Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to write a rhetorical analysis | Key concepts & examples

How to Write a Rhetorical Analysis | Key Concepts & Examples
Published on August 28, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on July 23, 2023.
A rhetorical analysis is a type of essay that looks at a text in terms of rhetoric. This means it is less concerned with what the author is saying than with how they say it: their goals, techniques, and appeals to the audience.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Key concepts in rhetoric, analyzing the text, introducing your rhetorical analysis, the body: doing the analysis, concluding a rhetorical analysis, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about rhetorical analysis.
Rhetoric, the art of effective speaking and writing, is a subject that trains you to look at texts, arguments and speeches in terms of how they are designed to persuade the audience. This section introduces a few of the key concepts of this field.
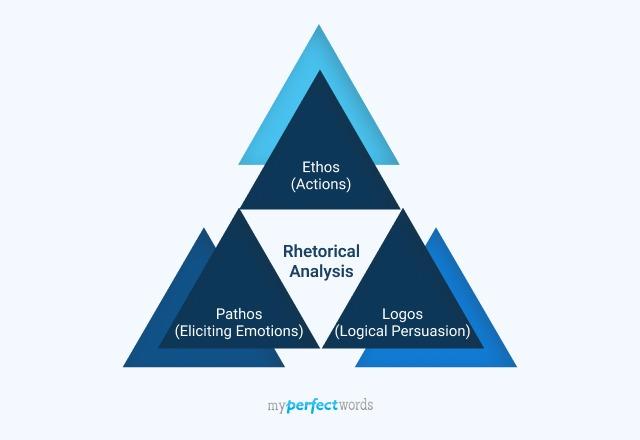
Appeals: Logos, ethos, pathos
Appeals are how the author convinces their audience. Three central appeals are discussed in rhetoric, established by the philosopher Aristotle and sometimes called the rhetorical triangle: logos, ethos, and pathos.
Logos , or the logical appeal, refers to the use of reasoned argument to persuade. This is the dominant approach in academic writing , where arguments are built up using reasoning and evidence.
Ethos , or the ethical appeal, involves the author presenting themselves as an authority on their subject. For example, someone making a moral argument might highlight their own morally admirable behavior; someone speaking about a technical subject might present themselves as an expert by mentioning their qualifications.
Pathos , or the pathetic appeal, evokes the audience’s emotions. This might involve speaking in a passionate way, employing vivid imagery, or trying to provoke anger, sympathy, or any other emotional response in the audience.
These three appeals are all treated as integral parts of rhetoric, and a given author may combine all three of them to convince their audience.
Text and context
In rhetoric, a text is not necessarily a piece of writing (though it may be this). A text is whatever piece of communication you are analyzing. This could be, for example, a speech, an advertisement, or a satirical image.
In these cases, your analysis would focus on more than just language—you might look at visual or sonic elements of the text too.
The context is everything surrounding the text: Who is the author (or speaker, designer, etc.)? Who is their (intended or actual) audience? When and where was the text produced, and for what purpose?
Looking at the context can help to inform your rhetorical analysis. For example, Martin Luther King, Jr.’s “I Have a Dream” speech has universal power, but the context of the civil rights movement is an important part of understanding why.
Claims, supports, and warrants
A piece of rhetoric is always making some sort of argument, whether it’s a very clearly defined and logical one (e.g. in a philosophy essay) or one that the reader has to infer (e.g. in a satirical article). These arguments are built up with claims, supports, and warrants.
A claim is the fact or idea the author wants to convince the reader of. An argument might center on a single claim, or be built up out of many. Claims are usually explicitly stated, but they may also just be implied in some kinds of text.
The author uses supports to back up each claim they make. These might range from hard evidence to emotional appeals—anything that is used to convince the reader to accept a claim.
The warrant is the logic or assumption that connects a support with a claim. Outside of quite formal argumentation, the warrant is often unstated—the author assumes their audience will understand the connection without it. But that doesn’t mean you can’t still explore the implicit warrant in these cases.
For example, look at the following statement:
We can see a claim and a support here, but the warrant is implicit. Here, the warrant is the assumption that more likeable candidates would have inspired greater turnout. We might be more or less convinced by the argument depending on whether we think this is a fair assumption.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Rhetorical analysis isn’t a matter of choosing concepts in advance and applying them to a text. Instead, it starts with looking at the text in detail and asking the appropriate questions about how it works:
- What is the author’s purpose?
- Do they focus closely on their key claims, or do they discuss various topics?
- What tone do they take—angry or sympathetic? Personal or authoritative? Formal or informal?
- Who seems to be the intended audience? Is this audience likely to be successfully reached and convinced?
- What kinds of evidence are presented?
By asking these questions, you’ll discover the various rhetorical devices the text uses. Don’t feel that you have to cram in every rhetorical term you know—focus on those that are most important to the text.
The following sections show how to write the different parts of a rhetorical analysis.
Like all essays, a rhetorical analysis begins with an introduction . The introduction tells readers what text you’ll be discussing, provides relevant background information, and presents your thesis statement .
Hover over different parts of the example below to see how an introduction works.
Martin Luther King, Jr.’s “I Have a Dream” speech is widely regarded as one of the most important pieces of oratory in American history. Delivered in 1963 to thousands of civil rights activists outside the Lincoln Memorial in Washington, D.C., the speech has come to symbolize the spirit of the civil rights movement and even to function as a major part of the American national myth. This rhetorical analysis argues that King’s assumption of the prophetic voice, amplified by the historic size of his audience, creates a powerful sense of ethos that has retained its inspirational power over the years.
The body of your rhetorical analysis is where you’ll tackle the text directly. It’s often divided into three paragraphs, although it may be more in a longer essay.
Each paragraph should focus on a different element of the text, and they should all contribute to your overall argument for your thesis statement.
Hover over the example to explore how a typical body paragraph is constructed.
King’s speech is infused with prophetic language throughout. Even before the famous “dream” part of the speech, King’s language consistently strikes a prophetic tone. He refers to the Lincoln Memorial as a “hallowed spot” and speaks of rising “from the dark and desolate valley of segregation” to “make justice a reality for all of God’s children.” The assumption of this prophetic voice constitutes the text’s strongest ethical appeal; after linking himself with political figures like Lincoln and the Founding Fathers, King’s ethos adopts a distinctly religious tone, recalling Biblical prophets and preachers of change from across history. This adds significant force to his words; standing before an audience of hundreds of thousands, he states not just what the future should be, but what it will be: “The whirlwinds of revolt will continue to shake the foundations of our nation until the bright day of justice emerges.” This warning is almost apocalyptic in tone, though it concludes with the positive image of the “bright day of justice.” The power of King’s rhetoric thus stems not only from the pathos of his vision of a brighter future, but from the ethos of the prophetic voice he adopts in expressing this vision.
The conclusion of a rhetorical analysis wraps up the essay by restating the main argument and showing how it has been developed by your analysis. It may also try to link the text, and your analysis of it, with broader concerns.
Explore the example below to get a sense of the conclusion.
It is clear from this analysis that the effectiveness of King’s rhetoric stems less from the pathetic appeal of his utopian “dream” than it does from the ethos he carefully constructs to give force to his statements. By framing contemporary upheavals as part of a prophecy whose fulfillment will result in the better future he imagines, King ensures not only the effectiveness of his words in the moment but their continuing resonance today. Even if we have not yet achieved King’s dream, we cannot deny the role his words played in setting us on the path toward it.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
The goal of a rhetorical analysis is to explain the effect a piece of writing or oratory has on its audience, how successful it is, and the devices and appeals it uses to achieve its goals.
Unlike a standard argumentative essay , it’s less about taking a position on the arguments presented, and more about exploring how they are constructed.
The term “text” in a rhetorical analysis essay refers to whatever object you’re analyzing. It’s frequently a piece of writing or a speech, but it doesn’t have to be. For example, you could also treat an advertisement or political cartoon as a text.
Logos appeals to the audience’s reason, building up logical arguments . Ethos appeals to the speaker’s status or authority, making the audience more likely to trust them. Pathos appeals to the emotions, trying to make the audience feel angry or sympathetic, for example.
Collectively, these three appeals are sometimes called the rhetorical triangle . They are central to rhetorical analysis , though a piece of rhetoric might not necessarily use all of them.
In rhetorical analysis , a claim is something the author wants the audience to believe. A support is the evidence or appeal they use to convince the reader to believe the claim. A warrant is the (often implicit) assumption that links the support with the claim.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, July 23). How to Write a Rhetorical Analysis | Key Concepts & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved March 27, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/rhetorical-analysis/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, how to write an argumentative essay | examples & tips, how to write a literary analysis essay | a step-by-step guide, comparing and contrasting in an essay | tips & examples, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”

Ethos Definition
What is ethos? Here’s a quick and simple definition:
Ethos , along with logos and pathos , is one of the three "modes of persuasion" in rhetoric (the art of effective speaking or writing). Ethos is an argument that appeals to the audience by emphasizing the speaker's credibility and authority. If the speaker has a high-ranking position, is an expert in his or her field, or has had life experience relevant to a particular topic, anything the speaker says or does to ensure that the audience knows about and remembers these qualifications is an example of ethos .
Some additional key details about ethos:
- Ethos shares a root with the word "ethics ." This is helpful to remember because speakers often try to establish their own strong moral character by using ethos.
- The word "ethos" is also often used to refer to a community or organization's characteristic belief or spirit, as in the sentence, "We will not give you a larger bonus than your coworkers: that is against our company's ethos of fairness." However, this guide focuses specifically on the rhetorical technique of ethos used in literature and public speaking.
- The three "modes of persuasion"— pathos , logos , and ethos —were originally defined by Aristotle.
- While ethos appeals to an audience's instinctive respect for authority, logos appeals to the audience's sense of reason, and pathos appeals to the audience's emotions.
- Ethos is used in advertising just as often as it is used in public speaking and literature. Any commercial in which a celebrity endorses a product, for example, hopes to persuade its target audience by cultivating an aura of authority or expertise through its association with the celebrity—and is therefore an example of ethos.
How to Pronounce Ethos
Here's how to pronounce ethos: ee -thos
Ethos Explained
Aristotle (the ancient Greek philosopher and scientist) first defined e thos , along with logos and pathos , in his treatise on rhetoric, Ars Rhetorica. Together, he referred to e thos , logos , and pathos as the three modes of persuasion, or sometimes simply as "the appeals." Aristotle believed that in order to have ethos a good speaker must demonstrate three things:
- Phronesis : Sound reasoning, and relevant experience or expertise.
- Arete : Moral character.
- Eunoia : Good intentions towards the audience.
Aristotle argued that a speaker in possession of these three attributes will naturally impress the audience with his or her ethos , and as a result will be better able to influence that audience. Over time, however, the definition of ethos has broadened, and the significance of the three qualities Aristotle named is now lost on anyone who hasn't studied classical Greek. So it may give more insight into the meaning of ethos to translate Aristotle's three categories into a new set of categories that make more sense in the modern era. A speaker or writer's credibility can be said to rely on each of the following:
- Within literature, it's interesting to notice when characters attempt to invoke their own authority and enhance their ethos by reminding other characters of the titles they possess. Often, this can be an indication that the character citing his or her own credentials actually feels his or her authority being threatened or challenged.
- In literature, this form of ethos is particularly relevant with respect to narrators. Authors often have their narrators profess impartiality or objectivity at the outset of a book in order to earn the reader's trust in the narrator's reliability regarding the story he or she is about to tell.
- This type of ethos translates into literature quite easily, in the sense that characters' opinions are often evaluated within the framework of their professions.
- Literary characters often use ethos to communicate similarity or likemindedness to other characters, and you can detect this by certain changes in their speech. In these situations, characters (as well as real-life speakers) often use a shibboleth— a specialized term or word used by a specific group of people—to show that they belong. For example, if you knew the name of a special chemical used to make jello, and you wanted to impress the head of a jello company, the name of that chemical would count as a shibboleth and saying it would help you show the jello executive that you're "in the know."
The Stagecraft of Ethos
In order to impress their positive personal qualities upon audiences, public speakers can use certain techniques that aren't available to writers. These include:
- Speaking in a certain manner or even with a certain accent.
- Demonstrating confident stage presence.
- Having reputable people to introduce the speaker in a positive light.
- Listing their credentials and achievements.
Put another way, the ethos of a speech can be heavily impacted by the speaker's confidence and manner of presenting him or herself.
Ethos and Ad Hominem
An ad hominem argument is a specific type of argument which involves attacking someone else's character or ethos, rather than attacking that person's position or point of view on the subject being discussed. Ad hominem attacks usually have the goal of swaying an audience away from an opponent's views and towards one's own by degrading the audience's perception of the opponent's character. For instance, if one politician attacks another as being "elite," the attacker may be seeking to make voters question whether the other politician is trustworthy or actually has the public's interest at heart. But the first politician is not in any way attacking their opponent's positions on matters of policy.
An ad hominem argument is not necessarily "wrong" or even a bad strategy, but it's generally seen as more dignified (another component of ethos ) for speakers to focus on strengthening their own ethos, and to debate their opponents based on the substance of the opposition's counterarguments. When a literary character uses an ad hominem argument, this can sometimes indicate that he or she is insecure about his or her own position regarding a certain issue.
Ethos Examples
Examples of ethos in literature.
Characters in novels often use ethos , as well as logos and pathos , to convince one another of certain arguments in the same way that a speaker in reality might use these techniques. In addition, authors often use a subtler form of ethos when establishing a narrator's reliability at the outset of a novel.
Ethos in Ayn Rand's Atlas Shrugged
In Atlas Shrugged, a group of pioneering American industrialists, financiers, and artists go on strike against a corrupt government. As the strike nears its end, its leader—John Galt—delivers a speech to the nation about his ideals. He promises that the strike will end only if Americans allow him to remake the country according to his moral code, which he explains in the following lines:
Just as I support my life, neither by robbery nor alms, but by my own effort, so I do not seek to derive my happiness from the injury or the favor of others, but earn it by my own achievement. Just as I do not consider the pleasure of others as the goal of my life, so I do not consider my pleasure as the goal of the lives of others. Just as there are no contradictions in my values and no conflicts among my desires—so there are no victims and no conflicts of interest among rational men, men who do not desire the unearned and do not view one another with a cannibal's lust, men who neither make sacrifices nor accept them.
Galt not only creates an impression of moral rectitude, but also emphasizes his own self-sufficiency. He assures his audience that he expects nothing in return from them for sharing his personal views. In this way, his ability to cultivate an aura of impartiality and objectivity enhances his ethos.
Ethos in Nathaniel Hawthorne's The Scarlet Letter
The Scarlet Letter opens with a chapter called "The Custom-House," in which the unnamed narrator—who has a similar biography to Hawthorne—describes his job in a Custom House, a place where taxes were paid on imports in 18th century Massachusetts. The narrator's stories about his job have no relation to the actual narrative of The Scarlet Letter, except that he finds the scarlet letter of the title in the Custom House attic. This discovery inspired him to research the life of the woman who wore the embroidered letter, and to tell her story. By presenting himself as someone who merely discovered, researched, and "edited" the story the reader is about to begin, the narrator effectively creates the impression that his is a reliable historical account, thereby strengthening his ethos.
It will be seen, likewise, that this Custom-House sketch has a certain propriety, of a kind always recognised in literature, as explaining how a large portion of the following pages came into my possession, and as offering proofs of the authenticity of a narrative therein contained. This, in fact—a desire to put myself in my true position as editor, or very little more, of the most prolix among the tales that make up my volume—this, and no other, is my true reason for assuming a personal relation with the public.
Ethos in F. Scott Fitzgerald's The Great Gatsby
In the opening lines of The Great Gatsby , the narrator, Nick Carraway, claims that he has followed one piece of his father's advice throughout his life:
In my younger and more vulnerable years my father gave me some advice that I've been turning over in my mind ever since. 'Whenever you feel like criticizing any one,' he told me, just remember that all the people in this world haven't had the advantages that you've had.'... In consequence I'm inclined to reserve all judgements, a habit that has opened up many curious natures to me and also made me the victim of not a few veteran bores. The abnormal mind is quick to detect and attach itself to this quality when it appears in a normal person, and so it came about that in college I was unjustly accused of being a politician, because I was privy to the secret griefs of wild, unknown men...
Nick's tendency to reserve judgement makes him an ideal, objective narrator, while his awareness of his own economic and social advantages makes him a perfect guide to the privileged world of The Great Gatsby. Though he describes his non-judgmental, "neutral" affect with self-deprecating humor, it's a subtle way of strengthening his ethos as a narrator, and of causing the reader to eagerly anticipate hearing the stories that "wild, unknown men" have shared with him.
Examples of Ethos in Political Speeches
Every politician recognizes that a speaker must earn an audience's respect and trust if he or she expects to be listened to. As a result, it's difficult to find a political speech that doesn't contain an example of ethos. It's particularly easy to spot ethos in action when listening to speeches by candidates for office.
Ethos in Mitt Romney's Acceptance Speech at the 2012 Republican National Convention
When he accepted the Republican presidential nomination in 2012, Romney pointed to his business success as relevant experience that would serve him well if he were to take office:
I learned the real lessons about how America works from experience. When I was 37, I helped start a small company. My partners and I had been working for a company that was in the business of helping other businesses. So some of us had this idea that if we really believed our advice was helping companies, we should invest in companies. We should bet on ourselves and on our advice. So we started a new business called Bain Capital...That business we started with 10 people has now grown into a great American success story. Some of the companies we helped start are names you know. An office supply company called Staples – where I'm pleased to see the Obama campaign has been shopping; The Sports Authority, which became a favorite of my sons. We started an early childhood learning center called Bright Horizons that First Lady Michelle Obama rightly praised.
In addition to strengthening his ethos by pointing to his past achievements, Romney also hopes to portray himself as principled, rational, and daring when he explains how his company decided to "bet on ourselves and on our advice."
Ethos in John Kasich's 2016 Ohio Primary Victory Speech
After winning his first campaign victory, 2016 presidential candidate John Kasich told his supporters about his disadvantaged yet hardworking relatives to contextualize his own rise to success:
And you know, ladies and gentlemen, my whole life has been about trying to create a climate of opportunity for people. You know, as my father carried that mail on his back and his father was a coal miner, and you know, I was just told by my cousin—I didn't realize this—that my mother, one of four [children]‚ was the only one to graduate from high school. The other three barely made it out of the eighth grade because they were poor... And you know, as I've traveled the country and I look into your eyes... You want to believe that your children are going to have ultimately a better America than what we got from our mothers and fathers. That's the great American legacy: that our kids will be better than we are.
By saying that he comes from a modest background, Kasich hopes to convey that he is "just a regular American" and that he will advocate for other hard working Americans.
Ethos in Winston Churchill's 1941 Address to Joint Session of the US Congress
In this speech to the US Congress during World War II, British Prime Minister Winston Churchill enhances the ethos of his speech by emphasizing both the qualities he shares in common with the American people and the American Democratic values instilled in him by his parents:
I am a child of the House of Commons. I was brought up in my father's house to believe in democracy. "Trust the people." That was his message. I used to see him cheered at meetings and in the streets by crowds of workingmen way back in those aristocratic Victorian days when as Disraeli said "the world was for the few, and for the very few." Therefore I have been in full harmony all my life with the tides which have flowed on both sides of the Atlantic against privilege and monopoly and I have steered confidently towards the Gettysburg ideal of government of the people, by the people, for the people.
Examples of Ethos in Advertisements
Advertisers often attempt to use ethos to influence people to buy their product. Dressing up an actor as a doctor who then extols the benefits a medication is a way that advertisers used to try to gin up a little ethos , but such obvious practices of what might be called "fake ethos" are now regularly mocked. However, any celebrity endorsement or testimonial from an expert are also attempts to build up ethos around a product's endorsement. For instance, here's a Prudential Financial commercial that ups its ethos with an appearance by Harvard social psychologist Dan Gilbert.
Why Do Writers Use Ethos?
Politicians, activists, and advertisers use ethos because they recognize that it is impossible to convince an audience of anything if its members do not believe in the speaker's credibility, morality, or authority.
The use of e thos in fiction is often different from real-world examples. Authors are not usually trying to directly influence their audience in the way politicians or advertisers are. Rather, authors often show one of their characters making use of ethos . In doing so, the author gives insight into characters' perceptions of one another, their values, and their motives.
In addition, e thos is an especially useful tool for authors looking to establish a narrator's credibility. Having a credible narrator is hugely important to the success of a literary work. Books with narrators that never establish a reasonable claim to an objective viewpoint are nearly impossible to read because everything they say is cast in doubt, so that readers come to feel like they're being lied to or "jerked around," which is fatiguing. Although often enough readers simply assume that a narrator has credibility , if you've ever read a book where you felt you simply didn't like the narrator very much—or watched a television show where you felt that none of the characters were likable or believable—that might be another sign that the writer has failed to establish a character's ethos . There are circumstances in which a writer creates an unreliable narrator —a narrator who is either purposefully or subconsciously offering a slanted narrative—but ethos is just as crucial in creating such a narrator: the author must first establish the narrator's ethos and then slowly undermine it over the course of the book.
Other Helpful Ethos Resources
- The Wikipedia Page on Ethos: An in-depth explanation of ethos , and how the concept has changed over time.
- The Dictionary Definition of Ethos: A definition and etymology of the term, which comes from the Greek ethos meaning "character, custom, or habit."
- Ethos on Youtube: An excellent video from TED-Ed about the three modes of persuasion.

- PDFs for all 136 Lit Terms we cover
- Downloads of 1895 LitCharts Lit Guides
- Teacher Editions for every Lit Guide
- Explanations and citation info for 39,904 quotes across 1895 books
- Downloadable (PDF) line-by-line translations of every Shakespeare play
- Bildungsroman
- Antimetabole
- Figurative Language
- Climax (Figure of Speech)
- Pathetic Fallacy
- Climax (Plot)
- Antanaclasis
- Deus Ex Machina
- Rhetorical Question
- Tragic Hero


An Example for Rhetorical Analysis
A publish.illinois.edu site
What is Ethos?
Ethos implies credit of an argument to readers when it tries to persuade them of certain ideas. When reading an argument, readers mainly judge the Ethos by the identity of the author and the credibility of the sources used in the argument.
An Analysis Example:
Sara Peres works in Geography and Environment at the University of Southampton. And what’s important is that she has previously focused on how agricultural seeds are banked and circulated for conservation purposes for her Ph.D. (UCL, 2017), the history of seed banks, which was exactly where this paper comes from. And I think this experience and her occupation grant the basic credit of her claims in this paper, indicating that she was trustworthy to her readers.
However, there would not be enough authority if she hasn’t quoted other experts’ claims and research results. She mainly depends on the vision of the plant breeder and emphatic advocate of gene banking, Otto H. Frankel (1900–1998) and there are also some views of other experts to support the advantages of seed banks.
ps: Those two are undeveloped paragraphs! In my essay, they appear in the same paragraph, but here I just separate them for the convenience of my explanation below.
Rhetorical Analysis Sample Essay
Harriet Clark
Ms. Rebecca Winter
13 Feb. 2015
Not Quite a Clean Sweep: Rhetorical Strategies in
Grose's "Cleaning: The Final Feminist Frontier”
A woman’s work is never done: many American women grow up with this saying and feel it to be true. 1 One such woman, author Jessica Grose, wrote “Cleaning: The Final Feminist Frontier,” published in 2013 in the New Republic, 2 and she argues that while the men recently started taking on more of the childcare and cooking, cleaning still falls unfairly on women. 3 Grose begins building her credibility with personal facts and reputable sources, citing convincing facts and statistics, and successfully employing emotional appeals; however, toward the end of the article, her attempts to appeal to readers’ emotions weaken her credibility and ultimately, her argument. 4
In her article, Grose first sets the stage by describing a specific scenario of house-cleaning with her husband after being shut in during Hurricane Sandy, and then she outlines the uneven distribution of cleaning work in her marriage and draws a comparison to the larger feminist issue of who does the cleaning in a relationship. Grose continues by discussing some of the reasons that men do not contribute to cleaning: the praise for a clean house goes to the woman; advertising and media praise men’s cooking and childcare, but not cleaning; and lastly, it is just not fun. Possible solutions to the problem, Grose suggests, include making a chart of who does which chores, dividing up tasks based on skill and ability, accepting a dirtier home, and making cleaning more fun with gadgets. 5
Throughout her piece, Grose uses many strong sources that strengthen her credibility and appeal to ethos, as well as build her argument. 6 These sources include, “sociologists Judith Treas and Tsui-o Tai,” “a 2008 study from the University of New Hampshire,” and “P&G North America Fabric Care Brand Manager, Matthew Krehbiel” (qtd. in Grose). 7 Citing these sources boosts Grose’s credibility by showing that she has done her homework and has provided facts and statistics, as well as expert opinions to support her claim. She also uses personal examples from her own home life to introduce and support the issue, which shows that she has a personal stake in and first-hand experience with the problem. 8
Adding to her ethos appeals, Grose uses strong appeals to logos, with many facts and statistics and logical progressions of ideas. 9 She points out facts about her marriage and the distribution of household chores: “My husband and I both work. We split midnight baby feedings ...but ... he will admit that he’s never cleaned the bathroom, that I do the dishes nine times out of ten, and that he barely knows how the washer and dryer work in the apartment we’ve lived in for over eight months.” 10 These facts introduce and support the idea that Grose does more household chores than her husband. Grose continues with many statistics:
[A]bout 55 percent of American mothers employed full time do some housework on an average day, while only 18 percent of employed fathers do. ... [W]orking women with children are still doing a week and a half more of “second shift” work each year than their male partners. ... Even in the famously gender-neutral Sweden, women do 45 minutes more housework a day than their male partners. 11
These statistics are a few of many that logically support her claim that it is a substantial and real problem that men do not do their fair share of the chores. The details and numbers build an appeal to logos and impress upon the reader that this is a problem worth discussing. 12
Along with strong logos appeals, Grose effectively makes appeals to pathos in the beginning and middle sections. 13 Her introduction is full of emotionally-charged words and phrases that create a sympathetic image; Grose notes that she “was eight months pregnant” and her husband found it difficult to “fight with a massively pregnant person.” 14 The image she evokes of the challenges and vulnerabilities of being so pregnant, as well as the high emotions a woman feels at that time effectively introduce the argument and its seriousness. Her goal is to make the reader feel sympathy for her. Adding to this idea are words and phrases such as, “insisted,” “argued,” “not fun,” “sucks” “headachey,” “be judged,” “be shunned” (Grose). All of these words evoke negative emotions about cleaning, which makes the reader sympathize with women who feel “judged” and shunned”—very negative feelings. Another feeling Grose reinforces with her word choice is the concept of fairness: “fair share,” “a week and a half more of ‘second shift’ work,” “more housework,” “more gendered and less frequent.” These words help establish the unfairness that exists when women do all of the cleaning, and they are an appeal to pathos, or the readers’ feelings of frustration and anger with injustice. 15
However, the end of the article lacks the same level of effectiveness in the appeals to ethos. 16 For example, Grose notes that when men do housework, they are considered to be “’enacting “small instances of gender heroism,” or ‘SIGH’s’—which, barf.” 17 The usage of the word “barf” is jarring to the reader; unprofessional and immature, it is a shift from the researched, intelligent voice she has established and the reader is less likely to take the author seriously. This damages the strength of her credibility and her argument. 18
Additionally, her last statement in the article refers to her husband in a way that weakens the argument. 19 While returning to the introduction’s hook in the conclusion is a frequently-used strategy, Grose chooses to return to her discussion of her husband in a humorous way: Grose discusses solutions, and says there is “a huge, untapped market ... for toilet-scrubbing iPods. I bet my husband would buy one.” 20 Returning to her own marriage and husband is an appeal to ethos or personal credibility, and while that works well in the introduction, in the conclusion, it lacks the strength and seriousness that the topic deserves and was given earlier in the article. 21
Though Grose begins the essay by effectively persuading her readers of the unfair distribution of home-maintenance cleaning labor, she loses her power in the end, where she most needs to drive home her argument. Readers can see the problem exists in both her marriage and throughout the world; however, her shift to humor and sarcasm makes the reader not take the problem as seriously in the end. 22 Grose could have more seriously driven home the point that a woman’s work could be done: by a man. 23
Works Cited
Grose, Jessica. “Cleaning: The Final Feminist Frontier.” New Republic. The New Republic, 19 Mar. 2013. Web. 28 Mar. 2014.
- Article author's claim or purpose
- Summary of the article's main point in the second paragraph (could also be in the introduction)
- Third paragraph begins with a transition and topic sentence that reflects the first topic in the thesis
- Quotes illustrate how the author uses appeals to ethos
- Analysis explains how the quotes show the effective use of ethos as noted in the thesis
- Transition and topic sentence about the second point from the thesis
- Quote that illustrates appeals to logos
- Analysis explains how the quotes show the effective use of logos, as noted in the thesis
- Transition and topic sentence about the third point from the thesis
- Quotes that illustrate appeals to pathos
- Analysis explains how the quotes show the effective use of pathos, as noted in the thesis
- Transition and topic sentence about fourth point from the thesis
- Quote illustrates how the author uses appeal to ethos
- Analysis explains how quote supports thesis
- Transition and topic sentence about fourth point from thesis
- Conclusion returns to the ideas in the thesis and further develops them
- Last sentence returns to the hook in the introduction
Learn more about the " Rhetorical Analysis Graphic Organizer ."
Learn more about " Pathos, Logos, and Ethos ."
Rhetorical Analysis Essay
Ethos Pathos And Logos
Ethos, Pathos, and Logos - Structure, Usage & Examples
People also read
Rhetorical Analysis Essay - A Complete Guide With Examples
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Topics – 120+ Unique Ideas
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example - Free Samples
Crafting an Effective Rhetorical Analysis Essay Outline - Free Samples!
Are your arguments falling flat? Struggling to persuade your audience effectively? You're not alone!
Many students face this challenge when trying to convey their ideas convincingly. Whether it's in a class discussion, a persuasive essay , or a presentation, the art of persuasion often seems elusive.
But fear not!
In this blog, we're going to delve deep into the world of ethos, pathos, and logos, the three pillars of persuasive communication.
By the end, you'll not only understand these concepts but also know how to wield them skillfully.
Let’s get started!
- 1. Ethos, Pathos, and Logos Definition
- 2. Usage of Ethos, Pathos, and Logos
- 3. How To Identify Whether An Author Is Using Ethos, Pathos, Or Logos While Analyzing A Text?
- 4. Ethos, Pathos, and Logos Examples
Ethos, Pathos, and Logos Definition
Ethos, pathos, and logos are three essential components in rhetorical analysis . It can be a very effective tool for influencing and convincing others.
These concepts have been employed by great speakers, writers, and thinkers throughout history and continue to play a pivotal role in communication today.
Here are the key differences between ethos, pathos, and logos:
Let's break down each section one at a time, getting to know what ethos, pathos, and logos mean.
Ethos
Ethos is all about establishing credibility and trustworthiness. When you use ethos in your argument, you aim to convince your audience that you are a credible and reliable source of information. It also means you have the expertise needed to speak on a particular subject.
This can be achieved through the use of references to your qualifications, expertise, or by citing reputable sources to support your claims.
Pathos
Pathos appeals to the emotions and feelings of your audience. When you employ pathos, you're aiming to elicit an emotional response, whether it's sympathy, anger, happiness, or any other emotion that can strengthen any type of argument .
This is often achieved through storytelling, vivid language, and relatable anecdotes that connect with the audience on a personal level.
Logos is the appeal to logic and reason. When you use logos, you provide your audience with clear, rational, and well-structured arguments supported by evidence, facts, and statistics.
This appeals to the logical side of your audience's thinking, encouraging them to see the soundness of your position and the validity of your claims.
Usage of Ethos, Pathos, and Logos
Understanding the definitions of ethos, pathos, and logos is a solid foundation, but knowing how to apply these modes of persuasion effectively is equally important.
In this section, we'll delve into practical examples and strategies for utilizing ethos, pathos, and logos to make your persuasive communication more compelling.
Ethos in Action
One of the most common ways to establish ethos is by citing credible sources. Whether you're writing an academic paper or delivering a persuasive speech , referencing reputable experts, institutions, or publications can lend authority to your argument.
If you have personal expertise in the subject matter, don't be shy about showcasing it. Share your qualifications, relevant experiences, or your journey of learning and growth to build trust with your audience.
The following examples of the usage of ethos in the content will help you understand the concept better.
- "My three decades of experience in public service, my tireless commitment to the people of this community, and my willingness to reach across the aisle and cooperate with the opposition make me the ideal candidate for your mayor."
- "Our expertise in roofing contracting is evidenced not only by our 50 years in the business and our staff of qualified technicians. But in the decades of satisfied customers who have come to expect nothing but the best."
- "Based on the dozens of archaeological expeditions I've made all over the world, I am confident that those potsherds are Mesopotamian in origin."
2. Eliciting Emotions with Pathos
Personal anecdotes or emotionally charged stories can engage your audience on a deeper level. They create a connection by allowing the audience to empathize with the characters or situations in your narrative.
Use descriptive language that paints a vivid picture in the minds of your audience. This can help evoke specific emotions and make your message more memorable.
Here are some examples of how to use pathos for persuasion:
- "They've worked against everything we've worked so hard to build, and they don't care who gets hurt in the process. Make no mistake, they're the enemy, and they won't stop until we're all destroyed."
- "You will never be satisfied in life if you don't seize this opportunity. Do you want to live the rest of your year’s yearning to know what would have happened if you just jumped when you had the chance?"
- "After years of this type of disrespect from your boss, countless hours wasted, and birthdays missed, it's time that you took a stand."
Logos for Logical Persuasion
Logos require you to incorporate relevant data, statistics, and evidence to support your claims. This provides a logical foundation for your argument and demonstrates that your position is well-informed and substantiated.
Using logos can be a bit hard compared to the other two devices, but the following examples can help you understand.
- "Ladies and gentlemen of the jury: we have not only the fingerprints, the lack of an alibi, a clear motive, and an expressed desire to commit the robbery. We also have a video of the suspect breaking in. The case could not be more open and shut."
- "More than one hundred peer-reviewed studies have been conducted over the past decade. None of them suggests that this is an effective treatment for hair loss."
- "Research compiled by analysts from NASA, as well as organizations from five other nations with space programs, suggests that a moon colony is viable with international support."

Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers!
How To Identify Whether An Author Is Using Ethos, Pathos, Or Logos While Analyzing A Text?
Identifying whether an author is using Ethos, Pathos, or Logos in a text involves a careful analysis of the writing's persuasive techniques.
Here's how to recognize each of these elements:
- Look for the author's credentials, expertise, or reputation. Do they cite reputable sources, and are they qualified to speak on the subject?
- Assess whether the author employs a professional and trustworthy tone throughout the text.
- Check for citations and references to authoritative figures, institutions, or research.
- Identify emotionally charged language, vivid imagery, or personal anecdotes that elicit feelings in the reader.
- Pay attention to words that trigger empathy, sympathy, or strong emotional responses.
- Notice if the author appeals to values, hopes, fears, or desires to sway the reader's emotions.
- Analyze the use of statistics, data, and facts in the text. Does the author support their argument with evidence?
- Look for clear and structured reasoning. Is the argument well-organized and does it follow a logical sequence?
- Consider whether the author uses syllogisms, analogies, or deductive reasoning to make their point.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
Ethos, Pathos, and Logos Examples
Still uncertain about making a try on your argumentative essay or analysis paper?
Here are some additional examples of ethos, pathos, and logos to help you make your content convincing and persuasive.
Ethos, Pathos, and Logos in Advertising
Ethos, Pathos, and Logos Worksheet
Ethos, Pathos, and Logos in Movies
Ethos, Pathos, and Logos in Speeches
Ethos, Pathos, Logos Kairos Example
In summary, using ethos, pathos, and logos is essential to strengthen your point and persuade the audience. Without using these rhetorical devices, the readers will not understand the frame of mind of the writer.
If you are still unclear about the concept and its usage, it is advised to get help from expert analytical essay writer. MyPerfectWords.com is an expert essay writer service that helps students with all their academic assignments.
Be it a rhetorical paper or a persuasive speech, our analytical essay writing service knows how to assist students. Simply place an order at our essay writing service to get in touch with an expert writer at the most reasonable price.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can logos build ethos.
Logos are appealing to logic by offering evidence in support of your argument. It also makes you look knowledgeable because the information demonstrates intelligence on your part, developing ethos for yourself.
Which is more important: ethos logos or pathos?
Aristotle believed that logos should be the most important of three persuasive appeals. As a philosopher and master of logical reasoning, he thought it was unnecessary to use either ethos or pathos if you present your argument with good reason supported by facts.

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Nova Allison is a Digital Content Strategist with over eight years of experience. Nova has also worked as a technical and scientific writer. She is majorly involved in developing and reviewing online content plans that engage and resonate with audiences. Nova has a passion for writing that engages and informs her readers.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading

- Features for Creative Writers
- Features for Work
- Features for Higher Education
- Features for Teachers
- Features for Non-Native Speakers
- Learn Blog Grammar Guide Community Events FAQ
- Grammar Guide
What Is a Rhetorical Analysis and How to Write a Great One

Helly Douglas

Do you have to write a rhetorical analysis essay? Fear not! We’re here to explain exactly what rhetorical analysis means, how you should structure your essay, and give you some essential “dos and don’ts.”
What is a Rhetorical Analysis Essay?
How do you write a rhetorical analysis, what are the three rhetorical strategies, what are the five rhetorical situations, how to plan a rhetorical analysis essay, creating a rhetorical analysis essay, examples of great rhetorical analysis essays, final thoughts.
A rhetorical analysis essay studies how writers and speakers have used words to influence their audience. Think less about the words the author has used and more about the techniques they employ, their goals, and the effect this has on the audience.

In your analysis essay, you break a piece of text (including cartoons, adverts, and speeches) into sections and explain how each part works to persuade, inform, or entertain. You’ll explore the effectiveness of the techniques used, how the argument has been constructed, and give examples from the text.
A strong rhetorical analysis evaluates a text rather than just describes the techniques used. You don’t include whether you personally agree or disagree with the argument.
Structure a rhetorical analysis in the same way as most other types of academic essays . You’ll have an introduction to present your thesis, a main body where you analyze the text, which then leads to a conclusion.
Think about how the writer (also known as a rhetor) considers the situation that frames their communication:
- Topic: the overall purpose of the rhetoric
- Audience: this includes primary, secondary, and tertiary audiences
- Purpose: there are often more than one to consider
- Context and culture: the wider situation within which the rhetoric is placed
Back in the 4th century BC, Aristotle was talking about how language can be used as a means of persuasion. He described three principal forms —Ethos, Logos, and Pathos—often referred to as the Rhetorical Triangle . These persuasive techniques are still used today.
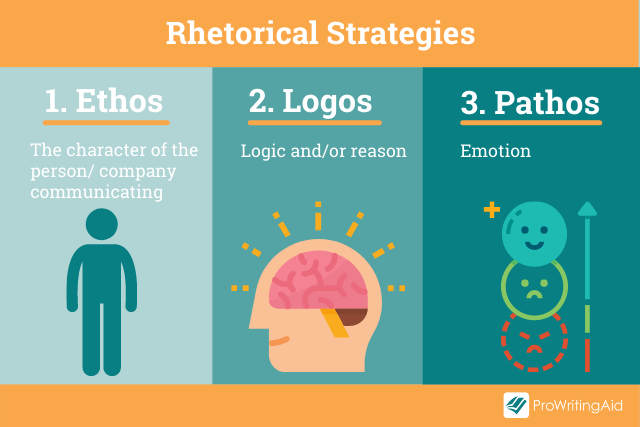
Rhetorical Strategy 1: Ethos
Are you more likely to buy a car from an established company that’s been an important part of your community for 50 years, or someone new who just started their business?
Reputation matters. Ethos explores how the character, disposition, and fundamental values of the author create appeal, along with their expertise and knowledge in the subject area.
Aristotle breaks ethos down into three further categories:
- Phronesis: skills and practical wisdom
- Arete: virtue
- Eunoia: goodwill towards the audience
Ethos-driven speeches and text rely on the reputation of the author. In your analysis, you can look at how the writer establishes ethos through both direct and indirect means.
Rhetorical Strategy 2: Pathos
Pathos-driven rhetoric hooks into our emotions. You’ll often see it used in advertisements, particularly by charities wanting you to donate money towards an appeal.
Common use of pathos includes:
- Vivid description so the reader can imagine themselves in the situation
- Personal stories to create feelings of empathy
- Emotional vocabulary that evokes a response
By using pathos to make the audience feel a particular emotion, the author can persuade them that the argument they’re making is compelling.
Rhetorical Strategy 3: Logos
Logos uses logic or reason. It’s commonly used in academic writing when arguments are created using evidence and reasoning rather than an emotional response. It’s constructed in a step-by-step approach that builds methodically to create a powerful effect upon the reader.
Rhetoric can use any one of these three techniques, but effective arguments often appeal to all three elements.
The rhetorical situation explains the circumstances behind and around a piece of rhetoric. It helps you think about why a text exists, its purpose, and how it’s carried out.
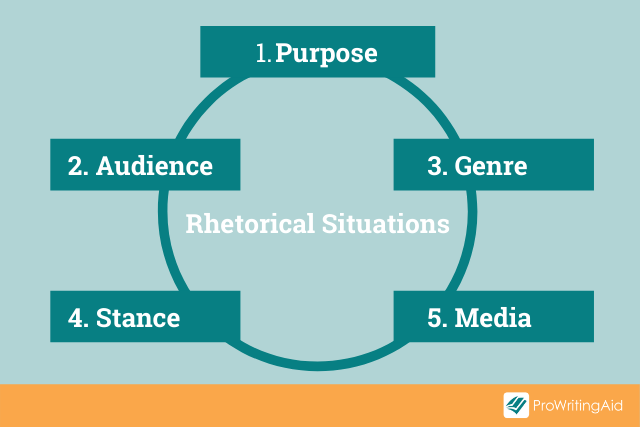
The rhetorical situations are:
- 1) Purpose: Why is this being written? (It could be trying to inform, persuade, instruct, or entertain.)
- 2) Audience: Which groups or individuals will read and take action (or have done so in the past)?
- 3) Genre: What type of writing is this?
- 4) Stance: What is the tone of the text? What position are they taking?
- 5) Media/Visuals: What means of communication are used?
Understanding and analyzing the rhetorical situation is essential for building a strong essay. Also think about any rhetoric restraints on the text, such as beliefs, attitudes, and traditions that could affect the author's decisions.
Before leaping into your essay, it’s worth taking time to explore the text at a deeper level and considering the rhetorical situations we looked at before. Throw away your assumptions and use these simple questions to help you unpick how and why the text is having an effect on the audience.

1: What is the Rhetorical Situation?
- Why is there a need or opportunity for persuasion?
- How do words and references help you identify the time and location?
- What are the rhetoric restraints?
- What historical occasions would lead to this text being created?
2: Who is the Author?
- How do they position themselves as an expert worth listening to?
- What is their ethos?
- Do they have a reputation that gives them authority?
- What is their intention?
- What values or customs do they have?
3: Who is it Written For?
- Who is the intended audience?
- How is this appealing to this particular audience?
- Who are the possible secondary and tertiary audiences?
4: What is the Central Idea?
- Can you summarize the key point of this rhetoric?
- What arguments are used?
- How has it developed a line of reasoning?
5: How is it Structured?
- What structure is used?
- How is the content arranged within the structure?
6: What Form is Used?
- Does this follow a specific literary genre?
- What type of style and tone is used, and why is this?
- Does the form used complement the content?
- What effect could this form have on the audience?
7: Is the Rhetoric Effective?
- Does the content fulfil the author’s intentions?
- Does the message effectively fit the audience, location, and time period?
Once you’ve fully explored the text, you’ll have a better understanding of the impact it’s having on the audience and feel more confident about writing your essay outline.
A great essay starts with an interesting topic. Choose carefully so you’re personally invested in the subject and familiar with it rather than just following trending topics. There are lots of great ideas on this blog post by My Perfect Words if you need some inspiration. Take some time to do background research to ensure your topic offers good analysis opportunities.

Remember to check the information given to you by your professor so you follow their preferred style guidelines. This outline example gives you a general idea of a format to follow, but there will likely be specific requests about layout and content in your course handbook. It’s always worth asking your institution if you’re unsure.
Make notes for each section of your essay before you write. This makes it easy for you to write a well-structured text that flows naturally to a conclusion. You will develop each note into a paragraph. Look at this example by College Essay for useful ideas about the structure.
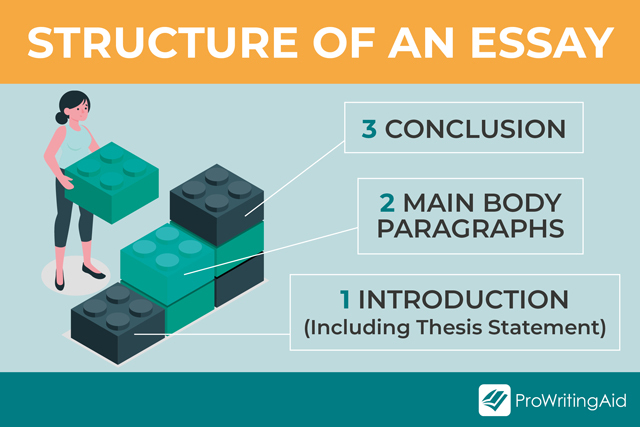
1: Introduction
This is a short, informative section that shows you understand the purpose of the text. It tempts the reader to find out more by mentioning what will come in the main body of your essay.
- Name the author of the text and the title of their work followed by the date in parentheses
- Use a verb to describe what the author does, e.g. “implies,” “asserts,” or “claims”
- Briefly summarize the text in your own words
- Mention the persuasive techniques used by the rhetor and its effect
Create a thesis statement to come at the end of your introduction.
After your introduction, move on to your critical analysis. This is the principal part of your essay.
- Explain the methods used by the author to inform, entertain, and/or persuade the audience using Aristotle's rhetorical triangle
- Use quotations to prove the statements you make
- Explain why the writer used this approach and how successful it is
- Consider how it makes the audience feel and react
Make each strategy a new paragraph rather than cramming them together, and always use proper citations. Check back to your course handbook if you’re unsure which citation style is preferred.
3: Conclusion
Your conclusion should summarize the points you’ve made in the main body of your essay. While you will draw the points together, this is not the place to introduce new information you’ve not previously mentioned.
Use your last sentence to share a powerful concluding statement that talks about the impact the text has on the audience(s) and wider society. How have its strategies helped to shape history?
Before You Submit
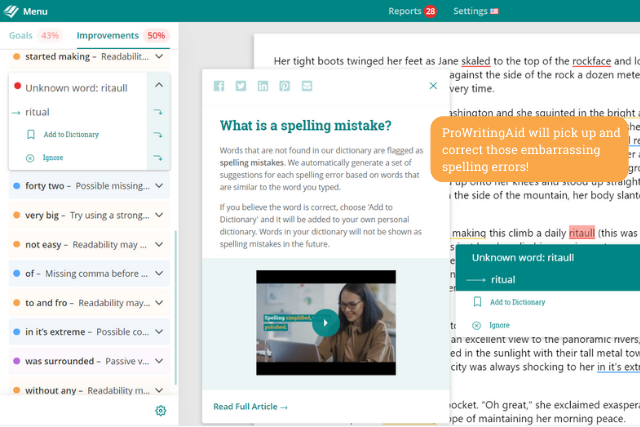
Poor spelling and grammatical errors ruin a great essay. Use ProWritingAid to check through your finished essay before you submit. It will pick up all the minor errors you’ve missed and help you give your essay a final polish. Look at this useful ProWritingAid webinar for further ideas to help you significantly improve your essays. Sign up for a free trial today and start editing your essays!
You’ll find countless examples of rhetorical analysis online, but they range widely in quality. Your institution may have example essays they can share with you to show you exactly what they’re looking for.
The following links should give you a good starting point if you’re looking for ideas:
Pearson Canada has a range of good examples. Look at how embedded quotations are used to prove the points being made. The end questions help you unpick how successful each essay is.
Excelsior College has an excellent sample essay complete with useful comments highlighting the techniques used.
Brighton Online has a selection of interesting essays to look at. In this specific example, consider how wider reading has deepened the exploration of the text.

Writing a rhetorical analysis essay can seem daunting, but spending significant time deeply analyzing the text before you write will make it far more achievable and result in a better-quality essay overall.
It can take some time to write a good essay. Aim to complete it well before the deadline so you don’t feel rushed. Use ProWritingAid’s comprehensive checks to find any errors and make changes to improve readability. Then you’ll be ready to submit your finished essay, knowing it’s as good as you can possibly make it.
Try ProWritingAid's Editor for Yourself
Be confident about grammar
Check every email, essay, or story for grammar mistakes. Fix them before you press send.
Helly Douglas is a UK writer and teacher, specialising in education, children, and parenting. She loves making the complex seem simple through blogs, articles, and curriculum content. You can check out her work at hellydouglas.com or connect on Twitter @hellydouglas. When she’s not writing, you will find her in a classroom, being a mum or battling against the wilderness of her garden—the garden is winning!
Get started with ProWritingAid
Drop us a line or let's stay in touch via :
- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources
How to Write a Rhetorical Analysis Essay–Examples & Template
What is a Rhetorical Analysis Essay?
A rhetorical analysis essay is, as the name suggests, an analysis of someone else’s writing (or speech, or advert, or even cartoon) and how they use not only words but also rhetorical techniques to influence their audience in a certain way. A rhetorical analysis is less interested in what the author is saying and more in how they present it, what effect this has on their readers, whether they achieve their goals, and what approach they use to get there.
Its structure is similar to that of most essays: An Introduction presents your thesis, a Body analyzes the text you have chosen, breaks it down into sections and explains how arguments have been constructed and how each part persuades, informs, or entertains the reader, and a Conclusion section sums up your evaluation.
Note that your personal opinion on the matter is not relevant for your analysis and that you don’t state anywhere in your essay whether you agree or disagree with the stance the author takes.
In the following, we will define the key rhetorical concepts you need to write a good rhetorical analysis and give you some practical tips on where to start.
Key Rhetorical Concepts
Your goal when writing a rhetorical analysis is to think about and then carefully describe how the author has designed their text so that it has the intended effect on their audience. To do that, you need to consider a number of key rhetorical strategies: Rhetorical appeals (“Ethos”, “Logos”, and “Pathos”), context, as well as claims, supports, and warrants.
Ethos, Logos, and Pathos were introduced by Aristotle, way back in the 4th century BC, as the main ways in which language can be used to persuade an audience. They still represent the basis of any rhetorical analysis and are often referred to as the “rhetorical triangle”.
These and other rhetorical techniques can all be combined to create the intended effect, and your job as the one analyzing a text is to break the writer’s arguments down and identify the concepts they are based on.
Rhetorical Appeals
Rhetorical appeal #1: ethos.
Ethos refers to the reputation or authority of the writer regarding the topic of their essay or speech and to how they use this to appeal to their audience. Just like we are more likely to buy a product from a brand or vendor we have confidence in than one we don’t know or have reason to distrust, Ethos-driven texts or speeches rely on the reputation of the author to persuade the reader or listener. When you analyze an essay, you should therefore look at how the writer establishes Ethos through rhetorical devices.
Does the author present themselves as an authority on their subject? If so, how?
Do they highlight how impeccable their own behavior is to make a moral argument?
Do they present themselves as an expert by listing their qualifications or experience to convince the reader of their opinion on something?
Rhetorical appeal #2: Pathos
The purpose of Pathos-driven rhetoric is to appeal to the reader’s emotions. A common example of pathos as a rhetorical means is adverts by charities that try to make you donate money to a “good cause”. To evoke the intended emotions in the reader, an author may use passionate language, tell personal stories, and employ vivid imagery so that the reader can imagine themselves in a certain situation and feel empathy with or anger towards others.
Rhetorical appeal #3: Logos
Logos, the “logical” appeal, uses reason to persuade. Reason and logic, supported by data, evidence, clearly defined methodology, and well-constructed arguments, are what most academic writing is based on. Emotions, those of the researcher/writer as well as those of the reader, should stay out of such academic texts, as should anyone’s reputation, beliefs, or personal opinions.
Text and Context
To analyze a piece of writing, a speech, an advertisement, or even a satirical drawing, you need to look beyond the piece of communication and take the context in which it was created and/or published into account.
Who is the person who wrote the text/drew the cartoon/designed the ad..? What audience are they trying to reach? Where was the piece published and what was happening there around that time?
A political speech, for example, can be powerful even when read decades later, but the historical context surrounding it is an important aspect of the effect it was intended to have.
Claims, Supports, and Warrants
To make any kind of argument, a writer needs to put forward specific claims, support them with data or evidence or even a moral or emotional appeal, and connect the dots logically so that the reader can follow along and agree with the points made.
The connections between statements, so-called “warrants”, follow logical reasoning but are not always clearly stated—the author simply assumes the reader understands the underlying logic, whether they present it “explicitly” or “implicitly”. Implicit warrants are commonly used in advertisements where seemingly happy people use certain products, wear certain clothes, accessories, or perfumes, or live certain lifestyles – with the connotation that, first, the product/perfume/lifestyle is what makes that person happy and, second, the reader wants to be as happy as the person in the ad. Some warrants are never clearly stated, and your job when writing a rhetorical analysis essay is therefore to identify them and bring them to light, to evaluate their validity, their effect on the reader, and the use of such means by the writer/creator.

What are the Five Rhetorical Situations?
A “rhetorical situation” refers to the circumstance behind a text or other piece of communication that arises from a given context. It explains why a rhetorical piece was created, what its purpose is, and how it was constructed to achieve its aims.
Rhetorical situations can be classified into the following five categories:
Asking such questions when you analyze a text will help you identify all the aspects that play a role in the effect it has on its audience, and will allow you to evaluate whether it achieved its aims or where it may have failed to do so.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Outline
Analyzing someone else’s work can seem like a big task, but as with every assignment or writing endeavor, you can break it down into smaller, well-defined steps that give you a practical structure to follow.
To give you an example of how the different parts of your text may look when it’s finished, we will provide you with some excerpts from this rhetorical analysis essay example (which even includes helpful comments) published on the Online Writing Lab website of Excelsior University in Albany, NY. The text that this essay analyzes is this article on why one should or shouldn’t buy an Ipad. If you want more examples so that you can build your own rhetorical analysis template, have a look at this essay on Nabokov’s Lolita and the one provided here about the “Shitty First Drafts” chapter of Anne Lamott’s writing instruction book “Bird by Bird”.
Analyzing the Text
When writing a rhetorical analysis, you don’t choose the concepts or key points you think are relevant or want to address. Rather, you carefully read the text several times asking yourself questions like those listed in the last section on rhetorical situations to identify how the text “works” and how it was written to achieve that effect.
Start with focusing on the author : What do you think was their purpose for writing the text? Do they make one principal claim and then elaborate on that? Or do they discuss different topics?
Then look at what audience they are talking to: Do they want to make a group of people take some action? Vote for someone? Donate money to a good cause? Who are these people? Is the text reaching this specific audience? Why or why not?
What tone is the author using to address their audience? Are they trying to evoke sympathy? Stir up anger? Are they writing from a personal perspective? Are they painting themselves as an authority on the topic? Are they using academic or informal language?
How does the author support their claims ? What kind of evidence are they presenting? Are they providing explicit or implicit warrants? Are these warrants valid or problematic? Is the provided evidence convincing?
Asking yourself such questions will help you identify what rhetorical devices a text uses and how well they are put together to achieve a certain aim. Remember, your own opinion and whether you agree with the author are not the point of a rhetorical analysis essay – your task is simply to take the text apart and evaluate it.
If you are still confused about how to write a rhetorical analysis essay, just follow the steps outlined below to write the different parts of your rhetorical analysis: As every other essay, it consists of an Introduction , a Body (the actual analysis), and a Conclusion .
Rhetorical Analysis Introduction
The Introduction section briefly presents the topic of the essay you are analyzing, the author, their main claims, a short summary of the work by you, and your thesis statement .
Tell the reader what the text you are going to analyze represents (e.g., historically) or why it is relevant (e.g., because it has become some kind of reference for how something is done). Describe what the author claims, asserts, or implies and what techniques they use to make their argument and persuade their audience. Finish off with your thesis statement that prepares the reader for what you are going to present in the next section – do you think that the author’s assumptions/claims/arguments were presented in a logical/appealing/powerful way and reached their audience as intended?
Have a look at an excerpt from the sample essay linked above to see what a rhetorical analysis introduction can look like. See how it introduces the author and article , the context in which it originally appeared , the main claims the author makes , and how this first paragraph ends in a clear thesis statement that the essay will then elaborate on in the following Body section:
Cory Doctorow ’s article on BoingBoing is an older review of the iPad , one of Apple’s most famous products. At the time of this article, however, the iPad was simply the latest Apple product to hit the market and was not yet so popular. Doctorow’s entire career has been entrenched in and around technology. He got his start as a CD-ROM programmer and is now a successful blogger and author. He is currently the co-editor of the BoingBoing blog on which this article was posted. One of his main points in this article comes from Doctorow’s passionate advocacy of free digital media sharing. He argues that the iPad is just another way for established technology companies to control our technological freedom and creativity . In “ Why I Won’t Buy an iPad (and Think You Shouldn’t, Either) ” published on Boing Boing in April of 2010, Cory Doctorow successfully uses his experience with technology, facts about the company Apple, and appeals to consumer needs to convince potential iPad buyers that Apple and its products, specifically the iPad, limit the digital rights of those who use them by controlling and mainstreaming the content that can be used and created on the device .
Doing the Rhetorical Analysis
The main part of your analysis is the Body , where you dissect the text in detail. Explain what methods the author uses to inform, entertain, and/or persuade the audience. Use Aristotle’s rhetorical triangle and the other key concepts we introduced above. Use quotations from the essay to demonstrate what you mean. Work out why the writer used a certain approach and evaluate (and again, demonstrate using the text itself) how successful they were. Evaluate the effect of each rhetorical technique you identify on the audience and judge whether the effect is in line with the author’s intentions.
To make it easy for the reader to follow your thought process, divide this part of your essay into paragraphs that each focus on one strategy or one concept , and make sure they are all necessary and contribute to the development of your argument(s).
One paragraph of this section of your essay could, for example, look like this:
One example of Doctorow’s position is his comparison of Apple’s iStore to Wal-Mart. This is an appeal to the consumer’s logic—or an appeal to logos. Doctorow wants the reader to take his comparison and consider how an all-powerful corporation like the iStore will affect them. An iPad will only allow for apps and programs purchased through the iStore to be run on it; therefore, a customer must not only purchase an iPad but also any programs he or she wishes to use. Customers cannot create their own programs or modify the hardware in any way.
As you can see, the author of this sample essay identifies and then explains to the reader how Doctorow uses the concept of Logos to appeal to his readers – not just by pointing out that he does it but by dissecting how it is done.
Rhetorical Analysis Conclusion
The conclusion section of your analysis should restate your main arguments and emphasize once more whether you think the author achieved their goal. Note that this is not the place to introduce new information—only rely on the points you have discussed in the body of your essay. End with a statement that sums up the impact the text has on its audience and maybe society as a whole:
Overall, Doctorow makes a good argument about why there are potentially many better things to drop a great deal of money on instead of the iPad. He gives some valuable information and facts that consumers should take into consideration before going out to purchase the new device. He clearly uses rhetorical tools to help make his case, and, overall, he is effective as a writer, even if, ultimately, he was ineffective in convincing the world not to buy an iPad .
Frequently Asked Questions about Rhetorical Analysis Essays
What is a rhetorical analysis essay.
A rhetorical analysis dissects a text or another piece of communication to work out and explain how it impacts its audience, how successfully it achieves its aims, and what rhetorical devices it uses to do that.
While argumentative essays usually take a stance on a certain topic and argue for it, a rhetorical analysis identifies how someone else constructs their arguments and supports their claims.

What is the correct rhetorical analysis essay format?
Like most other essays, a rhetorical analysis contains an Introduction that presents the thesis statement, a Body that analyzes the piece of communication, explains how arguments have been constructed, and illustrates how each part persuades, informs, or entertains the reader, and a Conclusion section that summarizes the results of the analysis.
What is the “rhetorical triangle”?
The rhetorical triangle was introduced by Aristotle as the main ways in which language can be used to persuade an audience: Logos appeals to the audience’s reason, Ethos to the writer’s status or authority, and Pathos to the reader’s emotions. Logos, Ethos, and Pathos can all be combined to create the intended effect, and your job as the one analyzing a text is to break the writer’s arguments down and identify what specific concepts each is based on.
Let Wordvice help you write a flawless rhetorical analysis essay!
Whether you have to write a rhetorical analysis essay as an assignment or whether it is part of an application, our professional proofreading services feature professional editors are trained subject experts that make sure your text is in line with the required format, as well as help you improve the flow and expression of your writing. Let them be your second pair of eyes so that after receiving paper editing services or essay editing services from Wordvice, you can submit your manuscript or apply to the school of your dreams with confidence.
And check out our editing services for writers (including blog editing , script editing , and book editing ) to correct your important personal or business-related work.
Reference management. Clean and simple.
How to write a rhetorical analysis

What is a rhetorical analysis?
What are the key concepts of a rhetorical analysis, rhetorical situation, claims, supports, and warrants.
- Step 1: Plan and prepare
- Step 2: Write your introduction
- Step 3: Write the body
- Step 4: Write your conclusion
Frequently Asked Questions about rhetorical analysis
Related articles.
Rhetoric is the art of persuasion and aims to study writers’ or speakers' techniques to inform, persuade, or motivate their audience. Thus, a rhetorical analysis aims to explore the goals and motivations of an author, the techniques they’ve used to reach their audience, and how successful these techniques were.
This will generally involve analyzing a specific text and considering the following aspects to connect the rhetorical situation to the text:
- Does the author successfully support the thesis or claims made in the text? Here, you’ll analyze whether the author holds to their argument consistently throughout the text or whether they wander off-topic at some point.
- Does the author use evidence effectively considering the text’s intended audience? Here, you’ll consider the evidence used by the author to support their claims and whether the evidence resonates with the intended audience.
- What rhetorical strategies the author uses to achieve their goals. Here, you’ll consider the word choices by the author and whether these word choices align with their agenda for the text.
- The tone of the piece. Here, you’ll consider the tone used by the author in writing the piece by looking at specific words and aspects that set the tone.
- Whether the author is objective or trying to convince the audience of a particular viewpoint. When it comes to objectivity, you’ll consider whether the author is objective or holds a particular viewpoint they want to convince the audience of. If they are, you’ll also consider whether their persuasion interferes with how the text is read and understood.
- Does the author correctly identify the intended audience? It’s important to consider whether the author correctly writes the text for the intended audience and what assumptions the author makes about the audience.
- Does the text make sense? Here, you’ll consider whether the author effectively reasons, based on the evidence, to arrive at the text’s conclusion.
- Does the author try to appeal to the audience’s emotions? You’ll need to consider whether the author uses any words, ideas, or techniques to appeal to the audience’s emotions.
- Can the author be believed? Finally, you’ll consider whether the audience will accept the arguments and ideas of the author and why.
Summing up, unlike summaries that focus on what an author said, a rhetorical analysis focuses on how it’s said, and it doesn’t rely on an analysis of whether the author was right or wrong but rather how they made their case to arrive at their conclusions.
Although rhetorical analysis is most used by academics as part of scholarly work, it can be used to analyze any text including speeches, novels, television shows or films, advertisements, or cartoons.
Now that we’ve seen what rhetorical analysis is, let’s consider some of its key concepts .
Any rhetorical analysis starts with the rhetorical situation which identifies the relationships between the different elements of the text. These elements include the audience, author or writer, the author’s purpose, the delivery method or medium, and the content:
- Audience: The audience is simply the readers of a specific piece of text or content or printed material. For speeches or other mediums like film and video, the audience would be the listeners or viewers. Depending on the specific piece of text or the author’s perception, the audience might be real, imagined, or invoked. With a real audience, the author writes to the people actually reading or listening to the content while, for an imaginary audience, the author writes to an audience they imagine would read the content. Similarly, for an invoked audience, the author writes explicitly to a specific audience.
- Author or writer: The author or writer, also commonly referred to as the rhetor in the context of rhetorical analysis, is the person or the group of persons who authored the text or content.
- The author’s purpose: The author’s purpose is the author’s reason for communicating to the audience. In other words, the author’s purpose encompasses what the author expects or intends to achieve with the text or content.
- Alphabetic text includes essays, editorials, articles, speeches, and other written pieces.
- Imaging includes website and magazine advertisements, TV commercials, and the like.
- Audio includes speeches, website advertisements, radio or tv commercials, or podcasts.
- Context: The context of the text or content considers the time, place, and circumstances surrounding the delivery of the text to its audience. With respect to context, it might often also be helpful to analyze the text in a different context to determine its impact on a different audience and in different circumstances.
An author will use claims, supports, and warrants to build the case around their argument, irrespective of whether the argument is logical and clearly defined or needs to be inferred by the audience:
- Claim: The claim is the main idea or opinion of an argument that the author must prove to the intended audience. In other words, the claim is the fact or facts the author wants to convince the audience of. Claims are usually explicitly stated but can, depending on the specific piece of content or text, be implied from the content. Although these claims could be anything and an argument may be based on a single or several claims, the key is that these claims should be debatable.
- Support: The supports are used by the author to back up the claims they make in their argument. These supports can include anything from fact-based, objective evidence to subjective emotional appeals and personal experiences used by the author to convince the audience of a specific claim. Either way, the stronger and more reliable the supports, the more likely the audience will be to accept the claim.
- Warrant: The warrants are the logic and assumptions that connect the supports to the claims. In other words, they’re the assumptions that make the initial claim possible. The warrant is often unstated, and the author assumes that the audience will be able to understand the connection between the claims and supports. In turn, this is based on the author’s assumption that they share a set of values and beliefs with the audience that will make them understand the connection mentioned above. Conversely, if the audience doesn’t share these beliefs and values with the author, the argument will not be that effective.
Appeals are used by authors to convince their audience and, as such, are an integral part of the rhetoric and are often referred to as the rhetorical triangle. As a result, an author may combine all three appeals to convince their audience:
- Ethos: Ethos represents the authority or credibility of the author. To be successful, the author needs to convince the audience of their authority or credibility through the language and delivery techniques they use. This will, for example, be the case where an author writing on a technical subject positions themselves as an expert or authority by referring to their qualifications or experience.
- Logos: Logos refers to the reasoned argument the author uses to persuade their audience. In other words, it refers to the reasons or evidence the author proffers in substantiation of their claims and can include facts, statistics, and other forms of evidence. For this reason, logos is also the dominant approach in academic writing where authors present and build up arguments using reasoning and evidence.
- Pathos: Through pathos, also referred to as the pathetic appeal, the author attempts to evoke the audience’s emotions through the use of, for instance, passionate language, vivid imagery, anger, sympathy, or any other emotional response.
To write a rhetorical analysis, you need to follow the steps below:
With a rhetorical analysis, you don’t choose concepts in advance and apply them to a specific text or piece of content. Rather, you’ll have to analyze the text to identify the separate components and plan and prepare your analysis accordingly.
Here, it might be helpful to use the SOAPSTone technique to identify the components of the work. SOAPSTone is a common acronym in analysis and represents the:
- Speaker . Here, you’ll identify the author or the narrator delivering the content to the audience.
- Occasion . With the occasion, you’ll identify when and where the story takes place and what the surrounding context is.
- Audience . Here, you’ll identify who the audience or intended audience is.
- Purpose . With the purpose, you’ll need to identify the reason behind the text or what the author wants to achieve with their writing.
- Subject . You’ll also need to identify the subject matter or topic of the text.
- Tone . The tone identifies the author’s feelings towards the subject matter or topic.
Apart from gathering the information and analyzing the components mentioned above, you’ll also need to examine the appeals the author uses in writing the text and attempting to persuade the audience of their argument. Moreover, you’ll need to identify elements like word choice, word order, repetition, analogies, and imagery the writer uses to get a reaction from the audience.
Once you’ve gathered the information and examined the appeals and strategies used by the author as mentioned above, you’ll need to answer some questions relating to the information you’ve collected from the text. The answers to these questions will help you determine the reasons for the choices the author made and how well these choices support the overall argument.
Here, some of the questions you’ll ask include:
- What was the author’s intention?
- Who was the intended audience?
- What is the author’s argument?
- What strategies does the author use to build their argument and why do they use those strategies?
- What appeals the author uses to convince and persuade the audience?
- What effect the text has on the audience?
Keep in mind that these are just some of the questions you’ll ask, and depending on the specific text, there might be others.
Once you’ve done your preparation, you can start writing the rhetorical analysis. It will start off with an introduction which is a clear and concise paragraph that shows you understand the purpose of the text and gives more information about the author and the relevance of the text.
The introduction also summarizes the text and the main ideas you’ll discuss in your analysis. Most importantly, however, is your thesis statement . This statement should be one sentence at the end of the introduction that summarizes your argument and tempts your audience to read on and find out more about it.
After your introduction, you can proceed with the body of your analysis. Here, you’ll write at least three paragraphs that explain the strategies and techniques used by the author to convince and persuade the audience, the reasons why the writer used this approach, and why it’s either successful or unsuccessful.
You can structure the body of your analysis in several ways. For example, you can deal with every strategy the author uses in a new paragraph, but you can also structure the body around the specific appeals the author used or chronologically.
No matter how you structure the body and your paragraphs, it’s important to remember that you support each one of your arguments with facts, data, examples, or quotes and that, at the end of every paragraph, you tie the topic back to your original thesis.
Finally, you’ll write the conclusion of your rhetorical analysis. Here, you’ll repeat your thesis statement and summarize the points you’ve made in the body of your analysis. Ultimately, the goal of the conclusion is to pull the points of your analysis together so you should be careful to not raise any new issues in your conclusion.
After you’ve finished your conclusion, you’ll end your analysis with a powerful concluding statement of why your argument matters and an invitation to conduct more research if needed.
A rhetorical analysis aims to explore the goals and motivations of an author, the techniques they’ve used to reach their audience, and how successful these techniques were. Although rhetorical analysis is most used by academics as part of scholarly work, it can be used to analyze any text including speeches, novels, television shows or films, advertisements, or cartoons.
The steps to write a rhetorical analysis include:
Your rhetorical analysis introduction is a clear and concise paragraph that shows you understand the purpose of the text and gives more information about the author and the relevance of the text. The introduction also summarizes the text and the main ideas you’ll discuss in your analysis.
Ethos represents the authority or credibility of the author. To be successful, the author needs to convince the audience of their authority or credibility through the language and delivery techniques they use. This will, for example, be the case where an author writing on a technical subject positions themselves as an expert or authority by referring to their qualifications or experience.
Appeals are used by authors to convince their audience and, as such, are an integral part of the rhetoric and are often referred to as the rhetorical triangle. The 3 types of appeals are ethos, logos, and pathos.


- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

5.5: Rhetorical Appeals- Logos, Pathos, and Ethos Defined
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 219009

- Terri Pantuso, Emilie Zickel, & Melanie Gagich
- Texas A&M Univesrity
Rhetoric, as the previous sections have discussed, is the way that authors use and manipulate language in order to persuade an audience. Once we understand the rhetorical situation out of which a text is created (why it was written, for whom it was written, by whom it was written, how the medium in which it was written creates certain constraints, or perhaps freedom of expression), we can look at how all of those contextual elements shape the author’s creation of the text.
We can look first at the classical rhetorical appeals which are the three ways to classify an author’s intellectual, moral, and emotional approaches to getting the audience to react in the manner in which the author may have intended.
Rhetorical Appeals
In composition studies, the term rhetorical appeals refers to the use of ethos, pathos, and logos. These are classical Greek terms dating back to Aristotle who is traditionally viewed as the creator of rhetoric. To be rhetorically effective (and thus persuasive), an author must engage the audience in a variety of compelling ways which involves carefully choosing how to craft their argument so that the intended outcome is achieved. Often that outcome occurs when the audience agrees with the argument or point being presented. Aristotle defined these modes of engagement and gave them the terms that we still use today: logos, pathos, and ethos.
Logos: Appeal to Logic
Logic. Reason. Rationality. Logos is brainy and intellectual, cool, calm, collected, objective.
When an author relies on logos, it means that they are using logic, careful structure, and objective evidence to appeal to the audience. Objective evidence is anything that can be proven with statistics or other facts via more than one source. Oftentimes that evidence has been validated by more than one authority in the field of study.
For example, if Dr. Smith was trying to convince her students to complete their homework, she might explain that she understands everyone is busy and they have other classes (non-biased), but that completing their homework will help them get a better grade on their test (explanation). She could add to this explanation by providing statistics showing the number of students who failed and didn’t complete their homework versus the number of students who passed and did complete their homework (factual evidence). This is an example of logos employed for the purposes of argument and persuasion.
Logical appeals rest on rational modes of thinking , such as:
- Comparison: a comparison between one thing (with regard to your topic) and another, similar thing to help support your claim. It is important that the comparison is fair and valid – the things being compared must share significant traits of similarity.
- Cause/effect thinking: you argue that X has caused Y, or that X is likely to cause Y to help support your claim. Be careful with the latter – it can be difficult to predict that something “will” happen in the future.
- Deductive reasoning: starting with a broad, general claim/example and using it to support a more specific point or claim (picture an hourglass where the sands gather in the middle)
- Inductive reasoning: using several specific examples or cases to make a broad generalization (consider the old question of “if your friend jumped off of a bridge, would you” to make the sweeping claim that all young people are easily persuaded to follow the crowd)
- Analogical reasoning: moves from one particular claim/example to another, seemingly sequential (sometimes this line of reasoning is used to make a guilt by association claim)
- Exemplification: use of many examples or a variety of evidence to support a single point
- Elaboration: moving beyond just including a fact, but explaining the significance or relevance of that fact
- Coherent thought: maintaining a well-organized line of reasoning; not repeating ideas or jumping around
Pathos: Appeal to Emotions
When an author relies on pathos, it means that they are trying to tap into the audience’s emotions to get them to agree with the author’s claim. An author using pathos appeals wants the audience to feel something: anger, pride, joy, rage, or happiness. For example, many of us have seen the ASPCA commercials that use photographs of injured puppies, or sad-looking kittens, and slow, depressing music to emotionally persuade their audience to donate money. This is a classic example of the use of pathos in argument.
Pathos-based rhetorical strategies are any strategies that get the audience to “open up” to the topic, the argument, or to the author through an emotional connection. Emotions can make us vulnerable and an author can use this vulnerability to get the audience to believe that their argument is a compelling one.
Pathos appeals might include:
- Expressive descriptions of people, places, or events that help the reader to feel or experience those events
- Vivid imagery of people, places or events that help the reader to feel like they are seeing those events
- Sharing personal stories that make the reader feel a connection to, or empathy for, the person being described
- Using emotion-laden vocabulary as a way to put the reader into that specific emotional mindset (what is the author trying to make the audience feel? and how are they doing that?)
- Using any information that will evoke an emotional response from the audience. This could involve making the audience feel empathy or disgust for the person/group/event being discussed, or perhaps connection to or rejection of the person/group/event being discussed.
When reading a text, try to locate where the author is trying to convince the reader by strictly using emotions because, if used to excess, pathos appeals can indicate a lack of substance or emotional manipulation of the audience. If the only way in which an author can persuade the reader is by making him/her sad or angry, does that make for a solid, valid argument?
Ethos: Appeal to Values/Trust
Appeals using ethos are typically two faceted focusing on audience values and authorial credibility/character.
On the one hand, when an author makes an ethical appeal, they are attempting to tap into the values or ideologies that the audience holds. Examples include patriotism, tradition, justice, equality, dignity for all humankind, self-preservation, or other specific social, religious or philosophical values (Christian values, socialism, capitalism, feminism, etc.). These values can sometimes feel very close to emotions, but they are felt on a social level rather than only on a personal level. When an author evokes the values that the audience cares about as a way to justify or support their argument, we classify that as ethos. The audience will feel that the author is making an argument that is “right” (in the sense of moral “right”-ness, i.e., My argument rests upon the values that matter to you. Therefore, you should accept my argument ). This first part of the definition of ethos, then, is focused on the audience’s values.
On the other hand, this sense of referencing what is “right” in an ethical appeal connects to the other sense of ethos, the author. Ethos that is centered on the author revolves around two concepts: the credibility of the author and their character.
Credibility of the speaker/author is determined by their knowledge and expertise in the subject at hand. For example, if you are learning about Einstein’s Theory of Relativity, would you rather learn from a professor of physics or a cousin who took two science classes in high school thirty years ago? It is fair to say that, in general, the professor of physics would have more credibility to discuss the topic of physics than your cousin. To establish their credibility, an author may draw attention to who they are or what kinds of experience they have with the topic being discussed as an ethical appeal (i.e., Because I have experience with this topic – and I know my stuff! – you should trust what I am saying about this topic ). Some authors do not have to establish their credibility because the audience already knows who they are and that they are credible.
Character is another aspect of ethos that is different from credibility because it involves personal history and sometimes personality traits. A person can be credible but lack character or vice versa. For example, in politics, sometimes the most experienced candidates – those who might be the most credible candidates – fail to win elections because voters do not accept their character. Politicians take pains to shape their character as leaders who have the interests of the voters at heart. The candidate who successfully proves to the voters (the audience) that they have the type of character that they can trust is more likely to win.
Thus, ethos comes down to trust. How can the author get the audience to trust him or her so that they will accept their argument? How can the author make himself or herself appear as a credible speaker who embodies the character traits that the audience values?
In building ethical appeals, we may see authors:
- Referring either directly or indirectly to the values that matter to the intended audience (so that the audience will trust the speaker)
- Using language, phrasing, imagery, or other writing styles common to people who hold those values, thereby “talking the talk” of people with those values (again, so that the audience is inclined to trust the speaker)
- Referring to their experience and/or authority with the topic (and therefore demonstrating their credibility)
- Referring to their own character, or making an effort to build their character in the text
When reading, you should always think about the author’s credibility regarding the subject as well as their character. Here is an example of a rhetorical move that connects with ethos: when reading an article about abortion, the author mentions that she has had an abortion. That is an example of an ethical move because the author is creating credibility via anecdotal evidence and first person narrative. In a rhetorical analysis project, it would be up to you, the analyzer, to point out this move and associate it with a rhetorical strategy.
When Writers Misuse Logos, Pathos, or Ethos, Arguments can be Weakened
Above, we defined and described what logos, pathos, and ethos are and why authors may use those strategies. Sometimes, using a combination of appeals leads to a sound, balanced, and persuasive argument. It is important to understand, though, that using rhetorical appeals does not always lead to a sound, balanced argument. In fact, any of the appeals could be misused or overused. When that happens, arguments can be weakened.
Using a social media platform, find a topic that is trending for today and create an argument using ethos, pathos, and logos for that topic.
Practice Activity
The original version of this chapter contained H5P content. You may want to remove or replace this element.
This section contains material from:
Gagich, Melanie and Emilie Zickel. “Rhetorical Appeals: Logos, Pathos, and Ethos Defined.” In A Guide to Rhetoric, Genre, and Success in First-Year Writing , by Melanie Gagich and Emilie Zickel. Cleveland: MSL Academic Endeavors. Accessed July 2019. https://pressbooks.ulib.csuohio.edu/csu-fyw-rhetoric/chapter/rhetorical-strategies-building-compelling-arguments/ Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License .

Chapter 6: Thinking and Analyzing Rhetorically
6.4 Rhetorical Appeals: Logos, Pathos, and Ethos Defined
Melanie Gagich & Emilie Zickel
Rhetoric, as the previous chapters have discussed, is the way that authors use and manipulate language in order to persuade an audience. Once we understand the rhetorical situation out of which a text is created (why it was written, for whom it was written, by whom it was written, how the medium in which it was written creates certain constraints, or perhaps freedoms of expression), we can look at how all of those contextual elements shape the author’s creation of the text.
We can look first at the classical rhetorical appeals, which are the three ways to classify authors’ intellectual, moral, and emotional approaches to getting the audience to have the reaction that the author hopes for.
Rhetorical Appeals
Rhetorical appeals refer to ethos, pathos, and logos. These are classical Greek terms, dating back to Aristotle, who is traditionally seen as the father of rhetoric. To be rhetorically effective (and thus persuasive), an author must engage the audience in a variety of compelling ways, which involves carefully choosing how to craft his or her argument so that the outcome, audience agreement with the argument or point, is achieved. Aristotle defined these modes of engagement and gave them the terms that we still use today: logos, pathos, and ethos.
Logos: Appeal to Logic
Logic. Reason. Rationality. Logos is brainy and intellectual, cool, calm, collected, objective.
When an author relies on logos, it means that he or she is using logic, careful structure, and objective evidence to appeal to the audience. An author can appeal to an audience’s intellect by using information that can be fact checked (using multiple sources) and thorough explanations to support key points. Additionally, providing a solid and non-biased explanation of one’s argument is a great way for an author to invoke logos.
For example, if I were trying to convince my students to complete their homework, I might explain that I understand everyone is busy and they have other classes (non-biased), but the homework will help them get a better grade on their test (explanation). I could add to this explanation by providing statistics showing the number of students who failed and didn’t complete their homework versus the number of students who passed and did complete their homework (factual evidence).
Logical appeals rest on rational modes of thinking , such as
- Comparison – a comparison between one thing (with regard to your topic) and another, similar thing to help support your claim. It is important that the comparison is fair and valid – the things being compared must share significant traits of similarity.
- Cause/effect thinking – you argue that X has caused Y, or that X is likely to cause Y to help support your claim. Be careful with the latter – it can be difficult to predict that something “will” happen in the future.
- Deductive reasoning – starting with a broad, general claim/example and using it to support a more specific point or claim
- Inductive reasoning – using several specific examples or cases to make a broad generalization
- Exemplification – use of many examples or a variety of evidence to support a single point
- Elaboration – moving beyond just including a fact, but explaining the significance or relevance of that fact
- Coherent thought – maintaining a well organized line of reasoning; not repeating ideas or jumping around
Pathos: Appeal to Emotions
When an author relies on pathos, it means that he or she is trying to tap into the audience’s emotions to get them to agree with the author’s claim. An author using pathetic appeals wants the audience to feel something: anger, pride, joy, rage, or happiness. For example, many of us have seen the ASPCA commercials that use photographs of injured puppies, or sad-looking kittens, and slow, depressing music to emotionally persuade their audience to donate money.
Pathos-based rhetorical strategies are any strategies that get the audience to “open up” to the topic, the argument, or to the author. Emotions can make us vulnerable, and an author can use this vulnerability to get the audience to believe that his or her argument is a compelling one.
Pathetic appeals might include
- Expressive descriptions of people, places, or events that help the reader to feel or experience those events
- Vivid imagery of people, places or events that help the reader to feel like he or she is seeing those events
- Sharing personal stories that make the reader feel a connection to, or empathy for, the person being described
- Using emotion-laden vocabulary as a way to put the reader into that specific emotional mindset (what is the author trying to make the audience feel? and how is he or she doing that?)
- Using any information that will evoke an emotional response from the audience . This could involve making the audience feel empathy or disgust for the person/group/event being discussed, or perhaps connection to or rejection of the person/group/event being discussed.
When reading a text, try to locate when the author is trying to convince the reader using emotions because, if used to excess, pathetic appeals can indicate a lack of substance or emotional manipulation of the audience. See the links below about fallacious pathos for more information.
Ethos: Appeal to Values/Trust
Ethical appeals have two facets: audience values and authorial credibility/character.
On the one hand, when an author makes an ethical appeal, he or she is attempting to tap into the values or ideologies that the audience holds , for example, patriotism, tradition, justice, equality, dignity for all humankind, self preservation, or other specific social, religious or philosophical values (Christian values, socialism, capitalism, feminism, etc.). These values can sometimes feel very close to emotions, but they are felt on a social level rather than only on a personal level. When an author evokes the values that the audience cares about as a way to justify or support his or her argument, we classify that as ethos. The audience will feel that the author is making an argument that is “right” (in the sense of moral “right”-ness, i.e., “My argument rests upon that values that matter to you. Therefore, you should accept my argument”). This first part of the definition of ethos, then, is focused on the audience’s values.
On the other hand, this sense of referencing what is “right” in an ethical appeal connects to the other sense of ethos: the author. Ethos that is centered on the author revolves around two concepts: the credibility of the author and his or her character.
Credibility of the speaker/author is determined by his or her knowledge and expertise in the subject at hand. For example, if you are learning about Einstein’s Theory of Relativity, would you rather learn from a professor of physics or a cousin who took two science classes in high school thirty years ago? It is fair to say that, in general, the professor of physics would have more credibility to discuss the topic of physics. To establish his or her credibility, a n author may draw attention to who he or she is or what kinds of experience he or she has with the topic being discussed as an ethical appeal (i.e., “Because I have experience with this topic – and I know my stuff! – you should trust what I am saying about this topic”). Some authors do not have to establish their credibility because the audience already knows who they are and that they are credible.
Character is another aspect of ethos, and it is different from credibility because it involves personal history and even personality traits. A person can be credible but lack character or vice versa. For example, in politics, sometimes the most experienced candidates – those who might be the most credible candidates – fail to win elections because voters do not accept their character. Politicians take pains to shape their character as leaders who have the interests of the voters at heart. The candidate who successfully proves to the voters (the audience) that he or she has the type of character that they can trust is more likely to win.
Thus, ethos comes down to trust. How can the author get the audience to trust him or her so that they will accept his or her argument? How can the the author make him or herself appear as a credible speaker who embodies the character traits that the audience values?
In building ethical appeals, we see authors
- Referring either directly or indirectly to the values that matter to the intended audience (so that the audience will trust the speaker)
- Using language, phrasing, imagery, or other writing styles common to people who hold those values, thereby “talking the talk” of people with those values (again, so that the audience is inclined to trust the speaker)
- Referring to their experience and/or authority with the topic (and therefore demonstrating their credibility)
- Referring to their own character, or making an effort to build their character in the text
When reading, you should always think about the author’s credibility regarding the subject as well as his or her character. Here is an example of a rhetorical move that connects with ethos: when reading an article about abortion, the author mentions that she has had an abortion. That is an example of an ethical move because the author is creating credibility via anecdotal evidence and first person narrative. In a rhetorical analysis project, it would be up to you, the analyzer, to point out this move and associate it with a rhetorical strategy.
When writers misuse Logos, Pathos, or Ethos, arguments can be weakened
Above, we defined and described what logos, pathos, and ethos are and why authors may use those strategies. Sometimes, using a combination of logical, pathetic, and ethical appeals leads to a sound, balanced, and persuasive argument. It is important to understand, though, that using rhetorical appeals does not always lead to a sound, balanced argument.
In fact, any of the appeals could be misused or overused. When that happens, arguments can be weakened.
To see what a misuse of logical appeals might consist of, see the next chapter, Logical Fallacies.
To see how authors can overuse emotional appeals and turn-off their target audience, visit the following link from WritingCommons.org : Fallacious Pathos .
To see how ethos can be misused or used in a manner that may be misleading, visit the following link to WritingCommons.org : Fallacious Ethos
A Guide to Rhetoric, Genre, and Success in First-Year Writing by Melanie Gagich & Emilie Zickel is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Feedback/Errata
Comments are closed.

Part 4: Rhetorical Modes
16 Rhetorical Analysis
What is a rhetorical analysis.
A Rhetorical analysis begins with the examination of the content and the style of the author. A rhetorical analysis is an examination of the topic, purpose, audience, and context of a piece of text. A text can be written, spoken, or conveyed in some other manner.
Sometimes, the best way to learn how to write a good argument is to start by analyzing other arguments. When you do this, you get to see what works, what doesn’t, what strategies another author uses, what structures seem to work well and why, and more.
In the paragraphs that follow, you will learn about analyzing arguments for both content and rhetorical strategies. The content analysis may come a little easier for you, but the rhetorical analysis is extremely important. To become a good writer, we must develop the language of writing and learn how to use that language to talk about the “moves” other writers make.
When we understand the decisions other writers make and why, it helps us make more informed decisions as writers. We can move from being the “accidental” writer, where we might do well but are not sure why, to being a “purposeful” writer, where we have an awareness of the impact our writing has on our audience at all levels.
The ultimate goal of a rhetorical analysis is twofold:
- to analyze how well the rhetorical elements work together to create a fitting response, and
- to evaluate the overall effectiveness of that response.
To examine that goal, there are a couple of approaches that can be made in writing an analysis. The first is to ask some basic questions.
- How has the place affected the writing?
- How have the rhetorical elements (rhetorical appeals) affected the writing?
- Do the means of delivery, genre, or medium impact the audience?
As you begin, search your answers for an idea that can serve as your claim or thesis. For example, you might focus on the declared goal—if there is one—of the creator of the text and whether it has been achieved.
You might evaluate how successfully that creator has identified the rhetorical audience, shaped a fitting response, or employed the best available means.
Or you might focus on the use of the rhetorical appeals and the overall success of their use.
Whether or not you agree with the text is beside the point. Your job is to analyze how and how well the text’s creator has accomplished the purpose of that text.
- HOW is the analysis of the parts
- HOW WELL is the overall evaluation
Thinking Rhetorically

To add to this trickiness, you can write a rhetorical analysis of any piece of information, not just an essay. You may be asked to write a rhetorical analysis of an ad, an image, or a commercial.
The key is to start now! Rhetorical analysis is going to help you think about strategies other authors have made and how or why these strategies work or don’t work. In turn, your goal is to be more aware of these things in your own writing.
When you analyze a work rhetorically, you are going to explore the following concepts in a piece:
- Style or Voice
You will be thinking about the decisions an author has made along these lines and thinking about whether these decisions are effective or ineffective.
Types of Argument
Just as there many types of essays you will write in college and many types of writing in general, argumentative essays come in many forms as well. There are three basic structures or types of an argument you are likely to encounter in college: the Toulmin argument, the Rogerian argument, and the Classical or Aristotelian argument. Although the Toulmin method was originally developed to analyze arguments, some professors will ask you to model its components. Each of these serves a different purpose, and deciding which type to use depends upon the rhetorical situation: In other words, you have to think about what is going to work best for your audience given your topic and the situation in which you are writing.
Toulmin Argument

The Toulmin method, developed by philosopher Stephen Toulmin , is essentially a structure for analyzing arguments. But the elements for analysis are so clear and structured that many professors now have students write argumentative essays with the elements of the Toulmin method in mind.
This type of argument works well when there are no clear truths or absolute solutions to a problem. Toulmin arguments take into account the complex nature of most situations.
There are six elements for analyzing, and, in this case, presenting arguments that are important to the Toulmin method.
These elements of a Toulmin analysis can help you as both a reader and a writer. When you’re analyzing arguments as a reader, you can look for these elements to help you understand the argument and evaluate its validity. When you’re writing an argument, you can include these same elements to ensure your audience will see the validity in your claims.

The claim is a statement of opinion that the author is asking her or his audience to accept as true.
There should be more laws to regulate texting while driving in order to cut down on dangerous car accidents.
The grounds are the facts, data, or reasoning upon which the claim is based. Essentially, the grounds are the facts making the case for the claim.
The National Safety Council estimates that 1.6 million car accidents per year are caused by cell phone use and texting.
The warrant is what links the grounds to the claim. This is what makes the audience understand how the grounds are connected to supporting the claim. Sometimes, the warrant is implicit (not directly stated), but the warrant can be stated directly as well. As a writer, you are making assumptions about what your audience already believes, so you have to think about how clear your warrant is and if you need to state it directly for your audience. You must also think about whether or not a warrant is actually an unproven claim.
The backing gives additional support for the claim by addressing different questions related to your claim.
The qualifier is essentially the limits to the claim or an understanding that the claim is not true in all situations. Qualifiers add strength to claims because they help the audience understand the author does not expect her or his opinion to be true all of the time or for her or his ideas to work all of the time. If writers use qualifiers that are too broad, such as “always” or “never,” their claims can be really difficult to support. Qualifiers like “some” or “many” help limit the claim, which can add strength to the claim.
The rebuttal is when the author addresses the opposing views. The author can use a rebuttal to pre-empt counter-arguments, making the original argument stronger.

Aristotelian Argument

The Aristotelian or classical argument is a style of argument developed by the famous Greek philosopher and rhetorician, Aristotle . In this style of argument, your goal as a writer is to convince your audience of something. The goal is to use a series of strategies to persuade your audience to adopt your side of the issue. Although ethos , pathos , and logos play a role in any argument, this style of argument utilizes them in the most persuasive ways possible.
Of course, your professor may require some variations, but here is the basic format for an Aristotelian, or classical, argumentative essay:
- Introduce your issue. At the end of your introduction, most professors will ask you to present your thesis. The idea is to present your readers with your main point and then dig into it.
- Present your case by explaining the issue in detail and why something must be done or a way of thinking is not working. This will take place over several paragraphs.
- Address the opposition. Use a few paragraphs to explain the other side. Refute the opposition one point at a time.
- Provide your proof. After you address the other side, you’ll want to provide clear evidence that your side is the best side.
- Present your conclusion. In your conclusion, you should remind your readers of your main point or thesis and summarize the key points of your argument. If you are arguing for some kind of change, this is a good place to give your audience a call to action. Tell them what they could do to make a change.
For a visual representation of this type of argument, check out the Aristotelian infographic below.

Rogerian Argument

When most of us think of arguments, we think about winners of arguments and losers of arguments. Arguments, even sometimes academic arguments, can be strong and forceful. An Aristotelian or classical argument is a strong, “this is my assertion and here’s why I am right” kind of argument. But that kind of argument isn’t going to work in all situations. When your audience is a really difficult one in the sense that you know your audience isn’t going to completely agree with your side of the issue, it can be a good idea to try to find a middle ground. The Rogerian argument finds that middle ground.
Based on the work of psychologist Carl Rogers (pictured on the right), a Rogerian argument focuses on finding a middle ground between the author and the audience. This type of argument can be extremely persuasive and can help you, as a writer, understand your own biases and how you might work to find common ground with others.
Here is a summary of the basic strategy for a Rogerian argument, and the infographic on the following page should be helpful as well.
- In your essay, first, introduce the problem .
- Acknowledge the other side before you present your side of the issue. This may take several paragraphs.
- Next, you should carefully present your side of the issue in a way that does not dismiss the other side. This may also take several paragraphs.
- You should then work to bring the two sides together . Help your audience see the benefits of the middle ground. Make your proposal for the middle ground here, and be sure to use an even, respectful tone. This should be a key focus of your essay and may take several paragraphs.
- Finally, in your conclusion, remind your audience of the balanced perspective you have presented and make it clear how both sides benefit when they meet in the middle.
For a visual representation of this type of argument, check out the Rogerian infographic below.

Types of Argument Activity
This interaction will give you a chance to practice what you have learned about the different types of argument and when it might be most appropriate to use one type over another. Read the scenarios and, then, choose a rhetorical style. You will be told if you are correct or not, and which type of argument would work best in that scenario, and why.
After completing this activity, you may download or print a completion report that summarizes your results.
Analyze This
You have learned about some of the most common organizational structures for academic arguments and learned about the benefits of each one—as well as when it might be best to use each one.
Before you begin working with your own academic argument structure, it might be helpful to review another academic argument for its organizational structure.
In the following video, watch as one student analyzes a traditional academic argumentative essay ( Cheap Thrills: The Price of Fast Fashion ), one that most closely follows the Aristotelian structure.
See It in Practice
Although there are many options for organizing your argument, understanding these three basic argumentative types can help you make a good decision about which type of argument would work best given your topic and audience.
Watch as our student writer makes notes and comes to a decision about which type of argument she’ll use as she works with a controversial topic and a potentially difficult audience.
Thinking About Content

The Toulmin method described in this learning area is a great tool for analyzing the content of an argument. In fact, it was developed as a tool for analyzing the content of an argument. Using the different concepts we learn in the Toulmin model, we are able to examine an argument by thinking about what claim is being made, what evidence is being used to support that claim, the warrants behind that evidence, and more.
When you analyze an argument, there is a good chance your professor will have you review and use the Toulmin information provided in the Excelsior OWL.
However, the lessons you have learned about logical fallacies will also help you analyze the content of an argument. You’ll want to look closely at the logic being presented in the claims and evidence. Does the logic hold up, or do you see logical fallacies? Obviously, if you see fallacies, you should really question the argument.
Basic Questions for a Rhetorical Analysis
What is the rhetorical situation?
- What occasion gives rise to the need or opportunity for persuasion?
- What is the historical occasion that would give rise to the composition of this text?
Who is the author/speaker?
- How does he or she establish ethos (personal credibility)?
- Does he/she come across as knowledgeable? fair?
- Does the speaker’s reputation convey a certain authority?
What is his/her intention in speaking?
- To attack or defend?
- To exhort or dissuade from certain action?
- To praise or blame?
- To teach, to delight, or to persuade?
Who makes up the audience?
- Who is the intended audience?
- What values does the audience hold that the author or speaker appeals to?
- Who have been or might be secondary audiences?
- If this is a work of fiction, what is the nature of the audience within the fiction?
What is the content of the message?
- Can you summarize the main idea?
- What are the principal lines of reasoning or kinds of arguments used?
- What topics of invention are employed?
- How does the author or speaker appeal to reason? to emotion?
What is the form in which it is conveyed?
- What is the structure of the communication; how is it arranged?
- What oral or literary genre is it following?
- What figures of speech (schemes and tropes) are used?
- What kind of style and tone is used and for what purpose?
How do form and content correspond?
- Does the form complement the content?
- What effect could the form have, and does this aid or hinder the author’s intention?
Does the message/speech/text succeed in fulfilling the author’s or speaker’s intentions?
- Does the author/speaker effectively fit his/her message to the circumstances, times, and audience?
- Can you identify the responses of historical or contemporary audiences?
What does the nature of the communication reveal about the culture that produced it?
- What kinds of values or customs would the people have that would produce this?
- How do the allusions, historical references, or kinds of words used place this in a certain time and location?
Sample Rhetorical Analysis
Seeing rhetorical analysis in action is one of the best ways to understand it. Read the sample rhetorical analysis of an article . If you like, you can read the original article the student analyzes: Why I won’t buy an iPad (and think you shouldn’t, either) .
Time to Write
Purpose: This assignment will demonstrate the understanding of Rhetorical Analysis and Preliminary Research. This assignment will connect to the course competencies of writing for specific rhetorical contexts, using appropriate conventions in writing, an
This assignment frames the topic, purpose, audience, and context for the approved research topic from Research Prospectus 1.
At this time you will utilize two or three sources as in-text citations and on the References.
Choose a single source (selection) for rhetorical analysis that meets the following criteria.
- Is the text responding to an opportunity to make a change? (Does it look at solving a problem?)
- What is the rhetorical opportunity for change?
- How is it identified?
- How is it connected to your research proposal topic?
After you have selected a text, read it carefully, keeping in mind that the ultimate goal of a rhetorical analysis is twofold: (1) to analyze how well the rhetorical elements work together to create a fitting response, and (2) to assess the overall effectiveness of that response. Then, write answers to the following questions, citing material from the text itself to support each answer:
Are the available means anchored to the writer’s place?
- Who created the text? What credentials or expertise does that person or group have? Why is the creator of the text engaged with this opportunity? Is this an opportunity that can be modified through language? What opinions or biases did the person or group bring to the text?
- What is the place (physical, social, academic, economic, and so on) from which the creator of the text forms and sends the response? What are the resources of that place? What are its constraints (or limitations)?
- Who is the audience for the message? What relationship is the creator of the text trying to establish with the audience? What opinions or biases might the audience hold? How might the audience feel about this rhetorical opportunity? And, most important, can this audience modify or help bring about a modification of the rhetorical opportunity? How?
Do the available means include the rhetorical elements of the message itself?
- Identify the rhetorical elements of the message itself. In other words, where and how does the person or group employ the rhetorical appeals of ethos, pathos, and logos? How are credentials, goodwill, or good sense evoked to establish ethos? How is evidence (examples, statistics, data, and so forth) used to establish logos? And how is an emotional connection created to establish pathos? Keep in mind that the rhetorical appeals can sometimes overlap.
- What kind of language does the creator of the text use? Is it plain or specialized, slang or formal? How does the choice of language reveal how the person or group views the intended audience?
Do the available means deliver a message in a genre and medium that reaches the audience?
- Is the intended audience for the text a rhetorical audience? Draw on evidence from the text to support your answer.
- If the audience is a rhetorical one, what can it do to resolve the problem?
- Does the response address and fit the rhetorical opportunity? How exactly? If not, how might the response be reshaped so that it does fit?
- Is the response delivered in an appropriate medium that reaches its intended audience? Why is that medium appropriate? Or how could it be adjusted to be appropriate?
- Can you think of other responses to similar rhetorical situations? What genre is commonly used? Does the creator of this text use that genre? If not, what is the effect of going against an audience’s expectations?
Now that you have carefully read the text and answered all of the questions, you are ready to write your rhetorical analysis. How does your analysis of the use of the available means reveal
- How well the rhetorical elements work together to create a fitting response to an opportunity for change?
- How effective the response is?
As you begin, search your answers for an idea that can serve as your claim or thesis. For example, you might focus on the declared goal—if there is one—of the creator of the text and whether it has been achieved. You might assess how successfully that creator has identified the rhetorical audience, shaped a fitting response, or employed the best available means. Or you might focus on the use of the rhetorical appeals and the overall success of their use.
Whether or not you agree with the text is beside the point.
Your job is to analyze an essay, examining how, and how well, the text’s creator has accomplished the purpose of that text.
Key Grading Considerations
- The intro provides context for the rest of the paper
- The thesis is explicit, specific, and clear
- The thesis is analytical in nature
- The conclusion recasts the thesis and provides cohesion to the whole paper
- rhetorical triangle (audience, author, purpose)
- and rhetorical appeals (logos, ethos, pathos)
- focus is on an analysis (not a summary or the author’s own ideas of the issue)
- Smooth flow of ideas ordered in a logical sequence that effectively guides the reader
- Each paragraph has a well-supported clearly-stated main point
- The topic sentences focus on analysis
- There is an effective use of transitions.
- Uses the Rhetorical Triangle to Target the Audience
- Language Use & Mechanics
- Fully in APA Format
ATTRIBUTIONS
- Content Adapted from Excelsior Online Writing Lab (OWL). (2020). Excelsior College. Retrieved from https://owl.excelsior.edu/ licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-4.0 International License .
- Basic Questions for Rhetorical Analysis. Authored by : Gideon O. Burton. Provided by : Brigham Young University. Located at : http://rhetoric.byu.edu . Project : Silva Rhetoricae. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Original Content from Christine Jones. (2021). Rhetorical Analysis. Licensed under a CC0 1.0 Universal (CC0 1.0) Public Domain Dedication .
English 102: Journey Into Open Copyright © 2021 by Christine Jones is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Rhetorical Analysis Definition and Examples
The analysis can be used on any communication, even a bumper sticker
- An Introduction to Punctuation
Sample Rhetorical Analyses
Examples and observations, analyzing effects, analyzing greeting card verse, analyzing starbucks, rhetorical analysis vs. literary criticism.
- Ph.D., Rhetoric and English, University of Georgia
- M.A., Modern English and American Literature, University of Leicester
- B.A., English, State University of New York
Rhetorical analysis is a form of criticism or close reading that employs the principles of rhetoric to examine the interactions between a text, an author, and an audience . It's also called rhetorical criticism or pragmatic criticism.
Rhetorical analysis may be applied to virtually any text or image—a speech , an essay , an advertisement, a poem, a photograph, a web page, even a bumper sticker. When applied to a literary work, rhetorical analysis regards the work not as an aesthetic object but as an artistically structured instrument for communication. As Edward P.J. Corbett has observed, rhetorical analysis "is more interested in a literary work for what it does than for what it is."
- A Rhetorical Analysis of Claude McKay's "Africa"
- A Rhetorical Analysis of E.B. White's "The Ring of Time"
- A Rhetorical Analysis of U2's "Sunday Bloody Sunday"
- "Our response to the character of the author—whether it is called ethos, or 'implied author,' or style , or even tone—is part of our experience of his work, an experience of the voice within the masks, personae , of the work...Rhetorical criticism intensifies our sense of the dynamic relationships between the author as a real person and the more or less fictive person implied by the work." (Thomas O. Sloan, "Restoration of Rhetoric to Literary Study." The Speech Teacher )
- "[R]hetorical criticism is a mode of analysis that focuses on the text itself. In that respect, it is like the practical criticism that the New Critics and the Chicago School indulge in. It is unlike these modes of criticism in that it does not remain inside the literary work but works outward from the text to considerations of the author and the audience...In talking about the ethical appeal in his 'Rhetoric,' Aristotle made the point that although a speaker may come before an audience with a certain antecedent reputation, his ethical appeal is exerted primarily by what he says in that particular speech before that particular audience. Likewise, in rhetorical criticism, we gain our impression of the author from what we can glean from the text itself—from looking at such things as his ideas and attitudes, his stance, his tone, his style. This reading back to the author is not the same sort of thing as the attempt to reconstruct the biography of a writer from his literary work. Rhetorical criticism seeks simply to ascertain the particular posture or image that the author is establishing in this particular work in order to produce a particular effect on a particular audience." (Edward P.J. Corbett, "Introduction" to " Rhetorical Analyses of Literary Works ")
"[A] complete rhetorical analysis requires the researcher to move beyond identifying and labeling in that creating an inventory of the parts of a text represents only the starting point of the analyst's work. From the earliest examples of rhetorical analysis to the present, this analytical work has involved the analyst in interpreting the meaning of these textual components—both in isolation and in combination—for the person (or people) experiencing the text. This highly interpretive aspect of rhetorical analysis requires the analyst to address the effects of the different identified textual elements on the perception of the person experiencing the text. So, for example, the analyst might say that the presence of feature x will condition the reception of the text in a particular way. Most texts, of course, include multiple features, so this analytical work involves addressing the cumulative effects of the selected combination of features in the text." (Mark Zachry, "Rhetorical Analysis" from " The Handbook of Business Discourse , " Francesca Bargiela-Chiappini, editor)
"Perhaps the most pervasive type of repeated-word sentence used in greeting card verse is the sentence in which a word or group of words is repeated anywhere within the sentence, as in the following example:
In quiet and thoughtful ways , in happy and fun ways , all ways , and always , I love you.
In this sentence, the word ways is repeated at the end of two successive phrases, picked up again at the beginning of the next phrase, and then repeated as part of the word always . Similarly, the root word all initially appears in the phrase 'all ways' and is then repeated in a slightly different form in the homophonic word always . The movement is from the particular ('quiet and thoughtful ways,' 'happy and fun ways'), to the general ('all ways'), to the hyperbolic ('always')." (Frank D'Angelo, "The Rhetoric of Sentimental Greeting Card Verse." Rhetoric Review )
"Starbucks not just as an institution or as a set of verbal discourses or even advertising but as a material and physical site is deeply rhetorical...Starbucks weaves us directly into the cultural conditions of which it is constitutive. The color of the logo, the performative practices of ordering, making, and drinking the coffee, the conversations around the tables, and the whole host of other materialities and performances of/in Starbucks are at once the rhetorical claims and the enactment of the rhetorical action urged. In short, Starbucks draws together the tripartite relationships among place, body, and subjectivity. As a material/rhetorical place, Starbucks addresses and is the very site of a comforting and discomforting negotiation of these relationships." (Greg Dickinson, "Joe's Rhetoric: Finding Authenticity at Starbucks." Rhetoric Society Quarterly )
"What essentially are the differences between literary criticism analysis and rhetorical analysis? When a critic explicates Ezra Pound's Canto XLV , for example, and shows how Pound inveighs against usury as an offense against nature that corrupts society and the arts, the critic must point out the 'evidence'—the 'artistic proofs' of example and enthymeme [a formal syllogistic argument that is incompletely stated}—that Pound has drawn upon for his fulmination. The critic will also call attention to the 'arrangement' of the parts of that argument as a feature of the 'form' of the poem just as he may inquire into the language and syntax. Again these are matters that Aristotle assigned mainly to rhetoric...
"All critical essays dealing with the persona of a literary work are in reality studies of the 'Ethos' of the 'speaker' or 'narrator'—the voice—source of the rhythmic language which attracts and holds the kind of readers the poet desires as his audience, and the means this persona consciously or unconsciously chooses, in Kenneth Burke's term, to 'woo' that reader-audience." (Alexander Scharbach, "Rhetoric and Literary Criticism: Why Their Separation." College Composition and Communication )
- Audience Analysis in Speech and Composition
- Definition and Examples of Ethos in Classical Rhetoric
- A Rhetorical Analysis of U2's 'Sunday Bloody Sunday'
- Invented Ethos (Rhetoric)
- Rhetoric: Definitions and Observations
- What Is Phronesis?
- Feminist Literary Criticism
- An Introduction to Rhetorical Questions
- Enthymeme - Definition and Examples
- Deliberative Rhetoric
- Persuasion and Rhetorical Definition
- Use Social Media to Teach Ethos, Pathos and Logos
- Pathos in Rhetoric
- Definition and Examples of Rhetorical Stance
- Definition and Examples of Analysis in Composition
- Definition and Examples of Senders in Communication
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Using Rhetorical Strategies for Persuasion

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
These OWL resources will help you develop and refine the arguments in your writing.
There are three types of rhetorical appeals, or persuasive strategies, used in arguments to support claims and respond to opposing arguments. A good argument will generally use a combination of all three appeals to make its case.
Logos or the appeal to reason relies on logic or reason. Logos often depends on the use of inductive or deductive reasoning.
Inductive reasoning takes a specific representative case or facts and then draws generalizations or conclusions from them. Inductive reasoning must be based on a sufficient amount of reliable evidence. In other words, the facts you draw on must fairly represent the larger situation or population. Example:
In this example the specific case of fair trade agreements with coffee producers is being used as the starting point for the claim. Because these agreements have worked the author concludes that it could work for other farmers as well.
Deductive reasoning begins with a generalization and then applies it to a specific case. The generalization you start with must have been based on a sufficient amount of reliable evidence.Example:
In this example the author starts with a large claim, that genetically modified seeds have been problematic everywhere, and from this draws the more localized or specific conclusion that Mexico will be affected in the same way.
Avoid Logical Fallacies
These are some common errors in reasoning that will undermine the logic of your argument. Also, watch out for these slips in other people's arguments.
Slippery slope: This is a conclusion based on the premise that if A happens, then eventually through a series of small steps, through B, C,..., X, Y, Z will happen, too, basically equating A and Z. So, if we don't want Z to occur A must not be allowed to occur either. Example:
In this example the author is equating banning Hummers with banning all cars, which is not the same thing.
Hasty Generalization: This is a conclusion based on insufficient or biased evidence. In other words, you are rushing to a conclusion before you have all the relevant facts. Example:
In this example the author is basing their evaluation of the entire course on only one class, and on the first day which is notoriously boring and full of housekeeping tasks for most courses. To make a fair and reasonable evaluation the author must attend several classes, and possibly even examine the textbook, talk to the professor, or talk to others who have previously finished the course in order to have sufficient evidence to base a conclusion on.
Post hoc ergo propter hoc: This is a conclusion that assumes that if 'A' occurred after 'B' then 'B' must have caused 'A.' Example:
In this example the author assumes that if one event chronologically follows another the first event must have caused the second. But the illness could have been caused by the burrito the night before, a flu bug that had been working on the body for days, or a chemical spill across campus. There is no reason, without more evidence, to assume the water caused the person to be sick.
Genetic Fallacy: A conclusion is based on an argument that the origins of a person, idea, institute, or theory determine its character, nature, or worth. Example:
In this example the author is equating the character of a car with the character of the people who built the car.
Begging the Claim: The conclusion that the writer should prove is validated within the claim. Example:
Arguing that coal pollutes the earth and thus should be banned would be logical. But the very conclusion that should be proved, that coal causes enough pollution to warrant banning its use, is already assumed in the claim by referring to it as "filthy and polluting."
Circular Argument: This restates the argument rather than actually proving it. Example:
In this example the conclusion that Bush is a "good communicator" and the evidence used to prove it "he speaks effectively" are basically the same idea. Specific evidence such as using everyday language, breaking down complex problems, or illustrating his points with humorous stories would be needed to prove either half of the sentence.
Either/or: This is a conclusion that oversimplifies the argument by reducing it to only two sides or choices. Example:
In this example where two choices are presented as the only options, yet the author ignores a range of choices in between such as developing cleaner technology, car sharing systems for necessities and emergencies, or better community planning to discourage daily driving.
Ad hominem: This is an attack on the character of a person rather than their opinions or arguments. Example:
In this example the author doesn't even name particular strategies Green Peace has suggested, much less evaluate those strategies on their merits. Instead, the author attacks the characters of the individuals in the group.
Ad populum: This is an emotional appeal that speaks to positive (such as patriotism, religion, democracy) or negative (such as terrorism or fascism) concepts rather than the real issue at hand. Example:
In this example the author equates being a "true American," a concept that people want to be associated with, particularly in a time of war, with allowing people to buy any vehicle they want even though there is no inherent connection between the two.
Red Herring: This is a diversionary tactic that avoids the key issues, often by avoiding opposing arguments rather than addressing them. Example:
In this example the author switches the discussion away from the safety of the food and talks instead about an economic issue, the livelihood of those catching fish. While one issue may affect the other, it does not mean we should ignore possible safety issues because of possible economic consequences to a few individuals.
Ethos or the ethical appeal is based on the character, credibility, or reliability of the writer. There are many ways to establish good character and credibility as an author:
- Use only credible, reliable sources to build your argument and cite those sources properly.
- Respect the reader by stating the opposing position accurately.
- Establish common ground with your audience. Most of the time, this can be done by acknowledging values and beliefs shared by those on both sides of the argument.
- If appropriate for the assignment, disclose why you are interested in this topic or what personal experiences you have had with the topic.
- Organize your argument in a logical, easy to follow manner. You can use the Toulmin method of logic or a simple pattern such as chronological order, most general to most detailed example, earliest to most recent example, etc.
- Proofread the argument. Too many careless grammar mistakes cast doubt on your character as a writer.
Pathos , or emotional appeal, appeals to an audience's needs, values, and emotional sensibilities. Pathos can also be understood as an appeal to audience's disposition to a topic, evidence, or argument (especially appropriate to academic discourse).
Argument emphasizes reason, but used properly there is often a place for emotion as well. Emotional appeals can use sources such as interviews and individual stories to paint a more legitimate and moving picture of reality or illuminate the truth. For example, telling the story of a single child who has been abused may make for a more persuasive argument than simply the number of children abused each year because it would give a human face to the numbers. Academic arguments in particular benefit from understanding pathos as appealing to an audience's academic disposition.
Only use an emotional appeal if it truly supports the claim you are making, not as a way to distract from the real issues of debate. An argument should never use emotion to misrepresent the topic or frighten people.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example

Top 15+ Rhetorical Analysis Essay Examples for Students
Published on: Mar 10, 2023
Last updated on: Jan 29, 2024

People also read
How To Write A Rhetorical Analysis Essay That Stands Out
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Topics & Ideas for Students
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Outline - Tips & Examples
Understanding Ethos, Pathos, Logos - The Three Rhetorical Appeals
Share this article
Writing a rhetorical analysis essay can be tough. You want to engage your reader, but you also need to provide clear and concise analysis of the text.
It's hard to know where to start, what information is important, and how to make your argument clear.
Don't fret! We've got you covered.
In this blog post, we'll give you 15+ Rhetorical analysis essay examples to help you craft a winning essay. Plus, we'll give you some tips on how to make your essay stand out.
So without a further delay, let's start!
On This Page On This Page -->
Good Rhetorical Analysis Essay Examples
Examples help the readers to understand things in a better way. They also help a writer to compose an essay just like professionals.
Here are some amazing rhetorical analysis examples on different topics. Use them as a helping hand to understand the concept and write a good essay.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example: AP Language
Rhetorical analysis done in AP Language and Composition is one of the biggest tasks a student can ever get. On the same hand, drafting it in a proper way is also necessary to get good grades.
Look at these rhetorical analysis essay example AP language given below to see how a well-written rhetorical essay is written.
AP Rhetorical analysis essay example
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example Ap Lang 2020
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example Ap Lang 2021
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example AP Lang 2022
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example AP Lang 2023
These rhetorical analysis essay example college board will help you to win over your panel in no time!
Want to start from the basics? Head over to our Rhetorical essay guide to solidify your base.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example: Ted Talk
A rhetorical analysis can be done on nearly anything. Here is a good example of a rhetorical essay in which a ted talk is being analyzed.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example: Ethos, Pathos, Logos
The first impression of these three terms sounds just like a conjuration in some kind of a magical story. But in fact, these elements of persuasion were created by Aristotle and have been used for a very long time.
According to Aristotle, they were the primary persuasive strategies that authors should use in their papers. These elements are further elaborated as follows:
- The ethos appeals to ethics.
- Pathos appeals to emotions.
- Logos mean the use of rational thinking.
Here is an example of a rhetorical essay written using these elements.
Understand Ethos,Pathos and Logos to write a compelling essay.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example for College
College students often get to write a rhetorical analysis essay. They find it hard to write such an essay because it is a bit more technical than other essay types.
Here is an example of a well-written rhetorical essay for college students.
Comparative Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example
A rhetorical analysis essay can be written to show a comparison between two objects. Here is a compare-and-contrast rhetorical analysis essay example.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
Visual Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example
The visual rhetorical essay determines how pictures and images communicate messages and persuade the audience. Usually, visual rhetorical essays are written for advertisements. They use strong images to convince the audience to behave in a certain way.
Visual Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example Pdf
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example: Letter from Birmingham Jail
Here is another good example of a rhetorical essay. Most of us know about the history of âletter from a Birmingham jailâ. Read the given example to see how rhetorical analysis is done on it.
Struggling for a similar good topic? Check out our amazing rhetorical essay topics to select the perfect theme for your essay.
Great Influenza: Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example
Influenza has been one of the scariest pandemics the world has faced in history. Here is a rhetorical essay on great influenza.
Great influenza: Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example
Condoleezza Rice Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example
The speech given by Condoleezza Rice has become a classic example of effective oratory. Here is an example of a rhetorical analysis essay on the speech given by Condoleezza Rice at a commencement ceremony.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example: Condoleezza Riceâs Commencement Speech
This example explores the effectiveness of Rice's speech and features an in-depth analysis.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example High School
High school essays involve the analysis of different texts and the application of rhetorical tools to those texts. Here is an example that focuses on a high school essay about the effects of television on society.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example (Pdf)
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example MLA
MLA format is one of the most commonly used formats for essays. Here is an example of a rhetorical essay written in MLA format that focuses on the effectiveness of advertisements.
MLA Rhetorical Analysis Essay PDF
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example Outline
Outline helps to organize the ideas and arguments that you want to present in your essay. Here is a sample outline that can help you write an effective rhetorical analysis essay.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example Outline sample
Hop on to our rhetorical essay outline guide to learn the step-by-step process of crafting an exemplary outline.
How to Start a Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example
When starting a rhetorical analysis essay, it is important to provide a brief overview of the topic that you are analyzing. This should include the overall message being conveyed, the target audience and the rhetorical devices used in the text.
Here is a rhetorical analysis introduction example for your ease.
Thesis Statement Example for Rhetorical Analysis Essay
The thesis statement of a rhetorical analysis essay should explain the primary argument being made in the text. Here is an example of a thesis statement for a rhetorical analysis essay for your ease.
Example of Rhetorical Analysis Thesis Statement
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example Conclusion
The conclusion of a rhetorical analysis essay is an important part of the overall essay. It should summarize your main points and provide some final thoughts on the topic.
Here is an example of conclusion for a rhetorical analysis essay for your ease.
Download this Rhetorical Analysis Essay Writing Manual to help gather all the relevant guidance for your rhetorical essay.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Writing Manual (PDF)
Watch this video to understand how to select Rhetorical analysis essay evidences.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Writing Tips
To write a rhetorical analysis essay, you must have good writing skills. Writing a rhetorical essay is a technical task to do. This is why many students find it really difficult.
There are the following things that you should do to write a good rhetorical analysis essay. Those important things are as follows:
- Determine the Rhetorical Strategy
To write a rhetorical essay, the writer needs to follow a specific method for research. The typical research methods used for this particular essay are as follows:
- Choose a Topic
For any essay type, it is very important to have a good topic. A good topic seeks the readers of attention and convinces them to read the complete essay.
- Create a Rhetorical Analysis Outline
An outline is an essential part of essay writing. The outline provides a definite structure to the essay and also guides the reader throughout the essay. A rhetorical analysis outline has the following elements in it:
- Introduction
- Body paragraphs
These three elements let you describe the entire idea of your rhetorical analysis essay. These three elements are further written with the help of sub-elements.
- Develop a Thesis Statement
The thesis statement is yet another important part of essay writing. It is the essence of the entire essay. It may be a sentence or two explaining the whole idea of your essay. However, not give background information about the topic.
- Proofread and Edit
The formal terminology used for essay revision is known as proofreading. To make sure that your essay is error-free, repeat this process more than once.
Now let's wrap up , shall we?
So far we have provided you with the best rhetorical analysis examples that are sure to win over your panel. With our help, you can surely sfe guard your academic success journey in no time!
In case you think you can not write such an essay on your own, consult an essay writing service.
At CollegeEssay.org , we provide the best rhetorical analysis essay writing service to every student. We have an extensive team of professional writers who can handle all your essay writing assignments.
We make sure that the content we provide you is 100% unique and help you get the best grade.
So why delay when our essay writer can provide you with a top-notch rhetorical essay right away?
Hire our essay service and avail yourself 50% OFF on your first order today!
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the 3 parts of rhetorical analysis.
The three parts of rhetorical analysis are:
- Ethos
- Logos
- Pathos
What are the elements of a rhetorical analysis?
The main elements of a rhetorical analysis essay are:
- Situation
- Audience
- Purpose
- Medium
- Context
Is there any difference between AP lang rhetorical analysis essay example 2020 and AP lang rhetorical analysis essay example 2021?
Yes, there are differences between 2020 and 2021 AP Language and Composition rhetorical analysis essay examples.
- In 2020 the essay prompts revolved around various social issues related to public discourse. In 2021 they mainly focused on the ideas of justice or progress.
- In 2020 students were encouraged to write a multi-paragraph essay shifting back and forth between creative devices of rhetoric. While in 2021 more emphasis was placed on analyzing how well an author's argument is structured.
Cathy A. (Literature, Marketing)
For more than five years now, Cathy has been one of our most hardworking authors on the platform. With a Masters degree in mass communication, she knows the ins and outs of professional writing. Clients often leave her glowing reviews for being an amazing writer who takes her work very seriously.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!

Keep reading

- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Terms of Use
- Refunds & Cancellations
- Our Writers
- Success Stories
- Our Guarantees
- Affiliate Program
- Referral Program
- AI Essay Writer
Disclaimer: All client orders are completed by our team of highly qualified human writers. The essays and papers provided by us are not to be used for submission but rather as learning models only.
Home — Essay Samples — Government & Politics — Malala — I Am Malala Rhetorical Analysis
I Am Malala Rhetorical Analysis
- Categories: Malala
About this sample

Words: 520 |
Published: Mar 25, 2024
Words: 520 | Page: 1 | 3 min read

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Dr. Heisenberg
Verified writer
- Expert in: Government & Politics

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
2 pages / 1020 words
2 pages / 756 words
6 pages / 2944 words
2 pages / 1017 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Malala
The stories of individuals who have made a difference highlight the extraordinary capacity of human agency to transform lives, communities, and even the world. By nurturing the seed of change within ourselves and acting on [...]
Malala Yousafzai, a young Pakistani activist for female education, delivered a powerful speech at the United Nations in 2013. Her speech, commonly known as the "Malala Rhetorical Analysis," is a prime example of effective [...]
Malala Yousafzai is a Pakistani activist for women's education and the youngest Nobel Prize laureate. Her speech to the United Nations Youth Assembly on July 12, 2013, is a powerful call to action for education and activism. [...]
I chose to illustrate two scenes from the bookI Am Malalaby Malala Yousafzai and Christina Lamb. The two scenes I have chosen to depict are Malala lying on her hospital bed after being shot in the head by a member of the Taliban [...]
Malala's Advocacy for Girls' Education: Analyze Malala Yousafzai's passionate advocacy for girls' education as expressed in her speeches, and discuss the impact of her message on global awareness and action. [...]
In a world where education is often taken for granted, the story of Malala Yousafzai serves as a powerful reminder of the transformative power of knowledge and courage. "I Am Malala" by Malala Yousafzai and Christina Lamb is a [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
Free Rhetorical Analysis Generator
- 🌟 Intro to Rhetorical Analysis Generator
🤔 What Is Rhetorical Analysis?
- ✒️ Components of Rhetorical Analysis
- 💎 SOAPSTone Template
- 📝 Essay Outline
🔗 References
🌟 intro to our free rhetorical analysis generator.
Rhetoric refers to the use of language that helps motivate, persuade, or get the point across to a particular audience. Rhetorical analysis involves studying and evaluating strategies authors and speakers use to achieve this goal. Here, you’ll learn how to use our generator, the fundamentals of rhetorical analysis, and the components of making a great essay.
Rhetorical Analysis Generator & Reasons to Try
It’s not always easy to conduct a good rhetorical analysis. Many students struggle with it and may even fail to submit their work on time. Our rhetorical analysis generator is here to help! It has many benefits that help you finish your work faster:
A rhetorical analysis evaluates a piece of work and the effectiveness with which the author communicated their ideas. It can be anything from a novel to a movie, as long as the work wants to persuade an audience. In other words, instead of discussing the events of The Count of Monte Cristo, you explore what Alexander Dumas wanted to tell his readers, which techniques were used to convey the message, and whether it was successful.
11 Common Rhetorical Analysis Devices
Look at some of the most popular rhetorical devices you can encounter in written and spoken works. They will help you better identify and include them in your upcoming papers.
✒️ Rhetorical Analysis Components & Their Meaning
You can come across several rhetorical analysis methods in your professional and academic work. The rhetorical triangle is the most popular type but has several lesser-known subtypes.
Its components are:
- Ethos . This notion appeals to the author or speaker’s credibility. It evaluates a person’s authority on a subject and tells the audience if they should trust them.
- Pathos . Pathos deals with emotions. It’s the most effective rhetorical device as it’s used to connect the speaker and the audience. For example, an emotional appeal over the use of facts is a tell-tale sign of propaganda.
- Logos . This element backs up a claim with logical and reasonable substance. Through it, the author provides factual evidence that supports their claims.
- Kairos . When a writer or a speaker addresses a particular time and place, they use kairos to provide specific context. To illustrate, an address concerning the First Amendment is most effective during a political debate.
- Stasis . The final segment of the rhetorical analysis lets people view arguments from different perspectives. This adds an impact and makes the audience more likely to side with the writer or speaker.
💎 Rhetorical Analysis: SOAPSTone Template
Like any analysis, evaluating a person’s rhetorical capabilities requires structure. Without it, you may fail to address some aspects of the work, making your paper incomplete. You can make this process easier with the SOAPSTone template and its components:
📝 Rhetorical Analysis Essay Outline
Writing any type of essay requires structure and cohesion. While you may have encountered this structure before, it’s worth to remember the basics. A rhetorical analysis paper outline requires the following elements:
- Introduction . This paragraph introduces the text and its author. Some experts recommend including a summary of the work and elements of the SOAPStone analysis you uncovered. Explain why you’re conducting the research and give a clear thesis statement.
- Body . The section where you present arguments about work and what makes it persuasive. Here you discuss the methods, strategies, and rhetorical and literary devices the author used to convey their message.
- Conclusion . The conclusive paragraph ties your analysis together by driving home the main arguments provided in its body. It can also explain how the work impacted society or its target audience.
3 Good Rhetorical Analysis Essay Examples
Here we have picked up some samples with rhetorical analysis of different types of works that can inspire you to create own impressive essay.
- Rhetorical Analysis of Paypal’s Online Payments Commercial Essay . PayPal's online payments commercial employs a potent blend of rhetorical techniques to convey its message effectively. The ad emotionally connects with the audience through vibrant visuals, stirring music, and relatable scenarios. Using real-life situations highlights the convenience and security of PayPal's services, appealing to the ethos and building trust. Additionally, persuasive language and a call to action stimulate a sense of urgency, prompting viewers to adopt PayPal as their preferred online payment platform. By artfully combining pathos, ethos, and logos, the commercial convinces viewers that PayPal is a trustworthy and convenient decision for their online payment requirements.
- “The Myth of Multitasking” by Rosen: Rhetorical Analysis Essay . The author adeptly employs rhetorical strategies to debunk the notion of multitasking. Christine Rosen dismantles the prevalent belief in multitasking efficiency through persuasive arguments and compelling evidence, revealing its detrimental effects on productivity and cognitive abilities. Her skillful use of logic and reasoning challenges readers to question their habits and consider a more focused approach to tasks. By strategically dismantling this cultural trend, Rosen urges her audience to reassess their attitudes toward multitasking, prompting a profound reevaluation of its impact on daily life and productivity.
- A Rhetorical Analysis: “Chevy Commercial 2014” Essay . Chevy Commercial from 2014 is a captivating piece of rhetoric that skillfully employs various persuasive techniques to resonate with its audience. The ad establishes an immediate connection with viewers through emotional storytelling. The commercial artfully weaves heartwarming scenes of people's lives, accompanied by an inspiring soundtrack, evoking a sense of nostalgia and relatability. Ethos is reinforced by showcasing real people in everyday situations, enhancing the credibility of Chevy's brand positioning as an integral part of consumers' lives. Furthermore, logos strategically highlights the car's innovative features and performance. By aligning Chevy with moments of happiness and adventure, the ad compels viewers to consider Chevy as the vehicle that can accompany them on their life journeys.
We hope our tool will facilitate your rhetorical analysis of books, commercials, or speeches, so you'll create a unique essay! Besides, you may try our hook generator to engage the audience to read your paper from the beginning.
📌 Rhetorical Analysis Generator – FAQ
Updated: Oct 25th, 2023
- Rhetorical Analysis – Jessica Allee, University of Arkansas
- How To Write a Rhetorical Analysis in 8 Simple Steps – Jennifer Herrity, Indeed
- Rhetorical Analysis – Blinn College District
- What Is a Rhetorical Device? Definition, List, Examples – Jeffrey Somers, ThoughtCo
- Rhetorical Analysis Essay: Formatting – Brandon Everett, California State University, East Bay
- What is Rhetorical Analysis? – Melanie Gagich & Emilie Zickel, PressBooks
- SOAPStone Graphic Organizer for Rhetorical Analysis – Sacramento City Unified School District
- Free Essays
- Writing Tools
- Lit. Guides
- Donate a Paper
- Referencing Guides
- Free Textbooks
- Tongue Twisters
- Job Openings
- Expert Application
- Video Contest
- Writing Scholarship
- Discount Codes
- IvyPanda Shop
- Terms and Conditions
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Copyright Principles
- DMCA Request
- Service Notice
This page contains a free tool for conducting rhetorical analysis. It is user-friendly, accurate, and fast. You can customize the analysis according to your text type and context. Also, we have prepared a guide where you can find out about literary devices, components of rhetorical analysis, and the structure of your future essay.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A rhetorical analysis is a type of essay that looks at a text in terms of rhetoric. This means it is less concerned with what the author is saying than with how they say it: their goals, techniques, and appeals to the audience. A rhetorical analysis is structured similarly to other essays: an introduction presenting the thesis, a body analyzing ...
This article will find some examples that will help you with your rhetorical analysis essay writing effortlessly. On This Page. 1. Good Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example. 2. Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example AP Lang 2023. 3. Rhetorical Analysis Essay Examples for Students. 4.
Ethos, along with logos and pathos, is one of the three "modes of persuasion" in rhetoric (the art of effective speaking or writing). Ethos is an argument that appeals to the audience by emphasizing the speaker's credibility and authority. If the speaker has a high-ranking position, is an expert in his or her field, or has had life experience ...
An Analysis Example: Sara Peres works in Geography and Environment at the University of Southampton. And what's important is that she has previously focused on how agricultural seeds are banked and circulated for conservation purposes for her Ph.D. (UCL, 2017), the history of seed banks, which was exactly where this paper comes from.
Rhetorical Analysis Sample Essay. A woman's work is never done: many American women grow up with this saying and feel it to be true. 1 One such woman, author Jessica Grose, wrote "Cleaning: The Final Feminist Frontier," published in 2013 in the New Republic, 2 and she argues that while the men recently started taking on more of the ...
Ethos, Pathos, and Logos Definition. Ethos, pathos, and logos are three essential components in rhetorical analysis. It can be a very effective tool for influencing and convincing others. These concepts have been employed by great speakers, writers, and thinkers throughout history and continue to play a pivotal role in communication today.
Body Paragraph #1: Ethos. Describe how the speaker makes an appeal to ethos (the audience's sense of ethical responsibility) Use specific examples, referring to word choice, tone, anecdotes, and other devices. Body Paragraph #2: Pathos. Describe how the speaker makes an appeal to pathos (the audience's emotions)
Name the author of the text and the title of their work followed by the date in parentheses. Use a verb to describe what the author does, e.g. "implies," "asserts," or "claims". Briefly summarize the text in your own words. Mention the persuasive techniques used by the rhetor and its effect.
Rhetorical appeal #2: Pathos. The purpose of Pathos-driven rhetoric is to appeal to the reader's emotions. A common example of pathos as a rhetorical means is adverts by charities that try to make you donate money to a "good cause". To evoke the intended emotions in the reader, an author may use passionate language, tell personal stories ...
To write a rhetorical analysis, you need to follow the steps below: Step 1: Plan and prepare. With a rhetorical analysis, you don't choose concepts in advance and apply them to a specific text or piece of content. Rather, you'll have to analyze the text to identify the separate components and plan and prepare your analysis accordingly.
Updated on March 10, 2019. In classical rhetoric, ethos is a persuasive appeal (one of the three artistic proofs) based on the character or projected character of the speaker or writer. Also called ethical appeal or ethical argument. According to Aristotle, the chief components of a compelling ethos are goodwill, practical wisdom, and virtue.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay: Ethos, Pathos, Logos Created by: Brandon Everett Summer 2019 An appeal is an author's attempt to earn audience approval. Authors will utilize specific devices and techniques to appeal to emotion, values, character, and reason in their writing in order to make their arguments more persuasive.
Rhetorical Appeals. In composition studies, the term rhetorical appeals refers to the use of ethos, pathos, and logos. These are classical Greek terms dating back to Aristotle who is traditionally viewed as the creator of rhetoric. To be rhetorically effective (and thus persuasive), an author must engage the audience in a variety of compelling ...
A Simplified Guide to Writing a Rhetorical Analysis ETHOS - Ethos uses the writer's credibility or expertise to make an argument. Here the writer may be a credible source or may incorporate credible sources to support the writer's argument. Example: A heart surgeon from Johns Hopkins Hospital makes a credible argument linking heart disease to
6.4 Rhetorical Appeals: Logos, Pathos, and Ethos Defined Melanie Gagich & Emilie Zickel. ... Here is an example of a rhetorical move that connects with ethos: when reading an article about abortion, the author mentions that she has had an abortion. ... In a rhetorical analysis project, it would be up to you, the analyzer, to point out this move ...
RHETORICAL ANALYSIS SAMPLE ESSAY. Harriet Clark. Ms. Rebecca Winter. CWC 101. 13 Feb. 2015 Not Quite a Clean Sweep: Rhetorical Strategies in Grose's "Cleaning: The Final Feminist Frontier" A woman's work is never done: many American women grow up with this saying and feel it to be true. One such woman, author Jessica Grose, wrote ...
The ultimate goal of a rhetorical analysis is twofold: to analyze how well the rhetorical elements work together to create a fitting response, and. to evaluate the overall effectiveness of that response. To examine that goal, there are a couple of approaches that can be made in writing an analysis. The first is to ask some basic questions.
Analyzing Effects "[A] complete rhetorical analysis requires the researcher to move beyond identifying and labeling in that creating an inventory of the parts of a text represents only the starting point of the analyst's work.From the earliest examples of rhetorical analysis to the present, this analytical work has involved the analyst in interpreting the meaning of these textual components ...
Using Rhetorical Strategies for Persuasion. There are three types of rhetorical appeals, or persuasive strategies, used in arguments to support claims and respond to opposing arguments. A good argument will generally use a combination of all three appeals to make its case.
Pathos appeals to emotions. Logos mean the use of rational thinking. Here is an example of a rhetorical essay written using these elements. Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example: Ethos, Pathos, Logos. Expert Tip. Understand Ethos,Pathos and Logos to write a compelling essay.
Examples of weak rhetorical analysis thesis statements: Abortion is a big issue in the United States. The author claims abortion is a big issue in the United States. I'm going to examine how this author uses pathos, ethos, and logos to convince his audience. The author uses pathos, ethos and logos.
Published: Mar 25, 2024. In her compelling memoir "I Am Malala," Malala Yousafzai recounts her journey as an advocate for girls' education, her survival of a brutal attack by the Taliban, and her continued fight for equality and justice. Through her use of rhetorical devices, Malala effectively conveys her message of resilience, courage, and ...
The five components of rhetorical analysis are ethos, pathos, logos, kairos, and stasis. In plain terms, they evaluate the work's credibility, logical and emotional appeals, context, and perspective. Any argument or claim can be analyzed by examining these elements. You can use them to evaluate a speech, a novel, or a movie.
A rhetorical analysis reveals the varying degrees of success with which Suzuki employs logos, pathos, and ethos: while Suzuki9s ethos is strong because of the reputation he brings to his writing and his use of pathos to appeal to his target audience of parents and educators, his use of logos is weak.
3. Finally, two important pieces this morning take a crack at what Trump's sledgehammer approach means politically.. The WSJ looks at how Trump's hush money trial, which begins April 15, might ...