Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to write a rhetorical analysis | Key concepts & examples

How to Write a Rhetorical Analysis | Key Concepts & Examples
Published on August 28, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on July 23, 2023.
A rhetorical analysis is a type of essay that looks at a text in terms of rhetoric. This means it is less concerned with what the author is saying than with how they say it: their goals, techniques, and appeals to the audience.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Key concepts in rhetoric, analyzing the text, introducing your rhetorical analysis, the body: doing the analysis, concluding a rhetorical analysis, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about rhetorical analysis.
Rhetoric, the art of effective speaking and writing, is a subject that trains you to look at texts, arguments and speeches in terms of how they are designed to persuade the audience. This section introduces a few of the key concepts of this field.
Appeals: Logos, ethos, pathos
Appeals are how the author convinces their audience. Three central appeals are discussed in rhetoric, established by the philosopher Aristotle and sometimes called the rhetorical triangle: logos, ethos, and pathos.
Logos , or the logical appeal, refers to the use of reasoned argument to persuade. This is the dominant approach in academic writing , where arguments are built up using reasoning and evidence.
Ethos , or the ethical appeal, involves the author presenting themselves as an authority on their subject. For example, someone making a moral argument might highlight their own morally admirable behavior; someone speaking about a technical subject might present themselves as an expert by mentioning their qualifications.
Pathos , or the pathetic appeal, evokes the audience’s emotions. This might involve speaking in a passionate way, employing vivid imagery, or trying to provoke anger, sympathy, or any other emotional response in the audience.
These three appeals are all treated as integral parts of rhetoric, and a given author may combine all three of them to convince their audience.
Text and context
In rhetoric, a text is not necessarily a piece of writing (though it may be this). A text is whatever piece of communication you are analyzing. This could be, for example, a speech, an advertisement, or a satirical image.
In these cases, your analysis would focus on more than just language—you might look at visual or sonic elements of the text too.
The context is everything surrounding the text: Who is the author (or speaker, designer, etc.)? Who is their (intended or actual) audience? When and where was the text produced, and for what purpose?
Looking at the context can help to inform your rhetorical analysis. For example, Martin Luther King, Jr.’s “I Have a Dream” speech has universal power, but the context of the civil rights movement is an important part of understanding why.
Claims, supports, and warrants
A piece of rhetoric is always making some sort of argument, whether it’s a very clearly defined and logical one (e.g. in a philosophy essay) or one that the reader has to infer (e.g. in a satirical article). These arguments are built up with claims, supports, and warrants.
A claim is the fact or idea the author wants to convince the reader of. An argument might center on a single claim, or be built up out of many. Claims are usually explicitly stated, but they may also just be implied in some kinds of text.
The author uses supports to back up each claim they make. These might range from hard evidence to emotional appeals—anything that is used to convince the reader to accept a claim.
The warrant is the logic or assumption that connects a support with a claim. Outside of quite formal argumentation, the warrant is often unstated—the author assumes their audience will understand the connection without it. But that doesn’t mean you can’t still explore the implicit warrant in these cases.
For example, look at the following statement:
We can see a claim and a support here, but the warrant is implicit. Here, the warrant is the assumption that more likeable candidates would have inspired greater turnout. We might be more or less convinced by the argument depending on whether we think this is a fair assumption.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Rhetorical analysis isn’t a matter of choosing concepts in advance and applying them to a text. Instead, it starts with looking at the text in detail and asking the appropriate questions about how it works:
- What is the author’s purpose?
- Do they focus closely on their key claims, or do they discuss various topics?
- What tone do they take—angry or sympathetic? Personal or authoritative? Formal or informal?
- Who seems to be the intended audience? Is this audience likely to be successfully reached and convinced?
- What kinds of evidence are presented?
By asking these questions, you’ll discover the various rhetorical devices the text uses. Don’t feel that you have to cram in every rhetorical term you know—focus on those that are most important to the text.
The following sections show how to write the different parts of a rhetorical analysis.
Like all essays, a rhetorical analysis begins with an introduction . The introduction tells readers what text you’ll be discussing, provides relevant background information, and presents your thesis statement .
Hover over different parts of the example below to see how an introduction works.
Martin Luther King, Jr.’s “I Have a Dream” speech is widely regarded as one of the most important pieces of oratory in American history. Delivered in 1963 to thousands of civil rights activists outside the Lincoln Memorial in Washington, D.C., the speech has come to symbolize the spirit of the civil rights movement and even to function as a major part of the American national myth. This rhetorical analysis argues that King’s assumption of the prophetic voice, amplified by the historic size of his audience, creates a powerful sense of ethos that has retained its inspirational power over the years.
The body of your rhetorical analysis is where you’ll tackle the text directly. It’s often divided into three paragraphs, although it may be more in a longer essay.
Each paragraph should focus on a different element of the text, and they should all contribute to your overall argument for your thesis statement.
Hover over the example to explore how a typical body paragraph is constructed.
King’s speech is infused with prophetic language throughout. Even before the famous “dream” part of the speech, King’s language consistently strikes a prophetic tone. He refers to the Lincoln Memorial as a “hallowed spot” and speaks of rising “from the dark and desolate valley of segregation” to “make justice a reality for all of God’s children.” The assumption of this prophetic voice constitutes the text’s strongest ethical appeal; after linking himself with political figures like Lincoln and the Founding Fathers, King’s ethos adopts a distinctly religious tone, recalling Biblical prophets and preachers of change from across history. This adds significant force to his words; standing before an audience of hundreds of thousands, he states not just what the future should be, but what it will be: “The whirlwinds of revolt will continue to shake the foundations of our nation until the bright day of justice emerges.” This warning is almost apocalyptic in tone, though it concludes with the positive image of the “bright day of justice.” The power of King’s rhetoric thus stems not only from the pathos of his vision of a brighter future, but from the ethos of the prophetic voice he adopts in expressing this vision.
The conclusion of a rhetorical analysis wraps up the essay by restating the main argument and showing how it has been developed by your analysis. It may also try to link the text, and your analysis of it, with broader concerns.
Explore the example below to get a sense of the conclusion.
It is clear from this analysis that the effectiveness of King’s rhetoric stems less from the pathetic appeal of his utopian “dream” than it does from the ethos he carefully constructs to give force to his statements. By framing contemporary upheavals as part of a prophecy whose fulfillment will result in the better future he imagines, King ensures not only the effectiveness of his words in the moment but their continuing resonance today. Even if we have not yet achieved King’s dream, we cannot deny the role his words played in setting us on the path toward it.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
The goal of a rhetorical analysis is to explain the effect a piece of writing or oratory has on its audience, how successful it is, and the devices and appeals it uses to achieve its goals.
Unlike a standard argumentative essay , it’s less about taking a position on the arguments presented, and more about exploring how they are constructed.
The term “text” in a rhetorical analysis essay refers to whatever object you’re analyzing. It’s frequently a piece of writing or a speech, but it doesn’t have to be. For example, you could also treat an advertisement or political cartoon as a text.
Logos appeals to the audience’s reason, building up logical arguments . Ethos appeals to the speaker’s status or authority, making the audience more likely to trust them. Pathos appeals to the emotions, trying to make the audience feel angry or sympathetic, for example.
Collectively, these three appeals are sometimes called the rhetorical triangle . They are central to rhetorical analysis , though a piece of rhetoric might not necessarily use all of them.
In rhetorical analysis , a claim is something the author wants the audience to believe. A support is the evidence or appeal they use to convince the reader to believe the claim. A warrant is the (often implicit) assumption that links the support with the claim.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, July 23). How to Write a Rhetorical Analysis | Key Concepts & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 2, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/rhetorical-analysis/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, how to write an argumentative essay | examples & tips, how to write a literary analysis essay | a step-by-step guide, comparing and contrasting in an essay | tips & examples, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources
How to Write a Rhetorical Analysis Essay–Examples & Template
What is a Rhetorical Analysis Essay?
A rhetorical analysis essay is, as the name suggests, an analysis of someone else’s writing (or speech, or advert, or even cartoon) and how they use not only words but also rhetorical techniques to influence their audience in a certain way. A rhetorical analysis is less interested in what the author is saying and more in how they present it, what effect this has on their readers, whether they achieve their goals, and what approach they use to get there.
Its structure is similar to that of most essays: An Introduction presents your thesis, a Body analyzes the text you have chosen, breaks it down into sections and explains how arguments have been constructed and how each part persuades, informs, or entertains the reader, and a Conclusion section sums up your evaluation.
Note that your personal opinion on the matter is not relevant for your analysis and that you don’t state anywhere in your essay whether you agree or disagree with the stance the author takes.
In the following, we will define the key rhetorical concepts you need to write a good rhetorical analysis and give you some practical tips on where to start.
Key Rhetorical Concepts
Your goal when writing a rhetorical analysis is to think about and then carefully describe how the author has designed their text so that it has the intended effect on their audience. To do that, you need to consider a number of key rhetorical strategies: Rhetorical appeals (“Ethos”, “Logos”, and “Pathos”), context, as well as claims, supports, and warrants.
Ethos, Logos, and Pathos were introduced by Aristotle, way back in the 4th century BC, as the main ways in which language can be used to persuade an audience. They still represent the basis of any rhetorical analysis and are often referred to as the “rhetorical triangle”.
These and other rhetorical techniques can all be combined to create the intended effect, and your job as the one analyzing a text is to break the writer’s arguments down and identify the concepts they are based on.
Rhetorical Appeals
Rhetorical appeal #1: ethos.
Ethos refers to the reputation or authority of the writer regarding the topic of their essay or speech and to how they use this to appeal to their audience. Just like we are more likely to buy a product from a brand or vendor we have confidence in than one we don’t know or have reason to distrust, Ethos-driven texts or speeches rely on the reputation of the author to persuade the reader or listener. When you analyze an essay, you should therefore look at how the writer establishes Ethos through rhetorical devices.
Does the author present themselves as an authority on their subject? If so, how?
Do they highlight how impeccable their own behavior is to make a moral argument?
Do they present themselves as an expert by listing their qualifications or experience to convince the reader of their opinion on something?
Rhetorical appeal #2: Pathos
The purpose of Pathos-driven rhetoric is to appeal to the reader’s emotions. A common example of pathos as a rhetorical means is adverts by charities that try to make you donate money to a “good cause”. To evoke the intended emotions in the reader, an author may use passionate language, tell personal stories, and employ vivid imagery so that the reader can imagine themselves in a certain situation and feel empathy with or anger towards others.
Rhetorical appeal #3: Logos
Logos, the “logical” appeal, uses reason to persuade. Reason and logic, supported by data, evidence, clearly defined methodology, and well-constructed arguments, are what most academic writing is based on. Emotions, those of the researcher/writer as well as those of the reader, should stay out of such academic texts, as should anyone’s reputation, beliefs, or personal opinions.
Text and Context
To analyze a piece of writing, a speech, an advertisement, or even a satirical drawing, you need to look beyond the piece of communication and take the context in which it was created and/or published into account.
Who is the person who wrote the text/drew the cartoon/designed the ad..? What audience are they trying to reach? Where was the piece published and what was happening there around that time?
A political speech, for example, can be powerful even when read decades later, but the historical context surrounding it is an important aspect of the effect it was intended to have.
Claims, Supports, and Warrants
To make any kind of argument, a writer needs to put forward specific claims, support them with data or evidence or even a moral or emotional appeal, and connect the dots logically so that the reader can follow along and agree with the points made.
The connections between statements, so-called “warrants”, follow logical reasoning but are not always clearly stated—the author simply assumes the reader understands the underlying logic, whether they present it “explicitly” or “implicitly”. Implicit warrants are commonly used in advertisements where seemingly happy people use certain products, wear certain clothes, accessories, or perfumes, or live certain lifestyles – with the connotation that, first, the product/perfume/lifestyle is what makes that person happy and, second, the reader wants to be as happy as the person in the ad. Some warrants are never clearly stated, and your job when writing a rhetorical analysis essay is therefore to identify them and bring them to light, to evaluate their validity, their effect on the reader, and the use of such means by the writer/creator.

What are the Five Rhetorical Situations?
A “rhetorical situation” refers to the circumstance behind a text or other piece of communication that arises from a given context. It explains why a rhetorical piece was created, what its purpose is, and how it was constructed to achieve its aims.
Rhetorical situations can be classified into the following five categories:
Asking such questions when you analyze a text will help you identify all the aspects that play a role in the effect it has on its audience, and will allow you to evaluate whether it achieved its aims or where it may have failed to do so.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Outline
Analyzing someone else’s work can seem like a big task, but as with every assignment or writing endeavor, you can break it down into smaller, well-defined steps that give you a practical structure to follow.
To give you an example of how the different parts of your text may look when it’s finished, we will provide you with some excerpts from this rhetorical analysis essay example (which even includes helpful comments) published on the Online Writing Lab website of Excelsior University in Albany, NY. The text that this essay analyzes is this article on why one should or shouldn’t buy an Ipad. If you want more examples so that you can build your own rhetorical analysis template, have a look at this essay on Nabokov’s Lolita and the one provided here about the “Shitty First Drafts” chapter of Anne Lamott’s writing instruction book “Bird by Bird”.
Analyzing the Text
When writing a rhetorical analysis, you don’t choose the concepts or key points you think are relevant or want to address. Rather, you carefully read the text several times asking yourself questions like those listed in the last section on rhetorical situations to identify how the text “works” and how it was written to achieve that effect.
Start with focusing on the author : What do you think was their purpose for writing the text? Do they make one principal claim and then elaborate on that? Or do they discuss different topics?
Then look at what audience they are talking to: Do they want to make a group of people take some action? Vote for someone? Donate money to a good cause? Who are these people? Is the text reaching this specific audience? Why or why not?
What tone is the author using to address their audience? Are they trying to evoke sympathy? Stir up anger? Are they writing from a personal perspective? Are they painting themselves as an authority on the topic? Are they using academic or informal language?
How does the author support their claims ? What kind of evidence are they presenting? Are they providing explicit or implicit warrants? Are these warrants valid or problematic? Is the provided evidence convincing?
Asking yourself such questions will help you identify what rhetorical devices a text uses and how well they are put together to achieve a certain aim. Remember, your own opinion and whether you agree with the author are not the point of a rhetorical analysis essay – your task is simply to take the text apart and evaluate it.
If you are still confused about how to write a rhetorical analysis essay, just follow the steps outlined below to write the different parts of your rhetorical analysis: As every other essay, it consists of an Introduction , a Body (the actual analysis), and a Conclusion .
Rhetorical Analysis Introduction
The Introduction section briefly presents the topic of the essay you are analyzing, the author, their main claims, a short summary of the work by you, and your thesis statement .
Tell the reader what the text you are going to analyze represents (e.g., historically) or why it is relevant (e.g., because it has become some kind of reference for how something is done). Describe what the author claims, asserts, or implies and what techniques they use to make their argument and persuade their audience. Finish off with your thesis statement that prepares the reader for what you are going to present in the next section – do you think that the author’s assumptions/claims/arguments were presented in a logical/appealing/powerful way and reached their audience as intended?
Have a look at an excerpt from the sample essay linked above to see what a rhetorical analysis introduction can look like. See how it introduces the author and article , the context in which it originally appeared , the main claims the author makes , and how this first paragraph ends in a clear thesis statement that the essay will then elaborate on in the following Body section:
Cory Doctorow ’s article on BoingBoing is an older review of the iPad , one of Apple’s most famous products. At the time of this article, however, the iPad was simply the latest Apple product to hit the market and was not yet so popular. Doctorow’s entire career has been entrenched in and around technology. He got his start as a CD-ROM programmer and is now a successful blogger and author. He is currently the co-editor of the BoingBoing blog on which this article was posted. One of his main points in this article comes from Doctorow’s passionate advocacy of free digital media sharing. He argues that the iPad is just another way for established technology companies to control our technological freedom and creativity . In “ Why I Won’t Buy an iPad (and Think You Shouldn’t, Either) ” published on Boing Boing in April of 2010, Cory Doctorow successfully uses his experience with technology, facts about the company Apple, and appeals to consumer needs to convince potential iPad buyers that Apple and its products, specifically the iPad, limit the digital rights of those who use them by controlling and mainstreaming the content that can be used and created on the device .
Doing the Rhetorical Analysis
The main part of your analysis is the Body , where you dissect the text in detail. Explain what methods the author uses to inform, entertain, and/or persuade the audience. Use Aristotle’s rhetorical triangle and the other key concepts we introduced above. Use quotations from the essay to demonstrate what you mean. Work out why the writer used a certain approach and evaluate (and again, demonstrate using the text itself) how successful they were. Evaluate the effect of each rhetorical technique you identify on the audience and judge whether the effect is in line with the author’s intentions.
To make it easy for the reader to follow your thought process, divide this part of your essay into paragraphs that each focus on one strategy or one concept , and make sure they are all necessary and contribute to the development of your argument(s).
One paragraph of this section of your essay could, for example, look like this:
One example of Doctorow’s position is his comparison of Apple’s iStore to Wal-Mart. This is an appeal to the consumer’s logic—or an appeal to logos. Doctorow wants the reader to take his comparison and consider how an all-powerful corporation like the iStore will affect them. An iPad will only allow for apps and programs purchased through the iStore to be run on it; therefore, a customer must not only purchase an iPad but also any programs he or she wishes to use. Customers cannot create their own programs or modify the hardware in any way.
As you can see, the author of this sample essay identifies and then explains to the reader how Doctorow uses the concept of Logos to appeal to his readers – not just by pointing out that he does it but by dissecting how it is done.
Rhetorical Analysis Conclusion
The conclusion section of your analysis should restate your main arguments and emphasize once more whether you think the author achieved their goal. Note that this is not the place to introduce new information—only rely on the points you have discussed in the body of your essay. End with a statement that sums up the impact the text has on its audience and maybe society as a whole:
Overall, Doctorow makes a good argument about why there are potentially many better things to drop a great deal of money on instead of the iPad. He gives some valuable information and facts that consumers should take into consideration before going out to purchase the new device. He clearly uses rhetorical tools to help make his case, and, overall, he is effective as a writer, even if, ultimately, he was ineffective in convincing the world not to buy an iPad .
Frequently Asked Questions about Rhetorical Analysis Essays
What is a rhetorical analysis essay.
A rhetorical analysis dissects a text or another piece of communication to work out and explain how it impacts its audience, how successfully it achieves its aims, and what rhetorical devices it uses to do that.
While argumentative essays usually take a stance on a certain topic and argue for it, a rhetorical analysis identifies how someone else constructs their arguments and supports their claims.
What is the correct rhetorical analysis essay format?
Like most other essays, a rhetorical analysis contains an Introduction that presents the thesis statement, a Body that analyzes the piece of communication, explains how arguments have been constructed, and illustrates how each part persuades, informs, or entertains the reader, and a Conclusion section that summarizes the results of the analysis.
What is the “rhetorical triangle”?
The rhetorical triangle was introduced by Aristotle as the main ways in which language can be used to persuade an audience: Logos appeals to the audience’s reason, Ethos to the writer’s status or authority, and Pathos to the reader’s emotions. Logos, Ethos, and Pathos can all be combined to create the intended effect, and your job as the one analyzing a text is to break the writer’s arguments down and identify what specific concepts each is based on.
Let Wordvice help you write a flawless rhetorical analysis essay!
Whether you have to write a rhetorical analysis essay as an assignment or whether it is part of an application, our professional proofreading services feature professional editors are trained subject experts that make sure your text is in line with the required format, as well as help you improve the flow and expression of your writing. Let them be your second pair of eyes so that after receiving paper editing services or essay editing services from Wordvice, you can submit your manuscript or apply to the school of your dreams with confidence.
And check out our editing services for writers (including blog editing , script editing , and book editing ) to correct your important personal or business-related work.
- Features for Creative Writers
- Features for Work
- Features for Higher Education
- Features for Teachers
- Features for Non-Native Speakers
- Learn Blog Grammar Guide Community Events FAQ
- Grammar Guide
What Is a Rhetorical Analysis and How to Write a Great One

Helly Douglas

Do you have to write a rhetorical analysis essay? Fear not! We’re here to explain exactly what rhetorical analysis means, how you should structure your essay, and give you some essential “dos and don’ts.”
What is a Rhetorical Analysis Essay?
How do you write a rhetorical analysis, what are the three rhetorical strategies, what are the five rhetorical situations, how to plan a rhetorical analysis essay, creating a rhetorical analysis essay, examples of great rhetorical analysis essays, final thoughts.
A rhetorical analysis essay studies how writers and speakers have used words to influence their audience. Think less about the words the author has used and more about the techniques they employ, their goals, and the effect this has on the audience.

In your analysis essay, you break a piece of text (including cartoons, adverts, and speeches) into sections and explain how each part works to persuade, inform, or entertain. You’ll explore the effectiveness of the techniques used, how the argument has been constructed, and give examples from the text.
A strong rhetorical analysis evaluates a text rather than just describes the techniques used. You don’t include whether you personally agree or disagree with the argument.
Structure a rhetorical analysis in the same way as most other types of academic essays . You’ll have an introduction to present your thesis, a main body where you analyze the text, which then leads to a conclusion.
Think about how the writer (also known as a rhetor) considers the situation that frames their communication:
- Topic: the overall purpose of the rhetoric
- Audience: this includes primary, secondary, and tertiary audiences
- Purpose: there are often more than one to consider
- Context and culture: the wider situation within which the rhetoric is placed
Back in the 4th century BC, Aristotle was talking about how language can be used as a means of persuasion. He described three principal forms —Ethos, Logos, and Pathos—often referred to as the Rhetorical Triangle . These persuasive techniques are still used today.
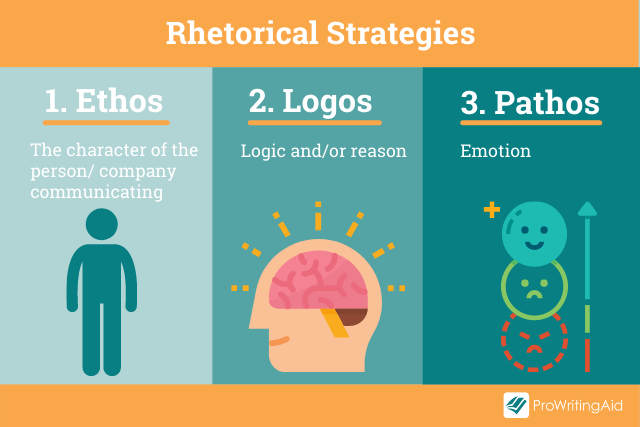
Rhetorical Strategy 1: Ethos
Are you more likely to buy a car from an established company that’s been an important part of your community for 50 years, or someone new who just started their business?
Reputation matters. Ethos explores how the character, disposition, and fundamental values of the author create appeal, along with their expertise and knowledge in the subject area.
Aristotle breaks ethos down into three further categories:
- Phronesis: skills and practical wisdom
- Arete: virtue
- Eunoia: goodwill towards the audience
Ethos-driven speeches and text rely on the reputation of the author. In your analysis, you can look at how the writer establishes ethos through both direct and indirect means.
Rhetorical Strategy 2: Pathos
Pathos-driven rhetoric hooks into our emotions. You’ll often see it used in advertisements, particularly by charities wanting you to donate money towards an appeal.
Common use of pathos includes:
- Vivid description so the reader can imagine themselves in the situation
- Personal stories to create feelings of empathy
- Emotional vocabulary that evokes a response
By using pathos to make the audience feel a particular emotion, the author can persuade them that the argument they’re making is compelling.
Rhetorical Strategy 3: Logos
Logos uses logic or reason. It’s commonly used in academic writing when arguments are created using evidence and reasoning rather than an emotional response. It’s constructed in a step-by-step approach that builds methodically to create a powerful effect upon the reader.
Rhetoric can use any one of these three techniques, but effective arguments often appeal to all three elements.
The rhetorical situation explains the circumstances behind and around a piece of rhetoric. It helps you think about why a text exists, its purpose, and how it’s carried out.
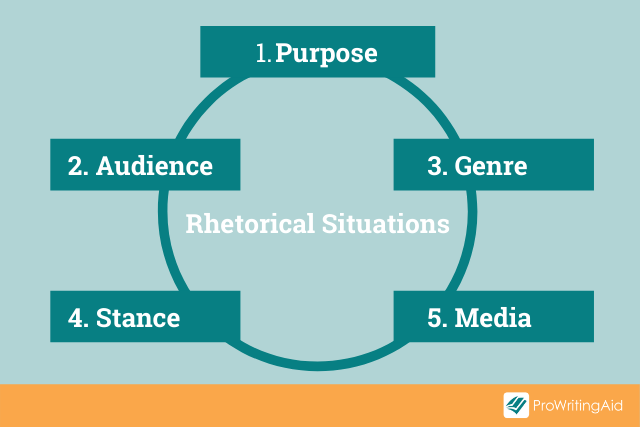
The rhetorical situations are:
- 1) Purpose: Why is this being written? (It could be trying to inform, persuade, instruct, or entertain.)
- 2) Audience: Which groups or individuals will read and take action (or have done so in the past)?
- 3) Genre: What type of writing is this?
- 4) Stance: What is the tone of the text? What position are they taking?
- 5) Media/Visuals: What means of communication are used?
Understanding and analyzing the rhetorical situation is essential for building a strong essay. Also think about any rhetoric restraints on the text, such as beliefs, attitudes, and traditions that could affect the author's decisions.
Before leaping into your essay, it’s worth taking time to explore the text at a deeper level and considering the rhetorical situations we looked at before. Throw away your assumptions and use these simple questions to help you unpick how and why the text is having an effect on the audience.

1: What is the Rhetorical Situation?
- Why is there a need or opportunity for persuasion?
- How do words and references help you identify the time and location?
- What are the rhetoric restraints?
- What historical occasions would lead to this text being created?
2: Who is the Author?
- How do they position themselves as an expert worth listening to?
- What is their ethos?
- Do they have a reputation that gives them authority?
- What is their intention?
- What values or customs do they have?
3: Who is it Written For?
- Who is the intended audience?
- How is this appealing to this particular audience?
- Who are the possible secondary and tertiary audiences?
4: What is the Central Idea?
- Can you summarize the key point of this rhetoric?
- What arguments are used?
- How has it developed a line of reasoning?
5: How is it Structured?
- What structure is used?
- How is the content arranged within the structure?
6: What Form is Used?
- Does this follow a specific literary genre?
- What type of style and tone is used, and why is this?
- Does the form used complement the content?
- What effect could this form have on the audience?
7: Is the Rhetoric Effective?
- Does the content fulfil the author’s intentions?
- Does the message effectively fit the audience, location, and time period?
Once you’ve fully explored the text, you’ll have a better understanding of the impact it’s having on the audience and feel more confident about writing your essay outline.
A great essay starts with an interesting topic. Choose carefully so you’re personally invested in the subject and familiar with it rather than just following trending topics. There are lots of great ideas on this blog post by My Perfect Words if you need some inspiration. Take some time to do background research to ensure your topic offers good analysis opportunities.

Remember to check the information given to you by your professor so you follow their preferred style guidelines. This outline example gives you a general idea of a format to follow, but there will likely be specific requests about layout and content in your course handbook. It’s always worth asking your institution if you’re unsure.
Make notes for each section of your essay before you write. This makes it easy for you to write a well-structured text that flows naturally to a conclusion. You will develop each note into a paragraph. Look at this example by College Essay for useful ideas about the structure.
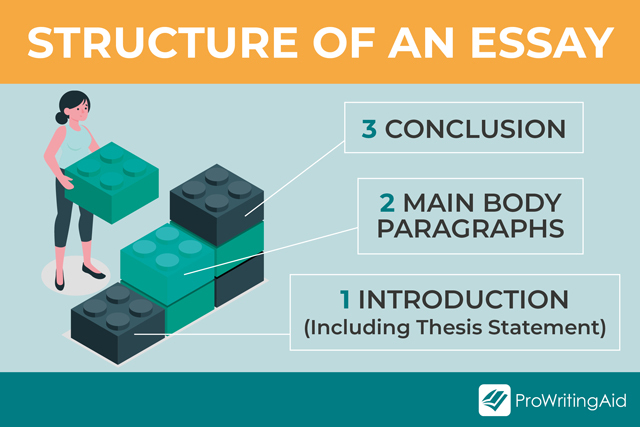
1: Introduction
This is a short, informative section that shows you understand the purpose of the text. It tempts the reader to find out more by mentioning what will come in the main body of your essay.
- Name the author of the text and the title of their work followed by the date in parentheses
- Use a verb to describe what the author does, e.g. “implies,” “asserts,” or “claims”
- Briefly summarize the text in your own words
- Mention the persuasive techniques used by the rhetor and its effect
Create a thesis statement to come at the end of your introduction.
After your introduction, move on to your critical analysis. This is the principal part of your essay.
- Explain the methods used by the author to inform, entertain, and/or persuade the audience using Aristotle's rhetorical triangle
- Use quotations to prove the statements you make
- Explain why the writer used this approach and how successful it is
- Consider how it makes the audience feel and react
Make each strategy a new paragraph rather than cramming them together, and always use proper citations. Check back to your course handbook if you’re unsure which citation style is preferred.
3: Conclusion
Your conclusion should summarize the points you’ve made in the main body of your essay. While you will draw the points together, this is not the place to introduce new information you’ve not previously mentioned.
Use your last sentence to share a powerful concluding statement that talks about the impact the text has on the audience(s) and wider society. How have its strategies helped to shape history?
Before You Submit
Poor spelling and grammatical errors ruin a great essay. Use ProWritingAid to check through your finished essay before you submit. It will pick up all the minor errors you’ve missed and help you give your essay a final polish. Look at this useful ProWritingAid webinar for further ideas to help you significantly improve your essays. Sign up for a free trial today and start editing your essays!
You’ll find countless examples of rhetorical analysis online, but they range widely in quality. Your institution may have example essays they can share with you to show you exactly what they’re looking for.
The following links should give you a good starting point if you’re looking for ideas:
Pearson Canada has a range of good examples. Look at how embedded quotations are used to prove the points being made. The end questions help you unpick how successful each essay is.
Excelsior College has an excellent sample essay complete with useful comments highlighting the techniques used.
Brighton Online has a selection of interesting essays to look at. In this specific example, consider how wider reading has deepened the exploration of the text.

Writing a rhetorical analysis essay can seem daunting, but spending significant time deeply analyzing the text before you write will make it far more achievable and result in a better-quality essay overall.
It can take some time to write a good essay. Aim to complete it well before the deadline so you don’t feel rushed. Use ProWritingAid’s comprehensive checks to find any errors and make changes to improve readability. Then you’ll be ready to submit your finished essay, knowing it’s as good as you can possibly make it.
Try ProWritingAid's Editor for Yourself
Be confident about grammar
Check every email, essay, or story for grammar mistakes. Fix them before you press send.
Helly Douglas is a UK writer and teacher, specialising in education, children, and parenting. She loves making the complex seem simple through blogs, articles, and curriculum content. You can check out her work at hellydouglas.com or connect on Twitter @hellydouglas. When she’s not writing, you will find her in a classroom, being a mum or battling against the wilderness of her garden—the garden is winning!
Get started with ProWritingAid
Drop us a line or let's stay in touch via :
Reference management. Clean and simple.
How to write a rhetorical analysis

What is a rhetorical analysis?
What are the key concepts of a rhetorical analysis, rhetorical situation, claims, supports, and warrants.
- Step 1: Plan and prepare
- Step 2: Write your introduction
- Step 3: Write the body
- Step 4: Write your conclusion
Frequently Asked Questions about rhetorical analysis
Related articles.
Rhetoric is the art of persuasion and aims to study writers’ or speakers' techniques to inform, persuade, or motivate their audience. Thus, a rhetorical analysis aims to explore the goals and motivations of an author, the techniques they’ve used to reach their audience, and how successful these techniques were.
This will generally involve analyzing a specific text and considering the following aspects to connect the rhetorical situation to the text:
- Does the author successfully support the thesis or claims made in the text? Here, you’ll analyze whether the author holds to their argument consistently throughout the text or whether they wander off-topic at some point.
- Does the author use evidence effectively considering the text’s intended audience? Here, you’ll consider the evidence used by the author to support their claims and whether the evidence resonates with the intended audience.
- What rhetorical strategies the author uses to achieve their goals. Here, you’ll consider the word choices by the author and whether these word choices align with their agenda for the text.
- The tone of the piece. Here, you’ll consider the tone used by the author in writing the piece by looking at specific words and aspects that set the tone.
- Whether the author is objective or trying to convince the audience of a particular viewpoint. When it comes to objectivity, you’ll consider whether the author is objective or holds a particular viewpoint they want to convince the audience of. If they are, you’ll also consider whether their persuasion interferes with how the text is read and understood.
- Does the author correctly identify the intended audience? It’s important to consider whether the author correctly writes the text for the intended audience and what assumptions the author makes about the audience.
- Does the text make sense? Here, you’ll consider whether the author effectively reasons, based on the evidence, to arrive at the text’s conclusion.
- Does the author try to appeal to the audience’s emotions? You’ll need to consider whether the author uses any words, ideas, or techniques to appeal to the audience’s emotions.
- Can the author be believed? Finally, you’ll consider whether the audience will accept the arguments and ideas of the author and why.
Summing up, unlike summaries that focus on what an author said, a rhetorical analysis focuses on how it’s said, and it doesn’t rely on an analysis of whether the author was right or wrong but rather how they made their case to arrive at their conclusions.
Although rhetorical analysis is most used by academics as part of scholarly work, it can be used to analyze any text including speeches, novels, television shows or films, advertisements, or cartoons.
Now that we’ve seen what rhetorical analysis is, let’s consider some of its key concepts .
Any rhetorical analysis starts with the rhetorical situation which identifies the relationships between the different elements of the text. These elements include the audience, author or writer, the author’s purpose, the delivery method or medium, and the content:
- Audience: The audience is simply the readers of a specific piece of text or content or printed material. For speeches or other mediums like film and video, the audience would be the listeners or viewers. Depending on the specific piece of text or the author’s perception, the audience might be real, imagined, or invoked. With a real audience, the author writes to the people actually reading or listening to the content while, for an imaginary audience, the author writes to an audience they imagine would read the content. Similarly, for an invoked audience, the author writes explicitly to a specific audience.
- Author or writer: The author or writer, also commonly referred to as the rhetor in the context of rhetorical analysis, is the person or the group of persons who authored the text or content.
- The author’s purpose: The author’s purpose is the author’s reason for communicating to the audience. In other words, the author’s purpose encompasses what the author expects or intends to achieve with the text or content.
- Alphabetic text includes essays, editorials, articles, speeches, and other written pieces.
- Imaging includes website and magazine advertisements, TV commercials, and the like.
- Audio includes speeches, website advertisements, radio or tv commercials, or podcasts.
- Context: The context of the text or content considers the time, place, and circumstances surrounding the delivery of the text to its audience. With respect to context, it might often also be helpful to analyze the text in a different context to determine its impact on a different audience and in different circumstances.
An author will use claims, supports, and warrants to build the case around their argument, irrespective of whether the argument is logical and clearly defined or needs to be inferred by the audience:
- Claim: The claim is the main idea or opinion of an argument that the author must prove to the intended audience. In other words, the claim is the fact or facts the author wants to convince the audience of. Claims are usually explicitly stated but can, depending on the specific piece of content or text, be implied from the content. Although these claims could be anything and an argument may be based on a single or several claims, the key is that these claims should be debatable.
- Support: The supports are used by the author to back up the claims they make in their argument. These supports can include anything from fact-based, objective evidence to subjective emotional appeals and personal experiences used by the author to convince the audience of a specific claim. Either way, the stronger and more reliable the supports, the more likely the audience will be to accept the claim.
- Warrant: The warrants are the logic and assumptions that connect the supports to the claims. In other words, they’re the assumptions that make the initial claim possible. The warrant is often unstated, and the author assumes that the audience will be able to understand the connection between the claims and supports. In turn, this is based on the author’s assumption that they share a set of values and beliefs with the audience that will make them understand the connection mentioned above. Conversely, if the audience doesn’t share these beliefs and values with the author, the argument will not be that effective.
Appeals are used by authors to convince their audience and, as such, are an integral part of the rhetoric and are often referred to as the rhetorical triangle. As a result, an author may combine all three appeals to convince their audience:
- Ethos: Ethos represents the authority or credibility of the author. To be successful, the author needs to convince the audience of their authority or credibility through the language and delivery techniques they use. This will, for example, be the case where an author writing on a technical subject positions themselves as an expert or authority by referring to their qualifications or experience.
- Logos: Logos refers to the reasoned argument the author uses to persuade their audience. In other words, it refers to the reasons or evidence the author proffers in substantiation of their claims and can include facts, statistics, and other forms of evidence. For this reason, logos is also the dominant approach in academic writing where authors present and build up arguments using reasoning and evidence.
- Pathos: Through pathos, also referred to as the pathetic appeal, the author attempts to evoke the audience’s emotions through the use of, for instance, passionate language, vivid imagery, anger, sympathy, or any other emotional response.
To write a rhetorical analysis, you need to follow the steps below:
With a rhetorical analysis, you don’t choose concepts in advance and apply them to a specific text or piece of content. Rather, you’ll have to analyze the text to identify the separate components and plan and prepare your analysis accordingly.
Here, it might be helpful to use the SOAPSTone technique to identify the components of the work. SOAPSTone is a common acronym in analysis and represents the:
- Speaker . Here, you’ll identify the author or the narrator delivering the content to the audience.
- Occasion . With the occasion, you’ll identify when and where the story takes place and what the surrounding context is.
- Audience . Here, you’ll identify who the audience or intended audience is.
- Purpose . With the purpose, you’ll need to identify the reason behind the text or what the author wants to achieve with their writing.
- Subject . You’ll also need to identify the subject matter or topic of the text.
- Tone . The tone identifies the author’s feelings towards the subject matter or topic.
Apart from gathering the information and analyzing the components mentioned above, you’ll also need to examine the appeals the author uses in writing the text and attempting to persuade the audience of their argument. Moreover, you’ll need to identify elements like word choice, word order, repetition, analogies, and imagery the writer uses to get a reaction from the audience.
Once you’ve gathered the information and examined the appeals and strategies used by the author as mentioned above, you’ll need to answer some questions relating to the information you’ve collected from the text. The answers to these questions will help you determine the reasons for the choices the author made and how well these choices support the overall argument.
Here, some of the questions you’ll ask include:
- What was the author’s intention?
- Who was the intended audience?
- What is the author’s argument?
- What strategies does the author use to build their argument and why do they use those strategies?
- What appeals the author uses to convince and persuade the audience?
- What effect the text has on the audience?
Keep in mind that these are just some of the questions you’ll ask, and depending on the specific text, there might be others.
Once you’ve done your preparation, you can start writing the rhetorical analysis. It will start off with an introduction which is a clear and concise paragraph that shows you understand the purpose of the text and gives more information about the author and the relevance of the text.
The introduction also summarizes the text and the main ideas you’ll discuss in your analysis. Most importantly, however, is your thesis statement . This statement should be one sentence at the end of the introduction that summarizes your argument and tempts your audience to read on and find out more about it.
After your introduction, you can proceed with the body of your analysis. Here, you’ll write at least three paragraphs that explain the strategies and techniques used by the author to convince and persuade the audience, the reasons why the writer used this approach, and why it’s either successful or unsuccessful.
You can structure the body of your analysis in several ways. For example, you can deal with every strategy the author uses in a new paragraph, but you can also structure the body around the specific appeals the author used or chronologically.
No matter how you structure the body and your paragraphs, it’s important to remember that you support each one of your arguments with facts, data, examples, or quotes and that, at the end of every paragraph, you tie the topic back to your original thesis.
Finally, you’ll write the conclusion of your rhetorical analysis. Here, you’ll repeat your thesis statement and summarize the points you’ve made in the body of your analysis. Ultimately, the goal of the conclusion is to pull the points of your analysis together so you should be careful to not raise any new issues in your conclusion.
After you’ve finished your conclusion, you’ll end your analysis with a powerful concluding statement of why your argument matters and an invitation to conduct more research if needed.
A rhetorical analysis aims to explore the goals and motivations of an author, the techniques they’ve used to reach their audience, and how successful these techniques were. Although rhetorical analysis is most used by academics as part of scholarly work, it can be used to analyze any text including speeches, novels, television shows or films, advertisements, or cartoons.
The steps to write a rhetorical analysis include:
Your rhetorical analysis introduction is a clear and concise paragraph that shows you understand the purpose of the text and gives more information about the author and the relevance of the text. The introduction also summarizes the text and the main ideas you’ll discuss in your analysis.
Ethos represents the authority or credibility of the author. To be successful, the author needs to convince the audience of their authority or credibility through the language and delivery techniques they use. This will, for example, be the case where an author writing on a technical subject positions themselves as an expert or authority by referring to their qualifications or experience.
Appeals are used by authors to convince their audience and, as such, are an integral part of the rhetoric and are often referred to as the rhetorical triangle. The 3 types of appeals are ethos, logos, and pathos.

How to Write the AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay (With Example)
November 27, 2023

Feeling intimidated by the AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay? We’re here to help demystify. Whether you’re cramming for the AP Lang exam right now or planning to take the test down the road, we’ve got crucial rubric information, helpful tips, and an essay example to prepare you for the big day. This post will cover 1) What is the AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay? 2) AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Rubric 3) AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis: Sample Prompt 4) AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example 5)AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example: Why It Works
What is the AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay?
The AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay is one of three essays included in the written portion of the AP English Exam. The full AP English Exam is 3 hours and 15 minutes long, with the first 60 minutes dedicated to multiple-choice questions. Once you complete the multiple-choice section, you move on to three equally weighted essays that ask you to synthesize, analyze, and interpret texts and develop well-reasoned arguments. The three essays include:
Synthesis essay: You’ll review various pieces of evidence and then write an essay that synthesizes (aka combines and interprets) the evidence and presents a clear argument. Read our write up on How to Write the AP Lang Synthesis Essay here.
Argumentative essay: You’ll take a stance on a specific topic and argue your case.
Rhetorical essay: You’ll read a provided passage, then analyze the author’s rhetorical choices and develop an argument that explains why the author made those rhetorical choices.
AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Rubric
The AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay is graded on just 3 rubric categories: Thesis, Evidence and Commentary, and Sophistication . At a glance, the rubric categories may seem vague, but AP exam graders are actually looking for very particular things in each category. We’ll break it down with dos and don’ts for each rubric category:
Thesis (0-1 point)
There’s nothing nebulous when it comes to grading AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay thesis. You either have one or you don’t. Including a thesis gets you one point closer to a high score and leaving it out means you miss out on one crucial point. So, what makes a thesis that counts?
- Make sure your thesis argues something about the author’s rhetorical choices. Making an argument means taking a risk and offering your own interpretation of the provided text. This is an argument that someone else might disagree with.
- A good test to see if you have a thesis that makes an argument. In your head, add the phrase “I think that…” to the beginning of your thesis. If what follows doesn’t logically flow after that phrase (aka if what follows isn’t something you and only you think), it’s likely you’re not making an argument.
- Avoid a thesis that merely restates the prompt.
- Avoid a thesis that summarizes the text but does not make an argument.
Evidence and Commentary (0-4 points)
This rubric category is graded on a scale of 0-4 where 4 is the highest grade. Per the AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis rubric, to get a 4, you’ll want to:
- Include lots of specific evidence from the text. There is no set golden number of quotes to include, but you’ll want to make sure you’re incorporating more than a couple pieces of evidence that support your argument about the author’s rhetorical choices.
- Make sure you include more than one type of evidence, too. Let’s say you’re working on your essay and have gathered examples of alliteration to include as supporting evidence. That’s just one type of rhetorical choice, and it’s hard to make a credible argument if you’re only looking at one type of evidence. To fix that issue, reread the text again looking for patterns in word choice and syntax, meaningful figurative language and imagery, literary devices, and other rhetorical choices, looking for additional types of evidence to support your argument.
- After you include evidence, offer your own interpretation and explain how this evidence proves the point you make in your thesis.
- Don’t summarize or speak generally about the author and the text. Everything you write must be backed up with evidence.
- Don’t let quotes speak for themselves. After every piece of evidence you include, make sure to explain your interpretation. Also, connect the evidence to your overarching argument.
Sophistication (0-1 point)
In this case, sophistication isn’t about how many fancy vocabulary words or how many semicolons you use. According to College Board , one point can be awarded to AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis essays that “demonstrate sophistication of thought and/or a complex understanding of the rhetorical situation” in any of these three ways:
- Explaining the significance or relevance of the writer’s rhetorical choices.
- Explaining the purpose or function of the passage’s complexities or tensions.
- Employing a style that is consistently vivid and persuasive.
Note that you don’t have to achieve all three to earn your sophistication point. A good way to think of this rubric category is to consider it a bonus point that you can earn for going above and beyond in depth of analysis or by writing an especially persuasive, clear, and well-structured essay. In order to earn this point, you’ll need to first do a good job with your thesis, evidence, and commentary.
- Focus on nailing an argumentative thesis and multiple types of evidence. Getting these fundamentals of your essay right will set you up for achieving depth of analysis.
- Explain how each piece of evidence connects to your thesis.
- Spend a minute outlining your essay before you begin to ensure your essay flows in a clear and cohesive way.
- Steer clear of generalizations about the author or text.
- Don’t include arguments you can’t prove with evidence from the text.
- Avoid complex sentences and fancy vocabulary words unless you use them often. Long, clunky sentences with imprecisely used words are hard to follow.
AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis: Sample Prompt
The sample prompt below is published online by College Board and is a real example from the 2021 AP Exam. The prompt provides background context, essay instructions, and the text you need to analyze. For sake of space, we’ve included the text as an image you can click to read. After the prompt, we provide a sample high scoring essay and then explain why this AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis essay example works.
Suggested time—40 minutes.
(This question counts as one-third of the total essay section score.)
On February 27, 2013, while in office, former president Barack Obama delivered the following address dedicating the Rosa Parks statue in the National Statuary Hall of the United States Capitol building. Rosa Parks was an African American civil rights activist who was arrested in 1955 for refusing to give up her seat on a segregated bus in Montgomery, Alabama. Read the passage carefully. Write an essay that analyzes the rhetorical choices Obama makes to convey his message.
In your response you should do the following:
- Respond to the prompt with a thesis that analyzes the writer’s rhetorical choices.
- Select and use evidence to support your line of reasoning.
- Explain how the evidence supports your line of reasoning.
- Demonstrate an understanding of the rhetorical situation.
- Use appropriate grammar and punctuation in communicating your argument.
AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example
In his speech delivered in 2013 at the dedication of Rosa Park’s statue, President Barack Obama acknowledges everything that Parks’ activism made possible in the United States. Telling the story of Parks’ life and achievements, Obama highlights the fact that Parks was a regular person whose actions accomplished enormous change during the civil rights era. Through the use of diction that portrays Parks as quiet and demure, long lists that emphasize the extent of her impacts, and Biblical references, Obama suggests that all of us are capable of achieving greater good, just as Parks did.
Although it might be a surprising way to start to his dedication, Obama begins his speech by telling us who Parks was not: “Rosa Parks held no elected office. She possessed no fortune” he explains in lines 1-2. Later, when he tells the story of the bus driver who threatened to have Parks arrested when she refused to get off the bus, he explains that Parks “simply replied, ‘You may do that’” (lines 22-23). Right away, he establishes that Parks was a regular person who did not hold a seat of power. Her protest on the bus was not part of a larger plan, it was a simple response. By emphasizing that Parks was not powerful, wealthy, or loud spoken, he implies that Parks’ style of activism is an everyday practice that all of us can aspire to.
AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example (Continued)
Even though Obama portrays Parks as a demure person whose protest came “simply” and naturally, he shows the importance of her activism through long lists of ripple effects. When Parks challenged her arrest, Obama explains, Martin Luther King, Jr. stood with her and “so did thousands of Montgomery, Alabama commuters” (lines 27-28). They began a boycott that included “teachers and laborers, clergy and domestics, through rain and cold and sweltering heat, day after day, week after week, month after month, walking miles if they had to…” (lines 28-31). In this section of the speech, Obama’s sentences grow longer and he uses lists to show that Parks’ small action impacted and inspired many others to fight for change. Further, listing out how many days, weeks, and months the boycott lasted shows how Parks’ single act of protest sparked a much longer push for change.
To further illustrate Parks’ impact, Obama incorporates Biblical references that emphasize the importance of “that single moment on the bus” (lines 57-58). In lines 33-35, Obama explains that Parks and the other protestors are “driven by a solemn determination to affirm their God-given dignity” and he also compares their victory to the fall the “ancient walls of Jericho” (line 43). By of including these Biblical references, Obama suggests that Parks’ action on the bus did more than correct personal or political wrongs; it also corrected moral and spiritual wrongs. Although Parks had no political power or fortune, she was able to restore a moral balance in our world.
Toward the end of the speech, Obama states that change happens “not mainly through the exploits of the famous and the powerful, but through the countless acts of often anonymous courage and kindness” (lines 78-81). Through carefully chosen diction that portrays her as a quiet, regular person and through lists and Biblical references that highlight the huge impacts of her action, Obama illustrates exactly this point. He wants us to see that, just like Parks, the small and meek can change the world for the better.
AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example: Why It Works
We would give the AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis essay above a score of 6 out of 6 because it fully satisfies the essay’s 3 rubric categories: Thesis, Evidence and Commentary, and Sophistication . Let’s break down what this student did:
The thesis of this essay appears in the last line of the first paragraph:
“ Through the use of diction that portrays Parks as quiet and demure, long lists that emphasize the extent of her impacts, and Biblical references, Obama suggests that all of us are capable of achieving greater good, just as Parks did .”
This student’s thesis works because they make a clear argument about Obama’s rhetorical choices. They 1) list the rhetorical choices that will be analyzed in the rest of the essay (the italicized text above) and 2) include an argument someone else might disagree with (the bolded text above).
Evidence and Commentary:
This student includes substantial evidence and commentary. Things they do right, per the AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis rubric:
- They include lots of specific evidence from the text in the form of quotes.
- They incorporate 3 different types of evidence (diction, long lists, Biblical references).
- After including evidence, they offer an interpretation of what the evidence means and explain how the evidence contributes to their overarching argument (aka their thesis).
Sophistication
This essay achieves sophistication according to the AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis essay rubric in a few key ways:
- This student provides an introduction that flows naturally into the topic their essay will discuss. Before they get to their thesis, they tell us that Obama portrays Parks as a “regular person” setting up their main argument: Obama wants all regular people to aspire to do good in the world just as Rosa Parks did.
- They organize evidence and commentary in a clear and cohesive way. Each body paragraph focuses on just one type of evidence.
- They explain how their evidence is significant. In the final sentence of each body paragraph, they draw a connection back to the overarching argument presented in the thesis.
- All their evidence supports the argument presented in their thesis. There is no extraneous evidence or misleading detail.
- They consider nuances in the text. Rather than taking the text at face value, they consider what Obama’s rhetorical choices imply and offer their own unique interpretation of those implications.
- In their final paragraph, they come full circle, reiterate their thesis, and explain what Obama’s rhetorical choices communicate to readers.
- Their sentences are clear and easy to read. There are no grammar errors or misused words.
AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay—More Resources
Looking for more tips to help your master your AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay? Brush up on 20 Rhetorical Devices High School Students Should Know and read our Tips for Improving Reading Comprehension . If you’re ready to start studying for another part of the AP English Exam, find more expert tips in our How to Write the AP Lang Synthesis blog post.
Considering what other AP classes to take? Read up on the Hardest AP Classes .
- High School Success

Christina Wood
Christina Wood holds a BA in Literature & Writing from UC San Diego, an MFA in Creative Writing from Washington University in St. Louis, and is currently a Doctoral Candidate in English at the University of Georgia, where she teaches creative writing and first-year composition courses. Christina has published fiction and nonfiction in numerous publications, including The Paris Review , McSweeney’s , Granta , Virginia Quarterly Review , The Sewanee Review , Mississippi Review , and Puerto del Sol , among others. Her story “The Astronaut” won the 2018 Shirley Jackson Award for short fiction and received a “Distinguished Stories” mention in the 2019 Best American Short Stories anthology.
- 2-Year Colleges
- Application Strategies
- Best Colleges by Major
- Best Colleges by State
- Big Picture
- Career & Personality Assessment
- College Essay
- College Search/Knowledge
- College Success
- Costs & Financial Aid
- Dental School Admissions
- Extracurricular Activities
- Graduate School Admissions
- High Schools
- Law School Admissions
- Medical School Admissions
- Navigating the Admissions Process
- Online Learning
- Private High School Spotlight
- Summer Program Spotlight
- Summer Programs
- Test Prep Provider Spotlight

“Innovative and invaluable…use this book as your college lifeline.”
— Lynn O'Shaughnessy
Nationally Recognized College Expert
College Planning in Your Inbox
Join our information-packed monthly newsletter.
Sign Up Now
Explore your training options in 10 minutes Get Started
- Graduate Stories
- Partner Spotlights
- Bootcamp Prep
- Bootcamp Admissions
- University Bootcamps
- Coding Tools
- Software Engineering
- Web Development
- Data Science
- Tech Guides
- Tech Resources
- Career Advice
- Online Learning
- Internships
- Apprenticeships
- Tech Salaries
- Associate Degree
- Bachelor's Degree
- Master's Degree
- University Admissions
- Best Schools
- Certifications
- Bootcamp Financing
- Higher Ed Financing
- Scholarships
- Financial Aid
- Best Coding Bootcamps
- Best Online Bootcamps
- Best Web Design Bootcamps
- Best Data Science Bootcamps
- Best Technology Sales Bootcamps
- Best Data Analytics Bootcamps
- Best Cybersecurity Bootcamps
- Best Digital Marketing Bootcamps
- Los Angeles
- San Francisco
- Browse All Locations
- Digital Marketing
- Machine Learning
- See All Subjects
- Bootcamps 101
- Full-Stack Development
- Career Changes
- View all Career Discussions
- Mobile App Development
- Cybersecurity
- Product Management
- UX/UI Design
- What is a Coding Bootcamp?
- Are Coding Bootcamps Worth It?
- How to Choose a Coding Bootcamp
- Best Online Coding Bootcamps and Courses
- Best Free Bootcamps and Coding Training
- Coding Bootcamp vs. Community College
- Coding Bootcamp vs. Self-Learning
- Bootcamps vs. Certifications: Compared
- What Is a Coding Bootcamp Job Guarantee?
- How to Pay for Coding Bootcamp
- Ultimate Guide to Coding Bootcamp Loans
- Best Coding Bootcamp Scholarships and Grants
- Education Stipends for Coding Bootcamps
- Get Your Coding Bootcamp Sponsored by Your Employer
- GI Bill and Coding Bootcamps
- Tech Intevriews
- Our Enterprise Solution
- Connect With Us
- Publication
- Reskill America
- Partner With Us
- Resource Center
- Bachelor’s Degree
- Master’s Degree
How to Write a Rhetorical Analysis: Tips, Guidelines, and Rhetorical Analysis Examples
A rhetorical analysis essay is one of the different types of academic essays written for a specific audience. This essay examines the intentions and techniques of the author and promotes critical thinking.
This article explains how to write a rhetorical analysis and identifies some fundamental rhetorical principles while giving you rhetorical analysis examples to aid your writing process.
Find your bootcamp match
What is a rhetorical analysis.
In rhetorical analysis, a text is examined from the perspective of rhetoric. Therefore, the essay is less concerned with what the author says and more concerned with how they say it. It focuses on their goals, strategies, and audience appeals.
A rhetorical analysis follows the same format as other essays, including an introduction that states the thesis, a body that analyzes the text in detail, and a conclusion that summarizes the main points and wraps up the essay.
What Are the 4 Features of a Rhetorical Analysis?
- Rhetorical appeals. Authors use rhetorical appeals to persuade their audience in a rhetorical analysis essay. The three major rhetorical appeals are logos, also known as the logic appeal, ethos, also known as the ethical appeal, and pathos, also known as the pathetic appeal. Aristotle developed rhetorical appeals, also known as the rhetorical triangle.
- Text. Any piece of communication you are studying is known as a text. A speech, an advertisement, or a satirical image could all be examples of this type of communication. Most of the time, your analysis would include more than just language. You could also look at the text’s visual or auditive aspects.
- Context. The rhetorical analysis takes into account the author, the intended or actual audience, the time and place of the work, and the reason for its creation. Your rhetorical analysis can be strengthened by considering the context.
- Claims, supports, and warrants. There are always arguments in rhetorical analysis essays, and these arguments are based on claims, supports, and warrants. A claim is a fact or idea the author intends to convince the audience of support is the evidence used to support a claim, and the warrant is the logic or assumption supporting the claim.
How to Write a Rhetorical Analysis: Beginning and Ending
How you begin and end your entire essay will determine whether it is accepted by the audience or not. To write an effective rhetorical analysis essay, you need to pay attention to every detail. The following is a detailed description of how to begin and end a strong rhetorical essay.
How to Begin a Rhetorical Analysis
A rhetorical analysis, like any other essay, begins with an introduction. The introductory paragraph informs readers about the literature for discussion, gives significant background information, and provides your thesis statement in an objective tone.
In your paper, your argument begins with the first few words. As a result, your introduction should provide context that allows the reader to see the importance of your argument. Always begin your rhetorical analysis essay by providing factual data that leads smoothly into your argument.
How to End a Rhetorical Analysis
Your conclusion should explain your primary argument briefly. It should then apply your argument to a higher level, explaining why it is essential and what it implies in practice.
The conclusion of a rhetorical analysis summarizes the essay by demonstrating its production process through your analysis. Your conclusion may also attempt to link the text and your study of it to more significant issues.
How to Write a Rhetorical Analysis: 5 More Useful Tips

Collate Information
When writing a rhetorical analysis, ensure that you gather accurate facts using the SOAPSTone technique to identify the components of the work and arrange your analysis and essay outline.
SOAPSTone is a literary analysis acronym that stands for speaker, occasion, audience, purpose, subject, and tone. When you collate accurate information, you set the foundation for a strong essay.
Study the Appeals
A writer uses appeals, also known as persuasive strategies, to generate specific responses from their audience. The three appeals include ethos appeals, logos appeals, and pathos appeals.
The appeal to ethos involves ethical appeals, such as emphasizing one’s qualifications, that build the writer’s credibility. Logos refers to logical appeals such as evidence and statistics, which writers use to make an argument. Pathos appeals include personal and relatable data about a subject that provokes an emotional appeal in the audience.
Determine Style Choices and Details
Style choices and details are tools the writer can use to generate a specific emotion from the reader. Word choice, word order, tone, repetition, imagery, analogies, and figurative language are examples of these tools.
Build an Analysis
When building an analysis, ask yourself about the information you’ve gathered. Your responses will assist you in determining the reasons for the writer’s selections and how well they support the argument of the writer.
Consider the intended audience, the author’s intentions, the argument, the writer’s rhetorical strategy, the appeals the writer uses, and the effect the essay has on the reader.
Write the Body Text
Include at least three body paragraphs that provide evidence for your thesis when writing the body of your essay. Each paragraph should cover a new, well-defined topic. You could divide your body paragraphs based on the appeals, chronologically, and by techniques.
Each paragraph should contain facts and quotes rather than opinions, emotions, and rhetorical devices. You should also pay careful attention to grammar to ensure that your rhetorical analysis essay does not contain grammatical errors.
Rhetorical Analysis Examples to Help You Make an Effective Argument
A rhetorical analysis seeks to understand how an author communicates their message to a specific audience by studying their intentions, explaining the tactics or tools they use, and analyzing their effectiveness. Below are examples of rhetorical analysis.
Rhetorical Analysis Example 1: Visual Rhetorical Analysis Essay
An essay that uses visual rhetorical analysis examines how images and pictures convey messages and influence the audience. Visual rhetorical analysis papers are typically for commercials and so they are useful if you want to break into a field such as digital marketing .
Baker College provides a sample visual rhetorical essay to assist students in understanding its writing process. They break it down piece by piece to make learning and writing easier and more understandable.
Rhetorical Analysis Example 2: AP Language Rhetorical Analysis Essay
Writing a rhetorical analysis for an AP language and composition course can be challenging. As a result, it is critical to compose it appropriately if you want to get top grades. To write a successful and winning essay, make sure you grasp the prompt, follow the format, and use rhetorical components to form an argument.
Texas A&M provides a rhetorical analysis example guide for their students to break down the proper composition using easy-to-understand instructions.
How to Use Rhetorical Analysis Examples to Write Your Own
If you examine different examples of rhetorical analysis essays, you will be able to use different rhetorical techniques in writing your own. You will also be able to give a critical analysis of subjects and present a strong academic paper .
How to Write a Rhetorical Analysis FAQ
When writing a rhetorical analysis, you should address the goal or purpose of the essay; arguments, evidence, and strategies used, and why; examples of these arguments, evidence, and strategies, and your explanation of why they worked or did not work.
When selecting a topic for a rhetorical essay, consider one that interests you. It should also provide sufficient information for you to reference in your essay. Famous poetry, speeches, movies, art, and literature are popular topics to choose from.
To develop an argument about communication, a brief rhetorical analysis evaluates all parts of the rhetorical situation, including the audience, purpose, medium, and context in which it was made and presented.

"Career Karma entered my life when I needed it most and quickly helped me match with a bootcamp. Two months after graduating, I found my dream job that aligned with my values and goals in life!"
Venus, Software Engineer at Rockbot
The five central elements of rhetorical analysis are the text, the author, the audience, the purpose(s), and the setting.
About us: Career Karma is a platform designed to help job seekers find, research, and connect with job training programs to advance their careers. Learn about the CK publication .
What's Next?
Get matched with top bootcamps
Ask a question to our community, take our careers quiz.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
How to Write a Rhetorical Analysis: Full Guide

Have you ever been completely fascinated by a speech or ad, wondering how it managed to convince you so effectively? From powerful political speeches to catchy commercials, persuasion is all around us, shaping our thoughts and choices every day.
In this guide, we'll explain all about a rhetorical analysis essay. We'll break down the clever tricks writers and speakers use to win over their audience, like how they choose their words carefully and play with our emotions. This article will give you the tools you need to understand and analyze texts more deeply. So, let’s jump right in and start by understanding the nature of this assignment first.
What is a Rhetorical Analysis Essay
A rhetorical analysis essay is a type of essay where you examine how authors or speakers use words, phrases, and other techniques to influence or persuade their audience. This type of essay focuses on analyzing the strategies used by the writer or speaker to achieve their purpose, whether it's to inform, persuade, entertain, or provoke.
You'll dissect the text or speech into its components, looking at how each part contributes to the overall message. This might involve examining the introduction, thesis statement, body paragraphs, evidence, and conclusion.
Once you've identified the strategies used, you'll assess their effectiveness in achieving the author's or speaker's purpose. This involves considering the intended audience, context, and the impact of the communication.
As per our essay writing service , some common topics for rhetorical analysis include analyzing speeches by influential leaders, dissecting political advertisements, or examining the rhetoric used in literary works.
Do You Want to Ease Your Academic Burden?
Order a rhetorical analysis essay from our expert writers today and experience the power of top-notch academic writing.
Rhetorical Analysis Topic Ideas
Now that we've grasped the essence of a rhetorical analysis essay let's explore some potential topics you might consider for your own analysis. Here are 15 specific ideas to get you started:
- The Use of Metaphors in Barack Obama's 'Yes We Can' Speech
- Visual Rhetoric in Dove's 'Real Beauty' Advertising Campaign
- The Role of Irony in Jonathan Swift's 'A Modest Proposal'
- The Manipulation of Emotions in Coca-Cola's 'Share a Coke' Campaign
- The Repetition Technique in Winston Churchill's 'We Shall Fight on the Beaches' Speech
- The Argument Structure in Michelle Obama's Speech on Education
- The Use of Imagery in Edgar Allan Poe's 'The Raven'
- Gender Stereotypes in Old Spice's 'The Man Your Man Could Smell Like' Ad
- Satirical Elements in George Orwell's 'Animal Farm'
- The Influence of Tone in Greta Thunberg's Climate Change Speeches
- Political Symbolism in Banksy's Street Art
- Humor as Persuasion in Ellen DeGeneres' Stand-Up Comedy
- The Power of Silence in Emma Watson's UN Speech on Gender Equality
- Ethical Appeals in ASPCA's Animal Rights Advertisements
- The Cultural References in Super Bowl Commercials: A Case Study
How to Write a Rhetorical Analysis
Understanding how to start a rhetorical analysis essay involves dissecting a piece of communication to learn how it works and what effect it aims to achieve. This analytical process typically includes five paragraphs and three main parts: an introduction, three body paragraphs, and a conclusion. Below, our analytical essay writing service will explain each in more detail
.webp)
Major Rhetorical Elements
Before heading towards the analysis process, it's essential to grasp some key rhetorical concepts that will help guide your examination of the text or speech. These concepts provide a framework for understanding how authors and speakers use language to persuade and influence their audience.
Ethos, pathos logos in rhetorical analysis form the foundation of persuasive communication and are often intertwined in rhetorical strategies. Ethos refers to the credibility or authority of the speaker or author. Pathos involves appealing to the audience's emotions, while logos appeals to reason and logic.
There are also other rhetorical devices that are specific techniques or patterns of language used to convey meaning or evoke particular responses. Examples include metaphor, simile, imagery, irony, repetition, and hyperbole. Recognizing and analyzing these devices can provide insight into the author's intended message and its impact on the audience.
Tone and mood also play crucial roles in shaping the audience's perception and response to the communication. Tone refers to the author's attitude toward the subject matter, while mood describes the emotional atmosphere created by the text.
Whether you ask us - write my essay , or tackle the task yourself, familiarizing yourself with these concepts will help you analyze the text and persuade the audience more effectively.
Understanding Rhetorical Appeals
.webp)
First off, what is ethos in rhetorical analysis? Well, it revolves around establishing the credibility and authority of the speaker or author. This appeal seeks to convince the audience that the communicator is trustworthy, knowledgeable, and reliable. Ethos in rhetorical analysis can be built through various means, including:
- Professional Credentials : Demonstrating expertise in the subject matter through relevant qualifications or experience.
- Personal Character : Highlighting traits such as honesty, integrity, and sincerity to engender trust and respect.
- Association : Aligning oneself with respected individuals, institutions, or causes to enhance credibility by association.
For instance, in a health-related speech, a doctor might leverage their medical expertise and professional experience (credentials) to establish ethos. Similarly, a celebrity endorsing a product is using their fame and reputation (association) to persuade consumers.
Now, let's understand what is pathos in rhetorical analysis. Pathos involves appealing to the audience's emotions, aiming to evoke feelings such as empathy, sympathy, joy, anger, or fear. This emotional connection can be a powerful tool for persuasion, as it resonates with the audience on a personal level. Strategies for employing pathos in rhetorical analysis include:
- Vivid Imagery : Painting a vivid picture or narrative that elicits strong emotional responses from the audience.
- Anecdotes : Sharing personal stories or anecdotes that evoke empathy or sympathy and make the message more relatable.
- Language Choice : Using emotive language, sensory details, and rhetorical devices to evoke specific emotional reactions.
For example, in a charity advertisement for children in need, images of impoverished and suffering children coupled with heart-wrenching stories (anecdotes) are used to evoke feelings of compassion and a desire to help.
Lastly, what is logos in rhetorical analysis, you may ask. It appeals to reason and logic, aiming to persuade the audience through rational argumentation and evidence. This appeal relies on facts, statistics, logical reasoning, and sound arguments to convince the audience of the validity of the message. Strategies for employing logos in rhetorical analysis include:
- Factual Evidence : Providing empirical data, research findings, or expert opinions to support the argument.
- Logical Reasoning : Presenting a well-structured argument with clear premises and conclusions that logically follow one another.
- Counterarguments : Addressing potential counterarguments and refuting them with logical reasoning and evidence.
For instance, in a persuasive essay advocating for environmental conservation, the author might present scientific data on climate change (factual evidence) and use logical reasoning to explain the consequences of inaction.

Text and Context
Text analysis involves closely examining the language, structure, and rhetorical devices employed within the communication. This includes identifying key themes, rhetorical appeals, persuasive strategies, and stylistic elements used by the author or speaker to convey their message.
For example, in a political speech advocating for healthcare reform, text analysis might involve identifying the use of rhetorical appeals such as ethos (e.g., highlighting the speaker's experience in healthcare policy), pathos (e.g., sharing anecdotes of individuals struggling with medical costs), and logos (e.g., presenting statistics on healthcare affordability).
Contextual analysis involves considering the broader social, cultural, and historical factors that shape communication and influence its reception. This includes examining the audience demographics, the political and cultural climate, the historical events surrounding the communication, and any relevant societal norms or values.
For instance, when analyzing a historical speech advocating for civil rights, contextual research paper writers might involve considering the social and political context of the time, including prevailing attitudes towards race, ongoing civil rights movements, and recent legislative developments.
Claims, Supports, and Warrants
A claim is a statement or assertion that the author or speaker is advocating for or seeking to prove. Claims can take various forms, including factual claims (assertions of fact), value claims (judgments about what is good or bad), and policy claims (proposals for action). For example, in an argumentative essay about the importance of exercise, the claim might be that regular physical activity is essential for maintaining good health.
Supports are the evidence, reasoning, or examples provided to substantiate and strengthen the claims being made. Supports can take many forms, including empirical data, expert testimony, personal anecdotes, logical reasoning, and analogies. The quality and relevance of the supports provided play a critical role in the persuasiveness of the argument.
Continuing with the example of the argumentative essay about exercise, supports might include scientific studies demonstrating the health benefits of physical activity, testimonials from fitness experts, and personal stories of individuals who have experienced positive changes from incorporating exercise into their routine.
Warrants are the underlying assumptions or principles that connect the supports to the claims. They provide the reasoning or justification for why the supports are relevant and valid evidence for supporting the claims. Warrants are often implicit rather than explicit and require careful analysis to uncover. In the context of the essay on exercise, the warrant connecting the supports to the claim might be the assumption that actions that promote good health are inherently valuable and worthy of pursuit.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Outline
Whether you opt for the option to buy essay or start writing it yourself, it's important to use a clear plan to organize your thoughts well. This plan usually includes four main steps, each looking at different parts of your analysis.
Analyzing the Text
Before writing a rhetorical analysis, take the time to thoroughly analyze the text you'll be examining. This means more than just skimming through it; it requires a thorough understanding of its subtleties and complexities. Here are some questions to guide your analysis:
- How does the text try to sway its audience? What methods does it use to convince or influence them?
- Which rhetorical appeals—ethos (credibility), pathos (emotion), logos (logic)—does the author use, and how do they contribute to the overall argument?
- What specific rhetorical devices and strategies does the author employ to effectively convey their message? Are there any patterns or recurring motifs?
- How does the structure of the text contribute to its persuasive power or overall impact?
- Are there any cultural, historical, or contextual factors that influence how the text is perceived or understood?
By scrutinizing the text in this manner, you'll gain a deeper understanding of how it functions and the techniques employed by the author to achieve their desired effect.
Rhetorical Analysis Introduction
The introduction sets the stage for your analysis by providing essential context and framing the discussion. Start by introducing the text you're analyzing, including the author's name and the title of the work. Provide some background information to give context to your analysis. For example, if you're analyzing a speech, mention the occasion or event where it was delivered.
Next, summarize the main arguments or claims made by the author. Highlight the rhetorical techniques they use to persuade their audience. Are they appealing to logic, emotion, credibility, or a combination of these? Use specific examples from the text to illustrate these techniques discussed by our dissertation service .
For instance, if you're analyzing a speech on climate change, mention the speaker's expertise in environmental science to establish credibility. Summarize the key points they make about the consequences of inaction and the urgent need for change.
Finally, conclude your introduction with a clear thesis statement. This statement should encapsulate the main argument or purpose of your analysis.
Rhetorical Analysis Body Paragraph
The body paragraphs form the crux of your analysis, where you delve into the details of the text and dissect its rhetorical strategies. Each paragraph should focus on a specific aspect of the text, such as the use of ethos, pathos, logos, or specific rhetorical devices.
Utilize Aristotle's rhetorical triangle and other key concepts introduced earlier to guide your analysis. Provide quotations or examples from the text to illustrate your points and explain why the author chose certain approaches. Evaluate the effectiveness of these strategies in achieving the author's goals and persuading the audience.
For instance, if you're discussing the use of pathos in a marketing campaign, analyze the emotional appeal of the imagery or language used and consider how it resonates with the target audience.
Rhetorical Analysis Conclusion
In the conclusion, it's crucial to reinforce your main arguments and evaluate the author's effectiveness in achieving their goals, whether you're writing an MLA or APA essay format . Reflect on the overall impact of the text on both its immediate audience and society at large, underscoring the importance of your analysis.
Resist the temptation to introduce new ideas in the conclusion. Instead, draw upon the points you've already explored in the body of your essay to strengthen your analysis. Conclude with a poignant statement that resonates with your readers, encapsulating the essence of your interpretation and leaving a lasting impression. This final remark should tie together the threads of your analysis, leaving the reader with a deeper understanding of the text's rhetorical strategies and significance.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example
In this section, you'll discover two essay samples that skillfully demonstrate the application of rhetorical analysis. These examples offer insightful insights into the effective use of rhetorical techniques in writing.
5 Rhetorical Analysis Essay Tips
Here are five focused tips that will help you lay a solid foundation for your examination.
- Dissect Rhetorical Strategies : Break down the text to identify specific rhetorical devices such as metaphor, simile, or parallelism.
- Evaluate Tone and Diction : Pay attention to the author's tone and word choice. Analyze how these elements contribute to the overall mood of the text.
- Probe Ethos, Pathos, Logos : Explore how the author establishes credibility (ethos), evokes emotions (pathos), and employs logic (logos) to sway the audience.
- Contextualize Historical Significance : Consider the historical, cultural, and social backdrop against which the text was written.
- Craft a Structured Analysis : Organize your essay with a clear introduction, body paragraphs focusing on specific rhetorical elements, and a conclusion that synthesizes your findings.
Final Words
As we near the end, it's important to analyze carefully whether you're examining a speech, an advertisement, or a story. Pay attention to the smart tactics that influence our thinking. It's all about revealing how we communicate and relate to one another. Ultimately, understanding rhetoric offers a fresh perspective on the world beyond just academic success.
Looking to Take Your Academic Performance to the Next Level?
Say goodbye to stress, endless research, and sleepless nights - and hello to a brighter academic future.
What is a Rhetorical Analysis Essay?
How to structure a rhetorical analysis essay, how to write a rhetorical analysis essay, related articles.
.webp)

- Customer Reviews
- Extended Essays
- IB Internal Assessment
- Theory of Knowledge
- Literature Review
- Dissertations
- Essay Writing
- Research Writing
- Assignment Help
- Capstone Projects
- College Application
- Online Class
How to Write a Rhetorical Analysis: A Step-by-Step Guide
by Antony W
September 13, 2022

If you’re looking for a guide on how to write a rhetorical analysis the right way, this article is for you.
Journalists and reporters love to throw the word 'rhetoric' around, as in 'political rhetoric' and 'empty rhetoric. The word serves their purpose quite well because its dictionary meaning is 'the art of effective persuasive writing or speaking.'
In this case, rhetorical analysis is the study of how effectively a writer or speaker communicates and how they use various techniques and tools to accomplish it.
As a student in the arts, literature, history, and other similar disciplines, you will be called to write a rhetorical analysis essay on works, mostly nonfiction publications.
This article will take you on a step-by-step journey through the exciting world of rhetorical analysis, what form your assignment should take, and how you can ensure that your own writing passes the threshold of great rhetoric.
What Is a Rhetorical Analysis
Given that rhetoric is the study of how writers use words to influence an audience, a rhetorical analysis is a detailed breakdown of how a writer achieves his goal in a written work.
Specifically, it is an essay that breaks down such a work into parts and shows each plays a part individually and in the whole to bring about the intended effect.
Even though we refer to nonfiction works, any type of communication can be subjected to this form of analysis.
A politician's speech might be weighed based on how effectively he manages to rouse his audience. A video or piece of art might be analyzed based on how the creator managed to express their intended message.
For the sake of simplicity, let us retain the word ‘writer’ to refer to the person whose work is under rhetorical scrutiny. You can remain the student, and we will limit ourselves to purely nonfiction written work.
Most rhetorical analysis essays are a few pages long of mostly unstructured work, following the flow of ideas as you (the one analyzing) sees fit.
Just as you are analyzing how another writer is effectively communicating, you are also striving to pass on your own ideas successfully.
What a rhetorical analysis is not: it is not a summary of a published work.
You are not seeking to reword the work, not summarize the message for readers. You will not put so much emphasis on what the work has to say as in how it says it.
It is not an easy task to break down a full-length book, journal, article, or other publication into its various literary devices without first having a working strategy.
If you would prefer to have expert writers and acclaimed academicians help you complete your rhetorical analysis assignment, get in touch with the team at Help for Assessments.
Parts of a Rhetorical Analysis
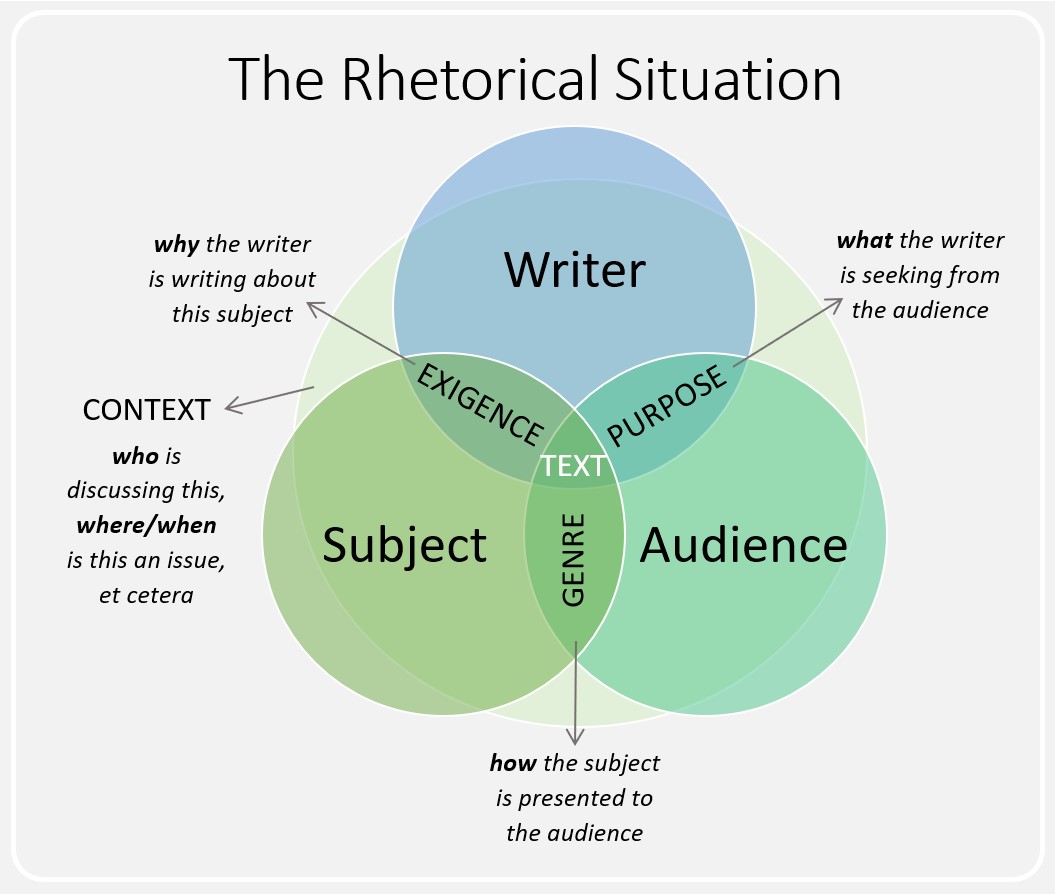
Credit: Open English SLCC
Like most other essays, a rhetorical analysis essay is made up of three parts: an introduction , body, and conclusion.
However, these will not be of much help if you have no previous experience. The logical parts of such an essay are much more useful.
1. Thesis/Claim
A rhetorical analysis essay rests on a few major arguments you make based on what your opinion regarding the work is.
Each of these arguments is part of your thesis statement and should come from your strongest claims about the work.
Your thesis statement argues the most important rhetorical features in the work. You can write one or several statements, each one expressing a major point.
Remember to make the thesis statement debatable, specific, and be ready to back it up later in the text with a lot of evidence.
You will essentially be explaining and expounding your thesis statements later in the text.
One approach is to give your whole argument upfront in the thesis statements and then explain them later in the text. This is your claim you will be talking about, not what the author claims in the text.
We can take the example of Horace Miner's article titled Body Rituals Among the Nacirema. To start with, you might summarize your argument thus:
"The article uses sociological imagination to distance the reader with what he considers an inferior culture to effectively deliver the message before he realizes that he is the subject. It also uses a didactic tone to give credibility and emphasis on his message, while infusing an objectivity that would otherwise not be present given the sensitive nature of the topic ... "
The author(s) of the text are in control of what the flow of the text is, what the reader sees, and the overall outcome of the work.
Thus, you should think about discussing the author’s motivation for writing the word, what their goal is, and what their qualifications are.
Talking about the writer establishes what is referred to as the rhetorical situation.
Answer the following questions to help you figure out what you need to mention.
- Who is the writer?
- What issue are they addressing?
- What is their purpose for creating the work? Is it to raise awareness? To critique? Defend? Is it to persuade or dissuade?
- How does the writer go about achieving this purpose? Is it satirical? Humorous?
- What figures of speech does he use?
- What effect does the chosen form have on the entire work?
For example, in the work Body Rituals Among the Nacirema, you might say about the author:
“Horace Miner uses cryptic language to conceal the fact that the culture he is actually talking about is the American one. He makes the reader assume moral superiority in judging what he considers an inferior culture, only to reveal in the end that the subject under scrutiny is himself. In the work, he seeks to address America’s obsession with cosmetic beauty at any cost, even their own health. He does this subtly by using … “
3. Audience
If writing is a performance, the reader is the audience you have to think about to make your communication effective.
The author had to think about who was going to read his work, who it was meant to influence, and what pressure points he would manipulate to deliver the message.
You can talk about how the writer's strategies influence the audience and help to bring the message home. How do his techniques appeal to the reader?
As it is, look through the writer's lens and share their angle of view to effectively dissect, describe, and critique their approach.
4. Summary of The Text
In as much as the main goal is to describe and analyze how the work puts its message across, the message itself is important for the reader to understand what you are talking about.
The essay is not meant to be abstract but rather practical and with a hands-on approach.
The summary also gives the context of the work. Use your own words to tell what you believe to be the main message of the work, taking care to remain as brief as possible.
Break the message into parts and tell what each part is conveying.
In this section, you should also use descriptive words like metaphor, analogy, common ground, metonymy, euphemism, foreshadowing, among other literary devices.
You will likely have learned these already in class, and this is a chance to prove to your instructor that you were listening.
Taking Miner’s example again, you might have a few statements such as:
The author uses common ground to place himself and the author or a superior level, thus creating engagement to help the reader identify with his message, before finally revealing that he was, in fact, analyzing himself.
This is where you back up your claims/thesis statements with arguments and facts from the text. This is done through emotional appeals, quoting or paraphrasing the text, evidence from other sources and texts, among others.
The goal is to make the appeal as solid and credible as possible.
One of the most important forms of support comes in three forms of claims called pathos, ethos, and logos.
We shall take a deeper look at each and what they entail, but for now, remember that support for the statements takes a structured form.
This support comes in the body of the essay. You will be writing it in paragraphs beginning with a strong topic sentence , then followed by a few explanatory or expository sentences.
Each paragraph will be describing one form of stylistic choice used in the text. The entire support section should flow logically and the arguments link into each other.
A rhetorical analysis isn’t usually long, a few pages at most. Most instructors will have you write about five pages or so.
As such, there is no need for sub-sections in the body. The support sets the stage for the final part; the warrant.
A warrant in rhetoric writing is the connection between the claim and the arguments made in the text.
It is usually an assumed kind of support or belief, inference, experience, or value that ties the writer to the assumption they share with the audience.
If this belief were wrong, the entire argument would be wrong and out of place.
In our example text, Miner assumes that other Americans share the same superiority complex with him and will thus assume an elevated state, a moral pedestal, as they read the article.
If this were a wrong assumption, his techniques would daily dramatically.
The Rhetorical Triangle: Ethos, Pathos, and Logos
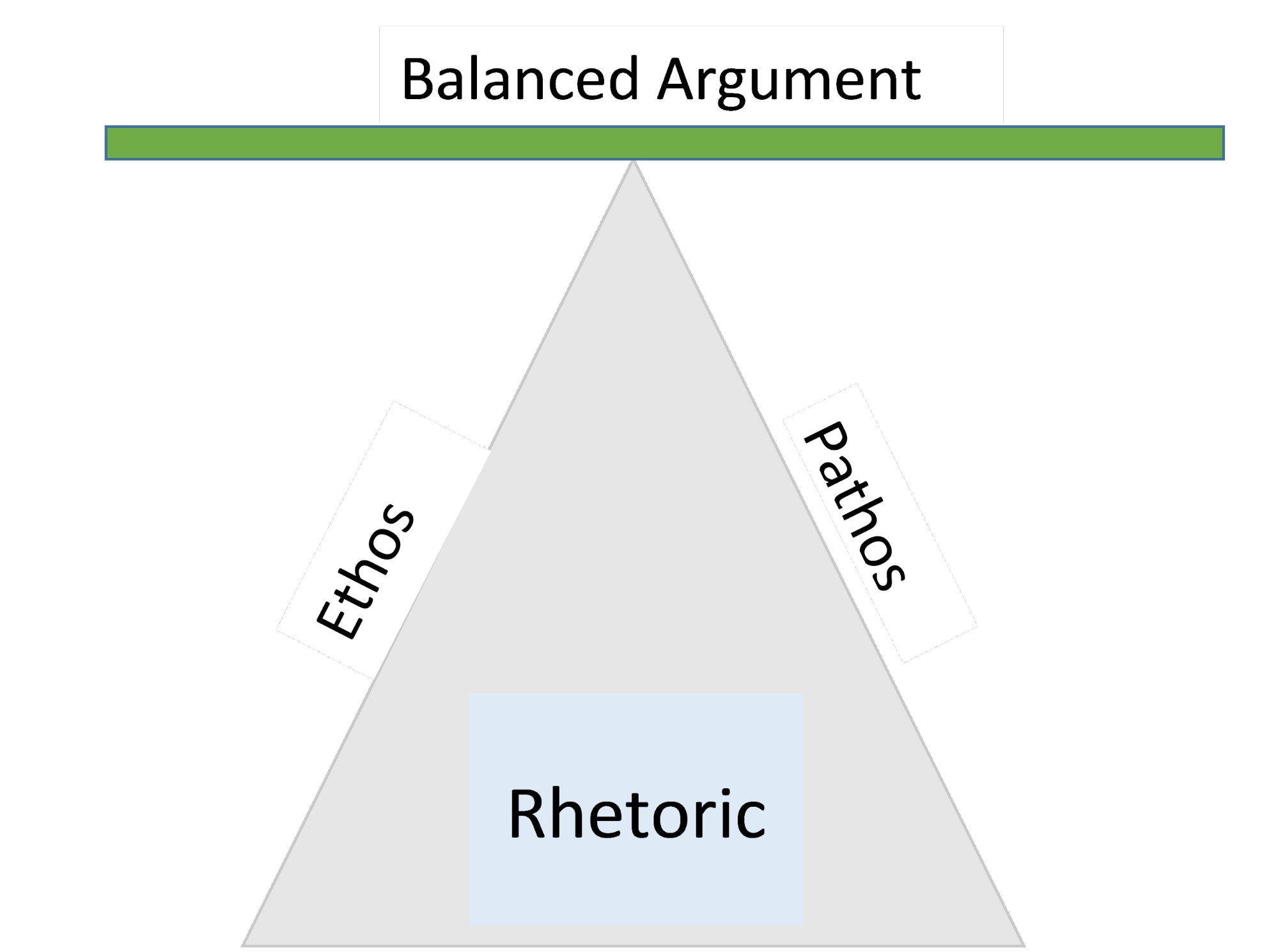
The support in a rhetorical analysis essay is dynamic and each part relies on the others to stand.
The three major parts mentioned: ethos, pathos, and logos, form a kind of rhetorical triangle where this relationship is apparent.
A final look at these three devices, also called claims, will help you craft an A-grade essay.
Ethos refers to the author’s authority or credibility as established in the essay.
Thus, an ethical appeal uses the writer’s own credibility, expertise, knowledge, or other position of higher regard compared to his audience to give importance to the work.
This position of importance can be achieved in different ways.
Some authors prefer to negotiate with the audience beforehand, others set forth their credibility with convincing arguments, while others prefer to set up a different persona in the text to assume this authoritarian position to invoke ethos.
- What can you say about the author based on the text only?
- How does the author establish credibility in the text?
- What qualifies the author to write with authority on the subject?
Pathos, as in the word pathetic, refers to an emotional appeal to the audience’s feelings.
Here, the writer would be looking to evoke pity, angler, sympathy, tenderness, sorrow, or any other emotion to elicit a reaction or achieve a goal.
Advertisements and political propaganda do this to great effect.
Pathos is also a valid appeal in academic work, but it must be backed by a lot of facts and hard evidence.
Otherwise, a work rich in pathos but lacking in either ethos or logos is empty and risks polarizing the audience or losing them completely.
As you might guess, logos is the same word used in 'logic.' it involves a practical appeal or demonstration to the mind and intellect of the audience.
Using facts, figures, and fact-based evidence, the writer seeks to draw connections that the audience is meant to see as logical arguments.
Logos is a major device used in scholarly work.
Scientific minds rely on hard evidence and logical facts to prove a point, but it would be unappealing unless it was garnished skillfully with a bit of pathos.
As the rhetorical triangle shows, the three major parts are fully co-dependent. However, a few others are also worth a mention:
Kairos means 'right time.' The most effective writers build the tempo up to the time when they can deliver the main argument.
If it were given too early or too late, it would not have the effect desired and might even be detrimental to the work.
Thus, a good writer knows how to time their acts perfectly. That is kairos in action.
Stasis means 'resting place.'
A writer may move the arguments away from his main idea in such a way that they seem to differ, but will actually rest on one firm point that seems irrefutable.
Such is the mark of a skilled writer, and this common point or foundation is what is called stasis.
Remember to include a ‘Works Cited’ section at the end of your essay.
It will be your bibliography of both the text under analysis and any other sources you have relied on during in the essay. Use an approved citation style for this section.
How to Write a Good Rhetorical Analysis Step-by-Step
Rhetorical essays are typically unstructured, at least not in the way that other assignments can be.
The way to approach them if you want to write an excellent essay is through a planned logical approach. Here is one way to go about it:
1. Pre-writing
The first part, one that you will include in the essay, is a general explanation of what you think the work is about.
Start with a broad approach and talk about the impression the work has had on you.
However, remember that you will later have to defend each of these opinions.
2. Breakdown
Pick out the major strategies or techniques that the writer uses to bring his message home.
They will be techniques you have already covered in your schoolwork, so be lookout as you are reading the work.
3. Craft Your Thesis Statement
Write down a few sentences explaining what the major strategies used in the text are.
As you do, note down the textual evidence you will use to support them.
Remember that you should also be doing this as you read through the work, preferably on a notepad for future reference.
4. Write the Draft
Make sure that you have your thesis statements put down and polished because there will be little room to change them later.
Then write as if you are trying to debate or convince your colleagues regarding the literary devices and techniques in use.
5. Edit and Proofread Your Work
Go through your work once or thrice to make sure that there is a natural flow of ideas. Of course, there should be no grammatical errors in the work.
About the author
Antony W is a professional writer and coach at Help for Assessment. He spends countless hours every day researching and writing great content filled with expert advice on how to write engaging essays, research papers, and assignments.

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

5.6: Rhetorical Analysis
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 219010
Overview of Rhetorical Analysis
A RHETORICAL ANALYSIS REFERS TO THE PROCESS OF ANALYZING A TEXT, GIVEN SOURCE OR ARTIFACT. The text, source, or artifact may be in written form or in some different sort of communication. The goal of a rhetorical analysis is to take into consideration the purpose, audience, genre, stance, and media/design of the given rhetorical situation. In other words, the analysis explores not only what everything means in the given source (content), but also why the author wrote about it (the purpose), who the author is (background), how the piece was organized (structure), where and/or when it was published (forum), and the intended message conveyed to the audience (topic).
A rhetorical analysis is one of the more challenging assignments in any writing class. Students often confuse a rhetorical analysis with a review because both assignments work to analyze a text. However, a rhetorical analysis reserves judgment on whether they agree/disagree with the topic presented. A review, of course, invites the reviewer to critique how "good" or "bad" the content of the text is. The PROCESS of completing a rhetorical analysis requires the use of different rhetorical strategies. These strategies are: critical reading, strategies for effective communication, persuasive appeals, argumentation, and avoidance of logical fallacies. These specific strategies are discussed in depth throughout the remainder of this page.
The PURPOSE of a rhetorical analysis is to engage in critical thinking with the intention of effectively communicating an intended message to a predetermined audience. In order to successfully determine the intended message of a particular text a good question to guide your analysis is: how did the author craft his/her argument?
Rhetoric is a term that is widely used in many forms, and by itself can mean a great many things. Some use the term in association with political rhetoric, to name the voice and stance, as well as the language that becomes the nature of politics. Rhetoric can be thought of as the way in which you phrase what you are saying, and the forces that impact what you are saying. At its very core RHETORIC IS THE ABILITY TO EFFECTIVELY COMMUNICATE AN INTENDED MESSAGE , whether it is via argumentation, persuasion, or another form of communication.
Critical Reading
Critical reading is the first step in a rhetorical analysis. In order to make a reasonable and logical analysis, you need to apply critical reading skills to a text, given source, or artifact that you intend on analyzing. For example, when reading, you can break the whole text down into several parts. Then, try to determine what the writer is attempting to achieve with the message they are conveying to a predetermined audience; then work to identify the writing strategies s/he is using. Once the text, artifact or given source has been thoroughly analyzed you can determine whether the intended message was effectively communicated.
Reading critically does not simply mean being moved, affected, informed, influenced, and persuaded by a piece of writing; it is much more than that. It refers to analyzing and understanding of how the writing has achieved its effect on the audience. Some specific questions can guide you in your critical reading process. You can use them in reading the text, and if asked to, you can use them in writing a formal analysis. In terms of engaging in critical reading, it is important to begin with broad questions and then work towards asking more specific questions, but in the end the purpose of engaging in critical reading is so that as an analyzer you are asking questions that work to develop the purpose of the artifact, text, or given source you are choosing to analyze.
The following is a list of suggested questions that you may find useful for when you engage in critical reading. However, you do not need to apply all of these questions to every text, artifact, or given source. Rather, you may use them selectively according to the specific reading at hand. The main questions listed below are considered to be broad in nature; with the questions listed via bullet points underneath the broad questions are meant to get at more the specific details of the intended message. Please remember that this is simply one method for getting you started on reading (and then writing) more critically.
POTENTIAL QUESTIONS TO ASK WHEN ENGAGING IN CRITICAL READING:
What is the subject?
- Does the subject bring up any personal associations? Is it a controversial one?
What is the thesis (the overall main point)?
- How does the thesis interpret the subject? If asked, could you summarize the main idea?
Who is the intended audience?
- What values and/or beliefs do they hold that the writer could appeal to?
What is the tone of the text?
- What is your reaction to the text, emotional or rational (think of pathos)? Does this reaction change at all throughout the text?
What is the writer's purpose?
- To explain? Inform? Anger? Persuade? Amuse? Motivate? Sadden? Ridicule? Attack? Defend?
- Is there more than one purpose? Does the purpose shift at all throughout the text?
What methods does the writer use to develop his/her ideas?
- Narration? Description? Definition? Comparison? Analogy? Cause and Effect? Example?
- Why does the writer use these methods? Do these methods help in his/her development of ideas?
What pattern does the author use for the arrangement of ideas?
- Particular to general, broad to specific, spatial, chronological, alternating, or block?
- Does the format enhance or detract from the content? Does it help the piece along or distract from it?
Does the writer use adequate transitions to make the text unified and coherent?
- Do you think the transitions work well? In what ways do they work well?
Are there any patterns in the sentence structure that make the writer's purpose clear to you?
- What are these patterns like if there are some? Does the writer use any fragments or run-on sentences?
Is there any dialog and/or quotations used in the text?
- To what effect? For what purpose is this dialog or quotations used?
In what way does the writer use diction?
- Is the language emotionally evocative? Does the language change throughout the piece? How does the language contribute to the writer's aim?
Is there anything unusual in the writer's use of punctuation?
- What punctuation or other techniques of emphasis (italics, capitals, underlining, ellipses, parentheses) does the writer use?
- Is punctuation over- or under-used? Which marks does the writer use where, and to what effect?
Are there any repetitions of important terms throughout the text?
- Are these repetitions effective, or do they detract from the text?
Does the writer present any particularly vivid images that stand out?
- What is the effect of these images on the writer's purpose?
Are there any tropes--similes, metaphors, personification, hyperbole, comparisons, contrasts, etc. that are employed by the writer?
- When does he/she use them? For what reason(s)? Are those devices used to convey or enhance meaning?
Are there any other devices such as humor, wordplay, irony, sarcasm, understatement, or parody that are used in the text?
- Is the effect comic relief? Pleasure? Hysteria? Ridicule?
Is there any information about the background of the writer?
- Is the writer an acceptable authority on the subject? How do you know?
Basic Rhetorical Strategies for Effective Communication
After engaging in a critical analysis or reading of your intended artifact, text, or given source, the next step in the process of completing an effective rhetorical analysis is to discuss your discoveries. For the purposes of writing, when we refer to rhetoric, we often talk about it as the art of persuasion or the ability to communicate effectively. There are many different strategies a communicator may employ to effectively communicate his/her message to his/her intended audience. While the rhetorical strategies for effective communication are discussed in terms of writing about your findings, pertaining to your rhetorical analysis, it should be noted that these rhetorical strategies can be employed during the critical analysis or reading portion of your rhetorical analysis project.
Below is a table that breaks down some rhetorical strategies, what they mean, and how to analyze them critically. This table can be used when rhetorically analyzing a text or artifact or when you begin the process of writing about your findings. The purpose of this table is to provide a breakdown of rhetorical strategies and how one can identify them in a message.
Persuasive Appeals
The persuasive appeals, or what could also be known as the rhetorical triangle, were developed by Aristotle to ensure effective communication, and are a cornerstone within the field of Rhetoric and Writing. It is common to see the three persuasive appeals depicted as the points of a triangle because like the points of triangle they each play a role in the ability to hold the message together. Aristotle was a Greek philosopher that believed all three of these rhetorical appeals were needed to effectively communicate an intended message to a pre-determined audience. Aristotle's three rhetorical appeals are: Logos, Ethos, and Pathos; they are discussed in detail throughout the remainder of this section.
Logos is most easily defined as the logical appeal of an argument. It relies on logic or reason and depends on deductive and/or inductive reasoning. Deductive reasoning begins with a generalization and then applies it to a specific case. The generalization you start with must be based on a sufficient amount of reliable evidence. Inductive reasoning takes a specific representative case, or facts, and then draws generalizations or conclusions from them. Inductive reasoning must be based on a sufficient amount of reliable evidence. In other words, the facts you draw on must fairly represent the larger situation or population. Both deductive and inductive reasoning are discussed more in depth further down on this page.
Example of Logos: Say that you are writing a paper on immigration and you say "55,000 illegal immigrants entered this country last year, of those, only 23,000 did it legally." There is obviously something wrong here. Although saying 55,000 immigrants were "illegal" makes for an impressive statistic, it is apparently not correct if you admit that 23,000 of these people immigrated legally. The actual number of illegal immigrants would then be only 32,000, a significantly lower number. The purpose of this example is to demonstrate how having logical progression to an argument is essential in effectively communicating your intended message.
Ethos is the appeal to ethics, the use of authority to persuade an audience to believe in their character. And while ethos is called an ethical appeal, be careful not to confuse it solely with ethics; it encompasses a large number of different things which can include what a person wears, says, the words they use, their tone, their credentials, their experience, their charge over the audience, verbal and nonverbal behavior, criminal records, etc. Ethos gives the author credibility. It is important to build credibility with your audience because without it, readers are less inclined to trust you or accept the argument presented to them. Using credible sources is one method of building credibility. A certain amount of ethos may be implied solely from the author's reputation, but a writer should not rely only on reputation to prop up his/her work. A sure way to damage your ethos is by attacking or insulting an opponent or opposing viewpoint. The most effective ethos should develop from what is said, whether it is in spoken or written form. The most persuasive rhetoricians are the ones that understand this concept.
Example of Ethos: To elaborate, the construction of authority is reflected in how the rhetorician presents herself, what diction she uses, how she phrases her ideas, what other authorities she refers to, how she composes herself under stress, her experience within the context of her message, her personal or academic background, and more. In academia, ethos can be constructed not only by diction, tone, phrasing, and the like, but by what the rhetorician knows. A works cited page reflects this. It says: this author has read these sources, and knows their contents. And if those sources are relevant, reputable, and well regarded, the author has just benefited from that association. At the same time, authors want to make sure they properly introduce their sources within their writing to establish the authority they are drawing from.
Pathos is the appeal to passion, the use of emotion to persuade readers’ or listeners’ opinions in a rhetorical argument. Pathetic appeals (the use of pathos) are characterized by evocative imagery, description, visuals, and the like to create within the reader or listener a sense of emotion: outrage, sorrow, excitement, etc. Pathos is often easily recognizable because audiences tend to know when what they hear or read swells emotion within their hearts and minds. Be careful to distinguish between pathos as a rhetorical vehicle to persuade using emotion and the logical fallacy “appeal to pity” (discussed more in depth further down the page). Both use emotion to make their point, but the fallacy diverts the audience from the issue to the self while the appeal emphasizes the impact of the issue.
Although argument emphasizes reason, there is usually a place for emotion as well. Emotional appeals can use sources such as interviews and individual stories to paint a moving picture of reality, or to illuminate the truth. For example, telling the story of a specific child who has been abused may make for a more persuasive argument than simply stating the number of children abused each year. The story provides the numbers with a human face. However, a writer must be careful not to employ emotional appeals which distract from the crux of the debate, argument, or point trying to be made.
Example of Pathos: A good example of pathos is in public services announcements. Some of the most popular include drug warnings: A woman is at the stove in the kitchen with a skillet. She holds up an egg and says, “This is your brain.” She cracks the egg into the skillet where it immediately begins to cook. “This is your brain on drugs.” Or the more recent billboards cautioning against (meth)amphetamines which show an attractive young person juxtaposed against a mug-shot of the same person at a later date but with pustules, open sores, missing teeth, unkempt hair, acne, running makeup, and any other assortment of detrimental and hideous signs of the drug’s ruinous capabilities. Audiences are not meant to pity these individuals; rather, the audience is meant to reel in horror at the destruction meth can cause to a person in a short amount of time. In this case, horror or shock is the emotional tool rhetoric wields to persuade. It should be noted that people with acne, unkempt hair, or other traits listed are not necessarily uncommon—in fact, these traits can be found in vast numbers of high school students; the traits are merely shown in conjunction with the normative “before” picture to elicit the desired emotion. Either of the pictures alone would not be rhetorically effective, it is only by placing them together that the audience is passionately moved.
Argumentation
DEDUCTIVE LOGICAL ARGUMENT
A deductive logical argument is one that works from the top to the bottom. It begins with what is known as a "major premise," adds a "minor premise," and attempts to reach a conclusion. A major premise is a statement that names something about a large group, a minor premise takes a single member, and the conclusion attempts to prove that because this single member is a part of the larger group, they must also have the trait named in the original statement. For example:
Now, if it is true that men are tall, and that Bob is a man, then we can safely infer that Bob must be tall. However, beware the logical fallacy. Though it may be true that in certain cultures men are, on average, taller than women, certainly this is not always the case. Being that our major premise is not altogether true, we can now say that this argument is flawed. Furthermore, we might ask what our definition of "tall" is. Tall is different if we are talking about the average population, or basketball players. Also, what is a man? Do transgendered individuals count? We see that the problem becomes far more complex the more we look into it.
INDUCTIVE LOGICAL ARGUMENT
As some would argue that a deductive argument works from the top down, toward a conclusion, some comment that an inductive argument works from the bottom up. This is mildly misleading. What is meant by this is that an inductive logical argument begins with a firm affirmation of truth, a conclusive statement. By getting the audience to agree with this statement, the argument moves to the next "logical" step. It proceeds in this manner until the argument has led you from one seemingly reasonable conclusion to another that you may not have originally agreed with. Take the following as an example. Move through the argument slowly, making sure you understand and agree with each step in the process (and please forgive the religious content, you'll come to see it is irrelevant anyway).
A sample inductive argument by Ben Doberstein
The human soul is inherently free. This is its very nature. We are confined to our mortal, earthly bodies, but our souls must be kept free, or the nature of the soul is entirely negated. If one chooses to believe in a soul, they can only believe that it embraces this (vague idea of ) freedom.
At conception, a child is given a soul. Some may argue that it is not until birth, but if those very same persons are pro-life, they confuse their arguments. Thus, if someone is pro-life, and believes in a soul, they must believe in the freedom of that soul, and also accept that the soul is granted upon conception.
A soul cannot die. By the same means by which it is free over the body, a soul claims immortality while the body decomposes and is ruined. To deny that a soul is immortal is again to deny the very essence of a soul. Thus, if someone is pro-life, and believes in a soul, they must believe in the freedom of that soul, the immortality of the soul, and also accept that the soul is granted upon conception.
A soul cannot be born. It is immortal and cannot die, it is not earthly, it forever exists, and cannot be born. There are tales in Greek mythology of Athena’s birth, yet she bounds from her father’s head a fully decorated woman. She was not born. She existed previously, as Milton writes the Son in Paradise Lost. If one accepts the Bible’s teachings, there can be no reincarnation, another form of birth, a rebirth. Thus, if someone is pro-life, and believes in a soul, and does not accept reincarnation, they must believe in the freedom of that soul, the immortality of the soul that is always and forever (which cannot be born and cannot die), and also accept that the soul is granted upon conception.
A soul being always an essence, and not being able to be reincarnated, can only exist outside of the body, somewhere, until the act of conception occurs. That soul must then be placed in the body that was forever intended to receive it, as it belongs nowhere else. The soul is fated to that one body. Thus, if someone is pro-life, and believes in a soul, and does not accept reincarnation, namely a practicing Catholic, they must also believe in the freedom of the soul, and in the concept of fate. Fate, however, completely opposes the idea of freedom. One cannot then believe in a soul, for it immediately enforces a belief if fate which directly negates the belief in the soul. If our actions are written in a Divine plan, we are not free to make our own choices. Every action has been scripted.
Do not worry, it must be that you were meant to read this.
Having seen this, some might say that the argument defeats Catholicism from an atheist standpoint. Others might find that it argues for the secularization of religion. Still, there are ways in which it supports Catholicism at the same time. Though the argument might seem as if it is disagreeing with the Catholic religion, and some would agree that it is, we must always be looking for the logical fallacy. Upon closer inspection, you may notice that all this argument truly does, in one reading of the text, is to explain the complexity of God through the mind of a human. Catholicism has argued since the beginning that God is impossible to fully explain using the conceptions of man. In that way, this argument only supports that conclusion. Be aware that there will be logic fallacies hidden in almost every argument. If there is more than one side to an argument, such as in religious or political debates, it is most likely because the argument is impossible to prove. Hence, there will be a logical fallacy present.
Logical Fallacies
Logical fallacies, often referred to by their Latin name “non sequitur” (which translates to “it does not follow”), are powerful tools in logic and rhetoric. When an arguer is able to identify her opponent’s fallacious positions, she can point them out and expose a weakness. She undermines her opponent’s position. Arguers comfortable with fallacies have an easier time avoiding them, thus making their positions more tenable. Missteps in logic can be confusing for students: sometimes a fallacy will be called by its Latin name, other times they will be referred to by a synonym; some are clumped together, and others are overly specific. For example: “Argument against the person” is often called an “Ad hominem” argument; a “Complex question” can be referred to as a “Loaded question”; “Appeal to the people” occasionally loses its distinction between direct and indirect (referred to only as “Bandwagon fallacy”); and “Begging the question” many times implies only its aspect of circular reasoning and not the other aspects. However, more important than agreeing on a name is the recognition of these non sequiturs. While a logician might dedicate her life to this topic, as a student you are expected only to avoid fallacies in your own writing and identify them in others’.
The following is a fairly comprehensive table of fallacies, and its purpose if for you to use a reference to ensure that you do not create a logical fallacy as your are writing about your discoveries throughout your rhetorical analysis. Having said that, this table can be used for more than just the completion of a rhetorical analysis; rather this table could be used as a reference for any argument or persuasion you are attempting to effectively communicate to an intended audience.

- Writing Center
- Current Students
- Online Only Students
- Faculty & Staff
- Parents & Family
- Alumni & Friends
- Community & Business
- Student Life
- Video Introduction
- Become a Writing Assistant
- All Writers
- Graduate Students
- ELL Students
- Campus and Community
- Testimonials
- Encouraging Writing Center Use
- Incentives and Requirements
- Open Educational Resources
- How We Help
- Get to Know Us
- Conversation Partners Program
- Workshop Series
- Professors Talk Writing
- Computer Lab
- Starting a Writing Center
- A Note to Instructors
- Annotated Bibliography
- Literature Review
- Research Proposal
- Argument Essay
Rhetorical Analysis

Almost every text makes an argument. Rhetorical analysis is the process of evaluating elements of a text and determining how those elements impact the success or failure of that argument. Often rhetorical analyses address written arguments, but visual, oral, or other kinds of “texts” can also be analyzed.
Rhetorical Features—What to Analyze
Asking the right questions about how a text is constructed will help you determine the focus of your rhetorical analysis. A good rhetorical analysis does not try to address every element of a text; discuss just those aspects with the greatest [positive or negative] impact on the text’s effectiveness.
The Rhetorical Situation
Remember that no text exists in a vacuum. The rhetorical situation of a text refers to the context in which it is written and read, the audience to whom it is directed, and the purpose of the writer.
The Rhetorical Appeals
A writer makes many strategic decisions when attempting to persuade an audience. Considering the following rhetorical appeals will help you understand some of these strategies and their effect on an argument. Generally, writers should incorporate a variety of different rhetorical appeals rather than relying on only one kind.
Ethos (appeal to the writer’s credibility)
- What is the writer’s purpose (to argue, explain, teach, defend, call to action, etc.)?
- Do you trust the writer? Why?
- Is the writer an authority on the subject? What credentials does the writer have?
- Does the writer address other viewpoints?
- How does the writer’s word choice or tone affect how you view the writer?
Pathos (appeal to emotion or to an audience’s values or beliefs)
- Who is the target audience for the argument?
- How is the writer trying to make the audience feel (i.e., sad, happy, angry, guilty)?
- Is the writer making any assumptions about the background, knowledge, values, etc. of the audience?
Logos (appeal to logic)
- Is the writer’s evidence relevant to the purpose of the argument? Is the evidence current (if applicable)? Does the writer use a variety of sources to support the argument?
- What kind of evidence is used (i.e., expert testimony, statistics, proven facts)?
- Do the writer’s points build logically upon each other?
- Where in the text is the main argument stated? How does that placement affect the success of the argument?
- Does the writer’s thesis make that purpose clear?
Kairos (appeal to timeliness)
- When was the argument originally presented?
- Where was the argument originally presented?
- What circumstances may have motivated the argument?
- Does the particular time or situation in which this text is written make it more compelling or persuasive?
- What would an audience at this particular time understand about this argument?
Writing a Rhetorical Analysis Essay
No matter the kind of text you are analyzing, remember that the text’s subject matter is never the focus of a rhetorical analysis. The most common error writers make when writing rhetorical analyses is to address the topic or opinion expressed by an author instead of focusing on how that author constructs an argument.
You must read and study a text critically in order to distinguish its rhetorical elements and strategies from its content or message. By identifying and understanding how audiences are persuaded, you become more proficient at constructing your own arguments and in resisting faulty arguments made by others.
A thesis for a rhetorical analysis does not address the content of the writer’s argument. Instead, the thesis should be a statement about specific rhetorical strategies the writer uses and whether or not they make a convincing argument.
Incorrect: Smith’s editorial promotes the establishment of more green space in the Atlanta area through the planting of more trees along major roads.
This statement is summarizing the meaning and purpose of Smith’s writing rather than making an argument about how – and how effectively – Smith presents and defends his position.
Correct: Through the use of vivid description and testimony from affected citizens, Smith makes a powerful argument for establishing more green space in the Atlanta area.
Correct: Although Smith’s editorial includes vivid descriptions of the destruction of green space in the Atlanta area, his argument will not convince his readers because his claim is not backed up with factual evidence.
These statements are both focused on how Smith argues, and both make a claim about the effectiveness of his argument that can be defended throughout the paper with examples from Smith’s text.
Introduction
The introduction should name the author and the title of the work you are analyzing. Providing any relevant background information about the text and state your thesis (see above). Resist the urge to delve into the topic of the text and stay focused on the rhetorical strategies being used.
Summary of argument
Include a short summary of the argument you are analyzing so readers not familiar with the text can understand your claims and have context for the examples you provide.
The body of your essay discusses and evaluates the rhetorical strategies (elements of the rhetorical situation and rhetorical appeals – see above) that make the argument effective or not. Be certain to provide specific examples from the text for each strategy you discuss and focus on those strategies that are most important to the text you are analyzing. Your essay should follow a logical organization plan that your reader can easily follow.
Go beyond restating your thesis; comment on the effect or significance of the entire essay. Make a statement about how important rhetorical strategies are in determining the effectiveness of an argument or text.
Analyzing Visual Arguments
The same rhetorical elements and appeals used to analyze written texts also apply to visual arguments. Additionally, analyzing a visual text requires an understanding of how design elements work together to create certain persuasive effects (or not). Consider how elements such as image selection, color, use of space, graphics, layout, or typeface influence an audience’s reaction to the argument that the visual was designed to convey.
This material was developed by the KSU Writing Center and is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License . All materials created by the KSU Writing Center are free to use and can be adopted, remixed, and shared at will as long as the materials are attributed. Please keep this information on materials you adapt or adopt for attribution purposes.
Contact Info
Kennesaw Campus 1000 Chastain Road Kennesaw, GA 30144
Marietta Campus 1100 South Marietta Pkwy Marietta, GA 30060
Campus Maps
Phone 470-KSU-INFO (470-578-4636)
kennesaw.edu/info
Media Resources
Resources For
Related Links
- Financial Aid
- Degrees, Majors & Programs
- Job Opportunities
- Campus Security
- Global Education
- Sustainability
- Accessibility
470-KSU-INFO (470-578-4636)
© 2024 Kennesaw State University. All Rights Reserved.
- Privacy Statement
- Accreditation
- Emergency Information
- Reporting Hotline
- Open Records
- Human Trafficking Notice
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Organizing Your Analysis

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
This resource covers how to write a rhetorical analysis essay of primarily visual texts with a focus on demonstrating the author’s understanding of the rhetorical situation and design principles.
There is no one perfect way to organize a rhetorical analysis essay. In fact, writers should always be a bit leery of plug-in formulas that offer a perfect essay format. Remember, organization itself is not the enemy, only organization without considering the specific demands of your particular writing task. That said, here are some general tips for plotting out the overall form of your essay.
Introduction
Like any rhetorical analysis essay, an essay analyzing a visual document should quickly set the stage for what you’re doing. Try to cover the following concerns in the initial paragraphs:
- Make sure to let the reader know you’re performing a rhetorical analysis. Otherwise, they may expect you to take positions or make an evaluative argument that may not be coming.
- Clearly state what the document under consideration is and possibly give some pertinent background information about its history or development. The intro can be a good place for a quick, narrative summary of the document. The key word here is “quick, for you may be dealing with something large (for example, an entire episode of a cartoon like the Simpsons). Save more in-depth descriptions for your body paragraph analysis.
- If you’re dealing with a smaller document (like a photograph or an advertisement), and copyright allows, the introduction or first page is a good place to integrate it into your page.
- Give a basic run down of the rhetorical situation surrounding the document: the author, the audience, the purpose, the context, etc.
Thesis Statements and Focus
Many authors struggle with thesis statements or controlling ideas in regards to rhetorical analysis essays. There may be a temptation to think that merely announcing the text as a rhetorical analysis is purpose enough. However, especially depending on your essay’s length, your reader may need a more direct and clear statement of your intentions. Below are a few examples.
1. Clearly narrow the focus of what your essay will cover. Ask yourself if one or two design aspects of the document is interesting and complex enough to warrant a full analytical treatment.
The website for Amazon.com provides an excellent example of alignment and proximity to assist its visitors in navigating a potentially large and confusing amount of information.
2. Since visual documents often seek to move people towards a certain action (buying a product, attending an event, expressing a sentiment), an essay may analyze the rhetorical techniques used to accomplish this purpose. The thesis statement should reflect this goal.
The call-out flyer for the Purdue Rowing Team uses a mixture of dynamic imagery and tantalizing promises to create interest in potential, new members.
3. Rhetorical analysis can also easily lead to making original arguments. Performing the analysis may lead you to an argument; or vice versa, you may start with an argument and search for proof that supports it.
A close analysis of the female body images in the July 2007 issue of Cosmopolitan magazine reveals contradictions between the articles’ calls for self-esteem and the advertisements’ unrealistic, beauty demands.
These are merely suggestions. The best measure for what your focus and thesis statement should be the document itself and the demands of your writing situation. Remember that the main thrust of your thesis statement should be on how the document creates meaning and accomplishes its purposes. The OWl has additional information on writing thesis statements.
Analysis Order (Body Paragraphs)
Depending on the genre and size of the document under analysis, there are a number of logical ways to organize your body paragraphs. Below are a few possible options. Which ever you choose, the goal of your body paragraphs is to present parts of the document, give an extended analysis of how that part functions, and suggest how the part ties into a larger point (your thesis statement or goal).
Chronological
This is the most straight-forward approach, but it can also be effective if done for a reason (as opposed to not being able to think of another way). For example, if you are analyzing a photo essay on the web or in a booklet, a chronological treatment allows you to present your insights in the same order that a viewer of the document experiences those images. It is likely that the images have been put in that order and juxtaposed for a reason, so this line of analysis can be easily integrated into the essay.
Be careful using chronological ordering when dealing with a document that contains a narrative (i.e. a television show or music video). Focusing on the chronological could easily lead you to plot summary which is not the point of a rhetorical analysis.
A spatial ordering covers the parts of a document in the order the eye is likely to scan them. This is different than chronological order, for that is dictated by pages or screens where spatial order concerns order amongst a single page or plane. There are no unwavering guidelines for this, but you can use the following general guidelines.
- Left to right and top to down is still the normal reading and scanning pattern for English-speaking countries.
- The eye will naturally look for centers. This may be the technical center of the page or the center of the largest item on the page.
- Lines are often used to provide directions and paths for the eye to follow.
- Research has shown that on web pages, the eye tends to linger in the top left quadrant before moving left to right. Only after spending a considerable amount of time on the top, visible portion of the page will they then scroll down.
Persuasive Appeals
The classic, rhetorical appeals are logos, pathos, and ethos. These concepts roughly correspond to the logic, emotion, and character of the document’s attempt to persuade. You can find more information on these concepts elsewhere on the OWL. Once you understand these devices, you could potentially order your essay by analyzing the document’s use of logos, ethos, and pathos in different sections.
The conclusion of a rhetorical analysis essay may not operate too differently from the conclusion of any other kind of essay. Still, many writers struggle with what a conclusion should or should not do. You can find tips elsewhere on the OWL on writing conclusions. In short, however, you should restate your main ideas and explain why they are important; restate your thesis; and outline further research or work you believe should be completed to further your efforts.
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Write a Rhetorical Analysis
Last Updated: April 2, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Megan Morgan, PhD . Megan Morgan is a Graduate Program Academic Advisor in the School of Public & International Affairs at the University of Georgia. She earned her PhD in English from the University of Georgia in 2015. There are 7 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 1,376,265 times.
A rhetorical analysis can be written about other texts, television shows, films, collections of artwork, or a variety of other communicative mediums that attempt to make a statement to an intended audience. In order to write a rhetorical analysis, you need to be able to determine how the creator of the original work attempts to make his or her argument. You can also include information about whether or not that argument is successful. To learn more about the right way to write a rhetorical analysis, continue reading.
Gathering Information

- The speaker refers to the first and last name of the writer. If the writer has any credentials that lend to his or her authority on the matter at hand, you should also briefly consider those. Note that if the narrator is different from the writer, though, it could also refer to the narrator.
- The occasion mostly refers to the type of text and the context under which the text was written. For instance, there is a big difference between an essay written for a scholarly conference and a letter written to an associate in the field.
- The audience is who the text was written for. This is related to the occasion, since the occasion can include details about the audience. In the example above, the audience would be a conference of scholars versus an associate in the field.
- The purpose refers to what the writer wants to accomplish in the text. It usually includes selling a product or point of view.
- The subject is simply the topic the writer discusses in the text.

- Ethos, or ethical appeals, rely on the writer's credibility and character in the garnering of approval. Mentions of a writer's character or qualifications usually qualify as ethos. For instance, if a family therapist with 20 years of practice writes an article on improving familial relations, mention of that experience would be using ethos. Despite their name, these appeals don't have anything to do with "ethics" as we usually think of them.
- Logos, or logical appeals, use reason to make an argument. Most academic discourse should make heavy use of logos. A writer who supports an argument with evidence, data, and undeniable facts uses logos.
- Pathos, or pathetic appeals, seek to evoke emotion in order to gain approval. These emotions can include anything from sympathy and anger to the desire for love. If an article about violent crime provides personal, human details about victims of violent crime, the writer is likely using pathos.

- Analogies and figurative language, including metaphors and similes, demonstrate an idea through comparison.
- Repetition of a certain point or idea is used to make that point seem more memorable.
- Imagery often affects pathos. The image of a starving child in a low income country can be a powerful way of evoking compassion or anger.
- Diction refers to word choice. Emotionally-charged words have greater impact, and rhythmic word patterns can establish a theme more effectively.
- Tone essentially means mood or attitude. A sarcastic essay is vastly different from a scientific one, but depending on the situation, either tone could be effective.
- Addressing the opposition demonstrates that the writer is not afraid of the opposing viewpoint. It also allows the writer to strengthen his or her own argument by cutting down the opposing one. This is especially powerful when the author contrasts a strong viewpoint he or she holds with a weak viewpoint on the opposing side.

- Ask yourself how the rhetorical strategies of appeals and style help the author achieve his or her purpose. Determine if any of these strategies fail and hurt the author instead of helping.
- Speculate on why the author may have chosen those rhetorical strategies for that audience and that occasion. Determine if the choice of strategies may have differed for a different audience or occasion.
- Remember that in a rhetorical analysis, you do not need to agree with the argument being presented. Your task is to analyze how well the author uses the appeals to present her or his argument.
Writing the Introduction

- By letting the reader know that your paper is a rhetorical analysis, you let him or her know exactly what to expect. If you do not let the reader know this information beforehand, he or she may expect to read an evaluative argument instead.
- Do not simply state, "This paper is a rhetorical analysis." Weave the information into the introduction as naturally as possible.
- Note that this may not be necessary if you are writing a rhetorical analysis for an assignment that specifically calls for a rhetorical analysis.

- The introduction is a good place to give a quick summary of the document. Keep it quick, though. Save the majority of the details for your body paragraphs, since most of the details will be used in defending your analysis.

- You do not necessarily need to mention these details in this order. Include the details in a matter that makes sense and flows naturally within your introductory paragraph.

- Try stating which rhetorical techniques the writer uses in order to move people toward his or her desired purpose. Analyze how well these techniques accomplish this goal.
- Consider narrowing the focus of your essay. Choose one or two design aspects that are complex enough to spend an entire essay analyzing.
- Think about making an original argument. If your analysis leads you to make a certain argument about the text, focus your thesis and essay around that argument and provide support for it throughout the body of your paper.
- Try to focus on using words such as "effective" or "ineffective" when composing your thesis, rather than "good" or "bad." You want to avoid seeming like you are passing value judgments.
Writing the Body

- The order of logos, ethos, and pathos is not necessarily set in stone. If you intend to focus on one more than the other two, you could briefly cover the two lesser appeals in the first two sections before elaborating on the third in greater detail toward the middle and end of the paper.
- For logos, identify at least one major claim and evaluate the document's use of objective evidence.
- For ethos, analyze how the writer or speaker uses his or her status as an "expert" to enhance credibility.
- For pathos, analyze any details that alter the way that the viewer or reader may feel about the subject at hand. Also analyze any imagery used to appeal to aesthetic senses, and determine how effective these elements are.
- Wrap things up by discussing the consequences and overall impact of these three appeals.

- Start from the beginning of the document and work your way through to the end. Present details about the document and your analysis of those details in the order the original document presents them in.
- The writer of the original document likely organized the information carefully and purposefully. By addressing the document in this order, your analysis is more likely to make more coherent sense by the end of your paper.

- Evidence often include a great deal of direct quotation and paraphrasing.
- Point to spots in which the author mentioned his or her credentials to explain ethos. Identify emotional images or words with strong emotional connotations as ways of supporting claims to pathos. Mention specific data and facts used in analysis involving logos.

- Avoid use of the first-person words "I" and "we." Stick to the more objective third-person.
Writing the Conclusion

- When restating your thesis, you should be able to quickly analyze how the original author's purpose comes together.
- When restating your thesis, try to bring more sophistication or depth to it than you had in the beginning. What can the audience now understand about your thesis that they would not have without reading your analysis?

- Keep this information brief. You spent an entire essay supporting your thesis, so these restatements of your main ideas should only serve as summaries of your support.

- Indicate what that research must entail and how it would help.
- Also state why the subject matter is important enough to continue researching and how it has significance to the real world.
Writing Help

Community Q&A
- Avoid the use of "In conclusion..." While many writers may be taught to end conclusion paragraphs with this phrase as they first learn to write essays, you should never include this phrase in an essay written at a higher academic level. This phrase and the information that usually follows it is empty information that only serves to clutter up your final paragraph. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- Do not introduce any new information in your conclusion. Summarize the important details of the essay. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- Do not argue in an analysis. Focus on the "how" they made their point, not if it's good or not. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/academic_writing/establishing_arguments/rhetorical_strategies.html
- ↑ https://writingcenter.tamu.edu/Students/Writing-Speaking-Guides/Alphabetical-List-of-Guides/Academic-Writing/Analysis/Rhetorical-Analysis
- ↑ https://courses.lumenlearning.com/englishcomp1/chapter/text-an-overview-of-the-rhetorical-modes/
- ↑ https://oer.pressbooks.pub/informedarguments/chapter/rhetorical-modes-of-writing/
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/visual_rhetoric/analyzing_visual_documents/organizing_your_analysis.html
- ↑ https://www.pfw.edu/offices/learning-support/documents/WriteARhetoricalAnalysis.pdf
About This Article

To write a rhetorical analysis, start by determining what the author of the work you're analyzing is trying to argue. Then, ask yourself if they succeeded in making their argument. Whether you think they did or didn't, include quotes and specific examples in your analysis to back up your opinion. When you're writing your analysis, use the third-person to appear objective as opposed to using "I" or "we." Also, make sure you include the author's name, profession, and purpose for writing the text at the beginning of your analysis to give reader's some context. To learn different ways to structure your rhetorical analysis from our English Ph.D. co-author, keep reading! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Dec 15, 2016
Did this article help you?
Theophilus Ndubisi Chukwu
Aug 13, 2016
Pamela Austin
Sep 28, 2017
John Cornelius
Jul 13, 2016
McKenzie Jameson
Oct 18, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter
Rhetorical Analysis Definition and Examples
The analysis can be used on any communication, even a bumper sticker
- An Introduction to Punctuation
Sample Rhetorical Analyses
Examples and observations, analyzing effects, analyzing greeting card verse, analyzing starbucks, rhetorical analysis vs. literary criticism.
- Ph.D., Rhetoric and English, University of Georgia
- M.A., Modern English and American Literature, University of Leicester
- B.A., English, State University of New York
Rhetorical analysis is a form of criticism or close reading that employs the principles of rhetoric to examine the interactions between a text, an author, and an audience . It's also called rhetorical criticism or pragmatic criticism.
Rhetorical analysis may be applied to virtually any text or image—a speech , an essay , an advertisement, a poem, a photograph, a web page, even a bumper sticker. When applied to a literary work, rhetorical analysis regards the work not as an aesthetic object but as an artistically structured instrument for communication. As Edward P.J. Corbett has observed, rhetorical analysis "is more interested in a literary work for what it does than for what it is."
- A Rhetorical Analysis of Claude McKay's "Africa"
- A Rhetorical Analysis of E.B. White's "The Ring of Time"
- A Rhetorical Analysis of U2's "Sunday Bloody Sunday"
- "Our response to the character of the author—whether it is called ethos, or 'implied author,' or style , or even tone—is part of our experience of his work, an experience of the voice within the masks, personae , of the work...Rhetorical criticism intensifies our sense of the dynamic relationships between the author as a real person and the more or less fictive person implied by the work." (Thomas O. Sloan, "Restoration of Rhetoric to Literary Study." The Speech Teacher )
- "[R]hetorical criticism is a mode of analysis that focuses on the text itself. In that respect, it is like the practical criticism that the New Critics and the Chicago School indulge in. It is unlike these modes of criticism in that it does not remain inside the literary work but works outward from the text to considerations of the author and the audience...In talking about the ethical appeal in his 'Rhetoric,' Aristotle made the point that although a speaker may come before an audience with a certain antecedent reputation, his ethical appeal is exerted primarily by what he says in that particular speech before that particular audience. Likewise, in rhetorical criticism, we gain our impression of the author from what we can glean from the text itself—from looking at such things as his ideas and attitudes, his stance, his tone, his style. This reading back to the author is not the same sort of thing as the attempt to reconstruct the biography of a writer from his literary work. Rhetorical criticism seeks simply to ascertain the particular posture or image that the author is establishing in this particular work in order to produce a particular effect on a particular audience." (Edward P.J. Corbett, "Introduction" to " Rhetorical Analyses of Literary Works ")
"[A] complete rhetorical analysis requires the researcher to move beyond identifying and labeling in that creating an inventory of the parts of a text represents only the starting point of the analyst's work. From the earliest examples of rhetorical analysis to the present, this analytical work has involved the analyst in interpreting the meaning of these textual components—both in isolation and in combination—for the person (or people) experiencing the text. This highly interpretive aspect of rhetorical analysis requires the analyst to address the effects of the different identified textual elements on the perception of the person experiencing the text. So, for example, the analyst might say that the presence of feature x will condition the reception of the text in a particular way. Most texts, of course, include multiple features, so this analytical work involves addressing the cumulative effects of the selected combination of features in the text." (Mark Zachry, "Rhetorical Analysis" from " The Handbook of Business Discourse , " Francesca Bargiela-Chiappini, editor)
"Perhaps the most pervasive type of repeated-word sentence used in greeting card verse is the sentence in which a word or group of words is repeated anywhere within the sentence, as in the following example:
In quiet and thoughtful ways , in happy and fun ways , all ways , and always , I love you.
In this sentence, the word ways is repeated at the end of two successive phrases, picked up again at the beginning of the next phrase, and then repeated as part of the word always . Similarly, the root word all initially appears in the phrase 'all ways' and is then repeated in a slightly different form in the homophonic word always . The movement is from the particular ('quiet and thoughtful ways,' 'happy and fun ways'), to the general ('all ways'), to the hyperbolic ('always')." (Frank D'Angelo, "The Rhetoric of Sentimental Greeting Card Verse." Rhetoric Review )
"Starbucks not just as an institution or as a set of verbal discourses or even advertising but as a material and physical site is deeply rhetorical...Starbucks weaves us directly into the cultural conditions of which it is constitutive. The color of the logo, the performative practices of ordering, making, and drinking the coffee, the conversations around the tables, and the whole host of other materialities and performances of/in Starbucks are at once the rhetorical claims and the enactment of the rhetorical action urged. In short, Starbucks draws together the tripartite relationships among place, body, and subjectivity. As a material/rhetorical place, Starbucks addresses and is the very site of a comforting and discomforting negotiation of these relationships." (Greg Dickinson, "Joe's Rhetoric: Finding Authenticity at Starbucks." Rhetoric Society Quarterly )
"What essentially are the differences between literary criticism analysis and rhetorical analysis? When a critic explicates Ezra Pound's Canto XLV , for example, and shows how Pound inveighs against usury as an offense against nature that corrupts society and the arts, the critic must point out the 'evidence'—the 'artistic proofs' of example and enthymeme [a formal syllogistic argument that is incompletely stated}—that Pound has drawn upon for his fulmination. The critic will also call attention to the 'arrangement' of the parts of that argument as a feature of the 'form' of the poem just as he may inquire into the language and syntax. Again these are matters that Aristotle assigned mainly to rhetoric...
"All critical essays dealing with the persona of a literary work are in reality studies of the 'Ethos' of the 'speaker' or 'narrator'—the voice—source of the rhythmic language which attracts and holds the kind of readers the poet desires as his audience, and the means this persona consciously or unconsciously chooses, in Kenneth Burke's term, to 'woo' that reader-audience." (Alexander Scharbach, "Rhetoric and Literary Criticism: Why Their Separation." College Composition and Communication )
- Audience Analysis in Speech and Composition
- Definition and Examples of Ethos in Classical Rhetoric
- A Rhetorical Analysis of U2's 'Sunday Bloody Sunday'
- Invented Ethos (Rhetoric)
- Rhetoric: Definitions and Observations
- What Is Phronesis?
- Feminist Literary Criticism
- An Introduction to Rhetorical Questions
- Enthymeme - Definition and Examples
- Deliberative Rhetoric
- Persuasion and Rhetorical Definition
- Use Social Media to Teach Ethos, Pathos and Logos
- Pathos in Rhetoric
- Definition and Examples of Rhetorical Stance
- Definition and Examples of Analysis in Composition
- Definition and Examples of Senders in Communication
Rhetorical Analysis Essay
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example - Free Samples
11 min read

People also read
Rhetorical Analysis Essay - A Complete Guide With Examples
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Topics – 120+ Unique Ideas
Crafting an Effective Rhetorical Analysis Essay Outline - Free Samples!
Ethos, Pathos, and Logos - Structure, Usage & Examples
Writing a rhetorical analysis essay for academics can be really demanding for students. This type of paper requires high-level analyzing abilities and professional writing skills to be drafted effectively.
As this essay persuades the audience, it is essential to know how to take a strong stance and develop a thesis.
This article will find some examples that will help you with your rhetorical analysis essay writing effortlessly.
- 1. Good Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example
- 2. Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example AP Lang 2023
- 3. Rhetorical Analysis Essay Examples for Students
- 4. Writing a Visual Rhetorical Analysis Essay with Example
- 5. Rhetorical Analysis Essay Writing Tips
Good Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example
The step-by-step writing process of a rhetorical analysis essay is far more complicated than ordinary academic essays. This essay type critically analyzes the rhetorical means used to persuade the audience and their efficiency.
The example provided below is the best rhetorical analysis essay example:
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Sample
In this essay type, the author uses rhetorical approaches such as ethos, pathos, and logos . These approaches are then studied and analyzed deeply by the essay writers to weigh their effectiveness in delivering the message.
Let’s take a look at the following example to get a better idea;
The outline and structure of a rhetorical analysis essay are important.
According to the essay outline, the essay is divided into three sections:
- Introduction
- Ethos
- Logos
A rhetorical analysis essay outline is the same as the traditional one. The different parts of the rhetorical analysis essay are written in the following way:
Rhetorical Analysis Introduction Example
The introductory paragraph of a rhetorical analysis essay is written for the following purpose:
- To provide basic background information about the chosen author and the text.
- Identify the target audience of the essay.
An introduction for a rhetorical essay is drafted by:
- Stating an opening sentence known as the hook statement. This catchy sentence is prepared to grab the audience’s attention to the paper.
- After the opening sentence, the background information of the author and the original text are provided.
For example, a rhetorical analysis essay written by Lee Jennings on“The Right Stuff” by David Suzuki. Lee started the essay by providing the introduction in the following way:
Analysis of the Example:
- Suzuki stresses the importance of high school education. He prepares his readers for a proposal to make that education as valuable as possible.
- A rhetorical analysis can show how successful Suzuki was in using logos, pathos, and ethos. He had a strong ethos because of his reputation.
- He also used pathos to appeal to parents and educators. However, his use of logos could have been more successful.
- Here Jennings stated the background information about the text and highlighted the rhetorical techniques used and their effectiveness.
Thesis Statement Example for Rhetorical Analysis Essay
A thesis statement of a rhetorical analysis essay is the writer’s stance on the original text. It is the argument that a writer holds and proves it using the evidence from the original text.
A thesis statement for a rhetorical essay is written by analyzing the following elements of the original text:
- Diction - It refers to the author’s choice of words and the tone
- Imagery - The visual descriptive language that the author used in the content.
- Simile - The comparison of things and ideas
In Jennings's analysis of “The Right Stuff,” the thesis statement was:
Example For Rhetorical Analysis Thesis Statement
Rhetorical Analysis Body Paragraph Example
In the body paragraphs of your rhetorical analysis essay, you dissect the author's work, analyze their use of rhetorical techniques, and provide evidence to support your analysis.
Let's look at an example that analyzes the use of ethos in David Suzuki's essay:
Rhetorical Analysis Conclusion Example
All the body paragraphs lead the audience towards the conclusion.
For example, the conclusion of “The Right Stuff” is written in the following way by Jennings:
In the conclusion section, Jennings summarized the major points and restated the thesis statement to prove them.
Rhetorical Essay Example For The Right Stuff by David Suzuki
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example AP Lang 2023
Writing a rhetorical analysis for the AP Language and Composition course can be challenging. So drafting it correctly is important to earn good grades.
To make your essay effective and winning, follow the tips provided by professionals below:
Step #1: Understand the Prompt
Understanding the prompt is the first thing to produce an influential rhetorical paper. It is mandatory for this academic writing to read and understand the prompt to know what the task demands from you.
Step #2: Stick to the Format
The content for the rhetorical analysis should be appropriately organized and structured. For this purpose, a proper outline is drafted.
The rhetorical analysis essay outline divides all the information into different sections, such as the introduction, body, and conclusion. The introduction should explicitly state the background information and the thesis statement.
All the body paragraphs should start with a topic sentence to convey a claim to the readers. Provide a thorough analysis of these claims in the paragraph to support your topic sentence.
Step #3: Use Rhetorical Elements to Form an Argument
Analyze the following things in the text to form an argument for your essay:
- Language (tone and words)
- Organizational structure
- Rhetorical Appeals ( ethos, pathos, and logos)
Once you have analyzed the rhetorical appeals and other devices like imagery and diction, you can form a strong thesis statement. The thesis statement will be the foundation on which your essay will be standing.
AP Language Rhetorical Essay Sample
AP Rhetorical Analysis Essay Template
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example AP Lang
AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Examples for Students
Here are a few more examples to help the students write a rhetorical analysis essay:
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example Ethos, Pathos, Logos
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example Outline
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example College
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example APA Format
Compare and Contrast Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example
Comparative Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example
How to Start Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example High School
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example APA Sample
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example Of a Song
Florence Kelley Speech Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example MLA
Writing a Visual Rhetorical Analysis Essay with Example
The visual rhetorical analysis essay determines how pictures and images communicate messages and persuade the audience.
Usually, visual rhetorical analysis papers are written for advertisements. This is because they use strong images to convince the audience to behave in a certain way.
To draft a perfect visual rhetorical analysis essay, follow the tips below:
- Analyze the advertisement deeply and note every minor detail.
- Notice objects and colors used in the image to gather every detail.
- Determine the importance of the colors and objects and analyze why the advertiser chose the particular picture.
- See what you feel about the image.
- Consider the objective of the image. Identify the message that the image is portraying.
- Identify the targeted audience and how they respond to the picture.
An example is provided below to give students a better idea of the concept.
Simplicity Breeds Clarity Visual Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Writing Tips
Follow the tips provided below to make your rhetorical writing compelling.
- Choose an engaging topic for your essay. The rhetorical analysis essay topic should be engaging to grab the reader’s attention.
- Thoroughly read the original text.
- Identify the SOAPSTone. From the text, determine the speaker, occasions, audience, purpose, subject, and tone.
- Develop a thesis statement to state your claim over the text.
- Draft a rhetorical analysis essay outline.
- Write an engaging essay introduction by giving a hook statement and background information. At the end of the introductory paragraph, state the thesis statement.
- The body paragraphs of the rhetorical essay should have a topic sentence. Also, in the paragraph, a thorough analysis should be presented.
- For writing a satisfactory rhetorical essay conclusion, restate the thesis statement and summarize the main points.
- Proofread your essay to check for mistakes in the content. Make your edits before submitting the draft.
Following the tips and the essay's correct writing procedure will guarantee success in your academics.
We have given you plenty of examples of a rhetorical analysis essay. But if you are still struggling to draft a great rhetorical analysis essay, it is suggested to take a professional’s help.
MyPerfectWords.com can assist you with all your academic assignments. The top essay writer service that we provide is reliable. If you are confused about your writing assignments and have difficulty meeting the deadline, get help from the legal essay writing service .
Hire our analytical essay writing service today at the most reasonable prices.

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Nova Allison is a Digital Content Strategist with over eight years of experience. Nova has also worked as a technical and scientific writer. She is majorly involved in developing and reviewing online content plans that engage and resonate with audiences. Nova has a passion for writing that engages and informs her readers.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading

Table of Contents
Collaboration, information literacy, writing process, breaking down an image.
- CC BY-NC-ND 4.0 by Jenna Pack Sheffield

We come across many images on a daily basis, but we rarely stop to think about what those images mean or about how they persuade us. Yet, images have power, which is why we need to understand how to analyze them. When you’re analyzing an image to understand the message it portrays, this is called visual rhetoric . Visual rhetoric is a means of communication that uses images to create meaning or to make an argument .
The first thing to consider when breaking down, or analyzing, an image is the rhetorical situation : the audience , context , and purpose .
Each of these elements is essential in order to understand the message an image portrays. It is important to remember that you can analyze all different types of images, including advertisements, Public Service Announcements (PSAs), websites, paintings, photographs, and more. Here, we will look at an advertisement:
Belviso, Luciano, “Day 34” June 11, 2011 via Flickr. Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY 2.0)
The audience consists of who is being targeted by the author, designer, or creator. In the above image, it appears that the audience is men. How do we know this? Not only is the person running in the background a man, but the color of the watch and the size of the watch face indicate that the watch is likely a man’s watch. Of course, women could indirectly be an audience, too, since they might want to buy this watch for someone or wear it themselves. In addition, the audience might be male athletes or outdoor enthusiasts . If you pay close attention to the watch features, it includes North, South, East, and West orientations; it is digital with various modes that likely include a stopwatch, and it has a light for when it is dark. All of these features are likely to appeal to outdoors types, athletes, or both.
The context includes any background information that will help you understand and analyze an image. In the above image, the most important context is that the watch is a Pro Trek watch. If you did some research, you would find out that Pro Trek watches are part of Casio, an electronics manufacturing company. Knowing that Casio is an electronics company, we might assume that they value functionality over aesthetics; therefore, this might be the reason why the above watch is not very decorative or complex, but is still the focal point of the image. This is because Casio wants to feature the watch’s functionality.
Purpose refers to the overall goal for creating an image. With advertisements, that goal is fairly easy to understand. Advertisements are almost always made to sell items. In our example image, the purpose is to sell the Pro Trek watch.
There are many other strategies to consider when breaking down an image. It’s always important to consider the rhetorical situation first, since that will help you interpret the purpose of the other strategies the designer uses. Then, you can begin to interpret the other persuasive techniques that influence the overall message of the image, including the tone, arrangement, text, typography, and color.
In literature, tone refers to the author’s attitude toward the subject. So, with regard to images, tone can also refer to the photographer/artist’s/designer’s perspective on the issue. In our image above, the tone is a bit hard to interpret. However, the fact that the watch is focused and up close while the background image of a person is blurred gives us a clue: it seems that the designer is portraying that the wearer of the watch is not that important. The watch is what’s significant. Perhaps the message is that anyone can wear these watches. Whether or not this is an effective approach to selling the watch is up for debate!
Arrangement
Arrangement refers to the placement of images, graphics, and text in an image. There are two key elements of arrangement—location and scale. Location refers to where a text or image is placed, whereas scale refers to the relative size of the visual components.
Typically, our eyes scan an image, text, and/or webpage from left to right and from top to bottom. The designer of this advertisement has placed the Pro Trek logo and the image of the watch to the right side of the page—top and bottom, respectively. If the designer wanted our eyes to go to the logo first, he or she probably should have placed the logo at the top left corner so our eyes would catch that logo first. However, because the size of the watch is so large, it is obvious that the focus is the watch. This brings us to the term scale.
As discussed, image of the watch is both large and focused (compared to the blurred image of the man). Thus, the scale of the watch (its size in relation to everything else on the page), along with the sharp focus, indicates that the designer wants to viewer to focus on the watch, ensuring that viewers can see all the neat features this watch has to offer, while not getting distracted by other text or images.
Text is another important element to analyze, assuming an image includes text. If it does, the text is obviously there for a purpose. Now, the only text on this advertisement is the company logo. This is obviously there for the purpose of showing viewers what type of watch it is so they can find it online or in a store. However, it is possible that this image could have been more effective if it included a catch phrase like those we often see in print ads or in commercials (think of Skittles’ “Taste the Rainbow” or Subway’s “Eat Fresh” slogans). If you see an image with text, consider the connotations of the words, the possible underlying assumptions of the phrase, and the effect the words are meant to have on the audience.
Typography refers to the font size and font type choices that are made in a visual composition.
Notice that the font size of Pro Trek is actually smaller than the time indicated on the watch! This seems to actually reduce the importance of the company as compared to the importance of the watch itself. Do you think this is an effective visual strategy to persuade the audience to buy a Pro Trek watch?
The font type we see with the words Pro Trek is strong, bolded, and in ALL CAPS. Since this advertisement is for a men’s athletic watch, the STRONG, SERIOUS FONT TYPE is probably more effective than a silly or playful font type .
Color choices can really affect your audience, too. Colors can have different meanings ( connotations ) that implicitly portray a message. Colors can also enhance or detract from an image’s readability depending on the level of contrast used.
Connotation
Notice that this advertisement has red hues in the background and orange/yellow hues in the background and on the watch. The orange/yellow hues from the background tie in nicely with this same color in the watch, creating a sense of coherence that makes the design feel professional and therefore convincing. The red hues could connote warmth, raising the heart beat, getting the blood pumping, which all symbolize that the watch is effective for athletes.
Readability
You also should think about practical concerns with color, such as whether or not the text color is contrasted well enough with the background so that it is readable. For instance, THIS is more effective than THIS .
The white/black contrast of the Pro Trek logo makes it easy to read.
Ultimately, the image we have just broken down has both effective and ineffective rhetorical effects (persuasive effects). For instance, the absence of a catchy phrase might detract from its persuasiveness, or the blurred image of the man might indirectly signal that the company cares more about the watch than who its users are. On the other hand, though, the absence of text might send the message that the watch is so amazing it speaks for itself. The blurred image might simply reflect the movement of a man running, further emphasizing that this man is using the watch for athletic purposes. These decisions about the effectiveness of each strategy really depend on your individual analysis of the image. This is how you will make an argument about its effectiveness. While the above terminology will be helpful for analysis, regardless of the terminology, the most important thing to remember is this: visuals portray meaning, just as language does. If you take the time to understand the strategies used in images to create meaning, then you will become a stronger critical thinker, understanding how images are persuading you on a daily basis.

Brevity – Say More with Less

Clarity (in Speech and Writing)

Coherence – How to Achieve Coherence in Writing

Flow – How to Create Flow in Writing

Inclusivity – Inclusive Language

The Elements of Style – The DNA of Powerful Writing

Suggested Edits
- Please select the purpose of your message. * - Corrections, Typos, or Edits Technical Support/Problems using the site Advertising with Writing Commons Copyright Issues I am contacting you about something else
- Your full name
- Your email address *
- Page URL needing edits *
- Email This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Featured Articles

Academic Writing – How to Write for the Academic Community

Professional Writing – How to Write for the Professional World

Authority – How to Establish Credibility in Speech & Writing

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A rhetorical analysis is a type of essay that looks at a text in terms of rhetoric. This means it is less concerned with what the author is saying than with how they say it: their goals, techniques, and appeals to the audience. A rhetorical analysis is structured similarly to other essays: an introduction presenting the thesis, a body analyzing ...
5. State your thesis. Now that you've completed your analysis of the material, try to summarize it into one clear, concise thesis statement that will form the foundation of your essay. Your thesis statement should summarize: 1) the argument or purpose of the speaker; 2) the methods the speaker uses; and 3) the effectiveness of those methods ...
A rhetorical analysis essay is a type of analytical essay that examines how an author uses language and persuasion to get their message across. It involves analyzing speeches or essays to understand how authors use strategies within the rhetorical triangle to influence their intended audience. These techniques usually involve logical appeal ...
Rhetorical appeal #2: Pathos. The purpose of Pathos-driven rhetoric is to appeal to the reader's emotions. A common example of pathos as a rhetorical means is adverts by charities that try to make you donate money to a "good cause". To evoke the intended emotions in the reader, an author may use passionate language, tell personal stories ...
Like all other essays, your rhetorical analysis essay will have an introduction with a thesis, body paragraphs, and a conclusion. WRITE - write your essay. Asher AP ELAC Name: _____ Step 3: Organizing and Writing Your Essay: Some of this is redundant, but this breaks down some of the steps from MAD TO WRITE even further. ...
Name the author of the text and the title of their work followed by the date in parentheses. Use a verb to describe what the author does, e.g. "implies," "asserts," or "claims". Briefly summarize the text in your own words. Mention the persuasive techniques used by the rhetor and its effect.
Follow this step-by-step guide to write your own effective rhetorical analysis essay. 1. Choose and study a text. Review the work you're analyzing more than once to become as familiar as possible with the author's argument and writing style. Make sure you have read the text thoroughly, and that you fully understand each point that the ...
To write a rhetorical analysis, you need to follow the steps below: Step 1: Plan and prepare. With a rhetorical analysis, you don't choose concepts in advance and apply them to a specific text or piece of content. Rather, you'll have to analyze the text to identify the separate components and plan and prepare your analysis accordingly.
Her story "The Astronaut" won the 2018 Shirley Jackson Award for short fiction and received a "Distinguished Stories" mention in the 2019 Best American Short Stories anthology. How to write the AP Lang rhetorical analysis essay. We look at a AP lang rhetorical analysis essay example and explore do's and don'ts.
A rhetorical analysis, like any other essay, begins with an introduction. The introductory paragraph informs readers about the literature for discussion, gives significant background information, and provides your thesis statement in an objective tone. In your paper, your argument begins with the first few words.
A rhetorical analysis essay is a type of essay where you examine how authors or speakers use words, phrases, and other techniques to influence or persuade their audience. This type of essay focuses on analyzing the strategies used by the writer or speaker to achieve their purpose, whether it's to inform, persuade, entertain, or provoke. ...
Understand there are two voices in a rhetorical analysis: the author's and your own. Some ways to differentiate are by saying, "The author states," "The author thinks," or "The article states." Then, follow up with your own analysis, but avoid "I" phrases. Part 2: Writing 1. Write your introduction.
Given that rhetoric is the study of how writers use words to influence an audience, a rhetorical analysis is a detailed breakdown of how a writer achieves his goal in a written work. Specifically, it is an essay that breaks down such a work into parts and shows each plays a part individually and in the whole to bring about the intended effect.
Rhetorical Analysis. Rhetoric is the study of how writers and speakers use words to influence an audience. A rhetorical analysis is an essay that breaks a work of non-fiction into parts and then explains how the parts work together to create a certain effect—whether to persuade, entertain or inform. You can also conduct a rhetorical analysis ...
A rhetorical analysis is one of the more challenging assignments in any writing class. Students often confuse a rhetorical analysis with a review because both assignments work to analyze a text. However, a rhetorical analysis reserves judgment on whether they agree/disagree with the topic presented. A review, of course, invites the reviewer to ...
Almost every text makes an argument. Rhetorical analysis is the process of evaluating elements of a text and determining how those elements impact the success or failure of that argument. Often rhetorical analyses address written arguments, but visual, oral, or other kinds of "texts" can also be analyzed.
How Do I Write a Rhetorical Analysis? Take the following four steps to develop content and plan your rhetorical analysis essay draft. 1. Analyze the rhetorical appeals. 2. Brainstorm your introduction. 3. Develop your body paragraphs. 4. Draw a Conclusion. From the Prompt: Questions to Think about before Writing
There may be a temptation to think that merely announcing the text as a rhetorical analysis is purpose enough. However, especially depending on your essay's length, your reader may need a more direct and clear statement of your intentions. Below are a few examples. 1. Clearly narrow the focus of what your essay will cover.
rhetorical analysis essay. Below is one way that is a good, simple format to help you get started. You may find as you become more comfortable with analysis that you want to deviate from this format. That's fine as long as you are still focusing on numbers 1-3 from above. Introduction The introductory paragraph to an analysis essay is usually ...
The purpose refers to what the writer wants to accomplish in the text. It usually includes selling a product or point of view. The subject is simply the topic the writer discusses in the text. 2. Examine the appeals. Appeals are the first classification of rhetorical strategy and involve the ethos, logos, and pathos.
Rhetorical analysis is a form of criticism or close reading that employs the principles of rhetoric to examine the interactions between a text, an author, and an audience. It's also called rhetorical criticism or pragmatic criticism. Rhetorical analysis may be applied to virtually any text or image—a speech, an essay, an advertisement, a poem ...
Step #2: Stick to the Format. The content for the rhetorical analysis should be appropriately organized and structured. For this purpose, a proper outline is drafted. The rhetorical analysis essay outline divides all the information into different sections, such as the introduction, body, and conclusion.
Visual rhetoric is a means of communication that uses images to create meaning or to make an argument. The first thing to consider when breaking down, or analyzing, an image is the rhetorical situation: the audience , context, and purpose. Each of these elements is essential in order to understand the message an image portrays.