Immigration Topic Journals List of journals that cover immigration from our catalog listings.
- AlterNative Journal Internationally peer-reviewed interdisciplinary journal on latest thinking and practice in Indigenous scholarship, on Indigenous worldviews and experiences of decolonization from Indigenous perspectives from around the world.
- Google Scholar Google Scholar is a freely accessible web search engine that indexes the full text or metadata of scholarly literature across an array of publishing formats and disciplines.
The information provided below will help you access and use the Libraries' online resources when you are not connected to the campus computer network.
- Connect from off-campus : The majority of the library online materials are available only to current UC Irvine students, faculty and staff. Authenticate yourself with your UCInet ID and password in order to use them remotely.
- Ask a Librarian : There are lots of ways to get help from a librarian.
- Find Articles: The Databases To Get You Started guide provides links to resources (called databases) that will help you find scholarly and popular articles.
- Citations: A Beginners Guide : This guide provides basic information on how to cite the materials you use for your writing assignments.
- Need more help? Ask a Librarian
- << Previous: Encyclopedias and Handbooks
- Next: U.S. Immigration Law >>
- Last Updated: Mar 21, 2024 9:34 AM
- URL: https://guides.lib.uci.edu/immigrants
Off-campus? Please use the Software VPN and choose the group UCIFull to access licensed content. For more information, please Click here
Software VPN is not available for guests, so they may not have access to some content when connecting from off-campus.
Research Our Records

Immigrant Records at the National Archives
Please note: Although some of these records have been digitized and made available online, there are many records that are only available in paper or microfilm format at NARA locations.
Among the billions of historical records housed at the National Archives throughout the country, researchers can find information relating to immigrants from the late 1700s through the early 2000s. The National Archives preserves and makes available documents created by Federal agencies in the course of their daily business.
As you plan your research, consider this question: how does my research topic intersect with the US Federal Government?
What are you researching?

Immigration Records


Naturalization Records

Visa Records

Alien Files (A-Files)
Enemy Alien Records

Passport Records

Other Immigrant Topics

Ethnic Heritage
What are people asking on history hub about immigration and naturalization records.

- Passenger manifests for the ship Charles Joseph leaving Liverpool, England and arriving in New York, New York in April of 1830. Looking for the William Smith family - William, Mary, Hannah, Joseph, Frances, John & George. Thank you.
- How do I locate my deceased mother's alien registration registration? She came to US from Germany on or about June 1966. So far, I've had no luck with FOIA request.
- Need help finding more information about an elusive grandmother and family immigration
- Naturalization Records for Italian Immigrants around 1911
- Eutizi from Italy
Find answers to your research questions at History Hub
Enjoy a completely custom, expertly-written dissertation. Choose from hundreds of writers, all of whom are career specialists in your subject.
110 Immigration Research Paper Topics

Immigration is the process of people moving to a country and can be either voluntary or involuntary. Immigration is a very interesting aspect of education, and you may be asked at one point or another to come up with a research paper in the immigration niche.
Immigration is a broad topic, and it can be difficult to choose immigration research paper topics. Here are some broad categories of immigration.
- Voluntary migration : This refers to people who move to another country on their own accord and are not forced by the government. It could be for health reasons, lifestyle change, economic reasons, educational reasons, tax evasion, etc.
- Involuntary migration : This refers to people who are forced to move to another country because there is no other option for them. Examples include migration during a crisis, migration due to fear of persecution, etc.
- Emigration : This refers to people who decide on their own not to stay in a particular country and return home.
- Internal migration : This refers to people who move within a country for work or school purposes or simply for personal reasons, such as living closer to family members or friends.
Why Do You Need Help Choosing Immigration Research Paper Topics?
You’re ready to write your immigration research paper, but you’re scared. It’s easy to get overwhelmed when you’re looking for research paper topics. Why? Because there are so many things that you can write about, it can be hard to know where to start.
You’ve put a lot of thought into the topic, but you’re not sure how to start. Maybe you have a great idea but don’t know where to start writing. Or maybe you’ve already written the outline, but it’s not working out. You feel stuck.
Whatever the case may be, it’s normal to get stressed out when writing a research paper on an important topic like immigration. When you’re in this situation, it can be really helpful to have someone who can point out what works and what doesn’t work with your outline or subject matter. And that’s where we come in.
There are many benefits to getting help with your immigration paper research topics.
- Immigration research paper topics are hard to come by.
Immigration has been a hot topic for quite some time now. Since the government has been putting a heavy focus on it, there are a lot of different angles to research. This can make it difficult to find a topic that is interesting and relevant to your own life experience.
- Immigration research paper topics are often controversial.
Immigration is a very touchy subject, which means that it can be hard to find something that accurately reflects your views on the issue without being too extreme or inflammatory.
- You’ll save time.
If your research paper is due soon, you might not have enough time to do the necessary research and choose topics yourself. Seeking help out there makes your work easier and saves you from stress!
- It will be well detailed.
Other than just looking at things from your point of view, seeking help from other sources can help you get detailed in-depth approaches.
Immigration Research Paper Topics
As a result of the Covid-19 Pandemic and other global military wars, the difficulties associated with immigration are now more widely recognized in the world. Are you looking for good topics to write about for your immigration research paper? If so, the list below includes some of the top options:
- How did the Covid-19 pandemic affect immigration into the UK and the United States?
- How does immigration affect the global economy?
- What are the benefits and disadvantages of immigration?
- What are the top five benefits of being an immigrant?
- What is the relationship between immigration and crime?
- How does the cost of immigration compare with other factors that influence business?
- How do illegal immigrants affect our economy and society, and how can they be made legal?
- What are the most common reasons people apply for a U.S. visa?
- What are some of the benefits of having an immigration visa program in the U.S.?
- How many countries have a visa waiver program with the U.S. and how does it work?
Simple Immigration Essay Topics
Selecting a simple topic for an immigration essay is not always an easy thing to do. At times, it requires you to spend a lot of time doing research here and there. To save you from this stress, we have compiled the top ten simple immigration essay topics for you!
- How has immigration impacted your life?
- What are your thoughts on illegal immigration?
- How would you improve the process for naturalized citizens?
- What are some of the challenges associated with immigration?
- Give some examples of how immigration benefits the U.S.
- What is the motivation for immigration?
- Discuss the attitude of nativism towards immigrants.
- How has being an immigrant changed the way you think about yourself?
- What is the greatest barrier to becoming a citizen?
- What would you say to people who believe that immigrants should not be allowed into the U.S.?
International Immigration Essay Topics
We have compiled 10 international immigration essay topics for your essay because when it comes to choosing topics about immigration internationally, you need to make sure it covers the entire world of immigration. This can often be a difficult process.
- How have international immigration policies changed over time?
- How can we increase our understanding of the diversity of the world’s cultures?
- What are some of the benefits of allowing more immigration?
- Describe the UK’s current immigration system.
- Discuss Canada’s 20th-century immigration policies.
- Talk about the EU’s current immigration problems and how they affect the terrorism rate.
- Examine the connection between immigration and Australian national identity.
- Describe Switzerland’s newest immigration law.
- Examine the effects of Muslim immigration on Britain.
- Examine the importance of gender in Irish immigration.
Best Immigration Research Topics
Do you want to come up with the best topic for your essay in your class? We also want you to be the best, so we’ve put together a list of some of the best topics on immigration that you could pick from.
- The impact of immigration on wages and employment levels
- The impact of immigration on public health and other social outcomes
- The impact of immigration on local governments and their budgets
- How immigrants help contribute to economic growth
- What are the best ways to attract immigrants to your country?
- The impact of immigration on education and health care
- What is the relationship between immigration and terrorism?
- Does immigration increase or decrease social cohesion?
- What effect immigration has on things like forests, water sources, and wildlife habitats.
- What are the best ways to encourage new immigrants to stay in their new home country?
Immigration Argumentative Essay Topics
Because you would need to compare and view the issue from all sides, choosing an argumentative immigration topics to write about could be challenging. To make your job easier, we have compiled a list of 10 argumentative immigration essay ideas for you below.
- Immigrants are taking jobs away from American citizens who deserve them.
- Should an immigrant be given a path to citizenship?
- Do you think that it is important for countries to take in refugees who are fleeing war-torn countries?
- Immigrants contribute to the growth of our economy, our culture, and our society.
- Should immigrants pay taxes?
- Should immigration from certain countries be limited based on their economic impact on the country?
- Should incentives be given to people who want to immigrate legally instead of illegally?
- Should businesses be permitted to hire foreign workers over Americans if they can’t find any eligible Americans?
- Should immigrants be allowed to stay in the country indefinitely?
- Should people be treated differently based on their immigration status?
Controversial Immigration Topics
When we discuss contentious topics, we typically engage in debate or discussion of divergent viewpoints. Finding a topic on this can be difficult at times, but don’t worry; to relieve some of your tension, we’ve selected 10 contentious immigration topics for research paper that you can choose from or use as a reference:
- Should gay couples be allowed to marry?
- Race and Immigration
- Ethnicity and Immigration
- Should non-citizens be able to vote?
- Is it okay for parents to get deported because they refuse to pay child support?
- Undocumented immigrants and identity theft.
- Deportation rates for undocumented immigrants
- Immigration: Illegals vs. Legal Immigrants
- The wall between the U.S. and Mexico.
Immigration Thesis Topics
Choosing a thesis topic on immigration requires extensive research because the paper needs to be outstanding and well written. Do you need a thesis for an academic degree? Here are 10 thesis immigration topics for essays that could help you.
- The historical impact of immigration on America
- The impact of immigration on the economy
- The impact of immigration on our culture and society
- Why should immigrants be allowed into the United States?
- How can we make sure that immigrants are treated fairly and humanely in America?
- Immigration is a major issue that affects Americans in many ways.
- Immigrants are less likely to commit crimes
- Immigrants do not make any significant difference in the unemployment rate of native-born Americans
- Immigrants create more jobs than they take
- Immigrants need government assistance to survive
Global Politics Immigration Paper Topics
Global politics is a large topic. So, finding suitable global political immigration topics may be a bit tiresome. Here are 10 global research topics on immigration that you can choose from!
- Immigration policies in the U.S., Canada, and Australia.
- International trade and immigration policies.
- The diversity of immigrants: A look at America’s immigrant population.
- The social structure of immigrants in the Netherlands.
- Globalization and migration patterns: A case study of Australia.
- Global recessions, financial crises, and the labor market.
- Immigration policy and human rights violations
- Migration patterns around the world
- The history of immigration in the U.S.
- Political and economic implications of immigration in Europe
Illegal Immigration Research Paper Topics
Illegal immigration is a big problem for law enforcement and the national security of many countries. It also often leads to violations of the human rights of the most vulnerable people.
Would you like to investigate this for a research paper? Here are some illegal immigration topics to research that can help.
- The effects of illegal immigration on businesses
- Illegal immigration and public safety
- Illegal immigration and workplace discrimination
- The impact of illegal immigration on the American workforce
- How does illegal immigration affect the U.S?
- Should illegal immigration be legalized?
- What are some of the consequences of legalizing illegal immigrants?
- What are some benefits of legalizing illegal immigrants?
- How many people illegally immigrate to the U.S. every year?
- How are illegal immigrants treated by society?
Research Paper Topics on Immigration in America
Are you seeking a topic to write about for a research paper about immigration in America? Here are 10 excellent American immigration research paper topics for you.
- Why America’s immigration policies are unfair and unproductive, and why we need to change them.
- Why the Mexican border is a good immigration channel
- Border security and border policy in the U.S.
- How does immigrant crime compare to native crime?
- Immigrants are more likely to have good grades than native-born Americans
- Which groups of immigrants have been most affected by the rise in deportations and why?
- Are immigrants more likely to start businesses than native-born Americans?
- Immigrants have made incredible contributions to the U.S., like Levi Strauss and Albert Einstein
- Should undocumented immigrants have health insurance coverage in the U.S.?
- The Effect of Immigration on Social Security in the U.S.
Persuasive Speech Topics About Immigration
You need to make sure the topics you choose for your persuasive speeches are compelling enough to win over your audience. Finding a topic like this could be difficult, but we have nonetheless put together a list of the top 10 persuasive immigration topics for essay from which you can choose.
- Should immigration be a human right?
- Can immigrants help economies grow and make countries better
- Why immigration is not a threat to our culture but a benefit
- We need more immigrants in this country because it’s not sustainable otherwise!
- Immigrants are an asset to any country, not a burden.
- Are most immigrants hard-working, honest, and law-abiding citizens?
- Illegal immigration is not a problem—it’s a solution to problems—like unemployment and poverty
- The U.S. needs immigrants to keep growing and stay strong in the world economy
- Are immigrants good for business and do they make great contributions to society?
- Immigrants bring in new ideas and experiences that enrich culture and nation growth.
How to Choose a Topic on Immigration
Choosing a topic for your immigration research paper is a big decision. You have to consider your audience, the content of the paper, and how much time you have to write it. Here are some tips for choosing the best immigration research paper topics.
- Know your audience.
You can’t write an immigration research paper if you don’t know who you’re writing it for! Before you start writing, sit down with the person in charge of your assignment (usually the professor) and get their feedback on what they need from you. This will help you narrow down topics that they’ll find interesting and relevant, which will make them more excited about reading your work!
- Look at what’s already out there.
You may want to try writing something new, but don’t forget about other people’s work! Go online and check out any papers written by professors on similar topics in your field. Have them give their opinions about whether or not those papers are good examples of quality work done well. If they love something else, maybe those details can help inspire yours!
- Do your research.
Do some research on current events. This is where most of the immigration news comes from, so it’s a great way to find out what’s happening in your community.
Read blogs and articles from reliable sources like newspapers or websites that focus on profiling immigrants and people who are looking for asylum.
Immigration research paper topics could be challenging to find. Sometimes they are complex and require an in-depth understanding. Here are 110 immigration research paper topics you can choose from. Sometimes, you might need help in writing your research paper. You can always outsource your research paper to a trusted writing company to help you!
Frequently Asked Questions
Richard Ginger is a dissertation writer and freelance columnist with a wealth of knowledge and expertise in the writing industry. He handles every project he works on with precision while keeping attention to details and ensuring that every work he does is unique.

Succeed With A Perfect Dissertation

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
As Putin continues killing civilians, bombing kindergartens, and threatening WWIII, Ukraine fights for the world's peaceful future.
Ukraine Live Updates
Questions? Call us:
Email:
- How it works
- Testimonials
Essay Writing
- Essay service
- Essay writers
- College essay service
- Write my essay
- Pay for essay
- Essay topics
Term Paper Writing
- Term paper service
- Buy term papers
- Term paper help
- Term paper writers
- College term papers
- Write my term paper
- Pay for term paper
- Term paper topic
Research Paper Writing
- Research paper service
- Buy research paper
- Research paper help
- Research paper writers
- College research papers
- Write my research paper
- Pay for research paper
- Research paper topics
Dissertation Writing
- Dissertation service
- Buy dissertation
- Dissertation help
- Dissertation writers
- College thesis
- Write my dissertation
- Pay for dissertation
- Dissertation topics
Other Services
- Custom writing services
- Speech writing service
- Movie review writing
- Editing service
- Assignment writing
- Article writing service
- Book report writing
- Book review writing
Popular request:
Comprehensive guide to writing a winning research paper on immigration.
July 16, 2020
One of the hot button issues in the globe today is immigration. On July 5th, 2019, people all over the globe were angered by images of an infant being separated from her mother by Border Patrol police in the US-Mexico border. However, it is not just the US-Mexico border that has the problem of immigration. From Africans trying to cross to Europe via the Mediterranean Sea in makeshift boats to refugees freeing war-torn Middle East countries, the problem of immigration appears to have no end.

To assess students’ understanding of current affairs and global problems, most lecturers in colleges, at some point, ask their students to write a research paper on immigration. Notably, most students find writing this type of paper an uphill task, but we are here to help. This post is a comprehensive guide on how to write a research paper on immigration.
Select a Good Title for Your Research Paper on Immigration
When your professor asks you to write an essay on immigration, he/she may give you the topic to work on. However, you need to pick one on your own if the titles are not provided. Make sure to identify a topic that is interesting, and that has ample resources to help you complete the work effectively. Here are some great research paper topics on immigration in America, Europe, and around the globe.
Do illegal immigrants in the US deserve civil rights? Comparing illegal immigration to the US and Europe. Illegal immigration: What are the impacts in the society? Compare the immigration policy of the United States and Canada. Are illegal immigrants good or bad for the US Economy?
Study Your Topic and Craft a Thesis for Your Research Paper on Immigration
Depending on the topic you select, it is important to study it widely, ensuring to identify the key points that will form the basis of your paper. When analyzing the selected topic, make sure also to develop a powerful thesis about your paper. The thesis you adopt will be your stand and evident in the entire paper. Here are some examples of good thesis statements when writing research papers on immigration.
- “ Migrant workers have played an important role in the history of the United States, so they should not be treated as undeserving persons.”
- “ In light of the escalating immigration problem in Europe, the primary focus should be on universal human rights and respect for human dignity.”
Develop and Use a Good Outline for Your Essay on Immigration Research Paper
Whether you are working on a research paper on illegal immigration, policy on immigration, human rights for immigrants, or other topics, it is important to start by developing a good format or outline. The outline tells you what to discuss at different stages of the essay. Here is a sample outline that you can use to craft a winning research paper on immigration:
- Introduction: This is the first section after the paper title, and you should use it to set the stage for the entire paper. So, open the essay with a strong hook statement, and capture the background of the study. You should also highlight the thesis statement, and tell the reader what to expect in the research paper.
- Body: In the body of the paper, you should discuss the main points about the topic of interest. Make sure that every point is discussed in its own paragraph and use evidence, such as quotes and statistics, to support your argument. To make your essay sound more professional, you should also bring out counterarguments.
- Conclusion: The conclusion is the last part of your research paper on immigration and should be used to wrap up your key points. Start by restating the thesis statement (of course, using different words to avoid sounding repetitive) and summarizing the main points in one or two paragraphs. Note that you should not introduce new points when writing the conclusion of your paper. However, you can call for further studies if you found gaps in the current literature on immigration.
Special Tips for Writing a Great Research Paper on Illegal Immigration
To make your research paper on immigration reforms or other topics earn you more marks, the most important tip is following your professor’s instructions. For example, you should stick to the teacher’s guideline on the right research paper length and formatting. Here are other tips to consider.
- Make sure to identify and work on a topic that is interesting to avoid getting bored midway.
- Use excellent secondary resources to support your arguments when writing the paper. The best resources are those published within the last five years.
- Start by writing a draft before refining it to create the final copy.
- If you find writing the paper challenging, consider seeking help from a writing professional .
When you are faced with the task of writing a research paper on immigration, this guide is all that you need to rake high marks. Make sure to select a topic that is interesting, follow the outline we have discussed above, and ensure your points are flowing well from the beginning to the end.

Take a break from writing.
Top academic experts are here for you.
- How To Write An Autobiography Guideline And Useful Advice
- 182 Best Classification Essay Topics To Learn And Write About
- How To Manage Stress In College: Top Practical Tips
- How To Write A Narrative Essay: Definition, Tips, And A Step-by-Step Guide
- How To Write Article Review Like Professional
- Great Problem Solution Essay Topics
- Creating Best Stanford Roommate Essay
- Costco Essay – Best Writing Guide
- How To Quote A Dialogue
- Wonderful Expository Essay Topics
- Research Paper Topics For 2020
- Interesting Persuasive Essay Topics
- (888) 777-9102
- Learning Center

- How It Works
- All Packages & Pricing
- I-90 Application to Replace Permanent Resident Card
- I-129F Petition for Alien Fiancé
- I-130 Petition for Alien Relative
- I-131 Application for Travel Document
- I-485 Adjustment of Status Application
- I-751 Remove Conditions on Residence
- I-765 Application for Employment Authorization
- I-821D DACA Application Package
- I-864 Affidavit of Support
- N-400 Application for Naturalization
- N-565 Application to Replace Citizenship Document
- Citizenship Through Naturalization
- Citizenship Through Parents
- Apply For Citizenship (N-400)
- Apply for Certificate of Citizenship (N-600)
- Replace Citizenship Document (N-565)
- Apply for a Green Card
- Green Card Renewal
- Green Card Replacement
- Renew or Replace Green Card (I-90)
- Remove Conditions on Green Card (I-751)
- Green Card through Adjustment of Status
- Adjustment of Status Application (I-485)
- Affidavit of Support (I-864)
- Employment Authorization (I-765)
- Advance Parole Application (I-131)
- Adjustment of Status Fee
- Family-Based Immigration Explained
- Search the Learning Center
- Request Support
- Find an Immigration Attorney

Home » Blog » Immigration Papers: Your Proof of Immigration Status
Immigration Papers: Your Proof of Immigration Status
July 20, 2021 Citizenship Humanitarian Immigration News Replace/Renew Green Card Working in the U.S.

It is becoming increasingly important to have proof of your immigration status in the United States. Having immigration papers, documentation or proof of your legal status is essential if you have contact with law enforcement or immigration officials. In the current environment, even natural-born U.S. citizens can run into problems with identification. What’s more, immigration paperwork can be necessary to gain access to many government benefits, secure housing, obtaining driving privileges, just to name a few.
Foreign nationals who wish to work, get a driver’s license, … must have the appropriate immigration papers to prove status. These papers come in a variety of types and can be confusing. However, in virtually all uses, the immigration documents must be valid and unexpired. If you have an expired document, you’ll need to renew or replace it.
Documentation for U.S. Employment
In 1986, Congress enacted the Immigration Reform and Control Act (IRCA) in an effort to address the problem of people illegally immigrating to the United States and becoming employed by U.S. employers. IRCA requires all employers, regardless of number of employees, to verify the identity of new employees and their eligibility for employment in the United States.
All employers, regardless of size, must complete a Form I-9 upon hiring a new employee to work in the United States. Re-verification of eligibility for employment in the United States may also be required under certain circumstances.
To verify identity and prove employment authorization, foreign nationals may use a variety of documents . Employees can show a List A Document that proves identity and employment authorization. Alternatively, employees can show a List B Document to prove identity and a List C Document to prove employment authorization.
Examples of List A Documents for Foreign Nationals
Permanent resident card, employment authorization card.
- Foreign passport with I-551 stamp
- Foreign passport with I-94 record and work endorsement
Examples of List B Documents for Foreign Nationals
- U.S. driver license
- State-issued ID card
- School ID with photograph
- U.S. military ID
Examples of List C Documents for Foreign Nationals
- Social Security Card (nonrestrictive)
- Form I-94 (if employment authorization is part of the class)
The lists of examples above are not inclusive of all possible immigration papers for use in employment. Additional documents and some restrictions may apply. Please refer to USCIS I-9 Central for details.
Proof of Status for Driving
In the United States, driver’s licenses are not issued by the federal government. Each state issues their own driver’s license. Consequently, there may be slightly different requirements in each state that affect foreign nationals.
Resident non-citizens who wish to driver must obtain a driver’s license from the state where they live. Again, each state may have different requirements. Generally, the following immigration papers may be used to apply for a driver’s license:
- Foreign passport with an approved I-94 Arrival/Departure Record
- Foreign passport with an I-551 stamp
- Re-entry Permit
- Refugee Travel Document
- Form I-94 stamped “REFUGEE,” “PAROLE”, or “PAROLEE,” “ASYLEE,” “HP,” “PIP,” Section(s) 207, 208, 209, or 212d(2).
- Form I-94 with attached photo stamped “Temporary evidence of lawful admission for permanent residence.”
- Immigration judge’s order granting asylum
For the specific driver’s license requirements for your state, check your state’s department of motor vehicles .
Immigration Papers for Health Insurance
Like natural-born U.S. citizens, foreign-born U.S. citizens are also generally eligible for health insurance through the Affordable Care Act (ACA) – also known as Obamacare. However, permanent residents and many other lawfully present immigrants are eligible. To qualify, applicants will be required to provide immigration papers that prove their status.
For a complete list of acceptable immigration document types, please visit Healthcare.gov .
Replacing Immigration Documents
Citizenship documents.
Foreign-born persons who become U.S. citizens may prove their immigration status with a variety of documents including: Certificate of Citizenship, Certificate of Naturalization, or U.S. passport.

To replace a Certificate of Naturalization or Certificate of Citizenship, you may file Form N-565, Application for Replacement Naturalization/Citizenship Document .
RECOMMENDED: Certificate of Naturalization Replacement Process
To replace a U.S. passport, you can submit an application directly on the U.S. Department of State website.
Also known as a green card or resident alien card, the permanent resident card if proof of a foreign national’s right to permanently live and work in the United States.

To replace or renew a 10-year permanent resident card, you may file Form I-90, Application to Replace Permanent Resident Card . Conditional residents with a 2-year green card may replace a lost/stolen green card with Form I-90 but should not a renew a card with Form I-90. Instead, conditional residents file Form I-751, Petition to Remove Conditions on Residence , in the 90-day period before the 2-year card expires.
RECOMMENDED: My Green Card Was Lost Or Stolen
It can take several months to obtain a new green card. When attending the biometrics appointment, USCIS will place a sticker on an existing green card to extend its validity for another year. If you have lost your card, you may request an I-551 stamp in your valid foreign passport. File Form I-90 first and get your receipt number. Upon confirmation that you have successfully filed, call USCIS at 1-800-375-5283 to schedule an appointment at your local office. CitizenPath can provide you more detailed directions in your filing instructions.
A variety of foreign nationals with a nonimmigrant status may be eligible for an employment authorization document. Also known as a work permit, the card is proof of employment authorization for several visa types and other status. Some common immigration statuses eligible for an EAD include: adjustment of status applicant, DACA, TPS, asylum/refugee, and certain F-1 students with special permission to work.

To replace or renew an employment authorization card, you may file Form I-765, Application for Employment Authorization . You must continue to qualify for employment authorization within the eligibility category for which you are applying. If your status has expired, you may also need to submit forms related to renewing your status.
RECOMMENDED: Lost EAD and How to Replace It
I-94 Arrival Departure Record
The I-94 Arrival/Departure Record, also known as Form I-94, confirms that a foreign visitor has been lawfully admitted (or paroled) into the United States. It also includes information about the visitor’s visa status and permitted duration of stay.
Most people are issued an electronic I-94 and can replace it by simply visiting the I-94 website . Enter your information to get an instant copy. Read more for information about how to find an electronic I-94 record .
RECOMMENDED: How to Find an I-94 Record
If CBP issued you a paper I-94, you may file Form I-102, Application for Replacement/Initial Nonimmigrant Arrival/Departure Document .
Foreign Passport
Foreign passports are not under the purview of the United States government. In other words, you will need to contact your country’s embassy here in the United States. Each country has its own rules on replacing or renewing a passport.
About CitizenPath
CitizenPath provides simple, affordable, step-by-step guidance through USCIS immigration applications. Individuals, attorneys and non-profits use the service on desktop or mobile device to prepare immigration forms accurately, avoiding costly delays. CitizenPath allows users to try the service for free and provides a 100% money-back guarantee that USCIS will approve the application. We provide support for Citizenship Document Replacement (Form N-565) , Green Card Replacement (Form I-90) , EAD Replacement (I-765) , and several other immigration packages .
Note to Reader: This post was originally published on October 1, 2019, and has been modified with improvements.
Want more immigration tips and how-to information for your family?
Sign up for CitizenPath’s FREE immigration newsletter and
on our immigration services
Related Posts

New USCIS Fee Increase Published by Biden Administration
The USCIS fee increase affects many family-based immigration applications. Find out which forms are affected and what you may be able to do to beat the fee hike.… Continue Reading →

U.S. Income Taxes and Immigration Consequences
As a general rule, U.S. tax law applies to you if you live in the United States or spend a significant amount of time here. And income taxes can affect immigration status.… Continue Reading →
Immigration Form Guides Form I-90 Form I-129F Form I-130 Form I-131 Form I-131A Form I-134 Form I-485 Form I-751 Form I-765 Form I-821D Form I-864 Form N-400 Form N-565 Form N-600
Sign Up to Receive Free Monthly Information for Your Immigration Journey
© Copyright 2013-2024, CitizenPath, LLC. All rights reserved. CitizenPath is a private company that provides self-directed immigration services at your direction. We are not affiliated with USCIS or any government agency. The information provided in this site is not legal advice, but general information on issues commonly encountered in immigration. CitizenPath is not a law firm and is not a substitute for an attorney or law firm. Your access to and use of this site is subject to additional Terms of Use .

- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
Texas' immigration law is being challenged in court amid racial profiling concerns

Adrian Florido
Texas' immigration law has raised fear that it'll promote racial profiling by police. The concerns evoke memories of what happened after Arizona passed its so-called "show me your papers" law in 2010.
ARI SHAPIRO, HOST:
A federal appeals court today heard arguments over the Texas immigration enforcement law known as SB4. It empowers local law enforcement to arrest and deport people who are in the state illegally. SB4 is currently on hold while the Biden administration's legal challenge makes its way through the federal courts. Many of the measure's critics worry that, if it takes effect, it will lead to rampant racial profiling by police. It all sounds very similar to a battle over a law that Arizona passed in 2010 which made it a crime to be undocumented in the state and required police to check the status of people they suspected. NPR's Adrian Florido has this look-back.
ADRIAN FLORIDO, BYLINE: When Arizona's SB1070 was passed in 2010, Reyna Montoya was a college student, undocumented, living with her parents. And the so-called show me your papers law had them in constant fear.
REYNA MONTOYA: My mom, for example, didn't allow me to go to the movie theaters with my friends, and she said that it was better to be cautious and to be safe than sorry.
FLORIDO: When she did go out, avoiding the police became vital.
MONTOYA: Whenever I would get to a stop sign, I started counting five Mississippis very slowly. So I just remember that my hands would start sweating, and I would be extra cautious to ensure that I wouldn't get in any type of encounter with law enforcement.
FLORIDO: Latinos and immigrants like Montoya knew that just the way they looked or spoke could give police a reason to suspect they were undocumented. The law even put Native Americans on alert, along with other U.S. citizens. Mario Carrillo, who's Mexican American, remembers that, when he took a road trip to Tucson from his home in Texas, he made sure to pack his U.S. passport.
MARIO CARRILLO: I can tell you for a fact that if SB1070 had not been put into law right around that time - that I would not have taken my passport. I wouldn't have felt the need to take it.
FLORIDO: As it turned out, he says that, once in Arizona, he was pulled over by a Border Patrol agent who asked if he was a U.S. citizen and who took his passport back to his patrol truck to verify it.
CARRILLO: I'm sure if I had been blond, blue-eyed, you know, I doubt that that same question would have come up.
FLORIDO: Just like the federal government is challenging Texas' law today, it also challenged Arizona's on the grounds that immigration enforcement was a federal responsibility. But a coalition of civil rights groups filed a separate lawsuit in Arizona on different legal grounds. Nicholas Espiritu is one of the attorneys who litigated that case. He's with the National Immigration Law Center. And he says the goal of the lawsuit was to show that SB1070 would have racist outcomes and that it was written with racist intent.
NICHOLAS ESPIRITU: We also wanted to highlight that the whole law was designed in part because of a desire to discriminate against Latinos, and we presented a large amount of evidence in the record to that effect.
FLORIDO: They found emails, writings and speeches in which the law's Republican authors talked about an invasion from Mexico and used other stereotypes to talk about Latinos. Ultimately, in 2012, the Supreme Court ruled, though only on the government's challenge.
(SOUNDBITE OF ARCHIVED NPR BROADCAST)
MELISSA BLOCK: To the Supreme Court now and a much-anticipated decision on Arizona's controversial immigration law.
FLORIDO: It struck down parts of the law that criminalized being in the state as an undocumented immigrant, but it upheld the section allowing police to investigate people's immigration status if they suspected they were in the country illegally. The civil rights groups spent several more years fighting that provision and eventually settled with the state's attorney general after he agreed to instruct police departments to essentially ignore that part of the law. While it remains on the books today, attorney Nicholas Espiritu says...
ESPIRITU: It can't be used as a mechanism to engage in racial profiling.
FLORIDO: Lisa Magana, a political scientist at Arizona State University, says one reason state officials threw in the towel was because of the immense public backlash. The state gained a reputation as racist. Artists and corporations boycotted.
LISA MAGANA: The state lost lots of money. The impact of boycotts and cancellations of conventions and concerts is what I think had the state rethink these types of laws.
FLORIDO: SB1070 also led many young Latinos and immigrants to activism. That wave of organizing helped turn Republican Arizona into the battleground state it is today. Reyna Montoya, who used to count to five at stop signs, founded a nonprofit called Aliento that helps young undocumented immigrants work through trauma stemming from their status. Many were children during the years of SB1070 and remember worrying their parents might not come home. She says the recent news about Texas' immigration law...
MONTOYA: This has been very triggering and opening up old wounds.
FLORIDO: And also opening up a deep worry, she says, that police could once again get a license to racially profile people who look like them.
Adrian Florido, NPR News.
Copyright © 2024 NPR. All rights reserved. Visit our website terms of use and permissions pages at www.npr.org for further information.
NPR transcripts are created on a rush deadline by an NPR contractor. This text may not be in its final form and may be updated or revised in the future. Accuracy and availability may vary. The authoritative record of NPR’s programming is the audio record.
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( A locked padlock ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- Create Account
Downloading and Printing Immigration Forms
We provide free fillable forms through our website in PDF format, which means you can type your answers directly on the form instead of printing a blank form and writing your answers by hand. For the best results, we suggest you download the PDF to your computer and complete the form using the latest version of Adobe Acrobat Reader rather than completing the PDF through your web browser. You can download Adobe Acrobat Reader for free from the Adobe website . Download Instructions After opening the form in your web browser:
- In Microsoft Edge, click the Save icon (second from the right) in the ribbon at the top of the page, or press Ctrl (or Command ) and S on your keyboard. After saving the form to your computer, click on the form icon to reopen it in Adobe Acrobat Reader.
- If you receive the error message: “An error occurred. An error was encountered while processing the file. Some features might not work.”, the Chrome extension might be on.
You can remove or disable the Chrome extension by: 1. Opening Chrome; 2. Clicking the ellipsis in the right corner; 3. Clicking "Settings"; 4. Selecting “Extensions”; and 5. Removing or turning off the Chrome extension on the “Adobe Acrobat: PDF edit, convert, sign tools” tab.
- In Safari, open the form, hover your mouse toward the bottom-center of the screen to bring up the gray icon, and click the Download icon on the right corner of the gray icon, or press Command and S on your keyboard. After saving the form to your computer, click on the form icon to reopen it in Adobe Acrobat Reader.
If you complete and print the form to mail, make sure that the form edition date and page numbers are visible at the bottom of all pages and that all pages are from the same form edition. If any of the form’s pages are missing or are from a different form edition, we may reject your form.
If you are required to sign the form , you must write your signature by hand before submitting your form. We will not accept a stamped or typewritten name in place of a signature.
USCIS forms are available for free on our website. You can find the latest version of any USCIS form on our Forms page. Warning : Many non-USCIS websites offer immigration forms for downloading. These sites may ask you to pay for immigration forms and may not have the correct form version. Do not pay for any USCIS form. In some circumstances, your case may be delayed or rejected if you use an outdated form.

Texas immigration controversy rekindles fight over Arizona’s ‘show me your papers’ law
T he legal battle over a controversial Texas immigration law could eventually give the Supreme Court a chance to revisit a historic ruling that largely struck down Arizona’s “show me your papers” law and reaffirmed the federal government’s “broad, undoubted power” over immigration.
Texas’ SB 4, which allows state officials to arrest and detain people they suspect of entering the country illegally, was back in court Wednesday at the 5th US Circuit Court of Appeals in New Orleans.
The law is on hold after three judges blocked it while they consider whether it is constitutional. That same panel heard arguments on Wednesday.
The majority ruling in the 2-1 decision last month leaned heavily on the 2012 Supreme Court case known as Arizona v. United States, in which the high court struck down several provisions of an Arizona law, SB 1070, intended to deter illegal immigration.
Legal experts believe the Texas case could eventually give the majority-conservative Supreme Court an opportunity to take another look at the federal government’s long-held control over immigration policy.
“This would be probably one of the most radical changes the Supreme Court has made in the immigration field,” said Andrew Schoenholtz, a professor at Georgetown Law and an expert on immigration law, referring to the possibility that the high court overturns its 2012 ruling. “It’s that much of a change that Texas is asking for.”
When he signed the law, Texas Republican Gov. Greg Abbott acknowledged that the issue could end up back at the Supreme Court.
“We think that Texas already has the constitutional authority to do this, but we also welcome a Supreme Court decision that would overturn the precedent set in the Arizona case,” Abbott told CNN’s Rosa Flores.
Denise Gilman, a professor at the University of Texas School of Law, agreed that the state’s goal is to get the justices to reverse the Arizona decision.
“It would have been incredibly difficult for the 5th Circuit to let this law stand under existing Supreme Court precedent,” she said. “The Supreme Court is another matter. The Supreme Court can overturn its own precedent, and that’s clearly what the state of Texas wants it to do.”
SB 4 was initially blocked by a federal judge in late February in a pair of cases brought by the Biden administration, two immigrant advocacy groups and El Paso County. Texas quickly appealed that decision to the 5th Circuit. In the meantime, the Supreme Court had allowed the state to enforce the law for a brief time on March 19, only for the appeals court to put it back on hold hours later.
‘Show me your papers’ law
The Arizona law is a high-profile example of what happens when states attempt to take immigration policy into their own hands.
Then-Arizona Republican Gov. Jan Brewer signed the Support Our Law Enforcement and Safe Neighborhoods Act, known as SB 1070, into law in 2010.
Chief among the law’s provisions was one that allowed police to check a person’s immigration status during traffic stops or other law enforcement actions if the official had “reasonable suspicion” to believe the person was in the country unlawfully. That part of SB 1070 led critics to dub it the “show me your papers” law.
SB 1070 also made it a state crime for “unauthorized immigrants” to fail to carry registration papers and other government identification; forbade people unauthorized for employment in the US to apply, solicit or perform work; and authorized police to arrest undocumented immigrants without a warrant when “probable cause” existed that they committed a crime that made them deportable.
Legal challenges to the law quickly ensued. The Supreme Court upheld the “show me your papers” part of the law and struck down the three other parts.
Perhaps most importantly, the majority ruling penned by Justice Anthony Kennedy reaffirmed the federal government’s authority over immigration matters. The five-justice bloc said that “federal power to determine immigration policy is well settled” and that its “authority rests, in part, on the National Government’s constitutional power to ‘establish an uniform Rule of Naturalization.’ ”
“The National Government has significant power to regulate immigration,” Kennedy wrote. “Arizona may have understandable frustrations with the problems caused by illegal immigration while that process continues, but the State may not pursue policies that undermine federal law.”
Gilman said the court’s decision in Arizona is significant because Texas’ SB 4 essentially contains the concepts the court struck down in that case.
“The (Arizona) law that made a crime out of immigration status was struck down by the Supreme Court as being in conflict with federal authority to govern immigration enforcement,” she said. “And that’s a really significant part of what the Texas law has in place.”
Among the three justices who dissented in the 2012 case, two are still on the court: Justices Clarence Thomas and Samuel Alito. Justice Antonin Scalia died in 2016. (Justice Elena Kagan disqualified herself from the 2012 case.)
Jessica Bulman-Pozen, a professor at Columbia Law School who specializes in federalism, said the arguments pushed by Texas in defense of SB 4 hew most closely to the dissent penned by Scalia, which concluded that Arizona’s law was enacted in an effort to enforce federal immigration law “more effectively.”
“The court did not think that was right as a descriptive matter about what was happening in Arizona, and I think it’s even more clearly incorrect here with respect to Texas,” Bulman-Pozen said, referring to the majority’s rejection of Arizona’s argument that it was attempting to address the Obama administration’s alleged inaction on immigration issues.
“The idea that what (Texas is) doing is in fact vindicating some kind of congressional judgment or congressional law against an executive that’s not enforcing (those laws), I don’t think that that’s a fair description of what’s happening here,” she said.
Abbott cited the Scalia dissent when he signed the law.
“Remembering that Justice Scalia wrote a dissenting opinion in that case, pretty much laying out a pathway that he thought would be a legal way for a state to go about the process of enforcing immigration laws,” Abbott told CNN.
Oldham’s dissent
A considerable amount of daylight exists between the divided 5th Circuit panel that is weighing the legality of SB 4.
“Supreme Court authorities and the detailed statutory scheme governing who will be permitted to remain in the United States and removal procedures strongly indicate that Congress ‘occupies [the] entire field’ of unlawful entry and reentry of noncitizens as well as removal,” Chief Judge Priscilla Richman wrote in a decision that was joined by Circuit Judge Irma Carrillo Ramirez.
But Circuit Judge Andrew Oldham – a former Alito clerk – wrote in a lengthy dissent last week that he would have let Texas enforce the law while the legal challenges continue.
Oldham leaned into a more limited reading of the Supreme Court’s 2012 decision in Arizona, saying it “certainly does not suggest States may never supplement any federal immigration laws.”
He argued the Arizona decision leaves some room for parts of SB 4 to withstand scrutiny, particularly the policy that allows Texas judges to order immigrants to be deported.
“The Arizona Court did not hold – as plaintiffs seem to believe – that the State was preempted from the field of removal because of ‘some brooding federal interest’ like foreign policy or national security,” wrote Oldham, who was also previously general counsel to Abbott.
Texas’ attorneys have raised those same claims.
“Arizona did not find that state laws concerning entry and removal were field preempted, and nothing in Arizona precludes States from regulating entry and reentry or issuing return orders,” the attorneys wrote.
Whether those arguments have any salience before the nation’s highest court if the case comes before the justices is another question.
“To the extent the court revisited Arizona in this context, it would basically be making states authorities with respect to entry and removal in the immigration space. And that would be an extreme departure from precedent in our nation’s history,” Bulman-Pozen said. “It’d be quite shocking.”
This story has been updated with additional details.
CNN’s Rosa Flores contributed to this report.
For more CNN news and newsletters create an account at CNN.com

- Weather
Search location by ZIP code
Texas immigration controversy rekindles fight over arizona’s ‘show me your papers’ law.
- Copy Link Copy {copyShortcut} to copy Link copied!

GET OUR POLITICS NEWSLETTER
Stay up to speed on all the latest local and national political news.
The legal battle over a controversial Texas immigration law could eventually give the Supreme Court a chance to revisit a historic ruling that largely struck down Arizona’s “show me your papers” law and reaffirmed the federal government’s “broad, undoubted power” over immigration.
Texas’ SB 4, which allows state officials to arrest and detain people they suspect of entering the country illegally, is back in court Wednesday at the 5th U.S Circuit Court of Appeals in New Orleans.
The law is on hold after three judges blocked it while they consider whether it is constitutional. That same panel will hear Wednesday’s arguments.
The majority ruling in the 2-1 decision last month leaned heavily on the 2012 Supreme Court case known as Arizona v. United States, in which the high court struck down several provisions of an Arizona law, SB 1070, intended to deter illegal immigration.
Legal experts believe the Texas case could eventually give the majority-conservative Supreme Court an opportunity to take another look at the federal government’s long-held control over immigration policy.
“This would be probably one of the most radical changes the Supreme Court has made in the immigration field,” said Andrew Schoenholtz, a professor at Georgetown Law and an expert on immigration law, referring to the possibility that the high court overturns its 2012 ruling. “It’s that much of a change that Texas is asking for.”
When he signed the law, Texas Republican Gov. Greg Abbott acknowledged that the issue could end up back at the Supreme Court.
“We think that Texas already has the constitutional authority to do this, but we also welcome a Supreme Court decision that would overturn the precedent set in the Arizona case,” Abbott told CNN’s Rosa Flores.
Denise Gilman, a professor at the University of Texas School of Law, agreed that the state’s goal is to get the justices to reverse the Arizona decision.
“It would have been incredibly difficult for the 5th Circuit to let this law stand under existing Supreme Court precedent,” she said. “The Supreme Court is another matter. The Supreme Court can overturn its own precedent, and that’s clearly what the state of Texas wants it to do.”
Video below: Securing the southern border continues to be a challenge
SB 4 was initially blocked by a federal judge in late February in a pair of cases brought by the Biden administration, two immigrant advocacy groups and El Paso County. Texas quickly appealed that decision to the 5th Circuit. In the meantime, the Supreme Court had allowed the state to enforce the law for a brief time on March 19, only for the appeals court to put it back on hold hours later.
‘Show me your papers’ law
The Arizona law is a high-profile example of what happens when states attempt to take immigration policy into their own hands.
Then-Arizona Republican Gov. Jan Brewer signed the Support Our Law Enforcement and Safe Neighborhoods Act, known as SB 1070, into law in 2010.
Chief among the law’s provisions was one that allowed police to check a person’s immigration status during traffic stops or other law enforcement actions if the official had “reasonable suspicion” to believe the person was in the country unlawfully. That part of SB 1070 led critics to dub it the “show me your papers” law.
SB 1070 also made it a state crime for “unauthorized immigrants” to fail to carry registration papers and other government identification; forbade people unauthorized for employment in the U.S. to apply, solicit or perform work; and authorized police to arrest undocumented immigrants without a warrant when “probable cause” existed that they committed a crime that made them deportable.
Legal challenges to the law quickly ensued. The Supreme Court upheld the “show me your papers” part of the law and struck down the three other parts.

Perhaps most importantly, the majority ruling penned by Justice Anthony Kennedy reaffirmed the federal government’s authority over immigration matters. The five-justice bloc said that “federal power to determine immigration policy is well settled” and that its “authority rests, in part, on the National Government’s constitutional power to ‘establish an uniform Rule of Naturalization.’ ”
“The National Government has significant power to regulate immigration,” Kennedy wrote. “Arizona may have understandable frustrations with the problems caused by illegal immigration while that process continues, but the State may not pursue policies that undermine federal law.”
Gilman said the court’s decision in Arizona is significant because Texas’ SB 4 essentially contains the concepts the court struck down in that case.
“The (Arizona) law that made a crime out of immigration status was struck down by the Supreme Court as being in conflict with federal authority to govern immigration enforcement,” she said. “And that’s a really significant part of what the Texas law has in place.”
Among the three justices who dissented in the 2012 case, two are still on the court: Justices Clarence Thomas and Samuel Alito. Justice Antonin Scalia died in 2016. (Justice Elena Kagan disqualified herself from the 2012 case.)
Jessica Bulman-Pozen, a professor at Columbia Law School who specializes in federalism, said the arguments pushed by Texas in defense of SB 4 hew most closely to the dissent penned by Scalia, which concluded that Arizona’s law was enacted in an effort to enforce federal immigration law “more effectively.”
“The court did not think that was right as a descriptive matter about what was happening in Arizona, and I think it’s even more clearly incorrect here with respect to Texas,” Bulman-Pozen said, referring to the majority’s rejection of Arizona’s argument that it was attempting to address the Obama administration’s alleged inaction on immigration issues.
“The idea that what (Texas is) doing is in fact vindicating some kind of congressional judgment or congressional law against an executive that’s not enforcing (those laws), I don’t think that that’s a fair description of what’s happening here,” she said.

Abbott cited the Scalia dissent when he signed the law.
“Remembering that Justice Scalia wrote a dissenting opinion in that case, pretty much laying out a pathway that he thought would be a legal way for a state to go about the process of enforcing immigration laws,” Abbott told CNN.
Oldham’s dissent
A considerable amount of daylight exists between the divided 5th Circuit panel that is weighing the legality of SB 4.
“Supreme Court authorities and the detailed statutory scheme governing who will be permitted to remain in the United States and removal procedures strongly indicate that Congress ‘occupies [the] entire field’ of unlawful entry and reentry of noncitizens as well as removal,” Chief Judge Priscilla Richman wrote in a decision that was joined by Circuit Judge Irma Carrillo Ramirez.
But Circuit Judge Andrew Oldham – a former Alito clerk – wrote in a lengthy dissent last week that he would have let Texas enforce the law while the legal challenges continue.
Oldham leaned into a more limited reading of the Supreme Court’s 2012 decision in Arizona, saying it “certainly does not suggest States may never supplement any federal immigration laws.”
He argued the Arizona decision leaves some room for parts of SB 4 to withstand scrutiny, particularly the policy that allows Texas judges to order immigrants to be deported.
“The Arizona Court did not hold – as plaintiffs seem to believe – that the State was preempted from the field of removal because of ‘some brooding federal interest’ like foreign policy or national security,” wrote Oldham, who was also previously general counsel to Abbott.
Texas’ attorneys have raised those same claims.
“Arizona did not find that state laws concerning entry and removal were field preempted, and nothing in Arizona precludes States from regulating entry and reentry or issuing return orders,” the attorneys wrote.
Whether those arguments have any salience before the nation’s highest court if the case comes before the justices is another question.
“To the extent the court revisited Arizona in this context, it would basically be making states authorities with respect to entry and removal in the immigration space. And that would be an extreme departure from precedent in our nation’s history,” Bulman-Pozen said. “It’d be quite shocking.”
Texas immigration controversy rekindles fight over Arizona’s ‘show me your papers’ law
South carolina defeats the wolfpack 78-59 to head to the national championship, phoenix from the ashes: just like '83, destiny and resolve fuel nc state's trip west, hurricanes rally for 4-2 victory over slumping caps. ovechkin scores both goals for washington., shrimp walk by bulls, 9-6, dt derrick brown to sign contract extension with panthers worth up to $96 million.

WRAL Late News

WRAL WeatherCenter Forecast

Evening Pick 3 Pick 4 and Cash 5

Mega Millions Drawing

Food vendors prep for Dreamville Festival

IMAGES
COMMENTS
In. the U.S. context, the immigrant share of the population almost tripled from a historic low of. 4.7 percent in 1970 to 13.7 percent by 2017. It is sometimes claimed that the immigration surge has been a key contributor to. economic growth, and that an even larger number of immigrants would increase our.
1. Introduction. The United States is, once again, in the midst of an age of immigration. In 2010, there were 40 million foreign-born persons living in the United States (Grieco et al. 2012).Of the 220 million international migrants in the world in 2010—defined as persons living outside their country of birth—almost one in five were residents in the United States (UN Population Division 2013).
This paper reviews and explains the growing literature focused on the political effects of immigration, and highlights fruitful avenues for future research. When compared to potential labor market competition and other economic forces, broadly defined cultural factors have a stronger political and social impact. 03 Nov 2020.
What we know about unauthorized immigrants living in the U.S. The unauthorized immigrant population in the United States reached 10.5 million in 2021. That was a modest increase over 2019 but nearly identical to 2017. short reads | Sep 28, 2023.
U.S. immigration policy is governed largely by the Immigration and Nationality Act (INA), which was first codified in 1952 and has been amended significantly several times since.2. Implementation of INA policies is carried out by executive branch agencies. The Department of Homeland Security (DHS) has primary responsibility for immigration ...
The paper supports a well-resourced and independent immigration court system devoted to producing the right decisions under the law. Following a short introduction, a long section on "Causes and Solutions to the Backlog" examines the multi-faceted causes of the backlog, and offers an integrated, wide-ranging set of recommendations to reverse and ultimately eliminate the backlog.
Beyond Economic Barriers: Conceptualizing Food Insecurity among Resettled Refugees Living in the United States. Hannah Stokes-Ramos. Article | Published online: 27 Feb 2024. Explore the current issue of Journal of Immigrant & Refugee Studies, Volume 22, Issue 1, 2024.
Portes Jonathan. 2018. "The Economic Impacts of Immigration to the UK" and "New Evidence on the Economics of Immigration to the UK," VoxEU (April and October, respectively). News summaries of the research evidence on the economic impacts of migration to the UK on jobs, wages, productivity, and more. Google Scholar.
The Immigration Research Library is a free, online collection of contemporary, U.S. immigration reports, briefs, fact sheets, infographics, news and events. The Library hosts (with links to original sources) more than 1,500 U.S. immigration research reports with simple, straightforward abstracts drawn from respected universities and research institutes from across the country.
The history of immigration to the United States has been shaped both by changes in the. underlying costs and benefits of migration as well as by substantial shifts in immigration policy. The high cost of crossing the Atlantic in the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries gave rise to a. long. period. of.
Immigration-control skeptics argue that international migration is mainly driven by structural economic and political factors such as labor market demand, ... South- and South East Asia, and the EU. By synthesizing the DEMIG findings previously published as working papers, journal articles, and book chapters, this article aims to enhance ...
Background Immigration has a strong impact on the development of health systems, medicine and science worldwide. Therefore, this article provides a descriptive study on the overall research output ...
The U.S. foreign-born population reached a record 44.8 million in 2018. Since 1965, when U.S. immigration laws replaced a national quota system, the number of immigrants living in the U.S. has more than quadrupled. Immigrants today account for 13.7% of the U.S. population, nearly triple the share (4.8%) in 1970.
immigration and wage inequality, focusing on the evidence derived from comparisons across 1 The founding president of the American Economic Association, Francis A. Walker, wrote a well-known article arguing in favor of restricting immigration (Walker 1896). Walker believed that a particular problem was the declin-
In fiscal 2019, the U.S. government awarded more than 139,000 employment-based green cards to foreign workers and their families. The Biden administration's proposed legislation could boost the number of employment-based green cards, which are capped at about 140,000 per year. The proposal would allow the use of unused visa slots from ...
Publication Date: 2022. The Criminalization of Immigration: Truth, Lies, Tragedy, and Consequences by Robert Hartmann McNamara. Call Number: eBook. Publication Date: 2020. Building Walls: Excluding Latin people in the United States by Ernesto Castañeda. Call Number: eBook.
The changing culture, discussion and challenges of migrants and refugees issues covers many disciplines; see these interdisciplinary databases to search many disciplines and resource types, like newspapers, trade journals or scholarly journals, at once. List of journals that cover immigration from our catalog listings.
Among the billions of historical records housed at the National Archives throughout the country, researchers can find information relating to immigrants from the late 1700s through the early 2000s. The National Archives preserves and makes available documents created by Federal agencies in the course of their daily business.
An immigration research paper will either deal with a particular pair of countries or take a global approach. Depending on your course and research paper type, you may come up with assumptions or focus on a title that reflects certain similarities of some problem. The most important is to discuss the causes of immigration.
110 Immigration Research Paper Topics. Immigration is the process of people moving to a country and can be either voluntary or involuntary. Immigration is a very interesting aspect of education, and you may be asked at one point or another to come up with a research paper in the immigration niche. Immigration is a broad topic, and it can be ...
Here is a sample outline that you can use to craft a winning research paper on immigration: Introduction: This is the first section after the paper title, and you should use it to set the stage for the entire paper. So, open the essay with a strong hook statement, and capture the background of the study. You should also highlight the thesis ...
To qualify, applicants will be required to provide immigration papers that prove their status. Permanent Resident Card. Foreign passport with an approved I-94 Arrival/Departure Record. Employment Authorization Card. Foreign passport with an I-551 stamp. Re-entry Permit.
Texas' immigration law has raised fear that it'll promote racial profiling by police. The concerns evoke memories of what happened after Arizona passed its so-called "show me your papers" law in 2010.
2. Clicking the ellipsis in the right corner; 3. Clicking "Settings"; 4. Selecting "Extensions"; and. 5. Removing or turning off the Chrome extension on the "Adobe Acrobat: PDF edit, convert, sign tools" tab. In Safari, open the form, hover your mouse toward the bottom-center of the screen to bring up the gray icon, and click the ...
'Show me your papers' law. The Arizona law is a high-profile example of what happens when states attempt to take immigration policy into their own hands.
In the meantime, the Supreme Court had allowed the state to enforce the law for a brief time on March 19, only for the appeals court to put it back on hold hours later.'Show me your papers ...
'Show me your papers' law. The Arizona law is a high-profile example of what happens when states attempt to take immigration policy into their own hands.
The legal battle over a controversial Texas immigration law could eventually give the Supreme Court a chance to revisit a historic ruling that largely struck down Arizona's "show me your ...