Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Assignments
- Annotated Bibliography
- Analyzing a Scholarly Journal Article
- Group Presentations
- Dealing with Nervousness
- Using Visual Aids
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
- Types of Structured Group Activities
- Group Project Survival Skills
- Leading a Class Discussion
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Works
- Writing a Case Analysis Paper
- Writing a Case Study
- About Informed Consent
- Writing Field Notes
- Writing a Policy Memo
- Writing a Reflective Paper
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Generative AI and Writing
- Acknowledgments

Definition and Introduction
Journal article analysis assignments require you to summarize and critically assess the quality of an empirical research study published in a scholarly [a.k.a., academic, peer-reviewed] journal. The article may be assigned by the professor, chosen from course readings listed in the syllabus, or you must locate an article on your own, usually with the requirement that you search using a reputable library database, such as, JSTOR or ProQuest . The article chosen is expected to relate to the overall discipline of the course, specific course content, or key concepts discussed in class. In some cases, the purpose of the assignment is to analyze an article that is part of the literature review for a future research project.
Analysis of an article can be assigned to students individually or as part of a small group project. The final product is usually in the form of a short paper [typically 1- 6 double-spaced pages] that addresses key questions the professor uses to guide your analysis or that assesses specific parts of a scholarly research study [e.g., the research problem, methodology, discussion, conclusions or findings]. The analysis paper may be shared on a digital course management platform and/or presented to the class for the purpose of promoting a wider discussion about the topic of the study. Although assigned in any level of undergraduate and graduate coursework in the social and behavioral sciences, professors frequently include this assignment in upper division courses to help students learn how to effectively identify, read, and analyze empirical research within their major.
Franco, Josue. “Introducing the Analysis of Journal Articles.” Prepared for presentation at the American Political Science Association’s 2020 Teaching and Learning Conference, February 7-9, 2020, Albuquerque, New Mexico; Sego, Sandra A. and Anne E. Stuart. "Learning to Read Empirical Articles in General Psychology." Teaching of Psychology 43 (2016): 38-42; Kershaw, Trina C., Jordan P. Lippman, and Jennifer Fugate. "Practice Makes Proficient: Teaching Undergraduate Students to Understand Published Research." Instructional Science 46 (2018): 921-946; Woodward-Kron, Robyn. "Critical Analysis and the Journal Article Review Assignment." Prospect 18 (August 2003): 20-36; MacMillan, Margy and Allison MacKenzie. "Strategies for Integrating Information Literacy and Academic Literacy: Helping Undergraduate Students make the most of Scholarly Articles." Library Management 33 (2012): 525-535.
Benefits of Journal Article Analysis Assignments
Analyzing and synthesizing a scholarly journal article is intended to help students obtain the reading and critical thinking skills needed to develop and write their own research papers. This assignment also supports workplace skills where you could be asked to summarize a report or other type of document and report it, for example, during a staff meeting or for a presentation.
There are two broadly defined ways that analyzing a scholarly journal article supports student learning:
Improve Reading Skills
Conducting research requires an ability to review, evaluate, and synthesize prior research studies. Reading prior research requires an understanding of the academic writing style , the type of epistemological beliefs or practices underpinning the research design, and the specific vocabulary and technical terminology [i.e., jargon] used within a discipline. Reading scholarly articles is important because academic writing is unfamiliar to most students; they have had limited exposure to using peer-reviewed journal articles prior to entering college or students have yet to gain exposure to the specific academic writing style of their disciplinary major. Learning how to read scholarly articles also requires careful and deliberate concentration on how authors use specific language and phrasing to convey their research, the problem it addresses, its relationship to prior research, its significance, its limitations, and how authors connect methods of data gathering to the results so as to develop recommended solutions derived from the overall research process.
Improve Comprehension Skills
In addition to knowing how to read scholarly journals articles, students must learn how to effectively interpret what the scholar(s) are trying to convey. Academic writing can be dense, multi-layered, and non-linear in how information is presented. In addition, scholarly articles contain footnotes or endnotes, references to sources, multiple appendices, and, in some cases, non-textual elements [e.g., graphs, charts] that can break-up the reader’s experience with the narrative flow of the study. Analyzing articles helps students practice comprehending these elements of writing, critiquing the arguments being made, reflecting upon the significance of the research, and how it relates to building new knowledge and understanding or applying new approaches to practice. Comprehending scholarly writing also involves thinking critically about where you fit within the overall dialogue among scholars concerning the research problem, finding possible gaps in the research that require further analysis, or identifying where the author(s) has failed to examine fully any specific elements of the study.
In addition, journal article analysis assignments are used by professors to strengthen discipline-specific information literacy skills, either alone or in relation to other tasks, such as, giving a class presentation or participating in a group project. These benefits can include the ability to:
- Effectively paraphrase text, which leads to a more thorough understanding of the overall study;
- Identify and describe strengths and weaknesses of the study and their implications;
- Relate the article to other course readings and in relation to particular research concepts or ideas discussed during class;
- Think critically about the research and summarize complex ideas contained within;
- Plan, organize, and write an effective inquiry-based paper that investigates a research study, evaluates evidence, expounds on the author’s main ideas, and presents an argument concerning the significance and impact of the research in a clear and concise manner;
- Model the type of source summary and critique you should do for any college-level research paper; and,
- Increase interest and engagement with the research problem of the study as well as with the discipline.
Kershaw, Trina C., Jennifer Fugate, and Aminda J. O'Hare. "Teaching Undergraduates to Understand Published Research through Structured Practice in Identifying Key Research Concepts." Scholarship of Teaching and Learning in Psychology . Advance online publication, 2020; Franco, Josue. “Introducing the Analysis of Journal Articles.” Prepared for presentation at the American Political Science Association’s 2020 Teaching and Learning Conference, February 7-9, 2020, Albuquerque, New Mexico; Sego, Sandra A. and Anne E. Stuart. "Learning to Read Empirical Articles in General Psychology." Teaching of Psychology 43 (2016): 38-42; Woodward-Kron, Robyn. "Critical Analysis and the Journal Article Review Assignment." Prospect 18 (August 2003): 20-36; MacMillan, Margy and Allison MacKenzie. "Strategies for Integrating Information Literacy and Academic Literacy: Helping Undergraduate Students make the most of Scholarly Articles." Library Management 33 (2012): 525-535; Kershaw, Trina C., Jordan P. Lippman, and Jennifer Fugate. "Practice Makes Proficient: Teaching Undergraduate Students to Understand Published Research." Instructional Science 46 (2018): 921-946.
Structure and Organization
A journal article analysis paper should be written in paragraph format and include an instruction to the study, your analysis of the research, and a conclusion that provides an overall assessment of the author's work, along with an explanation of what you believe is the study's overall impact and significance. Unless the purpose of the assignment is to examine foundational studies published many years ago, you should select articles that have been published relatively recently [e.g., within the past few years].
Since the research has been completed, reference to the study in your paper should be written in the past tense, with your analysis stated in the present tense [e.g., “The author portrayed access to health care services in rural areas as primarily a problem of having reliable transportation. However, I believe the author is overgeneralizing this issue because...”].
Introduction Section
The first section of a journal analysis paper should describe the topic of the article and highlight the author’s main points. This includes describing the research problem and theoretical framework, the rationale for the research, the methods of data gathering and analysis, the key findings, and the author’s final conclusions and recommendations. The narrative should focus on the act of describing rather than analyzing. Think of the introduction as a more comprehensive and detailed descriptive abstract of the study.
Possible questions to help guide your writing of the introduction section may include:
- Who are the authors and what credentials do they hold that contributes to the validity of the study?
- What was the research problem being investigated?
- What type of research design was used to investigate the research problem?
- What theoretical idea(s) and/or research questions were used to address the problem?
- What was the source of the data or information used as evidence for analysis?
- What methods were applied to investigate this evidence?
- What were the author's overall conclusions and key findings?
Critical Analysis Section
The second section of a journal analysis paper should describe the strengths and weaknesses of the study and analyze its significance and impact. This section is where you shift the narrative from describing to analyzing. Think critically about the research in relation to other course readings, what has been discussed in class, or based on your own life experiences. If you are struggling to identify any weaknesses, explain why you believe this to be true. However, no study is perfect, regardless of how laudable its design may be. Given this, think about the repercussions of the choices made by the author(s) and how you might have conducted the study differently. Examples can include contemplating the choice of what sources were included or excluded in support of examining the research problem, the choice of the method used to analyze the data, or the choice to highlight specific recommended courses of action and/or implications for practice over others. Another strategy is to place yourself within the research study itself by thinking reflectively about what may be missing if you had been a participant in the study or if the recommended courses of action specifically targeted you or your community.
Possible questions to help guide your writing of the analysis section may include:
Introduction
- Did the author clearly state the problem being investigated?
- What was your reaction to and perspective on the research problem?
- Was the study’s objective clearly stated? Did the author clearly explain why the study was necessary?
- How well did the introduction frame the scope of the study?
- Did the introduction conclude with a clear purpose statement?
Literature Review
- Did the literature review lay a foundation for understanding the significance of the research problem?
- Did the literature review provide enough background information to understand the problem in relation to relevant contexts [e.g., historical, economic, social, cultural, etc.].
- Did literature review effectively place the study within the domain of prior research? Is anything missing?
- Was the literature review organized by conceptual categories or did the author simply list and describe sources?
- Did the author accurately explain how the data or information were collected?
- Was the data used sufficient in supporting the study of the research problem?
- Was there another methodological approach that could have been more illuminating?
- Give your overall evaluation of the methods used in this article. How much trust would you put in generating relevant findings?
Results and Discussion
- Were the results clearly presented?
- Did you feel that the results support the theoretical and interpretive claims of the author? Why?
- What did the author(s) do especially well in describing or analyzing their results?
- Was the author's evaluation of the findings clearly stated?
- How well did the discussion of the results relate to what is already known about the research problem?
- Was the discussion of the results free of repetition and redundancies?
- What interpretations did the authors make that you think are in incomplete, unwarranted, or overstated?
- Did the conclusion effectively capture the main points of study?
- Did the conclusion address the research questions posed? Do they seem reasonable?
- Were the author’s conclusions consistent with the evidence and arguments presented?
- Has the author explained how the research added new knowledge or understanding?
Overall Writing Style
- If the article included tables, figures, or other non-textual elements, did they contribute to understanding the study?
- Were ideas developed and related in a logical sequence?
- Were transitions between sections of the article smooth and easy to follow?
Overall Evaluation Section
The final section of a journal analysis paper should bring your thoughts together into a coherent assessment of the value of the research study . This section is where the narrative flow transitions from analyzing specific elements of the article to critically evaluating the overall study. Explain what you view as the significance of the research in relation to the overall course content and any relevant discussions that occurred during class. Think about how the article contributes to understanding the overall research problem, how it fits within existing literature on the topic, how it relates to the course, and what it means to you as a student researcher. In some cases, your professor will also ask you to describe your experiences writing the journal article analysis paper as part of a reflective learning exercise.
Possible questions to help guide your writing of the conclusion and evaluation section may include:
- Was the structure of the article clear and well organized?
- Was the topic of current or enduring interest to you?
- What were the main weaknesses of the article? [this does not refer to limitations stated by the author, but what you believe are potential flaws]
- Was any of the information in the article unclear or ambiguous?
- What did you learn from the research? If nothing stood out to you, explain why.
- Assess the originality of the research. Did you believe it contributed new understanding of the research problem?
- Were you persuaded by the author’s arguments?
- If the author made any final recommendations, will they be impactful if applied to practice?
- In what ways could future research build off of this study?
- What implications does the study have for daily life?
- Was the use of non-textual elements, footnotes or endnotes, and/or appendices helpful in understanding the research?
- What lingering questions do you have after analyzing the article?
NOTE: Avoid using quotes. One of the main purposes of writing an article analysis paper is to learn how to effectively paraphrase and use your own words to summarize a scholarly research study and to explain what the research means to you. Using and citing a direct quote from the article should only be done to help emphasize a key point or to underscore an important concept or idea.
Business: The Article Analysis . Fred Meijer Center for Writing, Grand Valley State University; Bachiochi, Peter et al. "Using Empirical Article Analysis to Assess Research Methods Courses." Teaching of Psychology 38 (2011): 5-9; Brosowsky, Nicholaus P. et al. “Teaching Undergraduate Students to Read Empirical Articles: An Evaluation and Revision of the QALMRI Method.” PsyArXi Preprints , 2020; Holster, Kristin. “Article Evaluation Assignment”. TRAILS: Teaching Resources and Innovations Library for Sociology . Washington DC: American Sociological Association, 2016; Kershaw, Trina C., Jennifer Fugate, and Aminda J. O'Hare. "Teaching Undergraduates to Understand Published Research through Structured Practice in Identifying Key Research Concepts." Scholarship of Teaching and Learning in Psychology . Advance online publication, 2020; Franco, Josue. “Introducing the Analysis of Journal Articles.” Prepared for presentation at the American Political Science Association’s 2020 Teaching and Learning Conference, February 7-9, 2020, Albuquerque, New Mexico; Reviewer's Guide . SAGE Reviewer Gateway, SAGE Journals; Sego, Sandra A. and Anne E. Stuart. "Learning to Read Empirical Articles in General Psychology." Teaching of Psychology 43 (2016): 38-42; Kershaw, Trina C., Jordan P. Lippman, and Jennifer Fugate. "Practice Makes Proficient: Teaching Undergraduate Students to Understand Published Research." Instructional Science 46 (2018): 921-946; Gyuris, Emma, and Laura Castell. "To Tell Them or Show Them? How to Improve Science Students’ Skills of Critical Reading." International Journal of Innovation in Science and Mathematics Education 21 (2013): 70-80; Woodward-Kron, Robyn. "Critical Analysis and the Journal Article Review Assignment." Prospect 18 (August 2003): 20-36; MacMillan, Margy and Allison MacKenzie. "Strategies for Integrating Information Literacy and Academic Literacy: Helping Undergraduate Students Make the Most of Scholarly Articles." Library Management 33 (2012): 525-535.
Writing Tip
Not All Scholarly Journal Articles Can Be Critically Analyzed
There are a variety of articles published in scholarly journals that do not fit within the guidelines of an article analysis assignment. This is because the work cannot be empirically examined or it does not generate new knowledge in a way which can be critically analyzed.
If you are required to locate a research study on your own, avoid selecting these types of journal articles:
- Theoretical essays which discuss concepts, assumptions, and propositions, but report no empirical research;
- Statistical or methodological papers that may analyze data, but the bulk of the work is devoted to refining a new measurement, statistical technique, or modeling procedure;
- Articles that review, analyze, critique, and synthesize prior research, but do not report any original research;
- Brief essays devoted to research methods and findings;
- Articles written by scholars in popular magazines or industry trade journals;
- Pre-print articles that have been posted online, but may undergo further editing and revision by the journal's editorial staff before final publication; and
- Academic commentary that discusses research trends or emerging concepts and ideas, but does not contain citations to sources.
Journal Analysis Assignment - Myers . Writing@CSU, Colorado State University; Franco, Josue. “Introducing the Analysis of Journal Articles.” Prepared for presentation at the American Political Science Association’s 2020 Teaching and Learning Conference, February 7-9, 2020, Albuquerque, New Mexico; Woodward-Kron, Robyn. "Critical Analysis and the Journal Article Review Assignment." Prospect 18 (August 2003): 20-36.
- << Previous: Annotated Bibliography
- Next: Giving an Oral Presentation >>
- Last Updated: Mar 6, 2024 1:00 PM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/assignments

How to Write an Article Analysis

What Are the Five Parts of an Argumentative Essay?
As you write an article analysis, focus on writing a summary of the main points followed by an analytical critique of the author’s purpose.
Knowing how to write an article analysis paper involves formatting, critical thinking of the literature, a purpose of the article and evaluation of the author’s point of view. In an article analysis critique, you integrate your perspective of the author about a specific topic into a mix of reasoning and arguments. So, you develop an argumentative approach to the point of view of the author. However, a careful distinction occurs between summary and analysis.
When presenting your findings of the article analysis, you might want to summarize the main points, which allows you to formulate a thesis statement. Then, inform the readers about the analytical aspects the author presents in his arguments. Most likely, developing ideas on how to write an article analysis entails a meticulous approach to the critical thinking of the author.
Writing Steps for an Article Analysis
As with any formal paper, you want to begin by quickly reading the article to get the main points. Once you generate a general idea of the point of view of the author, start analyzing the main ideas of each paragraph. An ideal way to take notes based on the reading is to jot them down in the margin of the article. If that's not possible, include notes on your computer or a separate piece of paper. Interact with the text you're reading.
Becoming an active reader helps you decide the relevant information the author intends to communicate. At this point, you might want to include a summary of the main ideas. After you finish writing down the main points, read them to yourself and decide on a concise thesis statement. To do so, begin with the author’s name followed by the title of the article. Next, complete the sentence with your analytical perspective.
Ideally, you want to use outlines, notes and concept mapping to draft your copy. As you progress through the body of the critical part of the paper, include relevant information such as literature references and the author’s purpose for the article. Formal documents, such as an article analysis, also use in-text citation and proofreading. Any academic paper includes a grammar, spelling and mechanics proofreading. Make sure you double-check your paper before submission.
When you write the summary of the article, focus on the purpose of the paper and develop ideas that inform the reader in an unbiased manner. One of the most crucial parts of an analysis essay is the citation of the author and the title of the article. First, introduce the author by first and last name followed by the title of the article. Add variety to your sentence structure by using different formats. For example, you can use “Title,” author’s name, then a brief explanation of the purpose of the piece. Also, many sentences might begin with the author, “Title,” then followed by a description of the main points. By implementing active, explicit verbs into your sentences, you'll show a clear understanding of the material.
Much like any formal paper, consider the most substantial points as your main ideas followed by evidence and facts from the author’s persuasive text. Remember to use transition words to guide your readers in the writing. Those transition phrases or words encourage readers to understand your perspective of the author’s purpose in the article. More importantly, as you write the body of the analysis essay, use the author’s name and article title at the beginning of a paragraph.
When you write your evidence-based arguments, keep the author’s last name throughout the paper. Besides writing your critique of the author’s purpose, remember the audience. The readers relate to your perspective based on what you write. So, use facts and evidence when making inferences about the author’s point of view.
Description of an Article Analysis Essay
When you analyze an article based on the argumentative evidence, generate ideas that support or not the author’s point of view. Although the author’s purpose to communicate the intentions of the article may be clear, you need to evaluate the reasons for writing the piece. Since the basis of your analysis consists of argumentative evidence, elaborate a concise and clear thesis. However, don't rely on the thesis to stay the same as you research the article.
At many times, you'll find that you'll change your argument when you see new facts. In this way, you might want to use text, reader, author, context and exigence approaches. You don't need elaborate ideas. Just use the author’s text so that the reader understands the point of views. However, evaluate the strong tone of the author and the validity of the claims in the article. So, use the context of the article.
Then, ask yourself if the author explains the purpose of his or her persuasive reasons. As you discern the facts and evidence of the article, analyze the point of views carefully. Look for assumptions without basis and biased ideas that aren't valid. An analysis example paragraph easily includes your perspective of the author’s purpose and whether you agree or not. Don't be surprised if your critique changes as you research other authors about the article.
Consequently, your response might end up agreeing, disagreeing or being somewhat in between despite your efforts of finding supporting evidence. Regardless of the consequences of your research of the literature and the perspective of the author’s point of view, maintain a definite purpose in writing. Don't fluctuate from agreement and disagreement. Focusing your analysis on presenting the points of view of the author so readers understand it and disseminating that critique is the basis of your paper.
When reading the text carefully, analyze the main points and explain the reasons of the author. Also, as you describe the document, offer evidence and facts to eliminate any biases. In an argumentative analysis, the focus of the writer can quickly shift. Avoid ineffective ways of approaching the author’s point of view that make the writing vague and lack supporting evidence. A clear way to stay away from biases is to use quotes from the author. However, using excessive amounts of quotes is counterproductive. Use author quotes sparingly.
As you develop your own ideas about the author’s viewpoints, use deductive reasoning to analyze the various aspects of the article. Often, you'll find the historical background influenced the author or persuaded the author to challenge the ideals of the time. Distinguishing between writing a summary and an analysis paper is crucial to your essay. You might find that using a review at the beginning of your article indicates a clear perspective to your analysis. Hence, a summary explains the main points of a paper in a concise manner.
You condense the original text, describe the main points, write your thesis and form no opinion about the article. On the other hand, an analysis is the breakdown of the author’s arguments that you use to derive the purpose of the author. When analyzing an article, you're dissecting the main points to draw conclusions about the persuasive ideas of the author. Furthermore, you offer argumentative evidence, strengths and weaknesses of the main points. More importantly, you don't give your opinion. Rather than providing comments on the author’s point of views, you compile evidence of how the author persuades readers to think about a particular topic and whether the author elaborates it adequately.
Examples of an Article Analysis
A summary and analysis essay example illustrates the arguments the author makes and how those claims are valid. For instance, a sample article analysis of “Sex, Lies, and Conversation; Why Is It So Hard for Men and Women to Talk to Each Other” by Deborah Tannen begins with a summary of the main critical points followed by an analytical perspective. One of the precise ways to summarize is to focus on the main ideas that Tannen uses to distinguish between men and women.
The writer of the summary also clearly states how one idea correlates to the other without presenting biases or opinions. Also, the writer doesn't take any sides on whether men or women are to blame for miscommunication. Instead, the summary points to the communication differences between men and women. In the analytical section of the sample, the writer immediately takes a transparent approach to the article and the author. The analysis shows apparent examples from the article with quotes and refers back to the article connecting miscommunication with misinterpretation. Finally, the writer poses various questions that Tannen didn't address, such as strategies for effective communication. However, the writer gives the reader the purpose of Tannen’s article and the reasons the author wrote it.
Another example of an article analysis is “The Year That Changed Everything” by Lance Morrow. The writer presents a concise summary of the elected government positions of Nixon, Kennedy and Johnson. Furthermore, the writer distinguishes between the three elected men's positions and discusses the similarities. The summary tends to lean toward a more powerful tone but effectively explains the author’s point of view for each one of these men. Then, the writer further describes the ideals of the period between morality and immoral values. The analytical aspect of the sample shows the reader the author’s powerful message.
The writer immediately lets the reader know about the persuasive nature of the article and the relevance of the time. For instance, the writer shows the reader in various parts of the article by suggesting examples in specific paragraph numbers. The writer also makes a powerful impact with the use of quotes embedded into the text. The writer uses transition words and active verbs, such as more examples, links, uncovering and secrets, and backs this claim up to describe Morrow’s purpose for the article. The analysis has the audience in mind.
The writer points out the specific details of the time era that only people of the time would relate. More importantly, the writer analyzes Morrow’s ideas as critical to formulating an opinion about Nixon, Kennedy and Johnson. However, the writer points out the assumptions Morrow makes between personal lifestyle and how it affects the political arena. Moreover, the writer suggests that Morrow’s claims aren't entirely valid just because the author mentions historical events. Unlike Tannen’s analytical example, the writer lets the readers know the misconnection between moral value and the lifestyle of many people at the time.
Both article analyses show a clear way to present different persuasive points of view. Unlike a summary, an analysis approach offers the reader an explicit representation of the author’s viewpoints without any opinions. The writers of each sample focus on providing evidence, facts and reasonable statements. Consequently, each example demonstrates the proper use of the critical analysis of the literature and evaluates the purpose of the author. Without seeking an agreement or not, the writer clearly distinguishes between a summary and an analysis of each article.
Related Articles

What Are Two Types of Research Papers?

How to Set Up a Rhetorical Analysis

How to Write a Thesis & Introduction for a Critical Reflection Essay

The Parts of an Argument

How to Write a Technical Essay

How to Write a Critical Summary of an Article

How to Analyze Expository Writing

How to Do a Summary for a Research Paper
- Owlcation: How to Write a Summary, Analysis, and Response Essay Paper with Examples
- Education: One How To: How to Write a Text Analysis Essay
Barbara earned a B. S. in Biochemistry and Chemistry from the Univ. of Houston and the Univ. of Central Florida, respectively. Besides working as a chemist for the pharmaceutical and water industry, she pursued her degree in secondary science teaching. Barbara now writes and researches educational content for blogs and higher-ed sites.
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you’re on board with our cookie policy

- A Research Guide
- Writing Guide
- Article Writing
How to Analyze an Article
- What is an article analysis
- Outline and structure
- Step-by-step writing guide
- Article analysis format
- Analysis examples
- Article analysis template
What Is an Article Analysis?
- Summarize the main points in the piece – when you get to do an article analysis, you have to analyze the main points so that the reader can understand what the article is all about in general. The summary will be an overview of the story outline, but it is not the main analysis. It just acts to guide the reader to understand what the article is all about in brief.
- Proceed to the main argument and analyze the evidence offered by the writer in the article – this is where analysis begins because you must critique the article by analyzing the evidence given by the piece’s author. You should also point out the flaws in the work and support where it needs to be; it should not necessarily be a positive critique. You are free to pinpoint even the negative part of the story. In other words, you should not rely on one side but be truthful about what you are addressing to the satisfaction of anyone who would read your essay.
- Analyze the piece’s significance – most readers would want to see why you need to make article analysis. It is your role as a writer to emphasize the importance of the article so that the reader can be content with your writing. When your audience gets interested in your work, you will have achieved your aim because the main aim of writing is to convince the reader. The more persuasive you are, the more your article stands out. Focus on motivating your audience, and you will have scored.
Outline and Structure of an Article Analysis
What do you need to write an article analysis, how to write an analysis of an article, step 1: analyze your audience, step 2: read the article.
- The evidence : identify the evidence the writer used in the article to support their claim. While looking into the evidence, you should gauge whether the writer brings out factual evidence or it is personal judgments.
- The argument’s validity: a writer might use many pieces of evidence to support their claims, but you need to identify the sources they use and determine whether they are credible. Credible sources are like scholarly articles and books, and some are not worth relying on for research.
- How convictive are the arguments? You should be able to judge the writer’s persuasion of the audience. An article is usually informative and therefore has to be persuasive to the readers to be considered worthy. If it does not achieve this, you should be able to critique that and illustrate the same.
Step 3: Make the plan
Step 4: write a critical analysis of an article, step 5: edit your essay, article analysis format, article analysis example, what didn’t you know about the article analysis template.
- Read through the piece quickly to get an overview.
- Look for confronting words in the article and note them down.
- Read the piece for the second time while summarizing major points in the literature piece.
- Reflect on the paper’s thesis to affirm and adhere to it in your writing.
- Note the arguments and the evidence used.
- Evaluate the article and focus on your audience.
- Give your opinion and support it to the satisfaction of your audience.

Receive paper in 3 Hours!
- Choose the number of pages.
- Select your deadline.
- Complete your order.
Number of Pages
550 words (double spaced)
Deadline: 10 days left
By clicking "Log In", you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We'll occasionally send you account related and promo emails.
Sign Up for your FREE account

Forget about ChatGPT and get quality content right away.
- Essay Topic Generator
- Summary Generator
- Thesis Maker Academic
- Sentence Rephraser
- Read My Paper
- Hypothesis Generator
- Cover Page Generator
- Text Compactor
- Essay Scrambler
- Essay Plagiarism Checker
- Hook Generator
- AI Writing Checker
- Notes Maker
- Overnight Essay Writing
- Topic Ideas
- Writing Tips
- Essay Writing (by Genre)
- Essay Writing (by Topic)
How to Analyze a Research Article: Guide & Analysis Examples
Analyzing a scientific paper is a complicated task that requires knowledge and systematic preparation. This process favors patience over haste and offers a deep and nuanced exploration of the presented research. Fully understanding the peculiarities of content analysis may seem complicated, especially when it comes to evaluating the results.
Our team has developed a thorough guide to make your writing process more comfortable and focused. We offer helpful tips and examples to help you create a paper worthy of admiration from college professors. This guide has everything for a stellar and in-depth argument analysis.
🤔 What Is a Research Article Analysis?
🎯 analysis of a paper: main goals.
- 📑 How to Analyze a Research Article
📝 Research Analysis Template: Essay Outline
- ✨ 5 Tips for Writing an Analysis
- ✒️ 7 Research Paper Analysis Examples
🔗 References
A research genre analysis is a genre of academic writing that lets students assess issues and arguments presented in research articles. They review the text’s content and determine its validity through critical thinking . It involves a great deal of topic analysis. After studying the source, they provide an assessment of the claims with evidence that support or disprove them. It’s their job to establish which of the statements are flawed and which are valid. Students also summarize the article and explain its relevance to the field of study.
📑 How to Analyze a Research Article – 4 Key Steps
Research paper analysis is often both educational and complicated. Taking a structured approach to this task makes it a lot easier. This section of our guide discloses the four stages that help better understand the content of a scientific paper. Follow our analysis plan to learn how to write about things like results and methodology analysis .

Research Paper Analysis: Read an Article & Take Notes
You can’t critique a research piece without reading the source material first. Skimming over the paper won’t do, as you’ll miss crucial details for your analysis. Follow these steps to ensure you get the most out of the paper while critically evaluating its contents.
- Read the paper once to have a general understanding of what it’s about. Ensure you are familiar with the topic beyond elementary knowledge. You may also read up on related literature beforehand.
- Read the second time and take notes. Read the entire research paper carefully, paying attention to the results, discussion, and conclusion sections. It’s better to take detailed notes as you read, summarizing each section in your own words.
- Outline the results of the study. Write a short rundown of what the author found during the search.
Research Paper Analysis: Comprehend & Reveal the Methodology
Once you’re done with the first step, it’s time to move on to the second stage of research paper analysis: comprehending and revealing the methodology. You can’t possibly remember everything about the article so that you can revise your notes.
- Explore key terms and concepts of an article . If you don’t fully understand them, take the time to familiarize yourself with them.
- Find the hypothesis or the research question the author decided to tackle . Check the facts, arguments, and logic behind their thinking to view the paper critically.
- Look at the validity of the arguments . Research sources used in the article and assess the credibility of the supporting evidence.
- Identify the study’s methodology . Find out how the author approached the research and what its results were. Once you establish the methodology, evaluate the quality of the information, including the methods of data gathering and analysis.
Research Paper Analysis: Assess the Results
After completing the second part of the analysis, it’s time to assess the research results. Establish if the findings support the paper’s hypothesis and their statistical relevance. Address any limitations of the study . For example, a writing on psychology that uses a small group of participants that cannot be considered representative of a larger population. It may be true that the researcher did this intentionally to skew their findings. However, it’s best to be balanced in your article critique and talk about the strong sides of the paper as well. Look at similar studies and see if they came to the same conclusions.
Research Paper Analysis: Draw Conclusions
After you’ve completed the previous steps, you’re ready to make conclusions about the research paper as a whole. Don’t forget to include the following information when working on this part of the analysis:
- Determine the theoretical and practical meaning of the results. For example, if the paper found a particular treatment effective, emphasize that it should be used more often.
- Consider the applications of the research results. Try to find out how they can be applied to the broader field and what ethical implications they may lead to.
- Show how they relate to the big picture. Finally, your analysis should show how the article expands the knowledge of the subject and what it means to further studies.
Writing a research paper analysis can be demanding. These papers have several characteristics that set them apart from other types of academic writing. We’ve created this simple template to explain the content each part of your assessment should have.

✨ 5 Tips for Writing an Analysis of Paper
Mastering the art of writing a research paper analysis takes time and practice. We’ve decided to provide five great tips that will make this process easier and more enjoyable:
- Take the time to establish the right angle for your analysis. If you can choose its direction, study the paper first and choose the best subject for your work. You can develop several ideas and select the right one later.
- Connect all evidence to your argument. When conducting the analysis, find facts and data supporting your point of view. Explain the connection of each piece of evidence to your statement and showcase what makes it particularly significant.
- Stay balanced. A good analysis covers all facts and looks at them objectively. When confronted with data that clashes with your stance, check it and use evidence to bolster the credibility of your arguments.
- Work on an outline . Good analysis is often grounded in well-structured outline. Write down ideas and topic sentences that connect to various parts of the research sample and its general idea.
- Evaluate all evidence. All evidence has a place in your analysis. Use all of it, even if you come across contradictory facts. Include information that doesn’t fully support the main idea of your analysis and build compelling counterarguments.

️ ✒️ 7 Great Research Paper Analysis Examples
Seeing an example of a finished article can point you in the right direction. Our team has collected seven excellent essays to inspire your subsequent work and show how to approach its structure correctly.
- Hybridization Trends for Main Group Elements: Article Analysis Research Paper. This paper analysis deals with a paper on hybridization in chemistry. It shows the relationship between hybridization and electronegativity concerning the bond’s strengths and atomic size.
- Globalization by Peter Temin: Article Analysis. This analysis deals with an article on globalization published in 1999. It examines research objectives, approach, methodology, key findings, and recommendations for future research on this issue.
- Effectiveness of Hand Hygiene Interventions in Reducing Illness Absence : Article Analysis. Researchers behind this paper tried to find out if hand washing effectively decreases diseases among children in educational institutions. Its significance lies in the fact that there’s a limited pool of studies on this subject.
- Analysis of The Five Dysfunctions of a Team Article . This paper concerns the pitfalls of team building in a business environment. In particular, how to overcome this environment’s five most common dysfunctions.
- When Altruism Isn’t Moral by Sally Satel : Article Analysis. The author demonstrates altruistic behavior is not always sufficient to explain human interaction. It discusses what drives people to help others for free or for money.
- Article Analysis Perceptions of ADHD Among Diagnosed Children and Their Parents. In this work, the author evaluates the findings on the perception of ADHD-diagnosed children in developed countries.
- School Dress Code: Articles Analysis. This article critique has different points of view on the use of the school dress code. It showcases a comparative analysis of positions that point to increased safety vs. increased diversity.
Research Article Analysis Topics
Now that you understand how to write a research paper analysis, it’s time to find the right topic for your paper. Below, you’ll find fifteen exciting ideas to inspire your analytical pursuits.
- Review a research paper on the effects of carbon emissions.
- Explore a recent research article on the use of opioids in American healthcare .
- Assess a research paper on the applications of the Large Hadron Collider.
- Discuss quantitative research about mental health rates in developed countries.
- Examine a scientific article about the problems of space exploration .
- Investigate a recent research paper about the rise of surveillance technology.
- Analyze a qualitative research paper on the effectiveness of biofuels as an alternative energy source.
- Study quantitative methods of research on the housing market in Canada.
- Scrutinize a research article about the use of pesticides in food production .
- Evaluate a paper on the efficiency of anti-climate change measures.
- Assess a recent study on the dangers of sugar consumption .
- Survey the latest research on fast food advertising tactics.
- Consider a paper on the most recent developments in string theory .
- Address a recent research article about artificial intelligence .
- Cover research about the benefits of using nuclear power.
We did our best to cover all crucial points of research article analysis and prepare you for this kind of academic work. When you have the time, share our guide with fellow students who can benefit from the content of our work!
- Analyzing Scholarly Articles. – University Writing Center
- How to Write an Analysis (With Examples and Tips). – Indeed
- Complete Guide on Article Analysis (with 1 Analysis Example). – Nerdify, Medium
- How to Read and Understand a Scientific Paper: A Guide for Non-scientists. – Jennifer Raff, LSE
- How to Review a Journal Article. – The Board of Trustees of the University of Illinois
- Critique/Review of Research Articles. – University of Calgary
- How to Summarize a Research Article. – University of Connecticut
- A Guide for Critique of Research Articles – California State Universite, Long Beach
Article Analysis Essay
by Stephanie Johnson | Apr 4, 2018 | tips | 0 comments
Recently, I’ve seen a lot of papers where the student is asked to read an article and write an analytical paper. This is a new concept for some people, and the tendency to summarize instead of analyze is strong. Here are some key tips for analyzing an article in most subjects without falling in to the trap of summarizing instead.
1) Read through your professor’s essay prompt first before you begin writing. Keep it in mind as you read the article. Underline or circle key words. Rephrase and rewrite in your own words what it is the professor is asking you to do.
2) Read the whole article more than once. It’s surprising how often students come to me and say, “well, I haven’t quite finished reading the article, but I started writing my paper.” It is impossible to have a complete grasp of the article in question without reading the article in completion.
3) Be an active, not passive, reader. How many people simply read through an article without highlighting, underlining, making marginal notes, or otherwise engaging in the text and expect full understanding? Too many!
Your paper should bleed ink by the time you’re done reading the article (see image for an example of marginal annotations). The best strategy is not simply to highlight indiscriminately, but to take the time to write summaries, questions, and connections in the margins first. Keeping in mind your professor’s essay prompt, mark evidence that helps answer some of the questions in your assignment.
Then, you can also highlight if you find that helps you. In my own experience, I find most articles to be set up in such a way that the things I’d like to highlight (vocabulary, important dates, etc.) are already made significant in the text in some way already (by bold text, or italics, or headings, etc.).
4) Now that you’ve thoroughly marked your article, quiz yourself on the important concepts covered in it. For example, cover the article and see if you can accurately identify the author’s thesis and main points without referencing back to the article. Studies show that testing or quizzing yourself on material is far more effective than simply rereading a source.
5) Now that you’ve effectively spent time on understanding your article, you may begin thinking about writing. Don’t skimp on steps 1-4! You cannot write an effective article analysis essay without first analyzing your article!
6) Reread the assignment/prompt sheet. Begin by outlining how you will answer the questions outlined by your professor using evidence from the article as support. Identify the author’s thesis and synthesize your own wording of what it was the author was attempting to argue. Then, create your own thesis. This should argue whether or not the article was effective in proving the article’s thesis, why or why not.
7) Begin writing an introduction paragraph that includes necessary article information (author, title, subject, brief summary), and concludes with the author’s thesis and your thesis.
8) In a logical order (chronologically, thematically, other), begin presenting evidence from the original article that supports either the author’s thesis or your thesis about the effectiveness of the article.
9) Read through and remove unnecessary summary. Make sure you focus on presenting evidence (by way of quotations with correct citations) and then explain why that evidence supports your thesis. You can use signal phrases such as, “This quote shows…”, or “As evidenced by this quote…”, etc.
10) Visit your writing center to revise for clarity and coherence.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Social Media
Need help with your papers.
- Annotating Texts
- Attribution & Paraphasing
- Business and Thank-you Letters
- Conquering Writer’s Block
- How to Write a Thesis
- How to Write an Introduction and Thesis
- Lab Reports
- Organization and Transition
- Outlining Your Paper
- Paragraph Structure
- Passive and Active Voice
- Personal Statement
- Proofreading
- Proper Punctuation
- Sentence Structure
- Using Pronouns Effectively
- Using Quotations Effectively
Recent Posts
- Writing Pitfalls: Weak Theses
- Write, Revise, then Revise Some More
- Night Against Procrastination Spring ’19
- PowerPoint Presentation Tips
- Sample Cover Letter
How to Write an Analytical Essay in 6 Steps
An analytical essay is an essay that meticulously and methodically examines a single topic to draw conclusions or prove theories. Although they are used in many fields, analytical essays are often used with art and literature to break down works’ creative themes and explore their deeper meanings and symbolism .
Analytical essays are a staple in academics, so if you’re a student, chances are you’ll write one sooner or later. This guide addresses all the major concerns about how to write an analytical essay, such as the preferred structure and what to put in the outline. Let’s start with an in-depth answer to the question, what is an analytical essay? Give your writing extra polish Grammarly helps you communicate confidently Write with Grammarly
What is an analytical essay?
One of the seven main types of essay , analytical essays intricately examine a single topic to explain specific arguments or prove the author’s theories. They commonly deal with creative works like art, literature, film, or music, dissecting the creator’s artistic themes and revealing hidden meanings. However, they can also address other issues in realms like science, politics, and society.
Analytical essays are a type of expository essay , so they’re not supposed to express bias, opinions , or persuasions . Even when the author is trying to prove their own theory (or disprove an opposing theory), their argument should stick solely to facts and logic and keep the author’s personal feelings to a minimum.
An analytical essay example could be a deep dive into the character of Hamlet, but this topic itself could have multiple interpretations. Your essay could focus on whether or not Hamlet truly loved Ophelia, question the motives for his constant hesitation, or even attempt to prove the theory that he was mentally ill—after all, he did see apparitions!
How to structure an analytical essay
Although analytical essays tend to be more detailed, specific, or technical than other essays, they still follow the same loose essay structure as the rest:
1 Introduction
3 Conclusion
The introduction is where you present your thesis statement and prepare your reader for what follows. Because analytical essays focus on a single topic, the introduction should give all the background information and context necessary for the reader to understand the writer’s argument. Save the actual analysis of your topic for the body.
The body is the nucleus of your essay. Here you explain each separate point and offer evidence to support the thesis, breaking up your argument into paragraphs. While the introduction and conclusion are each usually just a single paragraph, the body is composed of many different paragraphs and often stretches out over pages, thereby making up most of the essay.
Every paragraph in the body still relates to your chosen topic and your thesis, but each paragraph should make a different point or focus on a different piece of evidence. For example, if your topic is about how Edgar Allan Poe uses the theme of death in his writing, one paragraph could explore the use of death in “The Tell-Tale Heart,” while a different paragraph could explore death in “The Raven,” and so on.
Finally, the conclusion wraps everything up. Conclusions usually don’t introduce new evidence or supporting details but instead reiterate the previous points and bring them all together to strengthen your original thesis. At this point your reader has sufficient background to understand the topic. With your evidential examples in mind, they’ll be more receptive to your main argument when you present it one last time.
How to write an analytical essay in 6 steps
The process of writing an analytical essay largely follows the same guidelines as all essay writing . Here we break down each individual step from start to finish.
1 Choose your topic
This step may be optional if your topic has been given to you as an assignment. If not, though, you should choose your topic with care.
Your topic should be specific enough that you’re able to discuss it thoroughly. If you choose a broad topic like “love in novels from Victorian England,” it’s unlikely you’ll be able to cover all Victorian novels in a single analytical essay (or even ten analytical essays!). However, narrowing the topic down to something such as “love in Jane Austen novels” makes your task more achievable.
That said, don’t be too specific, or you won’t have enough material to cover. Try to find a good middle ground: specific enough that you can discuss everything but general enough that you’ll be able to find enough research and supporting evidence.
2 Research your topic
Once you know your topic, you can begin collecting data and evidence to discuss it. If your analytical essay is about a creative work, you may want to spend time reviewing or evaluating that work, such as watching a film closely or studying the details of a painting. It’s also useful to review other people’s critiques of that work to inspire new ideas or reveal details you hadn’t noticed before.
Don’t forget to write down where you get your information, including page numbers for books or time codes if you’re watching visual media. You may need to reference these in your essay, so making a quick note about where you find your information while researching saves time later when you’re citing your sources .
It helps to know your thesis from the onset. However, you may realize during your research that your original thesis is not as strong as you thought. If this happens, don’t be afraid to modify it or choose a new one. In any case, by the time your research is finished, you should know what your thesis will be.
3 Create an outline
An essay outline gives you the opportunity to organize all your thoughts and research so you can put them in the optimal order. Ideally, you’ll have finished your research by now and made notes of everything you want to say in your analytical essay. The outline is your chance to decide when to talk about each point.
Outlines are typically broken up by paragraph. Each paragraph should explore an individual point you’re making and include your evidence or statistical data to back up that particular point. Be careful about trying to squeeze too much information into a single paragraph; if it looks excessive, try to break up the information into two or more paragraphs.
Feel free to move around or rearrange the order of paragraphs while outlining—that’s what this step is for! It’s much easier to fix structural problems now in the outline phase than later when writing.
4 Write your first draft
Now is the time you sit down and actually write the rough draft of your analytical essay. This step is by far the longest, so be sure to set aside ample time.
If you wrote your outline thoroughly, all you have to do is follow it paragraph by paragraph. Be sure to include each piece of evidence and data you had planned to include. Don’t worry about details like choosing the perfect wording or fixing every grammar mistake—you can do those later in the revisions phase. For now, focus solely on getting everything down.
Pay particular attention to how you start an essay. The introduction serves different purposes, such as telling the reader what to expect, providing background information, and above all presenting your thesis statement. Make sure your introduction checks all those boxes.
Likewise, be extra careful with your conclusion. There are special techniques for how to write a conclusion, such as using a powerful clincher and avoiding certain cliches like “in summary.” Conclusions usually hold more weight than the other paragraphs because they’re the last thing a person reads and can leave a lasting impression on them.
Finally, don’t forget to include transition sentences in between your body paragraphs when needed. Moving abruptly from one topic to the next can be jarring for the reader; transition sentences improve the essay’s flow and remove distractions.
5 Revise your draft
Your first draft is never meant to be perfect. Once you have all your ideas down on paper, it’s much easier to go back and revise . Now is the perfect time to improve your phrasing and word choice and edit out any unnecessary or tangential parts.
When you revise, pay particular attention to details. Try to find areas that you can remove to make your essay more succinct or passages that aren’t clear that need more explanation. Put yourself in the reader’s shoes: Will someone with no background knowledge still understand your points?
6 Proofread your essay
Last, it’s time to fix any grammar and spelling mistakes by proofreading . While it’s tempting to do this at the same time as your revisions, it’s best to do them separately so you don’t split your attention. This allows you to focus only on word choice, phrasing, and adding/removing content while revising and to concentrate solely on language mistakes during proofreading.
If you’re not confident in your grammar or spelling expertise, you can always use an app like Grammarly . Our app highlights any spelling or grammar mistakes directly in your text and gives proper suggestions on how to fix them. There are even features that help you choose the perfect word or adjust your writing to fit a certain tone. You can also copy and paste your writing to check your grammar and get instant feedback on grammar, spelling, punctuation, and other mistakes you might have missed.
Analytical essay outline example
If you’re having trouble, here’s an analytical essay example that shows how a proper outline or structure should look. The format here uses a five-paragraph essay structure, but for more complicated topics, you can add as many body paragraphs as you need.
Topic: Who is the real villain: Macbeth or Lady Macbeth?
Introduction
- Briefly describe the plot of Macbeth for those who aren’t familiar with it
- Thesis statement : Lady Macbeth is the real villain of Macbeth because she manipulates her husband into committing an atrocious crime
Body Paragraph 1
- Murdering the king is all Lady Macbeth’s idea
- Macbeth is initially against it until Lady Macbeth convinces him
Body Paragraph 2
- Lady Macbeth has her own individual character arc where she is driven mad by her guilt
- Her guilt insinuates she knows her actions are villainous, with appropriate consequences
- Cite quotations from her “Out, damned spot!” speech
Body Paragraph 3
- Macbeth decides to listen to Lady Macbeth, so he is still guilty
- Speculate that he still would not have murdered the king if not for Lady Macbeth
- Macbeth remains the main character because most scenes revolve around him, but the person acting against him most is Lady Macbeth
- Remind reader that Macbeth didn’t want to murder the king until Lady Macbeth convinced him
- Clincher : Macbeth is still the hero albeit a tragic one. But his main antagonist is not Macduff or the king or even the prophecy itself; it’s his wife.
Analytical essay FAQs
An analytical essay is an essay that deeply examines a single topic, often a creative work, to reveal certain conclusions or prove theories held by the essay’s author.
How is an analytical essay structured?
Analytical essays are structured like most other essays: an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. However, the body paragraphs have a stricter emphasis on facts, logic, and empirical evidence compared to other essays.
What are the steps to writing an analytical essay?
As with all essays, you first research and then organize all your points into a working outline. Next, you write the rough draft with all the data and evidence collected during your research. Revise the rough draft when it’s finished to improve the phrasing and add/remove certain parts. Last, proofread the essay for any grammar or spelling mistakes.

Research Paper Analysis: How to Analyze a Research Article + Example
Why might you need to analyze research? First of all, when you analyze a research article, you begin to understand your assigned reading better. It is also the first step toward learning how to write your own research articles and literature reviews. However, if you have never written a research paper before, it may be difficult for you to analyze one. After all, you may not know what criteria to use to evaluate it. But don’t panic! We will help you figure it out!
In this article, our team has explained how to analyze research papers quickly and effectively. At the end, you will also find a research analysis paper example to see how everything works in practice.
- 🔤 Research Analysis Definition
📊 How to Analyze a Research Article
✍️ how to write a research analysis.
- 📝 Analysis Example
- 🔎 More Examples
🔗 References
🔤 research paper analysis: what is it.
A research paper analysis is an academic writing assignment in which you analyze a scholarly article’s methodology, data, and findings. In essence, “to analyze” means to break something down into components and assess each of them individually and in relation to each other. The goal of an analysis is to gain a deeper understanding of a subject. So, when you analyze a research article, you dissect it into elements like data sources , research methods, and results and evaluate how they contribute to the study’s strengths and weaknesses.
📋 Research Analysis Format
A research analysis paper has a pretty straightforward structure. Check it out below!
Research articles usually include the following sections: introduction, methods, results, and discussion. In the following paragraphs, we will discuss how to analyze a scientific article with a focus on each of its parts.

How to Analyze a Research Paper: Purpose
The purpose of the study is usually outlined in the introductory section of the article. Analyzing the research paper’s objectives is critical to establish the context for the rest of your analysis.
When analyzing the research aim, you should evaluate whether it was justified for the researchers to conduct the study. In other words, you should assess whether their research question was significant and whether it arose from existing literature on the topic.
Here are some questions that may help you analyze a research paper’s purpose:
- Why was the research carried out?
- What gaps does it try to fill, or what controversies to settle?
- How does the study contribute to its field?
- Do you agree with the author’s justification for approaching this particular question in this way?
How to Analyze a Paper: Methods
When analyzing the methodology section , you should indicate the study’s research design (qualitative, quantitative, or mixed) and methods used (for example, experiment, case study, correlational research, survey, etc.). After that, you should assess whether these methods suit the research purpose. In other words, do the chosen methods allow scholars to answer their research questions within the scope of their study?
For example, if scholars wanted to study US students’ average satisfaction with their higher education experience, they could conduct a quantitative survey . However, if they wanted to gain an in-depth understanding of the factors influencing US students’ satisfaction with higher education, qualitative interviews would be more appropriate.
When analyzing methods, you should also look at the research sample . Did the scholars use randomization to select study participants? Was the sample big enough for the results to be generalizable to a larger population?
You can also answer the following questions in your methodology analysis:
- Is the methodology valid? In other words, did the researchers use methods that accurately measure the variables of interest?
- Is the research methodology reliable? A research method is reliable if it can produce stable and consistent results under the same circumstances.
- Is the study biased in any way?
- What are the limitations of the chosen methodology?
How to Analyze Research Articles’ Results
You should start the analysis of the article results by carefully reading the tables, figures, and text. Check whether the findings correspond to the initial research purpose. See whether the results answered the author’s research questions or supported the hypotheses stated in the introduction.
To analyze the results section effectively, answer the following questions:
- What are the major findings of the study?
- Did the author present the results clearly and unambiguously?
- Are the findings statistically significant ?
- Does the author provide sufficient information on the validity and reliability of the results?
- Have you noticed any trends or patterns in the data that the author did not mention?
How to Analyze Research: Discussion
Finally, you should analyze the authors’ interpretation of results and its connection with research objectives. Examine what conclusions the authors drew from their study and whether these conclusions answer the original question.
You should also pay attention to how the authors used findings to support their conclusions. For example, you can reflect on why their findings support that particular inference and not another one. Moreover, more than one conclusion can sometimes be made based on the same set of results. If that’s the case with your article, you should analyze whether the authors addressed other interpretations of their findings .
Here are some useful questions you can use to analyze the discussion section:
- What findings did the authors use to support their conclusions?
- How do the researchers’ conclusions compare to other studies’ findings?
- How does this study contribute to its field?
- What future research directions do the authors suggest?
- What additional insights can you share regarding this article? For example, do you agree with the results? What other questions could the researchers have answered?

Now, you know how to analyze an article that presents research findings. However, it’s just a part of the work you have to do to complete your paper. So, it’s time to learn how to write research analysis! Check out the steps below!
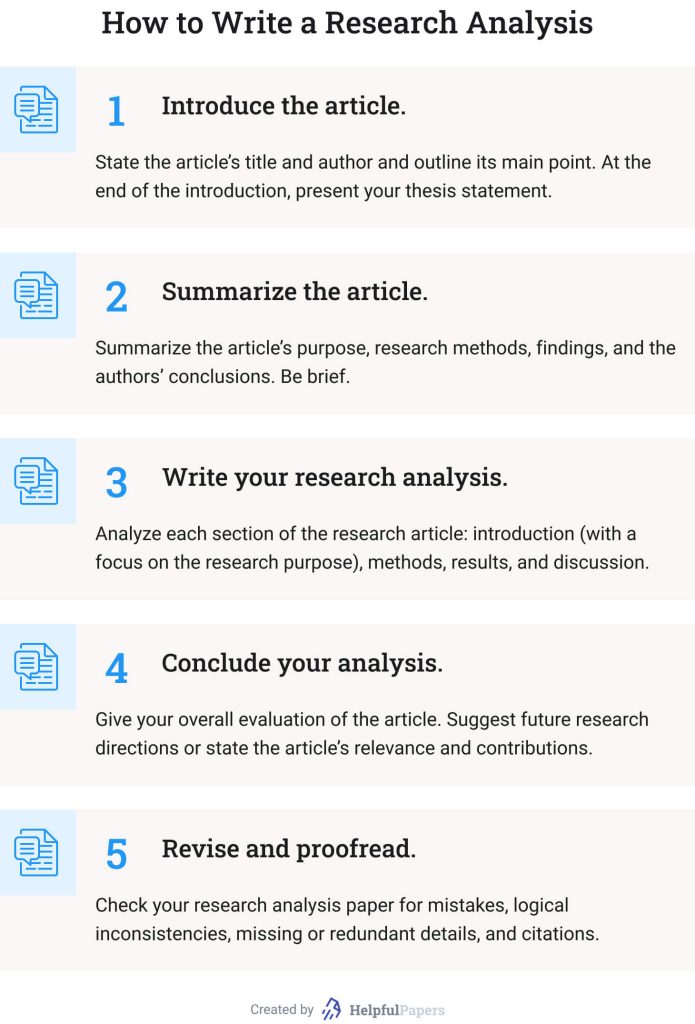
1. Introduce the Article
As with most academic assignments, you should start your research article analysis with an introduction. Here’s what it should include:
- The article’s publication details . Specify the title of the scholarly work you are analyzing, its authors, and publication date. Remember to enclose the article’s title in quotation marks and write it in title case .
- The article’s main point . State what the paper is about. What did the authors study, and what was their major finding?
- Your thesis statement . End your introduction with a strong claim summarizing your evaluation of the article. Consider briefly outlining the research paper’s strengths, weaknesses, and significance in your thesis.
Keep your introduction brief. Save the word count for the “meat” of your paper — that is, for the analysis.
2. Summarize the Article
Now, you should write a brief and focused summary of the scientific article. It should be shorter than your analysis section and contain all the relevant details about the research paper.
Here’s what you should include in your summary:
- The research purpose . Briefly explain why the research was done. Identify the authors’ purpose and research questions or hypotheses .
- Methods and results . Summarize what happened in the study. State only facts, without the authors’ interpretations of them. Avoid using too many numbers and details; instead, include only the information that will help readers understand what happened.
- The authors’ conclusions . Outline what conclusions the researchers made from their study. In other words, describe how the authors explained the meaning of their findings.
If you need help summarizing an article, you can use our free summary generator .
3. Write Your Research Analysis
The analysis of the study is the most crucial part of this assignment type. Its key goal is to evaluate the article critically and demonstrate your understanding of it.
We’ve already covered how to analyze a research article in the section above. Here’s a quick recap:
- Analyze whether the study’s purpose is significant and relevant.
- Examine whether the chosen methodology allows for answering the research questions.
- Evaluate how the authors presented the results.
- Assess whether the authors’ conclusions are grounded in findings and answer the original research questions.
Although you should analyze the article critically, it doesn’t mean you only should criticize it. If the authors did a good job designing and conducting their study, be sure to explain why you think their work is well done. Also, it is a great idea to provide examples from the article to support your analysis.
4. Conclude Your Analysis of Research Paper
A conclusion is your chance to reflect on the study’s relevance and importance. Explain how the analyzed paper can contribute to the existing knowledge or lead to future research. Also, you need to summarize your thoughts on the article as a whole. Avoid making value judgments — saying that the paper is “good” or “bad.” Instead, use more descriptive words and phrases such as “This paper effectively showed…”
Need help writing a compelling conclusion? Try our free essay conclusion generator !
5. Revise and Proofread
Last but not least, you should carefully proofread your paper to find any punctuation, grammar, and spelling mistakes. Start by reading your work out loud to ensure that your sentences fit together and sound cohesive. Also, it can be helpful to ask your professor or peer to read your work and highlight possible weaknesses or typos.
📝 Research Paper Analysis Example
We have prepared an analysis of a research paper example to show how everything works in practice.
No Homework Policy: Research Article Analysis Example
This paper aims to analyze the research article entitled “No Assignment: A Boon or a Bane?” by Cordova, Pagtulon-an, and Tan (2019). This study examined the effects of having and not having assignments on weekends on high school students’ performance and transmuted mean scores. This article effectively shows the value of homework for students, but larger studies are needed to support its findings.
Cordova et al. (2019) conducted a descriptive quantitative study using a sample of 115 Grade 11 students of the Central Mindanao University Laboratory High School in the Philippines. The sample was divided into two groups: the first received homework on weekends, while the second didn’t. The researchers compared students’ performance records made by teachers and found that students who received assignments performed better than their counterparts without homework.
The purpose of this study is highly relevant and justified as this research was conducted in response to the debates about the “No Homework Policy” in the Philippines. Although the descriptive research design used by the authors allows to answer the research question, the study could benefit from an experimental design. This way, the authors would have firm control over variables. Additionally, the study’s sample size was not large enough for the findings to be generalized to a larger population.
The study results are presented clearly, logically, and comprehensively and correspond to the research objectives. The researchers found that students’ mean grades decreased in the group without homework and increased in the group with homework. Based on these findings, the authors concluded that homework positively affected students’ performance. This conclusion is logical and grounded in data.
This research effectively showed the importance of homework for students’ performance. Yet, since the sample size was relatively small, larger studies are needed to ensure the authors’ conclusions can be generalized to a larger population.
🔎 More Research Analysis Paper Examples
Do you want another research analysis example? Check out the best analysis research paper samples below:
- Gracious Leadership Principles for Nurses: Article Analysis
- Effective Mental Health Interventions: Analysis of an Article
- Nursing Turnover: Article Analysis
- Nursing Practice Issue: Qualitative Research Article Analysis
- Quantitative Article Critique in Nursing
- LIVE Program: Quantitative Article Critique
- Evidence-Based Practice Beliefs and Implementation: Article Critique
- “Differential Effectiveness of Placebo Treatments”: Research Paper Analysis
- “Family-Based Childhood Obesity Prevention Interventions”: Analysis Research Paper Example
- “Childhood Obesity Risk in Overweight Mothers”: Article Analysis
- “Fostering Early Breast Cancer Detection” Article Analysis
- Lesson Planning for Diversity: Analysis of an Article
- Journal Article Review: Correlates of Physical Violence at School
- Space and the Atom: Article Analysis
- “Democracy and Collective Identity in the EU and the USA”: Article Analysis
- China’s Hegemonic Prospects: Article Review
- Article Analysis: Fear of Missing Out
- Article Analysis: “Perceptions of ADHD Among Diagnosed Children and Their Parents”
- Codependence, Narcissism, and Childhood Trauma: Analysis of the Article
- Relationship Between Work Intensity, Workaholism, Burnout, and MSC: Article Review
We hope that our article on research paper analysis has been helpful. If you liked it, please share this article with your friends!
- Analyzing Research Articles: A Guide for Readers and Writers | Sam Mathews
- Summary and Analysis of Scientific Research Articles | San José State University Writing Center
- Analyzing Scholarly Articles | Texas A&M University
- Article Analysis Assignment | University of Wisconsin-Madison
- How to Summarize a Research Article | University of Connecticut
- Critique/Review of Research Articles | University of Calgary
- Art of Reading a Journal Article: Methodically and Effectively | PubMed Central
- Write a Critical Review of a Scientific Journal Article | McLaughlin Library
- How to Read and Understand a Scientific Paper: A Guide for Non-scientists | LSE
- How to Analyze Journal Articles | Classroom
How to Write an Animal Testing Essay: Tips for Argumentative & Persuasive Papers
Descriptive essay topics: examples, outline, & more.
Analytical Essay: Tips, Structure, Examples

Analytical essays could be perfect for you if you enjoy immersing yourself in tasks and excel at thinking creatively. By conducting thorough analysis and employing innovative writing techniques, you can discover new viewpoints and enhance your understanding of the subject.
In this article, our research paper writer will explain what it entails, learn how to structure your paper for top marks, snag some snazzy topic ideas, and glean practical examples. This guide has got all the essentials you need for writing success!

What Is an Analytical Essay
To write an effective analytical essay, it is important to understand its purpose and method. In basic terms, it requires using textual evidence to logically support the author's arguments rather than relying on emotions or personal anecdotes. Compared to persuasive essays that advocate for one specific viewpoint, a quality analytical essay example should delve into all aspects of the subject. This involves examining different perspectives, dissecting arguments, and assessing evidence thoughtfully. Ultimately, you will have to express your viewpoint after conducting your analysis. This requires combining your research and determining if you agree with the conclusions made or have a different interpretation.
Wondering How to Impress Your Professor with Your Essay?
Let our writers craft you a winning essay, no matter the subject, field, type, or length!
How to Structure an Analytical Essay
Now it's time to ace the process of crafting an excellent paper. To make writing easier, organize your thoughts and structure your arguments clearly. An analytical essay needs the introduction, body, and conclusion of an outline, which acts as a guide from start to finish. Here's the simple breakdown of an analytical essay outline:
.webp)
Introduction
- Background information
- Thesis statement
Body paragraph 1
- Topic sentence
- Supporting evidence
- Transition to the body paragraph to
Body paragraph 2
- Transition to body paragraph 3
Body paragraph 3
- Transition to conclusion
- Summary of major points
- Restate the thesis
- Key takeaways
Introduction: To begin your essay successfully (see our analytical essay example), captivate the reader's interest from the very start and clearly outline the topic. A good beginning should give some background information, outline the essay's purpose, and suggest the main arguments that will be made. Grab the reader's attention with an engaging and pertinent opening sentence, such as a surprising fact, a funny story, or a challenging question. After that, introduce your thesis statement, which summarizes your main point in the essay.
Body Paragraphs: In an analysis essay, each paragraph begins with a topic sentence that helps guide the reader. The paragraph then provides evidence to support the thesis, concentrating on a single issue. By summarizing the main point at the end of each paragraph, the essay flows smoothly from one idea to the next, maintaining clarity and coherence in the argument.
Conclusion: The final paragraph of an analytical essay usually adheres to a specific structure:
- Reiterating the main argument
- Outlining the main ideas discussed in the essay
- Providing thoughts on the overall significance of the analysis
It is crucial to include your perspective on the topic's relevance and how your analysis adds to the understanding of it. This approach can strongly impact the reader's perception of the essay.
Meanwhile, you might also be interested in how to write a reflection paper , so check out the article for more information!
How to Write an Analytical Essay
Once you understand the structure, there are some steps you can take to make writing an analytical essay easier. Preparing beforehand can simplify the process and improve the overall flow and structure of your essay. Here are some tips from our experts. Meanwhile, you can also request from our experts - write my essay for me . And we'll take care of it right away.
.webp)
- Think Ahead : Before writing, a good analytical essay writer should spend some time thinking about the topic. Make a list of ideas or themes related to it. This helps you find interesting angles for your essay.
- Create a Thesis Statement : Develop a clear and concise thesis statement that outlines the main argument of your essay. This will guide you in how to write an analytical essay introduction and keep your writing focused.
- Visualize Information : Use graphs or charts to organize your thoughts visually. This makes your research easier to understand. For example, you can compare ideas with a chart.
- Consider Different Views : Address opposing viewpoints in your essay. This shows you've thought about different perspectives and strengthens your argument.
- Use Original Sources : Include interviews, presentations, or original documents in your research. They give a unique insight into your topic. For instance, old letters can offer personal views on historical events.
- Analyze Cause and Effect : Explore the cause-and-effect relationships within your topic. Analyze how different factors contribute to certain outcomes or phenomena.
Analytical Essay Topics
Choosing the right one among lots of analytical essay topic ideas is crucial when tackling your essay. Here's a guide to help you pick wisely:
- Find a topic that piques your interest. It's easier to dive into analysis when you're passionate about the subject.
- Look for topics that catch the reader's eye. Think about what would make someone stop and want to read more.
- Avoid topics that are too broad. Focus on something specific that you can thoroughly analyze within the scope of your essay.
- Ensure there's enough quality research available to support your analysis. You'll need evidence to back up your points.
- Your topic should raise questions worth exploring. Aim for something that sparks curiosity and has significance.
Now, here's a mix of engaging topics from our dissertation services to consider:
- Analyzing the Impact of Blue Light from Screens on Sleep Quality
- Exploring the Environmental Effects of Microplastics in Ocean Ecosystems
- Understanding the Benefits of Deep Breathing Exercises for Anxiety Relief
- Analyzing the Influence of Instagram Filters on Body Image Perception
- Exploring the Health Risks of Artificial Sweeteners in Diet Soda
- Understanding the Psychological Effects of High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT)
- Analyzing the Environmental Impact of Fast Food Packaging Waste
- Exploring the Effects of Social Media Validation on Self-Esteem
- Understanding the Benefits of Indoor Plants for Air Quality Improvement
- Analyzing the Relationship Between Sugar Consumption and Dental Health
- Exploring the Psychological Effects of Online Shopping Addiction
- Understanding the Environmental Impact of Fast Fashion Textile Dyes
- Analyzing the Effects of Smartphone Notifications on Focus and Productivity
- Exploring the Benefits of Outdoor Exercise for Vitamin D Production
- Understanding the Relationship Between Noise Pollution and Cardiovascular Health
- Analyzing the Psychological Effects of Colorful Food Presentation on Appetite
- Exploring the Impact of Petting Therapy Dogs on Stress Reduction
- Understanding the Benefits of Classical Music for Concentration While Studying
- Analyzing the Effects of Lavender Aromatherapy on Sleep Quality
- Exploring the Health Risks of Prolonged Sitting and Sedentary Lifestyles
Analytical Essay Examples
Here is our analytical writing sample to see theory in action. Notice how analytical thinking applies to real-world situations, improving your understanding of concepts. By studying these examples, you'll learn to analyze complex issues, build strong arguments, and sharpen your critical thinking skills.
Final Thoughts
With our tips on how to write an analytical essay and examples, you're ready to boost your writing skills and craft essays that captivate your audience. With practice, you'll become a pro at analytical writing, ready to tackle any topic with confidence.
And hey, if you need help to buy essay online , just drop us a line saying ' do my homework for me ' and we'll jump right in!
Do Analytical Essays Tend to Intimidate You?
Give us your assignment to uncover a deeper understanding of your chosen analytical essay topic!
How to Write an Analytical Essay?
What is an analytical essay, what is the purpose of an analytical essay, related articles.
.webp)

McNair Scholars: 10. Scholarly Journal Article Analysis
- Before Your Library Visit...
- 1. Review the Literature
- 2. Identify Appropriate Resources
- 3. Organize Sources
- 4. Write & Cite in Style
- 5. Search Smarter
- 6. Search More Strategically
- 7. Use Databases
- 8. Find Your Librarian
- 9. Borrow From Other Libraries
- 10. Scholarly Journal Article Analysis
Anatomy of a Scholarly Article
Watch this video to learn about the structure of scholarly articles. Knowing this structure will help you to quickly find the type of information you want to read about.
The video was created by the staff of the D. H. Hill Jr. Library at NCSU and is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareALike 3.0 United States License .
Components of a Scientific Paper
The " IMRAD" (Introduction, Methods, Results, and Discussion) format of scientific research papers is widely-accepted, though there are variations within each discipline. This list adds a few additional sections that are typically found in scientific research papers.
- Title - Succinctly describes the topic of the paper and includes appropriate terminology to help readers retrieve the paper and understand its contents.
- Abstract - In paragraph format, this summarizes the main ideas, methods, results, and conclusions of the paper.
- Introduction - The purpose of the paper is clearly stated, along with background information on the topic and a summary of research that is relevant to the topic.
- Methods - Explains the type of scientific methods or procedures that were used in the research.
- Results - The data collected in the study are presented here in text, charts and graphs.
- Discussion/Conclusion - This section contains the analysis and discussion of the data presented in the results and draws conclusions based on the data.
- Acknowledgements - Any person or organization who helped with the study through funding or other support is mentioned here.
- References - All the sources used in the paper are cited in the style that is appropriate to the discipline.
How to Read Scientific Articles
Watch this video from the Univ. of Minnesota Libraries for tips on reading scientific articles effectively.
Article Analysis Takeaways
Article assignments.
- Bau, S., Toussaint, A., Payet, R., & Witschger, O. (2017). Performance study of various Condensation Particle Counters (CPCs): Development of a methodology based on steady-state airborne DEHS particles and application to a series of handheld and stationary CPCs . Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 838 , 1-11. https:// doi:10.1088/1742-6596/838/1/012002
- Holt-Lunstad, J., Birmingham, W. & Light, K. C. (2011). The influence of depressive symptomatology and perceived stress on plasma and salivary oxytocin before, during and after a support enhancement intervention . Psychoneuroendocrinology, 36 (8), 1249-1256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psyneuen.2011.03.007 [Group 1]
- Huang, K.-L., Liu, T.-Y., Huang, Y.-C., Leong, C.-P., Lin, W.-C., & Pong, Y.-P. (2014). Functional outcome in acute stroke patients with oropharyngeal Dysphagia after swallowing therapy . Journal of Stroke and Cerebrovascular Diseases: The Official Journal of National Stroke Association, 23 (10), 2547-2553. https:// doi:10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2014.05.031 [Group 2]
- Jiang, L., Kondo, A., Shigeta, M., Endoh, S., Uejima, M., Ogura, I., & Naito, M. (2014). Evaluation of particles released from single-wall carbon nanotube/polymer composites with or without thermal aging by an accelerated abrasion test . Journal of Occupational and Environmental Hygiene, 11 (10), 658-664. https:// doi:10.1080/15459624.2014.902953 [Group 3]
- Lalander, C. H., Hill, G. B., & Vinnerås, B. (2013). Hygienic quality of faeces treated in urine diverting vermicomposting toilets . Waste Management (New York, N.Y.), 33 (11), 2204-2210. https:// doi:10.1016/j.wasman.2013.07.007
- Laskowski, D., Strzelecki, J., Pawlawk K., Dahm, H., & Balter, A.. (2018). Effect of ampicillin on adhesive properties of bacteria examined by atomic force microscopy. . Micron, 112, 84-90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micron.2018.05.005
- Pavlova, E. V., Kirilyuk, V. E., & Naidenko, S. V. (2015). Patterns of seroprevalence of feline viruses among domestic cats (Felis catus) and Pallas' cats (Otocolobus manul) in Daursky Reserve, Russia . Canadian Journal of Zoology, 93 (11), 849-855. https:// doi:10.1139/cjz-2015-0006
- Peters, E., Fennema, M., & Tiede, K. E. (2019). The loss‐bet paradox: Actuaries, accountants, and other numerate people rate numerically inferior gambles as superior . Journal of Behavioral Decision Making, 32 (1), 15–29. https://doi.org/10.1002/bdm.2085
- Trinkner, R., Mays, R. D., Cohn, E. S., Van Gundy, K. T., & Rebellon, C. J. (2019). Turning the corner on procedural justice theory: Exploring reverse causality with an experimental vignette in a longitudinal survey. Journal of Experimental Criminology, 15 (4), 661–671. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11292-019-09358-1
- << Previous: 9. Borrow From Other Libraries
- Last Updated: Feb 19, 2024 12:01 PM
- URL: https://libguides.uww.edu/mcnair
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to write a rhetorical analysis | Key concepts & examples
How to Write a Rhetorical Analysis | Key Concepts & Examples
Published on August 28, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on July 23, 2023.
A rhetorical analysis is a type of essay that looks at a text in terms of rhetoric. This means it is less concerned with what the author is saying than with how they say it: their goals, techniques, and appeals to the audience.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Key concepts in rhetoric, analyzing the text, introducing your rhetorical analysis, the body: doing the analysis, concluding a rhetorical analysis, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about rhetorical analysis.
Rhetoric, the art of effective speaking and writing, is a subject that trains you to look at texts, arguments and speeches in terms of how they are designed to persuade the audience. This section introduces a few of the key concepts of this field.
Appeals: Logos, ethos, pathos
Appeals are how the author convinces their audience. Three central appeals are discussed in rhetoric, established by the philosopher Aristotle and sometimes called the rhetorical triangle: logos, ethos, and pathos.
Logos , or the logical appeal, refers to the use of reasoned argument to persuade. This is the dominant approach in academic writing , where arguments are built up using reasoning and evidence.
Ethos , or the ethical appeal, involves the author presenting themselves as an authority on their subject. For example, someone making a moral argument might highlight their own morally admirable behavior; someone speaking about a technical subject might present themselves as an expert by mentioning their qualifications.
Pathos , or the pathetic appeal, evokes the audience’s emotions. This might involve speaking in a passionate way, employing vivid imagery, or trying to provoke anger, sympathy, or any other emotional response in the audience.
These three appeals are all treated as integral parts of rhetoric, and a given author may combine all three of them to convince their audience.
Text and context
In rhetoric, a text is not necessarily a piece of writing (though it may be this). A text is whatever piece of communication you are analyzing. This could be, for example, a speech, an advertisement, or a satirical image.
In these cases, your analysis would focus on more than just language—you might look at visual or sonic elements of the text too.
The context is everything surrounding the text: Who is the author (or speaker, designer, etc.)? Who is their (intended or actual) audience? When and where was the text produced, and for what purpose?
Looking at the context can help to inform your rhetorical analysis. For example, Martin Luther King, Jr.’s “I Have a Dream” speech has universal power, but the context of the civil rights movement is an important part of understanding why.
Claims, supports, and warrants
A piece of rhetoric is always making some sort of argument, whether it’s a very clearly defined and logical one (e.g. in a philosophy essay) or one that the reader has to infer (e.g. in a satirical article). These arguments are built up with claims, supports, and warrants.
A claim is the fact or idea the author wants to convince the reader of. An argument might center on a single claim, or be built up out of many. Claims are usually explicitly stated, but they may also just be implied in some kinds of text.
The author uses supports to back up each claim they make. These might range from hard evidence to emotional appeals—anything that is used to convince the reader to accept a claim.
The warrant is the logic or assumption that connects a support with a claim. Outside of quite formal argumentation, the warrant is often unstated—the author assumes their audience will understand the connection without it. But that doesn’t mean you can’t still explore the implicit warrant in these cases.
For example, look at the following statement:
We can see a claim and a support here, but the warrant is implicit. Here, the warrant is the assumption that more likeable candidates would have inspired greater turnout. We might be more or less convinced by the argument depending on whether we think this is a fair assumption.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Rhetorical analysis isn’t a matter of choosing concepts in advance and applying them to a text. Instead, it starts with looking at the text in detail and asking the appropriate questions about how it works:
- What is the author’s purpose?
- Do they focus closely on their key claims, or do they discuss various topics?
- What tone do they take—angry or sympathetic? Personal or authoritative? Formal or informal?
- Who seems to be the intended audience? Is this audience likely to be successfully reached and convinced?
- What kinds of evidence are presented?
By asking these questions, you’ll discover the various rhetorical devices the text uses. Don’t feel that you have to cram in every rhetorical term you know—focus on those that are most important to the text.
The following sections show how to write the different parts of a rhetorical analysis.
Like all essays, a rhetorical analysis begins with an introduction . The introduction tells readers what text you’ll be discussing, provides relevant background information, and presents your thesis statement .
Hover over different parts of the example below to see how an introduction works.
Martin Luther King, Jr.’s “I Have a Dream” speech is widely regarded as one of the most important pieces of oratory in American history. Delivered in 1963 to thousands of civil rights activists outside the Lincoln Memorial in Washington, D.C., the speech has come to symbolize the spirit of the civil rights movement and even to function as a major part of the American national myth. This rhetorical analysis argues that King’s assumption of the prophetic voice, amplified by the historic size of his audience, creates a powerful sense of ethos that has retained its inspirational power over the years.
The body of your rhetorical analysis is where you’ll tackle the text directly. It’s often divided into three paragraphs, although it may be more in a longer essay.
Each paragraph should focus on a different element of the text, and they should all contribute to your overall argument for your thesis statement.
Hover over the example to explore how a typical body paragraph is constructed.
King’s speech is infused with prophetic language throughout. Even before the famous “dream” part of the speech, King’s language consistently strikes a prophetic tone. He refers to the Lincoln Memorial as a “hallowed spot” and speaks of rising “from the dark and desolate valley of segregation” to “make justice a reality for all of God’s children.” The assumption of this prophetic voice constitutes the text’s strongest ethical appeal; after linking himself with political figures like Lincoln and the Founding Fathers, King’s ethos adopts a distinctly religious tone, recalling Biblical prophets and preachers of change from across history. This adds significant force to his words; standing before an audience of hundreds of thousands, he states not just what the future should be, but what it will be: “The whirlwinds of revolt will continue to shake the foundations of our nation until the bright day of justice emerges.” This warning is almost apocalyptic in tone, though it concludes with the positive image of the “bright day of justice.” The power of King’s rhetoric thus stems not only from the pathos of his vision of a brighter future, but from the ethos of the prophetic voice he adopts in expressing this vision.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
The conclusion of a rhetorical analysis wraps up the essay by restating the main argument and showing how it has been developed by your analysis. It may also try to link the text, and your analysis of it, with broader concerns.
Explore the example below to get a sense of the conclusion.
It is clear from this analysis that the effectiveness of King’s rhetoric stems less from the pathetic appeal of his utopian “dream” than it does from the ethos he carefully constructs to give force to his statements. By framing contemporary upheavals as part of a prophecy whose fulfillment will result in the better future he imagines, King ensures not only the effectiveness of his words in the moment but their continuing resonance today. Even if we have not yet achieved King’s dream, we cannot deny the role his words played in setting us on the path toward it.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
The goal of a rhetorical analysis is to explain the effect a piece of writing or oratory has on its audience, how successful it is, and the devices and appeals it uses to achieve its goals.
Unlike a standard argumentative essay , it’s less about taking a position on the arguments presented, and more about exploring how they are constructed.
The term “text” in a rhetorical analysis essay refers to whatever object you’re analyzing. It’s frequently a piece of writing or a speech, but it doesn’t have to be. For example, you could also treat an advertisement or political cartoon as a text.
Logos appeals to the audience’s reason, building up logical arguments . Ethos appeals to the speaker’s status or authority, making the audience more likely to trust them. Pathos appeals to the emotions, trying to make the audience feel angry or sympathetic, for example.
Collectively, these three appeals are sometimes called the rhetorical triangle . They are central to rhetorical analysis , though a piece of rhetoric might not necessarily use all of them.
In rhetorical analysis , a claim is something the author wants the audience to believe. A support is the evidence or appeal they use to convince the reader to believe the claim. A warrant is the (often implicit) assumption that links the support with the claim.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, July 23). How to Write a Rhetorical Analysis | Key Concepts & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 8, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/rhetorical-analysis/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, how to write an argumentative essay | examples & tips, how to write a literary analysis essay | a step-by-step guide, comparing and contrasting in an essay | tips & examples, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
16+ SAMPLE Article Analysis Templates in PDF | MS Word
Article analysis templates | ms word, 16+ sample article analysis templates, what is an article analysis, the three main purposes of writing, how to process an effective article analysis, what is apa format in article analysis, what is mla format in article analysis, what does it mean to analyze an article.

Journal Article Analysis Assignment

Article Analysis Worksheet
Article Analysis Essay Template

Content Analysis of Articles

Analysis of Empirical Article

Journal Article Analysis Example

Article Analysis Questions

Newspaper Article Analysis

Critical Analysis of an Article

Business Article Analysis Template

Nonfiction Article Analysis Template

Article Summary Analysis Template

Article Research Analysis Template

Legal Analysis of Article
Sample Article Analysis Template

Research Article Analysis Template

Basic Article Analysis Template

A Quick Look into the Origins of Writing
Article analysis: why is it important, step 1: read the article twice, step 2: analyze the article, step 3: summarize the gist in your words, step 4: be critical; do not personalize, step 5: observe a sense of open-mindedness, step 6: polish your work, share this post on your network, file formats, word templates, google docs templates, excel templates, powerpoint templates, google sheets templates, google slides templates, pdf templates, publisher templates, psd templates, indesign templates, illustrator templates, pages templates, keynote templates, numbers templates, outlook templates, you may also like these articles, 25+ sample business impact analysis templates in pdf | ms word.
As the COVID-19 continues and has already affected many lives of people worldwide, there is also big economic damage that negatively affected the global economy. According to Statista's estimate,…
53+ SAMPLE Analysis Report Templates in PDF | MS Word | Google Docs | Apple Pages
Are you familiar with those complex statistical graphs, detailed organizational charts, or tables presented in business? Such visual representations are useful to give information, define relationships, and show patterns of…
browse by categories
- Questionnaire
- Description
- Reconciliation
- Certificate
- Spreadsheet
Information
- privacy policy
- Terms & Conditions
Newspaper Article Analysis Term Paper
Newspapers are a means through which information is conveyed to the reader. However, there are different facets that are involved while conveying messages to the reader. The Washington Post is an example of a newspaper which will be used in this context for analysis with regard to “Philadelphia Escalated its Conflict with an Anarchist Group”.
The topic can make one to believe that there is a certain group trying to overthrow the government in place but, this is not the case. This is a newspaper analysis on the aspect of class differences, which apparently has been painted a different picture by the newspaper headlines.
The photograph depicts two different racial groups, the black and the whites. This is an implication that there exist two different types of classes. A photograph is an “object that has been chosen, composed, structured, worked on and treated based on professional, ideological and aesthetic norms, which are various factors of connotation” (cited in Bignell 98).
The two racial groups are a representation of the different classes that exist in Philadelphia. Price (431) has shown how the two groups suggest two types of classes: the wealthy and superior verses the poor and suppressed. This is illustrated by the white man who is neatly dressed and represents formality and authority while the three other men are a symbol of informality and submission.
Classism is also endorsed by the fact that there is unequal representation brought out by the two groups. The three black men as opposed to one white man tell it all about the inequality and injustice that prevails. The two groups are paradigms of the different cultural affiliations and social classes present in Philadelphia.
Cultural differences should not be used to point out a certain group of people as an anarchist as reported in the article. Unfortunately, this is the case in Philadelphia as the poor are seen as ‘White trash’ (Price, 431-435).
The photograph as declared by Carter in his ‘Semiotic Analysis of Newspaper Front-Page Photographs’, is used to portray a certain kind of attitude. Both groups connote lack of sentimentality. This can be attributed to the fact that there is some kind of resentment towards each other due to the differences in social class, not forgetting the conflicts involved.
The white man in the photograph is MOVE’s lawyer, a responsibility he has assumed out of obligation. He does not care about the black people who in this case are the suppressed minority characterized by poverty, illiteracy and ignorance.
The white lawyer is therefore representing the group due to the returns associated with this position and not because he cares for the black people, the poor. Robert Guzzardi has also been referred to as MOVE’s lawyer but his talk as indicated in the article, does not correspond to this role (Quinn and Flood A4).
According to the headlines, one expects to find an incomparable level of conflict between Philadelphia state and the ‘MOVE’ group. Apparently, this is not the case and the setting up of the blockade is not called for.
The demeanor of the ‘MOVE’ is one that is connoted by poverty, ignorance and illiteracy, away from the upheld perception that they rebel against the authority set in place. The cause of conflict as implied in the article can be solved through a consensus after arriving at a conclusion as implied by the photograph, despite not being the case.
The main theme of the article as observed from the headlines is that there is escalated dispute between the state of Philadelphia and the supposed ‘anarchist group’ going by the name ‘move’. Typographic coding has been used to grasp the attention of the reader.
In showing the emphasis of the conflict between Philadelphia state and the ‘MOVE’, the article has used capital letters while referring to these two groups. On the contrary, a detailed examination of the contents of the newspaper indicates that the move group is not an anarchist as reported. The difference is with reference to cultural beliefs, values and social class.
The large sized photograph and the eye catching headlines leave the reader in an indecisive status. What is what? Conflict, or there is more to the façade of conflict that has been pointed out in the headlines. The picture, contrary to the headlines, shows some dialogue taking place between two sides. At a glance, it is quite obvious that something is amiss here as the headlines and the photograph convey different messages.
The main war is on equality with regard to power and culture, and not treason. Contrary to what one may expect, there is no exchange of fire between MOVE and the blockade. This is a clear show that ‘MOVE’ is not an anarchist as stated.
Linguistically, the term ‘escalates’ and ‘anarchist group’ have been used to suggest tension and segregation thereby indicating resentment, hostility and displeasure. The article implies a connection with Philadelphia but maintains a distance with the anarchist group. Familiarity of the elite individuals in state is evident whereas details about ‘MOVE’ are lacking hence, maintaining a distance between this group and the reader.
MOVE is seen as a criminal gang and at no one time has the article supported this group in any way. Several allegations have been made and are thought to be linked with ‘MOVE’ but there is no single evidence of this.
Photographs, typographic codes and language are some of the elements that are used to analyze a newspaper. These elements can present a certain picture based on composition and appropriate structuring. However, it takes more than a mere glimpse to actually get the actual message. A thorough content analysis of any paper is very essential so as to obtain the actual message being conveyed.
Works Cited
Bignell, J. Media Semiotics: An Introduction. Manchester: Manchester Press. 1997.
Carter, Paul . A Semiotic Analysis of Newspaper Front-Page Photographs . 2000. Web.
Price, Angelina. Working Class Whites. In Readings for Analytical Writings . Farris, Christine. (Ed). Bloomington: Indiana University Press, 2007.
Quinn, Jim & Flood, Ralph. Philadelphia Escalates its Conflict with an Anarchist Group. The Washington Post . 1978.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2023, November 2). Newspaper Article Analysis. https://ivypanda.com/essays/news-stories-analytics/
"Newspaper Article Analysis." IvyPanda , 2 Nov. 2023, ivypanda.com/essays/news-stories-analytics/.
IvyPanda . (2023) 'Newspaper Article Analysis'. 2 November.
IvyPanda . 2023. "Newspaper Article Analysis." November 2, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/news-stories-analytics/.
1. IvyPanda . "Newspaper Article Analysis." November 2, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/news-stories-analytics/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Newspaper Article Analysis." November 2, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/news-stories-analytics/.
- Taking Credit for Writing
- Nineteenth-Century Women in "The Yellow Wallpaper" and "An Anarchist Looks at Life"
- Neville Brody and the Fact of Typography
- “Do Designers Show Categorical Perception of Typefaces?" by Dyson
- Text Messaging as a Communication Form
- Understanding Violence: Different Perspectives
- Headlines twice the size of the events
- "The Dispossessed" Story by Ursula K. Le Guin
- Framing Effects of Television News Coverage of Social Protest
- The U.S. Decision to Blockade Cuba
- The History of Print Media and Its Competition With the Internet
- How the range and value of news have been influenced by technological advances in news production
- Content analysis: Why is it that many US citizens are not well informed about international events
- What Makes a Successful Situation Comedy?
- Changes in Telecommunications & Workings of the Media Industries
Log in using your username and password
- Search More Search for this keyword Advanced search
- Latest content
- Current issue
- Write for Us
- BMJ Journals More You are viewing from: Google Indexer
You are here
- Volume 24, Issue 2
- Five tips for developing useful literature summary tables for writing review articles
- Article Text
- Article info
- Citation Tools
- Rapid Responses
- Article metrics
- http://orcid.org/0000-0003-0157-5319 Ahtisham Younas 1 , 2 ,
- http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7839-8130 Parveen Ali 3 , 4
- 1 Memorial University of Newfoundland , St John's , Newfoundland , Canada
- 2 Swat College of Nursing , Pakistan
- 3 School of Nursing and Midwifery , University of Sheffield , Sheffield , South Yorkshire , UK
- 4 Sheffield University Interpersonal Violence Research Group , Sheffield University , Sheffield , UK
- Correspondence to Ahtisham Younas, Memorial University of Newfoundland, St John's, NL A1C 5C4, Canada; ay6133{at}mun.ca
https://doi.org/10.1136/ebnurs-2021-103417
Statistics from Altmetric.com
Request permissions.
If you wish to reuse any or all of this article please use the link below which will take you to the Copyright Clearance Center’s RightsLink service. You will be able to get a quick price and instant permission to reuse the content in many different ways.
Introduction
Literature reviews offer a critical synthesis of empirical and theoretical literature to assess the strength of evidence, develop guidelines for practice and policymaking, and identify areas for future research. 1 It is often essential and usually the first task in any research endeavour, particularly in masters or doctoral level education. For effective data extraction and rigorous synthesis in reviews, the use of literature summary tables is of utmost importance. A literature summary table provides a synopsis of an included article. It succinctly presents its purpose, methods, findings and other relevant information pertinent to the review. The aim of developing these literature summary tables is to provide the reader with the information at one glance. Since there are multiple types of reviews (eg, systematic, integrative, scoping, critical and mixed methods) with distinct purposes and techniques, 2 there could be various approaches for developing literature summary tables making it a complex task specialty for the novice researchers or reviewers. Here, we offer five tips for authors of the review articles, relevant to all types of reviews, for creating useful and relevant literature summary tables. We also provide examples from our published reviews to illustrate how useful literature summary tables can be developed and what sort of information should be provided.
Tip 1: provide detailed information about frameworks and methods
- Download figure
- Open in new tab
- Download powerpoint
Tabular literature summaries from a scoping review. Source: Rasheed et al . 3
The provision of information about conceptual and theoretical frameworks and methods is useful for several reasons. First, in quantitative (reviews synthesising the results of quantitative studies) and mixed reviews (reviews synthesising the results of both qualitative and quantitative studies to address a mixed review question), it allows the readers to assess the congruence of the core findings and methods with the adapted framework and tested assumptions. In qualitative reviews (reviews synthesising results of qualitative studies), this information is beneficial for readers to recognise the underlying philosophical and paradigmatic stance of the authors of the included articles. For example, imagine the authors of an article, included in a review, used phenomenological inquiry for their research. In that case, the review authors and the readers of the review need to know what kind of (transcendental or hermeneutic) philosophical stance guided the inquiry. Review authors should, therefore, include the philosophical stance in their literature summary for the particular article. Second, information about frameworks and methods enables review authors and readers to judge the quality of the research, which allows for discerning the strengths and limitations of the article. For example, if authors of an included article intended to develop a new scale and test its psychometric properties. To achieve this aim, they used a convenience sample of 150 participants and performed exploratory (EFA) and confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) on the same sample. Such an approach would indicate a flawed methodology because EFA and CFA should not be conducted on the same sample. The review authors must include this information in their summary table. Omitting this information from a summary could lead to the inclusion of a flawed article in the review, thereby jeopardising the review’s rigour.
Tip 2: include strengths and limitations for each article
Critical appraisal of individual articles included in a review is crucial for increasing the rigour of the review. Despite using various templates for critical appraisal, authors often do not provide detailed information about each reviewed article’s strengths and limitations. Merely noting the quality score based on standardised critical appraisal templates is not adequate because the readers should be able to identify the reasons for assigning a weak or moderate rating. Many recent critical appraisal checklists (eg, Mixed Methods Appraisal Tool) discourage review authors from assigning a quality score and recommend noting the main strengths and limitations of included studies. It is also vital that methodological and conceptual limitations and strengths of the articles included in the review are provided because not all review articles include empirical research papers. Rather some review synthesises the theoretical aspects of articles. Providing information about conceptual limitations is also important for readers to judge the quality of foundations of the research. For example, if you included a mixed-methods study in the review, reporting the methodological and conceptual limitations about ‘integration’ is critical for evaluating the study’s strength. Suppose the authors only collected qualitative and quantitative data and did not state the intent and timing of integration. In that case, the strength of the study is weak. Integration only occurred at the levels of data collection. However, integration may not have occurred at the analysis, interpretation and reporting levels.
Tip 3: write conceptual contribution of each reviewed article
While reading and evaluating review papers, we have observed that many review authors only provide core results of the article included in a review and do not explain the conceptual contribution offered by the included article. We refer to conceptual contribution as a description of how the article’s key results contribute towards the development of potential codes, themes or subthemes, or emerging patterns that are reported as the review findings. For example, the authors of a review article noted that one of the research articles included in their review demonstrated the usefulness of case studies and reflective logs as strategies for fostering compassion in nursing students. The conceptual contribution of this research article could be that experiential learning is one way to teach compassion to nursing students, as supported by case studies and reflective logs. This conceptual contribution of the article should be mentioned in the literature summary table. Delineating each reviewed article’s conceptual contribution is particularly beneficial in qualitative reviews, mixed-methods reviews, and critical reviews that often focus on developing models and describing or explaining various phenomena. Figure 2 offers an example of a literature summary table. 4
Tabular literature summaries from a critical review. Source: Younas and Maddigan. 4
Tip 4: compose potential themes from each article during summary writing
While developing literature summary tables, many authors use themes or subthemes reported in the given articles as the key results of their own review. Such an approach prevents the review authors from understanding the article’s conceptual contribution, developing rigorous synthesis and drawing reasonable interpretations of results from an individual article. Ultimately, it affects the generation of novel review findings. For example, one of the articles about women’s healthcare-seeking behaviours in developing countries reported a theme ‘social-cultural determinants of health as precursors of delays’. Instead of using this theme as one of the review findings, the reviewers should read and interpret beyond the given description in an article, compare and contrast themes, findings from one article with findings and themes from another article to find similarities and differences and to understand and explain bigger picture for their readers. Therefore, while developing literature summary tables, think twice before using the predeveloped themes. Including your themes in the summary tables (see figure 1 ) demonstrates to the readers that a robust method of data extraction and synthesis has been followed.
Tip 5: create your personalised template for literature summaries
Often templates are available for data extraction and development of literature summary tables. The available templates may be in the form of a table, chart or a structured framework that extracts some essential information about every article. The commonly used information may include authors, purpose, methods, key results and quality scores. While extracting all relevant information is important, such templates should be tailored to meet the needs of the individuals’ review. For example, for a review about the effectiveness of healthcare interventions, a literature summary table must include information about the intervention, its type, content timing, duration, setting, effectiveness, negative consequences, and receivers and implementers’ experiences of its usage. Similarly, literature summary tables for articles included in a meta-synthesis must include information about the participants’ characteristics, research context and conceptual contribution of each reviewed article so as to help the reader make an informed decision about the usefulness or lack of usefulness of the individual article in the review and the whole review.
In conclusion, narrative or systematic reviews are almost always conducted as a part of any educational project (thesis or dissertation) or academic or clinical research. Literature reviews are the foundation of research on a given topic. Robust and high-quality reviews play an instrumental role in guiding research, practice and policymaking. However, the quality of reviews is also contingent on rigorous data extraction and synthesis, which require developing literature summaries. We have outlined five tips that could enhance the quality of the data extraction and synthesis process by developing useful literature summaries.
- Aromataris E ,
- Rasheed SP ,
Twitter @Ahtisham04, @parveenazamali
Funding The authors have not declared a specific grant for this research from any funding agency in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
Competing interests None declared.
Patient consent for publication Not required.
Provenance and peer review Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Read the full text or download the PDF:
- Business Templates
- Sample Analysis
FREE 10+ Article Analysis Samples in PDF
Preparing and formatting an article analysis paper requires critical thinking of the literature, identifying the purpose statement of the article, and evaluating the point of view of the author. As numerous pieces of information are being spread today, it is an important skill for a reader to know how to analyze an article correctly to identify its most important points. By analyzing an article, readers can easily remember what they learned, increase their critical thinking capabilities, and will add value to their professionalism.
Article Analysis
Free 10+ article analysis samples, 1. business article analysis, 2. article analysis grading, 3. journal article analysis, 4. empirical article analysis, 5. standard article analysis, 6. article analysis example, 7. article analysis worksheet, 8. research article analysis, 9. basic article analysis, 10. multimodal news article analysis, 11. article analysis in pdf, what is an article analysis, how to write an article analysis, what are the examples of an author’s purpose in writing, what are the key points to remember in writing an article analysis, why do we analyze an article.

Size: 209 KB

Size: 316 KB

Size: 40 KB

Size: 346 KB

Size: 149 KB

Size: 58 KB

Size: 577 KB
Size: 46 KB

Size: 443 KB

Size: 51 KB
An article analysis is a summarization of literature’s main points as well as the analytical critique of the writer’s purpose of the article writing and determines if the reader has read, understood, and can apply the article to their tasks which also helps in determining their critical thinking skills. Analyzing an article means understanding the type of literature you are going to analyze so you can proceed with the correct tone and format for your paper. This paper is usually used for business management, data journalism , strategic planning , and project management.
Writing an article analysis aims to understand the thesis statement and contents of an article which means the reader should have to break down and study each of its parts. You must also ensure that the article project analysis paper’s readers will understand its key points easily while expressing your critical thinking skills so you can proceed with clear opinions and conclusions.
1. Understand the Content of the Article
To start analyzing an article, you must first read and understand its content. By reading the entire article, you will be able to determine the purpose of the author or the main points of the literature as well as the secondary points and verifications he used to support his arguments.
2. Conduct Your Own Research to Verify any Information
One feature of a good article is that includes a piece of new information that you must investigate to acquire a full understanding of the matter. You can conduct your own research to investigate the authority of the writer, the validity of their claims, and provide meaning to terms you do not understand.
3. Provide the Summarized Main Points of the Article
You must be able to give the summarized main points of the literature using your own words after reading, researching, and investigating the article’s information. Summarizing the article will show how much you have learned and understand the article and its author’s points.
4. Construct Your Own Opinion on the Subject
When you gain an understanding of the article, you can now construct your own opinion on the subject matter. You can accept the author’s argument, oppose it, or somewhere between the two. Constructing your own opinion means you can now implement your own understanding of the article.
Some of the several purposes why an author writes is to inform the reader by providing clear structure and enough evidence to support facts, to persuade them by presenting logical reasoning, or to entertain them by showing them emotions that articles can cause.
In writing an article, convey your ideas in a subjective way, ensure to properly introduce your subject in your paper, use evidence and facts to support your claims and ideas, convey the literature’s value and relevance by using critical analysis writing, and be unbiased as you read, analyze, and write your article analysis paper.
Analyzing an article provides an opportunity to explain its main points to the readers, the importance of its evidence and facts, its purpose, and its connection to other ideas in the article.
Article analysis enables its readers to increase their understanding of an article’s content because it conveys the author’s point of view, and analysis or provides a completed evaluation sheet of a given literature. It is also important to understand what type of article a writer is working with as there can be various types of articles to analyze.
Related Posts
Free 10+ make or buy analysis samples in pdf, free 10+ fishbone root cause analysis samples in pdf, free 11+ cost volume profit analysis samples & templates in pdf | ms word, free 6+ corporate portfolio analysis samples in pdf, free 10+ fault tree analysis samples in pdf, free 10+ comp analysis samples in pdf, free 10+ fishbone analysis samples in pdf, free 10+ individual swot analysis samples in pdf, free 10+ 5 year analysis samples in pdf, free 10+ benefit costs analysis samples in pdf, free 10+ job hazard analysis samples in pdf, free 10+ primary source analysis samples in pdf, free 10+ literary analysis samples in pdf, free 10+ critical path analysis samples in pdf, free 10+ competition analysis samples in pdf, free 12+ customer service swot analysis templates in pdf, free 11+ functional behavioral analysis samples in pdf, free 10+ research analysis report samples in ms word pdf, free 10+ sample employee swot analysis templates in pdf ....
- Bihar Board
SRM University
Ap inter results.
- AP Board Results 2024
- UP Board Result 2024
- CBSE Board Result 2024
- MP Board Result 2024
- Rajasthan Board Result 2024
- Shiv Khera Special
- Education News
- Web Stories
- Current Affairs
- नए भारत का नया उत्तर प्रदेश
- School & Boards
- College Admission
- Govt Jobs Alert & Prep
- GK & Aptitude
- CBSE Class 12
CBSE Class 12 Computer Science Paper Analysis 2024: Exam Review, Student Feedback and Expert View
Cbse class 12 computer science paper analysis 2024: in this article, students can find cbse class 12 computer science exam analysis 2024 and get to know about the overall difficulty level of the paper. also, find students reactions on cbse 12th computer science exam 2024. .

CBSE Class 12 Computer Science Exam Paper Analysis 2024: The Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) Board Exam 2024 has now come to an end on April 2, 2024. Today, CBSE had scheduled Class 12 Computer Science Exam 2024 and with the completion of this exam, CBSE Board Exams 2024 has been successfully ended. All the students who have appeared for today’s exam can check the CBSE Class 12 Computer Science exam analysis 2024. As a part of the analysis, students will get to know about the overall difficulty level of the question paper, section-wise challenges faced by students, types of questions asked in the exam, paper pattern followed, and a lot more. Also, get to know the students’ reactions on today’s CBSE 12th Computer Science question paper 2024 along with experts’ opinion on the same.
CBSE Class 12 Computer Science Exam 2024 Key Highlights
Cbse class 12 computer science paper review 2024.
- The CBSE Class 12 Computer Science Question Paper 2024 was moderate
- It would fall under easy to moderate category
- The programming questions were moderately challenging
- MCQs were a combination of easy and tricky ones
- Very short answer type questions, short answer type questions, long answer type questions were also a good mix of easy and tricky questions.
CBSE Class 12 Computer Science Paper Review 2024: Students’ Reactions
- Challenging Areas in Computer Science Questions: The entire paper was a combination of mixed questions
- Type of Questions asked in Today’s Computer Science Exam: MCQs, Very short answer type questions, short answer type questions, long answer type questions, Programming based questions
- Section-wise Class 12 Computer Science Exam Review: Section A was average, B and C were easy, Section D was moderately hard
CBSE Class 12 Computer Science Paper Analysis 2024 - Experts' Review
- Experts have agreed to students’ reaction on the paper. They have said that the question paper was moderate
- The paper was completely based on the format of the sample paper
- There was no out-of-syllabus question. Everything was asked from within the curriculum laid down by the board.
- MCQs were a good mix of easy and tricky questions
- Programming based questions were also quite easy
- Overall, the paper was quite doable
CBSE Class 12 Computer Science Question Paper 2024
Cbse class 12 computer science answer key 2024.
Check the CBSE Class 12 Computer Science answer key 2024 here and verify your answers from the article link attached above.
Also Check:
CBSE Class 12 Syllabus 2023-2024 (All Subjects)
CBSE Class 12 Sample Paper 2023-2024 (All Subjects)
CBSE Class 12 Practice Papers 2023-2024
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 (All Subjects and Chapters)
Important Questions for Class 12 Board Exam 2024 (All Subjects)
Get here latest School , CBSE and Govt Jobs notification in English and Hindi for Sarkari Naukari and Sarkari Result . Download the Jagran Josh Sarkari Naukri App . Check Board Result 2024 for Class 10 and Class 12 like CBSE Board Result , UP Board Result , Bihar Board Result , MP Board Result , Rajasthan Board Result and Other States Boards.
- NDA 1 Admit Card 2024
- TSPSC AE Answer Key 2024
- NDA Admit Card 2024
- CTET Correction Window 2024
- NTA NITTT Result 2024
- APPSC Group 2 Result 2024
- CUET PG Answer Key 2024
- TN SET Application Form 2024
Latest Education News
[Current] Orange Cap and Purple Cap Holders in IPL 2024
IPL Orange Cap 2024: दिलचस्प हो गयी है ऑरेंज कैप की रेस, ये युवा बल्लेबाज रेस में है शामिल
Surya Grahan 2024 Live: अपने मोबाइल पर LIVE देखें साल के पहले सूर्यग्रहण का यह अद्भुत नजारा
Genius IQ Test: Find the missing number in 5 seconds!
Picture Puzzle IQ Test: Can You Spot The Hidden Paintbrush In 12 Seconds?
NDA Admit Card 2024 Live Updates: UPSC NDA 1 Hall Ticket Download Link on upsc.gov.in Soon
SBI Clerk Mains Result 2024 Delayed: Check Latest Updates Here
UPPSC Agriculture Officer Recruitment 2024: यूपी एग्रीकल्चर ऑफिसर परीक्षा के लिए शार्ट नोटिस जारी
Google Tests "Lookup" Button for Unknown Callers: Know What it is
Today’s School Assembly Headlines (9 April): Total Solar Eclipse 2024, Right Against Climate Change, Heat Wave Alert in India and Other News in English
ISRO URSC Admit Card 2024 Released at isro.gov.in, Check Download Link
MUHS Result 2024 OUT at muhs.ac.in; Direct Link to Download UG and PG Marksheet PDF
IIM Bangalore holds 49th Convocation Ceremony; award degrees to 706 students
IPL Points Table 2024: आईपीएल 2024 अपडेटेड पॉइंट टेबल यहां देखें
CUET PG 2024 Answer Key OUT LIVE: NTA Releases Provisional Answer Keys and Response Sheets, Check Latest Updates
Optical Illusion: Find the hidden frog in the picture in 8 seconds!
SSC Revised Exam Dates 2024 for JE, Selection Post 12, CPO and CHSL Released at ssc.gov.in, Check New Schedule Here
Purple Cap in IPL 2024: इन पांच गेंदबाजों में है पर्पल कैप की रेस, कौन निकलेगा सबसे आगे?
RGPV Diploma Results 2024 OUT on rgpvdiploma.in; Direct Link to Download All Semester Marksheet PDF
ISRO URSC Admit Card 2024 OUT: जारी हुआ इसरो यूआरएससी परीक्षा का हॉल टिकट, cdn.digialm.com से करें डाउनलोड

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A journal article analysis paper should be written in paragraph format and include an instruction to the study, your analysis of the research, and a conclusion that provides an overall assessment of the author's work, along with an explanation of what you believe is the study's overall impact and significance. ... Examples can include ...
The analysis shows that you can evaluate the evidence presented in the research and explain why the research could be important. Summary. The summary portion of the paper should be written with enough detail so that a reader would not have to look at the original research to understand all the main points. At the same time, the summary section ...
One of the most crucial parts of an analysis essay is the citation of the author and the title of the article. First, introduce the author by first and last name followed by the title of the article. Add variety to your sentence structure by using different formats. For example, you can use "Title," author's name, then a brief explanation ...
Step 4: Write a critical analysis of an article. Follow your plan and write the paper. Do not be afraid to express your point of view and give examples. It is also important to correctly cite the article you are analyzing and all additional materials.
Table of contents. Step 1: Reading the text and identifying literary devices. Step 2: Coming up with a thesis. Step 3: Writing a title and introduction. Step 4: Writing the body of the essay. Step 5: Writing a conclusion. Other interesting articles.
Analyzing Research Articles: A Guide for Readers and Writers1 Sam Mathews, Ph.D. Department of Psychology The University of West Florida The critical reader of a research report expects the writer to provide logical and coherent rationales for conducting the study, concrete descriptions of methods, procedures, design, and analyses, accurate and clear reports of the findings, and plausible ...
A critical analysis essay requires you to analyze a subject and determine its meaning, backing it with evidence and ideas of your own. ... believing (and understanding). We can't help you with your actual critical analyzing, but we can at least give you an example of a critical analysis essay to show you how it might look. Note that we're ...
In writing an analysis, you begin by prewriting; then, you formulate a thesis and offer support from the article. Prewriting Begin by reading the article carefully. Then make notes about the various parts of the article and how they contribute to its thesis, or argument. Title. Consider the title of the journal article or essay.
Give a rundown of the main ideas from the research article. It should answer five questions: what, why, who, when, and how. Additionally, it would help if you talked about the paper's structure, point of view, and style. Ensure that you properly identify the research methods used in the study.
Here are some key tips for analyzing an article in most subjects without falling in to the trap of summarizing instead. 1) Read through your professor's essay prompt first before you begin writing. Keep it in mind as you read the article. Underline or circle key words. Rephrase and rewrite in your own words what it is the professor is asking ...
2 Research your topic. Once you know your topic, you can begin collecting data and evidence to discuss it. If your analytical essay is about a creative work, you may want to spend time reviewing or evaluating that work, such as watching a film closely or studying the details of a painting.
Save the word count for the "meat" of your paper — that is, for the analysis. 2. Summarize the Article. Now, you should write a brief and focused summary of the scientific article. It should be shorter than your analysis section and contain all the relevant details about the research paper.
Here is our analytical writing sample to see theory in action. Notice how analytical thinking applies to real-world situations, improving your understanding of concepts. By studying these examples, you'll learn to analyze complex issues, build strong arguments, and sharpen your critical thinking skills. Health Risks.
Summary Writing Steps. A summary is telling the main ideas of the article in your own words. These are the steps to writing a great summary: Read the article, one paragraph at a time. For each paragraph, underline the main idea sentence (topic sentence). If you can't underline the book, write that sentence on your computer or a piece of paper.
The "IMRAD" (Introduction, Methods, Results, and Discussion) format of scientific research papers is widely-accepted, though there are variations within each discipline.This list adds a few additional sections that are typically found in scientific research papers. Title - Succinctly describes the topic of the paper and includes appropriate terminology to help readers retrieve the paper and ...
The following two sample papers were published in annotated form in the Publication Manual and are reproduced here as PDFs for your ease of use. The annotations draw attention to content and formatting and provide the relevant sections of the Publication Manual (7th ed.) to consult for more information.. Student sample paper with annotations (PDF, 4.95MB)
A rhetorical analysis is a type of essay that looks at a text in terms of rhetoric. This means it is less concerned with what the author is saying than with how they say it: their goals, techniques, and appeals to the audience. A rhetorical analysis is structured similarly to other essays: an introduction presenting the thesis, a body analyzing ...
Writing a critical analysis involves evaluating and interpreting a text, such as a book, article, or film, and expressing your opinion about its quality and significance. Here are some steps you can follow to write a critical analysis: Read and re-read the text: Before you begin writing, make sure you have a good understanding of the text. Read ...
In a critical analysis essay, you systematically evaluate a work's effectiveness including what it does well and what it does poorly. It can be used to discuss a book, article or even a film. You must read the piece carefully and may need to look up terms or concepts you are unfamiliar with or research related reading prior to writing your essay.
A critical analysis paper asks the writer to make an argument about a particular book, essay, movie, etc. The goal is two fold: one, identify and explain the argument that the author is making, and two, provide your own argument about that argument. One of the key directions of these assignments is often to avoid/minimize summary - you are ...
Step 2: Analyze the Article. As you insert questions and analyze the whole article, never forget to be guided by our article analysis templates. How the format and design look like is introduced to you by the templates up for grabs. A common idea on how to scrutinize articles is by recognizing the article structure, voice, tone, metaphors, and ...
The Washington Post is an example of a newspaper which will be used in this context for analysis with regard to "Philadelphia Escalated its Conflict with an Anarchist Group". The topic can make one to believe that there is a certain group trying to overthrow the government in place but, this is not the case. This is a newspaper analysis on ...
Literature reviews offer a critical synthesis of empirical and theoretical literature to assess the strength of evidence, develop guidelines for practice and policymaking, and identify areas for future research.1 It is often essential and usually the first task in any research endeavour, particularly in masters or doctoral level education. For effective data extraction and rigorous synthesis ...
Preparing and formatting an article analysis paper requires critical thinking of the literature, identifying the purpose statement of the article, and evaluating the point of view of the author. As numerous pieces of information are being spread today, it is an important skill for a reader to know how to analyze an article correctly to identify its most important points.
Check what experts' think about today's CBSE Class 12 Computer Science paper 2024. Experts have agreed to students' reaction on the paper. They have said that the question paper was moderate ...