Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- How to Write an Abstract | Steps & Examples

How to Write an Abstract | Steps & Examples
Published on February 28, 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on July 18, 2023 by Eoghan Ryan.

An abstract is a short summary of a longer work (such as a thesis , dissertation or research paper ). The abstract concisely reports the aims and outcomes of your research, so that readers know exactly what your paper is about.
Although the structure may vary slightly depending on your discipline, your abstract should describe the purpose of your work, the methods you’ve used, and the conclusions you’ve drawn.
One common way to structure your abstract is to use the IMRaD structure. This stands for:
- Introduction
Abstracts are usually around 100–300 words, but there’s often a strict word limit, so make sure to check the relevant requirements.
In a dissertation or thesis , include the abstract on a separate page, after the title page and acknowledgements but before the table of contents .
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Abstract example, when to write an abstract, step 1: introduction, step 2: methods, step 3: results, step 4: discussion, tips for writing an abstract, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about abstracts.
Hover over the different parts of the abstract to see how it is constructed.
This paper examines the role of silent movies as a mode of shared experience in the US during the early twentieth century. At this time, high immigration rates resulted in a significant percentage of non-English-speaking citizens. These immigrants faced numerous economic and social obstacles, including exclusion from public entertainment and modes of discourse (newspapers, theater, radio).
Incorporating evidence from reviews, personal correspondence, and diaries, this study demonstrates that silent films were an affordable and inclusive source of entertainment. It argues for the accessible economic and representational nature of early cinema. These concerns are particularly evident in the low price of admission and in the democratic nature of the actors’ exaggerated gestures, which allowed the plots and action to be easily grasped by a diverse audience despite language barriers.
Keywords: silent movies, immigration, public discourse, entertainment, early cinema, language barriers.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
You will almost always have to include an abstract when:
- Completing a thesis or dissertation
- Submitting a research paper to an academic journal
- Writing a book or research proposal
- Applying for research grants
It’s easiest to write your abstract last, right before the proofreading stage, because it’s a summary of the work you’ve already done. Your abstract should:
- Be a self-contained text, not an excerpt from your paper
- Be fully understandable on its own
- Reflect the structure of your larger work
Start by clearly defining the purpose of your research. What practical or theoretical problem does the research respond to, or what research question did you aim to answer?
You can include some brief context on the social or academic relevance of your dissertation topic , but don’t go into detailed background information. If your abstract uses specialized terms that would be unfamiliar to the average academic reader or that have various different meanings, give a concise definition.
After identifying the problem, state the objective of your research. Use verbs like “investigate,” “test,” “analyze,” or “evaluate” to describe exactly what you set out to do.
This part of the abstract can be written in the present or past simple tense but should never refer to the future, as the research is already complete.
- This study will investigate the relationship between coffee consumption and productivity.
- This study investigates the relationship between coffee consumption and productivity.
Next, indicate the research methods that you used to answer your question. This part should be a straightforward description of what you did in one or two sentences. It is usually written in the past simple tense, as it refers to completed actions.
- Structured interviews will be conducted with 25 participants.
- Structured interviews were conducted with 25 participants.
Don’t evaluate validity or obstacles here — the goal is not to give an account of the methodology’s strengths and weaknesses, but to give the reader a quick insight into the overall approach and procedures you used.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Next, summarize the main research results . This part of the abstract can be in the present or past simple tense.
- Our analysis has shown a strong correlation between coffee consumption and productivity.
- Our analysis shows a strong correlation between coffee consumption and productivity.
- Our analysis showed a strong correlation between coffee consumption and productivity.
Depending on how long and complex your research is, you may not be able to include all results here. Try to highlight only the most important findings that will allow the reader to understand your conclusions.
Finally, you should discuss the main conclusions of your research : what is your answer to the problem or question? The reader should finish with a clear understanding of the central point that your research has proved or argued. Conclusions are usually written in the present simple tense.
- We concluded that coffee consumption increases productivity.
- We conclude that coffee consumption increases productivity.
If there are important limitations to your research (for example, related to your sample size or methods), you should mention them briefly in the abstract. This allows the reader to accurately assess the credibility and generalizability of your research.
If your aim was to solve a practical problem, your discussion might include recommendations for implementation. If relevant, you can briefly make suggestions for further research.
If your paper will be published, you might have to add a list of keywords at the end of the abstract. These keywords should reference the most important elements of the research to help potential readers find your paper during their own literature searches.
Be aware that some publication manuals, such as APA Style , have specific formatting requirements for these keywords.
It can be a real challenge to condense your whole work into just a couple of hundred words, but the abstract will be the first (and sometimes only) part that people read, so it’s important to get it right. These strategies can help you get started.
Read other abstracts
The best way to learn the conventions of writing an abstract in your discipline is to read other people’s. You probably already read lots of journal article abstracts while conducting your literature review —try using them as a framework for structure and style.
You can also find lots of dissertation abstract examples in thesis and dissertation databases .
Reverse outline
Not all abstracts will contain precisely the same elements. For longer works, you can write your abstract through a process of reverse outlining.
For each chapter or section, list keywords and draft one to two sentences that summarize the central point or argument. This will give you a framework of your abstract’s structure. Next, revise the sentences to make connections and show how the argument develops.
Write clearly and concisely
A good abstract is short but impactful, so make sure every word counts. Each sentence should clearly communicate one main point.
To keep your abstract or summary short and clear:
- Avoid passive sentences: Passive constructions are often unnecessarily long. You can easily make them shorter and clearer by using the active voice.
- Avoid long sentences: Substitute longer expressions for concise expressions or single words (e.g., “In order to” for “To”).
- Avoid obscure jargon: The abstract should be understandable to readers who are not familiar with your topic.
- Avoid repetition and filler words: Replace nouns with pronouns when possible and eliminate unnecessary words.
- Avoid detailed descriptions: An abstract is not expected to provide detailed definitions, background information, or discussions of other scholars’ work. Instead, include this information in the body of your thesis or paper.
If you’re struggling to edit down to the required length, you can get help from expert editors with Scribbr’s professional proofreading services or use the paraphrasing tool .
Check your formatting
If you are writing a thesis or dissertation or submitting to a journal, there are often specific formatting requirements for the abstract—make sure to check the guidelines and format your work correctly. For APA research papers you can follow the APA abstract format .
Checklist: Abstract
The word count is within the required length, or a maximum of one page.
The abstract appears after the title page and acknowledgements and before the table of contents .
I have clearly stated my research problem and objectives.
I have briefly described my methodology .
I have summarized the most important results .
I have stated my main conclusions .
I have mentioned any important limitations and recommendations.
The abstract can be understood by someone without prior knowledge of the topic.
You've written a great abstract! Use the other checklists to continue improving your thesis or dissertation.
If you want to know more about AI for academic writing, AI tools, or research bias, make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
Research bias
- Anchoring bias
- Halo effect
- The Baader–Meinhof phenomenon
- The placebo effect
- Nonresponse bias
- Deep learning
- Generative AI
- Machine learning
- Reinforcement learning
- Supervised vs. unsupervised learning
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
An abstract is a concise summary of an academic text (such as a journal article or dissertation ). It serves two main purposes:
- To help potential readers determine the relevance of your paper for their own research.
- To communicate your key findings to those who don’t have time to read the whole paper.
Abstracts are often indexed along with keywords on academic databases, so they make your work more easily findable. Since the abstract is the first thing any reader sees, it’s important that it clearly and accurately summarizes the contents of your paper.
An abstract for a thesis or dissertation is usually around 200–300 words. There’s often a strict word limit, so make sure to check your university’s requirements.
The abstract is the very last thing you write. You should only write it after your research is complete, so that you can accurately summarize the entirety of your thesis , dissertation or research paper .
Avoid citing sources in your abstract . There are two reasons for this:
- The abstract should focus on your original research, not on the work of others.
- The abstract should be self-contained and fully understandable without reference to other sources.
There are some circumstances where you might need to mention other sources in an abstract: for example, if your research responds directly to another study or focuses on the work of a single theorist. In general, though, don’t include citations unless absolutely necessary.
The abstract appears on its own page in the thesis or dissertation , after the title page and acknowledgements but before the table of contents .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, July 18). How to Write an Abstract | Steps & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 2, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/abstract/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a thesis or dissertation introduction, shorten your abstract or summary, how to write a literature review | guide, examples, & templates, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
Writing an Abstract for Your Research Paper
Definition and Purpose of Abstracts
An abstract is a short summary of your (published or unpublished) research paper, usually about a paragraph (c. 6-7 sentences, 150-250 words) long. A well-written abstract serves multiple purposes:
- an abstract lets readers get the gist or essence of your paper or article quickly, in order to decide whether to read the full paper;
- an abstract prepares readers to follow the detailed information, analyses, and arguments in your full paper;
- and, later, an abstract helps readers remember key points from your paper.
It’s also worth remembering that search engines and bibliographic databases use abstracts, as well as the title, to identify key terms for indexing your published paper. So what you include in your abstract and in your title are crucial for helping other researchers find your paper or article.
If you are writing an abstract for a course paper, your professor may give you specific guidelines for what to include and how to organize your abstract. Similarly, academic journals often have specific requirements for abstracts. So in addition to following the advice on this page, you should be sure to look for and follow any guidelines from the course or journal you’re writing for.
The Contents of an Abstract
Abstracts contain most of the following kinds of information in brief form. The body of your paper will, of course, develop and explain these ideas much more fully. As you will see in the samples below, the proportion of your abstract that you devote to each kind of information—and the sequence of that information—will vary, depending on the nature and genre of the paper that you are summarizing in your abstract. And in some cases, some of this information is implied, rather than stated explicitly. The Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association , which is widely used in the social sciences, gives specific guidelines for what to include in the abstract for different kinds of papers—for empirical studies, literature reviews or meta-analyses, theoretical papers, methodological papers, and case studies.
Here are the typical kinds of information found in most abstracts:
- the context or background information for your research; the general topic under study; the specific topic of your research
- the central questions or statement of the problem your research addresses
- what’s already known about this question, what previous research has done or shown
- the main reason(s) , the exigency, the rationale , the goals for your research—Why is it important to address these questions? Are you, for example, examining a new topic? Why is that topic worth examining? Are you filling a gap in previous research? Applying new methods to take a fresh look at existing ideas or data? Resolving a dispute within the literature in your field? . . .
- your research and/or analytical methods
- your main findings , results , or arguments
- the significance or implications of your findings or arguments.
Your abstract should be intelligible on its own, without a reader’s having to read your entire paper. And in an abstract, you usually do not cite references—most of your abstract will describe what you have studied in your research and what you have found and what you argue in your paper. In the body of your paper, you will cite the specific literature that informs your research.
When to Write Your Abstract
Although you might be tempted to write your abstract first because it will appear as the very first part of your paper, it’s a good idea to wait to write your abstract until after you’ve drafted your full paper, so that you know what you’re summarizing.
What follows are some sample abstracts in published papers or articles, all written by faculty at UW-Madison who come from a variety of disciplines. We have annotated these samples to help you see the work that these authors are doing within their abstracts.
Choosing Verb Tenses within Your Abstract
The social science sample (Sample 1) below uses the present tense to describe general facts and interpretations that have been and are currently true, including the prevailing explanation for the social phenomenon under study. That abstract also uses the present tense to describe the methods, the findings, the arguments, and the implications of the findings from their new research study. The authors use the past tense to describe previous research.
The humanities sample (Sample 2) below uses the past tense to describe completed events in the past (the texts created in the pulp fiction industry in the 1970s and 80s) and uses the present tense to describe what is happening in those texts, to explain the significance or meaning of those texts, and to describe the arguments presented in the article.
The science samples (Samples 3 and 4) below use the past tense to describe what previous research studies have done and the research the authors have conducted, the methods they have followed, and what they have found. In their rationale or justification for their research (what remains to be done), they use the present tense. They also use the present tense to introduce their study (in Sample 3, “Here we report . . .”) and to explain the significance of their study (In Sample 3, This reprogramming . . . “provides a scalable cell source for. . .”).
Sample Abstract 1
From the social sciences.
Reporting new findings about the reasons for increasing economic homogamy among spouses
Gonalons-Pons, Pilar, and Christine R. Schwartz. “Trends in Economic Homogamy: Changes in Assortative Mating or the Division of Labor in Marriage?” Demography , vol. 54, no. 3, 2017, pp. 985-1005.
![article abstract template “The growing economic resemblance of spouses has contributed to rising inequality by increasing the number of couples in which there are two high- or two low-earning partners. [Annotation for the previous sentence: The first sentence introduces the topic under study (the “economic resemblance of spouses”). This sentence also implies the question underlying this research study: what are the various causes—and the interrelationships among them—for this trend?] The dominant explanation for this trend is increased assortative mating. Previous research has primarily relied on cross-sectional data and thus has been unable to disentangle changes in assortative mating from changes in the division of spouses’ paid labor—a potentially key mechanism given the dramatic rise in wives’ labor supply. [Annotation for the previous two sentences: These next two sentences explain what previous research has demonstrated. By pointing out the limitations in the methods that were used in previous studies, they also provide a rationale for new research.] We use data from the Panel Study of Income Dynamics (PSID) to decompose the increase in the correlation between spouses’ earnings and its contribution to inequality between 1970 and 2013 into parts due to (a) changes in assortative mating, and (b) changes in the division of paid labor. [Annotation for the previous sentence: The data, research and analytical methods used in this new study.] Contrary to what has often been assumed, the rise of economic homogamy and its contribution to inequality is largely attributable to changes in the division of paid labor rather than changes in sorting on earnings or earnings potential. Our findings indicate that the rise of economic homogamy cannot be explained by hypotheses centered on meeting and matching opportunities, and they show where in this process inequality is generated and where it is not.” (p. 985) [Annotation for the previous two sentences: The major findings from and implications and significance of this study.]](https://writing.wisc.edu/wp-content/uploads/sites/535/2019/08/Abstract-1.png)
Sample Abstract 2
From the humanities.
Analyzing underground pulp fiction publications in Tanzania, this article makes an argument about the cultural significance of those publications
Emily Callaci. “Street Textuality: Socialism, Masculinity, and Urban Belonging in Tanzania’s Pulp Fiction Publishing Industry, 1975-1985.” Comparative Studies in Society and History , vol. 59, no. 1, 2017, pp. 183-210.
![article abstract template “From the mid-1970s through the mid-1980s, a network of young urban migrant men created an underground pulp fiction publishing industry in the city of Dar es Salaam. [Annotation for the previous sentence: The first sentence introduces the context for this research and announces the topic under study.] As texts that were produced in the underground economy of a city whose trajectory was increasingly charted outside of formalized planning and investment, these novellas reveal more than their narrative content alone. These texts were active components in the urban social worlds of the young men who produced them. They reveal a mode of urbanism otherwise obscured by narratives of decolonization, in which urban belonging was constituted less by national citizenship than by the construction of social networks, economic connections, and the crafting of reputations. This article argues that pulp fiction novellas of socialist era Dar es Salaam are artifacts of emergent forms of male sociability and mobility. In printing fictional stories about urban life on pilfered paper and ink, and distributing their texts through informal channels, these writers not only described urban communities, reputations, and networks, but also actually created them.” (p. 210) [Annotation for the previous sentences: The remaining sentences in this abstract interweave other essential information for an abstract for this article. The implied research questions: What do these texts mean? What is their historical and cultural significance, produced at this time, in this location, by these authors? The argument and the significance of this analysis in microcosm: these texts “reveal a mode or urbanism otherwise obscured . . .”; and “This article argues that pulp fiction novellas. . . .” This section also implies what previous historical research has obscured. And through the details in its argumentative claims, this section of the abstract implies the kinds of methods the author has used to interpret the novellas and the concepts under study (e.g., male sociability and mobility, urban communities, reputations, network. . . ).]](https://writing.wisc.edu/wp-content/uploads/sites/535/2019/08/Abstract-2.png)
Sample Abstract/Summary 3
From the sciences.
Reporting a new method for reprogramming adult mouse fibroblasts into induced cardiac progenitor cells
Lalit, Pratik A., Max R. Salick, Daryl O. Nelson, Jayne M. Squirrell, Christina M. Shafer, Neel G. Patel, Imaan Saeed, Eric G. Schmuck, Yogananda S. Markandeya, Rachel Wong, Martin R. Lea, Kevin W. Eliceiri, Timothy A. Hacker, Wendy C. Crone, Michael Kyba, Daniel J. Garry, Ron Stewart, James A. Thomson, Karen M. Downs, Gary E. Lyons, and Timothy J. Kamp. “Lineage Reprogramming of Fibroblasts into Proliferative Induced Cardiac Progenitor Cells by Defined Factors.” Cell Stem Cell , vol. 18, 2016, pp. 354-367.
![article abstract template “Several studies have reported reprogramming of fibroblasts into induced cardiomyocytes; however, reprogramming into proliferative induced cardiac progenitor cells (iCPCs) remains to be accomplished. [Annotation for the previous sentence: The first sentence announces the topic under study, summarizes what’s already known or been accomplished in previous research, and signals the rationale and goals are for the new research and the problem that the new research solves: How can researchers reprogram fibroblasts into iCPCs?] Here we report that a combination of 11 or 5 cardiac factors along with canonical Wnt and JAK/STAT signaling reprogrammed adult mouse cardiac, lung, and tail tip fibroblasts into iCPCs. The iCPCs were cardiac mesoderm-restricted progenitors that could be expanded extensively while maintaining multipo-tency to differentiate into cardiomyocytes, smooth muscle cells, and endothelial cells in vitro. Moreover, iCPCs injected into the cardiac crescent of mouse embryos differentiated into cardiomyocytes. iCPCs transplanted into the post-myocardial infarction mouse heart improved survival and differentiated into cardiomyocytes, smooth muscle cells, and endothelial cells. [Annotation for the previous four sentences: The methods the researchers developed to achieve their goal and a description of the results.] Lineage reprogramming of adult somatic cells into iCPCs provides a scalable cell source for drug discovery, disease modeling, and cardiac regenerative therapy.” (p. 354) [Annotation for the previous sentence: The significance or implications—for drug discovery, disease modeling, and therapy—of this reprogramming of adult somatic cells into iCPCs.]](https://writing.wisc.edu/wp-content/uploads/sites/535/2019/08/Abstract-3.png)
Sample Abstract 4, a Structured Abstract
Reporting results about the effectiveness of antibiotic therapy in managing acute bacterial sinusitis, from a rigorously controlled study
Note: This journal requires authors to organize their abstract into four specific sections, with strict word limits. Because the headings for this structured abstract are self-explanatory, we have chosen not to add annotations to this sample abstract.
Wald, Ellen R., David Nash, and Jens Eickhoff. “Effectiveness of Amoxicillin/Clavulanate Potassium in the Treatment of Acute Bacterial Sinusitis in Children.” Pediatrics , vol. 124, no. 1, 2009, pp. 9-15.
“OBJECTIVE: The role of antibiotic therapy in managing acute bacterial sinusitis (ABS) in children is controversial. The purpose of this study was to determine the effectiveness of high-dose amoxicillin/potassium clavulanate in the treatment of children diagnosed with ABS.
METHODS : This was a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Children 1 to 10 years of age with a clinical presentation compatible with ABS were eligible for participation. Patients were stratified according to age (<6 or ≥6 years) and clinical severity and randomly assigned to receive either amoxicillin (90 mg/kg) with potassium clavulanate (6.4 mg/kg) or placebo. A symptom survey was performed on days 0, 1, 2, 3, 5, 7, 10, 20, and 30. Patients were examined on day 14. Children’s conditions were rated as cured, improved, or failed according to scoring rules.
RESULTS: Two thousand one hundred thirty-five children with respiratory complaints were screened for enrollment; 139 (6.5%) had ABS. Fifty-eight patients were enrolled, and 56 were randomly assigned. The mean age was 6630 months. Fifty (89%) patients presented with persistent symptoms, and 6 (11%) presented with nonpersistent symptoms. In 24 (43%) children, the illness was classified as mild, whereas in the remaining 32 (57%) children it was severe. Of the 28 children who received the antibiotic, 14 (50%) were cured, 4 (14%) were improved, 4(14%) experienced treatment failure, and 6 (21%) withdrew. Of the 28children who received placebo, 4 (14%) were cured, 5 (18%) improved, and 19 (68%) experienced treatment failure. Children receiving the antibiotic were more likely to be cured (50% vs 14%) and less likely to have treatment failure (14% vs 68%) than children receiving the placebo.
CONCLUSIONS : ABS is a common complication of viral upper respiratory infections. Amoxicillin/potassium clavulanate results in significantly more cures and fewer failures than placebo, according to parental report of time to resolution.” (9)
Some Excellent Advice about Writing Abstracts for Basic Science Research Papers, by Professor Adriano Aguzzi from the Institute of Neuropathology at the University of Zurich:

Academic and Professional Writing
This is an accordion element with a series of buttons that open and close related content panels.
Analysis Papers
Reading Poetry
A Short Guide to Close Reading for Literary Analysis
Using Literary Quotations
Play Reviews
Writing a Rhetorical Précis to Analyze Nonfiction Texts
Incorporating Interview Data
Grant Proposals
Planning and Writing a Grant Proposal: The Basics
Additional Resources for Grants and Proposal Writing
Job Materials and Application Essays
Writing Personal Statements for Ph.D. Programs
- Before you begin: useful tips for writing your essay
- Guided brainstorming exercises
- Get more help with your essay
- Frequently Asked Questions
Resume Writing Tips
CV Writing Tips
Cover Letters
Business Letters
Proposals and Dissertations
Resources for Proposal Writers
Resources for Dissertators
Research Papers
Planning and Writing Research Papers
Quoting and Paraphrasing
Writing Annotated Bibliographies
Creating Poster Presentations
Thank-You Notes
Advice for Students Writing Thank-You Notes to Donors
Reading for a Review
Critical Reviews
Writing a Review of Literature
Scientific Reports
Scientific Report Format
Sample Lab Assignment
Writing for the Web
Writing an Effective Blog Post
Writing for Social Media: A Guide for Academics

Magnum Proofreading Services
- Jake Magnum
- Jan 2, 2021
Writing an Abstract for a Research Paper: Guidelines, Examples, and Templates
There are six steps to writing a standard abstract. (1) Begin with a broad statement about your topic. Then, (2) state the problem or knowledge gap related to this topic that your study explores. After that, (3) describe what specific aspect of this problem you investigated, and (4) briefly explain how you went about doing this. After that, (5) describe the most meaningful outcome(s) of your study. Finally, (6) close your abstract by explaining the broad implication(s) of your findings.
In this article, I present step-by-step guidelines for writing an abstract for an academic paper. These guidelines are fo llowed by an example of a full abstract that follows these guidelines and a few fill-in-the-blank templates that you can use to write your own abstract.
Guidelines for Writing an Abstract
The basic structure of an abstract is illustrated below.
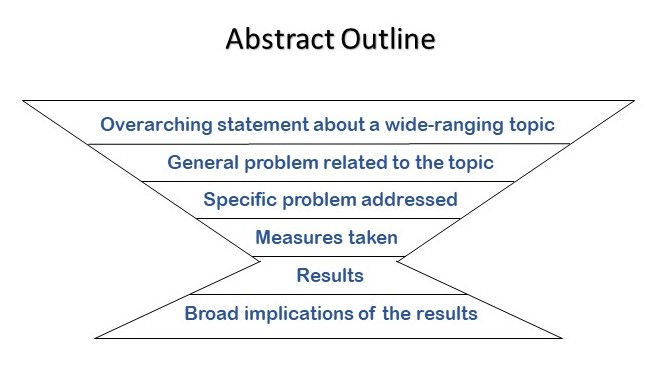
A standard abstract starts with a very general statement and becomes more specific with each sentence that follows until once again making a broad statement about the study’s implications at the end. Altogether, a standard abstract has six functions, which are described in detail below.
Start by making a broad statement about your topic.
The first sentence of your abstract should briefly describe a problem that is of interest to your readers. When writing this first sentence, you should think about who comprises your target audience and use terms that will appeal to this audience. If your opening sentence is too broad, it might lose the attention of potential readers because they will not know if your study is relevant to them.
Too broad : Maintaining an ideal workplace environment has a positive effect on employees.
The sentence above is so broad that it will not grab the reader’s attention. While it gives the reader some idea of the area of study, it doesn’t provide any details about the author’s topic within their research area. This can be fixed by inserting some keywords related to the topic (these are underlined in the revised example below).
Improved : Keeping the workplace environment at an ideal temperature positively affects the overall health of employees.
The revised sentence is much better, as it expresses two points about the research topic—namely, (i) what aspect of workplace environment was studied, (ii) what aspect of employees was observed. The mention of these aspects of the research will draw the attention of readers who are interested in them.
Describe the general problem that your paper addresses.
After describing your topic in the first sentence, you can then explain what aspect of this topic has motivated your research. Often, authors use this part of the abstract to describe the research gap that they identified and aimed to fill. These types of sentences are often characterized by the use of words such as “however,” “although,” “despite,” and so on.
However, a comprehensive understanding of how different workplace bullying experiences are associated with absenteeism is currently lacking.
The above example is typical of a sentence describing the problem that a study intends to tackle. The author has noticed that there is a gap in the research, and they briefly explain this gap here.
Although it has been established that quantity and quality of sleep can affect different types of task performance and personal health, the interactions between sleep habits and workplace behaviors have received very little attention.
The example above illustrates a case in which the author has accomplished two tasks with one sentence. The first part of the sentence (up until the comma) mentions the general topic that the research fits into, while the second part (after the comma) describes the general problem that the research addresses.
Express the specific problem investigated in your paper.
After describing the general problem that motivated your research, the next sentence should express the specific aspect of the problem that you investigated. Sentences of this type are often indicated by the use of phrases like “the purpose of this research is to,” “this paper is intended to,” or “this work aims to.”
Uninformative : However, a comprehensive understanding of how different workplace bullying experiences are associated with absenteeism is currently lacking. The present article aimed to provide new insights into the relationship between workplace bullying and absenteeism .
The second sentence in the above example is a mere rewording of the first sentence. As such, it adds nothing to the abstract. The second sentence should be more specific than the preceding one.
Improved : However, a comprehensive understanding of how different workplace bullying experiences are associated with absenteeism is currently lacking. The present article aimed to define various subtypes of workplace bullying and determine which subtypes tend to lead to absenteeism .
The second sentence of this passage is much more informative than in the previous example. This sentence lets the reader know exactly what they can expect from the full research article.
Explain how you attempted to resolve your study’s specific problem.
In this part of your abstract, you should attempt to describe your study’s methodology in one or two sentences. As such, you must be sure to include only the most important information about your method. At the same time, you must also be careful not to be too vague.
Too vague : We conducted multiple tests to examine changes in various factors related to well-being.
This description of the methodology is too vague. Instead of merely mentioning “tests” and “factors,” the author should note which specific tests were run and which factors were assessed.
Improved : Using data from BHIP completers, we conducted multiple one-way multivariate analyses of variance and follow-up univariate t-tests to examine changes in physical and mental health, stress, energy levels, social satisfaction, self-efficacy, and quality of life.
This sentence is very well-written. It packs a lot of specific information about the method into a single sentence. Also, it does not describe more details than are needed for an abstract.
Briefly tell the reader what you found by carrying out your study.
This is the most important part of the abstract—the other sentences in the abstract are there to explain why this one is relevant. When writing this sentence, imagine that someone has asked you, “What did you find in your research?” and that you need to answer them in one or two sentences.
Too vague : Consistently poor sleepers had more health risks and medical conditions than consistently optimal sleepers.
This sentence is okay, but it would be helpful to let the reader know which health risks and medical conditions were related to poor sleeping habits.
Improved : Consistently poor sleepers were more likely than consistently optimal sleepers to suffer from chronic abdominal pain, and they were at a higher risk for diabetes and heart disease.
This sentence is better, as the specific health conditions are named.
Finally, describe the major implication(s) of your study.
Most abstracts end with a short sentence that explains the main takeaway(s) that you want your audience to gain from reading your paper. Often, this sentence is addressed to people in power (e.g., employers, policymakers), and it recommends a course of action that such people should take based on the results.
Too broad : Employers may wish to make use of strategies that increase employee health.
This sentence is too broad to be useful. It does not give employers a starting point to implement a change.
Improved : Employers may wish to incorporate sleep education initiatives as part of their overall health and wellness strategies.
This sentence is better than the original, as it provides employers with a starting point—specifically, it invites employers to look up information on sleep education programs.
Abstract Example
The abstract produced here is from a paper published in Electronic Commerce Research and Applications . I have made slight alterations to the abstract so that this example fits the guidelines given in this article.
(1) Gamification can strengthen enjoyment and productivity in the workplace. (2) Despite this, research on gamification in the work context is still limited. (3) In this study, we investigated the effect of gamification on the workplace enjoyment and productivity of employees by comparing employees with leadership responsibilities to those without leadership responsibilities. (4) Work-related tasks were gamified using the habit-tracking game Habitica, and data from 114 employees were gathered using an online survey. (5) The results illustrated that employees without leadership responsibilities used work gamification as a trigger for self-motivation, whereas employees with leadership responsibilities used it to improve their health. (6) Work gamification positively affected work enjoyment for both types of employees and positively affected productivity for employees with leadership responsibilities. (7) Our results underline the importance of taking work-related variables into account when researching work gamification.
In Sentence (1), the author makes a broad statement about their topic. Notice how the nouns used (“gamification,” “enjoyment,” “productivity”) are quite general while still indicating the focus of the paper. The author uses Sentence (2) to very briefly state the problem that the research will address.
In Sentence (3), the author explains what specific aspects of the problem mentioned in Sentence (2) will be explored in the present work. Notice that the mention of leadership responsibilities makes Sentence (3) more specific than Sentence (2). Sentence (4) gets even more specific, naming the specific tools used to gather data and the number of participants.
Sentences (5) and (6) are similar, with each sentence describing one of the study’s main findings. Then, suddenly, the scope of the abstract becomes quite broad again in Sentence (7), which mentions “work-related variables” instead of a specific variable and “researching” instead of a specific kind of research.
Abstract Templates
Copy and paste any of the paragraphs below into a word processor. Then insert the appropriate information to produce an abstract for your research paper.
Template #1
Researchers have established that [Make a broad statement about your area of research.] . However, [Describe the knowledge gap that your paper addresses.] . The goal of this paper is to [Describe the purpose of your paper.] . The achieve this goal, we [Briefly explain your methodology.] . We found that [Indicate the main finding(s) of your study; you may need two sentences to do this.] . [Provide a broad implication of your results.] .
Template #2
It is well-understood that [Make a broad statement about your area of research.] . Despite this, [Describe the knowledge gap that your paper addresses.] . The current research aims to [Describe the purpose of your paper.] . To accomplish this, we [Briefly explain your methodology.] . It was discovered that [Indicate the main finding(s) of your study; you may need two sentences to do this.] . [Provide a broad implication of your results.] .
Template #3
Extensive research indicates that [Make a broad statement about your area of research.] . Nevertheless, [Describe the knowledge gap that your paper addresses.] . The present work is intended to [Describe the purpose of your paper.] . To this end, we [Briefly explain your methodology.] . The results revealed that [Indicate the main finding(s) of your study; you may need two sentences to do this.] . [Provide a broad implication of your results.] .
- How to Write an Abstract
Related Posts
How to Write a Research Paper in English: A Guide for Non-native Speakers
How to Write an Abstract Quickly
Using the Present Tense and Past Tense When Writing an Abstract

- Walden University
- Faculty Portal
Writing for Publication: Abstracts
An abstract is "a brief, comprehensive summary of the contents of the paper" (American Psychological Association [APA], 2020, p. 38). This summary is intended to share the topic, argument, and conclusions of a research study or course paper, similar to the text on the back cover of a book. When submitting your work for publication, an abstract is often the first piece of your writing a reviewer will encounter. An abstract may not be required for course papers.
Read on for more tips on making a good first impression with a successful abstract.
An abstract is a single paragraph preceded by the heading " Abstract ," centered and in bold font. The abstract does not begin with an indented line. APA (2020) recommends that abstracts should generally be less than 250 words, though many journals have their own word limits; it is always a good idea to check journal-specific requirements before submitting. The Writing Center's APA templates are great resources for visual examples of abstracts.
Abstracts use the present tense to describe currently applicable results (e.g., "Results indicate...") and the past tense to describe research steps (e.g., "The survey measured..."), and they do not typically include citations.
Key terms are sometimes included at the end of the abstract and should be chosen by considering the words or phrases that a reader might use to search for your article.
An abstract should include information such as
- The problem or central argument of your article
- A brief exposition of research design, methods, and procedures.
- A brief summary of your findings
- A brief summary of the implications of the research on practice and theory
It is also appropriate, depending on the type of article you are writing, to include information such as:
- Participant number and type
- Study eligibility criteria
- Limitations of your study
- Implications of your study's conclusions or areas for additional research
Your abstract should avoid unnecessary wordiness and focus on quickly and concisely summarizing the major points of your work. An abstract is not an introduction; you are not trying to capture the reader's attention with timeliness or to orient the reader to the entire background of your study. When readers finish reading your abstract, they should have a strong sense of your article's purpose, approach, and conclusions. The Walden Office of Research and Doctoral Services has additional tutorial material on abstracts .
Clinical or Empirical Study Abstract Exemplar
In the following abstract, the article's problem is stated in red , the approach and design are in blue , and the results are in green .
End-stage renal disease (ESRD) patients have a high cardiovascular mortality rate. Precise estimates of the prevalence, risk factors and prognosis of different manifestations of cardiac disease are unavailable. In this study a prospective cohort of 433 ESRD patients was followed from the start of ESRD therapy for a mean of 41 months. Baseline clinical assessment and echocardiography were performed on all patients. The major outcome measure was death while on dialysis therapy. Clinical manifestations of cardiovascular disease were highly prevalent at the start of ESRD therapy: 14% had coronary artery disease, 19% angina pectoris, 31% cardiac failure, 7% dysrhythmia and 8% peripheral vascular disease. On echocardiography 15% had systolic dysfunction, 32% left ventricular dilatation and 74% left ventricular hypertrophy. The overall median survival time was 50 months. Age, diabetes mellitus, cardiac failure, peripheral vascular disease and systolic dysfunction independently predicted death in all time frames. Coronary artery disease was associated with a worse prognosis in patients with cardiac failure at baseline. High left ventricular cavity volume and mass index were independently associated with death after two years. The independent associations of the different echocardiographic abnormalities were: systolic dysfunction--older age and coronary artery disease; left ventricular dilatation--male gender, anemia, hypocalcemia and hyperphosphatemia; left ventricular hypertrophy--older age, female gender, wide arterial pulse pressure, low blood urea and hypoalbuminemia. We conclude that clinical and echocardiographic cardiovascular disease are already present in a very high proportion of patients starting ESRD therapy and are independent mortality factors.
Foley, R. N., Parfrey, P. S., Harnett, J. D., Kent, G. M., Martin, C. J., Murray, D. C., & Barre, P. E. (1995). Clinical and echocardiographic disease in patients starting end-stage renal disease therapy. Kidney International , 47 , 186–192. https://doi.org/10.1038/ki.1995.22
Literature Review Abstract Exemplar
In the following abstract, the purpose and scope of the literature review are in red , the specific span of topics is in blue , and the implications for further research are in green .
This paper provides a review of research into the relationships between psychological types, as measured by the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI), and managerial attributes, behaviors and effectiveness. The literature review includes an examination of the psychometric properties of the MBTI and the contributions and limitations of research on psychological types. Next, key findings are discussed and used to advance propositions that relate psychological type to diverse topics such as risk tolerance, problem solving, information systems design, conflict management and leadership. We conclude with a research agenda that advocates: (a) the exploration of potential psychometric refinements of the MBTI, (b) more rigorous research designs, and (c) a broadening of the scope of managerial research into type.
Gardner, W. L., & Martinko, M. J. (1996). Using the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator to study managers: A literature review and research agenda. Journal of Management, 22 (1), 45–83. https://doi.org/10.1177/014920639602200103
Didn't find what you need? Search our website or email us .
Read our website accessibility and accommodation statement .
- Previous Page: Cover Letters
- Next Page: Formatting and Editing
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.
- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers

Abstract Writing: A Step-by-Step Guide With Tips & Examples

Table of Contents

Introduction
Abstracts of research papers have always played an essential role in describing your research concisely and clearly to researchers and editors of journals, enticing them to continue reading. However, with the widespread availability of scientific databases, the need to write a convincing abstract is more crucial now than during the time of paper-bound manuscripts.
Abstracts serve to "sell" your research and can be compared with your "executive outline" of a resume or, rather, a formal summary of the critical aspects of your work. Also, it can be the "gist" of your study. Since most educational research is done online, it's a sign that you have a shorter time for impressing your readers, and have more competition from other abstracts that are available to be read.
The APCI (Academic Publishing and Conferences International) articulates 12 issues or points considered during the final approval process for conferences & journals and emphasises the importance of writing an abstract that checks all these boxes (12 points). Since it's the only opportunity you have to captivate your readers, you must invest time and effort in creating an abstract that accurately reflects the critical points of your research.
With that in mind, let’s head over to understand and discover the core concept and guidelines to create a substantial abstract. Also, learn how to organise the ideas or plots into an effective abstract that will be awe-inspiring to the readers you want to reach.
What is Abstract? Definition and Overview
The word "Abstract' is derived from Latin abstractus meaning "drawn off." This etymological meaning also applies to art movements as well as music, like abstract expressionism. In this context, it refers to the revealing of the artist's intention.
Based on this, you can determine the meaning of an abstract: A condensed research summary. It must be self-contained and independent of the body of the research. However, it should outline the subject, the strategies used to study the problem, and the methods implemented to attain the outcomes. The specific elements of the study differ based on the area of study; however, together, it must be a succinct summary of the entire research paper.
Abstracts are typically written at the end of the paper, even though it serves as a prologue. In general, the abstract must be in a position to:
- Describe the paper.
- Identify the problem or the issue at hand.
- Explain to the reader the research process, the results you came up with, and what conclusion you've reached using these results.
- Include keywords to guide your strategy and the content.
Furthermore, the abstract you submit should not reflect upon any of the following elements:
- Examine, analyse or defend the paper or your opinion.
- What you want to study, achieve or discover.
- Be redundant or irrelevant.
After reading an abstract, your audience should understand the reason - what the research was about in the first place, what the study has revealed and how it can be utilised or can be used to benefit others. You can understand the importance of abstract by knowing the fact that the abstract is the most frequently read portion of any research paper. In simpler terms, it should contain all the main points of the research paper.
What is the Purpose of an Abstract?
Abstracts are typically an essential requirement for research papers; however, it's not an obligation to preserve traditional reasons without any purpose. Abstracts allow readers to scan the text to determine whether it is relevant to their research or studies. The abstract allows other researchers to decide if your research paper can provide them with some additional information. A good abstract paves the interest of the audience to pore through your entire paper to find the content or context they're searching for.
Abstract writing is essential for indexing, as well. The Digital Repository of academic papers makes use of abstracts to index the entire content of academic research papers. Like meta descriptions in the regular Google outcomes, abstracts must include keywords that help researchers locate what they seek.
Types of Abstract
Informative and Descriptive are two kinds of abstracts often used in scientific writing.
A descriptive abstract gives readers an outline of the author's main points in their study. The reader can determine if they want to stick to the research work, based on their interest in the topic. An abstract that is descriptive is similar to the contents table of books, however, the format of an abstract depicts complete sentences encapsulated in one paragraph. It is unfortunate that the abstract can't be used as a substitute for reading a piece of writing because it's just an overview, which omits readers from getting an entire view. Also, it cannot be a way to fill in the gaps the reader may have after reading this kind of abstract since it does not contain crucial information needed to evaluate the article.
To conclude, a descriptive abstract is:
- A simple summary of the task, just summarises the work, but some researchers think it is much more of an outline
- Typically, the length is approximately 100 words. It is too short when compared to an informative abstract.
- A brief explanation but doesn't provide the reader with the complete information they need;
- An overview that omits conclusions and results
An informative abstract is a comprehensive outline of the research. There are times when people rely on the abstract as an information source. And the reason is why it is crucial to provide entire data of particular research. A well-written, informative abstract could be a good substitute for the remainder of the paper on its own.
A well-written abstract typically follows a particular style. The author begins by providing the identifying information, backed by citations and other identifiers of the papers. Then, the major elements are summarised to make the reader aware of the study. It is followed by the methodology and all-important findings from the study. The conclusion then presents study results and ends the abstract with a comprehensive summary.
In a nutshell, an informative abstract:
- Has a length that can vary, based on the subject, but is not longer than 300 words.
- Contains all the content-like methods and intentions
- Offers evidence and possible recommendations.
Informative Abstracts are more frequent than descriptive abstracts because of their extensive content and linkage to the topic specifically. You should select different types of abstracts to papers based on their length: informative abstracts for extended and more complex abstracts and descriptive ones for simpler and shorter research papers.
What are the Characteristics of a Good Abstract?
- A good abstract clearly defines the goals and purposes of the study.
- It should clearly describe the research methodology with a primary focus on data gathering, processing, and subsequent analysis.
- A good abstract should provide specific research findings.
- It presents the principal conclusions of the systematic study.
- It should be concise, clear, and relevant to the field of study.
- A well-designed abstract should be unifying and coherent.
- It is easy to grasp and free of technical jargon.
- It is written impartially and objectively.
What are the various sections of an ideal Abstract?
By now, you must have gained some concrete idea of the essential elements that your abstract needs to convey . Accordingly, the information is broken down into six key sections of the abstract, which include:
An Introduction or Background
Research methodology, objectives and goals, limitations.
Let's go over them in detail.
The introduction, also known as background, is the most concise part of your abstract. Ideally, it comprises a couple of sentences. Some researchers only write one sentence to introduce their abstract. The idea behind this is to guide readers through the key factors that led to your study.
It's understandable that this information might seem difficult to explain in a couple of sentences. For example, think about the following two questions like the background of your study:
- What is currently available about the subject with respect to the paper being discussed?
- What isn't understood about this issue? (This is the subject of your research)
While writing the abstract’s introduction, make sure that it is not lengthy. Because if it crosses the word limit, it may eat up the words meant to be used for providing other key information.
Research methodology is where you describe the theories and techniques you used in your research. It is recommended that you describe what you have done and the method you used to get your thorough investigation results. Certainly, it is the second-longest paragraph in the abstract.
In the research methodology section, it is essential to mention the kind of research you conducted; for instance, qualitative research or quantitative research (this will guide your research methodology too) . If you've conducted quantitative research, your abstract should contain information like the sample size, data collection method, sampling techniques, and duration of the study. Likewise, your abstract should reflect observational data, opinions, questionnaires (especially the non-numerical data) if you work on qualitative research.
The research objectives and goals speak about what you intend to accomplish with your research. The majority of research projects focus on the long-term effects of a project, and the goals focus on the immediate, short-term outcomes of the research. It is possible to summarise both in just multiple sentences.
In stating your objectives and goals, you give readers a picture of the scope of the study, its depth and the direction your research ultimately follows. Your readers can evaluate the results of your research against the goals and stated objectives to determine if you have achieved the goal of your research.
In the end, your readers are more attracted by the results you've obtained through your study. Therefore, you must take the time to explain each relevant result and explain how they impact your research. The results section exists as the longest in your abstract, and nothing should diminish its reach or quality.
One of the most important things you should adhere to is to spell out details and figures on the results of your research.
Instead of making a vague assertion such as, "We noticed that response rates varied greatly between respondents with high incomes and those with low incomes", Try these: "The response rate was higher for high-income respondents than those with lower incomes (59 30 percent vs. 30 percent in both cases; P<0.01)."
You're likely to encounter certain obstacles during your research. It could have been during data collection or even during conducting the sample . Whatever the issue, it's essential to inform your readers about them and their effects on the research.
Research limitations offer an opportunity to suggest further and deep research. If, for instance, you were forced to change for convenient sampling and snowball samples because of difficulties in reaching well-suited research participants, then you should mention this reason when you write your research abstract. In addition, a lack of prior studies on the subject could hinder your research.
Your conclusion should include the same number of sentences to wrap the abstract as the introduction. The majority of researchers offer an idea of the consequences of their research in this case.
Your conclusion should include three essential components:
- A significant take-home message.
- Corresponding important findings.
- The Interpretation.
Even though the conclusion of your abstract needs to be brief, it can have an enormous influence on the way that readers view your research. Therefore, make use of this section to reinforce the central message from your research. Be sure that your statements reflect the actual results and the methods you used to conduct your research.
Good Abstract Examples
Abstract example #1.
Children’s consumption behavior in response to food product placements in movies.
The abstract:
"Almost all research into the effects of brand placements on children has focused on the brand's attitudes or behavior intentions. Based on the significant differences between attitudes and behavioral intentions on one hand and actual behavior on the other hand, this study examines the impact of placements by brands on children's eating habits. Children aged 6-14 years old were shown an excerpt from the popular film Alvin and the Chipmunks and were shown places for the item Cheese Balls. Three different versions were developed with no placements, one with moderately frequent placements and the third with the highest frequency of placement. The results revealed that exposure to high-frequency places had a profound effect on snack consumption, however, there was no impact on consumer attitudes towards brands or products. The effects were not dependent on the age of the children. These findings are of major importance to researchers studying consumer behavior as well as nutrition experts as well as policy regulators."
Abstract Example #2
Social comparisons on social media: The impact of Facebook on young women’s body image concerns and mood. The abstract:
"The research conducted in this study investigated the effects of Facebook use on women's moods and body image if the effects are different from an internet-based fashion journal and if the appearance comparison tendencies moderate one or more of these effects. Participants who were female ( N = 112) were randomly allocated to spend 10 minutes exploring their Facebook account or a magazine's website or an appearance neutral control website prior to completing state assessments of body dissatisfaction, mood, and differences in appearance (weight-related and facial hair, face, and skin). Participants also completed a test of the tendency to compare appearances. The participants who used Facebook were reported to be more depressed than those who stayed on the control site. In addition, women who have the tendency to compare appearances reported more facial, hair and skin-related issues following Facebook exposure than when they were exposed to the control site. Due to its popularity it is imperative to conduct more research to understand the effect that Facebook affects the way people view themselves."
Abstract Example #3
The Relationship Between Cell Phone Use and Academic Performance in a Sample of U.S. College Students
"The cellphone is always present on campuses of colleges and is often utilised in situations in which learning takes place. The study examined the connection between the use of cell phones and the actual grades point average (GPA) after adjusting for predictors that are known to be a factor. In the end 536 students in the undergraduate program from 82 self-reported majors of an enormous, public institution were studied. Hierarchical analysis ( R 2 = .449) showed that use of mobile phones is significantly ( p < .001) and negative (b equal to -.164) connected to the actual college GPA, after taking into account factors such as demographics, self-efficacy in self-regulated learning, self-efficacy to improve academic performance, and the actual high school GPA that were all important predictors ( p < .05). Therefore, after adjusting for other known predictors increasing cell phone usage was associated with lower academic performance. While more research is required to determine the mechanisms behind these results, they suggest the need to educate teachers and students to the possible academic risks that are associated with high-frequency mobile phone usage."
Quick tips on writing a good abstract
There exists a common dilemma among early age researchers whether to write the abstract at first or last? However, it's recommended to compose your abstract when you've completed the research since you'll have all the information to give to your readers. You can, however, write a draft at the beginning of your research and add in any gaps later.
If you find abstract writing a herculean task, here are the few tips to help you with it:
1. Always develop a framework to support your abstract
Before writing, ensure you create a clear outline for your abstract. Divide it into sections and draw the primary and supporting elements in each one. You can include keywords and a few sentences that convey the essence of your message.
2. Review Other Abstracts
Abstracts are among the most frequently used research documents, and thousands of them were written in the past. Therefore, prior to writing yours, take a look at some examples from other abstracts. There are plenty of examples of abstracts for dissertations in the dissertation and thesis databases.
3. Avoid Jargon To the Maximum
When you write your abstract, focus on simplicity over formality. You should write in simple language, and avoid excessive filler words or ambiguous sentences. Keep in mind that your abstract must be readable to those who aren't acquainted with your subject.
4. Focus on Your Research
It's a given fact that the abstract you write should be about your research and the findings you've made. It is not the right time to mention secondary and primary data sources unless it's absolutely required.
Conclusion: How to Structure an Interesting Abstract?
Abstracts are a short outline of your essay. However, it's among the most important, if not the most important. The process of writing an abstract is not straightforward. A few early-age researchers tend to begin by writing it, thinking they are doing it to "tease" the next step (the document itself). However, it is better to treat it as a spoiler.
The simple, concise style of the abstract lends itself to a well-written and well-investigated study. If your research paper doesn't provide definitive results, or the goal of your research is questioned, so will the abstract. Thus, only write your abstract after witnessing your findings and put your findings in the context of a larger scenario.
The process of writing an abstract can be daunting, but with these guidelines, you will succeed. The most efficient method of writing an excellent abstract is to centre the primary points of your abstract, including the research question and goals methods, as well as key results.
Interested in learning more about dedicated research solutions? Go to the SciSpace product page to find out how our suite of products can help you simplify your research workflows so you can focus on advancing science.

The best-in-class solution is equipped with features such as literature search and discovery, profile management, research writing and formatting, and so much more.
But before you go,
You might also like.

Consensus GPT vs. SciSpace GPT: Choose the Best GPT for Research

Literature Review and Theoretical Framework: Understanding the Differences

Types of Essays in Academic Writing - Quick Guide (2024)
How to Write an Abstract APA Format
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
An APA abstract is a brief, comprehensive summary of the contents of an article, research paper, dissertation, or report.
It is written in accordance with the guidelines of the American Psychological Association (APA), which is a widely used format in social and behavioral sciences.
An APA abstract summarizes, usually in one paragraph of between 150–250 words, the major aspects of a research paper or dissertation in a prescribed sequence that includes:
- The rationale: the overall purpose of the study, providing a clear context for the research undertaken.
- Information regarding the method and participants: including materials/instruments, design, procedure, and data analysis.
- Main findings or trends: effectively highlighting the key outcomes of the hypotheses.
- Interpretations and conclusion(s): solidify the implications of the research.
- Keywords related to the study: assist the paper’s discoverability in academic databases.
The abstract should stand alone, be “self-contained,” and make sense to the reader in isolation from the main article.
The purpose of the abstract is to give the reader a quick overview of the essential information before reading the entire article. The abstract is placed on its own page, directly after the title page and before the main body of the paper.
Although the abstract will appear as the very first part of your paper, it’s good practice to write your abstract after you’ve drafted your full paper, so that you know what you’re summarizing.
Note : This page reflects the latest version of the APA Publication Manual (i.e., APA 7), released in October 2019.
Structure of the Abstract
[NOTE: DO NOT separate the components of the abstract – it should be written as a single paragraph. This section is separated to illustrate the abstract’s structure.]
1) The Rationale
One or two sentences describing the overall purpose of the study and the research problem(s) you investigated. You are basically justifying why this study was conducted.
- What is the importance of the research?
- Why would a reader be interested in the larger work?
- For example, are you filling a gap in previous research or applying new methods to take a fresh look at existing ideas or data?
- Women who are diagnosed with breast cancer can experience an array of psychosocial difficulties; however, social support, particularly from a spouse, has been shown to have a protective function during this time. This study examined the ways in which a woman’s daily mood, pain, and fatigue, and her spouse’s marital satisfaction predict the woman’s report of partner support in the context of breast cancer.
- The current nursing shortage, high hospital nurse job dissatisfaction, and reports of uneven quality of hospital care are not uniquely American phenomena.
- Students with special educational needs and disabilities (SEND) are more likely to exhibit behavioral difficulties than their typically developing peers. The aim of this study was to identify specific risk factors that influence variability in behavior difficulties among individuals with SEND.
2) The Method
Information regarding the participants (number, and population). One or two sentences outlining the method, explaining what was done and how. The method is described in the present tense.
- Pretest data from a larger intervention study and multilevel modeling were used to examine the effects of women’s daily mood, pain, and fatigue and average levels of mood, pain, and fatigue on women’s report of social support received from her partner, as well as how the effects of mood interacted with partners’ marital satisfaction.
- This paper presents reports from 43,000 nurses from more than 700 hospitals in the United States, Canada, England, Scotland, and Germany in 1998–1999.
- The study sample comprised 4,228 students with SEND, aged 5–15, drawn from 305 primary and secondary schools across England. Explanatory variables were measured at the individual and school levels at baseline, along with a teacher-reported measure of behavior difficulties (assessed at baseline and the 18-month follow-up).
3) The Results
One or two sentences indicating the main findings or trends found as a result of your analysis. The results are described in the present or past tense.
- Results show that on days in which women reported higher levels of negative or positive mood, as well as on days they reported more pain and fatigue, they reported receiving more support. Women who, on average, reported higher levels of positive mood tended to report receiving more support than those who, on average, reported lower positive mood. However, average levels of negative mood were not associated with support. Higher average levels of fatigue but not pain were associated with higher support. Finally, women whose husbands reported higher levels of marital satisfaction reported receiving more partner support, but husbands’ marital satisfaction did not moderate the effect of women’s mood on support.
- Nurses in countries with distinctly different healthcare systems report similar shortcomings in their work environments and the quality of hospital care. While the competence of and relation between nurses and physicians appear satisfactory, core problems in work design and workforce management threaten the provision of care.
- Hierarchical linear modeling of data revealed that differences between schools accounted for between 13% (secondary) and 15.4% (primary) of the total variance in the development of students’ behavior difficulties, with the remainder attributable to individual differences. Statistically significant risk markers for these problems across both phases of education were being male, eligibility for free school meals, being identified as a bully, and lower academic achievement. Additional risk markers specific to each phase of education at the individual and school levels are also acknowledged.
4) The Conclusion / Implications
A brief summary of your conclusions and implications of the results, described in the present tense. Explain the results and why the study is important to the reader.
- For example, what changes should be implemented as a result of the findings of the work?
- How does this work add to the body of knowledge on the topic?
Implications of these findings are discussed relative to assisting couples during this difficult time in their lives.
- Resolving these issues, which are amenable to managerial intervention, is essential to preserving patient safety and care of consistently high quality.
- Behavior difficulties are affected by risks across multiple ecological levels. Addressing any one of these potential influences is therefore likely to contribute to the reduction in the problems displayed.
The above examples of abstracts are from the following papers:
Aiken, L. H., Clarke, S. P., Sloane, D. M., Sochalski, J. A., Busse, R., Clarke, H., … & Shamian, J. (2001). Nurses’ reports on hospital care in five countries . Health affairs, 20(3) , 43-53.
Boeding, S. E., Pukay-Martin, N. D., Baucom, D. H., Porter, L. S., Kirby, J. S., Gremore, T. M., & Keefe, F. J. (2014). Couples and breast cancer: Women’s mood and partners’ marital satisfaction predicting support perception . Journal of Family Psychology, 28(5) , 675.
Oldfield, J., Humphrey, N., & Hebron, J. (2017). Risk factors in the development of behavior difficulties among students with special educational needs and disabilities: A multilevel analysis . British journal of educational psychology, 87(2) , 146-169.
5) Keywords
APA style suggests including a list of keywords at the end of the abstract. This is particularly common in academic articles and helps other researchers find your work in databases.
Keywords in an abstract should be selected to help other researchers find your work when searching an online database. These keywords should effectively represent the main topics of your study. Here are some tips for choosing keywords:
Core Concepts: Identify the most important ideas or concepts in your paper. These often include your main research topic, the methods you’ve used, or the theories you’re discussing.
Specificity: Your keywords should be specific to your research. For example, suppose your paper is about the effects of climate change on bird migration patterns in a specific region. In that case, your keywords might include “climate change,” “bird migration,” and the region’s name.
Consistency with Paper: Make sure your keywords are consistent with the terms you’ve used in your paper. For example, if you use the term “adolescent” rather than “teen” in your paper, choose “adolescent” as your keyword, not “teen.”
Jargon and Acronyms: Avoid using too much-specialized jargon or acronyms in your keywords, as these might not be understood or used by all researchers in your field.
Synonyms: Consider including synonyms of your keywords to capture as many relevant searches as possible. For example, if your paper discusses “post-traumatic stress disorder,” you might include “PTSD” as a keyword.
Remember, keywords are a tool for others to find your work, so think about what terms other researchers might use when searching for papers on your topic.
The Abstract SHOULD NOT contain:
Lengthy background or contextual information: The abstract should focus on your research and findings, not general topic background.
Undefined jargon, abbreviations, or acronyms: The abstract should be accessible to a wide audience, so avoid highly specialized terms without defining them.
Citations: Abstracts typically do not include citations, as they summarize original research.
Incomplete sentences or bulleted lists: The abstract should be a single, coherent paragraph written in complete sentences.
New information not covered in the paper: The abstract should only summarize the paper’s content.
Subjective comments or value judgments: Stick to objective descriptions of your research.
Excessive details on methods or procedures: Keep descriptions of methods brief and focused on main steps.
Speculative or inconclusive statements: The abstract should state the research’s clear findings, not hypotheses or possible interpretations.
- Any illustration, figure, table, or references to them . All visual aids, data, or extensive details should be included in the main body of your paper, not in the abstract.
- Elliptical or incomplete sentences should be avoided in an abstract . The use of ellipses (…), which could indicate incomplete thoughts or omitted text, is not appropriate in an abstract.
APA Style for Abstracts
An APA abstract must be formatted as follows:
Include the running head aligned to the left at the top of the page (professional papers only) and page number. Note, student papers do not require a running head. On the first line, center the heading “Abstract” and bold (do not underlined or italicize). Do not indent the single abstract paragraph (which begins one line below the section title). Double-space the text. Use Times New Roman font in 12 pt. Set one-inch (or 2.54 cm) margins. If you include a “keywords” section at the end of the abstract, indent the first line and italicize the word “Keywords” while leaving the keywords themselves without any formatting.
Example APA Abstract Page
Download this example as a PDF

Further Information
- APA 7th Edition Abstract and Keywords Guide
- Example APA Abstract
- How to Write a Good Abstract for a Scientific Paper or Conference Presentation
- How to Write a Lab Report
- Writing an APA paper
How long should an APA abstract be?
An APA abstract should typically be between 150 to 250 words long. However, the exact length may vary depending on specific publication or assignment guidelines. It is crucial that it succinctly summarizes the essential elements of the work, including purpose, methods, findings, and conclusions.

Where does the abstract go in an APA paper?
In an APA formatted paper, the abstract is placed on its own page, directly after the title page and before the main body of the paper. It’s typically the second page of the document. It starts with the word “Abstract” (centered and not in bold) at the top of the page, followed by the text of the abstract itself.
What are the 4 C’s of abstract writing?
The 4 C’s of abstract writing are an approach to help you create a well-structured and informative abstract. They are:
Conciseness: An abstract should briefly summarize the key points of your study. Stick to the word limit (typically between 150-250 words for an APA abstract) and avoid unnecessary details.
Clarity: Your abstract should be easy to understand. Avoid jargon and complex sentences. Clearly explain the purpose, methods, results, and conclusions of your study.
Completeness: Even though it’s brief, the abstract should provide a complete overview of your study, including the purpose, methods, key findings, and your interpretation of the results.
Cohesion: The abstract should flow logically from one point to the next, maintaining a coherent narrative about your study. It’s not just a list of disjointed elements; it’s a brief story of your research from start to finish.
What is the abstract of a psychology paper?
An abstract in a psychology paper serves as a snapshot of the paper, allowing readers to quickly understand the purpose, methodology, results, and implications of the research without reading the entire paper. It is generally between 150-250 words long.
- - Google Chrome
Intended for healthcare professionals
- Access provided by Google Indexer
- My email alerts
- BMA member login
- Username * Password * Forgot your log in details? Need to activate BMA Member Log In Log in via OpenAthens Log in via your institution

Search form
- Advanced search
- Search responses
- Search blogs
- How to write an...
How to write an abstract that will be accepted
- Related content
- Peer review
- Mary Higgins , fellow in maternal fetal medicine 1 ,
- Maeve Eogan , consultant obstetrician and gynaecologist 2 ,
- Keelin O’Donoghue , consultant obstetrician and gynaecologist, and senior lecturer 3 ,
- Noirin Russell , consultant obstetrician and gynaecologist 3
- 1 Mount Sinai Hospital, Toronto, Ontario, Canada
- 2 Rotunda Hospital Dublin, Ireland
- 3 Cork University Maternity Hospital, Ireland
- mairenihuigin{at}gmail.com
Researchers do not always appreciate the importance of producing a good abstract or understand the best way of writing one. Mary Higgins and colleagues share some of the lessons they have learnt as both researchers and reviewers of abstracts
Effective abstracts reflect the time, work, and importance of the scientific research performed in the course of a study. A last minute approach and poor writing may not reflect the good quality of a study.
Between the four of us we have written over 150 published papers, as well as having reviewed numerous abstracts for national and international meetings. Nevertheless, we have all had abstracts rejected, and this experience has emphasised a number of teaching points that could help maximise the impact of abstracts and success on the world, or other, stage.
An abstract is the first glimpse an audience has of a study, and it is the ticket to having research accepted for presentation to a wider audience. For a study to receive the respect it deserves, the abstract should be as well written as possible. In practice, this means taking time to write the abstract, keeping it simple, reading the submission guidelines, checking the text, and showing the abstract to colleagues.
It is important to take the necessary time to write the abstract. Several months or years have been spent on this groundbreaking research, so take the time to show this. Five minutes before the call for abstracts closes is not the time to start putting it together.
Keep it simple, and think about the message that needs to be communicated. Some abstracts churn out lots of unrelated results and then have a conclusion that does not relate to the results, and this is just confusing. Plan what points need to be made, and then think about them a little more.
Read the submission guidelines and keep to the instructions provided in the call for abstracts. Don’t submit an unstructured abstract if the guidance has asked for a structured one. Comply with the word or letter count, and do not go over this.
An abstract comprises five parts of equal importance: the title, introduction and aims, methods, results, and conclusion. Allow enough time to write each part well.
The title should go straight to the point of the study. Make the study sound interesting so that it catches people’s attention. The introduction should include a brief background to the research and describe its aims. For every aim presented there needs to be a corresponding result in the results section. There is no need to go into detail in terms of the background to the study, as those who are reviewing the abstract will have some knowledge of the subject. The methods section can be kept simple—it is acceptable to write “retrospective case-control study” or “randomised controlled trial.”
The results section should be concrete and related to the aims. It is distracting and irritating to read results that have no apparent relation to the professed aims of the study. If something is important, highlight it or put it in italics to make it stand out. Include the number of participants, and ensure recognition is given if 10 000 charts have been reviewed. Equally, a percentage without a baseline number is not meaningful.
In the conclusion, state succinctly what can be drawn from the results, but don’t oversell this. Words like “possibly” and “may” can be useful in this part of the abstract but show that some thought has been put into what the results may mean. This is what divides the good from the not so good. Many people are capable of doing research, but the logical formation of a hypothesis and the argument of its proof are what make a real researcher.
Once you have written the abstract, check the spelling and grammar. Poor spelling or grammar can give the impression that the research is also poor. Show the abstract to the supervisor or principal investigator of the study, as this person’s name will go on the abstract as well. Then show the abstract to someone who knows nothing about the particular area of research but who knows something about the subject. Someone detached from the study might point out the one thing that needs to be said but that has been forgotten.
Then let it go; abstracts are not life and death scenarios. Sometimes an abstract will not be accepted no matter how wonderful it is. Perhaps there is a theme to the meeting, into which the research does not fit. Reviewers may also be looking for particular things. For one conference, we limited the number of case reports so that only about 10% were accepted. It may be that your research is in a popular or topical area and not all abstracts in that area can be chosen. On occasions, politics play a part, and individual researchers have little control over that.
Finally, remember that sometimes even the best reviewer may not appreciate the subtleties of your research and another audience may be more appreciative.
Competing interests: We have read and understood the BMJ Group policy on declaration of interests and have no relevant interests to declare.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Scholars often write abstracts for various applications: conference presentations may require an abstract or other short summary for a program; journal articles almost always require abstracts; invited talks and lectures are often advertised using an abstract. While the application may necessarily change the length of the abstract (a conference program may only allow for 50-75 words, for instance), the purpose and structure remains fairly constant.
Abstracts are generally kept brief (approximately 150-200 words). They differ by field, but in general, they need to summarize the article so that readers can decide if it is relevant to their work. The typical abstract includes these elements:
- A statement of the problem and objectives
- A statement of the significance of the work
- A summary of employed methods or your research approach
- A summary of findings or conclusions of the study
- A description of the implications of the findings
Regardless of field, abstract authors should explain the purpose of the work, methods used, the results and the conclusions that can be drawn. However, each field purports slightly different ways to structure the abstract. A reliable strategy is to write the abstract as a condensed version of your article, with 1-2 sentences summarizing each major section. This means that in many of the sciences and a large portion of the humanities, abstracts follow a version of the IMRAD structure: Introduction, Methods, Results, and Discussion.
Most scientific journals require authors to submit such abstracts. It is generally advisable to write the abstract in the English language. That is because most papers in other languages, especially Asian nations, tend to publish an English abstract with common search engines, such as, the MLA site.
Example Abstract
This example abstract follows the IMRAD structure closely. The first two sentences are the introduction and background information. Sentences 3-5 describe the methods used in the study. Sentence 6 summarizes the results, while the last two sentences summarize the discussion and conclusion of the study; they also indicate the significance of the results.
Usability and User-Centered Theory for 21 st Century OWLs — by Dana Lynn Driscoll, H. Allen Brizee, Michael Salvo, and Morgan Sousa from The Handbook of Research on Virtual Workplaces and the New Nature of Business Practices . Eds. Kirk St. Amant and Pavel Zemlansky. Hershey, PA: Idea Group Publishing, 2008.
This article describes results of usability research conducted on the Purdue Online Writing Lab (OWL). The Purdue OWL is an information-rich educational website that provides free writing resources to users worldwide. Researchers conducted two generations of usability tests. In the first test, participants were asked to navigate the OWL and answer questions. Results of the first test and user-centered scholarship indicated that a more user-centered focus would improve usability. The second test asked participants to answer writing-related questions using both the OWL website and a user-centered OWL prototype. Participants took significantly less time to find information using the prototype and reported a more positive response to the user-centered prototype than the original OWL. Researchers conclude that a user-centered website is more effective and can be a model for information-rich online resources. Researchers also conclude that usability research can be a productive source of ideas, underscoring the need for participatory invention.
How to Write an Abstract?
- Open Access
- First Online: 24 October 2021
Cite this chapter
You have full access to this open access chapter

- Samiran Nundy 4 ,
- Atul Kakar 5 &
- Zulfiqar A. Bhutta 6
55k Accesses
5 Altmetric
An abstract is a crisp, short, powerful, and self-contained summary of a research manuscript used to help the reader swiftly determine the paper’s purpose. Although the abstract is the first paragraph of the manuscript it should be written last when all the other sections have been addressed.
Research is formalized curiosity. It is poking and prying with a purpose. — Zora Neale Hurston, American Author, Anthropologist and Filmmaker (1891–1960)
You have full access to this open access chapter, Download chapter PDF
Similar content being viewed by others

Writing the Abstract

Abstract and Keywords

Additional Commentaries
1 what is an abstract.
An abstract is usually a standalone document that informs the reader about the details of the manuscript to follow. It is like a trailer to a movie, if the trailer is good, it stimulates the audience to watch the movie. The abstract should be written from scratch and not ‘cut –and-pasted’ [ 1 ].
2 What is the History of the Abstract?
An abstract, in the form of a single paragraph, was first published in the Canadian Medical Association Journal in 1960 with the idea that the readers may not have enough time to go through the whole paper, and the first abstract with a defined structure was published in 1991 [ 2 ]. The idea sold and now most original articles and reviews are required to have a structured abstract. The abstract attracts the reader to read the full manuscript [ 3 ].
3 What are the Qualities of a Good Abstract?
The quality of information in an abstract can be summarized by four ‘C’s. It should be:
C: Condensed
C: Critical
4 What are the Types of Abstract?
Before writing the abstract, you need to check with the journal website about which type of abstract it requires, with its length and style in the ‘Instructions to Authors’ section.
The abstract types can be divided into:
Descriptive: Usually written for psychology, social science, and humanities papers. It is about 50–100 words long. No conclusions can be drawn from this abstract as it describes the major points in the paper.
Informative: The majority of abstracts for science-related manuscripts are informative and are surrogates for the research done. They are single paragraphs that provide the reader an overview of the research paper and are about 100–150 words in length. Conclusions can be drawn from the abstracts and in the recommendations written in the last line.
Critical: This type of abstract is lengthy and about 400–500 words. In this, the authors’ own research is discussed for reliability, judgement, and validation. A comparison is also made with similar studies done earlier.
Highlighting: This is rarely used in scientific writing. The style of the abstract is to attract more readers. It is not a balanced or complete overview of the article with which it is published.
Structured: A structured abstract contains information under subheadings like background, aims, material and methods, results, conclusion, and recommendations (Fig. 15.1 ). Most leading journals now carry these.
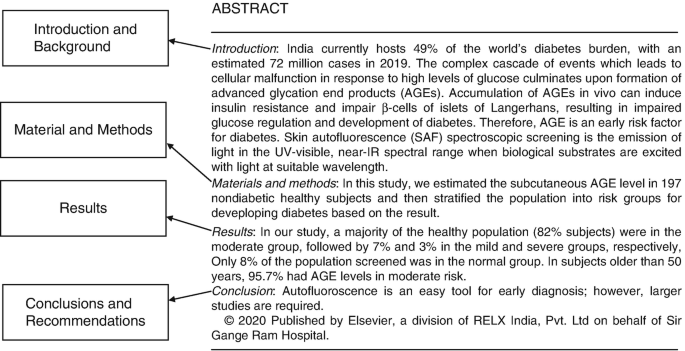
Example of a structured abstract (with permission editor CMRP)
5 What is the Purpose of an Abstract?
An abstract is written to educate the reader about the study that follows and provide an overview of the science behind it. If written well it also attracts more readers to the article. It also helps the article getting indexed. The fate of a paper both before and after publication often depends upon its abstract. Most readers decide if a paper is worth reading on the basis of the abstract. Additionally, the selection of papers in systematic reviews is often dependent upon the abstract.
6 What are the Steps of Writing an Abstract?
An abstract should be written last after all the other sections of an article have been addressed. A poor abstract may turn off the reader and they may cause indexing errors as well. The abstract should state the purpose of the study, the methodology used, and summarize the results and important conclusions. It is usually written in the IMRAD format and is called a structured abstract [ 4 , 5 ].
I: The introduction in the opening line should state the problem you are addressing.
M: Methodology—what method was chosen to finish the experiment?
R: Results—state the important findings of your study.
D: Discussion—discuss why your study is important.
Mention the following information:
Important results with the statistical information ( p values, confidence intervals, standard/mean deviation).
Arrange all information in a chronological order.
Do not repeat any information.
The last line should state the recommendations from your study.
The abstract should be written in the past tense.
7 What are the Things to Be Avoided While Writing an Abstract?
Cut and paste information from the main text
Hold back important information
Use abbreviations
Tables or Figures
Generalized statements
Arguments about the study

8 What are Key Words?
These are important words that are repeated throughout the manuscript and which help in the indexing of a paper. Depending upon the journal 3–10 key words may be required which are indexed with the help of MESH (Medical Subject Heading).
9 How is an Abstract Written for a Conference Different from a Journal Paper?
The basic concept for writing abstracts is the same. However, in a conference abstract occasionally a table or figure is allowed. A word limit is important in both of them. Many of the abstracts which are presented in conferences are never published in fact one study found that only 27% of the abstracts presented in conferences were published in the next five years [ 6 ].
Table 15.1 gives a template for writing an abstract.
10 What are the Important Recommendations of the International Committees of Medical Journal of Editors?
The recommendations are [ 7 ]:
An abstract is required for original articles, metanalysis, and systematic reviews.
A structured abstract is preferred.
The abstract should mention the purpose of the scientific study, how the procedure was carried out, the analysis used, and principal conclusion.
Clinical trials should be reported according to the CONSORT guidelines.
The trials should also mention the funding and the trial number.
The abstract should be accurate as many readers have access only to the abstract.
11 Conclusions
An Abstract should be written last after all the other sections of the manuscript have been completed and with due care and attention to the details.
It should be structured and written in the IMRAD format.
For many readers, the abstract attracts them to go through the complete content of the article.
The abstract is usually followed by key words that help to index the paper.
Andrade C. How to write a good abstract for a scientific paper or conference presentation? Indian J Psychiatry. 2011;53:172–5.
Article Google Scholar
Squires BP. Structured abstracts of original research and review articles. CMAJ. 1990;143:619–22.
CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Pierson DJ. How to write an abstract that will be accepted for presentation at a national meeting. Respir Care. 2004 Oct;49:1206–12.
PubMed Google Scholar
Tenenbein M. The abstract and the academic clinician. Pediatr Emerg Care. 1995;11:40–2.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Bahadoran Z, Mirmiran P, Kashfi K, Ghasemi A. The principles of biomedical scientific writing: abstract and keywords. Int J Endocrinol Metab. 2020;18:e100159.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Grover S, Dalton N. Abstract to publication rate: do all the papers presented in conferences see the light of being a full publication? Indian J Psychiatry. 2020;62:73–9.
Preparing a manuscript for submission to a medical journal. Available on http://www.icmje.org/recommendations/browse/manuscript-preparation/preparing-for-submission.html . Accessed 10 May 2020.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Surgical Gastroenterology and Liver Transplantation, Sir Ganga Ram Hospital, New Delhi, India
Samiran Nundy
Department of Internal Medicine, Sir Ganga Ram Hospital, New Delhi, India
Institute for Global Health and Development, The Aga Khan University, South Central Asia, East Africa and United Kingdom, Karachi, Pakistan
Zulfiqar A. Bhutta
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Rights and permissions
Open Access This chapter is licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ ), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license and indicate if changes were made.
The images or other third party material in this chapter are included in the chapter's Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the chapter's Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder.
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s)
About this chapter
Nundy, S., Kakar, A., Bhutta, Z.A. (2022). How to Write an Abstract?. In: How to Practice Academic Medicine and Publish from Developing Countries?. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-5248-6_15
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-5248-6_15
Published : 24 October 2021
Publisher Name : Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN : 978-981-16-5247-9
Online ISBN : 978-981-16-5248-6
eBook Packages : Medicine Medicine (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- J Indian Prosthodont Soc
- v.13(3); 2013 Sep
How to Write a Scientific Abstract
Suhasini nagda.
Nair Hospital Dental College, Mumbai, India
Scientific publications are an important source of information and knowledge in Academics, Research and development. When articles are submitted for publication, the 1st part that comes across and causes an impact on the minds of the readers is the abstract. It is a concise summary of the paper and must convey the right message. It is a quick overview of the entire paper and giving a gist of the paper and also gives us and insight into whether the paper fulfills the expectations of the reader.
Abstracts are significant parts of academic assignments and research papers. The abstract is written at the end and by this time, the author has a clear picture regarding the findings and conclusions and hence the right message can be put forward.
Types of Scientific Abstracts [ 1 ]
- Descriptive
- Informative
- Semi-structured
- Non structured
Descriptive Abstracts
This type of abstract is usually very short (50–100 words). Most descriptive abstracts have certain key parts in common. They are:
□ Background
□ Purpose
□ Particular interest/focus of paper
□ Overview of contents (not always included)
These abstracts are inconvenient in that, by not including a detailed presentation of the results, it is necessary to have access to the complete article ; they may present the results via a phrase synthesizing them, without contributing numerical or statistical data. Ultimately, these guide readers on the nature of the contents of the article, but it is necessary to read the whole manuscript to know further details [ 1 ].
Informative Abstracts
From these abstracts, you must get the essence of what your report is about, usually in about 200 words. Most informative abstracts also have key parts in common. Each of these parts might consist of 1–2 sentences. The parts include:
□ Aim or purpose of research
□ Method used
□ Findings/results
□ Conclusion
The abstracts provide accurate data on the contents of the work, especially on the results section. Informative abstracts are short scientific productions, since they follow the IMRaD structure [ 2 ] and can in fact replace the whole text, because readers extract from these the most valuable information and in many instances it is not necessary to read the complete text.
Recommendations by the CONSORT [ 3 ] declaration, in its adaptation for abstracts, offer a guide for the elaboration of an abstract of a clinical trial in structured and informative manner, using up to 400 words and briefly including the Title, Methods (participants, interventions, objective, outcomes, randomization, blind tests), Results (number of randomizations, recruitment, number of analyses, outcome, important adverse effects), and Conclusions, registry of the clinical trial and conflict of interests.
Structured Abstracts
A structured abstract has a paragraph for each section: Introduction, Materials and Methods, Results, and Conclusion (it may even include paragraphs for the objectives or other sections). This type of presentation is often required for informative abstracts. The CONSORT [ 3 ] declaration suggests the presentation of clinical trials with structured abstracts . Structuring an abstract permits its informative development
Semi-structured Abstract
A semi-structured abstract is written in only one paragraph, where each sentence corresponds to a section . All the sections of the article are present as in the structured abstract [ 1 ].
Non-structured Abstract
When the abstract does not present divisions between each section , and it may not even present any of them, it is a non-structured abstract. The sentences are included in a sole paragraph. This type of presentation is ideal for descriptive abstracts [ 1 ].
Key Steps to Plan Writing an Abstract [ 4 ]
- Introduction—what is the topic?
- Statement of purpose?
- Summarize why have other studies not tackled similar research questions?
- How has the research question been tackled?
- How was the research done?
- What is the key impact of the research?
Errors in the Creation of an Abstract [ 1 ]
- The abstract of an article should contribute to readers the most relevant aspects of each part of the whole manuscript, maintaining a balance between excessive detail and a vague contribution of information.
- The abstract should be written by adequately selecting the words and sentences to accomplish coherent, clear, and concise contents.
- A common defect is including adequate information like abbreviations, excessive acronyms, bibliographic references, or figures.
- The length of an abstract will be determined by the instructions to authors by each journal; an excessively lengthy abstract is the most frequent error.
- Sections should maintain coherence and order and that the conclusions must be substantiated by the results revealed and respond to the objectives proposed.
- Frequently, abstracts have poorly defined objectives, excessive numerical data and statistical results, and conclusions not based on results presented.
In short, a good abstract is one that:
- Is coherent and concise
- Covers all the essential academic elements of the full-length paper
- Contains no information not included in the paper;
- Is written in plain English and is understandable to a wider audience and discipline-specific audience;
- Uses passive structures in order to report on findings
- Uses the language of the original paper, in a more simplified form
- Usually does not include any referencing; and
- In publications such as journals, it is found at the beginning of the text, but in academic assignments, it is placed on a separate preliminary page.
A good abstract usually ensures a good article, but a bad abstract often points towards an undesirable article. Scientific abstracts are a challenge to write and for the success of our publications, careful and planned writing of the abstract is absolutely essential.
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
Formatting guide
This guide describes how to prepare contributions for submission. We recommend you read this in full if you have not previously submitted a contribution to Nature . We also recommend that, before submission, you familiarize yourself with Nature ’s style and content by reading the journal, either in print or online, particularly if you have not submitted to the journal recently.
Formats for Nature contributions
Articles are the main format for original research contributions to Nature . In addition, Nature publishes other submitted material as detailed below.
Articles are original reports whose conclusions represent a substantial advance in understanding of an important problem and have immediate, far-reaching implications. In print, physical sciences papers do not normally exceed 6 pages on average, and biological, clinical and social-sciences papers do not normally exceed 8 pages on average. However, the final print length is at the editor’s discretion.
Articles start with a fully referenced summary paragraph, ideally of no more than 200 words, which is separate from the main text and avoids numbers, abbreviations, acronyms or measurements unless essential. It is aimed at readers outside the discipline. This summary paragraph should be structured as follows: 2-3 sentences of basic-level introduction to the field; a brief account of the background and rationale of the work; a statement of the main conclusions (introduced by the phrase 'Here we show' or its equivalent); and finally, 2-3 sentences putting the main findings into general context so it is clear how the results described in the paper have moved the field forwards. Please refer to our annotated example to see how the summary paragraph should be constructed.
The typical length of a 6-page article with 4 modest display items (figures and tables) is 2500 words (summary paragraph plus body text). The typical length of an 8-page article with 5-6 modest display items is 4300 words. A ‘modest’ display item is one that, with its legend, occupies about a quarter of a page (equivalent to ~270 words). If a composite figure (with several panels) needs to occupy at least half a page in order for all the elements to be visible, the text length may need to be reduced accordingly to accommodate such figures. Keep in mind that essential but technical details can be moved into the Methods or Supplementary Information.
As a guideline, articles typically have no more than 50 references. (There is no such constraint on any additional references associated with Methods or Supplementary Information.)
Sections are separated with subheadings to aid navigation. Subheadings may be up to 40 characters (including spaces).
Word counts refer to the text of the paper. Title, author list, acknowledgements and references are not included in total word counts.
Matters Arising and Corrections
Matters Arising are exceptionally interesting or important comments and clarifications on original research papers or other peer-reviewed material published within the past 18 months in Nature . They are published online but not in print.
For further details of and instructions for how to submit such comments on peer-reviewed material published in Nature — or to notify editors of the potential need for a correction — please consult our Matters Arising page.
Other contributions to Nature
Please access the other submitted material pages for further details on any of the contribution types below:
News and Comment
Correspondence
Books & Arts
News & Views
Insights, Reviews and Perspectives
Technology Features
The editorial process
See this section for an explanation of Nature 's editorial criteria for publication, refereeing policy and how editors handle papers after submission. Submission to a Nature journal is taken by the journal to mean that all the listed authors have agreed to all of the contents. See authorship policy for more details.
Presubmission enquiries
If you wish to enquire whether your Article might be suitable for consideration by Nature , please use our online presubmission enquiry service . All presubmission enquiries must include a cover paragraph to the editor stating the interest to a broad scientific readership, a fully referenced summary paragraph, and a reference list.
Readability
Nature is an international journal covering all the sciences. Contributions should therefore be written clearly and simply so that they are accessible to readers in other disciplines and to readers for whom English is not their first language. Thus, technical jargon should be avoided as far as possible and clearly explained where its use is unavoidable. Abbreviations, particularly those that are not standard, should also be kept to a minimum. The background, rationale and main conclusions of the study should be clearly explained. Titles and abstracts in particular should be written in language that will be readily intelligible to any scientist. Essential but specialized terms should be explained concisely but not didactically.
For gene, protein and other specialized names authors can use their preferred terminology so long as it is in current use by the community, but they must give all known names for the entity at first use in the paper. Nature prefers authors to use internationally agreed nomenclature. Papers containing new or revised formal taxonomic nomenclature for animals, whether living or extinct, are accepted conditional on the provision of LSIDs (Life Science Identifiers) by means of registration of such nomenclature with ZooBank, the proposed online registration system for the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN).
Even though no paper will be rejected because of poor language, non–native English speakers occasionally receive feedback from editors and reviewers regarding language and grammar usage in their manuscripts. You may wish to consider asking colleagues to read your manuscript and/or to use a professional editing service such as those provided by our affiliates Nature Research Editing Service or American Journal Experts . You can also get a fast, free grammar check of your manuscript that takes into account all aspects of readability in English. Please note that the use of a language editing service is not a requirement for publication in Nature .
Nature 's editors provide detailed advice about the expected print length when asking for the final version of the manuscript. Nature 's editors often suggest revised titles and rewrite the summary paragraphs of Articles so the conclusions are clear to a broad readership.
After acceptance, Nature 's subeditors (copyeditors) ensure that the text and figures are readable and clear to those outside the field, and edit papers into Nature 's house style. They pay particular attention to summary paragraphs, overall clarity, figures, figure legends and titles.
Proofs are sent before publication; authors are welcome to discuss proposed changes with Nature 's subeditors, but Nature reserves the right to make the final decision about matters of style and the size of figures.
A useful set of articles providing general advice about writing and submitting scientific papers can be found on the SciDev.Net website.
Format of Articles
Contributions should be double-spaced and written in English (spellings as in the Oxford English Dictionary ).
Contributions should be organized in the sequence: title, authors, affiliations (plus present addresses), bold first paragraph, main text, main references, tables, figure legends, methods (including separate data and code availability statements), methods references, acknowledgements, author contributions, competing interest declaration, additional information (containing supplementary information line (if any) and corresponding author line), extended data figure/table legends. In order to facilitate the review process, for initial submissions we encourage authors to present the manuscript text and figures together in a single file (Microsoft Word or PDF, up to 30 MB in size). The figures may be inserted within the text at the appropriate positions or grouped at the end, and each figure legend should be presented together with its figure. Also, please include line numbers within the text.
Titles do not exceed two lines in print. This equates to 75 characters (including spaces). Titles do not normally include numbers, acronyms, abbreviations or punctuation. They should include sufficient detail for indexing purposes but be general enough for readers outside the field to appreciate what the paper is about.
An uninterrupted page of text contains about 1250 words.
A typical 6-page Article contains about 2,500 words of text and, additionally, 4 modest display items (figures and/or tables) with brief legends, reference list and online-only methods section if applicable. A composite figure (with several panels) usually needs to take about half a page, equivalent to about 600 words, in order for all the elements to be visible (see section 5.9 for instructions on sizing figures).
A typical 8-page Article contains about 4300 words of text and, additionally, 5-6 modest display items (figures and/or tables) with brief legends, reference list and online-only methods section if applicable. A composite figure (with several panels) usually needs to take about half a page, equivalent to about 600 words, in order for all the elements to be visible (see section 5.9 for instructions on sizing figures).
Authors of contributions that significantly exceed the limits stated here (or as specified by the editor) will have to shorten their papers before acceptance, inevitably delaying publication.
Nature requires authors to specify the contribution made by their co-authors in the end notes of the paper (see section 5.5). If authors regard it as essential to indicate that two or more co-authors are equal in status, they may be identified by an asterisk symbol with the caption ‘These authors contributed equally to this work’ immediately under the address list. If more than three co-authors are equal in status, this should be indicated in the author contributions statement. Present addresses appear immediately below the author list (below the footnote rule at the bottom of the first page) and may be identified by a dagger symbol; all other essential author-related explanation is placed in the acknowledgements.
Our preferred format for text is Microsoft Word, with the style tags removed.
TeX/LaTeX: If you have prepared your paper using TeX/LaTeX, we will need to convert this to Word after acceptance, before your paper can be typeset. All textual material of the paper (including references, tables, figure captions, online methods, etc.) should be included as a single .tex file.
We prefer the use of a ‘standard’ font, preferably 12-point Times New Roman. For mathematical symbols, Greek letters and other special characters, use normal text or Symbol font. Word Equation Editor/MathType should be used only for formulae that cannot be produced using normal text or Symbol font.
The ‘Methods’ section is in the main text file, following the figure legends. This Methods section will appear in the PDF and in the full-text (HTML) version of the paper online, but will not appear in the printed issue. The Methods section should be written as concisely as possible but should contain all elements necessary to allow interpretation and replication of the results. As a guideline, the Methods section does not typically exceed 3,000 words. To increase reproducibility, authors are encouraged to deposit a detailed description of protocols used in their study in a protocol sharing platform of their choice. Springer Nature’s protocols.io is a free and open service designed to help researchers share experimental know-how. Protocols deposited by the authors in www.protocols.io will be linked to the online Methods section upon publication
Detailed descriptions of methods already published should be avoided; a reference number can be provided to save space, with any new addition or variation stated.
The Methods section should be subdivided by short bold headings referring to methods used and we encourage the inclusion of specific subsections for statistics, reagents and animal models. If further references are included in this section their numbering should continue from the end of the last reference number in the rest of the paper and they are listed after the Methods section.
Please provide separate Data Availability and Code Availability statements after the main text statements and before the Extended Data legends; detailed guidance can be found in our data availability and data citations policy . Certain data types must be deposited in an appropriate public structured data depository (details are available here ), and the accession number(s) provided in the manuscript. Full access is required at the time of publication. Should full access to data be required for peer review, authors must provide it.
The Methods section cannot contain figures or tables (essential display items should be included in the Extended Data or exceptionally in the Supplementary Information).
References are each numbered, ordered sequentially as they appear in the text, tables, boxes, figure legends, Methods, Extended Data tables and Extended Data figure legends.
When cited in the text, reference numbers are superscript, not in brackets unless they are likely to be confused with a superscript number.
Do not use linked fields (produced by EndNote and similar programs). Please use the one-click button provided by EndNote to remove EndNote codes before saving your file.
As a guideline, Articles allow up to 50 references in the main text if needed and within the average page budget. Only one publication can be listed for each number. Additional references for Methods or Supplementary Information are not included in this count.
Only articles that have been published or accepted by a named publication, or that have been uploaded to a recognized preprint server (for example, arXiv, bioRxiv), should be in the reference list; papers in preparation should be mentioned in the text with a list of authors (or initials if any of the authors are co-authors of the present contribution).
Published conference abstracts, numbered patents, preprints on recognized servers, papers in press, and research datasets that have been assigned a digital object identifier may be included in reference lists, but text, grant details and acknowledgements may not. (An exception is the highlighted references which we ask authors of Reviews, Perspectives and Insights articles to provide.)
All authors should be included in reference lists unless there are more than five, in which case only the first author should be given, followed by ‘et al.’.
Please follow the style below in the published edition of Nature in preparing reference lists.
Authors should be listed surname first, followed by a comma and initials of given names.
Titles of all cited articles are required. Titles of articles cited in reference lists should be in upright, not italic text; the first word of the title is capitalized, the title written exactly as it appears in the work cited, ending with a full stop. Book titles are italic with all main words capitalized. Journal titles are italic and abbreviated according to common usage. Volume numbers are bold. The publisher and city of publication are required for books cited. (Refer to published papers in Nature for details.)
Research datasets may be cited in the reference list if they have been assigned digital object identifiers (DOIs) and include authors, title, publisher (repository name), identifier (DOI expressed as a URL). Example: Hao, Z., AghaKouchak, A., Nakhjiri, N. & Farahmand, A. Global Integrated Drought Monitoring and Prediction System (GIDMaPS) data sets. figshare http://dx.doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.853801 (2014).
Recognized preprints may be cited in the reference list. Example: Babichev, S. A., Ries, J. & Lvovsky, A. I. Quantum scissors: teleportation of single-mode optical states by means of a nonlocal single photon. Preprint at http://arXiv.org/quant-ph/0208066 (2002).
References to web-only journals should give authors, article title and journal name as above, followed by URL in full - or DOI if known - and the year of publication in parentheses.
References to websites should give authors if known, title of cited page, URL in full, and year of posting in parentheses.
End notes are brief and follow the Methods (or Methods References, if any).
Acknowledgements should be brief, and should not include thanks to anonymous referees and editors, inessential words, or effusive comments. A person can be thanked for assistance, not “excellent” assistance, or for comments, not “insightful” comments, for example. Acknowledgements can contain grant and contribution numbers.
Author Contributions: Authors are required to include a statement to specify the contributions of each co-author. The statement can be up to several sentences long, describing the tasks of individual authors referred to by their initials. See the authorship policy page for further explanation and examples.
Competing interests statement.
Additional Information: Authors should include a set of statements at the end of the paper, in the following order:
Papers containing Supplementary Information contain the statement: “Supplementary Information is available for this paper.”
A sentence reading "Correspondence and requests for materials should be addressed to XX.” Nature expects this identified author to respond to readers’ enquiries and requests for materials, and to coordinate the handling of any other matters arising from the published contribution, including corrections complaints. The author named as corresponding author is not necessarily the senior author, and publication of this author’s name does not imply seniority. Authors may include more than one e-mail address if essential, in which event Nature will communicate with the first-listed address for any post-publication matters, and expect that author to coordinate with the other co-authors.
Peer review information includes the names of reviewers who agree to be cited and is completed by Nature staff during proofing.
A sentence reading “Reprints and permissions information is available at www.nature.com/reprints.”
Life sciences and behavioural & social sciences reporting guidelines
To improve the transparency of reporting and the reproducibility of published results, authors of life sciences and behavioural & social sciences Articles must provide a completed Reporting Summary that will be made available to editors and reviewers during manuscript assessment. The Reporting Summary will be published with all accepted manuscripts.
Please note: because of the advanced features used in these forms, you must use Adobe Reader to open the documents and fill them out.
Guidance and resources related to the use and reporting of statistics are available here .
Tables should each be presented on a separate page, portrait (not landscape) orientation, and upright on the page, not sideways.
Tables have a short, one-line title in bold text. Tables should be as small as possible. Bear in mind the size of a Nature page as a limiting factor when compiling a table.
Symbols and abbreviations are defined immediately below the table, followed by essential descriptive material as briefly as possible, all in double-spaced text.
Standard table formats are available for submissions of cryo-EM , NMR and X-ray crystallography data . Authors providing these data must use these standard tables and include them as Extended Data.
Figure legends
For initial submissions, we encourage authors to present the manuscript text and figures together in a single Word doc or PDF file, and for each figure legend to be presented together with its figure. However, when preparing the final paper to be accepted, we require figure legends to be listed one after the other, as part of the text document, separate from the figure files, and after the main reference list.
Each figure legend should begin with a brief title for the whole figure and continue with a short description of each panel and the symbols used. If the paper contains a Methods section, legends should not contain any details of methods. Legends should be fewer than 300 words each.
All error bars and statistics must be defined in the figure legend, as discussed above.
Nature requires figures in electronic format. Please ensure that all digital images comply with the Nature journals’ policy on image integrity .
Figures should be as small and simple as is compatible with clarity. The goal is for figures to be comprehensible to readers in other or related disciplines, and to assist their understanding of the paper. Unnecessary figures and parts (panels) of figures should be avoided: data presented in small tables or histograms, for instance, can generally be stated briefly in the text instead. Avoid unnecessary complexity, colouring and excessive detail.
Figures should not contain more than one panel unless the parts are logically connected; each panel of a multipart figure should be sized so that the whole figure can be reduced by the same amount and reproduced on the printed page at the smallest size at which essential details are visible. For guidance, Nature ’s standard figure sizes are 90 mm (single column) and 180 mm (double column) and the full depth of the page is 170 mm.
Amino-acid sequences should be printed in Courier (or other monospaced) font using the one-letter code in lines of 50 or 100 characters.
Authors describing chemical structures should use the Nature Research Chemical Structures style guide .
Some brief guidance for figure preparation:
Lettering in figures (labelling of axes and so on) should be in lower-case type, with the first letter capitalized and no full stop.
Units should have a single space between the number and the unit, and follow SI nomenclature or the nomenclature common to a particular field. Thousands should be separated by commas (1,000). Unusual units or abbreviations are defined in the legend.
Scale bars should be used rather than magnification factors.
Layering type directly over shaded or textured areas and using reversed type (white lettering on a coloured background) should be avoided where possible.
Where possible, text, including keys to symbols, should be provided in the legend rather than on the figure itself.
Figure quality
At initial submission, figures should be at good enough quality to be assessed by referees, preferably incorporated into the manuscript text in a single Word doc or PDF, although figures can be supplied separately as JPEGs if authors are unable to include them with the text. Authors are advised to follow the initial and revised submissions guidelines with respect to sizing, resolution and labelling.
Please note that print-publication quality figures are large and it is not helpful to upload them at the submission stage. Authors will be asked for high-quality figures when they are asked to submit the final version of their article for publication.At that stage, please prepare figures according to these guidelines .
Third party rights
Nature discourages the use or adaptation of previously published display items (for example, figures, tables, images, videos or text boxes). However, we recognize that to illustrate some concepts the use of published data is required and the reuse of previously published display items may be necessary. Please note that in these instances we might not be able to obtain the necessary rights for some images to be reused (as is, or adapted versions) in our articles. In such cases, we will contact you to discuss the sourcing of alternative material.
Figure costs
In order to help cover some of the additional cost of four-colour reproduction, Nature Portfolio charges our authors a fee for the printing of their colour figures. Please contact our offices for exact pricing and details. Inability to pay this charge will not prevent publication of colour figures judged essential by the editors, but this must be agreed with the editor prior to acceptance.
Production-quality figures
When a manuscript is accepted in principle for publication, the editor will ask for high-resolution figures. Do not submit publication-quality figures until asked to do so by an editor. At that stage, please prepare figures according to these guidelines .
Extended Data
Extended Data figures and tables are online-only (appearing in the online PDF and full-text HTML version of the paper), peer-reviewed display items that provide essential background to the Article but are not included in the printed version of the paper due to space constraints or being of interest only to a few specialists. A maximum of ten Extended Data display items (figures and tables) is typically permitted. See Composition of a Nature research paper .
Extended Data tables should be formatted along similar lines to tables appearing in print (see section 5.7) but the main body (excluding title and legend, which should be included at the end of the Word file) should be submitted separately as an image rather than as an editable format in Word, as Extended Data tables are not edited by Nature’s subediting department. Small tables may also be included as sub-panels within Extended Data figures. See Extended Data Formatting Guide .
Extended Data figures should be prepared along slightly different guidelines compared to figures appearing in print, and may be multi-panelled as long as they fit to size rules (see Extended Data Formatting Guide ). Extended Data figures are not edited or styled by Nature’s art department; for this reason, authors are requested to follow Nature style as closely as possible when preparing these figures. The legends for Extended Data figures should be prepared as for print figures and should be listed one after the other at the end of the Word file.
If space allows, Nature encourages authors to include a simple schematic, as a panel in an Extended Data figure, that summarizes the main finding of the paper, where appropriate (for example, to assist understanding of complex detail in cell, structural and molecular biology disciplines).
If a manuscript has Extended Data figures or tables, authors are asked to refer to discrete items at an appropriate place in the main text (for example, Extended Data Fig. 1 and Extended Data Table 1).
If further references are included in the Extended Data tables and Extended Data figure legends, the numbering should continue from the end of the last reference number in the main paper (or from the last reference number in the additional Methods section if present) and the list should be added to the end of the list accompanying the additional Methods section, if present, or added below the Extended Data legends if no additional Methods section is present.
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Information (SI) is online-only, peer-reviewed material that is essential background to the Article (for example, large data sets, methods, calculations), but which is too large or impractical, or of interest only to a few specialists, to justify inclusion in the printed version of the paper. See the Supplementary Information page for further details.
Supplementary Information should not contain figures (any figures additional to those appearing in print should be formatted as Extended Data figures). Tables may be included in Supplementary Information, but only if they are unsuitable for formatting as Extended Data tables (for example, tables containing large data sets or raw data that are best suited to Excel files).
If a manuscript has accompanying SI, either at submission or in response to an editor’s letter that requests it, authors are asked to refer to discrete items of the SI (for example, videos, tables) at an appropriate point in the main manuscript.
Chemical structures and characterization of chemical materials
For guidelines describing Nature ’s standards for experimental methods and the characterization of new compounds, please see the information sheet on the characterization of chemical materials .
We aim to produce chemical structures in a consistent format throughout our articles. Please use the Nature Portfolio Chemical Structures Guide and ChemDraw template to ensure that you prepare your figures in a format that will require minimal changes by our art and production teams. Submit final files at 100% as .cdx files.
Registered Reports
Registered Reports are empirical articles testing confirmatory hypotheses in which the methods and proposed analyses are pre-registered and peer reviewed prior to research being conducted. For further details about Registered Reports and instructions for how to submit such articles to Nature please consult our Registered Reports page.
All contributions should be submitted online , unless otherwise instructed by the editors. Please be sure to read the information on what to include in your cover letter as well as several important content-related issues when putting a submission together.
Before submitting, all contributors must agree to all of Nature's publication policies .
Nature authors must make data and materials publicly available upon publication. This includes deposition of data into the relevant databases and arranging for them to be publicly released by the online publication date (not after). A description of our initiative to improve the transparency and the reproducibility of published results is available here . A full description of Nature’s publication policies is at the Nature Portfolio Authors and Referees website .
Other Nature Research journals
An account of the relationship between all the Nature journals is provided at the Nature family page .
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Chemical Communications
Nak alloy as a versatile reagent for template-free synthesis of porous metal- and metalloid-based nanostructures.
Using the strong reduction potential of the liquid NaK-78 alloy, we present a new versatile template-free approach to the synthesis of porous metal- and metalloid-based nanomaterials. With this novel approach, NaK can be simultaneously used as an agent for reduction, structure directing, and pore formation without the use of additional reagents.
Supplementary files
- Supplementary information PDF (1576K)
Article information
Download citation, permissions.
S. S. Leonchuk, A. S. Falchevskaya, P. Morozova, N. V. Gromov and V. V. Vinogradov, Chem. Commun. , 2024, Accepted Manuscript , DOI: 10.1039/D4CC00966E
To request permission to reproduce material from this article, please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page .
If you are an author contributing to an RSC publication, you do not need to request permission provided correct acknowledgement is given.
If you are the author of this article, you do not need to request permission to reproduce figures and diagrams provided correct acknowledgement is given. If you want to reproduce the whole article in a third-party publication (excluding your thesis/dissertation for which permission is not required) please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page .
Read more about how to correctly acknowledge RSC content .
Social activity
Search articles by author.
This article has not yet been cited.
Advertisements
- Open supplemental data
- Reference Manager
- Simple TEXT file
People also looked at
Original research article, purification of linearized template plasmid dna decreases double-stranded rna formation during ivt reaction.

- RNA Synthesis and Development Department, Certest Pharma, Certest Biotec, Zaragoza, Spain
After the COVID-19 pandemic, messenger RNA (mRNA) has revolutionized traditional vaccine manufacturing. With the increasing number of RNA-based therapeutics, valuable new scientific insights into these molecules have emerged. One fascinating area of study is the formation of double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) during in vitro transcription (IVT) which is considered a significant impurity, as it has been identified as a major trigger in the cellular immune response pathway. Therefore, there is a growing importance placed to develop and optimize purification processes for the removal of this by-product. Traditionally, efforts have primarily focused on mRNA purification after IVT through chromatographic separations, with anion exchange and reverse phase chromatography emerging as effective tools for this purpose. However, to the best of our knowledge, the influence and significance of the quality of the linearized plasmid have not been thoroughly investigated. Plasmids production involves the growth of bacterial cultures, bacterial harvesting and lysis, and multiple filtration steps for plasmid DNA purification. The inherent complexity of these molecules, along with the multitude of purification steps involved in their processing, including the subsequent linearization and the less-developed purification techniques for linearized plasmids, often result in inconsistent batches with limited control over by-products such as dsRNA. This study aims to demonstrate how the purification process employed for linearized plasmids can impact the formation of dsRNA. Several techniques for the purification of linearized plasmids based on both, resin filtration and chromatographic separations, have been studied. As a result of that, we have optimized a chromatographic method for purifying linearized plasmids using monolithic columns with C4 chemistry (butyl chains located in the surface of the particles), which has proven successful for mRNAs of various sizes. This chromatographic separation facilitates the generation of homogeneous linearized plasmids, leading to mRNA batches with lower levels of dsRNA during subsequent IVT processes. This finding reveals that dsRNA formation is influenced not only by RNA polymerase and IVT conditions but also by the quality of the linearized template. The results suggest that plasmid impurities may contribute to the production of dsRNA by providing additional templates that can be transcribed into sequences that anneal with the mRNA molecules. This highlights the importance of considering the quality of plasmid purification in relation to dsRNA generation during transcription. Further investigation is needed to fully understand the mechanisms and implications of plasmid-derived dsRNA. This discovery could shift the focus in mRNA vaccine production, placing more emphasis on the purification of linearized plasmids and potentially saving, in some instances, a purification step for mRNA following IVT.
1 Introduction
In recent years, mRNA-based therapies have emerged as highly promising tools in combating infectious diseases, correcting malfunctioning genes, and offering new approaches to tackle pathogens and tumors. The SARS-CoV-2 pandemic has served as a catalyst, propelling advancements in this technology and necessitating the development of production techniques with stringent timelines to address a global health crisis. ( Schlake et al., 2012 ; Kis et al., 2020 ; Whitley et al., 2020 ; Ouranidis et al., 2021 ; Park et al., 2021 ; Sousa et al., 2021 ; Verbeke et al., 2021 ).
Due to the urgent need for mRNA production, IVT processes were developed at a rapid pace, often surpassing the understanding of the molecule itself and the by-products that arise during the transcription process. The transcription of DNA templates into mRNA is facilitated by phage RNA polymerases, such as T7 RNA polymerase (T7 RNAP), which exhibit high fidelity in RNA synthesis. However, the biological process is not entirely efficient, resulting in the generation of certain by-products, albeit at a low frequency. Common non-target molecules include abortive sequences, short transcripts, and dsRNA. ( Mu and Hur, 2021 ).
From the above described, dsRNA moieties have special interest due to inherent immunogenicity that is not desirable in mRNA therapeutic applications. The innate cellular response to dsRNA byproducts, recognized by receptors like TLR3, can adversely affect mRNA therapy efficacy. TLR3 activation by dsRNA involves multiple steps, including dimerization and activation upon dsRNA recognition. This recruits cytoplasmic adapter TRIF, initiating downstream signaling with adaptors like TRAF3 and RIP1. This leads to intracellular signaling events, activating transcription factors IRF3 and NF-κB, which promote immune gene transcription. Additionally, a Src-mediated, adapter-independent TLR3 branch influences cellular properties. In summary, TLR3 activation by dsRNA initiates a complex cascade involving TRIF and transcription factors, inducing immune genes. Src’s adapter-independent branch modulates cellular properties beyond gene induction ( Mu and Hur, 2021 ).
Origin of this double stranded molecule is being studied and is not very well stablished yet. Most of the authors described a great dependence of the T7 RNAP enzyme. It has been described during the initiation of transcription; 5- to 11-nt-long RNA by-products are generated as the enzyme aborts the synthesis with a certain probability ( Milligan et al., 1987 ; Dousis et al., 2022 ).
Several mechanisms have been described to explain the different pathways that lead to these kinds of molecules. One of them, explains that RNA transcript that has been synthesized by the T7 RNAP serves as a template for the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase activity of the T7 RNAP in subsequent rounds of transcription ( Roy and Wu, 2019 ). If the 3′-end of the runoff transcript has sufficient complementarity (in cis), it will fold back and result in extension of the runoff transcript ( Figure 1A ). Another explanation claims that T7 RNAP might use the resulting RNA molecule as template to synthesize the complementary strand in a promoter-independent manner ( Figure 1B ) ( Triana-Alonso et al., 1995 ; Gholamalipour et al., 2018 ). Another mechanism considers that T7 RNAP also has subjacent RNA-dependent as well as template-independent RNA polymerase activity ( Konarska and Sharp, 1989 ; Krupp, 1989 ; Cazenave and Uhlenbeck, 1994 ; Triana-Alonso et al., 1995 ; Biebricher and Luce, 1996 ; Arnaud-Barbe, 1998 ; Nacheva and Berzal-Herranz, 2003 ; Gholamalipour et al., 2018 ). Indeed, the short abortive RNA fragments and the 3‘-end of the full-length RNA can prime complementary RNA synthesis from the primary transcripts that leads to the generation of dsRNA contaminant ( Figure 1C ). However, it is crucial to acknowledge that dsRNA is not a precisely defined individual molecule, but rather a diverse population of molecules with varying sizes and annealing levels.
FIGURE 1 . dsRNA generation mechanisms during IVT. (A) Template strand of DNA is transcribed into mRNA, 3’-extreme loops due to complementarity and T7RNAP uses mRNA as template to continue transcription. (B) Polymerase might switch to the non-template strand and generate the complementary strand of the original mRNA. (C) Abortive fragments during IVT with complementary sequences anneals with the run-off transcript.
The permissible thresholds of dsRNA content exhibit variability contingent upon the designated application, whether within investigative, preclinical, or clinical contexts. Furthermore, these thresholds are inherently contingent upon the inherent characteristics of the mRNA in question. Presently, regulatory entities are diligently engaged in the endeavor to attain a harmonious consensus regarding the precise delineation of specifications governing mRNA vaccines. In accordance with prevailing conventions, it is widely acknowledged that dsRNA content should ideally remain below 0.5% for applications within clinical settings. However, the attainment of such modest dsRNA levels may prove to be a formidable undertaking through mere refinement of IVT conditions. As such, the implementation of supplementary purification protocols invariably becomes imperative to surmount this challenge effectively.
The presence of dsRNA impurities, which share similar physicochemical properties with single-stranded RNA (ssRNA) molecules, poses challenges in their removal during purification processes. Conventional purification methods such as lithium chloride precipitation, size exclusion chromatography, affinity chromatography, or diafiltration are not effective in eliminating dsRNA moieties. Anion exchange chromatography has emerged as good option for dsRNA removal in mRNA polishing (Levanova and Poranen, 2018; Baiersdörfer et al., 2019; Romanovskaya et al., 2013). However, scaling up these chromatographic purifications for industrial production is problematic. Recently, cellulose-based matrix purification methods have been proposed as suitable and simple approaches for dsRNA removal, irrespective of length and nucleoside composition (Baiersdörfer et al., 2019). Another strategy focuses on optimizing the transcription reaction conditions to minimize the production of dsRNA contaminants during IVT instead of relying solely on additional purification steps. Parameters such as reducing Mg2+ concentration (below 10 mM), using modified nucleosides, employing thermally stable T7 RNAP or mutated T7 RNAP, sequence optimization with depletion of U-rich sequences, or RNAse III treatment have been explored to address this issue (Wu et al., 2020; Cavac et al., 2021). It is important to note that the DNA template used in IVT also plays a crucial role, and the generation of dsRNA by-products could be influenced by the quality of the linearized DNA template in addition to the transcription enzyme.
In this study, we have successfully produced a wide range of constructs encompassing different sizes and scales. Additionally, we have thoroughly investigated various reaction conditions and purification methodologies. Commercially available plasmids are manufactured to meet specific customer requirements, and therefore, it is advisable to assess their compliance with specifications and determine the isoform status before commencing work with a new plasmid. The quality of plasmids directly impacts the quality of the resulting linearized template following the digestion step. Throughout our development process, we have observed significant heterogeneity in linearized plasmids, which appears to be dependent on the specific plasmid used. Interestingly, we have discovered a noteworthy correlation between the quality of linearized plasmids and the production of dsRNA. To the best of our knowledge, this study represents the first evidence linking plasmid quality to dsRNA generation during IVT.
One of the primary objectives of optimization is to obtain RNA constructs of exceptionally high quality, with a specific focus on reducing levels of dsRNA. Initially, our efforts were directed towards the purification and refinement of mRNA, as many RNA producers and researchers have done in recent years.( Dickman and Hornby, 2006 ; Jacoby, 2006 ; Mccarthy and Gilar, 2008 ; Karikó et al., 2011 ; Weissman et al., 2013 ; Azarani and Hecker, 2021 ).
Various purification methodologies were combined for both linearized templates and mRNA to determine the optimal combination that would result in the lowest levels of dsRNA. Additionally, considering that dsRNA generation may be influenced by the length of the RNA, we investigated the impact of different construct sizes encoding three different proteins: Green Fluorescence Protein (GFP, 1,000 NTPs long aprox.), Firefly Luciferase (FLuc, 2000 NTPs long aprox.), and the Spike protein for SARS-CoV-2 (COV, 4,000 NTPs long aprox.). To minimize variables in the study and due to therapeutic mRNAs commonly contains modified nucleosides, we chose to employ N1-Me-ψUTP as the modified UTP for the production of all mRNA in this study ( Knezevic et al., 2021 ; Kim et al., 2022 ).
At the first stage, our purification efforts were focused on mRNA that encoded COVID spike protein. After plasmid linearization, IVT crudes were purified by affinity chromatography (Oligo-dT) and levels of dsRNA were measured. It was founded that dsRNA contents were always above 2% and that most of them were higher than 3% ( Figure 2 ). These impurity contents are unacceptable for therapy application, so it was mandatory to set up an additional step of polishing to reduce these amounts.
FIGURE 2 . Comparison of the influence of the template purification method in the content of dsRNA in COVID transcripts. Pointed line represents threshold 1%.
On this regard, it was deemed interesting to compare dsRNA levels when an additional specific dsRNA removing polishing step was added after the DNA resin purification. Typically, tandem affinity (capture step) and anion exchange chromatography (polishing step) is very well known and accepted as a good path to obtain mRNA constructs with low levels of dsRNA and high purity ( Gagnon, 2020 ). It is important to point out, that separation of dsRNA in AEX is usually performed by pH gradient, from 7.2 to 11. It is widely recognized that basic pH enhances RNA degradation by means of internal nucleophilic attack of 2’ hydroxyl to the nearest electrophilic phosphorus breaking the phosphodiester bond ( Chatterjee et al., 2022 ; Fang et al., 2022 ). For this reason, the prompt neutralization of the collected fractions becomes crucially important. However, despite these efforts, a certain degree of degradation was observed. In an attempt to mitigate this degradation during our research, it was discovered that by reversing the order of these steps, improvements in purity were achieved as a result of reduced degradation. ( Figure 3 ).
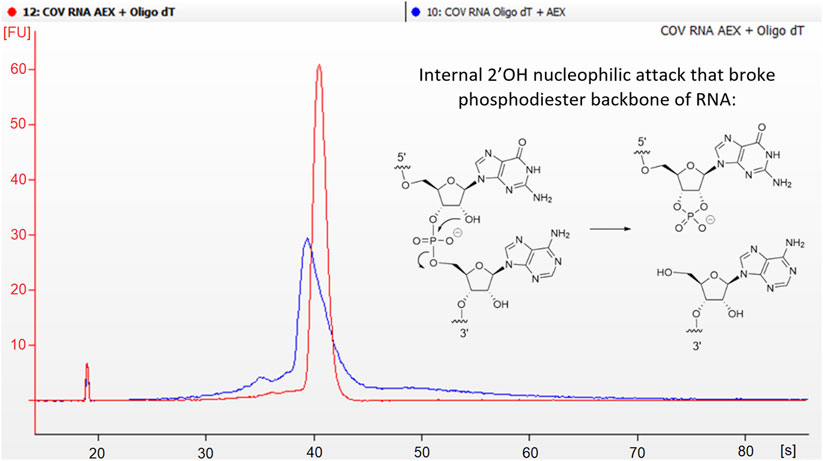
FIGURE 3 . Degradation of mRNA is influenced by the type of purification method employed. Electropherogram comparison between tandem Oligo-dT + AEX (blue line) vs. AEX + Oligo-dT (red line). Blue line shows more degraded profiles. Mechanism of intramolecular hydrolysis of RNA phosphodiester bond.
In order to prevent the loss of integrity, the decision was made to reverse the order of the purification process, starting with anion exchange chromatography (AEX) followed by affinity chromatography. Another commonly employed polishing strategy involves incorporating hydrophobic interaction chromatography (HIC) after affinity purification. Consequently, two additional polishing methods were employed: anion exchange chromatography using either the CIMmultus ® PrimaS ® 1 mL Monolithic Column (2 μm) or the CIMmultus ® C4HLD - 1 mL (2 µm). Both methods have been recognized for their effectiveness in removing dsRNA ( Dickman and Hornby, 2006 ; Jacoby, 2006 ; Mccarthy and Gilar, 2008 ; Karikó et al., 2011 ; Weissman et al., 2013 ; Gagnon, 2020 ; Azarani and Hecker, 2021 ) (Urbas, 2015) ( Mccarthy and Gilar, 2008 ; Podgornik et al., 2013 ; Lee and Barton, 2015 ; Separations, 2020 ).
By implementing the purification and polishing steps as mentioned earlier, we were able to reduce degradation in the final isolated constructs ( Figure 2 ). As anticipated, the additional AEX step resulted in lower levels of dsRNA, with some cases falling below the 1% threshold, thus confirming its efficacy in removing such impurities. However, it was quite surprising to find that HIC was not as effective as AEX in reducing dsRNA levels.
2.1 Influence of purification of linear plasmids in dsRNA content
At this juncture, it is pertinent to recall that the prevailing methodologies employed for dsRNA removal primarily focus on the purification and polishing of mRNA post IVT, often overlooking the significance of purifying the initial linearized plasmid. However, we emphasize the importance of obtaining linear templates with high purity and quality, as they directly impact the levels of dsRNA. In order to investigate this, several batches of linear plasmids were isolated using a resin filtration method employing silica resin (Wizard ® Megapreps DNA Purification Resin, Promega, Cat#A7361) or by hydrophobic chromatography (CIMmultus ® C4HLD—1 mL (2 µm), Sartorius, Cat# 311.8136-2). Then IVT was carried out and the resulting crudes were purified and polished in some cases by Affinity (Oligo-dT) and AEX.
Surprisingly, the linearized plasmids isolated through chromatographic purification exhibited dsRNA levels below the 1% threshold. As anticipated, the subsequent polishing steps further reduced the presence of dsRNA. However, the tandem Oligo-dT/C4 HIC method was not as effective as the Prima S Oligo-dT method in removing double-stranded impurities, as demonstrated in Figure 2 . These findings highlight the significant impact of template purification, which appears to have more influence than previously acknowledged.
These results suggest that based on a good purification method of the starting linearized plasmids, such as hydrophobic chromatography, it is possible to obtain mRNA transcripts that does not require any further polishing step to obtain less percentage of dsRNA.
3 Discussion
The primary objective of this study was to optimize our internal purification methods in order to reduce the presence of dsRNA and enhance the quality of the mRNA. As mentioned previously, significant efforts were dedicated to the polishing step following IVT. Until now, the generation of dsRNA has been largely attributed to the transcription process itself, with a substantial reliance on the polymerase enzyme. ( Konarska and Sharp, 1989 ; Krupp, 1989 ; Cazenave and Uhlenbeck, 1994 ; Triana-Alonso et al., 1995 ; Biebricher and Luce, 1996 ; Arnaud-Barbe, 1998 ; Nacheva and Berzal-Herranz, 2003 ; Gholamalipour et al., 2018 ). According to this theory, it is suggested that pre-IVT processes, such as plasmid linearization, do not have an impact on dsRNA levels Nevertheless, we decided to explore also how pre-IVT factors such as plasmid linearization isolation methods could affect to the production of this important impurity. The recent findings regarding COVID have been highly informative, prompting us to investigate whether the purification of linearized plasmids using hydrophobic C4 columns could also reduce the dsRNA content in transcripts of various lengths or sizes. It is well-known that AEX chromatography has proven to be an effective technique for removing dsRNA. However, we aimed to determine if chromatographic purification of DNA templates alone could achieve dsRNA levels below 1% without the need for an additional mRNA polishing step, relying solely on Oligo-dT purification for the transcripts. In this study, our objective was to establish baseline levels of dsRNA generated without the inclusion of supplementary purification steps aimed at its removal or mitigation. To achieve this, we initiated the synthesis of respective mRNA strands for three designated protein targets from their corresponding linearized templates, followed by template purification utilizing the Wizard ® Megapreps DNA Purification Resin or chromatographic methodologies involving the CIMmultus ® C4HLD matrix. After the purification of templates, an Oligo-dT affinity chromatography process was employed to refine the mRNA constructs, ultimately leading to the acquisition of purified mRNA entities. Subsequently, dsRNA quantification was performed using Dot Blot analysis, as depicted in Figure 4 .
FIGURE 4 . %dsRNA obtained for GFP, Fluc and COV. Linearized DNA was isolated by Wizard ® Megapreps DNA Purification Resin, Promega, Cat#A7361 and RNA crudes were purified by POROS™ Oligo (dT)25 Affinity column. Pointed line represents threshold 1%.
We observed that the constructs encoding GFP and COV displayed elevated levels of dsRNA, whereas Fluc exhibited more favorable levels around 1%. As previously mentioned, in the absence of a polishing step, the RNA transcripts for GFP and COV exhibited higher dsRNA values compared to Fluc. These findings captured our attention, as the capillary electrophoresis, HPLC, and AGE analyses revealed linearized plasmids targeting COV and GFP with decreased purity and an increased number of peaks that do not correspond with target mRNA. ( Figure 5 ). This observation led us to speculate about a potential relationship between the impurities of the initial template and the production of endogenous dsRNA during IVT.
FIGURE 5 . AEX-HPLC (CIMac™ pDNA 0.3 mL Analytical Column (1.4 µm)) profile comparison GFP (green line), Fluc (red line) and COV (blue line) linearized plasmids purified by resin (0.5ug each template injected). Chromatogram shows more intense impurity peaks for COV and GFP.
To assess the impact of linearized template quality, we sought to employ a more specific and reliable purification technique instead of depending solely on simple filtration or resin retention methods. While several options exist for the chromatographic purification of circular plasmids, limited information is available regarding the purification of linearized plasmids. In this study, we investigated the efficacy of CIMmultus C4 HLD columns, which utilize hydrophobic interactions to fractionate proteins from nucleic acids, commonly applied in the polishing of purified mRNA.
To evaluate the performance of C4 columns, we enzymatically opened several circular plasmids of varying lengths using BspQI enzyme, followed by purification using this monolithic column. One example of purification is described in ( Supplementary Figure S1 ). In the supplementary image, the chromatogram depicts a multi-stage process. Initially, during the loading phase, no breakthrough is observed, indicating that all components of the loaded sample (linearized DNA + restriction enzyme) adhere tightly to the column. The elution of the restriction enzyme only occurs after a final treatment involving CIP with 0.1M NaOH. Subsequent to the loading phase, a washing phase with buffer A is employed, followed by elution using a 100% B. This elution process yields a primary peak alongside a minor tail consisting of highly diluted fractions. It is noteworthy that the UV signal within these dilute fraction’s ranges from 20 to 0 mAU. Our extensive experience has shown that the quantity of DNA present in these extremely diluted fractions is negligible compared to the total content of the primary peak, rendering them unsuitable for further analysis and thus necessitating their exclusion. The presence of this tailing-off effect in the chromatogram is attributed to residual components firmly bound to the column, which ultimately detach due to the decreasing conductivity values as the elution progresses. To further investigate these tail fractions, they were consolidated, concentrated, and subjected to preliminary analysis using HPLC CIMac pDNA. This analysis revealed an overlap with the target linear DNA, leading us to conclude that the main peak and the tail were essentially identical ( Supplementary Figure S2 ). However, the mass obtained from these tail fractions constituted less than 5% of the total, prompting their exclusion from further analysis.
When comparing the purified fractions to templates purified using Megapreps DNA Resin, it became evident that C4 provided superior results. Capillary electrophoresis (CE) profiles exhibited reduced tailing (smearing in the simulated gel) at the right side and higher intensity, indicating improved template purity. Furthermore, HPLC analysis using ClMac™ pDNA demonstrated more prominent main peaks corresponding to the template and decreased impurities ( Figure 6 ).
FIGURE 6 . Template characterization. (A) AEX-HPLC (CIMac™ pDNA) analytical profile of linear DNA profiles for encoded GFP, Fluc and COV purified by Megapreps DNA Resin (blue lines) and CIMmultus C4 HLD column (red lines) (0.5ug each template injected). (B) Capillary electrophoresis for the same samples.
To further characterize the purified templates, we subjected them to AEX-HPLC and capillary electrophoresis ( Figure 6 ). Comparative analysis revealed improved profiles for the chromatographically purified templates, with reduced degradation and fewer impurity peaks. Notably, the profiles of Fluc templates exhibited greater similarity and lower impurity levels, aligning with the lower dsRNA values observed in the corresponding transcripts.
These results highlight the importance of template purification in obtaining high-quality linearized plasmids. The use of C4 columns offers significant advantages in terms of template integrity and purity, ultimately contributing to the production of mRNA transcripts with reduced levels of impurities, such as dsRNA.
The purified linearized plasmids obtained through C4 chromatography were used as the starting material for the subsequent IVT reactions. Following IVT, mRNA crudes were isolated exclusively using affinity chromatography. As anticipated, the levels of dsRNA were significantly reduced, regardless of the size of the resulting mRNA molecules. Notably, the most substantial reduction in dsRNA content was observed for the COVID construct ( Figure 7 ).
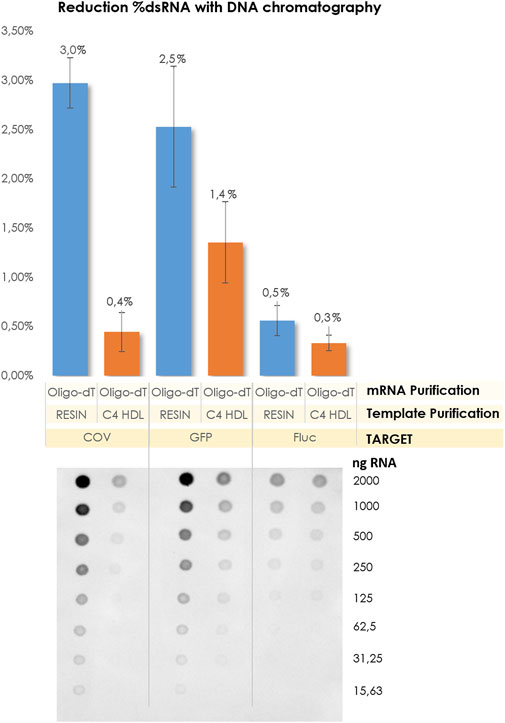
FIGURE 7 . Comparison of dsRNA content related to the template purification method and transcript size. Corresponding dot blot membranes.
To the best of our knowledge, our findings represent the first direct evidence of a correlation between the plasmid purification method and the levels of dsRNA generated during the subsequent IVT process. While it is evident that the use of high-quality linearized plasmids leads to a significant reduction in double-stranded impurities, the underlying explanation for this phenomenon remains unclear.
As previously mentioned, two main mechanisms have been proposed to explain the origin of dsRNA. The first mechanism is associated with the occasional mispriming of the T7 RNA polymerase (T7RNAP) ( Triana-Alonso et al., 1995 ; Gholamalipour et al., 2018 ; Mu et al., 2018 ; Mu and Hur, 2021 ), and the second one in which the antisense strand can be transcribed in a promoter-independent manner, leading to the generation of a complete complementary sequence that anneals to the sense strand ( Mu and Hur, 2021 ) ( Figure 1 ). However, until now, no studies have investigated the influence of impurities on dsRNA generation.
While our study does not aim to elucidate the specific mechanisms or origins of dsRNA, it highlights the critical role of the quality of linearized templates in obtaining transcripts with reduced levels of dsRNA. Importantly, our results suggest that the poor purification of the starting plasmid results in the presence of impurities that the T7 RNAP can potentially use as alternative templates for transcription ( Figure 8 ). Each of these alternative templates could generate RNA fragments that are complementary to different regions of the properly transcribed mRNA sequence. Consequently, a heterogeneous population of dsRNA transcripts would coexist with the dsRNA produced through the aforementioned mechanisms.
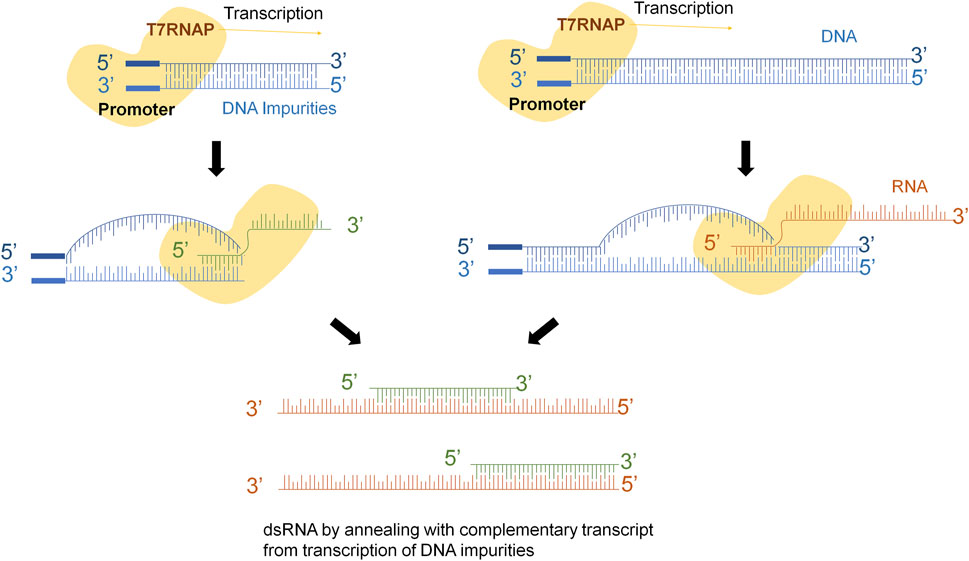
FIGURE 8 . dsRNA generation mechanisms during IVT. Not removed impurities of DNA might be treated as the linearized complete plasmid producing sequences of RNA that could anneal with the original transcript. That might lead to a population of different dsRNA species.
The significant reduction of dsRNA observed during the purification of linearized plasmids highlights the substantial contribution of this impurity from the DNA fragments themselves. This finding emphasizes the importance of employing effective purification techniques for linearized templates. The data presented in this study demonstrate the successful application of chromatography, specifically using C4 columns, for this purpose.
In conclusion, our study demonstrates the importance of implementing both purification and polishing steps in the production of mRNA constructs. The use of AEX chromatography proved to be highly effective in reducing dsRNA levels, with some constructs achieving levels below the recommended threshold. However, it was observed that HIC was not as efficient in reducing dsRNA content compared to AEX. The results suggest that by employing a robust purification method for the initial linearized plasmids, such as hydrophobic chromatography, it is possible to obtain mRNA transcripts with lower dsRNA percentages without the need for additional polishing steps. This highlights the importance of optimizing the purification process of the starting linearized plasmid to achieve high-quality mRNA constructs with reduced dsRNA impurities. Further investigations should focus on understanding the underlying mechanisms and factors influencing dsRNA formation, as well as exploring alternative purification strategies for even more efficient removal of dsRNA.
4 Materials and methods
4.1 synthetic methods, 4.1.1 plasmid linearization.
Prior to RNA IVTs, pDNAs encoding firefly luciferase (pTLuc), spike 2p SARS-CoV-2 (pTCOV01), and green fluorescent protein (pTGFP) were linearized using BspQI (NEB) enzyme, according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
4.1.2 IVT mRNA synthesis
Triphosphate-derivatives of N -methylpseudouridine (Hongene) were used to generate modified nucleoside containing RNA. All RNAs were capped using Cleancap™ (Trilink Biotechnologies). All IVT reagents except enzymes listed in ( Table 1 ) were preheated to 37°C, mixed in a 1.5 mL plastic tube in Thermomixer TM C (Eppendorf) and incubated at 37°C with shaking at 300 rpm. The reaction was quenched after 180 min by addition of 5 mM EDTA, pH 8.0 for its subsequent purification by the different methods.
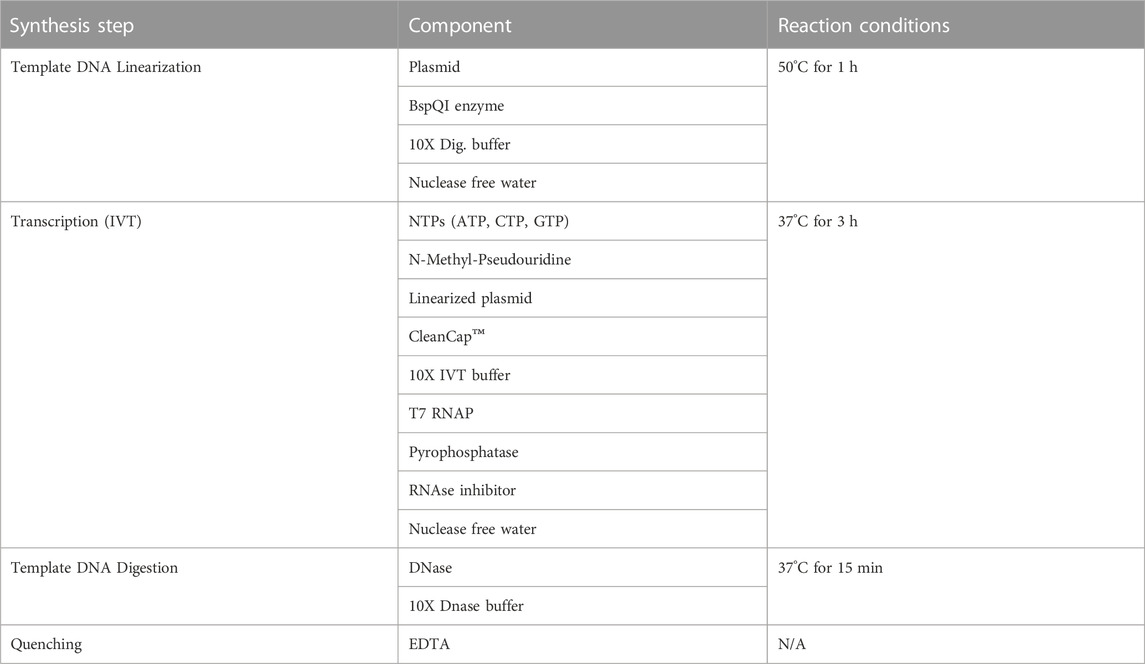
TABLE 1 . Components for upstream production.
4.2 Purification methods
4.2.1 purification of linearized plasmids with silica resin.
The Wizard ® Plus Maxipreps DNA Purification System provides a rapid resin-based batch column method for purification of plasmid DNA. The purification procedure was carried out following the manufacturer’s protocol.
4.2.2 Hydrophobic interaction chromatography of linearized plasmids
Chromatographic purification was performed on the ÄKTA Start (GE Healthcare) FPLC system composed of two pumps and a multiwavelength UV-Vis detector (2 mm flow cell path length). Unicorn software (GE Healthcare) was used for instrument control and data acquisition. DNA template linearized was diluted once in sample loading buffer (75 mM Tris + 15 mM EDTA + 3.75 M SA (ammonium sulphate) pH = 7.2 and loaded onto CIMmultus C4 HDL 1 mL column (Sartorius) equilibrated in mobile phase containing 50 mM Tris + 10 mM EDTA + 2.5 M SA pH = 7.2. After the UV 260 nm signal and conductivity was stabilized, an elution step was performed with 50 mM Tris + 10 mM EDTA pH = 7.2 DNA content from desired fractions was concentrated and desalted using Amicon Ultra-15 centrifugal filter units (30K membrane) (Millipore) by successive centrifugation at 1,000 g for 10 min RT in a 5804R centrifuge (Eppendorf).
4.2.3 Purification of mRNA by lithium chloride precipitation
RNA precipitation is an easy and cost-effective method for the concentration of RNA, leaving a pellet that can be resuspended in the buffer of choice. An equal volume of LiCl 7.5 M solution was added, and the resulting solution was stored at −80°C overnight. Next day, it was centrifuged at top speed for 20 min and the supernatant was discarded. The pellet was washed twice with ice-cold 70% ethanol to remove residual salt and dried with SpeedVac for 5 min. The pellet was then resuspended in a suitable buffer and stored at −80°C.
4.2.4 Affinity chromatography of mRNA
The ssRNA fraction from CIMmultus PrimaS was purified by affinity chromatography using POROS Oligo (dT)25 (ThermoFisher) as polishing step.
Buffer A contained 50 mM sodium phosphate, 0.5 M NaCl, 5 mM EDTA, pH = 7.0 and Buffer B contained 50 mM sodium phosphate, 5 mM EDTA, pH = 7.0. Column was equilibrated with 100% Buffer A, loaded with RNA, washed with buffer B, and finally eluted by step elution of polyadenylated mRNA with double-deionized water.
4.2.5 RNA isolation from column fractions
RNA content from desired fractions was concentrated and desalted using Amicon Ultra-15 centrifugal filter units (30K membrane) (Millipore) by successive centrifugation at 2,100 g for 10 min in a 5804R centrifuge (Eppendorf), and dilution with nuclease free water.
4.2.6 Anion exchange chromatography of mRNA
CIMmultus PrimaS is used for one-step purification of research grade of ssRNA, to process in vitro transcription mixtures. Purification performance is enhanced by a high-salt wash that removes the majority of dsRNA, DNA, and proteins in advance of elution. IVT mixture was diluted once in sample loading/equilibrate buffer A (20 mM Tris, 20 mM BTP, 20 mM glycine, 50 mM NaCl, 10 mM EDTA, pH = 8.0) and loaded onto CIMmultus PrimaS (BIA Separations). After unbound IVT components eluted in flow-through, a wash 1 with equilibration buffer was necessary, followed by a high-salt wash with 50 mM Tris, 3.0 M guanidine-HCl, 20 mM EDTA, pH 8.0. DNA, dsRNA, and proteins typically elute on the ascending side of the guanidine-EDTA peak. And after a wash 3 with buffer A until UV returns to baseline, a step elution was performed with buffer C (20 mM Tris, 20 mM BTP, 20 mM glycine, 50 mM NaCl, 10 mM EDTA, pH = 11.0). Fractions were neutralized immediately after elution.
4.3 Analytical methods
4.3.1 hplc analysis of pdna.
Linear pDNA was analyzed by HPLC using a CIMac TM pDNA-0.3 Analytical Column (Pores 1.4 µm) (BIA Separations) connected to an HPLC WATERS e2695.
The separations of the isoforms were performed in a linear gradient of NaCl with the temperature of the whole system controlled to 15.0+/- 0.5°C. Using the followed mobile phases in standard protocol for the column (MPA: 100 mM Tris-HCl, 0.6 M NaCl, pH = 8, MPB: 100 mM Tris-HCl, 1 M NaCl, pH = 8). A linear gradient was performed, 5% MPB to 30% MPB in 6 min at a flow rate 1 mL/min. The column was eluted with 100% MPB for 1 min before re-equilibration in 5% MPB.
4.3.2 Dot blot
Purified IVT RNA samples were spotted onto positively charged nylon membranes (Nytran SC, Sigma Aldrich). The membranes were blocked with 5% (w/v) non-fat dried milk in TBS-T buffer (20 mM Tris-HCl, 150 mM NaCl, 0.1% [v/v] Tween-20, pH 7.4), and incubated with dsRNA-specific mAb J2 (Jena Bioscience) 4°C ON. Membranes were washed three times with TBS-T and reacted with HRP-conjugated goat anti-mouse Ig (Abcam), washed three times, and detected with ECL Plus Western blot detection reagent (Amersham). Images were captured on an iBright 750 digital imaging system.
dsRNA Ladder (Biolabs) (25 ng) was used as a positive control.
4.3.3 Capillary electrophoresis
DNA and RNA samples were loaded into the corresponding kits; Agilent DNA 12000 Kit and Agilent RNA 6000 Nano Kit, both designed for use with the Agilent 2,100 Bioanalyzer instrument, according to guide instructions. Results were analyzed with the 2,100 Expert Software.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusion of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
VL, AL, and HM, designed, performed and analyzed the experiments. DC and JM supervised the project and DC wrote the manuscript. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their sincere appreciation to Elena Mata and her dedicated team for their invaluable assistance in performing the mRNA transfections in cell lines and providing us with crucial protein expression results. Their expertise and commitment have greatly contributed to the success of this study. The authors thanks Gobierno de Aragón (Spain) for financial funding through project IDMF/2021/0009 (Nuevas tecnologías para el diseño y obtención de vacunas de ARN en Aragón).
Conflict of interest
JM, VL, AL, HM, and DC were employed by the Company Certest Pharma, Certest Biotec.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmolb.2023.1248511/full#supplementary-material
Arnaud-Barbe, N., Cheynet-Sauvion, V., Oriol, G., Mandrand, B., and Mallet, F. (1998). Transcription of RNA templates by T7 RNA polymerase. Nucleic Acids Res. 26, 3550–3554. doi:10.1093/nar/26.15.3550
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Azarani, A., and Hecker, K. H. (2021). RNA analysis by ion-pair reversed-phase high performance liquid chromatography. Nucleic Acids Res. 29, E7–E9. doi:10.1093/nar/29.2.e7
Biebricher, C. K., and Luce, R. (1996). Template-free generation of RNA species that replicate with bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase. EMBO J. 15, 3458–3465. doi:10.1002/j.1460-2075.1996.tb00712.x
Cazenave, C., and Uhlenbeck, O. C. (1994). RNA template-directed RNA synthesis by T7 RNA polymerase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 91, 6972–6976. doi:10.1073/pnas.91.15.6972
Chatterjee, S., Shioi, R., and Kool, E. T. (2022). Sulfonylation of RNA 2′-OH groups. ACS Cent. Sci. 9, 531–539. doi:10.1021/acscentsci.2c01237
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Dickman, M. J., and Hornby, D. P. (2006). Enrichment and analysis of RNA centered on ion pair reverse phase methodology. Rna 12, 691–696. doi:10.1261/rna.2278606
Dousis, A., Ravichandran, K., Hobert, E. M., Moore, M. J., and Rabideau, A. E. (2022). An engineered T7 RNA polymerase that produces mRNA free of immunostimulatory byproducts. Nat. Biotechnol. 41, 560–568. doi:10.1038/s41587-022-01525-6
Fang, L., Xiao, L., Jun, Y. W., Onishi, Y., and Kool, E. T. (2022). Reversible 2’-OH acylation enhances RNA stability. Res. Sq. , 0–20. doi:10.1038/s41557-023-01246-6
Gagnon, P. (2020). Purification of nucleic acids: a handbook for purification of plasmid DNA and mRNA for gene therapy and vaccines - Sartorius BIA separations. Available at: https://www.biaseparations.com/en/products/monolithic-columns/books/226/purification-of-nucleic-acids-a-handbook-for-purification-of-plasmid-dna-and-mrna-for-gene-therapy-and-vaccines .
Google Scholar
Gholamalipour, Y., Karunanayake Mudiyanselage, A., and Martin, C. T. (2018). 3' end additions by T7 RNA polymerase are RNA self-templated, distributive and diverse in character-RNA-Seq analyses. Nucleic Acids Res. 46, 9253–9263. doi:10.1093/nar/gky796
Jacoby, M. (2006). Monolithic chromatography. Chem. Eng. News 84, 14–19. doi:10.1021/cen-v084n050.p014
Karikó, K., Muramatsu, H., Ludwig, J., and Weissman, D. (2011). Generating the optimal mRNA for therapy: HPLC purification eliminates immune activation and improves translation of nucleoside-modified, protein-encoding mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 39, e142. doi:10.1093/nar/gkr695
Kim, K. Q., Burgute, B. D., Tzeng, S. C., Jing, C., Jungers, C., Zhang, J., et al. (2022). N1-methylpseudouridine found within COVID-19 mRNA vaccines produces faithful protein products. Cell Rep. 40, 111300. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111300
Kis, Z., Kontoravdi, C., Dey, A. K., Shattock, R., and Shah, N. (2020). Rapid development and deployment of high-volume vaccines for pandemic response. J. Adv. Manuf. Process. 2, 100600–e10110. doi:10.1002/amp2.10060
Knezevic, I., Liu, M. A., Peden, K., Zhou, T., and Kang, H. N. (2021). Development of mRNA vaccines: scientific and regulatory issues. Vaccines 9, 81–11. doi:10.3390/vaccines9020081
Konarska, M. M., and Sharp, P. A. (1989). Replication of RNA by the DNA-dependent RNA polymerase of phage T7. Cell 57, 423–431. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(89)90917-3
Krupp, G. (1989). Unusual promoter-independent transcription reactions with bacteriophage RNA polymerases. Nucleic Acids Res. 17, 3023–3036. doi:10.1093/nar/17.8.3023
Lee, B. L., and Barton, G. M. (2015). Trafficking of endosomal Toll-like receptors , 360–369. S0962-8924(13)00226-2.pdf. 24. doi:10.1016/j.tcb.2013.12.002
Mccarthy, S. M., and Gilar, M. (2008). Semi-preparative scale single-stranded RNA purification. 2–4 .
Milligan, J. F., Groebe, D. R., Witherell, G. W., and Uhlenbeck, O. C. (1987). Oligoribonucleotide synthesis using T7 RNA polymerase and synthetic DNA templates. Nucleic Acids Res. 15, 8783–8798. doi:10.1093/nar/15.21.8783
Mu, X., Greenwald, E., Ahmad, S., and Hur, S. (2018). An origin of the immunogenicity of in vitro transcribed RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 46, 5239–5249. doi:10.1093/nar/gky177
Mu, X., and Hur, S. (2021). Immunogenicity of in vitro -transcribed RNA. Acc. Chem. Res. 54, 4012–4023. doi:10.1021/acs.accounts.1c00521
Nacheva, G. A., and Berzal-Herranz, A. (2003). Preventing nondesired RNA-primed RNA extension catalyzed by T7 RNA polymerase. Eur. J. Biochem. 270, 1458–1465. doi:10.1046/j.1432-1033.2003.03510.x
Ouranidis, A., Davidopoulou, C., Tashi, R. K., and Kachrimanis, K. (2021). Pharma 4.0 continuous mRNA drug products manufacturing. Pharmaceutics 13, 1371. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics13091371
Park, J. W., Lagniton, P. N. P., Liu, Y., and Xu, R.-H. (2021). mRNA vaccines for COVID-19: what, why and how. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 17, 1446–1460. doi:10.7150/ijbs.59233
Podgornik, A. Š., Yamamoto, S., Peterka, M. Ž., and Krajnc, N. L. (2013). Fast separation of large biomolecules using short monolithic columns. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 927, 80–89. doi:10.1016/j.jchromb.2013.02.004
Roy, B., and Wu, M. Z. (2019). Understanding and overcoming the immune response from synthetic mRNAs. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. News 39, 56–58. doi:10.1089/gen.39.12.15
Schlake, T., Thess, A., Fotin-mleczek, M., and Kallen, K. (2012). Developing mRNA-vaccine technologies. RNA Biol. 9 (11), 1319–1330. doi:10.4161/rna.22269
Separations, B. I. A. (2020). Purification of single-stranded mRNA: The toolbox for the next generation .
Sousa, S., Prazeres, D. M. F., Azevedo, A. M., and Marques, M. P. C. (2021). mRNA vaccines manufacturing: challenges and bottlenecks. Vaccine 39, 2190–2200. doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2021.03.038
Triana-Alonso, F. J., Dabrowski, M., Wadzack, J., and Nierhaus, K. H. (1995). Self-coded 3’-extension of run-off transcripts produces aberrant products during in vitro transcription with T7 RNA polymerase. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 6298–6307. doi:10.1074/jbc.270.11.6298
Verbeke, R., Lentacker, I., De Smedt, S. C., and Dewitte, H. (2021). The dawn of mRNA vaccines: the COVID-19 case. J. Control. Release 333, 511–520. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2021.03.043
Weissman, D., Pardi, N., Muramatsu, H., and Karikó, K. (2013). HPLC purification of in vitro transcribed long RNA. Methods Mol. Biol. 969, 43–54. doi:10.1007/978-1-62703-260-5_3
Whitley, J., Zwolinski, C., Denis, C., Maughan, M., Hayles, L., Clarke, D., et al. (2020). Development of mRNA manufacturing for vaccines and therapeutics: mRNA platform requirements and development of a scalable production process to support early phase clinical trials. Transaltional Res. 242, 38–55. doi:10.1016/j.trsl.2021.11.009
Keywords: dsRNA, chromatography, polishing, IVT, immunogenicity, vaccines, mRNA
Citation: Martínez J, Lampaya V, Larraga A, Magallón H and Casabona D (2023) Purification of linearized template plasmid DNA decreases double-stranded RNA formation during IVT reaction. Front. Mol. Biosci. 10:1248511. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1248511
Received: 27 June 2023; Accepted: 19 September 2023; Published: 29 September 2023.
Reviewed by:
Copyright © 2023 Martínez, Lampaya, Larraga, Magallón and Casabona. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Diego Casabona, [email protected]
This article is part of the Research Topic
In Vitro Transcription (IVT) Reaction – The Gateway to New Therapeutic Modalities

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Write clearly and concisely. A good abstract is short but impactful, so make sure every word counts. Each sentence should clearly communicate one main point. To keep your abstract or summary short and clear: Avoid passive sentences: Passive constructions are often unnecessarily long.
Definition and Purpose of Abstracts An abstract is a short summary of your (published or unpublished) research paper, usually about a paragraph (c. 6-7 sentences, 150-250 words) long. A well-written abstract serves multiple purposes: an abstract lets readers get the gist or essence of your paper or article quickly, in order to decide whether to….
There are six steps to writing a standard abstract. (1) Begin with a broad statement about your topic. Then, (2) state the problem or knowledge gap related to this topic that your study explores. After that, (3) describe what specific aspect of this problem you investigated, and (4) briefly explain how you went about doing this.
Developing such a skill takes practice. Here is an exercise to help you develop this skill. Pick a scientific article in your field. Read the paper with the abstract covered. Then try to write an abstract based on your reading. Compare your abstract to the author's. Repeat until you feel confident.
Authors abstract various longer works, including book proposals, dissertations, and online journal articles. There are two main types of abstracts: descriptive and informative. A descriptive abstract briefly describes the longer work, while an informative abstract presents all the main arguments and important results.
The abstract does not begin with an indented line. APA (2020) recommends that abstracts should generally be less than 250 words, though many journals have their own word limits; it is always a good idea to check journal-specific requirements before submitting. The Writing Center's APA templates are great resources for visual examples of abstracts.
You can, however, write a draft at the beginning of your research and add in any gaps later. If you find abstract writing a herculean task, here are the few tips to help you with it: 1. Always develop a framework to support your abstract. Before writing, ensure you create a clear outline for your abstract.
Use Times New Roman font in 12 pt. Set one-inch (or 2.54 cm) margins. If you include a "keywords" section at the end of the abstract, indent the first line and italicize the word "Keywords" while leaving the keywords themselves without any formatting.
How to write a structured abstract. Let's start with a few essential points to remember when writing your abstract. You should: Report the essential facts contained within the document. Avoid exaggerating or including material that doesn't feature in the main text. Avoid abbreviations that are only explained in the main text.
The abstract is the most important piece of your scientific article. In this post, you'll get your hands on the scientific abstract template that normally only members of our scientific writing program, the Researchers' Writing Academy, get access to!Writing a scientific abstract according to the suggested scientific abstract structure will make your paper more likely to get accepted, read ...
Informative Abstract Example 1. Emotional intelligence (EQ) has been correlated with leadership effectiveness in organizations. Using a mixed-methods approach, this study assesses the importance of emotional intelligence on academic performance at the high school level. The Emotional Intelligence rating scale was used, as well as semi ...
The recipe. Consider an abstract a 5-part structure consisting of 1) introduction, 2) problem/objective, 3) "Here we show", 4) main results & conclusions, and 5) implications. 1) Introduction (2 sentences): --> Sentence 1: Basic introduction to the field; accessible to scientists of any discipline. --> Sentence 2: Background of the specific ...
An abstract comprises five parts of equal importance: the title, introduction and aims, methods, results, and conclusion. Allow enough time to write each part well. The title should go straight to the point of the study. Make the study sound interesting so that it catches people's attention. The introduction should include a brief background ...
INTRODUCTION. This paper is the third in a series on manuscript writing skills, published in the Indian Journal of Psychiatry.Earlier articles offered suggestions on how to write a good case report,[] and how to read, write, or review a paper on randomized controlled trials.[2,3] The present paper examines how authors may write a good abstract when preparing their manuscript for a scientific ...
Abstracts are generally kept brief (approximately 150-200 words). They differ by field, but in general, they need to summarize the article so that readers can decide if it is relevant to their work. The typical abstract includes these elements: A statement of the problem and objectives. A statement of the significance of the work.
Authors abstract various longer works, including book proposals, dissertations, and online journal articles. There are two main types of abstracts: descriptive and informative. A descriptive abstract briefly describes the longer work, while an informative abstract presents all the main arguments and important results.
The goal of this video is to discuss how to prepare your abstract for the symposium. The first step and probably most important is to check the rules and regulations to confirm key components. These include the word count, templates and other information related to the rules. The AMA specifically requires that all abstracts must be submitted ...
An abstract, in the form of a single paragraph, was first published in the Canadian Medical Association Journal in 1960 with the idea that the readers may not have enough time to go through the whole paper, and the first abstract with a defined structure was published in 1991 [].The idea sold and now most original articles and reviews are required to have a structured abstract.
Download free graphical abstract templates and view other science images. Sign up for free courses on graphical abstract and scientific illustration. Step 3. Adjust the design formatting and colors until the main story of your research is clear. Read articles to learn more about data visualization design best practices and data storytelling.
How to Write a Scientific Abstract. Scientific publications are an important source of information and knowledge in Academics, Research and development. When articles are submitted for publication, the 1st part that comes across and causes an impact on the minds of the readers is the abstract. It is a concise summary of the paper and must ...
For guidance, Nature 's standard figure sizes are 90 mm (single column) and 180 mm (double column) and the full depth of the page is 170 mm. Amino-acid sequences should be printed in Courier (or ...
Abstract The ion extraction and electro/photo catalysis are promising methods to address environmental and energy issues. Covalent organic frameworks (COFs) are a class of promising template to construct absorbents and catalysts because of their stable frameworks, high surface areas, controllable pore environments, and well-defined catalytic sites.
Abstract. Using the strong reduction potential of the liquid NaK-78 alloy, we present a new versatile template-free approach to the synthesis of porous metal- and metalloid-based nanomaterials. With this novel approach, NaK can be simultaneously used as an agent for reduction, structure directing, and pore formation without the use of ...
After the COVID-19 pandemic, messenger RNA (mRNA) has revolutionized traditional vaccine manufacturing. With the increasing number of RNA-based therapeutics, valuable new scientific insights into these molecules have emerged. One fascinating area of study is the formation of double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) during in vitro transcription (IVT) which is considered a significant impurity, as it has ...
Wikipedia articles (content pages) are commonly used corpora in Natural Language Processing (NLP) research, especially in low-resource languages other than English. Yet, a few research studies have studied the three Arabic Wikipedia editions, Arabic Wikipedia (AR), Egyptian Arabic Wikipedia (ARZ), and Moroccan Arabic Wikipedia (ARY), and documented issues in the Egyptian Arabic Wikipedia ...