Comparative Essay

How to Write a Comparative Essay – A Complete Guide
10 min read
People also read
Learn How to Write an Editorial on Any Topic
Best Tips on How to Avoid Plagiarism
How to Write a Movie Review - Guide & Examples
A Complete Guide on How to Write a Summary for Students
Write Opinion Essay Like a Pro: A Detailed Guide
Evaluation Essay - Definition, Examples, and Writing Tips
How to Write a Thematic Statement - Tips & Examples
How to Write a Bio - Quick Tips, Structure & Examples
How to Write a Synopsis – A Simple Format & Guide
Visual Analysis Essay - A Writing Guide with Format & Sample
List of Common Social Issues Around the World
Writing Character Analysis - Outline, Steps, and Examples
11 Common Types of Plagiarism Explained Through Examples
Article Review Writing: A Complete Step-by-Step Guide with Examples
A Detailed Guide on How to Write a Poem Step by Step
Detailed Guide on Appendix Writing: With Tips and Examples
Comparative essay is a common assignment for school and college students. Many students are not aware of the complexities of crafting a strong comparative essay.
If you too are struggling with this, don't worry!
In this blog, you will get a complete writing guide for comparative essay writing. From structuring formats to creative topics, this guide has it all.
So, keep reading!
- 1. What is a Comparative Essay?
- 2. Comparative Essay Structure
- 3. How to Start a Comparative Essay?
- 4. How to Write a Comparative Essay?
- 5. Comparative Essay Examples
- 6. Comparative Essay Topics
- 7. Tips for Writing A Good Comparative Essay
- 8. Transition Words For Comparative Essays
What is a Comparative Essay?
A comparative essay is a type of essay in which an essay writer compares at least two or more items. The author compares two subjects with the same relation in terms of similarities and differences depending on the assignment.
The main purpose of the comparative essay is to:
- Highlight the similarities and differences in a systematic manner.
- Provide great clarity of the subject to the readers.
- Analyze two things and describe their advantages and drawbacks.
A comparative essay is also known as compare and contrast essay or a comparison essay. It analyzes two subjects by either comparing them, contrasting them, or both. The Venn diagram is the best tool for writing a paper about the comparison between two subjects.
Moreover, a comparative analysis essay discusses the similarities and differences of themes, items, events, views, places, concepts, etc. For example, you can compare two different novels (e.g., The Adventures of Huckleberry Finn and The Red Badge of Courage).
However, a comparative essay is not limited to specific topics. It covers almost every topic or subject with some relation.
Comparative Essay Structure
A good comparative essay is based on how well you structure your essay. It helps the reader to understand your essay better.
The structure is more important than what you write. This is because it is necessary to organize your essay so that the reader can easily go through the comparisons made in an essay.
The following are the two main methods in which you can organize your comparative essay.
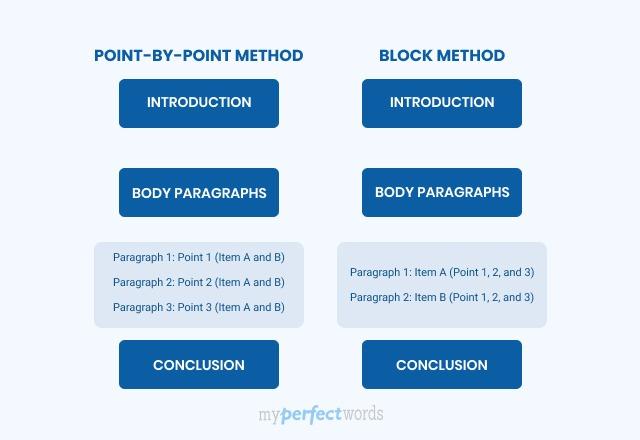
Point-by-Point Method
The point-by-point or alternating method provides a detailed overview of the items that you are comparing. In this method, organize items in terms of similarities and differences.
This method makes the writing phase easy for the writer to handle two completely different essay subjects. It is highly recommended where some depth and detail are required.
Below given is the structure of the point-by-point method.
Block Method
The block method is the easiest as compared to the point-by-point method. In this method, you divide the information in terms of parameters. It means that the first paragraph compares the first subject and all their items, then the second one compares the second, and so on.
However, make sure that you write the subject in the same order. This method is best for lengthy essays and complicated subjects.
Here is the structure of the block method.
Therefore, keep these methods in mind and choose the one according to the chosen subject.
Mixed Paragraphs Method
In this method, one paragraph explains one aspect of the subject. As a writer, you will handle one point at a time and one by one. This method is quite beneficial as it allows you to give equal weightage to each subject and help the readers identify the point of comparison easily.
How to Start a Comparative Essay?
Here, we have gathered some steps that you should follow to start a well-written comparative essay.
Choose a Topic
The foremost step in writing a comparative essay is to choose a suitable topic.
Choose a topic or theme that is interesting to write about and appeals to the reader.
An interesting essay topic motivates the reader to know about the subject. Also, try to avoid complicated topics for your comparative essay.
Develop a List of Similarities and Differences
Create a list of similarities and differences between two subjects that you want to include in the essay. Moreover, this list helps you decide the basis of your comparison by constructing your initial plan.
Evaluate the list and establish your argument and thesis statement .
Establish the Basis for Comparison
The basis for comparison is the ground for you to compare the subjects. In most cases, it is assigned to you, so check your assignment or prompt.
Furthermore, the main goal of the comparison essay is to inform the reader of something interesting. It means that your subject must be unique to make your argument interesting.
Do the Research
In this step, you have to gather information for your subject. If your comparative essay is about social issues, historical events, or science-related topics, you must do in-depth research.
However, make sure that you gather data from credible sources and cite them properly in the essay.
Create an Outline
An essay outline serves as a roadmap for your essay, organizing key elements into a structured format.
With your topic, list of comparisons, basis for comparison, and research in hand, the next step is to create a comprehensive outline.
Here is a standard comparative essay outline:
How to Write a Comparative Essay?
Now that you have the basic information organized in an outline, you can get started on the writing process.
Here are the essential parts of a comparative essay:
Comparative Essay Introduction
Start off by grabbing your reader's attention in the introduction . Use something catchy, like a quote, question, or interesting fact about your subjects.
Then, give a quick background so your reader knows what's going on.
The most important part is your thesis statement, where you state the main argument , the basis for comparison, and why the comparison is significant.
This is what a typical thesis statement for a comparative essay looks like:
Comparative Essay Body Paragraphs
The body paragraphs are where you really get into the details of your subjects. Each paragraph should focus on one thing you're comparing.
Start by talking about the first point of comparison. Then, go on to the next points. Make sure to talk about two to three differences to give a good picture.
After that, switch gears and talk about the things they have in common. Just like you discussed three differences, try to cover three similarities.
This way, your essay stays balanced and fair. This approach helps your reader understand both the ways your subjects are different and the ways they are similar. Keep it simple and clear for a strong essay.
Comparative Essay Conclusion
In your conclusion , bring together the key insights from your analysis to create a strong and impactful closing.
Consider the broader context or implications of the subjects' differences and similarities. What do these insights reveal about the broader themes or ideas you're exploring?
Discuss the broader implications of these findings and restate your thesis. Avoid introducing new information and end with a thought-provoking statement that leaves a lasting impression.
Below is the detailed comparative essay template format for you to understand better.
Comparative Essay Format
Comparative Essay Examples
Have a look at these comparative essay examples pdf to get an idea of the perfect essay.
Comparative Essay on Summer and Winter
Comparative Essay on Books vs. Movies
Comparative Essay Sample
Comparative Essay Thesis Example
Comparative Essay on Football vs Cricket
Comparative Essay on Pet and Wild Animals
Comparative Essay Topics
Comparative essay topics are not very difficult or complex. Check this list of essay topics and pick the one that you want to write about.
- How do education and employment compare?
- Living in a big city or staying in a village.
- The school principal or college dean.
- New Year vs. Christmas celebration.
- Dried Fruit vs. Fresh. Which is better?
- Similarities between philosophy and religion.
- British colonization and Spanish colonization.
- Nuclear power for peace or war?
- Bacteria or viruses.
- Fast food vs. homemade food.
Tips for Writing A Good Comparative Essay
Writing a compelling comparative essay requires thoughtful consideration and strategic planning. Here are some valuable tips to enhance the quality of your comparative essay:
- Clearly define what you're comparing, like themes or characters.
- Plan your essay structure using methods like point-by-point or block paragraphs.
- Craft an introduction that introduces subjects and states your purpose.
- Ensure an equal discussion of both similarities and differences.
- Use linking words for seamless transitions between paragraphs.
- Gather credible information for depth and authenticity.
- Use clear and simple language, avoiding unnecessary jargon.
- Dedicate each paragraph to a specific point of comparison.
- Summarize key points, restate the thesis, and emphasize significance.
- Thoroughly check for clarity, coherence, and correct any errors.
Transition Words For Comparative Essays
Transition words are crucial for guiding your reader through the comparative analysis. They help establish connections between ideas and ensure a smooth flow in your essay.
Here are some transition words and phrases to improve the flow of your comparative essay:
Transition Words for Similarities
- Correspondingly
- In the same vein
- In like manner
- In a similar fashion
- In tandem with
Transition Words for Differences
- On the contrary
- In contrast
- Nevertheless
- In spite of
- Notwithstanding
- On the flip side
- In contradistinction
Check out this blog listing more transition words that you can use to enhance your essay’s coherence!
In conclusion, now that you have the important steps and helpful tips to write a good comparative essay, you can start working on your own essay.
However, if you find it tough to begin, you can always hire our professional essay writing service .
Our skilled writers can handle any type of essay or assignment you need. So, don't wait—place your order now and make your academic journey easier!
Frequently Asked Question
How long is a comparative essay.
A comparative essay is 4-5 pages long, but it depends on your chosen idea and topic.
How do you end a comparative essay?
Here are some tips that will help you to end the comparative essay.
- Restate the thesis statement
- Wrap up the entire essay
- Highlight the main points

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Dr. Barbara is a highly experienced writer and author who holds a Ph.D. degree in public health from an Ivy League school. She has worked in the medical field for many years, conducting extensive research on various health topics. Her writing has been featured in several top-tier publications.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Write a Comparative Essay
Last Updated: May 19, 2023 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Christopher Taylor, PhD . Christopher Taylor is an Adjunct Assistant Professor of English at Austin Community College in Texas. He received his PhD in English Literature and Medieval Studies from the University of Texas at Austin in 2014. There are 8 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 1,682,513 times.
Perhaps you have been assigned a comparative essay in class, or need to write a comprehensive comparative report for work. In order to write a stellar comparative essay, you have to start off by picking two subjects that have enough similarities and differences to be compared in a meaningful way, such as two sports teams or two systems of government. Once you have that, then you have to find at least two or three points of comparison and use research, facts, and well-organized paragraphs to impress and captivate your readers. Writing the comparative essay is an important skill that you will use many times throughout your scholastic career.
Comparative Essay Outline and Example

How to Develop the Essay Content

- Many comparative essay assignments will signal their purpose by using words such as "compare," "contrast," "similarities," and "differences" in the language of the prompt.
- Also see whether there are any limits placed on your topic.

- The assignment will generally ask guiding questions if you are expected to incorporate comparison as part of a larger assignment. For example: "Choose a particular idea or theme, such as love, beauty, death, or time, and consider how two different Renaissance poets approach this idea." This sentence asks you to compare two poets, but it also asks how the poets approach the point of comparison. In other words, you will need to make an evaluative or analytical argument about those approaches.
- If you're unclear on what the essay prompt is asking you to do, talk with your instructor. It's much better to clarify questions up front than discover you've written the entire essay incorrectly.

- The best place to start is to write a list of things that the items you are comparing have in common as well as differences between them. [3] X Research source

- You may want to develop a system such as highlighting different types of similarities in different colors, or use different colours if you are using an electronic device.
- For example, if you are comparing two novels, you may want to highlight similarities in characters in pink, settings in blue, and themes or messages in green.

- The basis for your comparison may be assigned to you. Be sure to check your assignment or prompt.
- A basis for comparison may have to do with a theme, characteristics, or details about two different things. [7] X Research source
- A basis for comparison may also be known as the “grounds” for comparison or a frame of reference.
- Keep in mind that comparing 2 things that are too similar makes it hard to write an effective paper. The goal of a comparison paper is to draw interesting parallels and help the reader realize something interesting about our world. This means your subjects must be different enough to make your argument interesting.

- Research may not be required or appropriate for your particular assignment. If your comparative essay is not meant to include research, you should avoid including it.
- A comparative essay about historical events, social issues, or science-related topics are more likely to require research, while a comparison of two works of literature are less likely to require research.
- Be sure to cite any research data properly according to the discipline in which you are writing (eg, MLA, APA, or Chicago format).

- Your thesis needs to make a claim about your subjects that you will then defend in your essay. It's good for this claim to be a bit controversial or up for interpretation, as this allows you to build a good argument.
How to Organize the Content

- Use a traditional outline form if you would like to, but even a simple list of bulleted points in the order that you plan to present them would help.
- You can also write down your main points on sticky notes (or type them, print them, and then cut them out) so that you can arrange and rearrange them before deciding on a final order.

- The advantages of this structure are that it continually keeps the comparison in the mind of the reader and forces you, the writer, to pay equal attention to each side of the argument.
- This method is especially recommended for lengthy essays or complicated subjects where both the writer and reader can easily become lost. For Example: Paragraph 1: Engine power of vehicle X / Engine power of vehicle Y Paragraph 2: Stylishness of vehicle X / Stylishness of vehicle Y Paragraph 3: Safety rating of vehicle X / Safety rating of vehicle Y

- The advantages of this structure are that it allows you to discuss points in greater detail and makes it less jarring to tackle two topics that radically different.
- This method is especially recommended for essays where some depth and detail are required. For example: Paragraph 1: Engine power of vehicle X Paragraph 2: Engine power of vehicle Y Paragraph 3: Stylishness of vehicle X Paragraph 4: Stylishness of vehicle Y Paragraph 5: Safety rating of vehicle X Paragraph 6: Safety rating of vehicle Y

- This method is by far the most dangerous, as your comparison can become both one-sided and difficult for the reader to follow.
- This method is only recommended for short essays with simplistic subjects that the reader can easily remember as (s)he goes along. For example: Paragraph 1: Engine power of vehicle X Paragraph 2: Stylishness of vehicle X Paragraph 3: Safety rating of vehicle X Paragraph 4: Engine power of vehicle Y Paragraph 5: Stylishness of vehicle Y Paragraph 6: Safety rating of vehicle Y
How to Write the Essay

- Body paragraphs first . Work through all that information you've been compiling and see what kind of story it tells you. Only when you've worked with your data will you know what the larger point of the paper is.
- Conclusion second . Now that you've done all the heavy lifting, the point of your essay should be fresh in your mind. Strike while the iron’s hot. Start your conclusion with a restatement of your thesis.
- Intro last . Open your introduction with a "hook" to grab the reader's attention. Since you've already written your essay, choose a hook that reflects what you will talk about, whether it's a quote, statistic, factoid, rhetorical question, or anecdote. Then, write 1-2 sentences about your topic, narrowing down to your thesis statement, which completes your introduction.

- Organize your paragraphs using one of the approaches listed in the "Organizing the Content" part below. Once you have defined your points of comparison, choose the structure for the body paragraphs (where your comparisons go) that makes the most sense for your data. To work out all the organizational kinks, it’s recommended that you write an outline as a placeholder.
- Be very careful not to address different aspects of each subject. Comparing the color of one thing to the size of another does nothing to help the reader understand how they stack up. [15] X Research source

- Be aware that your various comparisons won’t necessarily lend themselves to an obvious conclusion, especially because people value things differently. If necessary, make the parameters of your argument more specific. (Ex. “Though X is more stylish and powerful, Y’s top safety ratings make it a more appropriate family vehicle .”)
- When you have two radically different topics, it sometimes helps to point out one similarity they have before concluding. (i.e. "Although X and Y don't seem to have anything in common, in actuality, they both ....”)

- Even the best writers know editing is important to produce a good piece. Your essay will not be your best effort unless you revise it.
- If possible, find a friend to look over the essay, as he or she may find problems that you missed.
- It sometimes helps to increase or decrease the font size while editing to change the visual layout of the paper. Looking at the same thing for too long makes your brain fill in what it expects instead of what it sees, leaving you more likely to overlook errors.
Expert Q&A

- The title and introduction really catch the reader's attention and make them read the essay. Make sure you know how to write a catchy essay title . Thanks Helpful 6 Not Helpful 1
- Quotes should be used sparingly and must thoroughly complement the point they are being used to exemplify/justify. Thanks Helpful 5 Not Helpful 2
- The key principle to remember in a comparative paragraph or essay is that you must clarify precisely what you are comparing and keep that comparison alive throughout the essay. Thanks Helpful 3 Not Helpful 2

- Avoid vague language such as "people," "stuff," "things," etc. Thanks Helpful 4 Not Helpful 0
- Avoid, at all costs, the conclusion that the two subjects are "similar, yet different." This commonly found conclusion weakens any comparative essay, because it essentially says nothing about the comparison. Most things are "similar, yet different" in some way. Thanks Helpful 4 Not Helpful 0
- Some believe that an "unbalanced" comparison - that is, when the essay focuses predominantly on one of the two issues, and gives less importance to the other - is weaker, and that writers should strive for 50/50 treatment of the texts or issues being examined. Others, however, value emphasis in the essay that reflects the particular demands of the essay's purpose or thesis. One text may simply provide context, or historical/artistic/political reference for the main text, and therefore need not occupy half of the essay's discussion or analysis. A "weak" essay in this context would strive to treat unequal texts equally, rather than strive to appropriately apportion space to the relevant text. Thanks Helpful 3 Not Helpful 0
- Beware of the "Frying Pan Conclusion" in which you simply recount everything that was said in the main body of the essay. While your conclusion should include a simple summary of your argument, it should also emphatically state the point in a new and convincing way, one which the reader will remember clearly. If you can see a way forward from a problem or dilemma, include that as well. Thanks Helpful 2 Not Helpful 1
You Might Also Like

- ↑ http://writingcenter.unc.edu/handouts/comparing-and-contrasting/
- ↑ http://www.writing.utoronto.ca/advice/specific-types-of-writing/comparative-essay
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/comparing-and-contrasting/
- ↑ http://writingcenter.fas.harvard.edu/pages/how-write-comparative-analysis
- ↑ https://www.butte.edu/departments/cas/tipsheets/style_purpose_strategy/compare_contrast.html
- ↑ https://open.lib.umn.edu/writingforsuccess/chapter/10-7-comparison-and-contrast/
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/the_writing_process/proofreading/steps_for_revising.html
- How to Structure Paragraphs in an Essay
About This Article

To write a comparative essay, start by writing an introduction that introduces the 2 subjects you'll be comparing. You should also include your thesis statement in the introduction, which should state what you've concluded based on your comparisons. Next, write the body of your essay so that each paragraph focuses on one point of comparison between your subjects. Finally, write a conclusion that summarizes your main points and draws a larger conclusion about the two things you compared. To learn how to do research for your essay, read on! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Nov 21, 2017
Did this article help you?

Lisa Taylor
Aug 19, 2017
Brayden Ryan
Aug 10, 2016
Antwanette Nottage
Feb 5, 2019
Bernice Sangmortey
Nov 5, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter
VCE Study Tips
English Language

Private Tutoring

Only one more step to getting your FREE text response mini-guide!
Simply fill in the form below, and the download will start straight away
English & EAL
The Ultimate Guide to VCE Comparative
May 8, 2019

Want insider tips? Sign up here!
Go ahead and tilt your mobile the right way (portrait). the kool kids don't use landscape....
Updated 14/07/2022
- What Is a Comparative?
- What Are You Expected To Cover? (Comparative Criteria)
- School Assessed Coursework (SAC), Exams and Allocated Marks
- How To Prepare for Your Comparative SAC and Exam
- How To Write a Comparative Essay
1. What Is a Comparative?
Comparative is also known as 'Reading and Comparing', 'Comparative Essay' and less frequently, 'Compare and Contrast'. For our purposes, we'll just stick to 'Comparative'.
As its name may indicate, a Comparative is when you analyse and write on two texts, comparing their similarities and differences. In VCE, there are 8 pairs of texts Year 12s can choose from (or more accurately, your school chooses for you!). The most popular combination of texts include novels and films, however, plays also make it onto the list.
When you start doing Comparative at school, you will move through your texts just as you have for Text Response (except...instead of one text it's actually two) - from watching the film and/or reading the novel, participating in class discussions about similar and different themes and ideas, and finally, submitting one single essay based on the two texts. So yep, if you've only just gotten your head around Text Response, VCAA likes to throw a spanner in the works to keep you on your toes!
But, don't worry. The good news is all of your Text Response learning is applicable to VCE’s Comparative, and it's really not as hard as it might first appear. Here's a video I created introducing Comparative ( I've time-stamped it to start at 0:55 - when the Comparative section starts - thank me later! ).
2. What Are You Expected To Cover? (Comparative Criteria)
What are teachers and examiners expecting to see in your essays? Below are the VCE criteria for Comparative essays (sourced from the VCAA English examination page ).
Note: Some schools may express the following points differently, however, they should all boil down to the same points - what is necessary in a Comparative essay.
a) Knowledge and understanding of both texts, and the ideas and issues they present
Society, history and culture all shape and influence us in our beliefs and opinions. Authors use much of what they’ve obtained from the world around them and employ this knowledge to their writing. Understanding their values embodied in texts can help us, as readers, identify and appreciate theme and character representations.
For example: Misogyny is widespread in both Photograph 51 and The Penelopiad , and both writers explore the ways in which females deal with such an environment. Photograph 51 is set in the 1950s when women begun to enter the workforce, whereas The Penelopiad is set in Ancient Greece, a period when women were less likely to speak out against discrimination.
b) Discussion of meaningful connections, similarities or differences between the texts, in response to the topic;
More about this later in 4. How To Prepare for Your Comparative SAC and Exam, Step 2: Understand both your texts - as a pair (below) .
c) Use of textual evidence to support the comparative analysis
While you should absolutely know how to embed quotes in your essay like a boss , you want to have other types of evidence in your Comparative essay. You must discuss how the author uses the form that he/she is writing in to develop their discussion. This encompasses a huge breadth of things from metaphors to structure to language.
For example: "The personification of Achilles as ‘wolf, a violator of every law of men and gods', illustrates his descent from human to animal..." or "Malouf’s constant use of the present voice and the chapter divisions allow the metaphor of time to demonstrate the futility and omnipresence of war..."
To learn more about metalanguage, read our What Is Metalanguage? post.
d) Control and effectiveness of language use, as appropriate to the task.
When examiners read essays, they are expected to get through about 12-15 essays in an hour! This results in approximately 5 minutes to read, get their head around, and grade your essay - not much time at all! It is so vital that you don’t give the examiner an opportunity to take away marks because they have to reread certain parts of your essay due to poor expression and grammar.
3. School Assessed Coursework (SAC), Exams and Allocated Marks
Comparative is the first Area of Study (AoS 1) in Unit 2 (Year 11) and Unit 4 (Year 12) - meaning that majority of students will tackle the Comparative SAC in Term 3. The number of allocated marks are:
- Unit 2 – dependant on school
- Unit 4 – 60 marks (whopper!)
The time allocated to your SAC is school-based. Schools often use one or more periods combined, depending on how long each of your periods last. Teachers can ask you to write anywhere from 900 to 1200 words for your essay (keep in mind that it’s about quality, not quantity!)
In your exam, you get a whopping total of 3 hours to write 3 essays ( Text Response , Comparative, and Language Analysis ). The general guide is 60 minutes on Comparative, however, it is up to you exactly how much time you decide to dedicate to this section of the exam. Your Comparative essay will be graded out of 10 by two different examiners. Your two unique marks from these examiners will be combined, with 20 as the highest possible mark.

4. How To Prepare for Your Comparative SAC and Exam
Preparation is a vital component in how you perform in your SACs and exam so it’s always a good idea to find out what is your best way to approach assessments. This is just to get you thinking about the different study methods you can try before a SAC. Here are my top strategies (ones I actually used in VCE) for Comparative preparation that can be done any time of year (including holidays - see How To Recharge Your Motivation Over the School Holidays for more tips):
Step 1: Understand each text - individually
This doesn’t mean reading/watching your texts a specific amount of times (though twice is usually a recommended minimum), but rather, coming to an understanding of your texts. Besides knowing important sections, quotes, themes and characters (which are still important and which you should definitely know), here are some other matters which are also necessary to consider:
- Why has it been chosen by VCAA (out of literally millions of other books)?
- Why are you reading it (especially if it’s an old text, and how it’s still important throughout the ages)?
- Why did the author write it?
- What kind of social commentary exists within the text (especially on specific issues and themes)?
These kinds of questions are important because quite often in this area of study, you’ll be defending and interpreting your own ideas alongside the author’s. When you find a solid interpretation of the text as a whole, then no essay topic will really throw you off - because you’ll know already what you think about it. Moreover, because you’re comparing two texts in this section, understanding a text and being specific (e.g. 'both texts argue that equality is important' vs. 'while both texts A and B agree with the notion of equality, A focuses on ____ whereas B highlights ____') will help your writing improve in sophistication and depth.
If you need any more tips on how to learn your texts in-depth, Susan's (English study score 50) Steps for Success in Text Study guide provides a clear pathway for how to approach your texts and is a must read for VCE English students!
And, if you're studying texts you hate (ugh!), you'll also want to check out Lavinia's guide which teaches you how to do well even when you hate your texts .
Step 2: Understand both your texts - as a pair
Avoid simply drawing connections between the texts which are immediately obvious. When writing a Comparative, the key strategy that'll help you stand out from the crowd is the CONVERGENT and DIVERGENT strategy . I discuss this in more detail below, under 'eBooks'.
We'll use George Orwell's Animal Farm and Shakespeare's Macbeth as an example ( don't worry if you haven't studied either of these texts, it's just to prove a point ). The most obvious connection simply from reading the plot is that both Napoleon and Macbeth are powerful leaders. However, you want to start asking yourself more questions to develop an insightful comparison between the two men:
For example: In Macbeth and Animal Farm a common theme is power
Q: How do they achieve power?
A: In Animal Farm , Napoleon is sly about his intentions and slowly secures his power with clever manipulation and propaganda. However , Shakespeare’s Macbeth adopts very different methods as he uses violence and abuse to secure his power.
Q: How do they maintain power?
A: Both Napoleon and Macbeth are tyrants who go to great length to protect their power. They believe in killing or chasing away anyone who undermines their power.
Q: What is the effect of power on the two characters?
A: While Macbeth concentrates on Macbeth’s growing guilty conscience and his gradual deterioration to insanity, Animal Farm offers no insight into Napoleon’s stream of consciousness. Instead, George Orwell focuses on the pain and suffering of the animals under Napoleon’s reign. This highlights Shakespeare’s desire to focus on the inner conflict of a man, whereas Orwell depicted the repercussions of a totalitarian regime on those under its ruling.
Check out our comparative scene analysis of The Longest Memory & The 7 Stages of Grieving for another example of understanding texts as a pair!
Step 3: Know your comparative words
Having a list of comparative words will help you understand your texts as a pair, and helps make your life easier when you start writing your essays. Here's a list we've compiled below:
Similarities
- Additionally
- At the same time
- Correspondingly
- Furthermore
- In addition
- In parallel
Differences
- Compared to
- Despite that
- Even though
- In contrast
- Nevertheless
- On the contrary
- On the other hand
- Nonetheless
Feel free to download the PDF version of this list for your own studies as well!
Step 4: Understand the construction of your texts
Besides comparing ideas and themes, and having an understanding of what the text says, it’s also imperative that you understand HOW the texts say it. This type of analysis focuses on metalanguage (also known as literary devices or literary techniques). When you get technical with this and focus on metalanguage, it brings out more depth in your writing.
You could start asking yourself:
- What kind of description is used?
- What kind of sentences are used?
- Are they long and winding or rather short and bare?
- Are they dripping with adjectives or snappy?
- What is the structure of the text?
- Does one begin with a prologue/end with an epilogue?
- Is the text continuous or divided e.g. through letters or days or parts?
- Does the text end at a climax or end with a true finality?
- What reoccurs throughout the text? (specific lines, symbols or images)
These kinds of understanding are important as they are evidentiary material for your arguments. What you say and believe the authors have said, as well as how you believe the texts differ, may rely heavily on these techniques. You'd then translate this analysis to develop your arguments further in your essay. For example:
His depiction of Chapel serves as a subversion of the conventional type of slave; he is 'half a slave, half the master' and belongs to 'another way of life'. His defiance and rebellion against the dictations of society is exemplified through his speech, which consists of rhythmic and poetic couplets, filled with flowery language; which ultimately challenges the idea of illiterate slaves.
Step 5: Read and watch Lisa's Study Guides' resources
Doing this study all by yourself can be rather daunting, so we've got your back. We specialise in supporting VCE English students by creating helpful videos, study guides and ebooks. Here are some just to get your started:
YouTube Videos
We create general study advice videos like this:
We also create Comparative pair-specific videos:
If you prefer learning through videos, check out our entire YouTube channel (and don't forget to subscribe for regular new videos!).
Study Guides
Our awesome team of English high-achievers have written up study guides based on popular VCE texts. Here's a compilation of all the ones we've covered so far including current and older text pairs:
Bombshells and The Penelopiad
I Am Malala and Pride
Reckoning and The Namesake
Reckoning and The Namesake (Quote Analysis)
Ransom and Invictus
Ransom and The Queen
Stasiland and 1984
Stasiland and Never Let Me Go
Stasiland and Never Let Me Go (yes this is a different guide to the one above!)
The Crucible and The Dressmaker
The Crucible and The Dressmaker (Understanding Context)
The Crucible and Year of Wonders
The Hate Race and Charlie's Country
The Longest Memory and Black Diggers
The Longest Memory and The 7 Stages of Grieving
The Penelopiad and Photograph 51
Tracks and Charlie's Country
Tracks and Into the Wild
Tip: You can download and save the study guides for your own study use! How good is that?

And if that isn't enough, I'd highly recommend my How To Write A Killer Comparative ebook. What's often the most difficult part of Comparative is finding the right examples and evidence to ensure that you're standing out against hundreds of other students studying VCE.
Unlike Text Response where there are over 30 texts for schools to choose from, Comparative only has 8 pairs of texts. This means that the likelihood of other students studying the same texts as you is much higher. And what does that mean?
It means that your competition is going to be even tougher. It's likely the character or quote you plan to use will also be used by other students. So, this means that there needs to be a way for you to differentiate yourself. Enter my golden CONVERGENT and DIVERGENT strategy .
This strategy can be used for any example you wish to use, but by approaching your example with the CONVERGENT and DIVERGENT mindset, you'll immediately be able to establish a unique perspective that should earn you some bonus marks.
If you've ever had a teacher tell you that you needed to ‘elaborate’, ‘go into more detail’, or ‘more analysis’ needed in your essays - this strategy will help eliminate all those criticisms. It will also show your teacher how you are comfortable writing an in-depth analysis using fewer examples, rather than trying to overload your essay with as many examples as possible because you barely have anything to say about each one.
To learn more about the CONVERGENT and DIVERGENT strategy, get a free preview of this study guide on the Shop page or at the bottom of this blog.
Step 6: Brainstorm and write plans
Once you've done some preliminary revision, it's time to write plans! Plans will help ensure you stick to your essay topic, and have a clear outline of what your essay will cover. This clarity is crucial to success in a Comparative essay.
Doing plans is also an extremely time-efficient way to approach SACs. Rather than slaving away hours upon hours over writing essays, writing plans will save you the burnout and get you feeling confident faster.
I've also curated essay topic breakdown videos based on specific VCE texts. In these videos, I explore keywords, ideas and how I'd plan an essay with corresponding examples/evidence.
Step 7: Get your hands on essay topics
Often, teachers will provide you with a list of prompts to practice before your SAC. Some teachers can be kind enough to nudge you in the direction of a particular prompt that may be on the SAC. If your teacher hasn’t distributed any, don’t be afraid to ask.
We have a number of free essay topics curated by our team at LSG, check some of them out:
I Am Malala and Made In Dagenham Prompts
Ransom and Invictus Prompts
Stasiland and Never Let Me Go Prompts
The Crucible and Year Of Wonders Prompts
The Penelopiad and Photograph 51 Prompts
Psst...see these fully annotated sample essays where we show you exactly how we analysed the prompt, brainstormed our ideas and created a plan for our essay:
Comparing Photograph 51 and The Penelopiad: Essay Topic Breakdown
Ransom and The Queen: Comparative Essay Topic Breakdown
The Longest Memory and Black Diggers - A Comparative Essay Breakdown
Step 8: Write essays
Yes, sad but it’s a fact. Writers only get better by actually writing . Even if you just tackle a couple of essays then at least you will have started to develop a thinking process that will help you to set out arguments logically, utilise important quotes and time yourself against the clock. It will help you write faster as well – something that is a major problem for many students. With that said, let's get into how to write a Comparative next.
5. How To Write a Comparative Essay
Comparative essay structure.
Here are a couple of resources to get your Comparative essay structure sorted. Firstly a video (time-stamped at 1:38) :
Secondly, jump over to Sarah's (English study score 47) Compare the Pair: A Guide to Structuring a Reading and Comparing Essay post where she delves into two different types of Comparative essay structures.
Comparative Essay Example
Introduction.
In an introduction, you're expected to have the following:
- Context (or background)
- Both authors' (or director's) names
- Both text titles
- Main arguments
Here's an example from Mida (English study score 43), in her post The Longest Memory and Black Diggers - A Comparative Essay Breakdown :
The hopes and dreams of oppressed individuals can be fulfilled to a certain extent. This degree of fulfilment, however, can ultimately become restricted by the entrenched beliefs and dictations of society; and thus, this process of fulfilment is presented to be difficult and rare to achieve. In Fred D’Aguiar’s novella, The Longest Memory , the hopes and dreams for equality and racial acceptance is revealed to coerce oppressed individuals to subvert social norms, all in an attempt to gain liberty and fairness. Similarly, Tom Wright’s play, Black Diggers , explores the collective yearning of oppressed Indigenous Australians who seek to gain a sense of belonging and recognition in society. Both D’Aguiar and Wright expose how the obstacles of social inequality, deep-rooted prejudice and beliefs can essentially restrict the fulfilment of such desires and dreams.
Try to keep your introduction to the point. There's no need to prolong an introduction just to make a set number of sentences. It's always better to be concise and succinct, and move into your main body paragraphs where the juicy contents of your essay resides.
Body Paragraph
Most of you will be familiar with TEEL learnt in Text Response. TEEL can stand for:
- Topic sentence
- Linking sentence
If your teacher or school teaches you something slightly different that's okay too. At the end of the day, the foundations are the same.
In Comparative, you can still use TEEL, except that you'll be making comparisons between the two texts throughout your paragraph.
The below example adopts the 'Alternate' Comparative essay structure where the first part of the body paragraph focuses on Text 1 ( The Longest Memory ) and the second half of the body paragraph focuses on Text 2 ( Black Diggers ).
The ambitions of the oppressed are achieved to a certain extent. However, they are not maintained and thus become restricted due to the beliefs and conventions entrenched in society. D’Aguiar asserts that a sense of liberation can indeed be achieved in the unjust system of slavery, and this is demonstrated through his characterisation of Chapel. His depiction of Chapel serves as a subversion of the conventional type of slave; he is 'half a slave, half the master' and belongs to 'another way of life'. His defiance and rebellion against the dictations of society is exemplified through his speech, which consists of rhythmic and poetic couplets, filled with flowery language; which ultimately challenges the idea of illiterate slaves. D’Aguiar also associates the allusion of the 'two star-crossed lovers' in regards to the relationship between Lydia and Chapel; who were 'forbidden' to 'read together'. Despite this, the two characters take on a form of illicit, linguistic, sexual intercourse with each other, as they 'touch each other’s bodies in the dark' and 'memorise [their] lines throughout'. Here, D’Aguiar illustrates their close intimacy as a form of rebellion against the Eurocentric society, who believed such interrelation between blacks and whites was 'heinous' and 'wicked'. The individualistic nature of Chapel is also paralleled in Black Diggers , where Wright’s portrayal of Bertie expresses the yearning for a sense of belonging. Just like Chapel, Bertie desires free will, and he decides to 'fight for the country'. This aspiration of his however, is restrained by both his Mum and Grandad; who in a similar manner as Whitechapel, represent the voice of reality and reason. Wright employs the metaphor of the Narrandera Show to depict the marginalisation and exclusion of Aboriginal people, as they will never be 'allowed through the wire', or essentially, ever be accepted in Australia. This notion of exclusion is further reinforced through Bertie’s gradual loss of voice and mentality throughout Wright’s short vignettes, as he soon becomes desensitised and is 'unable to speak'. Here, Wright seems to suggest that the silenced voices of the Indigenous soldiers depict the eternal suffering they experienced; from both the horrors of war, but also the continual marginalisation and lack of recognition they faced back home. Consequently, D’Aguiar and Wright highlight how the ambitions of young individuals are limited by the truths and history of reality, and are essentially rarely achieved.
Conclusions should be short and sweet. Summarise your main points while comparing the two texts (just as you have throughout your entire essay).
D’Aguiar and Wright both illustrate oppressed individuals fighting against the beliefs and conventions of society; in order to gain their freedom and achieve their hopes and dreams. However, both reveal the harsh truths of reality that ultimately inhibit and restrict the capacity of people’s ambitions. D’Aguiar and Wright compel their readers to try and grasp an understanding of the past of slaves and Aboriginal soldiers, in order to seek remembrance and closure of this fundamental truth. They both convey the need for memories and the past to never be forgotten; and instead remembered and recognised in history.
For further detail from Sarah (English study score 45), read her advice on 5 Tips For A Mic-Drop Worthy Essay Conclusion .
If you're looking for more A+ Comparative essay examples, then you can also get your hands on any of our LSG study guide ebooks. Each study guide has 5 comparative essays, all fully annotated so you can see into the mind of a high achiever. These comparative essay examples also adopt different essay structures (block, alternating, and integrated) so you can see all three in action.
Ransom & The Queen
The Crucible & The Dressmaker
The 7 Stages of Grieving & The Longest Memory
I Am Malala & Pride
Photograph 51 & My Brilliant Career
This blog guide is fantastic to get you started - there are certain strategies you can implement to ensure your Comparative essay wows your examiner and gives you an A-grade ranking. These strategies have been adopted by high-achievers in the past few years and have resulted in student achieving study scores of 45+. Make sure you don't miss out on these strategies by accessing a free sample of our How To Write A Killer Comparative ebook. In the meantime, good luck!
Get our FREE VCE English Text Response mini-guide
Now quite sure how to nail your text response essays? Then download our free mini-guide, where we break down the art of writing the perfect text-response essay into three comprehensive steps. Click below to get your own copy today!

Unsure how to study for your Comparative SAC or exam?
- Learn LSG's unique CONVERGENT and DIVERGENT strategy which has helped hundreds of students achieve A+ in their assessments
- Includes sample A+ essays with EVERY essay annotated and broken down on HOW and WHY students achieved A+ so you reach your goals quicker
- Different types of essay structures broken down so you understand what to do and what not to do with confidence
- Learn how to stand out from other students with unique points of comparison
.png)
Are you a slow writer who struggles to write down all of the information that you hear in the listening audio clip? Have you ever been in a situation where the next sentence in the audio comes up way before you finish writing down information from the previous sentence? If yes, then this blog is for you!
You want to write down as much useful information as possible in a short period of time during your VCE EAL exam, so it is very useful to implement a system of techniques that works well for you personally. Here are some ideas and suggestions that you may want to use to increase the speed of your note-taking.
1. Use Different Coloured Pens or Keys for Different Speakers
Under the stress of exams/SACs, you might lose track of which speaker is talking. This is likely to happen if the speakers are of the same sex or they sound similar to each other (from personal experience, I had a listening task with 3 female speakers!) A simple way to remind yourself of who is speaking is to take side notes with different coloured pens and/or symbols for different speakers.
For example:
If in the audio: Lisa says, ‘The weather is lovely’ and Cici replies ‘Let’s go for a run’. We can write side notes using L (for Lisa) and C for Cici, which may look like:
L ‘weather is lovely’
C 'Let's go for a run’
Or, you could use a red pen for Lisa and blue pen for Cici.
2. Use Signs & Symbols to Replace Words
Using symbols is an efficient way to increase the speed of writing and ultimately increase the amount of information that you can record. Here are some examples of symbols I have used in the past and the meanings I gave them.
→ Leading to/Stimulate/Result in
↑ Increase
↓ Decrease
⇆ Exchangeable
☓ Cross/Incorrect
∴ Therefore OR Consequently
? Uncertain/Possibly/Disapprove
> Greater than/More than
< Less than/Fewer than
~ Approximately OR Around OR Similar to OR Not Equal OR Not the same as
c/b Could be
- Negative/Before
+ Positive/Plus
3.Use Abbreviations
Use abbreviations that work for you. There is no right or wrong here as the ‘blank space for scribbles’ will not be marked. Abbreviations can take the form of short notes or letters...you get to be creative here!
You can also choose to keep only the essential vowels and consonants in words. Or, leave out the double consonants and silent letters. The following list contains some abbreviations for common words or phases:
Answer = answ
About = abt
Morning = am
Afternoon = pm
As soon as possible = asap
Before = bef/b4
Between = bt
Because = bc
Common = com
Condition = cond
Diagnosis = diag
Regular = reg
Notes = nts
With respect to = wrt
Will be = w/b
Within = w/i
Without = w/o
Here are some examples of how you might use abbreviations and symbols:
‘You should remember to take notes in classes’
Can be abbreviated as:
‘U shld rmbr t tk nts in cls’
Example 2
‘Gidon has a rare blood condition which means he visits the hospital quite regularly. Since his diagnosis, Gidon’s family paid more than ten thousand dollars just to visit the hospital. Gidon initiated a petition that advocates for lowering the fees for parking in hospitals and putting a limit on how much the hospital can charge.’
- G has rare blood condi → he visits hosp. v. reg.
I've used G as an abbreviation for Gidon, and the arrow here represents that the stuff on the left side of the arrow (i.e. his rare blood condition), led to the events on the right side of the arrow (i.e. regular hospital visits).
- Since his diag. → G’s fam paid >$10K to visit hosp.
Here I’ve also used the arrow, indicating that the stuff on the left side of the arrow (i.e. his diagnosis), led to the events on the right side of the arrow (i.e. Gidon's family paid more than 10 thousand dollars). I’ve also used >$10K to indicate that the amount Gidon’s family paid is more than 10 thousand dollars.
- G → petition → advocates for ↓ $ parking & limit how much hosp. can charge
Using my symbols and abbreviations above, it’s your turn to work out how I’ve abbreviated this ;)
I hope these tips and tricks will assist you with note taking during the EAL listening SACs and exam. If you would like more practice on the listening section, check out the following blogs!
EAL Listening Practice and Resources
EAL Listening Practice
Tips on EAL Listening
- Plot Summaries
- Textual Features Analysis
- Themes (Convergent and Divergent Strategy)
- LSG’s Bubble Tea (BBT) Strategy for Unique Strategies
- Sample Essay Questions
Essay Topic Breakdown
For a detailed guide on Comparative, check out our Ultimate Guide to VCE Comparative.
1. Plot Summaries
In Stasiland , Anna Funder, the author and first-person narrator , meets and listens to the ordinary people of East Germany : those who resisted the GDR dictatorship, those who were crushed by it, and those who diligently and remorselessly worked for it as Stasi informants or officers. As Anna speaks with those whose lives have been traumatised by the Stasi, she reflects on how the reunified Germany has dealt with (or ignored) its citizens' trauma and whether memory can be reconciled . Anna is an Australian working for a television station in Berlin in 1996. As an outsider Anna is uniquely positioned to ask East Germans about their experiences , as they do not have to battle with prior knowledge and experience to share their stories. She is interested in the former German Democratic Republic and what has happened to the East German people since the country reunified with West Germany. She became curious after learning that there are people putting together documents that were shredded by the Stasi.
Anna travels to Leipzig and visits the former headquarters of East Germany’s secret police, the Stasi, which is now a museum. The Stasi were the East German secret police and internal surveillance and defense force . Headed by Erich Mielke, they conducted surveillance on the East German population, aided by a vast number of civilian informants. While in Leipzig, Anna meets with a woman called Miriam Weber, who attempted to sneak out of East Germany when she was just a teenager. Miriam, sleep deprived and tortured, lied about receiving help from an organisation to cross the Wall and was sentenced to jail time. Her husband Charlie was also imprisoned by the Stasi and died while in custody. Miriam was told he committed suicide by hanging, but she suspects he was killed after the Stasi refused to show her his body and went to great lengths to hide Charlie during the funeral.
Returning to the apartment she rents in Berlin, Anna puts an advertisement in the paper calling for former Stasi agents and informers to share their stories with her. She meets with several ex-Stasi men, including Herr Winz, Herr Christian, Herr Bohnsack and Hagen Koch. She also visits and speaks to Karl-Eduard von Schitzler, a hateful man who hosted a propaganda-filled television program that criticised West Germany and gave false information about Communist success. In their discussions the former Stasi agents are concerned with justifying their involvement with the Stasi, although many also remain committed to communist ideals and await with anticipation the next revolution and restoration of the communist government.
Anna rents her apartment from an unpredictable and evasive young woman called Julia. Over time, Julia comes to trust Anna and shares her story of the Stasi cruelly interfering with her life. Anna also speaks with her rock musician friend Klaus Renft – East Germany’s Mick Jagger, and a woman named Frau Paul who was separated overnight from her sick infant son when the Berlin Wall went up and was later imprisoned for inflated charges of assisting people to escape East Germany.
After Anna’s mother is diagnosed with cancer, she goes home to Australia for 3 years, returning to Berlin to meet with some of the people she spoke with during her earlier stay, including Hagen Koch and Miriam. She also finally visits the ‘puzzlers’ in Nuremberg, whose story first sparked her interest in investigating the lives of East Germans affected by the Stasi. Anna is disappointed in the puzzlers, realising that their work is futile and there is no real effort put towards uncovering the lost information.
Almost all East Germans were left reeling at the sudden collapse of their government. For many, the collapse of the GDR took with it ideological security and made them nostalgic for the past. For others, being confronted with the level of the Stasi’s intrusion into their lives was deeply traumatic, as people realised they had been grievously betrayed by their fellow citizens, neighbours and even family members. The nostalgia for the regime that Funder witnesses shows how people cling to certainty and position and sometimes struggle with new freedoms. However, having spoken with so many individuals whose lives were ruined by the Stasi, Anna feels that the old regime was oppressive and authoritarian, and that the East Germans are better off with the challenges of their freedom, rather than stuck with the certainties of their oppression.
Never Let Me Go
Never Let Me Go is set in a dystopian alternative reality in England in the 1990s. The narrator, Kathy H, is a thirty-one-year-old 'carer' – a clone who looks after other clones who are donating their organs. Kathy is about to retire after a long career as a carer to become a donor herself, meaning she will soon 'complete' ( a euphemism for dying ). However, this premise is not immediately apparent to the reader . At the start of the novel, Kathy informs us she will be leaving her role as carer in a few months and has started to write down memories of her life, sorting through her time as a 'student' at Hailsham. However, at the start of the novel the reader is not aware that Kathy is a clone, although she appears to be addressing an insider from her world.
In the first third of the novel Kathy reflects on her childhood and teenage years at Hailsham . Hailsham is an institution where clones are looked after by 'guardians' and referred to as 'students', and which at first appears to be a private boarding school with a heavy focus on the arts and creativity. Their best works of painting, pottery, drawing or poetry were selected and taken away by a woman known as 'Madame', for what the students presume, and what is later confirmed to be, a gallery. The students know they are different from their guardians and the people who live outside Hailsham, referred to as 'normals', but the truth of what the clones are and their certain fate is not fully articulated until the characters are adults.
Kathy is close friends with a confident and controlling girl called Ruth and a boy named Tommy, whose work is never selected for the Gallery – an acknowledgement that defines status at the school. Tommy, teased and excluded, struggles to control his temper and often explodes into furies of rage. The students collect items and other students’ artwork for their own memory boxes , bought or traded at the school’s Exchanges and Sales. Kathy buys a cassette tape by a woman named Judy Bridgewater that contains a song called ‘Never Let Me Go’. This song makes Kathy emotional, and one day she is caught dancing to it by Madame, who Kathy is surprised to see is in tears watching her. Kathy presumes Madame is upset because she knows Kathy can never have children.
Ruth and Tommy start dating and Part Two sees the three friends reach early adulthood and move to a place known as the Cottages, to live with other clones from around the country and experience some freedom before beginning their donations or training to become a carer. When Rodney, another Cottage resident, believes he saw Ruth’s 'possible' – an original that one of the clones was modelled off – the three friends along with Rodney and his girlfriend Chrissie, take a trip to Norfolk to find her. Norfolk exists in the imagination of the Hailsham students as a 'lost corner', where things they have lost will be found. While the 'possible' is not Ruth’s original, Kathy and Tommy find a copy of the Judy Bridgewater tape that Kathy had lost. Ruth was secretly desperate to find her possible and hoped to find her working in an office. Ruth dreams of working in an office and her wish that her possible will be an office worker is one of the only suggestions we have that the clones secretly long for more from their lives and view their possibles as versions of them and what they are capable of. Back at the Cottages, Ruth continues to be manipulative and self-promoting, leading to a falling out with Kathy where she decides to leave early to begin training as a carer and falls out of contact with Ruth and Tommy.
Part Three encompasses Kathy’s time as a carer. Years after the time at the Cottages, Kathy organises to be Ruth’s carer and Ruth reconnects Kathy and Tommy, admitting she knew they loved each other and deliberately kept them apart. She hopes they will attempt to get a deferral from Madame. After Ruth 'completes', Kathy and Tommy finally become a couple. They visit Madame to ask for a deferral, who informs them there is no such thing. They learn from Madame that Hailsham was an attempt to reform the treatment of clones in their youth by proving they had souls . In most centers, clones are reared in deplorable, abusive conditions. They also learn that Hailsham had to be shut down. The normals became too uncomfortable with the reality of the clones’ souls but were not prepared to lose their organ supply. Never Let Me Go is a story about injustice and social stratification, where one group is made to suffer for the benefit of another. The 'normals' can deny their mortality while forcing the clones to confront their death sooner than their natural life span , and by shutting down schools like Hailsham, they do not need to think about the ethics of their choices.
Tommy dies and Kathy resigns herself to her fate as a donor. At the end of the novel, Kathy misses Tommy and Ruth, but consoles herself that she will always have her memories with her . Ishiguro explores the extent to which people accept their predetermined fate and how they can find meaning and love within those often-cruel limitations.
2. Textual Features Analysis
A textual feature is a component of the text used by authors to give meaning to their work. It is necessary to engage with the actual construction of the texts and to discuss textual features using metalanguage (terms that describe and analyse language). To write a thorough and thoughtful essay, you need to understand the textual features and how they are connected to overall thematic ideas. Structural features and metalanguage can be used as evidence of authorial intent and deepen our understanding of how writers use literary techniques to develop ideas and create meaning. Let’s take a look at Genre .
Stasiland is an example of creative nonfiction, meaning it tells a story of factual events and real people using literary and poetic techniques. The word ‘creative’ doesn’t give authors permission to exaggerate or dramatise the truth, instead this genre is one of factually accurate prose about real people and events that is told in a vivid and compelling way.
The reason Stasiland is classified as creative nonfiction and not under the genre of memoir is because although the events follow Anna Funder’s experiences in Berlin, they are not predominantly about her. A memoir is the writer’s own personal journey and life, whereas creative nonfiction generally has more public relevance and commentary. In Stasiland , Funder’s experiences in Berlin structure the chronology of the narrative but take a thematic backseat to the stories of the East Germans she meets and the historical events she relays .
Never Let Me Go has elements of multiple genres: dystopian fiction, speculative historical fiction, science fiction and bildungsroman.
‘Dystopia’ means the opposite of ‘utopia’, but you’ll notice that most dystopian novels are set in societies where the ruling classes believe they are in a utopia. This is true of Never Let Me Go , as the clones pay with their lives and freedom for the utopian elimination of disease and extended life spans of the 'normals '. However, while clearly set in a horrific dystopian world, Never Let Me Go notably differs from other novels in the dystopian genre, as the oppressed clones never once consider rebelling against the status quo – the most Kathy and Tommy hope for is an extension before beginning their donations and 'completing'. Ishiguro has stated in multiple interviews that he was most interested in exploring why oppressed persons never consider rebelling against their fate – what leads them to passive acceptance of their position in society?
In his exploration of this question, Ishiguro explores the development and growing up of Kathy, Ruth, and Tommy, trying to understand why they all submit without protest to their fate . In this sense the novel is a bildungsroman. Bildungsroman is a genre concerned with the psychological and moral development of a protagonist from childhood to adulthood, focusing on a person’s formation or coming of age. Never Let Me Go follows Kathy, Ruth and Tommy throughout their childhood and adolescence at Hailsham, their experience of limited freedom at the Cottages as young adults, and finally the reality of their short adult life as organ donors.
Of course, Never Let Me Go also fits into the category of speculative historical fiction and science fiction. The novel is set in an alternate historical reality where genetic science rapidly advanced after World War Two (significantly outstripping the real-world) and clones have been used to extend life in the UK for decades. However, Ishiguro does not give much narrative weight to describing the political reality of his fictional world , and neither does he offer much scientific explanation for the existence of clones. As we’ve already discussed, Ishiguro was vastly more interested in using these scientific and political circumstances to create conditions within which to explore characters and, by extension, human nature, so Never Let Me Go fits uneasily in these genres.
3. Themes (Convergent and Divergent Strategy)
Now that we’ve looked closely at both Stasiland and Never Let Me Go , it’s time to discuss in depth the key themes and ideas. Themes are the big ideas about human experience that a text explores, and form part of the message the author is hoping to communicate. A sound knowledge of key themes is essential for developing a thoughtful essay. All essay topics will ask you to explore thematic ideas in one way or another. If you have a strong understanding of both texts’ themes and how they are communicated, you will be able to generate arguments for any essay topic with confidence.
I’ll be adhering to the CONVERGENT and DIVERGENT strategy. This guide doesn’t go into too much detail about using LSG’s CONVERGENT and DIVERGENT strategy, so perhaps familiarise yourself with it by reading How to Write a Killer Comparative .
Convergent Idea: The Importance of the Act of Remembering
Both Stasiland and Never Let Me Go illustrate the importance of remembering through the very construction of the text: in the narrative voice and narrative structure. Both narrators are looking into the past to try to make sense of history. For Kathy, this is a personal history whereas for Funder it is an act of witnessing a nation’s past and elevating the voices of the victims.
Stasiland is a compilation of the stories of all kinds of people involved and impacted by the GDR , including those who rebelled against the system, those who supported it and those crushed by it. Thus, ‘both sides’ of history are represented. Funder said in an interview with the Sydney Morning Herald after the publication of Stasiland that, 'When [Germans] read my book, people in the East are not proud of themselves. They'd rather not be reminded that other people were braver than they were. So there is a huge force to pretend that the Stasi regime was not as bad as it was.' This desire to forget the past so as to ignore confronting the terrible and terrifying truths contained within it is what Funder is working against by writing Stasiland . At one point in the text, she explicitly states what she’s doing:
'I’m making portraits of people, East Germans, of whom there will be none left in a generation. And I’m painting a picture of a city on the old fault-line of east and west. This is working against forgetting, and against time' ( Stasiland , 147).
Julia explains the importance of these portraits, telling Anna 'For anyone to understand a regime like the GDR, the stories of ordinary people must be told. …You have to look at how normal people manage with such things in their pasts' (144). These 'things in their pasts' are not just trauma and hardship, but the knowledge that people just like them – their spouses, children, friends and neighbours – were capable of such cowardice, betrayal, self-interest and cruelty. It is this knowledge that Funder wants to preserve – that ordinary people are capable of both extraordinary courage and extraordinary cowardice .
Anna comes across a sobbing man 'I don’t want to be German anymore!...We are terrible…They are terrible. The Germans are terrible' ( Stasiland , 253-4). Anna reflects that East Germans were 'long used to thinking the bad Germans were on the other side of the Wall' and now he is forced to ask 'were his people, now broke or drunk, shamed or fled or imprisoned or dead, any good at all?' ( Stasiland , 254).
Although Kathy’s narration is entirely from her perspective , her act of remembering is also in many ways a political statement that forces us to consider the inhumanity people are capable of .
Kathy recollects and structures her memories of her childhood and relationships to understand them as a unified whole, essentially establishing her identity . More importantly, it is evident in phrases such as 'I don’t know how it was where you were, but at Hailsham…' ( NLMG , 13) and 'I’m sure you’ve heard it said plenty more' ( NLMG , 4) that Kathy is positing a reader for her writing. Assuming a reader places her autobiography in a social framework with the purpose of communicating her life , which turns it into a historical account that exists beyond the limit of her death. Kathy’s attempt to leave a legacy by writing down her experiences and structuring her identity is an act of protest against a society that believes she is sub-human , without feelings or motivations, and that her life meant nothing.
Divergent Idea: The Role and Value of Nostalgia
The way memory can be distorted is particularly clear in relation to the idea of nostalgia for a brutal past. This idea is explored differently in Stasiland and Never Let Me Go , with Funder condemning nostalgia as blinding people to the horrors of the past, and Ishiguro illustrating how drawing comfort from the past can help people through difficult times .
In Stasiland , many disaffected former East Germans tell Anna that things were 'so much better before' ( Stasiland , 251) the country’s reunification. Anna reflects:
'I don’t doubt this genuine nostalgia, but I think it has coloured a cheap and nasty world golden; a world where they was nothing to buy, nowhere to go and anyone who wanted to do anything with their lives other than serve the Party risked persecution, or worse' ( Stasiland , 251-2).
Similarly, while working at the radio station on Ostalgie parties ( Ostalgie is nostalgia for life in Communist East Germany), Miriam observes 'a crazy nostalgia for the GDR – as if it had been a harmless welfare state that looked after people’s needs. Most of the people at these parties are too young to remember the GDR anyway. They are just looking for something to yearn for' ( Stasiland , 275). Funder is critical of nostalgia because it minimises past injustice .
Conversely, in Never Let Me Go , nostalgia and false memories are shown to be consolatory and even useful. Before Kathy begins to recount her childhood, she mentions a donor who was once under her care who 'knew he was close to completing' ( NLMG , 5). He asks Kathy to share memories of her childhood and 'What he wanted was not just to hear about Hailsham, but to remember Hailsham, just like it had been his own childhood. …so the line would blur between what were my memories and his' ( NLMG , 5). Although this man is falsifying his memories, he is not editing and revising history like some people in east Berlin , he is replacing them entirely to suppress the trauma of his own past. He is not yearning for a return to an idealised past the way some people in Stasiland do. For Kathy, nostalgia for her childhood helps her reconnect with her friends, creating a sense of belonging and identity. Her attachment to Hailsham strengthens her worldview, her relational bonds and gives meaning to her life. Nostalgic memory in Never Let Me Go brings comfort, although you could argue that it also fosters passivity and acceptance in the face of oppression .
4. LSG’s Bubble Tea (BBT) Strategy for Unique Strategies
Why is an interpretation important.
Your interpretation is what English is all about; it’s about getting you to think critically about the essay topic at hand, to formulate a contention (agree, disagree, or sit on the fence) and argue each of your points with the best pieces of evidence you can find - and it’s something you might already be starting to do naturally.
In this section, we aim to help you develop your own interpretation of the text, rather than relying on your teacher, tutor or even a study guide (including this one) author’s interpretation. By developing your own interpretation, you become a better English student by:
- Writing with meaning. For a text to be interpreted, you need a text and an interpreter (i.e. you!). Whenever we read a new text, our interpretation of a text is shaped by our pre-existing beliefs, knowledge and expectations. This should be reassuring because it means that you can leverage your own life experiences in developing a unique interpretation of the text! We’ll show you how this works in the next point.
- Remembering evidence (quotes or literary devices) more easily. If you know you admire a character for example (which is in itself an interpretation 😉), you can probably remember why you admire them. Perhaps the character’s selflessness reminds you of your Dad (see how you’re using real life experiences mentioned in Point 1 to develop an interpretation of the text?). You will then more easily recall something the character said or did in the text (i.e. evidence) that made you admire them.
- Having an analysis ready to use alongside the evidence. As a result of Point 2 , you’ll be able to write a few sentences based on your own interpretation. Rather than memorising entire essays ( we’ve talked about this before ) and regurgitating information from teachers, tutors, study guides and other resources - which can be labour intensive and actually detract from the originality of your essay - you’re approaching the essay with your own thoughts and opinions (which you can reuse over and over again across different essay topics).
Let’s look on the flip side. What happens when you don’t have your own interpretation?
When you don’t take the time to actively think for yourself - i.e. to think through your own interpretations (we’ve talked about the importance of THINK in the THINK and EXECUTE strategy here ) - when it finally comes to writing an essay, you may find it difficult:
a) to get started - formulating a contention in response to the essay topic is challenging because you have no strong opinion about the text ,
b) complete the essay - writing up arguments and using evidence in paragraphs becomes challenging because you have no strong opinion about the text ,
c) to score higher marks - ultimately, you end up regurgitating other people’s ideas (your teacher’s, tutor’s or from study guides) because you have (you guessed it) no strong opinion on the text .
Having your own interpretation means that you’ll eliminate issues a, b and c from above. Overall, you’ll have opinions (and therefore contentions) ready for any prompt when you go into your SACs or exams, which means it’ll be easier not only to write a full essay, but an original and insightful one as well.
To overcome the issues above, you need to be confident with your own interpretation of the text. This doesn’t come naturally to a lot of students, and it makes sense why. After all, so many subjects reward specific answers (2 + 2 = 4), whereas English is tricky because there’s so much more flexibility in what constitutes a ‘correct answer’. It’s scary treading the sea of different possible interpretations because you’ll ask yourself questions like:
- How do I know if my interpretation is correct?
- How do I know if my evidence actually backs up what I’m arguing?
- What if I disagree with my teacher, and they mark me down for a differing opinion?
- Or worse - I’m not smart enough to come up with my own interpretation!
Let me say that you are absolutely smart enough to develop your own interpretation, and I’ll show you how to do so in A Killer Comparative Guide: Stasiland & Never Let Me Go with LSG’s unique strategy - the BUBBLE TEA (BBT) strategy . By following our step-by-step framework, you can be confident that your interpretation is valid, that it backs up your argument, and that most importantly, you won’t lose marks for it!
5. Sample Essay Questions
1. ‘To conform is to be safe and to survive.’ Compare how this idea is examined in both texts.
2. 'The earlier years…blur into each other as a kind of golden time' ( Never Let Me Go ) 'I don’t doubt this genuine nostalgia, but I think it has coloured a cheap and nasty world golden.' ( Stasiland ) Compare what the two texts say about the dangers of willful ignorance.
3. 'For Miriam, the past stopped when Charlie died.' ( Stasiland ) '…I’d see it was Tommy, and he’d wave, maybe even call…and though the tears rolled down my face, I wasn’t sobbing…I just waited a bit, then turned back to the car, to drive off to wherever it was I was supposed to be.' ( Never Let Me Go ) What role do love and relationships play in helping people withstand persecution?
4. ‘It is impossible to be free when you are unaware of your confines.’ Compare how the two texts explore freedom and confinement.
4. ‘The past is always harder to access than we think’. Compare the ways in which Stasiland and Never Let Me Go depict the difficulties in uncovering the past.
As with all our essay topic breakdowns, we'll follow LSG's THINK and EXECUTE strategy , as taught in our How To Write A Killer Text Response study guide. The LSG's THINK and EXECUTE strategy follows three steps in the THINK phase - A nalyse, B rainstorm, and C reate a Plan. Learn more about this technique in this video:
'To remember or forget? Which is healthier? To demolish it or fence it off? To dig it up, or leave it to lie in the ground?' ( Stasiland ). 'What he wanted was not just to hear about Hailsham, but to remember Hailsham, just like it had been his own childhood' ( Never Let Me Go ). How does memory inform identity in Stasiland and Never Let Me Go ?
Step 1: Analyse
This quote-based prompt is constructed a bit like a theme-based prompt as it directs us to talk about memory’s role in forming identity. However, the quotes act as an additional hint in terms of what else we’re supposed to discuss. We need to identify where these quotes come from in the texts and why they might be significant. The Stasiland quote (from p. 52) comes from the question of what the nation should do with Hitler’s bunker. In the end the only decision was indecision, the mayor buried the bunker and hoped that people in 50 years might know what to do with it. Thus, this quote points to the difficulty countries have in creating a national identity when there is horror and trauma in their history. The Never Let Me Go quote (from p. 5) points towards an ill donor’s recreation of his identity using someone else’s memories. Therefore, this quote points to how memories, even false ones, can reconstruct individual identity.
Step 2: Brainstorm
Because of the direction of the two quotes, I am going to explore memory’s role in forming individual and group identity.
Individual identity:
- Kathy and Julia develop greater self-insight through sharing their memories in a structured, logical narrative.
- Kathy and Herr Koch fear that the loss of the physical presence of Hailsham and the Berlin Wall will undermine the significance of their memories of these places, which form a substantial part of their pasts and identities. They therefore pay much more attention to preserving their memories of these places to affirm their identity.
Group identity:
- East Germany’s rewriting and erasure of history meant that they no longer identified as the same Germans responsible for Hitler’s regime.
- The episode in which a distressed man sobs 'I don’t want to be German anymore!' reveals how difficult memories can generate confusion and internal conflict over an individual’s perception of their national identity.
- In NLMG , the country’s determined forgetting of the circumstances of the clones allows them to preserve their own interests and maintain an uncomplicated, guilt-free, but false, innocent national identity.
Step 3: Create a Plan
P1: Both texts show that the degree to which one’s memories have been investigated and illuminated impacts how well they understand their identity.
- Compare Kathy and Julia and the way they reconstruct their understanding of their identity by reflecting on their memories with the new information offered by hindsight.
- Conversely, the ill donor that Kathy cares for at the beginning of the novel sought to purposefully suppress his own identity by replacing his memories. This speaks to the same idea that memories can evolve and shape identity but shows how that can be misaligned with reality and truth (note: this discussion of the donor is your opportunity to use the quote from the prompt, which is a requirement of a quote-based topic).
P2: Sometimes people hold on tightly to particular memories as a way to affirm their identity as losing those memories is akin to erasing or denying the legitimacy of their experiences.
- Compare Hagen Koch’s obsession with the Berlin Wall and Kathy’s preoccupation with Hailsham.
P3: Choosing what gets remembered or forgotten in a nation’s ‘official history’ drastically impacts how their national identity is perceived and how well that identity aligns with reality.
- 'History was so quickly remade, and so successfully, that it can truly be said that the easterners did not feel then, and do not feel now, that they were the same Germans as those responsible for Hitler’s regime'
- 'I don’t want to be German anymore!'
- 'To remember or forget? Which is healthier?'
- 'The world didn’t want to be reminded how the donation program really worked.'
- 'They preferred to believe these organs appeared from nowhere.'
If you'd like to see the sample A+ essay we wrote up for this essay topic, then you might want to check out our A Killer Comparative Guide: Stasiland & Never Let Me Go study guide !
For an overview of the EAL study design plus tips and tricks for reading comprehension, time management and more, check out The Ultimate Guide to EAL .
The listening tasks of the EAL exam are worth 20% of the total exam marks. Since this section was introduced to the exam fairly recently, limited past exam questions are available for students to practice. In my blog post EAL Listening Practice and Resources , I provide you with some awesome listening resources that you should definitely check out! And more importantly, I teach you a step-by-step approach for how to use those listening resources to help you better prepare for EAL listening. If you haven’t already read that blog post, go and check it out before coming back to this one so that you understand the steps we’re following.
Here we’ll be working through another exam-style practice to help us improve on the EAL listening section. We will be adopting the same strategies introduced in EAL Listening Practice and Resources . For more advice on how to boost your skills in the listening section, check out Tips on EAL Listening .
Use this link to access the audio clip that we’ll be using in this listening practice: Hospital Parking Fees - Classroom - BTN (abc.net.au)
Download this worksheet so that you can work through this listening task on your own too!
1st Time Listening
Step 1: read and annotate background information (below).
- Highlight the name of the speakers.
- Underline important information.

Step 2: Read and Annotate the Questions
Develop a system that works well for you personally. For example, I usually underline the keywords that give me information on ‘what’, ‘why’, ‘how’, ‘where’, ‘when’. I highlight the speakers in the example below.

Step 3: Listen to the Audio (Without the Visual)
Hospital Parking Fees - Classroom - BTN (abc.net.au)
Step 4: Write Down Side Notes

2nd Time Listening
Step 1: Fill in the blanks and try to be aware of words you don’t quite ‘get’.
This is where you have the opportunity to fill in the blanks for the challenging words that you did not pick up in the first round. For example: petition, democratic, campaign, rare.
COMMON MISTAKE: check the spelling for ‘rare’, not ‘rear’
Step 2: Note down how the speakers convey their attitude, feeling, ideas, etc.
Let's take a look at this section of the audio clip:
GIDON: ‘ It gives me a really good feeling to know that I've made a change, that change has happened. I think what I would like to say to all the other people, especially kids who want to start change, is that it really does sometimes seem impossible that someone that doesn't have a vote and who doesn't have as much democratic power really as adults do, I think what this has shown is that it really is possible to do these things that we still can affect our country and that small people can make great change.’
Here’s one way I analysed the delivery of the audio:
The cheerful and hopeful tone used to deliver the message that the change brings him ‘a really good feeling’ demonstrates Gidon’s approval of the change in parking fees. Furthermore, Gidon states this in a high pitch and fast pace, unveiling that he is pleased and satisfied about the reduction in hospital parking fees .
Step 3: Interaction between speakers.
This step does not apply to this particular audio clip since the audio/ video is a recount of the event rather than direct conversation between two or more speakers.
3rd Time Listening
The transcript is available HERE .
Whilst reading through the transcript with the audio on, try and pick up any information that you missed in previous rounds of listening and also words that you might have spelt incorrectly.
Sample Questions and Answers
Have a go at these VCAA-style questions that I wrote up, and then check out my sample answers to see how your own answers compare. You will probably notice that a lot of the information you gather from the ‘W’ words actually provides you with the answers to the majority of the questions here.
Sample Questions
Sample answers.
1. Gidon’s petition is about lowering the fee for parking in hospitals and putting a limit on how much the hospital can charge.
2. Gidon has a rare blood condition which means he visits the hospital quite regularly. Since his diagnosis, Gidon’s family paid more than ten thousand dollars just to visit the hospital.
3. When hospital parking fees are too expensive, patients will buy food and other necessities instead of going to the hospital. Thus, patients may not go to the hospital because parking is too expensive, these poor patients need to choose between paying parking fees and buying food.
4. Regular hospital attendants will receive a 90% discount on what they are currently paying.
5. Families, patients and carers for regular visitors of public hospitals.
COMMON MISTAKE: check the spelling for ‘carer’, not ‘career’ or ‘carrier’
6. Gidon is very happy and proud of the change in hospital fees. Gidon uses a cheerful and hopeful tone (1st mark) to deliver the message that the change brings him ‘a really good feeling’ and he feels ‘unbelievably proud’ that ‘small people can make great change’ (2nd mark). In addition, Gidon states this in a high pitch and fast pace, demonstrating that he is pleased and satisfied with the reduction in hospital parking fees (3rd mark).
--- I hope you found this guide handy! For further tips and tricks on tackling the EAL Listening Exam, check out How To ACE the EAL Listening Exam .
The listening section of the curriculum was introduced by VCAA in 2017 and I highly recommend having a look at the examination reports from 2017 onwards as they provide valuable insight into what the examiners are looking for in high-scoring responses. In this blog, I will explain three key tips that helped me receive a perfect study score in EAL so that you can better prepare for EAL listening.
Tip #1: Pay Attention to the Choice of Delivery
Delivery of speech can be described from 5 aspects:
Pitch refers to the highness or lowness of a sound. High-pitch can be used to heighten the emotion; conversely, a low-pitched voice is often softer and quieter or used to make an important point.
Pace is the speed at which the speech is delivered. Pace can be described as ‘fast’ or ‘slow’.
- Presence of pauses, repetition, hesitation
These are often used in conjunction with pace and pitch of voice to illustrate the speaker’s feelings, attitude or views towards a certain issue.
- Emphasis/stress on certain words
The emphasis a speaker places on specific words or phrases serves to draw the listener’s attention to the most important information.
- Tone of voice
When I first started learning how to nail the listening component, I made an extensive list of descriptive words for tone of voice that can be incorporated into my answers when it comes to SACs and the exam:
.png)
It is, of course, awesome and somewhat satisfying to have a glorious list of A+ words under our belt, but they are of no use if we are not comfortable using them. By this, I mean we need to make sure we know the meaning of these fancy words and how to incorporate them into sentences.
Although the full list is very useful, I found myself frequently tending to use a certain few as highlighted below. This helped me to memorise the words I found most versatile, rather than trying to memorise ones I was unlikely to use. You can select the words that work best for you individually - no right or wrong here!
.png)
Tip #2: How To Tackle the 3 Marks Question!
Usually, towards the end of a listening task, you will get a 3 marks question that asks for ‘choice of language and delivery’.
.png)
Note: For background information on this ‘Gidon’ question, see this blog . And, if you’re not sure why we have highlighted and underlined certain words, see here .
So how do we formulate a cohesive response for this question and ensure we can get 3/3? The train of thought for answering this question is similar to that of analysing how language is tailored to persuade the readers.
.png)
The following is an example of what your final answer might look like:
Describe Gidon’s response to the change made to hospital fees. Support your answer with his word choice and delivery. 3 marks
Gidon is very happy and proud of the change in hospital fees. Gidon uses a cheerful and hopeful tone (1st mark) to deliver the message that the change brings him ‘a really good feeling’ and he feels ‘unbelievably proud’ that ‘small people can make great change’ (2nd mark). In addition, Gidon states this in a high pitch and at a fast pace, demonstrating that he is pleased and satisfied with the reduction in hospital parking fees (3rd mark).
For background information on this ‘Gidon’ question and its answer, see EAL Listening Practice .
Here is another sample answer question and answer (see this blog for background information):
What is Beverley Wang’s opinion on some apps showing many ‘likes’? Support your answer with an example of word choice and language. (3 marks)
Beverley Wang expresses her opinion that some apps can foster addictive behaviours and can be scary by using a frustrated and alarmed tone (1st mark). Additionally, by repeating the term ‘consuming’ four times in a row (2nd mark), delivered at a fast pace, Wang affirms the unethical and addictive nature of the apps (3rd mark).
Tip #3: Build Your Vocabulary to Describe the Interaction Between Speakers
In EAL listening, you are often expected to describe the interaction between two or more speakers. This allows you to comment on how multiple speakers express their ideas. There will typically be a question that asks you to describe the interaction between the speakers, such as, ‘Suggest 2 words to describe the interaction between A and B’. The answer you need to provide will typically be a two-word answer. Here is a list of words that I frequently used to answer questions like this:
Words to describe positive interactions include:
- Friendly, respectful
- Professional, formal, polite
- Relaxed, warm
- Amicable, sanguine
Words to describe negative interactions include:
- Embarrassed
- Teasing, childish
- Tense, unpleasant, disappointed
- Confrontational
Hint: You have probably noticed that a lot of the words used to describe the tone for language analysis overlap with the ones you employ to describe the interaction between speakers. This is a bonus since once you have learned these adjectives, you can use them for both sections of the exam.
I hope you found these tips useful! For further tips and tricks on tackling the EAL Listening Exam, check out How To ACE the EAL Listening Exam .
Why Is the Context Important?
Understanding the context of the texts you are studying is essential if you are to satisfactorily respond to any prompt ( learn about the 5 types of prompts here ). Not only does it provide an insight into the society of the time and their views and values , it also allows for greater awareness of the characters’ motivations, resulting in a richer discussion in your essays. Discussing the context of the texts also makes for an ideal comparison which can be incorporated in the introduction as well as the body paragraphs. Moreover, context paragraphs are a great tool to have up your sleeves, as they can easily be adapted to almost every essay question, a real asset when attempting to write an essay in an hour.
In this blog post, I will be giving a brief overview of the contexts of the play The Crucible by Arthur Miller and Rosalie Ham’s The Dressmaker . Further down , I have also provided a sample paragraph as an example of a way in which I would go about writing a context paragraph in response to an essay prompt concerning the two texts. Both of these texts are set in fascinating and significant eras of human history so I invite you to conduct your own research after reading this!
At first glance, the town of Salem, Massachusetts in 1692 and Dungatar, Victoria in 1950s Australia have little in common; however, both towns exist in stifling geographical isolation, allow myopic and parochial outlooks to flourish, and maintain an irrational but overwhelming fear of ‘the other.’
The Crucible, Arthur Miller
The Crucible is set in 1692 in Salem. The provincial, conservative town was established by English Puritans who, fearing persecution, fled from a Britain dominated by The Church of England. The first Puritans to arrive in Salem faced brutal conditions, including 'marauding Indians' and living on a 'barbaric frontier' that lay close to the 'dark and threatening…virgin forest' that they believed to be the 'devil’s last preserve'. In order to overcome these challenges, the people of Salem were forced to unify and remain diligent. In order to ensure efficiency, a strict and rigid way of life was adopted, where work and prayer were championed and individual freedoms and pleasures abhorred. Though this harsh way of life did allow the Salemites to stay alive, it forced them to suppress various natural human emotions such as joy and anger, so as to not detract from work and prayer. Further, the town had limited their interaction with the outside world, compelling them to instead be constantly surrounded by each other. This hazardous combination of repression of emotions and interaction with only a small pool of people spurred private jealousies and vengeance within the townspeople, and it is here that the play commences.
The Dressmaker, Rosalie Ham
In contrast, Ham’s novel takes place in 1950s rural Australia, in the fictional town of Dungatar. Despite being set centuries after The Crucible , Dungatar is rife with the same parochialism (great word to use for both texts, referring to a limited/ narrow outlook), resentment and gossip as Salem. The town’s physical isolation - it is surrounded by 'wheat, yellow plains' and seems to be a 'dark blot shimmering on the edge of flatness' - corresponded with their metaphoric isolation from global events, creating an intense fear of ‘the other’. Further, similarly to The Crucible , the stark physical isolation ensures that each individual’s social interactions are limited to the town’s small population, fostering a breeding ground for narrow-mindedness and prejudice. Ham’s description of the way 'the crowd screamed with lust, revenge, joy, hate and elation' after a local football match win reveals the underlying emotions of the town, repressed behind a veneer of respectability and perceived moral propriety. All it takes is a stimulus, which arrives in the form of outcast Tilly Dunnage, to uncover the malicious undertones of the provincial town.
Example Context Paragraph
During VCE, I tended to use my first paragraph (in response to an essay prompt) as a way to explore the context of the texts I was studying, and relate the context to the essay prompt being addressed ( learn more about the different types of essay prompts here ). In this case, the prompt I have responded to is:
Compare the ways in which The Crucible and The Dressmaker portray divided societies.
I was able to adapt much of this paragraph below to whatever essay prompts I came across.
The geographical isolation of rural, parochial towns can breed a kind of myopia amongst inhabitants and promote binary thinking. Salem is situated on the 'edge of wilderness’, with the 'American continent stretching endlessly West’. The 'dark and threatening' forest which ominously surrounds the town is believed to be 'the last place on earth not paying homage to God’, inciting the irrational fear that 'the virgin’s forest was the Devil’s last preserve' (1) . To combat the imminent threat of the 'marauding Indians' upon their arrival in Salem, the Salemites maintained that 'in unity…lay the best promise of safety’, and hence were governed as 'an autocracy by consent' (2) . Similarly, in The Dressmaker , the town of Dungatar 'stretches as far as the silos' and is described as a 'dark blot shimmering on the edge of flatness’. 'The green eye of the oval' is a physical representation of the town’s predilection for prejudice and endorsement of slyly watching others (3) . The stifling insularity experienced by both towns perpetuates a paucity of culture and 'parochial snobbery’, as well as fostering austere social expectations (4) . The totalitarian regime that governed Salem and their 'strict and sombre way of life' conditioned the people of Salem to repress natural human emotions so as to conform to the conservative and rigid values of society. Indeed, Miller’s description of the 'small windowed dark houses struggling against the raw Massachusetts winter' alludes to the Salemites’ dogmatically narrow-minded outlook and their repression of any individuality. Hence, despite the veneer of propriety upheld by Salem’s 'sect of fanatics’, the town is rife with hidden resentments and 'long-held hatreds of neighbours' (5) . Whilst moral respectability and piety conceal the true sentiments of the people of Salem, clothing is the mask for the 'liars, sinners and hypocrites' of Dungatar (6) . Though on the surface the town appears respectable, the true desires of 'the sour people of Dungatar' are revealed through their desire 'to look better than everybody else’. Their lack of connection with the outside world forces their constant interaction with one another and means that 'everybody knows everything about everyone' (7) . Thus, Miller and Ham postulate that geographical isolation inevitably forges unyielding social norms that repress human emotions and pits individuals against each other (8) .
Annotations (1) In these two sentences, I’ve provided the geographical context of Salem. (2) My description of the geographical location is followed quickly by describing the town’s beliefs and values, which have a large impact on the social context. (3) Here, I’ve used the geographical context as a metaphor to explain the social context of Dungatar. (4) I’ve described a similarity between the two towns - remember to use lots of meaningful comparisons in all paragraphs ( LSG’s CONVERGENT and DIVERGENT strategy is a useful strategy for this). (5) I’ve detailed how the societal expectations and values of the Salemites (the people of Salem) can impact the behaviour of the characters. (6) Here, I’ve outlined a subtle difference (or divergence ) between Dungatar and Salem. (7) Once again, I’ve related the townspeople’s values and beliefs, as well as the physical context, to their behaviour. (8) I’ve ended with a meaningful comparison between the intent of the two authors.
Looking for more? Check out our other blog posts on The Crucible and The Dressmaker :
The Crucible by Arthur Miller
The Dressmaker by Rosalie Ham
Comparing The Crucible and The Dressmaker
[Video Transcription]
Most people commonly mistake Comparative (also known as Reading and Comparing, and an array of other names) as just two Text Responses rolled into one essay. They think that Comparative is Text Response, except that instead of writing about one text, you’re writing about two.
And boy are they wrong.
Most people are also aware that the main difference is that Comparative looks at similarities and differences between the two texts. However, this is where the challenge begins.
As you study your texts in detail, you’ll come to realise that the majority of students keep using the same old examples – example X for similarities, and example Y for differences.
To stand out from hundreds of other students studying the same texts, you need a strategy. You need something that will wow your examiners and will catapult you to the top of the VCE cohort.
*Drum roll*
Introducing you to my golden rule, the CONVERGENT and DIVERGENT STRATEGY!
This strategy is simple. It’s simple to understand and it’s simple to incorporate into your essays. Its beauty is that despite its simplicity, it’ll advance your essay beyond the average English student. All my students who have applied this strategy have seen their English scores improve by at least one grade (from B+ to an A, or from an A to A+).
Let me explain.
PART 1 – CONVERGENT
The word, ‘convergent’ means coming closer together . When we start looking for similarities in Comparative, keep this word CONVERGENT in mind. Having CONVERGENT at the forefront of your mind will ensure that you are always aware of the fact that your examples are never the same. Notice how the blue arrows never touch:

Sometimes, students fall into the trap of referring to examples in each text as the ‘same,’ but this won’t ever happen to you if you keep CONVERGENT in mind. No two texts are ever exactly the same, no two examples are exactly the same , so avoid falling into this trap.
Instead, you’ll be using phrases like: "similarly to Text 1, Text 2 also…" or "likewise, in Text 2….’"
Awesome! So this is the simple part done. Let’s move onto the most powerful part of this strategy - DIVERGENT.
PART 2 – DIVERGENT
The word ‘divergent’ means developing in different directions. We can use the CONVERGENT and DIVERGENT strategy for any example you include in your essay. Since no examples from two texts are exactly the same, this means there is always an opportunity for you to first compare the similarities, then compare the differences.
Rather than just a simple ‘on the other hand’ or ‘however’, which you probably have written a dozen times, and felt like you’re repeating yourself, we show you advanced ways to DIVERGE as in this example for Photograph 51 and The Penelopiad:
In The Penelopiad , the resigned way in which Penelope confides in the reader alludes definitively to the ‘overlooked woman’ stereotype being, in fact, a very well-used one. Atwood (the author of The Penelopiad ) does, however, accord some power to Penelope by ensuring that she alone tells her own story, a privilege which is not given to Rosalind in Photograph 51 .
See how in this example, we don’t even use the overused comparative words such as ‘however’ or ‘on the other hand’ which can make a comparative feel simple. Instead, we show you unique ways to compare the two texts so that your essay stands out amongst all the others that are just using the same old words and methods to compare.
If you’ve ever received feedback that you needed to ‘elaborate,’ ‘go into more detail,’ or needed ‘more analysis ’ in your essays, this strategy will help eliminate those criticisms. It will also show your teacher that you are comfortable writing an in-depth analysis using fewer examples (because you’ll be spending more time on each example - firstly by discussing a similarity, then a difference), rather than swamping your essay with as many examples as possible because you barely have anything to say about each one.
Too many students miss out on the opportunity to elaborate or expand on an example because they only write about either the similarity or the difference. But with the CONVERGENT and DIVERGENT strategy, we can see that no matter what example you choose from each text, there is always an opportunity to discuss both similarities and differences . This is an extremely powerful approach to comparative because it enables you to spend time comparing, rather than getting lots of examples of for one text in the first half of your body paragraph, slapping in an ‘on the other hand’ in the middle, then lots of examples for the second text in the second half of the body. I see students doing this all the time, pretending to compare these examples when they’re not - you know what I mean right? We’ve all been there once or twice - so you’re not alone in doing this if you’ve tried in the past. The thing is, with examiners, in particular, they’re really good at noticing when a paragraph looks like it’s a comparison, rather than a truly in-depth comparison between the two texts.
That’s why in my How To Write A Killer Comparative , I show you how to use CONVERGENT and DIVERGENT in multiple essay examples across many text pairs. It’s not just about one way of comparing similarities too, it’s all the different ways to can discuss ‘similarities’ - what I mean is, it can be easy to slip into a template of ‘similarly to text A, text B does this by…’ but in this study guide, written by myself, and study scorers who have achieved 50 in English , we show you how to unique discuss comparisons. We also show you how to advance your comparative discussion through Advanced Essay Paragraph Structures which truly showcase the power of the CONVERGENT and DIVERGENT strategy.

COMPARATIVE GUIDES
How to Write a Killer Comparative Ebook
A Killer Comparative Guide: The Crucible and The Dressmaker
A Killer Comparative Guide: I am Malala and Pride
A Killer Comparative Guide: The 7 Stages of Grieving and The Longest Memory
A Killer Comparative Guide: Ransom and The Queen
USEFUL RESOURCES
The Ultimate Guide To VCE Comparative
Reading and Comparing essays
How to get A+ in Reading and Comparing
Compare the Pair: A guide to Structuring a Reading and Comparing essay
[Modified Video Transcription]
In a previous video , we covered some of the themes found in both The 7 Stages of Grieving and The Longest Memory. I’d recommend that you watch that video first (or read it’s accompanying blog post if you prefer reading) because once you know some of the themes, you can get even more out of this video. In this video, we’ll be looking at a scene each from both The 7 Stages of Grieving and The Longest Memory , and trying to compare them a little bit.
We’ll be applying the CONVERGENT and DIVERGENT strategy from LSG’s How To Write A Killer Comparative and exploring how ideas are developed in similar or different thematic directions in these texts. CONVERGENT ideas lead to similar conclusions and messages, while DIVERGENT ideas take us to different conclusions. If you’d like to learn more about this strategy which can help you build more insightful discussions of the text by finding unique points of comparison, then I’d recommend you check out the LSG’s How To Write A Killer Comparative study guide.
The Play ( The 7 Stages of Grieving )
Let’s go to scene 14 of the play - this should be the report of Daniel Yocke’s death in police custody. The woman recounts his death in a factual, impersonal style as if reading from a court report. She describes how the police pursued and arrested Yocke after he went out drinking with a group of friends, and how he was detained and taken to the watchhouse. He arrives without a pulse, but the report doesn’t go into detail about how that happened between his arrest and his arrival. The woman breaks into bursts of emotion toward the end of the scene.
While most of the play deals with issues that are universal and timeless for First Nations peoples, this scene looks at a specific real event . However, this doesn’t mean that this scene isn’t timeless - First Nations deaths in custody are still a major issue for which no police officer has been held legally accountable - but this scene chooses just one example out of several hundred.
The emotionally detached tone makes the situation feel serious, but in a way, that distances us and the woman from the brutality and the violence of what must’ve happened. After all, how exactly was Yocke dead upon arriving at the watchhouse? How badly must the police have mishandled him for that to have happened? Along the way, there are little outbursts of emotion (like the little outburst of ‘people called him Boonie!’) and these remind us that the detachment belies the true significance of what happened - the needless loss of yet another Aboriginal person’s life.
This has been such a persistent problem in our history - this scene happened in 1993, but even in today’s time we’re still dealing with the same problem. The institution of policing has been unaccountable and violent for decades, at least, and something desperately needs to change.
The Novel ( The Longest Memory )
Let’s go to the novel now and look at Chapter 6: Plantation Owners.
In this chapter, Mr. Whitechapel is talking to his peers about Chapel’s death in this clubhouse that his father had built for his own peers. Mr. Whitechapel is initially nervous that they’ll make fun of him, and they kind of do - they point out how hypocritical it is for him to think that he can treat the people he’s enslaved with humanity, and to stick to this argument even after Chapel had been whipped to death. At some point in this banter, he realises this physical violence is unjust and starts proposing ‘another way to organise the economy’ that isn’t slavery, but this draws even more mockery. He ultimately leaves feeling a little more convinced by the perspectives of his peers.
What does this chapter tell us, and how is it similar to the scene from the play?
Well, in both scenes, white men get away with murdering a Black man, and it comes down to socio-economic and institutional power. In this chapter, Mr. Whitechapel and his fellow enslavers all inherit significant wealth and extremely prejudiced attitudes from their fathers, and this creates not only pressure, but also a financial incentive, to conform to the system of slavery. He touches on the possibility of abolition, but this is seen as impossible - certainly, none of these men want to lose their power.
Looking more closely at this chapter, we also see how Mr. Whitechapel is exactly the hypocrite that everybody says he is - it’s ridiculous for him to pretend he’s treating black people fairly when they are dying under his watch. He says he’s feeding enslaved workers adequately and treating them with respect, but none of this is actually going to protect them from violence, and none of this is going to level the playing field so that white enslavers are held accountable. Ultimately, Mr. Whitechapel isn’t seriously interested in making substantive changes to slavery in the name of morality; he is simply trying to save face.
I’ve chosen these two scenes because they both illustrate the dynamics of race and power which pervade both texts, but these two scenes might not be the first ones that come to your mind as a pair that you can analyse together, and that’s totally fine! I encourage you to find your own scenes to compare because that’s what makes English powerful. If you, as a unique student, can compare two scenes that nobody else has compared, that’s going to give you an extra edge because you’re more likely to say something original.
If you’re interested in finding more unique ways to compare these two texts, I’d recommend LSG’s The 7 Stages of Grieving & The Longest Memory study guide. I know there aren’t many resources out there for this text pairing, so what we’ve done at LSG is work really hard at ensuring that all the information in this study guide will actually be beneficial for you. We’re not here just to make you read more guides - we’ve really thought about what would be meaningful for you as a student learning this pairing. That’s why you’ll see that I’ve used some of the ideas mentioned in this video and turned them into an A+ essay, so you can see exactly how knowing this information translates into your SAC/exam.
There’s a free sample of the study guide you can check out to see if it’s right for you!
Passage 1: Act 1 Scene 3
[Aside] Two truths are told,
As happy prologues to the swelling act
Of the imperial theme.--I thank you, gentlemen.
[Aside] This supernatural soliciting
Cannot be ill, cannot be good: if ill,
Why hath it given me earnest of success,
Commencing in a truth? I am thane of Cawdor:
If good, why do I yield to that suggestion
Whose horrid image doth unfix my hair
And make my seated heart knock at my ribs,
Against the use of nature? Present fears
Are less than horrible imaginings:
My thought, whose murder yet is but fantastical,
Shakes so my single state of man that function
Is smother'd in surmise, and nothing is
But what is not.
Passage One from Act 1 Scene 3 takes place just after Macbeth has just been announced as Thane of Cawdor proving part of the Witches’ prophecy true “All hail Macbeth…Thane of Cawdor…/that shalt be king hereafter.” This part of the play is the first insight we have on Macbeth’s inner thoughts.
Macbeth’s firm and thoughtful tone in the opening alliteration “two truths are told ” stresses how serious he takes the Witches’ predictions. Shakespeare presents this passage as a soliloquy in order to convey Macbeth’s true inner thoughts and motives. As this is Macbeth’s first soliloquy, it emphasises the strong possibility of Macbeth heading down a dark journey as he cannot forget the Witches’ predictions “(it) cannot be ill, cannot be good. If ill, / Why hath it given me earnest of success, Commencing in a truth?”
Shakespeare uses the metaphor of theatre for fate . The meta-theatrical reference, ‘as happy prologues to the swelling act’ makes the audience consider the action that will unfold in the following scenes through foreshadowing.
Macbeth feels that committing regicide will be a “supernatural soliciting”. The word “supernatural” demonstrates that Macbeth acknowledges that such an act is “against the use of nature.” It suggests that if Macbeth kills Duncan, he will forever be trapped in the supernatural world for his dishonourable action. The alliteration of “supernatural soliciting” sounds incredibly seductive, and therefore highlights Macbeth’s lust and thirst for the crown.
There is a physiological response to his unnerving thoughts as the ‘horrid image doth unfix my hair’ and ‘my seated heart knock at my ribs’ , emphasising the horror of Macbeth has with himself at his thoughts.
The personification “my seated heart knock at my ribs” once again depicts the increasing fear that Macbeth experiences as his heart is not “seated” with its connotations of calmness and steadiness but “knock(ing)” which is associated with alarming fear.
As Macbeth struggles with his conscience and fears “my thought, whose murder yet is but fantastical,/ Shakes so my single state of man,” he is uncertain whether or not he should take the prophecy into his own hands and murder Duncan or, let time decide his fate “time and the hour runs through the roughest day”. The consonance ’s’, Shakes so my single state of man”..
The alliteration “smothered in surmise” demonstrates how Macbeth’s vivid imagination causes him to struggle with fear and hesitate undergoing the action that is foreseen by him as a “horrid image.” These mental images are of significance throughout the play as it is evident that Macbeth’ conscience results in him “seeing” a dagger and also Banquo’s ghost.
The antithesis “and nothing is,/ But what is not” is deliberately broken up into two lines to demonstrate the ambiguity of Macbeth’s thoughts and the confusion which evidently contributes to his overall fear. Macbeth’s actions become overpowered by his imagination until ‘nothing is but what is not’ or imagination carries more weight than action. The partial alliteration of ‘smother’d in surmise’ and the antithesis of ‘nothing is but what is not’ makes this notion seem again, particularly seductive to the audience. The word ‘smother’d’ , with it’s connotations of oppression, further amplifies the notion and even suggests that Macbeth’s imagination takes the place of his will.
Hey everyone! This is Part 2 in a series of videos I will release on VCE Study Guides. The content goes through the sample VCAA Chickens Range Free article which you can find here . Feel free to analyse it yourself, then check out how I’ve analysed the article!
I’m super excited to share with you my first ever online tutorial course for VCE English/EAL students on How to achieve A+ for Language Analysis !!!
I created this course for a few reasons:
Language Analysis is often the key weakness for VCE English/EAL students, after my workshops, students always wish we had spent even more time on Language Analysis, many of you have come to me seeking private tuition however since I am fully booked out, I wanted to still offer you a chance to gain access to my ‘breakthrough’ method of tutoring Language Analysis,I am absolutely confident in my unique and straightforward way of teaching Language Analysis which has lead to my students securing exceptional A graded SAC and exam scores!
Are you a student who:
struggles to identify language techniques?
finds it difficult to identify which tones are adopted in articles?
has no idea explaining HOW the author persuades?
finds it difficult to structure your language analysis essay?
becomes even more unsure when comparing 2 or 3 articles?
feels like your teacher at school never explained language analysis properly?
prefers learning when it’s enjoyable and easy to understand?
wants to stand out from other students across the cohort?
wants to know the secrets of 45+ English high achievers?
wants to know what examiners are looking for?
sees room for improvement whether you’re an average student or a pro?
wants to get a head start and maximise your potential in VCE?
This is what you will accomplish by the end of the course:
Be able to successfully identify language techniques in articles and images
Be able to successfully identify tones adopted in articles and images
Be able to analyse a single article or image
Be able to analyse 2 or more articles and/or images
Be able to apply your new skills coherently and clearly in essay writing
You will be able to accurately describe HOW an author uses language to persuade
You will be able to plan and write a language analysis essay structure (single article/image)
You will be able to plan and write a language analysis essay structure (2 or more articles/images)
You will understand common pitfalls and how to avoid these in language analysis
Be confident when approaching your SACs and exam
Know exactly what examiners are looking for and how to ‘WOW’ them
Know how to distinguish yourself from other students
Have unlimited help in course forum from myself and other VCE students
You will become a better VCE English language analysis student!
To find out more, you can check out the full details of the course here !
See you in the course!
I am Malala and Made in Dagenham is usually studied in the Australian curriculum under Comparative (also known as Reading and Comparing). For a detailed guide on Comparative , check out our Ultimate Guide to VCE Comparative .
- Compare the importance and role of idols and role models in I am Malala and Made in Dagenham.
- Describe the role of fear and obligation as an obstacle to progress by comparing I am Malala and Made in Dagenham.
- ‘As we change the things around us, the things around us change us’. Discuss the extent to which this is true by comparing I am Malala and Made in Dagenham.
- Discuss the benefit of adversity in strengthening one’s will to persevere by comparing I am Malala and Made in Dagenham.
- Resilience is more important than success. Discuss whether this is true within the texts I am Malala and Made in Dagenham.
- Compare the role and importance of family within the texts I am Malala and Made in Dagenham.
- Compare both I am Malala and Made in Dagenham in relation to the importance of language as a device (spoken and written).
- Compare the forms of resistance displayed by protagonists Malala Yousafzai and Rita O’Grady in texts I am Malala and Made in Dagenham and decide why they chose these methods.
- Analyse the effectiveness of small triumphs creating ripple effects in wider communities by comparing I am Malala and Made in Dagenham.
- Discuss whether support networks are intrinsic for a single figure to create positive change by comparing I am Malala and Made in Dagenham.
- The main protagonists are galvanized by the people they wish not to be like rather than their role models. Discuss to what extent this is true by comparing the texts I am Malala and Made in Dagenham.
- Made in Dagenham and I am Malala explore the vices of deceit, appeasement and scapegoating. Discuss these by comparing both texts, commenting on how they pose a threat to the causes of both protagonists.
- What role do interpersonal relationships play in the texts I am Malala and Made in Dagenham? Can these relationships be both positive and negative? Discuss.
- Change cannot be immediate but gradual. To what extent is this true in texts I am Malala and Made in Dagenham .
- Examine the role of the media in driving social change by comparing texts I am Malala and Made in Dagenham
- A patriarchal society is invariably one that is repressive. Discuss this statement and its truths or falsities by comparing texts I am Malala and Made in Dagenham.
- Discuss solidarity in relation to social, historical and cultural progress and whether it can be both positive and negative by comparing texts I am Malala and Made in Dagenham.
The most overlooked aspect of English is probably the actual reading of your English novel. Shockingly, there are some students who believe that they can still do well in English without reading their texts – but that’s a topic for another blog post. Since VCE is about strategy, you should think about how you can maximise your learning while minimising the time spent reading. Some students only read their text once, while others read up to 5 or 6 times! For some one reading may be sufficient but in most circumstances it is definitely not enough. Conversely, reading more than 5 times might be a bit excessive. After asking ex-VCE students who have excelled in English, the overall consensus is that you should read your text 3 times before the English exam. Here’s why:
Reading 1 : The first reading should be done in the holidays prior to your school year. Yes, it is during the holidays but you will be thankful you started early when you’re in the middle of numerous SACs, assignments and homework during the year. You should take your time with the first reading in order to let the information soak in. Focus on exposing yourself to the characters and themes. Since many essay topics are based on characters or themes, this will help you foresee the types of prompts you’ll be asked. If it is a more difficult text to understand (such as Shakespeare), rather than pushing through your reading and trying to understand the plot, have a look at study guides first in order to gain a better understanding from the outset.
Reading 2 : This should be done while you are studying your text at school. Using the new information taught in class (such as character, theme, context and metalanguage analysis), a second reading will help you build on the knowledge from your first reading. During the reading, you should start to take note of key passages and draw out important quotes. This will set you up for the SAC and mean that you have read your text twice before your SAC.
Reading 3 : Your third and final reading is to be completed before your English exam. An ideal time is the term 3 holidays. Since it may have been a while since you studied the text, the third reading is crucial for knowledge consolidation. You should watch out for things that you missed during first two readings – usually small pieces of information that are unique and when used in essays, will separate you from other students. These include: not-so-popular quotes, passages that haven’t been discussed in class, fleeting descriptions of characters etc. Remember that the best essays involve interesting and original discussion of the text.
Summary
Reading 1 : Initial exposure to the text and an idea of what prompts may be asked in SACs and the English exam.
Reading 2 : Essential for identifying key details for SAC preparation.
Reading 3 : Vital for consolidation prior to the English exam and finding information that will distinguish yourself from other students.
So with this in mind, figure out how you will approach your readings throughout the year, and most importantly – get started early!
We’ve explored historical context, themes, essay planning and essay topics over on our Like a House on Fire by Cate Kennedy blog post. If you need a quick refresher or you’re new to studying this text, I highly recommend checking it out!
[Video Transcript]
‘Liz sits there helpless’
• From the beginning of the short story we can see that Liz isn’t, or doesn’t feel in control of her situation. The step by step process where she needs to ‘put the key in the ignition and turn it. Fire up the car and drive away’ showcases how the smallest details of starting the car, something that should be so simple instead requires immense mental effort on her behalf.
‘And he’s in there, alone, where she’s left him’.
• Her guilt bubbles to the surface here because it’s as though she’s the villain here, and she’s to blame for leaving him alone.
‘Abandoned him to a roomful of rampaging strangers’
• What’s really interesting here is her description of the other children. Instead of seeing this as an opportunity for Daniel to befriend others and have a great time, she describes them as ‘rampaging strangers’, giving us a sense that Daniel is subject to an unfamiliar environment that is wild, frenzied, rioting.
“Guerilla warfare”, “Jungle gym”, "seasoned commanders”
• These "fighter” phrases reveal Liz’s anxious mindset, as she imagines a world where her son is almost in the wilderness, every man for himself, as though it’s the survival of the fittest - and which Liz so fearfully express, “not that there’s going to be anybody with enough time to notice that Daniel needs help”, is not an environment where Daniel belongs.
“She digs in her bag for her lipstick, her fingers searching for the small cylinder, and pulls out a crayon, then a battery, then a tampon, then a gluestick.”
• Her everyday objects are splashed with Daniel’s belongings - the crayon, the gluestick, and demonstrate how intertwined her life is now with her child. This foreshadows her return to her pre-baby life - that things will not be the same.
“The smell of the place, that’s what throws her, the scent of it all, adult perfumes, air breathed out by computers and printers and photocopiers.”
• Even her sense of smell betrays her being away from Daniel. There’s a sense of alienation, of nausea that shows readers like us that Liz doesn’t feel like she belongs. This is in contrast to later in the story when she is reunited with Daniel and is comforted by ‘inhaling[ing] the scent of him again’.
“Same computer, same shiny worn spot on the space bar…"
• The repetition of ’same’ actually heightens how much has actually changed for Liz. Her entire world is now Daniel, whereas everything in the office is as it used to be. Therefore, there’s this sense that the people’s lives in the office remain unchanged, highlighting again Liz’s alienation.
“Yeah, yeah, yeah, they’re right, of course they are.”
• This sarcastic internal monologue reflects Liz’s current state of mind, where she’s experiencing a disconnect from her coworkers, and ’the land of the living’.
"Delete, she presses. Punching the key like a bird pecking. Delete, delete, delete.”
• We can feel Liz’s exasperation at this stage. The simile ‘like a bird pecking’ automates Liz’s actions in the workplace, as though she is doing it by switching to a ‘mechanical form’ of herself. The repetition of ‘delete, delete, delete’ gives us the sense that she’s frustratingly attempting to ‘delete’ her self-acknowledged, perhaps over-the-top anxiety surrounding Daniel, or trying to delete herself out of her situation. Whichever is unclear and left up to interpretation. Perhaps both ring true.
‘Returning to work after maternity leave’
• Liz’s narrative interspersed with new mum’s pamphlet. The juxtaposition of the pamphlet’s words ‘being a stay-at-home mum can begin to seem mundane and repetitive’ is contrasted with Liz’s love of motherhood - she is at odds with what society tells her she should be feeling.
‘[Daniel]’d have his thumb in his mouth right now. Not smiling, that’s for sure.’
• There’s a self-projection of anxiety here with Liz assuming that the childcarers are unable to look after Daniel properly, and that he’s suffering.
‘God, these endless extended moments where you’re left in limbo, the time dangling like a suspended toy on a piece of elastic.’
• This simile highlights how her mindset is completely consumed with Daniel, as she likens her daily experiences with objects and things related to Daniel and childhood. She struggles to switch between her identity as a mother, and her previous identity as a colleague in the workplace.
‘Caroline, Julie and Stella had laughed dutifully enough, but their faces had shown a kind of pained disappointment, something faintly aggrieved.’
• Perhaps this is Cate Kennedy's commentary on society and motherhood. The expectations others have on you as a new mother, and how you should be feeling.
‘He doesn’t run over when he sees her’.
• The opening of this chapter is blunt and brutal. Liz has longed to see Daniel all day, her anxiety getting the best of her, and yet at the moment of their reunion, it’s not as she expects. In this sense, we can to feel that Liz is very much alone in her anxiety and despair and, not the other way around with Daniel.
’She’s fighting a terrible nausea, feeling the sweat in the small of her back.’
• Unlike other stories in this collection, her pain isn’t because the absence of love, but because of its strength. Her love for Daniel is so intense that it’s physiological, making her unwell to have been away from him.
• The symbol of cake represents her pre-baby life, a time when she was concerned with the ‘account of Henderson’s’ and ‘delete fourth Excel column’. Her priorities have now shifted, and the celebrated ‘cake’ tradition in the workplace, one that is at the centre of several conversations, is no longer to significance to Liz. Her husband, Andrew’s attempt to celebrate Liz’s first day back at work with cake is highly ironic. The societal expectation that Liz is happy to be back at work even extends to her husband, and heightens how Liz is very much alone in her experience.
If you found this close analysis helpful, then you might want to check out our Like a House on Fire Study Guide where we analyse EVERY story in the text and pinpoint key quotes and symbols!
Watch our YouTube Video on Like A House On Fire Essay Topic and Body Paragraphs Breakdown
Like a House on Fire by Cate Kennedy
Like a House on Fire Essay Topic Breakdown
How To Get An A+ On Your Like A House On Fire Essay
Close Analysis Of 'Cake' From Like A House On Fire
Get exclusive weekly advice from Lisa, only available via email.
Power-up your learning with free essay topics, downloadable word banks, and updates on the latest VCE strategies.
latest articles
Check out our latest thought leadership on enterprise innovation., vce english unit 3, area of study 2: creating texts - what is it.

Breaking Down Themes & Key Quotes in The Erratics by Vicki Laveau-Harvie

Developing Interpretations SAC Guide: Interpreting Alias Grace
Keep in touch
Have questions? Get in touch with us here - we usually reply in 24 business hours.
Unfortunately, we won't be able to answer any emails here requesting personal help with your study or homework here!

Copyright © Lisa's Study Guides. All Rights Reserved. The VCAA does not endorse and is not affiliated with Lisa's Study Guides or vcestudyguides.com. The VCAA provides the only official, up to date versions of VCAA publications and information about courses including the VCE. VCE® is a registered trademark of the VCAA.
03 9028 5603 Call us: Monday to Friday between 3pm - 6pm or leave us a message and we'll call you back! Address: Level 2 Little Collins St Melbourne 3000 VIC
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Comparing and contrasting in an essay | Tips & examples
Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay | Tips & Examples
Published on August 6, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on July 23, 2023.
Comparing and contrasting is an important skill in academic writing . It involves taking two or more subjects and analyzing the differences and similarities between them.

Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
When should i compare and contrast, making effective comparisons, comparing and contrasting as a brainstorming tool, structuring your comparisons, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about comparing and contrasting.
Many assignments will invite you to make comparisons quite explicitly, as in these prompts.
- Compare the treatment of the theme of beauty in the poetry of William Wordsworth and John Keats.
- Compare and contrast in-class and distance learning. What are the advantages and disadvantages of each approach?
Some other prompts may not directly ask you to compare and contrast, but present you with a topic where comparing and contrasting could be a good approach.
One way to approach this essay might be to contrast the situation before the Great Depression with the situation during it, to highlight how large a difference it made.
Comparing and contrasting is also used in all kinds of academic contexts where it’s not explicitly prompted. For example, a literature review involves comparing and contrasting different studies on your topic, and an argumentative essay may involve weighing up the pros and cons of different arguments.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
As the name suggests, comparing and contrasting is about identifying both similarities and differences. You might focus on contrasting quite different subjects or comparing subjects with a lot in common—but there must be some grounds for comparison in the first place.
For example, you might contrast French society before and after the French Revolution; you’d likely find many differences, but there would be a valid basis for comparison. However, if you contrasted pre-revolutionary France with Han-dynasty China, your reader might wonder why you chose to compare these two societies.
This is why it’s important to clarify the point of your comparisons by writing a focused thesis statement . Every element of an essay should serve your central argument in some way. Consider what you’re trying to accomplish with any comparisons you make, and be sure to make this clear to the reader.
Comparing and contrasting can be a useful tool to help organize your thoughts before you begin writing any type of academic text. You might use it to compare different theories and approaches you’ve encountered in your preliminary research, for example.
Let’s say your research involves the competing psychological approaches of behaviorism and cognitive psychology. You might make a table to summarize the key differences between them.
Or say you’re writing about the major global conflicts of the twentieth century. You might visualize the key similarities and differences in a Venn diagram.
These visualizations wouldn’t make it into your actual writing, so they don’t have to be very formal in terms of phrasing or presentation. The point of comparing and contrasting at this stage is to help you organize and shape your ideas to aid you in structuring your arguments.
When comparing and contrasting in an essay, there are two main ways to structure your comparisons: the alternating method and the block method.
The alternating method
In the alternating method, you structure your text according to what aspect you’re comparing. You cover both your subjects side by side in terms of a specific point of comparison. Your text is structured like this:
Mouse over the example paragraph below to see how this approach works.
One challenge teachers face is identifying and assisting students who are struggling without disrupting the rest of the class. In a traditional classroom environment, the teacher can easily identify when a student is struggling based on their demeanor in class or simply by regularly checking on students during exercises. They can then offer assistance quietly during the exercise or discuss it further after class. Meanwhile, in a Zoom-based class, the lack of physical presence makes it more difficult to pay attention to individual students’ responses and notice frustrations, and there is less flexibility to speak with students privately to offer assistance. In this case, therefore, the traditional classroom environment holds the advantage, although it appears likely that aiding students in a virtual classroom environment will become easier as the technology, and teachers’ familiarity with it, improves.
The block method
In the block method, you cover each of the overall subjects you’re comparing in a block. You say everything you have to say about your first subject, then discuss your second subject, making comparisons and contrasts back to the things you’ve already said about the first. Your text is structured like this:
- Point of comparison A
- Point of comparison B
The most commonly cited advantage of distance learning is the flexibility and accessibility it offers. Rather than being required to travel to a specific location every week (and to live near enough to feasibly do so), students can participate from anywhere with an internet connection. This allows not only for a wider geographical spread of students but for the possibility of studying while travelling. However, distance learning presents its own accessibility challenges; not all students have a stable internet connection and a computer or other device with which to participate in online classes, and less technologically literate students and teachers may struggle with the technical aspects of class participation. Furthermore, discomfort and distractions can hinder an individual student’s ability to engage with the class from home, creating divergent learning experiences for different students. Distance learning, then, seems to improve accessibility in some ways while representing a step backwards in others.
Note that these two methods can be combined; these two example paragraphs could both be part of the same essay, but it’s wise to use an essay outline to plan out which approach you’re taking in each paragraph.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
Some essay prompts include the keywords “compare” and/or “contrast.” In these cases, an essay structured around comparing and contrasting is the appropriate response.
Comparing and contrasting is also a useful approach in all kinds of academic writing : You might compare different studies in a literature review , weigh up different arguments in an argumentative essay , or consider different theoretical approaches in a theoretical framework .
Your subjects might be very different or quite similar, but it’s important that there be meaningful grounds for comparison . You can probably describe many differences between a cat and a bicycle, but there isn’t really any connection between them to justify the comparison.
You’ll have to write a thesis statement explaining the central point you want to make in your essay , so be sure to know in advance what connects your subjects and makes them worth comparing.
Comparisons in essays are generally structured in one of two ways:
- The alternating method, where you compare your subjects side by side according to one specific aspect at a time.
- The block method, where you cover each subject separately in its entirety.
It’s also possible to combine both methods, for example by writing a full paragraph on each of your topics and then a final paragraph contrasting the two according to a specific metric.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, July 23). Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay | Tips & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 8, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/compare-and-contrast/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, how to write an expository essay, how to write an argumentative essay | examples & tips, academic paragraph structure | step-by-step guide & examples, unlimited academic ai-proofreading.
✔ Document error-free in 5minutes ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
- Forgot your Password?
First, please create an account
Writing effective comparison/contrast essays, 1. brainstorming and prewriting.
Recall that a comparison/contrast essay serves the purpose of examining the similarities and/or differences between two subjects. When you compare things, you show their similarities; when you contrast things, you show their differences.
The first step in writing a comparison/contrast essay is to brainstorm ideas and decide upon a topic. It's important that you find two things that have enough similarities or differences in order to be able to effectively compare or contrast them. If you choose two things that are too similar, you’ll struggle to find meaningful differences. If you choose two things that are too different, you’ll struggle to find meaningful comparisons.
During the brainstorming stage of the writing process, you can use a variety of activities to help you generate ideas for your topic. It can be helpful to make a list of similarities and differences between your two subjects, then choose the ones that are most important to use in your comparison/contrast essay.
This will help you to see the multitude of similarities and differences, and then focus in on the most important ones to use in your essay:
Clustering, or mapping, is another way to generate ideas using words, shapes, and lines that show the connections between those ideas.
- There are unending things that you can compare/contrast, and choosing two might seem overwhelming. Some common themes for a comparison/contrast essay may include events (Battle of Fort Sumter versus Battle of Sewell’s Point), situations (riding the bus versus driving to work), people (a CEO versus a CFO of a company), and places (London versus Tokyo).
- A good approach for beginner writers can be to pick two things that are in the same overarching category (foods, animals, locations, people, events, etc.) but differ in some significant ways. This can make it easier to see the similarities as well as the differences.
- Don’t forget to consider the "So what?" question when deciding on your topic. Why are you choosing this topic? Why should anyone care? Is it at all meaningful? You should be able to explain to your readers why it is useful that they understand the similarities or differences between these two topics.
- Ghandi and Martin Luther King Jr. (historical figures)
- The 1960s and today (two eras in time)
- Pop music and country music (genres of music)
- Oprah Winfrey and Ellen DeGeneres (talk show hosts)
- Online college courses and in-person college courses (ways to take college courses)
- Communism and socialism (belief systems)
- Solar power and wind energy (energy types)
As you narrow your focus, you will need to determine which points of comparison or contrast are most important. The number of points of comparison or contrast that you settle on will be driven by the topic you choose. However, for the comparison/contrast essay you’ll be writing for this course, you will need to focus in on two or three main points of comparison or contrast.
As you know, an outline can be a useful tool during prewriting to help you further develop the ideas and organization of your essay. Creating an outline will help you plan the way in which you want to organize your body paragraphs, and which details you want to include in each. This will help you to produce a sort of roadmap for your essay.
2. Drafting a Thesis Statement
A good thesis statement is the cornerstone of any academic essay. During the brainstorming and prewriting steps, you will have selected a topic and chosen your strongest main points to either compare or contrast within your essay. This will help you further develop your thesis statement.
A good thesis statement should convey the main points of your essay and should avoid being overly generic.
Instead, a good thesis statement should provide more information on which points of comparison or contrast will be discussed in the essay. Below are some templates you can consider as you begin to draft your thesis statement. A good thesis statement is not required to follow one of these patterns, but as a beginning writer, you may find that they provide a helpful starting point.
For an essay contrasting two subjects, your thesis statement may look something like this:
{Subject 1} and {Subject 2} may appear similar, but they differ in {first point of contrast}, {second point of contrast}, and {third point of contrast}.
Or, if you are comparing two subjects, your thesis statement might look something like this:
{Subject 1} and {Subject 2} do not appear to have a lot in common, but they are very similar in {first point of comparison}, {second point of comparison}, and {third point of comparison}.
A thesis statement might meaningfully contrast two subjects using the template above, like this:
Paris and Tokyo are both large metropolitan cities, but they differ in terms of their job opportunities, average income, and living expenses.
Notice how the primary emphasis in the above thesis is about how the two cities differ based on the three points the author chose to focus on: job opportunities, income, and living expenses. This thesis statement gives the reader a clear idea of the specific points of contrast that will be covered within the body of the essay.
3. Methods of Organization
Now that you have your working thesis statement, you’re ready to begin thinking about how to organize the body paragraphs within your essay.
- The point-by-point method
- The block method
You may also consider your particular approach to the subjects as well as the nature of the subjects themselves; some subjects might better lend themselves to one structure or the other.
3a. Point-by-Point Method
The point-by-point method, also known as the alternating format method, is one method of paragraph development and organization for a comparison/contrast essay.
When you use the point-by-point method, you are choosing one point of comparison and then writing one paragraph about each of your subjects that shows how they are similar or different.
IN CONTEXT If you are comparing two fast-food restaurants, McDonalds and Burger King, you would first determine your points of comparison. Let’s say you're going to focus on similarities in costs, menus, and taste. Your first body paragraph would consider the costs at McDonalds, and your second body paragraph would consider the costs at Burger King. Your third and fourth body paragraphs would consider the menus at McDonalds and Burger King, and your final two body paragraphs would consider the taste of the food at both restaurants.
This method of organizing is usually easier for the reader to follow, as the main points of the body paragraphs alternate in sequence between subjects.
To demonstrate this method, let’s take the thesis statement, "Paris and Tokyo are both large metropolitan cities, but they differ in terms of their job opportunities, average income, and living expenses." In this case, the author is focusing on the differences between the two cities in regard to three main points.
- Introduction + thesis statement
- Body paragraph 1: Job opportunities in Paris
- Body paragraph 2: Job opportunities in Tokyo
- Body paragraph 3: Average income in Paris
- Body paragraph 4: Average income in Tokyo
- Body paragraph 5: Living expenses in Paris
- Body paragraph 6: Living expenses in Tokyo
3b. Block Method
The block method, also known as the subject-by-subject method, is another method of paragraph development and organization in a comparison/contrast essay.
As the name implies, if you choose the block method, you will consider all of your points of comparison or contrast for one subject in the first two or three body paragraphs of your essay, and then discuss the same main points for the second subject in the remaining body paragraphs.
IN CONTEXT If you're contrasting your local grocery store with the giant superstore outside of town, you would first determine your points for contrast. You might choose to focus on the differences in prices, convenience, and atmosphere. You would begin the body of the essay by devoting one paragraph each to these three points about your local grocery store; then, you would write three paragraphs that show how the superstore is different according to those same points.
hint If you choose this method, pay special attention to transition use to help guide your reader.
To demonstrate this method, let’s again take the thesis statement, "Paris and Tokyo are both large metropolitan cities, but they differ in terms of their job opportunities, average income, and living expenses."
- Body paragraph 2: Average income in Paris
- Body paragraph 3: Living expenses in Paris
- Body paragraph 4: Job opportunities in Tokyo
- Body paragraph 5: Average income in Tokyo
4. Using Transitions
Given that comparison/contrast essays analyze the relationship between two subjects, it is also helpful to have some transitions on hand that will cue the reader to such analysis.
These words and phrases help to highlight the points you are trying to make by signaling the relationships between the subjects in a clear way.
Below are some sample transitional words and phrases that you may use to indicate a comparison or contrast.
summary In this lesson, you learned how to begin putting your comparison/contrast essay together by first starting with brainstorming and prewriting, then moving on to drafting a thesis statement . There are two methods of organization for the body of a comparison/contrast essay that you can choose from: the point-by-point method and the block method . The specific way in which you organize your body paragraphs will be largely determined by your topic and subjects, your audience, and your purpose. Whichever method you choose, using transitions effectively can help readers follow along with your main points. Best of luck in your learning!
Source: THIS TUTORIAL WAS AUTHORED BY SOPHIA LEARNING. PLEASE SEE OUR TERMS OF USE .
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Terms of Use
© 2024 SOPHIA Learning, LLC. SOPHIA is a registered trademark of SOPHIA Learning, LLC.
- Generating Ideas
- Drafting and Revision
- Sources and Evidence
- Style and Grammar
- Specific to Creative Arts
- Specific to Humanities
- Specific to Sciences
- Specific to Social Sciences
- CVs, Résumés and Cover Letters
- Graduate School Applications
- Other Resources
- Hiatt Career Center
- University Writing Center
- Classroom Materials
- Course and Assignment Design
- UWP Instructor Resources
- Writing Intensive Requirement
- Criteria and Learning Goals
- Course Application for Instructors
- What to Know about UWS
- Teaching Resources for WI
- FAQ for Instructors
- FAQ for Students
- Journals on Writing Research and Pedagogy
- University Writing Program
- Degree Programs
- Majors and Minors
- Graduate Programs
- The Brandeis Core
- School of Arts and Sciences
- Brandeis Online
- Brandeis International Business School
- Graduate School of Arts and Sciences
- Heller School for Social Policy and Management
- Rabb School of Continuing Studies
- Precollege Programs
- Faculty and Researcher Directory
- Brandeis Library
- Academic Calendar
- Undergraduate Admissions
- Summer School
- Financial Aid
- Research that Matters
- Resources for Researchers
- Brandeis Researchers in the News
- Provost Research Grants
- Recent Awards
- Faculty Research
- Student Research
- Centers and Institutes
- Office of the Vice Provost for Research
- Office of the Provost
- Housing/Community Living
- Campus Calendar
- Student Engagement
- Clubs and Organizations
- Community Service
- Dean of Students Office
- Orientation
- Spiritual Life
- Graduate Student Affairs
- Directory of Campus Contacts
- Division of Creative Arts
- Brandeis Arts Engagement
- Rose Art Museum
- Bernstein Festival of the Creative Arts
- Theater Arts Productions
- Brandeis Concert Series
- Public Sculpture at Brandeis
- Women's Studies Research Center
- Creative Arts Award
- Our Jewish Roots
- The Framework for the Future
- Mission and Diversity Statements
- Distinguished Faculty
- Nobel Prize 2017
- Notable Alumni
- Administration
- Working at Brandeis
- Commencement
- Offices Directory
- Faculty & Staff
- Alumni & Friends
- Parents & Families
- 75th Anniversary
- New Students
- Shuttle Schedules
- Support at Brandeis
Writing Resources
Comparative essays.
This handout is available for download in DOCX format and PDF format .
What is a comparative essay?
A comparative essay asks that you compare at least two (or possibly more) items. These items will differ depending on the assignment. You might be asked to compare
- positions on an issue (e.g., responses to midwifery in Canada and the United States)
- theories (e.g., capitalism and communism)
- figures (e.g., GDP in the United States and Britain)
- texts (e.g., Shakespeare’s Hamlet and Macbeth )
- events (e.g., the Great Depression and the global financial crisis of 2008-9)
Although the assignment may say “compare,” the assumption is that you will consider both the similarities and differences; in other words, you will compare and contrast.
Make sure you know the basis for comparison
The assignment sheet may say exactly what you need to compare, or it may ask you to come up with a basis for comparison yourself.
- Provided by the essay question: The essay question may ask that you consider the figure of the gentleman in Charles Dickens’s Great Expectations and Anne Brontë’s The Tenant of Wildfell Hall . The basis for comparison will be the figure of the gentleman.
- Developed by you: The question may simply ask that you compare the two novels. If so, you will need to develop a basis for comparison, that is, a theme, concern, or device common to both works from which you can draw similarities and differences.
Develop a list of similarities and differences
Once you know your basis for comparison, think critically about the similarities and differences between the items you are comparing, and compile a list of them. For example, you might decide that in Great Expectations , being a true gentleman is not a matter of manners or position but morality, whereas in The Tenant of Wildfell Hall , being a true gentleman is not about luxury and self-indulgence but hard work and productivity. Your list is not yet your outline for the essay, but it should provide you with enough similarities and differences to construct an initial plan.
Develop a thesis based on the relative weight of similarities and differences
Once you have listed similarities and differences, decide whether the similarities on the whole outweigh the differences or vice versa. Create a thesis statement that reflects their relative weights. A more complex thesis will usually include both similarities and differences and will argue that one of them (either the similarities or the differences) outweighs the other.
Come up with a structure for your essay
Alternating method: point-by-point pattern.
In the alternating method, you find points common to your central subjects A and B, and alternate between A and B on the basis of these points (ABABAB …). For instance, a comparative essay on the French and Russian revolutions might examine how both revolutions either encouraged or thwarted innovation in terms of new technology (body paragraphs 1 and 2), military strategy (body paragraphs 3 and 4), and the administrative system (body paragraphs 5 and 6).
Two notes about the alternating method:
- The two entities may be dissimilar in the themes you identify. To use this method, they need not be similar; you just need to have something to say about both A and B in each area.
- You may certainly include more than three pairs of alternating points: allow the subject matter to determine the number of points you develop in the body of your essay.
When do I use the alternating method?
The alternating method generally does a better job of highlighting similarities and differences between A and B. It also tends to produce a more tightly integrated and analytical paper. Consider the alternating method if you are able to identify clearly related points between A and B. Otherwise, if you attempt to impose the alternating method, you will probably find it counterproductive.
Block method: Subject-by-subject pattern
In the block method (AB), you discuss all of A, then all of B. For example, a comparative essay using the block method on the French and Russian revolutions would address the French Revolution in the first half of the essay and the Russian Revolution in the second half. If you choose the block method, however, make sure they are connected! The B block should refer to the A block and make clear points of comparison whenever comparisons are relevant: (“Unlike A, B . . .” or “Like A, B . . .”). This technique will allow for a higher level of critical engagement, continuity, and cohesion.
When do I use the block method?
The block method is particularly useful in the following cases:
- You are unable to find points about A and B that are closely related to each other.
- Your ideas about B build upon or extend your ideas about A.
- You are comparing three or more subjects as opposed to the traditional two.
Adapted from the University of Toronto, https://advice.writing.utoronto.ca/types-of-writing/comparative-essay/, 2020.
- Resources for Students
- Writing Intensive Instructor Resources
- Research and Pedagogy
Take 10% OFF— Expires in h m s Use code save10u during checkout.
Chat with us
- Live Chat Talk to a specialist
- Self-service options
- Search FAQs Fast answers, no waiting
- Ultius 101 New client? Click here
- Messenger
International support numbers
For reference only, subject to Terms and Fair Use policies.
- How it Works
Learn more about us
- Future writers
- Explore further
How to write a comparative essay
A step-by-step guide with instructions, outlines, and samples
Writing a great comparative essay means highlighting the similarities and differences between two things in a systematic manner. Start by choosing the parameters (items) to compare, write an outline, and fill in the details for each section. Make sure to have an introduction and conclusion.
The comparative essay is one form of document that you will probably be expected to write at some point over the course of your college career. The purpose of this article is to provide you with a thorough overview of the comparative essay. Specific things that will be addressed include:
Purpose of the comparative essay
Explanation of comparative models, how to analyze subjects, elements of a good comparative essay, how to write a great comparative essay.
- Samples/examples
- Best practices and advice
- Additional information
By the end of this article, you should feel more confident about your own knowledge of what a comparative essay is and the best ways to go about writing one (if you haven't decided to buy a comparative essay from Ultius ).

The fundamental purpose of a comparative essay is to elaborate the similarities and differences between two things in a systematic manner.
An effective comparative essay will leave the reader with much greater clarity about the natures and properties of the things that have been compared.
This could potentially serve as a basis for making a decision in favor of one or the other thing.
A comparative essay is different from, for example, an argumentative essay in that the comparative essay does not make a case for either of the two things under comparison. Rather, the point is to simply set up the comparison so that the reader will have as much information about the two things as possible.
Why are comparative essays important?
The comparative essay is an important form of document because when you have to make a decision or choose a side in an argument, you will want to know as much as possible about the two options under consideration—and a good comparative essay on the subject can bring out both the similarities and the differences between the options, thereby clarifying the stakes at play.
For example, a comparative essay could address the similarities and differences between any of the following pairs:
- The Republican Party and the Democratic Party
- Christianity and Marxism
- The Big Bang and creationism
- The Light or Dark side of the Force from Star Wars
- The revolutionary and the reformist perspectives on social change
By developing a comparative essay on any of these pairs, you can not only understand each item of under comparison is a more thorough way, you can also get closer to figuring out which item you prefer.
For example, a solid comparative essay on revolution vs. reformism could not only help you understand what each of these items entails, it can also help you figure out whether you would rather be a revolutionary or a reformist. Likewise, if you only have time to binge watch one show, then a comparative essay could help you figure out whether you would prefer to go with Game of Thrones or Westworld .
When writing a comparative essay, there are several models you can use in order to ensure that you set up your comparison as effectively as possible.
Venn diagram
The Venn diagram is a classic, and surely, you're familiar with it. This is the model of two overlapping circles, where each circle belongs to one item of comparison: features shared by both items (similarities) go in the overlapping middle zone, whereas features that are not shared go in the outer areas. For example, here is a Venn diagram that compares humans against gorillas.
When using the Venn diagram model, it is important to note that the differences must be symmetrical. In other words, every difference you list on one side of the comparison must be matched by a difference on the other side.
For example, if you were comparing Apple and Amazon, then for the parameter of "founder," you can list "Steve Jobs" in one circle and "Jeff Bezos" in the other. But it wouldn't make sense if you just listed one or the other: you must list something for each of the items of comparisons under the selected parameter of comparison.
In the Venn diagram above, the first parameter is "language," so for humans it is listed that we have a capacity of language, whereas for gorillas it is listed that they do not.
You don't need to worry about this kind of symmetry when it comes to the similarities, since you will list the same thing for both items of comparison (which means you only have to list it once, in the overlapping zone). In the example, above, the fact that both humans and gorillas are mammals is thus listed just once in the middle.
The dialectical method
The dialectical method is important within the discipline of philosophy, and it has been used to great effect by thinkers such as Socrates and Hegel and Kierkegaard.
This involves holding two ideas or items in tension with each other, to better clarify not only the ideas themselves but also the dynamic relationship that exist between the ideas. The first idea is called the thesis , and the second idea is called the antithesis .
For example, Romanticism could be dialectically compared against the Enlightenment that came before it, because Romanticism was in some ways a rejection of the previous worldview.
Need help? Essay writing services from Ultius can help you produce a great sample compare and contrast essay.
So, by setting up a comparison between Romanticism and the Enlightenment, it becomes possible to see both the continuities (or similarities) between the one and the other, as well as the contradictions (or differences) between them.
Berlin, Isaiah. The Roots of Romanticism . Princeton: Princeton U P, 2013. Print.
From the table above, it is clear that we are able to understand both Romanticism and the Enlightenment better if we set them up in terms of dialectical contrast.
Clearly, they are different in some important ways (logic vs. passion, for example), but we can also see that they are in continuity with each other (both happened in Western Europe and responded to previous developments). This comparison also leads one to wonder about whether it would be possible to make a synthesis that takes the best from both the thesis and the antithesis
A good comparative essay can lead one to ask such questions and pursue such lines of inquiry.
To analyze your subjects for a comparative essay, you need to identify clear parameters, or axes, in terms of which your two selected items can be compared. For example, in the table above, Romanticism and the Enlightenment were compared along the axis of " epistemology ". But that axis won't be relevant to all subjects.
Your job when preparing to write a comparative essay is to identify the specific axes that are relevant for the items that you are comparing. Why is the comparison interesting, and what insights are you trying produce? The answers to those questions will determine how you decide to frame your comparison.
For example, we could compare the Democratic Socialists of America (DSA) against the Democratic Party in terms of the axis of membership. This would reveal that the DSA has far fewer registered members than does the Democratic Party.
We could also compare them on the axis of healthcare policy, where it may be found that the DSA and the Democratic Party agree about the importance of universal coverage. When we look at the axis of economics, though, we may find that the DSA is much more radical in its proposals than the Democratic Party.
The problem of identifying relevance
In principle, any one thing in the world could be compared with any other thing in the world. For example, you could compare your shoe with the moon, and conclude that one similarity is that they both exist within the Milky Way galaxy.
But this would be a meaningless point (even if it may make for some interesting poetry). It is important for you to figure out what exactly you are trying to determine through your comparative essay. What is your purpose for writing it?
This will help you choose two items where setting up a dialectical contrast between them will produce actual insight, and it will also help you to choose the proper parameters by which to compare those items.
For example, suppose that you are running a business, and there are two expansion options open in front of you. It would be logical for you to compare and contrast these options, since this will help ensure that you are making your decision with as much knowledge and insight as possible.

Likewise, one parameter that you are sure to consider is: which option will make your business the most money? If you pick parameters that are meaningless, then you will obtain no real insight that can help you make the important decision.
Using a rubric
Once you have identified both the two items of comparison and the axes along which they will be compared, you can proceed to analyze the items by applying the axes in the form of a table or rubric.
This is what has been done, for example, in the tables that have been developed above in this article. In the left-most column, list the parameters you have selected in order to compare your items. Then, in the top-most row, list the items.
Then go ahead and list the relevant details for each parameter for each of the two items. This will produce a table where you can see how each item measures up against the other for each parameter.
The important thing is to be systematic when you are making your comparison: it should not seem random or arbitrary. Thus, it is important to carefully select both the items and the parameters for comparison, and then to proceed to address each item/parameter combo in turn.
There are several elements that are a part of any good comparative essay.
Effective selection of items
A strong comparative essay has well-chosen items for comparison, with the comparison producing actual insights of value through the juxtaposition of the two items. If the items appear to be chosen for no apparent reason, or if the comparison does not in fact produce insight, then the comparative essay would be quite weak (or at any rate pointless).
The comparative essay is not meant to make an argument in favor of one thing or another, but it is meant to produce knowledge and insight about the two things under comparison. In order to compare and contrast items in an effective way, the two items must be different enough from each other, but they should also not be so different that it just feels absurd to even compare them at all.
Effective selection of parameters of comparison
A good comparative essay not only includes well-selected items of comparison, it also includes well-selected parameters of comparison. Between any two selected items, you could theoretically make an endless number of comparisons.
But a good comparative essay identifies parameters of comparative in terms of salience , or the reasons why anyone would be interested in the comparison in the first place. This can be difficult, because in principle, any comparison could be interesting, depending on the audience of the comparative essay and the intended purpose of the essay.

For example, one could use the parameter of zodiac sign to compare Romantic artists against Enlightenment artists.
This could be very interesting to people who are very serious about the zodiac, but it would probably seem ridiculous to just about everyone else.
But if you were writing for an audience of zodiac fanatics, then this comparison could actually be a success.
So, there is no parameter of comparison that is "inherently" bad. Rather, the point is to find parameters that highlight specific salient aspects of the selected items.
For example, when comparing Romanticism against the Enlightenment, core values would be a solid parameter of comparison, because that will surely help produce insights about how worldviews changed from the one paradigm to another.
Strong organizational structure
If you want your comparative essay to be a success, then it absolutely must have strong organizational structure . This is because an effective comparison must be easy for your reader to follow. It can't just jump all over the place at random, which not only be confusing but could also result in the reader forgetting what the point of the comparison was in the first place.
In general, there are two ways in which you can organize your comparative essay. In the first format, each of the parameters would be considered in the section for similarities and the section for differences.
In the first format the comparative essay is organized in terms of similarities and differences, whereas in the second format the essay is organized in terms of parameters of comparison.

In the second format, both similarities and differences would be considered within each of the parameter sections.

Both these are formats are good, and a strong comparative essay could be built around either one.
The important thing is to have a clear system and to not make your comparisons random.
There needs to be an organizational structure that your reader can easily follow.
There are steps you can follow in order to ensure that your comparative essay has all the elements that will be required in order to make it great.
Ask yourself about your intention
If you have selected two items for your comparative essay, then you should start by asking yourself why you selected those two items. What is it about the two items that made you think it would be a good idea to compare them? (Or if you were assigned the two items, then why do you think those items were selected by your professor?)
The point here is that the items selected for a comparative essay are non-random. They are selected because that specific comparison should be able to yield interesting insights (unlike research papers ).
For example, if you are writing a comparative essay on the dogs vs. cats, then are you writing this from the perspective of evolutionary biology? Or are you perhaps writing it in order to inform potential pet owners who are debating whether they want a dog or a cat?
The purpose of your essay will determine what parameters you will select in order to compare your two items. This means that you should have an intended audience in mind, and you should also have specific questions you would like to know more about.
In short, in order to develop effective parameters for your comparative essay, you have to ask yourself why you are writing it and who would be interested in the insights produced by the essay. This can help ensure you select both appropriate items and appropriate parameters for comparison.
Develop a structural outline
It is very important that you do not just jump into your comparative essay and start writing it without a plan. That is a recipe for disaster, and the comparisons will almost certainly turn out random and confusing. Rather, you should begin with a solid outline .
A good outline will do three main things:
- 1. Identify the selected items of comparison in the introduction/thesis
- 2. Utilize one of the two organizational formats described above
- 3. Provide a roadmap for how you intend to systematically follow through on the comparison
For example, here is how an outline could look for a comparative essay on Romanticism vs. the Enlightenment.

In this sample outline, the format that is used dedicates a paragraph to each of three parameters of comparison, and both similarities and differences are addressed for each of those parameters.
This is the kind of logical flow that you will need to have in order for your comparative essay to turn out great.
Write in a systematic way
A comparative essay is not a place to get too creative with your writing, whether in terms of organization or in terms of style.
Rather, you should focus on simply carrying out your comparison, point-by-point and in a way that is easy for your reader to follow. This can get a little tedious, so if that is a problem for you, then you should make sure that you set aside enough time to work on your comparative essay little by little.
For example, if your essay has three parameters, then you could write a section on the first parameter today, the second parameter tomorrow, and the third parameter the next day.
The important thing is for you to ensure that you consider each of your two selected items in terms of each of your selected parameters. This needs to be done in a smooth and logical manner, such that your reader knows where you are in the comparison. There should be no jumping around, and there should be no departure from the basic format or structure.
Example comparative (compare/contrast) essay
Best practices/tips.
We have now arrived at the end of this guide, and you should have a much better idea of what makes a comparative essay successful and how you can go about writing one. It may be helpful to now summarize some of the main points that have been addressed here.
Let's address five main points.
1. Ensure that you select appropriate items for comparison
The two items that will be compared in your comparative essay should be carefully selected. The items should have some shared features and be in the same "class" of items, but they should also have substantial differences to which you are trying to call attention. If the items are too similar, then there would be no point in the comparison, but if they are too different, that can also make the comparison meaningless.
2. Select effective parameters of comparison
Your comparative essay shouldn't compare anything and everything between your two items; rather, the parameters should be specifically selected to highlight specific, salient similarities and differences. In order to determine what parameters would be effective, you have to ask yourself why you are writing your comparative essay and what sort of insights you intend to produce about the items being compared.
3. Use tools and models in an effective way
The Venn diagram is one tool that can be very helpful in conceptualizing your comparative essay, especially if you are a more visual kind of learner. Tables, rubrics, and outlines will also work to help ensure that you are developing a strong backbone of logic and systematic reasoning for your comparative essay. These and other tools may even help you reconsider your initial choices of items and parameters, if you realize that significant insights are not being produced.
4. Choose an organizational format, and stick with it
There are two main ways in which to structure an effective comparative essay, which have been described above. You can dedicate one section to similarities and one section to differences; or, you can dedicate a section to each of the parameters of comparison. This second option is usually more effective, especially if you are new to comparative essays. But either way, it is crucial that you stick to your chosen format and do not jump around and confuse the reader.
5. Seek assistance if you need it
If you are still uncertain about how to write a successful comparative essay, then Ultius is here to help. Our writer help section has many tools like this one available on various types of essays; we have a huge writer help section that contains all sorts of information on pretty much any writing-related questions you may have; and we also have elite professional writers who can produce a sample comparative essay for you on any subject of your choosing. We are here for you, and if you have any further questions about how to write a comparative essay, then you should feel free to reach out.

Tested Daily
Click to Verify
About The Author
This post was written by Ultius.

The Ultius Promise
With every order, you can count on the following:
- Delivered on time
- 100% original
- Free revisions
- Awesome 24/7 support
- World-class writers
- Writer Options
- Custom Writing
- Business Documents
- Support Desk
- +1-800-405-2972
- Submit bug report
- A+ BBB Rating!
Ultius is the trusted provider of content solutions for consumers around the world. Connect with great American writers and get 24/7 support.
© 2024 Ultius, Inc.
- Refund & Cancellation Policy
Free Money For College!
Yeah. You read that right —We're giving away free scholarship money! Our next drawing will be held soon.
Our next winner will receive over $500 in funds. Funds can be used for tuition, books, housing, and/or other school expenses. Apply today for your chance to win!
* We will never share your email with third party advertisers or send you spam.
** By providing my email address, I am consenting to reasonable communications from Ultius regarding the promotion.
Past winner

- Name Samantha M.
- From Pepperdine University '22
- Studies Psychology
- Won $2,000.00
- Award SEED Scholarship
- Awarded Sep. 5, 2018
Thanks for filling that out.
Check your inbox for an email about the scholarship and how to apply.
- Junior Cert
- Elizabeth Bishop
- Emily Dickinson
- Seamus Heaney
- Thomas Kinsella
- Derek Mahon
- All 2014 guides on CD
- Sylvia Plath
- Eavan Boland (LC 2012)
- Patrick Kavanagh (LC 2012)
- Adrienne Rich (LC 2013)
- Gerard Manley Hopkins (LC 2013)
- Cancelled Order
- Thank You for your order
Comparative essay structure
UPDATE – September 2014.
Again and again it’s been pointed out at marking conferences and in marking schemes that YOU MUST RESPOND TO THE QUESTION. Stock learned off answers are not being rewarded – and rightfully so! Using what you know to offer your opinion is what counts – agree, disagree, partially agree, partially disagree – it’s doesn’t matter as long as your essay is directly responding to the Q asked throughout and is doing so in a comparative way.
Here’s an extract from the Chief Examiner’s Report
“ examiners were pleased when they saw candidates trust in their own personal response and demonstrate a willingness to challenge the ‘fixed meaning’ of texts. The best answers managed to remain grounded, both in the question asked and in the texts ”.
Examiners complained that students had pre-prepared answers which they refused to adapt to the question asked. Don’t get confused here: in the comparative section you have to have done a lot of preparation prior to the exam. The similarities and differences are unlikely to simply occur to you on the day under exam conditions and the structure of comparing and contrasting, weaving the texts together using linking phrases and illustrating points using key moments is not something you can just DO with no practice. It’s a skill you have to learn. But you MUST be willing to change, adapt, and select from what you know to engage fully with the question asked.
This compliment, followed by a warning, was included in the 2013 report:
“ Many examiners reported genuine engagement with the terms of the questions, combined with a fluid comparative approach. As in previous years, examiners also noted that a significant minority of candidates were hampered by a rigid and formulaic approach “.
At the 2011 marking conference, a huge emphasis was placed on students engaging with the question – and the point was made that all too often they DON’T. You may have a general structure in your head but if this structure doesn’t suit the question that comes up DON’T just doggedly write what you’re prepared anyway. Use what you know to answer the Q. The basic structure will remain (text 1 key moment, link, text 2 km, link, text 3 km, general observation) – it’s not rocket science. But you must prove (if you want a grade above 70% in comparative) that you can engage with the question throughout your answer (not justthrow it in @ beginning and end) and conclude by showing how your essay engaged with the question asked. So the moral of the story is, if you puke up a pre-prepared answer & completely ignore the question, don’t be surprised when you then do badly!
Anyway, you still want to know what the basic comparative structure IS but remember you do not know what you will write until you see the question. Even then, your brain should be on fire non-stop as you write your answer. This is not about ‘remembering’ stuff – this is about knowing it so well, that it’s all there in your brain and you just have to shuffle it about so that it makes sense as a response to whatever question is asked.
Sorry, I don’t intend to scare you – but nor do I want to you be under some illusion that you just write one essay for each comparative mode during the year and that will do. IT WON’T…
UPDATE OVER
Right, here goes…
The quality of your links is REALLY SUPREMELY important. This section of the course is called ‘comparative studies’ for a reason. The more detailed a link is the more marks you’ll get for it. Thus just using the words ‘similarly’ or ‘by contrast’ isn’t really enough. Link individual characters from different texts, establish the ways they or their circumstances are similar but also point out subtle differences. You can extend this comparison throughout your paragraph/section if necessary (in fact this is a good idea) – but don’t simply repeat yourself.
Here’s some general advice on how you might structure your comparative essay, but I repeat, adapt, adapt adapt to the question asked .
Introduction:
Theme or Issue : Address the Q, introduce your theme, then your texts – genre, name, author and mention the central character who you will focus on in your discussion of this theme.
General Vision & Viewpoint : Address the Q, introduce the idea of GV&V (briefly), then your texts – genre, name, author and mention the major emotions you associate with each.
Cultural Context: Address the Q, introduce the idea of cultural context (briefly), then your texts – genre, name, author, plus where and when they are set. You may want to mention the aspects of cultural context you intend to discuss.
Literary Genre: Address the Q, briefly introduce what literary genre means, then introduce your texts – genre, name, author. Outline the aspects of literary genre you will discuss (depends on the Q asked).
Look at the following examples. Imagine the Q is “Exploring a theme or issue can add to our enjoyment of a text”
“I found it fascinating to explore the central theme of plagiarism in my comparative texts. In the novel ‘Old School ‘ (OS) by Tobias Wolff I was intrigued by the narrator’s self delusion after he entered a competition with a short story he had not written. By contrast, I found the film ‘Generous’ (GEN) directed by Frank Faulkner quite disturbing. It explores a young girl’s obsession with becoming famous as she ‘borrows’ outrageous online articles to make her blog more popular. Finally I found the play “IMHO” by Judy Price hilarious. It looks at how we all ‘copy’ ideas from others and pass them off as our own at dinner parties. Thus exploring this theme greatly added to my enjoyment of each text”.
Now look at how this changes for a different mode. Imagine the Q is “The general vision & viewpoint of a text often offers the reader both joy & despair”
“ All of my comparative texts took me on a rollercoaster ride through the highs and lows experienced by the central characters . In the novel “Old School” (OS) by Tobias Wolff I experienced the narrator’s joy at the visit of Robert Frost, and his despair when his cheating was uncovered. Similarly, the film “Generous” (GEN) directed by Frank Faulkner begins in elation for Emily as her blog goes viral but ends in complete mental and physical collapse. By contrast, the lighthearted play “IMOH” by Judy Price offers a hilarious look at the falseness of modern dinner parties and the only despair the audience feels is lamenting the complete lack of self-awareness of the central characters. Thus the vision & viewpoint of each text offered me a wide and varied range of emotions from joy to depair”.
Now look at how this changes again: Imagine the Q is: “Characters are often in conflict with the world or culture they inhabit”
“ The novel ‘Old School’ (OS) written by Tobias Wolff is set in an elite American boarding school in the 1960’s and the unnamed narrator certainly comes into conflict with his world. This text explores cultural issues such as social class, ethnic identity and authority figures. Similar issues are explored in the film “Generous” (GEN) directed by Frank Faulkner and set in modern day London as Emily comes into conflict with her parents, peers and teachers. My third text the play “IMOH” by Judy Price set in Celtic Tiger Ireland also looks at the conflicts which occur as a result of people’s social snobbery and their desire to escape their cultural identity and heritage. In this text the major authority figure is Susan, the host of the dinner party, who desperately tries to keep her guests in line. Thus I absolutely agree that these three texts made me more aware of the ways in which people can come into conflict with the world or culture they inhabit”.
Finally look at this literary genre question : “The creation of memorable characters is part of the art of good story-telling” .
The unnamed narrator in Tobias Wolff’s novel ‘Old School’ (OS) is a fascinating and memorable character because he is struggling to come to terms with his own flaws. Similarly, the film ‘Generous’ (GEN) directed by Frank Faulkner has a central character Emily who we emphathise with despite her many flaws. Finally, the play ‘IMHO’ by Judy Price with its emsemble cast creates many memorable characters but for the purposes of this essay I will focus on the dinner party host Susan. These characters live on in our memories because of the writer’s choice of narrative point of view, because of the vivid imagery we associate with them and because the climax of the action revolves around their character.
NEXT you need to think about structuring the essay itself. The most important thing to decide in advance is what aspect you wish to compare for each page/section but this may need to change to adapt to the Q.
For theme or issue you might plan it out like this but at all times focus on answering the Q:
- How is this theme introduced? How does this theme affect the central character/characters?
- How is this theme developed? Do the central characters embrace or fight against it? How?
- Do other characters influence how this theme unfolds?
- How does the text end & what are our final impressions of this theme as a result?
Asking the same question of each text allows you to come up with the all important links (similarities & differences).
For general vision & viewpoint you might plan as follows but at all times focus on answering the Q:
- What view is offered of humanity (are the main characters likable or deplorable?)
- What view is offered of society (is this society largely benign or does it negatively impact on the characters)
- How does the text end & what vision are we left with (positive or negative) as a result?
Alternatively you could just take a beginning, middle, end approach but you must at all times focus on whether the vision/feelings/atmosphere is positive or negative and how this impacts on the reader/viewers experience.
For literary genre you must focus on the aspects mentioned in the question – possibly some of these:
- Genre – diff between novel/play/film
- Narrator / point of view
- Characterisation
- Chronology – flashback / flashforward
- Climax / twist
For cultural context you must decide which of the following issues are most prominent in all three texts – try to find links before you decide. At all times focus on answering the Q asked
- Social class / social status
- Wealth / poverty
- Job opportunities / emigration
- Authority figures
- Sex / Marriage (attitudes towards)
- Gender roles
- Stereotypes / Ethnic identity
You may find some overlap between 2 of these – for example social class often influences a person’s wealth or poverty; religion often effects attitudes towards sex and marriage; marriage can often be a financial necessity for those with limited job opportunities (mostly women, so this overlaps with gender roles). Choose your sections carefully so you don’t end up repeating yourself.
You might plan as follows for the example given above but everything depends on the texts & the question.
- Social status
- Ethnic identity
- How does the text end? Do the main characters escape or remain constrained by their cultural context?
Once you’ve decided what sections to include your structure for each goes a little something like this:
STATEMENT – ALL 3 TEXTS e.g. All of the central characters are deeply aware of their social class and wish to ‘climb the ladder’ as it were in the hope that they will achieve recognition, the envy of their peers and ultimately a better life.
STATEMENT – TEXT 1 e.g. In OS, the narrator hides his background (he comes from a broken home) from his wealthier peers.
KEY MOMENT TEXT 1 e.g. This is evident when he discusses how, at school, your social class was defined not just by your clothes but also by how you spent your summers – in his case “working as a dishwasher in the kitchen crew at a YMCA camp” a fact which he vows never to reveal to his classmates.
LINKING PHRASE & STATEMENT TEXT 2 e.g. Similarly, in GEN, Emily comes from a broken home, but it is her family’s absolute impoverishment which she keeps hidden from her classmates. Like the narrator in OS, she fears their pity but unlike him she is already dealing with the harsh reality of being a social outcast at school.
KEY MOMENT TEXT 2 e.g. During one key moment she describes leaning down to tie her shoes, all the while talking, only to look up and find her friends have walked off and are now laughing at her for talking to thin air. Thus her desire to escape the limitations of her background is more urgent than in OS.
LINKING PHRASE & STATEMENT TEXT 3 e.g. By contrast, in IMHO, Jane, Lucy, Joel, Zach & Max all come from upper middle class backgrounds. Their social status is more secure than the narrator in OS or Emily in GEN, yet they are all obsessed with creating the impression that they have links to the aristocracy – or in Zach’s case, royalty.
KEY MOMENT TEXT 3 e.g. Several key moments spring to mind, the funniest of which is when Lucy boasts about the diamond necklace she’s wearing being a family heirloom bequeathed by her Aunt Tess, only to have one of the so-called diamonds fall into her soup. Joel the jeweller then delights in pointing out the evident ‘fake’ in the room (the woman AND the diamond).
STATEMENT ALL 3 & PERSONAL RESPONSE TO QUESTION ASKED e.g. Thus I found it fascinating, tragic and at times hilarious to see how all of these characters were so deeply affected by their obsession with their social status and to observe the conflicts – both internal & external – which resulted.
This all sounds very technical but if you break it down as follows it’s not so complicated (easy for me to say!)
STATEMENT ALL 3 TEXTS
STATEMENT TEXT 1 & KEY MOMENT
LINKING PHRASE & STATEMENT TEXT 2 & KEY MOMENT
LINKING PHRASE & STATEMENT TEXT 3 & KEY MOMENT
STATEMENT ALL 3 & PERSONAL RESPONSE TO QUESTION
Now look at how the paragraph/section flows when you put it all together.
All of the central characters are deeply aware of their social class and wish to ‘climb the ladder’ as it were in the hope that they will achieve recognition, the envy of their peers and ultimately a better life. In OS, the narrator hides his background (he comes from a broken home) from his wealthier peers. This is evident when he discusses how, at school, your social class was defined not just by your clothes but also by how you spent your summers – in his case “working as a dishwasher in the kitchen crew at a YMCA camp” a fact which he vows never to reveal to his classmates. Similarly, in GEN, Emily comes from a broken home, but it is her family’s absolute impoverishment which she keeps hidden from her classmates. Like the narrator in OS, she fears their pity but unlike him she is already dealing with the harsh reality of being a social outcast at school. During one key moment she describes leaning down to tie her shoes at her locker, all the while talking, only to look up and find her friends have walked off and are now laughing at her for talking to thin air. Thus her desire to escape the stigma of her background is more urgent than in OS. By contrast, in IMHO, Jane, Lucy, Joel, Zach & Max all come from upper middle class backgrounds. Their social status is more secure than for narrator in OS or Emily in GEN, yet they are all obsessed with creating the impression that they have links to the aristocracy – or in Zach’s case, royalty. S everal key moments spring to mind, the funniest of which is when Lucy boasts about the diamond necklace she’s wearing being a family heirloom bequeathed by her Aunt Tess, only to have one of the so-called diamonds fall into her soup. Joel the jeweller then delights in pointing out the evident ‘fakes’ in the room (the woman AND the diamond). Thus I found it fascinating, tragic and at times hilarious to see how all of these characters were so deeply affected by their obsession with their social status and to observe the conflicts – both internal & external – which resulted.
This paragraph only establishes that the characters want to hide or improve their social class. You could now look at some of their attempts to improve their social status.
If a paragraph gets too long, break it into two. The linking phrase will make it clear that you’re still talking about the same issue.
For the 30 / 40 marls question just take all of your statements & key moments for Text 1 and put them together, all the while answering the question and offering personal response. This is your 30 marks part.
Then take all of your statements & links for texts 2 & 3 and put them together, all the while answering the question and offering personal response. This is your 40 marks part. You will refer back, in passing, to Text 1 but only when establishing your links.
Also, I’ve said it before but I’ll say it again: the more detailed a link is the more marks you’ll get for it. Thus just using the words ‘similarly’ or ‘by contrast’ isn’t really enough. Link individual characters from different texts, establish the ways they or their circumstances are similar but also point out subtle differences.
This structure applies no matter what the mode – theme or issue / general vision or viewpoint / cultural context / literary genre.
P.S. If you’re wondering why you’ve never heard of the film Generous or the play IMHO, I can explain. I made them up.
65 responses to “ Comparative essay structure ”
Recent posts.
- A long slow goodbye…
- Lear’s journey
- Some themes in Lear…
- King Lear – Plot Chronology
- King Lear quotes (in translation!)
- Justice in King Lear – how to construct an answer…
- The Old Warrior and Me
- Single text options…
- Tackling the Comparative
- Reading Shakespeare (Othello)
- Game Based Learning
- Originality – Freshness – Energy – Style
- Discussions
- Comprehensions
- Comparative
- Studied poetry
- Unseen poetry
- Media Studies
- Uncategorized
Affiliations
Nominations.
How To Structure A Comparative Essay (VCE English Tips)
What is a comparative essay.
The comparative essay, in only its second year of being on the VCE English syllabus, is a cause for confusion for many students and teachers alike. Read on for one simple way to structure a comparative essay.
Comparative essay structure
How to write an introduction for a comparative essay.
This can be structured in much the same way as a text response essay. Here, the only difference is that you will need to introduce both texts. Do not forget to make use of comparative language, which is an element of the VCAA criteria, which requires that students discuss "meaningful connections , similarities or differences between the texts”. Your introduction must address your overall contention, specific to the prompt, which should be an idea or concept running through your essay.
How to write a body paragraph for a comparative essay
Aim for around two to four body paragraphs, which should be developed using breadth and a wide scope of ideas. A good way to construct these paragraphs is to base each around a premise or main idea, and you will explore both texts through the lens of this premise.
You can choose either to compare both texts throughout the paragraph, or to go into depth in one text and then transition into exploring the other. No matter which method you choose, make you mention to which extent the two texts are similar or different (it's not enough to say "they are different" or "they are similar").
Relate the end of your body paragraph back to the overall contention, bringing both texts explicitly into focus.
How to write a conclusion for a comparative essay
Like the intro, this can be very similar to a text response conclusion! Make sure to be clear and concise, and sum up your main points from your body paragraphs. Aim to end with a strong, clear point of analysis, shining new meaning on both texts.
Comparative Essay Writing Tips
- Create an Outline: Develop a well-organised outline to keep your essay focused and ensure a logical flow of arguments. This framework serves as a roadmap, guiding you from one point to the next. Always connect your arguments back to your thesis statement for coherence.
- Reference Throughout the Process: Avoid last-minute referencing by incorporating it into your writing process. Cite sources as you go to maintain accuracy and credibility. This practice helps in seamlessly integrating evidence to support your comparisons.
- Highlight Differences and Similarities: Emphasise both differences and similarities between the subjects you're comparing. Provide a clear analysis of how they relate, diverge, or intersect. This enhances the depth of your comparison and adds richness to your essay.
- Utilise Concrete Examples: Enhance the persuasiveness of your writing by using specific examples. Illustrate your points with concrete instances that support your comparisons. This not only reinforces your arguments but also adds clarity to your overall narrative.
- Incorporate Comparative Vocabulary: make sure your essay contains appropriate terminology and comparative words, such as: "On the contrary," "Although," "Furthermore," "Similar to," "Unlike," "In the same way," "Likewise," "Compared to," "In contrast," "Yet," and "On the one hand...on the other hand."
- Collaborate for Improvement: Seek input from others, whether through an English tutor or a study group. Collaborating with peers can provide valuable insights and help refine your work. Different perspectives contribute to a more comprehensive and polished essay.
- Prioritise Drafting: Aim to draft your essay as early as possible. Getting your initial thoughts on paper makes the editing process more manageable. Remember, a first draft is easier to edit than starting with a blank page
- Proofread and Edit: Finally, proofread and edit your essay. Pay attention to grammar, spelling, and overall clarity. A well-polished essay enhances the overall impact of your comparative analysis.
If you loved this article, you will LOVE all of our other articles, such as: How To Take Notes To Maximise Success , 2U Maths Tips from a Past Student (98 in 2U Maths)! and Tips on Studying for Exams – Learnmate Tutoring .
About Learnmate
Learnmate is a trusted Australian community platform that connects students who want 1:1 or small group study support, with tutors who are looking to share their knowledge and earn an income. From primary school to high school subjects — from science and maths to niche subjects like visual communication — Learnmate can help you improve academic performance or boost confidence, at your pace with the tutor that you choose.
We pride ourselves in offering a reliable and positive experience for both our students and tutors. Every tutor that joins the platform is vetted to meet a level of academic excellence, teaching qualification or relevant experience. All tutors are provided the opportunity to complete professional training.
Students and parents can easily find and screen for tutors based on their location, their subject results or skill level, and whether they provide in-person or online sessions. Learnmate is proud to provide tutors in Melbourne , Sydney , Geelong , Brisbane , Hobart , Canberra , Perth & Adelaide , and other locations.
Learnmate also has tutors for all curriculums: HSC , IB , QCE , BSSS, SACE , TASC, WACE , VCE and UMAT
Go online and let Learnmate help you get ahead. Start your search today.
"> "> share this post.
Article Author
Find online & in-person tutors near you, recent posts.

VCE SACs: Maximising Your Scores and Understanding Their Impact
Mastering VCE SACs: A Comprehensive Guide As part of the Victorian Certificate of Education (VCE), School Assessed Coursework (SACs) are...
March 26, 2024

Understanding Liquidity Analysis in VCE Accounting: Part One
In the latter part of the VCE Accounting course, students focus extensively on evaluating the financial performance of businesses. An...
Understanding Composite Functions in VCE Maths Methods: A Guide to Understanding and Applying Them
Hi there! My name is Daniela and I am a VCE Math Methods and Biology tutor on Learnmate. I graduated...
March 13, 2024


No products in the cart.
Insight: Engage
Writing a comparative essay.
This week, Insight writer and English teacher Melanie Flower outlines steps you can take to write your best comparative essay.
The comparative essay is still a relatively new element of VCE English, only becoming part of the Study Design in 2016. However, while the Area of Study is new, your essay should still have a clear and largely familiar structure, with an introduction, body and conclusion. Last year every topic in Section B of the VCE English examination included the word ‘compare’, and it is essential to note that the comparison of texts is the central requirement for this response, even if the word does not explicitly appear in the topic.
The comparative essay can be tackled in a variety of ways, and it is worth experimenting with different approaches throughout the semester to find the one that suits your strengths.
Read the topic carefully
Make sure that you understand exactly what the topic is asking you to do. The topic might invite a broad thematic comparison, which requires a thoughtful understanding of the ways a particular theme is explored in both texts. Other topics focus on an aspect of the texts’ construction, such as characterisation or setting, and require you to show an understanding of the texts’ form and genre.
You could also encounter a topic that contains one or two quotes. This type of topic necessitates a very thorough knowledge of your texts, as you need to recognise the context of each quote, identify the key ideas being addressed in each, and understand how these ideas are explored in both texts.
Give roughly equal weight to each text
Each text pairing has been carefully chosen to offer points of comparison, in terms of both similarities and differences. While you may have a preference for one text over the other, it is essential that you do not allow this to limit the scope of your discussion. One easy way to make sure that you are addressing both texts equally is to balance every point, example or quote from one text with an equivalent from the other. This can be done in the planning stages, giving you a wealth of material to use in your essay.
Choose your preferred structure
The broad structure of a comparative essay is already very familiar to you, and consists of an introduction, several body paragraphs and a conclusion. The introduction should include a clear contention that alerts the reader to your response to the topic, as well as the main ideas your essay will explore. It must contain references to both texts. Similarly, your conclusion should summarise the points you have made and leave the reader with a clear understanding of your position on the topic. These elements are common to all analytical text response essays. The difference in a comparative response is in the way the body paragraphs are structured and organised. You essentially have two basic options for the body: the block approach or the woven approach.
- The block approach: This approach involves devoting a paragraph or two to each text, examining the ways each of them address the ideas raised by the topic. The final body paragraphs pull this material together and discuss the similarities and differences between the texts’ approach to the central ideas explored in the essay. This structure appears straightforward, but it can be challenging to maintain a strong connection between the texts when discussing them in isolation. A careful use of linking words is essential to ensure that the essay is cohesive and the comparison of texts remains at the fore.
- The woven approach: Using a more sophisticated structure, the woven essay draws evidence from both texts within each body paragraph. Topic sentences focus on an aspect of the ideas raised by the topic rather than on individual texts or characters, leaving you free to explore material from both sources in the paragraph. It can be challenging to move between two texts, although with practice, this will become easier. One useful strategy is to begin your discussion of a particular idea with a sentence addressing text 1. Then start the next sentence with a linking word or phrase that leads to a statement about text 2’s perspective on the same idea. A third sentence links both texts, adding an overall position statement. This approach allows you to move smoothly between the texts while also engaging in deep analysis of their ideas.
Focus on differences as well as similarities
We tend to be very alert to similarities between texts, which are usually relatively simple to identify; however, often the most interesting discussion will devolve from a consideration of the differences. These provide an opportunity to explore contrasting situations and points of view, thus demonstrating your engagement with both the texts and the ideas they present.
Use linking words and phrases
When moving the discussion between texts, regardless of the overall essay structure you have chosen, use appropriate linking words and phrases to maintain fluency and cohesion. These links help your reader to understand the connection between the ideas you are discussing, whether they are similarities or contrasts.
Phrases that you can use to discuss similarities include:
similarly, likewise, in the same way, also, along similar lines, in the same fashion .
Phrases useful for indicating contrast include:
in contrast, on the other hand, unlike (text 1), regardless, however, conversely, on the contrary, nevertheless .
Used purposefully, these words and phrases help guide your reader through your discussion, ensuring that they understand the relationship between the texts and the ideas explored in your response.
Explore a range of elements
To add depth to your response, consider a variety of textual elements in your discussion. While the topic may prompt you to focus on character or theme, your response will have more depth if you are able to draw other aspects of the texts into your discussion. You could note the impact of the narrative voice, reflect on how structure shapes a reader’s responses, consider the influence of genre on the texts’ construction, or acknowledge differences in style or authorial purpose. All of these elements provide you with opportunities to consider the texts as constructs, leading to a more complex and sophisticated analysis.
_____________
The comparative essay is a challenging, but ultimately satisfying, opportunity to explore intertextual connections. By considering the different perspectives offered by carefully paired texts, you can enrich your understanding of both texts and draw new meanings from them. Ultimately, the best way to find an essay style that works for you is to experiment. Try a few different approaches, note the feedback you receive from your teacher, and use this to finetune your approach. Remember that examiners are not looking for a single, standard essay format. They are interested in your ideas and your genuine responses to the texts, and whichever structure best allows you to present these is the most appropriate structure for you.
Need help with your comparative essays? Insight has two Insight Sample Essays for each List 2 text comparison for English. Each high-level essay features annotations with assessor comments identifying the elements of the essay that work and areas for improvement, as well as tips on how to approach the essay topic and appropriate strategies for analysis.
Insight Sample Essays are produced by Insight Publications, an independent Australian educational publisher.
Photo credit: maradon333/shutterstock
Share this blog
*By using the Insight: Engage blog, you agree to the terms and conditions on this website .
Insight Engage Categories
- Argument and persuasive language
- Creative Text Response
- Creative Writing
- Exam preparation
- Handwriting
- Listening Comprehension
- Listening skills
- Queensland General English
- Reading and comparing texts
- Reading and creating texts
- Sample Essays & Text Articles
- Shakespeare
- Study techniques
- Text Analysis
- Text Guides & Comparisons
- Textbooks & Resources
- Theory of Knowledge
- Uncategorized
- VCE English
- VCE English as a Additional Language (EAL)
- VCE English Language
- VCE English Literature
- VCE text comparison
- Year 10 English
- Year 11 English
- Year 12 EAL
- Year 12 English
- Year 9 English
- 3/350 Charman Road Cheltenham, Victoria 3192
- [email protected]
Insight Publications is an independent Australian-owned company with over 50 years of experience publishing English resources for secondary teachers and students. We develop innovative, engaging and evolving English resources to challenge, to inspire and to enrich learning.
Information
- Credit Reporting Policy
- Insight Catalogue
- Privacy Policy
- Returns Policy
- Shipping Information
- Terms & Conditions
- +61 3 8571 4950
In the spirit of reconciliation, Insight Publications acknowledges the Traditional Custodians of Country throughout Australia and their connections to land, sea and community. We pay our respect to their Elders past and present and extend that respect to all Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples today.
- Utility Menu
GA4 Tracking Code
Gen ed writes, writing across the disciplines at harvard college.
- Comparative Analysis
What It Is and Why It's Useful
Comparative analysis asks writers to make an argument about the relationship between two or more texts. Beyond that, there's a lot of variation, but three overarching kinds of comparative analysis stand out:
- Coordinate (A ↔ B): In this kind of analysis, two (or more) texts are being read against each other in terms of a shared element, e.g., a memoir and a novel, both by Jesmyn Ward; two sets of data for the same experiment; a few op-ed responses to the same event; two YA books written in Chicago in the 2000s; a film adaption of a play; etc.
- Subordinate (A → B) or (B → A ): Using a theoretical text (as a "lens") to explain a case study or work of art (e.g., how Anthony Jack's The Privileged Poor can help explain divergent experiences among students at elite four-year private colleges who are coming from similar socio-economic backgrounds) or using a work of art or case study (i.e., as a "test" of) a theory's usefulness or limitations (e.g., using coverage of recent incidents of gun violence or legislation un the U.S. to confirm or question the currency of Carol Anderson's The Second ).
- Hybrid [A → (B ↔ C)] or [(B ↔ C) → A] , i.e., using coordinate and subordinate analysis together. For example, using Jack to compare or contrast the experiences of students at elite four-year institutions with students at state universities and/or community colleges; or looking at gun culture in other countries and/or other timeframes to contextualize or generalize Anderson's main points about the role of the Second Amendment in U.S. history.
"In the wild," these three kinds of comparative analysis represent increasingly complex—and scholarly—modes of comparison. Students can of course compare two poems in terms of imagery or two data sets in terms of methods, but in each case the analysis will eventually be richer if the students have had a chance to encounter other people's ideas about how imagery or methods work. At that point, we're getting into a hybrid kind of reading (or even into research essays), especially if we start introducing different approaches to imagery or methods that are themselves being compared along with a couple (or few) poems or data sets.
Why It's Useful
In the context of a particular course, each kind of comparative analysis has its place and can be a useful step up from single-source analysis. Intellectually, comparative analysis helps overcome the "n of 1" problem that can face single-source analysis. That is, a writer drawing broad conclusions about the influence of the Iranian New Wave based on one film is relying entirely—and almost certainly too much—on that film to support those findings. In the context of even just one more film, though, the analysis is suddenly more likely to arrive at one of the best features of any comparative approach: both films will be more richly experienced than they would have been in isolation, and the themes or questions in terms of which they're being explored (here the general question of the influence of the Iranian New Wave) will arrive at conclusions that are less at-risk of oversimplification.
For scholars working in comparative fields or through comparative approaches, these features of comparative analysis animate their work. To borrow from a stock example in Western epistemology, our concept of "green" isn't based on a single encounter with something we intuit or are told is "green." Not at all. Our concept of "green" is derived from a complex set of experiences of what others say is green or what's labeled green or what seems to be something that's neither blue nor yellow but kind of both, etc. Comparative analysis essays offer us the chance to engage with that process—even if only enough to help us see where a more in-depth exploration with a higher and/or more diverse "n" might lead—and in that sense, from the standpoint of the subject matter students are exploring through writing as well the complexity of the genre of writing they're using to explore it—comparative analysis forms a bridge of sorts between single-source analysis and research essays.
Typical learning objectives for single-sources essays: formulate analytical questions and an arguable thesis, establish stakes of an argument, summarize sources accurately, choose evidence effectively, analyze evidence effectively, define key terms, organize argument logically, acknowledge and respond to counterargument, cite sources properly, and present ideas in clear prose.
Common types of comparative analysis essays and related types: two works in the same genre, two works from the same period (but in different places or in different cultures), a work adapted into a different genre or medium, two theories treating the same topic; a theory and a case study or other object, etc.
How to Teach It: Framing + Practice
Framing multi-source writing assignments (comparative analysis, research essays, multi-modal projects) is likely to overlap a great deal with "Why It's Useful" (see above), because the range of reasons why we might use these kinds of writing in academic or non-academic settings is itself the reason why they so often appear later in courses. In many courses, they're the best vehicles for exploring the complex questions that arise once we've been introduced to the course's main themes, core content, leading protagonists, and central debates.
For comparative analysis in particular, it's helpful to frame assignment's process and how it will help students successfully navigate the challenges and pitfalls presented by the genre. Ideally, this will mean students have time to identify what each text seems to be doing, take note of apparent points of connection between different texts, and start to imagine how those points of connection (or the absence thereof)
- complicates or upends their own expectations or assumptions about the texts
- complicates or refutes the expectations or assumptions about the texts presented by a scholar
- confirms and/or nuances expectations and assumptions they themselves hold or scholars have presented
- presents entirely unforeseen ways of understanding the texts
—and all with implications for the texts themselves or for the axes along which the comparative analysis took place. If students know that this is where their ideas will be heading, they'll be ready to develop those ideas and engage with the challenges that comparative analysis presents in terms of structure (See "Tips" and "Common Pitfalls" below for more on these elements of framing).
Like single-source analyses, comparative essays have several moving parts, and giving students practice here means adapting the sample sequence laid out at the " Formative Writing Assignments " page. Three areas that have already been mentioned above are worth noting:
- Gathering evidence : Depending on what your assignment is asking students to compare (or in terms of what), students will benefit greatly from structured opportunities to create inventories or data sets of the motifs, examples, trajectories, etc., shared (or not shared) by the texts they'll be comparing. See the sample exercises below for a basic example of what this might look like.
- Why it Matters: Moving beyond "x is like y but also different" or even "x is more like y than we might think at first" is what moves an essay from being "compare/contrast" to being a comparative analysis . It's also a move that can be hard to make and that will often evolve over the course of an assignment. A great way to get feedback from students about where they're at on this front? Ask them to start considering early on why their argument "matters" to different kinds of imagined audiences (while they're just gathering evidence) and again as they develop their thesis and again as they're drafting their essays. ( Cover letters , for example, are a great place to ask writers to imagine how a reader might be affected by reading an their argument.)
- Structure: Having two texts on stage at the same time can suddenly feel a lot more complicated for any writer who's used to having just one at a time. Giving students a sense of what the most common patterns (AAA / BBB, ABABAB, etc.) are likely to be can help them imagine, even if provisionally, how their argument might unfold over a series of pages. See "Tips" and "Common Pitfalls" below for more information on this front.
Sample Exercises and Links to Other Resources
- Common Pitfalls
- Advice on Timing
- Try to keep students from thinking of a proposed thesis as a commitment. Instead, help them see it as more of a hypothesis that has emerged out of readings and discussion and analytical questions and that they'll now test through an experiment, namely, writing their essay. When students see writing as part of the process of inquiry—rather than just the result—and when that process is committed to acknowledging and adapting itself to evidence, it makes writing assignments more scientific, more ethical, and more authentic.
- Have students create an inventory of touch points between the two texts early in the process.
- Ask students to make the case—early on and at points throughout the process—for the significance of the claim they're making about the relationship between the texts they're comparing.
- For coordinate kinds of comparative analysis, a common pitfall is tied to thesis and evidence. Basically, it's a thesis that tells the reader that there are "similarities and differences" between two texts, without telling the reader why it matters that these two texts have or don't have these particular features in common. This kind of thesis is stuck at the level of description or positivism, and it's not uncommon when a writer is grappling with the complexity that can in fact accompany the "taking inventory" stage of comparative analysis. The solution is to make the "taking inventory" stage part of the process of the assignment. When this stage comes before students have formulated a thesis, that formulation is then able to emerge out of a comparative data set, rather than the data set emerging in terms of their thesis (which can lead to confirmation bias, or frequency illusion, or—just for the sake of streamlining the process of gathering evidence—cherry picking).
- For subordinate kinds of comparative analysis , a common pitfall is tied to how much weight is given to each source. Having students apply a theory (in a "lens" essay) or weigh the pros and cons of a theory against case studies (in a "test a theory") essay can be a great way to help them explore the assumptions, implications, and real-world usefulness of theoretical approaches. The pitfall of these approaches is that they can quickly lead to the same biases we saw here above. Making sure that students know they should engage with counterevidence and counterargument, and that "lens" / "test a theory" approaches often balance each other out in any real-world application of theory is a good way to get out in front of this pitfall.
- For any kind of comparative analysis, a common pitfall is structure. Every comparative analysis asks writers to move back and forth between texts, and that can pose a number of challenges, including: what pattern the back and forth should follow and how to use transitions and other signposting to make sure readers can follow the overarching argument as the back and forth is taking place. Here's some advice from an experienced writing instructor to students about how to think about these considerations:
a quick note on STRUCTURE
Most of us have encountered the question of whether to adopt what we might term the “A→A→A→B→B→B” structure or the “A→B→A→B→A→B” structure. Do we make all of our points about text A before moving on to text B? Or do we go back and forth between A and B as the essay proceeds? As always, the answers to our questions about structure depend on our goals in the essay as a whole. In a “similarities in spite of differences” essay, for instance, readers will need to encounter the differences between A and B before we offer them the similarities (A d →B d →A s →B s ). If, rather than subordinating differences to similarities you are subordinating text A to text B (using A as a point of comparison that reveals B’s originality, say), you may be well served by the “A→A→A→B→B→B” structure.
Ultimately, you need to ask yourself how many “A→B” moves you have in you. Is each one identical? If so, you may wish to make the transition from A to B only once (“A→A→A→B→B→B”), because if each “A→B” move is identical, the “A→B→A→B→A→B” structure will appear to involve nothing more than directionless oscillation and repetition. If each is increasingly complex, however—if each AB pair yields a new and progressively more complex idea about your subject—you may be well served by the “A→B→A→B→A→B” structure, because in this case it will be visible to readers as a progressively developing argument.
As we discussed in "Advice on Timing" at the page on single-source analysis, that timeline itself roughly follows the "Sample Sequence of Formative Assignments for a 'Typical' Essay" outlined under " Formative Writing Assignments, " and it spans about 5–6 steps or 2–4 weeks.
Comparative analysis assignments have a lot of the same DNA as single-source essays, but they potentially bring more reading into play and ask students to engage in more complicated acts of analysis and synthesis during the drafting stages. With that in mind, closer to 4 weeks is probably a good baseline for many single-source analysis assignments. For sections that meet once per week, the timeline will either probably need to expand—ideally—a little past the 4-week side of things, or some of the steps will need to be combined or done asynchronously.
What It Can Build Up To
Comparative analyses can build up to other kinds of writing in a number of ways. For example:
- They can build toward other kinds of comparative analysis, e.g., student can be asked to choose an additional source to complicate their conclusions from a previous analysis, or they can be asked to revisit an analysis using a different axis of comparison, such as race instead of class. (These approaches are akin to moving from a coordinate or subordinate analysis to more of a hybrid approach.)
- They can scaffold up to research essays, which in many instances are an extension of a "hybrid comparative analysis."
- Like single-source analysis, in a course where students will take a "deep dive" into a source or topic for their capstone, they can allow students to "try on" a theoretical approach or genre or time period to see if it's indeed something they want to research more fully.
- DIY Guides for Analytical Writing Assignments

- Types of Assignments
- Unpacking the Elements of Writing Prompts
- Formative Writing Assignments
- Single-Source Analysis
- Research Essays
- Multi-Modal or Creative Projects
- Giving Feedback to Students
Assignment Decoder

How to Write a Comparative Essay: Structure & Tips
A comparative essay may be something you are unfamiliar with in your schooling journey so far, the structure of the essay as a whole should be quite familiar to you. As you already know, having the correct structure and practices when writing is vital to having a good end product. This article will build on what you already know and teach you some new skills in how to write a comparative essay.
What Is a Comparative Essay?
A comparative essay is an essay that contains an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion. What makes a comparative essay different to other essays is that it compares and contrasts two different texts.
A comparative essay is usually completed by students in years 10, 11, and 12 undertaking General English. However, students in other English subjects and younger grades can also be asked to write comparative essays, or students may have similar assessments in other subjects, such as writing a history essay.

Comparative Essay Structure
In a comparative essay, much like other essays, there is your introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion. There are a few different ways you can structure your essay, but these elements stay the same.
- Introduction: In the introduction of a comparative essay, you should include; an overview and brief synopsis of the texts you are comparing, your thesis statement, and an outline of your arguments.
- Body paragraphs: The body paragraphs of your comparative essay contain all of your evidence and arguments, this is by far the longest part of your essay. This is where you actually compare and analyse the texts.
- Conclusion: Your conclusion should not introduce any new information, but rather summarise your arguments and restate your thesis.
How to Write a Comparative Essay Introduction
As mentioned above, your introduction should include: an overview and brief synopsis of the texts you are comparing, your thesis statement, and an outline of your arguments. A good practice to see if your introduction is long enough is to have your introduction be 10% of your total word count – so an 800-word essay would have an 80 word introduction.
Your introduction is the first thing people are going to read, so make sure it addresses the overall question clearly and succinctly. The easiest way to do this is in your thesis statement.
How to Write a Body Paragraph for a Comparative Essay
In the body of your essay you should have around two to four paragraphs. Each of your paragraphs should only surround one argument or idea that supports your thesis.
There are two different ways you can structure the body of your essay, you can either:
- Compare and contrast both texts in the same paragraph for each idea, or,
- Dedicate paragraphs to each text individually.
Both of these methods are perfectly acceptable, but there are limitations to both. For option one, it is important to remember you should be evenly analysing both texts, not favouring one over the other. It is also essential to remember for this option, to analyse in enough depth to support your argument. For option two, it is crucial that you are still comparing both texts. An easy way to do this is to us comparative language such as: however, conversely, in contrast, similarly. This is to ensure you are still meeting the requirements of the genre and task.
How to Write a Comparative Essay Conclusion
As mentioned above, your conclusion should not bring up any new arguments but should summarise everything you have said up to that point. This includes restating your thesis and arguments. Much like your introduction, it is good practice to have your conclusion be approximately 10% of your overall word count.
Comparative Essay Writing Tips
- Create an outline : A well-structured outline helps you stay focused and ensures that your arguments flow logically from one point to the next.
- Always link back to your thesis statement.
- Reference as you go , do not leave it to the last minute.
- Emphasise differences and similarities : Make sure to clearly highlight the differences and similarities between the two subjects.
- Use specific examples : Use concrete examples to illustrate your points and make your writing more persuasive.
- On the contrary
- Furthermore
- In the same way
- Compared to
- In contrast
- On the one hand … on the other hand.
- Work with others to edit and refine your work , this may be using the support of an English tutor, or joining a study group.
- The best way to work towards getting an A in English is drafting! Write a first draft as soon as possible – it is easier to edit than a blank piece of paper!
- Proofread and edit : Finally, make sure to proofread and edit your essay for grammar, spelling, and clarity.
Excel in Your Comparative Essay Writing!
The best way to improve your writing, whether it be comparative essays or any kind of essay, is to use the resources available to you. You can ask your teacher for help, form a study group with your friends and help each other, or you can get a tutor to help you!
Need a helping hand writing a comparative essay? A Team Tuition is here to help. With our tried and true tutoring methods, we can help you write impressive essays with our at-home and online tutoring. Find a tutor near you today!
Recent Posts
- Tutoring Jobs for University Students
- What is the Order of Operations? Definition, Tips & Examples
- Online Tutoring vs. In-Person Tutoring: Which One Is Better for Your Child?
- How to Write a Discursive Essay: Structure & Tips
- Complete Guide to the 10 Main Types of Essays for Students
- Advice For Parents
- Foundations of Learning
- How to Succeed
- Neurodivergent Learning
- ATAR for University Admissions
- Career Paths
- High School Programs and Classes
- Transformation Stories
Privacy Overview

Comparative Essay

Academic institutions always provide writing exercises to students so that the level of understanding that the students can have about a particular subject manner is widened. One of the most common academic essay examples that’s given as writing assignment to students is the comparative essay. A comparative essay, also known as comparison essay or compare and contrast essay, is the type of essay that specifically analyzes two subject matters. There are a lot of academic fields where writing a comparative essay can be beneficial to students and their educational undertaking.

Download Comparative Essay Bundle
A comparative essay can either compare or contrast two topics, theories, materials and other subjects of discussion. However, there are activities where both comparisons and contrasts are necessary to be presented. If you are required to write a comparative essay but is unaware on how you can do one effectively, you can browse through the samples that we have gathered for you so you can be more knowledgeable on how to structure both the content and layout of this kind of essay.

Free Download
Comparative Essay For High School

College Comparative Essay

Comparative Essay Plan Template

- Google Docs
- Apple Pages
Size: 28 KB
Compare and Contrast Sample Essay

Size: 109 KB
Sample Comparative Essay Format

Size: 249 KB
The Concept of Comparative Essays
Different college essay examples are written based on different sets of instructions. Depending on the writing task that you have at hand, the things that you may include in your comparative essay may vary. However, the concept of making a comparative essay remains the same. For it to be clearer in your mind, here is how a comparative essay works:
- A comparative essay is an academic essay that requires students to create a comprehensive and precise comparative report about two things.
- A comparative essay is an organized written material that is meant to provide a comparison that should be easily understood by the target readers. It is set to impress people by providing them the information that they need to be aware of about two subjects and how they differ and/or compare with each other.
- A comparative essay can be written if you have two objects or subjects that can be compared in a level where their similarities and/or differences are relevant or meaningful for a specific purpose.
- A comparative essay can be used in formal writing assignments and it can also be the basis for various research assessments.
- A comparative essay is created through pertaining precise points of comparison. These points should be backed by actual researchers, factual information, and other reliable evidence.
Block Comparative Essay Example

Size: 462 KB
Student Comparative Essay Sample

How to Develop the Content of Your Comparative Essay
Before writing a comparative essay, you first need to arm yourself with the information that you need. This will allow you to create a comparative essay that is filled with relevant and helpful information. More so, this can help you veer away from committing common essay mistakes if you are already in the process of actual content writing.
The way that you plan to present your ideas, especially if they are backed up with facts, can make your comparative essay more successful. Listed below are the steps that you may use when developing the content of your comparative essay.
- The first thing that you need to do is to be aware of the question that you need to answer. You need to be aware of the essay prompt so you can address the needs of your readers. It is essential for you to be fully knowledgeable of the essence of the question so you can interpret it accordingly. The content that you will write will only be effective if it is related to the question and if it matches the purpose on why the essay is necessary to be written.
- Know whether there are limits for your discussion . Always identify whether you need to know the similarities or the differences between your subjects. Also, you need to know whether the scope of your essay assignment requires you to do any of these or both.
- Select the ideas that you would like to compare. It is important for you to have an in-depth understanding of the kind of comparison that you will write. The framework of your essay should be based on an actual evaluation that can point out how you were able to perceive the similarities or differences of the subject.
- Assess whether you already have sufficient points for comparison. Your ability to present as many valid points as possible can make a lot of clarifications about the unanswered questions that you can enlighten your readers with.
- Once the points of your comparison are already specified, list down whether they are under the similarities or differences of the two subjects. This step can help you be organized throughout the writing process. With easy access to how subjects are compared, you can be guided on how to use them in your content development.
- Evaluate your list. Your list is only your initial view about the subjects being reviewed or assessed. Hence, further evaluation is necessary. Make sure that you will read through the entire list so you can rank them based on their impact and weight of thesis.
- Chronologically arrange your list based on your basis of comparison . Make sure that you will follow a metric when examining the items that you will place in your actual comparative essay.
- Know the approach that you will use when developing your essay content. Will you be theoretical? Will you focus on answering questions for comparison? It is essential for you to be aware of your basis so your approach can provide you with maximum benefits within the entirety of the content development process.
- Research further about your subjects so you can verify whether your claims and initial claims are correct. This can help you create more topics and gather more evidence that can support your comparison.
- Create a thesis statement where your discussion can set its foundation. This will enable you to start writing the comparative essay that you would like to achieve.
You may think that this is a very long process just for developing the ideas that you will present. In a way, you may be right. However, being prepared and ready on how you will attack and execute the writing assignment can make it easier for you to create a valid discussion.
Comparative Contrast Essay Template
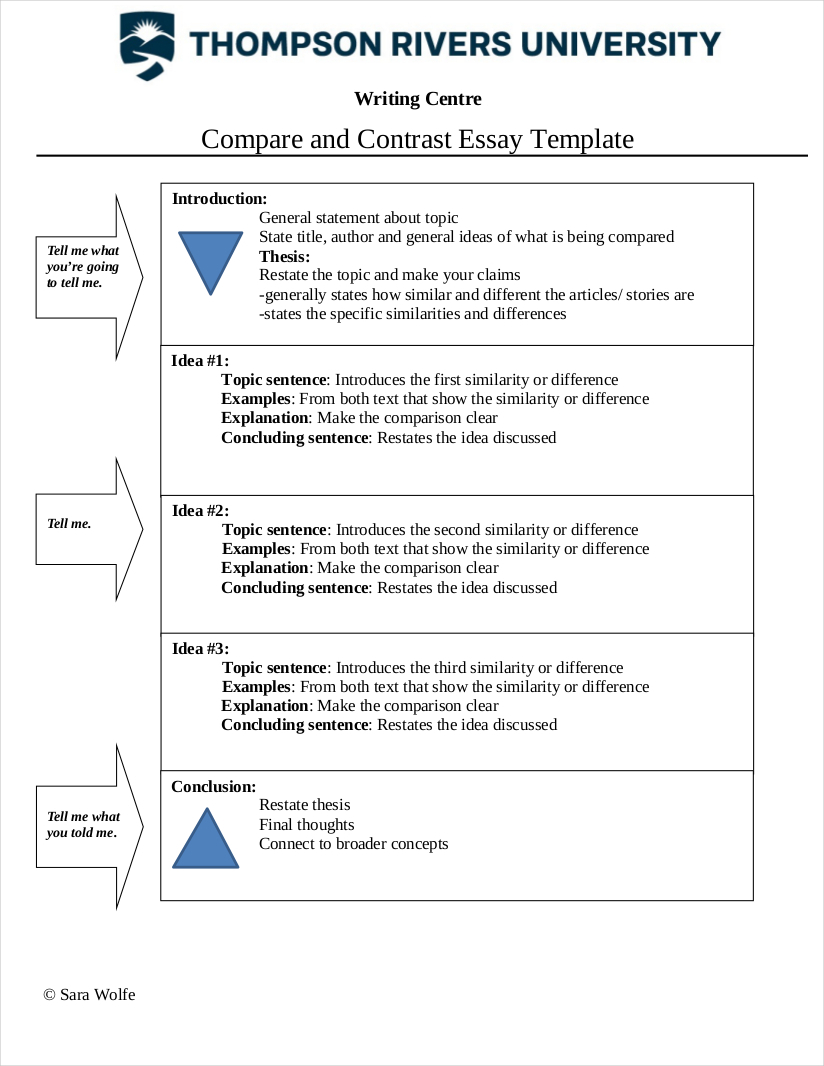
Size: 43 KB
Printable Comparative Essay Sample

Size: 148 KB
Steps in Organizing Your Comparative Essay Discussion
Aside from knowing the idea of what you will write about, the structure of your essay or the organization of your essay’s content can affect the smooth flow of your discussion. Even during last minute essay writing activities, you can still come up with an outstanding comparative essay if you are already knowledgeable on how you can organize your essay’s idea, content, structure, and discussion. Listed below are some of the ways on how you can efficiently organize your comparative essay’s content.
- Refer to the outline of your comparisons. This is where the items that we have discussed above can be helpful. If you are already guided by your comparisons, then you can easily rank their relevance to the essay that you will write. Referencing your comparisons can make it easier for you to have a thesis statement that you can further discuss.
- Organize your writing strategies. The strategies that you will incorporate into your discussion can make it easier for readers to relate to your point. You need to make sure that your strategies are aligned with your type of comparison and the subjects that you are comparing.
- Properly address your comparisons. For your comparative essay to be highly-usable, you need to make sure that you will implement simplicity within your discussion. Do not make it complicated. The content of your comparative essay should be as simple as possible so that it can be furthermore understood.
- Organize your paragraph structure. The way that you create your paragraph listing can be one of the factors that can either improve or destroy your comparative essay. You should create a draft that can specifically state the items that you will discuss per paragraph. Create statements that can address specific comparisons and divide them per paragraph. Each of your paragraphs should be talking about one subject so you can give focus per comparison aspect.
- Evaluate whether your writing guide is already organized enough. It is essential for you to not overlap subjects of discussion. When organizing your statements, make sure to cover one subject at a time. This will help you create a comparative essay that contains a list of carefully arranged and curated evidence which are further discussed and broken down into relevant specification pieces.
Simple Essay of Comparison Sample

Size: 19 KB
Sample Comparative Essay in PDF

Size: 539 KB
Writing Guide in Creating the Actual Comparative Essay
Just like descriptive essay examples and other kinds of academic essays, a comparative essay can be created in different ways. Each writer has various techniques that can be applied when doing this particular kind of essay. Since there are no strict rules when it comes to crafting a comparative essay, all you need to ensure is that your comparative essay is comprehensive, understandable and credible. Here is how you can effectively write your actual comparative essay:
- Create an introduction to the topic. Your thesis statement should contain the subjects that you will talk about. You also need to create an initial discussion of what your readers can expect to the reader within the content of your comparative essay. A strong validation of your comparison can make your readers more interested to browse through the entire essay document.
- Develop your next paragraphs for discussion. As mentioned above, work per paragraph. Arrange your topics of discussion in a way that each paragraph can specifically state one comparison topic per time. You have to create an interesting discussion so you need to ensure that all your paragraphs are organized and well-written.
- Finalize your comparative essay with a conclusion. Your last paragraph should contain the information about your final thoughts with regards the comparison. How different or similar are the two subjects from one another? How sure are you that your basis is factual and relevant? Create a great impact b
- y having a conclusion that can put together all your points of discussion.
Compare Contrast Essay Sample

Size: 86 KB
Sample Comparative Essay Guide

Size: 334 KB
Factors to Consider When Writing a Comparative Essay
In comparison to evaluation essay examples , a comparative essay is more keen with regards the assessment of two subjects. If you will write a comparative essay, you need to have an idea of the impacts of different factors to the result that you may get at the end of the writing activity. Listed below are some of the elements or factors that you need to take into consideration when writing a comparative essay.
- Your discussion’s organization. Within the entirety of the comparative essay creation, it is very evident that organization is key to success. As a writer, you need to ensure that you have a skeletal plan that can create your discussion more polished and coherent. The discussion of your organization can greatly affect the impression of your readers with regards your knowledge about your topic as well as your level of understanding with what you are talking about.
- Your thesis statement. When creating a comparative essay, you need to stick with an argument that can provide you the framework for the effective dissemination of information. Your thesis statement should be based on the results of your frame of references. You need to analyze your subjects properly so that you can create a stand on how you perceive them in levels of similarities and/or differences.
- Your claims or grounds for comparison. You should always be aware of your selection processes. At the end of the writing activity, you need to validate the importance of comparing two subjects. Always have your grounds of comparison ready so you can ensure your readers that you have followed a particular set of criteria that can enable the objectivity between the selection of two items for comparison. The rationale that you have behind your subject selection can make your comparative essay more appealing.
- Your reference frame. A comparative essay’s frame of reference deals with the way that the writer has created the groupings for the comparison. May it be talking about the similarities, differences, or both of these factors; a comparative essay should be able to have a reference that can identify how the characteristics of ideas, themes, theories or even problems are arranged.
With the samples that we have in this post, it will be faster for you to identify the points of discussion that you need to provide. Again, comparative essays vary from one another in terms of content. Ensure that you are fully aware of the writing instructions given to you so you can plan your comparative essay’s content and structure accordingly.
Always refer to the guidelines and tips that we have specified so you can create effective decisions in every step of your comparative essay development. Do not be afraid to write what your thoughts. As long as these thoughts are based on factual references, then it will be easy for you to have a comparative essay that can achieve its purpose or reason for creation.
the art of writing a comparative essay lies in the delicate balance of presenting similarities and differences in a clear, coherent manner. This type of essay encourages critical thinking and develops analytical skills, crucial for academic success. For further guidance on creating effective comparative essays, the UNC Writing Center offers a detailed resource on comparing and contrasting ( UNC Writing Center ). This link provides valuable insights and examples, helping students refine their comparative writing skills. By mastering the comparative essay, students not only enhance their writing abilities but also deepen their understanding of contrasting subjects, an essential skill in many academic and professional fields.
Comparative Essay Generator
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Write a comparative essay on cats vs. dogs as pets: which are better and why?
Compare in a comparative essay the effects of online learning vs. traditional classroom learning on students.

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

4.1: Introduction to Comparison and Contrast Essay
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 174873
The key to a good compare-and-contrast essay is to choose two or more subjects that connect in a meaningful way. Comparison and contrast is simply telling how two things are alike or different. The compare-and-contrast essay starts with a thesis that clearly states the two subjects that are to be compared, contrasted, or both. The thesis should focus on comparing, contrasting, or both.
Key Elements of the Compare and Contrast:
- A compare-and-contrast essay analyzes two subjects by either comparing them, contrasting them, or both.
- The purpose of writing a comparison or contrast essay is not to state the obvious but rather to illuminate subtle differences or unexpected similarities between two subjects.
- The thesis should clearly state the subjects that are to be compared, contrasted, or both, and it should state what is to be learned from doing so.
- Organize by the subjects themselves, one then the other.
- Organize by individual points, in which you discuss each subject in relation to each point.
- Use phrases of comparison or phrases of contrast to signal to readers how exactly the two subjects are being analyzed.
Objectives: By the end of this unit, you will be able to
- Identify compare & contrast relationships in model essays
- Construct clearly formulated thesis statements that show compare & contrast relationships
- Use pre-writing techniques to brainstorm and organize ideas showing a comparison and/or contrast
- Construct an outline for a five-paragraph compare & contrast essay
- Write a five-paragraph compare & contrast essay
- Use a variety of vocabulary and language structures that express compare & contrast essay relationships
Example Thesis: Organic vegetables may cost more than those that are conventionally grown, but when put to the test, they are definitely worth every extra penny.

Sample Paragraph:
Organic grown tomatoes purchased at the farmers’ market are very different from tomatoes that are grown conventionally. To begin with, although tomatoes from both sources will mostly be red, the tomatoes at the farmers’ market are a brighter red than those at a grocery store. That doesn’t mean they are shinier—in fact, grocery store tomatoes are often shinier since they have been waxed. You are likely to see great size variation in tomatoes at the farmers’ market, with tomatoes ranging from only a couple of inches across to eight inches across. By contrast, the tomatoes in a grocery store will be fairly uniform in size. All the visual differences are interesting, but the most important difference is the taste. The farmers’ market tomatoes will be bursting with flavor from ripening on the vine in their own time. However, the grocery store tomatoes are often close to being flavorless. In conclusion, the differences in organic and conventionally grown tomatoes are obvious in color, size and taste.

- English Grammar
Comparative and superlative adjectives
Level: beginner
Comparative adjectives
We use comparative adjectives to show change or make comparisons:
This car is certainly better , but it's much more expensive . I'm feeling happier now. We need a bigger garden.
We use than when we want to compare one thing with another :
She is two years older than me. New York is much bigger than Boston. He is a better player than Ronaldo. France is a bigger country than Britain.
When we want to describe how something or someone changes we can use two comparatives with and :
The balloon got bigger and bigger . Everything is getting more and more expensive . Grandfather is looking older and older .
We often use the with comparative adjectives to show that one thing depends on another :
The faster you drive, the more dangerous it is. (= When you drive faster, it is more dangerous.) The higher they climbed, the colder it got. (= When they climbed higher, it got colder.)
Matching_MTQxNzI=.
GapFillTyping_MTQxNzM=
Superlative adjectives
We use the with superlative adjectives :
It was the happiest day of my life. Everest is the highest mountain in the world. That’s the best film I have seen this year. I have three sisters: Jan is the oldest and Angela is the youngest .
MultipleChoice_MTk4Njg=
GapFillTyping_MTQxNzU=
How to form comparative and superlative adjectives.
We usually add –er and –est to one-syllable words to make comparatives and superlatives:
If an adjective ends in –e , we add –r or –st :
If an adjective ends in a vowel and a consonant , we double the consonant:
If an adjective ends in a consonant and –y , we change –y to –i and add –er or –est :
We use more and most to make comparatives and superlatives for most two syllable adjectives and for all adjectives with three or more syllables:
However, with these common two-syllable adjectives , you can either add –er / –r and –est / –st or use more and most :
He is certainly handsomer than his brother. His brother is handsome, but he is more handsome . She is one of the politest people I have ever met. She is the most polite person I have ever met.
The adjectives good , bad and far have irregular comparatives and superlatives:
GapFillTyping_MTQyMzc=
Could you check this sentence for me please? The maintenance cost of electric buses are lower than diesel buses.
- Log in or register to post comments
Hello Khangvo2812,
You can say 'The maintenance cost... is' or 'The maintenance costs... are'. Other than that, the sentence is fine.
Please note that we generally don't just check sentences. The site focuses on explaining usage and rules rather than proof-reading.
The LearnEnglish Team
Is 'more naughty than' correct?
Hello Paulinecwy,
Yes it is. Naughty is one of those adjectives where more than one form is possible: more naughty and naughtier .
Hello, Could you check this sentence for me pls? Vietnamese national football team is the strongest team among Asean countries.
Hi Khangvo2812,
It's good but a correction is needed: either add "the" ( The Vietnamese national football team ... ) or change the first word: Vietnam's national football team ...
I hope that helps.
LearnEnglish team
These exercises were helpful for me, I didn't find them so difficult
Hi sir, I'm grateful for this lesson, actually it was interesting and useful to me, thanks!
I hope this message finds you well. I wanted to reach out to express my satisfaction with the exercises that were assigned. I am pleased to inform you that I have successfully completed them and found them to be incredibly comprehensive and beneficial. They have provided me with valuable opportunities to apply and reinforce the concepts explained in our sessions.
Hello Emiliano,
We're very pleased to hear that you found the explanation and exercises useful!
Thanks for letting us know.
Best wishes, Kirk LearnEnglish team
I wanted to express my gratitude for the exercises you assigned. I have completed them and found them to be incredibly helpful in reinforcing the concepts we discussed. They provided me with a valuable learning experience and I feel more equipped as a result.
Thank you for offering such comprehensive exercises that allowed me to put theory into practice. The knowledge gained from these exercises will undoubtedly benefit me in the future.
Example: México is the best country of the world
For example: México is better than Venezuela
Hello, Sir I have already done the exercises and I find them very complete and very helpful to put into practice what is explained. I take with me a great experience and a new learning experience.
If we learnt that adjectives ending in a CVC pattern must be doubled the last consonant and then added with -er, why isn't "slowwer" or "newwer" correct?
Hi thatha.,
It's because although these adjectives end in "w" (a consonant), the "w" is actually part of the vowel sound ("ow" in "slow", and "ew" in "new").
Thaks yo this page, the subject became clearer to me, with the excercises what I new was reinforced.
I am trying to figure out why, in an English sentence, if there are multiple adjectives used for one noun, and one of those adjectives is superlative, it seems that all of them must be superlative.
For example, my student wrote the following: I bought the three large freshest looking cabbages to make Korean Kimchi.
I couldn't explain why that was incorrect, I just knew that I would say 'three of the largest, freshest-looking cabbages...'.
Could one of you provide an explanation? Thanks in advance!
I'm not sure if there's a grammatical explanation for this! It might be more about the conventional ideas that we tend to express. The student is saying that there were only three large cabbages in the shop, and they were also the freshest-looking ones, but this might be a bit unclear for listeners/readers to understand and your suggestion sounds clearer and more natural.
Good day, dear experts! Please, help me to understand why there is "elder" in the name of the game "The Elder Scrolls" when we know that the comparative of "old" is "older". Is there a mistake in this name? Thank you in advance!
Hello Iryna_hn,
I don't know much about this game, but I suspect 'elder' refers to an important or respected person in a group rather than being a comparative form of 'old'. Have a look at the Longman entry for 'elder' and scroll down to line 2 of the second meaning and you'll see what I mean.
All the best, Kirk LearnEnglish team
Hello! Can I ask you a question? So, I know that we can use the definite article with comparative adjectives for showing that one thing depends on another as it's written in this website too. But, what about this sentence "the farther side of the mountain"? What's the explanation for it since there are no things depending one another in that sentence? Maybe when we have an implied comparison we can use the definite article too? Thank you in advance. :)
Hello leo15722,
I don't think this is a question of two things being related in the way described above. I think this is simply an identified and specific item. Just as we would say 'the side of the mountain' (we know which side of which mountain we are talking about), so we say 'the farther side of the mountain'. You could use other articles if you conceive other contexts:
a farther side of the mountain > we know which mountain; it has several farther sides and we are talking about one of them but not saying which one. For example: " This side looks easy to climb. Now I don't know the mountain well, but I've heard that there's a farther side of the mountain which is harder to climb. "
the farther side of a mountain > we are imagining that there are only two sides (rather like we say 'the dark side of the moon') and are talking about any mountain. For example: " The farther side of a mountain is always tempting to a mountaineer. "
Could you please clarify the following:
Should we always use "the" with superlatives forms? Is it a mistake to say "She is most beautiful woman in this city", "He is smartest boy in the class?" or "They bought most delicious cake"?
I'm very very grateful for the work you are doing, thank you for your important help, and thank you for answering this post beforehand!!!
Hello howtosay_
Yes, you should always use 'the' with superlative forms. It is definitely necessary when there is a phrase like 'in this city', 'in the class', 'in the world, etc.
Your sentence about cake isn't actually a superlative construction. Instead, 'most' means 'very'.
It's also possible to see a sentence like 'They bought the most delicious cake'. There might be some rare exceptions, but normally a sentence like this is superlative because of the context. For example, perhaps in the previous sentences they were talking about all the different cakes in a bakery. So even though the sentence doesn't explicitly mention the other cakes, it's clear from context that there are many cakes.
Hope this helps.
Hello, Kirk!
Yes, it does help. I haven't known before that "most" also means "very".
Thank you very much indeed for your precious help!!!
Hello. Good morning sir/ma'am. This question has been bugging me lately.. Which one is correct? 1.he's the cleverest of *all the other* students. 2.he's the cleverest of *the other students* Or are they both correct??
Hello AydaChan2003,
They're both OK, though I think people would probably say 1 more often than 2.
All the best, Kirk The LearnEnglish Team
Hello, Kirk Thanks a lot!! You're a life saver
Both are grammatically correct and any difference would depend on the context in which they are used.
Peter The LearnEnglish Team
Hello sir! Could you please elaborate on what types of context? Also I have a vocabulary question.. I'm fairly new here and I don't know whether there's a separate page for asking vocabulary questions; is there really one? If there's not, then I might as well ask it here (sorry I know this isn't related to the subject but I got to know this) what's the difference between deadly, lethal, and fatal?
It's really a question of emphasis. 'All' adds rhetorical emphasis so if you want to make your statement stronger (e.g. when making a speech or trying to persuade someone of something) then it might be useful.
The main difference in the words is that fatal means someone died. Deadly and lethal can also describe potential - in other words they can also describe something is extremely dangerous. Thus, I could say 'It was a truly deadly situation and I was lucky to escape alive' but I could not use the word 'fatal' there.
There are some other differences in use, so you can talk about a deadly/lethal poison, for example, or use the words metaphorically to mean that someone is very good at performing a task: a footballer can be lethal in front of goal, or a lawyer can be deadly during cross-examination.
For differences like this, which are really about use rather than meaning, the best thing is to look each word up in an online dictionary, where you'll be able to compare the different entries.
Hello sir! Oh my God that was the BEST explanation I've ever seen; thanks a lot!!! I had looked up their differences before but still couldn't distinguish each separately but now with your awesome explanation, I can! Once again, thanks a lot! May God bless you 🙏
Hi Jonathan Fewer and smaller are comparative (forms)of inferiority ,aren't they?
Hi cooler48,
Yes, right!
Hello Team . The sentences He can run faster than me . or He can run faster than I . Which is the correct usage?
I can run faster than he or I can run faster than him . Which is the correct usage? Kindly guide. Thanks.
Hello paddyjosy,
The standard use is 'me' and 'him'. After 'than' we use an object pronoun not a subject pronoun.
You may find some instances where some users prefer 'I' as they interpret the sentence to be 'He can run faster than I can run', but this is very much a minority view.
Thank you Peter .
Hello paddyjosy, (than) actually considered as a proposition in modern English. As a result, we use after than a pronoun in object form (for example: me, you, him, her, us, them, and whom)
Hi . This is regarding the use of the adjective' late 'in the comparative and superlative degrees. Some sources have mentioned it as later and latest (time)or latter and last (position). Can u kindly explain it with example sentences. Thanks.
'Later' refers to time. It is often used as an adverb: See you later!
When used as an adjective it is the opposite of 'earlier': Do you want to go to the earlier performance or the later one?
'Latest' means the most recent: Have you heard the latest news? / I just bought her latest novel. It's great!
As you say, 'latter' is most often used to refer to the second item when two are mentioned. Its opposite is 'former': Would you prefer tea or coffee? > The latter, please.
'Latter' can also refer to the something occurring nearer to the end of something than the beginning: The latter part of the century was more stable / In his latter years he suffered from heart disease.
Thanks a lot Peter. It was helpful. But is there a comparative and superlative degree for the adjective 'late'?
Hello again paddyjosy,
The comparative and superlative forms of 'late' are later and latest .
'Latter' does not have comparative or superlative forms. There is an adverb ( latterly ) which is a formal synonym for recently .
Thanks once again for the prompt reply Peter. It's really confusing though that 'later' means afterwards and 'latest' means the most recent ,hence a change in meaning all together.
Hello Peter Is this usage correct ? No other programme is as late as ours. Our performance is later than all other programmes . Other programmes are the latest.
Yes, the use of the different forms of 'late' are all correct in these sentences. I might suggest 'The latest programmes are other ones' for the last sentence because 'latest' meaning 'most recent' is more common than the meaning that refers to time, but your sentence would be fine in context and in any case is grammatically correct.
Thanks for the explanation.Indeed a wonderful resoirce for grammar . Keep up.the good work.
Hello. In this sentence "Lisa is the........of the two sisters" the choices were "1.young 2.more young 3.as young as 4.younger" So I believe there's no correct answer of them because that's a superlative case not comparative as the "two sisters" is the whole group therefore "Lisa" isn't compared with the other sister but preferred over the whole group "the other sister" and the usage of "the" before the adjective and "of" after it means it's superlative and a colleague of mine think it's just comparative because they are only "two sisters" so my question is "Is it acceptable to use the preposition 'of' after the comparative form of adjective?". Thanks in advance.
Hi Roman...
Yes, you could say "Lisa is the youngest of the two sisters". However, it may be considered non-standard and incorrect. A more standard answer would be to say "Lisa is the younger of the two sisters". As there are only two sisters and one is compared with the other, it is a comparative case. Yes, it is fine to use "the + comparative adj. + of" if there are exactly two things being compared.
Online courses

Group and one-to-one classes with expert teachers.

Learn English in your own time, at your own pace.

One-to-one sessions focused on a personal plan.

Get the score you need with private and group classes.
The Study Blog
Term Paper Writing Help

If you aren't sure whether you are good at expressing yourself through writing, then if you find it difficult to do so (e.g., when trying to write an english essay), we can help you overcome those obstacles by assisting you in improving your communication through writing. We help students compose essays or other types of papers for their courses. Now is the time to come visit us!
How to Overcome the Complexity of a Nursing Essay
There aren't many alternatives for professional translations. Before writing a good summary of something, you need to know your subject well enough to be able to write an accurate one. A research paper requires mastery of research language, a deep understanding of their subjects to be able to write about them clearly, and a careful consideration of possible problems before proposing solutions. Students often have trouble understanding medical terminology when they first encounter it, because they have never heard of these words before. When writing a cohesive psychology essay, students must be familiar with some psychological concepts. We have a wealth of experience under our belt, so we know where they need help. Although you may be able to find better deals elsewhere, there is no way to tell if these sites offer superior customer service and top-quality results. Read customer reviews before making any online purchases. If you don't think there's a market for them, it's perhaps best to skip them.
Professional Help from Copywriters
If you would like us to write anything from an essay in history to a term paper for you, we’d be happy to oblige. When writing something, there's a precise formula for choosing the best word. You can rest assured that you'll receive an expertly written paper from those who know exactly what they're doing. No need to write anything down today; there are no reasons why you shouldn't let others edit your document for you. Don't waste your time trying to convince them to do it for you, instead, invest it in something more productive! Order term papers online and go there! Founded in a simple belief that we are capable of delivering top-quality content to you, we offer a range of guarantees. Test it out yourself! The results must be presented after all the research has been completed.
Cheap Business Essay Writing Services
Before being accepted into our company, we underwent extensive background checks. Check their credentials to confirm that they have been writing professionally for some time. If they are members of professional associations, check, for instance.

Fun Tips to Spend Orthodox Easter Away from Home
In "Student Life"
Welcome to the New Bloggers
In "Degree Essentials"
Mastering Warwick as a Postgraduate
In "Looking After You"
Comments are closed.
Copyright, 2023

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Comparative essay is a common assignment for school and college students. Many students are not aware of the complexities of crafting a strong comparative essay. If you too are struggling with this, don't worry! In this blog, you will get a complete writing guide for comparative essay writing. From structuring formats to creative topics, this ...
A comparative essay asks that you compare at least two (possibly more) items. These items will differ depending on the assignment. You might be asked to compare. positions on an issue (e.g., responses to midwifery in Canada and the United States) theories (e.g., capitalism and communism) figures (e.g., GDP in the United States and Britain)
2. Use a mixed paragraphs method. Address both halves of the comparison in each paragraph. This means that the first paragraph will compare the first aspect of each subject, the second will compare the second, and so on, making sure to always address the subjects in the same order.
Secondly, jump over to Sarah's (English study score 47) Compare the Pair: A Guide to Structuring a Reading and Comparing Essay post where she delves into two different types of Comparative essay structures. Comparative Essay Example Introduction. In an introduction, you're expected to have the following: Context (or background)
In the block method, you cover each of the overall subjects you're comparing in a block. You say everything you have to say about your first subject, then discuss your second subject, making comparisons and contrasts back to the things you've already said about the first. Your text is structured like this: Subject 1.
1. Brainstorming and Prewriting. Recall that a comparison/contrast essay serves the purpose of examining the similarities and/or differences between two subjects. When you compare things, you show their similarities; when you contrast things, you show their differences. The first step in writing a comparison/contrast essay is to brainstorm ...
A compare and contrast essay, also called a comparison or comparative essay, is used to explain the similarities and differences between two subjects. These types of essays usually use specific ...
For instance, a comparative essay on the French and Russian revolutions might examine how both revolutions either encouraged or thwarted innovation in terms of new technology (body paragraphs 1 and 2), military strategy (body paragraphs 3 and 4), and the administrative system (body paragraphs 5 and 6). Two notes about the alternating method:
comparative essay asks that you compare at least two (possibly more) items. These items will differ depending on the assignment. You might be asked to compare. events (e.g., the Great Depression and the global financial crisis of 2008-9) Although the assignment may say "compare," the assumption is that you will consider both the ...
Writing a great comparative essay means highlighting the similarities and differences between two things in a systematic manner. Start by choosing the parameters (items) to compare, write an outline, and fill in the details for each section. Make sure to have an introduction and conclusion. The comparative essay is one form of document that you ...
The basic structure will remain (text 1 key moment, link, text 2 km, link, text 3 km, general observation) - it's not rocket science. But you must prove (if you want a grade above 70% in comparative) that you can engage with the question throughout your answer (not justthrow it in @ beginning and end) and conclude by showing how your essay ...
The comparative essay, in only its second year of being on the VCE English syllabus, is a cause for confusion for many students and teachers alike. Read on for one simple way to structure a comparative essay. Comparative essay structure How to write an introduction for a comparative essay. This can be structured in much the same way as a text ...
The comparative essay is still a relatively new element of VCE English, only becoming part of the Study Design in 2016. However, while the Area of Study is new, your essay should still have a clear and largely familiar structure, with an introduction, body and conclusion.
Comparative analysis assignments have a lot of the same DNA as single-source essays, but they potentially bring more reading into play and ask students to engage in more complicated acts of analysis and synthesis during the drafting stages. With that in mind, closer to 4 weeks is probably a good baseline for many single-source analysis assignments.
A comparative essay is usually completed by students in years 10, 11, and 12 undertaking General English. However, students in other English subjects and younger grades can also be asked to write comparative essays, or students may have similar assessments in other subjects, such as writing a history essay. Comparative Essay Structure. In a ...
A comparative essay, also known as comparison essay or compare and contrast essay, is the type of essay that specifically analyzes two subject matters. There are a lot of academic fields where writing a comparative essay can be beneficial to students and their educational undertaking. Download Comparative Essay Bundle.
A compare-and-contrast essay analyzes two subjects by either comparing them, contrasting them, or both. The purpose of writing a comparison or contrast essay is not to state the obvious but rather to illuminate subtle differences or unexpected similarities between two subjects. The thesis should clearly state the subjects that are to be ...
In this article, we will teach you how to write a comparative essay, including Y12 Module A Textual Conversations requirements, different comparative essay structures, dos and don'ts, and an exemplar paragraph of both structures.
But really, a good essay structure that you use all the time can be applied to a comparative essay too. So if you normally write 1) an intro 2) paras agreeing with the question 3) paras arguing against the question 4) a conclusion this could work here as well. Or you can find a new structure. The important thing is that you simply have to ...
Level: beginner. Comparative adjectives. We use comparative adjectives to show change or make comparisons:. This car is certainly better, but it's much more expensive. I'm feeling happier now. We need a bigger garden.. We use than when we want to compare one thing with another:. She is two years older than me. New York is much bigger than Boston. He is a better player than Ronaldo.
Overview; Structuring a comparative essay; Comparing themes, ideas and attitudes; Compare the effect of form, structure and language; Comparing contexts
Cheap Business Essay Writing Services. Before being accepted into our company, we underwent extensive background checks. Check their credentials to confirm that they have been writing professionally for some time. If they are members of professional associations, check, for instance. Some students may have difficulty completing their research ...