What Is Comparative Analysis and How to Conduct It? (+ Examples)
Appinio Research · 30.10.2023 · 35min read

Have you ever faced a complex decision, wondering how to make the best choice among multiple options? In a world filled with data and possibilities, the art of comparative analysis holds the key to unlocking clarity amidst the chaos.
In this guide, we'll demystify the power of comparative analysis, revealing its practical applications, methodologies, and best practices. Whether you're a business leader, researcher, or simply someone seeking to make more informed decisions, join us as we explore the intricacies of comparative analysis and equip you with the tools to chart your course with confidence.

What is Comparative Analysis?
Comparative analysis is a systematic approach used to evaluate and compare two or more entities, variables, or options to identify similarities, differences, and patterns. It involves assessing the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats associated with each entity or option to make informed decisions.
The primary purpose of comparative analysis is to provide a structured framework for decision-making by:
- Facilitating Informed Choices: Comparative analysis equips decision-makers with data-driven insights, enabling them to make well-informed choices among multiple options.
- Identifying Trends and Patterns: It helps identify recurring trends, patterns, and relationships among entities or variables, shedding light on underlying factors influencing outcomes.
- Supporting Problem Solving: Comparative analysis aids in solving complex problems by systematically breaking them down into manageable components and evaluating potential solutions.
- Enhancing Transparency: By comparing multiple options, comparative analysis promotes transparency in decision-making processes, allowing stakeholders to understand the rationale behind choices.
- Mitigating Risks : It helps assess the risks associated with each option, allowing organizations to develop risk mitigation strategies and make risk-aware decisions.
- Optimizing Resource Allocation: Comparative analysis assists in allocating resources efficiently by identifying areas where resources can be optimized for maximum impact.
- Driving Continuous Improvement: By comparing current performance with historical data or benchmarks, organizations can identify improvement areas and implement growth strategies.
Importance of Comparative Analysis in Decision-Making
- Data-Driven Decision-Making: Comparative analysis relies on empirical data and objective evaluation, reducing the influence of biases and subjective judgments in decision-making. It ensures decisions are based on facts and evidence.
- Objective Assessment: It provides an objective and structured framework for evaluating options, allowing decision-makers to focus on key criteria and avoid making decisions solely based on intuition or preferences.
- Risk Assessment: Comparative analysis helps assess and quantify risks associated with different options. This risk awareness enables organizations to make proactive risk management decisions.
- Prioritization: By ranking options based on predefined criteria, comparative analysis enables decision-makers to prioritize actions or investments, directing resources to areas with the most significant impact.
- Strategic Planning: It is integral to strategic planning, helping organizations align their decisions with overarching goals and objectives. Comparative analysis ensures decisions are consistent with long-term strategies.
- Resource Allocation: Organizations often have limited resources. Comparative analysis assists in allocating these resources effectively, ensuring they are directed toward initiatives with the highest potential returns.
- Continuous Improvement: Comparative analysis supports a culture of continuous improvement by identifying areas for enhancement and guiding iterative decision-making processes.
- Stakeholder Communication: It enhances transparency in decision-making, making it easier to communicate decisions to stakeholders. Stakeholders can better understand the rationale behind choices when supported by comparative analysis.
- Competitive Advantage: In business and competitive environments , comparative analysis can provide a competitive edge by identifying opportunities to outperform competitors or address weaknesses.
- Informed Innovation: When evaluating new products , technologies, or strategies, comparative analysis guides the selection of the most promising options, reducing the risk of investing in unsuccessful ventures.
In summary, comparative analysis is a valuable tool that empowers decision-makers across various domains to make informed, data-driven choices, manage risks, allocate resources effectively, and drive continuous improvement. Its structured approach enhances decision quality and transparency, contributing to the success and competitiveness of organizations and research endeavors.
How to Prepare for Comparative Analysis?
1. define objectives and scope.
Before you begin your comparative analysis, clearly defining your objectives and the scope of your analysis is essential. This step lays the foundation for the entire process. Here's how to approach it:
- Identify Your Goals: Start by asking yourself what you aim to achieve with your comparative analysis. Are you trying to choose between two products for your business? Are you evaluating potential investment opportunities? Knowing your objectives will help you stay focused throughout the analysis.
- Define Scope: Determine the boundaries of your comparison. What will you include, and what will you exclude? For example, if you're analyzing market entry strategies for a new product, specify whether you're looking at a specific geographic region or a particular target audience.
- Stakeholder Alignment: Ensure that all stakeholders involved in the analysis understand and agree on the objectives and scope. This alignment will prevent misunderstandings and ensure the analysis meets everyone's expectations.
2. Gather Relevant Data and Information
The quality of your comparative analysis heavily depends on the data and information you gather. Here's how to approach this crucial step:
- Data Sources: Identify where you'll obtain the necessary data. Will you rely on primary sources , such as surveys and interviews, to collect original data? Or will you use secondary sources, like published research and industry reports, to access existing data? Consider the advantages and disadvantages of each source.
- Data Collection Plan: Develop a plan for collecting data. This should include details about the methods you'll use, the timeline for data collection, and who will be responsible for gathering the data.
- Data Relevance: Ensure that the data you collect is directly relevant to your objectives. Irrelevant or extraneous data can lead to confusion and distract from the core analysis.
3. Select Appropriate Criteria for Comparison
Choosing the right criteria for comparison is critical to a successful comparative analysis. Here's how to go about it:
- Relevance to Objectives: Your chosen criteria should align closely with your analysis objectives. For example, if you're comparing job candidates, your criteria might include skills, experience, and cultural fit.
- Measurability: Consider whether you can quantify the criteria. Measurable criteria are easier to analyze. If you're comparing marketing campaigns, you might measure criteria like click-through rates, conversion rates, and return on investment.
- Weighting Criteria : Not all criteria are equally important. You'll need to assign weights to each criterion based on its relative importance. Weighting helps ensure that the most critical factors have a more significant impact on the final decision.
4. Establish a Clear Framework
Once you have your objectives, data, and criteria in place, it's time to establish a clear framework for your comparative analysis. This framework will guide your process and ensure consistency. Here's how to do it:
- Comparative Matrix: Consider using a comparative matrix or spreadsheet to organize your data. Each row in the matrix represents an option or entity you're comparing, and each column corresponds to a criterion. This visual representation makes it easy to compare and contrast data.
- Timeline: Determine the time frame for your analysis. Is it a one-time comparison, or will you conduct ongoing analyses? Having a defined timeline helps you manage the analysis process efficiently.
- Define Metrics: Specify the metrics or scoring system you'll use to evaluate each criterion. For example, if you're comparing potential office locations, you might use a scoring system from 1 to 5 for factors like cost, accessibility, and amenities.
With your objectives, data, criteria, and framework established, you're ready to move on to the next phase of comparative analysis: data collection and organization.
Comparative Analysis Data Collection
Data collection and organization are critical steps in the comparative analysis process. We'll explore how to gather and structure the data you need for a successful analysis.
1. Utilize Primary Data Sources
Primary data sources involve gathering original data directly from the source. This approach offers unique advantages, allowing you to tailor your data collection to your specific research needs.
Some popular primary data sources include:
- Surveys and Questionnaires: Design surveys or questionnaires and distribute them to collect specific information from individuals or groups. This method is ideal for obtaining firsthand insights, such as customer preferences or employee feedback.
- Interviews: Conduct structured interviews with relevant stakeholders or experts. Interviews provide an opportunity to delve deeper into subjects and gather qualitative data, making them valuable for in-depth analysis.
- Observations: Directly observe and record data from real-world events or settings. Observational data can be instrumental in fields like anthropology, ethnography, and environmental studies.
- Experiments: In controlled environments, experiments allow you to manipulate variables and measure their effects. This method is common in scientific research and product testing.
When using primary data sources, consider factors like sample size, survey design, and data collection methods to ensure the reliability and validity of your data.
2. Harness Secondary Data Sources
Secondary data sources involve using existing data collected by others. These sources can provide a wealth of information and save time and resources compared to primary data collection.
Here are common types of secondary data sources:
- Public Records: Government publications, census data, and official reports offer valuable information on demographics, economic trends, and public policies. They are often free and readily accessible.
- Academic Journals: Scholarly articles provide in-depth research findings across various disciplines. They are helpful for accessing peer-reviewed studies and staying current with academic discourse.
- Industry Reports: Industry-specific reports and market research publications offer insights into market trends, consumer behavior, and competitive landscapes. They are essential for businesses making strategic decisions.
- Online Databases: Online platforms like Statista , PubMed , and Google Scholar provide a vast repository of data and research articles. They offer search capabilities and access to a wide range of data sets.
When using secondary data sources, critically assess the credibility, relevance, and timeliness of the data. Ensure that it aligns with your research objectives.
3. Ensure and Validate Data Quality
Data quality is paramount in comparative analysis. Poor-quality data can lead to inaccurate conclusions and flawed decision-making. Here's how to ensure data validation and reliability:
- Cross-Verification: Whenever possible, cross-verify data from multiple sources. Consistency among different sources enhances the reliability of the data.
- Sample Size: Ensure that your data sample size is statistically significant for meaningful analysis. A small sample may not accurately represent the population.
- Data Integrity: Check for data integrity issues, such as missing values, outliers, or duplicate entries. Address these issues before analysis to maintain data quality.
- Data Source Reliability: Assess the reliability and credibility of the data sources themselves. Consider factors like the reputation of the institution or organization providing the data.
4. Organize Data Effectively
Structuring your data for comparison is a critical step in the analysis process. Organized data makes it easier to draw insights and make informed decisions. Here's how to structure data effectively:
- Data Cleaning: Before analysis, clean your data to remove inconsistencies, errors, and irrelevant information. Data cleaning may involve data transformation, imputation of missing values, and removing outliers.
- Normalization: Standardize data to ensure fair comparisons. Normalization adjusts data to a standard scale, making comparing variables with different units or ranges possible.
- Variable Labeling: Clearly label variables and data points for easy identification. Proper labeling enhances the transparency and understandability of your analysis.
- Data Organization: Organize data into a format that suits your analysis methods. For quantitative analysis, this might mean creating a matrix, while qualitative analysis may involve categorizing data into themes.
By paying careful attention to data collection, validation, and organization, you'll set the stage for a robust and insightful comparative analysis. Next, we'll explore various methodologies you can employ in your analysis, ranging from qualitative approaches to quantitative methods and examples.
Comparative Analysis Methods
When it comes to comparative analysis, various methodologies are available, each suited to different research goals and data types. In this section, we'll explore five prominent methodologies in detail.
Qualitative Comparative Analysis (QCA)
Qualitative Comparative Analysis (QCA) is a methodology often used when dealing with complex, non-linear relationships among variables. It seeks to identify patterns and configurations among factors that lead to specific outcomes.
- Case-by-Case Analysis: QCA involves evaluating individual cases (e.g., organizations, regions, or events) rather than analyzing aggregate data. Each case's unique characteristics are considered.
- Boolean Logic: QCA employs Boolean algebra to analyze data. Variables are categorized as either present or absent, allowing for the examination of different combinations and logical relationships.
- Necessary and Sufficient Conditions: QCA aims to identify necessary and sufficient conditions for a specific outcome to occur. It helps answer questions like, "What conditions are necessary for a successful product launch?"
- Fuzzy Set Theory: In some cases, QCA may use fuzzy set theory to account for degrees of membership in a category, allowing for more nuanced analysis.
QCA is particularly useful in fields such as sociology, political science, and organizational studies, where understanding complex interactions is essential.
Quantitative Comparative Analysis
Quantitative Comparative Analysis involves the use of numerical data and statistical techniques to compare and analyze variables. It's suitable for situations where data is quantitative, and relationships can be expressed numerically.
- Statistical Tools: Quantitative comparative analysis relies on statistical methods like regression analysis, correlation, and hypothesis testing. These tools help identify relationships, dependencies, and trends within datasets.
- Data Measurement: Ensure that variables are measured consistently using appropriate scales (e.g., ordinal, interval, ratio) for meaningful analysis. Variables may include numerical values like revenue, customer satisfaction scores, or product performance metrics.
- Data Visualization: Create visual representations of data using charts, graphs, and plots. Visualization aids in understanding complex relationships and presenting findings effectively.
- Statistical Significance: Assess the statistical significance of relationships. Statistical significance indicates whether observed differences or relationships are likely to be real rather than due to chance.
Quantitative comparative analysis is commonly applied in economics, social sciences, and market research to draw empirical conclusions from numerical data.
Case Studies
Case studies involve in-depth examinations of specific instances or cases to gain insights into real-world scenarios. Comparative case studies allow researchers to compare and contrast multiple cases to identify patterns, differences, and lessons.
- Narrative Analysis: Case studies often involve narrative analysis, where researchers construct detailed narratives of each case, including context, events, and outcomes.
- Contextual Understanding: In comparative case studies, it's crucial to consider the context within which each case operates. Understanding the context helps interpret findings accurately.
- Cross-Case Analysis: Researchers conduct cross-case analysis to identify commonalities and differences across cases. This process can lead to the discovery of factors that influence outcomes.
- Triangulation: To enhance the validity of findings, researchers may use multiple data sources and methods to triangulate information and ensure reliability.
Case studies are prevalent in fields like psychology, business, and sociology, where deep insights into specific situations are valuable.
SWOT Analysis
SWOT Analysis is a strategic tool used to assess the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats associated with a particular entity or situation. While it's commonly used in business, it can be adapted for various comparative analyses.
- Internal and External Factors: SWOT Analysis examines both internal factors (Strengths and Weaknesses), such as organizational capabilities, and external factors (Opportunities and Threats), such as market conditions and competition.
- Strategic Planning: The insights from SWOT Analysis inform strategic decision-making. By identifying strengths and opportunities, organizations can leverage their advantages. Likewise, addressing weaknesses and threats helps mitigate risks.
- Visual Representation: SWOT Analysis is often presented as a matrix or a 2x2 grid, making it visually accessible and easy to communicate to stakeholders.
- Continuous Monitoring: SWOT Analysis is not a one-time exercise. Organizations use it periodically to adapt to changing circumstances and make informed decisions.
SWOT Analysis is versatile and can be applied in business, healthcare, education, and any context where a structured assessment of factors is needed.
Benchmarking
Benchmarking involves comparing an entity's performance, processes, or practices to those of industry leaders or best-in-class organizations. It's a powerful tool for continuous improvement and competitive analysis.
- Identify Performance Gaps: Benchmarking helps identify areas where an entity lags behind its peers or industry standards. These performance gaps highlight opportunities for improvement.
- Data Collection: Gather data on key performance metrics from both internal and external sources. This data collection phase is crucial for meaningful comparisons.
- Comparative Analysis: Compare your organization's performance data with that of benchmark organizations. This analysis can reveal where you excel and where adjustments are needed.
- Continuous Improvement: Benchmarking is a dynamic process that encourages continuous improvement. Organizations use benchmarking findings to set performance goals and refine their strategies.
Benchmarking is widely used in business, manufacturing, healthcare, and customer service to drive excellence and competitiveness.
Each of these methodologies brings a unique perspective to comparative analysis, allowing you to choose the one that best aligns with your research objectives and the nature of your data. The choice between qualitative and quantitative methods, or a combination of both, depends on the complexity of the analysis and the questions you seek to answer.
How to Conduct Comparative Analysis?
Once you've prepared your data and chosen an appropriate methodology, it's time to dive into the process of conducting a comparative analysis. We will guide you through the essential steps to extract meaningful insights from your data.
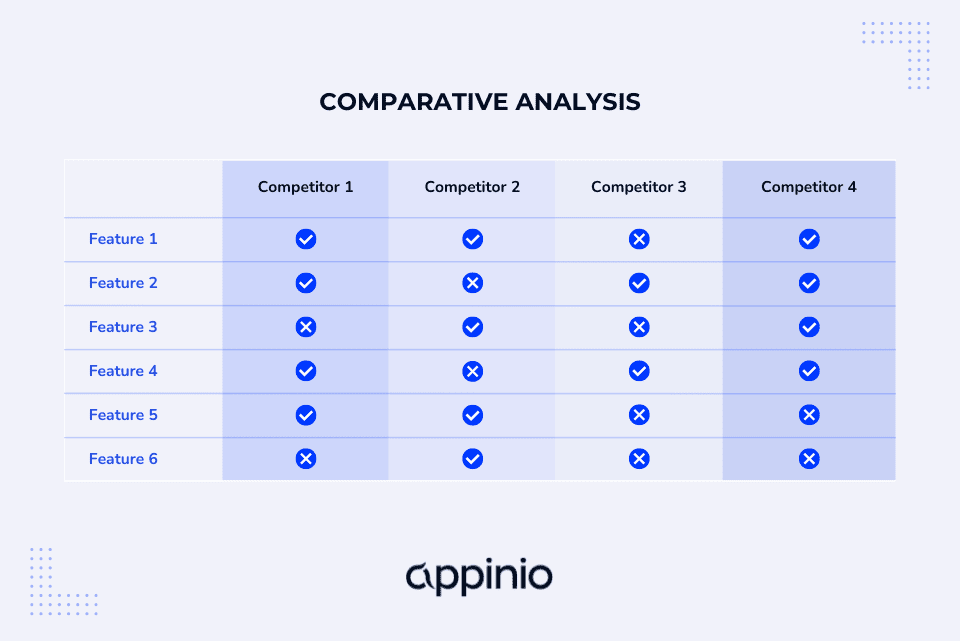
1. Identify Key Variables and Metrics
Identifying key variables and metrics is the first crucial step in conducting a comparative analysis. These are the factors or indicators you'll use to assess and compare your options.
- Relevance to Objectives: Ensure the chosen variables and metrics align closely with your analysis objectives. When comparing marketing strategies, relevant metrics might include customer acquisition cost, conversion rate, and retention.
- Quantitative vs. Qualitative : Decide whether your analysis will focus on quantitative data (numbers) or qualitative data (descriptive information). In some cases, a combination of both may be appropriate.
- Data Availability: Consider the availability of data. Ensure you can access reliable and up-to-date data for all selected variables and metrics.
- KPIs: Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are often used as the primary metrics in comparative analysis. These are metrics that directly relate to your goals and objectives.
2. Visualize Data for Clarity
Data visualization techniques play a vital role in making complex information more accessible and understandable. Effective data visualization allows you to convey insights and patterns to stakeholders. Consider the following approaches:
- Charts and Graphs: Use various types of charts, such as bar charts, line graphs, and pie charts, to represent data. For example, a line graph can illustrate trends over time, while a bar chart can compare values across categories.
- Heatmaps: Heatmaps are particularly useful for visualizing large datasets and identifying patterns through color-coding. They can reveal correlations, concentrations, and outliers.
- Scatter Plots: Scatter plots help visualize relationships between two variables. They are especially useful for identifying trends, clusters, or outliers.
- Dashboards: Create interactive dashboards that allow users to explore data and customize views. Dashboards are valuable for ongoing analysis and reporting.
- Infographics: For presentations and reports, consider using infographics to summarize key findings in a visually engaging format.
Effective data visualization not only enhances understanding but also aids in decision-making by providing clear insights at a glance.
3. Establish Clear Comparative Frameworks
A well-structured comparative framework provides a systematic approach to your analysis. It ensures consistency and enables you to make meaningful comparisons. Here's how to create one:
- Comparison Matrices: Consider using matrices or spreadsheets to organize your data. Each row represents an option or entity, and each column corresponds to a variable or metric. This matrix format allows for side-by-side comparisons.
- Decision Trees: In complex decision-making scenarios, decision trees help map out possible outcomes based on different criteria and variables. They visualize the decision-making process.
- Scenario Analysis: Explore different scenarios by altering variables or criteria to understand how changes impact outcomes. Scenario analysis is valuable for risk assessment and planning.
- Checklists: Develop checklists or scoring sheets to systematically evaluate each option against predefined criteria. Checklists ensure that no essential factors are overlooked.
A well-structured comparative framework simplifies the analysis process, making it easier to draw meaningful conclusions and make informed decisions.
4. Evaluate and Score Criteria
Evaluating and scoring criteria is a critical step in comparative analysis, as it quantifies the performance of each option against the chosen criteria.
- Scoring System: Define a scoring system that assigns values to each criterion for every option. Common scoring systems include numerical scales, percentage scores, or qualitative ratings (e.g., high, medium, low).
- Consistency: Ensure consistency in scoring by defining clear guidelines for each score. Provide examples or descriptions to help evaluators understand what each score represents.
- Data Collection: Collect data or information relevant to each criterion for all options. This may involve quantitative data (e.g., sales figures) or qualitative data (e.g., customer feedback).
- Aggregation: Aggregate the scores for each option to obtain an overall evaluation. This can be done by summing the individual criterion scores or applying weighted averages.
- Normalization: If your criteria have different measurement scales or units, consider normalizing the scores to create a level playing field for comparison.
5. Assign Importance to Criteria
Not all criteria are equally important in a comparative analysis. Weighting criteria allows you to reflect their relative significance in the final decision-making process.
- Relative Importance: Assess the importance of each criterion in achieving your objectives. Criteria directly aligned with your goals may receive higher weights.
- Weighting Methods: Choose a weighting method that suits your analysis. Common methods include expert judgment, analytic hierarchy process (AHP), or data-driven approaches based on historical performance.
- Impact Analysis: Consider how changes in the weights assigned to criteria would affect the final outcome. This sensitivity analysis helps you understand the robustness of your decisions.
- Stakeholder Input: Involve relevant stakeholders or decision-makers in the weighting process. Their input can provide valuable insights and ensure alignment with organizational goals.
- Transparency: Clearly document the rationale behind the assigned weights to maintain transparency in your analysis.
By weighting criteria, you ensure that the most critical factors have a more significant influence on the final evaluation, aligning the analysis more closely with your objectives and priorities.
With these steps in place, you're well-prepared to conduct a comprehensive comparative analysis. The next phase involves interpreting your findings, drawing conclusions, and making informed decisions based on the insights you've gained.
Comparative Analysis Interpretation
Interpreting the results of your comparative analysis is a crucial phase that transforms data into actionable insights. We'll delve into various aspects of interpretation and how to make sense of your findings.
- Contextual Understanding: Before diving into the data, consider the broader context of your analysis. Understand the industry trends, market conditions, and any external factors that may have influenced your results.
- Drawing Conclusions: Summarize your findings clearly and concisely. Identify trends, patterns, and significant differences among the options or variables you've compared.
- Quantitative vs. Qualitative Analysis: Depending on the nature of your data and analysis, you may need to balance both quantitative and qualitative interpretations. Qualitative insights can provide context and nuance to quantitative findings.
- Comparative Visualization: Visual aids such as charts, graphs, and tables can help convey your conclusions effectively. Choose visual representations that align with the nature of your data and the key points you want to emphasize.
- Outliers and Anomalies: Identify and explain any outliers or anomalies in your data. Understanding these exceptions can provide valuable insights into unusual cases or factors affecting your analysis.
- Cross-Validation: Validate your conclusions by comparing them with external benchmarks, industry standards, or expert opinions. Cross-validation helps ensure the reliability of your findings.
- Implications for Decision-Making: Discuss how your analysis informs decision-making. Clearly articulate the practical implications of your findings and their relevance to your initial objectives.
- Actionable Insights: Emphasize actionable insights that can guide future strategies, policies, or actions. Make recommendations based on your analysis, highlighting the steps needed to capitalize on strengths or address weaknesses.
- Continuous Improvement: Encourage a culture of continuous improvement by using your analysis as a feedback mechanism. Suggest ways to monitor and adapt strategies over time based on evolving circumstances.
Comparative Analysis Applications
Comparative analysis is a versatile methodology that finds application in various fields and scenarios. Let's explore some of the most common and impactful applications.
Business Decision-Making
Comparative analysis is widely employed in business to inform strategic decisions and drive success. Key applications include:
Market Research and Competitive Analysis
- Objective: To assess market opportunities and evaluate competitors.
- Methods: Analyzing market trends, customer preferences, competitor strengths and weaknesses, and market share.
- Outcome: Informed product development, pricing strategies, and market entry decisions.
Product Comparison and Benchmarking
- Objective: To compare the performance and features of products or services.
- Methods: Evaluating product specifications, customer reviews, and pricing.
- Outcome: Identifying strengths and weaknesses, improving product quality, and setting competitive pricing.
Financial Analysis
- Objective: To evaluate financial performance and make investment decisions.
- Methods: Comparing financial statements, ratios, and performance indicators of companies.
- Outcome: Informed investment choices, risk assessment, and portfolio management.
Healthcare and Medical Research
In the healthcare and medical research fields, comparative analysis is instrumental in understanding diseases, treatment options, and healthcare systems.
Clinical Trials and Drug Development opment
- Objective: To compare the effectiveness of different treatments or drugs.
- Methods: Analyzing clinical trial data, patient outcomes, and side effects.
- Outcome: Informed decisions about drug approvals, treatment protocols, and patient care.
Health Outcomes Research
- Objective: To assess the impact of healthcare interventions.
- Methods: Comparing patient health outcomes before and after treatment or between different treatment approaches.
- Outcome: Improved healthcare guidelines, cost-effectiveness analysis, and patient care plans.
Healthcare Systems Evaluation
- Objective: To assess the performance of healthcare systems.
- Methods: Comparing healthcare delivery models, patient satisfaction, and healthcare costs.
- Outcome: Informed healthcare policy decisions, resource allocation, and system improvements.
Social Sciences and Policy Analysis
Comparative analysis is a fundamental tool in social sciences and policy analysis, aiding in understanding complex societal issues.
Educational Research
- Objective: To compare educational systems and practices.
- Methods: Analyzing student performance, curriculum effectiveness, and teaching methods.
- Outcome: Informed educational policies, curriculum development, and school improvement strategies.
Political Science
- Objective: To study political systems, elections, and governance.
- Methods: Comparing election outcomes, policy impacts, and government structures.
- Outcome: Insights into political behavior, policy effectiveness, and governance reforms.
Social Welfare and Poverty Analysis
- Objective: To evaluate the impact of social programs and policies.
- Methods: Comparing the well-being of individuals or communities with and without access to social assistance.
- Outcome: Informed policymaking, poverty reduction strategies, and social program improvements.
Environmental Science and Sustainability
Comparative analysis plays a pivotal role in understanding environmental issues and promoting sustainability.
Environmental Impact Assessment
- Objective: To assess the environmental consequences of projects or policies.
- Methods: Comparing ecological data, resource use, and pollution levels.
- Outcome: Informed environmental mitigation strategies, sustainable development plans, and regulatory decisions.
Climate Change Analysis
- Objective: To study climate patterns and their impacts.
- Methods: Comparing historical climate data, temperature trends, and greenhouse gas emissions.
- Outcome: Insights into climate change causes, adaptation strategies, and policy recommendations.
Ecosystem Health Assessment
- Objective: To evaluate the health and resilience of ecosystems.
- Methods: Comparing biodiversity, habitat conditions, and ecosystem services.
- Outcome: Conservation efforts, restoration plans, and ecological sustainability measures.
Technology and Innovation
Comparative analysis is crucial in the fast-paced world of technology and innovation.
Product Development and Innovation
- Objective: To assess the competitiveness and innovation potential of products or technologies.
- Methods: Comparing research and development investments, technology features, and market demand.
- Outcome: Informed innovation strategies, product roadmaps, and patent decisions.
User Experience and Usability Testing
- Objective: To evaluate the user-friendliness of software applications or digital products.
- Methods: Comparing user feedback, usability metrics, and user interface designs.
- Outcome: Improved user experiences, interface redesigns, and product enhancements.
Technology Adoption and Market Entry
- Objective: To analyze market readiness and risks for new technologies.
- Methods: Comparing market conditions, regulatory landscapes, and potential barriers.
- Outcome: Informed market entry strategies, risk assessments, and investment decisions.
These diverse applications of comparative analysis highlight its flexibility and importance in decision-making across various domains. Whether in business, healthcare, social sciences, environmental studies, or technology, comparative analysis empowers researchers and decision-makers to make informed choices and drive positive outcomes.
Comparative Analysis Best Practices
Successful comparative analysis relies on following best practices and avoiding common pitfalls. Implementing these practices enhances the effectiveness and reliability of your analysis.
- Clearly Defined Objectives: Start with well-defined objectives that outline what you aim to achieve through the analysis. Clear objectives provide focus and direction.
- Data Quality Assurance: Ensure data quality by validating, cleaning, and normalizing your data. Poor-quality data can lead to inaccurate conclusions.
- Transparent Methodologies: Clearly explain the methodologies and techniques you've used for analysis. Transparency builds trust and allows others to assess the validity of your approach.
- Consistent Criteria: Maintain consistency in your criteria and metrics across all options or variables. Inconsistent criteria can lead to biased results.
- Sensitivity Analysis: Conduct sensitivity analysis by varying key parameters, such as weights or assumptions, to assess the robustness of your conclusions.
- Stakeholder Involvement: Involve relevant stakeholders throughout the analysis process. Their input can provide valuable perspectives and ensure alignment with organizational goals.
- Critical Evaluation of Assumptions: Identify and critically evaluate any assumptions made during the analysis. Assumptions should be explicit and justifiable.
- Holistic View: Take a holistic view of the analysis by considering both short-term and long-term implications. Avoid focusing solely on immediate outcomes.
- Documentation: Maintain thorough documentation of your analysis, including data sources, calculations, and decision criteria. Documentation supports transparency and facilitates reproducibility.
- Continuous Learning: Stay updated with the latest analytical techniques, tools, and industry trends. Continuous learning helps you adapt your analysis to changing circumstances.
- Peer Review: Seek peer review or expert feedback on your analysis. External perspectives can identify blind spots and enhance the quality of your work.
- Ethical Considerations: Address ethical considerations, such as privacy and data protection, especially when dealing with sensitive or personal data.
By adhering to these best practices, you'll not only improve the rigor of your comparative analysis but also ensure that your findings are reliable, actionable, and aligned with your objectives.
Comparative Analysis Examples
To illustrate the practical application and benefits of comparative analysis, let's explore several real-world examples across different domains. These examples showcase how organizations and researchers leverage comparative analysis to make informed decisions, solve complex problems, and drive improvements:
Retail Industry - Price Competitiveness Analysis
Objective: A retail chain aims to assess its price competitiveness against competitors in the same market.
Methodology:
- Collect pricing data for a range of products offered by the retail chain and its competitors.
- Organize the data into a comparative framework, categorizing products by type and price range.
- Calculate price differentials, averages, and percentiles for each product category.
- Analyze the findings to identify areas where the retail chain's prices are higher or lower than competitors.
Outcome: The analysis reveals that the retail chain's prices are consistently lower in certain product categories but higher in others. This insight informs pricing strategies, allowing the retailer to adjust prices to remain competitive in the market.
Healthcare - Comparative Effectiveness Research
Objective: Researchers aim to compare the effectiveness of two different treatment methods for a specific medical condition.
- Recruit patients with the medical condition and randomly assign them to two treatment groups.
- Collect data on treatment outcomes, including symptom relief, side effects, and recovery times.
- Analyze the data using statistical methods to compare the treatment groups.
- Consider factors like patient demographics and baseline health status as potential confounding variables.
Outcome: The comparative analysis reveals that one treatment method is statistically more effective than the other in relieving symptoms and has fewer side effects. This information guides medical professionals in recommending the more effective treatment to patients.
Environmental Science - Carbon Emission Analysis
Objective: An environmental organization seeks to compare carbon emissions from various transportation modes in a metropolitan area.
- Collect data on the number of vehicles, their types (e.g., cars, buses, bicycles), and fuel consumption for each mode of transportation.
- Calculate the total carbon emissions for each mode based on fuel consumption and emission factors.
- Create visualizations such as bar charts and pie charts to represent the emissions from each transportation mode.
- Consider factors like travel distance, occupancy rates, and the availability of alternative fuels.
Outcome: The comparative analysis reveals that public transportation generates significantly lower carbon emissions per passenger mile compared to individual car travel. This information supports advocacy for increased public transit usage to reduce carbon footprint.
Technology Industry - Feature Comparison for Software Development Tools
Objective: A software development team needs to choose the most suitable development tool for an upcoming project.
- Create a list of essential features and capabilities required for the project.
- Research and compile information on available development tools in the market.
- Develop a comparative matrix or scoring system to evaluate each tool's features against the project requirements.
- Assign weights to features based on their importance to the project.
Outcome: The comparative analysis highlights that Tool A excels in essential features critical to the project, such as version control integration and debugging capabilities. The development team selects Tool A as the preferred choice for the project.
Educational Research - Comparative Study of Teaching Methods
Objective: A school district aims to improve student performance by comparing the effectiveness of traditional classroom teaching with online learning.
- Randomly assign students to two groups: one taught using traditional methods and the other through online courses.
- Administer pre- and post-course assessments to measure knowledge gain.
- Collect feedback from students and teachers on the learning experiences.
- Analyze assessment scores and feedback to compare the effectiveness and satisfaction levels of both teaching methods.
Outcome: The comparative analysis reveals that online learning leads to similar knowledge gains as traditional classroom teaching. However, students report higher satisfaction and flexibility with the online approach. The school district considers incorporating online elements into its curriculum.
These examples illustrate the diverse applications of comparative analysis across industries and research domains. Whether optimizing pricing strategies in retail, evaluating treatment effectiveness in healthcare, assessing environmental impacts, choosing the right software tool, or improving educational methods, comparative analysis empowers decision-makers with valuable insights for informed choices and positive outcomes.
Comparative analysis is your compass in the world of decision-making. It helps you see the bigger picture, spot opportunities, and navigate challenges. By defining your objectives, gathering data, applying methodologies, and following best practices, you can harness the power of Comparative Analysis to make informed choices and drive positive outcomes.
Remember, Comparative analysis is not just a tool; it's a mindset that empowers you to transform data into insights and uncertainty into clarity. So, whether you're steering a business, conducting research, or facing life's choices, embrace Comparative Analysis as your trusted guide on the journey to better decisions. With it, you can chart your course, make impactful choices, and set sail toward success.
How to Conduct Comparative Analysis in Minutes?
Are you ready to revolutionize your approach to market research and comparative analysis? Appinio , a real-time market research platform, empowers you to harness the power of real-time consumer insights for swift, data-driven decisions. Here's why you should choose Appinio:
- Speedy Insights: Get from questions to insights in minutes, enabling you to conduct comparative analysis without delay.
- User-Friendly: No need for a PhD in research – our intuitive platform is designed for everyone, making it easy to collect and analyze data.
- Global Reach: With access to over 90 countries and the ability to define your target group from 1200+ characteristics, Appinio provides a worldwide perspective for your comparative analysis
Join the loop 💌
Be the first to hear about new updates, product news, and data insights. We'll send it all straight to your inbox.
Get the latest market research news straight to your inbox! 💌
Wait, there's more

05.04.2024 | 27min read
What is Field Research? Definition, Types, Methods, Examples

03.04.2024 | 29min read
What is Cluster Sampling? Definition, Methods, Examples

01.04.2024 | 26min read
Cross-Tabulation Analysis: A Full Guide (+ Examples)
Join thousands of product people at Insight Out Conf on April 11. Register free.
Insights hub solutions
Analyze data
Uncover deep customer insights with fast, powerful features, store insights, curate and manage insights in one searchable platform, scale research, unlock the potential of customer insights at enterprise scale.
Featured reads

Inspiration
Three things to look forward to at Insight Out
Tips and tricks
Make magic with your customer data in Dovetail

Four ways Dovetail helps Product Managers master continuous product discovery
Events and videos
© Dovetail Research Pty. Ltd.
What is comparative analysis? A complete guide
Last updated
18 April 2023
Reviewed by
Jean Kaluza
Comparative analysis is a valuable tool for acquiring deep insights into your organization’s processes, products, and services so you can continuously improve them.
Similarly, if you want to streamline, price appropriately, and ultimately be a market leader, you’ll likely need to draw on comparative analyses quite often.
When faced with multiple options or solutions to a given problem, a thorough comparative analysis can help you compare and contrast your options and make a clear, informed decision.
If you want to get up to speed on conducting a comparative analysis or need a refresher, here’s your guide.
Make comparative analysis less tedious
Dovetail streamlines comparative analysis to help you uncover and share actionable insights
- What exactly is comparative analysis?
A comparative analysis is a side-by-side comparison that systematically compares two or more things to pinpoint their similarities and differences. The focus of the investigation might be conceptual—a particular problem, idea, or theory—or perhaps something more tangible, like two different data sets.
For instance, you could use comparative analysis to investigate how your product features measure up to the competition.
After a successful comparative analysis, you should be able to identify strengths and weaknesses and clearly understand which product is more effective.
You could also use comparative analysis to examine different methods of producing that product and determine which way is most efficient and profitable.
The potential applications for using comparative analysis in everyday business are almost unlimited. That said, a comparative analysis is most commonly used to examine
Emerging trends and opportunities (new technologies, marketing)
Competitor strategies
Financial health
Effects of trends on a target audience
- Why is comparative analysis so important?
Comparative analysis can help narrow your focus so your business pursues the most meaningful opportunities rather than attempting dozens of improvements simultaneously.
A comparative approach also helps frame up data to illuminate interrelationships. For example, comparative research might reveal nuanced relationships or critical contexts behind specific processes or dependencies that wouldn’t be well-understood without the research.
For instance, if your business compares the cost of producing several existing products relative to which ones have historically sold well, that should provide helpful information once you’re ready to look at developing new products or features.
- Comparative vs. competitive analysis—what’s the difference?
Comparative analysis is generally divided into three subtypes, using quantitative or qualitative data and then extending the findings to a larger group. These include
Pattern analysis —identifying patterns or recurrences of trends and behavior across large data sets.
Data filtering —analyzing large data sets to extract an underlying subset of information. It may involve rearranging, excluding, and apportioning comparative data to fit different criteria.
Decision tree —flowcharting to visually map and assess potential outcomes, costs, and consequences.
In contrast, competitive analysis is a type of comparative analysis in which you deeply research one or more of your industry competitors. In this case, you’re using qualitative research to explore what the competition is up to across one or more dimensions.
For example
Service delivery —metrics like the Net Promoter Scores indicate customer satisfaction levels.
Market position — the share of the market that the competition has captured.
Brand reputation —how well-known or recognized your competitors are within their target market.
- Tips for optimizing your comparative analysis
Conduct original research
Thorough, independent research is a significant asset when doing comparative analysis. It provides evidence to support your findings and may present a perspective or angle not considered previously.
Make analysis routine
To get the maximum benefit from comparative research, make it a regular practice, and establish a cadence you can realistically stick to. Some business areas you could plan to analyze regularly include:
Profitability
Competition
Experiment with controlled and uncontrolled variables
In addition to simply comparing and contrasting, explore how different variables might affect your outcomes.
For example, a controllable variable would be offering a seasonal feature like a shopping bot to assist in holiday shopping or raising or lowering the selling price of a product.
Uncontrollable variables include weather, changing regulations, the current political climate, or global pandemics.
Put equal effort into each point of comparison
Most people enter into comparative research with a particular idea or hypothesis already in mind to validate. For instance, you might try to prove the worthwhileness of launching a new service. So, you may be disappointed if your analysis results don’t support your plan.
However, in any comparative analysis, try to maintain an unbiased approach by spending equal time debating the merits and drawbacks of any decision. Ultimately, this will be a practical, more long-term sustainable approach for your business than focusing only on the evidence that favors pursuing your argument or strategy.
Writing a comparative analysis in five steps
To put together a coherent, insightful analysis that goes beyond a list of pros and cons or similarities and differences, try organizing the information into these five components:
1. Frame of reference
Here is where you provide context. First, what driving idea or problem is your research anchored in? Then, for added substance, cite existing research or insights from a subject matter expert, such as a thought leader in marketing, startup growth, or investment
2. Grounds for comparison Why have you chosen to examine the two things you’re analyzing instead of focusing on two entirely different things? What are you hoping to accomplish?
3. Thesis What argument or choice are you advocating for? What will be the before and after effects of going with either decision? What do you anticipate happening with and without this approach?
For example, “If we release an AI feature for our shopping cart, we will have an edge over the rest of the market before the holiday season.” The finished comparative analysis will weigh all the pros and cons of choosing to build the new expensive AI feature including variables like how “intelligent” it will be, what it “pushes” customers to use, how much it takes off the plates of customer service etc.
Ultimately, you will gauge whether building an AI feature is the right plan for your e-commerce shop.
4. Organize the scheme Typically, there are two ways to organize a comparative analysis report. First, you can discuss everything about comparison point “A” and then go into everything about aspect “B.” Or, you alternate back and forth between points “A” and “B,” sometimes referred to as point-by-point analysis.
Using the AI feature as an example again, you could cover all the pros and cons of building the AI feature, then discuss the benefits and drawbacks of building and maintaining the feature. Or you could compare and contrast each aspect of the AI feature, one at a time. For example, a side-by-side comparison of the AI feature to shopping without it, then proceeding to another point of differentiation.
5. Connect the dots Tie it all together in a way that either confirms or disproves your hypothesis.
For instance, “Building the AI bot would allow our customer service team to save 12% on returns in Q3 while offering optimizations and savings in future strategies. However, it would also increase the product development budget by 43% in both Q1 and Q2. Our budget for product development won’t increase again until series 3 of funding is reached, so despite its potential, we will hold off building the bot until funding is secured and more opportunities and benefits can be proved effective.”
Get started today
Go from raw data to valuable insights with a flexible research platform
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 21 December 2023
Last updated: 16 December 2023
Last updated: 6 October 2023
Last updated: 17 February 2024
Last updated: 5 March 2024
Last updated: 19 November 2023
Last updated: 15 February 2024
Last updated: 11 March 2024
Last updated: 12 December 2023
Last updated: 6 March 2024
Last updated: 10 April 2023
Last updated: 20 December 2023
Latest articles
Related topics, log in or sign up.
Get started for free
- Why Blitzllama?
Comparative analysis: An essential guide (with examples) 2024
Transform your decision-making approach with our essential guide on comparative analysis, featuring real-world examples for practical insights.
In product management, understanding comparative analysis is crucial. Many struggle with how to effectively compare options and make informed decisions. Product owners and managers often face challenges in discerning the best choices among alternatives.
This article provides a practical guide, offering clear examples and actionable strategies. By mastering comparative analysis, professionals can confidently assess features, prices, and functionalities. Through concise explanations and real-world scenarios, this guide empowers decision-makers to streamline their evaluation processes.
With the right tools and insights, product owners and managers can navigate complex decision-making tasks efficiently. Let's delve into the essentials of comparative analysis for informed and effective decision-making.
What is comparative analysis?
Comparative analysis involves comparing two or more items to identify similarities and differences. It helps product owners and managers make informed decisions. By analyzing various aspects such as features, performance, and costs, they can assess which option best suits their needs.
Comparative analysis enables objective evaluation, aiding in selecting the most effective solutions for their products or services. It involves gathering data, organizing it systematically, and drawing meaningful conclusions.
Through this process, product owners and managers can understand market trends, competitor strengths, and areas for improvement. Ultimately, comparative analysis empowers decision-making by providing clear insights into available options and their respective merits.
Now that we understand the basics of comparative analysis, let's explore why it's crucial for product owners to leverage this approach.
Why is comparative analysis important to product owners?
Product owners rely on comparative analysis to make informed decisions about their products. By comparing features, performance, and user feedback, product owners can enhance their offerings and stay competitive in the market:

1) Informed decision-making
Comparative analysis equips product owners with vital insights to make informed decisions. By evaluating competitors, product owners gain clarity on market trends and consumer preferences. They can identify gaps in their offerings and adapt strategies accordingly. This analysis guides decisions on features, pricing, and positioning, ensuring products meet customer needs effectively.
2) Resource allocation
Efficient resource allocation is paramount for product success. Through comparative analysis, product owners discern where to allocate resources for maximum impact. By evaluating competitors' strengths and weaknesses, they optimize resource distribution across development, marketing, and support functions. This ensures resources are utilized effectively, driving product performance and profitability.
3) Continuous improvement
Continuous improvement is fundamental in the competitive business landscape. Comparative analysis enables product owners to benchmark against industry standards and identify areas for enhancement. By evaluating competitors' innovations and customer feedback, they refine product features and user experience iteratively. This iterative process fosters continuous improvement, keeping products relevant and competitive in evolving markets.
4) Stakeholder communication
Effective stakeholder communication is vital for product success. Comparative analysis provides product owners with valuable insights to communicate effectively with stakeholders. By presenting competitive intelligence, they substantiate strategic decisions and gain stakeholders' confidence. Clear communication of market dynamics and competitive positioning fosters alignment among stakeholders, facilitating collective efforts towards product goals.
Understanding why comparative analysis is essential sets the stage for distinguishing it from competitive analysis. Let's dissect this difference in the upcoming section.
Comparative vs. competitive analysis—what’s the difference?
Comparative analysis and competitive analysis are two distinct approaches utilized by product owners and managers to evaluate their products and understand market dynamics. While both methods involve assessing various aspects of products and their market environment, they differ in the following aspects:
Now that we've clarified the disparity between comparative and competitive analysis, let's pinpoint when product owners should employ comparative analysis in their decision-making process.
When to use comparative analysis?
Product owners should utilize comparative analysis when assessing market trends, understanding customer preferences, or evaluating new features. Recognizing the right time to employ this method ensures strategic decision-making and product improvement:

1) Evaluating competitor products
Comparative analysis is crucial when evaluating competitor products. It helps product owners and managers understand how their offerings stack up against others in the market.
By comparing features, pricing, and performance metrics, businesses can identify competitive advantages and areas for improvement. This analysis enables informed decision-making and enhances strategic planning for staying ahead in the market.
2) Analyzing different marketing strategies
Comparative analysis is instrumental in analyzing different marketing strategies. By comparing the effectiveness of various approaches, product owners and managers can determine which strategies yield the highest return on investment.
This analysis involves evaluating metrics such as customer engagement, conversion rates, and brand visibility across different marketing channels. Through comparative analysis, businesses can optimize their marketing efforts and allocate resources more efficiently.
3) Assessing design approaches
Comparative analysis plays a crucial role in assessing design approaches. It allows product owners and managers to evaluate the user experience, aesthetic appeal, and functionality of different design options.
By comparing prototypes or design concepts, businesses can gather valuable insights into customer preferences and usability. This analysis helps identify strengths and weaknesses in design, facilitating iterative improvements and ensuring that the final product meets user expectations.
4) Making informed product development decisions
Comparative analysis is essential for making informed product development decisions. By comparing market trends, customer feedback, and technological advancements, product owners and managers can identify opportunities for innovation and differentiation.
This analysis enables businesses to prioritize features, allocate resources effectively, and mitigate risks associated with product development. By leveraging comparative analysis, organizations can streamline the product development process and deliver solutions that resonate with their target audience.
With a clear understanding of when to leverage comparative analysis, let's explore the key steps involved in conducting a thorough comparative analysis.
Key steps in conducting a comparative analysis
Conducting a comparative analysis involves defining objectives, selecting criteria, gathering data, analyzing findings, and drawing conclusions. These steps provide a systematic approach for product owners to derive actionable insights and drive product innovation:
Step 1: Define Your Goals and Questions
When embarking on a comparative analysis, it's crucial to start with a clear understanding of your goals and the specific questions you aim to answer. This initial step lays the foundation for a focused and purposeful comparison.
What are you trying to achieve with the analysis?
Clearly articulate the overarching objectives of your comparative analysis. Are you seeking insights to enhance your product's features, understand market positioning, or identify potential areas for improvement? Defining your goals provides a roadmap for the entire process.
What specific questions do you need answers to?
List down the precise questions that need resolution. For instance, if you're comparing products, inquire about specific functionalities, user experience, or pricing strategies. This clarity ensures that your analysis remains targeted, saving time and resources.
Step 2: Identify Relevant Subjects for Comparison
Selecting the right subjects for comparison is pivotal to obtaining meaningful insights. Consider exploring the following categories:
Direct Competitors
Identify products or services that directly compete with yours in the market. This could include similar solutions with overlapping functionalities or offerings.
Alternative Solutions
Look beyond direct competitors and explore alternative solutions that cater to similar needs. This widens your perspective, allowing you to understand diverse approaches to solving user problems.
Industry Benchmarks
Include industry benchmarks to gauge where your product stands in comparison to the broader market standards. This broader context aids in recognizing areas of excellence or potential gaps.
Step 3: Gather Data and Information
Accurate and comprehensive data collection forms the backbone of any comparative analysis. The information you gather should cover various aspects of the subjects under consideration.
Product Features and Functionalities
Compile a detailed inventory of features and functionalities for each subject. This includes both core and unique attributes that contribute to the product's value proposition.
Pricing and Market Positioning
Examine the pricing strategies of your subjects and understand their market positioning. This information is critical for evaluating your product's competitiveness in terms of value.
User Reviews and Feedback
Aggregate user reviews and feedback to grasp the real-world experiences of consumers with each subject. This qualitative data provides insights into user satisfaction, pain points, and expectations.
Financial Performance and Market Share
Analyze the financial performance and market share of each subject. This quantitative data aids in understanding the overall success and reach of the products in the market.
Step 4: Choose the Right Comparison Framework
Selecting an appropriate framework for comparison ensures a systematic and meaningful evaluation. Tailor your approach based on the nature of your analysis.
Feature-by-Feature Comparison
Break down the analysis by comparing specific features and functionalities. This granular approach helps in identifying strengths and weaknesses in each area.
SWOT Analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats)
Conduct a SWOT analysis to comprehensively assess the internal strengths and weaknesses of your product, alongside external opportunities and threats in the market.
Value Proposition Analysis
Evaluate the unique value propositions of each subject. This analysis focuses on what sets each product apart and how it addresses user needs in a distinctive way.
Step 5: Analyze and Interpret the Data
With data in hand, delve into the analysis phase, aiming to draw meaningful insights and actionable conclusions.
Identify Key Similarities and Differences
Highlight the commonalities and disparities across the subjects. This provides a clear snapshot of the landscape, aiding in understanding the market dynamics.
Uncover Trends and Patterns
Look for trends or recurring patterns in the data. This could include customer preferences, market shifts, or emerging industry norms. Identifying these trends helps in future-proofing your product strategy.
Evaluate Strengths and Weaknesses of Each Subject
Assess the strengths and weaknesses of each subject objectively. This critical evaluation sets the stage for informed decision-making and strategic planning.
Step 6: Draw Conclusions and Recommendations
Synthesize the findings into actionable conclusions and recommendations that directly inform your product strategy.
How Do the Findings Inform Your Product Strategy?
Clearly articulate how the analysis findings impact your product strategy. Identify areas for improvement, potential areas for innovation, and strategies for staying competitive in the market.
What Actionable Insights Can Be Derived?
Translate insights into concrete actions. Whether it's enhancing specific features, adjusting pricing strategies, or refining marketing approaches, provide actionable steps based on your analysis.
Present Your Findings in a Clear and Concise Manner
Communication is key. Present your conclusions and recommendations in a clear and concise manner. Use visuals, charts, and graphs to enhance understanding and facilitate decision-making.
Having outlined the key steps, let's delve into best practices that can enhance the effectiveness of comparative analysis for product owners.
Best practices for effective comparative analysis
To maximize the benefits of comparative analysis, product owners should prioritize clear objectives, select relevant criteria, ensure data accuracy, and remain open to insights. By adhering to best practices, product owners can streamline decision-making and propel their products towards success:

1) Focus on relevant and comparable data
Effective comparative analysis hinges on focusing solely on data that is pertinent and can be compared directly. Ensure that the data you gather is relevant to the specific aspects you're analyzing.
Avoid including extraneous information that might obscure the comparison process. By narrowing your focus, you can better understand the nuances of the comparison and draw more actionable insights.
2) Use multiple sources of information for triangulation
To enhance the reliability and accuracy of your comparative analysis, utilize diverse sources of information. Triangulating data from various reputable sources helps validate your findings and minimizes the risk of bias.
Incorporate data from different perspectives or methodologies to gain a comprehensive understanding of the subject under analysis. By cross-referencing multiple sources, you can identify patterns, trends, and discrepancies more effectively.
3) Be objective and avoid bias in your analysis
Maintain objectivity throughout your comparative analysis process to ensure that your conclusions are grounded in factual evidence rather than personal opinions or preconceptions. Guard against biases that may skew your interpretation of data.
Approach the analysis with an open mind and remain impartial in your assessments. Objectivity fosters credibility and trust in the validity of your findings, enabling stakeholders to make informed decisions based on the analysis.
4) Visualize your data using charts and graphs for clarity
Enhance the clarity and comprehensibility of your comparative analysis by visualizing data through charts, graphs, and other visual representations. Visual aids facilitate the interpretation of complex information, enabling stakeholders to grasp key insights at a glance.
Choose appropriate visualization techniques based on the nature of the data and the comparisons being made. Well-designed visuals not only simplify complex concepts but also highlight important trends and patterns for easier interpretation.
5) Tailor your analysis to your specific audience and goals
Customize your comparative analysis to align with the needs, preferences, and expectations of your target audience. Consider the knowledge level, interests, and priorities of stakeholders when presenting findings and insights.
Tailoring the analysis ensures relevance and resonance with the intended audience, maximizing its impact and utility. Furthermore, clarify the goals and objectives of the analysis from the outset to guide the selection of data, methodologies, and presentation formats. Aligning the analysis with specific goals enhances its relevance and actionable outcomes for decision-making.
In conclusion, conducting comparative analysis empowers product owners and managers to make informed decisions. By evaluating similarities and differences, they gain valuable insights into market trends and consumer preferences.
Through practical examples, this guide illustrates the significance of comparing data, features, and performance metrics. Implementing a structured approach to analysis enhances product development strategies and fosters competitive advantage.
As decision-makers prioritize resources and optimize strategies, they foster innovation and adaptability in their products. Embracing comparative analysis as a fundamental practice ensures continual improvement and relevance in a dynamic marketplace. In essence, it is a cornerstone for effective decision-making and sustained success in product management.
Latest articles

Implementing a CSAT Survey Strategy: A Guide for Product Leaders

What is CSAT

15 Essential Customer Satisfaction Survey Questions for Actionable Insights

How to Do Comparative Analysis in Research ( Examples )
Comparative analysis is a method that is widely used in social science . It is a method of comparing two or more items with an idea of uncovering and discovering new ideas about them. It often compares and contrasts social structures and processes around the world to grasp general patterns. Comparative analysis tries to understand the study and explain every element of data that comparing.

We often compare and contrast in our daily life. So it is usual to compare and contrast the culture and human society. We often heard that ‘our culture is quite good than theirs’ or ‘their lifestyle is better than us’. In social science, the social scientist compares primitive, barbarian, civilized, and modern societies. They use this to understand and discover the evolutionary changes that happen to society and its people. It is not only used to understand the evolutionary processes but also to identify the differences, changes, and connections between societies.
Most social scientists are involved in comparative analysis. Macfarlane has thought that “On account of history, the examinations are typically on schedule, in that of other sociologies, transcendently in space. The historian always takes their society and compares it with the past society, and analyzes how far they differ from each other.
The comparative method of social research is a product of 19 th -century sociology and social anthropology. Sociologists like Emile Durkheim, Herbert Spencer Max Weber used comparative analysis in their works. For example, Max Weber compares the protestant of Europe with Catholics and also compared it with other religions like Islam, Hinduism, and Confucianism.
To do a systematic comparison we need to follow different elements of the method.
1. Methods of comparison The comparison method
In social science, we can do comparisons in different ways. It is merely different based on the topic, the field of study. Like Emile Durkheim compare societies as organic solidarity and mechanical solidarity. The famous sociologist Emile Durkheim provides us with three different approaches to the comparative method. Which are;
- The first approach is to identify and select one particular society in a fixed period. And by doing that, we can identify and determine the relationship, connections and differences exist in that particular society alone. We can find their religious practices, traditions, law, norms etc.
- The second approach is to consider and draw various societies which have common or similar characteristics that may vary in some ways. It may be we can select societies at a specific period, or we can select societies in the different periods which have common characteristics but vary in some ways. For example, we can take European and American societies (which are universally similar characteristics) in the 20 th century. And we can compare and contrast their society in terms of law, custom, tradition, etc.
- The third approach he envisaged is to take different societies of different times that may share some similar characteristics or maybe show revolutionary changes. For example, we can compare modern and primitive societies which show us revolutionary social changes.
2 . The unit of comparison
We cannot compare every aspect of society. As we know there are so many things that we cannot compare. The very success of the compare method is the unit or the element that we select to compare. We are only able to compare things that have some attributes in common. For example, we can compare the existing family system in America with the existing family system in Europe. But we are not able to compare the food habits in china with the divorce rate in America. It is not possible. So, the next thing you to remember is to consider the unit of comparison. You have to select it with utmost care.
3. The motive of comparison
As another method of study, a comparative analysis is one among them for the social scientist. The researcher or the person who does the comparative method must know for what grounds they taking the comparative method. They have to consider the strength, limitations, weaknesses, etc. He must have to know how to do the analysis.
Steps of the comparative method
1. Setting up of a unit of comparison
As mentioned earlier, the first step is to consider and determine the unit of comparison for your study. You must consider all the dimensions of your unit. This is where you put the two things you need to compare and to properly analyze and compare it. It is not an easy step, we have to systematically and scientifically do this with proper methods and techniques. You have to build your objectives, variables and make some assumptions or ask yourself about what you need to study or make a hypothesis for your analysis.
The best casings of reference are built from explicit sources instead of your musings or perceptions. To do that you can select some attributes in the society like marriage, law, customs, norms, etc. by doing this you can easily compare and contrast the two societies that you selected for your study. You can set some questions like, is the marriage practices of Catholics are different from Protestants? Did men and women get an equal voice in their mate choice? You can set as many questions that you wanted. Because that will explore the truth about that particular topic. A comparative analysis must have these attributes to study. A social scientist who wishes to compare must develop those research questions that pop up in your mind. A study without those is not going to be a fruitful one.
2. Grounds of comparison
The grounds of comparison should be understandable for the reader. You must acknowledge why you selected these units for your comparison. For example, it is quite natural that a person who asks why you choose this what about another one? What is the reason behind choosing this particular society? If a social scientist chooses primitive Asian society and primitive Australian society for comparison, he must acknowledge the grounds of comparison to the readers. The comparison of your work must be self-explanatory without any complications.
If you choose two particular societies for your comparative analysis you must convey to the reader what are you intended to choose this and the reason for choosing that society in your analysis.
3 . Report or thesis
The main element of the comparative analysis is the thesis or the report. The report is the most important one that it must contain all your frame of reference. It must include all your research questions, objectives of your topic, the characteristics of your two units of comparison, variables in your study, and last but not least the finding and conclusion must be written down. The findings must be self-explanatory because the reader must understand to what extent did they connect and what are their differences. For example, in Emile Durkheim’s Theory of Division of Labour, he classified organic solidarity and Mechanical solidarity . In which he means primitive society as Mechanical solidarity and modern society as Organic Solidarity. Like that you have to mention what are your findings in the thesis.
4. Relationship and linking one to another
Your paper must link each point in the argument. Without that the reader does not understand the logical and rational advance in your analysis. In a comparative analysis, you need to compare the ‘x’ and ‘y’ in your paper. (x and y mean the two-unit or things in your comparison). To do that you can use likewise, similarly, on the contrary, etc. For example, if we do a comparison between primitive society and modern society we can say that; ‘in the primitive society the division of labour is based on gender and age on the contrary (or the other hand), in modern society, the division of labour is based on skill and knowledge of a person.
Demerits of comparison
Comparative analysis is not always successful. It has some limitations. The broad utilization of comparative analysis can undoubtedly cause the feeling that this technique is a solidly settled, smooth, and unproblematic method of investigation, which because of its undeniable intelligent status can produce dependable information once some specialized preconditions are met acceptably.
Perhaps the most fundamental issue here respects the independence of the unit picked for comparison. As different types of substances are gotten to be analyzed, there is frequently a fundamental and implicit supposition about their independence and a quiet propensity to disregard the mutual influences and common impacts among the units.
One more basic issue with broad ramifications concerns the decision of the units being analyzed. The primary concern is that a long way from being a guiltless as well as basic assignment, the decision of comparison units is a basic and precarious issue. The issue with this sort of comparison is that in such investigations the depictions of the cases picked for examination with the principle one will in general turn out to be unreasonably streamlined, shallow, and stylised with contorted contentions and ends as entailment.
However, a comparative analysis is as yet a strategy with exceptional benefits, essentially due to its capacity to cause us to perceive the restriction of our psyche and check against the weaknesses and hurtful results of localism and provincialism. We may anyway have something to gain from history specialists’ faltering in utilizing comparison and from their regard for the uniqueness of settings and accounts of people groups. All of the above, by doing the comparison we discover the truths the underlying and undiscovered connection, differences that exist in society.
Also Read: How to write a Sociology Analysis? Explained with Examples

Sociology Group
The Sociology Group is an organization dedicated to creating social awareness through thoughtful initiatives like "social stories" and the "Meet the Professor" insightful interview series. Recognized for our book reviews, author interviews, and social sciences articles, we also host annual social sciences writing competition. Interested in joining us? Email [email protected] . We are a dedicated team of social scientists on a mission to simplify complex theories, conduct enlightening interviews, and offer academic assistance, making Social Science accessible and practical for all curious minds.
- Utility Menu
GA4 Tracking Code
Gen ed writes, writing across the disciplines at harvard college.
- Comparative Analysis
What It Is and Why It's Useful
Comparative analysis asks writers to make an argument about the relationship between two or more texts. Beyond that, there's a lot of variation, but three overarching kinds of comparative analysis stand out:
- Coordinate (A ↔ B): In this kind of analysis, two (or more) texts are being read against each other in terms of a shared element, e.g., a memoir and a novel, both by Jesmyn Ward; two sets of data for the same experiment; a few op-ed responses to the same event; two YA books written in Chicago in the 2000s; a film adaption of a play; etc.
- Subordinate (A → B) or (B → A ): Using a theoretical text (as a "lens") to explain a case study or work of art (e.g., how Anthony Jack's The Privileged Poor can help explain divergent experiences among students at elite four-year private colleges who are coming from similar socio-economic backgrounds) or using a work of art or case study (i.e., as a "test" of) a theory's usefulness or limitations (e.g., using coverage of recent incidents of gun violence or legislation un the U.S. to confirm or question the currency of Carol Anderson's The Second ).
- Hybrid [A → (B ↔ C)] or [(B ↔ C) → A] , i.e., using coordinate and subordinate analysis together. For example, using Jack to compare or contrast the experiences of students at elite four-year institutions with students at state universities and/or community colleges; or looking at gun culture in other countries and/or other timeframes to contextualize or generalize Anderson's main points about the role of the Second Amendment in U.S. history.
"In the wild," these three kinds of comparative analysis represent increasingly complex—and scholarly—modes of comparison. Students can of course compare two poems in terms of imagery or two data sets in terms of methods, but in each case the analysis will eventually be richer if the students have had a chance to encounter other people's ideas about how imagery or methods work. At that point, we're getting into a hybrid kind of reading (or even into research essays), especially if we start introducing different approaches to imagery or methods that are themselves being compared along with a couple (or few) poems or data sets.
Why It's Useful
In the context of a particular course, each kind of comparative analysis has its place and can be a useful step up from single-source analysis. Intellectually, comparative analysis helps overcome the "n of 1" problem that can face single-source analysis. That is, a writer drawing broad conclusions about the influence of the Iranian New Wave based on one film is relying entirely—and almost certainly too much—on that film to support those findings. In the context of even just one more film, though, the analysis is suddenly more likely to arrive at one of the best features of any comparative approach: both films will be more richly experienced than they would have been in isolation, and the themes or questions in terms of which they're being explored (here the general question of the influence of the Iranian New Wave) will arrive at conclusions that are less at-risk of oversimplification.
For scholars working in comparative fields or through comparative approaches, these features of comparative analysis animate their work. To borrow from a stock example in Western epistemology, our concept of "green" isn't based on a single encounter with something we intuit or are told is "green." Not at all. Our concept of "green" is derived from a complex set of experiences of what others say is green or what's labeled green or what seems to be something that's neither blue nor yellow but kind of both, etc. Comparative analysis essays offer us the chance to engage with that process—even if only enough to help us see where a more in-depth exploration with a higher and/or more diverse "n" might lead—and in that sense, from the standpoint of the subject matter students are exploring through writing as well the complexity of the genre of writing they're using to explore it—comparative analysis forms a bridge of sorts between single-source analysis and research essays.
Typical learning objectives for single-sources essays: formulate analytical questions and an arguable thesis, establish stakes of an argument, summarize sources accurately, choose evidence effectively, analyze evidence effectively, define key terms, organize argument logically, acknowledge and respond to counterargument, cite sources properly, and present ideas in clear prose.
Common types of comparative analysis essays and related types: two works in the same genre, two works from the same period (but in different places or in different cultures), a work adapted into a different genre or medium, two theories treating the same topic; a theory and a case study or other object, etc.
How to Teach It: Framing + Practice
Framing multi-source writing assignments (comparative analysis, research essays, multi-modal projects) is likely to overlap a great deal with "Why It's Useful" (see above), because the range of reasons why we might use these kinds of writing in academic or non-academic settings is itself the reason why they so often appear later in courses. In many courses, they're the best vehicles for exploring the complex questions that arise once we've been introduced to the course's main themes, core content, leading protagonists, and central debates.
For comparative analysis in particular, it's helpful to frame assignment's process and how it will help students successfully navigate the challenges and pitfalls presented by the genre. Ideally, this will mean students have time to identify what each text seems to be doing, take note of apparent points of connection between different texts, and start to imagine how those points of connection (or the absence thereof)
- complicates or upends their own expectations or assumptions about the texts
- complicates or refutes the expectations or assumptions about the texts presented by a scholar
- confirms and/or nuances expectations and assumptions they themselves hold or scholars have presented
- presents entirely unforeseen ways of understanding the texts
—and all with implications for the texts themselves or for the axes along which the comparative analysis took place. If students know that this is where their ideas will be heading, they'll be ready to develop those ideas and engage with the challenges that comparative analysis presents in terms of structure (See "Tips" and "Common Pitfalls" below for more on these elements of framing).
Like single-source analyses, comparative essays have several moving parts, and giving students practice here means adapting the sample sequence laid out at the " Formative Writing Assignments " page. Three areas that have already been mentioned above are worth noting:
- Gathering evidence : Depending on what your assignment is asking students to compare (or in terms of what), students will benefit greatly from structured opportunities to create inventories or data sets of the motifs, examples, trajectories, etc., shared (or not shared) by the texts they'll be comparing. See the sample exercises below for a basic example of what this might look like.
- Why it Matters: Moving beyond "x is like y but also different" or even "x is more like y than we might think at first" is what moves an essay from being "compare/contrast" to being a comparative analysis . It's also a move that can be hard to make and that will often evolve over the course of an assignment. A great way to get feedback from students about where they're at on this front? Ask them to start considering early on why their argument "matters" to different kinds of imagined audiences (while they're just gathering evidence) and again as they develop their thesis and again as they're drafting their essays. ( Cover letters , for example, are a great place to ask writers to imagine how a reader might be affected by reading an their argument.)
- Structure: Having two texts on stage at the same time can suddenly feel a lot more complicated for any writer who's used to having just one at a time. Giving students a sense of what the most common patterns (AAA / BBB, ABABAB, etc.) are likely to be can help them imagine, even if provisionally, how their argument might unfold over a series of pages. See "Tips" and "Common Pitfalls" below for more information on this front.
Sample Exercises and Links to Other Resources
- Common Pitfalls
- Advice on Timing
- Try to keep students from thinking of a proposed thesis as a commitment. Instead, help them see it as more of a hypothesis that has emerged out of readings and discussion and analytical questions and that they'll now test through an experiment, namely, writing their essay. When students see writing as part of the process of inquiry—rather than just the result—and when that process is committed to acknowledging and adapting itself to evidence, it makes writing assignments more scientific, more ethical, and more authentic.
- Have students create an inventory of touch points between the two texts early in the process.
- Ask students to make the case—early on and at points throughout the process—for the significance of the claim they're making about the relationship between the texts they're comparing.
- For coordinate kinds of comparative analysis, a common pitfall is tied to thesis and evidence. Basically, it's a thesis that tells the reader that there are "similarities and differences" between two texts, without telling the reader why it matters that these two texts have or don't have these particular features in common. This kind of thesis is stuck at the level of description or positivism, and it's not uncommon when a writer is grappling with the complexity that can in fact accompany the "taking inventory" stage of comparative analysis. The solution is to make the "taking inventory" stage part of the process of the assignment. When this stage comes before students have formulated a thesis, that formulation is then able to emerge out of a comparative data set, rather than the data set emerging in terms of their thesis (which can lead to confirmation bias, or frequency illusion, or—just for the sake of streamlining the process of gathering evidence—cherry picking).
- For subordinate kinds of comparative analysis , a common pitfall is tied to how much weight is given to each source. Having students apply a theory (in a "lens" essay) or weigh the pros and cons of a theory against case studies (in a "test a theory") essay can be a great way to help them explore the assumptions, implications, and real-world usefulness of theoretical approaches. The pitfall of these approaches is that they can quickly lead to the same biases we saw here above. Making sure that students know they should engage with counterevidence and counterargument, and that "lens" / "test a theory" approaches often balance each other out in any real-world application of theory is a good way to get out in front of this pitfall.
- For any kind of comparative analysis, a common pitfall is structure. Every comparative analysis asks writers to move back and forth between texts, and that can pose a number of challenges, including: what pattern the back and forth should follow and how to use transitions and other signposting to make sure readers can follow the overarching argument as the back and forth is taking place. Here's some advice from an experienced writing instructor to students about how to think about these considerations:
a quick note on STRUCTURE
Most of us have encountered the question of whether to adopt what we might term the “A→A→A→B→B→B” structure or the “A→B→A→B→A→B” structure. Do we make all of our points about text A before moving on to text B? Or do we go back and forth between A and B as the essay proceeds? As always, the answers to our questions about structure depend on our goals in the essay as a whole. In a “similarities in spite of differences” essay, for instance, readers will need to encounter the differences between A and B before we offer them the similarities (A d →B d →A s →B s ). If, rather than subordinating differences to similarities you are subordinating text A to text B (using A as a point of comparison that reveals B’s originality, say), you may be well served by the “A→A→A→B→B→B” structure.
Ultimately, you need to ask yourself how many “A→B” moves you have in you. Is each one identical? If so, you may wish to make the transition from A to B only once (“A→A→A→B→B→B”), because if each “A→B” move is identical, the “A→B→A→B→A→B” structure will appear to involve nothing more than directionless oscillation and repetition. If each is increasingly complex, however—if each AB pair yields a new and progressively more complex idea about your subject—you may be well served by the “A→B→A→B→A→B” structure, because in this case it will be visible to readers as a progressively developing argument.
As we discussed in "Advice on Timing" at the page on single-source analysis, that timeline itself roughly follows the "Sample Sequence of Formative Assignments for a 'Typical' Essay" outlined under " Formative Writing Assignments, " and it spans about 5–6 steps or 2–4 weeks.
Comparative analysis assignments have a lot of the same DNA as single-source essays, but they potentially bring more reading into play and ask students to engage in more complicated acts of analysis and synthesis during the drafting stages. With that in mind, closer to 4 weeks is probably a good baseline for many single-source analysis assignments. For sections that meet once per week, the timeline will either probably need to expand—ideally—a little past the 4-week side of things, or some of the steps will need to be combined or done asynchronously.
What It Can Build Up To
Comparative analyses can build up to other kinds of writing in a number of ways. For example:
- They can build toward other kinds of comparative analysis, e.g., student can be asked to choose an additional source to complicate their conclusions from a previous analysis, or they can be asked to revisit an analysis using a different axis of comparison, such as race instead of class. (These approaches are akin to moving from a coordinate or subordinate analysis to more of a hybrid approach.)
- They can scaffold up to research essays, which in many instances are an extension of a "hybrid comparative analysis."
- Like single-source analysis, in a course where students will take a "deep dive" into a source or topic for their capstone, they can allow students to "try on" a theoretical approach or genre or time period to see if it's indeed something they want to research more fully.
- DIY Guides for Analytical Writing Assignments

- Types of Assignments
- Unpacking the Elements of Writing Prompts
- Formative Writing Assignments
- Single-Source Analysis
- Research Essays
- Multi-Modal or Creative Projects
- Giving Feedback to Students
Assignment Decoder
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case NPS+ Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research Research Tools and Apps
Comparative Analysis: What It Is & How to Conduct It

When a business wants to start a marketing campaign or grow, a comparative analysis can give them information that helps them make crucial decisions. This analysis gathers different data sets to compare different options so a business can make good decisions for its customers and itself. If you or your business want to make good decisions, learning about comparative analyses could be helpful.
In this article, we’ll explain the comparative analysis and its importance. We’ll also learn how to do a good in-depth analysis .
What is comparative analysis?
Comparative analysis is a way to look at two or more similar things to see how they are different and what they have in common.
It is used in many ways and fields to help people understand the similarities and differences between products better. It can help businesses make good decisions about key issues.
One meaningful way it’s used is when applied to scientific data. Scientific data is information that has been gathered through scientific research and will be used for a certain purpose.
When it is used on scientific data, it determines how consistent and reliable the data is. It also helps scientists make sure their data is accurate and valid.
Importance of comparative analysis
Comparative analyses are important if you want to understand a problem better or find answers to important questions. Here are the main goals businesses want to reach through comparative analysis.
- It is a part of the diagnostic phase of business analytics. It can answer many of the most important questions a company may have and help you figure out how to fix problems at the company’s core to improve performance and even make more money.
- It encourages a deep understanding of the opportunities that apply to specific processes, departments, or business units. This analysis also ensures that we’re addressing the real reasons for performance gaps.
- It is used a lot because it helps people understand the challenges an organization has faced in the past and the ones it faces now. This method gives objective, fact-based information about performance and ways to improve it.
How to successfully conduct it
Consider using the advice below to carry out a successful comparative analysis:
Conduct research
Before doing an analysis, it’s important to do a lot of research . Research not only gives you evidence to back up your conclusions, but it might also show you something you hadn’t thought of before.
Research could also tell you how your competitors might handle a problem.
Make a list of what’s different and what’s the same.
When comparing two things in a comparative analysis, you need to make a detailed list of the similarities and differences.
Try to figure out how a change to one thing might affect another. Such as how increasing the number of vacation days affects sales, production, or costs.
A comparative analysis can also help you find outside causes, such as economic conditions or environmental analysis problems.
Describe both sides
Comparative analysis may try to show that one argument or idea is better, but the analysis must cover both sides equally. The analysis shows both sides of the main arguments and claims.
For example, to compare the benefits and drawbacks of starting a recycling program, one might examine both the positive effects, such as corporate responsibility and the potential negative effects, such as high implementation costs, to make wise, practical decisions or come up with alternate solutions.
Include variables
A thorough comparison unit of analysis is usually more than just a list of pros and cons because it usually considers factors that affect both sides.
Variables can be both things that can’t be changed, like how the weather in the summer affects shipping speeds, and things that can be changed, like when to work with a local shipper.
Do analyses regularly
Comparative analyses are important for any business practice. Consider the different areas and factors that a comparative analysis looks at:
- Competitors
- How well do stocks
- Financial position
- Profitability
- Dividends and revenue
- Development and research
Because a comparative analysis can help more than one department in a company, doing them often can help you keep up with market changes and stay relevant.
We’ve talked about how good a comparative analysis is for your business. But things always have two sides. It is a good workaround, but still do your own user interviews or user tests if you can.
We hope you have fun doing comparative analyses! Comparative analysis is always a method you like to use, and the point of learning from competitors is to add your own ideas. In this way, you are not just following but also learning and making.
QuestionPro can help you with your analysis process, create and design a survey to meet your goals, and analyze data for your business’s comparative analysis.
At QuestionPro, we give researchers tools for collecting data, like our survey software and a library of insights for all kinds of l ong-term research . If you want to book a demo or learn more about our platform, just click here.
LEARN MORE FREE TRIAL
MORE LIKE THIS

Top 17 UX Research Software for UX Design in 2024
Apr 5, 2024

Healthcare Staff Burnout: What it Is + How To Manage It
Apr 4, 2024

Top 15 Employee Retention Software in 2024

Top 10 Employee Development Software for Talent Growth
Apr 3, 2024
Other categories
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Uncategorized
- Video Learning Series
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence
We use cookies
This website uses cookies to provide better user experience and user's session management. By continuing visiting this website you consent the use of these cookies.
ChartExpo Survey

How to Conduct Comparative Analysis? Guide with Examples
Evaluating the differences and similarities in your data is one of the most straightforward analyses you can ever conduct.
You only need to compare data points side-by-side.
It gets better.
One of the comparative analysis example strategies we recommend is using charts and graphs.
Our brains process visual data 60,000 times faster than texts and figures. And this creates a concrete argument for using comparison-oriented charts and graphs, such as Matrix and Radar Graphs.
These charts are amazingly easy to read and interpret.
Excel is one of the freemium tools you can use to visualize your data for insights. But it lacks ready-to-go graphs for conducting a comparative analysis, such as Radar Chart.
You don’t have to dump Excel for other expensive data visualization tools.
You can supercharge your Excel by installing a particular add-in to access ready-made graphs for comparative analysis.
You don’t want to miss this.
In this blog, you’ll learn:
- How to conduct comparative analysis using our easy-to-follow steps?
- We’ll take you through comparative analysis examples.
- What is comparative analysis?
- The tested and recommended Comparative Charts.
- We’ll recommend the proven add-in to install to access ready-made graphs for comparative analysis.
How to Conduct Comparative Analysis? (Easy Steps)
Before jumping right into the how-to guide, we’ll address the following question: what is comparative analysis?
What is Comparative Analysis?
Definition : Comparison analysis is a methodology that entails comparing data variables to one another for similarities and differences.
Conducting a comparative analysis can help you understand the problem in-depth and form strategies. More so, you can efficiently conduct this analysis to investigate data points with noticeable differences and commonalities.
Car factories can leverage this analysis to examine two production processes to determine cost-effectiveness.
In the education section, policymakers can use comparative analysis to compare the efficacy of different curriculums.
Other practical uses of comparative analysis include:
- Evaluating emerging opportunities versus risks among micro and small
- Comparing performance relative to the competition.
- Compare revenue versus costs in your business.
Comparative analysis is critical to your data storytelling. In other words, you can use this methodology to create compelling narratives for your audience. Let’s check out the benefits of the analysis.
Why is Comparative Analysis Important?
Comparative analysis is important to better understand the problem and answer related questions. The main goals companies try to achieve by comparing records, documents or processes are:
Keep up with Your Competition’s Every Move
You can quickly evaluate the competition for more insights by conducting a comparative analysis.
Establish What’s Working and What’s Not
It’s very important for you to know what’s working well and what is not working well for you if your goal is to maximize returns and cut costs in the long term. So, flexibility and quickness in adopting changes are vital. The longer you take, the less valuable these improvements become. Besides, you risk losing your market to the competition.
Save Time and Resources
Comparative analysis helps you save time and valuable resources by providing a versatile way of comparing data using easy-to-read charts and graphs.
Explore Opportunities using Data
Comparative analysis helps you explore valuable opportunities in your data that are constantly appearing.
Real-Life Examples of Comparative Analysis
Data analysts in weather stations use comparison-based charts, such as Line Charts and Bar Charts , to compare weather patterns across different periods.
Recession Indicators
Federal and central banks worldwide use comparison charts to closely follow the global economy’s performance. Growth is depicted by two consecutive peaks of the line curve.
On the other hand, two consecutive trough quarters in a year are a sign recession is on the corner.

The Tested and Recommended Comparison Charts
For you to conduct a comparative analysis, you need different types of comparison charts and graphs. Yes, because we interpret visual data faster than text and figures.
We’ve put together a list of comparison-based charts and graphs you’ve to try.
Comparison Bar Chart
A Comparison Bar Chart is one of the best charts you can use to draw comparative analysis examples.
Remember, drawing comparisons is something that humans do naturally. So, by conducting comparative analysis using charts, you gain far more insights than relying on intuition or mere observation. This chart is the go-to if your goal is to compare two or more data sets or items within the same data set.
The key objective of this comparative chart is to help you visually depict data side by side, allowing you to see how data points stack up against one another.

Matrix Charts
Matrix Chart is a Comparison Chart example you can use to display relationships in your dataset, irrespective of the complexity. The chart has a grid-like format to display insights into relationships between two or more variables.
The Matrix Chart is effective at displaying many-to-many relationships in data. In other words, you can draw comparisons insights into multiple groups or specific components in your data.

Multi Axis Comparison Line Graph
A Multi Axis Line Graph function uses two y-axes. And this gives you more flexibility to use one chart to display more insights using limited space.
You can easily visualize data with varying metrics because the chart has two different scales.

How to Conduct Comparative Analysis Using Charts with Examples?
Comparative analysis is a form of analysis that entails comparing a data point against others. One of the standard tools for conducting comparative analysis uses charts, graphs, and maps in Excel.
But, the spreadsheet application lacks ready-made Comparative Charts.
We’re not advising you to do away with Excel in favor of other expensive tools.
And this is because there’s an amazingly affordable visualization tool that comes as an add-in you can easily install in Excel to access insightful and easy-to-customize Comparison-based charts . The application is called ChartExpo.
What is ChartExpo?
ChartExpo is an add-in you can easily install in your Excel to access ready-made and visually appealing Comparative Charts in Excel , such as Multi Axis Line and Radar Charts .
Features and benefits
- You have maximum freedom to customize your charts and graphs to your liking.
- You don’t need sophisticated design or coding skills to generate stunning, insightful charts for your stories. Save time with this drag-and-drop application.
- The tool has many templates to ensure a wider selection of charts. And this means you don’t have to waste time moving from one tool to another looking for charts.
- With just a few clicks, you can turn overwhelming tables and spreadsheets into stunning, insightful charts and graphs.
- ChartExpo comes with a free 7-day trial. Essentially, if you’re unsatisfied with the tool within a week, you can opt-out as easily as signing up for a trial.
In the coming section, we’ll take you through how to visualize data using Multi Axis Chart using ChartExpo add-in.
You don’t want to miss this!

This section will use a Multi Axis Line Graph (one of the Comparative Analysis Charts) to display insights into the table below.
To get started with ChartExpo in Excel, follow the steps below:
- Open your Excel desktop application.
- Open the worksheet and click the Insert button to access the My Apps option.
- Select ChartExpo add-in and click the Insert button .
- In this case, look for “ Multi Axis Line Chart ” in the list of charts as shown below.

- Highlight your data and click the Create Chart From Selection button, as shown below.

- To edit the chart, click the Edit Chart button .

- Once the Chart Header Properties window shows, click the Line 1 button, and fill in your header.

- Toggle the small button below Line 2 to the right side.
- Click the Apply button .
- Check out the final chart below.
When is it most appropriate to use a secondary chart axis?
Charts with a secondary axis can help you emphasize the key data points within categories. More so, you can make comparisons between categories using a highly contrasting color scheme.
If you want to use limited space in your data visualization dashboard, your go-to visualization design should be a Multi Axis Line Chart.
What is the difference between a Dual Axis Chart and a Combined Axis Chart?
A Combined Axis Graph merges two or more measures into a single axis. And this means you can display insights into multiple variables using the same chart.
The Dual Axis Chart (one of the comparative analysis charts) comes with two y-axes and a single x-axis.

Investigating the differences and similarities in your data is one of the most straightforward analyses you can ever conduct. You only need to compare data points side-by-side.
One of the comparative analysis strategies we recommend is using charts and graphs.
Remember, our brains process visual data faster than texts and figures. And this creates a concrete argument for using comparison-oriented charts and graphs, such as Matrix and Radar Graphs.
How much did you enjoy this article?

Related articles
Goal Chart Templates: Unlock Your Productivity Potential
Unlock productivity potential with our customizable Goal Chart templates, designed to empower insightful analysis & strategic planning for achieving objectives.
Return on Assets vs. Return on Equity: Core Differences
Discover the key differences between Return on Assets (ROA) vs. Return on Equity (ROE) and discover how to calculate and examine these financial metrics.
Master 3-Statement Financial Modeling: Unlock Success
Discover the power of 3-statement financial modeling in unlocking insights for business success. Master techniques to simplify forecasting and drive growth.
KPIs for Manufacturing Industry: Top 15 Metrics & Insights
Unlock the potential of key performance indicators for manufacturing industry with our guide. Learn how metrics and insights drive continuous improvement.
KPIs for Operations: Unlocking Operational Insights
Elevate your operational strategies with our in-depth analysis of key performance indicators for operations. Uncover actionable insights to enhance efficiency.
This website may not work correctly because your browser is out of date. Please update your browser .
Qualitative comparative analysis
Qualitative Comparative Analysis (QCA) is a means of analysing the causal contribution of different conditions (e.g. aspects of an intervention and the wider context) to an outcome of interest.
QCA starts with the documentation of the different configurations of conditions associated with each case of an observed outcome. These are then subject to a minimisation procedure that identifies the simplest set of conditions that can account for all the observed outcomes, as well as their absence.
The results are typically expressed in statements expressed in ordinary language or as Boolean algebra. For example:
- A combination of Condition A and condition B or a combination of condition C and condition D will lead to outcome E.
- In Boolean notation this is expressed more succinctly as A*B + C*D→E
QCA results are able to distinguish various complex forms of causation, including:
- Configurations of causal conditions, not just single causes. In the example above, there are two different causal configurations, each made up of two conditions.
- Equifinality, where there is more than one way in which an outcome can happen. In the above example, each additional configuration represents a different causal pathway
- Causal conditions which are necessary, sufficient, both or neither, plus more complex combinations (known as INUS causes – insufficient but necessary parts of a configuration that is unnecessary but sufficient), which tend to be more common in everyday life. In the example above, no one condition was sufficient or necessary. But each condition is an INUS type cause
- Asymmetric causes – where the causes of failure may not simply be the absence of the cause of success. In the example above, the configuration associated with the absence of E might have been one like this: A*B*X + C*D*X →e Here X condition was a sufficient and necessary blocking condition.
- The relative influence of different individual conditions and causal configurations in a set of cases being examined. In the example above, the first configuration may have been associated with 10 cases where the outcome was E, whereas the second might have been associated with only 5 cases. Configurations can be evaluated in terms of coverage (the percentage of cases they explain) and consistency (the extent to which a configuration is always associated with a given outcome).
QCA is able to use relatively small and simple data sets. There is no requirement to have enough cases to achieve statistical significance, although ideally there should be enough cases to potentially exhibit all the possible configurations. The latter depends on the number of conditions present. In a 2012 survey of QCA uses the median number of cases was 22 and the median number of conditions was 6. For each case, the presence or absence of a condition is recorded using nominal data i.e. a 1 or 0. More sophisticated forms of QCA allow the use of “fuzzy sets” i.e. where a condition may be partly present or partly absent, represented by a value of 0.8 or 0.2 for example. Or there may be more than one kind of presence, represented by values of 0, 1, 2 or more for example. Data for a QCA analysis is collated in a simple matrix form, where rows = cases and columns = conditions, with the rightmost column listing the associated outcome for each case, also described in binary form.
QCA is a theory-driven approach, in that the choice of conditions being examined needs to be driven by a prior theory about what matters. The list of conditions may also be revised in the light of the results of the QCA analysis if some configurations are still shown as being associated with a mixture of outcomes. The coding of the presence/absence of a condition also requires an explicit view of that condition and when and where it can be considered present. Dichotomisation of quantitative measures about the incidence of a condition also needs to be carried out with an explicit rationale, and not on an arbitrary basis.
Although QCA was originally developed by Charles Ragin some decades ago it is only in the last decade that its use has become more common amongst evaluators. Articles on its use have appeared in Evaluation and the American Journal of Evaluation.
For a worked example, see Charles Ragin’s What is Qualitative Comparative Analysis (QCA)? , slides 6 to 15 on The bare-bones basics of crisp-set QCA.
[A crude summary of the example is presented here]
In his presentation Ragin provides data on 65 countries and their reactions to austerity measures imposed by the IMF. This has been condensed into a Truth Table (shown below), which shows all possible configurations of four different conditions that were thought to affect countries’ responses: the presence or absence of severe austerity, prior mobilisation, corrupt government, rapid price rises. Next to each configuration is data on the outcome associated with that configuration – the numbers of countries experiencing mass protest or not. There are 16 configurations in all, one per row. The rightmost column describes the consistency of each configuration: whether all cases with that configuration have one type of outcome, or a mixed outcome (i.e. some protests and some no protests). Notice that there are also some configurations with no known cases.

Ragin’s next step is to improve the consistency of the configurations with mixed consistency. This is done either by rejecting cases within an inconsistent configuration because they are outliers (with exceptional circumstances unlikely to be repeated elsewhere) or by introducing an additional condition (column) that distinguishes between those configurations which did lead to protest and those which did not. In this example, a new condition was introduced that removed the inconsistency, which was described as “not having a repressive regime”.
The next step involves reducing the number of configurations needed to explain all the outcomes, known as minimisation. Because this is a time-consuming process, this is done by an automated algorithm (aka a computer program) This algorithm takes two configurations at a time and examines if they have the same outcome. If so, and if their configurations are only different in respect to one condition this is deemed to not be an important causal factor and the two configurations are collapsed into one. This process of comparisons is continued, looking at all configurations, including newly collapsed ones, until no further reductions are possible.
[Jumping a few more specific steps] The final result from the minimisation of the above truth table is this configuration:
SA*(PR + PM*GC*NR)
The expression indicates that IMF protest erupts when severe austerity (SA) is combined with either (1) rapid price increases (PR) or (2) the combination of prior mobilization (PM), government corruption (GC), and non-repressive regime (NR).
This slide show from Charles C Ragin, provides a detailed explanation, including examples, that clearly demonstrates the question, 'What is QCA?'
This book, by Schneider and Wagemann, provides a comprehensive overview of the basic principles of set theory to model causality and applications of Qualitative Comparative Analysis (QCA), the most developed form of set-theoretic method, for research ac
This article by Nicolas Legewie provides an introduction to Qualitative Comparative Analysis (QCA). It discusses the method's main principles and advantages, including its concepts.
COMPASSS (Comparative methods for systematic cross-case analysis) is a website that has been designed to develop the use of systematic comparative case analysis as a research strategy by bringing together scholars and practitioners who share its use as
This paper from Patrick A. Mello focuses on reviewing current applications for use in Qualitative Comparative Analysis (QCA) in order to take stock of what is available and highlight best practice in this area.
Marshall, G. (1998). Qualitative comparative analysis. In A Dictionary of Sociology Retrieved from https://www.encyclopedia.com/social-sciences/dictionaries-thesauruses-pictures-and-press-releases/qualitative-comparative-analysis
Expand to view all resources related to 'Qualitative comparative analysis'
- An introduction to applied data analysis with qualitative comparative analysis
- Qualitative comparative analysis: A valuable approach to add to the evaluator’s ‘toolbox’? Lessons from recent applications
'Qualitative comparative analysis' is referenced in:
- 52 weeks of BetterEvaluation: Week 34 Generalisations from case studies?
- Week 18: is there a "right" approach to establishing causation in advocacy evaluation?
Framework/Guide
- Rainbow Framework : Check the results are consistent with causal contribution
- Data mining
Back to top
© 2022 BetterEvaluation. All right reserved.

Comparative Analysis
Flipped learning module.
Each Flipped Learning Module (FLM) is a set of short videos and online activities that can be used (in whole or in part) to free up class time from content delivery for greater student interaction. At the end of the module, students are asked to fill out a brief survey, in which we adopt the minute paper strategy . In this approach, students are asked to submit their response to two brief questions regarding their knowledge of the module.
In this FLM, students are asked to complete a fill-in-the-blank outline which accompanies all three videos, covering the topics of comparative analysis, grounds for comparison, and the structure of comparative analysis. The completed outline will enhance the students’ note-taking skills and will serve as a summary of the FLM that they may refer to in the future.
comparative analysis goals, analytical discussion, interpretation, evaluation, grounds for comparison, organization, point-by-point & block-by-block structure
Module Overview Introduction to Comparative Analysis What is comparative analysis? Reading for and entering the conversation The goal of comparative analysis Grounds for Comparison The 5 grounds for comparison Identifying the significance Organization Point-by-point Block-by-block Download Video Transcripts
Worksheet: Comparative Analysis Outline
- Comparative analysis is different than a traditional compare/contrast essay in the following way: __________________________________________________________________________
- The goal of comparative analysis is to: __________________________________________________________________________
- When you put two articles in conversation with one another in order to shed light on a topic, continue a discussion, or potentially resolve a problem, you are: __________________________________________________________________________
- (Question 1):__________________________________________________
- (Question 2):__________________________________________________
- (Question 3):__________________________________________________
- (Question 4):__________________________________________________
- Once you have identified the conversation your authors are participating in, the next step is to: __________________________________________________________________________
- (Method 1):__________________________________________________
- (Method 2):__________________________________________________
- (Method 3):__________________________________________________
- (Method 4):__________________________________________________
- (Method 5):__________________________________________________
- Establishing the grounds for comparison is so important because: __________________________________________________________________________
Download Outline
Video 1: Introduction to Comparative Analysis
Comparative analysis online activity 1.
- What is each author’s claim?
- What claims are these authors responding to?
- What larger conversation are these authors participating in?
- How might you enter that conversation?
Video 2: Grounds for Comparison
Comparative analysis online activity 2.
- Describe the relationship between the two texts (the grounds for comparison).
- What aspects of this relationship could you analyze?
- What new ideas could your analysis present by exploring the relationship you identified within the context of the conversation you are entering?
- Why do you think it is important to engage in this conversation? Who needs to understand this issue? Why does it matter?
Video 3: Organization
Comparative analysis online activity 3.
- What are the main points you want to make?
- Looking at your main claims, can you more easily divide them into different ideas (point-by-point) or into different voices (block-by-block)?
- Write out a topic sentence for each of your main points following the method of organization you chose.
Comparative Analysis Survey
- What was the one most important thing you learned from this module?
- Do you have any unanswered questions for me?
Comparative Relationships Between Texts Chart
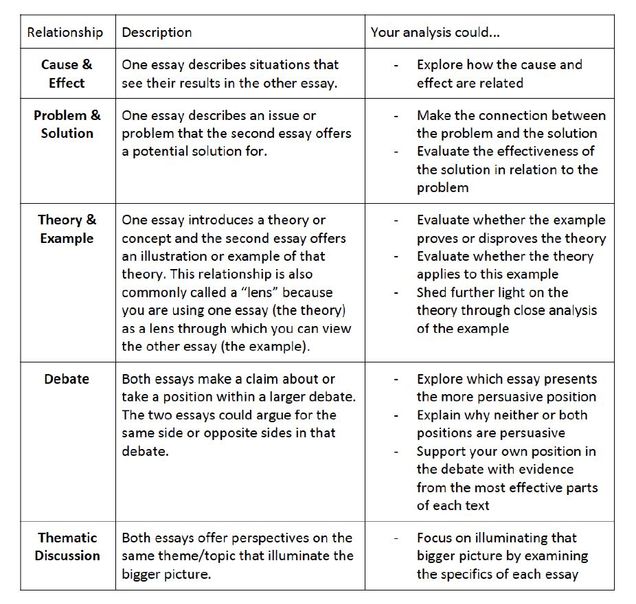
Comparative Analysis In-Class Activity
Goal: To practice writing and evaluating comparative analysis claims.
Materials: One laptop per group; your notes/annotations on reading material; Google doc link sent by your instructor.
Download Worksheet
Download Digital Implementation of the Activity
Graff, Gerald, and Cathy Birkenstein. They Say/I Say: The Moves That Matter in Academic Writing . 3rd ed., W.W. Norton & Co., 2014.
Tompkins, Case. “ Writing in Literature: Writing the Prompt Paper .” The Purdue OWL , Purdue U Writing Lab, 06 December 2013.
Walk, Kerry. “ How to Write a Comparative Analysis .” Harvard College Writing Center , 1998.
Endnote : This module follows the philosophy of the Writing Program and refers to the work of Kevin Barents, Holly Schaff, and Lesley Yoder for specific guidelines, categories, and best practices.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it's official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Browse Titles
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
Lau F, Kuziemsky C, editors. Handbook of eHealth Evaluation: An Evidence-based Approach [Internet]. Victoria (BC): University of Victoria; 2017 Feb 27.

Handbook of eHealth Evaluation: An Evidence-based Approach [Internet].
Chapter 10 methods for comparative studies.
Francis Lau and Anne Holbrook .
10.1. Introduction
In eHealth evaluation, comparative studies aim to find out whether group differences in eHealth system adoption make a difference in important outcomes. These groups may differ in their composition, the type of system in use, and the setting where they work over a given time duration. The comparisons are to determine whether significant differences exist for some predefined measures between these groups, while controlling for as many of the conditions as possible such as the composition, system, setting and duration.
According to the typology by Friedman and Wyatt (2006) , comparative studies take on an objective view where events such as the use and effect of an eHealth system can be defined, measured and compared through a set of variables to prove or disprove a hypothesis. For comparative studies, the design options are experimental versus observational and prospective versus retrospective. The quality of eHealth comparative studies depends on such aspects of methodological design as the choice of variables, sample size, sources of bias, confounders, and adherence to quality and reporting guidelines.
In this chapter we focus on experimental studies as one type of comparative study and their methodological considerations that have been reported in the eHealth literature. Also included are three case examples to show how these studies are done.
10.2. Types of Comparative Studies
Experimental studies are one type of comparative study where a sample of participants is identified and assigned to different conditions for a given time duration, then compared for differences. An example is a hospital with two care units where one is assigned a cpoe system to process medication orders electronically while the other continues its usual practice without a cpoe . The participants in the unit assigned to the cpoe are called the intervention group and those assigned to usual practice are the control group. The comparison can be performance or outcome focused, such as the ratio of correct orders processed or the occurrence of adverse drug events in the two groups during the given time period. Experimental studies can take on a randomized or non-randomized design. These are described below.
10.2.1. Randomized Experiments
In a randomized design, the participants are randomly assigned to two or more groups using a known randomization technique such as a random number table. The design is prospective in nature since the groups are assigned concurrently, after which the intervention is applied then measured and compared. Three types of experimental designs seen in eHealth evaluation are described below ( Friedman & Wyatt, 2006 ; Zwarenstein & Treweek, 2009 ).
Randomized controlled trials ( rct s) – In rct s participants are randomly assigned to an intervention or a control group. The randomization can occur at the patient, provider or organization level, which is known as the unit of allocation. For instance, at the patient level one can randomly assign half of the patients to receive emr reminders while the other half do not. At the provider level, one can assign half of the providers to receive the reminders while the other half continues with their usual practice. At the organization level, such as a multisite hospital, one can randomly assign emr reminders to some of the sites but not others. Cluster randomized controlled trials ( crct s) – In crct s, clusters of participants are randomized rather than by individual participant since they are found in naturally occurring groups such as living in the same communities. For instance, clinics in one city may be randomized as a cluster to receive emr reminders while clinics in another city continue their usual practice. Pragmatic trials – Unlike rct s that seek to find out if an intervention such as a cpoe system works under ideal conditions, pragmatic trials are designed to find out if the intervention works under usual conditions. The goal is to make the design and findings relevant to and practical for decision-makers to apply in usual settings. As such, pragmatic trials have few criteria for selecting study participants, flexibility in implementing the intervention, usual practice as the comparator, the same compliance and follow-up intensity as usual practice, and outcomes that are relevant to decision-makers.
10.2.2. Non-randomized Experiments
Non-randomized design is used when it is neither feasible nor ethical to randomize participants into groups for comparison. It is sometimes referred to as a quasi-experimental design. The design can involve the use of prospective or retrospective data from the same or different participants as the control group. Three types of non-randomized designs are described below ( Harris et al., 2006 ).
Intervention group only with pretest and post-test design – This design involves only one group where a pretest or baseline measure is taken as the control period, the intervention is implemented, and a post-test measure is taken as the intervention period for comparison. For example, one can compare the rates of medication errors before and after the implementation of a cpoe system in a hospital. To increase study quality, one can add a second pretest period to decrease the probability that the pretest and post-test difference is due to chance, such as an unusually low medication error rate in the first pretest period. Other ways to increase study quality include adding an unrelated outcome such as patient case-mix that should not be affected, removing the intervention to see if the difference remains, and removing then re-implementing the intervention to see if the differences vary accordingly. Intervention and control groups with post-test design – This design involves two groups where the intervention is implemented in one group and compared with a second group without the intervention, based on a post-test measure from both groups. For example, one can implement a cpoe system in one care unit as the intervention group with a second unit as the control group and compare the post-test medication error rates in both units over six months. To increase study quality, one can add one or more pretest periods to both groups, or implement the intervention to the control group at a later time to measure for similar but delayed effects. Interrupted time series ( its ) design – In its design, multiple measures are taken from one group in equal time intervals, interrupted by the implementation of the intervention. The multiple pretest and post-test measures decrease the probability that the differences detected are due to chance or unrelated effects. An example is to take six consecutive monthly medication error rates as the pretest measures, implement the cpoe system, then take another six consecutive monthly medication error rates as the post-test measures for comparison in error rate differences over 12 months. To increase study quality, one may add a concurrent control group for comparison to be more convinced that the intervention produced the change.
10.3. Methodological Considerations
The quality of comparative studies is dependent on their internal and external validity. Internal validity refers to the extent to which conclusions can be drawn correctly from the study setting, participants, intervention, measures, analysis and interpretations. External validity refers to the extent to which the conclusions can be generalized to other settings. The major factors that influence validity are described below.
10.3.1. Choice of Variables
Variables are specific measurable features that can influence validity. In comparative studies, the choice of dependent and independent variables and whether they are categorical and/or continuous in values can affect the type of questions, study design and analysis to be considered. These are described below ( Friedman & Wyatt, 2006 ).
Dependent variables – This refers to outcomes of interest; they are also known as outcome variables. An example is the rate of medication errors as an outcome in determining whether cpoe can improve patient safety. Independent variables – This refers to variables that can explain the measured values of the dependent variables. For instance, the characteristics of the setting, participants and intervention can influence the effects of cpoe . Categorical variables – This refers to variables with measured values in discrete categories or levels. Examples are the type of providers (e.g., nurses, physicians and pharmacists), the presence or absence of a disease, and pain scale (e.g., 0 to 10 in increments of 1). Categorical variables are analyzed using non-parametric methods such as chi-square and odds ratio. Continuous variables – This refers to variables that can take on infinite values within an interval limited only by the desired precision. Examples are blood pressure, heart rate and body temperature. Continuous variables are analyzed using parametric methods such as t -test, analysis of variance or multiple regression.
10.3.2. Sample Size
Sample size is the number of participants to include in a study. It can refer to patients, providers or organizations depending on how the unit of allocation is defined. There are four parts to calculating sample size. They are described below ( Noordzij et al., 2010 ).
Significance level – This refers to the probability that a positive finding is due to chance alone. It is usually set at 0.05, which means having a less than 5% chance of drawing a false positive conclusion. Power – This refers to the ability to detect the true effect based on a sample from the population. It is usually set at 0.8, which means having at least an 80% chance of drawing a correct conclusion. Effect size – This refers to the minimal clinically relevant difference that can be detected between comparison groups. For continuous variables, the effect is a numerical value such as a 10-kilogram weight difference between two groups. For categorical variables, it is a percentage such as a 10% difference in medication error rates. Variability – This refers to the population variance of the outcome of interest, which is often unknown and is estimated by way of standard deviation ( sd ) from pilot or previous studies for continuous outcome.
Sample Size Equations for Comparing Two Groups with Continuous and Categorical Outcome Variables.
An example of sample size calculation for an rct to examine the effect of cds on improving systolic blood pressure of hypertensive patients is provided in the Appendix. Refer to the Biomath website from Columbia University (n.d.) for a simple Web-based sample size / power calculator.
10.3.3. Sources of Bias
There are five common sources of biases in comparative studies. They are selection, performance, detection, attrition and reporting biases ( Higgins & Green, 2011 ). These biases, and the ways to minimize them, are described below ( Vervloet et al., 2012 ).
Selection or allocation bias – This refers to differences between the composition of comparison groups in terms of the response to the intervention. An example is having sicker or older patients in the control group than those in the intervention group when evaluating the effect of emr reminders. To reduce selection bias, one can apply randomization and concealment when assigning participants to groups and ensure their compositions are comparable at baseline. Performance bias – This refers to differences between groups in the care they received, aside from the intervention being evaluated. An example is the different ways by which reminders are triggered and used within and across groups such as electronic, paper and phone reminders for patients and providers. To reduce performance bias, one may standardize the intervention and blind participants from knowing whether an intervention was received and which intervention was received. Detection or measurement bias – This refers to differences between groups in how outcomes are determined. An example is where outcome assessors pay more attention to outcomes of patients known to be in the intervention group. To reduce detection bias, one may blind assessors from participants when measuring outcomes and ensure the same timing for assessment across groups. Attrition bias – This refers to differences between groups in ways that participants are withdrawn from the study. An example is the low rate of participant response in the intervention group despite having received reminders for follow-up care. To reduce attrition bias, one needs to acknowledge the dropout rate and analyze data according to an intent-to-treat principle (i.e., include data from those who dropped out in the analysis). Reporting bias – This refers to differences between reported and unreported findings. Examples include biases in publication, time lag, citation, language and outcome reporting depending on the nature and direction of the results. To reduce reporting bias, one may make the study protocol available with all pre-specified outcomes and report all expected outcomes in published results.
10.3.4. Confounders
Confounders are factors other than the intervention of interest that can distort the effect because they are associated with both the intervention and the outcome. For instance, in a study to demonstrate whether the adoption of a medication order entry system led to lower medication costs, there can be a number of potential confounders that can affect the outcome. These may include severity of illness of the patients, provider knowledge and experience with the system, and hospital policy on prescribing medications ( Harris et al., 2006 ). Another example is the evaluation of the effect of an antibiotic reminder system on the rate of post-operative deep venous thromboses ( dvt s). The confounders can be general improvements in clinical practice during the study such as prescribing patterns and post-operative care that are not related to the reminders ( Friedman & Wyatt, 2006 ).
To control for confounding effects, one may consider the use of matching, stratification and modelling. Matching involves the selection of similar groups with respect to their composition and behaviours. Stratification involves the division of participants into subgroups by selected variables, such as comorbidity index to control for severity of illness. Modelling involves the use of statistical techniques such as multiple regression to adjust for the effects of specific variables such as age, sex and/or severity of illness ( Higgins & Green, 2011 ).
10.3.5. Guidelines on Quality and Reporting
There are guidelines on the quality and reporting of comparative studies. The grade (Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation) guidelines provide explicit criteria for rating the quality of studies in randomized trials and observational studies ( Guyatt et al., 2011 ). The extended consort (Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials) Statements for non-pharmacologic trials ( Boutron, Moher, Altman, Schulz, & Ravaud, 2008 ), pragmatic trials ( Zwarestein et al., 2008 ), and eHealth interventions ( Baker et al., 2010 ) provide reporting guidelines for randomized trials.
The grade guidelines offer a system of rating quality of evidence in systematic reviews and guidelines. In this approach, to support estimates of intervention effects rct s start as high-quality evidence and observational studies as low-quality evidence. For each outcome in a study, five factors may rate down the quality of evidence. The final quality of evidence for each outcome would fall into one of high, moderate, low, and very low quality. These factors are listed below (for more details on the rating system, refer to Guyatt et al., 2011 ).
Design limitations – For rct s they cover the lack of allocation concealment, lack of blinding, large loss to follow-up, trial stopped early or selective outcome reporting. Inconsistency of results – Variations in outcomes due to unexplained heterogeneity. An example is the unexpected variation of effects across subgroups of patients by severity of illness in the use of preventive care reminders. Indirectness of evidence – Reliance on indirect comparisons due to restrictions in study populations, intervention, comparator or outcomes. An example is the 30-day readmission rate as a surrogate outcome for quality of computer-supported emergency care in hospitals. Imprecision of results – Studies with small sample size and few events typically would have wide confidence intervals and are considered of low quality. Publication bias – The selective reporting of results at the individual study level is already covered under design limitations, but is included here for completeness as it is relevant when rating quality of evidence across studies in systematic reviews.
The original consort Statement has 22 checklist items for reporting rct s. For non-pharmacologic trials extensions have been made to 11 items. For pragmatic trials extensions have been made to eight items. These items are listed below. For further details, readers can refer to Boutron and colleagues (2008) and the consort website ( consort , n.d.).
Title and abstract – one item on the means of randomization used. Introduction – one item on background, rationale, and problem addressed by the intervention. Methods – 10 items on participants, interventions, objectives, outcomes, sample size, randomization (sequence generation, allocation concealment, implementation), blinding (masking), and statistical methods. Results – seven items on participant flow, recruitment, baseline data, numbers analyzed, outcomes and estimation, ancillary analyses, adverse events. Discussion – three items on interpretation, generalizability, overall evidence.
The consort Statement for eHealth interventions describes the relevance of the consort recommendations to the design and reporting of eHealth studies with an emphasis on Internet-based interventions for direct use by patients, such as online health information resources, decision aides and phr s. Of particular importance is the need to clearly define the intervention components, their role in the overall care process, target population, implementation process, primary and secondary outcomes, denominators for outcome analyses, and real world potential (for details refer to Baker et al., 2010 ).
10.4. Case Examples
10.4.1. pragmatic rct in vascular risk decision support.
Holbrook and colleagues (2011) conducted a pragmatic rct to examine the effects of a cds intervention on vascular care and outcomes for older adults. The study is summarized below.
Setting – Community-based primary care practices with emr s in one Canadian province. Participants – English-speaking patients 55 years of age or older with diagnosed vascular disease, no cognitive impairment and not living in a nursing home, who had a provider visit in the past 12 months. Intervention – A Web-based individualized vascular tracking and advice cds system for eight top vascular risk factors and two diabetic risk factors, for use by both providers and patients and their families. Providers and staff could update the patient’s profile at any time and the cds algorithm ran nightly to update recommendations and colour highlighting used in the tracker interface. Intervention patients had Web access to the tracker, a print version mailed to them prior to the visit, and telephone support on advice. Design – Pragmatic, one-year, two-arm, multicentre rct , with randomization upon patient consent by phone, using an allocation-concealed online program. Randomization was by patient with stratification by provider using a block size of six. Trained reviewers examined emr data and conducted patient telephone interviews to collect risk factors, vascular history, and vascular events. Providers completed questionnaires on the intervention at study end. Patients had final 12-month lab checks on urine albumin, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and A1c levels. Outcomes – Primary outcome was based on change in process composite score ( pcs ) computed as the sum of frequency-weighted process score for each of the eight main risk factors with a maximum score of 27. The process was considered met if a risk factor had been checked. pcs was measured at baseline and study end with the difference as the individual primary outcome scores. The main secondary outcome was a clinical composite score ( ccs ) based on the same eight risk factors compared in two ways: a comparison of the mean number of clinical variables on target and the percentage of patients with improvement between the two groups. Other secondary outcomes were actual vascular event rates, individual pcs and ccs components, ratings of usability, continuity of care, patient ability to manage vascular risk, and quality of life using the EuroQol five dimensions questionnaire ( eq-5D) . Analysis – 1,100 patients were needed to achieve 90% power in detecting a one-point pcs difference between groups with a standard deviation of five points, two-tailed t -test for mean difference at 5% significance level, and a withdrawal rate of 10%. The pcs , ccs and eq-5D scores were analyzed using a generalized estimating equation accounting for clustering within providers. Descriptive statistics and χ2 tests or exact tests were done with other outcomes. Findings – 1,102 patients and 49 providers enrolled in the study. The intervention group with 545 patients had significant pcs improvement with a difference of 4.70 ( p < .001) on a 27-point scale. The intervention group also had significantly higher odds of rating improvements in their continuity of care (4.178, p < .001) and ability to improve their vascular health (3.07, p < .001). There was no significant change in vascular events, clinical variables and quality of life. Overall the cds intervention led to reduced vascular risks but not to improved clinical outcomes in a one-year follow-up.
10.4.2. Non-randomized Experiment in Antibiotic Prescribing in Primary Care
Mainous, Lambourne, and Nietert (2013) conducted a prospective non-randomized trial to examine the impact of a cds system on antibiotic prescribing for acute respiratory infections ( ari s) in primary care. The study is summarized below.
Setting – A primary care research network in the United States whose members use a common emr and pool data quarterly for quality improvement and research studies. Participants – An intervention group with nine practices across nine states, and a control group with 61 practices. Intervention – Point-of-care cds tool as customizable progress note templates based on existing emr features. cds recommendations reflect Centre for Disease Control and Prevention ( cdc ) guidelines based on a patient’s predominant presenting symptoms and age. cds was used to assist in ari diagnosis, prompt antibiotic use, record diagnosis and treatment decisions, and access printable patient and provider education resources from the cdc . Design – The intervention group received a multi-method intervention to facilitate provider cds adoption that included quarterly audit and feedback, best practice dissemination meetings, academic detailing site visits, performance review and cds training. The control group did not receive information on the intervention, the cds or education. Baseline data collection was for three months with follow-up of 15 months after cds implementation. Outcomes – The outcomes were frequency of inappropriate prescribing during an ari episode, broad-spectrum antibiotic use and diagnostic shift. Inappropriate prescribing was computed by dividing the number of ari episodes with diagnoses in the inappropriate category that had an antibiotic prescription by the total number of ari episodes with diagnosis for which antibiotics are inappropriate. Broad-spectrum antibiotic use was computed by all ari episodes with a broad-spectrum antibiotic prescription by the total number of ari episodes with an antibiotic prescription. Antibiotic drift was computed in two ways: dividing the number of ari episodes with diagnoses where antibiotics are appropriate by the total number of ari episodes with an antibiotic prescription; and dividing the number of ari episodes where antibiotics were inappropriate by the total number of ari episodes. Process measure included frequency of cds template use and whether the outcome measures differed by cds usage. Analysis – Outcomes were measured quarterly for each practice, weighted by the number of ari episodes during the quarter to assign greater weight to practices with greater numbers of relevant episodes and to periods with greater numbers of relevant episodes. Weighted means and 95% ci s were computed separately for adult and pediatric (less than 18 years of age) patients for each time period for both groups. Baseline means in outcome measures were compared between the two groups using weighted independent-sample t -tests. Linear mixed models were used to compare changes over the 18-month period. The models included time, intervention status, and were adjusted for practice characteristics such as specialty, size, region and baseline ari s. Random practice effects were included to account for clustering of repeated measures on practices over time. P -values of less than 0.05 were considered significant. Findings – For adult patients, inappropriate prescribing in ari episodes declined more among the intervention group (-0.6%) than the control group (4.2%)( p = 0.03), and prescribing of broad-spectrum antibiotics declined by 16.6% in the intervention group versus an increase of 1.1% in the control group ( p < 0.0001). For pediatric patients, there was a similar decline of 19.7% in the intervention group versus an increase of 0.9% in the control group ( p < 0.0001). In summary, the cds had a modest effect in reducing inappropriate prescribing for adults, but had a substantial effect in reducing the prescribing of broad-spectrum antibiotics in adult and pediatric patients.
10.4.3. Interrupted Time Series on EHR Impact in Nursing Care
Dowding, Turley, and Garrido (2012) conducted a prospective its study to examine the impact of ehr implementation on nursing care processes and outcomes. The study is summarized below.
Setting – Kaiser Permanente ( kp ) as a large not-for-profit integrated healthcare organization in the United States. Participants – 29 kp hospitals in the northern and southern regions of California. Intervention – An integrated ehr system implemented at all hospitals with cpoe , nursing documentation and risk assessment tools. The nursing component for risk assessment documentation of pressure ulcers and falls was consistent across hospitals and developed by clinical nurses and informaticists by consensus. Design – its design with monthly data on pressure ulcers and quarterly data on fall rates and risk collected over seven years between 2003 and 2009. All data were collected at the unit level for each hospital. Outcomes – Process measures were the proportion of patients with a fall risk assessment done and the proportion with a hospital-acquired pressure ulcer ( hapu ) risk assessment done within 24 hours of admission. Outcome measures were fall and hapu rates as part of the unit-level nursing care process and nursing sensitive outcome data collected routinely for all California hospitals. Fall rate was defined as the number of unplanned descents to the floor per 1,000 patient days, and hapu rate was the percentage of patients with stages i-IV or unstageable ulcer on the day of data collection. Analysis – Fall and hapu risk data were synchronized using the month in which the ehr was implemented at each hospital as time zero and aggregated across hospitals for each time period. Multivariate regression analysis was used to examine the effect of time, region and ehr . Findings – The ehr was associated with significant increase in document rates for hapu risk (2.21; 95% CI 0.67 to 3.75) and non-significant increase for fall risk (0.36; -3.58 to 4.30). The ehr was associated with 13% decrease in hapu rates (-0.76; -1.37 to -0.16) but no change in fall rates (-0.091; -0.29 to 011). Hospital region was a significant predictor of variation for hapu (0.72; 0.30 to 1.14) and fall rates (0.57; 0.41 to 0.72). During the study period, hapu rates decreased significantly (-0.16; -0.20 to -0.13) but not fall rates (0.0052; -0.01 to 0.02). In summary, ehr implementation was associated with a reduction in the number of hapu s but not patient falls, and changes over time and hospital region also affected outcomes.
10.5. Summary
In this chapter we introduced randomized and non-randomized experimental designs as two types of comparative studies used in eHealth evaluation. Randomization is the highest quality design as it reduces bias, but it is not always feasible. The methodological issues addressed include choice of variables, sample size, sources of biases, confounders, and adherence to reporting guidelines. Three case examples were included to show how eHealth comparative studies are done.
- Baker T. B., Gustafson D. H., Shaw B., Hawkins R., Pingree S., Roberts L., Strecher V. Relevance of consort reporting criteria for research on eHealth interventions. Patient Education and Counselling. 2010; 81 (suppl. 7):77–86. [ PMC free article : PMC2993846 ] [ PubMed : 20843621 ]
- Columbia University. (n.d.). Statistics: sample size / power calculation. Biomath (Division of Biomathematics/Biostatistics), Department of Pediatrics. New York: Columbia University Medical Centre. Retrieved from http://www .biomath.info/power/index.htm .
- Boutron I., Moher D., Altman D. G., Schulz K. F., Ravaud P. consort Group. Extending the consort statement to randomized trials of nonpharmacologic treatment: Explanation and elaboration. Annals of Internal Medicine. 2008; 148 (4):295–309. [ PubMed : 18283207 ]
- Cochrane Collaboration. Cochrane handbook. London: Author; (n.d.) Retrieved from http://handbook .cochrane.org/
- consort Group. (n.d.). The consort statement . Retrieved from http://www .consort-statement.org/
- Dowding D. W., Turley M., Garrido T. The impact of an electronic health record on nurse sensitive patient outcomes: an interrupted time series analysis. Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association. 2012; 19 (4):615–620. [ PMC free article : PMC3384108 ] [ PubMed : 22174327 ]
- Friedman C. P., Wyatt J.C. Evaluation methods in biomedical informatics. 2nd ed. New York: Springer Science + Business Media, Inc; 2006.
- Guyatt G., Oxman A. D., Akl E. A., Kunz R., Vist G., Brozek J. et al. Schunemann H. J. grade guidelines: 1. Introduction – grade evidence profiles and summary of findings tables. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology. 2011; 64 (4):383–394. [ PubMed : 21195583 ]
- Harris A. D., McGregor J. C., Perencevich E. N., Furuno J. P., Zhu J., Peterson D. E., Finkelstein J. The use and interpretation of quasi-experimental studies in medical informatics. Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association. 2006; 13 (1):16–23. [ PMC free article : PMC1380192 ] [ PubMed : 16221933 ]
- The Cochrane Collaboration. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Higgins J. P. T., Green S., editors. London: 2011. (Version 5.1.0, updated March 2011) Retrieved from http://handbook .cochrane.org/
- Holbrook A., Pullenayegum E., Thabane L., Troyan S., Foster G., Keshavjee K. et al. Curnew G. Shared electronic vascular risk decision support in primary care. Computerization of medical practices for the enhancement of therapeutic effectiveness (compete III) randomized trial. Archives of Internal Medicine. 2011; 171 (19):1736–1744. [ PubMed : 22025430 ]
- Mainous III A. G., Lambourne C. A., Nietert P.J. Impact of a clinical decision support system on antibiotic prescribing for acute respiratory infections in primary care: quasi-experimental trial. Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association. 2013; 20 (2):317–324. [ PMC free article : PMC3638170 ] [ PubMed : 22759620 ]
- Noordzij M., Tripepi G., Dekker F. W., Zoccali C., Tanck M. W., Jager K.J. Sample size calculations: basic principles and common pitfalls. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation. 2010; 25 (5):1388–1393. Retrieved from http://ndt .oxfordjournals .org/content/early/2010/01/12/ndt .gfp732.short . [ PubMed : 20067907 ]
- Vervloet M., Linn A. J., van Weert J. C. M., de Bakker D. H., Bouvy M. L., van Dijk L. The effectiveness of interventions using electronic reminders to improve adherence to chronic medication: A systematic review of the literature. Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association. 2012; 19 (5):696–704. [ PMC free article : PMC3422829 ] [ PubMed : 22534082 ]
- Zwarenstein M., Treweek S., Gagnier J. J., Altman D. G., Tunis S., Haynes B., Oxman A. D., Moher D. for the consort and Pragmatic Trials in Healthcare (Practihc) groups. Improving the reporting of pragmatic trials: an extension of the consort statement. British Medical Journal. 2008; 337 :a2390. [ PMC free article : PMC3266844 ] [ PubMed : 19001484 ] [ CrossRef ]
- Zwarenstein M., Treweek S. What kind of randomized trials do we need? Canadian Medical Association Journal. 2009; 180 (10):998–1000. [ PMC free article : PMC2679816 ] [ PubMed : 19372438 ]
Appendix. Example of Sample Size Calculation
This is an example of sample size calculation for an rct that examines the effect of a cds system on reducing systolic blood pressure in hypertensive patients. The case is adapted from the example described in the publication by Noordzij et al. (2010) .
(a) Systolic blood pressure as a continuous outcome measured in mmHg
Based on similar studies in the literature with similar patients, the systolic blood pressure values from the comparison groups are expected to be normally distributed with a standard deviation of 20 mmHg. The evaluator wishes to detect a clinically relevant difference of 15 mmHg in systolic blood pressure as an outcome between the intervention group with cds and the control group without cds . Assuming a significance level or alpha of 0.05 for 2-tailed t -test and power of 0.80, the corresponding multipliers 1 are 1.96 and 0.842, respectively. Using the sample size equation for continuous outcome below we can calculate the sample size needed for the above study.
n = 2[(a+b)2σ2]/(μ1-μ2)2 where
n = sample size for each group
μ1 = population mean of systolic blood pressures in intervention group
μ2 = population mean of systolic blood pressures in control group
μ1- μ2 = desired difference in mean systolic blood pressures between groups
σ = population variance
a = multiplier for significance level (or alpha)
b = multiplier for power (or 1-beta)
Providing the values in the equation would give the sample size (n) of 28 samples per group as the result
n = 2[(1.96+0.842)2(202)]/152 or 28 samples per group
(b) Systolic blood pressure as a categorical outcome measured as below or above 140 mmHg (i.e., hypertension yes/no)
In this example a systolic blood pressure from a sample that is above 140 mmHg is considered an event of the patient with hypertension. Based on published literature the proportion of patients in the general population with hypertension is 30%. The evaluator wishes to detect a clinically relevant difference of 10% in systolic blood pressure as an outcome between the intervention group with cds and the control group without cds . This means the expected proportion of patients with hypertension is 20% (p1 = 0.2) in the intervention group and 30% (p2 = 0.3) in the control group. Assuming a significance level or alpha of 0.05 for 2-tailed t -test and power of 0.80 the corresponding multipliers are 1.96 and 0.842, respectively. Using the sample size equation for categorical outcome below, we can calculate the sample size needed for the above study.
n = [(a+b)2(p1q1+p2q2)]/χ2
p1 = proportion of patients with hypertension in intervention group
q1 = proportion of patients without hypertension in intervention group (or 1-p1)
p2 = proportion of patients with hypertension in control group
q2 = proportion of patients without hypertension in control group (or 1-p2)
χ = desired difference in proportion of hypertensive patients between two groups
Providing the values in the equation would give the sample size (n) of 291 samples per group as the result
n = [(1.96+0.842)2((0.2)(0.8)+(0.3)(0.7))]/(0.1)2 or 291 samples per group
From Table 3 on p. 1392 of Noordzij et al. (2010).
This publication is licensed under a Creative Commons License, Attribution-Noncommercial 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC 4.0): see https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/
- Cite this Page Lau F, Holbrook A. Chapter 10 Methods for Comparative Studies. In: Lau F, Kuziemsky C, editors. Handbook of eHealth Evaluation: An Evidence-based Approach [Internet]. Victoria (BC): University of Victoria; 2017 Feb 27.
- PDF version of this title (4.5M)
- Disable Glossary Links
In this Page
- Introduction
- Types of Comparative Studies
- Methodological Considerations
- Case Examples
- Example of Sample Size Calculation
Related information
- PMC PubMed Central citations
- PubMed Links to PubMed
Recent Activity
- Chapter 10 Methods for Comparative Studies - Handbook of eHealth Evaluation: An ... Chapter 10 Methods for Comparative Studies - Handbook of eHealth Evaluation: An Evidence-based Approach
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
Turn recording back on
Connect with NLM
National Library of Medicine 8600 Rockville Pike Bethesda, MD 20894
Web Policies FOIA HHS Vulnerability Disclosure
Help Accessibility Careers

Global Encyclopedia of Public Administration, Public Policy, and Governance pp 1–6 Cite as
Comparative Historical Analysis, A Methodological Perspective
- Frank L. K. Ohemeng 2
- Living reference work entry
- First Online: 14 July 2020
288 Accesses
Approximate ; Comparable ; Equivalent ; Provisional
Definitions
Comparative historical analysis is concerned with causal analysis, an emphasis on processes over time, and the use of systematic and contextualized comparison (Mahoney and Rueschemeyer 2003a ).
Comparative historical analysis is a field of research characterized by the use of systematic comparison and the analysis of processes over time to explain large-scale outcomes such as revolutions, political regimes, and welfare states. It can be distinguished from other approaches within historical sociology, such as rational choice analysis and interpretive analysis (Mahoney and Rueschemeyer 2003a ).
Introduction
Among ways of understanding social issues, one that has best stood the test of time is comparative historical analysis (CHA) (Lange 2013 ; Mahoney and Rueschemeyer 2003a ; Mahoney and Terrie 2008 ). Although it has been around as long as anyone can remember, it is, as a number of scholars have noted, only in the past 30...
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution .
Acemoglu D, Johnson S, Robinson J (2001) Colonial origins of comparative development: an empirical investigation. Am Econ Rev 91(5):1369–1401
Article Google Scholar
Amenta E (2003) What we know about the development of social policy: comparative and historical research in comparative and historical perspective. In: Mahoney J, Rueschemeyer D (eds) Comparative historical analysis in the social sciences. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Google Scholar
Barzelay M, Gallego R (2010) The comparative historical analysis of public management policy cycles in France, Italy, and Spain: symposium introduction. Governance 23(2):209–223
Bennett A (2008) Process tracing: a Bayesian perspective. In: Box-Steffensmeier JM, Brady HE, Collier D (eds) The Oxford handbook of political methodology. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Boas TC (2017) Potential mistakes, plausible options: establishing the legacy of hypothesized critical junctures. Qual Multi-Method Res 15(1):18–20
Castles FG (ed) (1989) The comparative history of public policy. Oxford University Press, New York
Collier D (1998) Comparative historical analysis: where do we stand? APSA-CP Newsl APSA Organ Section Comp Polit 9(2):1–2, 4–5
Collier D (2011) Understanding process tracing. PS: Polit Sci Pol 44(4):823–830
Collier RB, Collier D (1991) Shaping the political arena: critical junctures, the labor movement, and regime dynamics in latin america. Princeton University Press, Princeton
George AL, Bennett A (2005) Case studies and theory development in social sciences. MIT Press, Cambridge
Goldstone JA (2003) Comparative historical analysis and knowledge accumulation in the study of revolutions. In: Mahoney J, Rueschemeyer D (eds) Comparative historical analysis in the social sciences. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Hodgson GM (2007) Meanings of methodological individualism. J Econ Methodol 14(2):211–226
Jaramillo G (2020) Comparing historical cases: advances in comparative historical research. In: Guy Peters B, Fontaine G (eds) Handbook of research methods and applications in comparative policy analysis. Cheltenham, Edward Elgar, pp 113–133
Lange M (2013) Comparative-historical methods. Los Angeles, California, Sage
Lijphart A (1971) Comparative politics and the comparative method. Am Polit Sci Rev 65(3):682–693
Mahoney J (2003) Knowledge accumulation in comparative historical research: the case of democracy and authoritarianism. In Mahoney J, Rueschemeyer D (eds) Comparative historical analysis in the social sciences. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 131–174
Mahoney J (2004) Comparative-historical methodology. Annu Rev Sociol 30:81–101
Mahoney J (2015) Comparative-historical analysis and development studies: methods, findings, future. Sociol Dev 1(1):77–90
Mahoney J, Rueschemeyer D (eds) (2003a) Comparative historical analysis in the social sciences. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Mahoney J, Rueschemeyer D (2003b) Comparative historical analysis: achievements and agendas. In: Mahoney J, Rueschemeyer D (eds) Comparative historical analysis in the social sciences. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Chapter Google Scholar
Mahoney J, Terrie PL (2008) Comparative-historical analysis in contemporary political science. In: Box-Steffensmeier JM, Brady H, Collier D (eds) Oxford handbook of political methodology. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Offen K (1988) Defining feminism: a comparative historical approach. Signs 14(1):119–157
Paterson BL (2010) Within case analysis. In: Mills AJ, Durepos G, Wiebe E (eds) Encyclopedia of case study research. SAGE, Thousand Oaks
Paul C, Clarke CP, Grill B, Savitsky T (2013) Between large-N and small-N analyses: historical comparison of thirty insurgency case studies. Hist Methods 46(4): 220–239
Pepinsky TB (2019) The return of the single-country study. Annu Rev Polit Sci 22:187–203
Risks J, Liu AH (2018) Process-tracing research designs: a practical guide. Polit Sci Polit 51(4):1–5
Ritter DP (2014) Comparative historical analysis. In: Porta Dd (ed) Methodological practices in social movement research. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Rueschemeyer D (2003) Can one or a few cases yield theoretical gains? In: Mahoney J, Rueschemeyer D (eds) Comparative Historical Analysis in the Social Sciences. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 203–336
Skocpol T (2003) Doubly engage social science: the promise of comparative historical analysis. In: Mahoney J, Rueschemeyer D (eds) Comparative historical analysis in the social sciences. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Smith PL, Little DR (2018) Small is beautiful: in defense of the small-N design. Psychon Bull Rev 25:2083–2101
Thelen K, Mahoney J (2015) Comparative-historical analysis in contemporary political science. In: Mahoney J, Thelen K (eds) Advances in comparative-historical analysis. Cambridge University Press, New York
Zaks S (2016) The logic of process tracing: contributions, pitfalls and future directions. In: Keman H, Woldendorp JJ (eds) Handbook of research methods and applications in political science. Edward Elgar, Cheltenham
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Political Science, Concordia University, Montreal, QC, Canada
Frank L. K. Ohemeng
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Frank L. K. Ohemeng .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Florida Atlantic University, Boca Raton, FL, USA
Ali Farazmand
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this entry
Cite this entry.
Ohemeng, F.L.K. (2020). Comparative Historical Analysis, A Methodological Perspective. In: Farazmand, A. (eds) Global Encyclopedia of Public Administration, Public Policy, and Governance. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-31816-5_1205-1
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-31816-5_1205-1
Received : 20 May 2020
Accepted : 24 June 2020
Published : 14 July 2020
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-319-31816-5
Online ISBN : 978-3-319-31816-5
eBook Packages : Springer Reference Economics and Finance Reference Module Humanities and Social Sciences Reference Module Business, Economics and Social Sciences
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Comparing and contrasting in an essay | Tips & examples
Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay | Tips & Examples
Published on August 6, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on July 23, 2023.
Comparing and contrasting is an important skill in academic writing . It involves taking two or more subjects and analyzing the differences and similarities between them.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
When should i compare and contrast, making effective comparisons, comparing and contrasting as a brainstorming tool, structuring your comparisons, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about comparing and contrasting.
Many assignments will invite you to make comparisons quite explicitly, as in these prompts.
- Compare the treatment of the theme of beauty in the poetry of William Wordsworth and John Keats.
- Compare and contrast in-class and distance learning. What are the advantages and disadvantages of each approach?
Some other prompts may not directly ask you to compare and contrast, but present you with a topic where comparing and contrasting could be a good approach.
One way to approach this essay might be to contrast the situation before the Great Depression with the situation during it, to highlight how large a difference it made.
Comparing and contrasting is also used in all kinds of academic contexts where it’s not explicitly prompted. For example, a literature review involves comparing and contrasting different studies on your topic, and an argumentative essay may involve weighing up the pros and cons of different arguments.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
As the name suggests, comparing and contrasting is about identifying both similarities and differences. You might focus on contrasting quite different subjects or comparing subjects with a lot in common—but there must be some grounds for comparison in the first place.
For example, you might contrast French society before and after the French Revolution; you’d likely find many differences, but there would be a valid basis for comparison. However, if you contrasted pre-revolutionary France with Han-dynasty China, your reader might wonder why you chose to compare these two societies.
This is why it’s important to clarify the point of your comparisons by writing a focused thesis statement . Every element of an essay should serve your central argument in some way. Consider what you’re trying to accomplish with any comparisons you make, and be sure to make this clear to the reader.
Comparing and contrasting can be a useful tool to help organize your thoughts before you begin writing any type of academic text. You might use it to compare different theories and approaches you’ve encountered in your preliminary research, for example.
Let’s say your research involves the competing psychological approaches of behaviorism and cognitive psychology. You might make a table to summarize the key differences between them.
Or say you’re writing about the major global conflicts of the twentieth century. You might visualize the key similarities and differences in a Venn diagram.
These visualizations wouldn’t make it into your actual writing, so they don’t have to be very formal in terms of phrasing or presentation. The point of comparing and contrasting at this stage is to help you organize and shape your ideas to aid you in structuring your arguments.
When comparing and contrasting in an essay, there are two main ways to structure your comparisons: the alternating method and the block method.
The alternating method
In the alternating method, you structure your text according to what aspect you’re comparing. You cover both your subjects side by side in terms of a specific point of comparison. Your text is structured like this:
Mouse over the example paragraph below to see how this approach works.
One challenge teachers face is identifying and assisting students who are struggling without disrupting the rest of the class. In a traditional classroom environment, the teacher can easily identify when a student is struggling based on their demeanor in class or simply by regularly checking on students during exercises. They can then offer assistance quietly during the exercise or discuss it further after class. Meanwhile, in a Zoom-based class, the lack of physical presence makes it more difficult to pay attention to individual students’ responses and notice frustrations, and there is less flexibility to speak with students privately to offer assistance. In this case, therefore, the traditional classroom environment holds the advantage, although it appears likely that aiding students in a virtual classroom environment will become easier as the technology, and teachers’ familiarity with it, improves.
The block method
In the block method, you cover each of the overall subjects you’re comparing in a block. You say everything you have to say about your first subject, then discuss your second subject, making comparisons and contrasts back to the things you’ve already said about the first. Your text is structured like this:
- Point of comparison A
- Point of comparison B
The most commonly cited advantage of distance learning is the flexibility and accessibility it offers. Rather than being required to travel to a specific location every week (and to live near enough to feasibly do so), students can participate from anywhere with an internet connection. This allows not only for a wider geographical spread of students but for the possibility of studying while travelling. However, distance learning presents its own accessibility challenges; not all students have a stable internet connection and a computer or other device with which to participate in online classes, and less technologically literate students and teachers may struggle with the technical aspects of class participation. Furthermore, discomfort and distractions can hinder an individual student’s ability to engage with the class from home, creating divergent learning experiences for different students. Distance learning, then, seems to improve accessibility in some ways while representing a step backwards in others.
Note that these two methods can be combined; these two example paragraphs could both be part of the same essay, but it’s wise to use an essay outline to plan out which approach you’re taking in each paragraph.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
Some essay prompts include the keywords “compare” and/or “contrast.” In these cases, an essay structured around comparing and contrasting is the appropriate response.
Comparing and contrasting is also a useful approach in all kinds of academic writing : You might compare different studies in a literature review , weigh up different arguments in an argumentative essay , or consider different theoretical approaches in a theoretical framework .
Your subjects might be very different or quite similar, but it’s important that there be meaningful grounds for comparison . You can probably describe many differences between a cat and a bicycle, but there isn’t really any connection between them to justify the comparison.
You’ll have to write a thesis statement explaining the central point you want to make in your essay , so be sure to know in advance what connects your subjects and makes them worth comparing.
Comparisons in essays are generally structured in one of two ways:
- The alternating method, where you compare your subjects side by side according to one specific aspect at a time.
- The block method, where you cover each subject separately in its entirety.
It’s also possible to combine both methods, for example by writing a full paragraph on each of your topics and then a final paragraph contrasting the two according to a specific metric.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, July 23). Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay | Tips & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 2, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/compare-and-contrast/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, how to write an expository essay, how to write an argumentative essay | examples & tips, academic paragraph structure | step-by-step guide & examples, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”

What is Qualitative Comparative Analysis (QCA)?

Introduction
A brief introduction to qualitative comparative analysis, what does qca do, when do researchers use qca, examples of qualitative comparative analysis, what is the qualitative comparative analysis method, strengths of qualitative comparative analysis, weaknesses of qualitative comparative analysis.
Qualitative comparative analysis (QCA) stands as a pivotal approach in the realm of social science research. Designed to bridge the gap between qualitative and quantitative analysis , QCA offers a unique way to systematically study complex social phenomena by analyzing qualitative data. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of its concepts, applications, strengths, and weaknesses to give you a clearer grasp of what QCA is and why it's essential in today's research landscape.

Qualitative comparative analysis is a research methodology primarily rooted in the social sciences, yet its applicability spans across diverse fields. It was originally developed by Charles Ragin in the 1980s as a method to address challenges faced when analyzing complex social situations. At its core, QCA is designed to systematically compare cases to identify patterns.
Unlike traditional qualitative research methods that focus on understanding individual cases in depth, or quantitative methods that seek generalizations from large datasets, QCA finds its niche in the middle ground. It aims to derive general patterns from a limited number of cases by treating them as configurations of attributes or conditions. Through this, qualitative researchers can identify which combinations of conditions lead to an outcome of interest, allowing for a nuanced understanding that both respects case specificity and seeks broader patterns.
Moreover, QCA models use Boolean algebra and set theory to make multiple comparisons. This mathematical approach ensures that the method remains rigorous and structured, granting researchers a solid foundation for building analyses and conclusions. As such, QCA is not just a method, but a fusion of deep insights from both qualitative and quantitative analysis .
At its essence, QCA allows researchers to discern relationships between conditions and outcomes across various cases. It serves a dual purpose: simplifying complex data while preserving the depth and richness of each case.
QCA helps in identifying "causal recipes." Unlike traditional variable oriented methods that seek a singular cause for an outcome, QCA acknowledges that multiple paths can lead to the same result. These paths or "recipes" are different configurations of conditions that lead to a particular outcome.
QCA emphasizes the importance of "conjunctural causation." This means that it's not just the presence or absence of individual conditions that matter, but the specific combination of these conditions. QCA thus recognizes the role of "equifinality" in social phenomena. This principle asserts that there can be multiple, equally valid paths leading to the same outcome.
Qualitative analysis made easy with ATLAS.ti
Analyze complex data with our cutting-edge qualitative analysis software, starting with a free trial.
Researchers often turn to QCA when they're faced with a complex interplay of conditions and outcomes. Given its unique blend of quantitative and qualitative methods , QCA provides a framework to embrace and understand this complexity.
In the realm of political science, for instance, research may want to study how policy-making, governance, and societal structures are intertwined. Imagine a study aiming to understand the factors leading to successful democratic transitions. Here, various combinations of historical, cultural, economic, and social conditions can be assessed to determine which specific combinations lead to a democracy.
Similarly, in health research, the factors affecting health outcomes can be manifold. For instance, when studying the impact of health campaigns hosted on web sites aiming to reduce smoking rates, researchers might find that cultural background, age, frequency of website interaction, and existing health beliefs all play a part. Instead of trying to find a single dominant factor, scholars can identify multiple pathways through which these campaigns might succeed or fail.
Additionally, this method can facilitate systematic cross case analysis in comparative research with multiple cases. Researchers can highlight patterns and relationships without losing sight of the unique intricacies of each case. Moreover, fuzzy set analysis enables researchers to deal with cases that don't fit neatly into binary categories. For instance, instead of classifying a country as simply democratic or not in the above example, fuzzy sets are based on degrees of membership, acknowledging the continuum of political systems.
Qualitative comparative analysis finds its utility in a diverse range of fields, and its flexibility makes it a favorite among researchers tackling intricate questions. Within research on politics and democratic transitions, the use of QCA, particularly "crisp set QCA", is evident. This version of QCA, which relies on binary distinctions (e.g., democratic vs. non-democratic), aids researchers in understanding the myriad conditions—such as civil unrest, economic stability, international influences, and historical legacies—that lead to a nation's democratic evolution. Utilizing crisp set QCA, researchers pinpoint combinations of these conditions that consistently catalyze democratic shifts.
In health care research, specifically studies analyzing the effectiveness of web-based campaigns promoting vaccination, "multi-value QCA" may be more suitable. Unlike its binary counterpart, multi-value QCA allows for more than two values in the causal conditions. This is particularly useful when examining a variety of factors, such as age groups, different socioeconomic brackets, and varying levels of prior beliefs. With this nuanced approach, researchers can systematically determine which combination of conditions are related to heightened vaccination rates.
Conducting QCA involves a series of structured steps that guide researchers from the initial phase of conceptualizing their study to the final interpretation of results . Here's a simplified breakdown of the process:
- Case selection : Begin by choosing the cases you wish to study. These cases should have varying outcomes concerning the research question , ensuring a mix of both positive and negative results.
- Define conditions and outcomes : Clearly define the causal conditions you believe influence the outcome. These can be binary (e.g., success/failure) in crisp set QCA or more nuanced in fuzzy set or multi-value QCA. Additionally, identify the outcome or outcomes of interest.
- Calibration : Assign values to each causal condition within each case. In crisp set QCA, this is a straightforward binary distinction. However, in fuzzy set QCA, the causal conditions need to be calibrated to indicate the degree of membership of each case in a given condition (i.e., given a value between 0 and 1, which refers to full membership). These set membership scores depend on each condition and the dataset, such that researchers' chosen cutoff points are a crucial aspect of fuzzy set analysis.
- Construct a truth table : After assigning values to each causal condition, create a truth table. This data matrix lists all possible combinations of conditions and their associated outcomes. It's a visual representation of how different conditions are related to the desired outcome.
- Analyze patterns : With the truth table at hand, identify patterns that lead to the outcome of interest. Look for combinations of conditions that consistently result in a particular outcome. Dedicated computer software for QCA can greatly facilitate this process by calculating and setting frequency and consistency values. Determining cutoff points (both for determining set membership and which possible configurations are related to the presence of the outcome) is often an iterative process, as researchers can try different combinations based on their causal inferences.
- Interpretation and presentation : After setting up the truth table and indicating the positive or negative outcomes of each combination, run the analysis and interpret the findings . The results convey which combinations of causal conditions are necessary or sufficient for the desired outcome. These findings can be presented in a manner that highlights the causal complexity and provides insights into the phenomenon under study. Researchers typically present the results of QCA in a table displaying the different causal configurations with symbols indicating the absence or presence of each condition within each configuration.
QCA boasts several strengths that make it a favored method in various research domains. Chief among these is its ability to bridge the gap between qualitative and quantitative research , allowing for in-depth case understanding while drawing broader, systematic conclusions. QCA analysis does not depend on having a high number of cases to assess causality. It adeptly handles the complexity of real-world scenarios by acknowledging multiple pathways to the same outcome (equifinality) and asymmetric causality, ensuring researchers capture the full spectrum of causal dynamics. Its emphasis on conjunctural causation enables the identification of unique combinations of conditions leading to outcomes, offering richer insights than traditional linear regression based on quantitative measures. Additionally, with set theory and robust statistical techniques at its foundation, QCA provides a structured and rigorous analytic technique.
While QCA offers a myriad of benefits, it's essential to recognize its limitations as well. Firstly, QCA can be data-intensive; each case requires meticulous detailing, which can be demanding when dealing with a large number of cases. The method's reliance on Boolean algebra and set theory, while providing structure, can also be a double-edged sword. Oversimplification or incorrect calibration can lead to misleading results. Furthermore, QCA, being primarily a cross-sectional analysis tool, might not be ideal for studies requiring a temporal or longitudinal perspective . Also, while it excels in identifying combinations of causal conditions, it may not always elucidate the deeper mechanisms or processes underlying those causalities. As with any research method, it's imperative for researchers to understand these constraints and apply QCA judiciously, ensuring that its application aligns with the research question and context.

Compare and analyze complex data sets with ATLAS.ti
Make your data work for you with our powerful data analysis interface. Download a free trial today.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Comparative analysis is a systematic approach used to evaluate and compare two or more entities, variables, or options to identify similarities, differences, and patterns. It involves assessing the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats associated with each entity or option to make informed decisions.
A comparative analysis is a side-by-side comparison that systematically compares two or more things to pinpoint their similarities and differences. The focus of the investigation might be conceptual—a particular problem, idea, or theory—or perhaps something more tangible, like two different data sets. For instance, you could use comparative ...
Comparative analysis equips product owners with vital insights to make informed decisions. By evaluating competitors, product owners gain clarity on market trends and consumer preferences. They can identify gaps in their offerings and adapt strategies accordingly. This analysis guides decisions on features, pricing, and positioning, ensuring ...
Comparative analysis is a method that is widely used in social science. It is a method of comparing two or more items with an idea of uncovering and discovering new ideas about them. It often compares and contrasts social structures and processes around the world to grasp general patterns. Comparative analysis tries to understand the study and ...
Comparative analyses can build up to other kinds of writing in a number of ways. For example: They can build toward other kinds of comparative analysis, e.g., student can be asked to choose an additional source to complicate their conclusions from a previous analysis, or they can be asked to revisit an analysis using a different axis of comparison, such as race instead of class.
Describe both sides. Comparative analysis may try to show that one argument or idea is better, but the analysis must cover both sides equally. The analysis shows both sides of the main arguments and claims. For example, to compare the benefits and drawbacks of starting a recycling program, one might examine both the positive effects, such as ...
What is Comparative Analysis? Comparative analysis can be defined as a method to compare similar items to one another and see their differences and what they have in common. It is used in many ...
His approach, Qualitative Comparative Analysis (QCA), is a configurational or holistic comparative method which considers each case (system, culture) as a complex entity, as a "whole," which needs to be studied in a case-sensitive way. It combines quantitative, variable-based logic and qualitative, case-based interpretation.
This module presents the macro-quantitative (statistical) methods by giving examples of recent research employing them. It analyzes the regression analysis and the various ways of analyzing data. Moreover, it concludes the course and opens to further perspectives on comparative research designs and methods.
Comparative analysis is a multidisciplinary method, which spans a wide cross-section of disciplines (Azarian, 2011).It is the process of comparing multiple units of study for the purpose of scientific discovery and for informing policy decisions (Rogers, 2014).Even though there has been a renewed interest in comparative analysis as a research method over the last decade in fields such as ...
Determine the focus of your piece. Determine if you will focus on the similarities, the differences, or both. Be sure you treat each individual the same; each person deserves the same amount of focus-meaning, do not place most of the emphasis on you or the other person. Find a balance.
One of the comparative analysis example strategies we recommend is using charts and graphs. Our brains process visual data 60,000 times faster than texts and figures. And this creates a concrete argument for using comparison-oriented charts and graphs, such as Matrix and Radar Graphs. These charts are amazingly easy to read and interpret.
In contrast to the chapters on survey research, experimentation, or content analysis that described a distinct set of skills, in this chapter, a variety of comparative research techniques are discussed. What makes a study comparative is not the particular techniques employed but the theoretical orientation and the sources of data.
comparative sociology and politics, but more recently it has been applied to policy analysis 6 and evaluation. After a few isolated attempts (see for example Befani et al. 2007), evaluators have started using QCA more often over the past 2 -3 years, including in meta- evaluations of approaches to evaluating interventions targeting violence ...
A comparative study is a kind of method that analyzes phenomena and then put them together. to find the points of differentiation and similarity (MokhtarianPour, 2016). A comparative perspective ...
This book, by Schneider and Wagemann, provides a comprehensive overview of the basic principles of set theory to model causality and applications of Qualitative Comparative Analysis (QCA), the most developed form of set-theoretic method, for research ac. An introduction to applied data analysis with qualitative comparative analysis.
Qualitative Comparative Analysis: An Introduction to Research Design and Application is a comprehensive guide to QCA. As QCA becomes increasingly popular across the social sciences, this textbook ...
In this FLM, students are asked to complete a fill-in-the-blank outline which accompanies all three videos, covering the topics of comparative analysis, grounds for comparison, and the structure of comparative analysis. The completed outline will enhance the students' note-taking skills and will serve as a summary of the FLM that they may ...
Experimental studies are one type of comparative study where a sample of participants is identified and assigned to different conditions for a given time duration, then compared for differences. ... Continuous variables are analyzed using parametric methods such as t-test, analysis of variance or multiple regression. 10.3.2. Sample Size.
The comparative method "involves the nonstatistical comparative analysis of a small number of cases" (George and Bennet 2005: 151). It is an interest in contextuality that causes CHA scholars to use the comparative method, which is to say they are context specific, since such context helps in understanding the different cases.
Comparative analysis, the process of comparing different products, companies, or systems, is a valuable practice for gaining insights and making decisions. At a basic level, comparative analysis provides a method for benchmarking performance and identifying strengths and areas for improvement.
Block method example. ... Jack is a Brit based in Amsterdam, with an MA in comparative literature. He writes for Scribbr about his specialist topics: grammar, linguistics, citations, and plagiarism. ... An argumentative essay presents a complete argument backed up by evidence and analysis. It is the most common essay type at university. 2264.
Qualitative comparative analysis is a research methodology primarily rooted in the social sciences, yet its applicability spans across diverse fields. It was originally developed by Charles Ragin in the 1980s as a method to address challenges faced when analyzing complex social situations. At its core, QCA is designed to systematically compare ...