- Grades 6-12
- School Leaders
FREE Poetry Worksheet Bundle! Perfect for National Poetry Month.

40 Strong Persuasive Writing Examples (Essays, Speeches, Ads, and More)
Learn from the experts.

The more we read, the better writers we become. Teaching students to write strong persuasive essays should always start with reading some top-notch models. This round-up of persuasive writing examples includes famous speeches, influential ad campaigns, contemporary reviews of famous books, and more. Use them to inspire your students to write their own essays. (Need persuasive essay topics? Check out our list of interesting persuasive essay ideas here! )
- Persuasive Essays
- Persuasive Speeches
- Advertising Campaigns
Persuasive Essay Writing Examples

From the earliest days of print, authors have used persuasive essays to try to sway others to their own point of view. Check out these top persuasive essay writing examples.
Professions for Women by Virginia Woolf
Sample lines: “Outwardly, what is simpler than to write books? Outwardly, what obstacles are there for a woman rather than for a man? Inwardly, I think, the case is very different; she has still many ghosts to fight, many prejudices to overcome. Indeed it will be a long time still, I think, before a woman can sit down to write a book without finding a phantom to be slain, a rock to be dashed against. And if this is so in literature, the freest of all professions for women, how is it in the new professions which you are now for the first time entering?”
The Crisis by Thomas Paine
Sample lines: “These are the times that try men’s souls. The summer soldier and the sunshine patriot will, in this crisis, shrink from the service of their country; but he that stands by it now, deserves the love and thanks of man and woman. Tyranny, like hell, is not easily conquered; yet we have this consolation with us, that the harder the conflict, the more glorious the triumph. What we obtain too cheap, we esteem too lightly: it is dearness only that gives every thing its value.”
Politics and the English Language by George Orwell
Sample lines: “As I have tried to show, modern writing at its worst does not consist in picking out words for the sake of their meaning and inventing images in order to make the meaning clearer. It consists in gumming together long strips of words which have already been set in order by someone else, and making the results presentable by sheer humbug.”
Letter From a Birmingham Jail by Dr. Martin Luther King Jr.
Sample lines: “We know through painful experience that freedom is never voluntarily given by the oppressor; it must be demanded by the oppressed. Frankly, I have yet to engage in a direct action campaign that was ‘well timed’ in the view of those who have not suffered unduly from the disease of segregation. For years now I have heard the word ‘Wait!’ It rings in the ear of every Negro with piercing familiarity. This ‘Wait’ has almost always meant ‘Never.’ We must come to see, with one of our distinguished jurists, that ‘justice too long delayed is justice denied.'”
Civil Disobedience by Henry David Thoreau
Sample lines: “Even voting for the right is doing nothing for it. It is only expressing to men feebly your desire that it should prevail. A wise man will not leave the right to the mercy of chance, nor wish it to prevail through the power of the majority. There is but little virtue in the action of masses of men.”
Go Gentle Into That Good Night by Roger Ebert
Sample lines: “‘Kindness’ covers all of my political beliefs. No need to spell them out. I believe that if, at the end of it all, according to our abilities, we have done something to make others a little happier, and something to make ourselves a little happier, that is about the best we can do. To make others less happy is a crime.”
The Way to Wealth by Benjamin Franklin
Sample lines: “Methinks I hear some of you say, must a man afford himself no leisure? I will tell thee, my friend, what Poor Richard says, employ thy time well if thou meanest to gain leisure; and, since thou art not sure of a minute, throw not away an hour. Leisure is time for doing something useful; this leisure the diligent man will obtain, but the lazy man never; so that, as Poor Richard says, a life of leisure and a life of laziness are two things.”
The Crack-Up by F. Scott Fitzgerald
Sample lines: “Of course all life is a process of breaking down, but the blows that do the dramatic side of the work—the big sudden blows that come, or seem to come, from outside—the ones you remember and blame things on and, in moments of weakness, tell your friends about, don’t show their effect all at once.”
Open Letter to the Kansas School Board by Bobby Henderson
Sample lines: “I am writing you with much concern after having read of your hearing to decide whether the alternative theory of Intelligent Design should be taught along with the theory of Evolution. … Let us remember that there are multiple theories of Intelligent Design. I and many others around the world are of the strong belief that the universe was created by a Flying Spaghetti Monster. … We feel strongly that the overwhelming scientific evidence pointing towards evolutionary processes is nothing but a coincidence, put in place by Him. It is for this reason that I’m writing you today, to formally request that this alternative theory be taught in your schools, along with the other two theories.”
Open Letter to the United Nations by Niels Bohr
Sample lines: “Humanity will, therefore, be confronted with dangers of unprecedented character unless, in due time, measures can be taken to forestall a disastrous competition in such formidable armaments and to establish an international control of the manufacture and use of the powerful materials.”
Persuasive Speech Writing Examples
Many persuasive speeches are political in nature, often addressing subjects like human rights. Here are some of history’s most well-known persuasive writing examples in the form of speeches.
I Have a Dream by Dr. Martin Luther King Jr.
Sample lines: “And so even though we face the difficulties of today and tomorrow, I still have a dream. It is a dream deeply rooted in the American dream. I have a dream that one day this nation will rise up and live out the true meaning of its creed: We hold these truths to be self-evident, that all men are created equal.”
Woodrow Wilson’s War Message to Congress, 1917
Sample lines: “There are, it may be, many months of fiery trial and sacrifice ahead of us. It is a fearful thing to lead this great peaceful people into war, into the most terrible and disastrous of all wars, civilization itself seeming to be in the balance. But the right is more precious than peace, and we shall fight for the things which we have always carried nearest our hearts—for democracy, for the right of those who submit to authority to have a voice in their own governments, for the rights and liberties of small nations, for a universal dominion of right by such a concert of free peoples as shall bring peace and safety to all nations and make the world itself at last free.”
Chief Seattle’s 1854 Oration
Sample lines: “I here and now make this condition that we will not be denied the privilege without molestation of visiting at any time the tombs of our ancestors, friends, and children. Every part of this soil is sacred in the estimation of my people. Every hillside, every valley, every plain and grove, has been hallowed by some sad or happy event in days long vanished. Even the rocks, which seem to be dumb and dead as they swelter in the sun along the silent shore, thrill with memories of stirring events connected with the lives of my people, and the very dust upon which you now stand responds more lovingly to their footsteps than yours, because it is rich with the blood of our ancestors, and our bare feet are conscious of the sympathetic touch.”
Women’s Rights Are Human Rights, Hillary Rodham Clinton
Sample lines: “What we are learning around the world is that if women are healthy and educated, their families will flourish. If women are free from violence, their families will flourish. If women have a chance to work and earn as full and equal partners in society, their families will flourish. And when families flourish, communities and nations do as well. … If there is one message that echoes forth from this conference, let it be that human rights are women’s rights and women’s rights are human rights once and for all.”
I Am Prepared to Die, Nelson Mandela
Sample lines: “Above all, My Lord, we want equal political rights, because without them our disabilities will be permanent. I know this sounds revolutionary to the whites in this country, because the majority of voters will be Africans. This makes the white man fear democracy. But this fear cannot be allowed to stand in the way of the only solution which will guarantee racial harmony and freedom for all. It is not true that the enfranchisement of all will result in racial domination. Political division, based on color, is entirely artificial and, when it disappears, so will the domination of one color group by another. … This then is what the ANC is fighting. Our struggle is a truly national one. It is a struggle of the African people, inspired by our own suffering and our own experience. It is a struggle for the right to live.”
The Struggle for Human Rights by Eleanor Roosevelt
Sample lines: “It is my belief, and I am sure it is also yours, that the struggle for democracy and freedom is a critical struggle, for their preservation is essential to the great objective of the United Nations to maintain international peace and security. Among free men the end cannot justify the means. We know the patterns of totalitarianism—the single political party, the control of schools, press, radio, the arts, the sciences, and the church to support autocratic authority; these are the age-old patterns against which men have struggled for 3,000 years. These are the signs of reaction, retreat, and retrogression. The United Nations must hold fast to the heritage of freedom won by the struggle of its people; it must help us to pass it on to generations to come.”
Freedom From Fear by Aung San Suu Kyi
Sample lines: “Saints, it has been said, are the sinners who go on trying. So free men are the oppressed who go on trying and who in the process make themselves fit to bear the responsibilities and to uphold the disciplines which will maintain a free society. Among the basic freedoms to which men aspire that their lives might be full and uncramped, freedom from fear stands out as both a means and an end. A people who would build a nation in which strong, democratic institutions are firmly established as a guarantee against state-induced power must first learn to liberate their own minds from apathy and fear.”
Harvey Milk’s “The Hope” Speech
Sample lines: “Some people are satisfied. And some people are not. You see there is a major difference—and it remains a vital difference—between a friend and a gay person, a friend in office and a gay person in office. Gay people have been slandered nationwide. We’ve been tarred and we’ve been brushed with the picture of pornography. In Dade County, we were accused of child molestation. It is not enough anymore just to have friends represent us, no matter how good that friend may be.”
The Union and the Strike, Cesar Chavez
Sample lines: “We are showing our unity in our strike. Our strike is stopping the work in the fields; our strike is stopping ships that would carry grapes; our strike is stopping the trucks that would carry the grapes. Our strike will stop every way the grower makes money until we have a union contract that guarantees us a fair share of the money he makes from our work! We are a union and we are strong and we are striking to force the growers to respect our strength!”
Nobel Lecture by Malala Yousafzai
Sample lines: “The world can no longer accept that basic education is enough. Why do leaders accept that for children in developing countries, only basic literacy is sufficient, when their own children do homework in algebra, mathematics, science, and physics? Leaders must seize this opportunity to guarantee a free, quality, primary and secondary education for every child. Some will say this is impractical, or too expensive, or too hard. Or maybe even impossible. But it is time the world thinks bigger.”
Persuasive Writing Examples in Advertising Campaigns
Ads are prime persuasive writing examples. You can flip open any magazine or watch TV for an hour or two to see sample after sample of persuasive language. Here are some of the most popular ad campaigns of all time, with links to articles explaining why they were so successful.
Nike: Just Do It

The iconic swoosh with the simple tagline has persuaded millions to buy their kicks from Nike and Nike alone. Teamed with pro sports-star endorsements, this campaign is one for the ages. Blinkist offers an opinion on what made it work.
Dove: Real Beauty
Beauty brand Dove changed the game by choosing “real” women to tell their stories instead of models. They used relatable images and language to make connections, and inspired other brands to try the same concept. Learn why Global Brands considers this one a true success story.
Wendy’s: Where’s the Beef?
Today’s kids are too young to remember the cranky old woman demanding to know where the beef was on her fast-food hamburger. But in the 1980s, it was a catchphrase that sold millions of Wendy’s burgers. Learn from Better Marketing how this ad campaign even found its way into the 1984 presidential debate.
De Beers: A Diamond Is Forever

A diamond engagement ring has become a standard these days, but the tradition isn’t as old as you might think. In fact, it was De Beers jewelry company’s 1948 campaign that created the modern engagement ring trend. The Drum has the whole story of this sparkling campaign.
Volkswagen: Think Small
Americans have always loved big cars. So in the 1960s, when Volkswagen wanted to introduce their small cars to a bigger market, they had a problem. The clever “Think Small” campaign gave buyers clever reasons to consider these models, like “If you run out of gas, it’s easy to push.” Learn how advertisers interested American buyers in little cars at Visual Rhetoric.
American Express: Don’t Leave Home Without It
AmEx was once better known for traveler’s checks than credit cards, and the original slogan was “Don’t leave home without them.” A simple word change convinced travelers that American Express was the credit card they needed when they headed out on adventures. Discover more about this persuasive campaign from Medium.
Skittles: Taste the Rainbow

These candy ads are weird and intriguing and probably not for everyone. But they definitely get you thinking, and that often leads to buying. Learn more about why these wacky ads are successful from The Drum.
Maybelline: Maybe She’s Born With It
Smart wordplay made this ad campaign slogan an instant hit. The ads teased, “Maybe she’s born with it. Maybe it’s Maybelline.” (So many literary devices all in one phrase!) Fashionista has more on this beauty campaign.
Coca-Cola: Share a Coke
Seeing their own name on a bottle made teens more likely to want to buy a Coke. What can that teach us about persuasive writing in general? It’s an interesting question to consider. Learn more about the “Share a Coke” campaign from Digital Vidya.
Always: #LikeaGirl

Talk about the power of words! This Always campaign turned the derogatory phrase “like a girl” on its head, and the world embraced it. Storytelling is an important part of persuasive writing, and these ads really do it well. Medium has more on this stereotype-bashing campaign.
Editorial Persuasive Writing Examples

Newspaper editors or publishers use editorials to share their personal opinions. Noted politicians, experts, or pundits may also offer their opinions on behalf of the editors or publishers. Here are a couple of older well-known editorials, along with a selection from current newspapers.
Yes, Virginia, There Is a Santa Claus (1897)
Sample lines: “Yes, Virginia, there is a Santa Claus. He exists as certainly as love and generosity and devotion exist, and you know that they abound and give to your life its highest beauty and joy. Alas! How dreary would be the world if there were no Santa Claus. It would be as dreary as if there were no Virginias.”
What’s the Matter With Kansas? (1896)
Sample lines: “Oh, this IS a state to be proud of! We are a people who can hold up our heads! What we need is not more money, but less capital, fewer white shirts and brains, fewer men with business judgment, and more of those fellows who boast that they are ‘just ordinary clodhoppers, but they know more in a minute about finance than John Sherman,’ we need more men … who hate prosperity, and who think, because a man believes in national honor, he is a tool of Wall Street.”
America Can Have Democracy or Political Violence. Not Both. (The New York Times)
Sample lines: “The nation is not powerless to stop a slide toward deadly chaos. If institutions and individuals do more to make it unacceptable in American public life, organized violence in the service of political objectives can still be pushed to the fringes. When a faction of one of the country’s two main political parties embraces extremism, that makes thwarting it both more difficult and more necessary. A well-functioning democracy demands it.”
The Booster Isn’t Perfect, But Still Can Help Against COVID (The Washington Post)
Sample lines: “The booster shots are still free, readily available and work better than the previous boosters even as the virus evolves. Much still needs to be done to build better vaccines that protect longer and against more variants, including those that might emerge in the future. But it is worth grabbing the booster that exists today, the jab being a small price for any measure that can help keep COVID at bay.”
If We Want Wildlife To Thrive in L.A., We Have To Share Our Neighborhoods With Them (Los Angeles Times)
Sample lines: “If there are no corridors for wildlife movement and if excessive excavation of dirt to build bigger, taller houses erodes the slope of a hillside, then we are slowly destroying wildlife habitat. For those people fretting about what this will do to their property values—isn’t open space, trees, and wildlife an amenity in these communities?”
Persuasive Review Writing Examples

Book or movie reviews are more great persuasive writing examples. Look for those written by professionals for the strongest arguments and writing styles. Here are reviews of some popular books and movies by well-known critics to use as samples.
The Great Gatsby (The Chicago Tribune, 1925)
Sample lines: “What ails it, fundamentally, is the plain fact that it is simply a story—that Fitzgerald seems to be far more interested in maintaining its suspense than in getting under the skins of its people. It is not that they are false: It is that they are taken too much for granted. Only Gatsby himself genuinely lives and breathes. The rest are mere marionettes—often astonishingly lifelike, but nevertheless not quite alive.”
Harry Potter and the Sorcerer’s Stone (The Washington Post, 1999)
Sample lines: “Obviously, Harry Potter and the Sorcerer’s Stone should make any modern 11-year-old a very happy reader. The novel moves quickly, packs in everything from a boa constrictor that winks to a melancholy Zen-spouting centaur to an owl postal system, and ends with a scary surprise. Yet it is, essentially, a light-hearted thriller, interrupted by occasional seriousness (the implications of Harry’s miserable childhood, a moral about the power of love).”
Twilight (The Telegraph, 2009)
Sample lines: “No secret, of course, at whom this book is aimed, and no doubt, either, that it has hit its mark. The four Twilight novels are not so much enjoyed, as devoured, by legions of young female fans worldwide. That’s not to say boys can’t enjoy these books; it’s just that the pages of heart-searching dialogue between Edward and Bella may prove too long on chat and too short on action for the average male reader.”
To Kill a Mockingbird (Time, 1960)
Sample lines: “Author Lee, 34, an Alabaman, has written her first novel with all of the tactile brilliance and none of the preciosity generally supposed to be standard swamp-warfare issue for Southern writers. The novel is an account of an awakening to good and evil, and a faint catechistic flavor may have been inevitable. But it is faint indeed; novelist Lee’s prose has an edge that cuts through cant, and she teaches the reader an astonishing number of useful truths about little girls and about Southern life.”
The Diary of Anne Frank (The New York Times, 1952)
Sample lines: “And this quality brings it home to any family in the world today. Just as the Franks lived in momentary fear of the Gestapo’s knock on their hidden door, so every family today lives in fear of the knock of war. Anne’s diary is a great affirmative answer to the life-question of today, for she shows how ordinary people, within this ordeal, consistently hold to the greater human values.”
What are your favorite persuasive writing examples to use with students? Come share your ideas in the WeAreTeachers HELPLINE group on Facebook .
Plus, the big list of essay topics for high school (120+ ideas) ..

You Might Also Like

101 Interesting Persuasive Essay Topics for Kids and Teens
Use your words to sway the reader. Continue Reading
Copyright © 2023. All rights reserved. 5335 Gate Parkway, Jacksonville, FL 32256

How to Write Perfect Persuasive Essays in 5 Simple Steps
WHAT IS A PERSUASIVE ESSAY?

A persuasive text presents a point of view around a topic or theme that is backed by evidence to support it.
The purpose of a persuasive text can be varied. Maybe you intend to influence someone’s opinion on a specific topic, or you might aim to sell a product or service through an advertisement.
The challenge in writing a good persuasive text is to use a mix of emotive language and, in some cases, images that are supported by hard evidence or other people’s opinions.
In a persuasive essay or argument essay, the student strives to convince the reader of the merits of their opinion or stance on a particular issue. The student must utilise several persuasive techniques to form a coherent and logical argument to convince the reader of a point of view or to take a specific action.

PERSUADING PEOPLE REQUIRES A CONSISTENT APPROACH…
Persuasive texts are simple in structure. You must clearly state your opinion around a specific topic and then repeatedly reinforce your opinions with external facts or evidence. A robust concluding summary should leave little doubt in the reader’s mind. ( Please view our planning tool below for a detailed explanation. )
TYPES OF PERSUASIVE TEXT
We cover the broad topic of writing a general persuasive essay in this guide, there are several sub-genres of persuasive texts students will encounter as they progress through school. We have complete guides on these text types, so be sure to click the links and read these in detail if required.
- Argumentative Essays – These are your structured “Dogs are better pets than Cats” opinion-type essays where your role is to upsell the positive elements of your opinions to your audience whilst also highlighting the negative aspects of any opposing views using a range of persuasive language and techniques.
- Advertising – Uses persuasive techniques to sell a good or service to potential customers with a call to action.
- Debating Speeches – A debate is a structured discussion between two teams on a specific topic that a moderator judges and scores. Your role is to state your case, sell your opinions to the audience, and counteract your opposition’s opinions.
- Opinion Articles, Newspaper Editorials. – Editorials often use more subtle persuasive techniques that blur the lines of factual news reporting and opinions that tell a story with bias. Sometimes they may even have a call to action at the end.
- Reviews – Reviews exist to inform others about almost any service or product, such as a film, restaurant, or product. Depending on your experiences, you may have firm opinions or not even care that much about recommending it to others. Either way, you will employ various persuasive techniques to communicate your recommendations to your audience.
- Please note a DISCUSSION essay is not a traditional persuasive text, as even though you are comparing and contrasting elements, the role of the author is to present an unbiased account of both sides so that the reader can make a decision that works best for them. Discussions are often confused as a form of persuasive writing.
A COMPLETE TEACHING UNIT ON PERSUASIVE WRITING SKILLS
Teach your students to produce writing that PERSUADES and INFLUENCES thinking with this HUGE writing guide bundle covering: ⭐ Persuasive Texts / Essays ⭐ Expository Essays⭐ Argumentative Essays⭐ Discussions.
A complete 140 PAGE unit of work on persuasive texts for teachers and students. No preparation is required.
THE STRUCTURE OF A PERSUASIVE ESSAY

1. Introduction
In the introduction, the student will naturally introduce the topic. Controversial issues make for great topics in this writing genre. It’s a cliche in polite society to discourage discussions involving politics, sex, or religion because they can often be very divisive. While these subjects may not be the best topics of conversation for the dinner table at Thanksgiving, they can be perfect when deciding on a topic for persuasive writing. Obviously, the student’s age and abilities should be considered, as well as cultural taboos, when selecting a topic for the essay. But the point holds, the more controversial, the better.
Let’s take a look at some of the critical elements of the introduction when writing a persuasive essay:
Title: Tell your audience what they are reading.
This will often be posed as a question; for example, if the essay is on the merits of a vegetarian lifestyle, it may be called something like: To Eat Meat or Not?
Hook : Provide your audience with a reason to continue reading.
As with any genre of writing, capturing the reader’s interest from the outset is crucial. There are several methods of doing this, known as hooks. Students may open their essays with anecdotes, jokes, quotations, or relevant statistics related to the topic under discussion.
Background: Provide some context to your audience.
In this introductory section, students will provide the reader with some background on the topic. This will place the issue in context and briefly weigh some opinions on the subject.
Thesis statement: Let the audience know your stance.
After surveying the topic in the first part of the introduction, it is now time for the student writer to express their opinion and briefly preview the points they will make later in the essay.
2. Body Paragraphs
The number of paragraphs forming this essay section will depend on the number of points the writer chooses to make to support their opinion. Usually three main points will be sufficient for beginning writers to coordinate. More advanced students can increase the number of paragraphs based on the complexity of their arguments, but the overall structure will largely remain intact.
Be sure to check out our complete guide to writing perfect paragraphs here .
The TEEL acronym is valuable for students to remember how to structure their paragraphs. Read below for a deeper understanding.
Topic Sentence:
The topic sentence states the central point of the paragraph. This will be one of the reasons supporting the thesis statement made in the introduction.
These sentences will build on the topic sentence by illustrating the point further, often by making it more specific.
These sentences’ purpose is to support the paragraph’s central point by providing supporting evidence and examples. This evidence may be statistics, quotations, or anecdotal evidence.
The final part of the paragraph links back to the initial statement of the topic sentence while also forming a bridge to the next point to be made. This part of the paragraph provides some personal analysis and interpretation of how the student arrived at their conclusions and connects the essay as a cohesive whole.
3. Conclusion
The conclusion weaves together the main points of the persuasive essay. It does not usually introduce new arguments or evidence but instead reviews the arguments made already and restates them by summing them up uniquely. It is important at this stage to tie everything back to the initial thesis statement. This is the writer’s last opportunity to drive home their point, to achieve the essay’s goal, to begin with – persuade the reader of their point of view.

Ending an essay well can be challenging, but it is essential to end strongly, especially for persuasive essays. As with the hooks of the essay’s opening, there are many tried and tested methods of leaving the reader with a strong impression. Encourage students to experiment with different endings, for example, concluding the essay with a quotation that amplifies the thesis statement.
Another method is to have the student rework their ending in simple monosyllabic words, as simple language often has the effect of being more decisive in impact. The effect they are striving for in the final sentence is the closing of the circle.
Several persuasive writing techniques can be used in the conclusion and throughout the essay to amp up the persuasive power of the writing. Let’s take a look at a few.
ETHOS, PATHOS & LOGOS TUTORIAL VIDEO (2:20)

TIPS FOR WRITING A GREAT PERSUASIVE ESSAY

PERSUASIVE TECHNIQUES
In this article, we have outlined a basic structure that will be helpful to students in approaching the organization of their persuasive writing. It will also be helpful for the students to be introduced to a few literary techniques that will help your students to present their ideas convincingly. Here are a few of the more common ones:
Repetition: There is a reason why advertisements and commercials are so repetitive – repetition works! Students can use this knowledge to their advantage in their persuasive writing. It is challenging to get the reader to fully agree with the writer’s opinion if they don’t fully understand it. Saying the same thing in various ways ensures the reader gets many bites at the ‘understanding’ cherry.
Repetition Example: “The use of plastic bags is not only bad for the environment, but it is also bad for our economy. Plastic bags are not biodegradable, meaning they will not decompose and will continue to take up space in landfills. Plastic bags are also not recyclable, meaning they will not be reused and will instead end up in landfills. Plastic bags are not only bad for the environment, but they are also bad for our economy as they are costly to dispose of and take up valuable space in landfills.”
In this example, the phrase “not only bad for the environment but also bad for our economy” is repeated multiple times to reinforce the idea that plastic bags are not just a problem for the environment but also the economy. The repetition of the phrase emphasizes the point and makes it more persuasive.
It is also important to note that repetition could be used differently, such as repeating a word or phrase to create rhythm or emphasis.
Storytelling: Humans tend to understand things better through stories. Think of how we teach kids important values through time-tested fables like Peter and the Wolf . Whether through personal anecdotes or references to third-person experiences, stories help climb down the ladder of abstraction and reach the reader on a human level.
Storytelling Example: “Imagine you are walking down the street, and you come across a stray dog clearly in need of food and water. The dog looks up at you with big, sad eyes, and you cannot help but feel a twinge of compassion. Now, imagine that same scenario, but instead of a stray dog, it’s a homeless person sitting on the sidewalk. The person is clearly in need of food and shelter, and their eyes also look up at her with a sense of hopelessness.
The point of this story is to show that just as we feel compelled to help a stray animal in need, we should also feel compelled to help a homeless person. We should not turn a blind eye to the suffering of our fellow human beings, and we should take action to address homelessness in our community. It is important to remember that everyone deserves a roof over their head and a warm meal to eat. The story is designed to elicit an emotional response in the reader and make the argument more relatable and impactful.
By using storytelling, this passage creates an image in the reader’s mind and creates an emotional connection that can be more persuasive than just stating facts and figures.

Dissent: We live in a cynical age, so leaving out the opposing opinion will smack of avoidance to the reader. Encourage your students to turn to that opposing viewpoint and deal with those arguments in their essays .
Dissent Example: “Many people argue that students should not have to wear uniforms in school. They argue that uniforms stifle creativity and individuality and that students should be able to express themselves through their clothing choices. While these are valid concerns, I strongly disagree.
In fact, uniforms can actually promote individuality by levelling the playing field and removing the pressure to dress in a certain way. Furthermore, uniforms can promote a sense of community and belonging within a school. They can also provide a sense of discipline and structure, which can help to create a more focused and productive learning environment. Additionally, uniforms can save families money and eliminate the stress of deciding what to wear daily .
While some may argue that uniforms stifle creativity and individuality, the benefits of uniforms far outweigh the potential drawbacks. It is important to consider the impact of uniforms on the school as a whole, rather than focusing solely on individual expression.”
In this example, the writer presents the opposing viewpoint (uniforms stifle creativity and individuality) and then provides counterarguments to refute it. By doing so, the writer can strengthen their own argument and present a more convincing case for why uniforms should be worn in school.
A Call to Action: A staple of advertising, a call to action can also be used in persuasive writing. When employed, it usually forms part of the conclusion section of the essay and asks the reader to do something, such as recycle, donate to charity, sign a petition etc.
A quick look around reveals to us the power of persuasion, whether in product advertisements, newspaper editorials, or political electioneering; persuasion is an ever-present element in our daily lives. Logic and reason are essential in persuasion, but they are not the only techniques. The dark arts of persuasion can prey on emotion, greed, and bias. Learning to write persuasively can help our students recognize well-made arguments and help to inoculate them against the more sinister manifestations of persuasion.
Call to Action Example: “Climate change is a pressing issue that affects us all, and it’s important that we take action now to reduce our carbon footprint and protect the planet for future generations. As a society, we have the power to make a difference and it starts with small changes that we can make in our own lives.
I urge you to take the following steps to reduce your carbon footprint:
- Reduce your use of single-use plastics
- Use public transportation, carpool, bike or walk instead of driving alone.
- Support clean energy sources such as solar and wind power
- Plant trees and support conservation efforts
It’s easy to feel like one person can’t make a difference, but the truth is that every little bit helps. Together, we can create a more sustainable future for ourselves and for the planet.
So, let’s take action today and make a difference for a better future, it starts with minor changes, but it all adds up and can make a significant impact. We need to take responsibility for our actions and do our part to protect the planet.”
In this example, the writer gives a clear and specific call to action and encourages the reader to take action to reduce their carbon footprint and protect the planet. By doing this, the writer empowers the reader to take action and enables them to change.
Now, go persuade your students of the importance of perfecting the art of persuasive writing!
A COMPLETE UNIT ON TEACHING FACT AND OPINION

This HUGE 120 PAGE resource combines four different fact and opinion activities you can undertake as a WHOLE GROUP or as INDEPENDENT READING GROUP TASKS in either DIGITAL or PRINTABLE TASKS.
20 POPULAR PERSUASIVE ESSAY TOPICS FOR STUDENTS
Writing an effective persuasive essay demonstrates a range of skills that will be of great use in nearly all aspects of life after school.

In essence, if you can influence a person to change their ideas or thoughts on a given topic through how you structure your words and thoughts, you possess a very powerful skill.
Be careful not to rant wildly. Use facts and other people’s ideas who think similarly to you in your essay to strengthen your concepts.
Your biggest challenge in getting started may be choosing a suitable persuasive essay topic. These 20 topics for a persuasive essay should make this process a little easier.
- WHY ARE WE FASCINATED WITH CELEBRITIES AND WEALTHY PEOPLE ON TELEVISION AND SOCIAL MEDIA?
- IS IT RIGHT FOR SCHOOLS TO RAISE MONEY BY SELLING CANDY AND UNHEALTHY FOODS TO STUDENTS?
- SHOULD GIRLS BE ALLOWED TO PLAY ON BOYS SPORTING TEAMS?
- IS TEACHING HANDWRITING A WASTE OF TIME IN THIS DAY AND AGE?
- SHOULD THERE BE FAR GREATER RESTRICTIONS AROUND WHAT CAN BE POSTED ON THE INTERNET?
- SHOULD PROFESSIONAL ATHLETES HAVE TO TAKE DRUG TESTS?
- ARE TEENAGE PREGNANCY SHOWS A NEGATIVE OR POSITIVE INFLUENCE ON VIEWERS?
- SHOULD GAMBLING BE PROMOTED IN ANY WAY IN SPORTS EVEN THOUGH IT BRINGS IN LARGE AMOUNTS OF REVENUE?
- SHOULD SPORTING TEAMS THAT LOSE BE REWARDED BY RECEIVING INCENTIVES SUCH AS HIGH DRAFT PICKS AND / OR FINANCIAL BENEFITS?
- SHOULD SHARKS THAT ATTACK PEOPLE BE DESTROYED? SHOULD WE GET INVOLVED IN FOREIGN CONFLICTS AND ISSUES THAT DON’T DIRECTLY AFFECT OUR COUNTRY?
- SHOULD WE GET INVOLVED IN FOREIGN CONFLICTS AND ISSUES THAT DON’T DIRECTLY AFFECT OUR COUNTRY?
- COULD VIDEO GAMES BE CONSIDERED AS A PROFESSIONAL SPORT?
- IF YOU WERE THE LEADER OF YOUR COUNTRY AND HAD A LARGE SURPLUS TO SPEND, WHAT WOULD YOU DO WITH IT?
- WHEN SHOULD A PERSON BE CONSIDERED AND TREATED AS AN ADULT?
- SHOULD SMOKING BECOME AN ILLEGAL ACTIVITY?
- SHOULD THE VOTING AGE BE LOWERED?
- DOES PROTECTIVE PADDING IN SPORTS MAKE IT MORE DANGEROUS?
- SHOULD CELL PHONES BE ALLOWED IN THE CLASSROOM?
- IS TEACHING A FOREIGN LANGUAGE A WASTE OF TIME?
- SHOULD WE TEACH ETIQUETTE IN SCHOOLS?
PERSUASIVE PROMPTS FOR RELUCTANT WRITERS
If your students need a little more direction and guidance, here are some journal prompts that include aspects to consider.
- Convince us that students would be better off having a three-day weekend . There are many angles you could take with this, such as letting children maximize their childhood or trying to convince your audience that a four-day school week might actually be more productive.
- Which is the best season? And why? You will really need to draw on the benefits of your preferred season and sell them to your audience. Where possible, highlight the negatives of the competing seasons. Use lots of figurative language and sensory and emotional connections for this topic.
- Aliens do / or don’t exist? We can see millions of stars surrounding us just by gazing into the night sky, suggesting alien life should exist, right? Many would argue that if there were aliens we would have seen tangible evidence of them by now. The only fact is that we just don’t know the answer to this question. It is your task to try and convince your audience through some research and logic what your point of view is and why.
- Should school uniforms be mandatory? Do your research on this popular and divisive topic and make your position clear on where you stand and why. Use plenty of real-world examples to support your thoughts and points of view.
- Should Smartphones be banned in schools? Whilst this would be a complete nightmare for most students’ social lives, maybe it might make schools more productive places for students to focus and learn. Pick a position, have at least three solid arguments to support your point of view, and sell them to your audience.
VISUAL JOURNAL PROMPTS FOR PERSUASIVE WRITING
Try these engaging, persuasive prompts with your students to ignite the writing process . Scroll through them.

Persuasive Essay Examples (Student Writing Samples)
Below are a collection of persuasive essay samples. Click on the image to enlarge and explore them in greater detail. Please take a moment to read the persuasive texts in detail and the teacher and student guides highlight some of the critical elements of writing a persuasion.
Please understand these student writing samples are not intended to be perfect examples for each age or grade level but a piece of writing for students and teachers to explore together to critically analyze to improve student writing skills and deepen their understanding of persuasive text writing.
We recommend reading the example either a year above or below, as well as the grade you are currently working with, to gain a broader appreciation of this text type.
VIDEO TUTORIALS FOR PERSUASIVE WRITING

OTHER GREAT ARTICLES RELATED TO PERSUASIVE ESSAY WRITING

Teaching Resources
Use our resources and tools to improve your student’s writing skills through proven teaching strategies.
WHERE CAN I FIND A COMPLETE UNIT OF WORK ON HOW TO WRITE PERSUASIVE ESSAYS?

We pride ourselves on being the web’s best resource for teaching students and teachers how to write a persuasive text. We value the fact you have taken the time to read our comprehensive guides to understand the fundamentals of writing skills.
We also understand some of you just don’t have the luxury of time or the resources to create engaging resources exactly when you need them.
If you are time-poor and looking for an in-depth solution that encompasses all of the concepts outlined in this article, I strongly recommend looking at the “ Writing to Persuade and Influence Unit. ”
Working in partnership with Innovative Teaching Ideas , we confidently recommend this resource as an all-in-one solution to teach how to write persuasively.
This unit will find over 140 pages of engaging and innovative teaching ideas.
PERSUASIVE ESSAY WRITING CHECKLIST AND RUBRIC BUNDLE

The Ultimate Guide to Opinion Writing for Students and Teachers

Top 5 Persuasive Writing Techniques for Students

5 Top Persuasive Writing Lesson Plans for Students and Teachers

23 Persuasive writing Topics for High School students

How to Write an Advertisement: A Complete Guide for Students and Teachers

How to Start an Essay with Strong Hooks and Leads
- Chess (Gr. 1-4)
- TV (Gr. 1-4)
- Metal Detectors (Gr. 2-6)
- Tetris (Gr. 2-6)
- Seat Belts (Gr. 2-6)
- The Coliseum (Gr. 2-6)
- The Pony Express (Gr. 2-6)
- Wintertime (Gr. 2-6)
- Reading (Gr. 3-7)
- Black Friday (Gr. 3-7)
- Hummingbirds (Gr. 3-7)
- Worst Game Ever? (Gr. 4-8)
- Carnivorous Plants (Gr. 4-8)
- Google (Gr. 4-8)
- Honey Badgers (Gr. 4-8)
- Hyperinflation (Gr. 4-8)
- Koko (Gr. 4-8)
- Mongooses (Gr. 5-9)
- Trampolines (Gr. 5-9)
- Garbage (Gr. 5-9)
- Maginot Line (Gr. 5-9)
- Asian Carp (Gr. 5-9)
- Tale of Two Countries (Gr. 6-10)
- Kevlar (Gr. 7-10)
- Tigers (Gr. 7-11)
- Statue of Liberty (Gr. 8-10)
- Submarines (Gr. 8-12)
- Castles (Gr. 9-13)
- Gutenberg (Gr. 9-13)
- Author's Purpose Practice 1
- Author's Purpose Practice 2
- Author's Purpose Practice 3
- Fact and Opinion Practice 1
- Fact and Opinion Practice 2
- Fact and Opinion Practice 3
- Idioms Practice Test 1
- Idioms Practice Test 2
- Figurative Language Practice 1
- Figurative Language Practice 2
- Figurative Language Practice 3
- Figurative Language Practice 4
- Figurative Language Practice 5
- Figurative Language Practice 6
- Figurative Language Practice 7
- Figurative Language Practice 8
- Figurative Language Practice 9
- Figurative Language of Edgar Allan Poe
- Figurative Language of O. Henry
- Figurative Language of Shakespeare
- Genre Practice 1
- Genre Practice 2
- Genre Practice 3
- Genre Practice 4
- Genre Practice 5
- Genre Practice 6
- Genre Practice 7
- Genre Practice 8
- Genre Practice 9
- Genre Practice 10
- Irony Practice 1
- Irony Practice 2
- Irony Practice 3
- Making Inferences Practice 1
- Making Inferences Practice 2
- Making Inferences Practice 3
- Making Inferences Practice 4
- Making Inferences Practice 5
- Main Idea Practice 1
- Main Idea Practice 2
- Point of View Practice 1
- Point of View Practice 2
- Text Structure Practice 1
- Text Structure Practice 2
- Text Structure Practice 3
- Text Structure Practice 4
- Text Structure Practice 5
- Story Structure Practice 1
- Story Structure Practice 2
- Story Structure Practice 3
- Author's Purpose
- Characterizations
- Context Clues
- Fact and Opinion
- Figurative Language
- Grammar and Language Arts
- Poetic Devices
- Point of View
- Predictions
- Reading Comprehension
- Story Structure
- Summarizing
- Text Structure
- Character Traits
- Common Core Aligned Unit Plans
- Teacher Point of View
- Teaching Theme
- Patterns of Organization
- Project Ideas
- Reading Activities
- How to Write Narrative Essays
- How to Write Persuasive Essays
- Narrative Essay Assignments
- Narrative Essay Topics
- Persuasive Essay Topics
- Research Paper Topics
- Rubrics for Writing Assignments
- Learn About Sentence Structure
- Grammar Worksheets
- Noun Worksheets
- Parts of Speech Worksheets
- Punctuation Worksheets
- Sentence Structure Worksheets
- Verbs and Gerunds
- Examples of Allitertion
- Examples of Hyperbole
- Examples of Onomatopoeia
- Examples of Metaphor
- Examples of Personification
- Examples of Simile
- Figurative Language Activities
- Figurative Language Examples
- Figurative Language Poems
- Figurative Language Worksheets
- Learn About Figurative Language
- Learn About Poetic Devices
- Idiom Worksheets
- Online Figurative Language Tests
- Onomatopoeia Worksheets
- Personification Worksheets
- Poetic Devices Activities
- Poetic Devices Worksheets
- About This Site
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Use
- Understanding CCSS Standards
- What's New?
Ereading Worksheets
Free reading worksheets, activities, and lesson plans., site navigation.
- Learn About Author’s Purpose
- Author’s Purpose Quizzes
- Character Types Worksheets and Lessons
- List of Character Traits
- Differentiated Reading Instruction Worksheets and Activities
- Fact and Opinion Worksheets
- Irony Worksheets
- Animal Farm Worksheets
- Literary Conflicts Lesson and Review
- New Home Page Test
- Lord of the Flies Chapter 2 Worksheet
- Lord of the Flies Chapter 5 Worksheet
- Lord of the Flies Chapter 6 Worksheet
- Lord of the Flies Chapter 10 Worksheet
- Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass
- Sister Carrie
- The Count of Monte Cristo
- The Odyssey
- The War of the Worlds
- The Wizard of Oz
- Mood Worksheets
- Context Clues Worksheets
- Inferences Worksheets
- Main Idea Worksheets
- Making Predictions Worksheets
- Nonfiction Passages and Functional Texts
- Setting Worksheets
- Summarizing Worksheets and Activities
- Short Stories with Questions
- Story Structure Activities
- Story Structure Worksheets
- Tone Worksheets
- Types of Conflict Worksheets
- Reading Games
- Figurative Language Poems with Questions
- Hyperbole and Understatement Worksheets
- Simile and Metaphor Worksheets
- Simile Worksheets
- Hyperbole Examples
- Metaphor Examples
- Personification Examples
- Simile Examples
- Understatement Examples
- Idiom Worksheets and Tests
- Poetic Devices Worksheets & Activities
- Alliteration Examples
- Allusion Examples
- Onomatopoeia Examples
- Onomatopoeia Worksheets and Activities
- Genre Worksheets
- Genre Activities
- Capitalization Worksheets, Lessons, and Tests
- Contractions Worksheets and Activities
- Double Negative Worksheets
- Homophones & Word Choice Worksheets
- ‘Was’ or ‘Were’
- Simple Subjects & Predicates Worksheets
- Subjects, Predicates, and Objects
- Clauses and Phrases
- Type of Sentences Worksheets
- Sentence Structure Activities
- Comma Worksheets and Activities
- Semicolon Worksheets
- End Mark Worksheets
- Noun Worksheets, Lessons, and Tests
- Verb Worksheets and Activities
- Pronoun Worksheets, Lessons, and Tests
- Adverbs & Adjectives Worksheets, Lessons, & Tests
- Preposition Worksheets and Activities
- Conjunctions Worksheets and Activities
- Interjections Worksheets
- Parts of Speech Activities
- Verb Tense Activities
- Past Tense Worksheets
- Present Tense Worksheets
- Future Tense Worksheets
- Point of View Activities
- Point of View Worksheets
- Teaching Point of View
- Cause and Effect Example Paragraphs
- Chronological Order
- Compare and Contrast
- Order of Importance
- Problem and Solution
- Text Structure Worksheets
- Text Structure Activities
- Essay Writing Rubrics
- Narrative Essay Topics and Story Ideas
- Narrative Essay Worksheets & Writing Assignments
- Persuasive Essay and Speech Topics
Persuasive Essay Worksheets & Activities
- Writing Narrative Essays and Short Stories
- Writing Persuasive Essays
- All Reading Worksheets
- Understanding Common Core State Standards
- Remote Learning Resources for Covid-19 School Closures
- What’s New?
- Ereading Worksheets | Legacy Versions
- Online Figurative Language Practice
- Online Genre Practice Tests
- Online Point of View Practice Tests
- 62 School Project Ideas
- 2nd Grade Reading Worksheets
- 3rd Grade Reading Worksheets
- 4th Grade Reading Worksheets
- 5th Grade Reading Worksheets
- 6th Grade Reading Worksheets
- 7th Grade Reading Worksheets
- 8th Grade Reading Worksheets
- 9th Grade Reading Worksheets
- 10th Grade Reading Worksheets
- Membership Billing
- Membership Cancel
- Membership Checkout
- Membership Confirmation
- Membership Invoice
- Membership Levels
- Your Profile
Want Updates?
84 comments.
Thank you so much. This has truly helped me in my exams and throughout the beneficial journey of my school year.
Ellen Davis
How will I be able to check my work, when I print it out to work on them? Where are the answers?
I guess it depends on what you are working on. On what are you working?
Kareema Coles
Ummm the pdf version is not working…is the link still valid?
Which link?
This is an amazing website with fabulous ideas and printable ready to go lessons!!! Thank you so much! I wish I could meet you!!!
Thank you very much for this amazing resource and great ideas. They are extremely comprehensive and well designed. Thank you very much for your kind consideration and not adding a Price-tag to your valuable resources. Highly appreciated.
Sandra Conner
Thank you so much for sharing your knowledge and your work with us. As teachers, we are always in need of fresh material. I teach college level creative writing classes, and your worksheets help my students. Sometimes I change the essay topics to fit their particular age group or interest, but having these examples laid out for us and made available for use in our classrooms is wonderful.
Lifesaver! Thank you for the great ideas and guidance. I am a new teacher, and finding this site has made a true turn around in my instruction. Thank you, thank you, thank you!!!
Thank you for these great step by step resources
Macca Malbrán
Despite all the negative comments above, you should keep up for the ones (like me) who are absolutely grateful for these material.
Thanks for sharing! Best.
I give this website 3stares only for the info but in general 1star
I give your comment 0 stars because your position lacks support or evidence of any kind. Complete some of these worksheets and begin your argument again.
that’s stupid from where do u get the worksheets
I wrote them.
I did not see any activities that required the student to write an entire essay.
https://www.ereadingworksheets.com/writing/persuasive-essay-topics/
Lamar Mohamed
Thank you for this information! They helped me in my exam so much!
These are fantastic resources! Thank you so much for sharing them. I only wish I had found them earlier in the school year!
There’s always next year…
Thank you so much for all you do for teachers. I love an use practically everything on your Website!
That’s awesome. Thanks for visiting my website.
I really like this website
Shenard McDougal
How can a teacher get the answers to the worksheets?
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Subscribe Now
Popular content.
- Author's Purpose Worksheets
- Characterization Worksheets
- Common Core Lesson and Unit Plans
- Online Reading Practice Tests
- Plot Worksheets
- Reading Comprehension Worksheets
- Summary Worksheets
- Theme Worksheets
New and Updated Pages
- Capitalization Worksheets
- Contractions Worksheets
- Double Negatives Worksheets
- Homophones & Word Choice Worksheets
BECOME A MEMBER!
- Primary Hub
- Art & Design
- Design & Technology
- Health & Wellbeing
- Secondary Hub
- Citizenship
- Primary CPD
- Secondary CPD
- Book Awards
- All Products
- Primary Products
- Secondary Products
- School Trips
- Trip Directory
- Trips by Subject
- Trips by Type
- Trips by Region
- Submit a Trip Venue
Trending stories

Top results

- Persuasive Writing Worksheets And Resources For Ks3 And Ks4 English
Persuasive writing techniques – Best resources & advice for KS3/4

Whether they're arguing for a good cause or selling the latest product, give your secondary students all the techniques and tricks they need to be able to write to persuade…

Effective communication skills are vital for life. What better way to empower your students than by helping them to master a range of persuasive writing techniques?
Here we embark on an exploration of engaging resources and valuable advice to transform your classroom into a hub of compelling arguments and articulate expression. (We also have a round-up of persuasive writing KS2 resources .)
Persuasive writing techniques resources
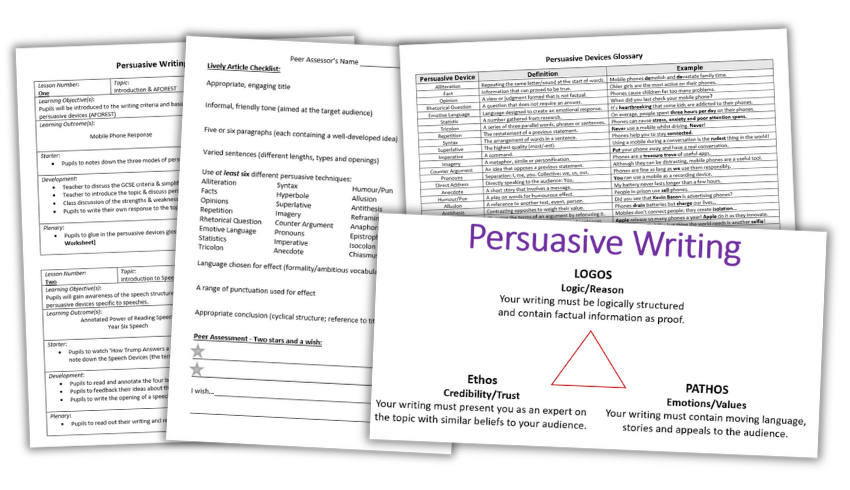
10 tips for better persuasive writing, persuasive writing full scheme of work.
This free persuasive writing scheme for KS3/4 by teacher James Tickle contains 17 lessons’ worth of material. It covers speeches, informal and formal letters, articles and more…
Write a letter of complaint
The GCSE syllabus encourages pupils to craft their writing to be imaginative and engaging. However, inspiring pupils to write a lively personal response can be a real challenge.
So, how can we enthuse our young people? Encourage teenagers to do what they do best: complain. This free lesson plan will encourage pupils to write a sophisticated, engaging, witty and highly persuasive protest worthy of a grade 9.
Persuasive writing techniques handout
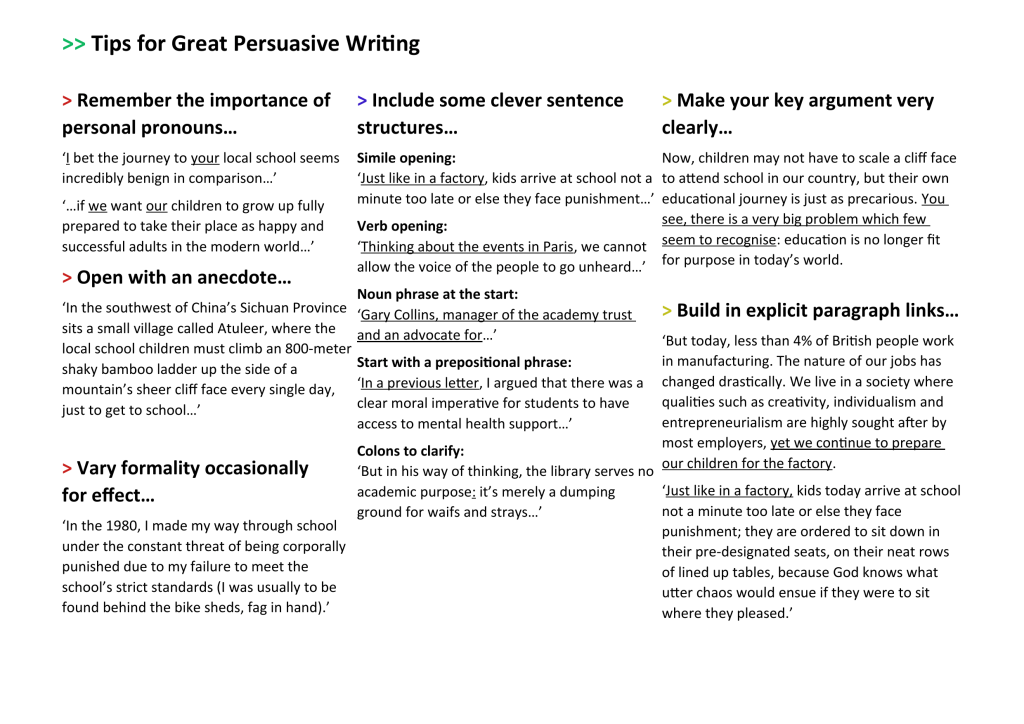
Print out this free handout and give it to your pupils to help them improve their use of persuasive writing techniques. It covers opening with an anecdote, including some clever sentence structures and more.
Charlie Chaplin’s The Great Dictator

How can Charlie Chaplin help students to become persuasive and voice their emotions? This free lesson plan looks at how he can help students to create a piece of persuasive writing. You can also easily adapt it for teaching descriptive, narrative and argumentative styles.
Persuasive techniques slideshow

This Slideshare presentation offers a great introduction to persuasive writing and its concepts and terms for students.
Persuasion techniques
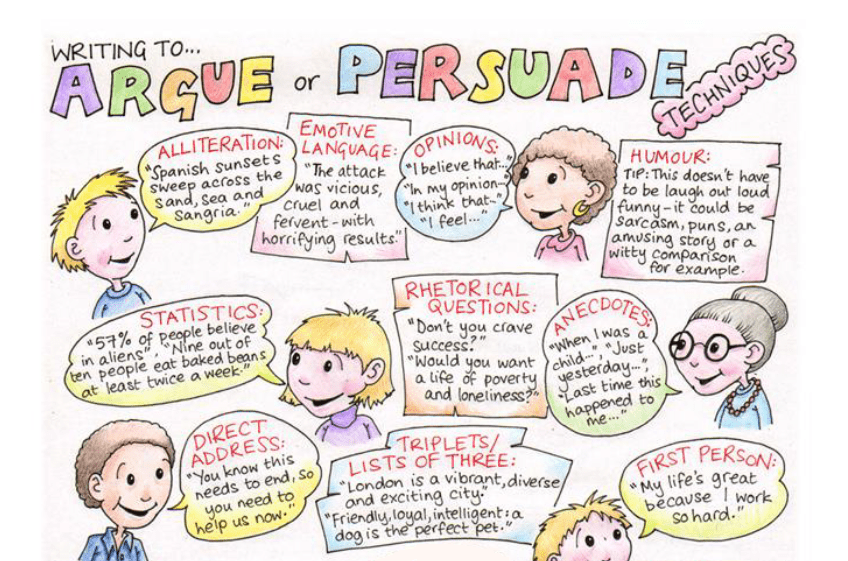
This handy printable PDF is packed with persuasive writing techniques. It will serve as a great introduction or reminder for your pupils.
It’s got everything from alliteration to hyperbole, and imperatives to repetition, all wrapped up with succinct descriptions and definitions.
Suffragettes and votes
This Votes for Women video and resource pack from UK Parliament contains activity ideas including a persuasive letter writing exercise. Pupils need to write a letter from an imprisoned Suffragette to their sibling. In it, they need to explain why they are willing to go to prison for their cause.
Influencing world leaders

This lesson plan is part of a range of free resources produced for Send My Friend to School. This is the schools activity of the UK Global Campaign for Education. It asks world leaders to keep their promise to get all children into school.
The main task for students is to write a letter persuading someone with influence to support the rights of all children to get an education. The resource includes activities, discussion points, and two example letters.

Students’ responses to persuasive writing assignments can become more considered and compelling by observing some key techniques, says Anthony Cockerill…
Throughout my teaching career, I’ve found that there’s a handful of topics for class discussion that never fail to get students to participate enthusiastically. Somewhat surprisingly, one of those is the topic of education itself.
I wanted to capitalise on my students’ eagerness to thrash out the pluses and minuses of their own experiences of schooling, and to teach them the process of planning, drafting and editing a piece of persuasive writing.
I also wanted to establish some maxims for great writing, without imposing a rigid framework or a list of success criteria.
To produce what AQA calls ‘ An enabling, provocative … controversial statement ’ to prompt students into writing a response offering their own viewpoint, I came up this: ‘Education is no longer fit for purpose’. This, I reasoned, could be a persuasive writing firecracker.
The following suggestions draw on my experiences of teaching what I eventually called ‘The Big School Debate’, though I’m sure you’ll also find them useful when applied to a topic of your choosing.
1 | Encourage students to plan broadly and gather ideas
Emphasise to students that to sustain their argument throughout the writing, they should develop a central idea and select reasons to support it. Examiners’ reports are clear that a crafted argument is crucial for success.
After screening stimulus material ranging from Sir Ken Robinson’s ‘Changing Paradigms’ lecture at the RSA and a Good Morning Britain interview with Katharine Birbalsingh, I fielded a classroom discussion in which I encouraged everyone to develop an individual response to the aforementioned controversial statement and to gather ideas in the form of a mind-map.
2 | Model the sequencing and structuring
I then gathered the students’ ideas into a series of on-screen text boxes to model how we might structure and sequence their ideas most powerfully.
Should we start with the strongest ideas first? Would the argument lose momentum this way? What about starting with the weakest ideas and building momentum as we go? What if we were to cluster them by theme?
The idea of clustering the ideas topically seemed like a sensible idea, but I suggested an alternative approach – grouping ideas by which mode of Aristotelian rhetoric they most suited.
A student proposed that in order to sustain powerful momentum throughout, we could open with the ‘ethos’ of the argument to establish a sense of virtue, followed by the ‘logos’ of the argument (an appeal to the reader’s sense of logic).
Last would be the ‘pathos’ of the argument, appealing to the reader’s emotions and contriving a powerful and lasting impact towards the end of the text.
3 | Open with an anecdote
A student in my class with an enviable grasp of writing to argue came up with this brilliant way to begin his piece:
‘ In the southwest of China’s Sichuan Province sits a small village called Atuleer, where the local schoolchildren must climb an 800m shaky bamboo ladder up the side of a mountain’s sheer cliff face every single day, just to get to school. ’
Another student who felt particularly strongly about school uniform produced a rather lacklustre opening, which contained the usual statistics about how many students in one school were sent home in the first week of term for flouting the rules.
But after reflecting on the importance of an immersive anecdote, she retooled it: ‘ Doting mum Julie Fowler had only just arrived at work when the telephone call came… ’
4 | Build explicit paragraph links to show visible cohesion
Students often productively employ the usual suspects, such as conjunctions or adverbials of time, within their writing. Another device that works really well is the explicit paragraph link, in which a motif or phrase in the last sentence of a paragraph is repeated in the first sentence of the next paragraph.
‘We live in a society where qualities such as creativity, individualism and entrepreneurialism are highly sought after by most employers, yet we continue to prepare our children for the factory,’ read the end of one student’s paragraph.
The next began: ‘Just like in a factory, kids today arrive at school not a minute too late or else they face punishment.’
This technique can help students employ much more bespoke and effective ways of linking ideas than the ubiquitous ‘Firstly… Secondly… Furthermore…’ approach.
5 | Emphasise the importance of personal pronouns
Students can create a rapport with the reader by addressing them directly. ‘We want our children to grow up fully prepared to take their place as happy and successful adults,’ wrote one student.
In this example, the first-person plural pronoun ‘we’ creates a sense of shared purpose and values, and also makes an assumption that the reader has already assented to the argument.
6 | Adopt the ‘tone’ of the powerful
The discourse of persuasion is the discourse of power. There are several gains a student might make in their own persuasive writing by ‘borrowing’ from powerful language.
I shared some examples from The Guardian , including the use of inverted commas to cast aspersions upon an idea, and posing a question immediately followed with a resoundingly clear answer.
I also encouraged my students to experiment with Latin connectives, such as ‘ergo’, ‘ad nauseam’ and ‘in perpetuum’ to suggest a sense of gravitas and bestow a high status ‘persona’ upon the writer.
7 | Experiment with sentence structures to showcase high-order thinking
Particular sentence structures can allow students to showcase sophisticated thinking. Subordinating conjunctions such as ‘however’ can allow a student to rebuff a counterargument, as can the preposition ‘despite’.
A student might use conjunctions such as ‘because’ and ‘since’ to demonstrate reasoning. Opening a sentence with a simile demonstrates understanding of loaded language.
8 | Change the level of formality for emphasis
A student might use parenthetical brackets to incorporate an informal joke or aside into their response. This can work extremely well, as the juxtaposition of humour or self-deprecation with the formal tone of argument can be an extremely sophisticated persuasive technique that gets the reader on side.
‘In the 1980s,’ wrote one student, ‘I made my way through school under the constant threat of being corporally punished, due to my failure to meet the school’s strict standards (I was usually to be found behind the bike sheds, fag in hand).’
I thought this student used a parenthetical aside to great effect. I also loved the way they adopted a ‘persona’ as part of their writing.
9 | Ensure students make thrifty use of persuasive devices
It’s important to ensure students don’t liberally scatter their responses with rhetorical devices.
Similarly, responses structured around mnemonics like DAFOREST can feel artificial and constrained.
Examiners’ reports are clear that a sustained argument should be led by the deeper structures of the argument itself, rather than simply signposted by persuasive devices.
10 | Write less, craft more
One student initially wrote over 2,000 words. The piece digressed at length about the merits of the education system in Finland, and in doing so really lost sight of the central thesis.
After cutting it down considerably, the student was still grappling with an overly long and unwieldy piece of writing. Offering verbal feedback as I sat with the student at a computer we pruned it brutally, then went back to edit and craft some more.
Anthony Cockerill is Head of English at Boroughbridge High School, North Yorkshire; for more information, visit anthonycockerill.com or follow @thecockerill .
Sign up to our newsletter
You'll also receive regular updates from Teachwire with free lesson plans, great new teaching ideas, offers and more. (You can unsubscribe at any time.)
Which sectors are you interested in?
Early Years
Thank you for signing up to our emails!
You might also be interested in...
Why join Teachwire?
Get what you need to become a better teacher with unlimited access to exclusive free classroom resources and expert CPD downloads.
Exclusive classroom resource downloads
Free worksheets and lesson plans
CPD downloads, written by experts
Resource packs to supercharge your planning
Special web-only magazine editions
Educational podcasts & resources
Access to free literacy webinars
Newsletters and offers
Create free account
I would like to receive regular updates from Teachwire with free lesson plans, great new teaching ideas, offers and more. (You can unsubscribe at any time.)
By signing up you agree to our terms and conditions and privacy policy .
Already have an account? Log in here
Thanks, you're almost there
To help us show you teaching resources, downloads and more you’ll love, complete your profile below.
Welcome to Teachwire!
Set up your account.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet consectetur adipisicing elit. Commodi nulla quos inventore beatae tenetur.

Log in to Teachwire
Not registered with Teachwire? Sign up for free
Reset Password
Remembered your password? Login here

Persuasive Essay Guide
Persuasive Essay Examples
30+ Free Persuasive Essay Examples To Get You Started

People also read
A Comprehensive Guide to Writing an Effective Persuasive Essay
200+ Persuasive Essay Topics to Help You Out
Learn How to Create a Persuasive Essay Outline
Read Excellent Examples of Persuasive Essay About Gun Control
How to Write a Persuasive Essay About Covid19 | Examples & Tips
Crafting a Convincing Persuasive Essay About Abortion
Learn to Write Persuasive Essay About Business With Examples and Tips
Check Out 12 Persuasive Essay About Online Education Examples
Persuasive Essay About Smoking - Making a Powerful Argument with Examples
Are you looking to improve your persuasive writing skills?
One of the best ways to do that is by reading persuasive essay examples. These examples can show you how to structure your arguments effectively.
But finding good examples can be a challenge. Don't worry, though – we've gathered some helpful persuasive essays for you right here!
So, if you're in search of persuasive essay examples to help you write your own, you're in the right place.
Keep reading this blog to explore various examples
- 1. Persuasive Essay Examples For Students
- 2. Persuasive Essay Examples for Different Formats
- 3. Persuasive Essay Outline Examples
- 4. Persuasive Essay Format Example
- 5. How to Write A Persuasive Essay With Examples
- 6. How to End a Persuasive Essay Examples
- 7. Catchy Persuasive Essay Topics
Persuasive Essay Examples For Students
A persuasive essay aims to convince the reader of the author’s point of view.
To find the right path for your essay, it's helpful to go through some examples. Similarly, good essay examples also help to avoid any potential pitfalls and offer clear information to the readers to adopt.
Here are some persuasive essay examples pdf:
3rd-grade Persuasive Essay Example
4th-grade Persuasive Essay Example
Persuasive Essay Example 5th-grade pdf
Persuasive Essay Examples for 6th Grade pdf
7th-grade Persuasive Essay Example
8th-grade Persuasive Essay Example
Persuasive Essay Examples Grade 10
11th-grade Persuasive Essay Example
Persuasive Writing Example For Kids
Persuasive Essay Examples High School
The following are good persuasive essay examples for high school. Having a look at them will help you understand better.
High-school Persuasive Essay Example
Examples of Persuasive Essay in Everyday Life
Persuasive Essay Examples for Middle School
Check out these persuasive essay examples for middle school to get a comprehensive idea of the format structure.
Persuasive Essay Examples Middle School
Short Persuasive Essay Example
Persuasive Essay Examples for College Students
Essay writing at the college level becomes more difficult and complicated. We have provided you with top-notch college persuasive and argumentative essay examples here.
Read them to understand the essay writing process easily.
Persuasive Essay Examples College
Higher English Persuasive Essay Example
Persuasive Essay About Smoking
Argumentative and Persuasive Examples
Persuasive Essay Examples For University
It becomes even more challenging to draft a perfect essay at the university level. Have a look at the below examples of a persuasive essay to get an idea of writing one.
University Persuasive Essay Example
5 Paragraph Persuasive Essay Example
Persuasive Essay Examples for Different Formats
A persuasive essay can be written in several formats. For instance, you can write the usual 5-paragraph essay, or even something longer or shorter.
Below are a few sample essays in various common formats.
Persuasive Essay Examples 5 Paragraph
Persuasive Essay Examples 3 Paragraph
Short Persuasive Essay Examples
These examples tell you how to remain convincing and persuasive regardless of the essay format you use.
Persuasive Essay Outline Examples
Creating an impressive outline is the most important step for writing a persuasive essay. It helps to organize thoughts and make the writing process easier.
A standard outline consists of the following sections.
- Introduction
- Body Paragraphs
Have a look at the following persuasive essay outline template examples.
Persuasive Essay Outline
Persuasive Essay Template
Persuasive Essay Format Example
A persuasive essay outline is bound to follow a specific format and structure. The main elements of a persuasive essay format are as follows.
- Font: Times New Roman, Georgia, or Arial
- Font Size: 16pt for the headlines and 12pt for the rest of the text
- Alignment: Justified
- Spacing: Double spacing
- Word Count: It usually contains 500 to 2000 words
How to Write A Persuasive Essay With Examples
Planning an essay before starting writing is essential to produce an organized and structured writing piece. So, it is better to understand the concept beforehand to impress your instructor.
The below example will show a good starting to an essay.
A Good Start for a Persuasive Essay - Short Example
How to Start a Persuasive Essay Examples
The introduction is the first part of an essay and your first chance to grab the reader's attention. It should clearly state the essay's purpose and give the reader a clear idea of what to expect.
A compelling persuasive essay introduction must have the following elements.
- Hook statement + topic
- A strong thesis statement
- Your arguments
Here are some examples of persuasive essay introductions to help you make a compelling start:
Introduction Persuasive Essay Example
Persuasive Essay Thesis Statement Examples
Persuasive Essay Hook Examples
How to End a Persuasive Essay Examples
Just like the introduction, the conclusion of the persuasive essay is equally important. It is considered as the last impression of your writing piece to the audience.
A good conclusion paragraph must include the following aspects.
- Restate the thesis statement or hypothesis
- Summarize the key arguments
- Avoid being obvious
- Include a call to action
Have a look at the document to explore the sample conclusions of a persuasive essay.
Conclusion Persuasive Essay Examples
Catchy Persuasive Essay Topics
Now that you have read some good examples, it's time to write your own persuasive essay.
But what should you write about? You can write persuasive essays about any topic, from business and online education to controversial topics like abortion , gun control , and more.
Here is a list of ten persuasive essay topics that you can use to grab your reader's attention and make them think:
- Should the government increase taxes to fund public health initiatives?
- Is the current education system effective in preparing students for college and the workplace?
- Should there be tighter gun control laws?
- Should schools have uniforms or a dress code?
- Are standardized tests an accurate measure of student performance?
- Should students be required to take physical education courses?
- Is undocumented immigration a legitimate cause for concern in the United States?
- Is affirmative action still necessary in today’s society?
- How much, if any, regulation should there be on technology companies?
- Is the death penalty an appropriate form of punishment for serious crimes?
Check out two examples on similar topics:
Political Persuasive Essay Examples
Persuasive Essay Examples About Life
Need more topic ideas? Check out our extensive list of unique persuasive essay topics and get started!
But if you're still feeling stuck, don't worry. Our persuasive essay writing service is here to the rescue!
Our experienced writers specialize in creating top-notch essays on a wide range of topics. Whether it's a challenging persuasive essay or any other type, we've got you covered.
Take advantage of our reliable essay writing service today!

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Caleb S. has been providing writing services for over five years and has a Masters degree from Oxford University. He is an expert in his craft and takes great pride in helping students achieve their academic goals. Caleb is a dedicated professional who always puts his clients first.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading

VCE Study Tips
English Language

Private Tutoring

Only one more step to getting your FREE text response mini-guide!
Simply fill in the form below, and the download will start straight away
English & EAL
The Ultimate Guide to Year 9 English
November 2, 2021

Want insider tips? Sign up here!
Go ahead and tilt your mobile the right way (portrait). the kool kids don't use landscape....
1. What’s the Difference Between Year 9 English and Year 7/8 (Junior years)? 2. What Are You Expected To Cover in Year 9? 3. Assessments and Exams 4. How To Prepare for the Assessments and Exams
Did you know that when you finish high school and you decide to apply for a part time job, you’re expected to recite every single essay you’ve ever written word for word?
Alright, you got me, I’m kidding!
You may be wondering why is the subject English mandatory? What’s the point of it? When am I ever going to apply the skills I’ll learn in English in real life?
Yes, math, science and even humanities subjects may have more apparent skill transfer to careers like medicine, politics and engineering, but the soft skills that many employers are after these days (such as strong communication skills and confident presentation skills) will develop as you continue with your English studies. And yes, if you plan on being a business owner, these skills are all the more important!
Of course, post-high school won’t involve writing essays and responding to essay topics but they help you build your critical thinking, creativity and understanding intentions (why people do what they do).
These skills will be extremely valuable to you regardless of the path you choose to pursue in life.
Let’s get straight into the nitty gritty of things then...
1. What’s the Difference Between Year 9 English and Year 7/8?
Achievement standards in the Victorian Curriculum from Years 7-9 build upon each other, and the skills learnt during the junior years will be expanded on in Year 9.
In Year 7 , students will be introduced to different text structures (novels, opinion pieces, editorials, speeches, etc.) and focus primarily on the audience, purpose and context of using these text structures.
You would have had the opportunity to:
- Explain ideas and issues explored in your texts (e.g. happiness, relationships, conflict, etc.)
- Begin looking at the implied meaning of evidence in your texts (this means forming your own interpretation of what you think the author is trying to say through characterising certain characters the way they are, or through the use of certain symbols, quotes, etc.)
The writing standard predominantly draws from:
- A mixture of your own personal knowledge and experiences
- Researched sources, such as news articles, reviews, etc.
- Your own analysis of the assigned texts (usually linking your analysis to a prompt)
Building on the grammatical and foundational writing skills taught in primary school, Year 7 students will need to apply them when writing and editing their work.
Year 8 English develops the students' critical thinking a bit more. You would have been expected to:
- Interpret assigned texts, ' questioning the reliability of sources of ideas and information ' (know that some texts you will come across may be biased and only expose one side of the argument)
- Make judgments about the effectiveness of language choices used by creators
- Understand how specific and selective choices of language are used by creators for different effects and purposes (be able to explain your reasoning as to how the conventions of language features used by an author enhance their point of view)
Year 9 English takes the previous two years’ worth of skills even further. This year you will be expected to:
- Analyse the ways in which different ' text structures can be manipulated for effect '
- Evaluate and integrate ideas from your assigned texts to create your own interpretations
- Realise the importance of planning before writing as well as the need for the drafting process in order to produce A+ level work (an introduction to writing will be provided)
- Be exposed to a wider range of forms of text compared to the junior years which are mainly novels and films
- Extend your lists of vocabulary and techniques
2. What Are You Expected To Cover in Year 9?
One of the most important skills needed in English is being able to write an analytical essay. This entails presenting an argument about your prompt based on your assigned texts. To do this well, you will need to discuss characters, literary features, structure, themes and big ideas .
The point of the analytical essay is for you to demonstrate your ability to analyse the evidence you choose to incorporate into your essay while linking it back to the idea you’re exploring in the body paragraph. One way to approach this is to provide your own interpretation of evidence.
This will be elaborated on with examples below.
Structure is also just as important as the content when writing an English essay. Most of the time, particularly in Year 9, your teacher will provide you with a specific structure to follow. This tends to include:
- An introduction (100 words)
- 3x body paragraphs (200 words each)
- A conclusion (50-100 words)
The amount of detail you include in each of your paragraphs will increase over the years. Once you reach Year 12, your essay will sit roughly around the 1000 words mark. For now, try to aim to write around 800 words. Just remember that quality always supersedes quantity . Ensure that the 800 words you write have relevance and are not just word vomit on a page.
The Introduction
Think of the introduction as a to-do list. You can always refer back to it to remind yourself of the points you need to cover and it will keep you on track so you don’t sway from the prompt in your essay. Your introduction sets the scene for the reader. All you have to do is introduce your overall stance (contention) and your three main points (arguments) you want to unpack in the essay. In some cases, teachers would also prefer for you to add in an introduction to the text(s) you’re studying and provide some background information or an overview of the text’s social or historical context.
The Body Paragraph
The most important components of your essay are the body paragraphs. That is where the bulk of your marks will come from - your analysis! Different schools have different acronyms they may follow for their body paragraphs, but the most common one is TEEL.
- T opic Sentence
- E xplanation
As you move up into Year 10, 11 and 12, many schools will extend the acronym to TEEEEEL , meaning that you will be expected to expand on the level and depth of your analysis.
Let’s break up TEEL a bit more…
‘T’ - Topic Sentence
Your topic sentence should support your stance (contention). Your contention should answer the prompt or topic, and your arguments (which form the basis for your topic sentences) should provide a reason for your stance . Because of this, your topic sentence should directly answer the prompt.
Examples of topic sentences include:
- 'Orwell indicates that for goals to be achieved, teamwork and cooperation among everyone involved will be necessary.' - taken from a Text Response Essay based on George Orwell’s Animal Farm
- The author portrays kindness and understanding as key factors that contribute to successful relationships.
‘E’ - Evidence
Most of the time, the evidence you embed into your body paragraphs will be in the form of quotes from the text . High scoring responses will also analyse evidence such as camera angles (film) or narrative conventions (novels).
Embedding quotes doesn’t always come easy to every student. Preferably, the quote you embed into your analysis will be no more than 10 words and no less than 2 words.
Rules to keep in mind when you incorporate a quote into your writing:
- Avoid using a quote to form the whole sentence.
- Don’t begin a sentence with a quote
- Single word quotes should rarely be used. They should only appear in your analysis if you’re exploring a unique, big idea that is conveyed by that one word.
- Use square brackets ‘[ ]’ if you want to change up the quote
It would be helpful to embed the quote into context first as this will help when you’re explaining its relevance to the idea you’re exploring in the body paragraph.
For Example:
Parallels can be drawn to the ways in which the pigs in the farm have the role of organisers 'naturally [fall] upon' them. Here, the pigs are portrayed as 'the cleverest of the animals', suggesting that they are the leaders who make the decisions on behalf of everyone…
- taken from a Text Response Essay based on George Orwell’s Animal Farm
‘E’ - Explanation
Listing all the quotes you can memorise from the text is not going to get you the marks. You need to analyse the quotes you embed and share your interpretation of the meaning they add to the idea you’re exploring.
Similar to math, where you need to show all the steps to prove that you know how to get the right answer, in English, the ‘explanation’ section is your opportunity to do just that. You need to explain your thought process regarding how you have reached this conclusion or interpretation.
Can you pinpoint the differences between the low-scoring response and the high-scoring response below?
Low-Scoring Example:
Big Brother’s lack of compassion is evident through its elimination of personal relationships between the Party members. A marriage is always refused 'if the couple concerned gave the impression of being physically attracted to one another'. This means that the institution of marriage has been manipulated to only serve Big Brother.
- taken from LSG’s How To Write A Killer Text Response study guide
High-Scoring Example:
The distortion of family relationships highlights the cruelty of Big Brother’s institution. Children are taught from an early age to be ‘spies’ for Big Brother. The children symbolise the eyes of Big Brother, as they are always watching members for 'any sign of betrayal to the Party'. Ironically, although Winston believes that 'another year, two years, and they (the children) will be watching (the mother) night and day for signs of unorthodox', it is shown soon after that the father, Parsons, is denounced for 'thoughtcrime'. *** Through this condemnation of their own father, the children also symbolise the destruction of family relationships in return for their loyalty to Big Brother. This unnerving vision of a complete disposal of relationships depicts how brutal a totalitarian society can be for its members in that the very fundamentals of human connection, such as love and family, are corrupted .***
- taken from LSG’s How To Write A Killer Text Response study guide*
***The ‘explanation’/analysis is located between the asterisks.
The linking sentence is the last sentence of your body paragraph and it should always ‘link’ back to the main idea you have explored (topic sentence) as well as the prompt. Avoid merely rewording your topic sentence, and a hint to do this well is to refer to the creator’s intent .
- 'Ultimately, the loss and alteration of meaning within marriage and sex demonstrates how brutal a dystopian society can be for individuals, and as Orwell forewarns, can be the destruction of humanity itself.' - taken from LSG’s How To Write A Killer Text Response study guide
- 'Orwell cautions his readers to be wary of societies such as the Big Brother regime by portraying the cruelty of the Party’s actions.' - taken from LSG’s How To Write A Killer Text Response study guide
Check out our video, ' What do year 9s learn in English? ' for a more in depth look at what's expected of you this year!
3. Year 9 Assessments and Exams
In Year 9, this is where you will gain exposure to an array of forms of texts, ranging from creative responses, speeches, analytical essays, film, poetry and persuasive pieces.
Throughout the year, you will study a range of different texts (the ones mentioned above) and the activities and assessment tasks you will receive will be based on these texts.
Generally, by the end of Year 9, you will have completed:
- A creative response,
- A persuasive essay (formatted as an opinion piece, editorial, or letter to the editor),
- An oral presentation about a particular issue,
- A film analysis , and/or
- An analytical essay based on a play, novel or poems
Throughout the year, you may receive different types of classwork, depending on your teacher. These may include:
- Performances
- Group presentations
- Comprehension questions
- Practise essays/paragraphs
- And so much more!
4. How To Prepare for the Assessments and Exams in Year 9?
Practise, practise, practise!
One of our most common sayings at LSG is 'study smarter, not harder'. This means knowing where your weaknesses lie and doing what you must to improve upon them. Don’t stick to your comfort zone too much - allow yourself to do the unfamiliar enough times to make it familiar. This will also help you build confidence within yourself when you see the progress you make.
Here are a couple of tips for you to help you prepare for any upcoming assessments and exams like an A+ student:
Reading more than your assigned texts can help you improve your spelling, vocabulary and expression when writing! The more you read, the more knowledge you will gain about fluency and structure. I would recommend reading widely. This means not confining your reading to just purely manga, but also newspaper articles, novels, non-fiction texts, etc.
If you want to become an expert on the text you’re studying and stand out from the rest of your classmates when you get to essay writing, read more about your text. This can include reading up on the background of the author who wrote the text, investigating the social, historical and cultural context of the text. Study guides, interviews, reviews and sample high scoring essays around the text are also very helpful resources!
Drafting and Essay Feedback
Drafting and getting essay feedback is an important cycle to come back to for the remainder of your high school career.
Going back to what I have just said, practise is key to success in English. English is often deemed to be one of the most confusing subjects because many students claim it to be subjective and will often complain that they have no idea what they’re doing. Generally, this isn’t a good sign. We understand that it can be difficult to know whether you’re on the right track or not, but it’s important we don’t just sit there and wonder the whole time. We must also seek feedback from our teachers or tutors about ways we can improve our work.
Upon receiving feedback from our teachers or tutors, we can’t just stop there. We must also incorporate this feedback into our re-draft or finalised copy of the work. Any questions or confusion must be addressed during this stage so you know exactly what to do next time.
At LSG, we have high-quality tutors who have received the marks you’re after and can walk you through your high school English journey.
What will we offer you?
- Regular English advice and support (whether that is homework help, essay feedback or if you just want to go the extra mile and get ahead with your English studies)
- A specialised LSG Signature Program that can cater to your goals and help you develop the knowledge and get all the consistent writing practise you need
- Guidance as we work through the necessary writing skills and strategies that will get you the A+ you desire
- Access to exclusive LSG resources that will save you time creating your own notes (planning and writing templates, sample high-scoring essays and so much more!)
If you want more information on why you should pick us, check out our tutoring page . Otherwise, click here to express your interest today!
Get our FREE VCE English Text Response mini-guide
Now quite sure how to nail your text response essays? Then download our free mini-guide, where we break down the art of writing the perfect text-response essay into three comprehensive steps. Click below to get your own copy today!

You're not alone. We're here with you.
We're here to support you. To learn more about Lisa's Study Guides' Private Tutoring, click on the button below!
.png)
Plans are one of the most ignored (and underestimated) steps in the essay writing process. Some people don’t do them simply because they don’t want to, some sacrifice them because they think they’ll run out of time, and some do ‘plans’, but in reality, they’re only a rough mental outline. Each of these situations place too many students time and time again in sticky situations come an English SAC or exam.
Why plans are essential for any good essay
- They ensure that you can’t mind blank — it’s all on the paper in front of you!
- They ensure that you always stay on topic.
Mental plans or not having a plan at all mean that you don’t have a true direction in which your essay is going. If you’re not sure where you’re going, well, how are you going to get anywhere?
They save you time in writing time.
Instead of wasting reading time, you’ve done most of your thinking right at the beginning of the SAC or exam, positioning you to do really well in your essay because you can focus on constructing some really juicy, coherent analysis in your body paragraphs, rather than remembering your basic points and/or making sure your essay is actually answering the question.
Let’s have a look at an essay topic that I’ve tackled in the past. This one is based on Kate Grenville’s The Lieutenant , a current VCE Year 12 English text. To learn more about themes, quotes, characters about this text, and to have a look at an essay topic breakdown, check out this blog post written by outstanding LSG tutor, Angelina !
“But a man could not travel along two different paths.” How does Grenville explore Rooke’s conflict of conscience in The Lieutenant ?
Step 1: Highlight key words

Now, it may seem like I've just highlighted the whole prompt, and I understand why you might think that! However, each of the words highlighted convey something meaningful within the prompt. If you're ever unsure about what could be considered a key word, consider whether the prompt would have the same meaning without the word in question.
Step 2: Define key words
In this topic, the main phrase that needs defining is ‘conflict of conscience’. For me, this signals that we must consider morality and the weighing up of right and wrong, especially when tough decisions have to be made.
I’d also take a moment to analyse the quote. This essay prompt is quote-based, so it’s imperative that we discuss the quote and consider the meaning of the quote throughout our essay. For some more detailed info on how to tackle different types of essay prompts, check out this blog post.
Step 3: Start essay plan
Next, I’d start tackling the plan itself. Although it seems like the above steps would take a while, my real-life planning process only takes about 5 minutes. You certainly don’t have to write everything down and you certainly don’t have to make it make sense to anyone but yourself.
Personally, I like to format my plans in dot-point form. I write 1, 2, 3 for each of my body paragraphs and I leave a space underneath each so I can plan each paragraph.
First, I’ll just write rough topic sentences under each, so I can really step back and consider whether my plan of action for the essay’s body paragraphs will do a good job at answering the prompt itself. Again, these are only rough topic sentences — fancying them up will come during the essay writing phase.
Step 4: Important things to include in each paragraph
Once I’ve decided on what each of my body paragraphs will be about, I can them go into a bit more depth for each of them individually.
These are the elements that I include for each:
Essentially, the points that I’ll argue and the reasoning behind the paragraph
The evidence that I’ll be using to reinforce my point(s).
Literary devices/metalanguage
In Year 12, I made a conscious effort to include one literary device or metalanguage example per body paragraph in all of my English essays. This really set me apart from the rest of the state because, in reality, not enough students really focused on the language of their texts, which can really impress examiners.
Strategy: Colour-coded plans

For me, using different colours in my plans helped me organise my thoughts, distinguish between them, and ensure that I had covered everything that I wanted to cover.
Obviously, you can come up with a colour system that works for you, but this is what I came up with:
- Green = metalanguage
- Red = quotes
- Black/blue = everything else!
And that’s it — my four-step but five minute essay planning process. Don’t be afraid to modify this to make it work for you and your needs. However, definitely DO be afraid of not planning — it’s absolutely essential for any good essay.
Happy planning!
[Video Transcription]
Hey guys. I've been doing a load of essay topic breakdowns for you guys, and we've been looking at plans for them, so I thought I would actually show you how I actually do a real life plan, one that I would do on paper if I was preparing for a SAC or an exam, as opposed to the ones that I do on YouTube because the ones that I do on YouTube are slightly different. I definitely go into more detail than I normally would. But at the same time I still do use the same concepts as I would when I do read the steps on YouTube. So I'm going to go and show you that today. And before I actually do that, I just want to preface this and tell you guys why doing a plan is so important. So I know that a plan is something that one, a lot of people just don't do, or two, they tend to sacrifice it if they feel like they don't have enough time, or three, they do a plan in their head, but they don't actually write it down on paper. Now, all of these things are pretty detrimental for you, especially because when you write a plan, it actually helps to secure you and ensure that one, you're not going to mind blank throughout your essay or let me rephrase that, if you do mind blank throughout your essay, you will still have a piece of paper in front of you telling you, "This is what you were thinking Lisa, just go and follow this method or what you've written down here." So that way you don't just get stuck in the middle of your essay and start having a freak out because you've forgotten what you were supposed to write. Second thing is that it ensures that you don't go off topic. This is something that happens quite frequently. If you don't have a plan, then you have this idea of, "Oh, I'll write this and this", and then somehow halfway through an essay, halfway through a paragraph, you realize, "Holy crap, I have completely veered off the topic or this has gone completely in the other direction from what I intended. This is not what I wanted." So in order to prevent that from happening, just do a plan, please! You will find that it ends up saving you so much time and it just gives you that reassurance that you need in situations where there are so many unpredictable factors, like what prompts you're actually going to get. And your focus and attention should be more about developing those ideas, rather than having a mind blank in the middle of your essay and then having a little bit of a freakout as a result. So I'm going to base this video on a previous essay topic breakdown in the past, and that is on Kate Grenville's The Lieutenant. I was going to say Lieutenant, because I always accidentally say that, but no, it is Lieutenant. Now, if you are not doing as text as always, don't stress about it because what I want you to take away from this video is how you actually do plans, the thinking that goes behind it and the formatting around it. So let's just get started. The essay topic that we're doing today is, "But a man could not travel along two different paths." How does Grenville explore Rooke's conflict of conscience in The Lieutenant. So as always, my first step is I will highlight the keywords that I see inside the prompt. Keywords are different for everyone, but these are the ones that I think are most important. Firstly, the actual quote itself, how Grenville, conflict of conscience. Pretty much in this case I could probably just highlight the entire thing, but for the sake of just defining some keywords, this is what I would do. So the next step is to define key words. I think the only big key word that I need to define here is conflict of conscience. And so to me, the conflict of conscience suggests internal conflict, which implies that we'll need to consider morality and the concepts of right and wrong, especially when a difficult decision must be made and sides need to be taken. So as you can see, I've written these words down next to the keyword and that will just help me ensure that I stay on topic or I stay in tune with what the keyword is about and I don't suddenly change my mind halfway through the essay. Then what I'll do is, I will analyze the quote itself. So this is unique because this particular essay prompt has a quote inside it, but I'll have to think about, okay, where did I see this quote? Who might've said it and what might it mean? And I'll draw it down a few notes for that. Then I'll pretty much just go straight into my plan. Now, my plans I've written within five minutes, most of the thinking is actually done during reading time. So personally, I've always found that just writing dot points is completely fine. I don't need to go more beyond that. And I'll show you a few examples now of real life year essay plans that I did during that time. And as you can see, they are pretty much just scribbles and if anybody else was to look at my essay plans, they would have no idea what I'm talking about. But you know what, for me it makes complete sense and that's all that matters. You're not graded on your plan, so just go ahead and do it your way. You do you. So what I'll do is I'll quickly dot down one, two, three, and these represent my body paragraphs. Then I'll just write down very quickly what the topic sentences will be. I don't actually write the full topic sentence itself, but I guess the essence of it, so the key things that I will mention in the topic sentence. By writing down the three topic sentences, this allows me to take a step back and look at the essay holistically and ensure that I am answering it the way that I want to. Then what I'll do is I'll move into each individual body paragraph and write down some things that I think are important for me to remember when I go ahead and write it. So I might write down a couple of ideas that I think are important. I will write down quotes that I think are essential to my discussion. And then what I'll do is I will throw in at least one literary device or a metalanguage that I think is important to discuss. So in this case, in this first body paragraph, it's limited omniscient third person perspective. By throwing this in, I will ensure that I can show my examiner or show my teacher that I can go on that deeper level. I'll repeat this method with both paragraph two and three. Of course for you, you might need to write down more dot points. You can write fewer dot points, it's really just dependent on every individual. If you are somebody who needs to write down the quotes more, then go ahead and do that. But for me, a lot of the quotes will stick in my head. I just need one point just to bounce off, and then from there, I'm able to pull in all of the other quotes that are necessary. You also notice that I do things in different colors. Now, I think this is a strategy that I implemented in order to make things a lot clearer for myself before jumping into an essay. So for example, for anything that's a metalanguage based, I'll write it in green. The whole purpose for that is to ensure that in every single body paragraph, I do cover some form of a literary device because that was always really important for me. I thought that it was one of the key things that helped me differentiate myself from other students. So if I took a step back from the plan and I looked at it overall, I could see, okay, there's a green color in every single body paragraph, done. I have ticked off that criteria. I also used to write quotes in red as well. So red just helped me do the same thing. It helps me take a step back and go, "Yep, there's a bit of red in every single body paragraph. I'm definitely including quotes," which might sound pretty stupid, but it's just that little bit of reassurance that I think really makes that difference when it comes to a stressful situation. That's pretty much it. It's just five minutes of your time, so we probably don't need to go into it in too much more detail than that. But as you can see from my essay plans, I'm quite minimal. I just keep things as short as possible because that's all I really need because a lot of the information is here, but I just need to reinforce it and ensure that it is concrete when it is on paper. So for yourself, I would recommend that you start practicing your plans. You can try my method and see if that works for you, but over time, I'm sure that you'll come to find your own way of writing plans that work for you. Next week I'm going to have another essay topic breakdown for you. Can you guess what it might be? If you want to take a stab, put it in the comment section below, but that's it for me in this week guys. I hope that was helpful for you, and don't forget plans are crucial to an amazing essay. If you needed any extra help, then my mailing list is always available for you guys. I send out emails every single week just giving you new advice and tips for your studies, so I'll put that in the description box below for you to sign up. Other than that, I will talk to you guys next week. Bye!
Stasiland and 1984 are studied as part of VCE English's Comparative. For one of most popular posts on Comparative (also known as Reading and Comparing), check out our Ultimate Guide to VCE Comparative.
1. Introductions
Stasiland is a memoir-style recollection of the author Anna Funder’s encounters with people affected by the years of the German Democratic Republic (GDR), or when Germany was divided into east and west. It marries the author’s personal growth and development during her period of research with the personal histories of those who acted as both perpetrator and victim of the regime’s atrocities. The result is an emotional and deeply human perspective of this heavily-documented period of history which delves into the lasting yet often invisible marks the GDR left on those it touched.
1984 is on the surface the dystopian narrative of the struggles and ultimate downfall of a man named Winston who lives in the depressingly grungy and hopeless world of Big Brother and The Party. In a more profound sense, however, it is author George Orwell’s warning concerning the possibilities inherent in the development of totalitarianism and how these might come to damage the human race.

3. Character Analysis and Comparison
When comparing the characters presented in these two texts, it is important to remember that Orwell’s are fictional and Funder’s are her retellings of real people’s stories. Take care to avoid discussing Funder’s characters as constructions, and focus instead on how she has chosen to portray them.

4. Sample Paragraphs
Prompt: Discuss the different ways in which the authors of Stasiland and 1984 explore the intricacies of state power and knowledge.
Sample Introduction
When significant knowledge in any form is gained, it follows that it can be used in any way an individual or group sees fit. Stasiland and 1984 both show that the same piece of information can be used in drastically different ways to suit the purpose of that information’s owner. In both texts, we can observe this in many areas: mass surveillance for security or espionage purposes, recordkeeping to retain the truth or warp it, and medical or physiological advancements used to solve humanity’s problems or deliberately harm and deform people. Such examples force us to consider two well-known maxims, and to decide between the bliss of ignorance and the power of knowledge.
Sample Body Paragraph
In theory, mass surveillance has many benefits; it could be used to prevent criminal activity such as large-scale terrorist attacks and ensure the happiness and wellbeing of citizens. However, it is almost never associated with anything positive. In George Orwell’s 1984 , we are introduced to his hypothesis concerning what it would be like if it were to become developed to its full extent. The concept can be divided into three levels; firstly there is the obvious, external activities that we observe in both texts, which include mail screening, a military or gendarme presence in the streets and a network of informers. Secondly there is the introduction of the state into the home, which is achieved by The Party mainly through the telescreen, the most prominent and sinister instrument of mass surveillance in Oceania which gives total access to individual behaviour in the privacy of the home. While Winston seems to have found a loophole in this area by being ‘able to remain outside the range of the telescreen’, The Party carries its mass surveillance to the truest sense of the expression by extending it to a seemingly impossible third level, which introduces the state into ‘the few cubic centimetres inside [the] skull’. Interestingly, while the Thought Police cannot truly ‘see’ what is inside someone’s head, they can still control it; as long as people think that someone can see their thoughts, they will censor them themselves. This shows that the beauty of mass surveillance is that it does not actually have to be universal or all-encompassing to be successful. This is why the Stasi did not need to go to the lengths of The Party to achieve a similar result; the people merely need to believe that it is so on the basis of some evidence, and through this they can be controlled. Ultimately, mass surveillance can never be anything but destructive for this reason; it could put a complete halt to all terrorist plots and it would still act against the people by insidiously forcing them to censor their own thoughts out of fear.
Sample Conclusion
Both Stasiland and 1984 show absolutely that knowledge is a fundamental and intrinsic part of power, as it cannot exist without knowledge. While it is true that knowledge can be held without exercising it in some external display of power, it always shapes the person who holds it in ways both subtle and direct. Knowledge can therefore be seen as similar to Pandora’s Box; once it exists in a mind, it alters it, and the actions it prompts depend only on the desires and will of that mind .
In order to properly understand either of these texts, you’ll need to put on your history hat. Both of them are very firmly rooted in historical events, and to get a good grasp on what they really mean, you need to understand these events. You should research communism and socialism fairly extensively as well as the GDR, but you don’t need to sit for hours and write a book on the subject. All you need to do is trawl through Wikipedia for half an hour, or as long as it takes to get a sense of the subject. They key is to not ignore things that you don’t understand; if you see terms like ‘Eastern Bloc’ or ‘Marxism’ or ‘The Iron Curtain’ and you’ve got no idea what they are, research them! Even terms that you might believe you’re familiar with, like ‘Communism’ could also use a refresher.
The other main point is that 1984 particularly deals very heavily in ideological and philosophical argument. Orwell constructed the events of the plot as one giant hypothetical situation, so try and think to yourself – could that really happen? Is that really possible, or is this whole thing just plain silly? Remember that this text is much, much more than a simple narrative, and address it as such
Want to download this study guide? Click the button below!
Let’s briefly discuss the background of the article before we dive into the analysis…
- So, the background information tells us that “Biodiversity is the term used to describe life on Earth — the variety of living things, the places they inhibit and the interactions between them.”
- The article at hand is a transcript of a speech given by Professor Chris Lee at the International Biodiversity Conference 2010.
- The purpose of this conference is to review the progress made towards achieving the target and to look beyond 2010.

Now, let’s analyse the opening of the speech. Take a second to read through Lee’s speech opener...

Firstly, we can analyse the way in which Lee addresses his audience. Rather than using a phrase like "Hi everyone" or a similar greeting, he actually refers to his audience as his "fellow delegates" which allows him to speak in a particularly candid and honest manner. He wants to be transparent about the reality of the situation with his peers, rather than trying to impress an audience or something similar.

Overall, this anecdote appeals to the emotions of the audience and plays on an apparent devotion/commitment presumably made to the environment by the delegates of a Biodiversity conference. Lee uniquely seeks to persuade his audience by using the information he knows about them – their past commitments.
More specifically, we can dive into the pejorative mood of the adjectives he uses to describe the second scene, which is one of destruction, especially compare to the images he presents first. The "lush jungle" with a variety of "interesting flora and fauna" on the banks of a "clear river" appears particularly idyllic in juxtaposition with the images of the "scorched earth", "gooey mudslide", "sepia tinge" and "barren sticks hopelessly groping for life."
In the last sentence, the repetition of the word "gone" reminds Lee's "fellow delegates" of what will be lost if action on biodiversity is not taken.
Now, we know that in any given Language Analysis article, there are so many things to analyse, which I’ve demonstrated with all of the things we managed to focus on in that single paragraph.
Often, students will be able to identify lots of techniques and as such, lots of elements to analyse, but they struggle to choose between these techniques when it comes to writing their responses.
I’d highly recommend that you download a free sample of my eBook, How To Write A Killer Language Analysis which talks about techniques you can use to pick what to write about in your essays. We won’t have enough time to talk about those techniques today, so we’ve written them down for you in the eBook.
Now that we’ve looked at how Lee has started his speech, let’s skip forward to a later section of the article. Take a second to read through the section.

One of the first things that may jump out at you is this repetition of inclusive language; "we are", "we have". However, this is way too obvious! For an upper level response, we want to steer clear of the cliche techniques and analyse ones that have more value and show off our own perspective of the article.
Utilising the statements, "everyone in the lecture theatre knows this" and "clearly, it is our lack of unity", Lee includes the audience and holds all of the delegates accountable through declaring the reasons for failure as simple matters of fact.
Here, Lee trivializes the actions of the organisation in creating "glossy brochures" with "wonderful words" as marketing tools to create the impression that meaningful action is being taken. Lee exposes such actions as deceitful and calls for "real action", seeking to persuade his audience into putting their effort into actual gains in the biodiversity fight.
Want to know more? I'd highly recommend checking out LSG's FREE Ultimate Guide to VCE Language Analysis for more great tips, resources and advice.
And that’s it! I hope this has been helpful in showing how to analyse a speech as a Language Analysis prompt.
Be sure to check out the free sample of my eBook below for more!
- Plot Summaries
- Themes, Motifs and Key Ideas
- LSG’s Bubble Tea (BBT) Strategy for Unique Strategies
- Structural Features Analysis
- Sample Essay Breakdown
For a detailed guide on Comparative, check out our Ultimate Guide to VCE Comparative.
1. Plot Summaries
Summary - the hate race .
Maxine Beneba Clarke’s seminal novel, The Hate Race, follows the childhood and adolescence of its author, who is the main protagonist. The book is a memoir, meaning that it is based around a recollection of her life and filtered through her psyche and experiences. The book begins with Clarke’s family, British citizens of Afro-Carribean descent, moving to Sydney, New South Wales. They settle in the town of Kellyville, which is known as a ‘white picket’ community. Although these communities largely don't exist anymore, what they once described was suburban environments where only Anglo-Australians lived. As you can probably imagine, this immediately caused problems for Clarke’s family, with suspicion from neighbours and racist interactions with other kids in the neighbourhood. Clarke initially focuses on her experiences in kindergarten, revealing how prejudice and discrimination can be inculcated (meaning, ‘taught to’) in children even from such a tender age. Clarke meets her first tormenter - Carlita Allen. Carlita makes every effort to exclude Clarke from participation in usual preschool activities, hurling insults across playgrounds and calling her ‘dirty’. Literally, of course, Carlita is referring to Clarke’s black skin colour, but, metaphorically, it reflects the deeply hateful implication that anyone with a dark complexion is inherently inferior and lesser than white Australians. The bullying doesn’t stop by the time Clarke reaches primary school. In fact, it intensifies, aided and abetted by teachers who consistently turn a blind eye to the constant, gut-wrenching racial abuse. One of the most salient (meaning, ‘important’) scenes arises when Clarke is asked by a teacher what her parents do for a living. Upon informing the teacher that her mother is an actor, and her father is a Mathematics Professor - the first British citizen of Afro-Carribean descent to attend a British university - she is met with the patronising assumption that she must be lying. Surely black people wouldn’t have the emotional and intellectual intelligence to perform such high-powered jobs? Clarke also develops eczema during her primary school years, leaving patches of lighter-coloured skin covering her face, and a newfound hope that, bit by bit, God is answering her prayers and making her white. In high school, the racist rot sets in even further. Clarke develops a new habit for scratching her skin at night to the point of bleeding and bruising. Looking back at this experience, Clarke theorises that this was her body’s way of expressing her extreme discomfort with being black. It gives us a picture of how horrific racism can truly be, and the ways in which it forces minorities into believing that there’s something wrong with them, instead of there being something wrong with the people hurling abuse in the first instance!
It is this stage of her life when Clarke deals with one of the most difficult parts of being a minority in a majority white country. Through her interactions with teachers, friends and boyfriends alike, she becomes deeply angry at those people who abhor racism themselves, but seem unable to step in when racist events are actually occurring. Clarke also deals with more nuanced experiences of racism - people who don’t intend to be racist, but end up making insensitive comments anyway. Whether intentional or not, these comments still hurt, and are still part of the challenges of growing up black in a white country. Nonetheless, Clarke continues to rise above the odds, becoming a prolific high school debater, maintaining her position at the top of the academic cohort, and forming a small but tight-knit group of friends whom she can trust.
Clarke’s recollection of her childhood ends on a relatively abrupt note, with Clarke returning home to realise that her father has left the family for another woman. In a note to the family, he provides no explanation other than that he had a secret affair for many years. Suddenly, Clarke, her brothers, sisters and mother are left to pick up the pieces. In the epilogue, Clarke is now an adult with a child of her own. Walking down Melbourne’s North Road, she reflects on the challenges and opportunities to which her child will be witness. Clarke portrays it as the dual sadness and happiness of knowing that, in Australia, her children will surely have access to more opportunity than in most parts of the world - but it will come at a cost. Namely, they will also have to contend with the remaining undercurrent of racism that, even now, still seeps through Australian society. The unsatisfying end to the novel reflects the nature of racism and the experience of a minority growing up in a white country itself: there is no happy ending. Rather, life becomes a series of painful incidents interspersed with minor victories; those who stand up against racism, those who fail to do so and the hundreds of thousands of Australians who will forever grapple with a society that sees them as ‘ lesser than’ due to the colour of their skin.
Summary - Charlie’s Country
Charlie’s Country , an Australian movie directed by Dutch-Australian Rolf De Heer, follows the story of Charlie, a First Nations man living in late-2000s Australia.
The movie is set in the wake of the 2007 Northern Territory Intervention. As a bit of quick context, this was an action taken by the Commonwealth Government under Coalition Prime Minister John Howard to send Australian Defence Force troops into the Northern Territory. It came in response to the ‘Little Children are Sacred’ report , which raised allegations of child sexual abuse and neglect of children in Aboriginal communities. The intervention also involved restricting alcohol consumption, quarantining a portion of welfare payments to Indigenous residents (with the justification that this would prevent it being spent on alcohol, pornography, cigarettes, etc.) and hefty fines as well as jail sentences for those forced to comply. It is important to note that, throughout the whole intervention, not a single person was prosecuted for child sexual abuse or any related offence. Nonetheless, this intervention had real world, drastic consequences - and that’s exactly what Charlie’s Country explores. At the time of de Heer’s film, Charlie lives in a remote Indigenous community. Signs of the intervention are all around - alcohol is banned from most communities, many individuals face personal bans on procuring alcohol, police officers dot the streets and citizens live under constant watch. Charlie, on a surface level, is a fairly happy-go-lucky individual; he exchanges jokes with police, is friendly with other elders and people in his community and doesn’t seem to do much else. As always with a movie like this - there’s a bigger story behind this all! Rolf de Heer takes us through an increasingly concerning image of Aboriginal communities in the wake of the intervention. Charlie visits his local housing officer and is unable to obtain a house. Here, we see that Charlie is willing to work and wants stable accommodation, but the government is unwilling to provide.
Going on a hunting trip with his friend, ‘Black Pete’, the two are stopped by police and have their guns, as well as the water buffalo they killed, confiscated. Yet again, two Indigenous men try to provide for themselves - but are stopped by a legal system more concerned with rules and procedure than listening to First Nations communities themselves. Charlie decides he’s had enough of having his every move and action monitored, and takes a stolen police car into the bush. Abandoning the car, he tries to live amongst nature for an unidentified amount of time. Cooking fish, performing traditional First Nations dances, painting on the bark and looking for shelter, Charlie finally appears to be home . Yet, as usual, it’s too good to be true - the extreme cold makes Charlie incredibly sick, and, before we know it, he wakes up in a Darwin hospital. After refusing further treatment from the white doctors who fail to understand Charlie’s situation and why he is so angry at what’s happened to him, the predictable cycle begins again: Charlie returns to his community, they all share alcohol as a way of coping with their current situation and flee when the police come running to confiscate the liquor. Charlie isn’t civil with the police this time. In a fit of anger - an outburst of emotion after decades upon decades of control and being denied access to any opportunity - he picks up a bat and smashes the police officer’s car window. Brutally beaten into submission, Charlie is imprisoned as the police officer remarks that he should never have 'gone soft on a blackfella’.
Dragged before the courts, Charlie is imprisoned for assault. When the judge asks him to make a comment, he gives a lengthy speech in his native language. For de Heer, this acts as a symbolic assertion of the First Nations’ rights to their own culture, and a proud statement against the many governments that have continually placed barriers in the way of Indigenous Australians having the same opportunities as any one of us. Eventually, Charlie is released on parole. He expresses a deep desire to go home - but also a sense of defeat . He resolves, in the end, to believe that even if he will always live under the watchful eyes of the Australian Government, he can at least fight back and contribute by doing his bit to maintain the many cultures of our First Nations Peoples. Charlie teaches young Indigenous boys traditional dances, speaking proudly of when he performed a dancing ceremony for Queen Elizabeth in 1973 at the Sydney Opera House. The movie ends with Charlie staring mournfully into the camera, almost looking at the audience themselves. There seems to be no happiness in his eyes - nothing left but a sense of sadness and resignation. I know that, upon approaching the end of the film, I started to feel the same sadness that Charlie so evidently shows us. It’s a different type of emotion; one centered around the pain of knowing that we live in a country that still has not made peace with its past, and refuses to listen to the First Nations Peoples who know it best. Charlie’s Country exposes to us that Australia is a country where, even today, our First Nations citizens are not treated as equals. As such, de Heer’s film is a stark reminder that this state of affairs is not good enough - and that the responsibility for change doesn’t just lie with politicians and decision-makers . It’s our job too: and failure is not an option .
2. Themes, Motifs and Key Ideas
Through discussing Themes, Motifs and Key Ideas, we’ll gain a clearer understanding of some super important ideas to include in your essays. Remember that, when it comes to themes, there’s a whole host of ways you can express your ideas, but this is what I’d suggest as the most impressive method to blow away the VCAA examiners. We’ll be adhering to the CONVERGENT and DIVERGENT strategy. While we don’t go into detail into how to use LSG’s CONVERGENT and DIVERGENT strategy in this guide, I’d highly recommend you get familiar with it by reading How To Write A Killer Comparative .
Connection to Culture (CONVERGENT)
Both de Heer and Clarke offer a unified idea around culture: that being connected to one’s culture is inherently good and positive, and should be encouraged. Let’s break this down. The Hate Race and Charlie’s Country are both works that explore the challenges of individuals maintaining their culture in surroundings which would otherwise see them revert to the ‘standard’. In this case, because we’re talking about Australia, de Heer and Clarke take us through the same story of an overarching, implicit acceptance that the Christian, Anglo way of life is the norm. This standard has deep roots in the colonisation of Australia, and the resulting claim of sovereignty by the Crown. Even as this country has evolved into a multicultural land, it still bears the marks of a ‘European’ country; whether that be our British legal system, Anglo-American democracy or any of the other institutions we have taken from the Western world.
It is in this context that de Heer and Clarke go to special lengths to explain why people should be empowered to connect to their culture. To our author and director, culture is an essential element of who you are, and it is this identity which carries people through life . For Maxine, the shock of realising that she may be the descendant of African slaves, and had lived so many years without having any idea this may be the case, is drawn from the fact that she, as a child, feels incredibly disconnected to who she is. Clarke’s memoir thus reminds us that ‘growing up black in a white country’ is an experience that often results in minority children not truly learning about who they are. Travelling through life, Maxine is continually disconnected from her culture, to the point where performing ‘African tribal dances’ to the school is nothing more than a joke. Even in her own estimation, Maxine has internalised (meaning, she’s adopted it herself) the view that her culture is irrelevant, and there’s no real reason for her to properly engage with all its complexity and beauty.
If we consider Charlie’s perspective, his involuntary burst of tears at the hospital stems from a recognition that his people have been denied the free opportunity to embrace the world’s longest-surviving culture; the First Nations traditions that date back 40,000 years. With his friend slowly dying of lung cancer, at that moment, the old man is more connected to the cigarettes that slowly sapped his life away than he is to the First Nations way of living. Unable to hunt, gather as a community, work the lands as the First Nations traditionally would or embark on any other activity that would keep them connected to their culture, this country’s first inhabitants are instead told to abandon ‘the old ways’ and embrace Anglocentric standards of life.
It is a shocking reminder that, without culture, people are left like driftwood swimming through a vast ocean. By that, I mean that people are left without an anchor through which they can independently experience the world. Instead, their understanding of themselves, their sense of self and their actions in life are all filtered through the preferences of the dominant majority.
Intergenerational Disadvantage (DIVERGENT)
Whilst Charlie’s Country and The Hate Race share many similarities in terms of the negative impacts of racism and prejudice, the texts carry different connotations when it comes to the notion of intergenerational disadvantage.
To explain this idea, let’s first define and unpack ‘intergenerational disadvantage’. We could spend days talking about this, but, simply, intergenerational disadvantage refers to cycles of poverty and criminality that pass from generation to generation, worsening with time. Think of it this way: assume you’re a teenager - or at least still financially reliant on your parents. If your parents were to lose everything they owned today in a massive financial crisis, you’d be in big trouble too, right? Suddenly, that part-time job you had that was helping you save money might be the only income for the entire family. You might even have to drop out of school, TAFE or university to care for everyone, denying you a higher paying job in the future.
You’ll have to work your tail off for years on end. Since you’re supporting an entire family, say goodbye to saving up for a house or to pay for your kid’s education in future. Your kids now have to start from square one with less opportunity than the people around them, meaning it’ll be harder for them to succeed in life.
When we apply this to Charlie’s Country, the analogy becomes quite clear. Charlie lives in a community where there is no opportunity. Because there are no jobs - and no real way to gain steady, meaningful employment - people fall into alcoholism, marijuana and anything else that’ll help them cope. Lung cancer and alcoholism shorten lifespans for people like the old man with failing kidneys, while no employer is going to waste a chance on those still living. There is simply no ability to ‘succeed’ here, because the local residents don’t see that there’s anything worth working towards. Hopeless, unheard and disillusioned, it becomes easier for Charlie’s community to just accept their sorry lot in life than futilely work towards changing it.
We aren’t made witness to this same cycle in The Hate Race. Instead, Bordeaux Clarke is the epitome of someone who has broken the cycle of intergenerational disadvantage; becoming the first individual in his community to attend a British university. Marrying a high-powered Guyanese actress in Cleopatra, the married couple represent success and a defiance of racist stereotypes, not the grinding poverty and disadvantage we see in Charlie’s Country. Although Maxine experiences terrible discrimination and prejudice as a child, there is always a sense that she will academically remain on top. Maxine uses the prejudice with which she’s faced as a motivator, giving her the impetus to consistently emerge successful; whether that be in her schooling, cross-country running, as a debater or any other academic endeavour. Sure, she faces racism that inhibits her from always succeeding - the Lions Club competition is a great example of such - but this isn’t so much about intergenerational disadvantage as it is about racism, plain and simple.
Ultimately, the difference between the two is a matter of emphasis. It’s not that intergenerational disadvantage doesn’t exist in The Hate Race, but more so that Clarke is choosing to focus on how even the most successful individuals can suffer from prejudice and racism. This in turn helps us to understand that racism impacts everyone , and we should never pretend it isn’t a massive problem. Conversely, Charlie’s Country is all about social disadvantage, and explores how prejudice can prevent oppressed individuals from becoming successful in the first place.
3. LSG’s Bubble Tea (BBT) Strategy for Unique Strategies
Why is an interpretation important.
Your interpretation is what English is all about; it’s about getting you to think critically about the essay topic at hand, to formulate a contention (agree, disagree, or sit on the fence) and argue each of your points with the best pieces of evidence you can find - and it’s something you might already be starting to do naturally.
In this section, we aim to help you develop your own interpretation of the text, rather than relying on your teacher, tutor or even a study guide (including this one) author’s interpretation. By developing your own interpretation, you become a better English student by:
- Writing with meaning. For a text to be interpreted, you need a text and an interpreter (i.e. you!). Whenever we read a new text, our interpretation of a text is shaped by our pre-existing beliefs, knowledge and expectations. This should be reassuring because it means that you can leverage your own life experiences in developing a unique interpretation of the text! We’ll show you how this works in the next point.
- Remembering evidence (quotes or literary devices) more easily. If you know you admire a character for example (which is in itself an interpretation 😉), you can probably remember why you admire them. Perhaps the character’s selflessness reminds you of your Dad (see how you’re using real life experiences mentioned in Point 1 to develop an interpretation of the text?). You will then more easily recall something the character said or did in the text (i.e. evidence) that made you admire them.
- Having an analysis ready to use alongside the evidence. As a result of Point 2 , you’ll be able to write a few sentences based on your own interpretation. Rather than memorising entire essays ( we’ve talked about this before ) and regurgitating information from teachers, tutors, study guides and other resources - which can be labour intensive and actually detract from the originality of your essay - you’re approaching the essay with your own thoughts and opinions (which you can reuse over and over again across different essay topics).
Let’s look on the flip side. What happens when you don’t have your own interpretation?
When you don’t take the time to actively think for yourself - i.e. to think through your own interpretations (we’ve talked about the importance of THINK in the THINK and EXECUTE strategy here ) - when it finally comes to writing an essay, you may find it difficult:
a) to get started - formulating a contention in response to the essay topic is challenging because you have no strong opinion about the text ,
b) complete the essay - writing up arguments and using evidence in paragraphs becomes challenging because you have no strong opinion about the text ,
c) to score higher marks - ultimately, you end up regurgitating other people’s ideas (your teacher’s, tutor’s or from study guides) because you have (you guessed it) no strong opinion on the text .
Having your own interpretation means that you’ll eliminate issues a, b and c from above. Overall, you’ll have opinions (and therefore contentions) ready for any prompt when you go into your SACs or exams, which means it’ll be easier not only to write a full essay, but an original and insightful one as well.
To overcome the issues above, you need to be confident with your own interpretation of the text. This doesn’t come naturally to a lot of students, and it makes sense why. After all, so many subjects reward specific answers (2 + 2 = 4), whereas English is tricky because there’s so much more flexibility in what constitutes a ‘correct answer’. It’s scary treading the sea of different possible interpretations because you’ll ask yourself questions like:
- How do I know if my interpretation is correct?
- How do I know if my evidence actually backs up what I’m arguing?
- What if I disagree with my teacher, and they mark me down for a differing opinion?
- Or worse - I’m not smart enough to come up with my own interpretation!
Let me say that you are absolutely smart enough to develop your own interpretation, and I’ll show you how to do so in A Killer Comparative Guide: The Hate Race & Charlie’s Country with LSG’s unique strategy - the BUBBLE TEA (BBT) strategy . By following our step-by-step framework, you can be confident that your interpretation is valid, that it backs up your argument, and that most importantly, you won’t lose marks for it!
4. Structural Features Analysis
In How To Write A Killer Text Response , we cover Metalanguage . A Structural Features Analysis and Comparison goes over a lot of the same material, and will help elevate your essays to the next level. Knowing quotes and themes is essential, but being able to pair that with analysis of the title, setting, narrator and overall structure - we'll cover title here - shows the examiner that you really know exactly what you’re talking about. This section will be especially crucial for metalanguage topics that are all about how Charlie’s Country and The Hate Race are structured , so, enjoy!
The title of a text is always significant - and this text pairing is no different. First, of course, please do keep in mind that there is no universally accurate interpretation of what a title means. I’m giving you my assessment, but the author and director could very well disagree themselves! That’s okay, because as long as we back it up properly, your interpretation is as valid as any. As always, that’s the beauty of English. Let’s first unpack The Hate Race. What this title signifies is that, for minorities in Australia, life is constantly akin to a race. There is no rest, no comfort and no sense of home when your mind is preoccupied with all the ways you don’t belong. Australia, as a colonial outpost representing the Crown in a region that is overwhelmingly non-white, was once proud of its discriminatory stances; holding itself as the 'White Man’s Paradise'. It is in this context that racism, for Clarke, is not just a reality that lurks beneath the surface, but rather, a guiding tenet of Australia since 1788. With this overarching narrative, it is also important to acknowledge that the mere experience of racism is immensely emotionally, physically and mentally taxing for Clarke, and all people of colour. Being denied a firm sense of self, and constantly being forced to justify one’s own existence isn’t easy, and becomes a ‘race against time’ to see who can cope and rise above, and who will be swept away along with the tide. This sorrowful reality is what engenders the never ending race against being consumed by such hatred, because, for non-white Australians, there simply is no other choice. If they stop running, they run the risk of being consumed by the hatred themselves and becoming so cynical and disillusioned that they forget their culture and accede to the Anglocentric, white majority.
Moving to de Heer’s film, Charlie’s Country, the title reflects a simple reality: this is Charlie’s country. However, when de Heer speaks of ‘country’, he is really talking about ‘Country’; the Indigenous notion of connection to and respect for one’s traditional lands. Nurturing this connection is a sacred responsibility, and the film reminds us that, despite Charlie’s many trials and tribulations, the land on which he lives is truly his own. Throughout the film, Charlie maintains a keen awareness that what is happening to him is unjust, and, unlike Maxine, he doesn’t need someone to convince him that he belongs. Whatever Anglo Australia does, it cannot change the continuing legacy of his people and their sovereignty. To Charlie, it is laughable to think that his Country - which the First Nations have nurtured and kept in common use for 40,000 years - could suddenly become someone else’s property in less than 200 years. He may not have any legal authority under the Crown, and his people may be dispossessed of their sovereignty and authority, but this cannot and will not change the remaining truth of First Nations sovereignty. De Heer’s film title thus challenges us to confront our own perceptions of Australia and remember that we all live on stolen land.
- Essay Topic Breakdown
As with all our essay topic breakdowns, we'll follow LSG's THINK and EXECUTE strategy , as taught in our How To Write A Killer Text Response study guide. The LSG's THINK and EXECUTE strategy follows three steps in the THINK phase - A nalyse, B rainstorm, and C reate a Plan. Learn more about this technique in this video:
'I’m free now!' ( Charlie’s Country ) 'My children are the descendants of the unbroken.' ( The Hate Race ) Compare the characters’ understanding of freedom in the two texts.
Step 1: Analyse
Let’s break down the prompt. This is a quote-based prompt, meaning the quote must feature somewhere in your essay . Ensure that you have a good understanding of the place from which the quote is drawn. In this case, Charlie’s exclamation of joy features when he escapes to the wilderness and is able to cook, dance and provide for himself. The quote from The Hate Race is the last line of the memoir, with Clarke expressing the sentiment that her children belong in Australia and will be as strong as their parents.
Step 2: Brainstorm
The next part is to establish the link between the quote and the topic. The essay topic at hand asks us how 'freedom' is understood, so we need to actually understand freedom itself in relation to the quotes provided. For de Heer and Clarke, freedom isn’t an abstract concept relating to rights, liberties and responsibilities. Rather, freedom is found when people have the ability to be themselves, own their culture and live their truth. For Charlie, that mainly relates to his right to live in his country and maintain the traditional ways of the First Nations Peoples. Clarke, however, is more focused on the balancing act of finding freedom through a multicultural society that includes all, and in doing so celebrates the contribution that all cultures make into the melting pot that is Australia.
Step 3: Create a Plan
There’s no one correct way to structure your paragraphs for Charlie’s Country and The Hate Race . However, I find it consistently helpful to follow a chronological structure. This refers to going through events of the memoir and film in the order they actually occur, and finding unique points of analysis based around these chronological groupings.
We also need to think of examples and points of comparison. Base these around the themes we’ve gone through, so you can easily identify DIVERGENT and CONVERGENT points of comparison. I’ll walk you through my thinking.
Paragraph 1 – unable to experience freedom because systems exist to stop individuals from embracing their own culture
- Kellyville and Alice Springs are immediately established as communities where rules and standards of association are both made and enforced by white authorities. The types of authorities and the prevalence of this overarching system of control differs between The Hate Race and Charlie’s Country , but are not any less harmful.
Paragraph 2 – attempts at pushback are rebuffed, resulting in further punishment for the simple crime of failing to conform
- Anglo Australia maintains its dominance through an assumption that minority Australians and First Nations Peoples will not question their place. Thus, when there is even the smallest semblance of resistance, punishment is the only solution.
- The difference here is that while Charlie wages an active resistance against white authorities, Maxine is moreso placed into submission by the repeated failure of her pleas to be heard by anyone in a position to change what is occurring. At the centre of both situations, though, is a desire to break free of white Australia’s chains.
Paragraph 3 – finding cultural freedom is a slow process of change, but one that begins with self acceptance
- There is no happy ending to either The Hate Race or Charlie’s Country. Freedom does not suddenly spring forth. Instead, our author and director elucidate that cultivating freedom is a slow process. For Charlie, that begins with embracing his culture again and seeking to keep it alive. On Maxine’s part, it is about refusing to be broken by her past, and instead using her trauma as a motivator to build a better future.
If you'd like to see the sample A+ essay we wrote up for this essay topic, then you might want to check out our A Killer Comparative Guide: The Hate Race & Charlie's Country study guide !
Don't forget to also check out Our Ultimate Guide to Oral Presentations for everything you need to know for Oral Presentations.
Since September 2015, the current affairs has been raging with numerous controversial topics - perfect for your oral presentation! Here are some of the more interesting issues that would be a good starting point for your oral. Remember to offer an interesting and unique argument, even if it may mean adopting the unconventional or unpopular point of view on the issue!
Oral presentation topics 2016
1. Should we have 24 hour public transport on weekends?
2. Gender selective abortion in Australia
3. Should the driving age in Australia be lowered?
4. Cricket star Chris Gayle’s treatment of journalist Mel McLaughlin
5. Should children be vaccinated?
6. Should the voting age in Australia be lowered to 16 years?
7. Should singer Chris Brown be denied entry to Australia?
8. Cultural appropriation in Australia
9. Should an Australian Prime Ministers be removed from office without a general election?
10. Should Australia be a republic?
11. Should the Australian flag be changed?
12. Is Australia Day racist against Indigenous Australians?
13. Adam Goodes booing: Are AFL football crowds racist?
14. Australian of the Year - Rosie Batty: Victim blaming
15. Should UBER be made legal in Australia?
16. Should baby formula be limited in sales?
17. Should greyhound racing be banned in Australia?
18. Is Australia’s border security policy justified?
19. Should Australian Open arenas have sports betting advertising?
20. See more Oral Presentation Topics 2017, click here .
- Symbols and Analysis
- Discussion Questions
- Sample Essay Topics
Go Went Gone revolves around an unlikely connection between a retired university professor , Richard, and a group of asylum seekers who come from all over the African continent . While he’s enjoyed a life of stability and privilege as a white male citizen, the lives of these asylum seekers could not be more different: no matter where they are in the world, uncertainty seems to follow. Richard initially sets out to learn their stories, but he is very quickly drawn into their histories of tragedy, as well as their dreams for the future.
However, the more he tries to help them, the more he realises what he’s up against: a potent mix of stringent legal bureaucracy and the ignorance of his peers . These obstacles are richly interwoven with the novel’s context in post-reunification Germany (more on this under Symbols: Borders ), but bureaucracy and ignorance are everywhere - Australia included . This novel, therefore, bears reflection on our own relationship with the refugees who seek protection and opportunity on our shores - refugees who are virtually imprisoned and cut off from the world .
Richard ultimately realises that these men are simply people , people who have the same complexities and inconsistencies as anyone else. They sometimes betray his trust; at other times, they help him in return despite their socio-economic standing. The end of the novel is thus neither perfect nor whole - while the asylum seekers develop a relationship with Richard and vice versa, neither is able to entirely solve the other’s problems, though both learn how to be there for each other in their own ways. We don’t get many solutions to everything the refugees are facing, but what we end up with is a lesson or two in human empathy.
The title of Jenny Erpenbeck’s novel Go Went Gone is a line she weaves into a couple of scenes. In one example, a group of asylum seekers in a repurposed nursing home learn to conjugate the verb in German. In another, a retired university professor reflects on this group, about to be relocated to another facility.
The various privileges Richard holds shape his identity in this text. It shapes how he approaches his retirement for example: now that “ he has time ”, he plans to spend it on highbrow pursuits like reading Proust and Dostoyevsky or listening to classical music. On the other hand, the asylum seekers sleep most of the time: “if you don’t sleep through half the morning, [a day] can be very long indeed.” Richard has the freedom to choose to spend his time on hobbies, but the asylum seekers face a daunting and seemingly-impossible array of tasks. After getting to know them more, he realises that while his to-do list includes menial things like “schedule repairman for dishwasher”, the refugees face daunting socio-political problems like needing to “eradicate corruption”.
Freedom in general is a useful way to think about privilege in this text, and besides freedom to choose how you spend your time, this can also look like the freedom to tell your story. While Richard helps the men with this to some degree, even he has a limited amount of power here (and power can be another useful way of thinking about privilege). Richard realises that “people with the freedom to choose…get to decide which stories to hold on to” - and those are the people who get to decide the future of the refugees, at least from a legal perspective.
Though Richard can’t necessarily help with these legal issues, he finds himself doing what he can for the refugees over time. He demonstrates a willingness to help them in quite substantial ways sometimes, for example buying a piece of land in Ghana for Karon and his family. In the end, we see him empathising with the refugees enough to offer them housing: though he is not a lawyer, he still finds ways to use his privilege for good and share what he can. He taps into his networks and finds housing for 147 refugees.
The tricky thing with empathy though is that it’s never one-sided, not in this book and not in real life either. It’s not simply a case of Richard taking pity on the refugees - we might think of this as sympathy rather than empathy - but he develops complex, reciprocal and ‘real’ friendships with all of them. This can challenge him, and us, and our assumptions about what is right. When Richard loses his wallet at the store, Rufu offers to pay for him. He initially insists he “can’t accept”, but when he does Rufu doesn’t let him pay him back in full. Erpenbeck challenges us to empathise without dehumanising, condescending or assuming anything in the process.
It’s an interesting way to think about social justice in general, particularly if you consider yourself an ‘ally’ of a marginalised group - how can we walk with people rather than speak for them and what they want?
Freedom of movement is sort of a form of privilege, but movement as a theme of its own is substantial enough to need a separate section. There are lots of different forms of movement in the novel, in particular movement between countries . In particular, it’s what brought the refugees to Germany at all, even though they didn’t necessarily have any control over that movement.
Contrast that with Richard’s friends, Jörg and Monika, who holiday in Italy and benefit from “freedom of movement [as] the right to travel”. Through this lens, we can see that this is really more of a luxury that the refugees simply do not have. Refugees experience something closer to forced displacement , rather than free travel, moving from one “temporary place” to the next often outside of their control. In this process, their lack of control often means they lose themselves in the rough-and-tumble of it all: “Becoming foreign. To yourself and others. So that’s what a transition looks like.”
3. Symbols & Analysis
Language and the law.
Many of the barriers faced by the refugees are reflected in their relationships with language; that is, their experiences learning German mirrors and sheds light on their relationship with other elements of German society. For example, there are times when they struggle to concentrate on learning: “It’s difficult to learn a language if you don’t know what it’s for”. This struggle reflects and symbolises the broader problems of uncertainty, unemployment and powerlessness in the men’s lives.
The symbol of language often intersects with the symbol of the “iron law”, so these are discussed together here. It’s hard on the one hand for these men to tell their stories in German, but it’s also hard for the German law to truly grapple with their stories. Indeed, Richard finds that the law doesn’t care if there are wars going on abroad or not: it only cares about “jurisdiction”, and about which country is technically responsible for the refugees. In this sense, the law mirrors and enables the callousness which runs through the halls of power - not to deter you from learning law if you want though! This might just be something to be aware of, and maybe something you’d want to change someday.
There’s one law mentioned in the novel stating that asylum seekers can simply be accepted “if a country, a government or a mayor so wishes”, but that one word in particular - “ if ” - puts all the power in lawyers and politicians who know the language and the law and how to navigate it all. These symbols thus reflect power and privilege.
Borders (+ Historical Context)
Throughout the novel, there’s a sense that borders between countries are somewhat arbitrary things. They can “suddenly become visible” and just as easily disappear; sometimes they’re easy to cross, sometimes they’re impossible to cross. Sometimes it’s easy physically, but harder in other ways - once you cross a border, you need housing, food, employment and so forth.
This complex understanding of borders draws on the history of Germany , and in particular of its capital Berlin, after World War II. After the war, Western powers (USA, UK, France) made a deal with the Soviet Union to each run half of Germany and half of Berlin. The Eastern half of Germany, and the Eastern half of Berlin, fell under Soviet control, and as East Germans started flocking to the West in search of better opportunities (sound familiar?), the Soviets built a wall around East Berlin. The Berlin Wall , built in 1961, became a border of its own, dividing a nation and a city and changing the citizenship of half of Germany overnight. Attempts to escape from the East continued for many years until the wall came down in 1989, changing all those citizenships right back, once again virtually overnight.
This history adds dimension to Erpenbeck’s novel. Refugees pass through many countries, but Erpenbeck draws on Germany’s history specifically as a once-divided nation itself. This helps to illustrate that national borders are just another arbitrary technicality that divides people, at the expense of these refugees.
Bodies of Water
One motif that comes back a few times in the novel is the drowned man in the lake by Richard’s house. This has a few layers of meaning.
Firstly, the man drowns despite the lake being a perfectly “placid” body of water, and for whatever reason, this bothers Richard immensely: “he can’t avoid seeing the lake”. There’s an interesting contrast here to be drawn between this one death in a still body of water and the hundreds of deaths at sea that are recounted in the novel. Rashid’s stories are particularly confronting: “Under the water I saw all the corpses”. Erpenbeck questions the limits of human empathy - whose deaths are we more affected by, and why - through contrasting these different bodies of water, and those who die within them. Richard is more affected than most, who visit the lake all summer leaving “just as happy as they came” - but even he has his limits with how much he can see and understand.
The next layer of meaning with this symbol then is more around the surface of the water itself: it is significant that in Rashid’s story, the casualties are below the surface. This reflects the common saying, “the tip of the iceberg” - the survivors who make it to Europe are really just the tip of the iceberg , only representing a fraction of the refugee experience. Often, that experience ends in death. Erpenbeck asks us to keep looking beneath the surface in order to empathise in full.
Music and the Piano
This symbol is specific to Richard’s relationship with Osarobo , to whom he teaches the piano. There’s one scene where this symbolism is particularly powerful, where they watch videos of pianists “us[ing] the black and white keys to tell stories that have nothing at all to do with the keys’ colours.”
It speaks to the power of music to bring people together, and also to the importance of storytelling in any form: Rosa Canales argues the keys’ colours, and the colour of the fingers playing them, “become irrelevant to the stories emanating from beneath them”.
- “What languages can you speak?”
- “The German language is my bridge into this country”
- “Empty phrases signify politeness in a language which neither of them is at home”
- “The things you’ve experienced become baggage you can’t get rid of, while others - people with the freedom to choose - get to decide which stories to hold on to”
- “He hears Apollo’s voice saying: They give us money, but what I really want is work. He hears Tristan’s voice saying: Poco lavoro . He hears the voice of Osaboro, the piano player, saying: Yes, I want to work but it is not allowed. The refugees’ protest has created half-time jobs for at least twelve Germans thus far”
- “Not so long ago, Richard thinks, this story of going abroad to find one's fortune was a German one”
- “Is it a rift between Black and White? Or Poor and Rich?”
- “Where can a person go when he doesn't know where to go?”
5. Discussion Questions
Here are some questions to think about before diving into essay-writing. There’s no right or wrong answer to any of these, and most will draw on your own experiences or reflections anyway. You may want to write some answers down, and brainstorm links between your responses and the novel. These reflections could be particularly useful if you’re writing a creative response to the text, but they’re also a really good way to get some personal perspective and apply the themes and lessons of this novel into your own life.
- Where do you ‘sit’ in the world? What privileges do you have or lack? What can you do that others cannot, and what can others do that you cannot?
- Think about the times you’ve travelled around the world - how many of those times were by choice? What might be the impact of moving across the world against your will?
- How do you show empathy to others? How do you receive empathy from others? What is that relationship ‘supposed’ to look like?
- What are some different names for where you live? How can you describe the same place in different languages or words? If you’re in Australia, what was your area called before 1788?
- Have you ever learned or spoken a language other than English? What language do you find easier to write, speak and think with? How might this impact someone’s ability to participate in different parts of life (school, work, friendships etc.)?
6. Sample Essay Topics
- Go Went Gone teaches us that anyone can be empathetic. Discuss.
- In Go Went Gone , Erpenbeck argues that storytelling can be powerful but only to an extent. Do you agree?
- How does Erpenbeck explore the different ways people see time?
- It’s possible to sympathise with Richard despite his relative privilege. Do you agree?
- Discuss the symbolic use of borders in Go Went Gone .
- Go Went Gone argues that the law is impartial. To what extent do you agree?
- “The German language is my bridge into this country.” How is language a privilege in Go Went Gone ?
- Who are the protagonists and antagonists of Go Went Gone ?
- Go Went Gone shows that it is impossible to truly understand another person’s experiences. To what extent do you agree?
In what ways do the people Richard meets challenge his assumptions about the world?
- Go Went Gone is less about borders between countries than it is about borders between people. Do you agree?
7. Essay Topic Breakdown
Whenever you get a new essay topic, you can use LSG’s THINK and EXECUTE strategy , a technique to help you write better VCE essays. This essay topic breakdown will focus on the THINK part of the strategy. If you’re unfamiliar with this strategy, then check it out in How To Write A Killer Text Response .
Within the THINK strategy, we have 3 steps, or ABC. These ABC components are:
Step 1: A nalyse
Step 2: B rainstorm
Step 3: C reate a Plan
This prompt alludes to certain assumptions that Richard might make about the world. If it’s hard to think of these off the top of your head, consider where our assumptions about the world come from: maybe from our jobs, our families and friends or our past experiences. Maybe there are some assumptions you’ve had in the past that you’ve since noticed or challenged.
Then it asks us how the people Richard meets challenges those assumptions. There’s no way to get out of this question without discussing the refugees, so this will inform our brainstorm.
I think some of Richard’s assumptions at the beginning come from his status: being a professor emeritus makes you pretty elite, and he can’t really empathise with the refugees because his experiences of life are so different. Part of the challenge with this prompt might be to break down what life experiences entail, and where those differences lie: particularly because it’s asking us ‘in what ways’. These experiences could be with language, employment, or personal relationships just to name a few ideas.
Because Richard’s life experiences are so vastly different, I’d contend that his assumptions are challenged in basically every way. However, I also think that his interest in the refugees exists because he knows they can challenge his assumptions. I want to use the motif of water surfaces to tie this argument together, particularly in the topic sentences, and this could look as follows:
Paragraph 1 : Richard realises that he only has a ‘surface-level’ appreciation of the refugees’ life experiences.
- He realises that he knows little about the African continent (“Nigeria has a coast?”)
- He suffers from a “poverty of experience” which means he hasn’t had to interact with this knowledge before
- His renaming of the refugees (Apollo, Tristan etc.) suggests that he still needs his own frame of reference to understand their experiences
- He learns about the hardships of migration through the tragic stories of those like Rashid
Paragraph 2 : He also realises that he has a ‘surface-level’ understanding of migration in general.
- This comes from the fact that he has never actually moved countries; he’s only been reclassified as an East German, and then again as a German. Neither happened because he wanted them to.
- On the other hand, the refugees want to settle in Europe: they want the right to work and make a living - it’s just that the “iron law” acts as a major barrier. Their powerlessness is different from Richard’s.
- Part of migration is also learning the language, and Richard is initially quite ignorant about this: he observes that the Ethiopian German teacher “for whatever reason speaks excellent German”, not realising this is necessary for any migrant to survive in the new country.
- We can think of this as the difference between migration and diaspora, the specific term for the dispersion of a people.
Paragraph 3 : Richard is more open than most people to looking beneath the surface though, meaning that his assumptions are challenged partly because he is willing for them to be.
- The symbol of the lake works well here to explain this: he is bothered by its still surface, and what lies underneath, while others aren’t
- We can also contrast this to characters like Monika and Jörg who remain quite ignorant the whole time: Richard’s views have departed from this throughout the course of the novel
- Ultimately, the novel is about visibility: Richard’s incorrect assumptions mean that he isn’t seeing reality, and his “research project” is all about making that reality visible.
Go Went Gone is usually studied in the Australian curriculum under Area of Study 1 - Text Response. For a detailed guide on Text Response, check out our Ultimate Guide to VCE Text Response .
Get exclusive weekly advice from Lisa, only available via email.
Power-up your learning with free essay topics, downloadable word banks, and updates on the latest VCE strategies.
latest articles
Check out our latest thought leadership on enterprise innovation., vce english unit 3, area of study 2: creating texts - what is it.

Breaking Down Themes & Key Quotes in The Erratics by Vicki Laveau-Harvie

Developing Interpretations SAC Guide: Interpreting Alias Grace
Keep in touch
Have questions? Get in touch with us here - we usually reply in 24 business hours.
Unfortunately, we won't be able to answer any emails here requesting personal help with your study or homework here!

Copyright © Lisa's Study Guides. All Rights Reserved. The VCAA does not endorse and is not affiliated with Lisa's Study Guides or vcestudyguides.com. The VCAA provides the only official, up to date versions of VCAA publications and information about courses including the VCE. VCE® is a registered trademark of the VCAA.
03 9028 5603 Call us: Monday to Friday between 3pm - 6pm or leave us a message and we'll call you back! Address: Level 2 Little Collins St Melbourne 3000 VIC
- Topical and themed
- Early years
- Special needs
- Schools directory
- Resources Jobs Schools directory News Search
Persuasive writing resources
Australia and new zealand, international schools, tes resources team.

Secondary English persuasive writing resources
Persuasive writing is a key topic which appears in all English language curriculum maps and is often one of the trickiest formats for students to master. From understanding what language features are, to highlighting them in a piece of text, analysing their use and implementing them in writing, persuasive writing draws in a range of skills for students to learn. So, to help you and your students out, we have gathered together a range of lessons and supportive materials to use in the classroom. For more English resources, take a look at the English hub .

Persuasive letter writing example

Travel Writing - Persuasive Articles
Persuasive Writing - school uniform

Persuasive Writing: TED Talks
Persuasive writing help sheet
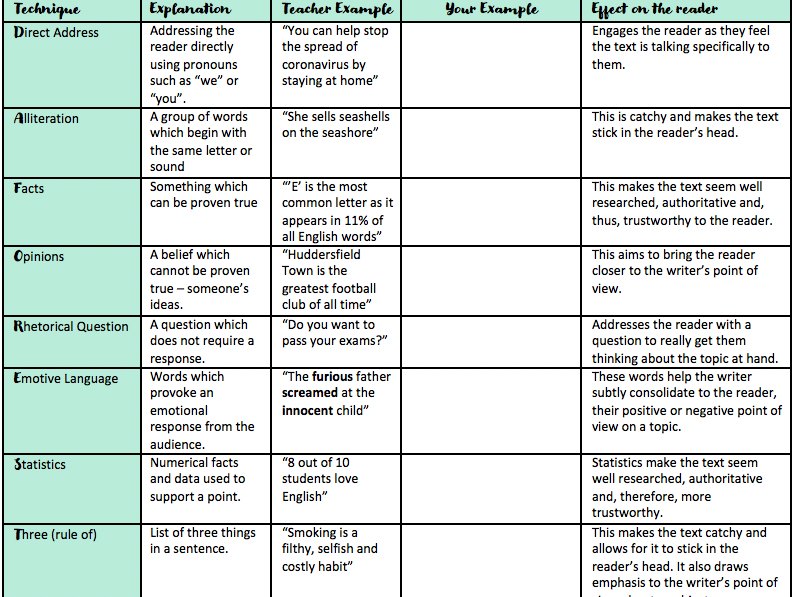
DAFOREST Techniques Grid/Persuasive Language Techniques Grid

Persuasive Speech Slow Write

Travel Writing Lesson

- About the Voiceless Grants Program
- Grants Criteria
- Expression of Interest Form
- 2023 Grant Recipients
- 2022 Grant Recipients
- 2004-2017 Grant Recipients
- Grants Frequently Asked Questions
- Prizes & Sponsorships
- Testimonials
- 2024 Grant Recipients
- Factory Farming
- Live Export
- Battery Hens
- Broiler Chickens
- Animal Sentience
- Animal Welfare Office
- Puppy Farming
- Truth in Labelling
- Animal Cruelty
Lesson Two: English, Yr 7/9
Identifying and using persuasive techniques in a text.
Curriculum links: Year 7 – ACELA1536 Year 9 – ACELA1770
Resources you will need
- Lesson 2 Persuasive Writing PowerPoint slides
- Techniques of persuasion worksheet (1 per student)
- Print-outs (1 per student) of the article: Lynn Simpson, ‘My 57 Voyages: Cruelty Onboard Australia’s Live Export Ships’ (2018), published on the Voiceless blog
- Animal Protection Encyclopedia
Lesson structure
- Using the Lesson 2 Persuasive Writing PowerPoint slides , teach students about the various different techniques used by writers to increase the persuasiveness of their writing.
- At the relevant point during the presentation, distribute to students the following text: Lynn Simpson, ‘My 57 Voyages: Cruelty Onboard Australia’s Live Export Ships’ (2018), published on the Voiceless blog
- Distribute the Techniques of persuasion worksheet to each student.
- Ask the students to fill in the worksheet by identifying the different techniques of persuasion used in the provided text. Students can work individually, or in groups.
- Using the Lesson 2 Persuasive Writing PowerPoint slides , discuss the different techniques used in the provided text.

SHARE THIS ON:
Australian curriculum alignment, join the voiceless community.
For academics, advocates, teachers and students, animal lovers, animal lawyers and everyone in between! Sign up below to learn more about our Voiceless Grants Program, our free library of resources on Animal Protection Education and Animal Law Education and other Voiceless related tidbits.
- First Name *
- Last Name *
- High School Education
- Name This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Thank you for providing your email. This allows us to record the number of downloads per resource, and determine its relative reach.
By downloading this file you agree to join our email list in accordance with our terms & conditions and privacy policy .
#FutureSTEMLeaders - Wiingy's $1200 scholarship for School and College Students

Book a Free Lesson

NAPLAN Year 9 Guide [Download of NAPLAN Year 9 Past Papers]
Written by Shefali Sundram

Year 9 is the second year in which students sit for the National Assessment Program – Literacy and Numeracy ( NAPLAN ). Students are tested for four testing domains through written and online assessments .
In this NAPLAN Year 9 exam guide, we have elaborated on the exam format and sample questions, provided resources to download Year 9 past papers and the exam dates for NAPLAN 2024 .
Need help with preparing for NAPLAN 2024? Register for a free demo with our online NAPLAN Tutor today .
What is NAPLAN Year 9?
The year 9 NAPLAN test is an annual assessment taken nationwide by all Australian students studying in year 9. The test includes assessments on four domains – Writing, Reading, Conventions of Language, and Numeracy.
In 2023 the NAPLAN Year 9 test will be conducted in a 13-day test window between Mar 15 and Mar 27.
The detailed format of the Year 9 NAPLAN assessment is as below:
What is the NAPLAN Year 9 exam format?
Students in Year 9 NAPLAN are tested on four testing domains through written and online assessments.
The four testing domains are: 1. Writing 2. Reading 3. Conventions of language 4. Numeracy or Math
NAPLAN Year 9 Writing
Students are provided with a ‘writing stimulus’ (sometimes called a ‘prompt’ – an idea or topic) and asked to write a response in a particular genre (narrative or persuasive writing).
The writing stimulus can be in two formats either:
- The persuasive writing, and
- The narrative writing
The NAPLAN Year 9 exam lasts 42 minutes. For the Year 9 NAPLAN test, writing is an online test.
NAPLAN Year 9 Persuasive Writing Examples
The question below is for reference purposes for the NAPLAN writing examples year 9 sample. The question below describes what to write and how to write.

NAPLAN Year 9 Narrative Writing Examples
The question below is from the NAPLAN 2016 Writing Test for Year 9. The question below describes what to write.

NAPLAN Year 9 Reading
Students read a range of informative, imaginative, and persuasive texts and then answer related questions. The reading section takes place after Writing. It is an online 65 minutes test.
NAPLAN Year 9 Reading Examples
The question below is from the NAPLAN 2016 Reading Test for Year 9. The question below describes what to write.

NAPLAN Year 9 Conventions of Language
Convention of language or Language conventions Year 9 of NAPLAN is held after the Reading Test of the NAPLAN exam. It is a 45 minutes test online test. This test assesses the spelling, grammar, and punctuation of the students. The sample question for language conventions NAPLAN year 9 is given below.
NAPLAN Year 9 Conventions of Language Examples
The question below is an example of NAPLAN practice Year 9 for Language Conventions for Year 9. Each question describes what to do.

NAPLAN Year 9 Numeracy
NAPLAN Numeracy Year 9 or Year 9 NAPLAN Maths is held after the Language Convention test of the NAPLAN exam. NAPLAN Maths Year 9 is a 65 minutes test online test. This test assesses numbers and algebra, measurement and geometry, and statistics and probability. The sample question for NAPLAN year 9 numeracy example test answers and questions are given below.
NAPLAN Year 9 Numeracy Examples
The question below is the NAPLAN year 9 example test answers with their Questions. Each question describes what to do.

- Jarrad will be paid $108 for working 6 hours.
- 3 2 × 2 2 = 36
- 8 horses will need 4 hectares of land.
- The value of the given expression will be -8.
- The maximum tickets Lara could buy are 10.

- Tammy was away for 8 hours 10 minutes.
- Mike has 2 1/4 cups left.
- The flash drive cost around $16.
How is NAPLAN Year 9 scored?
Results from the NAPLAN tests are reported on scales that compare student performance to established standards .
The scales are divided into 10 bands and apply to all academic years, from Year 3 to Year 9.
Not all bands are reported for each level of the year. For each year i.e. years 3, 5, 7, and 9, the scales and standards system are reported.
The band scale shown below reflects the standard marking pattern for the respective years i.e. years 3, 5, 7, and 9.

What is a good NAPLAN score for Year 9?
Each NAPLAN scale is divided into 10 bands used to report student progress through Years 3, 5, 7, and 9. Band 6 is the minimum standard for Year 9. Anything above Band 6 is considered to be a good score for Year 9. NAPLAN is not a test of intelligence, it only shows a snapshot of the reading, writing, and numeracy skills of the student.

NAPLAN 2023 Dates Year 9
In 2024, NAPLAN Year 9 will be conducted between 13 March to 25 March 2024 all across Australia.
Schools can complete practice tests in the assessment platform from Term 4. Prospective students can use the public demonstration site at any time during the year to familiarize themselves with the format of the test.
Tip : For more up-to-date information you can check out our article on NAPLAN 2O24 .
Resources to download NAPLAN Year 9 past papers
n addition to the comprehensive insights provided in our NAPLAN Year 9 exam guide, we recognize the importance of practice and preparation for NAPLAN exam.
We have made a downloadable resource for NAPLAN past test papers .
These past papers serve as a practice tool for students to familiarize themselves with the exam format, question types, and the level of difficulty they can expect.
Click on the link below to download NAPLAN year 9 past papers for all subjects and all years:

You can also download NAPLAN sample papers from the official website. The steps to download are as follows:
- Step 1: Go to the official ACARA website (Australian Curriculum, Assessment, and Reporting Authority).
- Step 2: Look through the Assessment section of the website.
- Step 3: Locate the NAPLAN section
- Step 4: Download the NAPLAN Year 9 past papers using the page’s link.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the highest band in naplan year 9.
Band 10 is the highest band for Year 9 and Band 5 is the lowest band for Year 9. Also, Band 6 is the minimum standard for Year 9.
Is Year 9 NAPLAN Important?
Yes, the Year 9 NAPLAN score is an important assessment criterion for appearing in the Year 10 Minimum Standard Literacy and Numeracy Test. The Higher School Certificate (HSC) cannot be awarded until the Year 9 NAPLAN test has been passed.
How to Practice for NAPLAN Year 9 ?
Download the past test papers using the link provided above and take NAPLAN Year 9 practice tests in a timed environment. Make sure to practice each test for NAPLAN year 9 within its specified time limit as defined by ACARA.
Reviewed by
Share article on

Summer Boarding Courses
100 Persuasive Writing Prompts for Writers aged 8 to 18

Being able to state your ideas and offer evidence for your arguments is an excellent skill to have! If you can convince people that you are right, you will be able to achieve so much more within your job, with your friends and new people that you meet.
Persuasive writing is about trying to get the reader to agree with your opinion or ideas. To be able to express what you want and what you believe to be true, we at Summer Boarding Courses have put together these 100 persuasive writing prompts to help you exercise your tactics!
Persuasive Writing Prompts for Writers
We have 25 fun writing prompts for each age group below that we teach at Summer Boarding Courses in the UK.
Present your arguments like a pro, build upon your critical thinking skills and communicate seamlessly through your writing with these opinion writing prompts.
But first, before you begin to write, you must consider the following…
Which audience are you trying to persuade?
Who are your trying to persuade? Is it your friends, your teachers, the manager of a company or the whole community that you live within? Different groups of people have different wishes, ideas, needs and wants. Think carefully about what appeals to the group you are trying to convince.
For example, if you are student arguing that school break times should be longer to your student friends, they may be easier to persuade than the teachers!
Students love to hang out with their friends, go outside, do sport and eat delicious food.
However, if you are trying to convince the teachers at your school that break times should be longer, they may feel stressed and unsure about this. They have lessons that they need to deliver to you, work goals to meet, and your education and learning is at the forefront of their minds.
If you can convince them that you can complete your learning is less time, they might just agree that longer break times are a good idea!
Always try and appeal to each person’s perspective so that you can convince as best as you can.
Be kind and respectful
We can all have different ideas about what is right, wrong, correct and unusual. Be respectful and kind when arguing in your speech or writing about what you are standing for. We are all entitled to our opinion, and for many issues, there are pros and cons for each side that we take.
Here are some key phrases that you can use to help yourself get your point across clearly and politely:
‘In my opinion…’
‘I feel that…’
‘Others must agree that…’
‘It seems to me that…’
‘Some people believe that…’
‘For this reason…’
‘I agree that…’
‘On the other hand…’
Firstly…Secondly….’

Introduce your argument in the first paragraph
Start your piece with an introductory paragraph that states your argument. This paragraph will clearly tell the reader what your opinion is and what you are standing for.
Support your argument with at least three pieces of evidence
Most people will not be convinced of your ideas unless you can show them evidence. This evidence can be qualitative or quantitative.
Qualitative evidence
Qualitative evidence is descriptive information that can come from a personal story, an interview, a drawing or a photograph. You can find this information from personally talking to people about their experiences.
Quantitative evidence
Quantitative evidence is about numbers, statistics and concrete data. This information can come from surveys, official records and experiments which carefully follow methods to try and ensure accurate information. Many people prefer to see quantitative evidence, as personal stories collected for qualitative evidence can sometimes be inaccurate.
Show that you understand the different sides to your argument
A clear and coherent writer who is putting their argument forward will have taken the time to consider other points of view different to their own. Show the reader that you understand and can see what else people may argue. Try and have a good answer back to these thoughts.
If you have evidence to support your counterargument, even better!
Ask questions
Ask your reader questions to get them to think about what you are arguing. This way, you can challenge their point of view.
They will start thinking about other perspectives that they may not have considered before.
If you’re stuck: think about a time where you did convince someone
Has there been a time in the past where you did successfully manage to persuade someone to see your point of view? Think about this time carefully.
How did you manage to convince the person? What strategies and language did you use?
Has there been a time where you were persuaded by someone?
Channel these techniques into your writing to put forward the best argument you can.

Finish your argument with a strong closing statement
Summarise your ideas and reinforce your argument so that readers are reminded about why your argument is valid. This is your last chance to sway their opinion!
Find below our 100 essay writing prompts to help you practice your persuasive skills.
25 Persuasive Young Kids Writing Prompts
Are you looking for 4th grade and 5th grade writing prompts? Or prompts for ages a little younger or older for kids? Here are our 20 writing persuasive prompts for students aged 8 to 12!
I should be able to go to bed when I want.
All classrooms should have a class pet.
There needs to a be a non-school uniform day every week.
You can only eat apples or oranges for the next week. Which one will you eat? Why?
I should be allowed to stay home alone.
There should be no homework at school.
Break times at school should be longer.
People should be fined for dropping litter.
I should be allowed to eat ice cream every day.
All students should learn how to cook.
Persuade your family to let you open a birthday present the day before your birthday.
Persuade your family to give you twice as much pocket money.
If you could have any pet, what would it be? Convince your family why you should care for it.
Convince your friend to swap their packed lunch with yours.
Students should be allowed to pick their own seats in class.
Persuade your family to watch the film you want to watch.
Dogs are better than cats.
School holidays should be longer.
Imagine in the future, you can live on land or underwater. Which one would you choose? Why?
You have to live in another country. Which one do you choose? Why?
Convince your family to let you watch your favourite TV programme.
Students should be allowed to choose their teacher.
Students should have 3-day weekends.
You can only play one sport for the next month. What is it? Why?
Students who are late to school should do a chore for their class.
You can choose one superhero power to help others: fly or stop time. Which one do you choose? Why?
Study English Abroad with Summer Boarding Courses
Find out more about how we can help you with your ESL writing, speaking, listening and reading.
25 Prompts for Persuasive Writing for Older Kids
Here are 25 writing persuasive prompts for students aged 11 to 15. If you’re looking for 7th grade and 8th grade writing prompts particularly, these are for you!
Mobile phones should be allowed to be used in the classroom.
It should be made mandatory to eat vegetables every day at school.
The school day should start later and end later in the day.
There should be a computer game room at school.
All students should learn at least 2 languages in school.
Students should be able to wear whatever they want at school.
Students should be taught only how to type; not write with pen and paper.
The first lesson of school every day should be exercise.
Facebook states that you must be at least 13 years old to have a Facebook account. Is this fair?
Persuade your brother/sister to do your house chores for one week.
Smoking should be banned in all public areas.
Teachers must wear a uniform to school. What is the uniform? Why?
Family should only give pocket money if chores are completed.
Persuade your teacher to let you eat your favourite snacks in class.
We should all learn how to grow our own fruit and vegetables.
Persuade your family to take you on holiday to a destination you want to go to.
Persuade your friend who doesn’t like sports to play your favourite sport with you.
Fast food like chips and pizza should be served everyday in the school canteen. Yes or no?
Persuade your family to let you stay at your friend’s house.
Teachers should not be allowed to have their cell phone in the classroom.
There should be one day per week where the whole nation must be vegetarian.
Fizzy drinks should be banned from school.
Students should be paid for getting good grades.
Is it better to have enough money, or too much money?
I should decide what time my bedtime is.

25 Ideas for Argumentative Writing Prompts for Teenagers
These writing prompts are great for students aged 13 to 16!
Teenagers should not do any chores at home.
All students should teach one lesson to their class each term.
Students should be allowed to use their mobile phones at any time in school.
All students should volunteer in their community once every week.
Persuade your friend to help you with your homework.
Imagine you can create a new class to be taught in your school. What subject would it be? Why should it be taught?
Students who commit cyber-bullying should be suspended from school. Yes or no? Why?
The voting age should be lowered to age 13.
Persuade your teacher to have their lessons outside in the Summer.
Persuade your family to let you redecorate your bedroom.
Imagine that you have been granted a ticket to live on Mars. If you go, you are not allowed to come back to Earth. Would you go? Why?
Textbooks should be replaced by tablets or e-readers.
Persuade your teacher to end their class 10 minutes early.
Persuade your teacher to let your class have a party.
Imagine that you are given 1 million pounds to improve your neighbourhood. What would you do with the money? Why are your ideas the right thing to do?
Persuade your teacher to not set your class homework for the next month.
Everyone under the age of 17 should have to stay in after 9pm.
People should only be allowed to drive their cars 4 days a week to minimise pollution.
Country life is better than city life.
All students should be allowed to study abroad once per year.
Teenagers under the age of 15 should not be allowed to have a Facebook page.
The internet should be free for everyone.
Everyone should eat vegan food one day per week.
All school classes should be outdoors in the forest.
25 Young Adult Persuasive Essay Prompts
These quick writing prompts for students aged 15 to 17 will have you scribbling away to get your point across!
All students should learn how to make YouTube videos.
People should pay extra tax when they buy drinks in plastic bottles.
Humans are living longer, to the point where we may become immortal in the future. Would living forever be a good? Argue your point of view.
Students should be allowed to listen to their own music on headphones when working in class. Argue your viewpoint.
Teenagers around the world should not be allowed to drive until they are 18.
You have been given money to hold a major event in your hometown. What would the event be about or for? Why should people come?
Imagine you want to be the next president of your country. Why should people vote for you?
Convince your friend to lend you something special of theirs.
Persuade your family to let you study overseas at a Summer School next year.
Imagine that you have been given the chance to interview for your dream job. Convince the boss that you are the person they should choose.
Persuade your family to watch a movie on Netflix that you want to watch.
You have just started a new business making a phone better than the iPhone. Explain what features your phone has, that makes it much better than Apple’s.
Persuade a friend to come to a new activity group with you that they are feeling anxious about.
Aliens exist. True or false? Argue your point of view.
All young adults should be required by law to volunteer in their community once every week. Yes or no?
Mathematics class is more important than music class. Yes or no? Why?
City life is better than country life.
Driving tests should be mandatory every year after you are 65 years old.
Students who bully others should be suspended from school.
There should be one currency for the whole world.
Recycling should be a legal requirement for every household.
Life is better than it was 10 years ago.
Girls and boys should study separately in school.
You can choose to put one celebrity on your country’s highest-value banknote. Who is the celebrity? Why should they be placed on the note?
Life is better without a computer.
Are you ready to improve your persuasive writing?
We hope you have enjoyed these free writing prompts! This is your chance to change the world in which we live through your thoughts!
If you want to work on your writing in English, try and aim to make these your daily writing prompts! We also recommend using pictures as writing prompts. Looking at pictures with writing prompts, rather than just seeing a sentence, can help you create your arguments and ideas if you are a visual learner .
And if you are ready to fully immerse yourself in a thriving and educational setting, come and study with us this Summer!
At Summer Boarding Courses, we run many courses for all international students aged 8 to 17 years old and would love for you to join us. We can help you improve your ESL writing as well as your English speaking, listening and reading skills with many other nationalities.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Part 10: How to Write Persuasive Essays | Year 9 English Guide. Are you unsure of how to approach writing persuasive writing? Don't worry! In this article, we will go through what persuasive writing is, what markers are looking for in your persuasive essays. We will then discuss planning and explain how to write persuasive essays.
This round-up of persuasive writing examples includes famous speeches, influential ad campaigns, contemporary reviews of famous books, and more. ... Sample lines: "Obviously, Harry Potter and the Sorcerer's Stone should make any modern 11-year-old a very happy reader. The novel moves quickly, packs in everything from a boa constrictor that ...
Persuasive writing, also known as the argument essay, utilizes logic and reason to show that one idea is more legitimate than another idea. It attempts to persuade a reader to adopt a certain point of view or to take a particular action. The argument must always use sound reasoning and solid evidence by stating facts, giving logical reasons ...
Thesis statement: Let the audience know your stance. After surveying the topic in the first part of the introduction, it is now time for the student writer to express their opinion and briefly preview the points they will make later in the essay. 2. Body Paragraphs.
Students practice arguing both sides of a four different topics. Arguing Both Sides Worksheet 2 - Here's another persuasive essay worksheet to help students practice approaching writing prompts logically. In this double-sided worksheet students practice arguing both sides of a selection of topics.
Give your secondary students all the persuasive writing techniques and tricks they need with this round-up of the best resources and advice. ... The resource includes activities, discussion points, and two example letters. 10 tips for better persuasive writing. ... Year 5 Year 6 Year 7 Year 8 Year 9 Year 10 Year 11 ...
Spelling and grammar. It goes without saying that to achieve a Band 8 or above in writing, you need to ensure your spelling and grammar are spotless (or close to being so). All sentences should be correctly structured, with a variety of sentences being used - e.g. simple, compound and truncated.
Part of English Non-fiction Year 5 Year 6. Save to My Bitesize Remove from My Bitesize. Jump to. Video: Persuasive writing ... Use your table to note down examples of persuasive writing as they ...
Analysis of a persuasive speech script; Generation of persuasive topics; Planning and writing pages, broken down into easily manageable steps; Sample essay marking schedule; Sample teaching plan; Teacher keys; And more… While originally created for Year 9 - Year 11 students in Australia and New Zealand, this versatile resource can be used ...
Persuasive Essay Format Example. A persuasive essay outline is bound to follow a specific format and structure. The main elements of a persuasive essay format are as follows. Font: Times New Roman, Georgia, or Arial. Font Size: 16pt for the headlines and 12pt for the rest of the text. Alignment: Justified.
The word persuade literally means to 'thoroughly sweeten.'. This is a great metaphor for the action of persuasion - when you persuade someone you try and make whatever it is you want seem ...
PERSUASIVE WRITING YEAR 9 BOOKLET - Free download as Word Doc (.doc / .docx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free.
Persuasive writing is a form of writing where the writer attempts to convince or persuade the audience to adopt a particular point of view or take a specific action by presenting logical reasoning, supporting evidence, and compelling arguments. This type of writing encourages students to formulate a clear viewpoint on a particular topic ...
Year 9 Assessments and Exams. In Year 9, this is where you will gain exposure to an array of forms of texts, ranging from creative responses, speeches, analytical essays, film, poetry and persuasive pieces. Throughout the year, you will study a range of different texts (the ones mentioned above) and the activities and assessment tasks you will ...
Persuasive writing is a key topic which appears in all English language curriculum maps and is often one of the trickiest formats for students to master. From understanding what language features are, to highlighting them in a piece of text, analysing their use and implementing them in writing, persuasive writing draws in a range of skills for ...
Part of English Non-fiction Year 3 Year 4. Save to My Bitesize Remove from My Bitesize. Jump to. ... Use your table to note down examples of persuasive writing that have been used in the article.
Year 9 English Page 2 of 23 December 2011 English Year 9 English - Work sample 1 Work sample 1: Persuasive speech - School uniforms should be compulsory Relevant parts of the achievement standard Receptive modes (listening, reading and viewing) By the end of Year 9, students analyse the ways that text structures can be manipulated for effect ...
Using the Lesson 2 Persuasive Writing PowerPoint slides, discuss the different techniques used in the provided text. ... Year 9 . Sequencing and developing an argument using basic language structures that suggest conclusions ('therefore', 'thus' and 'so') or give reasons ('since', 'because') or suggest conditionals ('if ...
Include a range of persuasive devices to do this. x See the list of twenty-five at the end of the booklet. x Please be advised not to overdo persuasive devices: you must have a well-constructed, detailed argument. Half a dozen persuasive devices per piece of writing is plenty - focus on placing them at key moments to make an idea memorable.
The narrative writing; The NAPLAN Year 9 exam lasts 42 minutes. For the Year 9 NAPLAN test, writing is an online test. NAPLAN Year 9 Persuasive Writing Examples. The question below is for reference purposes for the NAPLAN writing examples year 9 sample. The question below describes what to write and how to write. NAPLAN Persuasive Writing Year 9
Here are some key phrases that you can use to help yourself get your point across clearly and politely: 'In my opinion…'. 'I feel that…'. 'Others must agree that…'. 'It seems to me that…'. 'Some people believe that…'. 'For this reason…'. 'I agree that…'. 'On the other hand…'.