
39 Different Ways to Say ‘In Conclusion’ in an Essay (Rated)

The phrase “In conclusion …” sounds reductive, simple and … well, just basic.
You can find better words to conclude an essay than that!
So below I’ve outlined a list of different ways to say in conclusion in an essay using a range of analysis verbs . Each one comes with an explanation of the best time to use each phrase and an example you could consider.
Read Also: How to Write a Conclusion using the 5C’s Method
List of Ways to Say ‘In Conclusion’ in an Essay
The following are the best tips I have for to say in conclusion in an essay.
1. The Weight of the Evidence Suggests…
My Rating: 10/10
Overview: This is a good concluding phrase for an evaluative essay where you need to compare two different positions on a topic then conclude by saying which one has more evidence behind it than the other.
You could also use this phrase for argumentative essays where you’ve put forward all the evidence for your particular case.
Example: “The weight of the evidence suggests that climate change is a real phenomenon.”
2. A Thoughtful Analysis would Conclude…
My Rating: 9/10
Overview: I would use this phrase in either an argumentative essay or a comparison essay. As an argument, it highlights that you think your position is the most logical.
In a comparison essay, it shows that you have (or have intended to) thoughtfully explore the issue by looking at both sides.
Example: “A thoughtful analysis would conclude that there is substantial evidence highlighting that climate change is real.”
Related Article: 17+ Great Ideas For An Essay About Yourself
3. A Balanced Assessment of the Above Information…
Overview: This phrase can be used to show that you have made a thoughtful analysis of the information you found when researching the essay. You’re telling your teacher with this phrase that you have looked at all sides of the argument before coming to your conclusion.
Example: “A balanced assessment of the above information would be that climate change exists and will have a strong impact on the world for centuries to come.”
4. Across the Board…
My Rating: 5/10
Overview: I would use this phrase in a less formal context such as in a creative discussion but would leave it out of a formal third-person essay. To me, the phrase comes across as too colloquial.
Example: “Across the board, there are scientists around the world who consistently provide evidence for human-induced climate change.”
5. Logically…
My Rating: 7/10
Overview: This phrase can be used at the beginning of any paragraph that states out a series of facts that will be backed by clear step-by-step explanations that the reader should be able to follow to a conclusion.
Example: “Logically, the rise of the automobile would speed up economic expansion in the United States. Automobiles allowed goods to flow faster around the economy.
6. After all is Said and Done…
Overview: This is a colloquial term that is more useful in a speech than written text. If you feel that the phrase ‘In conclusion,’ is too basic, then I’d also avoid this term. However, use in speech is common, so if you’re giving a speech, it may be more acceptable.
Example: “After all is said and done, it’s clear that there is more evidence to suggest that climate change is real than a hoax.”
7. All in All…
Overview: ‘All in all’ is a colloquial term that I would use in speech but not in formal academic writing. Colloquialisms can show that you have poor command of the English language. However, I would consider using this phrase in the conclusion of a debate.
Example: “All in all, our debate team has shown that there is insurmountable evidence that our side of the argument is correct.”
8. All Things Considered…
My Rating: 6/10
Overview: This term is a good way of saying ‘I have considered everything above and now my conclusion is..’ However, it is another term that’s more commonly used in speech than writing. Use it in a high school debate, but when it comes to a formal essay, I would leave it out.
Example: “All things considered, there’s no doubt in my mind that climate change is man-made.”
9. As a Final Note…
My Rating: 3/10
Overview: This phrase gives me the impression that the student doesn’t understand the point of a conclusion. It’s not to simply make a ‘final note’, but to summarize and reiterate. So, I would personally avoid this one.
Example: “As a final note, I would say that I do think the automobile was one of the greatest inventions of the 20 th Century.”
10. As Already Stated…
My Rating: 2/10
Overview: I don’t like this phrase. It gives teachers the impression that you’re going around in circles and haven’t organized your essay properly. I would particularly avoid it in the body of an essay because I always think: “If you already stated it, why are you stating it again?” Of course, the conclusion does re-state things, but it also adds value because it also summarizes them. So, add value by using a phrase such as ‘summarizing’ or ‘weighing up’ in your conclusion instead.
Example: “As already stated, I’m going to repeat myself and annoy my teacher.”
11. At present, the Best Evidence Suggests…
My Rating: 8/10
Overview: In essays where the evidence may change in the future. Most fields of study do involve some evolution over time, so this phrase acknowledges that “right now” the best evidence is one thing, but it may change in the future. It also shows that you’ve looked at the latest information on the topic.
Example: “At present, the best evidence suggests that carbon dioxide emissions from power plants is the greatest influence on climate change.”
12. At the Core of the Issue…
Overview: I personally find this phrase to be useful for most essays. It highlights that you are able to identify the most important or central point from everything you have examined. It is slightly less formal than some other phrases on this list, but I also wouldn’t consider it too colloquial for an undergraduate essay.
Example: “At the core of the issue in this essay is the fact scientists have been unable to convince the broader public of the importance of action on climate change.”
13. Despite the shortcomings of…
Overview: This phrase can be useful in an argumentative essay. It shows that there are some limitations to your argument, but , on balance you still think your position is the best. This will allow you to show critical insight and knowledge while coming to your conclusion.
Often, my students make the mistake of thinking they can only take one side in an argumentative essay. On the contrary, you should be able to highlight the limitations of your point-of-view while also stating that it’s the best.
Example: “Despite the shortcomings of globalization, this essay has found that on balance it has been good for many areas in both the developed and developing world.”
14. Finally…
My Rating: 4/10
Overview: While the phrase ‘Finally,’ does indicate that you’re coming to the end of your discussion, it is usually used at the end of a list of ideas rather than in a conclusion. It also implies that you’re adding a point rather that summing up previous points you have made.
Example: “Finally, this essay has highlighted the importance of communication between policy makers and practitioners in order to ensure good policy is put into effect.”
15. Gathering the above points together…
Overview: While this is not a phrase I personally use very often, I do believe it has the effect of indicating that you are “summing up”, which is what you want out of a conclusion.
Example: “Gathering the above points together, it is clear that the weight of evidence highlights the importance of action on climate change.”
16. Given the above information…
Overview: This phrase shows that you are considering the information in the body of the piece when coming to your conclusion. Therefore, I believe it is appropriate for starting a conclusion.
Example: “Given the above information, it is reasonable to conclude that the World Health Organization is an appropriate vehicle for achieving improved health outcomes in the developing world.”
17. In a nutshell…
Overview: This phrase means to say everything in the fewest possible words. However, it is a colloquial phrase that is best used in speech rather than formal academic writing.
Example: “In a nutshell, there are valid arguments on both sides of the debate about socialism vs capitalism.”
18. In closing…
Overview: This phrase is an appropriate synonym for ‘In conclusion’ and I would be perfectly fine with a student using this phrase in their essay. Make sure you follow-up by explaining your position based upon the weight of evidence presented in the body of your piece
Example: “In closing, there is ample evidence to suggest that liberalism has been the greatest force for progress in the past 100 years.”
19. In essence…
Overview: While the phrase ‘In essence’ does suggest you are about to sum up the core findings of your discussion, it is somewhat colloquial and is best left for speech rather than formal academic writing.
Example: “In essence, this essay has shown that cattle farming is an industry that should be protected as an essential service for our country.”
20. In review…
Overview: We usually review someone else’s work, not our own. For example, you could review a book that you read or a film you watched. So, writing “In review” as a replacement for “In conclusion” comes across a little awkward.
Example: “In review, the above information has made a compelling case for compulsory military service in the United States.”
21. In short…
Overview: Personally, I find that this phrase is used more regularly by undergraduate student. As students get more confident with their writing, they tend to use higher-rated phrases from this list. Nevertheless, I would not take grades away from a student for using this phrase.
Example: “In short, this essay has shown the importance of sustainable agriculture for securing a healthy future for our nation.”
22. In Sum…
Overview: Short for “In summary”, the phrase “In sum” sufficiently shows that you are not coming to the moment where you will sum up the essay. It is an appropriate phrase to use instead of “In conclusion”.
But remember to not just summarize but also discuss the implications of your findings in your conclusion.
Example: “In sum, this essay has shown the importance of managers in ensuring efficient operation of medium-to-large enterprises.”
23. In Summary…
Overview: In summary and in sum are the same terms which can be supplemented for “In conclusion”. You will show that you are about to summarize the points you said in the body of the essay, which is what you want from an essay.
Example: “In summary, reflection is a very important metacognitive skill that all teachers need to master in order to improve their pedagogical skills.”
24. It cannot be conclusively stated that…
Overview: While this phrase is not always be a good fit for your essay, when it is, it does show knowledge and skill in writing. You would use this phrase if you are writing an expository essay where you have decided that there is not enough evidence currently to make a firm conclusion on the issue.
Example: “It cannot be conclusively stated that the Big Bang was when the universe began. However, it is the best theory so far, and none of the other theories explored in this essay have as much evidence behind them.”
25. It is apparent that…
Overview: The term ‘ apparent ’ means that something is ‘clear’ or even ‘obvious’. So, you would use this word in an argumentative essay where you think you have put forward a very compelling argument.
Example: “It is apparent that current migration patterns in the Americas are unsustainable and causing significant harm to the most vulnerable people in our society.”
26. Last but not least…
Overview: The phrase “last but not least” is a colloquial idiom that is best used in speech rather than formal academic writing. Furthermore, when you are saying ‘last’, you mean to say you’re making your last point rather than summing up all your points you already made. So, I’d avoid this one.
Example: “Last but not least, this essay has highlighted the importance of empowering patients to exercise choice over their own medical decisions.”
27. Overall…
My Rating: 7.5/10
Overview: This phrase means ‘taking everything into account’, which sounds a lot like what you would want to do in an essay. I don’t consider it to be a top-tier choice (which is why I rated it 7), but in my opinion it is perfectly acceptable to use in an undergraduate essay.
Example: “Overall, religious liberty continues to be threatened across the world, and faces significant threats in the 21 st Century.”
28. The above points illustrate…
Overview: This phrase is a good start to a conclusion paragraph that talks about the implications of the points you made in your essay. Follow it up with a statement that defends your thesis you are putting forward in the essay.
Example: “The above points illustrate that art has had an overwhelmingly positive impact on humanity since the renaissance.”
29. The evidence presented in this essay suggests that…
Overview: I like this phrase because it highlights that you are about to gather together the evidence from the body of the essay to put forward a final thesis statement .
Example: “The evidence presented in this essay suggests that the democratic system of government is the best for securing maximum individual liberty for citizens of a nation.”
30. This essay began by stating…
Overview: This phrase is one that I teach in my YouTube mini-course as an effective one to use in an essay conclusion. If you presented an interesting fact in your introduction , you can return to that point from the beginning of the essay to provide nice symmetry in your writing.
Example: “This essay began by stating that corruption has been growing in the Western world. However, the facts collected in the body of the essay show that institutional checks and balances can sufficiently minimize this corruption in the long-term.”
31. This essay has argued…
Overview: This term can be used effectively in an argumentative essay to provide a summary of your key points. Follow it up with an outline of all your key points, and then a sentence about the implications of the points you made. See the example below.
Example: “This essay has argued that standardized tests are damaging for students’ mental health. Tests like the SATs should therefore be replaced by project-based testing in schools.”
32. To close…
Overview: This is a very literal way of saying “In conclusion”. While it’s suitable and serves its purpose, it does come across as being a sophomoric term. Consider using one of the higher-rated phrases in this list.
Example: “To close, this essay has highlighted both the pros and cons of relational dialectics theory and argued that it is not the best communication theory for the 21 st Century.”
33. To Conclude…
Overview: Like ‘to close’ and ‘in summary’, the phrase ‘to conclude’ is very similar to ‘in conclusion’. It can therefore be used as a sufficient replacement for that term. However, as with the above terms, it’s just okay and you could probably find a better phrase to use.
Example: “To conclude, this essay has highlighted that there are multiple models of communication but there is no one perfect theory to explain each situation.”
34. To make a long story short…
My Rating: 1/10
Overview: This is not a good phrase to use in an academic essay. It is a colloquialism. It also implies that you have been rambling in your writing and you could have said everything more efficiently. I would personally not use this phrase.
Example: “To make a long story short, I don’t have very good command of academic language.”
35. To Sum up…
Overview: This phrase is the same as ‘In summary’. It shows that you have made all of your points and now you’re about to bring them all together in a ‘summary’. Just remember in your conclusion that you need to do more than summarize but also talk about the implications of your findings. So you’ll need to go beyond just a summary.
Example: “In summary, there is ample evidence that linear models of communication like Lasswell’s model are not as good at explaining 21 st Century communication as circular models like the Osgood-Schramm model .”
36. Ultimately…
Overview: While this phrase does say that you are coming to a final point – also known as a conclusion – it’s also a very strong statement that might not be best to use in all situations. I usually accept this phrase from my undergraduates, but for my postgraduates I’d probably suggest simply removing it.
Example: “Ultimately, new media has been bad for the world because it has led to the spread of mistruths around the internet.”
37. Undoubtedly…
Overview: If you are using it in a debate or argumentative essay, it can be helpful. However, in a regular academic essay, I would avoid it. We call this a ‘booster’, which is a term that emphasizes certainty. Unfortunately, certainty is a difficult thing to claim, so you’re better off ‘hedging’ with phrases like ‘It appears’ or ‘The best evidence suggests’.
Example: “Undoubtedly, I know everything about this topic and am one hundred percent certain even though I’m just an undergraduate student.”
38. Weighing up the facts, this essay finds…
Overview: This statement highlights that you are looking at all of the facts both for and against your points of view. It shows you’re not just blindly following one argument but being careful about seeing things from many perspectives.
Example: “Weighing up the facts, this essay finds that reading books is important for developing critical thinking skills in childhood.”
39. With that said…
Overview: This is another phrase that I would avoid. This is a colloquialism that’s best used in speech rather than writing. It is another term that feels sophomoric and is best to avoid. Instead, use a more formal term such as: ‘Weighing up the above points, this essay finds…’
Example: “With that said, this essay disagrees with the statement that you need to go to college to get a good job.”
Do you Need to Say Anything?
Something I often tell my students is: “Can you just remove that phrase?”
Consider this sentence:
- “In conclusion, the majority of scientists concur that climate change exists.”
Would it be possible to simply say:
- “ In conclusion, The majority of scientists concur that climate change exists.”
So, I’d recommend also just considering removing that phrase altogether! Sometimes the best writing is the shortest, simplest writing that gets to the point without any redundant language at all.
How to Write an Effective Conclusion
Before I go, I’d like to bring your attention to my video on ‘how to write an effective conclusion’. I think it would really help you out given that you’re looking for help on how to write a conclusion. It’s under 5 minutes long and has helped literally thousands of students write better conclusions for their essays:
You can also check out these conclusion examples for some copy-and-paste conclusions for your own essay.
In Conclusion…
Well, I had to begin this conclusion with ‘In conclusion…’ I liked the irony in it, and I couldn’t pass up that chance.
Overall, don’t forget that concluding an essay is a way to powerfully summarize what you’ve had to say and leave the reader with a strong impression that you’ve become an authority on the topic you’re researching.
So, whether you write it as a conclusion, summary, or any other synonym for conclusion, those other ways to say in conclusion are less important than making sure that the message in your conclusion is incredibly strong.

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 5 Top Tips for Succeeding at University
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 50 Durable Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 100 Consumer Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 30 Globalization Pros and Cons
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
5 Examples of Concluding Words for Essays

4-minute read
- 19th September 2022
If you’re a student writing an essay or research paper, it’s important to make sure your points flow together well. You’ll want to use connecting words (known formally as transition signals) to do this. Transition signals like thus , also , and furthermore link different ideas, and when you get to the end of your work, you need to use these to mark your conclusion. Read on to learn more about transition signals and how to use them to conclude your essays.
Transition Signals
Transition signals link sentences together cohesively, enabling easy reading and comprehension. They are usually placed at the beginning of a sentence and separated from the remaining words with a comma. There are several types of transition signals, including those to:
● show the order of a sequence of events (e.g., first, then, next)
● introduce an example (e.g., specifically, for instance)
● indicate a contrasting idea (e.g., but, however, although)
● present an additional idea (e.g., also, in addition, plus)
● indicate time (e.g., beforehand, meanwhile, later)
● compare (e.g., likewise, similarly)
● show cause and effect (e.g., thus, as a result)
● mark the conclusion – which we’ll focus on in this guide.
When you reach the end of an essay, you should start the concluding paragraph with a transition signal that acts as a bridge to the summary of your key points. Check out some concluding transition signals below and learn how you can use them in your writing.
To Conclude…
This is a particularly versatile closing statement that can be used for almost any kind of essay, including both formal and informal academic writing. It signals to the reader that you will briefly restate the main idea. As an alternative, you can begin the summary with “to close” or “in conclusion.” In an argumentative piece, you can use this phrase to indicate a call to action or opinion:
To conclude, Abraham Lincoln was the best president because he abolished slavery.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
As Has Been Demonstrated…
To describe how the evidence presented in your essay supports your argument or main idea, begin the concluding paragraph with “as has been demonstrated.” This phrase is best used for research papers or articles with heavy empirical or statistical evidence.
As has been demonstrated by the study presented above, human activities are negatively altering the climate system.
The Above Points Illustrate…
As another transitional phrase for formal or academic work, “the above points illustrate” indicates that you are reiterating your argument and that the conclusion will include an assessment of the evidence you’ve presented.
The above points illustrate that children prefer chocolate over broccoli.
In a Nutshell…
A simple and informal metaphor to begin a conclusion, “in a nutshell” prepares the reader for a summary of your paper. It can work in narratives and speeches but should be avoided in formal situations.
In a nutshell, the Beatles had an impact on musicians for generations to come.
Overall, It Can Be Said…
To recap an idea at the end of a critical or descriptive essay, you can use this phrase at the beginning of the concluding paragraph. “Overall” means “taking everything into account,” and it sums up your essay in a formal way. You can use “overall” on its own as a transition signal, or you can use it as part of a phrase.
Overall, it can be said that art has had a positive impact on humanity.
Proofreading and Editing
Transition signals are crucial to crafting a well-written and cohesive essay. For your next writing assignment, make sure you include plenty of transition signals, and check out this post for more tips on how to improve your writing. And before you turn in your paper, don’t forget to have someone proofread your work. Our expert editors will make sure your essay includes all the transition signals necessary for your writing to flow seamlessly. Send in a free 500-word sample today!
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
The benefits of using an online proofreading service.
Proofreading is important to ensure your writing is clear and concise for your readers. Whether...
2-minute read
6 Online AI Presentation Maker Tools
Creating presentations can be time-consuming and frustrating. Trying to construct a visually appealing and informative...
What Is Market Research?
No matter your industry, conducting market research helps you keep up to date with shifting...
8 Press Release Distribution Services for Your Business
In a world where you need to stand out, press releases are key to being...
3-minute read
How to Get a Patent
In the United States, the US Patent and Trademarks Office issues patents. In the United...
The 5 Best Ecommerce Website Design Tools
A visually appealing and user-friendly website is essential for success in today’s competitive ecommerce landscape....

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
How to End a College Essay – With Examples
June 16, 2023

Figuring out how to end a college essay can feel like the difference between success and failure. Common scenario: You’ve done the heavy lifting of brainstorming, developing, and revising your Common App essay, but now you sit and stare at the cursor pulsing on your screen, like a stress tick in your eye. What to say that you haven’t already said? How to tie it all together without sounding tired and stressed? It is true that your conclusion serves as a sort of benchmark for the strength of your overall essay. If your conclusion feels impossible to write after several attempts, this might be a sign that you need to go back and look over the strength or purpose of your essay overall.
The good news is, your final paragraph doesn’t need to be a graveyard of redundancy, clichés and tired summary! And even better, you have options about how to end a college essay. It doesn’t have to be formulaic or look like a friend’s conclusion. Amidst a dizzying array of “do’s and “don’ts,” here is a list of three straightforward options, along with examples, for how to successfully (and relatively painlessly) end your college essay.
Option 1: Save something for the end
It might be helpful to think of your essay like this: You are a tailor cutting a garment from a beautiful piece of fabric. You have plenty of fabric to work with because you are approaching your overall essay as a process: brainstorming, writing, revision, repeat. The writing process is cyclical. You begin with an idea, which leads you to another, and before you know it, you’re approaching your original idea from a different angle. In the midst of this process, you will unearth images, memories, meaningful moments, memorable things people in your life have said, and so on. When this happens, intentionally tuck away 1-2 of these items with the idea that you can use them to craft your final paragraph. Following are some examples of students who tried to save something for the end:
Strong Example:
Shortly before her death, my grandmother gave me a string of pearls. Whenever I look at these tiny treasures from the sea, I am reminded that despite our complex relationship, we made many meaningful memories together. Each pearl reminds me of an event, or place: Her 80th birthday party; deep sea diving in Florida; impromptu singing lessons around her piano. Along with the memories, the pearls are a symbol of her finest qualities—qualities she passed on to me: tenacity, loyalty, belief in the deep goodness of humanity—and a touchable reminder that I am in part who I am because of her.
This is a strong example because the student chose a concrete image—an image that we can imagine seeing or touching—and uses it to deepen his reflection on his relationship with his grandmother. Images are memorable, so this reflection will echo longer in the reader’s mind; this is a classic example of showing AND telling.
How to End a College Essay (Continued)
Weak example:.
Travel is a great way to learn about the world and ourselves. My family would go on amazing trips together, and thinking back on those trips is a really good reminder of all the special memories I have made with them. One time we went to Columbia as a family, and it was very special to me. I tried so many different foods and met so many new people. I even got to use some of the Spanish I learned in school on this trip. This trip really increased my passion for traveling. Having the opportunity to learn in a different setting while getting to experience new cultures is something I am really looking forward to during college.
This is a weak example because it does feel as if the student ran out of gas at the end. Notice the use of general adjectives such as amazing and special , and the fact that while a specific place is mentioned—Columbia—nothing specific is said about the country, or the family’s experience there. What foods did the student try? What, besides getting to speak Spanish, made the trip special? There are golden opportunities in this example for where the writer could have invoked one of the five senses—taste, touch, smell, site, or sound—and did not.
Option 2: Leave the reader with a thought to keep the conversation going
You can choose to end your college essay by saying something about your story or topic that you did not feel you had the opportunity to say before. Sometimes, at the end of an essay on a difficult or complex subject, you feel unable to just “wrap things up” like a pretty Christmas present. Is something still ambiguous for you? Does something still haunt you? Did you hold something back? Tell the reader about it. If it helps, imagine that you are having a conversation with a broader audience than an admissions counselor. If it helps, imagine that your audience is a friend, teacher, or family member.
The ideology behind color blindness doesn’t make you progressive, it makes you a coward. Talking about race should not be controversial. I shouldn’t be petrified to talk about racism to a group of white people . Petrified because I’ll most likely be shut down condescendingly like a parent scolding their child. I shouldn’t worry over the natural curls of my hair because it will seem ghetto and unprofessional.
Nor should I get excited when I see a movie that has at least one black person in a somewhat lead role. I should not have to read white literature, learn white history, and speak white English , but spend only one week learning about slavery. I shouldn’t have to read articles calling Edris Elba “too street” to play James Bond and Viola Davis “less classically beautiful.” So, why is it so hard to talk about racism? What about it make your spine tingle and the hairs on your skin raise?
This is a strong example because, wow! There is a lot of passion and specificity in this student’s reflection on race and racism. From her own curls, to literature and pop culture, this writer is not only giving her audience a piece of her mind, she is putting the ball in the reader’s court with that final question.
Also, think of it like this: What if this writer has hit upon the heart of her paper in her conclusion? What if, by “getting it all out,” she found a way to strengthen her thesis, and her overall purpose for her essay? In the lovely book on creative nonfiction called Tell it Slant , one writer describes the writing process this way: “The essayist attempts to surround a something—a subject, a mood, a problematic irritation, by coming at it from at all angles, wheeling and diving like a hawk, each seemingly digressive spiral actually taking us closer to the heart of the matter.” Trust your writing process, even if feels like you keep circling back to your starting point.
Speaking up for others is important. For example, after the death of George Floyd, Americans showed their support by protesting. Professional athletes have showed their support for the Black community by taking a knee during the national anthem, and regular people spread of awareness on social media. These are all crucial steps to the end of racial injustice in America. I learned that using your voice can make enormous impacts. In the future I’d really like to show my support in protests, by taking part in them, for these injustices.
This is a weak example because while it does mention several specifics, such as protests after the death of George Floyd, and professional athletes “taking the knee,” there isn’t enough of a connection between these examples and the writer. The details in this paragraph could really have been written by anyone (and those are the kind of conclusions you want to avoid writing at all costs!). In the sentence, for example, where the writer says, “I learned that using your voice can make enormous impacts,” s/he misses the opportunity to personalize this learning experience. Even if s/he did not have the opportunity to protest, etc., s/he could have delved deeper into his/her reactions and emotions to the events mentioned, or event discussed what they wished they’d have done to speak up.
Option 3: Don’t try to be fancy
Are you the kind of person who prefers facts and figures over emotions and descriptions? Do you dislike talking about yourself? Do you prefer taking apart machines to playing Wordle? Then this option is for you. When ending your college essay, being clear is better than being fancy. This doesn’t mean that you don’t have to write well. It just means that you can choose to focus more on being straightforward—describing a process, ending with a clear purpose for the future—than being colorful or edgy. The most important thing about the whole college essay writing process, after all, is about showing your authenticity.
It took time and patience, but by observing how various students worked and how I could best help them, I became an effective and efficient Homework Coach. Because I volunteered longer than anyone else, I became the lead Homework Coach. I passed on my hard-won knowledge about developing teaching strategies to the tutors in training so they too could be successful in teaching a variety of subjects. I enjoyed my time helping others and even received a community service award from the President of the United States. Going forward, I plan to continue using my skills as a tutor to help friends and classmates with their homework.
This is a strong example because the student clearly describes a learning experience, what he took from it, and what he hopes to do with it in the future. The writer is obviously proud of his accomplishments, but does not feel the need to “dress them up” by using fancy vocabulary, clichés or empty adjectives.
Which brings me to this point: You don’t need be the daughter of a professional clown, or have ridden an alpaca ten miles to school in order to have something worthwhile to say. Hard work speaks for itself, and often, being authentically you starts with acknowledging day-to-day life lessons and everyday accomplishments.
Weak Example
I started working as a lifeguard at my community pool as a skinny 16-year-old. I remember my first day like it was yesterday. It was 90 degrees, and my red Nike one-piece felt like a melting popsicle as I watched others having fun and cooling off in the water. I remember that there was a mom there with a set of twin toddlers, and I nervously kept an eye on them. Being a lifeguard is all about responsibility and teamwork. My lifeguard team has an outstanding record of keeping swimmers safe. As a student majoring in business, I know that having teamwork skills will be very important, especially because I will probably have to work with a team when I begin my career as well.
This is a weak example because the writer strays from her focus of being a lifeguard, and what she learned about responsibility and teamwork. The reflective, narrative details about the heat, the swimsuit, and the mom with twins, not to mention the cliché “I remember…like it was yesterday,” detract from her overall purpose. Don’t get me wrong: using narrative details to talk about life lessons is not a wrong approach; however, focus first on clarity and your overall purpose for writing.
How to End a College Essay – Final Thoughts
Remember, when ending your college essay, you have options! Consider trying each of these 3 approaches and see which you like best. And as you think about and brainstorm your essays, check out these links, too:
- How to Write the Overcoming Challenges Essay + Example ;
- 2023-2024 Common App Essay Prompts
- Why this College Essay—7 Tips for Success
- College Essay

Charity Gingerich
With a BA in English and an MFA in Creative Writing, Charity has served as an English and creative writing lecturer at several universities. Charity has received many awards for her work, including the Russell MacDonald Creative Writing Award, Tennessee Williams Scholarship in Poetry, and The Hopper Poetry Prize. Her writing has been featured in FIELD, The Kenyon Review, and Indiana Review, among others.
- 2-Year Colleges
- Application Strategies
- Best Colleges by Major
- Big Picture
- Career & Personality Assessment
- College Search/Knowledge
- College Success
- Costs & Financial Aid
- Dental School Admissions
- Extracurricular Activities
- Graduate School Admissions
- High School Success
- High Schools
- Law School Admissions
- Medical School Admissions
- Navigating the Admissions Process
- Online Learning
- Private High School Spotlight
- Summer Program Spotlight
- Summer Programs
- Test Prep Provider Spotlight

“Innovative and invaluable…use this book as your college lifeline.”
— Lynn O'Shaughnessy
Nationally Recognized College Expert
College Planning in Your Inbox
Join our information-packed monthly newsletter.
Sign Up Now
Have a language expert improve your writing
Check your paper for plagiarism in 10 minutes, generate your apa citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- College essay
How to End a College Admissions Essay | 4 Winning Strategies
Published on October 16, 2021 by Meredith Testa . Revised on May 31, 2023.
The ending of your college essay should leave your reader with a sense of closure and a strong final impression.
Table of contents
Endings to avoid, option 1: return to the beginning, option 2: look forward, option 3: reveal your main point, option 4: end on an action, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about college application essays.
A bad conclusion can bring your whole essay down, so make sure to avoid these common mistakes.
Summarizing
Unlike an academic essay, an admissions essay shouldn’t restate your points. Avoid ending with a summary; there’s no need to repeat what you’ve already written.
Phrases like “in conclusion,” “overall,” or “to sum it up” signal that you have nothing to add to what you’ve already written, so an admissions officer may stop reading.
Stating the obvious
Instead of stating the obvious, let your work speak for itself and allow readers to draw their own conclusions. If your essay details various times that you worked tirelessly to go above and beyond, don’t finish it by stating “I’m hardworking.” Admissions officers are smart enough to figure that out on their own.
You should also avoid talking about how you hope to be accepted. Admissions officers know you want to be accepted—that’s why you applied! It’s okay to connect what you discuss in the essay to your potential future career or college experience, but don’t beg for admission. Stay focused on your essay’s core topic.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Many successful essays follow a “sandwich,” or full-circle, structure , meaning that they start with some image or idea, veer away from it in the middle, and then return to it at the end.
This structure is clean, self-contained, and satisfying for readers, so it’s a great choice if it works with the topic you’ve chosen.
In the “sandwich” essay outlined below, a student discusses his passion for musical theater. Instead of simply stating that interest, his essay starts with a funny anecdote about a minor fire that erupted on set. At the end, it returns to this anecdote, creating a sense of closure.
- Intro: I may be the world’s worst firefighter.
- Flashback to working on the school musical
- Demonstrate my passion for theatre
- Detail the story of the theater set catching fire
- Show how I made the most of the situation
- Conclusion: I proved my value as a director, an actor, and a writer that week一even if I was a terrible firefighter.
Many successful essays end by looking forward to the future. These endings are generally hopeful and positive—always great qualities in an admissions essay—and often connect the student to the college or their academic goals.
Although these endings can be highly effective, it can be challenging to keep them from sounding cliché. Keep your ending specific to you, and don’t default to generalities, which can make your essay seem bland and unoriginal.
Below are a good and a bad example of how you could write a “looking forward” ending for the musical theater “firefighter” essay.
Sometimes, holding back your main point can be a good strategy. If your essay recounts several experiences, you could save your main message for the conclusion, only explaining what ties all the stories together at the very end.
When done well, this ending leaves the reader thinking about the main point you want them to take from your essay. It’s also a memorable structure that can stand out.
However, if you choose this approach, it can be challenging to keep the essay interesting enough that the reader pays attention throughout.
In the essay outlined below, a student gives us snapshots of her experience of gymnastics at different stages in her life. In the conclusion, she ties the stories together and shares the insight that they taught her about different aspects of her character and values.
- Passionate, excited
- Sister born that day—began to consider people beyond myself
- Realizing that no matter how much I love gymnastics, there are more important things
- I’d been working especially hard to qualify for that level
- It came after many setbacks and failures
- I had to give up time with friends, first homecoming dance of high school, and other activities, and I considered quitting
- Conclusion: I’m still all of those selves: the passionate 7-year-old, the caring 11-year-old, and the determined 15-year-old. Gymnastics has been a constant throughout my life, but beyond the balance beam, it has also shown me how to change and grow.
Ending on an action can be a strong way to wrap up your essay. That might mean including a literal action, dialogue, or continuation of the story.
These endings leave the reader wanting more rather than wishing the essay had ended sooner. They’re interesting and can help you avoid boring your reader.
Here’s an example of how this ending could work for the gymnastics essay.
If you want to know more about academic writing , effective communication , or parts of speech , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
Academic writing
- Writing process
- Transition words
- Passive voice
- Paraphrasing
Communication
- How to end an email
- Ms, mrs, miss
- How to start an email
- I hope this email finds you well
- Hope you are doing well
Parts of speech
- Personal pronouns
- Conjunctions
There are a few strategies you can use for a memorable ending to your college essay :
- Return to the beginning with a “full circle” structure
- Reveal the main point or insight in your story
- Look to the future
- End on an action
The best technique will depend on your topic choice, essay outline, and writing style. You can write several endings using different techniques to see which works best.
Unlike a five-paragraph essay, your admissions essay should not end by summarizing the points you’ve already made. It’s better to be creative and aim for a strong final impression.
You should also avoid stating the obvious (for example, saying that you hope to be accepted).
There are no set rules for how to structure a college application essay , but these are two common structures that work:
- A montage structure, a series of vignettes with a common theme.
- A narrative structure, a single story that shows your personal growth or how you overcame a challenge.
Avoid the five-paragraph essay structure that you learned in high school.
When revising your college essay , first check for big-picture issues regarding message, flow, tone, style , and clarity. Then, focus on eliminating grammar and punctuation errors.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Testa, M. (2023, May 31). How to End a College Admissions Essay | 4 Winning Strategies. Scribbr. Retrieved April 1, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/college-essay/conclusion-college-essay/
Is this article helpful?

Meredith Testa
Other students also liked, how to write a great college essay introduction | examples, college essay format & structure | example outlines, how to revise your college admissions essay | examples, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Applying for Tertiary Education
- Application Essays
How to End a College Essay: The Do’s and Don’ts
Last Updated: January 16, 2024 Fact Checked
Strategies to End Your College Essay
- Things to Avoid
Expert Interview
This article was co-authored by Alexander Ruiz, M.Ed. and by wikiHow staff writer, Sophie Burkholder, BA . Alexander Ruiz is an Educational Consultant and the Educational Director of Link Educational Institute, a tutoring business based in Claremont, California that provides customizable educational plans, subject and test prep tutoring, and college application consulting. With over a decade and a half of experience in the education industry, Alexander coaches students to increase their self-awareness and emotional intelligence while achieving skills and the goal of achieving skills and higher education. He holds a BA in Psychology from Florida International University and an MA in Education from Georgia Southern University. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources.
Deadlines are whizzing by, primary-colored pennants are waving, and keyboards are clicking and clacking…it’s college admissions season! Beyond the test scores and grade point averages, your personal statement is your one chance to show colleges who you are—and for some reason, wrapping up that essay can be the hardest part. We spoke to expert academic tutor and educational consultant Alexander Ruiz to give you strategies for concluding your college essay, along with the examples included in this comprehensive guide to college essay conclusions.
Things You Should Know
- End your college essay by returning to an idea or image you included in your intro or as your hook. This callback satisfies your reader with a full-circle effect.
- Look to the future to conclude your college essay on a positive and hopeful note. Describe your goals and the impact you’ll have on the world.
- Finish your college essay with a lesson learned. After sharing life experiences, describe what you’ve learned and how they’ve prepared you for your next step.
Ask the wikiHow College Coach
- As expert educational consultant Alexander Ruiz explains, universities are “trying to understand ‘How do you see that you fit within our school?’ Even though the prompt is asking ‘Why did you choose the school?’, it really is truly asking ‘How do you fit within the student body? How do you fit within our campus?’”
- Example of a “college address” conclusion: I want to be part of the long legacy of civil rights activists and leaders, from Martin Luther King, Jr. to Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez, who have studied within the walls of Boston University. I’ve planted the seeds of this work through my two years of volunteering and campaigning in local elections. If admitted to your globally renowned Political Science program, I will be thrilled to grow my skills in Public Policy Analysis and ultimately serve the dynamic and deserving communities of Greater Boston.

- Example of a “full circle” conclusion: This year was a challenge in many ways. But I know that when I drive across those state lines again next fall, I’ll be looking back at the swirling blues and grays of the Boise sky, already anxiously awaiting the next time I get to come back home.
- Example intro hook for above conclusion: As my parents drove us across the Idaho state line, I looked out at the cloud-covered sky and thought: Well, this sure doesn’t look like home.

- Example of a “lesson learned” conclusion: Having the opportunity to travel around Latin America—bouncing between coastal towns like Sayulita and sprawling cities like Buenos Aires—I learned the importance of understanding other cultures and their perspectives. In expanding the limits of my physical world, I also had the opportunity to expand my worldview.

- Example of a “look forward” conclusion: When my great-great-grandchildren fasten their shoes with a futuristic version of Velcro and head down the road to school, they will do so with excitement and purpose. They’ll look forward to the day’s tasks of digging in the garden for Biology, journaling on their socio-emotional well-being in Health class, and debating the issues of their times in Social Studies. An education system built around students, their needs, and their futures—as a hopeful member of your teaching college, that is a future I am enthusiastic to have a hand in.

- Example of a “last-minute reveal” conclusion: After multiple paragraphs of stories from swim meets throughout the writer’s life, they conclude with, I wasn’t just swimming to beat the stopwatch hanging around my coach’s neck. I was swimming because it gave me freedom, a place to reflect, and an ability to push back against even the strongest currents.
- This strategy is difficult to pull off, as our instinct is to put our thesis right at the top. However, when it comes to college admissions, academic tutor Alexander Ruiz warns against “the five-paragraph format, the intro, body, body, body, conclusion.”
- As Ruiz continues to explain, “When it comes to telling your story and sharing how valuable your experience will be to a school, [the five-paragraph format] is not going to be able to portray that in a way that's going to be very attractive. So I think that one of the main mistakes that people make is saying these quantitative measures are going to speak for themselves, and they don't put enough work into being able to tell their story in their essays.”

- Example of a “plot twist” conclusion: Every law office I interned at over the past four years, despite their intensity, was instrumental in shaping my path and who I am. They prepared me for college and a career and gave me a clear view of what I wanted to do: not study law. Don’t get me wrong, I enjoyed every minute of learning about the inner workings of our legal system, but now I want to put that knowledge toward my true passion: helping foster kids via a social services career.

- Example of a thought-question conclusion: After all, with no other world to compare ours to, who are we to say a better world isn’t possible?
- Example of a “call to action” conclusion: Now that I’ve spent some thousand-odd words advocating for voter rights, voter registration, and rattling off anecdotes of my door-to-door campaigning, I just have one question left: are you registered to vote?
Things to Avoid in Your College Essay Conclusion

- Don’t: In conclusion, my family’s struggle with poverty over the past five years taught me much about resilience.
- Do: Tonight, my dad will put food on the table, as he always manages to. My mom will kiss him on the cheek as soon as she walks in the door from work, sighing as she finally sits down for the day. Despite all the challenges of the last five years, I’ve watched my parents overcome every obstacle with resilience and grit—and what I’ve learned from them is something I wouldn’t give up for the world.

- Don’t: I’m a hard worker.
- Do: Juggling rigorous academics with grueling morning soccer practices has taught me the value of hard work and discipline.
- Don’t: Climate change is a problem.
- Do: My generation is already suffering the real-time effects of climate change, like our snow days turning to smoke days as wildfires burn around our homes.

- Don’t: Please consider me.
- Do: As shown by the four years I volunteered at my local children’s hospital, community service is a priority for me in my future personal and professional life. Seeing what your university does for its surrounding neighborhood and the people there, I feel confident I would be a natural fit at your school.

- Don’t: You miss 100% of the shots you don't take.
- Do: In my wildest dreams, I never imagined I would be the lead in my senior play. Cut to now, and I’m singing my heart out to an applauding audience of parents and peers. From this moment forward, I will always understand and uphold the value of betting on yourself, even when you don’t know the outcome.
- Don’t: College will help me reach my dreams.
- Do: I’m enthusiastic about starting my next chapter—attending a school that will help me grow, learn, and take my next step toward my dream of becoming a doctor.
Expert Q&A
- Be specific in your essay—admissions officers want to hear about you and your life, so tell details about who you are and your experiences. [10] X Research source Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- Be authentic—admissions officers have read enough college essays to know when someone is phoning it in. Be true to yourself, write how you speak, and let your personality shine through. [11] X Research source Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- Show enthusiasm—if you’re talking about the school or your future, show excitement for what the next four years will hold for you. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

You Might Also Like

Thanks for reading our article! If you’d like to learn more about preparing for graduation, check out our in-depth interview with Alexander Ruiz, M.Ed. .
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/conclusions/
- ↑ https://www.collegeessayadvisors.com/write-amazing-closing-line/
- ↑ https://essaypro.com/blog/how-to-write-a-conclusion
- ↑ https://students.tippie.uiowa.edu/sites/students.tippie.uiowa.edu/files/2022-05/effective_claims.pdf
- ↑ https://www.rochester.edu/newscenter/how-to-write-your-best-college-application-essay-493692/
About This Article

- Send fan mail to authors
Did this article help you?

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter
- Academic Proofreading
- Business Proofreading
- Content Creation
- Application Review
- Express Service
- Microsoft Track Changes
- Testimonials
- Areas of Expertise
- Our Editors
- Join Our Team
- English Writing Guides
- Academic Referencing Guides
- English Blog
- Instant Quote
- Your basket is currently empty.
How To Write A Conclusion For An Essay
Your conclusion paragraph should begin with a smooth transition from the body of your essay. The first sentence of your paragraph should include clear transition words to signal to your reader that you are beginning to wrap up your essay. Different transition words can have different effects, so be sure to choose a transition word or phrase that clearly communicates that you are closing your essay. Some common examples of conclusion transition words and phrases include:
- In conclusion,
- To conclude,
- As previously stated.
Once you have signalled that you are drawing your essay to a close, you can then restate the primary points of your essay. Depending on the length of your essay, this may be done in a single sentence, or it may require a few sentences. Be concise and clear; you should be able to summarise each main point in a simple phrase that avoids restating each detail and piece of evidence related to the point. Also, simply list off the point as a reminder to your audience about what they’ve just read.

Restate your main points
Finally, if you are writing an argumentative essay, you’ll want to clearly restate your main argument in order to leave readers with one final appeal. If you have provided enough evidence along the way, this restatement should make readers feel as if you’ve persuaded them fully.
Call to action
For some expository and argumentative essays, it’s appropriate to end with a call to action as your last sentence. For example, if you’re writing an informative essay about the sea creatures that live in the very deepest parts of the ocean, you may close with a sentence like this: “It’s clear that today’s scientists should continue to observe and document these mysterious creatures, so we may learn more about the life at the bottom of the ocean.” A call to action like this can make your reader feel inspired and informed after reading your essay.
What to avoid
When writing a strong conclusion paragraph, you want to keep it simple. Use a clear transition word or phrase, restate your main points and arguments, and possibly finish with a call to action. Be sure to avoid the following common mistakes:
- New information. Your conclusion is not the place to introduce anything new. Simply restate and summarise the main points clearly.
- Personal opinion. Unless you are writing an opinion piece that includes several “I” statements throughout, avoid ending your essay with a sudden “I think…” or “I feel…” If you haven’t been including your personal opinion throughout the essay, then you shouldn’t insert your opinion into the conclusion.
- Lots of detail. When you restate your main points, don’t worry about restating all the small details that make up your description or evidence. The place for details is in your body paragraphs. The conclusion is simply for summary and a possible call for action or next steps.
Obtain an instant quote for our proofreading and editing service
At Express Proofreading, we offer a professional academic proofreading and editing service . We are able to ensure that the entirety of your work is not only free from spelling mistakes and grammatical errors, but we also check syntax, sentence structure and are able to recommend improvements and suggestions that are relevant to your work. We will also check that your tables and footnotes are accurate and consistent with your bibliography.
To obtain an instant quote for us to proofread and edit your work, visit the ‘Instant Quote’ page and upload your document and our Quote Generator will calculate an instant quote for you based upon the word count of your document.
Places on our 2024 summer school are filling fast. Don’t miss out. Enrol now to avoid disappointment
- 40 Useful Words and Phrases for Top-Notch Essays

To be truly brilliant, an essay needs to utilise the right language. You could make a great point, but if it’s not intelligently articulated, you almost needn’t have bothered.
Developing the language skills to build an argument and to write persuasively is crucial if you’re to write outstanding essays every time. In this article, we’re going to equip you with the words and phrases you need to write a top-notch essay, along with examples of how to utilise them.
It’s by no means an exhaustive list, and there will often be other ways of using the words and phrases we describe that we won’t have room to include, but there should be more than enough below to help you make an instant improvement to your essay-writing skills.
If you’re interested in developing your language and persuasive skills, Oxford Royale offers summer courses at its Oxford Summer School , Cambridge Summer School , London Summer School , San Francisco Summer School and Yale Summer School . You can study courses to learn english , prepare for careers in law , medicine , business , engineering and leadership.
General explaining
Let’s start by looking at language for general explanations of complex points.
1. In order to
Usage: “In order to” can be used to introduce an explanation for the purpose of an argument. Example: “In order to understand X, we need first to understand Y.”
2. In other words
Usage: Use “in other words” when you want to express something in a different way (more simply), to make it easier to understand, or to emphasise or expand on a point. Example: “Frogs are amphibians. In other words, they live on the land and in the water.”
3. To put it another way
Usage: This phrase is another way of saying “in other words”, and can be used in particularly complex points, when you feel that an alternative way of wording a problem may help the reader achieve a better understanding of its significance. Example: “Plants rely on photosynthesis. To put it another way, they will die without the sun.”
4. That is to say
Usage: “That is” and “that is to say” can be used to add further detail to your explanation, or to be more precise. Example: “Whales are mammals. That is to say, they must breathe air.”
5. To that end
Usage: Use “to that end” or “to this end” in a similar way to “in order to” or “so”. Example: “Zoologists have long sought to understand how animals communicate with each other. To that end, a new study has been launched that looks at elephant sounds and their possible meanings.”
Adding additional information to support a point
Students often make the mistake of using synonyms of “and” each time they want to add further information in support of a point they’re making, or to build an argument . Here are some cleverer ways of doing this.
6. Moreover
Usage: Employ “moreover” at the start of a sentence to add extra information in support of a point you’re making. Example: “Moreover, the results of a recent piece of research provide compelling evidence in support of…”
7. Furthermore
Usage:This is also generally used at the start of a sentence, to add extra information. Example: “Furthermore, there is evidence to suggest that…”
8. What’s more
Usage: This is used in the same way as “moreover” and “furthermore”. Example: “What’s more, this isn’t the only evidence that supports this hypothesis.”
9. Likewise
Usage: Use “likewise” when you want to talk about something that agrees with what you’ve just mentioned. Example: “Scholar A believes X. Likewise, Scholar B argues compellingly in favour of this point of view.”
10. Similarly
Usage: Use “similarly” in the same way as “likewise”. Example: “Audiences at the time reacted with shock to Beethoven’s new work, because it was very different to what they were used to. Similarly, we have a tendency to react with surprise to the unfamiliar.”
11. Another key thing to remember
Usage: Use the phrase “another key point to remember” or “another key fact to remember” to introduce additional facts without using the word “also”. Example: “As a Romantic, Blake was a proponent of a closer relationship between humans and nature. Another key point to remember is that Blake was writing during the Industrial Revolution, which had a major impact on the world around him.”
12. As well as
Usage: Use “as well as” instead of “also” or “and”. Example: “Scholar A argued that this was due to X, as well as Y.”
13. Not only… but also
Usage: This wording is used to add an extra piece of information, often something that’s in some way more surprising or unexpected than the first piece of information. Example: “Not only did Edmund Hillary have the honour of being the first to reach the summit of Everest, but he was also appointed Knight Commander of the Order of the British Empire.”
14. Coupled with
Usage: Used when considering two or more arguments at a time. Example: “Coupled with the literary evidence, the statistics paint a compelling view of…”
15. Firstly, secondly, thirdly…
Usage: This can be used to structure an argument, presenting facts clearly one after the other. Example: “There are many points in support of this view. Firstly, X. Secondly, Y. And thirdly, Z.
16. Not to mention/to say nothing of
Usage: “Not to mention” and “to say nothing of” can be used to add extra information with a bit of emphasis. Example: “The war caused unprecedented suffering to millions of people, not to mention its impact on the country’s economy.”
Words and phrases for demonstrating contrast
When you’re developing an argument, you will often need to present contrasting or opposing opinions or evidence – “it could show this, but it could also show this”, or “X says this, but Y disagrees”. This section covers words you can use instead of the “but” in these examples, to make your writing sound more intelligent and interesting.
17. However
Usage: Use “however” to introduce a point that disagrees with what you’ve just said. Example: “Scholar A thinks this. However, Scholar B reached a different conclusion.”
18. On the other hand
Usage: Usage of this phrase includes introducing a contrasting interpretation of the same piece of evidence, a different piece of evidence that suggests something else, or an opposing opinion. Example: “The historical evidence appears to suggest a clear-cut situation. On the other hand, the archaeological evidence presents a somewhat less straightforward picture of what happened that day.”
19. Having said that
Usage: Used in a similar manner to “on the other hand” or “but”. Example: “The historians are unanimous in telling us X, an agreement that suggests that this version of events must be an accurate account. Having said that, the archaeology tells a different story.”
20. By contrast/in comparison
Usage: Use “by contrast” or “in comparison” when you’re comparing and contrasting pieces of evidence. Example: “Scholar A’s opinion, then, is based on insufficient evidence. By contrast, Scholar B’s opinion seems more plausible.”
21. Then again
Usage: Use this to cast doubt on an assertion. Example: “Writer A asserts that this was the reason for what happened. Then again, it’s possible that he was being paid to say this.”
22. That said
Usage: This is used in the same way as “then again”. Example: “The evidence ostensibly appears to point to this conclusion. That said, much of the evidence is unreliable at best.”
Usage: Use this when you want to introduce a contrasting idea. Example: “Much of scholarship has focused on this evidence. Yet not everyone agrees that this is the most important aspect of the situation.”
Adding a proviso or acknowledging reservations
Sometimes, you may need to acknowledge a shortfalling in a piece of evidence, or add a proviso. Here are some ways of doing so.
24. Despite this
Usage: Use “despite this” or “in spite of this” when you want to outline a point that stands regardless of a shortfalling in the evidence. Example: “The sample size was small, but the results were important despite this.”
25. With this in mind
Usage: Use this when you want your reader to consider a point in the knowledge of something else. Example: “We’ve seen that the methods used in the 19th century study did not always live up to the rigorous standards expected in scientific research today, which makes it difficult to draw definite conclusions. With this in mind, let’s look at a more recent study to see how the results compare.”
26. Provided that
Usage: This means “on condition that”. You can also say “providing that” or just “providing” to mean the same thing. Example: “We may use this as evidence to support our argument, provided that we bear in mind the limitations of the methods used to obtain it.”
27. In view of/in light of
Usage: These phrases are used when something has shed light on something else. Example: “In light of the evidence from the 2013 study, we have a better understanding of…”
28. Nonetheless
Usage: This is similar to “despite this”. Example: “The study had its limitations, but it was nonetheless groundbreaking for its day.”
29. Nevertheless
Usage: This is the same as “nonetheless”. Example: “The study was flawed, but it was important nevertheless.”
30. Notwithstanding
Usage: This is another way of saying “nonetheless”. Example: “Notwithstanding the limitations of the methodology used, it was an important study in the development of how we view the workings of the human mind.”
Giving examples
Good essays always back up points with examples, but it’s going to get boring if you use the expression “for example” every time. Here are a couple of other ways of saying the same thing.
31. For instance
Example: “Some birds migrate to avoid harsher winter climates. Swallows, for instance, leave the UK in early winter and fly south…”
32. To give an illustration
Example: “To give an illustration of what I mean, let’s look at the case of…”
Signifying importance
When you want to demonstrate that a point is particularly important, there are several ways of highlighting it as such.
33. Significantly
Usage: Used to introduce a point that is loaded with meaning that might not be immediately apparent. Example: “Significantly, Tacitus omits to tell us the kind of gossip prevalent in Suetonius’ accounts of the same period.”
34. Notably
Usage: This can be used to mean “significantly” (as above), and it can also be used interchangeably with “in particular” (the example below demonstrates the first of these ways of using it). Example: “Actual figures are notably absent from Scholar A’s analysis.”
35. Importantly
Usage: Use “importantly” interchangeably with “significantly”. Example: “Importantly, Scholar A was being employed by X when he wrote this work, and was presumably therefore under pressure to portray the situation more favourably than he perhaps might otherwise have done.”
Summarising
You’ve almost made it to the end of the essay, but your work isn’t over yet. You need to end by wrapping up everything you’ve talked about, showing that you’ve considered the arguments on both sides and reached the most likely conclusion. Here are some words and phrases to help you.
36. In conclusion
Usage: Typically used to introduce the concluding paragraph or sentence of an essay, summarising what you’ve discussed in a broad overview. Example: “In conclusion, the evidence points almost exclusively to Argument A.”
37. Above all
Usage: Used to signify what you believe to be the most significant point, and the main takeaway from the essay. Example: “Above all, it seems pertinent to remember that…”
38. Persuasive
Usage: This is a useful word to use when summarising which argument you find most convincing. Example: “Scholar A’s point – that Constanze Mozart was motivated by financial gain – seems to me to be the most persuasive argument for her actions following Mozart’s death.”
39. Compelling
Usage: Use in the same way as “persuasive” above. Example: “The most compelling argument is presented by Scholar A.”
40. All things considered
Usage: This means “taking everything into account”. Example: “All things considered, it seems reasonable to assume that…”
How many of these words and phrases will you get into your next essay? And are any of your favourite essay terms missing from our list? Let us know in the comments below, or get in touch here to find out more about courses that can help you with your essays.
At Oxford Royale Academy, we offer a number of summer school courses for young people who are keen to improve their essay writing skills. Click here to apply for one of our courses today, including law , business , medicine and engineering .
Comments are closed.

Essential Conclusion Transition Words to Master English Writing
By: Author ESLBUZZ
Posted on Last updated: September 5, 2023
Sharing is caring!
Hello and welcome! Today, we will explore the importance of conclusion transition words and how they can be used to effectively summarize and conclude a piece of writing. We will provide a comprehensive list of transition words and phrases that are commonly used in conclusions, along with examples of how they can be used in sentences. By the end of this article, you will have a better understanding of how to use conclusion transition words to create a strong and effective conclusion to your writing.
Conclusion Transition Words

Understanding Conclusion Transition Words
What are transition words.
Transition words are also known as discourse markers or connectives. They are words or phrases that signal a shift or connection between ideas. They help to create coherence and flow in writing and speaking by showing the relationship between different parts of a text.
Why are Transition Words Important?
Transition words are important because they help to create a clear and organized structure in writing and speaking. They make it easier for the reader or listener to follow along and understand the main points of the text. Additionally, using transition words can help to improve vocabulary and writing skills.
What are Conclusion Transition Words?
Conclusion transition words are words or phrases that are used to signal the end of a discussion or the conclusion of an argument. These words help to summarize the main points and provide closure to the reader or listener. Some examples of conclusion transition words include “in conclusion,” “to sum up,” “finally,” “in summary,” and “to conclude.” These words help to signal that the writer or speaker is wrapping up their thoughts and bringing the discussion to a close.
Examples of Transition Words in Context
Here are some example sentences that use transition words:
- Firstly, I would like to thank everyone for coming to my presentation.
- In addition to his academic achievements, John is also an accomplished musician.
- However, despite these challenges, we were able to complete the project on time.
- Therefore, it’s important to consider the environmental impact of our actions.
- In conclusion, I believe that the benefits of exercise outweigh the risks.
Focusing on Conclusion Transition Words
Conclusion transition words are phrases or words that indicate that you are about to conclude your writing. They signal to the reader that you are summarizing your thoughts and bringing your piece to a close.
Here are some commonly used conclusion transition words to help you wrap up your writing:
Using Conclusion Transition Words in Your Writing
Here are some examples of how to use them in a sentence:
- In conclusion, it’s important to remember that…
- In brief, the main takeaway from this piece is…
- To sum up, the key points to remember are…
- In summary, the main argument of this piece is…
- To conclude, it’s clear that…
- To summarize, the main points of this piece are…
Conclusion Paragraphs and Concluding Words
In addition to using conclusion transition words, it’s important to write a strong conclusion paragraph. This paragraph should summarize the main points of your piece and leave the reader with a clear understanding of your argument.
Concluding words can also be used to signal the end of your piece.
Here are some examples of concluding words to end your writing:
- To conclude
Comprehensive List of Conclusion Transition Words
Here is a list of conclusion transition words with their meanings:
Here are some example sentences that show how to use conclusion transition words in context:
- Example: “In conclusion, it is clear that climate change is a pressing issue that requires immediate action.”
- Finally: “Finally, after months of hard work, we were able to launch our new product.”
- Ultimately: “Ultimately, it was the team’s dedication and perseverance that led to our success.”
- Thus: “Thus, we can see that the data supports our hypothesis.”
- Overall: “Overall, the study found that there was a significant correlation between exercise and mental health.”
- In the final analysis: “In the final analysis, it was the company’s lack of transparency that led to the public’s distrust.”
- All things considered: “All things considered, the event was a success.”
- Therefore: “Therefore, we recommend that the company invest in renewable energy sources.”
- All in all: “All in all, it was a great vacation.”
- In the end: “In the end, it was the small details that made all the difference.”
- In a word: “In a word, the experience was unforgettable.”
- Given these points: “Given these points, it is clear that we need to make some changes to our strategy.”
- Generally speaking: “Generally speaking, people are more productive in the morning.”
- As a result: “As a result, we were able to increase our profits by 20%.”
- Noted: “Noted, we will take your feedback into consideration for future projects.”
- After all: “After all, it’s the thought that counts.”
- In the long run: “In the long run, investing in our employees will pay off.”
- For the most part: “For the most part, the study found that there was no significant difference between the two groups.”
- As has been noted: “As has been noted, there are still some unanswered questions regarding the effectiveness of the treatment.”
- On balance: “On balance, the pros outweigh the cons.”
- Usually: “Usually, I prefer to work alone.”
- By and large: “By and large, the event was a success.”
- Consequently: “Consequently, we had to make some changes to our plans.”
- Clearly: “Clearly, the data shows that there is a strong correlation between smoking and lung cancer.”
- Lastly: “Lastly, I would like to thank everyone for their hard work and dedication.”
- As shown above: “As shown above, there is a clear trend in the data.”
Using Conclusion Transition Words Effectively
Short and summarize.
When writing a conclusion, it is important to keep it short and summarize the main points of the paper. Using conclusion transition words such as “in summary” or “in brief” can help you achieve this. These words signal to the reader that you are summarizing the main points of the paper and preparing to conclude.
Remember to use the right conclusion transition words based on the formality of the writing. Here’s a simple guide:
- Informal: “So, yeah,” “Anyway,” “Well, that’s all for now,” “That’s it,” “Catch you later”
- Neutral: “In conclusion,” “To summarize,” “To sum up,” “Finally,” “In summary”
- Formal: “Thus,” “Therefore,” “Hence,” “Consequently,” “Accordingly”
Order and Connection
When using conclusion transition words, it is important to use them in a logical order that connects the main points of the paper. For example, you can use words like “therefore” or “hence” to connect the main points of the paper to the thesis statement. This helps the reader understand the connection between the main points and the overall purpose of the paper.
Purpose and Clarification
Conclusion transition words can also be used to clarify the purpose of the paper. For example, you can use words like “in order to” or “for the purpose of” to clarify the main idea of the paper. This helps the reader understand the purpose of the paper and the main points that support it.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some common conclusion transition words for essays?
Some common conclusion transition words for essays are “in conclusion,” “to sum up,” “finally,” “in summary,” “to conclude,” and “as a result.”
How can using transition words improve the clarity of my writing?
Using transition words can improve the clarity of your writing by helping to guide the reader through your ideas and making connections between them. They can also help to create a sense of flow and coherence in your writing.
What is the purpose of using transition words in writing?
The purpose of using transition words in writing is to help the reader follow your ideas and understand the connections between them. They can also help to create a sense of flow and coherence in your writing.
What are some examples of transitional phrases used in academic writing?
Some examples of transitional phrases used in academic writing are “on the other hand,” “in contrast,” “furthermore,” “moreover,” “in addition,” “nevertheless,” and “however.”
How can I effectively use transition words in the conclusion of my essay?
To effectively use transition words in the conclusion of your essay, you should choose words that help to summarize your main points and bring your argument to a close. Some effective transition words for conclusions include “in conclusion,” “to sum up,” and “finally.”
What are some commonly used transitional words and phrases for body paragraphs?
Some commonly used transitional words and phrases for body paragraphs include “firstly,” “secondly,” “in addition,” “furthermore,” “moreover,” “on the other hand,” “in contrast,” and “nevertheless.”
Some common conclusion transition words for essays are \"in conclusion,\" \"to sum up,\" \"finally,\" \"in summary,\" \"to conclude,\" and \"as a result.\"
"}},{"@type":"Question","name":"How can using transition words improve the clarity of my writing?","acceptedAnswer":{"@type":"Answer","text":"
"}},{"@type":"Question","name":"What is the purpose of using transition words in writing?","acceptedAnswer":{"@type":"Answer","text":"
"}},{"@type":"Question","name":"What are some examples of transitional phrases used in academic writing?","acceptedAnswer":{"@type":"Answer","text":"
Some examples of transitional phrases used in academic writing are \"on the other hand,\" \"in contrast,\" \"furthermore,\" \"moreover,\" \"in addition,\" \"nevertheless,\" and \"however.\"
"}},{"@type":"Question","name":"How can I effectively use transition words in the conclusion of my essay?","acceptedAnswer":{"@type":"Answer","text":"
To effectively use transition words in the conclusion of your essay, you should choose words that help to summarize your main points and bring your argument to a close. Some effective transition words for conclusions include \"in conclusion,\" \"to sum up,\" and \"finally.\"
"}},{"@type":"Question","name":"What are some commonly used transitional words and phrases for body paragraphs?","acceptedAnswer":{"@type":"Answer","text":"
Some commonly used transitional words and phrases for body paragraphs include \"firstly,\" \"secondly,\" \"in addition,\" \"furthermore,\" \"moreover,\" \"on the other hand,\" \"in contrast,\" and \"nevertheless.\"
Overall, using transition words and phrases can greatly improve the clarity and coherence of your writing. By guiding the reader through your ideas and making connections between them, you can create a more effective and engaging piece of writing.
- Recent Posts
- Mastering English Writing: Essential Transitional Words for Body Paragraphs - March 25, 2024
- 100+ Essential Contrast Transition Words for Exceptional English Writing - March 25, 2024
- Short E Words: Enhance Your Vocabulary with Easy Examples - March 23, 2024
Related posts:
- Brilliant Words that Start with B to Broaden Your Vocabulary
- 50 Words that Start with K: Kicking Off Your Vocabulary
- Sensational Words: Words that Start with S for Your Vocabulary Boost!
- Words Ending in B: Boost Your Vocabulary

Conclusion transition words: Phrases for summarizing and ending
Transition words help us structure our thoughts and guide the reader or listener through what we are saying. When it’s time to summarize your message or end a paragraph, conclusion transition words let you signal this closing.
It’s good to know some synonyms for ‘in conclusion’ and ‘to conclude’, because although these are good examples of concluding words, they can get repetitive.
Our comprehensive list of transition words for conclusion and summary should give you all the inspiration you need, whether you are writing an essay or speech, or just want to become more confident forming an argument. These signal words can also be helpful for restating ideas, drawing attention to key points as you conclude.
We have included plenty of examples of how you can use these transition words for concluding paragraphs or sentences, so by the end of this article, you should be clear on how to use them properly.

Conclusion transition words with examples
We have grouped these summarizing and concluding transition words according to how and where they can be used. For example, some should only be used when forming a final conclusion, whereas others can be used to summarize sections mid-way through your speech or writing.
First, let’s be clear about the difference between a summary and a conclusion .
Summary vs conclusion
A conclusion comes at the end of a speech, chapter, or piece of text, and it brings together all of the points mentioned. A summary, however, can be placed anywhere (even at the beginning). A summary gives a brief outline of the main points but is not as in-depth as a conclusion.
If you are giving a presentation or writing a blog, you may wish to summarize the main points in your introduction so that people know what you are going to cover. You could also summarize a section part-way through before moving on to another angle or topic.
In contrast, the conclusion always comes at the end, and you should only use specific conclusion transition words as you are drawing to a close.
Transition words for conclusion paragraphs
Let’s begin with some discourse markers that signal you are moving to the concluding paragraph in your presentation, speech, essay, or paper. These can all be used to start a conclusion paragraph.
- In conclusion
- To conclude
- We can conclude that
- Given these points
- In the final analysis
- As can be seen
- In the long run
- When all is said and done
- I’ll end by
- As we draw to a close
The last three on this list, the ‘closing’ transition words, would generally only be used in spoken discourse.
Some transition words for order and sequencing should also help with structuring what you want to say, including the ending.
Example conclusion sentences
The following sentences show how to use conclusion words correctly:
- In conclusion , we can say that plan A will be of greater benefit to the company.
- When all is said and done , it’s clear that we should steer clear of this investment strategy.
- Given these points , I believe the trial was a great success.
- I’ll end by reminding you all that this experiment was just the beginning of a much larger project.
- To wrap up , let’s look at how this learning can be applied.
- In the long run , we will make more profit by investing heavily in new machinery.
- Having analyzed seven of our competitors in detail, we can conclude that our content marketing strategy should be updated.
Transition words for summary
The following summary transition words may be used as part of a conclusion paragraph, but they are especially helpful for concisely drawing together several points.
- To summarize
- On the whole
- Generally speaking
- All things considered
- In a nutshell (informal)
- In any case
Note that although you can insert summary transition words anywhere, the specific phrases ‘In summary’, ‘To summarize’ and ‘To sum up’ are generally only used at the end, similar to conclusion phrases.
Example summary sentences
- In brief , this presentation is going to cover the pros and cons of the device and how we can apply this to our own product development.
- This new technology is, in a word , revolutionary.
- All things considered , we found that Berlin was a great city for a weekend break.
- To summarize , we can say that Shakespeare’s writing continues to have a global influence.
- We can say that the combustion engine was, on the whole , a good invention.
- In any case , we should put the necessary precautions in place.
- Generally speaking , girls are more thoughtful than boys.
Transition words to end a paragraph
You may wish to add ending transition words in the final sentence of a paragraph to conclude the ideas in that section of text, before moving on to another point.
Here are some transition words to conclude a paragraph:
- This means that
- With this in mind
- By and large
- For the most part
Note that some of these could equally be used to begin a new paragraph, so long as that paragraph is summarizing the points previously mentioned.
Cause and effect transition words could also be helpful in this context.
Examples of transition words for the end of a paragraph
- Jamie is a vegan and Sheryl has a lot of allergies. This means that we should be careful which restaurant we choose.
- The weather forecast said it would rain this afternoon. With this in mind , should we postpone our hike?
- Each of the students has their own opinion about where to go for the field trip. Ultimately , though, it’s the teacher who will decide.
Restating points as you conclude
Conclusion transition words can also signal that you are restating a point you mentioned earlier. This is common practice in both writing and speaking as it draws the reader or listener’s attention back to something you want them to keep in mind. These are, therefore, also examples of transition words for emphasizing a point .
Here are some helpful transition words for concluding or summarizing by restating points:
- As mentioned previously
- As stated earlier
- As has been noted
- As shown above
- As I have said
- As I have mentioned
- As we have seen
- As has been demonstrated
You may switch most of these between the passive and active voice, depending on which is most appropriate. For example, ‘As has been demonstrated’ could become ‘As I have demonstrated’ and ‘As shown above’ could become ‘As I have shown’.
Example sentences to restate a point in conclusion or summary
- As I stated earlier , the only way we can get meaningful results from this survey is by including at least a thousand people.
- As has been demonstrated throughout this conference, there are exciting things happening in the world of neuroscience.
- As shown by this study, the trials have been promising.
If you were researching these transition words for concluding an essay, you might find it helpful to read this guide to strong essay conclusions . Of course, there are many ways to use summary transition words beyond essays. They may be a little formal for casual conversation, but they certainly can be used in speech as part of a presentation, debate, or argument.
Can you think of any other concluding words or phrases that should be on this list? Leave a comment below to share them!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and site URL in my browser for next time I post a comment.
Sign me up for the newsletter!
- Features for Creative Writers
- Features for Work
- Features for Higher Education
- Features for Teachers
- Features for Non-Native Speakers
- Learn Blog Grammar Guide Community Events FAQ
- Grammar Guide
List of 50 "In Conclusion" Synonyms—Write Better with ProWritingAid

Alex Simmonds

Table of Contents
Why is it wrong to use "in conclusion" when writing a conclusion, what can i use instead of "in conclusion" for an essay, what are some synonyms for "in conclusion" in formal writing, what are some synonyms for "in conclusion" in informal writing, what is another word for "in conclusion", what should a conclusion do in an article or paper.
The final paragraphs of any paper can be extremely difficult to get right, and yet they are probably the most important. They offer you a chance to summarize the points you have made into a neat package and leave a good impression on the reader.
Many people choose to start the last paragraph with the phrase in conclusion , but this has its downsides.
Firstly, you should only use it once. Any more than that and your essay will sound horribly repetitive. Secondly, there is the question of whether you should even use the phrase at all?

Though it’s okay to use in conclusion in a speech or presentation, when writing an essay it comes across as stating the obvious. The phrase will come across as a bit unnecessary or "on the nose."
Its use in an essay is clichéd, and there are far cleaner and more elegant ways of indicating that you are going to be concluding the paper. Using in conclusion might even irritate and alienate your audience or readers.
Thankfully, there are hundreds of synonyms available in the English language which do a much better (and much more subtle) job of drawing a piece of writing to a close.
The key is to choose ones which suit the tone of the paper. Here we will look at both formal options for an essay or academic paper, and informal options for light-hearted, low key writing, or speeches.

If you are writing an academic essay, a white paper, a business paper, or any other formal text, you will want to use formal transitional expressions that successfully work as synonyms for in conclusion .
The following are some suggestions you could use:
As has been demonstrated
A simple way of concluding all your points and summarizing everything you have said is to confidently state that those points have convincingly proven your case:
As the research has demonstrated , kids really do love chocolate.
As all the above points have demonstrated , Dan Brown really was the most technically gifted writer of the 20th Century.
As has been demonstrated in this paper , the side-effects of the vaccine are mild in comparison to the consequences of the virus.
As has been shown
This is another way of saying as has been demonstrated , but perhaps less scientific and more literary. As has been shown would work well in literature, history, or philosophy essays.
For example:
As has been shown above , the First World War and industrialization were the drivers for a new way of seeing the world, reflected in Pound’s poetry.
In the final analysis
This is a great expression to use in your conclusion, since it’s almost as blunt as in conclusion , but is a more refined and far less clichéd way of starting the concluding paragraph.
Once you have finished your argument and started drawing things to a close, using in the final analysis allows you to tail nicely into your last summation.
In the final analysis , there can be little doubt that Transformers: Dark of the Moon represents a low point in the history of cinema.

Along with let’s review , this is short and blunt way of announcing that you intend to recap the points you have made so far, rather than actually drawing a conclusion.
It definitely works best when presenting or reading out a speech, but less well in an essay or paper.
However, it does work effectively in a scientific paper or if you wish to recap a long train of thought, argument, or sequence before getting to the final concluding lines.
To review , of the two groups of senior citizens, one was given a placebo and the other a large dose of amphetamines.

Another phrase you could consider is in closing . This is probably better when speaking or presenting because of how double-edged it is. It still has an in conclusion element to it, but arguably it could also work well when drawing an academic or scientific paper to a conclusion.
For example, it is particularly useful in scientific or business papers where you want to sum up your points, and then even have a call to action:
In closing then, it is clear that as a society, we all need to carefully monitor our consumption of gummy bears.
Or in an academic paper, it offers a slightly less blunt way to begin a paragraph:
In closing , how do we tie all these different elements of Ballard’s writing together?
Perhaps the most similar expression to in conclusion is in summary . In summary offers a clear indication to the reader that you are going to restate the main points of your paper and draw a conclusion from those points:
In summary , Existentialism is the only philosophy that has any real validity in the 21st century.
In summary , we believe that by switching to a subscription model...
On top of those previously mentioned, here are some other phrases that you can use as an alternative to in conclusion :
To summarize
Overall, it may be said
Taking everything into account
On the whole
In general, it can be said that
With this in mind
Considering all this
Everything considered
As a final observation
Considering all of the facts
For the most part
In light of these facts
When it comes to finishing up a speech, a light-hearted paper, blog post, or magazine article, there are a couple of informal phrases you can use rather than in conclusion :
In a nutshell
The phrase in a nutshell is extremely informal and can be used both in speech and in writing. However, it should never be used in academic or formal writing.
It could probably be used in informal business presentations, to let the audience know that you are summing up in a light-hearted manner:
In a nutshell , our new formula Pro Jazzinol shampoo does the same as our old shampoo, but we get to charge 20% more for it!
You can also use it if you want to get straight to the point at the end of a speech or article, without any fluff:
In a nutshell , our new SocialShocka app does what it says on the tin—gives you an electric shock every time you try to access your social media!
At the end of the day
This is a pretty useful expression if you want to informally conclude an argument, having made all your points. It basically means in the final reckoning or the main thing to consider is , but said in a more conversational manner:
At the end of the day , he will never make the national team, but will make a good living as a professional.
At the end of the day , the former President was never destined to unite the country…

Long story short
Another informal option when replacing in conclusion is to opt for to make a long story short —sometimes shortened to long story short .
Again, this is not one you would use when writing an academic or formal paper, as it is much too conversational. It’s a phrase that is far better suited to telling a joke or story to your friends:
Long story short , Billy has only gone and started his own religion!
Would you ever use it in writing? Probably not, except for at the end of friendly, low-key presentations:
Long story short , our conclusion is that you are spending far too much money on after work company bowling trips.
And possibly at the end of an offbeat magazine article or blog post:
Long story short , Henry VIII was a great king—not so great a husband though!
Other "In Conclusion" Synonyms for Informal Writing
You can use any of the synonyms in this article when writing informally, but these are particularly useful when you want your writing to sound conversational:
By and large
On a final note
Last but not least
For all intents and purposes
The bottom line is
To put it bluntly
To wrap things up
To come to the point
To wind things up

Instead of opting for one of the above expressions or idioms, there are several different singular transition words you can use instead. Here are a couple of examples:
The perfect word to tell the reader you are reaching the end of your argument. Lastly is an adverb that means "at the end" or "in summary." It is best used when you are beginning your conclusion:
Lastly , with all the previous points in mind, there is the question of why Philip K Dick was so fascinated with alternate history?
But can also be used at the very end of your conclusion too:
Lastly then, we are left with Eliot’s own words on his inspiration for "The Waste Land."
Finally does exactly the same job as lastly . It lets the reader know that you are at the final point of your argument or are about to draw your conclusion:
Finally , we can see from all the previous points that...
Another word that can be used at beginning of the conclusion is the adverb ultimately . Meaning "in the end" or "at the end of the day," it can be used as a conclusion to both informal and formal papers or articles:
Ultimately , it comes down to whether one takes an Old Testament view of capital punishment or...
It can also be used in more survey, scientific, or charity appeal style articles as a call to action of some sort:
Ultimately , we will all need to put some thought into our own carbon footprints over the next couple of years.
A good word to conclude a scientific, or survey style paper is overall . It can be used when discussing the points, arguments or results that have been outlined in the paper up until that point.
Thus, you can say:
Overall , our survey showed that most people believe you should spread the cream before you add the jam, when eating scones.
Other Transition Words to Replace "In Conclusion"
Here are a few transition word alternatives to add to your arsenal:
Considering
Essentially
Principally
Summarizing
Pro tip: You should use transition words throughout your essay, paper, or article to guide your reader through your ideas towards your conclusion. ProWritingAid’s Transitions Report tells you how many transition words you’ve used throughout your document so you can make sure you’re supporting your readers’ understanding.
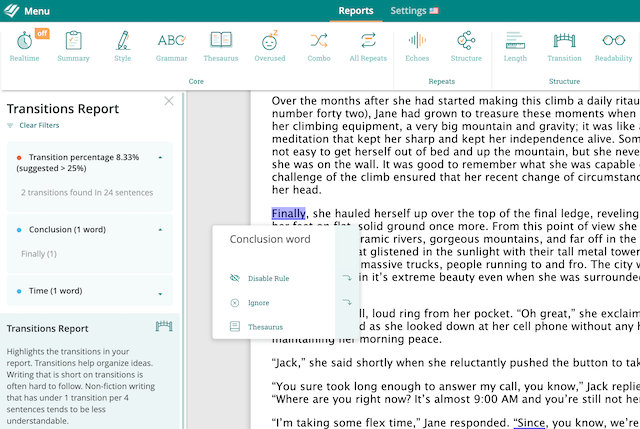
It’ll also tell you what type of transitions you’ve used. If there are no conclusion words in your writing, consider using one of the synonyms from this article.
Sign up for a free ProWritingAid account to try the Transitions Report.
One of the most effective ways of finishing up a piece of writing is to ask a question, or return to the question that was asked at the beginning of the paper using. This can be achieved using how , what , why , or who .
This is sometimes referred to as the "so what?" question. This takes all your points and moves your writing (and your reader) back to the broader context, and gets the reader to ask, why are these points important? Your conclusion should answer the question "so what?" .

To answer that, you circle back to the main concept or driving force of the essay / paper (usually found in the title) and tie it together with the points you have made, in a final, elegant few sentences:
How, then, is Kafka’s writing modernist in outlook?
Why should we consider Dickens’ work from a feminist perspective?
What, then , was Blake referring to, when he spoke of mind forged manacles?
In Conclusion
There are plenty of alternatives for drawing an effective and elegant close to your arguments, rather than simply stating in conclusion .
Whether you ask a question or opt for a transition expression or a single transition word, just taking the time to choose the right synonyms will make all the difference to what is, essentially, the most important part of your paper.
Want to improve your essay writing skills?
Use prowritingaid.
Are your teachers always pulling you up on the same errors? Maybe you’re losing clarity by writing overly long sentences or using the passive voice too much.
ProWritingAid helps you catch these issues in your essay before you submit it.

Be confident about grammar
Check every email, essay, or story for grammar mistakes. Fix them before you press send.
Alex Simmonds is a freelance copywriter based in the UK and has been using words to help people sell things for over 20 years. He has an MA in English Lit and has been struggling to write a novel for most of the last decade. He can be found at alexsimmonds.co.uk.
Get started with ProWritingAid
Drop us a line or let's stay in touch via :
- Homepage >
- Story Repository >
Words of inspiration from an inaugural poet
A world-class university with worldwide impact

The University at Buffalo, New York State’s flagship, is consistently recognized as one of the world's most exceptional, most affordable universities, making it a top choice for students and faculty around the globe.
- 4/1/24 Quick Facts About UB
- A Year in Pictures 📸
- 11/6/23 Diverse and Inclusive
- 3/1/24 Our Leadership
- 3/11/24 Our Campuses
- 9/21/23 Buffalo Niagara: Our Hometown
- 1/12/24 UB's Strategic Plan
- 10/17/23 Boldly Buffalo: The Campaign for UB
- 11/11/22 Resources for the WNY Community
Exceptional opportunities for extraordinary people (like you)

More choices. More challenges. More life-changing experiences. At UB, you'll find 500+ programs, world-renowned faculty and a diverse environment that prepares you for anything.
- 12/14/23 Superior Academics
- 5/12/23 Schools and Colleges
- 8/16/23 Degree Programs
- Study Abroad
- 1/8/24 Experiential Learning Opportunities
- Here to Career Initiative
- 3/22/24 Graduate Programs
- Undergraduate Catalog and Courses
- Class Schedule
Join our community of tenacious problem solvers

As a top 40 public research university, UB is a place where you’ll make a real difference. Here, you can follow your passion, apply your knowledge and collaborate with other top minds to tackle the world's most complex challenges.
- 3/25/24 Research and Economic Development Gateway
- 4/1/24 Research News
- 3/26/24 Podcast: Driven to Discover
- 3/1/24 Major research centers, institutes, and initiatives
- 3/7/24 Our cutting-edge facilities
Resources for:
- Researchers Get resources, services, and support for your research
- Information for Students Find research opportunities throughout UB
- Business and Entrepreneurs Connect with UB to grow or start your business
- Industry Partners Locate UB equipment, facilities and labs available for use
- The Community Learn how to participate in clinical trials at UB
- Entrepreneurially Minded Students, Faculty, Clinicians, and Researchers Explore UB's Innovation Hub to move your ideas from the lab, classroom, or clinic to the marketplace
You belong here!

Join one of our 400+ clubs. Go to a Division I basketball game. Kayak across our on-campus lake. There's always something to do at UB, and new friends to do it with. Share your True Blue pride with us every day, and wear your blue on Fridays!

- 12/1/23 Your Life at #UBuffalo
- 1/16/24 Students share their journeys 🎥
- 2/13/24 Where To Live
- Where To Eat

- Calendar of Events
- 9/21/23 Explore Buffalo Niagara

- 3/11/24 How True Blue Are You?
- 3/4/24 Student Clubs and Organizations
- 2/13/24 Find it in the Student Guide
- 2/13/24 Student Guide
- 12/21/22 Digital Backgrounds
Your journey begins here

Every success story has a starting point. This is yours. Take your first step toward an education that will put your grandest ambitions within reach.
- Undergraduate Admissions
- 1/27/24 International Undergraduate Admissions
- 10/24/22 Graduate Admissions
- 3/25/24 Summer Sessions
- 1/5/24 Winter Sessions
Due to Department of Education changes in the 2024 Free Application for Federal Student Aid, the University at Buffalo has extended the enrollment and tuition deposit deadline to May 15, 2024, and the housing application deadline has been extended to May 24, 2024. Learn more about your steps to enroll .
- Transfer to UB
- Make Your Deposit
campus news

Amanda Gorman was the final speaker in this year's Distinguished Speakers Series. Photo: Nancy J. Parisi
By VICKY SANTOS
Published March 28, 2024
The rainy weather didn’t deter a sold-out crowd from showing up for poet and activist Amanda Gorman’s appearance Tuesday night in the Center for the Arts to close the 2023-24 edition of UB’s Distinguished Speakers Series. And for their perseverance, audience members were rewarded with a night of inspirational, humorous and engaging dialogue.
Gorman received critical acclaim for performing her poem, “The Hill We Climb,” at the 2021 presidential inauguration. She is one of only six poets to ever do so and, at 22, was by far the youngest — the next youngest person, Richard Blanco, was 44.
In addition to her legendary performance at the U.S. Capitol, she has performed at the Library of Congress and Lincoln Center. She is the first National Youth Poet Laureate; the first poet to grace the cover of Vogue magazine; and the first poet to perform at the Super Bowl.
“We conclude another terrific season on an incredibly high note,” President Satish K. Tripathi said in his introduction of Gorman. “It’s been a little over three years since this evening’s speaker enthralled the world. In the midst of the COVID-19 pandemic, and only weeks after the Jan. 6 attack on the U.S. Capitol, Amanda Gorman delivered an electric performance of her poem, ‘The Hill we Climb,’ at President Biden’s inauguration. In five minutes, and with 723 words, Ms. Gorman managed to capture the moment and captivate millions with her message of hope, resilience and healing.”
Gorman received a rousing and enthusiastic round of applause as she walked on stage and joined the evening’s moderator, Cristanne Miller, SUNY Distinguished Professor and Edward H. Butler Professor of English.
“Thank you all so much for such a warm welcome to Buffalo! I had no idea upstate New York knew who I was! Thank you for stroking my pride and my ego,” Gorman joked.

Cristanne Miller (left), SUNY Distinguished Professor and Edward H. Butler Professor of English, moderated the Q&A portion of the evening. Photo: Nancy J. Parisi
Gorman said that while backstage, she had looked through Miller’s new book , “The Letters of Emily Dickinson.” Miller and Gorman spent a few moments talking about their love and admiration of Dickinson before moving onto the questions awaiting Gorman — most of which were submitted previously by audience members and covered topics ranging from overcoming a speech-and-hearing disorder in her youth to the power of poetry and social justice movements.
“Poetry is the language of revolution. I point out that there’s a reason that, at the base of the Statue of Liberty, there’s a poem and not an essay, and that is not to detract from prose, but just to say there’s something incredibly unique about poetry, which demands us to participate in envisioning our best selves,” Gorman said. “There’s an inherent engine behind poetry, which localizes us around the language that in and of itself is representative of activism. It is not latent; it is not static; it’s voicing the deepest versions of ourselves to improve the world.”
When asked which of her poems is her favorite, Gorman replied it’s “The Hill We Climb,” but probably not for the reasons people may think.
“I’m most proud of it because it’s my most banned poem. I never thought I’d be cool enough to be considered among the Toni Morrisons and James Baldwins and the Margaret Atwoods of the world. I’m like, the Instagramable one — and they’re all taking me so seriously.”
“The fact that this poem, that five minutes, could be that threatening that they’re revoking it from schools — it says something to how it speaks to the bedrock of America.”
Gorman says she reads the notorious poem differently each time she recites it — partly because of the environment and occasion, but also because of a speech impediment.
“Part of what causes my speech impediment is having an auditory-processing disorder, which means you hear things differently — sound is distorted, and that changes as your brain is wiring itself on how to develop speech. Even though I’ve gone through speech therapy, I still have a brain that’s wired to hear all the different versions of what someone might have said.”
Gorman gave the example that if someone said, “go sit on the couch,” a person with an auditory-processing disorder heard a couple different versions of that, including something along the lines of, “go hit the cow.”
“It was really confusing when I was a kid because I wasn’t always able to distinguish what I was hearing. I heard it as it was, but I was also hearing all the different versions of what it could be.”
Gorman says that process carries over to writing words and also when she’s speaking.
“I write whatever my brain is telling me to write, but when I speak, it comes out in different lattices and rhythms.”
Political ambitions
Gorman says she always wrote as if someday she might be writing a poem for an inauguration.
“I think I have always had a little bit of grandiose delusion in my life,” Gorman recalled. “I remember being a little kid and my mom was like, ‘where do you get this optimism from?’ Because every single time there was a raffle or some kind of drawing, I was always at the front of the line because I was sure I was going to win it.”
That same optimism is still guiding Gorman, who says she will be running for president of the United States in 2036.
“It’s not a dream; it’s a plan!” Gorman proclaimed. “My hashtag for my campaign is going to be #coAMANDA in chief.”
Humility accesses humanity
Gorman finished the night reading from her collection “What We Carry.”
“It deals with the pandemic, it deals with history, it deals with divisiveness, but more so it deals with how we move forward in spite of all these,” Gorman said.
“When I write my poems, I try to keep in mind that humility is how to access the humanity.”
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Guest Essay
Something Other Than Originalism Explains This Supreme Court

By Marc O. De Girolami
Mr. De Girolami is a law professor at the Catholic University of America. He is writing a book about traditionalism in constitutional law.
It is a sign of the polarizing nature of the current Supreme Court that even knowledgeable critics of its opinions make diametrically opposed arguments.
This week, for example, the former Supreme Court justice Stephen Breyer, in a new book, “Reading the Constitution,” chides the current court’s approach to the law, which he says fixates on the text of the Constitution and attaches too much significance to the meanings of its provisions at the time they were ratified. If only, Justice Breyer urges, justices would soften this “originalist” approach and take into account how “our values as a society evolve over time” — including by respecting the “longstanding practice” of the court and other organs of government.
Justice Breyer’s criticism follows on the heels of that of another judge, Kevin Newsom of the U.S. Court of Appeals for the 11th Circuit. In a talk last month at Harvard Law School, Judge Newsom made the opposite argument: He criticized the Supreme Court, when considering matters such as handgun regulation and abortion rights, for being insufficiently faithful to originalism and overly attuned to social practices that occurred or continued after constitutional ratification. Such traditions, he warned, “have no demonstrable connection to the original, written text.”
The current Supreme Court is the object of considerable controversy and confusion. To understand its decisions properly, especially over the past three or four years, the key is to realize that each critic is half right. Justice Breyer is right that the Constitution should be interpreted, in part, in light of practices that persisted after its ratification, but wrong to think that the current court is not doing this. Judge Newsom is right that the current court is doing this, but wrong to think that it should not be.
This court is conventionally thought of as originalist. But it is often more usefully and accurately understood as what I call “ traditionalist ”: In areas of jurisprudence as various as abortion, gun rights, free speech, religious freedom and the right to confront witnesses at trial, the court — led in this respect by Justices Samuel Alito, Clarence Thomas and Brett Kavanaugh — has indicated time and again that the meaning and law of the Constitution is often to be determined as much by enduring political and cultural practices as by the original meaning of its words.
The fact that the Supreme Court seems to be finding its way toward an open embrace of traditionalism should be broadly celebrated. To be sure, the court’s traditionalism has played a role in many decisions that have been popular with political conservatives, such as the Dobbs ruling in 2022 that overturned Roe v. Wade. But it is not a crudely partisan method. Justice Sonia Sotomayor, an Obama nominee, has used it in a decision for the court — and Justice Amy Coney Barrett, a Trump nominee, has expressed some skepticism about it.
Traditionalism may not be partisan, but it is political: It reflects a belief — one with no obvious party valence — that our government should strive to understand and foster the common life of most Americans. The Supreme Court has relied on traditionalism to good effect for many decades, though the justices have seldom explicitly acknowledged this. Traditionalism should be favored by all who believe that our legal system ought to be democratically responsive, concretely minded (rather than abstractly minded) and respectful of the shared values of Americans over time and throughout the country.
To get a better sense of what traditionalism is, it is useful to compare it with the two dominant approaches to constitutional interpretation in adjudication: originalism and what is often called “living constitutionalism.”
Sometimes the Constitution’s words are not clear and their application to a particular issue is also unclear. Consider the line “Congress shall make no law respecting an establishment of religion,” from the First Amendment. Judges face choices about how to determine what exactly Congress (and today, by extension, the states) is being forbidden from doing.
One option is to discern the meaning that those words would have had at the time of their adoption, using ratification-era dictionaries, contemporary documents by learned authorities, databases of usage, other linguistic and legal sources and perhaps activities closely confined to the founding period. That is originalism.
Another option is to understand those words by recourse to a high ideal or abstraction. For example, a judge might take that passage of the First Amendment to reflect a principle of separation of church and state and then apply that principle in light of the judge’s moral views or perceptions of contemporary moral standards in the case at hand. That is living constitutionalism.
Traditionalism offers a third option. Here, one would look at specific political and cultural practices — the activities of the organs of government and of individuals and groups across the country over long periods of time — to help determine constitutional meaning and law. For example, one might observe that the practice of legislative prayer (prayer that opens legislative assemblies) was pervasive long before and at the time of the First Amendment’s ratification, and that it continued for centuries afterward. For that reason, one would conclude that legislative prayer is unlikely to violate the prohibition against an “establishment of religion.”
The intuition is straightforward: It would be odd to think that the Establishment Clause of the First Amendment prohibits legislative prayer if legislative prayer was widely practiced before, during and for centuries after ratification. Were we supposed to put a stop to a practice many showed no sign of wanting to stop, and indeed, that a great many people were eager to continue and did continue? Sometimes, yes, moral reflection or changed circumstance prompts a re-evaluation of our practices. But in general, we do what we mean and we mean what we do, and constitutional law takes its shape accordingly.
In its 2021-2022 term, traditionalism was the Supreme Court’s preferred method in a number of high-profile cases. Consider New York State Rifle and Pistol Association v. Bruen, a 2022 decision that concerned a New York law that strictly limited the carrying of guns outside the home. Justice Thomas, writing for the majority, held that New York’s requirement to demonstrate a “special need for self-protection” before the state would issue a handgun permit for self-defense outside the home violated the Second Amendment.
The “historical tradition” of handgun regulation, Justice Thomas argued, established the limits of the right to keep and bear arms. He noted that the practices of regulation “from before, during and even after the founding” of the United States indicated “no such tradition in the historical materials,” which suggested that a long, unbroken line of tradition, stretching from medieval England to early 20th century America, was at odds with New York’s law. The opinion granted the existence of scattered 19th-century regulations akin to New York’s, but argued that these were dwarfed by the dearth of analogous traditions of gun regulation over time and across state and local communities.
One can see a similar traditionalist approach in Dobbs, where Justice Alito, writing for the court, examined the government practices of abortion regulation before, during and after ratification of the 14th Amendment, concluding that there is no constitutional right to abortion in part because there is “an unbroken tradition of prohibiting abortion” that persisted “from the earliest days of the common law until 1973.”
Likewise, in Kennedy v. Bremerton School District, the Supreme Court decided in 2022 that a public school football coach who prayed on the field after games was not in violation of the Establishment Clause by holding, in an opinion by Justice Neil Gorsuch, that this was not analogous to prayer practices long considered Establishment Clause violations. And in the unanimously decided case Houston Community College System v. Wilson, the court in 2022 held that “long settled and established practice” determined that elected bodies do not violate their members’ freedom of speech when they censure one of their members.
For some critics, the invocation of “tradition” sets off alarm bells. After all, our country looks very different today, demographically and otherwise, than it did hundreds of years ago, when political power was held by relatively few and denied to others for illegitimate reasons. These critics ask how well traditionalism deals with the contemporary realities of American democracy.
The answer to this legitimate question is: Compared to what? Consider again originalism and living constitutionalism. These approaches, different as they are from each other, are both suited to elite actors working at the nerve centers of legal and political power. Both depend on the preferences and findings of the legal professional class. Originalism privileges the centuries-old writings of illustrious figures of the founding or Reconstruction era as determined by today’s most brilliant legal historians and theorists. Living constitutionalism privileges the high ideals of today’s most prominent academics and judges.
Traditionalism, by contrast, looks to the ordinary practices of the American people across time and throughout the country. In democracies, people obey the law because they believe it is legitimate, and the law acquires legitimacy when the people believe they have had a hand, direct or indirect, in shaping it. True, the practices of “the people” may be repudiated or upended — no political tradition is perfect — but while they endure, their origin in popular sovereignty is a presumptive reason to preserve them.
Tradition, in the law and elsewhere, illuminates a basic fact of human life: We admire and want to unite ourselves with ways of being and of doing that have endured for centuries before we were born and that we hope will endure long after we are gone. At its core, this is what constitutional traditionalism is about: a desire for excellence, understood as human achievement over many generations and in many areas of life, that serves the common good of our society.
Not all traditions are worthy of preservation. Some are rightly jettisoned as the illegitimate vestiges of days gone by. But many, and perhaps most, deserve our solicitude and need a concerted defense.
Traditions can be fragile things. To the extent that a revitalized practice of constitutional interpretation is possible, it will depend on determining the content of the Constitution with an eye to their sustenance and restoration.
Marc O. De Girolami ( @MarcODeGirolami ) is a law professor at the Catholic University of America, where he is a co-director of the Center for Law and the Human Person.
The Times is committed to publishing a diversity of letters to the editor. We’d like to hear what you think about this or any of our articles. Here are some tips . And here’s our email: [email protected] .
Follow the New York Times Opinion section on Facebook , Instagram , TikTok , WhatsApp , X and Threads .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
1. The Weight of the Evidence Suggests…. My Rating: 10/10. Overview: This is a good concluding phrase for an evaluative essay where you need to compare two different positions on a topic then conclude by saying which one has more evidence behind it than the other.
Step 1: Return to your thesis. To begin your conclusion, signal that the essay is coming to an end by returning to your overall argument. Don't just repeat your thesis statement —instead, try to rephrase your argument in a way that shows how it has been developed since the introduction. Example: Returning to the thesis.
Finally, some advice on how not to end an essay: Don't simply summarize your essay. A brief summary of your argument may be useful, especially if your essay is long--more than ten pages or so. But shorter essays tend not to require a restatement of your main ideas. Avoid phrases like "in conclusion," "to conclude," "in summary," and "to sum up ...
End your essay with a call to action, warning, or image to make your argument meaningful. Keep your conclusion concise and to the point, so you don't lose a reader's attention. Do your best to avoid adding new information to your conclusion and only emphasize points you've already made in your essay. Method 1.
Overall, It Can Be Said…. To recap an idea at the end of a critical or descriptive essay, you can use this phrase at the beginning of the concluding paragraph. "Overall" means "taking everything into account," and it sums up your essay in a formal way. You can use "overall" on its own as a transition signal, or you can use it as ...
Option 1: Save something for the end. It might be helpful to think of your essay like this: You are a tailor cutting a garment from a beautiful piece of fabric. You have plenty of fabric to work with because you are approaching your overall essay as a process: brainstorming, writing, revision, repeat. The writing process is cyclical.
Option 4: End on an action. Ending on an action can be a strong way to wrap up your essay. That might mean including a literal action, dialogue, or continuation of the story. These endings leave the reader wanting more rather than wishing the essay had ended sooner. They're interesting and can help you avoid boring your reader.
Avoid stating the obvious. Avoid using statements like "I'm intelligent" if you've spent the essay giving examples of your smarts and academic skills. Likewise, avoid simplified statements that will seem obvious to the reader, like "High school is hard" or "People love dogs.". [8] Don't: I'm a hard worker.
4. Expository essay conclusion. This example of an essay conclusion revolves around a psychological phenomenon named the bandwagon effect and examines its potential ill effects on society: Restated thesis statement. Body paragraph summary. Closing statement
Highlight the "so what". At the beginning of your paper, you explain to your readers what's at stake—why they should care about the argument you're making. In your conclusion, you can bring readers back to those stakes by reminding them why your argument is important in the first place. You can also draft a few sentences that put ...
Different transition words can have different effects, so be sure to choose a transition word or phrase that clearly communicates that you are closing your essay. Some common examples of conclusion transition words and phrases include: In conclusion, To conclude, Finally, To sum up, As previously stated.
Pin. In Conclusion Meaning "In conclusion" is a transitional phrase used to indicate that you are approaching the end of your writing.It serves to summarize the main points or indicate a final thought or opinion. Using synonyms for "in conclusion" can help maintain your reader's interest and offer a sense of variety and sophistication in your writing.
It's true: there are other ways to say "in conclusion" that don't feel as trite. Can't think of any? Find 57 different words and phrases right here.
If you're struggling to choose the right words for your essay, don't worry—you've come to the right place! In this article, we've compiled a list of over 300 words and phrases to use in the introduction, body, and conclusion of your essay. Contents: Words to Use in the Essay Introduction. Words to Use in the Body of the Essay.
4. That is to say. Usage: "That is" and "that is to say" can be used to add further detail to your explanation, or to be more precise. Example: "Whales are mammals. That is to say, they must breathe air.". 5. To that end. Usage: Use "to that end" or "to this end" in a similar way to "in order to" or "so".
To effectively use transition words in the conclusion of your essay, you should choose words that help to summarize your main points and bring your argument to a close. Some effective transition words for conclusions include "in conclusion," "to sum up," and "finally."
In short. In essence. On balance. Overall. In any case. In effect. Note that although you can insert summary transition words anywhere, the specific phrases 'In summary', 'To summarize' and 'To sum up' are generally only used at the end, similar to conclusion phrases.
Other Transition Words to Replace "In Conclusion" Here are a few transition word alternatives to add to your arsenal: Briefly. Obviously. Considering. Therefore. Thus. Essentially. Indeed. Principally. Summarizing. Altogether. Pro tip: You should use transition words throughout your essay, paper, or article to guide your reader through your ...
3.Conclude with a summarizing sentence. Outline Example Introduction: Introduce the topics you'll be comparing and contrasting Body Paragraphs: You can have as many body paragraphs as necessary, each focusing on a different aspect of the subjects being compared. Block 1: (iPhone) A. Hardware and Performance B. Design and Build Quality C. Camera ...
Mr Huang's words should be taken with a pinch of salt: Nvidia's profits have soared because of the growing demand for its high-tech chips, which are used to train AI models. Promoting AI is ...
Taylor added the word to the order, but it would be the other Texan — a man with a fondness for using the N-word in private — who would most forcefully describe the moral rationale, the ...
"We conclude another terrific season on an incredibly high note," President Satish K. Tripathi said in his introduction of Gorman. ... 'The Hill we Climb,' at President Biden's inauguration. In five minutes, and with 723 words, Ms. Gorman managed to capture the moment and captivate millions with her message of hope, resilience and ...
Also read: How to Write a Thesis Statement. 2. Tying together the main points. Tying together all the main points of your essay does not mean simply summarizing them in an arbitrary manner. The key is to link each of your main essay points in a coherent structure. One point should follow the other in a logical format.
Guest Essay. Something Other Than Originalism Explains This Supreme Court. March 29, 2024 ... one would conclude that legislative prayer is unlikely to violate the prohibition against an ...