
20 Genetic Engineering Pros and Cons for the Biotechnology Era
Genetic engineering is part of the brave new world of biotechnology, but is changing the genes of living things the right thing to do?
Green Coast is supported by its readers. We may earn an affiliate commission at no extra cost to you if you buy through a link on this page . Learn more .

As the third decade of the twenty-first century rolls on, advancements in genetic engineering, a leading area of biotechnology, continue to gain momentum. Humans are now capable of making applied and consistently transmitted changes to the genetic composition of living things, with impacts on organisms and our environment that are already being felt.
Genetic engineering certainly offers a lot of promise, but many people are concerned that it may harbor devastating consequences that humanity has not yet comprehended. In this article, we’ll take a closer look at the genetic engineering pros and cons, to help you evaluate if it is truly a good thing.
What is genetic engineering?
The National Human Genome Institute defines genetic engineering as a process that uses laboratory-based technologies to change or manipulate the packaged DNA (genes) of an organism. Genetic engineering uses invasive techniques to change the genetic makeup of cells.
By moving genes within and across species boundaries, scientists can obtain their desired observable traits in the host organism’s phenotype. This video from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) explains the basics:
Scientists manipulate and modify sequences of DNA by removing them from organisms. They can also artificially synthesize RNA and complementary DNA strands using the polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Organisms can also be genetically modified (GM) through the removal of specific gene sequences, carried out using DNA-cutting enzymes known as restriction endonucleases.
Novel gene sequences can then be inserted or spliced into the DNA of a host organism. This is called recombinant technology. These genes encode instructions for the production of particular protein products. The host organism transcribes and translates the gene, leading to the production of the gene products with novel effects on the modified organism (gene expression).
What is a genetically modified organism?
A genetically modified organism or GMO is an organism that has undergone genetic engineering and is permanently different from the original wild-type or natural organism. This is because the genetic sequences added or removed change gene expression and protein production in the GMO organism leading to:
- An altered physical appearance
- The production of a specific substance, that may have positive or negative effects
- Increased resistance to a specific disease
- The eradication of specific genetic conditions in the organism or its offspring

A brief history of genetic engineering
The geneticists Stanley N. Cohen and Herbert W. Boyer were the first scientists to cut up DNA into fragments and insert gene sequences into an organism. In 1973 they successfully added new genes to the plasmid of E. Coli bacteria. A year later, Rudolf Jaenisch inserted foreign DNA into the genome of a mouse, creating the first GM animal.
By the end of the 1970s, the recombinant technology used by these scientists had already become commercialized with the production of human insulin by GM bacteria in 1982. Genetic engineering expanded to food crops and livestock, with GM food introduced to consumers in the 1990s. The Flavr Savr, a GM tomato introduced in 1994 was developed to have a longer shelf-life and by the early 21st century almost all the corn produced in the US was GM, with strained developed to be more resistant to drought and pests.
Genetic engineering technologies and techniques
Genetic engineering now uses several techniques to change the genes of living organisms. The methods vary in sophistication, cost, and application and certain jurisdictions may restrict their use. Here are some leading genetic engineering technologies:
- Recombination technology : This is the original form of genetic engineering that uses restriction enzymes that can cut sequences of DNA that are then inserted into the host organism’s genome.
- Zinc finger nucleases : This gene editing technology uses a special nuclease enzyme fused with a three base pair DNA-binding domains for more precise DNA binding site recognition when editing genes.
- CRISPR-Cas9 : Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats or CRISPR- based genome editing is one of the most advanced forms of genetic engineering. It adapts a technique used by bacteria to evade genetic damage from viruses. CRISPR has become widespread because of its accessibility, low cost, and precision. It is thought to have been used in some extremely controversial experiments including gain-of-function virology research, and the gene editing of embryos.
- Base editing : This simpler gene editing technique makes single base substitutions without inducing risky double-stranded breaks in the genome. Double-strand breaks are a serious form of DNA damage that can lead to the deletion of genes, cell death, or the development of cancer. Base editing offers the promise of curing genetic diseases caused by errors in a single base in the DNA (single nucleotide polymorphisms).
- Prime editing: This contemporary form of gene editing uses an enzyme that can create single-strand breaks in DNA (Cas9 nickase) along with a complex (pegRNA) that acts as a template for the reverse transaction attachment of the desired bases to the site where the DNA has been broken. This avoids double-strand breaks and is considered safer for human therapeutic uses.
Genetic engineering applications
Because all living things have DNA the applications and implications of genetic engineering are understandably vast. The rapid standardization and commercialization of genetic engineering techniques have enabled companies to develop applications in diverse sectors spanning agriculture, healthcare, environmental conservation, and industry, without any public consultation or consent.
Key applications of genetic engineering include:
- The study of gene expression and function using experiments to add or delete gene sequences and portions.
- The development of pharmaceutical products like antibiotics, hormones, and antibodies using GMOs.
- The creation of disease, pest, and drought-hardy crops.
- The production of potent enzymes for industrial detergents, cheese production, and fermentation.
Pros of genetic engineering
Genetic engineering is a key driver of the biotechnology sector which advocates that altering the expression of genes can be targeted, controlled, and beneficial to life on Earth. Here are some benefits of genetic engineering:
1. A greater understanding of how DNA and genes work
Genetic engineering evolved from the study of DNA, and experiments were undertaken to understand how genes work. Once eminent scientists like Watson and Crick and Rosalind Franklin had established the molecular structure of DNA in the 1950s, work began in earnest to understand its function.
The Discovery of the four key classes of enzymes that acted on DNA, helicase, primase, DNA polymerase, and ligase, equipped scientists with tools to work with DNA, cutting and splicing it in specific places. This experimentation with DNA and its effects on gene expression underpin genetic engineering and has continued to expand the field of genetics.
2. The production of medicines
Biotechnology is already an integral part of healthcare and genetic engineering is used to produce medicines for many common conditions. Medicines that are produced by genetic engineering are either:
- Biological medicines that a GMO has produced.
- GMOs that are used as medicinal agents.
Essential medicines that are derived from GMOs or are GM products include:
- Immunoglobulins
- Monoclonal antibodies
- Hormones including insulin and growth hormone
- Pancreatic enzymes
Genetic engineering has made it possible to produce these humanized biological agents at scale so that patients can access them when needed. For example, recombinant insulin is now the main type of insulin used by Type I diabetics rather than the animal-derived insulins that were originally used to treat this condition.

3. A promise of cures for genetic diseases
The manipulation and editing of gene sequences using genetic engineering technologies offer an as-yet-unrealized promise of curing genetic diseases. Point mutation diseases such as sickle cell disease and hemophilia A and B, caused by errors in a single or a limited number of nucleotides in a gene sequence could be frankly cured by having the genetic error corrected.
This type of genetic engineering is gene therapy. Though gene therapy has captured the public imagination, offering hope for cures for devastating genetic diseases, this area of science is not adequately advanced to treat patients in a consistent, reliable, or safe manner.
4. Development of more productive and resilient crops
Genetic engineering is considered a key area of innovation in agriculture. After millennia of painstaking cross-pollination and plant breeding, genetic engineering can achieve dramatic changes in the characteristics and performance of crops almost instantly.
Genetic engineering has been used to develop crops with novel gene insertions that confer protection against pests and diseases or raise the crop’s tolerance to pesticide use. GM crops achieve their enhanced resilience by producing protein products that have these beneficial effects, like plants that express proteins known to inhibit pests.
New breeding techniques (NBT) routinely use genetic engineering alongside conventional breeding to produce crops that are more resilient and productive. Examples of genetically engineered crops include non-browning potatoes, mushrooms, and apples, soybeans with an improved oil profile, and flavor-enhanced fruit and vegetables.

5. Enhanced livestock breeds
Genetic engineering has also extended to livestock, with modern techniques like CRISPR used on pre-implantation embryos to alter specific traits and characteristics. Scientists implant the gene-edited embryos in the womb of a surrogate animal to gestate, producing a generation of transgenic animals with an altered genetic profile.
The gene editing of animals is understandably controversial and governments restrict the use of these animals as food in many parts of the world. Advocates for transgenic livestock point to the enhancements that can be achieved, which can improve livestock health, fertility, resilience, and the nutritional content of meat.
6. The creation of new commercial sectors
Genetic engineering has been integral to developing biotechnology as an industry worth over $1 trillion globally. Genetic engineering has gained significant commercial traction because various industries can apply it to increase their productivity and generate revenue.
Even industries where genetic engineering may not seem relevant may demand the complex biological substances that genetic engineering can produce. For example, genetic engineering is being used to develop enzymes and microbiological organisms that can digest oil spills .
The commercial sector is a key driver of innovation in genetic engineering technologies, but governments are also funding and investing in genetic engineering technologies that can provide solutions to health problems, food security, and environmental challenges.
7. Reduced resource consumption
Genetic engineering may develop crops and livestock breeds that demand less water, fertilizer, and feed. Healthier livestock requires less medicine and adding hardiness traits may mean that farmers can rear them in challenging environments that would normally be more resource and labor-intensive.

Enhancing crop yields and animal productivity also means that the resources used for cultivation go further, leading to cost savings for farmers. Consumers benefit from lower prices and foods that may have a longer shelf-life.
8. Eradicating diseases
Genetic engineering is currently being used to develop solutions for eradicating serious parasite-borne diseases like malaria . In sub-Saharan Africa, Asia, and Latin America, malaria is a significant health and economic burden, causing hundreds of thousands of deaths annually.
Genetic engineering that targets mosquitos and the plasmodium parasite that causes malaria could lead to the eradication of this devastating disease. Oxitec, a British company, has already released male GM mosquitoes that carry an inserted gene that encodes a protein which is fatal to their female offspring.
Cons of genetic engineering
Genetic engineering shows a lot of promise, but at what cost should humanity seek to realize its potential? Interference with genes has implications for every living thing on Earth, yet the knowledge and control of these technologies are in the hands of a tiny number of people.
Here are the important downsides of genetic engineering that everyone should know about:
1. The science of genetics is not settled
Genetics is an incredibly expansive area of biology, but it’s important to know that scientists do not fully understand how genes work. Geneticists are continually working in disparate niche areas of this field to contribute to the body of knowledge in this area and regularly publish discoveries that challenge the mainstream understanding of genetics.
Consider this; until recently scientists believed that 99 percent of DNA, which did not code for proteins, was junk. They focused most of the field of genetic engineering on just 1 percent of the total amount of DNA in a cell.
But errors in non-coding DNA have now been implicated in the development of cancers like leukemia and the emerging field of epigenetics has also challenged conventional thinking on the nature and purpose of DNA.

2. Some claims of genetic engineering may be overstated
The promise of genetics as a solution to food shortages and diseases has captured the public imagination. However, the realization of these promises may take many years to achieve, and in some cases, may not be fulfilled at all.
Genetic engineering is still extremely experimental, and for every success reported, there are thousands of failed experiments in the lab. Geneticists work with cells, tissues, enzymes, and proteins that may not always behave as predicted. This means that it can take decades to develop genetic engineering techniques that produce consistent and reliable results.
3. The long-term effects of genetic engineering are unknown
Because genetics is an evolving field, it is impossible to know the long-term effects of gene editing on species, individuals, populations, and the wider environment. This is particularly important for GM crops which may produce harmful protein products that harm wildlife and even accumulate in human tissues causing health problems.
The introduction of GM species into ecosystems may also add novel selection pressure to the environment. GM crop species have out-competed their wild-type equivalents , or transferred their genes to them via hybridization, leading to a loss of biodiversity.
4. Genetic engineering is expensive
Genetic engineering is extremely expensive because of its experimental nature. Gene editing uses some of the world’s most expensive laboratory equipment , reagents, and technical expertise. Genetic engineering routinely takes years of investment before scientists develop commercially viable and safe applications.
This is one of the key limitations of even the most promising gene therapies. Even when a technique is found to work on patients, the costs are so high that few people can access them. Running clinical trials is also very expensive meaning many gene therapies do not obtain the funding to be developed properly.
5. Genetic engineering can lead to unregulated gene expression
Genetic engineering has mastered the technique of inserting a transgene into a host species’ genome, but regulation of the expression of the gene is much more sophisticated. This means that the transgenic organism may over or under-produce the protein product of the inserted gene.
Under-expression of an inserted gene may mean that scientists don’t achieve the desired effect of genetic modification, while over-expression may be harmful to the GMO and animals or people that consume it. In transgenic swine , overexpression of an inserted growth hormone gene resulted in an enlargement of the heart, arthritis, abnormal skeletal growth, and renal disease.
6. Genetic engineering can introduce insertional mutations
By breaking and annealing the ends of DNA with new gene frequencies, geneticists can introduce errors and mutations in DNA that produce disease in the host organism. Insertional mutations may affect the genes that control essential biological processes producing metabolic diseases and cancers.
Worse still, these mutations may be transmissible to subsequent generations, creating new diseases that could be introduced to wild-type organisms through hybridization or mating.
7. Transgene mosaicism or sex linkage may mean that not all offspring carry an inserted gene
Some gene-editing processes are failures, because the GMO does not transmit the inserted gene to all of its offspring.
This is usually because of mosaicism, where only some cells of the organism carry the inserted gene, making its expression inconsistent. Alternatively, in animals or humans, the inserted gene may become sex-chromosome linked (Y-chromosome) so that only males carry the transgene.
8. Genetic engineering requires time and resource-consuming planning to be successful
Genetic engineering projects have to be carefully designed and constructed to achieve the successful insertion of a genetic sequence into a host organism. The high failure rate of these experiments is often because of errors in the inserted gene or its integration site.
Scientists therefore repeatedly model and test the transgene and its insertion site, which can use significant resources and may risk the health and welfare of host organisms.
9. Rogue agents could use genetic engineering for biological warfare or terrorism
Genetic engineering is already being used for controversial ‘gain-of-function’ research, where the genomes of bacteria and viruses are edited to increase their transmissibility or virulence. This research has been taking place in academic settings with the purported objective of investigating pathogens to prevent them from starting pandemics.
Genetic engineering is largely unregulated, with restrictions on access to this technology varying widely between countries. It is not inconceivable that rogue states or nefarious organizations could procure the equipment and expertise to develop bacteria, viruses, or parasites that could infect targeted populations.
10. Genetic engineering could be used for eugenics
Eugenics is an ideology that believes that human reproduction can be controlled to produce populations with pre-determined desirable traits and eliminate individuals with undesirable characteristics. It is a form of scientific racism and has been associated with atrocities and genocides throughout history.
Many advocates of genetic engineering of human beings, point to its potential to ‘improve’ the human race by eradicating genetic abnormalities and introducing desirable traits. Unfortunately, small but powerful groups with little accountability to the wider population may decide what desirable or undesirable hereditable traits are, irrespective of the implications of this course of action.
In the wrong hands, genetic engineering could pursue a eugenics agenda, focused on specific racial groups or populations of people.
11. Genetic engineering enables genes and organisms to be copyrighted
Genetic engineering is a new and fast-evolving area of science and the ethical and legal frameworks that surround it are relatively immature. A key example of this is the patenting of genes and organisms developed through genetic engineering, with companies enforcing ownership of seeds and animal breeds they have developed.
In many jurisdictions, alteration of the genome of an organism makes it a patented product and subject to copyright law. In India, this has been a hotly contested issue, with Monsanto recently winning a Supreme Court case regarding the patents of its GMO cotton seeds.

12. Significant ethical, cultural, and religious concerns surround the use of genetic engineering
Despite its advances and benefits, genetic engineering continues to face deep public antipathy. Many people believe that interfering with genes that are passed from generation to generation is taboo. Even with comprehension of the science and its benefits, they believe that altering living things at a genetic level will harm them.
Religious groups who believe that God created the Earth, perceive generic engineering as a defilement of the Creator’s intelligent design.
With few consistent legal or regulatory boundaries for genetic engineering, ethicists join them in the concern that most people have no say over introducing GMOs into the environment and the genetic engineering of human beings.
In conclusion
As you can see the pros and cons of genetic engineering are a weighty matter, certainly worthy of further investigation. This issue is not only about science but touches on human, animal, and environmental health and welfare ongoing. This means that the evaluation of the societal benefit of genetic engineering should be rigorous with high ethical standards and stringent regulation.
Articles you might also like

How to Help Endangered Species: 16 Ways to Protect Vulnerable Species Anyone Can Do!

25+ Ways to Protect Forests and Fight Climate Changes

A Complete Guide to the Causes of Afforestation and Why This Process is Critical

20 Shocking Facts About Water Pollution

35 Ways to Reduce Air Pollution and Boost Air Quality for All

Top 3 Causes, Effects, and Solutions of Ozone Layer Depletion

Causes and Effects of Soil Erosion (And Why It’s Important)

16 Ways to Reduce Water Pollution

Prevention of Soil Pollution: What You Should Know

5 of the Critical Water Scarcity Solutions Addressing the Water Crisis

30 Interesting Facts About Air Pollution Everyone Needs to Know

How Does Deforestation Affect Humans? Social, Economic, and Health Impacts
- Branches of Biology
- Importance of Biology
- Domain Archaea
- Domain Eukarya
- Biological Organization
- Biological Species Concept
- Biological Weathering
- Cellular Organization
- Cellular Respiration
- Types of Plants
- Plant Cells Vs. Animal Cells
- Prokaryotic Cells Vs. Eukaryotic Cells
- Amphibians Vs. Reptiles
- Anatomy Vs. Physiology
- Diffusion vs. Osmosis
- Mitosis Vs. Meiosis
- Chromosome Vs. Chromatid
- History of Biology
- Biology News

- Pros and Cons
13 Important Genetic Engineering Pros And Cons

Over the last century, the field of genetics and biotechnology has greatly developed because of the better understanding of the gene. Because of the improvement of technology, scientists have already gone up until the manipulation of the genome (complete set of genes) of organisms. This process is called genetic engineering. In this article, we will explore 13 important genetic engineering pros and cons .
What Is Actually Genetic Engineering?
The “sharing” of genetic material among living organisms is known to be a natural event. This phenomenon is known to be very evident among bacteria, hence they are called “nature’s own genetic engineer”. Such phenomenon is the inspiration of scientists in this endeavor.
In literature, there are in fact many synonyms of the term “genetic engineering”: genetic modification , genome manipulation , genetic enhancement , and many more. However, this term shall not be confused with cloning because genetic engineering involves the production of new set of genes while the latter only involves the production of the same copies of genes in the organism.
Genetic engineering is the process of manipulating an organism’s genome using biotechnology and the products of it are either referred to as “genetically modified” or “transgenic” organisms. Check out the disadvantages of genetically modified foods here.
How Does Genetic Engineering Work?
Basically, genetic engineering is done by inserting a “gene of interest” from sources like bacteria, viruses , plants , and animals into the “target” organism. As a result, the organism with the inserted “gene of interest” is now able to carry out the new trait or characteristic.
This technology grants us the ability to overcome barriers, exchange genes among organisms, and produce new organisms with “favorable traits”.
Now we will dive into the pros and cons of Genetic Engineering now.
Pros of Genetic Engineering / Advantages of Genetic Engineering
Supporters of genetic engineering believe that genetic engineering is indeed safe and is still comparable to the traditional process of breeding in plants and animals. Advocates of genetic engineering support the technology primarily because of the following reasons:
1. Production of nutrient-rich foods

2. Increased resistance of plants to rotting and pests

3. Increased Meat Production

4. Production of novel drugs and vaccines
5. Development of new and favorable characters

6. Creation of humans with desirable features
Cons of Genetic Engineering / Disadvantages of Genetic Engineering
On the other hand, there are several types of potential health effects that could arise from the insertion of a novel gene into an organism. Critics disagree with the methods of genetic engineering because of:
1. The fear for unintended selection and any unwanted transfer of genes

2. Health issues like allergic reactions

3. Development of antibiotic resistance of disease causing organisms

4. Loss of biodiversity

5. The fear for the rise of “invasive species”

6. Economic consequences
Because of the technology used to create genetically modified crops and animals, private companies that produce them do not share their products at a reasonable cost with the public.
7. Social and Ethical Concerns

In addition, they believe that the process is somewhat disrupting the natural way and complexity of life. In addition to this, critics fear the misuse and abuse of biotechnology.
Genetic Engineering – Good, Bad & Ugly – An Infographics

What’s Next?
But there’s really no doubt that with the rapid advancements in technology, the creation of GM organisms are also increasing.
What do you think? Are GM organisms slowly becoming the future?
RELATED ARTICLES MORE FROM AUTHOR

Top 10 Genetics News of 2020

Top 10 BEST Genetics Discoveries of 2019

Top 12 Best Genetics Textbooks

Top 25 Most Recent Genetic Discoveries in 2018

Top 20 Biomass Energy Pros and Cons

Top 34 Gene Therapy Pros and Cons
this a really broadly informative article, I got lots of answers regarding the topic and it gives clear points as well. thank you
I used this for the k12 article great info
This is a great article and it is really informational, I love the videos that it includes to help you better understand the concept
really good article
Same for me, to do a Science essay from school
I got more information in this article nice article
LEAVE A REPLY Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
By using this form you agree with the storage and handling of your data by this website. *
Recent Posts

Blooming Texas: 25 Gorgeous Native Flowers Revealed!

Exploring the Top 50 Most Exquisite Purple Flowers in the World

Top 21 Holly Flowers For Sprucing Up Your Garden!

The Enchanting Beauty of the Top White Flowers

What Is Biological Magnification?

Top 34 Flightless Birds of All Times!

25 Reasons That Emphasizes The Importance of Biology

Top 27 Biology-themed Movies

Biology Boomtowns: 10 Best US Cities for Job Opportunities

Uncovering the Fathers of Biology: The Geniuses Who Unveiled Life’s Secrets

25 Mind-Blowing Biology Breakthroughs That Shaped Our World!

The Ultimate Guide: Discover 162+ Doctor Specialties for Every Health Need

40 Different Types of Birds


334 Types of Monkeys
Biology history.

History of Anatomy

History of Biochemistry

History of Biotechnology

History of Botany
History of Cell Biology

History of Ecology

Complete History of Evolution

History of Genetics

History of Immunology

History of Microbiology
- Privacy Policy
- Animal Profiles
- Amazing Places
- Conservation
- Endangered & Threatened Species
- Global Warming & Climate Change
- Food & Nutrition
- Home & Garden

- Earth Matters
Exploring the Pros and Cons of Genetic Engineering

Genetic engineering is the process of altering the genetic composition of plants, animals, and humans. The most practical application of genetic engineering is to create a more sustainable food system for the people of Earth, but there are other ways we can use it to our advantage as well.
Unfortunately, there are both pros and cons of genetic engineering. For every benefit, there is a list of concerns and potential problems we need to consider. There is a substantive argument on both sides of genetic engineering, and we’ll explore both ahead.
Positives of Genetic Engineering
Most people tend to focus on the negatives of genetic engineering, but there are some substantial positive we need to consider as well. Genetic engineering is a debate, and there are some good points on each side. You have to look at both the pros and cons of genetic engineering if you want to make an informed decision on the matter.
Extending Our Lives
Evolution takes thousands of years to adapt to our surroundings , but genetic engineering offers a quicker path forward. With the assistance of genetic engineering, we could force our bodies to adapt to the changing climate of our planet.
Additionally, we could tack-on some extra years to our lives by altering our cells, so our bodies don’t deteriorate as quickly as they currently do. The fountain of youth might be within our reach, and many look forward to advancements in the area of genetic engineering.
If we choose to go down this path, we’ll feel better as we age and be able to outlast some of the diseases that currently take us down. We still won’t be able to live forever, but genetic engineering shows promise in extending the prime of our lives.
Create New and Better Food

Food shortage is a massive problem in the world, especially with the growing population. We’re destroying natural habitats to make way for farmland, and overgrazing is causing current pastures to become dry and uninhabited.
The answer to this problem could come in the form of genetic engineering. If we can alter the composition of vegetables and animals, we can create new foods that might have more nutritional value than nature creates on its own.
We might even be able to advance to a point where foods give us medicines we need to combat widespread viruses and illnesses. Food is one of the most promising spaces when considering the prospect of genetic engineering.
Killing Hereditary Diseases
A lot of diseases depend on genetic predisposition. Some people are more likely to get cancer, Alzheimer’s and other diseases than their neighbor. With genetic engineering, we can get rid of these genetic predispositions once and for all.
There will likely still be some environmental concerns that will cause diseases, but if we start altering the genes of humans, we may become resistant to genetic abnormalities. Family history won’t mean anything when it comes to things like cancer, and we can start eliminating diseases that are completely based on genetics.
Making Every Child Healthy
There are already a handful of diseases and illnesses we can detect while a baby is still in the womb. We even can genetically engineer some diseases and illnesses out of a baby’s system before they’re born.
Finding out your baby has a disease can be devastating, and some parents make the difficult choice to spare their child possible pain. If you know that your baby might suffer and die a few months after they’re born, you have to decide whether or not you want to roll the dice.
In the future, we might be able to eliminate the chances of unhealthy babies. Diseases like Huntington’s offer a substantial chance that the carrier will pass it onto their child. If the child isn’t positive for the disease, they’ll still be a carrier and have to deal with the same dilemma when it comes time to have kids of their own.
Genetic engineering has the potential to stop these threats in their tracks. Parents won’t have to worry about birthing a healthy son or daughter. Science will guarantee that every baby is happy and healthy when they come into this world.
Negatives of Genetic Engineering

Of course, genetic engineering isn’t entirely positive. There is an upside to the ability to genetically alter humans and animals , but only in ideal situations.
Our world isn’t perfect, and scientists make mistakes all the time. We can’t assume that genetic engineering will be available to the entirety of the human population, which is a flaw in itself.
The negatives of genetic engineering seem to outweigh the positives, especially since there is so much room for error. We don’t know what we’re tampering with, which opens the door to a host of potential problems.
The Ethical Dilemma
There are a couple of ethical problems with genetic engineering that we need to consider as a society. Those who subscribe to religion will see genetic engineering as blasphemy, for instance. We’d be “playing God,” in a sense. Anyone who believes in creation will be expressly against genetic engineering – especially in human children.
Those who are on the opposite side of the spectrum from religious people probably won’t love genetic engineering either. Genetically engineered food might work, but changing the genes of people will add to the overpopulation problem we’re currently experiencing.
Diseases are one of the most effective forms of population control . We don’t have the heart to eliminate other humans in the name of population control, so disease does it for us. If we eliminate diseases, humans will have virtually no threat left on this planet.
Living longer lives might be ideal, but it isn’t practical. If we extend the prime of our lives, we’re opening the door to having more children. Since all children would be in perfect health, we’ll see a population increase that could have devastating consequences.
Limiting Diversity
If genetic engineering becomes a reality, it will likely only be available to the richest members of society. They’ll be able to extend their lives, limit diseases, and make sure their children are always healthy when they’re born
When this happens, natural selection is completely obsolete. Instead, the wealthiest in society will thrive while the poor will die-out. Eventually, genetic diversity will completely disappear as genetically engineered children all express the most desirable characteristics
This problem also arises in nature if we decide to engineer plants and animals genetically. These organisms might start as food, but could introduce themselves to the wild and take over. They’ll decimate natural species, and eventually be the only thing left.
The Possibility of Mistakes
One of the biggest hurdles in genetic engineering is the possibility of errors or genetic defects, especially in humans. Scientists have a general understanding of what creates a functioning human, but they don’t yet have all the pieces to the puzzle.
When it comes down to changing humans at a cellular level , scientists don’t yet have the understanding of how small changes can affect the development of a growing baby. Changing genes could result in more damaging birth defects or even miscarriages.
Furthermore, tampering with diseases could end up creating a super-disease that is even harder to combat. There are too many variables in the human body for genetic engineering to work to the fullest potential. Even if it could, people will probably be too nervous to trust scientists tampering with the cells of their future children.
The Logical Extreme
Science still isn’t at a point where they can alter the genes of humans to prevent all diseases in unborn children, but it might be there soon. When that time comes, some might take genetic engineering to its logical extreme.
Our priority will be to create healthy children. Once we perfect this process, though, where to, we go? The next logical step is the ability to pick certain traits that our children will have. We might be able to select whether we have a boy or girl. Then, we can decide what eye color and hair color they have.
Pretty soon, we’re selecting every trait that our child has before they leave the womb. Nature will be virtually out of the question at this point, and people with enough money will design their babies from scratch.
Is Genetic Engineering Good or Bad?
Since the pros and cons of genetic engineering are compelling, it’s worth it to explore the possibility further. We still haven’t reached a place where scientists fully understand the opportunities genetic engineering presents, so they still have years of research on their hands.
In the end, though, no system of genetically altering humans, animals, or plants will be perfect. There is a massive potential for errors, and we likely won’t have equal opportunities if and when scientists ever crack the case.
Although the positives of genetic engineering are convincing, the negatives can be terrifying. If we ever get to the point where we can genetically alter humans, we need to consider the moral, ethical, and practical application of technology before going any further.
RELATED ARTICLES MORE FROM AUTHOR

How Can Resource Conservation Benefit the Environment? 18 Helpful Components of Practice

10 Animals That Hibernate

What Is Point Source Pollution: Identifying the Culprit
Leave a reply cancel reply.
- How You Can Help
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Corrections
Genetic Engineering: Is It Ethical?
Genetic engineering is one of the most popular and controversial topics of our time. What are the pros and cons of genetic engineering, and do its achievements contradict ethics?

At present, genetic engineering is one of the most advanced technologies related to the scientific study of the living world. It enables us to interfere with the genetic code of organisms (including humans) and change it. As a result, genetic engineering has become a topic of heated discussions among specialists in various fields, the general public, international organizations, and legislators in different countries.
Its achievements, on the one hand, can save humanity from dangerous diseases, the threat of hunger, and chronic malnutrition. Still, on the other hand, genetic engineering gives rise to several moral, ethical, and philosophical problems. So, what are the pros and cons of genetic engineering, and do its achievements contradict ethics?
The Pros and Cons of Genetic Engineering: How Does It Even Work?

Genetic engineering is the process of manipulating genes in a living organism to change its characteristics. It can be done by introducing new DNA or deleting or replacing existing genes. Genetic engineering aims to create organisms with desirable traits, such as resistance to disease, tolerance of extreme environments, or increased yield.
Genetic engineering is a relatively new technology, and as such, it is still being perfected. For example, scientists have had some notable successes, such as the creation of “ golden rice ,” which is enriched with Vitamin A to help prevent blindness in developing countries. However, there have also been some controversial failures, such as the attempt to create a “Frankenstein” mouse by inserting human genes into its DNA.
Pros of Genetic Engineering for Crops and Humans
Get the latest articles delivered to your inbox
Please check your inbox to activate your subscription.
Genetic engineering is a powerful tool that can be used to improve the quality of our food supply. By modifying the genes of crops, we can make them more resistant to pests and diseases. We can also create new varieties of crops that are better suited to our climate and soil conditions.
In addition to improving the quality of our food supply, genetic engineering can also be used to create new medicines and treatments for diseases . By modifying the genes of cells, we can make them resistant to diseases, prevent them from spreading, and even cure them. For example, genetic engineering has already had a major impact on the treatment of cancer. By engineering immune cells to attack cancer cells, we have dramatically improved survival rates for many types of cancer. We are also using genetic engineering to develop new treatments for HIV and other viruses.
By understanding how genes work, we can create new drugs that target specific diseases. We can also use genetic engineering to produce vaccines and other medical products. This technology has the potential to save countless lives.
Transhumanism as a Profound Challenge to Traditional Ideas About the Human Condition

Due to the active development of genetic engineering, the concept of transhumanism has gained increasing traction in popular culture. Once relegated to the fringes of society, transhumanism is now being mainstreamed by tech giants like Elon Musk and Mark Zuckerberg. But what exactly is transhumanism? And what are its philosophical implications?
Transhumanism is a philosophical and social movement that seeks to use technology to enhance human physical and mental capabilities. Proponents of transhumanism believe that by using technology to augment our bodies and minds, we can overcome many of the limitations of the human condition, including disease, aging, and even death.
While transhumanism may initially sound like a far-fetched concept, it is actually rooted in a long history of human aspirations to improve ourselves. For centuries, we have used technology to enhance our physical abilities, from the invention of the wheel to the development of artificial limbs. In recent years, we have also begun to use technology to enhance our mental capabilities with devices like smartphones and smartwatches.
Still, transhumanism represents a profound challenge to our traditional ideas about the human condition. As we continue to develop new technologies that have the potential to change who we are, we will need to grapple with some tough philosophical questions about what it means to be human .
“Designer Babies”: Genetically Modified Humans

Designer babies are a controversial topic in the world of genetic engineering. Some people believe that parents should be able to choose the traits of their children, while others argue that this could lead to serious ethical issues.
The term “ designer baby ” refers to a baby whose genes have been artificially selected to produce specific traits. This process can be done using a variety of methods, but the most common method is the preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD). PGD is a procedure that is typically used to screen for genetic diseases. However, it can also be used to select embryos with certain eye colors, hair colors, or other desired physical traits.
There are many different ways that parents could create a designer baby. For example, they could use genetic screening to select embryos with desirable traits or alter their child’s genes after birth. However, there are also risks associated with these methods. For instance, there is a chance that genetic alterations could have unintended consequences or that parents may not be able to control which traits their child inherits.
Some people believe that designer babies are morally wrong because they involve manipulating the genes of a human embryo. Others argue that designer babies could have positive implications, such as reducing the likelihood of genetic diseases.
What Are the Ethical Implications of Creating “Designer Babies”?

As the technology to create designer babies rapidly becomes more sophisticated and accessible, the ethical consequences of this practice are becoming increasingly apparent. While some parents may see designer babies as a way to ensure their child has the best possible genes, others worry about the implications of playing God with human life.
Designer babies also raise significant questions about social inequality. If rich parents can afford to create genetically-modified children who are healthier and more intelligent than their peers, what does that mean for the future of humanity? There is a real risk that designer babies could further widen the gap between the haves and the have-nots, creating an even more unequal society.
There are also fears that designer babies could be used to create “superhumans” who are stronger, faster, and smarter than the rest of us. It could lead to a new form of eugenics , where only the wealthy can afford to create genetically-modified children, further exacerbating social inequality.
The ethical consequences of designer babies are complex and far-reaching. As we move closer to this technology becoming a reality, we must have an open and honest conversation about the implications of creating genetically-modified human beings. Otherwise, we may find ourselves in the future that none of us wants to live in.
Ethics of Genetic Engineering of Animals and Plants

Genetic engineering methods used in animal husbandry also give rise to a number of ethical problems. Scientists actively pursue profits from the intensification of agricultural production processes by applying genetic engineering methods to “improve” some breeds of agricultural animals.
However, such genetic experiments are striking in their cruelty. For example, the human growth gene that was introduced into the DNA of mice led to cancer cells’ appearance. So, there is an affinity between the “growth gene” and the “cancer gene.” Are these methods acceptable from the point of view of ethics?
In the genetic engineering of plants, fortunately, there are fewer ethical problems, but, nevertheless, they exist. In particular, the creation of hybrids of the most diverse organisms causes the anxiety of religious figures, in connection with which many difficult-to-solve problems arise.
For example, is it morally permissible to eat plant food with embedded animal genes during fasting? Is it okay to eat genetically modified products in which human genes are embedded, or should this be considered cannibalism? Is it impossible to consider food into which genes have been transferred, for example, pigs, to be partially pork, and if this is the case, do the prohibitions of some religions apply to it?
Religion Against Genetic Engineering

Religion provides the strongest grounds for protesting genetic engineering. So it is not surprising that most of the resistance to all new reproductive technologies comes from people with religious beliefs. This resistance is deeply rooted in fundamental religious norms.
According to the Judeo-Christian tradition, humans were created in the “image” and “likeness” of God ( Genesis 1:26-27 ), which, according to some interpreters, means both the given nature of man and their perfection, the goal towards which they must strive; and from the point of view of others, “image” and “likeness” are synonymous. Humans are likened to God, first of all, in that they were given power over nature ( Ps. 8 ), and also in that they received from the Creator the “breath of life.” Thanks to this, a person becomes a “living soul.” This concept means a living personality, the unity of vital forces, the “I” of a person. Soul and flesh are characterized by organic unity (in contrast to the Greek philosophical dualism, which contrasted spirit and flesh).
Some people believe genetic engineering is morally wrong because it interferes with God’s plan for humanity . They believe that we are playing with fire by altering the genes of living organisms and that this could have catastrophic consequences for both humans and the environment .
Others argue that genetic engineering is a tool that can be used for good and that it has the potential to help us solve some of the world’s most pressing problems, such as hunger and disease.
Final Verdict: Is It Ethical?

Currently, a wide range of problems is associated with the application of genetic engineering, covering almost all fundamental spheres of human life and activity. Ethical and moral problems come to the fore here, initiating many sharp discussions within and outside of scientific circles.
There are a lot of different opinions out there about whether genetic engineering is ethical or not. Some people believe that it is a helpful tool that can be used to improve the lives of people who have genetic disorders. Others believe that it is morally wrong to “ play with God ” and change a person’s DNA.
Still, an extensive class of these ethical problems requires a new adaptation to the surrounding reality. At this stage, the main task of genetic engineering is primarily to provide maximum benefits, both in the mental and physical development of a person, and not to harm humanity.

Should We Fear the Future? The Philosophy of Transhumanism

By Viktoriya Sus MA Philosophy Viktoriya is a writer from L’viv, Ukraine. She has knowledge about the main thinkers. In her free time, she loves to read books on philosophy and analyze whether ancient philosophical thought is relevant today. Besides writing, she loves traveling, learning new languages, and visiting museums.

Frequently Read Together

Posthumanism: A Philosophy for the 21st Century?

“Only a God Can Save Us”: Heidegger on Technology

Heinrich Himmler: The Architect of the Holocaust

- What is Genetic Engineering?
- What is DNA?
- The Process of Genetic Engineering
- Genetically Modified Food Example
- Genetically Modified Animals Example
- Edible Vaccines
- Biosimilar Medicine
- TB Resistant Cows
- Video of Pros
- Video of Cons
- Genetic Experimentation on Humans
- Patenting Genetic Material
- Genetic Modification as Aesthetics
- Discrimination of People with Genetic Anomalies
- Executive Summary
- Sources Consulted
Pros and Cons
In the table below you will find some of the important advantages and disadvantages of genetic engineering. You will realize that each benefit has a negative aspect. Basically, by modifying the genes, we can improve a condition at the cost of another. The modification of a specimen and its later introduction to the environment can negatively impact the nature.
Watch the following videos about the pros and cons of genetic engineering:
You are using an outdated browser. Upgrade your browser today or install Google Chrome Frame to better experience this site.
Is technological progress in genetic engineering mostly a threat or an opportunity?

Source: Composite by G_marius based on Bart 's and UK Ministry of Defence 's images
Is the technological progress in genetic engineering (in areas like food, health or chemistry) a threat or an opportunity? Here we discuss the issues.
Debate proposed by Pete Pajuheimo
We are discussing genetic engineering food in another debate, let's focus now on the technology that allows it possible. Men have been using Genetically Modified Organism (GMO) technologies since 1972, when United States Biochemists Herbert Boyer and Stanley Cohen used enzymes to cut a bacteria plasmid and insert another strand of DNA in the gap. Since then, genetic engineer technologies have helped us achieving many milestones in the fields of biology, medical sciences and chemistry. For example founding and utilization of green fluorescent protein (GFP)-gene is helping us in the fight against cancer and in the study of biology in a more precise manner. In field of chemistry, these technologies have helped in the development of bacteria that can produce oil from atmospheric CO. Biologists can use genetic engineer technologies to improve our crops by, for example, altering the vitamin/nutrition composition to make it more suitable for human consumption. Many scientists think there is great promise in GMO technologies and that much more can be achieved through these technologies in the future.
Genetic engineering pros and cons: threat or opportunity?
However, GMO technologies bring also important threats as well as legal and ethical issues that are far from being resolved. Some of the common cited risks are those of the development of mixed artificial species, or human engineering. Opponents to genetic engeneering warn of possible scenarios concerning runaway genes in our and other living organisms nature causing unexpected outcomes or the long term effects that the consumption of genetically modified food (GMF) may have on humans. What about parents or governments chosing the personality of the children? Although many within the scientific community dismiss these fears and risks, further research on GMO and its risks as well as improved and more transparent communication between the big laboratories behind GMO and the public is probably needed to improve the level of trust that the public have on these genetic engineering research and technologies.
Vote to see result and collect 1 XP. Your vote is anonymous. If you change your mind, you can change your vote simply by clicking on another option.
Voting results
New to netivist?
Join with confidence, netivist is completely advertisement free. You will not receive any promotional materials from third parties.
Or sign in with your favourite Social Network:
Join the debate
In order to join the debate you must be logged in.
Already have an account on netivist? Just login . New to netivist? Create your account for free .
Report Abuse and Offensive language
Was there any kind of offensive or inappropriate language used in this comment.
If you feel this user's conduct is unappropriate, please report this comment and our moderaters will review its content and deal with this matter as soon as possible.
NOTE: Your account might be penalized should we not find any wrongdoing by this user. Only use this feature if you are certain this user has infringed netivist's Terms of Service .
Our moderators will now review this comment and act accordingly. If it contains abusive or inappropriate language its author will be penalized.
Posting Comment
Your comment is being posted. This might take a few seconds, please wait.
Error Posting Comment
error.
We are having trouble saving your comment. Please try again .
Most Voted Debates
Start a Debate
Would you like to create a debate and share it with the netivist community? We will help you do it!
Found a technical issue?

Are you experiencing any technical problem with netivist? Please let us know!
Help netivist
Help netivist continue running free!
Please consider making a small donation today. This will allow us to keep netivist alive and available to a wide audience and to keep on introducing new debates and features to improve your experience.

- What is netivist?
- Entertainment
- Top Debates
- Top Campaigns
- Provide Feedback

Follow us on social media:

Share by Email
There was an error...
Email successfully sent to:

Join with confidence, netivist is completely advertisement free You will not recive any promotional materials from third parties
Join netivist
Already have a netivist account?
If you already created your netivist account, please log in using the button below.
If you are new to netivist, please create your account for free and start collecting your netivist points!
You just leveled up!
Congrats you just reached a new level on Netivist. Keep up the good work.

Together we can make a difference
Follow us and don't miss out on the latest debates!

13 Advantages and Disadvantages of Genetic Engineering
The process of genetic engineering allows for the structure of genes to be altered. It is a deliberate modification which occurs through the direct manipulation of the genetic material of an organism. DNA is either added or subtracted to produce one or more new traits that were not found in that organism before.
With genetic engineering, it becomes possible to create plants that can resist herbicides while they grow. It also becomes possible to create new threats to our food supply or personal health because viruses and bacteria continue to adapt to the changes that are produced through this process.
Here are the advantages and disadvantages of genetic engineering to consider.
What Are the Advantages of Genetic Engineering?
1. It allows for a faster growth rate. Genetic engineering allows of plants or animals to be modified so their maturity can occur at a quicker pace. Engineering can allow this maturity to occur outside of the normal growth conditions that are favorable without genetic changes as well. Even if there is higher levels of heat or lower levels of light, it becomes possible to expand what can be grown in those conditions.
2. It can create an extended life. Genetic modification can help to create resistance to common forms of organism death. Pest resistance can be included into the genetic profiles of plants so they can mature as a crop without any further additives. Animals can have their genetic profiles modified to reduce the risks of common health concerns that may affect the breed or species. This creates the potential for an extended lifespan for each organism.
3. Specific traits can be developed. Plants and animals can have specific traits developed through genetic engineering that can make them more attractive to use or consumption. Different colors can be created to produce a wider range of produce. Animals can be modified to produce more milk, grow more muscle tissue, or produce different coats so that a wider range of fabrics can be created.
4. New products can be created. With genetic engineering, new products can be created by adding or combining different profiles together. One example of this is to take a specific product, such as a potato, and alter its profile so that it can produce more nutrients per kcal than without the genetic engineering. This makes it possible for more people to get what they need nutritionally, even if their food access is limited, and this could potentially reduce global food insecurity.
5. Greater yields can be produced. Genetic engineering can also change the traits of plants or animals so that they produce greater yields per plant. More fruits can be produced per tree, which creates a greater food supply and more profits for a farmer. It also creates the potential for using modified organisms in multiple ways because there is a greater yield available. Modified corn, for example, can be used for specific purposes, such as animal feed, ethanol, or larger cobs for human consumption.
6. Risks to the local water supply are reduced. Because farmers and growers do not need to apply as many pesticides or herbicides to their croplands due to genetic engineering, fewer applications to the soil need to occur. This protects the local watershed and reduces the risk of an adverse event occurring without risking the yield and profitability that is needed.
7. It is a scientific practice that has been in place for millennia. Humans in the past may not have been able to directly modify the DNA of a plant or animal in a laboratory, but they still practiced genetic engineering through selective breeding and cross-species or cross-breeding. People would identify specific traits, seek out other plants or animals that had similar traits, and then breed them together to create a specific result. Genetic engineering just speeds up this process and can predict an outcome with greater regularity.
What Are the Disadvantages of Genetic Engineering?
1. The nutritional value of foods can be less. When animals grow, and mature quickly, the nutritional value of that product can be reduced. This can be seen in poultry products today with the white striping that is found in meat products. That striping is a fat deposit that was created, often in the breast meat, because of the rapid growth of the bird. In chickens, Good Housekeeping reports that this can increase the fat content of the meat consumed by over 220%. At the same time, the amount of protein that is received is also reduced.
2. Pathogens adapt to the new genetic profiles. Genetic engineering can create a natural resistance against certain pathogens for plants and animals, but the natural evolutionary process is geared toward creating pathways. Bacteria and viruses evolve a resistance to the resistance that is created by the genetic engineering efforts. This causes the pathogens to become stronger and more resistant than they normally would be, potentially creating future health concerns that are unforeseen.
3. There can be negative side effects that are unexpected. Genetic engineering is guaranteed to make a change. Many of those changes are positive, creating more and healthier foods. Some of those changes, however, can be negative and unexpected. Making a plant become more tolerant to drought might also make that plant become less tolerant to direct sunlight. Animals may be modified to produce more milk, but have a shortened lifespan at the same time so farmers suffer a greater livestock.
4. The amount of diversity developed can be less favorable. At some point, genetically engineered plants and animals make it “into the wild” and interact with domestic species. This results in a crossing of “natural” and “artificial” organisms. The engineered organisms often dominate, resulting in only a modified species over several generations, reducing the diversity that is available.
5. Copyrighted genetic engineering can have costly consequences. Many companies copyright their genetic engineering processes or products to maintain their profitability. If a farmer plants genetically modified crops and the pollination process causes another farmer in the field over to have those modified crops grow, there have been precedents for legal actions against the “unauthorized” farmer. This can have several costly consequences, from fewer farmers wanting to work to a higher cost for the seeds that are planted.
6. This knowledge and technology can be easily abused. At the moment, genetic engineering in humans is being used to treat specific disorders that threaten the health or wellbeing of individuals. In time, the approach in humans could be like what is already being done with plants and animals. Genetic engineering can change specific traits, which could create human outcomes that are ethically questionable or easily abused.
The advantages and disadvantages of genetic engineering show that the results can be generally positive, but there must be controls in place to manage the negative when it occurs.
- Testimonials
Genetic Engineering Pros and Cons
- Writing Services
- Essay Types
- Assignment Formatting
- Assignment Topics
- Assignment Help
- Assignment Writing Tips
- Cause and Effect Essay Topics
- College Admission Essay Writing
- Problem Solution Essay Topics
- Making Education Smarter in its Response to Students
- Recognizing Great High Schools By What They Actually Do

- Date: 31 July, 2013
- Category: Assignment Help
The process
Genetic engineering is a complex process whereby scientist separates a gene from a chromosome. This is done by using an enzyme called endonuclease that is used to split the gene that is required from the chromosome. This process can be used for various reasons like giving an animal immunity whereby scientists will find an organism that has an antiviral gene and implant it into an animal and that way their offspring will also carry that new gene.
The pros of genetic engineering are numerous; in animals, it enables hereditary diseases to be treated so as to avoid them passing to the offsprings. Genetic engineering has also enabled scientists to make animals have certain desirable characteristics and also enabled them to remove certain characteristics creating better animals
Disadvantages
The cons of genetic engineering in animals are that they disrupt nature which is not easy to understand. When scientist introduces these new genes to animals they may lead to disastrous consequences since they are never sure what they will form. The society has not fully accepted genetic engineering and most of them see it as an n insult to nature
Natural methods
There is also the natural method of genetic engineering which is not done in the lab. This whereby organism of the same species are taken based on characteristics and they are mate together. This may be done when certain characteristics are wanted in the offsprings like taking an animal that has a tendency to grow larger and another that has an unusual immunity and making them mate so that the offspring can have both characteristics.
Genetic Engineering in Agriculture
Genetic engineering is also used in agriculture with the aim of improving foods. Crops are being created whereby they are resistant to diseases and pests and also need less water to grow. These plants also tend to grow faster.
Advantages of genetic engineering in agriculture
The advantages of agriculture are also numerous as farmers are able to harvest more crops that have nutrients. It has enabled crops to be made to even grow in harsh conditions and therefore farming can be done any part of improving the economy of people. The crops are also engineered in a way that they are resistant to pests and diseases thereby reducing the cost of farming that includes buying pesticides. There is also the advantage of eliminating those characteristics that are undesirable
Disadvantages of genetic engineering in agriculture
There are however also the cons of genetic engineering which in agriculture they are quite many. One is that the despite not buying pesticides more fertilizers will be required and also as the plants grow equipment that is needed to crop these plants have to be modified. Genetic engineering also ignores certain steps in like pollination thereby disrupting the ecosystem. There is also the danger of pollution. Farmers also fear that any gene that is used for herbicide resistance may spread to other crops and create more dangerous weed leading them to use more money in farming.
Benefits and risks of genetic engineering
Applications
Genetic engineering has also been applied in medicine where it has been used to try and cure diseases like cancer. This is done by trying to replace those genes that are faulty with others that are working perfectly.
Pros of genetic engineering
It has tried to cure certain diseases and has lead to the elimination of faulty genes and replacing them with better ones. It also has been able to cure visual impairment.
Cons of genetic engineering
The gene therapy has a lot of dangers and has not been used widely. It can lead to other dangers in one’s life.
Genetic engineering and society
Most people in the society have been against genetic engineering claiming it is trying to change what is already there. This is because they have not seen the results that had been promised there before but scientists are not giving up because they continue advancing with technology.
Genetic engineering will be accepted if its benefits are more than its risks since nothing can be perfect.
- writing help
- essay writing

Arguing For and Against Genetic Engineering
Harvard philosopher Michael Sandel recently spoke at Stanford on the subject of his new book, The Case against Perfection: Ethics in the Age of Genetic Engineering. He focused on the “ethical problems of using biomedical technologies to determine and choose from the genetic material of human embryos,” an issue that has inspired much debate.
Having followed Sandel’s writings on genetic enhancement for several years, I think that this issue deserves special thought. For many years, the specter of human genetic engineering has haunted conservatives and liberals alike. Generally, their main criticisms run thus:
First, genetic engineering limits children’s autonomy to shape their own destinies. Writer Dinesh D’Souza articulates this position in a 2001 National Review Online article: “If parents are able to remake a child’s genetic makeup, they are in a sense writing the genetic instructions that shape his entire life. If my parents give me blue eyes instead of brown eyes, if they make me tall instead of medium height, if they choose a passive over an aggressive personality, their choices will have a direct, lifelong effect on me.” In other words, genetic enhancement is immoral because it artificially molds people’s lives, often pointing their destinies in directions that they themselves would not freely choose. Therefore, it represents a fundamental violation of their rights as human beings.
Second, some fear that genetic engineering will lead to eugenics. In a 2006 column, writer Charles Colson laments: “British medical researchers recently announced plans to use cutting-edge science to eliminate a condition my family is familiar with: autism. Actually, they are not ‘curing’ autism or even making life better for autistic people. Their plan is to eliminate autism by eliminating autistic people. There is no in utero test for autism as there is for Down syndrome…[Prenatal] testing, combined with abortion-on-demand, has made people with Down syndrome an endangered population…This utilitarian view of life inevitably leads us exactly where the Nazis were creating a master race. Can’t we see it?” The logic behind this argument is that human genetic enhancement perpetuates discrimination against the disabled and the “genetically unfit,” and that this sort of discrimination is similar to the sort that inspired the eugenics of the Third Reich.
A third argument is that genetic engineering will lead to vast social inequalities. This idea is expressed in the 1997 cult film Gattaca, which portrays a society where the rich enjoy genetic enhancements—perfect eyesight, improved height, higher intelligence—that the poor cannot afford. Therefore, the main character Vincent, a man from a poor background who aspires to be an astronaut, finds it difficult to achieve his goal because he is short-sighted and has a “weak heart.” This discrepancy is exacerbated by the fact that his brother, who is genetically-engineered, enjoys perfect health and is better able to achieve his dreams. To many, Gattaca is a dystopia where vast gaps between the haves and have-nots will become intolerable, due to the existence of not just material, but also genetic inequalities.
The critics are right that a world with genetic engineering will contain inequalities. On the other hand, it is arguable that a world without genetic engineering, like this one, is even more unequal. In Gattaca, a genetically “fit” majority of people can aspire to be astronauts, but an unfortunate “unfit” minority cannot. In the real world, the situation is the other way round: the majority of people don’t have the genes to become astronauts, and only a small minority with perfect eyesight and perfect physical fitness—the Neil Armstrong types—would qualify.
The only difference is that in the real world, we try to be polite about the unpleasant realities of life by insisting that the Average Joe has, at least theoretically, a Rocky-esque chance of becoming an astronaut. In that sense, our covert discrimination is much more polite than the overt discrimination of the Gattaca variety. But it seems that our world, where genetic privilege exists naturally among a tiny minority, could conceivably be less equal (and less socially mobile) than a world with genetic engineering, where genetic enhancements would be potentially available to the majority of people, giving them a chance to create better futures for themselves. Supporters of human genetic engineering thus ask the fair question: Are natural genetic inequalities, doled out randomly and sometimes unfairly by nature, more just than engineered ones, which might be earned through good old fashioned American values like hard work, determination, and effort?
“But,” the critics ask, “wouldn’t genetic engineering lead us to eugenics?” The pro-genetic engineering crowd thinks not. They suggest that genetic engineering, if done on a purely decentralized basis by free individuals and couples, will not involve any form of coercion. Unlike the Nazi eugenics program of the 1930s, which involved the forced, widespread killing of “unfit” peoples and disabled babies, the de facto effect of genetic engineering is to cure disabilities, not kill the disabled. This is a key moral difference. As pointed out by biologist Robert Sinsheimer, genetic engineering would “permit in principle the conversion of all the ‘unfit’ to the highest genetic level.” Too often, women choose to abort babies because pre-natal testing shows that they have Down syndrome or some other ailment. If anything, genetic engineering should be welcomed by pro-life groups because by converting otherwise-disabled babies into normal, healthy ones, it would reduce the number of abortions.
In addition, the world of Gattaca, for all its faults, features a world that, far from being defined along Hitler-esque racial lines, has in fact transcended racism. Being blond-haired and blue-eyed loses its racially elitist undertones because such traits are easily available on the genetic supermarket. Hair color, skin color, and eye color become a subjective matter of choice, no more significant than the color of one’s clothes. If anything, genetic engineering will probably encourage, not discourage, racial harmony and diversity.
It is true that genetic engineering may limit children’s autonomy to shape their own destinies. But it is equally true that all people’s destinies are already limited by their natural genetic makeup, a makeup that they are born with and cannot change. A short person, for example, would be unlikely to join the basketball team because his height makes it difficult for him to compete with his tall peers. An ugly person would be unable to achieve her dream of becoming a famous actress because the lead roles are reserved for the beautiful. A myopic kid who wears glasses will find it difficult to become a pilot. A student with an IQ of 75 will be unlikely to get into Harvard however hard he tries. In some way or another, our destinies are limited by the genes we are born with.
In this sense, it is arguable that genetic engineering might help to level the playing field. Genetic engineering could give people greater innate capacity to fulfill their dreams and pursue their own happiness. Rather than allow peoples’ choices to be limited by their genetic makeup, why not give each person the capability of becoming whatever he or she wants to, and let his or her eventual success be determined by effort, willpower, and perseverance? America has long represented the idea that people can shape their own destinies. To paraphrase Dr. King, why not have a society where people are judged not by the genes they inherit, but by the content of their character?
Looking at both sides, the genetic engineering controversy does raise questions that should be answered, not shouted down. Like all major scientific advances, it probably has some negative effects, and steps must be taken to ameliorate these outcomes. For example, measures should also be taken to ensure that genetic engineering’s benefits are, at least to some extent, available to the poor. As ethicists Maxwell Mehlman and Jeffrey Botkin suggest in their book Access to the Genome: The Challenge to Equality, the rich could be taxed on genetic enhancements, and the revenue from these taxes could be used to help pay for the genetic enhancement of the poor. To some extent, this will help to ameliorate the unequal effects of genetic engineering, allowing its benefits to be more equitably distributed. In addition, caution must be taken in other areas, such as ensuring that the sanctity of human life is respected at all times. In this respect, pro-life groups like Focus on the Family can take a leading role in ensuring that scientific advances do not come at the expense of moral ethics.
At the same time, we should not allow our fear of change to prevent our society from exploring this promising new field of science, one that promises so many medical and social benefits. A strategy that defines itself against the core idea of scientific progress cannot succeed. Instead of attempting to bury our heads in the sand, we should seek to harness genetic engineering for its positive benefits, even as we take careful steps to ameliorate its potential downsides.
The Pros and Cons of Genetic Engineering
Within the field of human embryo research lies a controversial science that could redefine prenatal care: genetic engineering. Genetic engineering not only offers the possibility of eliminating birth defects and genetic illness, but also presents the moral ambiguity of eugenics. The acceptabilities of genetic engineering, assuming that it will be available in the foreseeable future, must be explored if society is to fully benefit from it.
The most prominent and perhaps the most acceptable reason given for genetic engineering is its potential use in preventative medicine. A few cells from an embryo could be genetically analyzed to detect harmful mutation or predisposition towards disorder, at which point action could be taken either through somatic cell or germ-line gene modification. In 1993, the gene that causes Huntington’s Disease was located, and scientists are currently trying to determine its normal function (The Benefits of Genetic Engineering).
Assuming researchers succeed in this endeavor, genetic engineering could then be used to eliminate a debilitating and ultimately fatal disease that affects approximately 30000 Americans and that has the potential to affect 150000 more through genetic inheritance (Huntington’s Disease). In 1997, a group of scientists successfully diagnosed familial adenomatous polyposis coli, the dominant cancer predisposition syndrome, in three preimplantation embryos.
This type of cancer predisposition affects 1 in every 10000 people America, Britain, and Japan, making it a relatively common malady (Ao, 140). Schizophrenia has been shown to run in families; even adopted children of schizophrenic parents are ten times more likely to develop schizophrenia, regardless of whether or not their adoptive parents are affected (Bernstein, 518). Lastly, birth defects such as downs syndrome could be eliminated through genetic engineering (Resta).
A more ambiguous reason for genetic engineering is the elimination of common defects that vary in seriousness, such as sensory impairment. Dozens of chromosomes linked to hearing impairment have been located (Ruben, 33). Although treatment for such conditions initially looks promising, as the elimination of complete blindness or deafness would alleviate hardships caused by these disabilities, removing serious sensory conditions and actually raising sensory ability to a level above normal are separated by a fine line.
Due to relatively recent historical events, predominantly the practices of the Nazi party before and during World War 2, eugenics is rightly seen as a major risk to developing genetic engineering technology. Eighteen percent of people interviewed in the United Kingdom said that if they could choose, they would make their child less likely to exhibit aggressive or alcoholic behavior (Henig, 58).
Technically, if the gene for this behavior were isolated, it most likely could be altered, but it should be understood that a genetic predisposition towards a certain behavior neither guarantees that the behavior will manifest nor does it guarantee that the behavior will not be apparent even if the genetic predisposition is not present. Thus, not only is genetically engineering behavior morally and ethically questionable, it is highly unfeasible. Also, whether genetic engineering is undertaken for good or bad, the quality of the outcome must be considered.
In the recent experiments in cloning Dolly, many of the mistrials were largely oversized, causing undue pain to both the lamb and the mother (Wolfson). And finally, thought must be given to the psychological trauma that may result from any genetic choice made; family members of victims of Huntington’s disease sometimes display signs of guilt that they have escaped a positive diagnosis while their loved one must suffer, much like the survivor of a major natural disaster feeling guilty that they lived while many others did not (Ruben, 228).
More Essays
- Essay on The Pros And Cons Of Genetic Engineering
- Pros And Cons Of Genetic Testing Essay
- Genetic Engineering. Right or Wrong?
- Genetic Engineering
- Ethics Of Genetic Engineering
- Pros And Cons Of Gene Therapy Essay
- Human Genome Project Pros And Cons Essay
- Substance Abuse Pros And Cons Essay
- Essay on The Pros And Cons Of GMO Foods
- The Pros And Cons Of Biotechnology Essay
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Home — Essay Samples — Science — Technology & Engineering — Genetic Engineering
Essays on Genetic Engineering
What makes a good genetic engineering essay topic.
When it comes to writing a captivating genetic engineering essay, the topic you choose is paramount. It not only grabs the reader's attention but also allows for effective exploration of the subject matter. So, how can you brainstorm and select a standout essay topic? Here are some recommendations:
- Brainstorm: Kickstart your ideas by brainstorming topics related to genetic engineering. Consider the latest advancements, ethical concerns, controversial issues, or potential future applications. Jot down any ideas that come to mind.
- Research: Once you have a list of potential topics, conduct thorough research to gather relevant information and understand different perspectives. This will help you evaluate the feasibility and depth of each topic.
- Consider Interest: Choose a topic that genuinely piques your interest. Writing about something you are passionate about will make the entire process more enjoyable and motivate you to delve deeper into the subject matter.
- Relevance: Ensure that the chosen topic is relevant to genetic engineering. It should align with the scope of the subject and allow you to explore various aspects related to it.
- Uniqueness: Strive for a unique and imaginative topic that stands out from the ordinary. Steer clear of generic subjects and instead focus on specific areas or emerging trends within genetic engineering.
- Controversy: Controversial topics often generate more interest and discussion. Consider exploring ethical dilemmas, potential risks, or societal impacts of genetic engineering to add a thought-provoking element to your essay.
- Depth and Scope: Assess the depth and scope of each topic. Make sure it provides enough material for a comprehensive essay without being too broad or too narrow.
- Audience Appeal: Keep your target audience in mind. Choose a topic that would captivate readers, whether they are experts in the field or individuals with limited knowledge about genetic engineering.
- Originality: Strive for originality in your topic selection. Look for unique angles, lesser-known areas, or innovative applications of genetic engineering that can make your essay stand out.
- Personal Connection: If possible, choose a topic that connects with your personal experiences or future aspirations. This will enhance your engagement and make your essay more meaningful.
Igniting Thought: The Finest Genetic Engineering Essay Topics
Below are some of the most captivating genetic engineering essay topics to consider:
- Genetic Engineering and the Future of Human Evolution
- The Ethical Dilemmas of Designer Babies
- Genetic Engineering in Agriculture: Balancing Benefits and Concerns
- CRISPR-Cas9: Unleashing Revolutionary Potential in Genetic Engineering
- The Potential of Genetic Engineering in Cancer Treatment
- Genetic Engineering's Role in Creating Sustainable Food Sources
- Genetic Engineering and Animal Welfare: Navigating Ethical Considerations
- Genetic Engineering and its Impact on Biodiversity
- The Social and Economic Implications of Genetic Engineering
- Genetic Engineering's Influence on Human Longevity
- Enhancing Athletic Performance: The Power of Genetic Engineering
- Genetic Engineering Techniques for Disease Prevention and Treatment
- Genetic Engineering's Role in Environmental Conservation
- Genetic Engineering and the Preservation of Endangered Species
- The Psychological and Societal Effects of Genetic Engineering
- The Pros and Cons of Genetic Engineering for Non-Medical Purposes
- Exploring the Potential Risks and Benefits of Genetic Engineering in Space Exploration
- Genetic Engineering and the Creation of Biofuels
- The Morality of Genetic Engineering: Insights from Religious and Philosophical Perspectives
- Genetic Engineering's Role in Combating Climate Change
Thought-Provoking Genetic Engineering Essay Questions
Consider these stimulating questions for your genetic engineering essay:
- How does genetic engineering impact the concept of natural selection?
- What are the potential consequences of genetic engineering on human genetic diversity?
- Is it ethically justifiable to use genetic engineering for cosmetic purposes?
- How does genetic engineering contribute to the development of personalized medicine?
- What are the social implications of genetically modifying animals for human consumption?
- How does the use of genetic engineering in agriculture affect food security?
- Should genetic engineering be used to resurrect extinct species?
- What are the potential risks and benefits of genetically modifying viruses for medical purposes?
- How does genetic engineering influence the balance between individual rights and societal well-being?
- Can genetic engineering be the solution to eradicating genetic diseases?
Provocative Genetic Engineering Essay Prompts
Here are some imaginative and engaging prompts for your genetic engineering essay:
- Imagine a world where genetic engineering has eliminated all hereditary diseases. Discuss the potential benefits and drawbacks of such a scenario.
- You have been granted the ability to genetically engineer one aspect of yourself. What would you choose and why?
- Write a fictional story set in a future where genetic engineering is widespread and explore the consequences it has on society.
- Reflect on the ethical considerations of genetically modifying animals for entertainment purposes, such as creating glow-in-the-dark pets.
- Create a persuasive argument for or against the use of genetic engineering in enhancing human intelligence.
Answering Your Genetic Engineering Essay Queries
Q: Can I write about the history of genetic engineering?
A: Absolutely! Exploring the historical context of genetic engineering can provide valuable insights and set the foundation for your essay.
Q: How can I make my genetic engineering essay engaging for readers with limited scientific knowledge?
A: Simplify complex concepts and terminologies, provide relevant examples, and use relatable analogies to help readers grasp the information more easily.
Q: Can I express my personal opinion in a genetic engineering essay?
A: Yes, expressing your personal opinion is encouraged as long as you support it with logical reasoning and evidence from reputable sources.
Q: Are there any potential risks associated with genetic engineering that I should discuss in my essay?
A: Yes, incorporating a discussion on the potential risks and ethical concerns surrounding genetic engineering is essential to provide a balanced perspective.
Q: Can I include interviews or case studies in my genetic engineering essay?
A: Absolutely! Interviews or case studies can add depth and real-life examples to support your arguments and make your essay more compelling.
Remember, when writing your genetic engineering essay, let your creativity shine through while maintaining a formal and engaging tone.
Pros and Cons of Genetic Engineering: The Need for Proper Regulation
The pros and cons of genetic engineering and the need for regulation, made-to-order essay as fast as you need it.
Each essay is customized to cater to your unique preferences
+ experts online
The Ethics of Genetic Engineering in Human Enhancement
Genetic engineering, ethical issues of genetic engineering, the dangers of genetic engineering to humanity, let us write you an essay from scratch.
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
The Use and Ethics of Genetic Engineering
The potential and consequences of genetic engineering, the issue of the use of genetic modification of humans, reasons why genetic engineering should be banned, get a personalized essay in under 3 hours.
Expert-written essays crafted with your exact needs in mind
Genetic Engineering: an Overview of The Dna/rna and The Crispr/cas9 Technology
Review of human germline engineering, positional cloning of genetic disorders, engineering american society: the lesson of eugenics, bioethical issues related to genetic engineering, cloning and ethical controversies related to it, genetic editing as a possibility of same-sex parents to have children, adhering to natural processes retains the integrity of a natural human race , genetically modified organisms: soybeans, gene silencing to produce milk with reduced blg proteins, the role of crispr-cas9 gene drive in mosquitoes, the life of gregor mendel and his contributions to science, eugenics, its history and modern development, morphological operation hsv color space tree detetction, cytogenetics: analysis of comparative genomic hybridization and its implications, genetically engineered eucalyptus tree and crispr, review of the process of dna extraction, review of the features of the process of cloning, heterologous gene expression as an approach for fungal secondary metabolite discovery, review of the genetic algorithm searches.
Genetic engineering (also called genetic modification) is a process that uses laboratory-based technologies to alter the DNA makeup of an organism.
Genetic engineering as the direct manipulation of DNA by humans outside breeding and mutations has only existed since the 1970s. In 1972, Paul Berg created the first recombinant DNA molecules by combining DNA from the monkey virus SV40 with that of the lambda virus. The first field trials of genetically engineered plants occurred in France and the US in 1986, tobacco plants were engineered to be resistant to herbicides.
It is a set of technologies used to change the genetic makeup of cells, including the transfer of genes within and across species boundaries to produce improved or novel organisms. New DNA is obtained by either isolating and copying the genetic material of interest using recombinant DNA methods or by artificially synthesising the DNA. Used in research and industry, genetic engineering has been applied to the production of cancer therapies, brewing yeasts, genetically modified plants and livestock, and more.
Relevant topics
- Engineering
- Stephen Hawking
- Mathematics in Everyday Life
- Space Exploration
- Natural Selection
- Charles Darwin
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free

Genetic Engineering Pros and Cons
Genetic engineering is the process of methodically altering the nature and structure of an organism’s genes using methods like molecular cloning and cell transformation. This process can result in a considerable transformation of an organism’s characteristics due to the manipulation of genetic material (DNA), which determines how every cell functions. While Genetic engineering can result in better traits in organisms, it can also lead to undesirable after-effects. Let us first understand how genetic engineering can benefit individuals.
Pros of genetic engineering:
- Better varieties of crops
Scientists have genetically engineered crops like tomato, potato, rice, and soybean to new varieties with improved nutritional value and better yield. The genetically modified strains can grow on tough terrains, making the area suitable for cultivation. Engineered seeds can survive in harsh climatic conditions and are resistant to pests. Biotechnology, the science of producing genetically engineered foods, can slow down spoilage of perishable foods, resulting in the greater shelf life of fruits and vegetables.
- Create new substances
Genetic engineering can be applied to create totally new substances and food nutrients. The genetic modification can increase medicinal value of foods, thereby turning them into edible vaccines.
- Modification of human genes
Genetic engineering can be used to modify genotypes of humans before birth. This process can manipulate specific traits in a person, such as enhancing positive traits like boosting longevity and suppressing negative traits like genetic disorders. The discovery of genes associated with exceptional qualities in humans has allowed genetic engineers to artificially introduce genotypes to modify the DNA of human beings and desirable functional and structural changes in them.
- Fighting diseases
Some of the deadliest diseases in the world have resisted destruction till date. However, genetic engineering could wipe out these diseases forever from the human race. Genetic mutations are responsible for some dreaded diseases in humans. The sufferance can end with active intervention and genetically engineering, which can protect the next generation from these problems. Scientists are looking for a permanent cure for terrible diseases with the help of genetic engineering.
- Tackling diseases in unborn children
Advanced medical technology has enabled doctors to detect certain problems in unborn children. Prenatal examinations can detect whether the child will suffer from genetic diseases such as Down’s syndrome or sickle cell anaemia. If these issues are detected, doctors can use genetic engineering to cure diseases in children even before they are born. The infants would be born healthy with no diseases present at birth.
Genetic engineering can help people who are at risk of passing on awfully degenerative illnesses to their offspring. If people suffering from genetic disorders give birth, there are chances that the children will inherit the disease. Genetic engineering can ensure that the children born to these individuals live healthy and long lives and do not carry the disease to next generations.
- Enhanced longevity
Medical science had enhanced the lifespan of human beings but, there are certain illnesses that can appear later in life and kill individuals earlier than their expected lifetime. Genetic engineering can reverse body’s natural deterioration on a cellular level, improving the lifespan as well as the quality of life afterward. In addition, it could help individuals become accustomed to the growing inconvenience, like global warming. Thanks to genetic engineering, people can adapt to live in places that will be a lot colder or hotter in coming time.
Apart from its multiple benefits, genetic engineering has exposed human race to several disadvantages by allowing scientists to tread into territories that were better left untouched. Let us have a look at those disadvantages.
Cons of Genetic Engineering:
- Ethical and religious objections
When genetic engineering was introduced, many religions believed that the genetic engineers were trying to play god and forbade it to be used on their children. There are several ethical arguments that believe that the diseases exist for a reason. If humans fight against them and artificially extend their lifespan, the planet will become overpopulated and result in problems that cannot possibly be predicted.
- Genetic anomalies
It is known that genetic engineering can bring about changes at the cellular level but, what about the safety of these changes and repercussions of the slightest changes. Scientists are yet to fully understand the working of the human body and they cannot predict what would be the result of their actions. What will happen if erasing one disease introduces another brand new and more dangerous disease? If scientists genetically modify unborn babies, it could result in complications like stillbirth, premature birth or miscarriage.
- Genetic diversity hampered
Diversity is an important part of evolution that results in the continuation of fitter and better species. Genetically modifying species can have a negative impact on genetic diversity, just like cloning. Gene therapy is not an affordable process and makes it impossible for the common man to benefit from it. Additionally, some traits responsible for introducing diversity in species may eventually die out because of genetic engineering.
- Long-term use of genetic engineering
An important thing to consider is the scope of genetic engineering. The technique has been in use for years but, the question is how far can it go? While many scientists have been diligently using the process to eliminate worst illnesses, genetic engineering has remained at the centre of controversy for altering the DNA of living organisms. It has worked wonders for many but will it pan out real safe in the long run is something that remains to be seen.
- Hamper dietary value
Genetically engineering foods result from the contamination of genetic makeup of crops. The engineered crops supersede natural weeds but they might prove to be dangerous for natural vegetation. Unwanted genetic modifications can cause allergies in crops and hamper their dietary value while improving their appearance and taste.
- Entry of pathogens
Genetic engineering in crops is performed through horizontal gene transfer. While this process can boost disease-fighting capability of plants, it can produce new pathogens. The disease-resistant genes can get transferred to dangerous pathogens and make them stronger.
This shows that genetic engineering has its own set of benefits and disadvantages. It is up to the scientists using this technique to apply it after weighing it’s the pros and cons.
PraxiLabs A virtual world of science

Genetic Engineering in Humans: Between the Pros and Cons of that Magical Technique!
Last Updated on April 11, 2023 by Sara Assem
Try to mention the expression of genetic engineering in humans among a bunch of people, or a community gathering. Now try to escape the endless amount of questions, hurdles, and debates that will arise. technical
Since their first days, genetic engineering, gene modification, and traits selection have always been controversial and have always been questioned, whether socially, scientifically, or ethically. Questions and interrogations considering safety, individual liberties, and social inequality and aristocracy are the main ones surrounding this hot topic.
In this article, we will talk about the definition of genetic engineering, what genetic engineering in humans is, and how it can affect our lives. What are the pros and cons of genetic engineering? What is the importance of genetic engineering in humans life? That’s in addition to discussing ethical and safety considerations and regulations that are of a huge importance to everyone, from scientists and researchers to patients & parents… Let’s start!
Table of Contents
What is Genetic Engineering Used for?
Before knowing what genetic engineering is used for, let first things come first: what is genetic engineering in its essence? What is its definition?
Deep down the cells of any living organisms—whether it is a human being, an animal, a bacteria, or whatever—there are parts scientifically known as genes. Half of those genes are inherited from one parent; consequently the other half is passed from the other parent, and both parents transmit certain traits to their offspring. Genes control the cells, and they stimulate the chemical reactions responsible for their functioning and growth.
Genetic engineering “or genetic modification” is defined as:
“the process of altering the DNA through direct manipulation by using laboratory-based technologies, hence changing the organism’s phenotype (genome) in a certain way”
In other words, this can lead to changing only one base pair of DNA (A-T, or C-G), removing a complete region of DNA, or adding an additional copy of gene to the DNA. It can also mean extracting DNA from another genome and pasting it to another genome’s DNA.
The timeline tracing the history of genetic engineering does not date back to ancient old ages; rather, it dates back to the 1970s. To be specific, it was not until 1973 that the first successful genetically modified organism was created: bacterium .
Following that year, DNA experiments and modifications started to occur more often, where these techniques were applied on mice (in 1974), and that was followed by applying it on plants. In 1994, the first genetically modified food was available, and later on, human beings took their turn as well.
Genetic engineering is used for many purposes and applications. Examples are many, such as agriculture, animal characteristics, health, and scientific research.
Genetic Engineering in Humans
Due to its extraordinarily high costs and its unpopularity, the utilization of genetic engineering in humans and their embryos is slowly growing and spreading, at least among the society’s most privileged classes . Genetic engineering in humans helps in “Hacking Darwin” and his theory about the most important evolutionary pillars.
Darwin’s essential evolution pillars are two, which are:
- Natural selection
- Random mutation
while with the usage of genetic engineering in humans techniques, both the pillars are canceled and are replaced by other concepts that should be approached cautiously.
Under the umbrella of fighting and limiting certain diseases, this technology is receiving funds, supported, and continuing to evolve, giving humans the chance to cut off or add some genes. However, we do not know what this “selective selection” can bring to our race.
Book FREE Live Demo Now
Genetic Engineering in Humans Examples
Although examples of genetic engineering in humans and the modifications consequent on it are neither regularly, nor widely used techniques until today, we still have some examples to refer to, and here are some:
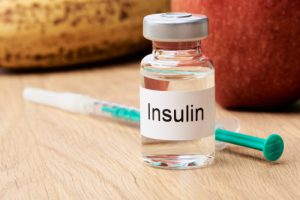
- Cavity formation in humans’ teeth was successfully able to be reduced with the help of transgenic bacteria. It was done because genetic scientists and engineers managed to control this type of bacteria and not allow it to produce tooth-corroding lactic acid.
- The weirdest thing is a banana vaccine, in which the bananas are genetically modified in a way that offers a vaccine against many diseases, such as cholera and hepatitis. It is a process similar to that of needle vaccine, where humans only need to eat the bananas in order to develop disease-combating antibodies; hence they gain immunity against these diseases.
- The most recent genetically modified vaccines were produced by Pfizer and Moderna, amid the pandemic of COVID-19. Such vaccines use mRNA genetic sequencing, to aid the human’s body recognizing the COVID virus.
Benefits of Genetic Engineering in Humans
All our genetic engineering technologies and advanced techniques are designed to help us overcome any genetically undesired diseases or traits caused by inheritance. In other words, genetically modified animals, food, and plants are also designed to facilitate human’s life and bring him the utmost benefits.
The benefits and pros are uncountable, but here are some examples:
- Limiting disease infections caused by insects, like dengue fever, malaria, and the Zika virus, through sterilizing insects, i.e., mosquitos.
- Reducing hunger and famines around the world, by improving crop quality and crop yields. This also helps in countries’ development.
- Getting rid of undesired personal traits, where humans favor intelligence, beauty, muscle growth, and many other features. We can choose and design our preferable traits with the help of genetic engineering techniques. This allows us to pave the way towards some very finely selected traits that cause natural selection to be canceled out.
- Cloning animals to preserve endangered species, as is the situation with the black-footed ferret, the only ferret native to North America. This species’ existence was threatened as its main source of food, the prairie dogs, has critically dropped. In 2020, scientists managed to complete the cloning project which started in 2013, and it resulted in the birth of Elizabeth Ann , a cloned kit. Elizabeth was cloned to bring some diversity amid the ferret members, which are 650 alive today.

Disadvantages of Genetic Engineering in Humans
Imagine if every human being started to prefer a certain trait and then managed to get it in the blink of an eye. We will end the broad window of genetic diversity we have by our own hands!
Genetic engineering may underlie many disadvantages, with some of them being crucial, while the others are some ethically asked questions which still have no answer. Some of these cons are listed below:
- Fear of spreading invasive species Genetically modified (GM) animals and plants are well-known for their ability to adapt to different environments better than the regular ones. There are concerns around the possibility of uncontrollable growth, turning the species into invasive ones, to an extent where they harm the environment and the organisms themselves.
- Uncontrollable population growth Since disease is a major factor and one of the most effective tools that accounts for controlling humans’ population. By extending the lifespan of everyone throughout using genetic engineering in humans, this may result in outgrown numbers of humans. Serious issues may arise as a consequence, i.e. problems with job availability, economic disparity, the necessity to provide higher levels of medical care, and the lack of agricultural products to cover everyone’s needs.
- Higher risk of increasing allergies The process here is a bit complicated, with the fact that allergens in GMO food are easily transferred from one crop to another. Hence, pregnant women eating GMO food might be endangering their offspring by altering their genetic codes and expressions. Genetic editing is an irreversible process; once taking place, it cannot be reversed. Unfavored effects may emerge from the immediate evolutionary alterations done by our genetic engineering techniques, and the danger can reach some critical scenarios, i.e., allergic reactions may develop some sort of spontaneous reactions that can jeopardize our entire planet and our existence.
Other cons and disadvantages can be furtherly discussed around this topic, but we still got the point. Technology and new scientific techniques are a double-edged weapon, since the silver lining lies in their many benefits to humans and facilitating their lives, but by using them unreasonably, we might be bringing our own death quicker than ever.
In addition to all the previously mentioned risks, genetic engineering and its techniques are continuously investigated, because of all the ethical issues it brings up to the surface every time. All in all, genetic engineering in humans laws are of a huge importance in civil society and human rights debates.
DNA extractions and genetic engineering experiments are costly, yet require scientific guidance and supervision…
Join PraxiLabs the best virtual labs and discover this world now!
About Sherouk Badr Shehata

COMMENTS
Genetic engineering technologies and techniques. Genetic engineering applications. Pros of genetic engineering. 1. A greater understanding of how DNA and genes work. 2. The production of medicines. 3. A promise of cures for genetic diseases.
2. Increased resistance of plants to rotting and pests. Increased Resistance To Pests. A common problem in farming and food production is the rapid infestation and rotting of crops. Using genetic engineering, scientists have already found a solution: by creating rot and pest resistant crops.
Pros of Genetic Engineering. A. Improved Crop Yield. Genetic engineering in agriculture has led to increased crop yield, where scientists have developed crops that are resistant to pests and diseases. This has led to a reduction in the use of pesticides, which is not only beneficial to the environment but also to the farmers and consumers.
3 A gene drive is a genetic engineering technology—adding, deleting, disrupting, or modifying genes—to rapidly spread a particular genetic trait to an entire offspring population. A gene drive ...
Genetic engineering is a debate, and there are some good points on each side. You have to look at both the pros and cons of genetic engineering if you want to make an informed decision on the matter. Extending Our Lives. Evolution takes thousands of years to adapt to our surroundings, but genetic engineering offers a quicker path forward. With ...
What are the pros and cons of genetic engineering, and do its achievements contradict ethics? Dec 10, 2022 • By Viktoriya Sus , MA Philosophy At present, genetic engineering is one of the most advanced technologies related to the scientific study of the living world.
Unlike selective breeding, modern genetic engineering is more gene-specific. One of the downsides of selective breeding is the possibility of generating traits that are less desirable. This is averted by modern genetic engineering that introduces specific genes. (Ref. 1) Since the process is rather straightforward, it is relatively faster than ...
Negative Side Effects The goal of genetic engineering is to solve an issue by transferring genes to the organism that will help combat the problem. Sometimes, this can cause side effects. For example, you can modify a plant to need less water, but that would make it intolerant to direct sunlight (Pros and Cons of Genetic Engineering, 2014).
Biologists can use genetic engineer technologies to improve our crops by, for example, altering the vitamin/nutrition composition to make it more suitable for human consumption. Many scientists think there is great promise in GMO technologies and that much more can be achieved through these technologies in the future.
Explore the different pros and cons of genetic engineering. Learn the benefits of genetic engineering and, through examples, understand its various applications. Updated: 11/21/2023
1. It allows for a faster growth rate. Genetic engineering allows of plants or animals to be modified so their maturity can occur at a quicker pace. Engineering can allow this maturity to occur outside of the normal growth conditions that are favorable without genetic changes as well.
This essay aims to explore the pros and cons of genetic engineering, the need for regulation, and the importance of genetic engineering in modern society. Say no to plagiarism. Get a tailor-made essay on
The cons of genetic engineering in animals are that they disrupt nature which is not easy to understand. When scientist introduces these new genes to animals they may lead to disastrous consequences since they are never sure what they will form. The society has not fully accepted genetic engineering and most of them see it as an n insult to nature.
Conclusion. In conclusion, genetic engineering is a complex and controversial topic that has both pros and cons. The benefits of genetic engineering in improved crop yield, medical advancements, and environmental conservation cannot be ignored.
The logic behind this argument is that human genetic enhancement perpetuates discrimination against the disabled and the "genetically unfit," and that this sort of discrimination is similar to the sort that inspired the eugenics of the Third Reich. A third argument is that genetic engineering will lead to vast social inequalities.
The Pros and Cons of Genetic Engineering. Within the field of human embryo research lies a controversial science that could redefine prenatal care: genetic engineering. Genetic engineering not only offers the possibility of eliminating birth defects and genetic illness, but also presents the moral ambiguity of eugenics.
There are also many consequences and beliefs that genetic engineering is wrong for moral or religious reasons. The first disadvantage of genetically engineering crops is the likelihood of genes transferring from GM (genetically modified) crops to other crops. For example, oilseed rape can cross-pollinate wild relatives.
Pros And Cons Of Genetic Engineering Philosophy Essay. Biotechnology has existed for many years, even since the prehistoric times and over the past few years it has benefited us immensely. With biotechnology we are able to create pest-resistant crops, developing new types of plant or animal species and therapeutic drugs for humans.
The Pros and Cons of Genetic Engineering for Non-Medical Purposes; ... Remember, when writing your genetic engineering essay, let your creativity shine through while maintaining a formal and engaging tone. 49 essay samples found. Sort & filter. 1 Pros and Cons of Genetic Engineering: The Need for Proper Regulation .
Pros of genetic engineering: Better varieties of crops. Scientists have genetically engineered crops like tomato, potato, rice, and soybean to new varieties with improved nutritional value and better yield. The genetically modified strains can grow on tough terrains, making the area suitable for cultivation.
Introduction to the Ethical Debate on Genetic Engineering. There are many misconceptions and oppositions on embryo alterations. There is a belief about it is unnatural and playing God. But it is important to recognise that this criticism relies on the belief that nature is good. If we used this belief, we would never use antibiotics or ...
Genetic engineering "or genetic modification" is defined as: "the process of altering the DNA through direct manipulation by using laboratory-based technologies, hence changing the organism's phenotype (genome) in a certain way". In other words, this can lead to changing only one base pair of DNA (A-T, or C-G), removing a complete ...
Essay On Pros And Cons Of Genetic Engineering. Improved Essays. 839 Words; 4 Pages; Open Document. ... This essay argues that genetic engineering does not allow tampering with evolution rather it is a novel and unique way of enhancing current biological systems by giving them additional abilities. It is an improved form of evolution and ...
The purpose of this study is to present a technique for enhancing multi-rotor spoke microphone array configurations through the utilisation of the Multiple Population Genetic Algorithm (MPGA) to meet the acoustic positioning demands of small UAVs. First, we analyse the pros and cons of both the Simple Genetic Algorithm (SGA) and the MPGA. Then, we construct the objective function using the ...