
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences

How to Write a Personal Essay for Your College Application

What does it take to land in the “accept” (instead of “reject”) pile?
How can you write an essay that helps advance you in the eyes of the admissions officers and makes a real impression? Here are some tips to get you started.
- Start early. Do not leave it until the last minute. Give yourself time when you don’t have other homework or extracurriculars hanging over your head to work on the essay.
- Keep the focus narrow. Your essay does not have to cover a massive, earth-shattering event. Some people in their teens haven’t experienced a major life event. Some people have. Either way, it’s okay.
- Be yourself. Whether writing about a painful experience or a more simple experience, use the narrative to be vulnerable and honest about who you are. Use words you would normally use. Trust your voice and the fact that your story is interesting enough in that no one else has lived it.
- Be creative. “Show, don’t tell,” and that applies here — to an extent. The best essays typically do both. You can help your reader see and feel what you are describing by using some figurative language throughout your piece.
- Make a point. As you finish your final body paragraphs ask yourself “So what?” This will help you hone in on how to end your essay in a way that elevates it into a story about an insight or discovery you made about yourself, rather than just being about an experience you had.
Where your work meets your life. See more from Ascend here .
We’ve all heard about the dreaded “college essay,” the bane of every high school senior’s existence. This daunting element of the college application is something that can create angst for even the most accomplished students.
- AA Amy Allen is a writer, educator, and lifelong learner. Her freelance writing business, All of the Write Words , focuses on providing high school students with one-on-one feedback to guide them through the college application process and with crafting a thoughtful personal essay. A dedicated poet, Amy’s work has also been published in several journals including Pine Row Press , Months to Years, and Atlanta Review .
Partner Center
Tips for Writing an Effective Application Essay

How to Write an Effective Essay
Writing an essay for college admission gives you a chance to use your authentic voice and show your personality. It's an excellent opportunity to personalize your application beyond your academic credentials, and a well-written essay can have a positive influence come decision time.
Want to know how to draft an essay for your college application ? Here are some tips to keep in mind when writing.
Tips for Essay Writing
A typical college application essay, also known as a personal statement, is 400-600 words. Although that may seem short, writing about yourself can be challenging. It's not something you want to rush or put off at the last moment. Think of it as a critical piece of the application process. Follow these tips to write an impactful essay that can work in your favor.
1. Start Early.
Few people write well under pressure. Try to complete your first draft a few weeks before you have to turn it in. Many advisers recommend starting as early as the summer before your senior year in high school. That way, you have ample time to think about the prompt and craft the best personal statement possible.
You don't have to work on your essay every day, but you'll want to give yourself time to revise and edit. You may discover that you want to change your topic or think of a better way to frame it. Either way, the sooner you start, the better.
2. Understand the Prompt and Instructions.
Before you begin the writing process, take time to understand what the college wants from you. The worst thing you can do is skim through the instructions and submit a piece that doesn't even fit the bare minimum requirements or address the essay topic. Look at the prompt, consider the required word count, and note any unique details each school wants.
3. Create a Strong Opener.
Students seeking help for their application essays often have trouble getting things started. It's a challenging writing process. Finding the right words to start can be the hardest part.
Spending more time working on your opener is always a good idea. The opening sentence sets the stage for the rest of your piece. The introductory paragraph is what piques the interest of the reader, and it can immediately set your essay apart from the others.
4. Stay on Topic.
One of the most important things to remember is to keep to the essay topic. If you're applying to 10 or more colleges, it's easy to veer off course with so many application essays.
A common mistake many students make is trying to fit previously written essays into the mold of another college's requirements. This seems like a time-saving way to avoid writing new pieces entirely, but it often backfires. The result is usually a final piece that's generic, unfocused, or confusing. Always write a new essay for every application, no matter how long it takes.
5. Think About Your Response.
Don't try to guess what the admissions officials want to read. Your essay will be easier to write─and more exciting to read─if you’re genuinely enthusiastic about your subject. Here’s an example: If all your friends are writing application essays about covid-19, it may be a good idea to avoid that topic, unless during the pandemic you had a vivid, life-changing experience you're burning to share. Whatever topic you choose, avoid canned responses. Be creative.
6. Focus on You.
Essay prompts typically give you plenty of latitude, but panel members expect you to focus on a subject that is personal (although not overly intimate) and particular to you. Admissions counselors say the best essays help them learn something about the candidate that they would never know from reading the rest of the application.
7. Stay True to Your Voice.
Use your usual vocabulary. Avoid fancy language you wouldn't use in real life. Imagine yourself reading this essay aloud to a classroom full of people who have never met you. Keep a confident tone. Be wary of words and phrases that undercut that tone.
8. Be Specific and Factual.
Capitalize on real-life experiences. Your essay may give you the time and space to explain why a particular achievement meant so much to you. But resist the urge to exaggerate and embellish. Admissions counselors read thousands of essays each year. They can easily spot a fake.
9. Edit and Proofread.
When you finish the final draft, run it through the spell checker on your computer. Then don’t read your essay for a few days. You'll be more apt to spot typos and awkward grammar when you reread it. After that, ask a teacher, parent, or college student (preferably an English or communications major) to give it a quick read. While you're at it, double-check your word count.
Writing essays for college admission can be daunting, but it doesn't have to be. A well-crafted essay could be the deciding factor─in your favor. Keep these tips in mind, and you'll have no problem creating memorable pieces for every application.
What is the format of a college application essay?
Generally, essays for college admission follow a simple format that includes an opening paragraph, a lengthier body section, and a closing paragraph. You don't need to include a title, which will only take up extra space. Keep in mind that the exact format can vary from one college application to the next. Read the instructions and prompt for more guidance.
Most online applications will include a text box for your essay. If you're attaching it as a document, however, be sure to use a standard, 12-point font and use 1.5-spaced or double-spaced lines, unless the application specifies different font and spacing.
How do you start an essay?
The goal here is to use an attention grabber. Think of it as a way to reel the reader in and interest an admissions officer in what you have to say. There's no trick on how to start a college application essay. The best way you can approach this task is to flex your creative muscles and think outside the box.
You can start with openers such as relevant quotes, exciting anecdotes, or questions. Either way, the first sentence should be unique and intrigue the reader.
What should an essay include?
Every application essay you write should include details about yourself and past experiences. It's another opportunity to make yourself look like a fantastic applicant. Leverage your experiences. Tell a riveting story that fulfills the prompt.
What shouldn’t be included in an essay?
When writing a college application essay, it's usually best to avoid overly personal details and controversial topics. Although these topics might make for an intriguing essay, they can be tricky to express well. If you’re unsure if a topic is appropriate for your essay, check with your school counselor. An essay for college admission shouldn't include a list of achievements or academic accolades either. Your essay isn’t meant to be a rehashing of information the admissions panel can find elsewhere in your application.
How can you make your essay personal and interesting?
The best way to make your essay interesting is to write about something genuinely important to you. That could be an experience that changed your life or a valuable lesson that had an enormous impact on you. Whatever the case, speak from the heart, and be honest.
Is it OK to discuss mental health in an essay?
Mental health struggles can create challenges you must overcome during your education and could be an opportunity for you to show how you’ve handled challenges and overcome obstacles. If you’re considering writing your essay for college admission on this topic, consider talking to your school counselor or with an English teacher on how to frame the essay.
Related Articles
Rochester News
- Science & Technology
- Society & Culture
- Campus Life
- University News
How to write your best college application essay

- Facebook Share on Facebook
- X/Twitter Share on Twitter
- LinkedIn Share on LinkedIn
University of Rochester dean of undergraduate admissions offers college applicants some dos and don’ts in writing the personal statement.
By robert alexander, the dean of undergraduate admissions, financial aid, and enrollment management for arts, sciences & engineering, university of rochester..
Many universities ask applicants to include a college application essay—usually a personal statement or similar essay—along with their application materials. With more students applying to selective colleges than ever, and with many of those colleges placing less emphasis on standardized test scores, the admissions essay can be a crucial component of the applicant’s file.
We’ve made that shift in emphasis away from testing at the University of Rochester . As a selective private research university with programs in the liberal arts, sciences, and engineering, the undergraduate college draws from a global pool of high-achieving students. Since nearly all of those candidates are at or near the top of their class, we use a holistic approach to select those with strong ethical character who align with our institutional values. So, as an applicant, how can you distinguish yourself?
One of the most important ways is through your college application essay.
Many students may dread this part of the process. Yet with the right attitude and strategy, you can write an essay that will improve your candidacy for admission. A good college application essay will not overcome poor grades for a student at the lowest end of a school’s applicant pool, but it can help a qualified candidate stand out from the crowd.

Tackle the college essay topic
The traditional college application essay usually requires an open-ended personal statement in response to broad or general prompts that might have you share a story, reflect on an event, or discuss a topic. The Common Application, Coalition for College Application, and other online college application forms typically provide a set of options from which you can choose.
Of course, some college and universities require you to respond to a specific prompt or question. In that case, you want to make sure to answer that prompt or question clearly and directly.
Whether the guidelines are open-ended or specific, the topic itself is less important than how you express yourself.
And above all: Don’t write an admissions essay about something you think sounds impressive or that you think the admissions officer wants to read. While it’s fine to look at college application essay examples, don’t simply mimic one. Write about something truly important to you.
Breadth versus depth?
- Dig deep into one aspect of your topic instead of trying to cover many aspects superficially in your college essay. Be brief in explaining who, what, and where; leave plenty of room for why and how .
→ For example : If you’re writing about a life-changing trip, don’t spend six paragraphs on where you traveled, how long it took to get there, and the weather. We want to know why you went and why the experience was meaningful. How are you different now because of it?
Details bring your application essay to life
- Be specific. It’s the details, rather than any general statements, that bring your essay—and hence, you—to life for an admissions officer who is reading hundreds of personal statements.
→ For example : If you’re writing about how much you loved playing your high school sport, tell a story about a specific game-winning play (or a devastating loss), how you felt, and what you learned.

Writing a college application essay: dos and don’ts
Here are a few guidelines for crafting a college application essay that effectively conveys who you are while also helping you stand out from the thousands of other applicants.
- Present yourself in a dimension that reaches beyond grades, recommendations, and test scores. Think of the things that built your character—maybe a special relationship in your life, your most meaningful extracurricular activity, or a class or idea that changed the way you think. We want to know what makes you tick, how you might fit into our community, and how your distinctive qualities and experiences would contribute to our interesting and dynamic campus.
- Be sure your essay reflects you. Ask yourself: Am I the only person who could have written this essay? Or could everyone else in my senior class have written it?
- Tell a story about yourself with a beginning, middle, and end. Hook the reader with a compelling opening paragraph—surprise us, teach us something we didn’t know, or share something vulnerable and make us curious to read more. Close with a clear ending that ties back to your opening or provides a captivating conclusion to your story.
- Ask someone to proofread your essay or to offer feedback—but be sure your essay is written in your own voice and style. It won’t serve you well for someone else to write your essay for you!
- Stay within the required—or suggested—length. Usually it is about 650 words. This shows that you can follow directions. Plus, good writers can adhere to a word limit and still get their point across.
- Pay attention to formatting. If you compose your essay in a word processing software program (like Microsoft Word or Google Docs) in order to use spellcheck or other features, be sure to review it again after copy-and-pasting into the application itself. Some of the original formatting might be lost because different combinations of word processing and web browsers can cause errors. Double-check before clicking “submit”!
And a few don’ts:
- Humor and creativity can work, provided they are not taken to an extreme. Remember: You don’t know your reader’s sense of humor—and it might not be the same as yours.
- Don’t be controversial or sensational for its own sake; but it’s OK to take a risk if you’re sharing a unique viewpoint or a particularly strong conviction that you hold dear.
- You’re not writing a legal brief for the Supreme Court or trying to sway the audience to your side of an argument. Instead, you’re attempting to share something of yourself with the admissions committee.
- Avoid using words that are not in your regular vocabulary. Again, be yourself.
- Don’t repeat information available in other parts of your application, unless you’re using your college admissions essay to expand upon an activity or academic opportunity that was particularly meaningful to you.
- Avoid regurgitating your resume or writing about your entire life’s history. Listing every award and semester you made honor roll is unnecessary, but sharing how you felt when a beloved yet demanding English teacher said you were his best student has more potential.
Ultimately, your college application essay is a chance to tell the admissions committee who you are and what is important to you. We want to know: What are your values?
At the University of Rochester, for example, we have a motto: Meliora, meaning “ever better.” So, it stands to reason that when we read an application essay, we want to know: How will you make yourself, your community, or the world better?
Tell us your story. This may be your best chance to come through as an individual, so make the most of this opportunity!
About Robert Alexander
Robert Alexander, the dean of undergraduate admissions, financial aid, and enrollment management for Arts, Sciences & Engineering at the University of Rochester, has more than 22 years of enrollment management experience in higher education. He joined Rochester in June 2020 and previously served in senior admissions, enrollment, and communications roles at Millsaps College, University of the Pacific, and Tulane University.

Rochester’s dean of undergraduate admissions offers advice on which courses to take, and why.

Grades. Clubs. Scores. Essays. Interviews. We’ve culled the advice of seasoned admissions professionals from the University of Rochester for a roadmap of what to do—and what to avoid.

Equitable access to internships helps University of Rochester students preview their futures.
More in Campus Life


How to Write an Application Letter to Study at a University

How do I Write an Application Letter to Study at a University?
According to Indiana University, a university application letter, also called a personal statement, serves three important purposes. The application letter serves to introduce yourself, outline your goals, past experiences and qualifications and display your writing skills. The university you are applying to might supply a specific topic, such as your greatest accomplishment or challenges you faced and overcame, or you might write a general letter saying why the university should consider your application. Regardless of the topic, the process of writing the letter is the same.
Read the instructions the university supplies for writing the application letter. Make sure you understand the topic or questions you must answer in the letter. According to Purdue University, the most common mistake applicants make is not taking the time to understand what the question is asking. In addition, look at specific writing requirements, such as length and formatting guidelines, and the time line for completing and submitting the letter.
Gather the information you need to complete the letter. Examples of supporting documentation you might find helpful include grade transcripts and a current resume that includes descriptions, names and dates of extracurricular activities, past jobs, internships or volunteer positions you held in the past or currently hold.
Write a few notes to yourself that you can refer to when writing the application letter. Purdue University provides examples of questions to consider that include defining how and why you developed an interest in your intended field of study and an outline of your career goals. Also consider skills and personal characteristics you possess that relate to, and improve your chance for success in your field of study, a description of obstacles you overcame to get where you are now and reasons why the admissions committee should consider your application.
Create an outline for your application letter. According to the University of Toronto, a good application letter is organized, focused and specific. Creating an outline can provide structure for your letter, help you identify the main points your letter will cover and serve as a checklist to ensure you include the supporting documentation required for evidence.
Write a first draft using the format your school requires. According to Indiana University, most application letters and personal statements are between 250 and 500 words and follow a format that includes an introduction, body and conclusion. In the introduction, mention the degree or field of study for which you are applying and include a short personal statement that, for example, describes a family member or experience that influenced your career decision. The body of your letter should address the topic and answer all required questions. The conclusion ties together the information you provided in your letter and restates your interest in the program.
Edit the content and structure of your letter. Start by reading the letter aloud and having another person do the same. Make sure your letter addresses the topic or questions and then spell and grammar check your letter.
Write the final draft and complete another spell and grammar check before you submit it.
Related Articles

How to Write the Objective in a CV for PhD Admissions

How to Write an Effective Letter of Complaint About a College

How to Write a Scholarship Letter

How to Write a Masters Degree Objective

How to Improve a Resume for Graduate School

How to Write a Letter of Protest

Does APA Style Recommend Using the Present Tense?

How to Write a Letter of Interest for Graduate Programs
- Berkeley: "Personal Statement"
- Univesity of Toronto: "Effective Admissions Letters"; Margaret Procter
Based in Green Bay, Wisc., Jackie Lohrey has been writing professionally since 2009. In addition to writing web content and training manuals for small business clients and nonprofit organizations, including ERA Realtors and the Bay Area Humane Society, Lohrey also works as a finance data analyst for a global business outsourcing company.
Sample Letter Of Interest For University Admission: Free & Effective
This article provides a detailed guide, including a customizable template and examples, to help you write a compelling university application letter based on my experience.
Key Takeaways Understanding the Purpose : Learn what a letter of interest is and why it’s crucial for your university application. Starting Strong : Tips for Crafting an Engaging Opening. Personalizing Your Story : How to weave in your unique experiences and aspirations. Structuring Your Letter : A step-by-step breakdown of each section. Finishing with Impact : Strategies for a Memorable Conclusion. Proofreading and Editing : ensuring your letter is flawless. Template for Success : A customizable template to get you started. Real-Life Examples : Insights from Successful Letters.
Step 1: Understanding the Purpose of Your Letter
A letter of interest, often mistaken for a personal statement, is a chance to show why you’re a perfect fit for the university and how the university aligns with your goals.
It’s more than just your achievements; it’s your story and aspirations and how they intertwine with what the university offers.
Step 2: Starting Strong
Your opening sentence sets the tone. Begin with something engaging and personal. For instance, “Ever since I witnessed my first solar eclipse, I knew astronomy was my calling—a passion I wish to explore at XYZ University.”
Table: Opening Statement Examples
Step 3: Personalizing Your Story
This is where you connect your past experiences, achievements, and future goals with what the university offers. Discuss specific programs, professors, or opportunities at the university that align with your interests.
For example, “Under the guidance of Professor Smith, an expert in medieval literature, I aim to deepen my understanding of Chaucer’s works.”
Step 4: Structuring Your Letter
- Introduction : Your opening statement and why you’re interested in this university.
- Body Paragraphs : Personal experiences, achievements, and how they connect with the university’s offerings.
- Conclusion : Reiterate your interest and how you would contribute to the university community.
Step 5: Finishing with Impact
Your conclusion should leave a lasting impression. Summarize your key points and express enthusiastic anticipation about the prospect of joining the university.
For instance, “I eagerly look forward to contributing to the vibrant community at XYZ University as both a learner and an active member.”
Step 6: Proofreading and Editing
Ensure your letter is free of grammatical errors and typos. It helps to have someone else read it for a fresh perspective.
Step 7: Template for Success
[Your Name] [Your Address] [City, State, Zip] [Email Address] [Phone Number] [Date]
[Admissions Office Name] [University Name] [University Address] [City, State, Zip]
Dear Admissions Committee,
Introduction: Start with an engaging opening that captures your interest in the specific field or program.
Example: Ever since I first visited [University Name] at the age of [Your Age], I have been captivated by its vibrant community and commitment to [specific field or program].
It is with great enthusiasm that I express my interest in applying to [specific program or major] at [University Name].
Body Paragraph 1 – Personal Background and Academic Interests: Describe your academic journey, key achievements, and how these have shaped your interest in your chosen field.
Example: My academic journey in [Your Field of Interest] began at [Your School or Experience]. Here, I was particularly drawn to [specific subjects or projects], which ignited my passion for [related topic].
My experience in [related experience or achievement] further solidified my desire to pursue [specific field or program] at a university that champions [specific qualities of the university/program].
Body Paragraph 2 – Connection with the University: Highlight specific aspects of the university or program that align with your interests and goals.
Example: What particularly excites me about [University Name] is [specific programs, facilities, faculty, research opportunities, or university values].
The [specific course or program feature] aligns perfectly with my academic interests and career aspirations.
Additionally, the work of [Professor’s Name or specific department] in [specific research or field] resonates deeply with my academic goals.
Body Paragraph 3 – Future Goals and Contributions: Discuss your future aspirations and how being a part of this university will help you achieve them. Also, mention how you plan to contribute to the university community.
Example: I am eager to bring my background in [Your Background] and experience in [Your Experience] to [University Name].
I look forward to contributing to [specific university clubs, groups, or activities], and engaging with the [University Name] community.
My goal is to [Your Future Goals], and I am confident that [University Name] is the ideal environment to achieve this.
Conclusion: Conclude by reiterating your interest and thanking the committee for considering your application.
Example: I am enthusiastic about the prospect of joining [University Name] and being part of its dynamic and innovative community. Thank you for considering my application.
I am looking forward to the opportunity to contribute to and learn from the esteemed faculty and talented student body at [University Name].
[Your Name]
Real-Life Example:
When I applied to ABC University, I highlighted my extensive work in community theater and linked it to their renowned theater program. This not only showcased my experience but also how I could contribute to their community.
Writing a letter of interest for university admission is your opportunity to showcase your unique story and how it intersects with what the university offers.
Personalize your experiences, highlight your aspirations, and demonstrate how you align with the university’s values and programs. Remember, this letter is about making a connection, so let your personality shine through.
I’d love to hear from you!
If you have any questions or would like to share your experiences in writing a letter of interest, please leave a comment below.
Your insights and queries not only enrich our discussion but also help others in their journey towards crafting their own compelling letters of interest.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)

Q: What is a Letter of Interest for University Admission?
Answer : A Letter of Interest for University Admission, often referred to as a Statement of Purpose or a Cover Letter, is a personal document submitted as part of your university application.
It outlines your academic and professional aspirations, explains why you are interested in a specific program and university, and highlights your relevant experiences and achievements.
This letter allows the admissions committee to understand your motivation, suitability for the program, and potential contributions to their academic community.
Q: How long should my letter of interest be?
Answer : Typically, a letter of interest should be concise and to the point, ideally not exceeding one page. It’s important to be clear and succinct, focusing on the most relevant details of your academic and extracurricular achievements and how they align with the program you are applying to. Avoid unnecessary details or overly complex language to ensure your letter is impactful and easy to read.
Q: Should I mention specific faculty or research projects in my letter of interest?
Answer : Yes, mentioning specific faculty members or research projects can be beneficial, especially if their work directly relates to your academic interests and career goals.
It shows that you have done your research and are genuinely interested in the specific opportunities offered by the university. However, make sure your references are relevant and demonstrate a clear connection to your aspirations.
Q: Can I use the same letter of interest for multiple university applications?
Answer : While it might be tempting to use the same letter for multiple applications, it’s not advisable. Each university and program has its own unique qualities and requirements.
Tailoring your letter to each specific institution shows that you have taken the time to understand what each program offers and how it aligns with your goals. A personalized letter can significantly increase your chances of making a strong impression.
Q: What are common mistakes to avoid in a letter of interest?
Answer : Common mistakes include being too vague or generic, failing to align your interests with the program, making grammatical errors, exceeding the recommended length, and not following the university’s specific guidelines.
Avoiding these mistakes is crucial for creating an effective letter. It’s also important to maintain a professional tone while allowing your personality to shine through.
Q: How important is the letter of interest in the admissions process?
Answer : The letter of interest is a critical component of your application. It’s your opportunity to speak directly to the admissions committee and provide context to your academic records and extracurricular activities.
A well-written letter can set you apart from other candidates by showcasing your unique perspective, motivation, and fit for the program. Therefore, investing time and effort in crafting a compelling letter is essential.
Related Articles
Sample letter of withdrawal of enrollment: free & effective, school transfer letter sample: free & effective, college admission letter example: free & effective, letter of withdrawal from college due to personal problems: free & effective, appeal letter for university rejection sample: free & effective, assignment extension request letter example: free & effective, leave a comment cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Important Addresses
Harvard College
University Hall Cambridge, MA 02138
Harvard College Admissions Office and Griffin Financial Aid Office
86 Brattle Street Cambridge, MA 02138
Social Links
If you are located in the European Union, Iceland, Liechtenstein or Norway (the “European Economic Area”), please click here for additional information about ways that certain Harvard University Schools, Centers, units and controlled entities, including this one, may collect, use, and share information about you.
Application Tips
- Navigating Campus
- Preparing for College
- How to Complete the FAFSA
- What to Expect After You Apply
- View All Guides
- Parents & Families
- School Counselors
- Información en Español
- Undergraduate Viewbook
- View All Resources
Search and Useful Links
Search the site, search suggestions.

Student walking up the steps of Widener
We consider each application with care.
When reading an application, we get to know the person behind the numbers. We take into consideration your academic achievements, extracurricular activities, personal qualities, and life experiences. Just as there is no typical Harvard student, there is no ideal Harvard applicant. We look forward to learning more about you.
Frequently asked questions about applying
Have my application materials been received (including common application forms, or supplemental materials).
Upon receipt of your application, we will send you a confirmation email with instructions on how to access the Applicant Portal . This portal allows you to view your record in our applicant database, to see which pieces of your application we've received and processed, and to make other changes to your application.
The data is updated nightly from the main admissions database and has the most up-to-date information available from our office. If you have sent us required materials that are shown in your status as not received, it is possible that those documents are being processed (along with thousands of others) in our office and simply have not yet made it to your file. Though we can not track each individual's materials upon request, we will conduct a thorough scrutiny of all files prior to committee evaluations. You will be contacted if you are missing required documents, and you will be given the opportunity to re-submit them without penalty.
How can I add new accomplishments/awards/accolades to my submitted application?
We understand that you might receive new recognitions or awards after you’ve submitted your application. We welcome the submission of this additional notable information. You may upload information about notable accomplishments and awards using the Applicant Portal .
When do I need to submit test scores if I want them considered in my application?
We are test optional for this admissions cycle. If you decide to submit scores for consideration, they need to be reported by the following deadlines: Scores from applicants applying for our Restrictive Early Action program must be reported by the end of November. Scores from applicants applying for our Regular Decision program must be reported by the end of February.
Do I need to complete an alumni interview for my first-year application?
Applicants are assigned interviews at the discretion of the Admissions Committee, based, in part, on availability of alumni in your local area. Nearly 10,000 alumni/ae volunteers help us recruit students from all 50 states and around the world, but most areas do not have the capacity to interview all applicants. Your application is considered complete without an interview and will receive a full and thorough evaluation. In most cases, the Admissions Committee has sufficient information in the student’s application materials to reach an admissions decision. If the Committee would like more information about a student or has questions about any application materials, someone may reach out to schedule an interview.
Starting an Application
For all first-year and transfer applicants, your first step will be to fill out and submit an application. You can do so through the Common Application or the Coalition Application - Powered by Scoir. For first-year applicants, the Common Application opens on August 1 and the Coalition Application opens on August 15. For transfer applicants, both applications open on September 1.
We have no preference and each application is treated equally by the Admissions Committee.
Application Requirements
All applicants—both international and U.S. candidates, first-year and transfer—must complete the following application components:
- Common Application or apply Coalition, Powered by Scoir
- Harvard College Questions for the Common Application, or Coalition Application Harvard supplement
- $85 fee (or request a fee waiver )
- SAT or ACT (with or without writing) - optional for 2022-2026 application cycles
- Optional: AP or other examination results
- School Report (which includes a counselor letter) and high school transcript
- Teacher Report (2)
- Midyear School Report (after your first semester grades)
- Final School Report (for admitted students only)
- College/Dean’s/Registrar’s report
- Official College Transcript
- College Instructor Recommendations (2)
- Official High School Transcript
Click below to learn more about each component.
No student with a bachelor's degree or other first university degree from any other university, whether American or foreign, is eligible for admission to Harvard College. Students interested in continuing their studies beyond the bachelor's degree might wish to consider one of the 12 Harvard University graduate schools .
Admissions Deadlines
Restrictive Early Action application deadline - learn more about Restrictive Early Action .
Regular Decision application deadline
Transfer application deadline

Get step-by-step tips on filling out your college application. From the application fee waiver to the writing supplement, we've gathered some tips to help you complete your application.
U.S. Military Veterans
Individuals who have served in the U.S. military bring valuable perspectives to our community and we welcome applications from veterans for both first-year and transfer admission. If you are a veteran, please review the information on our U.S. Military Veterans page. There, you'll find details on whether to apply as a first-year or transfer student, financial aid, and making the transition to college life.

International Applicants
We welcome applications from all over the world. Our admissions and financial aid processes are the same for all applicants - regardless of nationality or citizenship.
Related Topics
First-year applicants.
Here's everything you need to know about applying to Harvard College as a first-year applicant.
Transfer Applicants
Students who have completed at least one but not more than two continuous academic years in a full-time program may apply to transfer to Harvard.
Visiting Undergraduate Students
The Visiting Undergraduate Students (VUS) Program welcomes students enrolled in colleges around the world to spend a semester or year at Harvard.
Toggle Admissions Submenu

Academic Cover Letters
What is this handout about.
The long list of application materials required for many academic teaching jobs can be daunting. This handout will help you tackle one of the most important components: the cover letter or letter of interest. Here you will learn about writing and revising cover letters for academic teaching jobs in the United States of America.

What is an academic cover letter?
An academic cover letter describes your experiences and interest as a candidate for a specific position. It introduces you to the hiring committee and demonstrates how your academic background fits with the description of the position.
What do cover letters for academic teaching jobs typically contain?
At their most basic level, academic cover letters accomplish three things: one, they express your interest in the job; two, they provide a brief synopsis of your research and teaching; and three, they summarize your past experiences and achievements to illustrate your competence for the job. For early-career scholars, cover letters are typically no more than two pages (up to four pages for senior scholars). Occasionally, a third page may make sense for an early-career scholar if the application does not require a separate teaching statement and/or research statement. Digital versions of cover letters often contain hyperlinks to your CV or portfolio page. For some fields, cover letters may also include examples of your work, including music, popular articles, and other multimedia related to your research, service, or teaching available online. Typically, letters appear on departmental or university letterhead and include your signature. Above all, a strong cover letter presents your accomplishments and your familiarity with the institution and with the position.
How should I prepare to write my academic cover letter?
Like all writing, composing a cover letter is a process. The process may be as short as a few hours or as long as several weeks, but at the end the letter should present you as a strong candidate for the job. The following section has tips and questions for thinking through each stage of this writing process. You don’t need to answer all of these questions to write the letter; they are meant to help you brainstorm ideas.
Before you begin writing your cover letter, consider researching the institution, the department, and the student population. Incorporating all three aspects in your letter will help convey your interest in the position.
Get to know the institution. When crafting your cover letter, be aware of the type of institution to which you are applying. Knowing how the institution presents itself can help you tailor your letter and make it more specific.
- Where is the institution located?
- Is it on a quarter-system or semester-system?
- What type of institution is it? Is it an R1? Is it an R2? Is it a liberal arts college? Is it an HBCU? Is it a community college? A private high school?
- What is the institution’s culture? Is it teaching-focused or research-focused? Does it privilege experiential learning? Does it value faculty involvement outside the classroom? Is it affiliated with a specific religious tradition?
- Does it have any specific institutional commitments?
- How does the institution advocate for involvement in its local community?
- What are the professional development opportunities for new and junior faculty?
Learn about the department. Knowing the specific culture and needs of the department can help you reach your audience: the department members who will be reading your documents and vetting you as a candidate.
- Who is on the search committee? Who is the search committee chair?
- What is the official name of the department?
- Which different subfields make up the department?
- Is it a dual appointment or a position in a dual department?
- How does the department participate in specific types of student outreach?
- Does the department have graduate students? Does it offer a terminal Master’s degree, Ph.D., or both? How large are the cohorts? How are they funded?
- Does the department encourage or engage in interdisciplinary work?
- Does the majority of the department favor certain theoretical or methodological approaches?
- Does the department have partnerships with local institutions? If so, which ones?
- Is the department attempting to fill a specific vacancy, or is it an entirely new position?
- What are the typical course offerings in the department? Which courses might you be expected to teach? What courses might you be able to provide that are not currently available?
Consider the students. The search committee will often consider how you approach instructing and mentoring the student body. Sometimes committees will even reserve a position for a student or solicit student feedback on a candidate:
- What populations constitute the majority of the undergraduate population?
- Have there been any shifts in the student population recently?
- Do students largely come from in-state or out-of-state?
- Is there an international student population? If so, from which countries?
- Is the university recruiting students from traditionally underrepresented populations?
- Are students particularly active on campus? If so, how?
Many answers to these questions can be found both in the job description and on the institution’s website. If possible, consider contacting someone you know at the institution to ask about the culture directly. You can also use the institution’s course catalog, recruitment materials, alumni magazine, and other materials to get answers to these questions. The key is to understand the sort of institution to which you are applying, its immediate needs, and its future trajectory.
Remember, there is a resource that can help you with all three aspects—people. Reach out to your advisor, committee members, faculty mentors, and other contacts for insight into the prospective department’s culture and faculty. They might even help you revise your letter based on their expertise. Think of your job search as an opportunity to cultivate these relationships.
After you have done some initial research, think about how your experiences have prepared you for the job and identify the ones that seem the most relevant. Consider your previous research, internships, graduate teaching, and summer experiences. Here are some topics and questions to get you started thinking about what you might include.
Research Experiences. Consider how your research has prepared you for an academic career. Since the letter is a relatively short document, select examples of your research that really highlight who you are as a scholar, the direction you see your work going, and how your scholarship will contribute to the institution’s research community.
- What are your current research interests?
- What topics would you like to examine in the future?
- How have you pursued those research interests?
- Have you traveled for your research?
- Have you published any of your research? Have you presented it at a conference, symposium, or elsewhere?
- Have you worked or collaborated with scholars at different institutions on projects? If so, what did these collaborations produce?
- Have you made your research accessible to your local community?
- Have you received funding or merit-based fellowships for your research?
- What other research contributions have you made? This may include opinion articles, book chapters, or participating as a journal reviewer.
- How do your research interests relate to those of other faculty in the department or fill a gap?
Teaching Experience. Think about any teaching experience you may have. Perhaps you led recitations as a teaching assistant, taught your own course, or guest lectured. Pick a few experiences to discuss in your letter that demonstrate something about your teaching style or your interest in teaching.
- What courses are you interested in teaching for the department? What courses have you taught that discussed similar topics or themes?
- What new courses can you imagine offering the department that align with their aim and mission?
- Have you used specific strategies that were helpful in your instruction?
- What sort of resources do you typically use in the classroom?
- Do you have anecdotes that demonstrate your teaching style?
- What is your teaching philosophy?
- When have you successfully navigated a difficult concept or topic in the classroom, and what did you learn?
- What other opportunities could you provide to students?
Internships/Summer/Other Experiences. Brainstorm a list of any conferences, colloquiums, and workshops you have attended, as well as any ways you have served your department, university, or local community. This section will highlight how you participate in your university and scholarly community. Here are some examples of things you might discuss:
- Professional development opportunities you may have pursued over the summer or during your studies
- International travel for research or presentations
- Any research you’ve done in a non-academic setting
- Presentations at conferences
- Participation in symposia, reading groups, working groups, etc.
- Internships in which you may have implemented your research or practical skills related to your discipline
- Participation in community engagement projects
- Participation in or leadership of any scholarly and/or university organizations
In answering these questions, create a list of the experiences that you think best reflect you as a scholar and teacher. In choosing which experiences to highlight, consider your audience and what they would find valuable or relevant. Taking the time to really think about your reader will help you present yourself as an applicant well-qualified for the position.
Writing a draft
Remember that the job letter is an opportunity to introduce yourself and your accomplishments and to communicate why you would be a good fit for the position. Typically, search committees will want to know whether you are a capable job candidate, familiar with the institution, and a great future addition to the department’s faculty. As such, be aware of how the letter’s structure and content reflect your preparedness for the position.
The structure of your cover letter should reflect the typical standards for letter writing in the country in which the position is located (the list below reflects the standards for US letter writing). This usually includes a salutation, body, and closing, as well as proper contact information. If you are affiliated with a department, institution, or organization, the letter should be on letterhead.
- Use a simple, readable font in a standard size, such as 10-12pt. Some examples of fonts that may be conventional in your field include Arial, Garamond, Times New Roman, and Verdana, among other similar fonts.
- Do not indent paragraphs.
- Separate all paragraphs by a line and justify them to the left.
- Make sure that any included hyperlinks work.
- Include your signature in the closing.
Before you send in your letter, make sure you proofread and look for formatting mistakes. You’ll read more about proofreading and revising later in this handout!
The second most important aspect of your letter is its content. Since the letter is the first chance to provide an in-depth introduction, it should expand on who you are as a scholar and possible faculty member. Below are some elements to consider including when composing your letter.
Identify the position you are applying to and introduce yourself. Traditionally, the first sentence of a job letter includes the full name of the position and where you discovered the job posting. This is also the place to introduce yourself and describe why you are applying for this position. Since the goal of a job letter is to persuade the search committee to include you on the list of candidates for further review, you may want to include an initial claim as to why you are a strong candidate for the position. Some questions you might consider:
- What is your current status (ABD, assistant professor, post-doc, etc.)?
- If you are ABD, have you defended your dissertation? If not, when will you defend?
- Why are you interested in this position?
- Why are you a strong candidate for this position?
Describe your research experience and interests. For research-centered positions, such as positions at R1 or other types of research-centered universities, include information about your research experience and current work early in the letter. For many applicants, current work will be the dissertation project. If this is the case, some suggest calling your “dissertation research” your “current project” or “work,” as this may help you present yourself as an emerging scholar rather than a graduate student. Some questions about your research that you might consider:
- What research experiences have you had?
- What does your current project investigate?
- What are some of the important methods you applied?
- Have you collaborated with others in your research?
- Have you acquired specific skills that will be useful for the future?
- Have you received special funding? If so, what kind?
- Has your research received any accolades or rewards?
- What does your current project contribute to the field?
- Where have you presented your research?
- Have you published your research? If so, where? Or are you working on publishing your work?
- How does your current project fit the job description?
Present your plans for future research. This section presents your research agenda and usually includes a description of your plans for future projects and research publications. Detailing your future research demonstrates to the search committee that you’ve thought about a research trajectory and can work independently. If you are applying to a teaching-intensive position, you may want to minimize this section and/or consider including a sentence or two on how this research connects to undergraduate and/or graduate research opportunities. Some questions to get you started:
- What is your next research project/s?
- How does this connect to your current and past work?
- What major theories/methods will you use?
- How will this project contribute to the field?
- Where do you see your specialty area or subfield going in the next ten years and how does your research contribute to or reflect this?
- Will you be collaborating with anyone? If so, with whom?
- How will this future project encourage academic discourse?
- Do you already have funding? If so, from whom? If not, what plans do you have for obtaining funding?
- How does your future research expand upon the department’s strengths while simultaneously diversifying the university’s research portfolio? (For example, does your future research involve emerging research fields, state-of-the-art technologies, or novel applications?)
Describe your teaching experience and highlight teaching strategies. This section allows you to describe your teaching philosophy and how you apply this philosophy in your classroom. Start by briefly addressing your teaching goals and values. Here, you can provide specific examples of your teaching methods by describing activities and projects you assign students. Try to link your teaching and research together. For example, if you research the rise of feminism in the 19th century, consider how you bring either the methodology or the content of your research into the classroom. For a teaching-centered institution, such as a small liberal arts college or community college, you may want to emphasize your teaching more than your research. If you do not have any teaching experience, you could describe a training, mentoring, or coaching situation that was similar to teaching and how you would apply what you learned in a classroom.
- What is your teaching philosophy? How is your philosophy a good fit for the department in which you are applying to work?
- What sort of teaching strategies do you use in the classroom?
- What is your teaching style? Do you lecture? Do you emphasize discussion? Do you use specific forms of interactive learning?
- What courses have you taught?
- What departmental courses are you prepared to teach?
- Will you be able to fill in any gaps in the departmental course offerings?
- What important teaching and/or mentoring experiences have you had?
- How would you describe yourself in the classroom?
- What type of feedback have you gotten from students?
- Have you received any awards or recognition for your teaching?
Talk about your service work. Service is often an important component of an academic job description. This can include things like serving on committees or funding panels, providing reviews, and doing community outreach. The cover letter gives you an opportunity to explain how you have involved yourself in university life outside the classroom. For instance, you could include descriptions of volunteer work, participation in initiatives, or your role in professional organizations. This section should demonstrate ways in which you have served your department, university, and/or scholarly community. Here are some additional examples you could discuss:
- Participating in graduate student or junior faculty governance
- Sitting on committees, departmental or university-wide
- Partnerships with other university offices or departments
- Participating in community-partnerships
- Participating in public scholarship initiatives
- Founding or participating in any university initiatives or programs
- Creating extra-curricular resources or presentations
Present yourself as a future faculty member. This section demonstrates who you will be as a colleague. It gives you the opportunity to explain how you will collaborate with faculty members with similar interests; take part in departmental and/or institution wide initiatives or centers; and participate in departmental service. This shows your familiarity with the role of faculty outside the classroom and your ability to add to the departmental and/or institutional strengths or fill in any gaps.
- What excites you about this job?
- What faculty would you like to collaborate with and why? (This answer may be slightly tricky. See the section on name dropping below.)
- Are there any partnerships in the university or outside of it that you wish to participate in?
- Are there any centers associated with the university or in the community that you want to be involved in?
- Are there faculty initiatives that you are passionate about?
- Do you have experience collaborating across various departments or within your own department?
- In what areas will you be able to contribute?
- Why would you make an excellent addition to the faculty at this institution?
Compose a strong closing. This short section should acknowledge that you have sent in all other application documents and include a brief thank you for the reader’s time and/or consideration. It should also state your willingness to forward additional materials and indicate what you would like to see as next steps (e.g., a statement that you look forward to speaking with the search committee). End with a professional closing such as “Sincerely” or “Kind Regards” followed by your full name.
If you are finding it difficult to write the different sections of your cover letter, consider composing the other academic job application documents (the research statement, teaching philosophy, and diversity statement) first and then summarizing them in your job letter.
Different kinds of letters may be required for different types of jobs. For example, some jobs may focus on research. In this case, emphasize your research experiences and current project/s. Other jobs may be more focused on teaching. In this case, highlight your teaching background and skills. Below are two models for how you could change your letter’s organization based on the job description and the institution. The models offer a guide for you to consider how changing the order of information and the amount of space dedicated to a particular topic changes the emphasis of the letter.
Research-Based Position Job Letter Example:
Teaching-based position job letter example:.
Remember your first draft does not have to be your last. Try to get feedback from different readers, especially if it is one of your first applications. It is not uncommon to go through several stages of revisions. Check out the Writing Center’s handout on editing and proofreading and video on proofreading to help with this last stage of writing.
Potential pitfalls
Using the word dissertation. Some search committee members may see the word “dissertation” as a red flag that an applicant is too focused on their role as a graduate student rather than as a prospective faculty member. It may be advantageous, then, to describe your dissertation as current research, a current research project, current work, or some other phrase that demonstrates you are aware that your dissertation is the beginning of a larger scholarly career.
Too much jargon. While you may be writing to a specific department, people on the search committee might be unfamiliar with the details of your subfield. In fact, many committees have at least one member from outside their department. Use terminology that can easily be understood by non-experts. If you want to use a specific term that is crucial to your research, then you should define it. Aim for clarity for your reader, which may mean simplification in lieu of complete precision.
Overselling yourself. While your job letter should sell you as a great candidate, saying so (e.g., “I’m the ideal candidate”) in your letter may come off to some search committee members as presumptuous. Remember that although you have an idea about the type of colleague a department is searching for, ultimately you do not know exactly what they want. Try to avoid phrases or sentences where you state you are the ideal or the only candidate right for the position.
Paying too much attention to the job description. Job descriptions are the result of a lot of debate and compromise. If you have skills or research interests outside the job description, consider including them in your letter. It may be that your extra research interests; your outside skills; and/or your extracurricular involvements make you an attractive candidate. For example, if you are a Latin Americanist who also happens to be well-versed in the Spanish Revolution, it could be worth mentioning the expanse of your research interests because a department might find you could fill in other gaps in the curriculum or add an additional or complementary perspective to the department.
Improper sendoff. The closing of your letter is just as important as the beginning. The end of the letter should reflect the professionalism of the document. There should be a thank-you and the word sincerely or a formal equivalent. Remember, it is the very last place in your letter where you present yourself as a capable future colleague.
Small oversights. Make sure to proofread your letter not just for grammar but also for content. For example, if you use material from another letter, make sure you do not include the names of another school, department, or unassociated faculty! Or, if the school is in Chicago, make sure you do not accidentally reference it as located in the Twin Cities.
Name dropping. You rarely know the internal politics of the department or institution to which you are applying. So be cautious about the names you insert in your cover letters. You do not want to unintentionally insert yourself into a departmental squabble or add fire to an interdepartmental conflict. Instead, focus on the actions you will undertake and the initiatives you are passionate about.
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Ball, Cheryl E. 2013. “Understanding Cover Letters.” Inside Higher Ed , November 3, 2013. https://www.insidehighered.com/advice/2013/11/04/essay-cover-letter-academic-jobs .
Borchardt, John. 2014. “Writing a Winning Cover Letter.” Science Magazine , August 6, 2014. https://www.sciencemag.org/careers/2014/08/writing-winning-cover-letter# .
Helmreich, William. 2013. “Your First Academic Job.” Inside Higher Ed , June 17, 2013. https://www.insidehighered.com/advice/2013/06/17/essay-how-land-first-academic-job .
Kelsky, Karen. 2013. “How To Write a Journal Article Submission Cover Letter.” The Professor Is In (blog), April 26, 2013. https://theprofessorisin.com/2013/04/26/how-to-write-a-journal-article-submission-cover-letter/ .
Tomaska, Lubomir, and Josef Nosek. 2008. “Ten Simple Rules for Writing a Cover Letter to Accompany a Job Application for an Academic Position.” PLoS Computational Biology 14(5). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1006132 .
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift

Graduate School Application Tips & Advice

Applying to graduate school can be both exciting and a little overwhelming. You’re making a decision that could advance your career or allow you to dive deeper into a subject area that fulfills your personal goals, but you’re also making a significant investment of your time and finances.
With proper research, a clear head, and confidence, however, you can find the perfect program and submit an application that the admissions committee will be hard-pressed to reject.
Are you thinking about applying to graduate school? Here’s what every prospective student needs to know.
Tips for Applying to Graduate School
1. find a program that aligns with your goals ..
Finding the right graduate program can sometimes feel like the hardest part of the process. It’s important to find the right program for you, and with different degrees and certificates popping up at universities across the country, there are likely dozens of options available to you.
Write down the most important features of your ideal program before you begin your research. For example, do you want a full-time, on-campus experience or a flexible, online environment? Do you want research-based coursework or a program with experiential opportunities integrated into the curriculum? Once you have your list of non-negotiable features, you can kick off your research.
Learn More: How to Organize Your Grad School Search
After you’ve explored a range of programs, consider your career goals and how each program can help you achieve them. If you’d like to hone your skills to work in a specific focus area of a broader field, for instance, a program that offers a concentration or certificate aligned with those skills can be beneficial. On the other hand, if you’d like to have flexibility in your chosen career, pursuing a broader degree program that can be applied across various functions may be better suited to your needs.
Investing in this research upfront will help you find a graduate program that is right for your specific goals and allow you to feel more confident in your choice when it comes time to complete and submit your application.
2. Ask questions .
The old-school idea that the admissions office is a scary room filled with judgment is a falsehood. Today, graduate school admissions counselors are here to help guide you through the application process process. They want to be there to support your educational journey. If you have any questions, ask . Don’t worry that your interactions with the admissions team could impact your application. If anything, your interactions will only help improve your application before review and help demonstrate your sincere interest in the program.
Many colleges and universities offer online resources where prospective students can find information about the application process and requirements. Getting in touch with an admissions counselor, though, may be the most efficient way to find answers to specific questions you might have. Engaging with them will also give you a chance to get to know the school better and decide if what they offer is really the right fit for your needs.
Consider This: Admissions counselors are well-versed in the logistics of application requirements, individual programs, and financial aid and scholarships . If you have specific questions, be sure to reach out to them for the clarity and insight you need at any step of the process.
Prospective students should not be afraid of contacting faculty, either. If there’s a particular class you’re interested in taking or a lab you hope to work in, contact the faculty member in charge. Ask about that faculty member’s research and pose any questions about the degree program that you might have. You may have a better chance of standing out during the admissions process if you express interest early.
Ready to Get Your Questions Answered?
Reach out to our admissions team for personalized advice on the application process.
GET IN TOUCH
3. Understand the timeline.
Although the application process varies by college or university, the vast majority will require you to submit your transcript, letters of recommendation, professional resumé , and statement of purpose. Your transcript alone could take weeks to be delivered and processed, so don’t wait until the last minute to start applying.
In an effort to avoid procrastination, consider developing a calendar of deadlines. Map out when you need to apply to each of your desired schools and the specific requirements for that program. For example, if you need to submit your undergraduate grades, create a to-do at least a month before the application deadline that reminds you to order your transcript.
4. Update your resumé.
Before sending your resumé, make sure it’s optimized for your grad school application . In general, your experience should be listed in chronological order, starting with your current position, and described in bullet points using action-packed verbs, such as “achieved,” “improved,” “launched,” “negotiated,” or “trained.” Quantify any achievements and show your results, whether it’s the number of people you’ve managed, dollars you’ve raised, or articles you’ve written.
To help your resumé align with your grad school application, be sure to tailor it to the program you intend to pursue by showcasing your skills, highlighting relevant experience, and including your professional achievements.
5. Write a strong statement of purpose.
While some might think that a statement of purpose —or personal statement —is an afterthought during your application review, many admissions committees, consider it one of the most important components of your application. The statement of purpose can make or break your application for admission.
The key to crafting an impactful statement of purpose is to not get caught up in what you think the admissions committee wants to hear. Use this opportunity to tell the committee more about who you are and your background while also explaining specifically what you hope to get out of the program. Be sure to address the unique features the school offers that interest you most.
For Example: If you plan to apply to Northeastern, you might consider highlighting experiential learning as the unique feature that interests you about your program. In this case, you might explain that you’re excited to tackle real-world projects in your desired industry and learn from faculty who are experts in your field of study.
No matter where you apply, a strong statement of purpose should include:
- Insight into what drives you, whether that’s professional advancement, personal growth, or both
- The features about the school that appeal to you most
- Your expectations of the degree program and its potential impact
- Authenticity and a clear picture of what makes you unique
6 . Choose appropriate references .
Letters of recommendation are another piece of the application process that helps elevate your application for admission. When it comes to asking for letters of recommendation , carefully consider whom you’re contacting. You want to choose someone who knows you well and can speak to your strengths.
Reach out to a professor you regularly interacted with who can detail your academic accomplishments and describe why you were a standout student. You can also ask a former supervisor who’s working in a field that aligns with the graduate program you’re pursuing. No matter your choice, make sure it’s someone you know in a professional or academic capacity—not a friend or family member—who will to provide a positive recommendation representative of your character.
You can typically provide either a professional or academic recommendation in support of your application, but programs have specific requirements around who is writing the recommendation and what the content needs to address. Research what each program requires before you coordinate your references.
When asking for a recommendation, provide your chosen reference with as much information about your request as possible. The more insight you can provide, the better your recommendation letter will be. Include in your first outreach:
- The name of the school you’re applying to
- The degree you’re pursuing
- Why you want to enroll in that specific program
- Your resumé
Make sure you keep your timeline in mind as you embark on these communications, especially if you reach out to a professor. It’s likely your letter isn’t the only one he or she needs to write, so be respectful of their time by giving as much notice as possible. Four weeks is ideal.
7. Proofread your materials before applying.
You could be a perfect fit for your desired program, but if you submit materials that are riddled with spelling and grammar errors, the admissions team might dismiss your application before ever digging into it. Triple-check your materials and make sure that when you do press send, you’ve included all necessary documentation and hit all deadlines set in place by the university.
It’s easy for an individual to unknowingly overlook their own mistakes, so it can also be helpful to ask a friend to review your materials before you submit them, as well. Reading your materials out loud to yourself can also help you spot potential mistakes.
Though this may seem like a lot of effort, remember: Your application is the first impression you will make on the university, and it’s important to put your best foot forward.
8. Be true to yourself .
Of all the tips for applying to graduate school, the most important is being true to yourself. Being perfect is not the recipe for admission; admissions committees want to know the real you and understand your ambitions. Whether you’re a working professional hoping graduate school can bring you to the next level of your career or a recent graduate looking to further master your chosen skill, just be yourself, and you’ll start off in the right direction.
Applying to Northeastern’s Graduate Programs
If you are interested in applying to one of Northeastern University’s 200+ online, on-ground, or hybrid graduate degree and certificate programs , there are various resources available to help you along the way.
First, it is important to understand the application process and requirements. Specific application requirements vary by college and degree, so be sure to explore the admissions information for your desired program before getting started. In general, however, the application requirements for Northeastern’s graduate programs include:
- A completed online application
- Transcripts from all undergraduate and graduate schools you’ve previously attended
- A statement of purpose that details your goals and interest in the program
- One to three letters of recommendation (varies by program)
- Your updated professional resumé or curriculum vitae
- Your official GRE, GMAT, or LSAT test scores (if required)
- A non-refundable application fee
Additionally, international students who are non-native English speakers must submit proof of English proficiency in the form of TOEFL, IELTS, PTE, or Duolingo test scores, though the minimum scores vary by program. Students who do not meet the minimum requirement for these scores may also apply to the university’s Global Pathways program .
As always, students who intend to apply to a graduate program at Northeastern should also research the application deadlines for their program of interest. Be sure to set a timeline for yourself and avoid procrastination to ensure that you’re able to submit all of the required materials on time.
The faculty and admissions team at Northeastern are always available to help prospective students throughout this journey, and prospective students are always encouraged to reach out to ask questions and get personalized advice . Whether you need information about selecting the right program, the application process, program-specific requirements, financial aid, or anything in between, the admissions team is here to help.
The First Step Toward Grad School Success
Once you’ve made the decision to further your education and pursue a graduate degree or certificate, submitting your application is the first step toward being a successful graduate student.
No matter where you choose to apply and ultimately attend, there are countless resources available to help you throughout the process.
To learn more about the specific schools and programs you are interested in, it’s always best to start by reaching out to admissions teams and faculty to get to know what makes them unique and ask any questions you might have. Building these relationships early on will help you find a program that fits your personal and professional goals, and can ultimately help you through the process of getting accepted to a program that’s right for you.
Are you interested in applying to graduate school? Explore Northeastern’s degree and certificate programs , and contact us for personalized advice.
This article was originally published in August 2017. It has since been updated for accuracy and relevance.
Subscribe below to receive future content from the Graduate Programs Blog.
About shayna joubert, related articles.

Why Earn a Professional Doctoral Degree?

5 Tips to Get the Most out of Grad School

Is Earning a Graduate Certificate Worth It?
Did you know.
Advanced degree holders earn a salary an average 25% higher than bachelor's degree holders. (Economic Policy Institute, 2021)
Northeastern University Graduate Programs
Explore our 200+ industry-aligned graduate degree and certificate programs.
Most Popular:
Tips for taking online classes: 8 strategies for success, public health careers: what can you do with an mph, 7 international business careers that are in high demand, edd vs. phd in education: what’s the difference, 7 must-have skills for data analysts, in-demand biotechnology careers shaping our future, the benefits of online learning: 8 advantages of online degrees, how to write a statement of purpose for graduate school, the best of our graduate blog—right to your inbox.
Stay up to date on our latest posts and university events. Plus receive relevant career tips and grad school advice.
By providing us with your email, you agree to the terms of our Privacy Policy and Terms of Service.
Keep Reading:

The 8 Highest-Paying Master’s Degrees in 2024

How To Get a Job in Emergency Management

Join Us at Northeastern’s Virtual Graduate Open House | March 5–7, 2024
CV for University Application example
Getting into university and getting a degree will give you a huge head-start in your career, but getting into university isn’t easy
This guide contains an example University Applicant CV and plenty of tips on how to create your own winning CV, so you can stand out amongst the other candidates and get into the university of your dreams.
Guide contents
CV for University Application example 1
Cv for university application example 2.
- Structuring and formatting your CV
- Writing your CV profile
- Detailing work experience
- Your education
CV templates

Unsure of what your University Applicant CV should look like?
Have a look at the CV example above to get familiar with the structure, layout and format of a professional CV.
As you can see, it provides plenty of relevant information about the applicant but is still very easy to read, and brief – which will please busy university recruiters.
University Applicant CV structure and format
The format and structure of your CV is important because it will determine how easy it is for recruiters and employers to read your CV.
If they can find the information they need quickly, they’ll be happy; but if they struggle, your application could be overlooked.
A simple and logical structure will always create a better reading experience than a complex structure, and with a few simple formatting tricks, you’ll be good to go.

Formatting Tips
- Length: Recruiters will be immediately put off by lengthy CVs – with hundreds of applications to read through, they simply don’t have the time! Grabbing their attention with a short, snappy and highly relevant CV is far more likely to lead to success. Aim for two sides of A4 or less.
- Readability : Make sure your CV is easy to read and looks professional by applying some simple formatting tricks. Bullet points are great for making large paragraphs more digestible, while formatting your headings with bold or coloured text will help the reader to find the information they need, with speed.
- Design: It’s generally best to stick to a simple CV design, as funky or elaborate designs rarely add any value to your application. A clear, modern font and a subtle colour scheme work perfectly and allow your skills, experience and achievements to speak for themselves.
- Avoid photos: Logos, profile photos or other images aren’t necessary and rarely add any value – save the space for written content, instead!

Structuring your CV
As you write your CV , work to the simple but effective structure below:
- Name and contact details – Pop them at the top of your CV, so it’s easy for recruiters to contact you.
- CV profile – Write a snappy overview of what makes you a good fit for the role; discussing your key experience, skills and accomplishments.
- Core skills section – Add a short but snappy list of your relevant skills and knowledge.
- Work experience – A list of your relevant work experience, starting with your current role.
- Education – A summary of your relevant qualifications and professional/vocational training.
- Hobbies and interests – An optional sections, which you could use to write a short description of any relevant hobbies or interests.
Now I’ll guide you through exactly what you should include in each CV section.
CV Contact Details

Tuck your contact details into the corner of your CV, so that they don’t take up too much space. Stick to the basic details, such as:
- Mobile number
- Email address – It should sound professional, such as your full name.
- Location -Just write your rough location, rather than your full address.
- LinkedIn profile or portfolio URL – If you include these, ensure they’re sleek, professional and up-to-date.
University Applicant CV Profile
Recruiters read through countless applications every day.
If they don’t find what they’re looking for quickly, they’ll simply move onto the next one.
That’s what makes your CV profile (or personal statement , if you’re an entry-level/graduate candidate) so important.
This short and snappy summary sits at the top of your CV, and should give a high-level overview of why you’re a good match for the university.
This way, you can ensure that busy recruiters see your suitability from the outset, and so, feel your CV is worth their time.
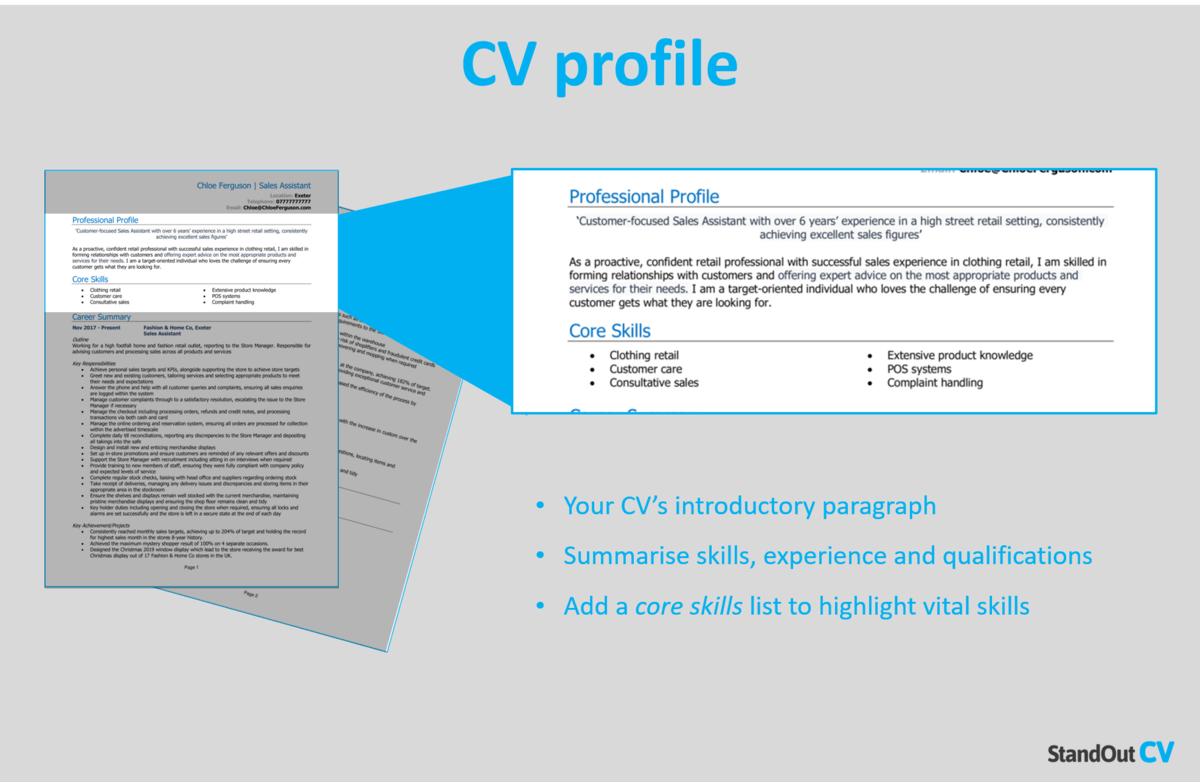
Tips for creating an impactful CV profile:
- Keep it brief: It might be tempting to submit a page-long CV profile, but recruiters won’t have the time to read it. To ensure every word gets read, it’s best to include high-level information only; sticking to a length of 3-5 lines.
- Tailor it: Before writing your CV, make sure to do some research. Figure out exactly what your desired employers are looking for and make sure that you are making those requirements prominent in your CV profile, and throughout.
- Don’t add an objective: Leave your career objectives or goals out of your profile. You only have limited space to work with, so they’re best suited to your cover letter .
- Avoid cliches: “Determined team player who always gives 110%” might seem like a good way to fill up your CV profile, but generic phrases like this won’t land you an interview. Recruiters hear them time and time again and have no real reason to believe them. Instead, pack your profile with your hard skills and tangible achievements.
What to include in your University Applicant CV profile?
- Summary of experience: Recruiters will want to know what type of companies you’ve worked for, industries you have knowledge of, and the type of work you’ve carried out in the past, so give them a summary of this in your profile.
- Relevant skills: Highlight your skills which are most relevant, to ensure that recruiters see your most in-demand skills as soon as they open your CV.
- Essential qualifications: Be sure to outline your relevant qualifications, so that anyone reading the CV can instantly see you are qualified for the universities you are applying to.
Quick tip: Your CV is your first impression on recruiters, so it’s vital to avoid spelling and grammar mistakes if you want to appear professional. Use our quick-and-easy CV Builder to add pre-written content that has been crafted by recruitment experts.
Core skills section
In addition to your CV profile, your core skills section provides an easily digestible snapshot of your skills – perfect for grabbing the attention of busy hiring managers.
As University places might receive a huge pile of applications, this is a great way to stand out and show off your suitability for the role.
It should be made up of 2-3 columns of bullet points and be made up of skills that are highly relevant to the universities you are targeting.

Work experience/Career history
Next up is your work experience section, which is normally the longest part of your CV.
Start with your current (or most recent) job and work your way backwards through your experience.
Can’t fit all your roles? Allow more space for your recent career history and shorten down descriptions for your older roles.

Structuring your roles
If you don’t pay attention to the structure of your career history section, it could quickly become bulky and overwhelming.
Get in recruiters’ good books by creating a pleasant reading experience, using the 3-step structure below:

Begin with a summary of your role, detailing what the purpose of your job was, who you reported to and what size of team you were part of (or led).
Key responsibilities
Next, write up a punchy list of your daily duties and responsibilities, using bullet points.
Wherever you can, point out how you put your hard skills and knowledge to use – especially skills which are applicable to your target role.
Key achievements
Finish off by showcasing 1-3 key achievements made within the role.
This could be anything that had a positive effect on your company, clients or customers, such as saving time or money, receiving exemplary feedback or receiving an award.
At the bottom of your CV is your full education section. You can list your formal academic qualifications, such as:
- GCSE’s
As well as any specific qualifications that are essential to the jobs you are applying for. Note down the name of the qualification, the organisation at which you studied, and the date of completion.
Interests and hobbies
This section is entirely optional, so you’ll have to use your own judgement to figure out if it’s worth including.
If your hobbies and interests could make you appear more suitable for your dream job, then they are definitely worth adding.
Interests which are related to the industry, or hobbies like sports teams or volunteering, which display valuable transferable skills might be worth including.
Writing your University Applicant CV
An interview-winning CV for a University Application needs to be both visually pleasing and packed with targeted content.
Whilst it needs to detail your experience, accomplishments and relevant skills, it also needs to be as clear and easy to read as possible.
Remember to research the role and review the university before applying, so you’re able to match yourself up to the requirements.
If you follow these guidelines and keep motivated in your university search, you should land an interview in no time.
Best of luck with your next application!
How Do I Apply to Law School?
- by Ryleigh J. Praker
- March 27, 2024

Well, here you are. You’ve decided you want to go to law school — but how do you get in? How do you know which schools to apply to? Will you need to take admission tests?
Having all these questions is normal. It’s also normal to feel lost and overwhelmed. But there’s nothing to be afraid of and no need for the process to seem opaque. Read on to learn about the application process, broken down into simple steps.
If you’re not sure about law school or want to learn more about what it’s like and whether you should apply, consider reading our article “ What You Need To Know About Law School .” If you don’t know much about law school, that article is a good place to start.
Applying to law school can be a daunting process, but it doesn’t have to be. Here are five steps to follow when setting off on your application journey.
1. Research many law schools

When searching for the right law school, there are a variety of factors you should consider. For example, you’ll want to think about location, cost of attendance and prestige. If you have an interest in a particular area of law, you should look for schools that have a strong program in that concentration.
As you build up your list of schools, you should organize them based on admissions statistics — acceptance rate, average GPA and average LSAT score. These factors will help you determine whether a school is in the safety, target or reach ranges for you.
A good place to start exploring law schools is the Law School Admission Council’s Official Guide . LSAC is an official organization on which law schools rely for admissions information coordination — sort of like the College Board for undergraduate institutions. LSAC administers the LSAT exam and manages the Credential Assembly Service, through which law schools accept applications.
2. Take the LSAT

The Law School Admission Test is a standardized test administered by LSAC. Offered several times throughout the year, the exam is divided into sections on reading comprehension, arguments and logic games. It’s designed to test your aptitude for the kind of reasoning that makes a good lawyer.
Your LSAT score will be a major factor law schools will consider when you apply. It will also offer a metric for you to determine whether a particular school is in your safety, target or reach ranges.
The LSAT is offered several times throughout the year. You should plan on taking it at least a few months before you send out applications, so you’ll have time to improve your score if necessary. Starting to prepare for the test at least two months in advance has been shown to improve outcomes. You’ll want to study the format of the test and, for the best results, take practice exams. You can start exploring official LSAT test preparation resources on the LSAC website.
3. Write a personal statement

In contrast to the LSAT’s quantitative metric of your aptitude, a personal statement offers a qualitative measure for schools. A personal statement is a short essay that you will submit with your application that discusses your personal history, interests, goals and strengths. It’s a chance for you to showcase what makes you unique.
For advice on this step, check out our article “ How to Write a Strong Personal Statement for Graduate School .” The UC Davis Office of Educational Opportunity and Enrichment Services also offers personal statement workshops and programs .
4. Request letters of recommendation

Letters of recommendation are another way for schools to qualitatively evaluate your academic success, work ethic and interests. They’re a way for you to stand out beyond the number on your LSAT report. Most schools will ask for two to three letters of recommendation, so start thinking early about who you’ll approach for them.
The key to receiving good letters of recommendation is building personal relationships with your professors and supervisors. Try out these tips:
- Attend office hours.
- Ask questions in class.
- Get involved in research.
- Share your interests.
- Ask for advice.
If you put in the effort to make genuine connections with them, your professors and supervisors will be happy to write passionate, personalized letters on your behalf.
For more advice on securing letters of recommendation, read our article “ How to Request Letters of Recommendation for Grad School .”
5. Keep on top of the admissions cycle

Just like applying to undergraduate studies, applying to law school is a lengthy process. You should plan to space out your application journey over at least six months. During this time, you’ll need to study for and take the LSAT, explore schools and prepare your application materials. Spacing the process out will allow you to keep a healthy balance with your studies and personal life.
Most law schools begin accepting applications in the fall of the preceding year and continue to accept them well into the spring. It’s recommended that you apply early in the cycle to have the best chance at securing a spot.
Now go on — you’ve got this
Applying to law school can be draining and nerve-wracking. Just remember that no matter what, you are good enough — it’s just about presenting your unique, talented self in the best way.
For more advice on the law school application process, read our article “ 6 Things I Wish I Knew When I Applied to Law School .”
How to apply to UC Davis School of Law
What you need to know about law school
R.J. Praker (she/her) is a third year pursuing a bachelor’s degree in political science with minors in professional writing and Russian . She currently works as a writing intern for UC Davis' Office of Strategic Communications and an academic peer advisor for the Department of Political Science . She also serves as chief copy editor at the Davis Political Review . R.J. is from Placerville, California and loves to hike in the Sierra Nevada with her family’s dogs.
Primary Category
The Ohio State University
Brushing through burnout, using ai to improve health care access, dedicated mentors inspiring student success, take your next step:.
- Schedule a visit
- Explore majors
Creating a world people need now.
The future is not only what you dream about; it’s what you create. Together, we’re finding solutions for challenges that can’t wait.
Important financial aid information
Get ready for the solar eclipse, ohio impact in all 88 counties, explore campus.
The Buckeye heart of The Ohio State University, located right in the heart of Ohio
Developing leaders with the resources and strength of the state’s top university
Bringing higher education opportunities to a broader community, throughout Ohio and beyond
Smaller campus, smaller class sizes but big opportunities to leverage the strength of Ohio State
Excellence in academics and innovative research opportunities paired with a supportive community
A critical component of our state-wide research enterprise with boundless opportunities
Ohio State News
Representatives discuss civility, compromise.
Disagree without being disagreeable. That was one of the central messages of a question-and-answer session with U.S. Reps. Joyce Beatty and Mike Carey.
Why prehistoric sharks got new names
Family engagement center to expand programs, parents, wealth, race impact girls’ sports, ohio state sets research spending record, key issues at ohio state.
Ohio State strongly condemns all terrorist groups and terrorist attacks, including those perpetrated by Hamas on Israeli civilians, Americans and others the weekend of October 7, 2023. The university is deeply committed to supporting all students, faculty and staff and will address national and global matters through direct actions and interventions that actively support the university community and afford educational dialogue in safe and supportive environments.
Strauss Investigation
Ohio State condemns Strauss' reprehensible conduct and the university's failure at the time to prevent the abuse.
Additional Links and Resources
Find it find it.
- Buckeye Link
Campuses Campuses
Health and wellness health and wellness.
- Wexner Medical Center
- Student Health Center
- Dental Clinics
- Optometry Services
- Buckeye Wellness
- Counseling Services
- Veterinary Medicine
Leadership Leadership
- Board of Trustees
- Strategic Plan
Around Campus Around Campus
- Visit, Stay and Dine
- Wexner Center for the Arts
- Schottenstein Center
- Ohio Stadium
Writers' Workshop
How to apply - summer, summer application deadline: march 3, 2024, to apply, please submit a manuscript of:.
10-12 poems for poetry 2 or 3 short stories or chapters of a novel for fiction
Applications for summer 2024 are now closed
Join Our Mailing List
Tuition for summer 2024 : undergraduate students: $1,128.00 per class; all other applicants: $1,878.00 per class *
* cost per class is based on University tuition rates; because we are a graduate program, you must be enrolled for credit to attend the class ** for international students, additional fees may apply in certain circumstances, for example if taking more than one class
For Admitted Students
Once you are admitted to the summer workshop, you will need to apply for admission to the University of Iowa as a Nondegree student. This application does not require a writing sample, but does require an official transcript. We will send an email with instructions to every admitted student.
Please be aware that acceptance to the summer program does not alter your chances of being admitted to the Writers' Workshop full-time graduate program.
Questions can be directed to: [email protected] .
The University has some level of available housing for undergraduate students. Most summer workshop students live in sublets and temporary housing (hotels, bed and breakfasts, Airbnbs). We will do our best to help.
Class Schedules
Typically, the 3-week poetry workshop meets on Tuesdays and Thursdays, from 10:00 a.m. to 1:00 p.m. Typically, the 3-week fiction workshops meets on Tuesdays and Thursdays, from 2:00 p.m. to 5:00 p.m.
In addition to classes, the summer program hosts readings and events during the week and occasionally over the weekend. Attendance at the events is not required, but they are a nice benefit of being in Iowa City.
International Students
International students should contact Andrew Wade in International Admissions for the complete requirements, by phone, at (319) 335-1534, or by email, at [email protected] .
Join the Summer Program Mailing List
To subscribe, click Yes, subscribe me to this list in the confirmation email we'll send.

Communications Specialist
- Madison, Wisconsin
- LAW SCHOOL/LAW SCHOOL-GEN
- Communications and Marketing
- Staff-Full Time
- Opening at: Mar 29 2024 at 13:45 CDT
- Closing at: Apr 14 2024 at 23:55 CDT
Job Summary:
The University of Wisconsin Law School's External Affairs (EA) team seeks a communications specialist to handle essential writing, editing, proofreading and publishing tasks. Primary focus areas include social media, newsletters, web posting and news stories/features. This person will also help fulfill other needs for creative and engaging print and digital content and overall provide support across EA, a collaborative, energetic team in charge of communications, events, Continuing Legal Education and alumni affairs. As a leader and innovator in legal education, UW Law boasts an abundance of stories to tell in multiple formats about our students, faculty, staff and alumni. This position will report to the Associate Director of Communications and receive guidance from the Communications Manager.
Responsibilities:
- 10% Monitors reach and effectiveness of communication campaigns, projects, and initiatives
- 10% Plans editorial content according to established goals and objects
- 10% Communicates with stakeholders to verify requests and identify editorial resources
- 50% Writes, edits, and publishes content for various communication projects and marketing platforms to align with strategic initiatives and established communication campaigns
- 20% Provides project management and execution of communications programs, initiatives, and tactical plans
Institutional Statement on Diversity:
Diversity is a source of strength, creativity, and innovation for UW-Madison. We value the contributions of each person and respect the profound ways their identity, culture, background, experience, status, abilities, and opinion enrich the university community. We commit ourselves to the pursuit of excellence in teaching, research, outreach, and diversity as inextricably linked goals. The University of Wisconsin-Madison fulfills its public mission by creating a welcoming and inclusive community for people from every background - people who as students, faculty, and staff serve Wisconsin and the world. For more information on diversity and inclusion on campus, please visit: Diversity and Inclusion
Preferred Bachelor's Degree
Qualifications:
The ideal candidate will be creative, productive and energetic. Strong written and verbal skills required. Experience with social media writing, campaigns, software and analytics required. Experience with newsletter campaigns and software strongly preferred. Experience with web publishing preferred. Experience with video creation and editing preferred.
Full Time: 100% It is anticipated this position requires work be performed in-person, onsite, at a designated campus work location. Some remote work flexibility may be possible after training and an evaluation period.
Appointment Type, Duration:
Ongoing/Renewable
Minimum $50,000 ANNUAL (12 months) Depending on Qualifications
How to Apply:
Applicants must submit a cover letter, along with 3 writing samples and a resume through the Jobs at UW website ( www.jobs.wisc.edu ) Job #295745 by the consideration date. The 3 writing samples should be attached as a part of the cover letter, or active links to a portfolio or work online. Samples could include a professional social media post or campaign, a professional newsletter and/or a brief news story.
Justin Boehm [email protected] 608-890-4466 Relay Access (WTRS): 7-1-1. See RELAY_SERVICE for further information.
Official Title:
Communications Specialist(CM004)
Department(s):
A45-LAW SCHOOL/LAW-EXTERNAL AFFAIRS
Employment Class:
Academic Staff-Renewable
Job Number:
The university of wisconsin-madison is an equal opportunity and affirmative action employer..
You will be redirected to the application to launch your career momentarily. Thank you!
Frequently Asked Questions
Applicant Tutorial
Disability Accommodations
Pay Transparency Policy Statement
Refer a Friend
You've sent this job to a friend!
Website feedback, questions or accessibility issues: [email protected] .
Learn more about accessibility at UW–Madison .
© 2016–2024 Board of Regents of the University of Wisconsin System • Privacy Statement

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Here are some tips to get you started. Start early. Do not leave it until the last minute. Give yourself time when you don't have other homework or extracurriculars hanging over your head to ...
Follow these tips to write an impactful essay that can work in your favor. 1. Start Early. Few people write well under pressure. Try to complete your first draft a few weeks before you have to turn it in. Many advisers recommend starting as early as the summer before your senior year in high school.
You will have a maximum number of words, so the secret is not to try to cover everything in your essay. Create a plan before you actually start writing, organize your essay in three parts (introduction, body and conclusion), and decide on the main ideas you want to express. 7. Ask someone to proofread your work.
Insert a quote from a well-known person. Challenge the reader with a common misconception. Use an anecdote, which is a short story that can be true or imaginary. Credibility is crucial when writing a personal statement as part of your college application process. If you choose a statistic, quote, or misconception for your hook, make sure it ...
college essay prompts: Colorado College: "Describe how your personal experiences with a particular community make you a student who would benefit from Colorado College's Block Plan." Tufts University: " I am applying to Tufts because…. Tulane University: "Describe why you are interested in joining the Tulane community.
One of the basic tasks of the application essay is to follow the directions. If you don't do what they ask, the reader may wonder if you will be able to follow directions in their program. Make sure you follow page and word limits exactly—err on the side of shortness, not length. The essay may take two forms:
Use a proper salutation. Begin your college application letter with a formal salutation. The standard, in this case, is "Dear". Be sure to avoid informal salutations such as "Hey", "Hi", and "Hello". 💡 Tip: Do your best to personalize your university application letter in every way that you can.
Making an all-state team → outstanding achievement. Making an all-state team → counting the cost of saying "no" to other interests. Making a friend out of an enemy → finding common ground, forgiveness. Making a friend out of an enemy → confront toxic thinking and behavior in yourself.
Here are a few guidelines for crafting a college application essay that effectively conveys who you are while also helping you stand out from the thousands of other applicants. Dos: Present yourself in a dimension that reaches beyond grades, recommendations, and test scores. Think of the things that built your character—maybe a special ...
Applying to university can seem very daunting. There's so much to do! But really, getting your application in is just a series of stages: do the research, narrow down your university choices, write the applications, and then play the waiting game. Then come the final decisions. Nobody else can help with the waiting game (start a new box set ...
University Application Letter Example Template. Dear Admissions Committee, I am writing to express my enthusiastic application for the [Program Name] at [University Name]. My interest in [Subject or Field of Study] was sparked by [brief personal anecdote or experience that ignited your passion in the field].
Click on the choices section and enter the universities and courses you've decided to apply to. Once you've added them all, click on the 'confirm choices' button on the bottom left to mark the section as complete. Your application will be linked to your college, so if your referee is one of your teachers they'll enter their reference into ...
Write a first draft using the format your school requires. According to Indiana University, most application letters and personal statements are between 250 and 500 words and follow a format that includes an introduction, body and conclusion. In the introduction, mention the degree or field of study for which you are applying and include a ...
A successful cover letter for a university application should contain specific elements that demonstrate the applicant's qualifications, achievements, and passion for the program. These elements include: Addressing the letter to the appropriate recipient. Crafting an engaging introduction that captures the reader's attention.
First, writing an application essay require a student aspiring to join college to prepare by reading and searching for information about the topic. Second, one should go through instructions, and ...
Just start by showing your enthusiasm for the subject, showcasing your knowledge and understanding, and sharing your ambitions of what you want to achieve. Avoid cliches! Remember, this opening part is simply about introducing yourself, so let the admissions tutor reading your personal statement get to know you. Keep it relevant and simple.
1. Write your name and street address. At the top of your cover letter, write your first and last name. On a separate line include your street address, followed by your city, state and zip code on another line. 2. Include the date. Below your contact information, write the date you plan on sending the cover letter.
Example. A personal anecdote. "My journey with community service began with a single, small act of kindness…". A career aspiration. "As a budding environmentalist, XYZ University's commitment to sustainability speaks to my deepest convictions.". An academic interest.
How to Write University Admission Application Letter. Some writing tips to help you craft a better application: Start with your personal information including your full name, address, the date, and the recipient's address. Open the letter with a formal salutation, addressing the admissions committee or specific admission officer, if known.
Common Application or apply Coalition, Powered by Scoir. Harvard College Questions for the Common Application, or Coalition Application Harvard supplement. $85 fee (or request a fee waiver) SAT or ACT (with or without writing) - optional for 2022-2026 application cycles. Optional: AP or other examination results. For first-year:
Follow these steps to compose a compelling application letter: 1. Research the company and job opening. Thoroughly research the company you're applying to and the specifications of the open position. The more you know about the job, the better you can customize your application letter. Look for details like:
The long list of application materials required for many academic teaching jobs can be daunting. This handout will help you tackle one of the most important components: the cover letter or letter of interest. Here you will learn about writing and revising cover letters for academic teaching jobs in the United States of America.
Instruction and resources for writing and rewriting your assignments and papers from the the Writing Studio. Financial aid and scholarships
3. Understand the timeline. Although the application process varies by college or university, the vast majority will require you to submit your transcript, letters of recommendation, professional resumé, and statement of purpose.Your transcript alone could take weeks to be delivered and processed, so don't wait until the last minute to start applying.
Structuring your CV. As you write your CV, work to the simple but effective structure below:. Name and contact details - Pop them at the top of your CV, so it's easy for recruiters to contact you.; CV profile - Write a snappy overview of what makes you a good fit for the role; discussing your key experience, skills and accomplishments.; Core skills section - Add a short but snappy list ...
A UC Davis School of Law student is lost in thought during class at King Hall. (Karin Higgins/UC Davis) In contrast to the LSAT's quantitative metric of your aptitude, a personal statement offers a qualitative measure for schools. A personal statement is a short essay that you will submit with your application that discusses your personal history, interests, goals and strengths.
Ohio State is a mission-driven land grant university that offers world-class graduate, undergraduate and research programs in various fields. Whether you are a domestic or international student, you can find the degree and program that suits your interests and goals. Explore Ohio State's academics, admissions, campus life and more.
Statement of Interest. In a concise statement of interest please address: Your writing goals and any personal information that you feel sheds light on your commitment to writing (e.g., details of your writing and reading practices, service to writing communities, artistic, professional, or academic objectives).
Class Schedules Typically, the 3-week poetry workshop meets on Tuesdays and Thursdays, from 10:00 a.m. to 1:00 p.m. Typically, the 3-week fiction workshops meets on Tuesdays and Thursdays, from 2:00 p.m. to 5:00 p.m.. In addition to classes, the summer program hosts readings and events during the week and occasionally over the weekend.
Job Summary: The University of Wisconsin Law School's External Affairs (EA) team seeks a communications specialist to handle essential writing, editing, proofreading and publishing tasks. Primary focus areas include social media, newsletters, web posting and news stories/features. This person will also help fulfill other needs for creative and engaging print and digital content and overall ...