Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to write a narrative essay | Example & tips

How to Write a Narrative Essay | Example & Tips
Published on July 24, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on July 23, 2023.
A narrative essay tells a story. In most cases, this is a story about a personal experience you had. This type of essay , along with the descriptive essay , allows you to get personal and creative, unlike most academic writing .
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
What is a narrative essay for, choosing a topic, interactive example of a narrative essay, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about narrative essays.
When assigned a narrative essay, you might find yourself wondering: Why does my teacher want to hear this story? Topics for narrative essays can range from the important to the trivial. Usually the point is not so much the story itself, but the way you tell it.
A narrative essay is a way of testing your ability to tell a story in a clear and interesting way. You’re expected to think about where your story begins and ends, and how to convey it with eye-catching language and a satisfying pace.
These skills are quite different from those needed for formal academic writing. For instance, in a narrative essay the use of the first person (“I”) is encouraged, as is the use of figurative language, dialogue, and suspense.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Narrative essay assignments vary widely in the amount of direction you’re given about your topic. You may be assigned quite a specific topic or choice of topics to work with.
- Write a story about your first day of school.
- Write a story about your favorite holiday destination.
You may also be given prompts that leave you a much wider choice of topic.
- Write about an experience where you learned something about yourself.
- Write about an achievement you are proud of. What did you accomplish, and how?
In these cases, you might have to think harder to decide what story you want to tell. The best kind of story for a narrative essay is one you can use to talk about a particular theme or lesson, or that takes a surprising turn somewhere along the way.
For example, a trip where everything went according to plan makes for a less interesting story than one where something unexpected happened that you then had to respond to. Choose an experience that might surprise the reader or teach them something.
Narrative essays in college applications
When applying for college , you might be asked to write a narrative essay that expresses something about your personal qualities.
For example, this application prompt from Common App requires you to respond with a narrative essay.
In this context, choose a story that is not only interesting but also expresses the qualities the prompt is looking for—here, resilience and the ability to learn from failure—and frame the story in a way that emphasizes these qualities.
An example of a short narrative essay, responding to the prompt “Write about an experience where you learned something about yourself,” is shown below.
Hover over different parts of the text to see how the structure works.
Since elementary school, I have always favored subjects like science and math over the humanities. My instinct was always to think of these subjects as more solid and serious than classes like English. If there was no right answer, I thought, why bother? But recently I had an experience that taught me my academic interests are more flexible than I had thought: I took my first philosophy class.
Before I entered the classroom, I was skeptical. I waited outside with the other students and wondered what exactly philosophy would involve—I really had no idea. I imagined something pretty abstract: long, stilted conversations pondering the meaning of life. But what I got was something quite different.
A young man in jeans, Mr. Jones—“but you can call me Rob”—was far from the white-haired, buttoned-up old man I had half-expected. And rather than pulling us into pedantic arguments about obscure philosophical points, Rob engaged us on our level. To talk free will, we looked at our own choices. To talk ethics, we looked at dilemmas we had faced ourselves. By the end of class, I’d discovered that questions with no right answer can turn out to be the most interesting ones.
The experience has taught me to look at things a little more “philosophically”—and not just because it was a philosophy class! I learned that if I let go of my preconceptions, I can actually get a lot out of subjects I was previously dismissive of. The class taught me—in more ways than one—to look at things with an open mind.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
If you’re not given much guidance on what your narrative essay should be about, consider the context and scope of the assignment. What kind of story is relevant, interesting, and possible to tell within the word count?
The best kind of story for a narrative essay is one you can use to reflect on a particular theme or lesson, or that takes a surprising turn somewhere along the way.
Don’t worry too much if your topic seems unoriginal. The point of a narrative essay is how you tell the story and the point you make with it, not the subject of the story itself.
Narrative essays are usually assigned as writing exercises at high school or in university composition classes. They may also form part of a university application.
When you are prompted to tell a story about your own life or experiences, a narrative essay is usually the right response.
The key difference is that a narrative essay is designed to tell a complete story, while a descriptive essay is meant to convey an intense description of a particular place, object, or concept.
Narrative and descriptive essays both allow you to write more personally and creatively than other kinds of essays , and similar writing skills can apply to both.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, July 23). How to Write a Narrative Essay | Example & Tips. Scribbr. Retrieved March 25, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/narrative-essay/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, how to write an expository essay, how to write a descriptive essay | example & tips, how to write your personal statement | strategies & examples, unlimited academic ai-proofreading.
✔ Document error-free in 5minutes ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
Narrative Essay
Narrative Essay Examples
10+ Interesting Narrative Essay Examples Plus Writing Tips!

People also read
Narrative Essay - A Complete Writing Guide with Examples
Writing a Personal Narrative Essay: Everything You Need to Know
Best Narrative Essay Topics 2023 for Students
Crafting a Winning Narrative Essay Outline: A Step-by-Step Guide
Many students struggle with crafting engaging and impactful narrative essays. They often find it challenging to weave their personal experiences into coherent and compelling stories.
If you’re having a hard time, don't worry!
We’ve compiled a range of narrative essay examples that will serve as helpful tools for you to get started. These examples will provide a clear path for crafting engaging and powerful narrative essays.
So, keep reading and find our expertly written examples!
- 1. Narrative Essay Definition
- 2. Narrative Essay Examples
- 3. Narrative Essay Examples for Students
- 4. Narrative Essay Topics
- 5. Narrative Essay Writing Tips
Narrative Essay Definition
Writing a narrative essay is a unique form of storytelling that revolves around personal experiences, aiming to immerse the reader in the author's world. It's a piece of writing that delves into the depths of thoughts and feelings.
In a narrative essay, life experiences take center stage, serving as the main substance of the story. It's a powerful tool for writers to convey a personal journey, turning experiences into a captivating tale. This form of storytelling is an artful display of emotions intended to engage readers, leaving the reader feeling like they are a part of the story.
By focusing on a specific theme, event, emotions, and reflections, a narrative essay weaves a storyline that leads the reader through the author's experiences.
The Essentials of Narrative Essays
Let's start with the basics. The four types of essays are argumentative essays , descriptive essays , expository essays , and narrative essays.
The goal of a narrative essay is to tell a compelling tale from one person's perspective. A narrative essay uses all components you’d find in a typical story, such as a beginning, middle, and conclusion, as well as plot, characters, setting, and climax.
The narrative essay's goal is the plot, which should be detailed enough to reach a climax. Here's how it works:
- It's usually presented in chronological order.
- It has a function. This is typically evident in the thesis statement's opening paragraph.
- It may include speech.
- It's told with sensory details and vivid language, drawing the reader in. All of these elements are connected to the writer's major argument in some way.
Before writing your essay, make sure you go through a sufficient number of narrative essay examples. These examples will help you in knowing the dos and don’ts of a good narrative essay.
It is always a better option to have some sense of direction before you start anything. Below, you can find important details and a bunch of narrative essay examples. These examples will also help you build your content according to the format.
Here is a how to start a narrative essay example:
Sample Narrative Essay
The examples inform the readers about the writing style and structure of the narration. The essay below will help you understand how to create a story and build this type of essay in no time.
Here is another narrative essay examples 500 words:
Narrative Essay Examples for Students
Narrative essays offer students a platform to express their experiences and creativity. These examples show how to effectively structure and present personal stories for education.
Here are some helpful narrative essay examples:
Narrative Essay Examples Middle School
Narrative Essay Examples for Grade 7
Narrative Essay Examples for Grade 8
Grade 11 Narrative Essay Examples
Narrative Essay Example For High School
Narrative Essay Example For College
Personal Narrative Essay Example
Descriptive Narrative Essay Example
3rd Person Narrative Essay Example
Narrative Essay Topics
Here are some narrative essay topics to help you get started with your narrative essay writing.
- When I got my first bunny
- When I moved to Canada
- I haven’t experienced this freezing temperature ever before
- The moment I won the basketball finale
- A memorable day at the museum
- How I talk to my parrot
- The day I saw the death
- When I finally rebelled against my professor
Need more topics? Check out these extensive narrative essay topics to get creative ideas!
Narrative Essay Writing Tips
Narrative essays give you the freedom to be creative, but it can be tough to make yours special. Use these tips to make your story interesting:
- Share your story from a personal viewpoint, engaging the reader with your experiences.
- Use vivid descriptions to paint a clear picture of the setting, characters, and emotions involved.
- Organize events in chronological order for a smooth and understandable narrative.
- Bring characters to life through their actions, dialogue, and personalities.
- Employ dialogue sparingly to add realism and progression to the narrative.
- Engage readers by evoking emotions through your storytelling.
- End with reflection or a lesson learned from the experience, providing insight.
Now you have essay examples and tips to help you get started, you have a solid starting point for crafting compelling narrative essays.
However, if storytelling isn't your forte, you can always turn to our essay writing service for help.
Our writers are specialists that can tackle any type of essay with great skill. With their experience, you get a top-quality, 100% plagiarism free essay everytime.
So, let our narrative essay writing service make sure your narrative essay stands out. Order now!

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Caleb S. has been providing writing services for over five years and has a Masters degree from Oxford University. He is an expert in his craft and takes great pride in helping students achieve their academic goals. Caleb is a dedicated professional who always puts his clients first.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading

- Features for Creative Writers
- Features for Work
- Features for Higher Education
- Features for Teachers
- Features for Non-Native Speakers
- Learn Blog Grammar Guide Community Events FAQ
- Grammar Guide
Telling the Story of Yourself: 6 Steps to Writing Personal Narratives

Jennifer Xue

Table of Contents
Why do we write personal narratives, 6 guidelines for writing personal narrative essays, inspiring personal narratives, examples of personal narrative essays, tell your story.
First off, you might be wondering: what is a personal narrative? In short, personal narratives are stories we tell about ourselves that focus on our growth, lessons learned, and reflections on our experiences.
From stories about inspirational figures we heard as children to any essay, article, or exercise where we're asked to express opinions on a situation, thing, or individual—personal narratives are everywhere.
According to Psychology Today, personal narratives allow authors to feel and release pains, while savouring moments of strength and resilience. Such emotions provide an avenue for both authors and readers to connect while supporting healing in the process.
That all sounds great. But when it comes to putting the words down on paper, we often end up with a list of experiences and no real structure to tie them together.
In this article, we'll discuss what a personal narrative essay is further, learn the 6 steps to writing one, and look at some examples of great personal narratives.
As readers, we're fascinated by memoirs, autobiographies, and long-form personal narrative articles, as they provide a glimpse into the authors' thought processes, ideas, and feelings. But you don't have to be writing your whole life story to create a personal narrative.
You might be a student writing an admissions essay , or be trying to tell your professional story in a cover letter. Regardless of your purpose, your narrative will focus on personal growth, reflections, and lessons.
Personal narratives help us connect with other people's stories due to their easy-to-digest format and because humans are empathising creatures.
We can better understand how others feel and think when we were told stories that allow us to see the world from their perspectives. The author's "I think" and "I feel" instantaneously become ours, as the brain doesn't know whether what we read is real or imaginary.
In her best-selling book Wired for Story, Lisa Cron explains that the human brain craves tales as it's hard-wired through evolution to learn what happens next. Since the brain doesn't know whether what you are reading is actual or not, we can register the moral of the story cognitively and affectively.
In academia, a narrative essay tells a story which is experiential, anecdotal, or personal. It allows the author to creatively express their thoughts, feelings, ideas, and opinions. Its length can be anywhere from a few paragraphs to hundreds of pages.
Outside of academia, personal narratives are known as a form of journalism or non-fiction works called "narrative journalism." Even highly prestigious publications like the New York Times and Time magazine have sections dedicated to personal narratives. The New Yorke is a magazine dedicated solely to this genre.
The New York Times holds personal narrative essay contests. The winners are selected because they:
had a clear narrative arc with a conflict and a main character who changed in some way. They artfully balanced the action of the story with reflection on what it meant to the writer. They took risks, like including dialogue or playing with punctuation, sentence structure and word choice to develop a strong voice. And, perhaps most important, they focused on a specific moment or theme – a conversation, a trip to the mall, a speech tournament, a hospital visit – instead of trying to sum up the writer’s life in 600 words.
In a nutshell, a personal narrative can cover any reflective and contemplative subject with a strong voice and a unique perspective, including uncommon private values. It's written in first person and the story encompasses a specific moment in time worthy of a discussion.
Writing a personal narrative essay involves both objectivity and subjectivity. You'll need to be objective enough to recognise the importance of an event or a situation to explore and write about. On the other hand, you must be subjective enough to inject private thoughts and feelings to make your point.
With personal narratives, you are both the muse and the creator – you have control over how your story is told. However, like any other type of writing, it comes with guidelines.
1. Write Your Personal Narrative as a Story
As a story, it must include an introduction, characters, plot, setting, climax, anti-climax (if any), and conclusion. Another way to approach it is by structuring it with an introduction, body, and conclusion. The introduction should set the tone, while the body should focus on the key point(s) you want to get across. The conclusion can tell the reader what lessons you have learned from the story you've just told.
2. Give Your Personal Narrative a Clear Purpose
Your narrative essay should reflect your unique perspective on life. This is a lot harder than it sounds. You need to establish your perspective, the key things you want your reader to take away, and your tone of voice. It's a good idea to have a set purpose in mind for the narrative before you start writing.
Let's say you want to write about how you manage depression without taking any medicine. This could go in any number of ways, but isolating a purpose will help you focus your writing and choose which stories to tell. Are you advocating for a holistic approach, or do you want to describe your emotional experience for people thinking of trying it?
Having this focus will allow you to put your own unique take on what you did (and didn't do, if applicable), what changed you, and the lessons learned along the way.
3. Show, Don't Tell
It's a narration, so the narrative should show readers what happened, instead of telling them. As well as being a storyteller, the author should take part as one of the characters. Keep this in mind when writing, as the way you shape your perspective can have a big impact on how your reader sees your overarching plot. Don't slip into just explaining everything that happened because it happened to you. Show your reader with action.
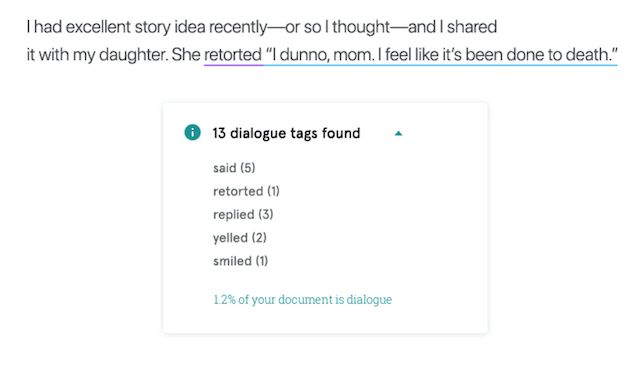
You can check for instances of telling rather than showing with ProWritingAid. For example, instead of:
"You never let me do anything!" I cried disdainfully.
"You never let me do anything!" To this day, my mother swears that the glare I levelled at her as I spat those words out could have soured milk.
Using ProWritingAid will help you find these instances in your manuscript and edit them without spending hours trawling through your work yourself.
4. Use "I," But Don't Overuse It
You, the author, take ownership of the story, so the first person pronoun "I" is used throughout. However, you shouldn't overuse it, as it'd make it sound too self-centred and redundant.
ProWritingAid can also help you here – the Style Report will tell you if you've started too many sentences with "I", and show you how to introduce more variation in your writing.
5. Pay Attention to Tenses
Tense is key to understanding. Personal narratives mostly tell the story of events that happened in the past, so many authors choose to use the past tense. This helps separate out your current, narrating voice and your past self who you are narrating. If you're writing in the present tense, make sure that you keep it consistent throughout.

6. Make Your Conclusion Satisfying
Satisfy your readers by giving them an unforgettable closing scene. The body of the narration should build up the plot to climax. This doesn't have to be something incredible or shocking, just something that helps give an interesting take on your story.
The takeaways or the lessons learned should be written without lecturing. Whenever possible, continue to show rather than tell. Don't say what you learned, narrate what you do differently now. This will help the moral of your story shine through without being too preachy.
GoodReads is a great starting point for selecting read-worthy personal narrative books. Here are five of my favourites.
Owl Moon by Jane Yolen
Jane Yolen, the author of 386 books, wrote this poetic story about a daughter and her father who went owling. Instead of learning about owls, Yolen invites readers to contemplate the meaning of gentleness and hope.
Night by Elie Wiesel
Elie Wiesel was a teenager when he and his family were sent to Auschwitz concentration camp in 1944. This Holocaust memoir has a strong message that such horrific events should never be repeated.
The Diary of a Young Girl by Anne Frank
This classic is a must-read by young and old alike. It's a remarkable diary by a 13-year-old Jewish girl who hid inside a secret annexe of an old building during the Nazi occupation of the Netherlands in 1942.
The Year of Magical Thinking by Joan Didion
This is a personal narrative written by a brave author renowned for her clarity, passion, and honesty. Didion shares how in December 2003, she lost her husband of 40 years to a massive heart attack and dealt with the acute illness of her only daughter. She speaks about grief, memories, illness, and hope.
Educated by Tara Westover
Author Tara Westover was raised by survivalist parents. She didn't go to school until 17 years of age, which later took her to Harvard and Cambridge. It's a story about the struggle for quest for knowledge and self-reinvention.
Narrative and personal narrative journalism are gaining more popularity these days. You can find distinguished personal narratives all over the web.
Curating the best of the best of personal narratives and narrative essays from all over the web. Some are award-winning articles.
Narratively
Long-form writing to celebrate humanity through storytelling. It publishes personal narrative essays written to provoke, inspire, and reflect, touching lesser-known and overlooked subjects.
Narrative Magazine
It publishes non,fiction narratives, poetry, and fiction. Among its contributors is Frank Conroy, the author of Stop-Time , a memoir that has never been out of print since 1967.
Thought Catalog
Aimed at Generation Z, it publishes personal narrative essays on self-improvement, family, friendship, romance, and others.
Personal narratives will continue to be popular as our brains are wired for stories. We love reading about others and telling stories of ourselves, as they bring satisfaction and a better understanding of the world around us.
Personal narratives make us better humans. Enjoy telling yours!

Write like a bestselling author
Love writing? ProWritingAid will help you improve the style, strength, and clarity of your stories.
Jennifer Xue is an award-winning e-book author with 2,500+ articles and 100+ e-books/reports published under her belt. She also taught 50+ college-level essay and paper writing classes. Her byline has appeared in Forbes, Fortune, Cosmopolitan, Esquire, Business.com, Business2Community, Addicted2Success, Good Men Project, and others. Her blog is JenniferXue.com. Follow her on Twitter @jenxuewrites].
Get started with ProWritingAid
Drop us a line or let's stay in touch via :
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- Autobiographies
How to Write a Life Story Essay
Last Updated: May 28, 2023 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Alicia Cook . Alicia Cook is a Professional Writer based in Newark, New Jersey. With over 12 years of experience, Alicia specializes in poetry and uses her platform to advocate for families affected by addiction and to fight for breaking the stigma against addiction and mental illness. She holds a BA in English and Journalism from Georgian Court University and an MBA from Saint Peter’s University. Alicia is a bestselling poet with Andrews McMeel Publishing and her work has been featured in numerous media outlets including the NY Post, CNN, USA Today, the HuffPost, the LA Times, American Songwriter Magazine, and Bustle. She was named by Teen Vogue as one of the 10 social media poets to know and her poetry mixtape, “Stuff I’ve Been Feeling Lately” was a finalist in the 2016 Goodreads Choice Awards. There are 11 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 101,075 times.
A life story essay involves telling the story of your life in a short, nonfiction format. It can also be called an autobiographical essay. In this essay, you will tell a factual story about some element of your life, perhaps for a college application or for a school assignment.
Preparing to Write Your Essay

- If you are writing a personal essay for a college application, it should serve to give the admissions committee a sense of who you are, beyond the basics of your application file. Your transcript, your letters of recommendation, and your resume will provide an overview of your work experience, interests, and academic record. Your essay allows you to make your application unique and individual to you, through your personal story. [2] X Research source
- The essay will also show the admissions committee how well you can write and structure an essay. Your essay should show you can create a meaningful piece of writing that interests your reader, conveys a unique message, and flows well.
- If you are writing a life story for a specific school assignment, such as in a composition course, ask your teacher about the assignment requirements.

- Include important events, such as your birth, your childhood and upbringing, and your adolescence. If family member births, deaths, marriages, and other life moments are important to your story, write those down as well.
- Focus on experiences that made a big impact on you and remain a strong memory. This may be a time where you learned an important life lesson, such as failing a test or watching someone else struggle and succeed, or where you felt an intense feeling or emotion, such as grief over someone’s death or joy over someone’s triumph.
- Have you faced a challenge in your life that you overcame, such as family struggles, health issues, a learning disability, or demanding academics?
- Do you have a story to tell about your cultural or ethnic background, or your family traditions?
- Have you dealt with failure or life obstacles?
- Do you have a unique passion or hobby?
- Have you traveled outside of your community, to another country, city, or area? What did you take away from the experience and how will you carry what you learned into a college setting?

- Remind yourself of your accomplishments by going through your resume. Think about any awards or experiences you would like spotlight in your essay. For example, explaining the story behind your Honor Roll status in high school, or how you worked hard to receive an internship in a prestigious program.
- Remember that your resume or C.V. is there to list off your accomplishments and awards, so your life story shouldn't just rehash them. Instead, use them as a jumping-off place to explain the process behind them, or what they reflect (or do not reflect) about you as a person.

- The New York Times publishes stellar examples of high school life story essays each year. You can read some of them on the NYT website. [8] X Research source
Writing Your Essay

- For example, you may look back at your time in foster care as a child or when you scored your first paying job. Consider how you handled these situations and any life lessons you learned from these lessons. Try to connect past experiences to who you are now, or who you aspire to be in the future.
- Your time in foster care, for example, may have taught you resilience, perseverance and a sense of curiosity around how other families function and live. This could then tie into your application to a Journalism program, as the experience shows you have a persistent nature and a desire to investigate other people’s stories or experiences.

- Certain life story essays have become cliche and familiar to admission committees. Avoid sports injuries stories, such as the time you injured your ankle in a game and had to find a way to persevere. You should also avoid using an overseas trip to a poor, foreign country as the basis for your self transformation. This is a familiar theme that many admission committees will consider cliche and not unique or authentic. [11] X Research source
- Other common, cliche topics to avoid include vacations, "adversity" as an undeveloped theme, or the "journey". [12] X Research source

- Try to phrase your thesis in terms of a lesson learned. For example, “Although growing up in foster care in a troubled neighborhood was challenging and difficult, it taught me that I can be more than my upbringing or my background through hard work, perseverance, and education.”
- You can also phrase your thesis in terms of lessons you have yet to learn, or seek to learn through the program you are applying for. For example, “Growing up surrounded by my mother’s traditional cooking and cultural habits that have been passed down through the generations of my family, I realized I wanted to discover and honor the traditions of other, ancient cultures with a career in archaeology.”
- Both of these thesis statements are good because they tell your readers exactly what to expect in clear detail.

- An anecdote is a very short story that carries moral or symbolic weight. It can be a poetic or powerful way to start your essay and engage your reader right away. You may want to start directly with a retelling of a key past experience or the moment you realized a life lesson.
- For example, you could start with a vivid memory, such as this from an essay that got its author into Harvard Business School: "I first considered applying to Berry College while dangling from a fifty-food Georgia pine tree, encouraging a high school classmate, literally, to make a leap of faith." [15] X Research source This opening line gives a vivid mental picture of what the author was doing at a specific, crucial moment in time and starts off the theme of "leaps of faith" that is carried through the rest of the essay.
- Another great example clearly communicates the author's emotional state from the opening moments: "Through seven-year-old eyes I watched in terror as my mother grimaced in pain." This essay, by a prospective medical school student, goes on to tell about her experience being at her brother's birth and how it shaped her desire to become an OB/GYN. The opening line sets the scene and lets you know immediately what the author was feeling during this important experience. It also resists reader expectations, since it begins with pain but ends in the joy of her brother's birth.
- Avoid using a quotation. This is an extremely cliche way to begin an essay and could put your reader off immediately. If you simply must use a quotation, avoid generic quotes like “Spread your wings and fly” or “There is no ‘I’ in ‘team’”. Choose a quotation that relates directly to your experience or the theme of your essay. This could be a quotation from a poem or piece of writing that speaks to you, moves you, or helped you during a rough time.

- Always use the first person in a personal essay. The essay should be coming from you and should tell the reader directly about your life experiences, with “I” statements.
- For example, avoid something such as “I had a hard time growing up. I was in a bad situation.” You can expand this to be more distinct, but still carry a similar tone and voice. “When I was growing up in foster care, I had difficulties connecting with my foster parents and with my new neighborhood. At the time, I thought I was in a bad situation I would never be able to be free from.”

- For example, consider this statement: "I am a good debater. I am highly motivated and have been a strong leader all through high school." This gives only the barest detail, and does not allow your reader any personal or unique information that will set you apart from the ten billion other essays she has to sift through.
- In contrast, consider this one: "My mother says I'm loud. I say you have to speak up to be heard. As president of my high school's debate team for the past three years, I have learned to show courage even when my heart is pounding in my throat. I have learned to consider the views of people different than myself, and even to argue for them when I passionately disagree. I have learned to lead teams in approaching complicated issues. And, most importantly for a formerly shy young girl, I have found my voice." This example shows personality, uses parallel structure for impact, and gives concrete detail about what the author has learned from her life experience as a debater.

- An example of a passive sentence is: “The cake was eaten by the dog.” The subject (the dog) is not in the expected subject position (first) and is not "doing" the expected action. This is confusing and can often be unclear.
- An example of an active sentence is: “The dog ate the cake.” The subject (the dog) is in the subject position (first), and is doing the expected action. This is much more clear for the reader and is a stronger sentence.

- Lead the reader INTO your story with a powerful beginning, such as an anecdote or a quote.
- Take the reader THROUGH your story with the context and key parts of your experience.
- End with the BEYOND message about how the experience has affected who you are now and who you want to be in college and after college.
Editing Your Essay

- For example, a sentence like “I struggled during my first year of college, feeling overwhelmed by new experiences and new people” is not very strong because it states the obvious and does not distinguish you are unique or singular. Most people struggle and feel overwhelmed during their first year of college. Adjust sentences like this so they appear unique to you.
- For example, consider this: “During my first year of college, I struggled with meeting deadlines and assignments. My previous home life was not very structured or strict, so I had to teach myself discipline and the value of deadlines.” This relates your struggle to something personal and explains how you learned from it.

- It can be difficult to proofread your own work, so reach out to a teacher, a mentor, a family member, or a friend and ask them to read over your essay. They can act as first readers and respond to any proofreading errors, as well as the essay as a whole.
Expert Q&A

You Might Also Like

- ↑ http://education.seattlepi.com/write-thesis-statement-autobiographical-essay-1686.html
- ↑ https://study.com/learn/lesson/autobiography-essay-examples-steps.html
- ↑ https://www.psychologytoday.com/blog/fulfillment-any-age/201101/writing-compelling-life-story-in-500-words-or-less
- ↑ Alicia Cook. Professional Writer. Expert Interview. 11 December 2020.
- ↑ https://mycustomessay.com/blog/how-to-write-an-autobiography-essay.html
- ↑ http://www.ahwatukee.com/community_focus/article_c79b33da-09a5-11e3-95a8-001a4bcf887a.html
- ↑ http://www.nytimes.com/2014/05/10/your-money/four-stand-out-college-essays-about-money.html
- ↑ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xY9AdFx0L4s
- ↑ https://www.medina-esc.org/Downloads/Practical%20Advice%20Writing%20College%20App%20Essay.pdf
- ↑ http://www.businessinsider.com/successful-harvard-business-school-essays-2012-11?op=1
- ↑ http://www.grammar-monster.com/glossary/passive_sentences.htm

About This Article

A life story essay is an essay that tells the story of your life in a short, nonfiction format. Start by coming up with a thesis statement, which will help you structure your essay. For example, your thesis could be about the influence of your family's culture on your life or how you've grown from overcoming challenging circumstances. You can include important life events that link to your thesis, like jobs you’ve worked, friendships that have influenced you, or sports competitions you’ve won. Consider starting your essay with an anecdote that introduces your thesis. For instance, if you're writing about your family's culture, you could start by talking about the first festival you went to and how it inspired you. Finish by writing about how the experiences have affected you and who you want to be in the future. For more tips from our Education co-author, including how to edit your essay effectively, read on! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Did this article help you?

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, 3 great narrative essay examples + tips for writing.
General Education

A narrative essay is one of the most intimidating assignments you can be handed at any level of your education. Where you've previously written argumentative essays that make a point or analytic essays that dissect meaning, a narrative essay asks you to write what is effectively a story .
But unlike a simple work of creative fiction, your narrative essay must have a clear and concrete motif —a recurring theme or idea that you’ll explore throughout. Narrative essays are less rigid, more creative in expression, and therefore pretty different from most other essays you’ll be writing.
But not to fear—in this article, we’ll be covering what a narrative essay is, how to write a good one, and also analyzing some personal narrative essay examples to show you what a great one looks like.
What Is a Narrative Essay?
At first glance, a narrative essay might sound like you’re just writing a story. Like the stories you're used to reading, a narrative essay is generally (but not always) chronological, following a clear throughline from beginning to end. Even if the story jumps around in time, all the details will come back to one specific theme, demonstrated through your choice in motifs.
Unlike many creative stories, however, your narrative essay should be based in fact. That doesn’t mean that every detail needs to be pure and untainted by imagination, but rather that you shouldn’t wholly invent the events of your narrative essay. There’s nothing wrong with inventing a person’s words if you can’t remember them exactly, but you shouldn’t say they said something they weren’t even close to saying.
Another big difference between narrative essays and creative fiction—as well as other kinds of essays—is that narrative essays are based on motifs. A motif is a dominant idea or theme, one that you establish before writing the essay. As you’re crafting the narrative, it’ll feed back into your motif to create a comprehensive picture of whatever that motif is.
For example, say you want to write a narrative essay about how your first day in high school helped you establish your identity. You might discuss events like trying to figure out where to sit in the cafeteria, having to describe yourself in five words as an icebreaker in your math class, or being unsure what to do during your lunch break because it’s no longer acceptable to go outside and play during lunch. All of those ideas feed back into the central motif of establishing your identity.
The important thing to remember is that while a narrative essay is typically told chronologically and intended to read like a story, it is not purely for entertainment value. A narrative essay delivers its theme by deliberately weaving the motifs through the events, scenes, and details. While a narrative essay may be entertaining, its primary purpose is to tell a complete story based on a central meaning.
Unlike other essay forms, it is totally okay—even expected—to use first-person narration in narrative essays. If you’re writing a story about yourself, it’s natural to refer to yourself within the essay. It’s also okay to use other perspectives, such as third- or even second-person, but that should only be done if it better serves your motif. Generally speaking, your narrative essay should be in first-person perspective.
Though your motif choices may feel at times like you’re making a point the way you would in an argumentative essay, a narrative essay’s goal is to tell a story, not convince the reader of anything. Your reader should be able to tell what your motif is from reading, but you don’t have to change their mind about anything. If they don’t understand the point you are making, you should consider strengthening the delivery of the events and descriptions that support your motif.
Narrative essays also share some features with analytical essays, in which you derive meaning from a book, film, or other media. But narrative essays work differently—you’re not trying to draw meaning from an existing text, but rather using an event you’ve experienced to convey meaning. In an analytical essay, you examine narrative, whereas in a narrative essay you create narrative.
The structure of a narrative essay is also a bit different than other essays. You’ll generally be getting your point across chronologically as opposed to grouping together specific arguments in paragraphs or sections. To return to the example of an essay discussing your first day of high school and how it impacted the shaping of your identity, it would be weird to put the events out of order, even if not knowing what to do after lunch feels like a stronger idea than choosing where to sit. Instead of organizing to deliver your information based on maximum impact, you’ll be telling your story as it happened, using concrete details to reinforce your theme.

3 Great Narrative Essay Examples
One of the best ways to learn how to write a narrative essay is to look at a great narrative essay sample. Let’s take a look at some truly stellar narrative essay examples and dive into what exactly makes them work so well.
A Ticket to the Fair by David Foster Wallace
Today is Press Day at the Illinois State Fair in Springfield, and I’m supposed to be at the fairgrounds by 9:00 A.M. to get my credentials. I imagine credentials to be a small white card in the band of a fedora. I’ve never been considered press before. My real interest in credentials is getting into rides and shows for free. I’m fresh in from the East Coast, for an East Coast magazine. Why exactly they’re interested in the Illinois State Fair remains unclear to me. I suspect that every so often editors at East Coast magazines slap their foreheads and remember that about 90 percent of the United States lies between the coasts, and figure they’ll engage somebody to do pith-helmeted anthropological reporting on something rural and heartlandish. I think they asked me to do this because I grew up here, just a couple hours’ drive from downstate Springfield. I never did go to the state fair, though—I pretty much topped out at the county fair level. Actually, I haven’t been back to Illinois for a long time, and I can’t say I’ve missed it.
Throughout this essay, David Foster Wallace recounts his experience as press at the Illinois State Fair. But it’s clear from this opening that he’s not just reporting on the events exactly as they happened—though that’s also true— but rather making a point about how the East Coast, where he lives and works, thinks about the Midwest.
In his opening paragraph, Wallace states that outright: “Why exactly they’re interested in the Illinois State Fair remains unclear to me. I suspect that every so often editors at East Coast magazines slap their foreheads and remember that about 90 percent of the United States lies between the coasts, and figure they’ll engage somebody to do pith-helmeted anthropological reporting on something rural and heartlandish.”
Not every motif needs to be stated this clearly , but in an essay as long as Wallace’s, particularly since the audience for such a piece may feel similarly and forget that such a large portion of the country exists, it’s important to make that point clear.
But Wallace doesn’t just rest on introducing his motif and telling the events exactly as they occurred from there. It’s clear that he selects events that remind us of that idea of East Coast cynicism , such as when he realizes that the Help Me Grow tent is standing on top of fake grass that is killing the real grass beneath, when he realizes the hypocrisy of craving a corn dog when faced with a real, suffering pig, when he’s upset for his friend even though he’s not the one being sexually harassed, and when he witnesses another East Coast person doing something he wouldn’t dare to do.
Wallace is literally telling the audience exactly what happened, complete with dates and timestamps for when each event occurred. But he’s also choosing those events with a purpose—he doesn’t focus on details that don’t serve his motif. That’s why he discusses the experiences of people, how the smells are unappealing to him, and how all the people he meets, in cowboy hats, overalls, or “black spandex that looks like cheesecake leotards,” feel almost alien to him.
All of these details feed back into the throughline of East Coast thinking that Wallace introduces in the first paragraph. He also refers back to it in the essay’s final paragraph, stating:
At last, an overarching theory blooms inside my head: megalopolitan East Coasters’ summer treats and breaks and literally ‘getaways,’ flights-from—from crowds, noise, heat, dirt, the stress of too many sensory choices….The East Coast existential treat is escape from confines and stimuli—quiet, rustic vistas that hold still, turn inward, turn away. Not so in the rural Midwest. Here you’re pretty much away all the time….Something in a Midwesterner sort of actuates , deep down, at a public event….The real spectacle that draws us here is us.
Throughout this journey, Wallace has tried to demonstrate how the East Coast thinks about the Midwest, ultimately concluding that they are captivated by the Midwest’s less stimuli-filled life, but that the real reason they are interested in events like the Illinois State Fair is that they are, in some ways, a means of looking at the East Coast in a new, estranging way.
The reason this works so well is that Wallace has carefully chosen his examples, outlined his motif and themes in the first paragraph, and eventually circled back to the original motif with a clearer understanding of his original point.
When outlining your own narrative essay, try to do the same. Start with a theme, build upon it with examples, and return to it in the end with an even deeper understanding of the original issue. You don’t need this much space to explore a theme, either—as we’ll see in the next example, a strong narrative essay can also be very short.
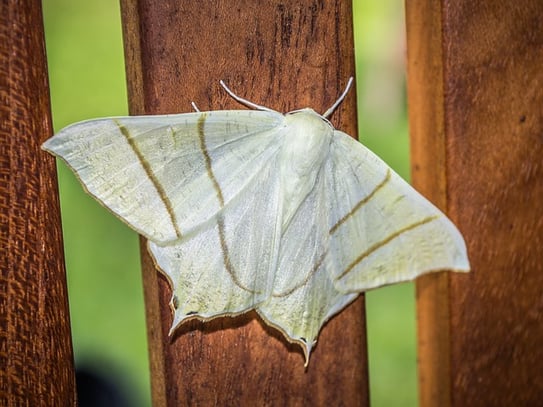

Death of a Moth by Virginia Woolf
After a time, tired by his dancing apparently, he settled on the window ledge in the sun, and, the queer spectacle being at an end, I forgot about him. Then, looking up, my eye was caught by him. He was trying to resume his dancing, but seemed either so stiff or so awkward that he could only flutter to the bottom of the window-pane; and when he tried to fly across it he failed. Being intent on other matters I watched these futile attempts for a time without thinking, unconsciously waiting for him to resume his flight, as one waits for a machine, that has stopped momentarily, to start again without considering the reason of its failure. After perhaps a seventh attempt he slipped from the wooden ledge and fell, fluttering his wings, on to his back on the window sill. The helplessness of his attitude roused me. It flashed upon me that he was in difficulties; he could no longer raise himself; his legs struggled vainly. But, as I stretched out a pencil, meaning to help him to right himself, it came over me that the failure and awkwardness were the approach of death. I laid the pencil down again.
In this essay, Virginia Woolf explains her encounter with a dying moth. On surface level, this essay is just a recounting of an afternoon in which she watched a moth die—it’s even established in the title. But there’s more to it than that. Though Woolf does not begin her essay with as clear a motif as Wallace, it’s not hard to pick out the evidence she uses to support her point, which is that the experience of this moth is also the human experience.
In the title, Woolf tells us this essay is about death. But in the first paragraph, she seems to mostly be discussing life—the moth is “content with life,” people are working in the fields, and birds are flying. However, she mentions that it is mid-September and that the fields were being plowed. It’s autumn and it’s time for the harvest; the time of year in which many things die.
In this short essay, she chronicles the experience of watching a moth seemingly embody life, then die. Though this essay is literally about a moth, it’s also about a whole lot more than that. After all, moths aren’t the only things that die—Woolf is also reflecting on her own mortality, as well as the mortality of everything around her.
At its core, the essay discusses the push and pull of life and death, not in a way that’s necessarily sad, but in a way that is accepting of both. Woolf begins by setting up the transitional fall season, often associated with things coming to an end, and raises the ideas of pleasure, vitality, and pity.
At one point, Woolf tries to help the dying moth, but reconsiders, as it would interfere with the natural order of the world. The moth’s death is part of the natural order of the world, just like fall, just like her own eventual death.
All these themes are set up in the beginning and explored throughout the essay’s narrative. Though Woolf doesn’t directly state her theme, she reinforces it by choosing a small, isolated event—watching a moth die—and illustrating her point through details.
With this essay, we can see that you don’t need a big, weird, exciting event to discuss an important meaning. Woolf is able to explore complicated ideas in a short essay by being deliberate about what details she includes, just as you can be in your own essays.

Notes of a Native Son by James Baldwin
On the twenty-ninth of July, in 1943, my father died. On the same day, a few hours later, his last child was born. Over a month before this, while all our energies were concentrated in waiting for these events, there had been, in Detroit, one of the bloodiest race riots of the century. A few hours after my father’s funeral, while he lay in state in the undertaker’s chapel, a race riot broke out in Harlem. On the morning of the third of August, we drove my father to the graveyard through a wilderness of smashed plate glass.
Like Woolf, Baldwin does not lay out his themes in concrete terms—unlike Wallace, there’s no clear sentence that explains what he’ll be talking about. However, you can see the motifs quite clearly: death, fatherhood, struggle, and race.
Throughout the narrative essay, Baldwin discusses the circumstances of his father’s death, including his complicated relationship with his father. By introducing those motifs in the first paragraph, the reader understands that everything discussed in the essay will come back to those core ideas. When Baldwin talks about his experience with a white teacher taking an interest in him and his father’s resistance to that, he is also talking about race and his father’s death. When he talks about his father’s death, he is also talking about his views on race. When he talks about his encounters with segregation and racism, he is talking, in part, about his father.
Because his father was a hard, uncompromising man, Baldwin struggles to reconcile the knowledge that his father was right about many things with his desire to not let that hardness consume him, as well.
Baldwin doesn’t explicitly state any of this, but his writing so often touches on the same motifs that it becomes clear he wants us to think about all these ideas in conversation with one another.
At the end of the essay, Baldwin makes it more clear:
This fight begins, however, in the heart and it had now been laid to my charge to keep my own heart free of hatred and despair. This intimation made my heart heavy and, now that my father was irrecoverable, I wished that he had been beside me so that I could have searched his face for the answers which only the future would give me now.
Here, Baldwin ties together the themes and motifs into one clear statement: that he must continue to fight and recognize injustice, especially racial injustice, just as his father did. But unlike his father, he must do it beginning with himself—he must not let himself be closed off to the world as his father was. And yet, he still wishes he had his father for guidance, even as he establishes that he hopes to be a different man than his father.
In this essay, Baldwin loads the front of the essay with his motifs, and, through his narrative, weaves them together into a theme. In the end, he comes to a conclusion that connects all of those things together and leaves the reader with a lasting impression of completion—though the elements may have been initially disparate, in the end everything makes sense.
You can replicate this tactic of introducing seemingly unattached ideas and weaving them together in your own essays. By introducing those motifs, developing them throughout, and bringing them together in the end, you can demonstrate to your reader how all of them are related. However, it’s especially important to be sure that your motifs and clear and consistent throughout your essay so that the conclusion feels earned and consistent—if not, readers may feel mislead.
5 Key Tips for Writing Narrative Essays
Narrative essays can be a lot of fun to write since they’re so heavily based on creativity. But that can also feel intimidating—sometimes it’s easier to have strict guidelines than to have to make it all up yourself. Here are a few tips to keep your narrative essay feeling strong and fresh.
Develop Strong Motifs
Motifs are the foundation of a narrative essay . What are you trying to say? How can you say that using specific symbols or events? Those are your motifs.
In the same way that an argumentative essay’s body should support its thesis, the body of your narrative essay should include motifs that support your theme.
Try to avoid cliches, as these will feel tired to your readers. Instead of roses to symbolize love, try succulents. Instead of the ocean representing some vast, unknowable truth, try the depths of your brother’s bedroom. Keep your language and motifs fresh and your essay will be even stronger!
Use First-Person Perspective
In many essays, you’re expected to remove yourself so that your points stand on their own. Not so in a narrative essay—in this case, you want to make use of your own perspective.
Sometimes a different perspective can make your point even stronger. If you want someone to identify with your point of view, it may be tempting to choose a second-person perspective. However, be sure you really understand the function of second-person; it’s very easy to put a reader off if the narration isn’t expertly deployed.
If you want a little bit of distance, third-person perspective may be okay. But be careful—too much distance and your reader may feel like the narrative lacks truth.
That’s why first-person perspective is the standard. It keeps you, the writer, close to the narrative, reminding the reader that it really happened. And because you really know what happened and how, you’re free to inject your own opinion into the story without it detracting from your point, as it would in a different type of essay.
Stick to the Truth
Your essay should be true. However, this is a creative essay, and it’s okay to embellish a little. Rarely in life do we experience anything with a clear, concrete meaning the way somebody in a book might. If you flub the details a little, it’s okay—just don’t make them up entirely.
Also, nobody expects you to perfectly recall details that may have happened years ago. You may have to reconstruct dialog from your memory and your imagination. That’s okay, again, as long as you aren’t making it up entirely and assigning made-up statements to somebody.
Dialog is a powerful tool. A good conversation can add flavor and interest to a story, as we saw demonstrated in David Foster Wallace’s essay. As previously mentioned, it’s okay to flub it a little, especially because you’re likely writing about an experience you had without knowing that you’d be writing about it later.
However, don’t rely too much on it. Your narrative essay shouldn’t be told through people explaining things to one another; the motif comes through in the details. Dialog can be one of those details, but it shouldn’t be the only one.
Use Sensory Descriptions
Because a narrative essay is a story, you can use sensory details to make your writing more interesting. If you’re describing a particular experience, you can go into detail about things like taste, smell, and hearing in a way that you probably wouldn’t do in any other essay style.
These details can tie into your overall motifs and further your point. Woolf describes in great detail what she sees while watching the moth, giving us the sense that we, too, are watching the moth. In Wallace’s essay, he discusses the sights, sounds, and smells of the Illinois State Fair to help emphasize his point about its strangeness. And in Baldwin’s essay, he describes shattered glass as a “wilderness,” and uses the feelings of his body to describe his mental state.
All these descriptions anchor us not only in the story, but in the motifs and themes as well. One of the tools of a writer is making the reader feel as you felt, and sensory details help you achieve that.
What’s Next?
Looking to brush up on your essay-writing capabilities before the ACT? This guide to ACT English will walk you through some of the best strategies and practice questions to get you prepared!
Part of practicing for the ACT is ensuring your word choice and diction are on point. Check out this guide to some of the most common errors on the ACT English section to be sure that you're not making these common mistakes!
A solid understanding of English principles will help you make an effective point in a narrative essay, and you can get that understanding through taking a rigorous assortment of high school English classes !

Melissa Brinks graduated from the University of Washington in 2014 with a Bachelor's in English with a creative writing emphasis. She has spent several years tutoring K-12 students in many subjects, including in SAT prep, to help them prepare for their college education.
Student and Parent Forum
Our new student and parent forum, at ExpertHub.PrepScholar.com , allow you to interact with your peers and the PrepScholar staff. See how other students and parents are navigating high school, college, and the college admissions process. Ask questions; get answers.

Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
Life’s Stories
How you arrange the plot points of your life into a narrative can shape who you are—and is a fundamental part of being human.
This article was featured in One Story to Read Today, a newsletter in which our editors recommend a single must-read from The Atlantic , Monday through Friday. Sign up for it here.
In Paul Murray’s novel Skippy Dies, there’s a point where the main character, Howard, has an existential crisis. “‘It’s just not how I expected my life would be,’” he says.
“‘What did you expect?’” a friend responds.
“Howard ponders this. ‘I suppose—this sounds stupid, but I suppose I thought there’d be more of a narrative arc .’”
But it’s not stupid at all. Though perhaps the facts of someone’s life, presented end to end, wouldn’t much resemble a narrative to the outside observer, the way people choose to tell the stories of their lives, to others and—crucially—to themselves, almost always does have a narrative arc. In telling the story of how you became who you are, and of who you’re on your way to becoming, the story itself becomes a part of who you are.
“Life stories do not simply reflect personality. They are personality, or more accurately, they are important parts of personality, along with other parts, like dispositional traits, goals, and values,” writes Dan McAdams, a professor of psychology at Northwestern University, along with Erika Manczak, in a chapter for the APA Handbook of Personality and Social Psychology.
In the realm of narrative psychology, a person’s life story is not a Wikipedia biography of the facts and events of a life, but rather the way a person integrates those facts and events internally—picks them apart and weaves them back together to make meaning. This narrative becomes a form of identity, in which the things someone chooses to include in the story, and the way she tells it, can both reflect and shape who she is. A life story doesn’t just say what happened, it says why it was important, what it means for who the person is, for who they’ll become, and for what happens next.
“Sometimes in cases of extreme autism, people don’t construct a narrative structure for their lives,” says Jonathan Adler, an assistant professor of psychology at Olin College of Engineering, “but the default mode of human cognition is a narrative mode.”
When people tell others about themselves, they kind of have to do it in a narrative way—that’s just how humans communicate. But when people think about their lives to themselves, is it always in a narrative way, with a plot that leads from one point to another? There’s an old adage that everyone has a book inside of them. (Christopher Hitchens once said that inside is “exactly where I think it should, in most cases, remain.” ) Is there anyone out there with a life story that’s not a story at all, but some other kind of more disjointed, avant-garde representation of their existence?
“This is an almost impossible question to address from a scientific approach,” says Monisha Pasupathi, a professor of developmental psychology at the University of Utah. Even if we are, as the writer Jonathan Gottschall put it, “storytelling animals,” what does that mean from one person to the next? Not only are there individual differences in how people think of their stories, there’s huge variation in the degree to which they engage in narrative storytelling in the first place.
“Some people write in their diaries and are very introspective, and some people are not at all,” says Kate McLean, an associate professor of psychology at Western Washington University. Journal-keeping, though a way of documenting the life story, doesn’t always make for a tightly-wound narrative. A writer I interviewed several months ago—Sarah Manguso—has kept a diary for 25 years, and still told me, “Narrative is not a mode that has ever come easily to me.”
Nevertheless, the researchers I spoke with were all convinced that even if it’s not 100 percent universal to see life as a story, it’s at least extremely common.
“I think normal, healthy adults have in common that they can all produce a life story,” Pasupathi says. “They can all put one together … In order to have relationships, we’ve all had to tell little pieces of our story. And so it’s hard to be a human being and have relationships without having some version of a life story floating around.”
But life rarely follows the logical progression that most stories—good stories—do, where the clues come together, guns left on mantles go off at the appropriate moments, the climax comes in the third act. So narrative seems like an incongruous framing method for life’s chaos, until you remember where stories came from in the first place. Ultimately, the only material we’ve ever had to make stories out of is our own imagination, and life itself.
Storytelling, then—fictional or nonfictional, realistic or embellished with dragons—is a way of making sense of the world around us.
“Life is incredibly complex, there are lots of things going on in our environment and in our lives at all times, and in order to hold onto our experience, we need to make meaning out of it,” Adler says. “The way we do that is by structuring our lives into stories.”
It’s hardly a simple undertaking. People contain multitudes, and by multitudes, I mean libraries. Someone might have an overarching narrative for her whole life, and different narratives for different realms of her life—career, romance, family, faith. She might have narratives within each realm that intersect, diverge, or contradict each other, all of them filled with the microstories of specific events. And to truly make a life story, she’ll need to do what researchers call “autobiographical reasoning” about the events—“identifying lessons learned or insights gained in life experiences, marking development or growth through sequences of scenes, and showing how specific life episodes illustrate enduring truths about the self,” McAdams and Manczak write.
“Stories don’t have to be really simple, like fairy-tale-type narratives,” McAdams says. “They can be complicated. It can be like James Joyce out there.”
If you really like James Joyce, it might be a lot like James Joyce. People take the stories that surround them—fictional tales, news articles, apocryphal family anecdotes—then identify with them and borrow from them while fashioning their own self-conceptions. It’s a Möbius strip: Stories are life, life is stories.
People aren’t writing their life stories from birth, though. The ability to create a life narrative takes a little while to come online—the development process gives priority to things like walking, talking, and object permanence. Young children can tell stories about isolated events, with guidance, and much of adolescence is dedicated to learning “what goes in a story … and what makes a good story in the first place,” Pasupathi says. “I don’t know how much time you’ve spent around little kids, but they really don’t understand that. I have a child who can really take an hour to tell you about Minecraft .” Through friends, family, and fiction, children learn what others consider to be good storytelling—and that being able to spin a good yarn has social value.
It’s in the late teens and early years of adulthood that story construction really picks up—because by then people have developed some of the cognitive tools they need to create a coherent life story. These include causal coherence—the ability to describe how one event led to another—and thematic coherence—the ability to identify overarching values and motifs that recur throughout the story. In a study analyzing the life stories of 8-, 12-, 16-, and 20-year-olds, these kinds of coherence were found to increase with age. As the life story enters its last chapters, it may become more set in stone. In one study by McLean , older adults had more thematic coherence, and told more stories about stability, while young adults tended to tell more stories about change.
McAdams conceives of this development as the layering of three aspects of the self. Pretty much from birth, people are “actors.” They have personality traits, they interact with the world, they have roles to play—daughter, sister, the neighbor’s new baby that cries all night and keeps you up. When they get old enough to have goals, they become “agents” too—still playing their roles and interacting with the world, but making decisions with the hopes of producing desired outcomes. And the final layer is “author,” when people begin to bundle ideas about the future with experiences from the past and present to form a narrative self.
This developmental trajectory could also explain why people enjoy different types of fictional stories at different ages. “When you’re a kid, it’s mostly about plot,” McAdams says. “This happens and this happens. You’re not tuned into the idea that a character develops.” Thus, perhaps, the appeal of cartoon characters who never get older.
Recently, McAdams says, his book club read Ethan Frome by Edith Wharton. “I read it in high school and hated it,” he says. “All I could remember about it was that this sled hits a tree. And we read it recently in the club, and whoa, is it fabulous. A sled does hit the tree, there’s no doubt that is a big scene, but how it changes these people’s lives and the tragedy of this whole thing, it’s completely lost on 18-year-olds. Things are lost on 8-year-olds that a 40-year-old picks up, and things that an 8-year-old found compelling and interesting will just bore a 40-year-old to tears sometimes.”
And like personal taste in books or movies, the stories we tell ourselves about ourselves are influenced by more than just, well, ourselves. The way people recount experiences to others seems to shape the way they end up remembering those events. According to Pasupathi’s research, this happens in a couple of ways. One is that people tailor the stories they tell to their audiences and the context. (For example, I tell the story of the time I crashed my mom’s car much differently now, to friends, than the way I told it to my mom at the time. Much less crying.)
The other is that the act of telling is a rehearsal of the story, Pasupathi says. “And rehearsal strengthens connections between some pieces of information in your mind and diminishes connections between others. So the things I tell you become more accessible to me and more memorable to me. Those can be pretty lasting effects.” So when people drop the cheesy pick-up line “What’s your story?” at a bar, like a man who nicks his carotid artery while shaving, they’ve accidentally hit upon something vital.
But just as there are consequences to telling, there are consequences to not telling . If someone is afraid of how people might react to a story, and they keep it to themselves, they’ll likely miss out on the enrichment that comes with a back-and-forth conversation. A listener “may give you other things to think about, or may acknowledge that this thing you thought was really bad is actually not a big deal, so you get this richer and more elaborated memory,” Pasupathi says. If you don’t tell, “your memory for that event may be less flexible and give you less chance for growth.” This is basically the premise of talk therapy.
And all of this doesn’t even account for all the conversations you plan to have, or elaborately imagine having and never have. The path from outside to inside and back out is winding, dark, and full of switchbacks.
Once certain stories get embedded into the culture, they become master narratives—blueprints for people to follow when structuring their own stories, for better or worse. One such blueprint is your standard “go to school, graduate, get a job, get married, have kids.”
That can be a helpful script in that it gives children a sense of the arc of a life, and shows them examples of tentpole events that could happen. But the downsides of standard narratives have been well-documented—they stigmatize anyone who doesn’t follow them to a T, and provide unrealistic expectations of happiness for those who do. If this approach were a blueprint for an IKEA desk instead of a life, almost everyone trying to follow it would end up with something wobbly and misshapen, with a few leftover bolts you find under the couch, boding ill for the structural integrity of the thing you built.
“I think that’s a particularly pernicious frame for people who become parents,” Pasupathi says. “That’s a narrative where the pinnacle is to get married and have kids and then everything will be sort of flatly happy from then on.”
And these scripts evolve as culture evolves. For example, in centuries past, stories of being possessed by demons might not have been out of place, but it’s unlikely most people would describe their actions in those terms nowadays.
Other common narrative structures seen in many cultures today are redemption sequences and contamination sequences. A redemption story starts off bad and ends better—“That horrible vacation ultimately brought us closer as a family”—while a contamination story does the opposite—“The cruise was amazing until we all got food poisoning.” Having redemption themes in one’s life story is generally associated with greater well-being, while contamination themes tend to coincide with poorer mental health.
Many people have some smaller stories of each type sprinkled throughout their greater life story, though a person’s disposition, culture, and environment can influence which they gravitate to. People can also see the larger arc of their lives as redemptive or contaminated, and redemption in particular is a popular, and particularly American, narrative. “Evolving from the Puritans to Ralph Waldo Emerson to Oprah Winfrey … Americans have sought to author their lives as redemptive tales of atonement, emancipation, recovery, self-fulfillment, and upward social mobility,” McAdams writes in an overview of life-story research . “The stories speak of heroic individual protagonists—the chosen people—whose manifest destiny is to make a positive difference in a dangerous world, even when the world does not wish to be redeemed.”
The redemption story is American optimism—things will get better!—and American exceptionalism—I can make things better!—and it’s in the water, in the air, and in our heads. This is actually a good thing a lot of the time. Studies have shown that finding a positive meaning in negative events is linked to a more complex sense of self and greater life satisfaction. And even controlling for general optimism, McAdams and his colleagues found that having more redemption sequences in a life story was still associated with higher well-being.
The trouble comes when redemption isn’t possible. The redemptive American tale is one of privilege, and for those who can’t control their circumstances, and have little reason to believe things will get better, it can be an illogical and unattainable choice. There are things that happen to people that cannot be redeemed.
It can be hard to share a story when it amounts to: “This happened, and it was terrible. The end.” In research McLean did, in which she asked people who’d had near-death experiences to tell their stories to others, “the people who told these unresolved stories had really negative responses,” she says. If there wasn’t some kind of uplifting, redemptive end to the story (beyond just the fact that they survived), “The listeners did not like that.
“The redemptive story is really valued in America, because for a lot of people it’s a great way to tell stories, but for people who just can’t do that, who can’t redeem their traumas for whatever reason, they’re sort of in a double bind,” she continues. “They both have this crappy story that’s hanging on, but they also can’t tell it and get acceptance or validation from people.”
In cases like this, for people who have gone through a lot of trauma, it might be better for them not to autobiographically reason about it at all.
“The first time I ever found this association, of reasoning associated with poor mental health, I thought that I had analyzed my data incorrectly,” McLean says. But after other researchers replicated her findings, she got more confident that something was going on. She thinks that people may repress traumatic events in a way that, while not ideal, is still “healthy enough.”
“The typical idea is that you can repress something but it’s going to come back and bite you if you don’t deal with it,” she says. “But that’s still under the assumption that people have the resources to deal with it.”
In one study, McLean and her colleagues interviewed adolescents attending a high school for vulnerable students. One subject, Josie, the 17-year-old daughter of a single mother, suffered from drug and alcohol abuse, bipolar disorder, rape, and a suicide attempt. She told the researchers that her self-defining memory was that her mother had promised not to have more children and then broke that promise.
“I’m the only person that I can rely on in my life because I’ve tried to rely on other people and I either get stabbed in the back or hurt, so I really know that I can only trust myself and rely on myself,” Josie said when recounting this memory.
“That’s pretty intensive reasoning,” McLean says. “So that’s meaningful in understanding who you are, but it doesn’t really give you a positive view of who you are. It may be true in the moment, but it’s not something that propels someone towards growth.”
It’s possible to over-reason about good things in your life as well. “There’s been some experimental research that shows that when people are asked to reflect on positive experiences, it makes them feel worse, because you’re like ‘Oh, why did I marry that person?’” McLean says. “Wisdom and maturity and cognitive complexity are all things that we value, but they don’t necessarily make you happy.”
Though sometimes autobiographical reasoning can lead to dark thoughts, other times it can help people find meaning. And while you may be able to avoid reasoning about a certain event, it would be pretty hard to leave all the pages of a life story unwritten.
“I think the act of framing our lives as a narrative is neither positive nor negative, it just is,” Adler says. “That said, there are better and worse ways of doing that narrative process for our mental health.”
In his research, Adler has noticed two themes in people’s stories that tend to correlate with better well-being: agency, or feeling like you are in control of your life, and communion, or feeling like you have good relationships in your life. The connection is “a little fuzzier” with communion, Adler says—there’s a strong relationship between communion and well-being at the same moment; it’s less clear if feeling communion now predicts well-being later.
But agency sure does. It makes sense, because feelings of helplessness and hopelessness are classic symptoms of depression, that feeling in control would be good for mental health. Adler did a longitudinal study of 47 adults undergoing therapy, having them write personal narratives and complete mental-health assessments over the course of 12 therapy sessions. What he found was not only that themes of agency in participants’ stories increased over time and that mental health increased, and that the two were related, but that increased agency actually appeared in stories before people’s mental health improved.
“It’s sort of like people put out a new version of themselves and lived their way into it,” Adler says.
(There’s something about the narrative form, specifically—while expressing thoughts and feelings about negative events seems to help people’s well-being, one study found that writing them in a narrative form helped more than just listing them.)
But, he continues, “I’m not like Mr. Agency, agency at all costs. I don’t believe that. If you have Stage 4 cancer, agency may be good for you, but is it a rational choice? And I do think [redemption] is good in the long term, but in the throes of really struggling with illness, I don’t know that it actually helps people.”
But I wondered: Though agency may be good for you, does seeing yourself as a strong protagonist come at a cost to the other characters in your story? Are there implications for empathy if we see other people as bit players instead of protagonists in their own right?
“That’s actually kind of an interesting empirical idea,” Pasupathi says. “I don’t know that anybody’s looking at that.”
As Adler’s work shows, people need to see themselves as actors to a certain degree. And Pasupathi’s work shows that other people play a big role in shaping life stories. The question, perhaps, is how much people recognize that their agency is not absolute.
According to one study, highly generative people—that is, people who are caring and committed to helping future generations— often tell stories about others who helped them in the past. McAdams suggests that narcissists are probably more likely to do the opposite—“People [who] are really good at talking about themselves and pushing their own narrative, but they’re not willing to listen to yours.”
“If our stories are about us as triumphant agents going through life and overcoming, and they underplay the role of other people and the role of institutional support in helping us do those things, we are likely to be less good at recognizing how other people’s lives are constrained by institutions and other people,” Pasupathi says. “I think that has real implications for how we think about inequity in our society. The more the whole world is designed to work for you, the less you are aware that it is working for you.”
It’s a dizzying problem: People use stories to make sense of life, but how much do those stories reflect life’s realities? Even allowing for the fact that people are capable of complex Joyce-ian storytelling, biases, personality differences, or emotions can lead different people to see the same event differently. And considering how susceptible humans are to false memories, who’s to say that the plot points in someone’s life story really happened, or happened the way she thought they did, or really caused the effects she saw from them?
Pasupathi’s not convinced that it matters that much whether life stories are perfectly accurate. A lot of false-memory research has to do with eyewitness testimony , where it matters a whole lot whether a person is telling a story precisely as it happened. But for narrative-psychology researchers, “What really matters isn’t so much whether it’s true in the forensic sense, in the legal sense,” she says. “What really matters is whether people are making something meaningful and coherent out of what happened. Any creation of a narrative is a bit of a lie. And some lies have enough truth.”
Organizing the past into a narrative isn’t a way just to understand the self but also to attempt to predict the future. Which is interesting, because the storytelling device that seems most incompatible with the realities of actual life is foreshadowing. Metaphors, sure. As college literature-class discussion sections taught me, you can see anything as a metaphor if you try hard enough. Motifs, definitely. Even if you’re living your life as randomly as possible, enough things will happen that, like monkeys with typewriters, patterns will start to emerge.
But no matter how hard you try, no matter how badly you want to, there is no way to truly know the future, and the world isn’t really organizing itself to give you hints. If you’re prone to overthinking, and playing out every possible scenario in your head in advance, you can see foreshadowing in everything. The look your partner gives you means a fight is on the horizon, that compliment from your boss means you’re on track for a promotion, all the little things you’ve forgotten over the years mean you’re definitely going to get dementia when you’re old.
“Actual life is full of false clues and signposts that lead nowhere,” E.M. Forster once wrote. These become obvious in the keeping of a diary: “Imagine a biography that includes not just a narrative but also all the events that failed to foreshadow,” Manguso writes in Ongoingness, the book about her 25-year diary . “ Most of what the diary includes foreshadows nothing.”
So what to do, then, with all the things that don’t fit tidily? There is evidence that finding some “unity” in your narrative identity is better, psychologically, than not finding it. And it probably is easier to just drop those things as you pull patterns from the chaos, though it may take some readjusting.
But Pasupathi rejects that. “I would want to see people do a good job of not trying to leave stuff out because they can’t make it fit,” she says. “We’re not trying to make pieces of your life go away.”
And so even with the dead ends and wrong turns, people can’t stop themselves. “We try to predict the future all the time,” Pasupathi says. She speculates that the reason there’s foreshadowing in fiction in the first place is because of this human tendency. The uncertainty of the future makes people uncomfortable , and stories are a way to deal with that.
“The future is never a direct replica of the past,” Adler says. “So we need to be able to take pieces of things that have happened to us and reconfigure them into possible futures.” For example, through experience, one learns that “We need to talk” rarely foreshadows anything good. (Life has its own clichés.)
There’s been some brain research supporting this link between the past and the future, showing that the same regions of the brain are activated when people are asked to remember something and when they’re asked to imagine an event that hasn’t happened yet. On the flip side, a patient with severe amnesia also had trouble imagining the future.
Similarly, the way someone imagines his future seems to affect the way he sees his past, at the same time as his past informs what he expects for the future.
“If you’re planning to be a doctor, and you’re a 25-year-old starting medical school, and you have expectations about what the next five to 10 years are going to be like, you’ve probably construed a narrative from your past that helps you understand how you got to this point,” McAdams says. “Then, say, you get into med school and you hate it and you drop out, you probably at the same time are going to change your past. You rewrite the history.”
A life story is written in chalk, not ink, and it can be changed. “You’re both the narrator and the main character of your story,” Adler says. “That can sometimes be a revelation—‘Oh, I’m not just living out this story; I am actually in charge of this story.’”
Whether it’s with the help of therapy, in the midst of an identity crisis, when you’ve been chasing a roadrunner of foreshadowing toward a tunnel that turns out to be painted on a wall, or slowly, methodically, day by day—like with all stories, there’s power in rewriting.
“The past is always up for grabs,” McAdams says.
Narrative Essay with Tips - a Detailed Guide

Defining What Is a Narrative Essay
We can explain a narrative essay definition as a piece of writing that tells a story. It's like a window into someone's life or a page torn from a diary. Similarly to a descriptive essay, a narrative essay tells a story, rather than make a claim and use evidence. It can be about anything – a personal experience, a childhood memory, a moment of triumph or defeat – as long as it's told in a way that captures the reader's imagination.
You might ask - 'which sentence most likely comes from a narrative essay?'. Let's take this for example: 'I could hear the waves crashing against the shore, their rhythm a soothing lullaby that carried me off to sleep.' You could even use such an opening for your essay when wondering how to start a narrative essay.
To further define a narrative essay, consider it storytelling with a purpose. The purpose of a narrative essay is not just to entertain but also to convey a message or lesson in first person. It's a way to share your experiences and insights with others and connect with your audience. Whether you're writing about your first love, a harrowing adventure, or a life-changing moment, your goal is to take the reader on a journey that will leave them feeling moved, inspired, or enlightened.
So if you're looking for a way to express yourself creatively and connect with others through your writing, try your hand at a narrative essay. Who knows – you might just discover a hidden talent for storytelling that you never knew you had!
Meanwhile, let's delve into the article to better understand this type of paper through our narrative essay examples, topic ideas, and tips on constructing a perfect essay.
Types of Narrative Essays
If you were wondering, 'what is a personal narrative essay?', know that narrative essays come in different forms, each with a unique structure and purpose. Regardless of the type of narrative essay, each aims to transport the reader to a different time and place and to create an emotional connection between the reader and the author's experiences. So, let's discuss each type in more detail:
- A personal narrative essay is based on one's unique experience or event. Personal narrative essay examples include a story about overcoming a fear or obstacle or reflecting on a particularly meaningful moment in one's life.
- A fictional narrative is a made-up story that still follows the basic elements of storytelling. Fictional narratives can take many forms, from science fiction to romance to historical fiction.
- A memoir is similar to personal narratives but focuses on a specific period or theme in a person's life. Memoirs might be centered around a particular relationship, a struggle with addiction, or a cultural identity. If you wish to describe your life in greater depth, you might look at how to write an autobiography .
- A literacy narrative essay explores the writer's experiences with literacy and how it has influenced their life. The essay typically tells a personal story about a significant moment or series of moments that impacted the writer's relationship with reading, writing, or communication.
You might also be interested in discovering 'HOW TO WRITE AN AUTOBIOGRAPHY'
Pros and Cons of Narrative Writing
Writing a narrative essay can be a powerful tool for self-expression and creative storytelling, but like any form of writing, it comes with its own set of pros and cons. Let's explore the pros and cons of narrative writing in more detail, helping you to decide whether it's the right writing style for your needs.
- It can be a powerful way to convey personal experiences and emotions.
- Allows for creative expression and unique voice
- Engages the reader through storytelling and vivid details
- It can be used to teach a lesson or convey a message.
- Offers an opportunity for self-reflection and growth
- It can be challenging to balance personal storytelling with the needs of the reader
- It may not be as effective for conveying factual information or arguments
- It may require vulnerability and sharing personal details that some writers may find uncomfortable
- It can be subjective, as the reader's interpretation of the narrative may vary
If sharing your personal stories is not your cup of tea, you can buy essays online from our expert writers, who will customize the paper to your particular writing style and tone.
20 Excellent Narrative Essay Topics and How to Choose One
Choosing a good topic among many narrative essay ideas can be challenging, but some tips can help you make the right choice. Here are some original and helpful tips on how to choose a good narrative essay topic:
- Consider your own experiences: One of the best sources of inspiration for a narrative essay is your own life experiences. Consider moments that have had a significant impact on you, whether they are positive or negative. For example, you could write about a memorable trip or a challenging experience you overcame.
- Choose a topic relevant to your audience: Consider your audience and their interests when choosing a narrative essay topic. If you're writing for a class, consider what topics might be relevant to the course material. If you're writing for a broader audience, consider what topics might be interesting or informative to them.
- Find inspiration in literature: Literature can be a great source of inspiration for a narrative essay. Consider the books or stories that have had an impact on you, and think about how you can incorporate elements of them into your own narrative. For example, you could start by using a title for narrative essay inspired by the themes of a favorite novel or short story.
- Focus on a specific moment or event: Most narrative essays tell a story, so it's important to focus on a specific moment or event. For example, you could write a short narrative essay about a conversation you had with a friend or a moment of realization while traveling.
- Experiment with different perspectives: Consider writing from different perspectives to add depth and complexity to your narrative. For example, you could write about the same event from multiple perspectives or explore the thoughts and feelings of a secondary character.
- Use writing prompts: Writing prompts can be a great source of inspiration if you struggle to develop a topic. Consider using a prompt related to a specific theme, such as love, loss, or growth.
- Choose a topic with rich sensory details: A good narrative essay should engage the senses and create a vivid picture in the reader's mind. Choose a topic with rich sensory details that you can use to create a vivid description. For example, you could write about a bustling city's sights, sounds, and smells.
- Choose a topic meaningful to you: Ultimately, the best narrative essays are meaningful to the writer. Choose a topic that resonates with you and that you feel passionate about. For example, you could write about a personal goal you achieved or a struggle you overcame.
Here are some good narrative essay topics for inspiration from our experts:
- A life-changing event that altered your perspective on the world
- The story of a personal accomplishment or achievement
- An experience that tested your resilience and strength
- A time when you faced a difficult decision and how you handled it
- A childhood memory that still holds meaning for you
- The impact of a significant person in your life
- A travel experience that taught you something new
- A story about a mistake or failure that ultimately led to growth and learning
- The first day of a new job or school
- The story of a family tradition or ritual that is meaningful to you
- A time when you had to confront a fear or phobia
- A memorable concert or music festival experience
- An experience that taught you the importance of communication or listening
- A story about a time when you had to stand up for what you believed in
- A time when you had to persevere through a challenging task or project
- A story about a significant cultural or societal event that impacted your life
- The impact of a book, movie, or other work of art on your life
- A time when you had to let go of something or someone important to you
- A memorable encounter with a stranger that left an impression on you
- The story of a personal hobby or interest that has enriched your life
Narrative Format and Structure
The narrative essay format and structure are essential elements of any good story. A well-structured narrative can engage readers, evoke emotions, and create lasting memories. Whether you're writing a personal essay or a work of fiction, the following guidelines on how to write a narrative essay can help you create a compelling paper:

- Introduction : The introduction sets the scene for your story and introduces your main characters and setting. It should also provide a hook to capture your reader's attention and make them want to keep reading. When unsure how to begin a narrative essay, describe the setting vividly or an intriguing question that draws the reader in.
- Plot : The plot is the sequence of events that make up your story. It should have a clear beginning, middle, and end, with each part building on the previous one. The plot should also have a clear conflict or problem the protagonist must overcome.
- Characters : Characters are the people who drive the story. They should be well-developed and have distinct personalities and motivations. The protagonist should have a clear goal or desire, and the antagonist should provide a challenge or obstacle to overcome.
- Setting : The setting is the time and place the story takes place. It should be well-described and help to create a mood or atmosphere that supports the story's themes.
- Dialogue : Dialogue is the conversation between characters. It should be realistic and help to reveal the characters' personalities and motivations. It can also help to move the plot forward.
- Climax : The climax is the highest tension or conflict point in the story. It should be the turning point that leads to resolving the conflict.
- Resolution : The resolution is the end of the story. It should provide a satisfying conclusion to the conflict and tie up any loose ends.
Following these guidelines, you can create a narrative essay structure that engages readers and leaves a lasting impression. Remember, a well-structured story can take readers on a journey and make them feel part of the action.
Want to Be Like an Expert Writer?
Order now and let our narrative essay service turn your experiences into a captivating and unforgettable tale
Narrative Essay Outline
Here is a detailed narrative essay outline from our custom term paper writing :
Introduction
A. Hook: Start with an attention-grabbing statement, question, or anecdote that introduces the topic and draws the reader in. Example: 'The sun beat down on my skin as I stepped onto the stage, my heart pounding with nervous excitement.'
B. Background information: Provide context for the story, such as the setting or the characters involved. Example: 'I had been preparing for this moment for weeks, rehearsing my lines and perfecting my performance for the school play.'
C. Thesis statement: State the essay's main point and preview the events to come. Example: 'This experience taught me that taking risks and stepping outside my comfort zone can lead to unexpected rewards and personal growth.'
Body Paragraphs
A. First event: Describe the first event in the story, including details about the setting, characters, and actions. Example: 'As I delivered my first lines on stage, I felt a rush of adrenaline and a sense of pride in my hard work paying off.'
B. Second event: Describe the second event in the story, including how it builds on the first event and moves the story forward. Example: 'As the play progressed, I became more comfortable in my role and connecting with the other actors on stage.'
C. Turning point: Describe the turning point in the story, when something unexpected or significant changes the course of events. Example: 'In the final act, my character faced a difficult decision that required me to improvise and trust my instincts.'
D. Climax: Describe the story's climax, the highest tension or conflict point. Example: 'As the play reached its climax, I delivered my final lines with confidence and emotion, feeling a sense of accomplishment and fulfillment.'
A. Restate thesis: Summarize the essay's main point and how the events in the story support it. Example: 'Through this experience, I learned that taking risks and pushing past my comfort zone can lead to personal growth and unexpected rewards.'
B. Reflection: Reflect on the significance of the experience and what you learned from it. Example: 'Looking back, I realize that this experience not only taught me about acting and performance but also about the power of perseverance and self-belief.'
C. Call to action: if you're still wondering how to write an essay conclusion , consider ending it with a call to action or final thought that leaves the reader with something to consider or act on. Example: 'I encourage everyone to take risks and embrace new challenges because you never know what kind of amazing experiences and growth they may lead to.
You might also be interested in getting detailed info on 'HOW TO WRITE AN ESSAY CONCLUSION'
Narrative Essay Examples
Are you looking for inspiration for your next narrative essay? Look no further than our narrative essay example. Through vivid storytelling and personal reflections, this essay takes the reader on a journey of discovery and leaves them with a powerful lesson about the importance of compassion and empathy. Use this sample from our expert essay writer as a guide for crafting your own narrative essay, and let your unique voice and experiences shine through.
Narrative Essay Example for College
College professors search for the following qualities in their students:
- the ability to adapt to different situations,
- the ability to solve problems creatively,
- and the ability to learn from mistakes.
Your work must demonstrate these qualities, regardless of whether your narrative paper is a college application essay or a class assignment. Additionally, you want to demonstrate your character and creativity. Describe a situation where you have encountered a problem, tell the story of how you came up with a unique approach to solving it, and connect it to your field of interest. The narrative can be exciting and informative if you present it in such fashion.
Narrative Essay Example for High School
High school is all about showing that you can make mature choices. You accept the consequences of your actions and retrieve valuable life lessons. Think of an event in which you believe your actions were exemplary and made an adult choice. A personal narrative essay example will showcase the best of your abilities. Finally, use other sources to help you get the best results possible. Try searching for a sample narrative essay to see how others have approached it.
Final Words
So now that you know what is a narrative essay you might want to produce high-quality paper. For that let our team of experienced writers help. Our research paper writing service offers a range of professional writing services that cater to your unique needs and requirements, from narrative essays to medical personal statement , also offering dissertation help and more.
With our flexible pricing options and fast turnaround times, you can trust that you'll receive great value for your investment. Contact us today to learn more about how we can help you succeed in your academic writing journey.
Unlock Your Potential with Our Essays!
Order now and take the first step towards achieving your academic goals
Related Articles
.webp)

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Unforgettable Day in My Life: Essay. Life Changing Experience ; Memories ; On Saturday we left Atlanta before dawn, and before his departure for Ghana, my father Anwar drive us by car, me Charbel, my mother Lina, my brother Alex, and my sister Rita; after parking the car, he took us on the hiking trail up to the top of the Stone Mountain from where we watched the sunrise in the eastern sky.
Interactive example of a narrative essay. An example of a short narrative essay, responding to the prompt “Write about an experience where you learned something about yourself,” is shown below. Hover over different parts of the text to see how the structure works. Narrative essay example.
Life is a journey filled with experiences that shape who we are. Throughout my life, I have encountered various challenges and triumphs that have significantly impacted my growth and development. In this essay, I will reflect on some of the most pivotal experiences in my life and explore how they have shaped me into the person I am today.
Here is a how to start a narrative essay example: A Leap of Faith. The air hung heavy with the promise of adventure as I stood on the precipice of the unknown. Below me, the water sparkled, inviting yet mysterious. My heart raced, echoing the uncertainty that rippled through my mind.
However, like any other type of writing, it comes with guidelines. 1. Write Your Personal Narrative as a Story. As a story, it must include an introduction, characters, plot, setting, climax, anti-climax (if any), and conclusion. Another way to approach it is by structuring it with an introduction, body, and conclusion.
1. Determine the goal of your essay. An autobiographical essay, also called a personal narrative essay, should tell the reader about your life, personality, values and goals. The essay should tell the reader what is important to you, what your values are, and any life experiences that influenced the way you experience the world. [1]
A narrative essay delivers its theme by deliberately weaving the motifs through the events, scenes, and details. While a narrative essay may be entertaining, its primary purpose is to tell a complete story based on a central meaning. Unlike other essay forms, it is totally okay—even expected—to use first-person narration in narrative essays.
In the realm of narrative psychology, a person’s life story is not a Wikipedia biography of the facts and events of a life, but rather the way a person integrates those facts and events ...
A personal narrative essay is based on one's unique experience or event. Personal narrative essay examples include a story about overcoming a fear or obstacle or reflecting on a particularly meaningful moment in one's life. A fictional narrative is a made-up story that still follows the basic elements of storytelling. Fictional narratives can ...