
How to Write a Character Analysis Essay

A character analysis essay is a challenging type of essay students usually write for literature or English courses. In this article, we will explain the definition of character analysis and how to approach it. We will also touch on how to analyze characters and guide you through writing character analysis essays.
Typically, this kind of writing requires students to describe the character in the story's context. This can be fulfilled by analyzing the relationship between the character in question and other personas. Although, sometimes, giving your personal opinion and analysis of a specific character is also appropriate.
Let's explain the specifics of how to do a character analysis by getting straight to defining what is a character analysis. Our term paper writers will have you covered with a thorough guide!
What Is a Character Analysis Essay?
The character analysis definition explains the in-depth personality traits and analyzes characteristics of a certain hero. Mostly, the characters are from literature, but sometimes other art forms, such as cinematography. In a character analysis essay, your main job is to tell the reader who the character is and what role they play in the story. Therefore, despite your personal opinion and preferences, it is really important to use your critical thinking skills and be objective toward the character you are analyzing. A character analysis essay usually involves the character's relationship with others, their behavior, manner of speaking, how they look, and many other characteristics.
Although it's not a section about your job experience or education on a resume, sometimes it is appropriate to give your personal opinion and analysis of a particular character.
What Is the Purpose of a Character Analysis Essay
More than fulfilling a requirement, this type of essay mainly helps the reader understand the character and their world. One of the essential purposes of a character analysis essay is to look at the anatomy of a character in the story and dissect who they are. We must be able to study how the character was shaped and then learn from their life.
A good example of a character for a character analysis essay is Daisy Buchanan from 'The Great Gatsby.' The essay starts off by explaining who Daisy is and how she relates to the main character, Jay Gatsby. Depending on your audience, you need to decide how much of the plot should be included. If the entire class writes an essay on Daisy Buchanan, it is logical to assume everyone has read the book. Although, if you know for certain that your audience has little to no knowledge of who she is, it is crucial to include as much background information as possible.
After that, you must explain the character through certain situations involving her and what she said or did. Make sure to explain to the reader why you included certain episodes and how they have showcased the character. Finally, summarize everything by clearly stating the character's purpose and role in the story.
We also highly recommend reading how to write a hook for an essay .
Still Need Help with Your Character Analysis Essay?
Different types of characters.
To make it clear how a reader learns about a character in the story, you should note that several characters are based on their behaviors, traits, and roles within a story. We have gathered some of them, along with vivid examples from famous literature and cinema pieces:

Types of Characters
- Major : These are the main characters; they run the story. Regularly, there are only one or two major characters. Major characters are usually of two types: the protagonist – the good guy, and the antagonist: the bad guy or the villain.
- Protagonist (s) (heroes): The main character around whom most of the plot revolves.
For example, Othello from Shakespeare's play, Frodo from The Lord of the Rings by J.R.R. Tolkien, Harry Potter from the Harry Potter series by J.K. Rowling, and Elizabeth Bennet from 'Pride and Prejudice' by Jane Austen.
- Antagonist (s): This is the person that is in opposition to the protagonist. This is usually the villain, but it could also be a natural power, set of circumstances, majestic being, etc.
For example, Darth Vader from the Star Wars series by George Lucas, King Joffrey from Game of Thrones, or the Wicked Queen from 'Snow White and Seven Dwarfs.'
- Minor : These characters help tell the major character's tale by letting them interact and reveal their personalities, situations, and/or stories. They are commonly static (unchanging). The minor characters in The Lord of the Rings by J.R.R. Tolkien would be the whole Fellowship of the ring. In their own way, each member of the Fellowship helps Frodo get the ring to Mordor; without them, the protagonist would not be a protagonist and would not be able to succeed. In the Harry Potter series by J.K. Rowling, minor characters are Ronald Weasley and Hermione Granger. They consistently help Harry Potter on his quests against Voldemort, and, like Frodo, he wouldn't have succeeded without them.
On top of being categorized as a protagonist, antagonist, or minor character, a character can also be dynamic, static, or foil.
- Dynamic (changing): Very often, the main character is dynamic.
An example would also be Harry Potter from the book series by J.K. Rowling. Throughout the series, we see Harry Potter noticing his likeness to Voldemort. Nevertheless, Harry resists these traits because, unlike Voldemort, he is a good person and resists any desire to become a dark wizard.
- Static (unchanging): Someone who does not change throughout the story is static.
A good example of a static character is Atticus Finch from “How to Kill a Mockingbird” by Harper Lee. His character and views do not change throughout the book. He is firm and steady in his beliefs despite controversial circumstances.
- Foils : These characters' job is to draw attention to the main character(s) to enhance the protagonist's role.
A great example of a foil charact e r is Dr. Watson from the Sherlock Holmes series by Arthur Conan Doyle.
How to Analyze a Character
While preparing to analyze your character, make sure to read the story carefully.
- Pay attention to the situations where the character is involved, their dialogues, and their role in the plot.
- Make sure you include information about what your character achieves on a big scale and how they influence other characters.
- Despite the categories above, try thinking outside the box and explore your character from around.
- Avoid general statements and being too basic. Instead, focus on exploring the complexities and details of your character(s).
How to Write a Character Analysis Essay?
To learn how to write a character analysis essay and gather a more profound sense of truly understanding these characters, one must completely immerse themself in the story or literary piece.
- Take note of the setting, climax, and other important academic parts.
- You must be able to feel and see through the characters. Observe how analysis essay writer shaped these characters into life.
- Notice how little or how vast the character identities were described.
- Look at the characters' morals and behaviors and how they have affected situations and other characters throughout the story.
- Finally, observe the characters whom you find interesting.
Meanwhile, if you need help writing a paper, leave us a message ' write my paper .'
How Do You Start a Character Analysis Essay
When writing a character analysis essay, first, you have to choose a character you'd like to write about. Sometimes a character will be readily assigned to you. It's wise to consider characters who play a dynamic role in the story. This will captivate the reader as there will be much information about these personas.
Read the Story
You might think that if you already have read the book, there is no need to do so again; however, now that you know the character you would like to focus on, reading it again will have plenty of benefits. It will give you an opportunity to be more precise while reading the scenes that relate directly to your character and are important for his/her analysis. While reading the book, pay attention to every tiny detail to make sure you grasp the whole array of your character's traits.
Consider the following things:
- What specific descriptions does the author provide for each character?
For example, when J.K. Rowling describes Harry Potter for the first time, she describes his clothes as old and oversized, his hair untidy, and his glasses as broken. It might seem just like a simple description, but she expresses compassion and pity for an orphan neglected by his only relatives.
- What kinds of relationships does your character have with others?
Think about how Harry builds up his friendships with others. First, he and Ron do not like Hermione because she acts like a know-it-all, but when she gets stuck in the dungeons with a horrendous troll, he rushes to save her regardless.
- How do the actions of the character move the plot forward?
In 'The Philosopher's Stone,' Harry is very observant of any events taking place at school. He analyzes people's actions, which builds up the plot around the stone and its importance for the magical world.
Get help with your character analysis from our experts.
Choose a Dynamic Character
Choosing a dynamic character is a great idea. This does not necessarily have to be the protagonist, but a character that undergoes many changes has grown throughout the story and is not boring and/or static. This gives you a perfect advantage to fully show the character and make your paper entertaining and engaging for the reader. If you choose a character that is not very dynamic, your essay might seem monotonous because your character will not end up doing much and will not be very involved in the story.
While you are reading, it is useful to take notes or highlight/underline any of the critical elements of the story. This will add depth to your character description(s). By providing vivid and specific examples, you connect your reader to the character, and the character comes alive in their eyes. Review your notes and formulate the main idea about your character when you're finished reading with your character in mind.
Make an initial draft while taking note of the character analysis essay outline provided by your instructor. You may follow the recommended character analysis essay format if you have not been provided with a sample.
Choose a Main Idea
While reading the story, make sure you keep track of your notes. It is a good idea to look at them, choose the ones that are the most representative of your character and find patterns. This will be your thesis. Then, you must support this idea with examples and situations involving your character.
If your character were Jem Finch from 'To Kill a Mockingbird' by Harper Lee, the main idea would be how his personal character is shaped through racial conflicts, social inequalities, and internal struggles between public opinion, his own views, and what is actually right. Essaypro offers you history essay help. Leave us a notice if you need to proofread, edit, or write your essay.
Character Analysis Questions
Now that you have jotted down some main concepts about your character, here is a list of questions that can help you fill in the blanks you might still have:
.webp)
- Where do the events involving your character take place?
- What are the relationships between your character and other significant characters?
- What is the primary change your character has gone through throughout the story?
- What is your character's background?
- What is your character's occupation?
- What kind of emotions does your character go through?
- What are your character's values?
- What is your character's value?
- Does your character have friends?
- Is there a lesson your character has learned by the end of the story?
- Does the character achieve the goals he/she has set for himself/herself?
Make a Character Analysis Essay Outline
When you're unsure how to write a character synopsis, remember that creating a literary analysis outline is one of the most critical steps. A well-constructed character analysis outline will keep your thoughts and ideas organized.
Character Analysis Essay Introduction:
Make the introduction to your paper brief and meaningful. It should hold together your entire essay and spark your audience's interest. Write a short description of the character in question. Don't forget to include a character analysis thesis statement which should make a case for the character's relevance within the narrative context.
Character Analysis Essay Body:
Subdivide your body paragraphs into different ideas or areas regarding the character. Look at your professor's rubric and ensure you'll be able to tackle all the requirements. You should also be provided with questions to be answered to formulate your analysis better. The body should answer the following questions:
- What is the character's physical appearance, personality, and background?
- What are the conflicts the character experiences, and how did he/she overcome them?
- What can we learn from this character?
- What is the meaning behind the character's actions? What motivates him/her?
- What does the character do? How does he/she treat others? Is he/she fair or unjust?
- What does the character say? What is his/her choice of words? Does he/she have a rich vocabulary?
- How does the character describe themself? How do others describe him/her?
- What words do you associate with the character? Perhaps a word like 'hope,' 'bravery,' or maybe even 'freedom'?
Character Analysis Essay Conclusion:
It's time to master the secrets of how to write character analysis essay conclusions. Your ending should also hold your ideas together and shape a final analysis statement. Mention things about the character's conflicts that we could experience in real life. Additionally, you can write about how a character should've reacted to a certain situation.
Character Analysis Essay Example
Read our blogs ‘Character Analysis of Jem Finch', 'The Great Gatsby Book Through Daisy Buchanan Character,' 'Analysis of Characters in Beowulf,' or simply use these character analysis essay examples to reference your paper. You might also be interested in a synthesis essay example .
Now that you know what is character analysis, it might be time to choose a character to write about. If you find yourself in a situation where you need to type ' do my homework for me ,' you should contact our writers. You also get a free plagiarism report, formatting, and citing when buying an essay from us!
STRUGGLE with Writing an Essay?
Address to our professional writers and get help asap!
Related Articles
.webp)
Writing a Character Analysis Essay | Step-by-Step Guide
I’m also going to give you a ton of examples.
This post is split into four parts for easy navigation:
- What is a Character Analysis Essay?
- What is the best Format to Use?
- 11 Character Analysis Example Ideas
- Template, Checklist and Outline for Your own Piece

In this post, I’m going to explain to you clearly and in a step-by-step way how to conduct a character analysis.
1. What is a Character Analysis Essay?
Let’s get you started with some really simple details about what a character analysis is:
- A Quick Definition: A character analysis essay zooms-in on a character in a book, movie or even real life. It provides what we sometimes call a ‘sketch’ of a character.
- The Purpose of a Character Analysis: The purpose of a character analysis is to reveal interesting details about the character that might contain a broader moral message about the human condition. For example, Atticus Finch is not just a lawyer in To Kill a Mockingbird. Rather, he provides us with a moral message about the importance of doing what you believe is right even though you know you will likely fail.
2. What is the best Character Analysis Essay Format?
Character analysis essays do not have just one format.
However, let me offer some advice that might act as a character analysis essay outline or ‘checklist’ of possible things you could discuss:
1. Start with the Simple Details.
You can start a character analysis by providing a simple, clear description of who your character is. Look at some basic identity traits such as:
- Race (if relevant)
- Social class (if relevant)
- Protagonist or Antagonist? A protagonist is the character who is our central character in the plot; the antagonist is often the protagonist’s opponent or challenger.
- Major or minor character?
2. What are the character’s distinctive personality features?
Your character might have some really clearly identifiable character traits. It’s best to highlight in your character analysis the exact traits that this character possesses. Some common character traits include:
I recommend you take a moment to write down what you think the top 3 to 5 words are that you’d use to explain your character’s personality traits. These will be important to discuss throughout your character analysis.
Sometimes a character may start out with some personality traits, but change over the course of the text. This is quite common; and one clear example of this is Lady Macbeth she deteriorates from a cutthroat power player to a guilt ridden shell of a person roaming the halls of the castle. This dramatic character change is something that makes her very interesting, and is worthy of discussion!
3. What are the character’s key relationships?
Does your character have a close relationship with a certain person in the storyline?
You might want to discuss the character’s relationships as a part of your character analysis. These relationships may reveal some key personality traits of your character.
For example, in Shakespeare’s play Hamlet, Horatio is the loyal offsider to Hamlet. Through his actions in staying by Hamlet through thick and thin, we learn that he is a deeply loyal character.
Examining the character’s relationships with their friends and foes therefore is very useful for digging deeper into who this character actually is, and what personality traits they have when they are put to the test within the narrative.
4. What are the character’s motivations?
Another thing you might want to examine are the character’s motivations . What do they desire most in the world? Some common motivations for characters in stories are:
- A simple life
- To serve others
This list really could be endless, but I hope the above examples give you a bit of an idea of the sorts of traits to look out for. By mentioning and examining the motivations of the character, we will come closer and closer to learning exactly what moral message this character might be able to tell us.
5. What are the character’s key conflicts?
Stories tend to have a beginning, a complication, and a resolution.
The complication involves conflicts and challenges that need to be overcome. For Edmund in Narnia, it’s cowardice. For Romeo and Juliet, it’s the conflict between love and family loyalty. Here’s some other common conflicts for characters:
- Whether to stay loyal to a friend;
- To overcome obstacles to love;
- To seek a way out of a challenging situation;
- To escape war or poverty;
- To persevere through imprisonment;
- To overcome personal fear
Again, this list is endless.
Knowing the character’s core conflict gets us even closer to knowing the moral that the character is trying to teach us.
For example, in Romeo and Juliet, the challenge of Romeo and Juliet being together despite their families’ objections teaches us something. Personally, I believe it teaches us the importance of letting go of old grudges in order to let love bloom.
This moral lesson was taught to us through conflict: namely, the conflict that Romeo and Juliet were right in the center of.
6. What are the character’s epiphanies?
Sometimes a character has an epiphany. This often happens towards the end of the story and helps the character overcome the challenge or conflict that we discussed in the point above.
Here’s an example of an epiphany:
- In the Lion King, Simba runs away from his tribe to live in exile. After a chance encounter with his childhood friend Nala, he has an epiphany that he has a duty to his tribe. This leads him back home to fight Scar and return freedom to Pride Rock.
Not all characters have an epiphany. But, if they do, I strongly encourage you to write about it in your character analysis.
7. Examine the moral message the character teaches us.
Finally, conclude by examining the moral message behind the character. Nearly every character has something to teach the reader. Authors put a lot of thought into creating complex characters with whom we can relate. We relate to the character and say “wow, they taught me a lesson about something!”
The lesson might be something like:
- Money doesn’t buy happiness;
- Loyalty to family comes above all else;
- Love gives life meaning;
- Honesty is always the best policy
This is the core of your character analysis essay. If you can pick out exactly what moral message the character teaches you, you’ll be well on your way to writing a strong character analysis.
Below I’m going to give you some examples to help you out. I know it can be hard to really get your head around a character, so sometimes the best thing is to look at some samples!
3. Here’s 13 Example Character Analysis Essay Ideas.
Most times when we create a character analysis, we’re exploring the deeper moral stories / aspects of humanity. Here’s some example ideas. I’ve tried to outline in less than a paragraph exactly what your key point will be about each character:
- Atticus Finch from To Kill a Mockingbird: A character who teaches us a lesson about standing up for what’s right, even if you know you’re likely to lose.
- Huckleberry Finn from Huckleberry Finn: A character who reveals our inner desire for freedom from the elements of society that constrain us.
- Dudley from Harry Potter: A character whose personality tells us a cautionary tale of the perils of middle-class narcissism, parents’ desire to wrap their children in cotton wool, and the lack of discipline we perceive in contemporary childhoods.
- Jack from Lord of the Flies: A character who represents the innate desire for power that seems to lurk not too far from the surface of the human condition. When social structures are stripped away, he quickly reverts to violence and superstition to assert control over his peers.
- Lady Macbeth from Macbeth: Lady Macbeth teaches us a valuable lesson about the perils of contravening our own morality. She starts out a cutthroat killer but is increasingly consumed by the guilt of her own actions. While we may be able to escape full punishment from outside forces, it is the inner guilt that might eat us away to our last.
- The Boy who Cried Wolf: The boy who cried wolf is a character whose fatal flaw is his desire for attention and adulation. His repeated attempts at gaining the attention of others leads the townspeople to no longer take him seriously, which causes him harm when he actually needs the villagers to take him seriously to save his life. He teaches us the virtue of honest and humility.
- Nick Carraway from the Great Gatsby: Nick shows us all the inner conflict between the trappings of wealth, glamor and spectacle; and the desire for simplicity, honesty and community. He is drawn by the dazzling world of East Egg, New York, but by the end of the novel sees live in East Egg as shallow and lacking the moral depth of his former life in small town Minnesota.
- Alice from Alice in Wonderland: In many ways, Alice represents the child within all of us. She is a character of goodwill to all and who looks upon the world (or, rather, Wonderland) with awe. Travelling with a cadre of flawed characters, she learns with them the importance of seeking strength from within.
- The Nurse in Romeo and Juliet: Like many Shakespearian characters, the nurse’s role is both as loyal confidante to a central character and comic relief. Shakespeare uses minor characters to regale his crowd and sustain viewer interest between scenes.
- Lucy in The Lion, the Witch and the Wardrobe: Lucy represents a surprising character whose youthfulness and small stature make her an underrated character by all around her. Nonetheless, she possesses within the bravery and loyalty necessary to carry out the quest for Aslan. Lucy represents the goodness in children and, by extension, all of mankind.
- Anne in Anne of Green Gables: Anne occupies the typical literary role of young girls in many classical novels: she represents innocence and wonder, and her contraventions of rules are seen through a prism of childhood innocence. This frames Anne not as a deviant but as a precious soul.
- Simba from The Lion King: Simba’s story follows his struggle with growing up, embracing his destiny and duty to his family, or fleeing towards freedom and a ‘no worries’ lifestyle. Simba flees Pride Rock and goes through an existential crisis with his existentialist friends Timon and Pumba. When he runs into an old childhood friend, he realizes how shallow his new carefree life has become and reflects upon his obligation to his community back home.
- Woody from Toy Story: Woody starts out Andy’s favorite toy, but when Andy gets a new flashier toy, Woody’s status amongst the toys falls apart. Woody’s key character challenge is to learn to be humble and inclusive living within the group. By the end of the movie, Woody realizes his duty to love and serve Andy is more important than his own status within the group.
4. Here’s an Example Template for your own Character Analysis Essay
Feel free to use this brainstorming template to get you started with your character analysis essay. I recommend filling out as many of these key points as you can, but remember sometimes you might have to skip some of these points if they’re not relevant to your character.
Once you’ve brainstormed the ideas in Table 1, follow the character analysis essay outline in Table 2 to stay on track for your character analysis essay. Do remember though that each assignment will be different and you should adjust it based on your teacher’s requirements.
Here’s Table 1, which is a brainstorming template for your character analysis essay:
And here’s Table 2, which is an example character analysis essay outline. This is for a 1500 word character analysis essay. Change the word count according to how long your essay should be:
Read Also: 39 Better Ways to Write ‘In Conclusion’ in an Essay
Character analyses can be really tough. You need to know your character really well. You might even need to re-read (or watch) your book or movie a few times over to get to know the character really well.
I recommend when you re-read or re-watch the text before you write your character analysis, have the checklist I provided above handy and take notes. Then, use the essay outline I provided above to put all of those notes together into a clear and thorough final character analysis essay.

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 5 Top Tips for Succeeding at University
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 50 Durable Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 100 Consumer Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 30 Globalization Pros and Cons
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- Essay Guides
- Main Academic Essays
How to Write a Character Analysis Essay: Guide with Examples
- Speech Topics
- Basics of Essay Writing
- Essay Topics
- Other Essays
- Research Paper Topics
- Basics of Research Paper Writing
- Miscellaneous
- Chicago/ Turabian
- Data & Statistics
- Methodology
- Admission Writing Tips
- Admission Advice
- Other Guides
- Student Life
- Studying Tips
- Understanding Plagiarism
- Academic Writing Tips
- Basics of Dissertation & Thesis Writing
- Research Paper Guides
- Formatting Guides
- Basics of Research Process
- Admission Guides
- Dissertation & Thesis Guides

Table of contents
Use our free Readability checker
A character analysis is a type of essay that requires you to analyze and evaluate the characteristics, traits, motivations, and decisions of a literary character. It involves closely examining such aspects as their personality, thoughts, behavior, and development. You should further explain how a character contributes to the overall meaning of the work.
When writing a character analysis essay, it is important to think critically and look beyond basic understanding of the character. For example, instead of simply describing their physical traits or explaining what happens in the plot, focus on how the characters think, feel, and interact with other characters. Examine the motivations behind their decisions and actions, as well as how they reflect a larger theme or idea in the work.
In this blog, we will explain how to write a character analysis essay. You will find a strtucture, outline and step-by-step guidelines along with examples.
If you don’t have much time for reading, we’ve got an easy solution for you. Entrust your assignment to essay writing services by StudyCrumb and get a custom paper tailored to your specific requirements.
What Is a Character Analysis Essay?
The main task of a character analysis essay is showing in detail key characteristics and certain person’s traits. Essay includes not just ordinary situations. It shows possible occasions for describing fictives fully and circumstantial. This type of essay helps understand how a hero will act in this or that situation, why would he do so, what were his reasons for these deeds? Analysis helps in figuring out what role a person plays in a story: great one or just secondary. Moreover, knowing the needed words of an analysis essay will enlarge students’ spoken literature.
What Is a Purpose of Character Analysis Essay?
Main purpose of a character analysis essay is helping the reader understand who's the bad one and who is among the good guys. This helps catch the idea of the story from the beginning. Knowing how a hero acts in this or that separate case, speaks a lot about his point of view. Essay divides all characters into main and minor ones. Detailed character analysis essay helps readers understand the nature of personages from an early beginning. Very often the story has several chapters, so the reader could discover much about a certain person from his doings/opinions.
Types of Character Using in Character Analysis Essay
While writing a character analysis essay, students have to remember two central personages: protagonist (key person) and antagonist. These are the main ones. The most striking roles are divided between them. Additional (minor) figures:
- confidante.
Each hero has special traits and behaviors. The round one is described as a person of passion having depth in feelings. Foil one is opposite one to positive, main one. Flat one is another side of round one: no vivid emotions, no changes while the story is being told. Use our college essay writing service to turn in the best character analysis your instructor has ever seen.
Protagonist — The Main Character
Protagonist in character analysis essays is the main story’s hero. This is a person all situations revolve around. They are the bearer of truth, the spokesman for the author's ideas, the main drive behind the plot. They don't have to even be a positive hero. After all, there is also an antihero - a protagonist with morally ambiguous or straight-up negative traits. Protagonist is a key figure, all other personages are considered minor ones. For better understanding of the protagonist, consider these examples: Romeo and Juliet, Katniss («Hunger Games»), Harry Potter, MacBeth. You can also consider Walter White («Breaking Bad»), Dexter Morgan («Dexter») and Hannibal Lecter («The Silence of the Lambs») to be antiheroes. All these examples are dynamic.
Antagonist — Character in the Opposite Position
Antagonist in character analysis essays is an opposite one to the protagonist. This type of character belongs to the dark side. Often, this can be a jealous, envious, bad, villain gossip person. They don't have to be the one ruining good protagonist’s plans, but they alway get in hero's way. Actually, there may even be more than one antagonist who may become hindrance for the protagonist. And if they are neutral in present, in the nearest future they will show their nature. Opposition between both protagonists and antagonists is clearly seen throughout the whole story. There is, of course, a catch. As with protagonists, there's more to know about antagonists' traits. After all, an anti-villain is also a thing! Basically it's when an antagonist has some heroic traits or can be sympathized with. One can also say that it's that type of person who has good intentions or their goal is pretty good, but their methods took a very wrong turn at some point. Othello, Captain Hook and Lord Voldemort — great antagonists’ examples. And those like John Silver, Khan («Star Trek») and Erik Lensherr («The X-Man») can be called anti-villain basically.
Major Characters
Major characters in character analysis essays are those who create a story. They play main (and clearly - important) parts, and have key roles. They make a so-called key set of personages. They are close confidants to the protagonist. If some conflict appears, major figures are mentioned first. Robinson Crusoe is a bright example.
Minor Characters
Minor characters in character analysis essays are often called supporting. They are important, but rarely are described in the story as key ones. This kind of fictives is represented by Yoda, Samwise Gamgee, Jabba the Hutt. They don’t remarkably influence the actual plot. Why flat? Because of no vivid progression.
Dynamic Characters
Talking about dynamic characters in character analysis essays - Shrek is a fine example. He is a dynamic personage because he changes: becomes softer and opens his heart to people. Fictives like him influence the story and make changes in the course of events. Their main feature: they change and grow throughout the story, making the reader sympathize with them. Another good example: Aladdin, Merida, Simba, Anakin Skywalker.
Static Characters
Static characters in character analysis essays do not change throughout whole story. They remain the same with their thoughts and opinions. Static personages are best described with the likes of Indiana Jones, Robin Hood, Sherlock Holmes. These personages are positive ones - though, unchangeable. Their points of view and tastes remain identical until a story ends.
Foils in character analysis essays are based on stereotypes and are opposite of main heroes. They have several key characteristics: they are wicked, distracted, conniving and scrooge. At the same time main personages are principled, focused, generous, and well-meaning. Foils are depressed and pessimistic, while main heroes — optimistic, kind, and good.
How to Analyze Characters in Character Analysis Essay?
While writing a character analysis essay, you should give a hero a general picture. Description has to grab appearance peculiarities and traits. Students must depict whether personage is good or bad. Are they pessimists or optimists? Do they have negative or positive thoughts? There are 3 main steps for analysis:
- Describing personality.
- Determining type of protagonist.
- Defining role in story.
To explore tiny personage’s quirks, all characteristics are taken into account. Just like in any literary analysis essay , you will need to pay special attention to literary devices that help reveal the true nature of a character.
How to Write a Character Analysis Essay Outline?
Character analysis essay outline includes 3 main parts: introduction, body, conclusion. Below you can find short description to understand some peculiarities:
- Introduction should be meaningful and brief. After reading this piece, essay’s idea should be understood.
- Main body is one that should be divided into paragraphs with described main heroes. It should give detailed answers to different questions concerning personality and appearance. Pay attention, separate paragraph depicts what we learn from hero or situation.
- Conclusion is the one where you should draw the final line of analysis. Summarize points you've given above, loop to your thesis statement or give your reader some food for thought. Just remember that this section should be brief.
Additionally, it will be good to write how a situation changed because of main hero's influence.
How to Write a Character Analysis Essay?
Instruction for writing character analysis essays is based on several steps. First, read a story carefully to find a person whom you are interested in. After reading the book, students should be able to completely grasp a key idea. Next steps include:
- choosing dynamic hero ;
- taking notes;
- defining main idea;
- answering analysis questions.
Concerning last point, think over next questions:
- What is hero's value?
- What kind of emotions does your hero go through?
- Does personage have a profound impact on plot?
- What are relationships between heroes and other significant figures?
Understanding an effect that main hero has on plot, it is easy to grasp the meaning the author put in their work.
How to Begin a Character Analysis Essay?
Character analysis essay introduction is the first step to start. It should describe whole essay in miniature. It's kind of a catchy hook for readers to get interested and proceed to explore chosen book. Introduction shows a completely full story in several paragraphs. To show all necessary information, make use of the thesis statement. These are rounded with text. It is fine to describe some catchy scenes and episodes to fuel readers’ interest.
Character Analysis Essay Body Paragraphs?
While introduction is a grand way to actually introduce the hero, character analysis essay body goal is identification of main personages features. Body should depict:
- Hero’s personality and physical appearance.
- Conflicts and ways of overcoming them.
- Lessons readers should learn.
- Meaning behind hero's actions.
Dynamic figure is key personage. Separate attention is given especially to them. Additional paragraph should describe a reader's feelings: what words are associated with a hero? Brave, modest, lucky, confident? Answers are key points to create a comprehensive description.
How to End a Character Analysis Essay?
How to write a conclusion paragraph for an essay ? Character analysis essay conclusion contains author’s point of view on course of events. Main ideas should be described shortly and clearly. Final part is a kind of review but with student's opinion. Lessons learned are described. For example, a story might teach how to live honestly, help poor people, feel merciful to others, etc. Remember that sheets’ personages teach us how to behave in real life. Many situations shown will be useful in everyday life. Hero’ deeds teach us how to cope with problems and find ways from tangled situations.
Character Analysis Essays: Final Thoughts
A character analysis essay is used for composing lines between parallel personages. It shows the present course of events that will make sense in future. Important traits and characteristics that are depicted in the book. They have a hidden idea, some kind of lesson. Comprehensive analysis helps to understand the meaning the author wanted to shed light on. Knowing main heros’ personal characteristics helps to explain their behavior and world perception. Buy essays for college in case this assignment isn't what you wanted to do this evening.
FAQs' for Character Analysis Essay
1. what is a good thesis statement for a character analysis essay.
Character analysis essay is saturated with essential messages. It appears at the end (in last sentence) of introductory paragraph. Its task is to inform reader about information they will get acquainted with. Every sentence has hidden meaning concerning heroes. Remember, introduction must be brief but meaningful. Student’s thesis statements should be specific — include only points that will be discussed. Good thesis statement should grab readers’ attention, make them read whole story.
2. What kind of essay is character analysis?
A character analysis essay mostly deals with certain books’ personages, though, figures from cinematography are involved. Its task is to explain in-depth key features of personages. Antagonist and protagonist are main ones. There also exist additional ones. This kind of an essay explains behavior and state of mind. Personal traits and preferences also make up whole picture described.
3. How do you write a literary character analysis essay?
Character analysis essay demands describing chosen personage in detail. Firstly though, it is needed to determine personage’s type. Next step include turning to plot for showing examples. Students have to explain why personages decide do act that way, after all.

Daniel Howard is an Essay Writing guru. He helps students create essays that will strike a chord with the readers.
You may also like

Character Analysis Guide: Master Literature
What is character analysis, how to identify characteristics of a character, how to analyze character development, how to analyze character interactions, how to analyze character motivations, how to analyze character influence on plot, how to analyze character influence on theme, how to analyze character arc and transformation.
- How to write character analysis essay
Picture your favorite book. Now, think about the characters that brought that story to life. Their actions, thoughts, and words paint a vivid picture in our minds, don't they? Well, the secret to understanding those characters, as well as the heart of the story, lies in mastering the art of analyzing characterization in literature. It's like a fun detective game where you gather clues about characters to uncover the deeper layers of the story. Let's jump right in!
Character analysis is a fascinating journey into the heart of a story. It's about looking closely at each character and understanding their traits, roles, and experiences. Imagine you are a detective and the character is a puzzle waiting to be solved. You're not just reading about who they are on the surface, but you're digging into their actions, words, and thoughts to see what makes them tick. Here's how you do it:
- Identify the character's traits: These are the qualities that make a character who they are. It could be anything from being brave, clever, kind, or stubborn.
- Understand their role in the story: Every character plays a part in moving the story forward. They could be the hero, the sidekick, the villain, or even the comic relief.
- Examine the conflicts they experience: Characters often face challenges or conflicts. How they deal with these situations can reveal a lot about their personality and growth.
Remember, analyzing characterization in literature isn't just about listing facts about the character. It's about understanding them in a way that brings the story to life. It's about seeing how they change, how they interact with others, and how they influence the plot and themes of the story. There's a whole world to explore within each character, so let's get started!
So, you're ready to start analyzing characterization in literature, and the first step is to identify the characteristics of a character. But how do you do it? Here is a straightforward plan:
- Observe their actions: What a character does can tell you a lot about who they are. For example, if a character always stands up for others, they're likely brave and compassionate.
- Pay attention to their words: Dialogue can reveal a lot about a character's personality, beliefs, and relationships with others. For instance, a character who always speaks kindly to others is likely a nice person.
- Consider their thoughts and feelings: Sometimes, a character's inner world — their thoughts and feelings — can tell you more about them than their actions or words.
- Take into account their appearance: How a character dresses or looks can give you clues about their personality or their role in the story.
Identifying characteristics is like collecting puzzle pieces about a character. It's not just about noting what you see or read, but about putting those pieces together to get a fuller picture of who the character really is. So, keep those detective glasses on and let's continue our journey in analyzing characterization in literature.
Now that you've got the basics down, let's move on to analyzing character development. This involves observing how a character changes and grows throughout the story. Here's the scoop:
- Track the character's journey: Look at where the character started at the beginning of the story and where they end up. Have they grown? Have they learned something new? Have their beliefs or attitudes changed? This can give you a sense of their development.
- Analyze key events: Major events in the story often trigger changes in characters. Examine these closely and consider how the character reacted, what choices they made, and how it affected them.
- Consider relationships: Relationships can greatly influence a character's development. How a character interacts with others, their reactions, and the changes in their relationships can all signify growth or change.
Remember, not all characters will develop or change in a story—that's okay. Some characters are static, meaning they stay the same throughout the story. Others are dynamic, meaning they undergo significant changes. Both are important and understanding this is a key part of analyzing characterization in literature.
Let's dive into another important part of analyzing characterization in literature: examining character interactions. This is all about how characters relate to each other. Let's break this down:
- Observe dialogues: So much can be uncovered from the way characters talk to each other. Do they argue? Are they supportive? Do they joke around? Dialogues can reveal a lot about relationships between characters.
- Look at their actions: Actions can speak louder than words. If a character helps another in a tough situation, or perhaps the opposite, betrays them, it can tell you much about their relationship and interactions.
- Consider their influence: Characters often influence each other's decisions and behaviors. If a character changes because of another, it shows the power and effect of their interaction.
When analyzing character interactions, it's important to note that these interactions can change over time—just like in real life. Characters can start off as friends and end up as enemies, or vice versa. Understanding these changing dynamics can give you a deeper understanding of the characters and the story as a whole.
It's time to explore the driving forces behind characters' actions. Understanding character motivations is a key part of analyzing characterization in literature. Here's what you need to watch out for:
- Desires and Goals: What does the character want more than anything? This could be anything from a physical object, a relationship, a change in their life, or even the resolution of a mystery. Their ultimate goal will heavily influence their actions.
- Fears and Worries: On the flip side, what does the character want to avoid? Fears and worries can be as motivating as desires and goals. They can push the character to take risks or to make safe choices.
- Values and Beliefs: What does the character believe in? What are their morals? These deeply held values can guide a character's decisions, even when they conflict with their desires or fears.
Remember, motivations can evolve as the story progresses. Characters might change their minds, achieve their goals, or face new fears. Keeping track of these changes can help you understand not just the characters, but also the bigger themes and messages of the story.
The plot of a story isn't just something that happens—it's often driven by the actions and decisions of its characters. That's why analyzing characterization in literature includes understanding how characters influence the plot. Here's how you can do it:
- Actions: Look at the key events in the story. How many of them are caused directly by the character's actions? A character who frequently makes things happen is likely to have a significant influence on the plot.
- Decisions: Similarly, consider the character's decisions. How do they affect the story's direction? Remember, a decision isn't always about doing something—sometimes, the decision to do nothing can be equally impactful!
- Reactions: Even passive characters can influence the plot through their reactions. How do other characters and events in the story change as a result of this character's responses? This can give you clues about their indirect influence on the plot.
As you can see, a character's influence on the plot goes beyond their actions. It's about how they shape the world around them, and how the world, in turn, shapes them. This give-and-take is a vital part of analyzing characterization in literature, and it can reveal a lot about the story's deeper meanings.
When analyzing characterization in literature, one often overlooked aspect is how characters can embody and influence the theme of the story. Themes are the underlying messages or big ideas of a story, and characters play a crucial role in expressing these. So how do you analyze a character's influence on theme? Here's a simple guide:
- Beliefs: What does the character believe in? Their beliefs can often mirror the theme of the story. For instance, if a character strongly believes in forgiveness, the theme of the story may revolve around redemption.
- Speech: The way a character speaks can reflect the theme. For example, a character who frequently talks about freedom and independence might hint at a theme of personal liberty.
- Behavior: How does the character behave? Do they consistently act in a way that supports the theme? In a story themed around courage, you might find a character who consistently stands up for what they believe in, no matter the cost.
Remember, characters are often vehicles for the author's themes. By diving into a character's beliefs, speech, and behavior, you can gain a deeper understanding of the story's larger messages. And that's the beauty of analyzing characterization in literature—it's not just about understanding the characters, but also the world they inhabit and the ideas they represent.
Another fascinating aspect of analyzing characterization in literature is the character arc and transformation. A character's arc is the journey they go through, the changes they undergo from the start of the story to the end. This can provide a wealth of insight into not only the character but also the story's overall message. Let's take a look at how to analyze this aspect:
- Identify the starting point: Where does the character begin in the story? Are they timid, confident, naive, cynical? This initial characterization sets the stage for their journey.
- Track the changes: As the story progresses, how does the character change? Do they become more confident? Do they lose their innocence? Identifying these changes can help you understand the character arc.
- Understand the catalysts: What events or experiences prompt these changes in the character? The reasons behind a character's transformation can be as revealing as the changes themselves.
- Analyze the end point: Where does the character end up at the end of the story? How do they differ from the character we met at the beginning? Assessing the end point of the character's journey can provide insight into the overall theme of the story.
Character transformation is one of the most compelling aspects of a story. It's what makes us root for characters, mourn their losses, and celebrate their victories. By analyzing a character's arc, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the intricacies of storytelling and the power of character development in literature.
How to write a character analysis essay
Now that we've covered the intricate process of analyzing characterization in literature, let's apply this knowledge to the final step: writing a character analysis essay. This task may seem daunting at first, but don't worry, we're in this together. Here's how you can approach it:
- Choose your character: Start by selecting the character you want to analyze. It could be a major character or a minor one—whatever sparks your interest!
- Identify key characteristics: Next, list down the key characteristics of your chosen character. Remember, these can include physical attributes, personality traits, and even their habits and quirks!
- Analyze character development: How does your character change over the course of the story? What experiences or events lead to these changes? This is where your understanding of character arcs comes into play.
- Consider character interactions: Look at how your character interacts with others. These interactions can reveal a lot about your character's motivations and their role in the story.
- Examine influence on plot and theme: How does your character influence the plot and the theme of the story? Their actions, decisions, and transformations can have significant impacts on the storyline and the underlying messages of the text.
- Organize your thoughts: Before you start writing, create an outline for your essay. This will help you structure your thoughts and ensure a smooth flow of ideas.
- Write, review, and revise: Now it's time to bring it all together! Write your essay, then take some time to review and revise it. Make sure your analysis is clear, your arguments are well-supported, and your writing is engaging.
And there you have it! With these steps, you're well on your way to writing a stellar character analysis essay. Remember, the goal is not to simply describe your character, but to delve into their personality, their changes, their motivations, and their impact on the story. So go ahead, flex those analytical muscles and dive into the wonderful world of character analysis!
If you enjoyed our Character Analysis Guide and want to dive deeper into the world of creating compelling characters, be sure to check out the workshop ' Creating Characters: The Design Process ' by Kit Buss. This workshop will provide you with valuable insights on how to design unique and memorable characters for your stories, further enhancing your understanding of literature.

Live classes every day
Learn from industry-leading creators
Get useful feedback from experts and peers
Best deal of the year
* billed annually after the trial ends.
*Billed monthly after the trial ends.
Start Writing a Character Analysis Essay with Us
- Essay Writing Guides

Characters are the cornerstones of stories in the broad world of literature; they are individuals with unique intricacies, motivations, and travels. But taking characters at their value only goes so far in revealing their significance. Exploring character analysis in depth reveals a wealth of knowledge that enhances reading and promotes a comprehensive comprehension of the story’s overall structure. In this article, we set out to discover the fundamentals of a character analysis essay , delving into its definition, significance, and constituent parts.
Understand Character Analysis Essay
What is a character analysis essay? Character analysis is a critical process that involves examining the traits, motivations, and development of characters in a literary work. It goes beyond mere observation, requiring readers to delve into the intricacies of characters’ personalities, actions, and relationships. Characters serve as conduits through which readers explore the depths of human nature, embodying universal themes and aspects of behavior.
Characters analysis offers profound insights into the human condition and enhances comprehension by enabling readers to grasp the underlying messages, themes, and conflicts within a story. Character analysis fosters critical thinking by encouraging readers to interpret evidence, form connections, and form informed opinions about the text.
Key components of the character analysis essay include personality traits, character development, motivations and goals, relationships, and symbolism and archetypes. Personality traits provide insights into the character’s strengths, weaknesses, virtues, and flaws, while character development examines how the character evolves and changes throughout the story. Understanding these components enhances the reading experience and instills a deeper appreciation for the artistry of storytelling.
Selecting the Character
What is a character analysis selection process? Selecting a character for analysis is crucial for crafting a compelling and insightful essay about a character . Some tips to guide in choosing the most suitable character include considering their significance, complexity, contrasts, personal interest, availability of textual evidence, and relevance.
Choosing a character integral to the plot is essential for conducting a meaningful character analysis essay that sheds light on the central themes and conflicts of the story. Characters are the driving force behind the plot, shaping events and conflicts that unfold within the story. Analyzing a character central to the plot allows for a deeper understanding of the story’s progression and thematic significance. They often embody the central themes and motifs of the narrative, allowing readers to uncover deeper layers of symbolism embedded within the text.
Analyzing a character central to the plot provides context for understanding the motivations, conflicts, and relationships that drive the narrative forward. Characters who play pivotal roles in the plot are often more compelling and memorable to readers, engaging them deeper and encouraging deeper engagement with the text.
Analyzing a character that resonates with the writer on a personal level can greatly enhance the depth and authenticity of the analysis. The benefits of choosing a character that resonates with the writer include emotional investment, empathy and understanding, authenticity, and insightful reflection.
Emotional investment allows for a deeper level of engagement with the text, fueling the passion for the analysis and inspiring insightful observations. Empathy and understanding enable readers to empathize with the character’s experiences, motivations, and struggles, leading to a more nuanced analysis.
Authenticity lends authenticity to the analysis, as it reflects genuine thoughts and feelings about the character. Insightful reflection prompts insights into one’s own experiences, beliefs, and values, enriching the analysis and adding depth to understanding both the character and oneself.
By choosing an essay about a character that resonates with the writer personally, one can infuse their analysis with authenticity, empathy, and emotional depth, resulting in a more compelling and insightful exploration of the text.
Gathering Evidence
Character analysis is a crucial process in understanding a character’s personality and behavior. To learn how to write a character analysis essay correctly, it is essential to gather textual evidence, such as close reading, note-taking, annotation, character profiles, comparative analysis, and archetypal analysis. These methods help extract relevant information from the text, providing a foundation for your analysis.
Archetypal analysis can explore how the character embodies archetypal traits or roles commonly found in literature, such as the hero, villain, mentor, or trickster. By carefully identifying and documenting the various traits exhibited by the character, you can develop a nuanced understanding of their personality and behavior.
Supporting details play a crucial role in bolstering your character analysis essay , providing concrete evidence to support your interpretations and arguments. To effectively utilize specific examples from the text to support your analysis, select relevant examples that directly relate to the traits, motivations, and actions you are analyzing.
Provide context by introducing each example with a brief explanation or summary of its significance within the larger narrative. Analyze the example in detail, pointing out specific details or language choices that illuminate the character’s traits or motivations. Incorporate quotations from the text whenever possible, using quotation marks to indicate the exact words spoken or written by the character.
When analyzing supporting details, consider multiple perspectives: Acknowledge alternative interpretations and perspectives, but provide reasons why your analysis is the most valid or persuasive. By effectively utilizing specific examples from the text to support your character analysis essay , you can strengthen your arguments and provide readers with a deeper understanding of the character’s role within the story.
Character Analysis Essay Outline
Let’s have a look at the character analysis essay outline and how to write it perfectly.
- Start with a hook or question about the character.
- Provide background information and the thesis statement.
- Describe the character’s role, appearance, and initial impressions.
- Identify and discuss the primary traits of the character.
- Explore the character’s desires, fears, and motivations.
- Analyze the character’s evolution throughout the story.
- Discuss key events or turning points that shape the character’s development.
- Examine the character’s interactions with other characters.
- Discuss the character’s role in the plot.
- Explore how the character embodies or reflects the story’s themes and symbols.
- Analyze how the character’s actions affect the plot’s progression.
- Provide specific quotes or passages from the text.
- Illustrate key character traits with examples of their actions or dialogue.
- Interpret symbols or imagery associated with the character.
- Restate the thesis.
- Recap key points
- End with a thought-provoking statement.
By following this outline for a character analysis essay , you can structure your essay effectively, providing a comprehensive analysis of the chosen character while engaging the reader from start to finish.
Character Analysis Essay Structure
Character analysis essay format typically follows a three-part format: introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion. The introduction serves to introduce the character being analysed and provide context for the analysis. Create a compelling introduction, start with a hook, write background information, and introduce the thesis statement. End the introduction with a clear and concise statement that outlines the purpose and focus of the essay. This will set the stage for a compelling and engaging character analysis essay.
The body paragraphs delve into the analysis of the character, each focusing on a specific aspect or trait. Each essay paragraph should begin with a topic sentence, followed by supporting evidence from the text and an analysis that explores the significance of the evidence in relation to the character’s development and role in the story. Organizing the analysis into coherent paragraphs is essential for presenting a logical and persuasive argument.
The conclusion of the character analysis essay summarises the analysis’s main points and reinforces the character’s significance within the narrative. It restates the thesis statement in different words, provides a brief recap of the main arguments presented in the essay, and offers final insights or reflections on the character’s importance and impact on the story.
By following these guidelines, you can craft a conclusion that reinforces the significance of the character and provides a satisfying conclusion to the essay.
Process of Analyzing a Character
Character Development:
- Initial Impression: Discuss the character’s introduction and personality traits.
- Growth and Change: Analyze how the character evolves and changes over the story.
- Internal Conflict: Explore internal struggles or conflicts the character faces.
- Relationships: Examine the character’s relationships with other characters and how they evolve.
- Resolution: Evaluate the character’s development at the end of the story.
Motivations and Actions:
- Identify Core Motivations: Understand what drives the character to act and the underlying reasons behind their behavior.
- External Influences: Analyze the external factors that influence the character’s motivations and actions.
- Internal Conflicts: Explore any internal conflicts or contradictions within the character that influence their motivations and actions.
- Character Consistency: Evaluate the consistency of the character’s motivations and actions throughout the text.
- Consequences of Actions: Discuss the consequences of the character’s actions and decisions within the narrative.
Impact on the Narrative:
- Plot Development: Examine the character’s role in advancing the plot and driving the story forward.
- Theme Exploration: Analyze how the character embodies or reflects the story’s central themes and motifs.
- Symbolic Significance: Explore any symbolic significance associated with the character and their role in the story.
- Influence on Other Characters: Discuss how their relationships, actions, and decisions impact the development and behavior of other characters.
- Resolution and Conclusion: Evaluate the character’s ultimate role in the resolution and conclusion of the story.
By discussing what is character analysis significance in shaping the story, you can provide a comprehensive analysis of their role and impact within the narrative, highlighting their contribution to the overall meaning and interpretation of the text.
Polishing and Refining
Proofreading is an important step in the editing process, ensuring your writing is free from errors and effectively communicates your ideas. To correct errors in grammar, punctuation, and syntax, take a break, read aloud, use editing tools, focus on one element at a time, print and review, and seek feedback from peers or instructors.
Polishing involves refining language, strengthening arguments, and enhancing the overall clarity and coherence of your work. Techniques for polishing your writing include clarifying your thesis, tightening your writing, strengthening your arguments, enhancing transitions, checking for consistency in tone, style, and formatting, and proofreading carefully.
Afterthoughts on Character Analysis Essay
A profound character analysis essay offers a profound understanding of the human psyche, storytelling, and the timeless relevance of literature. By examining character traits, motivations, and impact on the narrative, students gain a deeper understanding of universal themes, conflicts, and complexities of the human experience.
- Academic Writing Guides
- Citation Guides
- Essay Samples
- Essay Topics
- Research Paper Topics
- Research Paper Writing Guides
- Study Tips and Tricks
Featured articles

Start Writing Formal Emails
In today’s digital age, formal emails are a crucial form of communication in various professional settings. They reflect one’s professionalism and competence, making them essential for effective communication in workplaces, academic institutions, and business environments. Crafting well-written formal emails is invaluable for building and maintaining professional relationships, and they are often the initial point of […]
Author: Marina Kean

We’ll Help You Write Career Goals Essays
Career goals essays are important for expressing personal ambitions and objectives in the professional realm. They can greatly impact college applications, job interviews, scholarship submissions, and career advancement initiatives. These essays about career goals have the power to showcase an individual’s determination, visions, and unique brand, opening doors to academic programs, job opportunities, and funding. […]
How to Write a Character Analysis Essay?
14 August, 2020
14 minutes read
Author: Kate Smith
A character analysis essay is one of the most complicated academic assignments that students usually write for Literature or English classes. Generally, this kind of essay writing requires you to describe the character in the context of the story. This can be done through the analysis of the relationship between the major and secondary characters or through your personal opinion of a particular character.
So, there is something you should learn before getting down to work. What is a character analysis and how to approach it? Let’s try to find the answers in the information below.
What is a Character Analysis?
A character analysis is a kind of essay where you examine behaviors, motivations, and actions of characters. Also, a character analysis is an in-depth assignment that makes you think critically about one or more characters and make judgements after analyzing the text. In most cases, it is used for the analysis of literary works. This form of academic writing involves personalities’ descriptions and conflicts with others they experience throughout a story. This analysis aims to provide a critical assessment of characters and build up conclusions based on the storyline. You may analyze a personality through his or her behavioral patterns or internal and external conflicts.

When you’re asked to write a character analysis, you must look at that story from a different angle. How? This is not your average reading for fun. Your task is to focus on the character synopsis and everything that’s associated with the people involved in the story.
Aim of a Character Analysis
A character analysis aims to evaluate a character’s traits, their functions, and the conflicts they have to deal with throughout the story. During the analysis, you will need to think critically, ask questions, and make conclusions about the character. To make your analysis informative, you will have to go beyond available descriptions that are written by the author. To understand the meaning of every event, phrase, and action, you will have to read between the lines. Don’t be afraid of using some additional resources if you feel like knowing more about the epoch a character lives in. If you want to gain an alternative opinion about a character, do not hesitate to find out your friends’ or internet users’ thoughts. Thus, thorough research may help you develop some creative ideas that will add great value to your future paper.
General Types of Characters
You should have a deep understanding of a character before starting an in-depth analysis. While a good character has many sides, there are some standard features to be considered:
- Protagonist: Being the main figure in a story, this character has the whole plot based on their life, actions, events, and feelings.
- Antagonist: Being a villain in a story, this character is positioned as the opposite figure to the major hero. Their basic nature remains negative, which makes them even more interesting than the main character. An antagonist plays a significant role even in short stories.
- Major: This character dominates the story. While they are not the main one in the story, they are involved in all the events.
- Minor: This character appears in a story from time to time. Their role may be significant for the plot development, but then they may disappear for some time and pop up again.
- Dynamic and static characters: The existence of these two opposite characters is determined by their reflection of each other’s specifications. While one character of a story goes through an internal or external transformation, another one may have their basic characteristics unchanged. There is a common idea that an evolving character tends to be more interesting than a static one. However, you can also analyze a static character from the perspective that they are not sympathetic, smart, or deep enough to learn their lessons. Or on the contrary, they remain strong enough and can resist the system without going under it.
- Stereotypical: If you are familiar with stereotypes, you will know what type of character is meant here. Generally, this particular character serves as the representation of the social, national, as well as demographic background of the story.
- Foils: The main goal of this hero in the story is to stay in contrast with main characters and a protagonist in order to highlight the features of the main character.
- Multi-dimensional characters: This group of characters involves an unlimited number of personalities. They are one-dimensional characters in the story who usually are not particularly interesting for the reader or viewer and do not play a crucial role in the storyline.
How Do You Start a Character Analysis Essay?
Before you start writing, you may wonder how to do a character analysis. Of course, you need to select a character to describe. In some cases, your professor will give you a character to talk about. By reading a story several times, you may notice the tiniest details. Ideally, you can use a highlighter or marker to mark each spot where your character is mentioned. Here are some more details of how to start with a character analysis:
- Take notes while reading. Take notes by highlighting every significant element of the story.
- Introduce your character. Introduce your character by providing their detailed description.
- Describe your character. Provide a smooth transition from the general description of your character to the point of convergence of the story.
- Build up a thesis statement. Finish the presentation with your paper’s proposal.
Main Points of a Character Analysis
When you need to analyze one character, you can make it from the perspective of several types at once. The character’s ability to change can create an additional source of analysis. At the same time, the complex and changing personality will be more interesting for the detailed analysis. To make it easier to work with such characters, you should focus on their characteristics, namely their importance for a story, actions, events, and so on. In most cases, you have to cover three major points:
Personality
Reveal the main features of a character to provide the reader with a portrait. By adding some facts and descriptions of actions, you will enable a deeper understanding of the analyzed hero. There is no need to use some words with broad meanings like “bad,” “nice,” “honest,” etc.
Role in a story
Describe the importance of the particular character in the context of the general story. Also, you should pay attention to their actions and their ability to move the events forward.
Character development
Analyze the changes the character has gone through and what features they have now. You should focus on the progress of a person, even if it is regressive.
Character Analysis Outline
In the character analysis essay outline, you should describe two or maybe even three specific character categories. Your mission is to describe the personality of the character, their function in the story, and the value they have.
- Describe the personality of the character. The reader gets familiar with the characters of the story through the words the characters use, the emotions they express, and the actions they take. It is quite easy to build up an opinion about the personality of a character through the prism of their outward behaviors. Eventually, you will understand that the character fits into one of the character categories mentioned above.
- Explore the character’s role . While writing a character analysis, it is important to describe the role of that character in detail. Apart from expressing unique character traits, the character will also perform a specific function in the story. Whether it will be the major or minor role, the analysis should address all the aspects of the performed role.
- Outline the growth and development of the character . In order to write a professional analysis, you will explain how the character matures and transforms as the plot progresses.
The majority of characters will have to go through particular transformations until the end of the story. You should pay special attention to whether the character becomes better or worse, stronger or weaker, rich or poor. Mention any areas or scenes where these transformations occur. In the story, you will recognize them from the cues like “it was then that she understood…” or “for the first time in months, he…”
Do you need a more detailed analysis of your character?
To make your analysis essay correct, you need to explore your character deeply. If you set some points you will follow in your work, you will manage to be consequential in your analysis. So here are some crucial nuances you should remember to describe the character:
You should focus on the reasons that make the character in a story to make a particular decision or take a specific action. You have an opportunity to explore the rightfulness of those actions as well as their reasonability. While you are asked to express your thoughts about certain events and feelings, you should be objective by looking beyond the cover.
Every action taken by a character can say a lot about his/her personality. You should not skip any events because it can be important for the general story and reveal some info about the character, his/her attitude to things, etc.
You should pay attention to the words the person uses because they can say a lot about their personality. Their accents and phrases may provide you with valuable information about nationality, social status, education, or even age of a character.
Descriptions
There are two major sources of the description: from other people in a story and the author. The author can provide the reader with one attitude and description of the major character, while secondary heroes in a story may describe them from their own perspective. At that point, their conclusions may be totally different, yet they’ll provide you with an understanding of the person’s nature.
The way people refer to a person also determines the features of a character. They may have nicknames or other names that will demonstrate their background and the attitude of other characters toward them. You can also define the origin as well as other important nuances.
Character Analysis Examples
By using a readymade character analysis example, you can concentrate on the creative process itself. Here are some nice examples of written character analysis based on a couple of popular stories:
https://literatureessaysamples.com/joe-gargerys-character-analysis/
http://jmendelis.blogspot.com/p/sample-character-analysis-essay.html
Popular Topics for Character Analysis
- Hamlet Character Analysis
- The Crucible Character Analysis
- Macbeth Character Analysis
- Ophelia Character Analysis
- Iago Character Analysis
- 12 Angry Men Character Analysis
- The Great Gatsby Character Analysis
- Beowulf Character Analysis
- Lady Macbeth Character Analysis
- Atticus Finch Character Analysis
- Romeo Character Analysis
- Antigone Character Analysis
- Victor Frankenstein Character Analysis
- Pride And Prejudice Character Analysis
- Machinal By Sophie Treadwell Character Analysis
- Of Mice And Men Character Analysis
- Othello Character Analysis
- Macduff Character Analysis
- Lord Of The Flies Character Analysis
- To Kill A Mockingbird Character Analysis
- The Breakfast Club Character Analysis
- Charlie Brown Character Analysis
- Death Of A Salesman Character Analysis
- Hester Prynne Character Analysis
- Mr Darcy Character Analysis
- Desdemona Character Analysis
- Fahrenheit 451 Character Analysis
- Willy Loman Character Analysis
- A Raisin In The Sun Character Analysis
- The Things They Carried Character Analysis
- A Rose For Emily Character Analysis
- Nick Carraway Character Analysis
- Daisy Buchanan Character Analysis
- Boo Radley Character Analysis
- 13 Reasons Why Character Analysis
- King Lear Character Analysis
- Jay Gatsby Character Analysis
- Blanche Dubois Character Analysis
- Oedipus Character Analysis
- Claudius Character Analysis
Tips on Writing a Character Analysis from Handmadewriting Experts
Whether you follow a character analysis template yourself or ask a professional essay writer to complete this paper for you, you should not forget the common principles of work. Luckily, Handmadewriting’s specialists always follow the standard rules for character analysis writing:
- Support all your statements with evidence. Y ou should incorporate evidence for every single point you make, although it must be relevant to the story. By means of quotes taken from the story, you can easily support your ideas and increase your credibility.
- Point, illustrate, and explain. The so-called PIE method is a must for character analysis writing. Make sure to make a point, integrate quotations to support it, and explain how every quote creates the point.
- Use your own words to anchor the quote. A quotation should not be left alone in the sentence. You need to explain the eligibility of this quote and its meaning.
- Do not overuse quotes. You are allowed to use up to 10% of quotations in an academic paper, so remember this number. If you overuse quotes, you can hardly hope for a good grade.
Are you ready to proceed with your character analysis paper? Once you learn all writing rules and tips, you will be able to finish an excellent paper before the set deadline.

A life lesson in Romeo and Juliet taught by death
Due to human nature, we draw conclusions only when life gives us a lesson since the experience of others is not so effective and powerful. Therefore, when analyzing and sorting out common problems we face, we may trace a parallel with well-known book characters or real historical figures. Moreover, we often compare our situations with […]

Ethical Research Paper Topics
Writing a research paper on ethics is not an easy task, especially if you do not possess excellent writing skills and do not like to contemplate controversial questions. But an ethics course is obligatory in all higher education institutions, and students have to look for a way out and be creative. When you find an […]

Art Research Paper Topics
Students obtaining degrees in fine art and art & design programs most commonly need to write a paper on art topics. However, this subject is becoming more popular in educational institutions for expanding students’ horizons. Thus, both groups of receivers of education: those who are into arts and those who only get acquainted with art […]

Step-by-Step Guide for Writing a Character Analysis Essay

When assigned to write a character analysis essay or paper, you are expected to examine the actions, traits, behavior, and personalities of the antagonists and protagonists in a story, poem, song, film, or novel. You have to include a discussion of the characters' experiences, conflicts, roles, traits, and appearances. It is a full essay with introduction, body, and conclusion paragraphs.
Like a typical essay, when writing an essay that entails analyzing a character, you have to have a catchy sentence to grab the readers' attention at the very first paragraph-the introduction. You should also have an excellent thesis statement to announce what it is about.
If you want to know how to ace that character analysis essay or are unsure what to do next, you are in the right place.
Whether it is a character from a Movie or famous books such as Macbeth , A Rose for Emily , To Kill a Mockingbird , The Yellow Wallpaper, Romeo and Juliet, Alice in Wonderland, Huckleberry Finn, The Great Gatsby, Lord of the Flies, or any other story, you came to the right place.
This ultimate guide has everything to point you in the right direction. But before anything else, let�s first focus on the basics.
What is a Character Analysis Essay?
A character analysis essay is a piece of academic assignment where you critically analyze the traits, motivations, behaviors, and encounters of a specific character or characters from a TV show, book, play, novel, short story, poem, film, or in real-life scenarios. It is also known as a character analysis paper, character essay, characterization essay, or essay about characters.
The key focus of a character analysis essay is to narrow down to a specific character and provide their sketch so that someone who has read or has not read the story can get the role the character plays.
When writing this essay, your focus is on examining the actions and personalities (characteristics and traits) of the antagonists and protagonists in a story. It encompasses a description of the roles, traits, experiences, and conflicts of the specific characters, independently or relative to others.
Instead of offering light definitions and descriptions of a character, a character analysis entails synthesizing the driving force and personality of the character in question. You critically look at how these two influence the entire story, poem, song, or play.
A character essay is a common literary writing assignment for college students pursuing English and Literature. The true success of doing a character analysis comes when you view the characters as though they are real people who act, feel, and live as we do.
Therefore, there is no room for baseless interpretations and assumptions. You need to support every idea, concept, or observation with a proper quotation, summary, or paraphrased facts from the text or other credible scholarly sources . Again, since it is not your story, you must avoid writing in the first person , despite your personal preferences and opinions � being objective when writing a characterization essay is paramount.
Purpose of Character Analysis Essay
A character analysis aims to reveal some of the most interesting details about a character that can be applied to real-life situations.
Writing a character analysis essay allows you to see through a character from the lens of the author as it entails narrowing down the character�s traits, encounters, beliefs, and behavior.
You also get the chance to provide a sketch of the character, which can further help expound on the moral message the author is trying to pass to the audience that cares to interact with their piece of work.
A character analysis allows you to understand, contextualize, and evaluate the story from a broader perspective to determine the purpose of the story. In some stories, characters have symbolic meanings that are authors� ways of using literary devices to unmask different aspects of society. Some characters cause conflicts (i.e., the antagonists), while others play the role of progressing the story (i.e., the protagonist).
When your instructor or professor assigns you to write a characterization essay, they test whether you paid attention while reading, watching, or listening to a piece of work. It is also a strategy to assess your critical thinking depending on how best you write about the characters and the text's overall meaning.
Different Types of Characters to Consider when Writing
As you probably have learned in your literature or English class, there are several types of characters categorized based on factors such as roles, behavior, and traits in the story. Below, we explore some of these character types
1. Major characters
Major characters are the main characters that run the show or story. In most cases, you will find either one or a maximum of two major characters. A major character can either be a protagonist, otherwise known as the good guy, or an antagonist, who is the villain or bad person in the work of art or literature.
2. Protagonist characters
The protagonists are also known as the heroes, the main characters around whom the story's plot revolves.
3. Antagonist characters
The antagonists oppose the protagonist, also known as the villain. In some cases, antagonists� characters could be natural power, supernatural phenomena, or majestic beings.
4. Minor characters
The minor characters are those who help bring out the traits and personalities of the main characters. They are static and unchanging characters who maintain their stance, traits, and beliefs.
5. Dynamic/changing characters
Dynamic characters are the opposite of static characters, and they keep changing.
6. Static Characters
The static or unchanging characters are consistent in thought, behavior, allegiance, approach, and traits throughout a story, cinematography, or play. In How to Kill a Mockingbird , Atticus Finch fits the description of a static character, given he maintains his beliefs even in the most challenging situations. If you have read The Adventures of Huckleberry Finn by Mark Twain, you would agree that Jim is a static character, given that his personality remains the same throughout his journey. In Hamlet, Polpnius can be described as a static character because he remains sneaky throughout the story.
A foil character brings out the protagonist's qualities because they are the exact opposite of the protagonist's character. Foils are usually the opposite of the protagonist. For example, Draco Malfoy is a foil character in Harry Porter, and another example is Dr. Watson from the Sherlock Holmes Series.
7 Steps when writing a Character Analysis Essay
Character analysis essays follow the format and structure of a standard academic essay and have an introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion. Before writing a character essay, you need to read the assignment promptly to understand the scope of the essay. It also helps with choosing a character or knowing what to focus on and what to leave out.
Here are some steps to follow if you want to write a successful essay on a character.
1. Read the story or novel
Assuming you have gone through the character analysis essay prompt, you have to read the story, watch the film, play, theater performance, or listen to a narration. Reading with a general mindset enables you to contextualize the piece of work. You will be able to identify the author's thesis and how they use different characters to advance the themes that support the thesis. A general perspective of the story, novel, film, or poem helps you easily identify the characters. As you read, take notes on the different characters in the story, which will help you in the second step.
2. Identify the character of interest
After you have familiarized yourself with the story, song, or film, the next step is to select your specific character of focus.
In some cases, your instructor will likely assign a character of focus for your character analysis assignment. However, some professors will leave you the freedom to choose a character.
If this is the case, ensure that you consider a character that plays a dynamic role for you in writing a vivid character analysis paper. For example, if you are writing a character analysis essay based on Huckleberry Finn by Mark Twain, you can choose a character like Jim or Huck, who are both dynamic characters in the story.
To select a good character, refer to the notes you were taking as you initially read through the story or watched the film or play.
3. Re-read and Take notes
Even if you have already read the story or watched the performance, play, or film, you need to do it all over again, only that this time you will be taking notes based on your character.
With the instructions in mind, you can limit your scope, identify points quickly, and cover useful aspects when writing your analysis.
Focus on the description of your character, how the character relates to other characters, the conflicts the character faces, the struggles, wins, and failures of your character, and how the character advances through the story, film, or performance.
Taking notes while watching or reading helps you to identify rich pieces that will build up your paper. You can underline important passages or annotate important quotes.
4. Choose your thesis statement
At this stage, you are fully knowledgeable about your character and their role in your story or film. You should gather your notes and think of the main idea that links them, and the main idea that ties together these aspects is your thesis statement.
The thesis statement can be a sentence or two that tells the reader what your essay or paper is about, and it should promise the reader the purpose, scope, and direction of your paper.
An example of a good thesis statement for a character analysis is � Through Miss Maudie Atkinson�s open-mindedness, optimism, and compassion, she helps Jem and Scout better understand Atticus and their community.�
When writing your thesis, consider your character's motivations, actions, behavior, changes, and roles in the storyline. Your thesis can be aligned to a theme that your character advances.
5. Draft your essay outline
With the thesis at hand, you can now create an outline for your character analysis essay or paper. The outline will map out every section of your paper, which can help you determine your essay's flow, organization, and formatting.
Other people prefer writing an essay plan before creating an outline. We have given a template for an essay plan in this article in case it would help to simplify the pre-writing process.
The outline helps you organize your thoughts and maintain an effective flow of ideas as you write the analysis. And when writing it:
- Have an attention-grabber as your opening statement in the character analysis essay
- Ensure that your topic is clearly reflected in the essay title and thesis statement
- Come up with comprehensive topic sentences
- Organize the ideas in your essay
- Maintain one idea per paragraph
- Every idea in your essay must support your thesis statement
You are ready to put rubber on the road with such a solid outline. You can now comfortably write the essay. We recommend taking some break to cool your mind before beginning to write.
6. Write the essay
The writing stage should be enjoyable if you worked hard on the pre-writing phase. As you settle down to write your character analysis essay, follow your essay outline.
Write the introduction
Have the thesis in mind and begin by writing an attention-grabbing introduction. Strategically place your essay hook, such as a rhetorical question, quote, or fact, and the introduction should enthuse the reader to read your essay beyond the first paragraph.
The introduction should also give a background of your character and their role in the story. And to intrigue your readers, even more, write a thesis statement that describes what they should expect in your character analysis paper.
If allowed, you can give an outline where you signpost the rest of your paper in the introduction so that your readers are not ambushed with ideas.
Develop the body paragraphs
The body paragraph is where the real action takes place. It is where you answer the prompt, enabling your reader to find a link between your arguments and the thesis. Here, try to connect your character to the themes in the story, film, or performance. When writing the body, focus on these elements:
- Physical Appearance of your character. Describe how your chosen character looks and relate it to their traits, behavior, and personality. For instance, if a character appears formally dressed, it could mean that they are respectful, organized, and composed. If they appear rough and ragged, like Huck, you could conclude they are troublesome.
- Background of the character. Present the background of the character, including their history. History connects to character, personality, and personal development. Let your readers know how your character was raised, in what environment, and how these factors influence who they are.
- Their Personality. Explore the values, beliefs, behavior, and character traits of your character. As you explain their personality, use quotes from the story, play, or film. Some personalities include composed, mindful, articulate, ambitious, assertive, vengeful, forgiving, annoying, troublesome, etc.
- Their language. Let your readers know how your character speaks. Are they vulgar, or are they mindful of their words? Do they use formal language or slang? Also, the report of your character has an accent. Language can come in handy when connecting your character to a given culture.
- Relationship with others. Explore how your character relates to others. The interactions make it possible to frame the character of an individual. Examine how these relationships are important in the context of your analysis.
- Growth and transition. As you write the analysis, look at how your character develops, grows, or transitions through the story, film, or play. Examine your character's life and document how they progress as the story unfolds.
Finalize with a vivid conclusion
When all is done in the body of your character analysis, ensure that you wrap up your essay using a remarkable concluding paragraph . Here, you should restate your thesis using totally different words. You should then summarize your arguments from the body paragraphs related to the thesis. Summarize the role and personality of the character in the story. Finally, write a concluding statement that makes your analysis memorable or gets your readers thinking. The final statement could be the moral message from your character.
7. Proofread and edit the essay
When writing the first draft, we always insist on writing in raw form without bothering about other things such as grammar, spelling, or syntax. Writing is meant to achieve some flow and explore your creativity.
You need to take a break after writing to ensure that you develop an objective mindset. It could be hours or days, depending on your deadline.
Proofread your essay and edit it for grammar, spelling, and organization. Only submit an error-free paper. You can use editing software or Apps such as Ginger, Pro Writing Aid, or Hemingway editor. Besides, pass your essay through plagiarism checkers such as PlagScan to ensure that you submit a plagiarism-free character analysis essay.
Detailed Structure/Outline for Character Analysis Essay
Like a typical essay, having a character analysis essay outline or map helps you visualize the end and write a paper that comprehensively answers the assignment prompt questions. With a good outline, you have a map that will guide your writing process.
Paragraph #1: Introduction
Introduction � general comments about the character and/or novel lead you to your thesis statement (described above). Be sure you have identified the author and title of the book and the character you will be analyzing. Some questions you could address in your introduction include:
- Why did you pick this character?
- What do you like and/or dislike about this character?
- Do you identify with this character on any level? Do you know someone similar to them? Explain.
Paragraphs #2 - #4 (Body Paragraphs)
Three Body Paragraphs � the topic sentence for each body paragraph includes one character trait you chose to describe your character. For example, �Atticus Finch is a man of great integrity.� Follow the topic sentence with evidence from the novel: examples from the story that support your topic sentence and at least one direct quotation from the novel in each body paragraph. Next, explain how your examples support your topic sentence and conclude each body paragraph with a summarizing �clincher� sentence to wrap up your ideas.
Paragraph #5
Conclusion � restate your thesis statement and add some final thoughts about your character and/or the novel�leave the reader in awe of your wisdom!
Character Analysis Essay Plan
If you want something that can help you outline the contents of your essay, here is a format you could use. This plan can come in handy when you are writing a last-minute essay or do not have too much time to waste writing a full outline.
Great Starter������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������
Thesis Statement����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������.
Body Paragraph #1
Adjective #1���������������������������������������������������.
Example�����������������������������������������������������
Quote������������������������������������������������������.
Explanation���������������������������������������������������
Body Paragraph #2
Adjective #2���������������������������������������������������
Body Paragraph #3
Adjective #3���������������������������������������������������
Quote������������������������������������������������������
Great Finisher/conclusion�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������............
How to format Quotations in a Character Analysis Essay
A character analysis essay draws from the ideas and quotes from the story, play, or film. It is the best way to relate your character to your story, which helps contextualize your analysis. There are three approaches to formatting and framing quotes in a character analysis essay.
- Create an intro to your quotation that helps the reader understand its meaning. This is called a �tag line.�
Example : A change in Jem�s attitude toward the Radleys is shown when Scout reports, �Less than two weeks later we found a whole package of chewing gum, which we enjoyed, the fact that everything on the Radley Place was poison having slipped Jem�s memory� (Lee, 60).
- Double quotation marks around the entire quote; single quotation marks to show where the quotations exist already in the text.
Example: Jem�s frustration with the injustices of the world is shown in the courtroom. ?Doesn�t make it right,� said Jem stolidly. He beat his fist softly on his knee. �You just can�t convict a man on evidence like that � you can�t� (Lee, 220).
- Changing a word or two in a quotation to clarify its meaning.
Example: Harper Lee helps her readers understand why this neighbor is so mysterious to the children of the neighborhood when she states that �Mr. Radley kept [Boo] chained to the bed most of the time� (Lee, 16).
Final Words!
Writing a character analysis essay can be easy and tough at the same time. It is tough because you must read, research, and synthesize information on a specific character and relate it to the story. This might sound like too much work but not when you apply the tips we have shared above. It is also easy in that you have to focus on one character for every essay you are writing, which means limited research compared to when writing a book critique where you have to address aspects of the entire book or a movie review where you have to focus on all characters. To succeed, ensure that you read a text or watch a play or film before planning and organizing your ideas. Besides, with so many resources online, you can never miss information that helps you to write the best character essay.
If writing is not your thing, you do not have the time, or you don�t feel like writing a character essay, you can hire our custom writing professionals to help you. They contributed to this guide and understood what it takes to write a perfect essay that meets the highest grades in the rubric.

Gradecrest is a professional writing service that provides original model papers. We offer personalized services along with research materials for assistance purposes only. All the materials from our website should be used with proper references. See our Terms of Use Page for proper details.


Characterization

Characterization Definition
What is characterization? Here’s a quick and simple definition:
Characterization is the representation of the traits, motives, and psychology of a character in a narrative. Characterization may occur through direct description, in which the character's qualities are described by a narrator, another character, or by the character him or herself. It may also occur indirectly, in which the character's qualities are revealed by his or her actions, thoughts, or dialogue.
Some additional key details about characterization:
- Early studies of literature, such as those by the ancient Greek philosopher Aristotle, saw plot as more important than character. It wasn't until the 15th century that characters, and therefore characterization, became more crucial parts of narratives.
- Characterization became particularly important in the 19th century, with the rise of realist novels that sought to accurately portray people.
Characterization Pronunciation
Here's how to pronounce characterization: kar-ack-ter-ih- zey -shun
Direct and Indirect Characterization
Authors can develop characterization in two ways: directly and indirectly. It's important to note that these two methods are not mutually exclusive. Most authors can and do use both direct and indirect methods of characterization to develop their characters.
Direct Characterization
In direct characterization, the author directly describes a character's qualities. Such direct description may come from a narrator, from another character, or through self-description by the character in question. For instance, imagine the following dialogue between two characters:
"That guy Sam seems nice." "Oh, no. Sam's the worst. He acts nice when you first meet him, but then he'll ask you for money and never return it, and eat all your food without any offering anything in return, and I once saw him throw a rock at a puppy. Thank God he missed."
Here the second speaker is directly characterizing Sam as being selfish and cruel. Direct characterization is also sometimes called "explicit characterization."
Indirect Characterization
In indirect characterization, rather than explicitly describe a character's qualities, an author shows the character as he or she moves through the world, allowing the reader to infer the character's qualities from his or her behavior. Details that might contribute to the indirect characterization of a character are:
- The character's thoughts.
- The character's actions.
- What a character says (their choice of words)
- How a character talks (their tone, dialect, and manner of speaking)
- The character's appearance
- The character's movements and mannerisms
- How the character interacts with others (and how others react to the character)
Indirect characterization is sometimes called "implicit characterization."
Indirect Characterization in Drama
It's worth noting that indirect characterization has an additional layer in any art form that involves actors, including film, theater, and television. Actors don't just say the words on the script. They make choices about how to say those words, how to move their own bodies and in relation to other character. In other words, actors make choices about how to communicate all sorts of indirect details. As a result, different actors can portray the same characters in vastly different ways.
For instance, compare the way that the the actor Alan Bates plays King Claudius in this play-within-a-play scene from the 1990 movie of Hamlet, versus how Patrick Stewart plays the role in the same scene from a 2010 version. While Bates plays the scene with growing alarm and an outburst of terror that reveals his guilt, Stewart plays his Claudius as ice cold and offended, but by no means tricked by Hamlet's little play-within-a-play into revealing anything.
Round and Flat Characters
Characters are often described as being either round or flat.
- Round characters : Are complex, realistic, unique characters.
- Flat characters : Are one-dimensional characters, with a single overarching trait and otherwise limited personality or individuality.
Whether a character is round or flat depends on their characterization. In some cases, an author may purposely create flat characters, particularly if those characters will appear only briefly and only for a specific purpose. A bully who appears in a single scene of a television show, for instance, might never get or need more characterization than the fact that they act like a bully.
But other times authors may create flat characters unintentionally when round characters were necessary, and such characters can render a narrative dull, tensionless, and unrealistic.
Character Archetypes
Some types of characters appear so often in narratives that they come to seen as archetypes —an original, universal model of which each particular instance is a kind of copy. The idea of the archetype was first proposed by the psychologist Carl Jung, who proposed that there were twelve fundamental "patterns" that define the human psyche. He defined these twelve archetypes as the:
While many have disagreed with the idea that any such twelve patterns actually psychologically define people, the idea of archetypes does hold a lot of sway among both those who develop and analyze fictional characters. In fact, another way to define round and flat character is to think about them as they relate to archetypes:
- Flat characters are easy to define by a single archetype, and they do not have unique personal backgrounds, traits, or psychology that differentiates them from that archetype in a meaningful way.
- Round characters may have primary aspects that fit with a certain archetype, but they also may be the combination of several archetypes and also have unique personal backgrounds, behaviors, and psychologies that make them seem like individuals even as they may be identifiable as belonging to certain archetypes.
Good characterization often doesn't involve an effort to avoid archetype altogether—archetypes are archetypes, after all, because over human history they've proved to be excellent subjects for stories. But successful authors will find ways to make their characters not just archetypes. They might do so by playing with or subverting archetypes in order to create characters who are unexpected or new, or more generally create characters whose characterization makes them feel so unique and individual that their archetype feels more like a framework or background rather than the entirety of who that character is.
Characterization Examples
The characters of nearly every story—whether in literature, film, or any other narrative—have some characterization. Here are some examples of different types of characterization.
Characterization in Hamlet
The famous literary critic Harold Bloom has argued in his book The Invention of the Human that "Personality, in our sense, is a Shakespearean invention." Whether or not you agree with that, there's no doubting that Shakespeare was a master of characterization. One way he achieved such characterization was through his characters delivering soliloquies . The excerpt of a soliloquy below is from Hamlet , in which Hamlet considers suicide:
To be, or not to be? That is the question— Whether ’tis nobler in the mind to suffer The slings and arrows of outrageous fortune, Or to take arms against a sea of troubles, And, by opposing, end them? To die, to sleep— No more—and by a sleep to say we end The heartache and the thousand natural shocks That flesh is heir to—’tis a consummation Devoutly to be wished! To die, to sleep. To sleep, perchance to dream—ay, there’s the rub, For in that sleep of death what dreams may come When we have shuffled off this mortal coil, Must give us pause.
Hamlet's soliloquy is not simply him saying what he thinks. As he delivers the soliloquy, he discovers what he thinks. When he says "To die, to sleep. To sleep," he is all-in on the idea that suicide is the right course. His words "perchance to dream" flow directly out of his thoughts about death as being like "sleep." And with his positive thoughts of death as sleep, when he first says "perchance to dream" he's thinking about having good dreams. But as he says the words he realizes they are deeper than he originally thought, because in that moment he realizes that he doesn't actually know what sort of dreams he might experience in death—they might be terrible, never-ending nightmares. And suddenly the flow of his logic leaves him stuck.
In showing a character experiencing his own thoughts the way that real people experience their thoughts, not as a smooth flow but as ideas that spark new and different and unexpected ideas, Shakespeare gives Hamlet a powerful humanity as a character. By giving Hamlet a soliloquy on the possible joy of suicide he further captures Hamlet's current misery and melancholy. And in showing how much attention Hamlet pays to the detail of his logic, he captures Hamlet's rather obsessive nature. In other words, in just these 13 lines Shakespeare achieves a great deal of characterization.
Characterization in The Duchess of Malfi
In his play the The Duchess of Malfi , John Webster includes an excellent example of direct characterization. In this speech, the character Antonio tells his friend about Duke Ferdinand:
The Duke there? A most perverse and turbulent nature; What appears in him mirth is merely outside. If he laugh heartily, it is to laugh All honesty out of fashion. … He speaks with others' tongues, and hears men's suits With others' ears; will seem to sleep o’th' bench Only to entrap offenders in their answers; Dooms men to death by information, Rewards by hearsay.
Ferdinand directly describes the Duke as deceitful, perverse, and wild, and as a kind of hollow person who only ever laughs for show. It is a devastating description, and one that turns out to be largely accurate.
Characterization in The Great Gatsby
Here's another example of direct characterization, this time from The Great Gatsby . Here, Nick Carraway, the narrator of the novel, describes Tom and Daisy Buchanan near the end of the novel.
They were careless people, Tom and Daisy—they smashed up things and creatures and then retreated back into their money or their vast carelessness, or whatever it was that kept them together, and let other people clean up the mess they had made.
But The Great Gatsby, like essentially all other literature, doesn't solely rely on direct characterization. Here is Nick, earlier in the novel, describing Gatsby:
He stretched out his arms toward the dark water in a curious way, and, far as I was from him, I could have sworn he was trembling. Involuntarily I glanced seaward—and distinguished nothing except a single green light, minute and far away, that might have been the end of a dock.
This is an example of indirect characterization. Nick isn't describing Gatsby character directly, instead he's describing how Gatsby is behaving, what Gatsby is doing. But that physical description—Gatsby reaching out with trembling arms toward a distant and mysterious green light—communicates fundamental aspects of Gatsby's character: his overwhelming yearning and desire, and perhaps also the fragility inherent such yearning.
Why Do Writers Use Characterization?
Characterization is a crucial aspect of any narrative literature, for the simple reason that complex, interesting characters are vital to narrative literature. Writers therefore use the techniques of characterization to develop and describe characters':
- Motivations
- History and background
- Interests and desires
- Skills and talents
- Self-conception, quirks, and neuroses
Such characteristics in turn make characters seem realistic and also help to drive the action of the plot, as a plot is often defined by the clash of actions and desires of its various characters.
Other Helpful Characterization Resources
- Wikipedia entry on characterization: A brief but thorough entry.
- Archetypal characters: The website TV tropes has built a vast compendium of different archetypal characters that appear in film and television (and by extension to books).
- Encyclopedia Britannica on characters: A short entry on flat and round characters.

- PDFs for all 136 Lit Terms we cover
- Downloads of 1900 LitCharts Lit Guides
- Teacher Editions for every Lit Guide
- Explanations and citation info for 39,983 quotes across 1900 books
- Downloadable (PDF) line-by-line translations of every Shakespeare play
- Flat Character
- Round Character
- Climax (Plot)
- Climax (Figure of Speech)
- Deus Ex Machina
- Stream of Consciousness
- Understatement
- Falling Action
- Common Meter
- Point of View
- Static Character
- Epanalepsis

Character Analysis
Last updated on: May 29, 2023
Learn How to Write a Character Analysis Essay in Easy Steps
By: Nova A.
Reviewed By: Melisa C.
Published on: Jan 19, 2021

Writing a character analysis essay is a challenging type of assignment for students. It requires you to examine how the protagonist's personality and actions affect their development. Moreover, you have to explore the author's use of characterization.
So, you've decided to write a character analysis essay. If this is your first time writing one of these essays, don't worry!
Believing it's hard or that there are many rules can be intimidating, but it doesn't have to be difficult. If you know what steps need to be taken to write a great character analysis essay, you’ll be good to go.
So, if you want to know more about it, this blog can help. Read ahead to learn how to write a good character analysis essay.

On this Page
What is a Character Analysis?
A character analysis essay is a type of essay in which the writer explains the main traits of the character. It is based on the analysis and breakdown of the chosen character. It could be based on a drama, novel, or even poetry.
An essay analyzing a character is typically structured in the same way as other essays. Begin with an intro of that person. Later, discuss their traits and backstory. Then finish by explaining why you chose this particular character.
An analysis essay discusses the comprehensive characteristics of a character. These characters are from literature and art.
However, sum up everything clearly and explain the character’s role and purpose in the story. Avoid writing irrelevant and obscure details in the essay.
Purpose of a Character Analysis
The main purpose of the character analysis essay is to:
- Help the readers understand the characters better.
- Tell the people who the character is and what role they play.
- Make the people in the story more engaging.
- Give your personal opinion of a certain character.
- Allows you to analyze the relationship between a character with other characters.
How to do a Character Analysis?
It can be fun to learn more about a character by analyzing them. However, this is not the same as writing about them. In order to write a good analysis, you need to understand their personality.
You need to think about a few important things when doing a character analysis.
Actions : You need to know what are the actions of the character? Are the actions mindful or evil of others?
Inspiration: What are the motivations behind the character's actions? How do their choices reflect their personality? What ethical implications does their behavior have?
Choice of Words: Pay attention to these words as they will help you know more about the character.
Characters Names : The name and title of the story also help in understanding both minor as well major characters.
Different Types of Characters
There are many types of characters in stories, and each has its own traits, roles, or behaviors. Here is a list to help you know more about them:
Character Analysis Outline
One of the most critical steps in writing a good character analysis is organizing your thoughts and ideas. A well-constructed outline will help you stay on track with everything.
A good character analysis outline consists of an introduction, the main body, and a conclusion.
Let’s discuss them in detail.
Introduction
Your introduction should spark the interest of your audience and hold together all that follows. Use short sentences and interesting facts about the characters. Describe them clearly for people who might be reading this but haven't met those particular individuals before.
To write a well-structured analysis, you should first divide your body paragraphs into different areas or ideas according to the character. Make sure that all of the points are covered.
The body section should cover the below-mentioned questions:
- What does the character do?
- What’s the character’s physical appearance?
- How does the character describe themselves?
- What lesson do the characters give to the readers?
- What motivates the readers?
Conclusion
The conclusion of your character analysis should be well-written and cohesive. It’s time to take one last look at how the story unfolds, then draw some conclusions about what readers learn from it. Lastly, do not insert new details here and end it with closure instead.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job
How to Write a Character Analysis?
To understand these characters better, you need to immerse yourself in the story or piece of literature. Pay attention to its important parts, such as the setting, climax, and others. You need to be able to feel and see what the characters are going through.
Notice how the author developed the characters in the story. The writer can see how the characters were shaped and formed. The amount of information given about their identities is up to the writer.
Sometimes, writers can look at the different behaviors and morals of the characters. They are also able to see how these have affected different situations throughout the story. When you start writing a character analysis essay, you have to do some planning and preparation. Without it, you will never create a well-written essay.
For your help, we have gathered some steps that you should follow when you start writing the essay.
1. Read the Story
Reading is the key to all essay writing. It can give you insights into their development as a person or in life. You should read before you start describing the character.
2. Choose a Dynamic Character
Choosing the right character seems like the easiest part of writing a story, but it can be difficult. First, you need to understand what motivates your characters and what role they play.
If you choose to make your protagonist static and boring. In that case, the essay will likely turn out monotonous. It is because they won't undergo any changes during their journey throughout the story.
However, if you have characters with more depth than your main protagonists that are constantly changing and growing in different ways, there's no doubt that engaging content will appear in your work.
3. Take Proper Notes
When you are reading a book, you must take notes and highlight all the critical elements of the story. It will help in your entire writing phase, and you won’t forget any main points.
Therefore, when you take notes, you should cover;
- Childhood facts
- Physical traits
- Character traits
- Intonations, and Expressions
4. Create the Thesis Statement
In this step, create the thesis statement that covers the main essay purpose, which will be explained in the essay. A perfect character analysis thesis statement contains an idea about the character. Also, try to write it in an attention-grabbing way.
5. Create the Character Analysis Outlin e
Creating an outline is necessary for a character analysis essay, like all other essay types. The outline structure is also the same, but only the content is changed.
6. Write the Introduction
A good essay introduction is necessary to make the reader feel like part of what you're saying. Therefore, an introduction should have some kind of statement, question, or preview about your essay's content. It makes it effective and engaging.
To get readers interested before diving into an analysis, start by describing who that character is being analyzed? What motivates them? What makes their personality unique from others?
Give a brief introduction about the character, but don’t go into depth.
7. Write the Main Body Paragraphs
Your essay should be divided into three sections, each discussing a different important aspect of the character. The body paragraphs should answer the following questions:
- What can we learn from this character
- What are the main physical attributes
- What are the conflicts the character experiences?
- What does the character say?
- What is their background?
Therefore, keep these questions in your mind and answer them precisely without any confusion.
8. Write the Conclusion
The conclusion of a character analysis should conclude the character’s conflicts and what the reader can learn from them. Also, highlight the important personality traits of the character.
9. Proofreading and Editing
Proofreading is the last step of the essay. In this step, remove all the grammatical, punctuation, and vocabulary mistakes. Try to make it error-free and leave a good impression on the readers.
Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers!
Character Analysis Examples
Examples always make the writing task easier. Therefore, for your help, we gathered some professionally written examples that give you a better idea of a character analysis essay.
Character Analysis of Hamlet
Character Analysis Worksheet
Character Analysis of Oedipus Rex
Character Analysis of King Lear
Character Analysis of Maggie in Mill on the Floss
Character Analysis of Joseph Andrews
Character Analysis of Waiting for Godot
Lady Macbeth Character Analysis
Othello Character Analysis
Iago Character Analysis
Tips for Writing the Character Analysis
For your help, we compiled some great tips that will make your writing process easy. These are;
- Read the text carefully and pay attention to the major character.
- Explain the personality of the character in detail.
- Discuss the character's interaction with other characters.
- Elaborate on each character's role in the story.
- Never ignore the minor roles that the characters play.
- Character study is essential for writing a great essay.
Now you have a detailed guide on a character analysis essay. However, if you still need any help, consult MyPerfectPaper.net . All your ‘ do paper for me? ’ requests are managed by expert writers.
So, without thinking too much, contact us now.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the characteristics of good character analysis.
Below are some characteristics of good character analysis:
- Based on critical analysis
- Poses questions and answers them along
- Draws story-based conclusions
What are the 6 traits of good character?
The six traits of good character are:
- Responsibility
- Trustworthiness
- Citizenship
How do you start a character analysis?
The following are the steps that will help you start writing the character analysis essay.
- Identify whether the character is a protagonist, antagonist, or minor character.
- Introduce the character and explain their role.
- Discuss whether the character is static or dynamic.
What are the four major methods of analyzing characters?
Here are the four major methods of analyzing characters.
- What does the author say about the characters?
- What do the characters say?
- What do the characters do?
- What does the character say about other characters?

Literature, Marketing
Nova Allison is a Digital Content Strategist with over eight years of experience. Nova has also worked as a technical and scientific writer. She is majorly involved in developing and reviewing online content plans that engage and resonate with audiences. Nova has a passion for writing that engages and informs her readers.
Was This Blog Helpful?
Keep reading.
- Learn How to Write an Article Review Like a Pro

People Also Read
- expository essay topics
- how to write an abstract
- reflective essay topics
- 500 word essay
- cite a dissertation
Burdened With Assignments?

Advertisement
- LEGAL Privacy Policy
© 2024 - All rights reserved
What Is a Character Analysis Essay and How to Write It?

Different literary courses often require writing critical and analytical types of essays. One of such essays is a character analysis essay that a student has to perform on the chosen book character (in other cases, on the movie character). If you need to complete such an assignment, then our tips on this type of essay writing will definitely come in handy. Keep reading to know more about how to write such essays.
Preparing for Your Essay and Picking the Character
Every essay starts with a topic. In the case of a character analysis essay, you need to choose the character that you are going to describe and analyze. If the character is not specified and you need to make a choice, consider the following points:
- You might choose a major character or a secondary one
- Make sure to identify the relationship of your character with the others, his or her role in the story, the development through the plot and symbolism involved
- Find the quotes and description of the character in the text – details of the appearance, mentality, features, etc. Choose the character whom you can find enough information about in the source.
Consider the type of a character
Before making your choice of a character or multiple characters to analyze, pay attention to the type of the character:
- Protagonist — a positive character.
- Antagonist — a negative one.
- Foil — contrasts the major character.
- Major — leading characters who dominate in the story, the center of the plot.
- Minor — characters who appear in lesser episodes.
- Dynamic — the one who constantly changes.
- Static — the one who remains the same.
The type defines the place of the character in the story and should be mentioned in your essay as well as the significant meaning or the symbolism of the character.
Take your notes
Once you have decided on what specific character you are going to examine in your analysis essay, you can start gathering all the information that you can find. Look through the original source and write down:
- All of the scenes that your character appears in
- All of the characters he or she interacts with
- Description of the character that the author provides
- Scenes with the character
After you have all of your notes ready, you can start working on your essay.
Writing an Outline
Start your essay with creating a character analysis essay outline. Consider that character analysis essay has the structure that is pretty similar to any other type of academic writing that you usually perform.
- Introduction. Make sure to start your essay with a catchy sentence. Quotes, intriguing questions or interesting facts make a great hook for character analysis essay. Also make sure to include your thesis statement that will represent your opinion, thoughts and the main idea of your essay. You can take your inspiration for your hook sentence from our article.
- Body paragraphs. These paragraphs should contain the main information about the character, the description, facts, etc. Don’t forget to support your claims with the evidence – the quotes from the original source.
- Conclusion. The summary of your text that restates your thesis statement and concludes the ideas in your essay.
If you would like to improve your writing skills , make sure to check some useful tips.
Writing an Introduction
An introduction is the main part of your essay as it sets the tone for the whole paper and catches the reader’s attention. If your introduction is good enough, it is a reason for a reader to continue reading further.
Make sure to make your character analysis essay introduction clear. Mention the main idea of your paper, which character you have chosen and why, what makes this character significant or what distinguishes him or her from the rest of the characters.
Also, phrase and write down your thesis statement. Sometimes your thesis statement might be unclear until you finish the body of your essay. So, if you are not sure about it, set it aside and write your body paragraphs.
Sample character analysis thesis statement
“ In his novel ‘Lord of the Rings,’ J. R. R. Tolkien makes Sam devoted, faithful, optimistic and to some extent naive to contrast and emphasize the loneliness and the vulnerability of Frodo caused by the ring. ”
If you want to find some other character analysis thesis examples, make sure to take a look at the samples works performed by our writing team. Or, you might also be interested in writing methods that famous writers used in their work which you can use too.
Writing the Body Paragraphs
The body paragraphs of your essay are the main representation of the information that you have found in the original source. They must include the quotes that will support your claims and provide a description of the character from the author’s perspective. You can also write a character analysis of multiple characters and their relationships.
Find the quotes that will provide a detailed description not only of the appearance of the character but also their relationships and the place of the character in the story. Make sure to provide your opinion and evolve your thesis statement idea, referring to the particular parts of the original source.
Writing a Conclusion
The analysis essay conclusion should be a summary of your work. Make sure to repeat your thesis statement in other words and add a brief explanation of your findings. You might also mention the correlation between the experience of the character in the story and the experience that we might get in real life, you might make a conclusion about the mistakes that the character has made.
Proofread and edit your essay. Make sure to check if your essay follows the guidelines of your teacher or professor. If you are still confused about the process of writing this kind of essay or face difficulties with particular essay topics, you can always turn to a professional writing team and ask for help. You can order your essay or ask for editing service here.
Related posts

How to Write a Character Analysis Essay With Examples and Tips
11 December 2023
last updated
Essay writing is an exciting and valuable academic exercise for students at all levels of learning. Basically, the practice helps in developing students’ critical thinking skills. For example, when writing a character analysis essay, students use these skills to cover a specific character’s personality and mannerisms objectively. Moreover, this type of essay aims to analyze a character in a story in such a way that readers can develop a mental picture of them. In this case, the secret of writing a good character analysis essay involves choosing a dynamic character, such as a protagonist or an antagonist. Then, another tip is to write the first draft and read it at least twice to identify and correct errors and mistakes. In turn, the final draft should reflect a perfect document. Hence, students need to learn how to write a good character analysis essay with its features.
Definition of a Character Analysis Essay
Among many different types of essays is a character analysis essay, a text that describes a particular character in a story. When writing this essay, students analyze relationships between characters in question and other characters, paying particular attention to their mannerisms. Also, these mannerisms are exemplified by their behaviors, styles of speaking, physical appearances, and many other characteristics. Even though students may offer their personal opinions when analyzing specific characters, they must employ critical thinking and be objective. In essence, what matters in a character analysis essay is factual information about a character in question. In this case, the writer’s opinion should support rather than challenge the specific traits and characteristics of a character. Hence, a student writes this type of essay when instructions require them to discuss how a particular character is shaped in a story.

Types of Characters
When analyzing a character in a story, writers must first understand what kinds of characters are their subjects. Typically, there are different types of characters whose distinctions are based on particular behaviors, traits, and roles that they exemplify within a story. In turn, the main character types fall under five categories: major, minor, dynamic, static, and stoic.
1. Major Characters
In a story, major characters run a storyline, and they define a plot of this story. For example, there are two types of major characters: protagonists and antagonists. In this case, the former represents typical heroes, those characters that the audience is likely to admire. Then, the latter represents characters that take the role of a villain. Basically, the audience is likely to despise this type of character. Moreover, it is easier to spot protagonists because a story’s plot revolves around them. In literature, examples of protagonists include Harry Potter from the Harry Potter series by J.K. Rowling, Othello from the tragedy Othello by William Shakespeare, Elizabeth Bennet from “Pride and Prejudice” by Jane Austen, and Frodo from The Lord of the Rings by J.R.R. Tolkien. On the other hand, examples of antagonists from the literature include King Joffrey from Game of Thrones , Darth Vader from the Star Wars series by George Lucas, and the Wicked Queen from “Snow White and Seven Dwarfs.”
2. Minor Characters
As opposed to major characters, minor characters do not run stories. However, they are ones that help major characters to shine through storylines. In other words, minor characters in the course of their activities help main characters to create situations and circumstances that reveal the central characters’ personalities. As explained, this personality is defined by mannerism. Then, examples of minor characters in the literature include the whole Fellowship of the Ring in J.R.R Tolkien’s The Lord of the Rings. Individually, these characters help Frodo, a protagonist, to deliver the Ring to Mordor. In turn, another example of minor characters in literature is the duo Ronald Weasley and Hermione Granger in J.K. Rowling’s Harry Potter series. On several occasions, they help Harry Potter, a protagonist, in his battle against Voldemort.
3. Dynamic, Static, and Stoic Characters
Dynamic characters are those characters that change the course of a story in certain respects. In many cases, a protagonist is a dynamic character. Moreover, an example in the literature is Harry Potter from J.K. Rowling’s book series, who notices that he is similar to Voldemort in many ways throughout a storyline. Nevertheless, he resists “dark” traits that define Voldemort because he is a good person. As such, he resists any temptation to become a dark wizard. On the other hand, static characters never change in a story. Also, an excellent example in the literature is Atticus Finch from “How to Kill a Mockingbird” by Harper Lee. Despite finding himself in controversial circumstances, he remains firm in character and worldview throughout a story. Further on, stoic characters draw attention to the main character(s), and their role in a story is to fortify the protagonist’s role and image. In turn, a great example of a stoic character in literature is Dr. Watson from Sherlock Holmes by Arthur Conan Doyle.
Step 1: Preparation
Preparation is the starting step in writing a critical analysis essay. In essence, this step involves planning how to go about writing. Basically, a student reads a story, chooses a character, defines a topic, prepares ideas, and considers the audience and its needs. In this case, the essence of preparation is that it enables students to “get it right” from the beginning. Moreover, it is by preparing that students take into consideration requirements and seek clarification as necessary.
A. Reading a Story
In most instances, instructors guide students on which story to read and a character to analyze. However, if such guidance is not provided, a student should – as a matter of priority – choose a story and a character in this story to write about. About a story, writers should read it at least twice to have a good understanding of a plot and each character’s role.
B. Choosing a Character
The standard practice is that a character analysis essay focuses on major characters (protagonist and antagonist) as subjects of analysis. However, as indicated, an instructor may require students to analyze a specific character. In this case, instructions can require students to explore how a minor character enhances a major character’s image in a story. Also, the writer’s issue is to identify characters for analysis and read all about them in an assigned story.
C. Defining a Topic
Like any essay, a character analysis essay should have a topic. Basically, even though the goal is to analyze a specific character, writers must have a topic that underscores their work. When defining a topic, students may follow the instructor’s prompt or develop their own approach. Ultimately, a character analysis essay topic should align with the paper’s goal, which is to analyze a specific character.

D. Preparing Ideas
Typically, students get ideas about their work as soon as they read prompt requirements given by their instructors. When writing a character analysis essay, a student should generate ideas after reading instructions and reading through them. However, it is the latter exercise that serves as the foundation of ideas for writing a text. Indeed, this aspect exemplifies the essence of a character analysis essay, focusing on how a character emerges from a story. As discussed, a character can only be a protagonist, antagonist, minor, dynamic, or stoic. Understanding where characters fit helps a writer to generate ideas about effects of their roles in a story. Here, students should apply critical thinking to dissect characters objectively.
E. Considering an Audience
Every form of writing has an audience – readers that writers have in mind when writing their texts. In essay writing, the main audience is the instructor. However, in an application essay for college , the audience is the admission board of a college or university. Since instructors determine the quality of a character analysis essay, students should consider their requirements. Ideally, these requirements reflect what instructors, as the audience, need regarding a character analysis essay.
Step 2: Setting Up the Stage
The second step in writing a character analysis essay is setting the stage for the actual writing of a text. Here, students engage in several activities, including finding credible sources , making notes, creating an essay outline , and creating an annotated bibliography. As an academic text, a character analysis essay should satisfy all academic writing conventions, including backing up claims and arguments with evidence. Although a learner can write about a character in a story by simply reading a story, a character analysis reflects an in-depth discussion about a specific character. Hence, students should write about what others (scholars) have said about a story and a character.
A. Finding Sources
Reliable sources are external texts that writers rely on to find evidence supporting what they intend to write. Basically, when writers make claims or observations when composing a text, they must back it up with evidence to avoid making what they write seems like a personal opinion. Notably, subjective opinion is not encouraged in academic writing, unless writers are using it objectively. Moreover, the only way that students can demonstrate that their essays are free of bias is by providing evidence for their claims, arguments, opinions, and observations. In turn, this evidence comes from external academic sources – books and journal articles.
B. Making Notes
After finding sources, a student should read through them while making notes. Basically, these notes should be relevant to a task at hand. Therefore, when authors of a character analysis essay find sources pertinent to their mission, they should make notes as they read through them and write down what they find interesting about their characters. Given that the task at hand involves analyzing a character in question, students’ notes should reflect a deeper understanding of this character, such as what others say about their manner of speaking or effect in a story.
C. Creating an Outline and an Annotated Bibliography
Like any other academic text, such as a research paper , a term paper , a Master’s thesis , or a dissertation , essays have outlines that provide a structure. Typically, this outline involves having three main sections: introduction, body, and conclusion. When writing a character analysis essay, a student should stick to this essay structure . Then, an annotated bibliography summarizes study sources that writers intend to use to get evidence that backs up their claims and arguments. Although it is not needed in an essay, students who write a character analysis essay can develop one based on credible sources that they identified in the second step of essay writing. In this case, annotated bibliographies would provide quick access to evidence that learners need to strengthen their papers.
Step 3: Actual Writing of a Character Analysis Essay
After preparing and setting the stage, authors of a character analysis essay begin the actual writing of a paper. Here, students begin with the first draft, which provides an opportunity to organize thoughts, make mistakes, come up with new ideas, find new sources that back them up, and alter a critical analysis essay outline. Basically, this stage is about putting everything together to develop an essay that addresses the instructor’s requirements.
A. Writing a First Draft of a Character Analysis Essay
When writing a character analysis essay, students are likely to make numerous spelling and grammatical errors and other mistakes, such as inconsistent arguments and illogical conclusions. As such, writing the first draft provides writers with this allowance since they would have an opportunity to perfect their work. Nonetheless, the first draft’s content should mirror the expected work, which is dissecting a character’s personality.
Step 4: Wrapping Up
After writing the first draft of a character analysis essay, students must read and reread their work to identify all mistakes and errors. As discussed above, the chances of the first draft having spelling and grammatical errors, illogical conclusions, and inconsistent arguments are high. In turn, this fourth step in writing a character analysis essay provides students with an opportunity to perfect their work. Here, learners revise and edit the first draft to eliminate all errors and mistakes and ensure that their papers reflect a format of an academic text in all aspects. Also, body paragraphs should have topic and concluding sentences, transitions, and right formatting. Additionally, writers should subject their work to peer review and then write the final draft.
A. Revising and Editing the First Draft
The purpose of reading the first draft at least twice is to identify all errors and mistakes, as explained above. Basically, once writers note them down, they should revise their papers accordingly, ensuring that all inconsistencies are corrected. Moreover, students should edit all spelling and grammatical mistakes to give a written document to look like a professional appeal.
B. Topic Sentences.
The first statement that a student writes in every paragraph in the main text (body) should reflect a topic sentence. Basically, this sentence aims to introduce a single idea that a writer intends to develop in a paragraph. By considering a character analysis essay, this idea can be a claim or an observation about a subject under analysis. In this case, the standard practice is that a single idea that a writer expresses in a topic sentence should align with a paper’s thesis statement , as it is developed in the introduction part of a character analysis essay.
C. Concluding Sentences
While a topic sentence introduces a paragraph, a concluding sentence brings it to a close. For example, a reason why a student writes a concluding sentence is to finalize an intended message captured in a section. As such, it provides the writer’s concluding thoughts about a topic sentence and how it advances a thesis statement. Also, the content that comes between topic sentences and concluding sentences reinforces a sandwich rule: making a claim, backing it up with supporting facts, elaborating on it, and indicating its relevance in a context of a thesis.
D. Transitions
In writing a character analysis essay, students need to create a document with a natural flow from a beginning to an end. Basically, the aspect that enhances this flow is the use of transitions, which involve words and phrases, like “consequently,” “hence,” “thus,” “nonetheless,” “as such,” and “put differently.” In this case, a writer can use these words and phrases in any part of a text. However, using them in the main text is more appropriate as it is where writers need to create linkages between claims, evidence, and elaborations. Hence, transitions make such connections flawless and logical.
E. Formatting
When writing an academic text, it is critical for students to observe all academic writing rules. For example, one of these rules is writing a character analysis essay according to assigned rules that guide a paper format that learners are using to write their work. In this case, the main paper formats are APA 7, MLA 8, Harvard, and Chicago/Turabian, all of which differ in certain ways. For instance, they all have different requirements for citations and paragraph formation. Therefore, when writing a character analysis essay, a student should format a paper according to the appropriate writing format. Although learners may observe this rule when writing the first draft, they should certainly do so when creating the final draft.
F. Peer Reviewing
When writing a character analysis essay, students should ensure that their work is of high quality. Basically, what makes an academic text of high quality is peer review, which means subjecting a written work to a critical review by a friend, tutor, or mentor. For example, journal articles are regarded as peer-reviewed scholarly sources for a simple reason that they have been reviewed and made perfect. In turn, this perfection entails ensuring the absence of errors and mistakes and the use of credible and reliable sources.
Step 5: Writing a Final Draft of a Character Analysis Essay
The final draft represents the final work of a student in writing a character analysis essay. Basically, it is a document that students hand over to the audience by way of submission or publication. As such, writers must ensure that their texts are of the highest standard to eliminate the possibility of attracting penalties, such as a low grade or lousy review, in case they publish their work on online platforms. Also, to be clear that what students have is of the highest quality, they should read and reread their papers. In turn, it is the only way in which they can be sure that there are no errors or mistakes.
Simple Outline Example of a Character Analysis Essay
As indicated in the previous section, students should take time and create an outline for their work when writing an essay. This outline comprises three main sections: introduction, body, and conclusion as below.
I. Introduction Paragraph II. Body Section (this part may include several paragraphs) III. Conclusion Paragraph
While most academic texts follow this outline, some papers differ on features that writers address in each section. Basically, when writing a character analysis essay, students should ensure that the introduction section highlights its thesis. In turn, this statement guides the entire writing, meaning that it is the central claim or idea in a paper. In body paragraphs, writers should ensure that topic sentences open each paragraph while concluding sentences end them. Moreover, learners should ensure sufficient and appropriate use of transitions and observance of a sandwich rule. In the conclusion section, students should restate the thesis and summarize the paper’s main points.
How Students Know That They Write a Character Analysis Essay
Generally, the purpose of a character analysis essay is to provide an in-depth analysis of a specific character. As such, writers know that they write a character analysis essay if their texts describe a given character’s personality and mannerisms. In turn, the latter entails how a character in question behaves, speaks, looks like (physical features), and their familial and social relationships, as it is covered in a story.
How a Character Analysis Essay Differs From Other Papers
When it comes to an outline, a character analysis essay is similar to other types of papers . However, regarding the content, this type of essay differs from other papers significantly. For example, an argumentative essay focuses on making the writer’s argument acceptable to the audience, meaning that the content revolves around the writer’s perspective regarding an issue. In contrast, a character analysis essay focuses on providing the audience with a detailed picture of a specific character in a story, meaning that the content revolves around a subject (character). In an informative essay , the writer’s goal is to educate the audience about a topic or an issue, meaning that the content revolves around explaining concepts relating to a specific theme in question. Therefore, the point of difference between a character analysis essay and other essay types is content more than structure.
Easy Strategies for Writing Each Section of a Character Analysis Essay
When it comes to the introduction, authors of a character analysis essay should provide a hook, which can be a statement, quote, or a joke. Basically, a hook sentence aims to grab the reader’s attention and make them interested in reading the entire paper. Then, if students know how to write a hook , they provide a brief background of a text after it. Also, it is where they introduce a story and a character under investigation. In turn, writers should conclude this section with a thesis, thus outlining the purpose of writing. About the main text (body), if learners are familiar with the rules of how to write a topic sentence , they begin each paragraph with it, which establishes a claim. Further on, the feature that follows is evidence (supporting facts) and then an explanation. As a result, the last element is a concluding sentence.
1. Paying an Attention
Based on the above information, it is evident that authors of a character analysis essay must pay attention to several things. In the introduction, writers should pay attention to the thesis, and, in the body paragraphs, they should follow a sandwich rule. Basically, this rule reinforces the claim-evidence-explanation approach. In the conclusion section, students should pay attention to the main points’ summary to make sure no new information is captured in this paragraph. Additionally, learners should ensure that they provide closing remarks, which emphasize their objective opinions about subjects matter.
2. Major Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Besides spelling, grammatical and other mistakes, writers of essays make other mistakes, leading to the fact that their work becomes less than high-quality. In writing a character analysis essay, one mistake that students make is to focus on a single aspect, such as personality, thereby undermining the subject’s full image. In this case, the solution to this mistake for a writer is to focus on the character’s mannerisms – behavior, speaking style, and appearance. Then, another mistake that learners make is to focus on aspects that do not advance an in-depth analysis of a subject, such as a story’s plot. In turn, the solution to this mistake for students is to focus on the subject’s roles in a plot’s context.
An Example of Writing a Character Analysis Essay
Topic: Frodo and His Heroic Weakness
I. Sample Introduction of a Character Analysis Essay
In literature, characters play an essential role in enhancing the plot of a story. Basically, they do this through their actions, behaviors, relationships, and other aspects of personality. Moreover, their mannerisms define who they are within the context of a story. In The Lord of the Ring , J.R.R. Tolkien captures a heroic conscience that characterizes human existence. Then, the author reveals the destructive power of greed and envy, mainly where promises are concerned. Nonetheless, Tolkien shows how friendship and courage overcome these vices. At the center of a story , The Lord of the Ring, is Frodo Baggins, a protagonist, who, despite undergoing a series of challenging adventures, emerges as a hero.
II. Example of a Body in a Character Analysis Essay
A. frodo as a hero.
Tolkien develops Frodo as a young hobbit with a remarkable character. As a ring-bearer of a fellowship, Frodo has the Ring that belongs to Sauron, the Lord of the Rings. As such, Sauron is an antagonist in a story. For example, he is “a dark lord who lost the one Ring that held much of his power” (Tolkien, 2003, p. 54). Then, the author describes the Ring as precious and powerful enough to enslave Middle Earth. While everybody is scared of the Ring and no one wants to lead its destruction, Frodo courageously overcomes such fear. Despite a myth that absolute evil and frightening dark forces are likely to victimize anyone who attempts to destroy the Ring, the young hobbit is keen to prove everybody wrong. In turn, it is the anger toward myths and oppressions that they seemed to cause people that motivate Frodo to act to restore safety in Middle Earth.
B. Frodo’s Weakness
The first indication of Frodo’s inexperience comes when he faces his initial challenges in his quest. Basically, how he deals with them reveals his weak points. For example, when Frodo delays his departure from the Shire, in spite of the urgency of the task ahead, he comes out as an indecisive character (Tolkien, 2003). Although a protagonist has common sense, he lacks wisdom, which is evident when he chooses to face the Old Forest’s dangers. Besides getting himself into harm’s way, Frodo also endangers the lives of his friends. In this case, he comes out as a fool in Bree when he draws unnecessary attention to himself. At Weathertop, the main character gives in to the temptation of putting on the Ring, thus exposing himself to an attack by the Ringwraiths (Tolkien, 2003). Despite all these shortcomings, Frodo survives the dangers of his own mistakes and those of his quest. Moreover, the novel attributes this success to the fact that hobbits are tougher than they look and can endure hardships. More importantly, Frodo himself is not interested in possessing the Ring, which makes him avoid the dark forces it represents. In this respect, he emerges as a hero in the end.
III. Conclusion Example of a Character Analysis Essay
Frodo’s adventure in The Lord of the Ring is a selfless quest to bring good to society despite powerful myths that undermine people’s courage to act when needed. In this case, Tolkien describes specific events that characterize the protagonist’s quest to destroy Sauron’s Ring. Moreover, what is clear is that Frodo is a courageous hobbit who refuses to be defined by his weaknesses. Eventually, his actions display his heroic character, one that defies all odds against him. In turn, a lesson from a story is that people do not need to be perfect to be heroes, but they need to aspire to do what is right.
Arthur, S. (2003). Walking with Frodo: A devotional journey through the Lord of the Rings . Carol Stream, IL: Tyndale House Publishers, Inc.
Summing Up on How to Write a Good Character Analysis Essay
When writing a character analysis essay, students must understand that this type of paper is different from all others. While an argumentative essay focuses on convincing the audience about an issue, a character analysis essay covers telling the audience about a specific character’s personality and mannerisms within the context of a story’s plot. As such, it also differs from an informative essay that focuses on educating the audience about a topic or an issue. Nonetheless, all these essays assume the same outline, which entails three main sections: introduction, body, and conclusion. In turn, when writing a character analysis essay, a student must note the following tips:
- Read the instructions carefully.
- Read a story.
- If there is no instruction about a character, choose a dynamic character, who is either a protagonist or antagonist.
- Reread a story and make notes that are specific to a chosen character.
- Develop a thesis statement.
- Draft an outline.
- Write the first draft.
- Read and reread the first draft to identify and correct errors and mistakes.
- Subject the first draft to a peer review.
- Write the final draft.
- Read and reread the final draft.
To Learn More, Read Relevant Articles
How to write a critical response essay with examples and tips, free personal narrative examples: basic guidelines with tips.
Essay Contests: How to Stay Under the Character Count
How to Avoid Getting Disqualified
- Creative Contests
- Tips and Tricks
- Dream Vacations
- Win Electronics
- Home and Garden
- Win Vehicles
- Jewelry and Clothing
- Types of Contests
- Frugal Living
- Fine Arts & Crafts
- Card Games & Gambling
- Cars & Motorcycles
- Playing Music
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/LAbio-SandraG-71d952ecca9342619f0f66c0f4eff19c.jpeg)
- University of Maryland
Some writing contests set a limit on the number of characters your entry can contain. This happens most often with contests that are looking for short pieces of writing like poems, greeting card sentiments, or jingles, but character limits can occur in any kind of essay contest.
It's important to read the rules carefully and check if there are character limits before you start planning your entry. Judges will disqualify your entry if the character count is too long, wasting your efforts! Be sure you know what counts as a character so you can stay under the limit.
What "Characters" Are in Writing Contests
Characters are the basic building blocks of writing. Whether you're composing a writing contest entry, a headline, or a tweet, the number of characters you use in your writing is important. So what counts as a character? Do spaces count? What about commas and periods?
Most of the time, spaces, letters of the alphabet, numbers, and punctuation all count toward a character limit. For example, if you are composing a tweet, the 280-character limit includes everything you type.
When it comes to contests, however, the rules might be a bit different. Some writing contests don't count spaces or punctuation toward their character count, for example.
To know what to count as a character, check what the contest rules say. If the rules don't explicitly state that some characters are excluded from the character count, play it safe by counting them all.
It's better to trim a few letters from your entry than to be disqualified for exceeding the character count.
How to Count the Characters in Your Entry
If you're not sure whether your entry comes under the allowed character limit, don't worry — you don't have to count each letter by hand. There are several easy ways to count your characters:
- Use a Word Processor: Compose your entry in a word processor like MS Word or Apple Pages and click on the Word Count feature to how many characters your entry has.
- Use a Free Character Counter: Some websites offer a free character counter. All you need to do is copy-paste your text into their web form, and it will tell you how many characters it contains. Some even let you specify whether spaces should be counted or not. LetterCount.com is one site you can use, or you can do a Google search for "character counters" to see all your choices.
- Use a Writing-Specific Processor: Writing programs like Scrivener automatically track your character and word count at the bottom or side of your screen for you. This running total is handy to watch as you compose your essay.
Reducing Your Character Count
If your essay contest entry has too many characters, don't worry. With some editing, you can reduce your length to come under the limit.
There's a reason why kill your darlings is a popular motto among writers. It means to be ruthless in deleting words and sentences that don't serve your story, no matter how good they sound or how much work you put into writing them. This mindset can help a lot when you're trying to come under a tight character count.
Start by going through the essay to see where you can be more concise. Be ruthless about shrinking your character count by removing unnecessary repetition and by making your prose as clean and smooth as possible.
Next, look at the phrases you use to see if you can find shorter alternatives. For example, prepositions aren't necessary in phrases like "Open up the letter" — "Open the letter" works just as well. Similarly, you can replace phrases like "In order to..." with shorter ones like "To..."
When you can no longer sacrifice length without losing important content, look at the words themselves. Are you using character-heavy words that could be effectively replaced by something shorter? A website like thesaurus.com will help you with more concise synonyms.
For more tips, read the University of North Carolina's guide, Writing Concisely .
Character Counts Vs. Word Counts
Be careful not to confuse character count limits, which are usually used in shorter pieces of writing, with word count limits, which are used in longer essays.
A 500-word essay would be about a single page long, whereas a 500 character essay would be about 100 to 150 words long. It's important to be clear about your terminology before you plan out your essay.
You can use many of the same techniques listed above to stay under a tight word count. Sites like WordCounter.net can help you determine how many words your entry has.
- How to Win Essay Contests: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Red Mittens, Hooks, and Other Ways to Make Contest Entries Spectacular
- 13 Beautiful Free Wedding Fonts
- Formal Letter Closing and Signature Examples
- What to Give an Employer When They Request a Writing Sample
- Ideas for 'Price Is Right' T-Shirts
- Business Letter Format With Examples
- Professional Letter and Email Examples
- How Blackjack Card Counting Works
- How to Write Your Own Manga
- How to Write and Send Professional Emails
- 10 Twitter Terms to Know Before You Tweet
- How To Win Video Contests (Even If You're Not a Pro!)
- Tweet to Win: How to Enter and Win Twitter Sweepstakes
- How to Win Halloween Costume Contests
- What "Hashtags" Mean & How You Use Them
How to Write a Character Analysis Essay: Examples & Outline
A character analysis is an examination of the personalities and actions of protagonists and antagonists that make up a story. It discusses their role in the story, evaluates their traits, and looks at their conflicts and experiences. You might need to write this assignment in school or college. Like any other essay, your character analysis should contain an introduction, a conclusion, and a thesis.
Our specialists will write a custom essay specially for you!
Want to know how to write a character analysis essay? Not sure how to start? We understand. Whichever piece you choose – Lady Macbeth, A Rose for Emily, or something else, – analyzing a character for the first time might be challenging. No worries, we are here to help! In this guide by our custom writing experts, you will find a step-by-step guide, outlining and writing tips, as well as a number of character analysis examples.
- 📔 Character Analysis Definition
- 🧙 Types of Characters
- 📝 Writing Guide
- 🖥️ Formatting Tips
📑 Character Analysis Essay Examples
📔 what is a character analysis essay.
A character analysis essay is an assignment where you evaluate a character’s traits, behaviors, and motivations. It requires critical thinking and attention to detail. Unlike descriptions, analyses focus on a character’s personality and internal drives. It explains how those factors shape the narrated events.

So, what you need to do is to see the characters as if they were real people who feel and act just as we do. Ensure there are no baseless assumptions and interpretations: the ideas you present should be supported by quotes from the text.
Character: Definition (Literature)
How do you define a character? It is a person, a creature, or an animal that makes up the story’s world. A character can be based on a real-life person, or it can be entirely fictional. It is someone who thinks, feels, and acts.
We use the word “character” in many different contexts. For instance, it can denote someone eccentric or worthy of our admiration. In both contexts, the term “character” means a distinctive personality. Similarly, in an analysis, your task is to show what makes a character stand out.
Just in 1 hour! We will write you a plagiarism-free paper in hardly more than 1 hour
Characterization: Literary Definition & Examples
Characterization is the process by which a character’s personality is revealed. It presents characters’ traits, feelings, and motives to the reader. For this reason, characterization is closely connected to character analysis. It helps us to understand the characters better throughout the reading process.
Characterization can be direct and indirect .
- Direct characterization is when the narrator directly tells the audience what the personality of a character is.
- In contrast, indirect characterization shows things that hint at a character’s nature.
Here are some examples of direct characterization taken from Patti Smith’s Just Kids :
“But he always suppressed his real feelings, mimicking the stoic nature of his father.”
Here we see a direct description of a character. The author straightforwardly talks about Robert’s feelings. In comparison, look at the description of a woman taken from John Steinbeck’s The Snake :
“He looked around at her again. Her dark eyes seemed veiled with dust. She looked without expression at the cat’s open throat.”
These lines don’t directly reveal anything about the woman, but the reader can understand that she is cold and dangerous. It’s an indirect characterization that focuses on looks and actions to convey the message to the reader.
Receive a plagiarism-free paper tailored to your instructions. Cut 20% off your first order!
🧙 Types of Characters for Your Essay
When it comes to characters, they can be divided into several groups. For example, characters can be:
- Protagonists or antagonists,
- Static or dynamic,
- Flat or round.
These types define how much the characters change through the course of the story and their role in it.
Character Type: Definition
In psychology, a character type is defined by a combination of personality traits that coexist in an individual. Authors incorporate different types of characters into their works to convey the message and make the story more exciting or relatable to the reader.
There are three ways to categorize a character type:
- by archetypes,
- by their role in the narrative,
- by their ability to change throughout the story.
If you are about to write a character analysis essay, being familiar with character archetypes is essential. They have been categorized by a generation of writers, including the Swiss psychologist Carl Jung and the American literary theorist Joseph Campbell. A lot of characters we see in today’s literary works are rooted in them.
Get an originally-written paper according to your instructions!
Archetypes include the Trickster, the Ruler, the Lover, the Sage, and others. The Hero is one of the most notable archetypes. Hercules or Achilles can be good examples of heroic protagonists. They are strong and courageous; they meet challenges and save the day by helping others.
Main Character: Definition & Examples
The main character and the protagonist often get mixed up. Most narratives also have the figure of the antagonist , whose actions affect the plot and stimulate change. Let’s have a look at the similarities and differences between these types.
The main character is central in the narrative. We experience the story through their eyes. They don’t necessarily have to be protagonists, though it happens in many cases.
The crucial difference between the main character and the protagonist is that the protagonist goes through changes throughout the story. The main character, however, is there to guide the reader through the experience. Often they help to show a different, darker side of the protagonist.
To understand the difference better, let’s turn to some examples.
What’s a Static Character?
Now that we’ve learned about the main character and the protagonist, we will closely look at other types of character classifications. One of the ways to categorize a character is by their ability to change throughout the story.
A static or simple character is someone who undergoes little or no significant changes. They often exist for comedic purposes. Here are some examples:
Complex Character: Definition & Examples
Complex or dynamic characters are the opposite of static characters. Characters of this type change as the book progresses. They display different qualities, emotions, and motives. They become more complicated and interesting to the reader as the story unfolds.
Check out these examples of dynamic characters:
Other Kinds of Characters
You already know about several ways to define a type of character. Now, let’s go over some other types, starting with flat and round characters.
Similar to dynamic and static ones, round and flat characters represent two different ends of a spectrum. Round characters usually come with an in-depth background. They are traditionally protagonists, antagonists, or those close to them. In contrast, flat characters are two-dimensional, and there is not much depth to them.
For the examples, we will turn to the novel Pride and Prejudice by Jane Austen.
Finally, here are some bonus character types for you:
- Stock characters have a fixed set of traits and are flat. Most of the time, they exist for comical relief.
- Symbolic characters represent a concept or a theme that goes beyond them. They can be round and flat as long as they symbolize a particular notion or phenomena.
- Sidekick is a secondary character who supports the protagonist.
- The love interest is someone with whom the main character is infatuated.
- Foil is someone who’s set in contrast with the protagonist, thus putting more emphasis on the latter’s qualities.
Characterization Essay: Which Character Type to Choose
Before you start writing a paper, it essential to decide on the character you’re going to analyze. There are different types of characters in every story, so you need to choose which one suits your essay topic the best.
Usually, it’s best to choose a dynamic and round character . With static and flat ones, there may not be enough substance for you to analyze. However, some such personalities can be interesting to work with. For instance, a flat character such as Mr. Collins can be symbolic of something. Then, you can talk about how it embodies a specific idea or notion. You can also look at how they affect other characters in the story.
📝 How to Write a Character Analysis Step by Step
Now, we’re going to discuss how to write your paper step-by-step. But first, here are some pre-writing steps for you to consider:
- Choose a character for analysis.
- Take notes while reading;
- Define the type of the character and their role in the story;
- Pay attention to their descriptions and actions.
How to Analyze a Character: Description Examples
Knowing how to organize your work is an essential skill. Certain things need special attention if you are describing a character:
- physical appearance,
- emotional state,
- how the character speaks,
- behavior and personality traits,
- relationships with other characters.
When you analyze a character, try to look at them as if they were a real-life person. You want to know their motive, learn about how they feel, and understand why they think in a certain way. Ask yourself:
- How did the character change throughout the story (if at all)?
- What do other characters say about them? Can their words be trusted?
- Where is the character physically and emotionally? What brought them here?
- What is the character ready to do to achieve their goal?
Now, let’s look at the character of Franklin from the short story Just Before the War with the Eskimos by J.D. Salinger:
Character Profile Template for Writing
When writing your essay, use this character analysis template:

In the following sections, we’ll discuss each step in detail.
Character Analysis Outline: How to Start a Character Analysis
The beginning of your essay is its crucial part. It sets the mood and grabs the reader’s attention. There are many different ways to write a character analysis introduction, but here are the most effective ones:
- Use a quotation. It’s a great way to make a catchy hook. If it relates to the character and reflects their nature, it can also help to set the tone for analysis. In case you are using a quotation from somewhere else, mention the source in parentheses.
- Talk about the book or story. Mention the author, the name of the story, and the genre. Briefly describe the main events that are taking place in the story.
- Introduce the character. State their role in the story (define whether they are a protagonist, an antagonist, etc.) Then, explain whether the character is static or dynamic. Finally, describe them in 2-3 sentences.
The final part of an introduction is a thesis statement.Read on to learn how to write one!
Character Analysis Thesis Statement & Examples
A thesis is the key component of every essay, and character analysis is not an exception. It’s crucial to develop a good and clear thesis statement that includes all the aspects of your paper. For instance, if you plan to write a 4-paragraph body, including 4 points in your thesis.
What should a character analysis thesis include? Well, try to think of any trait that the character possesses that has to do with their downfall or somehow influences the story. Think about how this trait affects the character’s relationship with others or how it contributes to their motive or aspiration.
Take a look at the following examples:
How to Write Character Analysis Paragraphs for the Main Body
The main body of your essay can include as many paragraphs as you need. In this part, you introduce the character and analyze them. We have already talked in this article about what kind of questions should be answered in these paragraphs. The most important points are:
- Describe the character and their role within the story.
- Give the audience an explanation of the character’s motives.
- Show what message the author wanted to convey through this character.
Keep in mind that every paragraph should have a topic sentence that captures its main idea.
Tsukuru Tazaki’s spiritual rebirth also affects his physical appearance.
Character Analysis Conclusion: How to Write
The conclusion part of your essay summarizes all the information you have mentioned and restates the thesis. Here is some advice for your conclusion paragraph:
🖥️ Character Analysis Essay Format
Most college assignments and essays are written according to the APA or MLA format. Both styles have the same formatting, which requires:
- a double-spaced paper with 1-inch margins,
- a page header with page numbers flush right,
- an 11-12-point font.
While writing an essay on characters, pay special attention to quotations. Here are some tips for APA in-text citations:
- When you summarize or paraphrase the information, mention the author’s name and publication date in brackets. Example: According to Collins (1997.)
- When you quote directly from the source, add the number of the page, as well. Example: “There is a view that…” (Collins, 1997, pp. 134-135.)
- If the source includes three or more authors, use the abbreviation “et al.” after the first author’s name. Example: (Collins et al., 1997)
As for MLA format:
- You can write the author’s name in the sentence. Example: As Collins mentions in his essay<…>.
- You can mention the author’s name in the parentheses at the end of the sentence. Example: (Collins, J.K.)
- The last option is to use either footnotes or endnotes.
Below you’ll find a collection of character analysis essay examples and a downloadable sample to inspire you even more.
- The Grandmother in A Good Man Is Hard to Find: Character Analysis
- Willy Loman in Death of a Salesman: Character Analysis
- Jay Gatsby and Nick Carraway: Character Analysis
- Prospero in The Tempest: Character Analysis
- Agamemnon in the Iliad: Character Analysis
- Lord Pococurante in Candide: Character Analysis
- Andromache in the Iliad: Character Analysis
- Character Analysis of the Knight from The Canterbury Tales
- Essay on Soldier’s Home: Analysis of the Characters
Character Analysis Example (Downloadable)
Roald Dahl’s Matilda is one of the most famous children’s novels of the 20th century. The protagonist of this tale is Matilda Wormwood, a five and a half-year-old girl with a brilliant and lively mind that distances her from the rest of the family. Matilda’s character is particularly interesting as she has a powerful personality with extraordinary mental abilities, and she manages to overcome all the obstacles that surround her.
Character Analysis Essay Topics
- Character analysis of Abbas from A.D.: New Orleans After the Deluge .
- Jay Gatsby in The Great Gatsby by F. Scott Fitzgerald.
- Beowulf and Hamlet : similarity and diversity of the characters.
- Personal and social failures of Willy Loman in Death of a Salesman by Arthur Miller.
- Character analysis of Othello .
- Analyze the characters of Stanley and Blanche from A Streetcar Named Desire .
- The tragedy of Mathilde Loisel from The Necklace by Guy de Maupassant.
- Character analysis of Huck Finn from Mark Twain’s The Adventures of Huckleberry Finn .
- Moral force of Kate Lipton from Double Helix by Nancy Parker.
- Character analysis of Thorvald and Nora in Henrik Ibsen’s A Doll’s House .
- Discuss the character of king Creon in Antigone .
- Analyze the personality of Lydia from Jane Austen’s Pride and Prejudice .
- Compare Nick Carraway and Tom Buchanan from The Great Gatsby by F. Scott Fitzgerald.
- Describe the peculiarities of Lord Pococurante in Candide .
- Sarty Snopes in William Faulkner’s Barn Burning : character analysis.
- Analyze the character of Biff Loman in Death of a Salesman.
- Personality of Nora in A Doll House by Henrik Ibsen.
- Examine the main characters of The Yellow Paper by Charlotte Perkins Gilman.
- Personality change of the main character in Edgar Alan Poe’s The Black Cat .
- Analyze the characters of E. Hemingway’s A Clean, Well-Lighted Place .
- Describe the main characters of the novel The Overstory by Richard Powers.
- Controversial personality of Vladek in Maus: A Survivor’s Tale by Art Spiegelman.
- Character analysis of Victor Frankenstein in Frankenstein by Mary Shelley .
- Discuss the character of Creon in Oedipus the King .
- The manipulative character of Iago in Willian Shakespeare’s Othello .
- Analyze the characters of Nil and Kristine in A Doll’s House .
- Eccentricity of Grendel’s character in Beowulf .
- Describe the main characters of Four Summers by Joyce Carol Oates.
- Examine the characters of Harold Krebs and his mother in Ernest Hemingway’s Soldier’s Home .
- Analyze common and different traits of the characters in The Monkey’s Paw .
- Character peculiarities of Rostam and Sohrab in Shahnameh by Ferdowsi Tousi.
- How does the character of Elizabeth Bennet in Pride and Prejudice by Jane Austen differ from the rest of her family?
- The behavior and meaning of the characters in Nicholas Rowe’s The Tragedy of Jane Shore.
- Compare the characters of Victor Frankenstein and the monster in Frankenstein or the Modern Prometheus by Mary Shelley.
- Discuss the differences of main characters in Everyday Use by Alice Walker.
- Examine the character of Connie in Where Are You Going, Where Have You Been by Joyce Carol Oates.
- The influence of social pressure on the characters of Chopin’s Desirée’s Baby and Sedaris’ A Modest Proposal .
- Dynamic feminist characters of Delia and Jig in Sweat by Z. Hurston and Hills Like White Elephants by E. Hemingway.
- Analyze the personality traits of Emily in William Faulkner’s A Rose for Emily .
- Examine the characters of The Quiet American by Graham Greene.
- Henry ΙV by William Shakespeare : analysis of main characters.
Now you know everything necessary for writing an excellent character analysis. What character would you like to analyze? Let us know in the comments!
Further reading:
- How to Write a Literary Analysis Essay Step by Step
- Literature Review Outline: Examples, Approaches, & Templates
- Library Research Paper: Example & Writing Guide [2024]
- How to Write a Critique Paper: Tips + Critique Essay Examples
- 435 Literary Analysis Essay Topics and Prompts [2024 Upd]
- How to Write a Literature Review: Actionable Tips & Links
❓ Character Analysis FAQ
A character analysis involves:
1. description of a character; 2. explanation of how they change throughout the story; 3. their role in the narrative; 4. relationships with other characters; 5. what idea the author wanted to convey through the character.
A character analysis creates a description that contains their most important qualities. It provides a new perspective of a character that reveals more about what it’s like to be human. It can also point to a moral or a lesson.
Literary analysis uses the technique of tracing the character development. This technique is usually used to understand the theme of the work better. Through tracing a character’s development, we can learn more about the story’s message and how it’s conveyed.
A summary paragraph in a character study should include answers to the questions “what,” “who,” “where,” and “why.” You should mention who narrates the story, where the story is set, its theme, and the message it conveys.
- Critical Concepts: Character and Characterization: Kansas State University
- Analyzing Novels & Short Stories: Texas A&M University
- Guidelines for Writing a Character Analysis Essay: Tidewater Communite College
- Literary Criticism: Thesis Examples: The University of Texas at Arlington
- Writing a Literary Analysis Paper: Germanna Community College
- Flat and Round Characters: Encyclopedia Britannica
- Literature: University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
- How to Write a Book Analysis: Kean University
- Elements of Literary Analysis: Alamo Colleges District
- Defining Characterization: Read Write Think
- APA Style: General Format: Purdue University
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to LinkedIn
- Share to email
![characters in essay meaning Critical Writing: Examples & Brilliant Tips [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/02/fingers-note-report-journalist-filling-284x153.jpg)
Any critique is nothing more than critical analysis, and the word “analysis” does not have a negative meaning. Critical writing relies on objective evaluations of or a response to an author’s creation. As such, they can be either positive or negative, as the work deserves. To write a critique, you...

If you are assigned to write a rhetorical analysis essay, you have one significant advantage. You can choose a text from an almost infinite number of resources. The most important thing is that you analyze the statement addressed to an audience. The task of a rhetorical analysis essay is to...

Any literary analysis is a challenging task since literature includes many elements that can be interpreted differently. However, a stylistic analysis of all the figurative language the poets use may seem even harder. You may never realize what the author actually meant and how to comment on it! While analyzing...

As a student, you may be asked to write a book review. Unlike an argumentative essay, a book review is an opportunity to convey the central theme of a story while offering a new perspective on the author’s ideas. Knowing how to create a well-organized and coherent review, however, is...

The difference between an argumentative and persuasive essay isn’t always clear. If you’re struggling with either style for your next assignment, don’t worry. The following will clarify everything you need to know so you can write with confidence. First, we define the primary objectives of argumentative vs. persuasive writing. We...

You don’t need to be a nerd to understand the general idea behind cause and effect essays. Let’s see! If you skip a meal, you get hungry. And if you write an essay about it, your goal is achieved! However, following multiple rules of academic writing can be a tough...
![characters in essay meaning How to Write an Argumentative Essay: 101 Guide [+ Examples]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/young-writer-taking-notes-284x153.jpg)
An argumentative essay is a genre of academic writing that investigates different sides of a particular issue. Its central purpose is to inform the readers rather than expressively persuade them. Thus, it is crucial to differentiate between argumentative and persuasive essays. While composing an argumentative essay, the students have to...
![characters in essay meaning How to Title an Essay: Guide with Creative Examples [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/close-up-woman-making-greeting-card-new-year-christmas-2021-friends-family-scrap-booking-diy-writing-letter-with-best-wishes-design-her-homemade-card-holidays-celebration-284x153.jpg)
It’s not a secret that the reader notices an essay title first. No catchy hook or colorful examples attract more attention from a quick glance. Composing a creative title for your essay is essential if you strive to succeed, as it: Thus, how you name your paper is of the...

The conclusion is the last paragraph in your paper that draws the ideas and reasoning together. However, its purpose does not end there. A definite essay conclusion accomplishes several goals: Therefore, a conclusion usually consists of: Our experts prepared this guide, where you will find great tips on how to...
![characters in essay meaning How to Write a Good Introduction: Examples & Tips [2024 Upd.]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/closeup-shot-woman-working-studying-from-home-with-red-coffee-cup-nearby-284x153.jpg)
A five-paragraph essay is one of the most common academic assignments a student may face. It has a well-defined structure: an introduction, three body paragraphs, and a conclusion. Writing an introduction can be the most challenging part of the entire piece. It aims to introduce the main ideas and present...

Exemplification essays, also called illustration essays, are one of the easiest papers to write. However, even the simplest tasks require experience and practice. It is a good idea to find and analyze free exemplification essay examples. You can also ask your teacher to give you some sample exemplification essays from...
![characters in essay meaning How to Write about a Topic You Lack Interest in [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/Frustrated-exhausted-young-woman-blogger-284x153.jpg)
During their school years, students may not always have the opportunity to select a topic for their essay or research paper. Instructors tend to assign one or offer a list of ideas that might not seem engaging. Moreover, even the topic that you choose yourself can sometimes end up being...
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to write a literary analysis essay | A step-by-step guide
How to Write a Literary Analysis Essay | A Step-by-Step Guide
Published on January 30, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on August 14, 2023.
Literary analysis means closely studying a text, interpreting its meanings, and exploring why the author made certain choices. It can be applied to novels, short stories, plays, poems, or any other form of literary writing.
A literary analysis essay is not a rhetorical analysis , nor is it just a summary of the plot or a book review. Instead, it is a type of argumentative essay where you need to analyze elements such as the language, perspective, and structure of the text, and explain how the author uses literary devices to create effects and convey ideas.
Before beginning a literary analysis essay, it’s essential to carefully read the text and c ome up with a thesis statement to keep your essay focused. As you write, follow the standard structure of an academic essay :
- An introduction that tells the reader what your essay will focus on.
- A main body, divided into paragraphs , that builds an argument using evidence from the text.
- A conclusion that clearly states the main point that you have shown with your analysis.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Step 1: reading the text and identifying literary devices, step 2: coming up with a thesis, step 3: writing a title and introduction, step 4: writing the body of the essay, step 5: writing a conclusion, other interesting articles.
The first step is to carefully read the text(s) and take initial notes. As you read, pay attention to the things that are most intriguing, surprising, or even confusing in the writing—these are things you can dig into in your analysis.
Your goal in literary analysis is not simply to explain the events described in the text, but to analyze the writing itself and discuss how the text works on a deeper level. Primarily, you’re looking out for literary devices —textual elements that writers use to convey meaning and create effects. If you’re comparing and contrasting multiple texts, you can also look for connections between different texts.
To get started with your analysis, there are several key areas that you can focus on. As you analyze each aspect of the text, try to think about how they all relate to each other. You can use highlights or notes to keep track of important passages and quotes.
Language choices
Consider what style of language the author uses. Are the sentences short and simple or more complex and poetic?
What word choices stand out as interesting or unusual? Are words used figuratively to mean something other than their literal definition? Figurative language includes things like metaphor (e.g. “her eyes were oceans”) and simile (e.g. “her eyes were like oceans”).
Also keep an eye out for imagery in the text—recurring images that create a certain atmosphere or symbolize something important. Remember that language is used in literary texts to say more than it means on the surface.
Narrative voice
Ask yourself:
- Who is telling the story?
- How are they telling it?
Is it a first-person narrator (“I”) who is personally involved in the story, or a third-person narrator who tells us about the characters from a distance?
Consider the narrator’s perspective . Is the narrator omniscient (where they know everything about all the characters and events), or do they only have partial knowledge? Are they an unreliable narrator who we are not supposed to take at face value? Authors often hint that their narrator might be giving us a distorted or dishonest version of events.
The tone of the text is also worth considering. Is the story intended to be comic, tragic, or something else? Are usually serious topics treated as funny, or vice versa ? Is the story realistic or fantastical (or somewhere in between)?
Consider how the text is structured, and how the structure relates to the story being told.
- Novels are often divided into chapters and parts.
- Poems are divided into lines, stanzas, and sometime cantos.
- Plays are divided into scenes and acts.
Think about why the author chose to divide the different parts of the text in the way they did.
There are also less formal structural elements to take into account. Does the story unfold in chronological order, or does it jump back and forth in time? Does it begin in medias res —in the middle of the action? Does the plot advance towards a clearly defined climax?
With poetry, consider how the rhyme and meter shape your understanding of the text and your impression of the tone. Try reading the poem aloud to get a sense of this.
In a play, you might consider how relationships between characters are built up through different scenes, and how the setting relates to the action. Watch out for dramatic irony , where the audience knows some detail that the characters don’t, creating a double meaning in their words, thoughts, or actions.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Your thesis in a literary analysis essay is the point you want to make about the text. It’s the core argument that gives your essay direction and prevents it from just being a collection of random observations about a text.
If you’re given a prompt for your essay, your thesis must answer or relate to the prompt. For example:
Essay question example
Is Franz Kafka’s “Before the Law” a religious parable?
Your thesis statement should be an answer to this question—not a simple yes or no, but a statement of why this is or isn’t the case:
Thesis statement example
Franz Kafka’s “Before the Law” is not a religious parable, but a story about bureaucratic alienation.
Sometimes you’ll be given freedom to choose your own topic; in this case, you’ll have to come up with an original thesis. Consider what stood out to you in the text; ask yourself questions about the elements that interested you, and consider how you might answer them.
Your thesis should be something arguable—that is, something that you think is true about the text, but which is not a simple matter of fact. It must be complex enough to develop through evidence and arguments across the course of your essay.
Say you’re analyzing the novel Frankenstein . You could start by asking yourself:
Your initial answer might be a surface-level description:
The character Frankenstein is portrayed negatively in Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein .
However, this statement is too simple to be an interesting thesis. After reading the text and analyzing its narrative voice and structure, you can develop the answer into a more nuanced and arguable thesis statement:
Mary Shelley uses shifting narrative perspectives to portray Frankenstein in an increasingly negative light as the novel goes on. While he initially appears to be a naive but sympathetic idealist, after the creature’s narrative Frankenstein begins to resemble—even in his own telling—the thoughtlessly cruel figure the creature represents him as.
Remember that you can revise your thesis statement throughout the writing process , so it doesn’t need to be perfectly formulated at this stage. The aim is to keep you focused as you analyze the text.
Finding textual evidence
To support your thesis statement, your essay will build an argument using textual evidence —specific parts of the text that demonstrate your point. This evidence is quoted and analyzed throughout your essay to explain your argument to the reader.
It can be useful to comb through the text in search of relevant quotations before you start writing. You might not end up using everything you find, and you may have to return to the text for more evidence as you write, but collecting textual evidence from the beginning will help you to structure your arguments and assess whether they’re convincing.
To start your literary analysis paper, you’ll need two things: a good title, and an introduction.
Your title should clearly indicate what your analysis will focus on. It usually contains the name of the author and text(s) you’re analyzing. Keep it as concise and engaging as possible.
A common approach to the title is to use a relevant quote from the text, followed by a colon and then the rest of your title.
If you struggle to come up with a good title at first, don’t worry—this will be easier once you’ve begun writing the essay and have a better sense of your arguments.
“Fearful symmetry” : The violence of creation in William Blake’s “The Tyger”
The introduction
The essay introduction provides a quick overview of where your argument is going. It should include your thesis statement and a summary of the essay’s structure.
A typical structure for an introduction is to begin with a general statement about the text and author, using this to lead into your thesis statement. You might refer to a commonly held idea about the text and show how your thesis will contradict it, or zoom in on a particular device you intend to focus on.
Then you can end with a brief indication of what’s coming up in the main body of the essay. This is called signposting. It will be more elaborate in longer essays, but in a short five-paragraph essay structure, it shouldn’t be more than one sentence.
Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein is often read as a crude cautionary tale about the dangers of scientific advancement unrestrained by ethical considerations. In this reading, protagonist Victor Frankenstein is a stable representation of the callous ambition of modern science throughout the novel. This essay, however, argues that far from providing a stable image of the character, Shelley uses shifting narrative perspectives to portray Frankenstein in an increasingly negative light as the novel goes on. While he initially appears to be a naive but sympathetic idealist, after the creature’s narrative Frankenstein begins to resemble—even in his own telling—the thoughtlessly cruel figure the creature represents him as. This essay begins by exploring the positive portrayal of Frankenstein in the first volume, then moves on to the creature’s perception of him, and finally discusses the third volume’s narrative shift toward viewing Frankenstein as the creature views him.
Some students prefer to write the introduction later in the process, and it’s not a bad idea. After all, you’ll have a clearer idea of the overall shape of your arguments once you’ve begun writing them!
If you do write the introduction first, you should still return to it later to make sure it lines up with what you ended up writing, and edit as necessary.
The body of your essay is everything between the introduction and conclusion. It contains your arguments and the textual evidence that supports them.
Paragraph structure
A typical structure for a high school literary analysis essay consists of five paragraphs : the three paragraphs of the body, plus the introduction and conclusion.
Each paragraph in the main body should focus on one topic. In the five-paragraph model, try to divide your argument into three main areas of analysis, all linked to your thesis. Don’t try to include everything you can think of to say about the text—only analysis that drives your argument.
In longer essays, the same principle applies on a broader scale. For example, you might have two or three sections in your main body, each with multiple paragraphs. Within these sections, you still want to begin new paragraphs at logical moments—a turn in the argument or the introduction of a new idea.
Robert’s first encounter with Gil-Martin suggests something of his sinister power. Robert feels “a sort of invisible power that drew me towards him.” He identifies the moment of their meeting as “the beginning of a series of adventures which has puzzled myself, and will puzzle the world when I am no more in it” (p. 89). Gil-Martin’s “invisible power” seems to be at work even at this distance from the moment described; before continuing the story, Robert feels compelled to anticipate at length what readers will make of his narrative after his approaching death. With this interjection, Hogg emphasizes the fatal influence Gil-Martin exercises from his first appearance.
Topic sentences
To keep your points focused, it’s important to use a topic sentence at the beginning of each paragraph.
A good topic sentence allows a reader to see at a glance what the paragraph is about. It can introduce a new line of argument and connect or contrast it with the previous paragraph. Transition words like “however” or “moreover” are useful for creating smooth transitions:
… The story’s focus, therefore, is not upon the divine revelation that may be waiting beyond the door, but upon the mundane process of aging undergone by the man as he waits.
Nevertheless, the “radiance” that appears to stream from the door is typically treated as religious symbolism.
This topic sentence signals that the paragraph will address the question of religious symbolism, while the linking word “nevertheless” points out a contrast with the previous paragraph’s conclusion.
Using textual evidence
A key part of literary analysis is backing up your arguments with relevant evidence from the text. This involves introducing quotes from the text and explaining their significance to your point.
It’s important to contextualize quotes and explain why you’re using them; they should be properly introduced and analyzed, not treated as self-explanatory:
It isn’t always necessary to use a quote. Quoting is useful when you’re discussing the author’s language, but sometimes you’ll have to refer to plot points or structural elements that can’t be captured in a short quote.
In these cases, it’s more appropriate to paraphrase or summarize parts of the text—that is, to describe the relevant part in your own words:
The conclusion of your analysis shouldn’t introduce any new quotations or arguments. Instead, it’s about wrapping up the essay. Here, you summarize your key points and try to emphasize their significance to the reader.
A good way to approach this is to briefly summarize your key arguments, and then stress the conclusion they’ve led you to, highlighting the new perspective your thesis provides on the text as a whole:
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
By tracing the depiction of Frankenstein through the novel’s three volumes, I have demonstrated how the narrative structure shifts our perception of the character. While the Frankenstein of the first volume is depicted as having innocent intentions, the second and third volumes—first in the creature’s accusatory voice, and then in his own voice—increasingly undermine him, causing him to appear alternately ridiculous and vindictive. Far from the one-dimensional villain he is often taken to be, the character of Frankenstein is compelling because of the dynamic narrative frame in which he is placed. In this frame, Frankenstein’s narrative self-presentation responds to the images of him we see from others’ perspectives. This conclusion sheds new light on the novel, foregrounding Shelley’s unique layering of narrative perspectives and its importance for the depiction of character.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, August 14). How to Write a Literary Analysis Essay | A Step-by-Step Guide. Scribbr. Retrieved April 8, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/literary-analysis/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, how to write a thesis statement | 4 steps & examples, academic paragraph structure | step-by-step guide & examples, how to write a narrative essay | example & tips, what is your plagiarism score.
- Literary Terms
- Definition & Examples
- When & How to Write a Character
I. What is Character?
A character is a person, animal, being, creature, or thing in a story. Writers use characters to perform the actions and speak dialogue, moving the story along a plot line. A story can have only one character (protagonist) and still be a complete story. This character’s conflict may be an inner one (within him/herself), or a conflict with something natural, such as climbing a mountain. Most stories have multiple characters interacting, with one of them as the antagonist, causing a conflict for the protagonist.
II. Examples of Character
A popular television series that just ended is the show “Glee.” Each season had popular characters who had to learn to work together to create a good musical production. Various characters underwent a change, making them a dynamic character, such as Noah Puckerman. He appears to carry out the stereotype of a jock (strong but not so smart), but his character changes as it’s revealed that he can be hard working and intelligent.
A movie that features one character throughout most of it is “Castaway” with Tom Hanks. His character is on board a shipping plane when it crashes. He’s the only survivor, trapped on an island for four years. This movie focuses on his psychological (mental) and physical condition as he slowly adapts to a life of isolation, living alone on an island that is off all regular sea and airplane routes. It’s a great example of how a story can work with only one character, although many minor characters appear in the beginning and end.
III. Types of Character
A. major characters.
These are the most important characters in the story. There are two types, of which there may be a couple for each.
- Protagonist – This is the main character, around which the whole story revolves. The decisions made by this character will be affected by a conflict from within, or externally through another character, nature, technology, society, or the fates/God.
- Antagonist – This character, or group of characters, causes the conflict for the protagonist. However, the antagonist could be the protagonist, who is torn by a problem within. Most times, something external is causing the problem. A group of people causing the conflict would be considered society, perhaps the members of a team, community, or institution. Additionally, the antagonist could be a part of nature, such as an animal, the weather, a mountain or lake. A different kind of antagonist would be an item such as a pen, car, phone, carpet, etc. These are all considered technology, since they are instruments or tools to complete a job. Finally, if the conflict comes from something out of the character’s control, the antagonist is fate or God.
b. Minor characters
These are the other characters in a story. They are not as important as the major characters, but still play a large part in the story. Their actions help drive the story forward. They may impact the decisions the protagonist or antagonist make, either helping or interfering with the conflict.
Characters can have different traits. Major characters will usually be more dynamic, changing and growing through the story while minor characters may be more static.
- Foil – A foil is a character that has opposite character traits from another, meant to help highlight or bring out another’s positive or negative side. Many times, the antagonist is the foil for the protagonist.
- Static – Characters who are static do not change throughout the story. Their use may simply be to create or relieve tension, or they were not meant to change. A major character can remain static through the whole story.
- Dynamic – Dynamic characters change throughout the story. They may learn a lesson, become bad, or change in complex ways.
- Flat – A flat character has one or two main traits, usually only all positive or negative. They are the opposite of a round character. The flaw or strength has its use in the story.
- Round – These are the opposite of the flat character. These characters have many different traits, good and bad, making them more interesting.
- Stock – These are the stereotypical characters, such as the boy genius, ambitious career person, faithful sidekick, mad scientist, etc.
IV. The Importance of Character
Characters are what make stories. Without a character, there is no story to tell, only a lot of scenery. Many characters in literature, television series, and movies have a huge impact on people. Some people like to live their lives through these characters, who appear to have more exciting lives. Also, these characters may seem so real and inspirational, that people forget they are fictional.
Characters become so important to the audience, that cities across the country hold conventions in which people pay a lot of money to dress and act as their favorite characters from multiple types of shows, particularly of the comic magazine genre (type of literature).
V. Examples of Character in Pop Culture
The Teenage Mutant Ninja Turtles have been keeping the city safe since the 1980s, but are still just as popular today. They each have their own special fighting method as well as personality. Originally simple, small turtles, they became super human, err turtle, after an accident in which the fish bowl of water they were in got knocked out of their owner’s hands and fell down a sewer grate, along with a canister of radioactive material. The rest is history. Nickelodeon has brought the characters back to fame, as can be seen on the channel and in the Nickelodeon Hotel in Orlando, Florida. The hotel features suites based on characters from the Nickelodeon shows for kids, and kids can interact with their favorite characters, including the Turtles, during breakfast and fun events. It’s clear that characters are an important part of our culture.
The characters are named after famous painters, and each turtle has his own personality to which different kids may relate. For example, Leonardo is the wise leader, the one who can keep the group focused. Raphael is the hothead. His temper wants to get the best of him, just as most of us would like to jump into things! Michaelangelo is the comedian. Like our class clowns in school, he’s the group clown. Finally, no group is complete without the geeky nerd. Donatello is always inventing things to help our turtle heroes in their adventures .
VI. Examples of Character in Literature
A book whose character was inspired by a real teenage girl is “The Fault in Our Stars” by John Green. The protagonist is 16-year-old Hazel, who meets Gus, a fellow 16-year-old cancer patient, at a camp. Their young romance is doomed as they are fighting a losing battle with cancer. Their strong spirits overcome their parents’ fears as the determined Hazel gets her wish to go overseas to meet an author she has long admired. The book has both characters undergoing change, very dynamic, as they struggle to adapt to their fate. The minor characters are impacted by the decisions Hazel and Gus make, giving depth to the story line. This book is an example of how authors take real life situations to create believable and interesting characters. Green’s inspiration for the story, Esther Earl, was a young fan with cancer who had wanted to meet him. He became friends with her and her family. She was diagnosed with cancer at 12 and died at 16.

VII. Related Terms
Archetype: A standard or stock type of character that appears in fiction, such as the villain, the hero, the damsel-in-distress, or the sidekick. Each archetype has more categories within, as well. For example, the villain could be a tyrant, devil, schemer, etc. The hero could be the warrior, proto-female, scapegoat, etc. These are especially common in fairy and folk tales.
VIII. Conclusion
Characters are the whole reason for any story. They can be used to help teach a lesson, to entertain, to educate, and even to persuade, depending on the author’s goal for the story line. Characters can be based on real people and events, or be totally unrealistic, such as space aliens. People become attached to characters as if they are real, may develop favorites, and relate to those that have faced similar situations.
List of Terms
- Alliteration
- Amplification
- Anachronism
- Anthropomorphism
- Antonomasia
- APA Citation
- Aposiopesis
- Autobiography
- Bildungsroman
- Characterization
- Circumlocution
- Cliffhanger
- Comic Relief
- Connotation
- Deus ex machina
- Deuteragonist
- Doppelganger
- Double Entendre
- Dramatic irony
- Equivocation
- Extended Metaphor
- Figures of Speech
- Flash-forward
- Foreshadowing
- Intertextuality
- Juxtaposition
- Literary Device
- Malapropism
- Onomatopoeia
- Parallelism
- Pathetic Fallacy
- Personification
- Point of View
- Polysyndeton
- Protagonist
- Red Herring
- Rhetorical Device
- Rhetorical Question
- Science Fiction
- Self-Fulfilling Prophecy
- Synesthesia
- Turning Point
- Understatement
- Urban Legend
- Verisimilitude
- Essay Guide
- Cite This Website
Character Analysis
Writing Character Analysis - Outline, Steps, and Examples
12 min read

People also read
Learn How to Write an Editorial on Any Topic
Best Tips on How to Avoid Plagiarism
How to Write a Movie Review - Guide & Examples
A Complete Guide on How to Write a Summary for Students
Write Opinion Essay Like a Pro: A Detailed Guide
Evaluation Essay - Definition, Examples, and Writing Tips
How to Write a Thematic Statement - Tips & Examples
How to Write a Bio - Quick Tips, Structure & Examples
How to Write a Synopsis – A Simple Format & Guide
How to Write a Comparative Essay – A Complete Guide
Visual Analysis Essay - A Writing Guide with Format & Sample
List of Common Social Issues Around the World
11 Common Types of Plagiarism Explained Through Examples
Article Review Writing: A Complete Step-by-Step Guide with Examples
A Detailed Guide on How to Write a Poem Step by Step
Detailed Guide on Appendix Writing: With Tips and Examples
Have you ever struggled to understand characters beyond what meets the eye?
Character analysis is more than just explaining the character. It focuses on a particular character in a story and analyzes their strengths and weaknesses, and the depth of their character.
These assignments help students develop critical thinking, analytical skills, and writing skills. Analyzing characters from various backgrounds also helps encourage inclusivity.
Writing a character analysis might feel tricky, but fear not!
In this blog, you will learn how to write a character analysis, with tips and examples.
So without further ado, let’s dive right in!
- 1. What is Character Analysis
- 2. How to Write Character Analysis
- 3. Character Analysis Example
- 4. Tips for Writing a Character Analysis
What is Character Analysis
This type of analytical essay involves examining the traits, motivations, behaviors, and development of a character within a story or literary work.
Its purpose is to deeply understand and interpret the complexities of a character, going beyond surface-level descriptions.
Purpose of a Character Analysis
The key objectives of character analysis are:
- Understanding Depth: It aims to uncover the layers of a character's personality, motivations, and emotions to comprehend their role in the story comprehensively.
- Exploring Development: It involves tracking the character's journey throughout the narrative, identifying changes in their beliefs, attitudes, or actions.
- Identifying Motivations: Character analysis seeks to unearth the driving forces behind a character's choices, behaviors, and relationships within the story.
- Relating to Themes: Dissecting characters helps in exploring and understanding the themes, messages, and conflicts within the story.
- Enhancing Engagement: It encourages readers or students to engage more deeply with the narrative, fostering empathy and connection with the characters.
- Interpreting Author's Intentions: It aids in deciphering the author's purpose in creating specific characters, adding depth to the understanding of the literary work.
How to Write Character Analysis
Writing a good character analysis goes beyond just describing how a character looks or acts. It's like peeking into their thoughts, and feelings, and how they change as the story goes on.
Here are some steps you can follow to write a compelling character analysis;
Step 1: Choose a Character
When you pick a character to study, think if they change or if they stay the same throughout. Each character type brings its significance to the story.
When analyzing characters, knowing their type helps in understanding their roles, motivations, and impact on the narrative.
Here are different types of characters you can encounter:
Step 2: Gather Information
Gathering information is crucial for character analysis because it helps us understand the character better. By knowing about their physical attributes, personality traits, and what they do in the story to move the plot, we can identify the character better.
Look at the example of Harry Potter, the protagonist in J.K. Rowling’s Harry Potter series:
Step 3: Outline Your Analysis
Create a structured plan for your character analysis essay. Begin with an engaging introduction, introducing the character and their significance.
Proceed to discuss the character's development throughout the story and their interactions with other characters in the story.
Here is a basic outline structure you can follow for your essay:
Here is a template you can look at to understand the structure and flow of the analysis essay:
Character Analysis Template
Step 4: Support with Evidence
While analyzing characters, substantiate your observations with evidence from the text.
Quotes, descriptions, or scenes that depict the character's actions or character relationships provide strong evidence for your analysis.
Let’s take a look at the example below of a character analysis of Hamlet:
Step 5: Analyze, Don't Summarize
Remember, your goal is to analyze the character, not summarize the plot. Focus on interpreting their actions, decisions, and the types of characters they represent.
Let’s take a look at the example of character analysis of ‘Waiting for Godot’:
Step 6: Incorporate Critical Perspectives
Consider different interpretations of the character. Acknowledge how their character development influences the story's themes and the author's intentions for including them.
The character analysis of Joseph Andrews is a great example of understanding this factor:
Step 7: Write Your Character Analysis
Craft your analysis into a structured and coherent essay. Ensure your analysis contributes to a broader literary analysis of the work.
Here are some tips to help you:
- Avoid summarizing the plot extensively. Concentrate on interpreting the character's traits, actions, and their significance within the story.
- Contextualize your analysis within the broader themes or messages of the literary work.
Step 8: Conclusion
Conclude your analysis by summarizing the character's evolution, the impact of their character traits on the story, and their significance to the overall narrative.
Let’s take a look at the conclusion in the character analysis of Kurtz in Heart of Darkness:
Step 9 - Proofread and Refine
Though conclusions mark the end of an essay, it is considered a good practice to proofread. This step ensures the quality and readability of your essay.
Here are some tips to help you proofread and refine:
- Look for unclear or difficult sentences that might confuse the reader.
- Double-check formatting guidelines, citation styles, and bibliography entries if applicable.
- Correct any grammatical errors, punctuation mistakes, or spelling issues.
- Check that the quotes or scenes you've mentioned actually support your ideas.
Character Analysis Example
Examples of character analyses offer valuable insights into structuring an essay. They help to demonstrate how to organize thoughts systematically, from the introduction to the conclusion:
Let’s take a look at the character analysis of Oedipus Rex:
Let’s take a look at some more examples:
Character Analysis of Antigone
Mr. Birling's Character Analysis
The Crucible Character Analysis
Lady Macbeth Character Analysis
Jay Gatsby Character Analysis
Othello Character Analysis
Okonkwo Character Analysis
John Proctor Character Analysis
Tips for Writing a Character Analysis
Here are some tips that can help you improve your analysis:
- Focus on Subtleties: Pay attention to subtle character traits, gestures, or speech patterns that reveal deeper insights into the character's personality.
- Contextual Analysis: Consider the character within the context of their environment, era, or social background to understand how these factors shape their actions and beliefs.
- Contrast and Compare: Compare the character with others in the story to highlight unique attributes or to showcase how they contrast with different personalities.
- Symbolism and Imagery: Explore any symbolic elements or imagery associated with the character, as these can often convey deeper meanings or themes.
- Evolution over Time: Analyze how the character evolves or changes throughout the narrative, focusing on pivotal moments that drive their development.
- Impact on Plot Development: Highlight the character's role in advancing the story, influencing other characters, or triggering significant events.
- Narrative Perspective: Consider how the character's portrayal might differ based on the narrator's perspective or point of view.
So, there you have it!
By now you must have gotten an idea of how to write a character analysis.
By following these steps and tips, you'll grasp how to craft a thorough character analysis. You'll be able to understand and explain the complexities of the character effectively.
However, if you need help with it, then working with a professional essay writing service like MyPerfectWords.com, will save you time and help you learn better.

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Dr. Barbara is a highly experienced writer and author who holds a Ph.D. degree in public health from an Ivy League school. She has worked in the medical field for many years, conducting extensive research on various health topics. Her writing has been featured in several top-tier publications.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading
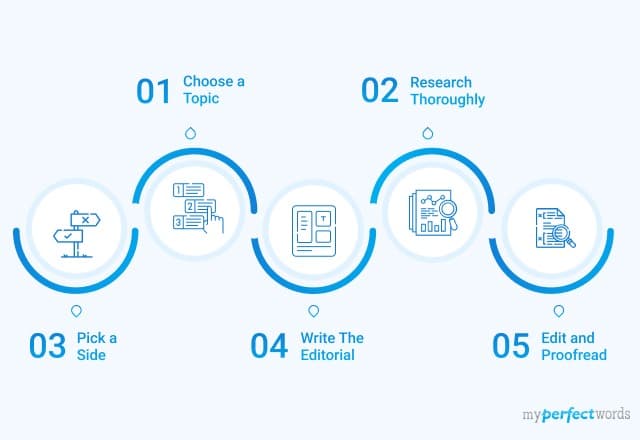

- Scriptwriting
What are Character Traits — Examples & How to Write Them
U nique descriptions, whether internal or external, are key to creating memorable and meaningful characters. And regardless of medium, character traits are critical considerations for any literary work. However, while they are typically noted in a character introduction, your chosen character traits should be noticeable throughout your characters’ presence on the page, and therefore, should be thoughtfully chosen and applied. Below, we’ll unpack character trait definitions and examples to help you gain a deeper understanding and how to implement them properly.
Watch: Anatomy of a Screenplay — Ultimate Guide
Subscribe for more filmmaking videos like this.
Character Traits Definition & Examples
First, let’s define character traits.
Character traits may seem pretty self-explanatory. But if you’re hoping to have a thoroughly built character (and who isn’t?), it’s crucial to understand the differences between character traits vs. other literary devices and techniques.
CHARACTER TRAITs DEFINITION
What are character traits.
C haracter trait are valued aspects of a person or character’s behavior, which are exemplified by individual characteristics or qualities like a person’s conduct, habits, or attitudes. Character traits can be considered positive or negative, and are commonly referred to by way of descriptive adjectives.
Character traits examples:
Character traits can be physical or mental/emotional, but what’s perhaps most important to note is the difference between character traits and say, personality. In writing, imbuing characters with these qualities is a process called characterization .
This can be done in two different ways — through direct characterization or indirect characterization . Essentially, it’s trustworthy information about a character given to the reader by the writer.
Learn more about direct and indirect characterization in the video below.
Character Traits for Stories
Up against character traits (and direct / indirect characterization) are personality traits . Personality traits are more so surface-level observations of whom a character is.
Noticeable from the outside, and not necessarily fortified over a set amount a time, personality traits can look something like, “ Constanza is effervescent and outgoing .” As opposed to the idea that she is an incredibly honest person who values transparency.
Applying Characterization
How to implement character traits.
The idea that you need to have strong character design shouldn’t surprise anyone. But the methodology of that implementation can make or break your characters (and you’ll need those). So how can you go about solidifying your characters over time using these defining traits?
To begin, we can look at notable examples from produced projects. Let’s take a look at Lady Bird .
Character traits meaning in action • Lady Bird
So, what are the main character traits in this coming of age movie ? Lady Bird, or Christine, is spontaneous and impulsive. Sure, we could be told this from the get-go; however, it’s something we come to understand as true throughout the duration of the film. In fact, we are introduced to this character trait of impulsiveness in the first scene of the movie.
Types of character traits in writing
Right away, we know that Lady Bird is going to do what she wants, when she wants, and that could be at literally any time. Throughout the rest of the film, she continues on this spontaneous path: she pulls a prank on her principal, interrupts a school assembly on abortion, etc.
So now that we’ve got some character traits examples to look at, what can we take from it? It’s clear that Gerwig implemented these characteristics not just as funny gags to liven up the story.
She did it to bring the character of Lady Bird to life by way of allowing these defining traits to guide Lady Bird’s choices.
So, here are some tips on how to use this technique for your next project:
- Build your character thoroughly, and be sure to differentiate between personality, physicality, morals, values, and belief.
- Decide how many character traits should a character have and which of those the character values most. Allow that to guide them through any decisions and obstacles they may face
- Be sure to include clear examples of those traits as essential to your characters’ journeys.
- Decide what tactics your character uses to act on their morals. Do they act out when they are lied to? Do they cut people off when they’ve been let down? How do they respond to aggressive confrontation?
You’ve chosen to follow your protagonists and supporting characters throughout your story for a reason: they are unique. These traits are an essential part of proving that. And when you use the above strategies to create your characters, the audience will thank you for it.
Related Posts
- What is Characterization →
- How to Write a Character Analysis →
- Characterization Examples in Movies →
Character Archetypes
You’ve just developed a deeper understanding of what character traits are and how to use them. But what other characters can guide your character development? Check out the classic character archetypes and how your characters measure up at the link below.
Up Next: Character Archetypes →
Write and produce your scripts all in one place..
Write and collaborate on your scripts FREE . Create script breakdowns, sides, schedules, storyboards, call sheets and more.
- Pricing & Plans
- Product Updates
- Featured On
- StudioBinder Partners
- The Ultimate Guide to Call Sheets (with FREE Call Sheet Template)
- How to Break Down a Script (with FREE Script Breakdown Sheet)
- The Only Shot List Template You Need — with Free Download
- Managing Your Film Budget Cashflow & PO Log (Free Template)
- A Better Film Crew List Template Booking Sheet
- Best Storyboard Softwares (with free Storyboard Templates)
- Movie Magic Scheduling
- Gorilla Software
- Storyboard That
A visual medium requires visual methods. Master the art of visual storytelling with our FREE video series on directing and filmmaking techniques.
We’re in a golden age of TV writing and development. More and more people are flocking to the small screen to find daily entertainment. So how can you break put from the pack and get your idea onto the small screen? We’re here to help.
- Making It: From Pre-Production to Screen
- What is Film Distribution — The Ultimate Guide for Filmmakers
- What is a Fable — Definition, Examples & Characteristics
- Whiplash Script PDF Download — Plot, Characters and Theme
- What Is a Talking Head — Definition and Examples
- What is Blue Comedy — Definitions, Examples and Impact
- 0 Pinterest
- My Storyboards
Character Analysis Essays
Without characters, there is no story. Without depth, the characters don't always contribute enough to the story, if at all. While character maps allow readers to track information about each character while reading, a character analysis lets them go deeper into the role they play in the story, the conflicts they encounter, and their traits, whether external or internal.
Writing a Character Analysis
Usually character analyses are a more in-depth assignment or short essay that require the student to think critically about one or more characters and make inferences from a careful reading of the text. It helps to have ways to visually organize the different parts of a character analysis with storyboards, graphic organizers, or with a character analysis worksheet . From there, the student can formulate their essay!
Defining the role, or function, of a character is an important first step. Are they the protagonist? The antagonist? The mentor? Do they change? Considering why a character may or may not change and how this affects character traits and conflicts is going to be important in a final analysis. You can ask students questions to guide them through the process of in depth analysis.
- What type of role does the character play in the story?
- How do they serve the story or other characters?
- Based on your initial read of the character, do they even change at all, or do they remain exactly the same as they were at the beginning?

If asked to describe the character, what sort of words would you use to describe them? Are they well educated, impulsive, or quiet? These answers contribute to the personality of the character and how they behave. They offer insight into why a character might make a certain decision, and alert us if something seems out of character. For instance, a quiet and cowardly character might suddenly make an impulsive or brave choice in the face of something. Why would they suddenly change?
- What physical traits define the character?
- How do they behave?
- Do they often fight other characters or are they overly helpful?
- How do they speak? What insight can you gain from their words?
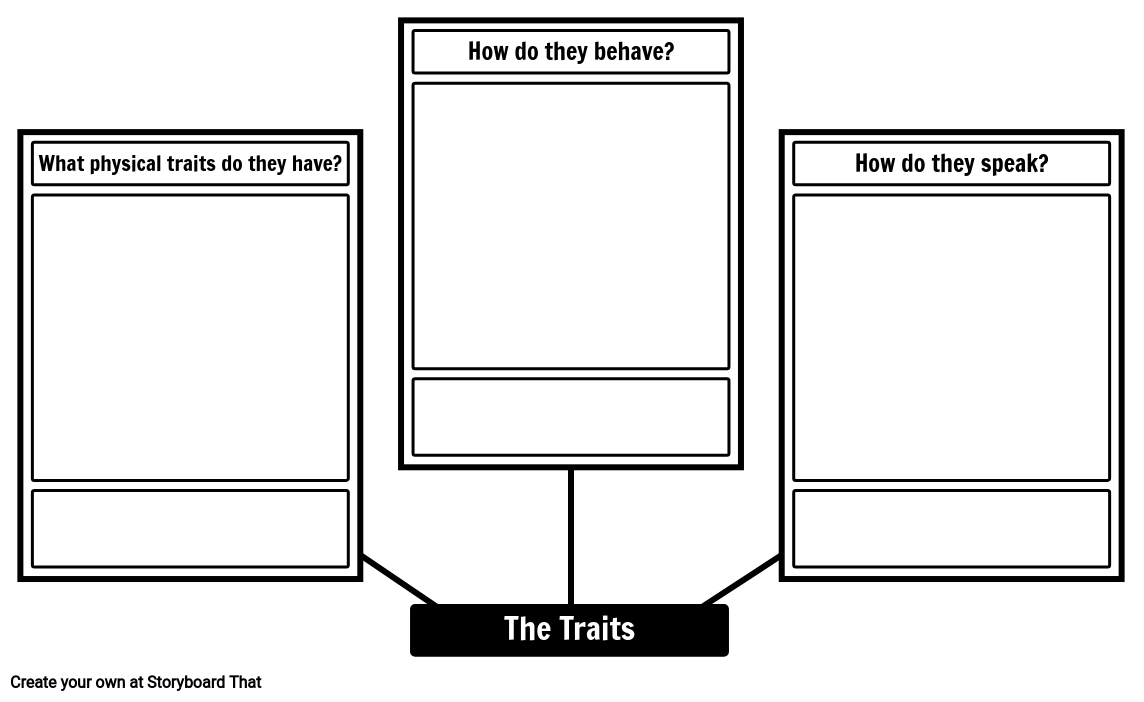
The Conflicts
Without conflict in a story, nothing changes. Conflicts, no matter the type, spur character development in at least one, if not all, of the characters in the story. When considering conflict in regards to an analysis, consider the following:
- What conflict(s) does the character encounter?
- What type of conflict is it?
- How does the character react?
- How is the character changed (or not changed) by the conflict?
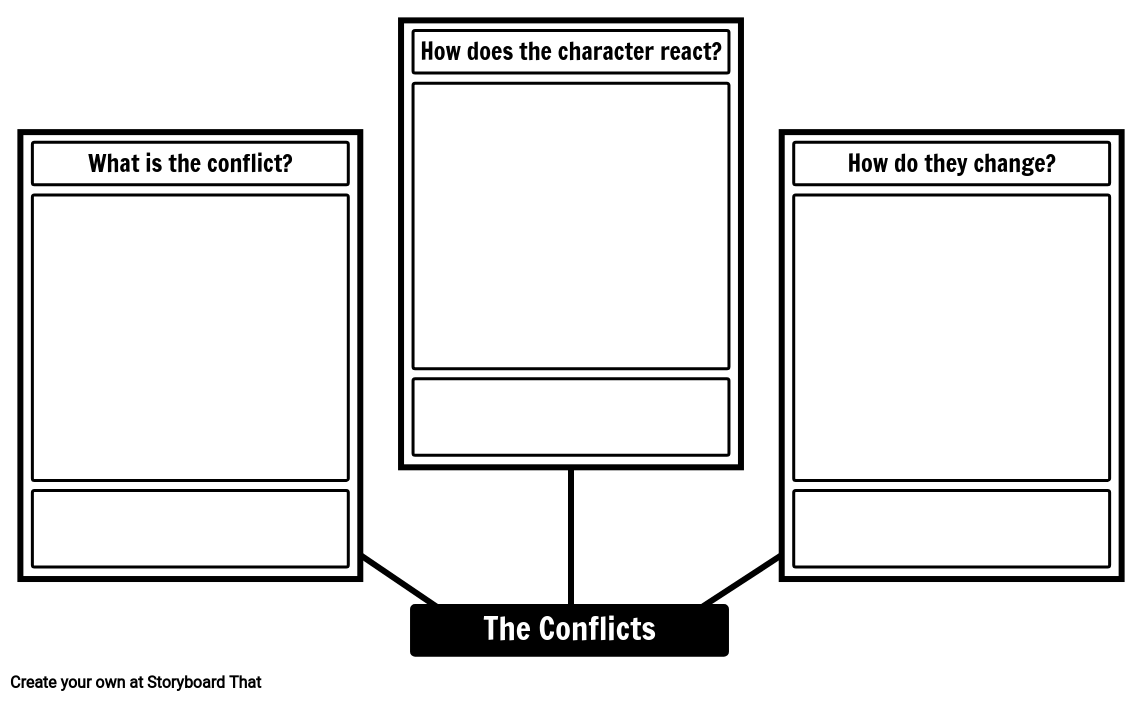
Character Maps
Character maps are a helpful tool for students to use as they're reading, although they can also be used after completing a book. In this activity, students will create a character map of the characters in the story, paying close attention to the physical attributes and the traits of both major and minor characters . They can also provide detailed information regarding the challenges the character faces, the challenges the character imposes, and the importance of the character to the plot of the story.
To scaffold or tailor this activity, teachers can change the questions, add more questions (the character map layout can be found under "Scenes" -> "Patterns"), provide the names of characters they want students to track, or let students start from scratch! Teachers may also provide the visuals for each character or let students pick their own from the Characters tab. Be sure to update the student instructions as necessary!
- What are the Character's Physical/Character Traits?
- How does this character interact with the other characters in the story?
- What challenges does this character face?

Many elements of these three main ideas will influence each other to offer further insight into a character. By creating a template for them, students will be able to keep track of the character while actively reading instead of having to comb back through when they've finished. They'll be able to easily see what connections exist between the information, and synthesize that into a comprehensive essay. Create scaffolded digital worksheets or use the spider map templates above as a starting point. You'll be surprised at what incredible things your students will find.
Related Activities

How to Write a Character Analysis Essay
Understand the role of the character.
Begin by defining the role of the character in the story. Determine whether they are the protagonist, antagonist, mentor, or another type of character. Consider how their role contributes to the overall story and other characters. Analyze whether the character undergoes any changes throughout the story or remains the same.
Identify and Describe the Character's Traits
Describe the character's traits by considering their personality, behavior, physical attributes, and speech. Use descriptive words to depict the character's qualities and explain how these traits shape their actions and decisions. Analyze any inconsistencies or changes in the character's behavior and examine the reasons behind them.
Explore the Conflicts Encountered by the Character
Examine the conflicts faced by the character and their significance in the story. Identify the type of conflicts, such as internal or external, and analyze how the character responds to these challenges. Assess the impact of the conflicts on the character's development and whether they undergo any transformations or remain unchanged.
Create a Character Map
Utilize a character map to visually organize information about the character. Include details about the character's physical attributes, traits, interactions with other characters, and challenges faced. Consider using pre-designed character map templates or creating a custom map to suit your analysis requirements. Adapt the questions and layout of the character map based on the specific needs of the assignment.
Synthesize the Analysis into an Essay
Take the gathered information from the character analysis and synthesize it into a comprehensive essay. Use the template or character map as a reference to maintain coherence and ensure all relevant connections and insights are included. Structure the essay with an introduction, body paragraphs discussing different aspects of the character analysis, and a conclusion that summarizes the key findings.
Frequently Asked Questions about Character Analysis Essays
What is a character analysis essay.
A character analysis essay is an assignment that requires the student to critically analyze one or more characters in a text and make inferences based on their traits, role in the story, and conflicts they encounter.
Why is it important to define the role of a character in a character analysis?
Defining the role of a character is important because it helps the student understand the character's purpose in the story and how they relate to other characters. It can also help identify if the character undergoes any changes and how it affects their traits and conflicts.
What are some questions to guide students in analyzing the role of a character?
Some questions to guide students in analyzing the role of a character are: What type of role does the character play in the story? How do they serve the story or other characters? Based on your initial read of the character, do they even change at all, or do they remain exactly the same as they were at the beginning?
- Czar Nicholas II • Museum of Photographic Arts Collections • License No known copyright restrictions (http://flickr.com/commons/usage/)
- Karl-Marx-Stadt auf Trab - Friedenslauf am Karl-Marx-Monument • Uwe Kaufmann1 • License Attribution (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0/)
- Kazan temple and Historical muzeum • akk_rus • License Attribution (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0/)
- Marx at Highgate • [Duncan] • License Attribution (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0/)
- STALIN-angry-JPG • snowlepard • License Attribution (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0/)
- Trotsky cor 06 • Luiz Fernando / Sonia Maria • License Attribution (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0/)
Try 1 Month For
30 Day Money Back Guarantee New Customers Only Full Price After Introductory Offer
Learn more about our Department, School, and District packages
- 30 Day Money Back Guarantee
- New Customers Only
- Full Price After Introductory Offer
Narrative Essay
Definition of narrative essay.
A narrative essay is a type of essay that has a single motif , or a central point, around which the whole narrative revolves. All incidents, happenings, and characters revolve around a single motif presented in the narrative. A narrative essay is similar to a simple five-paragraph essay, in that it has the same format. It is only different in that it is a narrative, having characters, incidents, and dialogues.
Difference Between a Narrative Essay and a Short Story
A narrative essay has a specific format, specific aspects to discover, and a specific motif. It revolves around that motif set by the writer prior to writing the essay. A short story , however, is different from a narrative essay in that it does not revolve around a pre-set motif, and that it does not have a specific format. Also, a short story always leaves readers at a critical juncture with the desire to discover more. In contrast , a narrative essay ends when the readers are fully satisfied. They do not wish to read anymore or do not want to discover anymore.
Elements of a Narrative Essay
A narrative essay has three required elements: character , theme , and dialogue :
Characters are an important part of a narrative essay. Even if the essay is autobiographical in nature, the person writing the essay is a character involving some other characters who act, behave, and do like all other characters presented in stories and novels .
Theme or Motif
A narrative essay revolves around a theme or a motif. This theme or motif is presented in its thesis statement, which breaks it down into three distinct pieces of evidence . These three distinct pieces of evidence are then further elaborated through characters in body paragraphs .
Dialogue is used to capture the conversation between characters. In a narrative essay, dialogue is the third important element, without which the characters lose their worth and liveliness.
How to Choose a Topic for Narrative Essay
There are four major steps to choosing the topic of a narrative essay:
- Choose a theme or thematic strand around which to weave a story.
- Outline the character, events, and happenings.
- Think about the conversation of the characters and place them in a setting and plot
- Synchronize the characters with the plot and the setting to see if they integrate with each other.
MLA and APA Formats in Narrative Essay
MLA and APA are used in all types of essays. However, APA is mostly used in social sciences, while MLA is used in humanities. Whereas the application of MLA in a narrative is concerned, it is used in the format, intext citation , and in the Works Cited page. The first page comprises the student’s name, class, tutor’s name, and date with the topic of the essay given after all of them. However, in APA, all this information appears on the cover page. Similarly, both MLA and APA differ in intext citation, with MLA having only the author’s name and page without any comma. In contrast, APA has the author’s name as well as page number with a comma and ‘p’ with a period before the number of the page, such as (Hardy, p. 45). Regarding the sources, MLA shows Works Cited page at the end, while APA shows Reference at the end.
Reflective Narrative Essay
As the name suggests, a reflection narrative is an essay that presents the reflections of a person who is writing that essay. He takes an incident from his life and gives it an organization on the pattern of an essay with a narrative having a beginning, middle, and an end. The essay may or may not have moral lessons, which does not make a lot of difference if the experiences carry the deeper meaning. What matters is that the writer reflects on his own life, taking out some significant moment to make it a storied essay or a narrative essay with a theme in it.
Examples of Narrative Essays in Literature
Example #1: new directions (by maya angelou).
“Annie, over six feet tall, big-boned, decided that she would not go to work as a domestic and leave her “precious babes” to anyone else’s care. There was no possibility of being hired at the town’s cotton gin or lumber mill, but maybe there was a way to make the two factories work for her. In her words, “I looked up the road I was going and back the way I come, and since I wasn’t satisfied, I decided to step off the road and cut me a new path.” She told herself that she wasn’t a fancy cook but that she could “mix groceries well enough to scare hungry away and keep from starving a man.”
This paragraph is an example from a narrative essay of Maya Angelou. She has described how a girl looks, and how she behaves. She has also written direct dialogues to show that it is a narrative.
Example #2: Saturday Evening Post (by Russell Baker)
“When I burst in that afternoon she was in conference with an executive of the Curtis Publishing Company. She introduced me. He bent low from the waist and shook my hand. Was it true as my mother had told him, he asked, that I longed for the opportunity to conquer the world of business? My Mother replied that I was blessed with a rare determination to make something of myself. ‘That’s right,’ I whispered. ‘But have you got the grit, the character, the never-say-quit spirit it takes to succeed in business?’ My Mother said I certainly did.”
In this piece from a narrative essay by Russell Baker of the famed Saturday Evening Post , the author has fully described the efforts of his mother by her dialogue. Both character and dialogue are very clear.
Example #3: Only Daughter (by Sandra Cisneros)
“Once several years ago, when I was just starting out my writing career, I was asked to write my own contributor’s note for an anthology I was part of, I wrote: ‘ I am the only daughter in a family of six sons. That explains everything.’ “Well, I’ve thought about that ever since, and yes, it explains a lot to me, but for the reader’s sake I should have written: ‘I am the only daughter in a Mexican family of six sons.’ Or even: ‘I am the only daughter of a Mexican father and a Mexican-American mother.’ Or: ‘I am the only daughter of a working-class family of nine.’ All of these had everything to do with who I am today.”
In this essay, the author has given a full description of a daughter – how she looks and how she behaves.
Function of Narrative Essay
A narrative essay describes people, presents their conversations, and narrates their experiences to teach lessons to readers. In fact, it is like a story, but different in that it is weaved around a motif. A motif is given before the incidents of the essay. Readers become aware of this single theme, central idea, or motif once they go through the essay. Its major aim is to provide information about life experiences and lessons learned from those experiences.
Synonyms of Narrative Essay
Some of the words closely related to the narrative essay are reflective account, chronicle, chronology , and historical narrative. However, these words cannot be interchangeably used to replace this title.
Related posts:
- Narrative Poem
- Elements of an Essay
- Definition Essay
- Descriptive Essay
- Types of Essay
- Analytical Essay
- Argumentative Essay
- Cause and Effect Essay
- Critical Essay
- Expository Essay
- Persuasive Essay
- Process Essay
- Explicatory Essay
- An Essay on Man: Epistle I
- Comparison and Contrast Essay
Post navigation
Things you buy through our links may earn Vox Media a commission
The Case for Marrying an Older Man
A woman’s life is all work and little rest. an age gap relationship can help..

In the summer, in the south of France, my husband and I like to play, rather badly, the lottery. We take long, scorching walks to the village — gratuitous beauty, gratuitous heat — kicking up dust and languid debates over how we’d spend such an influx. I purchase scratch-offs, jackpot tickets, scraping the former with euro coins in restaurants too fine for that. I never cash them in, nor do I check the winning numbers. For I already won something like the lotto, with its gifts and its curses, when he married me.
He is ten years older than I am. I chose him on purpose, not by chance. As far as life decisions go, on balance, I recommend it.
When I was 20 and a junior at Harvard College, a series of great ironies began to mock me. I could study all I wanted, prove myself as exceptional as I liked, and still my fiercest advantage remained so universal it deflated my other plans. My youth. The newness of my face and body. Compellingly effortless; cruelly fleeting. I shared it with the average, idle young woman shrugging down the street. The thought, when it descended on me, jolted my perspective, the way a falling leaf can make you look up: I could diligently craft an ideal existence, over years and years of sleepless nights and industry. Or I could just marry it early.
So naturally I began to lug a heavy suitcase of books each Saturday to the Harvard Business School to work on my Nabokov paper. In one cavernous, well-appointed room sat approximately 50 of the planet’s most suitable bachelors. I had high breasts, most of my eggs, plausible deniability when it came to purity, a flush ponytail, a pep in my step that had yet to run out. Apologies to Progress, but older men still desired those things.
I could not understand why my female classmates did not join me, given their intelligence. Each time I reconsidered the project, it struck me as more reasonable. Why ignore our youth when it amounted to a superpower? Why assume the burdens of womanhood, its too-quick-to-vanish upper hand, but not its brief benefits at least? Perhaps it came easier to avoid the topic wholesale than to accept that women really do have a tragically short window of power, and reason enough to take advantage of that fact while they can. As for me, I liked history, Victorian novels, knew of imminent female pitfalls from all the books I’d read: vampiric boyfriends; labor, at the office and in the hospital, expected simultaneously; a decline in status as we aged, like a looming eclipse. I’d have disliked being called calculating, but I had, like all women, a calculator in my head. I thought it silly to ignore its answers when they pointed to an unfairness for which we really ought to have been preparing.
I was competitive by nature, an English-literature student with all the corresponding major ambitions and minor prospects (Great American novel; email job). A little Bovarist , frantic for new places and ideas; to travel here, to travel there, to be in the room where things happened. I resented the callow boys in my class, who lusted after a particular, socially sanctioned type on campus: thin and sexless, emotionally detached and socially connected, the opposite of me. Restless one Saturday night, I slipped on a red dress and snuck into a graduate-school event, coiling an HDMI cord around my wrist as proof of some technical duty. I danced. I drank for free, until one of the organizers asked me to leave. I called and climbed into an Uber. Then I promptly climbed out of it. For there he was, emerging from the revolving doors. Brown eyes, curved lips, immaculate jacket. I went to him, asked him for a cigarette. A date, days later. A second one, where I discovered he was a person, potentially my favorite kind: funny, clear-eyed, brilliant, on intimate terms with the universe.
I used to love men like men love women — that is, not very well, and with a hunger driven only by my own inadequacies. Not him. In those early days, I spoke fondly of my family, stocked the fridge with his favorite pasta, folded his clothes more neatly than I ever have since. I wrote his mother a thank-you note for hosting me in his native France, something befitting a daughter-in-law. It worked; I meant it. After graduation and my fellowship at Oxford, I stayed in Europe for his career and married him at 23.
Of course I just fell in love. Romances have a setting; I had only intervened to place myself well. Mainly, I spotted the precise trouble of being a woman ahead of time, tried to surf it instead of letting it drown me on principle. I had grown bored of discussions of fair and unfair, equal or unequal , and preferred instead to consider a thing called ease.
The reception of a particular age-gap relationship depends on its obviousness. The greater and more visible the difference in years and status between a man and a woman, the more it strikes others as transactional. Transactional thinking in relationships is both as American as it gets and the least kosher subject in the American romantic lexicon. When a 50-year-old man and a 25-year-old woman walk down the street, the questions form themselves inside of you; they make you feel cynical and obscene: How good of a deal is that? Which party is getting the better one? Would I take it? He is older. Income rises with age, so we assume he has money, at least relative to her; at minimum, more connections and experience. She has supple skin. Energy. Sex. Maybe she gets a Birkin. Maybe he gets a baby long after his prime. The sight of their entwined hands throws a lucid light on the calculations each of us makes, in love, to varying degrees of denial. You could get married in the most romantic place in the world, like I did, and you would still have to sign a contract.
Twenty and 30 is not like 30 and 40; some freshness to my features back then, some clumsiness in my bearing, warped our decade, in the eyes of others, to an uncrossable gulf. Perhaps this explains the anger we felt directed at us at the start of our relationship. People seemed to take us very, very personally. I recall a hellish car ride with a friend of his who began to castigate me in the backseat, in tones so low that only I could hear him. He told me, You wanted a rich boyfriend. You chased and snuck into parties . He spared me the insult of gold digger, but he drew, with other words, the outline for it. Most offended were the single older women, my husband’s classmates. They discussed me in the bathroom at parties when I was in the stall. What does he see in her? What do they talk about? They were concerned about me. They wielded their concern like a bludgeon. They paraphrased without meaning to my favorite line from Nabokov’s Lolita : “You took advantage of my disadvantage,” suspecting me of some weakness he in turn mined. It did not disturb them, so much, to consider that all relationships were trades. The trouble was the trade I’d made struck them as a bad one.
The truth is you can fall in love with someone for all sorts of reasons, tiny transactions, pluses and minuses, whose sum is your affection for each other, your loyalty, your commitment. The way someone picks up your favorite croissant. Their habit of listening hard. What they do for you on your anniversary and your reciprocal gesture, wrapped thoughtfully. The serenity they inspire; your happiness, enlivening it. When someone says they feel unappreciated, what they really mean is you’re in debt to them.
When I think of same-age, same-stage relationships, what I tend to picture is a woman who is doing too much for too little.
I’m 27 now, and most women my age have “partners.” These days, girls become partners quite young. A partner is supposed to be a modern answer to the oppression of marriage, the terrible feeling of someone looming over you, head of a household to which you can only ever be the neck. Necks are vulnerable. The problem with a partner, however, is if you’re equal in all things, you compromise in all things. And men are too skilled at taking .
There is a boy out there who knows how to floss because my friend taught him. Now he kisses college girls with fresh breath. A boy married to my friend who doesn’t know how to pack his own suitcase. She “likes to do it for him.” A million boys who know how to touch a woman, who go to therapy because they were pushed, who learned fidelity, boundaries, decency, manners, to use a top sheet and act humanely beneath it, to call their mothers, match colors, bring flowers to a funeral and inhale, exhale in the face of rage, because some girl, some girl we know, some girl they probably don’t speak to and will never, ever credit, took the time to teach him. All while she was working, raising herself, clawing up the cliff-face of adulthood. Hauling him at her own expense.
I find a post on Reddit where five thousand men try to define “ a woman’s touch .” They describe raised flower beds, blankets, photographs of their loved ones, not hers, sprouting on the mantel overnight. Candles, coasters, side tables. Someone remembering to take lint out of the dryer. To give compliments. I wonder what these women are getting back. I imagine them like Cinderella’s mice, scurrying around, their sole proof of life their contributions to a more central character. On occasion I meet a nice couple, who grew up together. They know each other with a fraternalism tender and alien to me. But I think of all my friends who failed at this, were failed at this, and I think, No, absolutely not, too risky . Riskier, sometimes, than an age gap.
My younger brother is in his early 20s, handsome, successful, but in many ways: an endearing disaster. By his age, I had long since wisened up. He leaves his clothes in the dryer, takes out a single shirt, steams it for three minutes. His towel on the floor, for someone else to retrieve. His lovely, same-age girlfriend is aching to fix these tendencies, among others. She is capable beyond words. Statistically, they will not end up together. He moved into his first place recently, and she, the girlfriend, supplied him with a long, detailed list of things he needed for his apartment: sheets, towels, hangers, a colander, which made me laugh. She picked out his couch. I will bet you anything she will fix his laundry habits, and if so, they will impress the next girl. If they break up, she will never see that couch again, and he will forget its story. I tell her when I visit because I like her, though I get in trouble for it: You shouldn’t do so much for him, not for someone who is not stuck with you, not for any boy, not even for my wonderful brother.
Too much work had left my husband, by 30, jaded and uninspired. He’d burned out — but I could reenchant things. I danced at restaurants when they played a song I liked. I turned grocery shopping into an adventure, pleased by what I provided. Ambitious, hungry, he needed someone smart enough to sustain his interest, but flexible enough in her habits to build them around his hours. I could. I do: read myself occupied, make myself free, materialize beside him when he calls for me. In exchange, I left a lucrative but deadening spreadsheet job to write full-time, without having to live like a writer. I learned to cook, a little, and decorate, somewhat poorly. Mostly I get to read, to walk central London and Miami and think in delicious circles, to work hard, when necessary, for free, and write stories for far less than minimum wage when I tally all the hours I take to write them.
At 20, I had felt daunted by the project of becoming my ideal self, couldn’t imagine doing it in tandem with someone, two raw lumps of clay trying to mold one another and only sullying things worse. I’d go on dates with boys my age and leave with the impression they were telling me not about themselves but some person who didn’t exist yet and on whom I was meant to bet regardless. My husband struck me instead as so finished, formed. Analyzable for compatibility. He bore the traces of other women who’d improved him, small but crucial basics like use a coaster ; listen, don’t give advice. Young egos mellow into patience and generosity.
My husband isn’t my partner. He’s my mentor, my lover, and, only in certain contexts, my friend. I’ll never forget it, how he showed me around our first place like he was introducing me to myself: This is the wine you’ll drink, where you’ll keep your clothes, we vacation here, this is the other language we’ll speak, you’ll learn it, and I did. Adulthood seemed a series of exhausting obligations. But his logistics ran so smoothly that he simply tacked mine on. I moved into his flat, onto his level, drag and drop, cleaner thrice a week, bills automatic. By opting out of partnership in my 20s, I granted myself a kind of compartmentalized, liberating selfishness none of my friends have managed. I am the work in progress, the party we worry about, a surprising dominance. When I searched for my first job, at 21, we combined our efforts, for my sake. He had wisdom to impart, contacts with whom he arranged coffees; we spent an afternoon, laughing, drawing up earnest lists of my pros and cons (highly sociable; sloppy math). Meanwhile, I took calls from a dear friend who had a boyfriend her age. Both savagely ambitious, hyperclose and entwined in each other’s projects. If each was a start-up , the other was the first hire, an intense dedication I found riveting. Yet every time she called me, I hung up with the distinct feeling that too much was happening at the same time: both learning to please a boss; to forge more adult relationships with their families; to pay bills and taxes and hang prints on the wall. Neither had any advice to give and certainly no stability. I pictured a three-legged race, two people tied together and hobbling toward every milestone.
I don’t fool myself. My marriage has its cons. There are only so many times one can say “thank you” — for splendid scenes, fine dinners — before the phrase starts to grate. I live in an apartment whose rent he pays and that shapes the freedom with which I can ever be angry with him. He doesn’t have to hold it over my head. It just floats there, complicating usual shorthands to explain dissatisfaction like, You aren’t being supportive lately . It’s a Frenchism to say, “Take a decision,” and from time to time I joke: from whom? Occasionally I find myself in some fabulous country at some fabulous party and I think what a long way I have traveled, like a lucky cloud, and it is frightening to think of oneself as vapor.
Mostly I worry that if he ever betrayed me and I had to move on, I would survive, but would find in my humor, preferences, the way I make coffee or the bed nothing that he did not teach, change, mold, recompose, stamp with his initials, the way Renaissance painters hid in their paintings their faces among a crowd. I wonder if when they looked at their paintings, they saw their own faces first. But this is the wrong question, if our aim is happiness. Like the other question on which I’m expected to dwell: Who is in charge, the man who drives or the woman who put him there so she could enjoy herself? I sit in the car, in the painting it would have taken me a corporate job and 20 years to paint alone, and my concern over who has the upper hand becomes as distant as the horizon, the one he and I made so wide for me.
To be a woman is to race against the clock, in several ways, until there is nothing left to be but run ragged.
We try to put it off, but it will hit us at some point: that we live in a world in which our power has a different shape from that of men, a different distribution of advantage, ours a funnel and theirs an expanding cone. A woman at 20 rarely has to earn her welcome; a boy at 20 will be turned away at the door. A woman at 30 may find a younger woman has taken her seat; a man at 30 will have invited her. I think back to the women in the bathroom, my husband’s classmates. What was my relationship if not an inconvertible sign of this unfairness? What was I doing, in marrying older, if not endorsing it? I had taken advantage of their disadvantage. I had preempted my own. After all, principled women are meant to defy unfairness, to show some integrity or denial, not plan around it, like I had. These were driven women, successful, beautiful, capable. I merely possessed the one thing they had already lost. In getting ahead of the problem, had I pushed them down? If I hadn’t, would it really have made any difference?
When we decided we wanted to be equal to men, we got on men’s time. We worked when they worked, retired when they retired, had to squeeze pregnancy, children, menopause somewhere impossibly in the margins. I have a friend, in her late 20s, who wears a mood ring; these days it is often red, flickering in the air like a siren when she explains her predicament to me. She has raised her fair share of same-age boyfriends. She has put her head down, worked laboriously alongside them, too. At last she is beginning to reap the dividends, earning the income to finally enjoy herself. But it is now, exactly at this precipice of freedom and pleasure, that a time problem comes closing in. If she would like to have children before 35, she must begin her next profession, motherhood, rather soon, compromising inevitably her original one. The same-age partner, equally unsettled in his career, will take only the minimum time off, she guesses, or else pay some cost which will come back to bite her. Everything unfailingly does. If she freezes her eggs to buy time, the decision and its logistics will burden her singly — and perhaps it will not work. Overlay the years a woman is supposed to establish herself in her career and her fertility window and it’s a perfect, miserable circle. By midlife women report feeling invisible, undervalued; it is a telling cliché, that after all this, some husbands leave for a younger girl. So when is her time, exactly? For leisure, ease, liberty? There is no brand of feminism which achieved female rest. If women’s problem in the ’50s was a paralyzing malaise, now it is that they are too active, too capable, never permitted a vacation they didn’t plan. It’s not that our efforts to have it all were fated for failure. They simply weren’t imaginative enough.
For me, my relationship, with its age gap, has alleviated this rush , permitted me to massage the clock, shift its hands to my benefit. Very soon, we will decide to have children, and I don’t panic over last gasps of fun, because I took so many big breaths of it early: on the holidays of someone who had worked a decade longer than I had, in beautiful places when I was young and beautiful, a symmetry I recommend. If such a thing as maternal energy exists, mine was never depleted. I spent the last nearly seven years supported more than I support and I am still not as old as my husband was when he met me. When I have a child, I will expect more help from him than I would if he were younger, for what does professional tenure earn you if not the right to set more limits on work demands — or, if not, to secure some child care, at the very least? When I return to work after maternal upheaval, he will aid me, as he’s always had, with his ability to put himself aside, as younger men are rarely able.
Above all, the great gift of my marriage is flexibility. A chance to live my life before I become responsible for someone else’s — a lover’s, or a child’s. A chance to write. A chance at a destiny that doesn’t adhere rigidly to the routines and timelines of men, but lends itself instead to roomy accommodation, to the very fluidity Betty Friedan dreamed of in 1963 in The Feminine Mystique , but we’ve largely forgotten: some career or style of life that “permits year-to-year variation — a full-time paid job in one community, part-time in another, exercise of the professional skill in serious volunteer work or a period of study during pregnancy or early motherhood when a full-time job is not feasible.” Some things are just not feasible in our current structures. Somewhere along the way we stopped admitting that, and all we did was make women feel like personal failures. I dream of new structures, a world in which women have entry-level jobs in their 30s; alternate avenues for promotion; corporate ladders with balconies on which they can stand still, have a smoke, take a break, make a baby, enjoy themselves, before they keep climbing. Perhaps men long for this in their own way. Actually I am sure of that.
Once, when we first fell in love, I put my head in his lap on a long car ride; I remember his hands on my face, the sun, the twisting turns of a mountain road, surprising and not surprising us like our romance, and his voice, telling me that it was his biggest regret that I was so young, he feared he would lose me. Last week, we looked back at old photos and agreed we’d given each other our respective best years. Sometimes real equality is not so obvious, sometimes it takes turns, sometimes it takes almost a decade to reveal itself.
More From This Series
- Can You Still Sell Out in This Economy?
- 7 Stories of Dramatic Career Pivots
- My Mother’s Death Blew Up My Life. Opening a Book and Wine Store Helped My Grief
- newsletter pick
- first person
- relationships
- the good life
- best of the cut
- audio article
The Cut Shop
Most viewed stories.
- Madame Clairevoyant: Horoscopes for the Week of April 7–13
- Get Ready for the Solar Eclipse in Aries to Change You
- Behold, the Ballet Sneaker
- Cracks Are Back
- The Case for Marrying an Older Man
- What We Know About the Mommy Vlogger Accused of Child Abuse
- This Mercury Retrograde in Aries Will Be Peak Chaos
Editor’s Picks

Most Popular
What is your email.
This email will be used to sign into all New York sites. By submitting your email, you agree to our Terms and Privacy Policy and to receive email correspondence from us.
Sign In To Continue Reading
Create your free account.
Password must be at least 8 characters and contain:
- Lower case letters (a-z)
- Upper case letters (A-Z)
- Numbers (0-9)
- Special Characters (!@#$%^&*)
As part of your account, you’ll receive occasional updates and offers from New York , which you can opt out of anytime.
Screen Rant
Parish episode 2 recap: that major character death & 8 other reveals.
Parish episode 2 is finally here, and here are all of the biggest moments from the new episode explained, including this major character's death.
- Gray faces his son's death in a dramatic flashback, setting a dark tone for Parish episode 2.
- The gang's involvement in human trafficking is confirmed, adding a dark turn to the series.
- Gray's attempt to leave the criminal world is complicated as he gets pulled deeper into dangerous situations.
Parish episode 2 is out now, and here is a complete recap of the exciting new installment in the AMC series, breaking down that major character death from the end of the episode as well as eight other major reveals. Parish has been an exciting ride so far, with the first two episodes setting the stage for a complicated situation that Giancarlo Esposito's Gray Parish will have to find a way out of. Parish episode 2 ended with a bang, with this massive twist raising the stakes of the series and potentially throwing the world of Parish into chaos.
AMC has released an all-new crime thriller called Parish , with the series hoping to join the ranks of other beloved AMC series like Breaking Bad , Better Call Saul , Mad Men , and The Walking Dead . The series follows Giancarlo Esposito's Gracián "Gray" Parish , a retired criminal driver who rejoins the world of New Orleans gangs after running into some financial troubles at home. However, Gray soon realizes that he has gotten in far too deep, with Parish episode 2 chronicling the start of Gray's attempts to leave the Zimbabwean gang and return to his life as a family man.
9 Episode 2 Starts Out With A Flashback To The Death Of Gray’s Son
Although it isn't confirmed.
Much like episode 1, Parish episode 2 starts out with a flashback as well, establishing a potential trend for the AMC series. Parish episode 1's opening was actually a flash forward to a car chase that occurred later in the episode, and while this was a lot of fun and an exciting way to kick off the show, Parish episode 2's opening flashback is much darker. As it turns out, the opening scene of episode 2 gives viewers a first look at the death of Gray's son.
Giancarlo Esposito Just Perfected His 3rd Villain Since Breaking Bad Ended
The opening scene of Parish episode 2 sees several police cars and ambulances surrounding an undetermined crime scene late at night. Soon, Gray Parish arrives, with him frantically making his way through the crowd before erupting into tears upon seeing the scene. Although the series doesn't explicitly say that this is the death of Gray's son, it seems pretty clear due to context clues, with this storyline most likely being built off of in future episodes of Parish .
8 Gray Had A Dead Body In His Shop (& Has To Get Rid Of It)
Here's how he does it.
After the tragic opening flashback scene, Parish returns to the present timeline. Parish episode 2 picks up right where Parish episode 1 ended , with Gray and Colin finding themselves in Gray's garage. At the end of Parish episode 1, the Zimbabwean gang murders a man who was supposed to break into a safe, although he ended up throwing the entire heist off schedule. Because of this, the man is killed right in front of Gray, with this setup being played off of in episode 2.
At the beginning of episode 2, Gray and Colin find themselves tasked with getting rid of the body , a stressful job that causes the two of them to butt heads. They first decide to wash the blood off of the floor and burn any evidence. The duo is almost caught when a customer of Gray's walks in, although they evade the onlooker's suspicions and continue cleaning up the mess.
7 The Gang Is Starting To Question Zenzo
Things are becoming unstable.
Zenzo is one of the siblings that run the mob that Gray has found himself involved in, and as Parish episode 2 reveals, there is beginning to be trouble in the upper rankings of the organized crime ring. One scene shows Zenzo talking to his two siblings, with the two of them explaining their dissatisfaction with Zenzo's work and threatening to get rid of him.
Although not much comes from this conflict between Zenzo and the other heads of the gang in Parish episode 2, this will most likely play a bigger role in future episodes. Setting up a power struggle between Zenzo and his siblings could create an interesting dynamic that throws the antagonists of the series into chaos, with Zenzo potentially spending Parish looking for a way to gain more power within the gang.
6 Gray Learns That The Gang Deals In Human Trafficking
It has finally been confirmed.
When Gray first decided to do a job for the Zimbabwean gang in Parish episode 1, he intentionally didn't want to know much about their operation. Gray simply wanted to do the job, get paid, and leave, although things didn't go according to plan. Gray ended up learning that the heist was meant to steal several passports, causing him to question his involvement and leading to speculation that The Horse was operating in human trafficking .
As it turns out, this is officially the case. Skeet Ulrich's Parish character confirms this to Gray as they are driving after having cleaned up Gray's garage, explaining that the gang makes its money from trafficking humans. This is definitely a dark turn for the series, one that will most likely be explored more in future episodes of the series.
5 Gray Hides The Key Man’s Body In His Freezer, Then Dumps It In A Swamp
And he is almost caught.
One of the biggest points of tension in Parish episode 2 has to do with the body of the dead key man, with Gray spending much of the episode attempting to get rid of it. Gray first takes the body back to his house in the trunk of his car, unsure of what to do with it. Gray first puts the body in a freezer in his garage, covering the lid with a heavy sandbag so that his family won't find the body.
After storing the body at his house for a bit, Gray and Colin take the body to a swamp that seems to be near some sort of abandoned amusement park. The duo dumps the body but becomes stuck in the mud. Unable to get help due to the nearby dead body, Gray and Colin get creative, allowing them to escape the swamp without the corpse.
4 Parish Hints At Gray & Colin’s Shady Past
What happened between them.
Not much has yet been revealed about Gray and Colin's past, but hints are finally starting to be given in Parish episode 2. It is known that the two Parish main characters used to work together when they were leading criminal lifestyles, although Parish seemingly hadn't talked to him for a while upon leaving his life of crime. It was clear that the duo had a falling out, and details about the dissolution of their partnership are finally starting to be given.
As the two get into an argument while dumping the dead body, the name " Cleveland " gets brought up . Although nothing has been confirmed, it seems that they are referring to a person rather than the city, with it seeming like one of them messed up a hit. More information about the Cleveland case will surely get brought up soon, further shedding light on Gray and Colin's past.
3 The Gang Wants Gray To Continue Driving For Them
And gray can't get out.
Gray seriously showed off his skills as a criminal driver in Parish episode 1, but this may have backfired for him. After taking care of the botched heist, the gang asks Gray if he would continue driving for them, as they are in need of someone with his set of skills. Although Gray attempts to decline the offer, the gang won't take no for an answer, causing Gray to stay on as their driver.
This means that Gray has become stuck, with him most likely spending the next few episodes attempting to get out of the criminal underworld of Parish 's New Orleans location . However, Gray is now fully embroiled in the world of The Horse's gang, and the onset of what seems like a gang war at the end of the episode means that it will be even harder to escape.
2 Masked Gunmen Begin Firing At Gray’s Car
Gray has to use his skills to escape.
Parish's first job as an official member of the gang is to drive Zenzo's brother and his brother's son around, with this seeming like an easy task. However, Gray soon notices that several suspicious vehicles are following him, and his suspicions are right. Soon, several unknown masked gunmen hop out of the cars and open fire on Gray's vehicle, endangering everyone.
Recasting Gus Fring For A Breaking Bad Prequel: 9 Actors To Replace Giancarlo Esposito
Through some quick thinking, Gray is able to get the car out of the line of fire , crashing the car into the vehicle of the assailants before driving off. However, the vehicle did take serious damage, with Gray and the other two abandoning the vehicle. However, this doesn't end well for one of the characters involved in the fight. This exciting action scene is pretty tense, with it marking a big change in the story of Parish .
1 Zenzo’s Brother Is Killed By The Masked Gunmen
Episode 2's most tragic scene.
The end of Parish episode 2 ends with a shocking moment, as the gunmen are successful in their mission. Zenzo's brother attempts to hold off the masked gunmen , trying to give Gray a chance to escape with his son. Gray and the child run off and take cover as Zenzo's brother pulls out a gun and tries to fire back, although this only works for so long.
As Zenzo's brother is running back to Gray and the child, he is hit by the masked gunmen and falls down. Although it is possible that he could have lived through the shot, the episode treats it as if it is this character's final moment. The visual of this man dying right in front of his son is a dark one, with it setting up some big changes in the criminal underworld of Parish .
Parish is a crime thriller from AMC. The six-episode series focuses on Giancarlo Esposito's Gracian "Gray" Parish, a proud father and owner of a New Orleans luxury car service who goes to war with a violent crime syndicate when his son is murdered. Alongside Esposito stars Zackary Momoh, Paula Malcomson, Skeet Ulrich, and Bradley Whitford.
What is the difference between a solar eclipse and a lunar eclipse?

It almost time! Millions of Americans across the country Monday are preparing to witness the once-in-a-lifetime total solar eclipse as it passes over portions of Mexico, the United States and Canada.
It's a sight to behold and people have now long been eagerly awaiting what will be their only chance until 2044 to witness totality, whereby the moon will completely block the sun's disc, ushering in uncharacteristic darkness.
That being said, many are curious on what makes the solar eclipse special and how is it different from a lunar eclipse.
The total solar eclipse is today: Get the latest forecast and everything you need to know
What is an eclipse?
An eclipse occurs when any celestial object like a moon or a planet passes between two other bodies, obscuring the view of objects like the sun, according to NASA .
What is a solar eclipse?
A total solar eclipse occurs when the moon comes in between the Earth and the sun, blocking its light from reaching our planet, leading to a period of darkness lasting several minutes. The resulting "totality," whereby observers can see the outermost layer of the sun's atmosphere, known as the corona, presents a spectacular sight for viewers and confuses animals – causing nocturnal creatures to stir and bird and insects to fall silent.
Partial eclipses, when some part of the sun remains visible, are the most common, making total eclipses a rare sight.
What is a lunar eclipse?
A total lunar eclipse occurs when the moon and the sun are on exact opposite sides of Earth. When this happens, Earth blocks the sunlight that normally reaches the moon. Instead of that sunlight hitting the moon’s surface, Earth's shadow falls on it.
Lunar eclipses are often also referred to the "blood moon" because when the Earth's shadow covers the moon, it often produces a red color. The coloration happens because a bit of reddish sunlight still reaches the moon's surface, even though it's in Earth's shadow.
Difference between lunar eclipse and solar eclipse
The major difference between the two eclipses is in the positioning of the sun, the moon and the Earth and the longevity of the phenomenon, according to NASA.
A lunar eclipse can last for a few hours, while a solar eclipse lasts only a few minutes. Solar eclipses also rarely occur, while lunar eclipses are comparatively more frequent. While at least two partial lunar eclipses happen every year, total lunar eclipses are still rare, says NASA.
Another major difference between the two is that for lunar eclipses, no special glasses or gizmos are needed to view the spectacle and one can directly stare at the moon. However, for solar eclipses, it is pertinent to wear proper viewing glasses and take the necessary safety precautions because the powerful rays of the sun can burn and damage your retinas.
Contributing: Eric Lagatta, Doyle Rice, USA TODAY

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A character analysis essay is a challenging type of essay students usually write for literature or English courses. In this article, we will explain the definition of character analysis and how to approach it. We will also touch on how to analyze characters and guide you through writing character analysis essays.
Introduction: Introduce the character you are writing about using a good hook to get your reader curious. Body: In this section, use a few paragraphs to describe the character's traits, their role, and the transformation they undergo (you could write one paragraph for each of the sections outlined above). Conclusion: Summarize your essay in ...
Character analysis essays do not have just one format. However, let me offer some advice that might act as a character analysis essay outline or 'checklist' of possible things you could discuss: 1. Start with the Simple Details. You can start a character analysis by providing a simple, clear description of who your character is.
A character analysis is a type of essay that requires you to analyze and evaluate the characteristics, traits, motivations, and decisions of a literary character. It involves closely examining such aspects as their personality, thoughts, behavior, and development. You should further explain how a character contributes to the overall meaning of ...
Some characters are static, meaning they stay the same throughout the story. Others are dynamic, meaning they undergo significant changes. Both are important and understanding this is a key part of analyzing characterization in literature. ... writing a character analysis essay. This task may seem daunting at first, but don't worry, we're in ...
Character analysis fosters critical thinking by encouraging readers to interpret evidence, form connections, and form informed opinions about the text. Key components of the character analysis essay include personality traits, character development, motivations and goals, relationships, and symbolism and archetypes.
Step 1: Choose Your Individual for Analysis. Character evaluation is the first step to a great analysis. The role or persona you choose for your analysis is crucial to its success. Primary characters are sometimes easier to write since they have well-defined personalities, and their motivations may be evident.
A character analysis is an exploration of the traits, personality, and characteristics of a character within a story. A character analysis typically examines the conflicts a character faces and ...
A character analysis is a kind of essay where you examine behaviors, motivations, and actions of characters. Also, a character analysis is an in-depth assignment that makes you think critically about one or more characters and make judgements after analyzing the text. In most cases, it is used for the analysis of literary works.
A character essay is a common literary writing assignment for college students pursuing English and Literature. The true success of doing a character analysis comes when you view the characters as though they are real people who act, feel, and live as we do. ... In some stories, characters have symbolic meanings that are authors ways of using ...
Here's a quick and simple definition: Characterization is the representation of the traits, motives, and psychology of a character in a narrative. Characterization may occur through direct description, in which the character's qualities are described by a narrator, another character, or by the character him or herself.
A character analysis essay is a type of essay in which the writer explains the main traits of the character. It is based on the analysis and breakdown of the chosen character. It could be based on a drama, novel, or even poetry. An essay analyzing a character is typically structured in the same way as other essays.
Minor — characters who appear in lesser episodes. Dynamic — the one who constantly changes. Static — the one who remains the same. The type defines the place of the character in the story and should be mentioned in your essay as well as the significant meaning or the symbolism of the character. Take your notes
Definition of a Character Analysis Essay. Among many different types of essays is a character analysis essay, a text that describes a particular character in a story. When writing this essay, students analyze relationships between characters in question and other characters, paying particular attention to their mannerisms. ...
There are several easy ways to count your characters: Use a Word Processor: Compose your entry in a word processor like MS Word or Apple Pages and click on the Word Count feature to how many characters your entry has. Use a Free Character Counter: Some websites offer a free character counter. All you need to do is copy-paste your text into ...
If the source includes three or more authors, use the abbreviation "et al." after the first author's name. Example: (Collins et al., 1997) As for MLA format: You can write the author's name in the sentence. Example: As Collins mentions in his essay<…>.
Table of contents. Step 1: Reading the text and identifying literary devices. Step 2: Coming up with a thesis. Step 3: Writing a title and introduction. Step 4: Writing the body of the essay. Step 5: Writing a conclusion. Other interesting articles.
A character is a person, animal, being, creature, or thing in a story. Writers use characters to perform the actions and speak dialogue, moving the story along a plot line. A story can have only one character (protagonist) and still be a complete story. This character's conflict may be an inner one (within him/herself), or a conflict with ...
Step 3: Outline Your Analysis. Create a structured plan for your character analysis essay. Begin with an engaging introduction, introducing the character and their significance. Proceed to discuss the character's development throughout the story and their interactions with other characters in the story.
Character traits examples: Bossy. Joyful. Daring. Charming. Character traits can be physical or mental/emotional, but what's perhaps most important to note is the difference between character traits and say, personality. In writing, imbuing characters with these qualities is a process called characterization.
Character Maps. Character maps are a helpful tool for students to use as they're reading, although they can also be used after completing a book. In this activity, students will create a character map of the characters in the story, paying close attention to the physical attributes and the traits of both major and minor characters.They can also provide detailed information regarding the ...
Definition of Narrative Essay. A narrative essay is a type of essay that has a single motif, or a central point, around which the whole narrative revolves. All incidents, happenings, and characters revolve around a single motif presented in the narrative. A narrative essay is similar to a simple five-paragraph essay, in that it has the same format.
PDF (0.6 MB) Tools. Share. Abstract: There is a rapidly growing literature on the link between climate change and poverty. This study reviews the existing literature on whether the poor are more exposed to climate shocks and whether they are more adversely affected. About two-thirds of the studies in our analyzed sample find that the poor are ...
A series about ways to take life off "hard mode," from changing careers to gaming the stock market, moving back home, or simply marrying wisely. Illustration: Celine Ka Wing Lau. In the summer, in the south of France, my husband and I like to play, rather badly, the lottery. We take long, scorching walks to the village — gratuitous beauty ...
Andrea Riseborough's Agnes was the most sympathetic character in The Regime, with the palace manager remaining loyal to her chancellor despite the various messes she created. That changed when the chancellor snatched Agnes' young son Oskar (Louie Mynett) away from her. With the nation crumbling, Agnes was offered the chance to flee with Oskar ...
Summary. Death is only temporary in Star Wars, thanks to Force Ghosts and clever plot twists. Characters like Princess Leia and Darth Maul have been brought back to life in surprising ways. The power of the Force can reverse death, as seen with Rey Skywalker and Ben Solo's Force dyad bond. Death is only ever a temporary inconvenience in Star ...
Parish episode 2 is out now, and here is a complete recap of the exciting new installment in the AMC series, breaking down that major character death from the end of the episode as well as eight other major reveals.Parish has been an exciting ride so far, with the first two episodes setting the stage for a complicated situation that Giancarlo Esposito's Gray Parish will have to find a way out of.
The major difference between the two eclipses is in the positioning of the sun, the moon and the Earth and the longevity of the phenomenon, according to NASA. A lunar eclipse can last for a few ...