116 CyberCrime Topics & Essay Samples
If you are writing a cybercrime essay, our team prepared this article just for you. Here, you will find 115 unique topics for any type of paper.

Products & Resources
- JEE Main Knockout April
- Free Sample Papers
- Free Ebooks
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Syllabus
- NCERT Books
- RD Sharma Solutions
- Navodaya Vidyalaya Admission 2024-25
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11
- NCERT solutions for Class 10
- NCERT solutions for Class 9
- NCERT solutions for Class 8
- NCERT Solutions for Class 7
- JEE Main 2024
- JEE Advanced 2024
- BITSAT 2024
- View All Engineering Exams
- Colleges Accepting B.Tech Applications
- Top Engineering Colleges in India
- Engineering Colleges in India
- Engineering Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- Engineering Colleges Accepting JEE Main
- Top IITs in India
- Top NITs in India
- Top IIITs in India
- JEE Main College Predictor
- JEE Main Rank Predictor
- MHT CET College Predictor
- AP EAMCET College Predictor
- GATE College Predictor
- KCET College Predictor
- JEE Advanced College Predictor
- View All College Predictors
- JEE Main Question Paper
- JEE Main Mock Test
- JEE Main Registration
- JEE Main Syllabus
- Download E-Books and Sample Papers
- Compare Colleges
- B.Tech College Applications
- GATE 2024 Result
- MAH MBA CET Exam
- View All Management Exams
Colleges & Courses
- MBA College Admissions
- MBA Colleges in India
- Top IIMs Colleges in India
- Top Online MBA Colleges in India
- MBA Colleges Accepting XAT Score
- BBA Colleges in India
- XAT College Predictor 2024
- SNAP College Predictor
- NMAT College Predictor
- MAT College Predictor 2024
- CMAT College Predictor 2024
- CAT Percentile Predictor 2023
- CAT 2023 College Predictor
- CMAT 2024 Registration
- TS ICET 2024 Registration
- CMAT Exam Date 2024
- MAH MBA CET Cutoff 2024
- Download Helpful Ebooks
- List of Popular Branches
- QnA - Get answers to your doubts
- IIM Fees Structure
- AIIMS Nursing
- Top Medical Colleges in India
- Top Medical Colleges in India accepting NEET Score
- Medical Colleges accepting NEET
- List of Medical Colleges in India
- List of AIIMS Colleges In India
- Medical Colleges in Maharashtra
- Medical Colleges in India Accepting NEET PG
- NEET College Predictor
- NEET PG College Predictor
- NEET MDS College Predictor
- DNB CET College Predictor
- DNB PDCET College Predictor
- NEET Application Form 2024
- NEET PG Application Form 2024
- NEET Cut off
- NEET Online Preparation
- Download Helpful E-books
- LSAT India 2024
- Colleges Accepting Admissions
- Top Law Colleges in India
- Law College Accepting CLAT Score
- List of Law Colleges in India
- Top Law Colleges in Delhi
- Top Law Collages in Indore
- Top Law Colleges in Chandigarh
- Top Law Collages in Lucknow
Predictors & E-Books
- CLAT College Predictor
- MHCET Law ( 5 Year L.L.B) College Predictor
- AILET College Predictor
- Sample Papers
- Compare Law Collages
- Careers360 Youtube Channel
- CLAT Syllabus 2025
- CLAT Previous Year Question Paper
- AIBE 18 Result 2023
- NID DAT Exam
- Pearl Academy Exam
Animation Courses
- Animation Courses in India
- Animation Courses in Bangalore
- Animation Courses in Mumbai
- Animation Courses in Pune
- Animation Courses in Chennai
- Animation Courses in Hyderabad
- Design Colleges in India
- Fashion Design Colleges in Bangalore
- Fashion Design Colleges in Mumbai
- Fashion Design Colleges in Pune
- Fashion Design Colleges in Delhi
- Fashion Design Colleges in Hyderabad
- Fashion Design Colleges in India
- Top Design Colleges in India
- Free Design E-books
- List of Branches
- Careers360 Youtube channel
- NIFT College Predictor
- UCEED College Predictor
- NID DAT College Predictor
- IPU CET BJMC
- JMI Mass Communication Entrance Exam
- IIMC Entrance Exam
- Media & Journalism colleges in Delhi
- Media & Journalism colleges in Bangalore
- Media & Journalism colleges in Mumbai
- List of Media & Journalism Colleges in India
- CA Intermediate
- CA Foundation
- CS Executive
- CS Professional
- Difference between CA and CS
- Difference between CA and CMA
- CA Full form
- CMA Full form
- CS Full form
- CA Salary In India
Top Courses & Careers
- Bachelor of Commerce (B.Com)
- Master of Commerce (M.Com)
- Company Secretary
- Cost Accountant
- Charted Accountant
- Credit Manager
- Financial Advisor
- Top Commerce Colleges in India
- Top Government Commerce Colleges in India
- Top Private Commerce Colleges in India
- Top M.Com Colleges in Mumbai
- Top B.Com Colleges in India
- IT Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- IT Colleges in Uttar Pradesh
- MCA Colleges in India
- BCA Colleges in India
Quick Links
- Information Technology Courses
- Programming Courses
- Web Development Courses
- Data Analytics Courses
- Big Data Analytics Courses
- RUHS Pharmacy Admission Test
- Top Pharmacy Colleges in India
- Pharmacy Colleges in Pune
- Pharmacy Colleges in Mumbai
- Colleges Accepting GPAT Score
- Pharmacy Colleges in Lucknow
- List of Pharmacy Colleges in Nagpur
- GPAT Result
- GPAT 2024 Admit Card
- GPAT Question Papers
- NCHMCT JEE 2024
- Mah BHMCT CET
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Delhi
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Hyderabad
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Mumbai
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Maharashtra
- B.Sc Hotel Management
- Hotel Management
- Diploma in Hotel Management and Catering Technology
Diploma Colleges
- Top Diploma Colleges in Maharashtra
- UPSC IAS 2024
- SSC CGL 2024
- IBPS RRB 2024
- Previous Year Sample Papers
- Free Competition E-books
- Sarkari Result
- QnA- Get your doubts answered
- UPSC Previous Year Sample Papers
- CTET Previous Year Sample Papers
- SBI Clerk Previous Year Sample Papers
- NDA Previous Year Sample Papers
Upcoming Events
- NDA Application Form 2024
- UPSC IAS Application Form 2024
- CDS Application Form 2024
- CTET Admit card 2024
- HP TET Result 2023
- SSC GD Constable Admit Card 2024
- UPTET Notification 2024
- SBI Clerk Result 2024
Other Exams
- SSC CHSL 2024
- UP PCS 2024
- UGC NET 2024
- RRB NTPC 2024
- IBPS PO 2024
- IBPS Clerk 2024
- IBPS SO 2024
- Top University in USA
- Top University in Canada
- Top University in Ireland
- Top Universities in UK
- Top Universities in Australia
- Best MBA Colleges in Abroad
- Business Management Studies Colleges
Top Countries
- Study in USA
- Study in UK
- Study in Canada
- Study in Australia
- Study in Ireland
- Study in Germany
- Study in China
- Study in Europe
Student Visas
- Student Visa Canada
- Student Visa UK
- Student Visa USA
- Student Visa Australia
- Student Visa Germany
- Student Visa New Zealand
- Student Visa Ireland
- CUET PG 2024
- IGNOU B.Ed Admission 2024
- DU Admission
- UP B.Ed JEE 2024
- DDU Entrance Exam
- IIT JAM 2024
- IGNOU Online Admission 2024
- Universities in India
- Top Universities in India 2024
- Top Colleges in India
- Top Universities in Uttar Pradesh 2024
- Top Universities in Bihar
- Top Universities in Madhya Pradesh 2024
- Top Universities in Tamil Nadu 2024
- Central Universities in India
- CUET PG Admit Card 2024
- IGNOU Date Sheet
- CUET Mock Test 2024
- CUET Application Form 2024
- CUET PG Syllabus 2024
- CUET Participating Universities 2024
- CUET Previous Year Question Paper
- CUET Syllabus 2024 for Science Students
- E-Books and Sample Papers
- CUET Exam Pattern 2024
- CUET Exam Date 2024
- CUET Syllabus 2024
- IGNOU Exam Form 2024
- IGNOU Result
- CUET PG Courses 2024
Engineering Preparation
- Knockout JEE Main 2024
- Test Series JEE Main 2024
- JEE Main 2024 Rank Booster
Medical Preparation
- Knockout NEET 2024
- Test Series NEET 2024
- Rank Booster NEET 2024
Online Courses
- JEE Main One Month Course
- NEET One Month Course
- IBSAT Free Mock Tests
- IIT JEE Foundation Course
- Knockout BITSAT 2024
- Career Guidance Tool
Top Streams
- IT & Software Certification Courses
- Engineering and Architecture Certification Courses
- Programming And Development Certification Courses
- Business and Management Certification Courses
- Marketing Certification Courses
- Health and Fitness Certification Courses
- Design Certification Courses
Specializations
- Digital Marketing Certification Courses
- Cyber Security Certification Courses
- Artificial Intelligence Certification Courses
- Business Analytics Certification Courses
- Data Science Certification Courses
- Cloud Computing Certification Courses
- Machine Learning Certification Courses
- View All Certification Courses
- UG Degree Courses
- PG Degree Courses
- Short Term Courses
- Free Courses
- Online Degrees and Diplomas
- Compare Courses
Top Providers
- Coursera Courses
- Udemy Courses
- Edx Courses
- Swayam Courses
- upGrad Courses
- Simplilearn Courses
- Great Learning Courses
Access premium articles, webinars, resources to make the best decisions for career, course, exams, scholarships, study abroad and much more with
Plan, Prepare & Make the Best Career Choices
Cyber Crime Essay
The unlawful act of gaining unauthorised access to computer systems or digital devices is known as cybercrime. A detailed grasp of how to stop or recover from cyberattacks is provided by cyber security. Online courses offer guidance on how to avoid, safeguard against, and recover from cybercrime risks. Here are a few sample essays on the topic ‘Cyber Crime’.
100 Words Essay on Cyber Crime
200 words essay on cyber crime, 500 words essay on cyber crime.

Cybercrime is the most discussed problem in the twenty-first century. The usage of cellphones and the internet is increasing dramatically over the world, which is generating questions about consumers' security and privacy. Because of this, it is crucial for all users to understand cybercrime and security. Cybercrime is defined as organised criminal conduct carried out by attackers online. Cybercrime comes in numerous forms, such as fraud, computer viruses, cyberstalking, and others. Due to these, businesses and government organisations are spending more on maintaining and employing professionals in cybercrime.
There are millions and billions of users and websites in the vast community known as cyberspace. People utilise it for a variety of activities including e-commerce, transactions, shopping, movies, music, and video games. Anyone can simply access anything online in the current technological era owing to accessible internet connection. As a result, crime in general and cybercrime in particular have surged dramatically. Additionally, the faster internet connection has greatly boosted the rate of data circulation. All of these problems are responsible as to why cyber security has grown to be a significant issue for society.
The government has created a number of cybercrime-related laws in an effort to curb the spread of the crime and to protect people's interests. These laws also provide defence against cybercrime. Aside from that, the government has established cyber cells in police stations to combat cybercrime as quickly as possible.
Cybercrime is an attack that can be harmful to both an individual and a business. There have been several instances where a cyber attack led to a data leak that caused a significant loss for a business or a person. These cyber-attacks could have negative effects on the country and the business. The countless instances of cyberattacks that have taken place in India and other nations have necessitated increased security measures. There are four main categories of cybercrime, according to a popular definition—hacking, money, privacy, and cyber terrorism.
Cybercrime is a type of crime in which illegal activities are carried out online or using computers. Cybercrime comes in a variety of forms which involves harassing online users. Cybercrime is the most serious and rapidly expanding type of crime in this day and age. Any person's life may be negatively impacted for a very long time by becoming a cyber victim. Cybercrimes have a wide range of repercussions on financial and investment activity in digital organisations.
One typical tactic used by criminals is to lure online users in by creating attractive websites and sending phoney emails purporting to be from banks or other organisations and asking for personal information. It makes it easier for criminals to access a person's bank account and personal data. Due to viruses, mail fraud, account hacking, and software piracy, people have been victims of cybercrimes. They also run into problems with unauthorised access mailing, threats from pornographic emails, and video transmission.
Types of Cyber Crime
Cyberstalking | It is the use of electronic communication to track down a person or to make repeated attempts to get in touch with them in order to foster personal interaction despite their blatant lack of interest. Anyone who monitors the internet, email, or any other form of electronic communication is guilty of stalking.
Phishing | It is a sort of fraud that includes collecting personal data from recipients of emails that seem to be coming from a reliable source, including Customer ID, IPIN, Credit/Debit Card number, Card expiration date, CVV number, etc.
Vishing | It is an attempt when criminals attempt to obtain personal information over the phone, such as Customer ID, Net Banking password, ATM PIN, OTP, Card expiration date, CVV, etc.
Smishing | It is a sort of fraud that employs text messages sent to mobile devices to entice victims into dialling a fake phone number, going to a fake website, or downloading harmful software.
Impersonation And Identity Theft | This includes the dishonest or fraudulent use of another person's electronic signature, password, or other distinctive identification trait.
Virus, Worms, Trojan | A computer virus is a programme designed to infiltrate your computer, corrupt your files and data, and spread itself. Worms are malicious software applications that repeatedly duplicate themselves on local drives, network shares, etc. Trojan is a malicious programme that mimics a legitimate application. Trojans offer unauthorised people and applications access to your computer through a backdoor entry, allowing them to steal sensitive data.
How to Prevent Cyber Crime
Backup every piece of information—data, systems, and considerations—to make it easier for businesses to recover from unforeseen events with the help of prior data.
Pick a firewall that offers protection from viruses, malware, and dishonest hackers.
Never divulge private information to a stranger since they might exploit it for fraud.
To avoid cybercrime, check your security settings—in order to determine if someone has logged into your computer, a cyber firewall analyses your network settings.
Antivirus software aids in identifying potential threats and malware before they infect a computer system. Never use software that has been cracked since it poses a serious risk of data loss or malware attack.
Keep your information protected when accessing untrusted websites—information can readily bypass the data through phishing websites.
Explore Career Options (By Industry)
- Construction
- Entertainment
- Manufacturing
- Information Technology
Data Administrator
Database professionals use software to store and organise data such as financial information, and customer shipping records. Individuals who opt for a career as data administrators ensure that data is available for users and secured from unauthorised sales. DB administrators may work in various types of industries. It may involve computer systems design, service firms, insurance companies, banks and hospitals.
Bio Medical Engineer
The field of biomedical engineering opens up a universe of expert chances. An Individual in the biomedical engineering career path work in the field of engineering as well as medicine, in order to find out solutions to common problems of the two fields. The biomedical engineering job opportunities are to collaborate with doctors and researchers to develop medical systems, equipment, or devices that can solve clinical problems. Here we will be discussing jobs after biomedical engineering, how to get a job in biomedical engineering, biomedical engineering scope, and salary.
Ethical Hacker
A career as ethical hacker involves various challenges and provides lucrative opportunities in the digital era where every giant business and startup owns its cyberspace on the world wide web. Individuals in the ethical hacker career path try to find the vulnerabilities in the cyber system to get its authority. If he or she succeeds in it then he or she gets its illegal authority. Individuals in the ethical hacker career path then steal information or delete the file that could affect the business, functioning, or services of the organization.
GIS officer work on various GIS software to conduct a study and gather spatial and non-spatial information. GIS experts update the GIS data and maintain it. The databases include aerial or satellite imagery, latitudinal and longitudinal coordinates, and manually digitized images of maps. In a career as GIS expert, one is responsible for creating online and mobile maps.
Data Analyst
The invention of the database has given fresh breath to the people involved in the data analytics career path. Analysis refers to splitting up a whole into its individual components for individual analysis. Data analysis is a method through which raw data are processed and transformed into information that would be beneficial for user strategic thinking.
Data are collected and examined to respond to questions, evaluate hypotheses or contradict theories. It is a tool for analyzing, transforming, modeling, and arranging data with useful knowledge, to assist in decision-making and methods, encompassing various strategies, and is used in different fields of business, research, and social science.
Geothermal Engineer
Individuals who opt for a career as geothermal engineers are the professionals involved in the processing of geothermal energy. The responsibilities of geothermal engineers may vary depending on the workplace location. Those who work in fields design facilities to process and distribute geothermal energy. They oversee the functioning of machinery used in the field.
Database Architect
If you are intrigued by the programming world and are interested in developing communications networks then a career as database architect may be a good option for you. Data architect roles and responsibilities include building design models for data communication networks. Wide Area Networks (WANs), local area networks (LANs), and intranets are included in the database networks. It is expected that database architects will have in-depth knowledge of a company's business to develop a network to fulfil the requirements of the organisation. Stay tuned as we look at the larger picture and give you more information on what is db architecture, why you should pursue database architecture, what to expect from such a degree and what your job opportunities will be after graduation. Here, we will be discussing how to become a data architect. Students can visit NIT Trichy , IIT Kharagpur , JMI New Delhi .
Remote Sensing Technician
Individuals who opt for a career as a remote sensing technician possess unique personalities. Remote sensing analysts seem to be rational human beings, they are strong, independent, persistent, sincere, realistic and resourceful. Some of them are analytical as well, which means they are intelligent, introspective and inquisitive.
Remote sensing scientists use remote sensing technology to support scientists in fields such as community planning, flight planning or the management of natural resources. Analysing data collected from aircraft, satellites or ground-based platforms using statistical analysis software, image analysis software or Geographic Information Systems (GIS) is a significant part of their work. Do you want to learn how to become remote sensing technician? There's no need to be concerned; we've devised a simple remote sensing technician career path for you. Scroll through the pages and read.
Budget Analyst
Budget analysis, in a nutshell, entails thoroughly analyzing the details of a financial budget. The budget analysis aims to better understand and manage revenue. Budget analysts assist in the achievement of financial targets, the preservation of profitability, and the pursuit of long-term growth for a business. Budget analysts generally have a bachelor's degree in accounting, finance, economics, or a closely related field. Knowledge of Financial Management is of prime importance in this career.
Underwriter
An underwriter is a person who assesses and evaluates the risk of insurance in his or her field like mortgage, loan, health policy, investment, and so on and so forth. The underwriter career path does involve risks as analysing the risks means finding out if there is a way for the insurance underwriter jobs to recover the money from its clients. If the risk turns out to be too much for the company then in the future it is an underwriter who will be held accountable for it. Therefore, one must carry out his or her job with a lot of attention and diligence.
Finance Executive
Product manager.
A Product Manager is a professional responsible for product planning and marketing. He or she manages the product throughout the Product Life Cycle, gathering and prioritising the product. A product manager job description includes defining the product vision and working closely with team members of other departments to deliver winning products.
Operations Manager
Individuals in the operations manager jobs are responsible for ensuring the efficiency of each department to acquire its optimal goal. They plan the use of resources and distribution of materials. The operations manager's job description includes managing budgets, negotiating contracts, and performing administrative tasks.
Stock Analyst
Individuals who opt for a career as a stock analyst examine the company's investments makes decisions and keep track of financial securities. The nature of such investments will differ from one business to the next. Individuals in the stock analyst career use data mining to forecast a company's profits and revenues, advise clients on whether to buy or sell, participate in seminars, and discussing financial matters with executives and evaluate annual reports.
A Researcher is a professional who is responsible for collecting data and information by reviewing the literature and conducting experiments and surveys. He or she uses various methodological processes to provide accurate data and information that is utilised by academicians and other industry professionals. Here, we will discuss what is a researcher, the researcher's salary, types of researchers.
Welding Engineer
Welding Engineer Job Description: A Welding Engineer work involves managing welding projects and supervising welding teams. He or she is responsible for reviewing welding procedures, processes and documentation. A career as Welding Engineer involves conducting failure analyses and causes on welding issues.
Transportation Planner
A career as Transportation Planner requires technical application of science and technology in engineering, particularly the concepts, equipment and technologies involved in the production of products and services. In fields like land use, infrastructure review, ecological standards and street design, he or she considers issues of health, environment and performance. A Transportation Planner assigns resources for implementing and designing programmes. He or she is responsible for assessing needs, preparing plans and forecasts and compliance with regulations.
Environmental Engineer
Individuals who opt for a career as an environmental engineer are construction professionals who utilise the skills and knowledge of biology, soil science, chemistry and the concept of engineering to design and develop projects that serve as solutions to various environmental problems.
Safety Manager
A Safety Manager is a professional responsible for employee’s safety at work. He or she plans, implements and oversees the company’s employee safety. A Safety Manager ensures compliance and adherence to Occupational Health and Safety (OHS) guidelines.
Conservation Architect
A Conservation Architect is a professional responsible for conserving and restoring buildings or monuments having a historic value. He or she applies techniques to document and stabilise the object’s state without any further damage. A Conservation Architect restores the monuments and heritage buildings to bring them back to their original state.
Structural Engineer
A Structural Engineer designs buildings, bridges, and other related structures. He or she analyzes the structures and makes sure the structures are strong enough to be used by the people. A career as a Structural Engineer requires working in the construction process. It comes under the civil engineering discipline. A Structure Engineer creates structural models with the help of computer-aided design software.
Highway Engineer
Highway Engineer Job Description: A Highway Engineer is a civil engineer who specialises in planning and building thousands of miles of roads that support connectivity and allow transportation across the country. He or she ensures that traffic management schemes are effectively planned concerning economic sustainability and successful implementation.
Field Surveyor
Are you searching for a Field Surveyor Job Description? A Field Surveyor is a professional responsible for conducting field surveys for various places or geographical conditions. He or she collects the required data and information as per the instructions given by senior officials.
Orthotist and Prosthetist
Orthotists and Prosthetists are professionals who provide aid to patients with disabilities. They fix them to artificial limbs (prosthetics) and help them to regain stability. There are times when people lose their limbs in an accident. In some other occasions, they are born without a limb or orthopaedic impairment. Orthotists and prosthetists play a crucial role in their lives with fixing them to assistive devices and provide mobility.
Pathologist
A career in pathology in India is filled with several responsibilities as it is a medical branch and affects human lives. The demand for pathologists has been increasing over the past few years as people are getting more aware of different diseases. Not only that, but an increase in population and lifestyle changes have also contributed to the increase in a pathologist’s demand. The pathology careers provide an extremely huge number of opportunities and if you want to be a part of the medical field you can consider being a pathologist. If you want to know more about a career in pathology in India then continue reading this article.
Veterinary Doctor
Speech therapist, gynaecologist.
Gynaecology can be defined as the study of the female body. The job outlook for gynaecology is excellent since there is evergreen demand for one because of their responsibility of dealing with not only women’s health but also fertility and pregnancy issues. Although most women prefer to have a women obstetrician gynaecologist as their doctor, men also explore a career as a gynaecologist and there are ample amounts of male doctors in the field who are gynaecologists and aid women during delivery and childbirth.
Audiologist
The audiologist career involves audiology professionals who are responsible to treat hearing loss and proactively preventing the relevant damage. Individuals who opt for a career as an audiologist use various testing strategies with the aim to determine if someone has a normal sensitivity to sounds or not. After the identification of hearing loss, a hearing doctor is required to determine which sections of the hearing are affected, to what extent they are affected, and where the wound causing the hearing loss is found. As soon as the hearing loss is identified, the patients are provided with recommendations for interventions and rehabilitation such as hearing aids, cochlear implants, and appropriate medical referrals. While audiology is a branch of science that studies and researches hearing, balance, and related disorders.
An oncologist is a specialised doctor responsible for providing medical care to patients diagnosed with cancer. He or she uses several therapies to control the cancer and its effect on the human body such as chemotherapy, immunotherapy, radiation therapy and biopsy. An oncologist designs a treatment plan based on a pathology report after diagnosing the type of cancer and where it is spreading inside the body.
Are you searching for an ‘Anatomist job description’? An Anatomist is a research professional who applies the laws of biological science to determine the ability of bodies of various living organisms including animals and humans to regenerate the damaged or destroyed organs. If you want to know what does an anatomist do, then read the entire article, where we will answer all your questions.
For an individual who opts for a career as an actor, the primary responsibility is to completely speak to the character he or she is playing and to persuade the crowd that the character is genuine by connecting with them and bringing them into the story. This applies to significant roles and littler parts, as all roles join to make an effective creation. Here in this article, we will discuss how to become an actor in India, actor exams, actor salary in India, and actor jobs.
Individuals who opt for a career as acrobats create and direct original routines for themselves, in addition to developing interpretations of existing routines. The work of circus acrobats can be seen in a variety of performance settings, including circus, reality shows, sports events like the Olympics, movies and commercials. Individuals who opt for a career as acrobats must be prepared to face rejections and intermittent periods of work. The creativity of acrobats may extend to other aspects of the performance. For example, acrobats in the circus may work with gym trainers, celebrities or collaborate with other professionals to enhance such performance elements as costume and or maybe at the teaching end of the career.
Video Game Designer
Career as a video game designer is filled with excitement as well as responsibilities. A video game designer is someone who is involved in the process of creating a game from day one. He or she is responsible for fulfilling duties like designing the character of the game, the several levels involved, plot, art and similar other elements. Individuals who opt for a career as a video game designer may also write the codes for the game using different programming languages.
Depending on the video game designer job description and experience they may also have to lead a team and do the early testing of the game in order to suggest changes and find loopholes.
Radio Jockey
Radio Jockey is an exciting, promising career and a great challenge for music lovers. If you are really interested in a career as radio jockey, then it is very important for an RJ to have an automatic, fun, and friendly personality. If you want to get a job done in this field, a strong command of the language and a good voice are always good things. Apart from this, in order to be a good radio jockey, you will also listen to good radio jockeys so that you can understand their style and later make your own by practicing.
A career as radio jockey has a lot to offer to deserving candidates. If you want to know more about a career as radio jockey, and how to become a radio jockey then continue reading the article.
Choreographer
The word “choreography" actually comes from Greek words that mean “dance writing." Individuals who opt for a career as a choreographer create and direct original dances, in addition to developing interpretations of existing dances. A Choreographer dances and utilises his or her creativity in other aspects of dance performance. For example, he or she may work with the music director to select music or collaborate with other famous choreographers to enhance such performance elements as lighting, costume and set design.
Social Media Manager
A career as social media manager involves implementing the company’s or brand’s marketing plan across all social media channels. Social media managers help in building or improving a brand’s or a company’s website traffic, build brand awareness, create and implement marketing and brand strategy. Social media managers are key to important social communication as well.
Photographer
Photography is considered both a science and an art, an artistic means of expression in which the camera replaces the pen. In a career as a photographer, an individual is hired to capture the moments of public and private events, such as press conferences or weddings, or may also work inside a studio, where people go to get their picture clicked. Photography is divided into many streams each generating numerous career opportunities in photography. With the boom in advertising, media, and the fashion industry, photography has emerged as a lucrative and thrilling career option for many Indian youths.
An individual who is pursuing a career as a producer is responsible for managing the business aspects of production. They are involved in each aspect of production from its inception to deception. Famous movie producers review the script, recommend changes and visualise the story.
They are responsible for overseeing the finance involved in the project and distributing the film for broadcasting on various platforms. A career as a producer is quite fulfilling as well as exhaustive in terms of playing different roles in order for a production to be successful. Famous movie producers are responsible for hiring creative and technical personnel on contract basis.
Copy Writer
In a career as a copywriter, one has to consult with the client and understand the brief well. A career as a copywriter has a lot to offer to deserving candidates. Several new mediums of advertising are opening therefore making it a lucrative career choice. Students can pursue various copywriter courses such as Journalism , Advertising , Marketing Management . Here, we have discussed how to become a freelance copywriter, copywriter career path, how to become a copywriter in India, and copywriting career outlook.
In a career as a vlogger, one generally works for himself or herself. However, once an individual has gained viewership there are several brands and companies that approach them for paid collaboration. It is one of those fields where an individual can earn well while following his or her passion.
Ever since internet costs got reduced the viewership for these types of content has increased on a large scale. Therefore, a career as a vlogger has a lot to offer. If you want to know more about the Vlogger eligibility, roles and responsibilities then continue reading the article.
For publishing books, newspapers, magazines and digital material, editorial and commercial strategies are set by publishers. Individuals in publishing career paths make choices about the markets their businesses will reach and the type of content that their audience will be served. Individuals in book publisher careers collaborate with editorial staff, designers, authors, and freelance contributors who develop and manage the creation of content.
Careers in journalism are filled with excitement as well as responsibilities. One cannot afford to miss out on the details. As it is the small details that provide insights into a story. Depending on those insights a journalist goes about writing a news article. A journalism career can be stressful at times but if you are someone who is passionate about it then it is the right choice for you. If you want to know more about the media field and journalist career then continue reading this article.
Individuals in the editor career path is an unsung hero of the news industry who polishes the language of the news stories provided by stringers, reporters, copywriters and content writers and also news agencies. Individuals who opt for a career as an editor make it more persuasive, concise and clear for readers. In this article, we will discuss the details of the editor's career path such as how to become an editor in India, editor salary in India and editor skills and qualities.
Individuals who opt for a career as a reporter may often be at work on national holidays and festivities. He or she pitches various story ideas and covers news stories in risky situations. Students can pursue a BMC (Bachelor of Mass Communication) , B.M.M. (Bachelor of Mass Media) , or MAJMC (MA in Journalism and Mass Communication) to become a reporter. While we sit at home reporters travel to locations to collect information that carries a news value.
Corporate Executive
Are you searching for a Corporate Executive job description? A Corporate Executive role comes with administrative duties. He or she provides support to the leadership of the organisation. A Corporate Executive fulfils the business purpose and ensures its financial stability. In this article, we are going to discuss how to become corporate executive.
Multimedia Specialist
A multimedia specialist is a media professional who creates, audio, videos, graphic image files, computer animations for multimedia applications. He or she is responsible for planning, producing, and maintaining websites and applications.
Quality Controller
A quality controller plays a crucial role in an organisation. He or she is responsible for performing quality checks on manufactured products. He or she identifies the defects in a product and rejects the product.
A quality controller records detailed information about products with defects and sends it to the supervisor or plant manager to take necessary actions to improve the production process.
Production Manager
A QA Lead is in charge of the QA Team. The role of QA Lead comes with the responsibility of assessing services and products in order to determine that he or she meets the quality standards. He or she develops, implements and manages test plans.
Process Development Engineer
The Process Development Engineers design, implement, manufacture, mine, and other production systems using technical knowledge and expertise in the industry. They use computer modeling software to test technologies and machinery. An individual who is opting career as Process Development Engineer is responsible for developing cost-effective and efficient processes. They also monitor the production process and ensure it functions smoothly and efficiently.
AWS Solution Architect
An AWS Solution Architect is someone who specializes in developing and implementing cloud computing systems. He or she has a good understanding of the various aspects of cloud computing and can confidently deploy and manage their systems. He or she troubleshoots the issues and evaluates the risk from the third party.
Azure Administrator
An Azure Administrator is a professional responsible for implementing, monitoring, and maintaining Azure Solutions. He or she manages cloud infrastructure service instances and various cloud servers as well as sets up public and private cloud systems.
Computer Programmer
Careers in computer programming primarily refer to the systematic act of writing code and moreover include wider computer science areas. The word 'programmer' or 'coder' has entered into practice with the growing number of newly self-taught tech enthusiasts. Computer programming careers involve the use of designs created by software developers and engineers and transforming them into commands that can be implemented by computers. These commands result in regular usage of social media sites, word-processing applications and browsers.
Information Security Manager
Individuals in the information security manager career path involves in overseeing and controlling all aspects of computer security. The IT security manager job description includes planning and carrying out security measures to protect the business data and information from corruption, theft, unauthorised access, and deliberate attack
ITSM Manager
Automation test engineer.
An Automation Test Engineer job involves executing automated test scripts. He or she identifies the project’s problems and troubleshoots them. The role involves documenting the defect using management tools. He or she works with the application team in order to resolve any issues arising during the testing process.
Applications for Admissions are open.

Aakash iACST Scholarship Test 2024
Get up to 90% scholarship on NEET, JEE & Foundation courses

SAT® | CollegeBoard
Registeration closing on 19th Apr for SAT® | One Test-Many Universities | 90% discount on registrations fee | Free Practice | Multiple Attempts | no penalty for guessing

JEE Main Important Chemistry formulas
As per latest 2024 syllabus. Chemistry formulas, equations, & laws of class 11 & 12th chapters

Resonance Coaching
Enroll in Resonance Coaching for success in JEE/NEET exams

TOEFL ® Registrations 2024
Thinking of Studying Abroad? Think the TOEFL® test. Register now & Save 10% on English Proficiency Tests with Gift Cards

ALLEN JEE Exam Prep
Start your JEE preparation with ALLEN
Everything about Education
Latest updates, Exclusive Content, Webinars and more.
Download Careers360 App's
Regular exam updates, QnA, Predictors, College Applications & E-books now on your Mobile
Cetifications
We Appeared in
What to know about cybercrime
It's hard to protect yourself online if you don't know where to start. These insightful, info-packed talks offer a jumping off point.

Where is cybercrime really coming from?

The 1s and 0s behind cyber warfare

Governments don't understand cyber warfare. We need hackers

Your smartphone is a civil rights issue

How (and why) Russia hacked the US election

Everyday cybercrime -- and what you can do about it
- Home Products
- Small Business 1-49 employees
- Medium Business 50-999 employees
- Enterprise 1000+ employees
What is cybercrime? How to protect yourself

What is cybercrime?
Cybercrime is criminal activity that either targets or uses a computer, a computer network or a networked device. Most cybercrime is committed by cybercriminals or hackers who want to make money. However, occasionally cybercrime aims to damage computers or networks for reasons other than profit. These could be political or personal.
Cybercrime can be carried out by individuals or organizations. Some cybercriminals are organized, use advanced techniques and are highly technically skilled. Others are novice hackers.
What are the types of cybercrime?
Types of cybercrime include:
- Email and internet fraud.
- Identity fraud (where personal information is stolen and used).
- Theft of financial or card payment data.
- Theft and sale of corporate data.
- Cyberextortion (demanding money to prevent a threatened attack).
- Ransomware attacks (a type of cyberextortion).
- Cryptojacking (where hackers mine cryptocurrency using resources they do not own).
- Cyberespionage (where hackers access government or company data).
- Interfering with systems in a way that compromises a network.
- Infringing copyright.
- Illegal gambling.
- Selling illegal items online.
- Soliciting, producing, or possessing child pornography.
Cybercrime involves one or both of the following:
- Criminal activity targeting computers using viruses and other types of malware .
- Criminal activity using computers to commit other crimes.
Cybercriminals that target computers may infect them with malware to damage devices or stop them working. They may also use malware to delete or steal data. Or cybercriminals may stop users from using a website or network or prevent a business providing a software service to its customers, which is called a Denial-of-Service (DoS) attack.
Cybercrime that uses computers to commit other crimes may involve using computers or networks to spread malware, illegal information or illegal images.
Cybercriminals are often doing both at once. They may target computers with viruses first and then use them to spread malware to other machines or throughout a network. Some jurisdictions recognize a third category of cybercrime which is where a computer is used as an accessory to crime. An example of this is using a computer to store stolen data.

Examples of cybercrime
Here are some famous examples of different types of cybercrime attack used by cybercriminals:
1. Malware attacks
A malware attack is where a computer system or network is infected with a computer virus or other type of malware. A computer compromised by malware could be used by cybercriminals for several purposes. These include stealing confidential data, using the computer to carry out other criminal acts, or causing damage to data.
A famous example of a malware attack was the WannaCry ransomware attack, a global cybercrime committed in May 2017. WannaCry is a type of ransomware, malware used to extort money by holding the victim’s data or device to ransom. The ransomware targeted a vulnerability in computers running Microsoft Windows.
When the WannaCry ransomware attack hit, 230,000 computers were affected across 150 countries. Users were locked out of their files and sent a message demanding that they pay a Bitcoin ransom to regain access.
Worldwide, the WannaCry cybercrime is estimated to have caused $4 billion in financial losses. To this day, the attack stands out for its sheer size and impact.
2. Phishing
A phishing campaign is when spam emails, or other forms of communication, are sent with the intention of tricking recipients into doing something that undermines their security. Phishing campaign messages may contain infected attachments or links to malicious sites, or they may ask the receiver to respond with confidential information.
A famous example of a phishing scam took place during the World Cup in 2018. According to our report, 2018 Fraud World Cup , the World Cup phishing scam involved emails that were sent to football fans. These spam emails tried to entice fans with fake free trips to Moscow, where the World Cup was being hosted. People who opened and clicked on the links contained in these emails had their personal data stolen.
Another type of phishing campaign is known as spear-phishing . These are targeted phishing campaigns which try to trick specific individuals into jeopardizing the security of the organization they work for.
Unlike mass phishing campaigns, which are very general in style, spear-phishing messages are typically crafted to look like messages from a trusted source. For example, they are made to look like they have come from the CEO or the IT manager. They may not contain any visual clues that they are fake.
3. Distributed DoS attacks
Distributed DoS attacks (DDoS) are a type of cybercrime attack that cybercriminals use to bring down a system or network. Sometimes connected IoT (Internet of Things) devices are used to launch DDoS attacks.
A DDoS attack overwhelms a system by using one of the standard communication protocols it uses to spam the system with connection requests. Cybercriminals who are carrying out cyberextortion may use the threat of a DDoS attack to demand money. Alternatively, a DDoS may be used as a distraction tactic while another type of cybercrime takes place.
A famous example of this type of attack is the 2017 DDoS attack on the UK National Lottery website . This brought the lottery’s website and mobile app offline, preventing UK citizens from playing. The reason behind the attack remains unknown, however, it is suspected that the attack was an attempt to blackmail the National Lottery.

Impact of cybercrime
Generally, cybercrime is on the rise. According to Accenture’s State of Cybersecurity Resilience 2021 report , security attacks increased 31% from 2020 to 2021. The number of attacks per company increased from 206 to 270 year on year. Attacks on companies affect individuals too since many of them store sensitive data and personal information from customers.
A single attack – whether it’s a data breach, malware, ransomware or DDoS attack - costs companies of all sizes an average of $200,000, and many affected companies go out of business within six months of the attack, according to insurance company Hiscox .
Javelin Strategy & Research published an Identity Fraud Study in 2021 which found that identity fraud losses for the year totalled $56 billion.
For both individuals and companies, the impact of cybercrime can be profound – primarily financial damage, but also loss of trust and reputational damage.
How to report a cybercrime
File a report with the Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3) as soon as possible. Visit ic3.gov for more information.
Contact Action Fraud as soon as possible – find out more on their website here.
Europol has a useful website here which collates the relevant cybercrime reporting links for each EU member state.
You can find information about how to report cybercrime in the UAE on this official website here .
The Australian Cyber Security Centre has information about how to report a cybercrime here.
- How to protect yourself against cybercrime
Given its prevalence, you may be wondering how to stop cybercrime? Here are some sensible tips to protect your computer and your personal data from cybercrime:
1. Keep software and operating system updated
Keeping your software and operating system up to date ensures that you benefit from the latest security patches to protect your computer.
2. Use anti-virus software and keep it updated
Using anti-virus or a comprehensive internet security solution like Kaspersky Premium is a smart way to protect your system from attacks. Anti-virus software allows you to scan, detect and remove threats before they become a problem. Having this protection in place helps to protect your computer and your data from cybercrime, giving you piece of mind. Keep your antivirus updated to receive the best level of protection.
3. Use strong passwords
Be sure to use strong passwords that people will not guess and do not record them anywhere. Or use a reputable password manager to generate strong passwords randomly to make this easier.
4. Never open attachments in spam emails
A classic way that computers get infected by malware attacks and other forms of cybercrime is via email attachments in spam emails. Never open an attachment from a sender you do not know.
5. Do not click on links in spam emails or untrusted websites
Another way people become victims of cybercrime is by clicking on links in spam emails or other messages, or unfamiliar websites. Avoid doing this to stay safe online.
6. Do not give out personal information unless secure
Never give out personal data over the phone or via email unless you are completely sure the line or email is secure. Make certain that you are speaking to the person you think you are.
7. Contact companies directly about suspicious requests
If you are asked for personal information or data from a company who has called you, hang up. Call them back using the number on their official website to ensure you are speaking to them and not a cybercriminal. Ideally, use a different phone because cybercriminals can hold the line open. When you think you’ve re-dialed, they can pretend to be from the bank or other organization that you think you are speaking to.
8. Be mindful of which website URLs you visit
Keep an eye on the URLs you are clicking on. Do they look legitimate? Avoid clicking on links with unfamiliar or URLs that look like spam. If your internet security product includes functionality to secure online transactions, ensure it is enabled before carrying out financial transactions online.
9. Keep an eye on your bank statements
Spotting that you have become a victim of cybercrime quickly is important. Keep an eye on your bank statements and query any unfamiliar transactions with the bank. The bank can investigate whether they are fraudulent.
A good antivirus will protect you from the threat of cybercrime. Learn more about Kaspersky Premium.
Further reading:
- How to protect your data online by using a password manager
- What to do if you’ve been a victim of a phishing attack
- Ransomware protection: how to keep your data safe in 2024
Related videos:
Featured Articles

Black Friday Scams: How to Shop Safely Online

What is a dark web scan?

The Biggest Crypto Exchange Hacks: How to Make Sure You Protect Your Crypto Against Hacks

What Can Hackers Do With Your Email Address?

What is SIM Swapping?
We use cookies to make your experience of our websites better. By using and further navigating this website you accept this. Detailed information about the use of cookies on this website is available by clicking on more information .

Partner Overview
Join Us for Growth, Innovation and Cybersecurity Excellence.
Become a Channel Partner
Be a Valued Partner and Embark on a Journey of Profitability.
Partner Portal
Unified Security Platform
Latest Content and Resources
Threat Report 2023
NRGi Holding Case Study
Cybercrime Explained – A Brief Guide to the Dangers of the Online World
The Internet Can Be a Very Dangerous Place Nowadays. Here’s What You Need to Know About Cybercrime.
Last updated on September 13, 2023

It’s no secret that the expansion of the Internet benefitted the entire world in one way or another. Unfortunately, that also includes cybercrime. The digital world is ripe with opportunities for malicious activities, and there are individuals out there waiting to seize each one of them.
But what is cybercrime? And, more importantly, how can we collectively prevent it? Keep reading to find out.
What is Cybercrime?
Cybercrime is a type of criminal activity that involves the use of computers and the Internet . It represents the perpetuation of previous criminal activities in the digital age, as well as novel illicit behaviors that became possible with the advance of technology.
What this means is that the type of criminal behavior associated with cybercrime has existed long before computers were invented. However, the apparition of advanced electronic devices with the potential to connect to the Internet and reach anyone and anywhere in the world has exacerbated these wrongdoings.
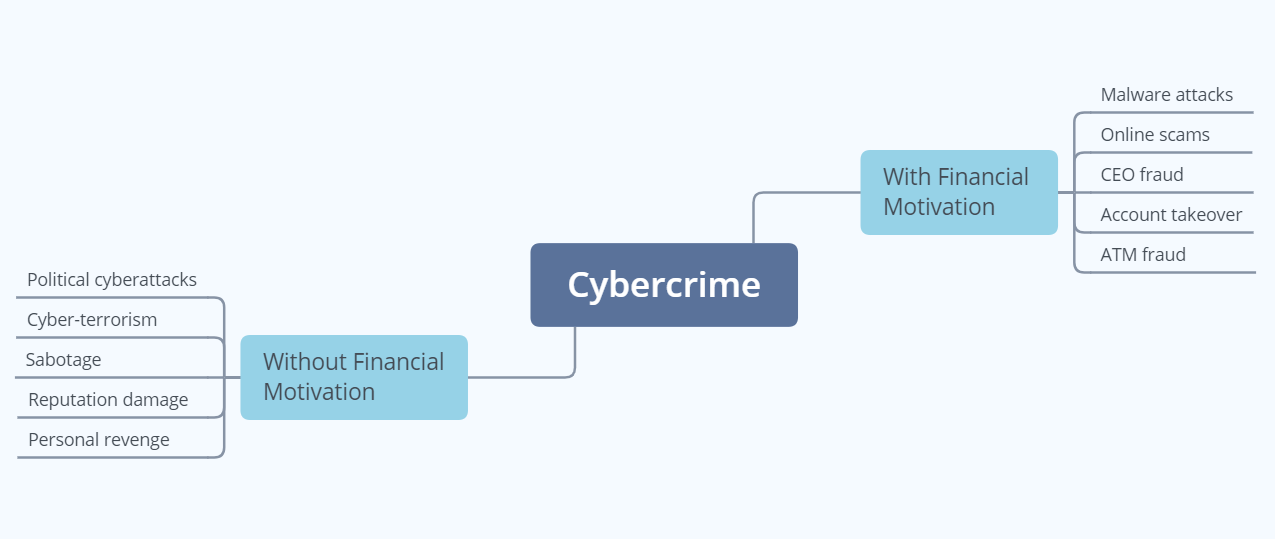
Types of Cybercrime
Cybercrime is split into two main categories according to the financial motivation behind it or lack thereof. While some malicious actors are in it for the cash, others have other incentives driving their actions. Below, you can find a list of the most widespread instances of cybercrime depending on whether they have a monetary component or not.
a. With Financial Motivation
When cybercrime has a financial motivation behind it, it means that hackers have a clear monetary gain following their actions. According to the Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report , a whopping 95% of all cyberattacks are driven by money. There are five subtypes to consider here:
- Malware attacks
- Online scams
- Account takeover fraud
Malware attacks on companies, especially those using ransomware, are the most widespread type of financially motivated cybercrime out there. A study led by Atlas VPN uncovered that 81% of all the financially motivated cyberattacks that took place in 2020 were perpetrated via ransomware.
Unfortunately, the Coronavirus pandemic exacerbated this hazard even more. According to the Ponemon Institute’s 2020 global risk report titled Cybersecurity in the Remote Work Era , the effectiveness of IT security in worldwide organizations dropped by 27% during this period.
Online scams are another common type of financially motivated cybercrime to watch out for, as they target enterprises and home users alike. Catfishing, hijacked Facebook profiles, or even the infamous Nigerian prince method are just a few examples.
CEO fraud is another insidious type of cyber fraud where hackers pose as figures of authority in a company to demand illicit money transfers. On the other end of the spectrum, account takeover fraud implies identity theft and the misuse of unlawfully obtained credentials to carry out fraudulent transactions.
Finally, ATM fraud might not seem like a cybercrime at first, but offenders use computers and other digital means to carry it out. Over time, they have developed methods to intercept both the user’s PIN and the data on the card’s magnetic strip. For this reason, it is still very lucrative for malicious actors to attempt it.
b. Without Financial Motivation
While it is true that the vast majority of cybercrime is driven by monetary gain, 5% of it has no financial motivation whatsoever. However, this doesn’t mean that its intent isn’t malicious. In fact, it might be even more so. This category contains the following five subtypes:
- Political cyberattacks
- Cyber-terrorism
- Reputation damage
- Personal revenge
The affairs of the state are an important driving force in cybercrime, and the stakes are higher than money. The Center for Strategic International Studies (CSIS) lists seven politically motivated cyberattacks in the last year alone. Malicious actors with this intent are mainly located in Russia, China, and Iran nowadays.
Closely linked to political cyberattacks is the matter of cyber-terrorism. The term refers to a type of cybercrime that makes use of computers to intimidate a country’s civilian population and influence the policy-making of its government.
Two other types of cybercrime that are intimately related are sabotage and reputation damage. While the former implies the damage of assets, the latter can take multiple forms. However, the end goal is the same, and it consists of tarnishing the name and standing of an organization.
Last, but certainly not least, personal revenge is another type of cybercrime that targets both enterprise or home users. Research published by Statista in 2021 showed that India alone registered nearly 1,200 cybercrime cases motivated by retaliation in one year.
What Methods Do Cybercriminals Use?
When it comes to attacking enterprises for financial gain, breaching organizations with ulterior motives, or even harassing home users for personal revenge, hackers have a wide array of tools under their belt. Examples include, but are not limited to:
- Social engineering
- Malicious code
- Denial of service attacks
- Credential theft
- Impersonation
- Online stalking
- Traffic sniffing
Countermeasures That Will Enhance Your Security
Knowing what the methods cybercriminals use to get to you are is the first step. The next focal point on your agenda should be prevention. Here are the three pillars of a strong defense that you need to implement as soon as possible.
#1 Secure Accounts
In terms of cybercrime prevention, what you first need to do is safeguard your organization against phishing attacks and implement an email security solution . Traditional email services such as Gmail, Outlook, or Yahoo! Mail already come with a few layers of defense that will detect malicious activity.
Credential theft is another threat you should consider in the prevention of cybercrime. Besides infecting the devices in your corporate network with malware, hackers are also looking to get their hands on as many login credentials as possible. This is a lucrative business opportunity for them, as they can further use them to steal your data or even sell them on the Dark Web . The shadiest corners of the Internet are swarming with password databases that anyone can purchase.
This is why your company needs a strong password policy. Credentials that contain both uppercase and lowercase letters, as well as alphanumeric characters are harder to crack. Create strict guidelines for this, and include cybersecurity tips on how often they should be changed as well.
Another way to make sure your accounts are bulletproof is through multi-factor authentication. The term refers to a verification system that sees users provide at least two if not more pieces of evidence that they are the owners of an account or have lawful access to it
The first step in a multi-factor authentication system is a standard one – you put in your username or email address, then your password. Additional layers of security then follow. Depending on the platform and method, you might be required to:
- Provide a biometric authentication vector such as facial recognition or fingerprint scanning.
- Use a verified mobile device like a smartphone or tablet to confirm the login attempt.
- Insert an additional PIN code that you get via email or text, etc.
#2 Cybersecurity Education
Other than protective tools and policies, your employees can be a valuable asset for your company in the prevention of cybercrime. Nonetheless, for them to be able to help, you must provide them with the appropriate cybersecurity education on issues that might pose a concern for your enterprise and industry. Here are but a few possible topics:
- how to recognize social engineering tactics,
- how to spot a malicious attachment or link,
- how to identify a cyberattack,
- how to create a strong password,
- and how to browse securely.
These are just a starting point. The field of cybersecurity is a lot vaster than these five pointers, which is why I recommend hiring an expert to hold these training sessions if you are not qualified to do it. Investing in your staff will pay off tenfold in the long run when they won’t fall victim to clever cyberattacks.
#3 Protected Systems
Having all your bases covered for the prevention of cybercrime requires a complete endpoint prevention, detection, and response solution . The particularity of this approach is that it takes protection one step beyond traditional EDR software, adding advanced threat hunting capabilities to your company network. This helps you prevent even the most cunning hackers from taking over your sensitive data and accounts.
HEIMDAL® ENDPOINT DETECTION AND RESPONSE SOFTWARE
- Next-gen Antivirus & Firewall which stops known threats;
- DNS traffic filter which stops unknown threats;
- Automatic patches for your software and apps with no interruptions;
- Privileged Access Management and Application Control, all in one unified dashboard
Our Heimdal™ EPDR offering consists of five modules:
- DNS traffic filtering
- Artificial intelligence
- Patch management
- Privileged access management
- Antivirus with firewall
By their powers combined, these state-of-the-art technologies not only detect and respond to cyberattacks but actively prevent them as well. Heimdal™ EPDR closes vulnerabilities in your system and keeps detailed lists of both known and unknown threats that keep your digital assets safe from cyber-harm.
Wrapping Up…
Cybercrime is a multi-faceted affair. Most attacks are financially motivated, but some are not. Regardless of their target, hackers have a nefarious purpose in mind and will stop at no lengths to fulfill it.
For this reason, prevention comes with several layers of defense that consist of both technologies and individuals. Having the appropriate cybersecurity tools under your belt should always be accompanied by relevant policies and cybersecurity training for your employees.
Heimdal™ Security can help you with the former, so don’t hesitate to reach out at [email protected] for more info.
Alina Georgiana Petcu
Product Marketing Manager
Alina Georgiana Petcu is a Product Marketing Manager within Heimdal™ Security and her main interest lies in institutional cybersecurity. In her spare time, Alina is also an avid malware historian who loves nothing more than to untangle the intricate narratives behind the world's most infamous cyberattacks.
Related Articles
A strong cybersecurity program should mean that plant infrastructure is also well connected. This opens up possibilities for leveraging plant solutions that can hit your bottom line quickly and efficiently. Solutions like artificial intelligence or augmented reality,
Leave a Reply (Cancel Reply)
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
CHECK OUR SUITE OF 11 CYBERSECURITY SOLUTIONS
- Cyber Resources And Beginners
- Cyber Security Glossary
- The Daily Security Tip
- Cyber Security For Small Business Owners
- Cybersecurity Webinars
- About Heimdal®
- Press Center
- Partner with us
- Affiliate Program
© 2024 Heimdal ®
Vat No. 35802495, Vester Farimagsgade 1, 2 Sal, 1606 København V
Doha Declaration
Education for justice.
- Agenda Day 1
- Agenda Day 2
- Agenda Day 3
- Agenda Day 4
- Registration
- Breakout Sessions for Primary and Secondary Level
- Breakout Sessions for Tertiary Level
- E4J Youth Competition
- India - Lockdown Learners
- Chuka, Break the Silence
- The Online Zoo
- I would like a community where ...
- Staying safe online
- Let's be respectful online
- We can all be heroes
- Respect for all
- We all have rights
- A mosaic of differences
- The right thing to do
- Solving ethical dilemmas
- UNODC-UNESCO Guide for Policymakers
- UNODC-UNESCO Handbooks for Teachers
- Justice Accelerators

Introduction
- Organized Crime
- Trafficking in Persons & Smuggling of Migrants
- Crime Prevention & Criminal Justice Reform
- Crime Prevention, Criminal Justice & SDGs
- UN Congress on Crime Prevention & Criminal Justice
- Commission on Crime Prevention & Criminal Justice
Conference of the Parties to UNTOC
Conference of the states parties to uncac.
- Rules for Simulating Crime Prevention & Criminal Justice Bodies
- Crime Prevention & Criminal Justice
- Engage with Us
- Contact Us about MUN
- Conferences Supporting E4J
- Cyberstrike
- Play for Integrity
- Running out of Time
- Zorbs Reloaded
- Developing a Rationale for Using the Video
- Previewing the Anti-Corruption Video
- Viewing the Video with a Purpose
- Post-viewing Activities
- Previewing the Firearms Video
- Rationale for Using the Video
- Previewing the Human Trafficking Video
- Previewing the Organized Crime Video
- Previewing the Video
- Criminal Justice & Crime Prevention
- Corruption & Integrity
- Human Trafficking & Migrant Smuggling
- Firearms Trafficking
- Terrorism & Violent Extremism
- Introduction & Learning Outcomes
- Corruption - Baseline Definition
- Effects of Corruption
- Deeper Meanings of Corruption
- Measuring Corruption
- Possible Class Structure
- Core Reading
- Advanced Reading
- Student Assessment
- Additional Teaching Tools
- Guidelines for Stand-Alone Course
- Appendix: How Corruption Affects the SDGs
- What is Governance?
- What is Good Governance?
- Corruption and Bad Governance
- Governance Reforms and Anti-Corruption
- Guidelines for Stand-alone Course
- Corruption and Democracy
- Corruption and Authoritarian Systems
- Hybrid Systems and Syndromes of Corruption
- The Deep Democratization Approach
- Political Parties and Political Finance
- Political Institution-building as a Means to Counter Corruption
- Manifestations and Consequences of Public Sector Corruption
- Causes of Public Sector Corruption
- Theories that Explain Corruption
- Corruption in Public Procurement
- Corruption in State-Owned Enterprises
- Responses to Public Sector Corruption
- Preventing Public Sector Corruption
- Forms & Manifestations of Private Sector Corruption
- Consequences of Private Sector Corruption
- Causes of Private Sector Corruption
- Responses to Private Sector Corruption
- Preventing Private Sector Corruption
- Collective Action & Public-Private Partnerships against Corruption
- Transparency as a Precondition
- Detection Mechanisms - Auditing and Reporting
- Whistle-blowing Systems and Protections
- Investigation of Corruption
- Introduction and Learning Outcomes
- Brief background on the human rights system
- Overview of the corruption-human rights nexus
- Impact of corruption on specific human rights
- Approaches to assessing the corruption-human rights nexus
- Human-rights based approach
- Defining sex, gender and gender mainstreaming
- Gender differences in corruption
- Theories explaining the gender–corruption nexus
- Gendered impacts of corruption
- Anti-corruption and gender mainstreaming
- Manifestations of corruption in education
- Costs of corruption in education
- Causes of corruption in education
- Fighting corruption in education
- Core terms and concepts
- The role of citizens in fighting corruption
- The role, risks and challenges of CSOs fighting corruption
- The role of the media in fighting corruption
- Access to information: a condition for citizen participation
- ICT as a tool for citizen participation in anti-corruption efforts
- Government obligations to ensure citizen participation in anti-corruption efforts
- Teaching Guide
- Brief History of Terrorism
- 19th Century Terrorism
- League of Nations & Terrorism
- United Nations & Terrorism
- Terrorist Victimization
- Exercises & Case Studies
- Radicalization & Violent Extremism
- Preventing & Countering Violent Extremism
- Drivers of Violent Extremism
- International Approaches to PVE &CVE
- Regional & Multilateral Approaches
- Defining Rule of Law
- UN Global Counter-Terrorism Strategy
- International Cooperation & UN CT Strategy
- Legal Sources & UN CT Strategy
- Regional & National Approaches
- International Legal Frameworks
- International Human Rights Law
- International Humanitarian Law
- International Refugee Law
- Current Challenges to International Legal Framework
- Defining Terrorism
- Criminal Justice Responses
- Treaty-based Crimes of Terrorism
- Core International Crimes
- International Courts and Tribunals
- African Region
- Inter-American Region
- Asian Region
- European Region
- Middle East & Gulf Regions
- Core Principles of IHL
- Categorization of Armed Conflict
- Classification of Persons
- IHL, Terrorism & Counter-Terrorism
- Relationship between IHL & intern. human rights law
- Limitations Permitted by Human Rights Law
- Derogation during Public Emergency
- Examples of States of Emergency & Derogations
- International Human Rights Instruments
- Regional Human Rights Instruments
- Extra-territorial Application of Right to Life
- Arbitrary Deprivation of Life
- Death Penalty
- Enforced Disappearances
- Armed Conflict Context
- International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights
- Convention against Torture et al.
- International Legal Framework
- Key Contemporary Issues
- Investigative Phase
- Trial & Sentencing Phase
- Armed Conflict
- Case Studies
- Special Investigative Techniques
- Surveillance & Interception of Communications
- Privacy & Intelligence Gathering in Armed Conflict
- Accountability & Oversight of Intelligence Gathering
- Principle of Non-Discrimination
- Freedom of Religion
- Freedom of Expression
- Freedom of Assembly
- Freedom of Association
- Fundamental Freedoms
- Definition of 'Victim'
- Effects of Terrorism
- Access to Justice
- Recognition of the Victim
- Human Rights Instruments
- Criminal Justice Mechanisms
- Instruments for Victims of Terrorism
- National Approaches
- Key Challenges in Securing Reparation
- Topic 1. Contemporary issues relating to conditions conducive both to the spread of terrorism and the rule of law
- Topic 2. Contemporary issues relating to the right to life
- Topic 3. Contemporary issues relating to foreign terrorist fighters
- Topic 4. Contemporary issues relating to non-discrimination and fundamental freedoms
- Module 16: Linkages between Organized Crime and Terrorism
- Thematic Areas
- Content Breakdown
- Module Adaptation & Design Guidelines
- Teaching Methods
- Acknowledgements
- 1. Introducing United Nations Standards & Norms on CPCJ vis-à-vis International Law
- 2. Scope of United Nations Standards & Norms on CPCJ
- 3. United Nations Standards & Norms on CPCJ in Operation
- 1. Definition of Crime Prevention
- 2. Key Crime Prevention Typologies
- 2. (cont.) Tonry & Farrington’s Typology
- 3. Crime Problem-Solving Approaches
- 4. What Works
- United Nations Entities
- Regional Crime Prevention Councils/Institutions
- Key Clearinghouses
- Systematic Reviews
- 1. Introduction to International Standards & Norms
- 2. Identifying the Need for Legal Aid
- 3. Key Components of the Right of Access to Legal Aid
- 4. Access to Legal Aid for Those with Specific Needs
- 5. Models for Governing, Administering and Funding Legal Aid
- 6. Models for Delivering Legal Aid Services
- 7. Roles and Responsibilities of Legal Aid Providers
- 8. Quality Assurance and Legal Aid Services
- 1. Context for Use of Force by Law Enforcement Officials
- 2. Legal Framework
- 3. General Principles of Use of Force in Law Enforcement
- 4. Use of Firearms
- 5. Use of “Less-Lethal” Weapons
- 6. Protection of Especially Vulnerable Groups
- 7. Use of Force during Assemblies
- 1. Policing in democracies & need for accountability, integrity, oversight
- 2. Key mechanisms & actors in police accountability, oversight
- 3. Crosscutting & contemporary issues in police accountability
- 1. Introducing Aims of Punishment, Imprisonment & Prison Reform
- 2. Current Trends, Challenges & Human Rights
- 3. Towards Humane Prisons & Alternative Sanctions
- 1. Aims and Significance of Alternatives to Imprisonment
- 2. Justifying Punishment in the Community
- 3. Pretrial Alternatives
- 4. Post Trial Alternatives
- 5. Evaluating Alternatives
- 1. Concept, Values and Origin of Restorative Justice
- 2. Overview of Restorative Justice Processes
- 3. How Cost Effective is Restorative Justice?
- 4. Issues in Implementing Restorative Justice
- 1. Gender-Based Discrimination & Women in Conflict with the Law
- 2. Vulnerabilities of Girls in Conflict with the Law
- 3. Discrimination and Violence against LGBTI Individuals
- 4. Gender Diversity in Criminal Justice Workforce
- 1. Ending Violence against Women
- 2. Human Rights Approaches to Violence against Women
- 3. Who Has Rights in this Situation?
- 4. What about the Men?
- 5. Local, Regional & Global Solutions to Violence against Women & Girls
- 1. Understanding the Concept of Victims of Crime
- 2. Impact of Crime, including Trauma
- 3. Right of Victims to Adequate Response to their Needs
- 4. Collecting Victim Data
- 5. Victims and their Participation in Criminal Justice Process
- 6. Victim Services: Institutional and Non-Governmental Organizations
- 7. Outlook on Current Developments Regarding Victims
- 8. Victims of Crime and International Law
- 1. The Many Forms of Violence against Children
- 2. The Impact of Violence on Children
- 3. States' Obligations to Prevent VAC and Protect Child Victims
- 4. Improving the Prevention of Violence against Children
- 5. Improving the Criminal Justice Response to VAC
- 6. Addressing Violence against Children within the Justice System
- 1. The Role of the Justice System
- 2. Convention on the Rights of the Child & International Legal Framework on Children's Rights
- 3. Justice for Children
- 4. Justice for Children in Conflict with the Law
- 5. Realizing Justice for Children
- 1a. Judicial Independence as Fundamental Value of Rule of Law & of Constitutionalism
- 1b. Main Factors Aimed at Securing Judicial Independence
- 2a. Public Prosecutors as ‘Gate Keepers’ of Criminal Justice
- 2b. Institutional and Functional Role of Prosecutors
- 2c. Other Factors Affecting the Role of Prosecutors
- Basics of Computing
- Global Connectivity and Technology Usage Trends
- Cybercrime in Brief
- Cybercrime Trends
- Cybercrime Prevention
- Offences against computer data and systems
- Computer-related offences
- Content-related offences
- The Role of Cybercrime Law
- Harmonization of Laws
- International and Regional Instruments
- International Human Rights and Cybercrime Law
- Digital Evidence
- Digital Forensics
- Standards and Best Practices for Digital Forensics
- Reporting Cybercrime
- Who Conducts Cybercrime Investigations?
- Obstacles to Cybercrime Investigations
- Knowledge Management
- Legal and Ethical Obligations
- Handling of Digital Evidence
- Digital Evidence Admissibility
- Sovereignty and Jurisdiction
- Formal International Cooperation Mechanisms
- Informal International Cooperation Mechanisms
- Data Retention, Preservation and Access
- Challenges Relating to Extraterritorial Evidence
- National Capacity and International Cooperation
- Internet Governance
- Cybersecurity Strategies: Basic Features
- National Cybersecurity Strategies
- International Cooperation on Cybersecurity Matters
- Cybersecurity Posture
- Assets, Vulnerabilities and Threats
- Vulnerability Disclosure
- Cybersecurity Measures and Usability
- Situational Crime Prevention
- Incident Detection, Response, Recovery & Preparedness
- Privacy: What it is and Why it is Important
- Privacy and Security
- Cybercrime that Compromises Privacy
- Data Protection Legislation
- Data Breach Notification Laws
- Enforcement of Privacy and Data Protection Laws
- Intellectual Property: What it is
- Types of Intellectual Property
- Causes for Cyber-Enabled Copyright & Trademark Offences
- Protection & Prevention Efforts
- Online Child Sexual Exploitation and Abuse
- Cyberstalking and Cyberharassment
- Cyberbullying
- Gender-Based Interpersonal Cybercrime
- Interpersonal Cybercrime Prevention
- Cyber Organized Crime: What is it?
- Conceptualizing Organized Crime & Defining Actors Involved
- Criminal Groups Engaging in Cyber Organized Crime
- Cyber Organized Crime Activities
- Preventing & Countering Cyber Organized Crime
- Cyberespionage
- Cyberterrorism
- Cyberwarfare
- Information Warfare, Disinformation & Electoral Fraud
- Responses to Cyberinterventions
- Framing the Issue of Firearms
- Direct Impact of Firearms
- Indirect Impacts of Firearms on States or Communities
- International and National Responses
- Typology and Classification of Firearms
- Common Firearms Types
- 'Other' Types of Firearms
- Parts and Components
- History of the Legitimate Arms Market
- Need for a Legitimate Market
- Key Actors in the Legitimate Market
- Authorized & Unauthorized Arms Transfers
- Illegal Firearms in Social, Cultural & Political Context
- Supply, Demand & Criminal Motivations
- Larger Scale Firearms Trafficking Activities
- Smaller Scale Trafficking Activities
- Sources of Illicit Firearms
- Consequences of Illicit Markets
- International Public Law & Transnational Law
- International Instruments with Global Outreach
- Commonalities, Differences & Complementarity between Global Instruments
- Tools to Support Implementation of Global Instruments
- Other United Nations Processes
- The Sustainable Development Goals
- Multilateral & Regional Instruments
- Scope of National Firearms Regulations
- National Firearms Strategies & Action Plans
- Harmonization of National Legislation with International Firearms Instruments
- Assistance for Development of National Firearms Legislation
- Firearms Trafficking as a Cross-Cutting Element
- Organized Crime and Organized Criminal Groups
- Criminal Gangs
- Terrorist Groups
- Interconnections between Organized Criminal Groups & Terrorist Groups
- Gangs - Organized Crime & Terrorism: An Evolving Continuum
- International Response
- International and National Legal Framework
- Firearms Related Offences
- Role of Law Enforcement
- Firearms as Evidence
- Use of Special Investigative Techniques
- International Cooperation and Information Exchange
- Prosecution and Adjudication of Firearms Trafficking
- Teaching Methods & Principles
- Ethical Learning Environments
- Overview of Modules
- Module Adaption & Design Guidelines
- Table of Exercises
- Basic Terms
- Forms of Gender Discrimination
- Ethics of Care
- Case Studies for Professional Ethics
- Case Studies for Role Morality
- Additional Exercises
- Defining Organized Crime
- Definition in Convention
- Similarities & Differences
- Activities, Organization, Composition
- Thinking Critically Through Fiction
- Excerpts of Legislation
- Research & Independent Study Questions
- Legal Definitions of Organized Crimes
- Criminal Association
- Definitions in the Organized Crime Convention
- Criminal Organizations and Enterprise Laws
- Enabling Offence: Obstruction of Justice
- Drug Trafficking
- Wildlife & Forest Crime
- Counterfeit Products Trafficking
- Falsified Medical Products
- Trafficking in Cultural Property
- Trafficking in Persons
- Case Studies & Exercises
- Extortion Racketeering
- Loansharking
- Links to Corruption
- Bribery versus Extortion
- Money-Laundering
- Liability of Legal Persons
- How much Organized Crime is there?
- Alternative Ways for Measuring
- Measuring Product Markets
- Risk Assessment
- Key Concepts of Risk Assessment
- Risk Assessment of Organized Crime Groups
- Risk Assessment of Product Markets
- Risk Assessment in Practice
- Positivism: Environmental Influences
- Classical: Pain-Pleasure Decisions
- Structural Factors
- Ethical Perspective
- Crime Causes & Facilitating Factors
- Models and Structure
- Hierarchical Model
- Local, Cultural Model
- Enterprise or Business Model
- Groups vs Activities
- Networked Structure
- Jurisdiction
- Investigators of Organized Crime
- Controlled Deliveries
- Physical & Electronic Surveillance
- Undercover Operations
- Financial Analysis
- Use of Informants
- Rights of Victims & Witnesses
- Role of Prosecutors
- Adversarial vs Inquisitorial Legal Systems
- Mitigating Punishment
- Granting Immunity from Prosecution
- Witness Protection
- Aggravating & Mitigating Factors
- Sentencing Options
- Alternatives to Imprisonment
- Death Penalty & Organized Crime
- Backgrounds of Convicted Offenders
- Confiscation
- Confiscation in Practice
- Mutual Legal Assistance (MLA)
- Extradition
- Transfer of Criminal Proceedings
- Transfer of Sentenced Persons
- Module 12: Prevention of Organized Crime
- Adoption of Organized Crime Convention
- Historical Context
- Features of the Convention
- Related international instruments
- Conference of the Parties
- Roles of Participants
- Structure and Flow
- Recommended Topics
- Background Materials
- What is Sex / Gender / Intersectionality?
- Knowledge about Gender in Organized Crime
- Gender and Organized Crime
- Gender and Different Types of Organized Crime
- Definitions and Terminology
- Organized crime and Terrorism - International Legal Framework
- International Terrorism-related Conventions
- UNSC Resolutions on Terrorism
- Organized Crime Convention and its Protocols
- Theoretical Frameworks on Linkages between Organized Crime and Terrorism
- Typologies of Criminal Behaviour Associated with Terrorism
- Terrorism and Drug Trafficking
- Terrorism and Trafficking in Weapons
- Terrorism, Crime and Trafficking in Cultural Property
- Trafficking in Persons and Terrorism
- Intellectual Property Crime and Terrorism
- Kidnapping for Ransom and Terrorism
- Exploitation of Natural Resources and Terrorism
- Review and Assessment Questions
- Research and Independent Study Questions
- Criminalization of Smuggling of Migrants
- UNTOC & the Protocol against Smuggling of Migrants
- Offences under the Protocol
- Financial & Other Material Benefits
- Aggravating Circumstances
- Criminal Liability
- Non-Criminalization of Smuggled Migrants
- Scope of the Protocol
- Humanitarian Exemption
- Migrant Smuggling v. Irregular Migration
- Migrant Smuggling vis-a-vis Other Crime Types
- Other Resources
- Assistance and Protection in the Protocol
- International Human Rights and Refugee Law
- Vulnerable groups
- Positive and Negative Obligations of the State
- Identification of Smuggled Migrants
- Participation in Legal Proceedings
- Role of Non-Governmental Organizations
- Smuggled Migrants & Other Categories of Migrants
- Short-, Mid- and Long-Term Measures
- Criminal Justice Reponse: Scope
- Investigative & Prosecutorial Approaches
- Different Relevant Actors & Their Roles
- Testimonial Evidence
- Financial Investigations
- Non-Governmental Organizations
- ‘Outside the Box’ Methodologies
- Intra- and Inter-Agency Coordination
- Admissibility of Evidence
- International Cooperation
- Exchange of Information
- Non-Criminal Law Relevant to Smuggling of Migrants
- Administrative Approach
- Complementary Activities & Role of Non-criminal Justice Actors
- Macro-Perspective in Addressing Smuggling of Migrants
- Human Security
- International Aid and Cooperation
- Migration & Migrant Smuggling
- Mixed Migration Flows
- Social Politics of Migrant Smuggling
- Vulnerability
- Profile of Smugglers
- Role of Organized Criminal Groups
- Humanitarianism, Security and Migrant Smuggling
- Crime of Trafficking in Persons
- The Issue of Consent
- The Purpose of Exploitation
- The abuse of a position of vulnerability
- Indicators of Trafficking in Persons
- Distinction between Trafficking in Persons and Other Crimes
- Misconceptions Regarding Trafficking in Persons
- Root Causes
- Supply Side Prevention Strategies
- Demand Side Prevention Strategies
- Role of the Media
- Safe Migration Channels
- Crime Prevention Strategies
- Monitoring, Evaluating & Reporting on Effectiveness of Prevention
- Trafficked Persons as Victims
- Protection under the Protocol against Trafficking in Persons
- Broader International Framework
- State Responsibility for Trafficking in Persons
- Identification of Victims
- Principle of Non-Criminalization of Victims
- Criminal Justice Duties Imposed on States
- Role of the Criminal Justice System
- Current Low Levels of Prosecutions and Convictions
- Challenges to an Effective Criminal Justice Response
- Rights of Victims to Justice and Protection
- Potential Strategies to “Turn the Tide”
- State Cooperation with Civil Society
- Civil Society Actors
- The Private Sector
- Comparing SOM and TIP
- Differences and Commonalities
- Vulnerability and Continuum between SOM & TIP
- Labour Exploitation
- Forced Marriage
- Other Examples
- Children on the Move
- Protecting Smuggled and Trafficked Children
- Protection in Practice
- Children Alleged as Having Committed Smuggling or Trafficking Offences
- Basic Terms - Gender and Gender Stereotypes
- International Legal Frameworks and Definitions of TIP and SOM
- Global Overview on TIP and SOM
- Gender and Migration
- Key Debates in the Scholarship on TIP and SOM
- Gender and TIP and SOM Offenders
- Responses to TIP and SOM
- Use of Technology to Facilitate TIP and SOM
- Technology Facilitating Trafficking in Persons
- Technology in Smuggling of Migrants
- Using Technology to Prevent and Combat TIP and SOM
- Privacy and Data Concerns
- Emerging Trends
- Demand and Consumption
- Supply and Demand
- Implications of Wildlife Trafficking
- Legal and Illegal Markets
- Perpetrators and their Networks
- Locations and Activities relating to Wildlife Trafficking
- Environmental Protection & Conservation
- CITES & the International Trade in Endangered Species
- Organized Crime & Corruption
- Animal Welfare
- Criminal Justice Actors and Agencies
- Criminalization of Wildlife Trafficking
- Challenges for Law Enforcement
- Investigation Measures and Detection Methods
- Prosecution and Judiciary
- Wild Flora as the Target of Illegal Trafficking
- Purposes for which Wild Flora is Illegally Targeted
- How is it Done and Who is Involved?
- Consequences of Harms to Wild Flora
- Terminology
- Background: Communities and conservation: A history of disenfranchisement
- Incentives for communities to get involved in illegal wildlife trafficking: the cost of conservation
- Incentives to participate in illegal wildlife, logging and fishing economies
- International and regional responses that fight wildlife trafficking while supporting IPLCs
- Mechanisms for incentivizing community conservation and reducing wildlife trafficking
- Critiques of community engagement
- Other challenges posed by wildlife trafficking that affect local populations
- Global Podcast Series
- Apr. 2021: Call for Expressions of Interest: Online training for academics from francophone Africa
- Feb. 2021: Series of Seminars for Universities of Central Asia
- Dec. 2020: UNODC and TISS Conference on Access to Justice to End Violence
- Nov. 2020: Expert Workshop for University Lecturers and Trainers from the Commonwealth of Independent States
- Oct. 2020: E4J Webinar Series: Youth Empowerment through Education for Justice
- Interview: How to use E4J's tool in teaching on TIP and SOM
- E4J-Open University Online Training-of-Trainers Course
- Teaching Integrity and Ethics Modules: Survey Results
- Grants Programmes
- E4J MUN Resource Guide
- Library of Resources
- Model United Nations (MUN)
- {{item.name}} ({{item.items.length}}) items
- Add new list
MUN Resource Guide - Home
Crime prevention & criminal justice for mun, crime prevention, criminal justice & sdgs, un congresses on crime prevention & criminal justice, commission on crime prevention and criminal justice, rules for simulating un bodies, model united nations topic.
Cybercrime is an evolving form of transnational crime.
The complex nature of the crime as one that takes place in the border-less realm of cyberspace is compounded by the increasing involvement of organized crime groups. Perpetrators of cybercrime and their victims can be located in different regions, and its effects can ripple through societies around the world, highlighting the need to mount an urgent, dynamic and international response.
What is cybercrime?
There is no international definition of cybercrime or cyberattacks. Offences typically cluster around the following categories:
Offences against the confidentiality, integrity and availability of computer data and systems;
- Computer-related offences;
- Content-related offences;
- Offences related to infringements of copyright and related rights.
Broadly, cybercrime can be described as having cyber-dependent offences, cyber-enabled offences and, as a specific crime-type, online child sexual exploitation and abuse.
- Cyber-dependent crime requires an information and communications technology infrastructure and is often typified as the creation, dissemination and deployment of malware, ransomware, attacks on critical national infrastructure (e.g. the cyber-takeover of a power-plant by an organised crime group) and taking a website offline by overloading it with data (a DDOS attack).
- Cyber-enabled crime is that which can occur in the offline world but can also be facilitated by information and communications technology. This typically includes online frauds, purchases of drugs online and online money laundering.
- Child sexual exploitation and abuse includes abuse on the clear internet, darknet forums and, increasingly, the exploitation of self-created imagery via extortion - known as "sextortion". We do not use the term "child pornography" as this creates a value judgment upon innocent children. You can read more about why language is important in the Luxembourg Guidelines here.
Combating cybercrime and the Sustainable Development Goals
While there is no specific Sustainable Development Goal to address cybercrime, it can be seen as an obstacle to achieving a number of targets, such as those under Goal 16, which relate to violence and other forms of crime, such as corruption and arms trafficking (Targets 16.1, 16.4, 16.5).
In addition, certain criminal activities can be facilitated by information and communications technology, such as the recruitment of victims of trafficking in persons (target 10.8) or sexual exploitation of women, which would characterize a form of violence against women (target 5.2).
By choosing to have cybercrime as a Model United Nations issue, participants can:
- Obtain more knowledge about the different phenomena relating to cybercrime, such as cyber-dependent, enabled and specific crime types;
- Increase their understanding of Member States' efforts to address cybercrime in intergovernmental fora;
- Increase their knowledge of best practices and ways in which Member States and society can cooperate to address cybercrime.
Suggested topics for a Model United Nations conference and related Sustainable Development Goals
Resources on cybercrime.
Back to top
Supported by the State of Qatar
60 years crime congress.
Cyber Crime Essay for Students and Children
500+ words essay on cyber crime.
Cyber Crime Essay – Everybody thinks that only stealing someone’s private data is Cyber Crime. But in defining terms we can say that ‘Cyber Crime refers to the use of an electronic device (computer, laptop, etc.) for stealing someone’s data or trying to harm them using a computer.
Besides, it is an illegal activity that involves a series of issues ranging from theft to using your system or IP address as a tool for committing a crime.

Types of Cyber Crime
Speaking in a broadway we can say that Cyber Crime are categorized into four major types. These are Financial, Privacy, Hacking, and Cyber Terrorism.
The financial crime they steal the money of user or account holders. Likewise, they also stole data of companies which can lead to financial crimes. Also, transactions are heavily risked because of them. Every year hackers stole lakhs and crores of rupees of businessmen and government.
Privacy crime includes stealing your private data which you do not want to share with the world. Moreover, due to it, the people suffer a lot and some even commit suicide because of their data’s misuse.
In, hacking they intentional deface a website to cause damage or loss to the public or owner. Apart from that, they destroy or make changes in the existing websites to diminish its value.
Modern-day terrorism has grown way beyond what it was 10-20 years ago. But cyber terrorism is not just related to terrorists or terrorist organizations. But to threat some person or property to the level of creating fear is also Cyber Terrorism.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Cyber Crime in India
Web world or cyberspace is a massive community of millions and billions of users and websites. Also, people access it for different uses like shopping, movies, music, video games, transactions, and e-commerce, etc.

In this Age of Technology and easy access to the internet, anyone can easily reach it. Because of this fast pace growth from the previous decade. Besides, the internet has opened a world of information on which anyone can connect.
Due to, this the rate of crime especially the rate of Cyber Crime has increased much fold. Moreover, the rate of circulation of data is also increased much fold due to the higher speed of internet. Above all, due to all these issues, the Cybersecurity has become a major concern for society.
Laws related to Cyber Crimes
To stop the spread of Cyber Crime and to safeguard the interest of people the government has made several laws related to Cyber Crimes. Also, these laws serve as protection against Cyber Crime. Apart from that, the government has also introduced cyber cells in police stations to counter the problem of Cyber Crime as fast as they can.
Ways of stopping Cyber Crime
Cyber Crime is not something which we cannot deal with our self. Likewise, with little use of our common sense and logic, we can stop Cyber Crimes from happening.
To conclude, we can say that Cyber Crime is a dangerous offense to someone’s privacy or any material. Also, we can avoid Cyber Crime by following some basic logical things and using our common sense. Above all, Cyber Crime is a violation of not only law but of human rights too.
{ “@context”: “https://schema.org”, “@type”: “FAQPage”, “mainEntity”: [{ “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “What is the main cause of Cyber Crime?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”: “The greed for quick money and the desire to get famous quickly are the two main reasons of Cyber Crime. Also, most of the targets of Cyber Crime banks, businessman, financial firms, etc.” } }, { “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “What is the punishment of Cyber Crime in India?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”:”If the person is found guilty then there are several punishments based on the level of crime. A simple crime can cost you a fine while a bigger crime can lead you to jail.”} }] }
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Lesson for Learners
Cyber crime.
STUDY FLASHCARDS: Cyber crime Review this lesson with Expemo Learn more
Cyber crime stays one step ahead
What started as the activity of geeky hacker s has become a multibillion-pound, international criminal industry.
Computer crime is not only exploding in volume but is mutating faster than it can be contained. Some 2.5 million new types of malicious programme have been launched in the past two months alone - more than in the entire last 15 years, according to the latest data from the security firm Trend Micro. The UK now has around 1.25 million "infected" computers. And the average number of PCs across the world sending out spam emails every month shot up to 10 million last year, more than double the 4.2 million in 2006, which was double the 2.1 million in 2005.
Cyber crime has become a multi-billion-pound, international criminal, industry including unsolicited email "phishing" campaigns to con people out of financial details and passwords.
In the age-old contest of good guys against bad guys, each side inspires the other to ever greater levels of sophistication. And as viruses evolve, taking root on everything from digital cameras to USB memory sticks, simply securing a corporate network may no longer be enough.
A key tool for the cyber-criminal is the botnet – a large number of computers that are recruited by a virus and can then be controlled from one place, often without their owner's knowledge. Botnets can include tens of thousands of individual PCs, and have a lot of different types of uses, including mass spamming, propagating yet more viruses , and crashing websites by bombarding them with visitors.
The current estimate is that there are 175 million infected computers live on the internet today. And cyber crime is worth billions of dollars. But scams are so diverse, and the techniques are evolving so quickly, that it is almost impossible to estimate the true scale of the problem.
In value terms, the biggest scam at the moment is "click fraud", where certain websites that are being paid by advertisers on a per-click basis use botnets to bombard the advertiser's site with apparent interest. Second is good, old-fashioned, fraud using credit-card details, online accounts or electronic transfers based on information stolen either from individuals' computers or from insecure company databases. Third is extortion - often against gambling sites just before major sporting events - where botnets are used to prove the site can be knocked down unless payment is received.
The criminals' techniques are continually developing. This month, for example, saw the first botnet involving both humans and machines. To bypass security measures in signing up free email accounts, a criminal group set up a high-tech sweatshop in India to process the part of the application that cannot be done automatically.
Original article by Sarah Arnott ©The Independent News and Media, first published in The Independent, 22/03/08
Study the following sentences and answer the questions below.
a) The criminals' techniques are continually developing . b) Cyber crime has become a multi-billion-pound, international criminal industry. c) 2.5 million new types of malicious programme have been launched in the past two months. d) ...where certain websites that are being paid by advertisers ..
Active: a, b
Passive: c, d
The passive is used when the cause of the action is unknown or unimportant.
The present continuous ( a and d ) is used to talk about an action or trend happening now or around the present time.
The present perfect simple ( b and c ) is used to talk about completed, recent actions or completed actions or trends that started in the past and continued to the present.
Now complete the sentences below by putting the verbs in brackets in their correct form. Decide if the meaning is active or passive.
The criminal who stole personal details of thousands of Internet users was finally caught yesterday. (steal, catch/finally)
Yesterday, Paul downloaded a malicious programme and his computer was infected with a virus. (download, infect)
Has somebody ever hacked into your computer? (somebody/ever/hack)
What is being done at the moment to stop cyber criminals from stealing money? (do)
I used a pay phone to call her this morning because my mobile phone had been stolen . (use, steal)
We were treated very well during our stay at the hotel last week. (treat)
When I was growing up, I was encouraged to become a doctor. (encourage)
Sally doesn't like being told what to do. (tell)
The construction of the new roundabout won’t be completed until May next year. (complete)
Taki's flat was burgled last month. His television and laptop were stolen . (burgle, steal)
Thousands of people were hurt when the earthquake struck last year. (hurt, strike)
Be the first to share your thoughts on this lesson
Leave a Comment
5 tips for users
Try to review your flashcards every 1-2 days.
Review lessons/pages that are still fresh in your memory.
Be honest with your grades.
Add and review one package at a time.
Relax and enjoy the review.
Rate this lesson

Use our Expemo flashcard app to review the language from our ESL worksheets and multi-language phrasebooks.
Expemo uses state-of-the-art spaced repetition algorithms that allow users to learn a new language from our resources without forgetting material from previous lessons.

Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Cyber Crime Essay

Essay on Cyber Crime
Cyber crime is the most discussed issue of the 21st century. The technology sector world wide is witnessing a boom in the consumer of smartphones and the internet which is raising concerns with regard to the privacy and security of the users. Owing to this reason, it is highly essential for all the users to know about cyber crime & security. As a result, thi topic has become the most favorite topic of the examiner and can often be seen asked in the exams. In this view, students must have information on cyber crime and stay prepared to tackle such topics in the essay question in the English paper.
Introduction
Cybercrime is a dangerous attack a company or an individual may face. There are many cases where the cyber attack has brought massive loss to the company and individuals due to the data hack. We live in a technology-driven era, and every piece of information is now fed on computers. Cybercrime involves an attack on computers and digital devices. These cyber-attacks can prove hazardous not just for the organization, but also for the nation. To date, there are many digital attack cases in India and global, pushing for more security measures. These attacks are also affecting the economy of the country if not controlled in the initial stage.
What is Cybercrime?
Cybercrime or attack is defined as the systematic criminal activity occurring digitally
and done by attackers. There are many examples of cybercrime, including fraud,
malware viruses, cyberstalking and others. Due to these, government agencies and
companies are investing more in the maintenance and hiring of cybercrime experts.
Earlier, cybercrime was committed only by individuals or by small groups. However, now a highly complex cybercriminals network work on attacking the system for data
collection.
Three groups of cybercrimes-
This is the form of cyberstalking, trafficking, and grooming. Over the years, this
This type of cybercrime has been taken seriously by law enforcement agencies. It is
now keeping a track over every such attack on an individual.
Similar to the real world where criminals steal the property, in the cyber world,
attackers steal data. Here, the attacker steals a person's bank details and
misuse the credit card for online purchase. By using malicious software, the
attacker attacks the property to disrupt the system of the organization.
These types of crimes are denoted as cyber terrorism. This can be a terror because
the attacker can get hold of essential documents related to government
projects. An enemy nation or terrorist usually makes such attacks. There are
many cases globally where a terrorist hacks government data.
Apart from these, there is a financial crime where the hacker steals the money of the
user account holder. Moreover, they steal company data and finance.
In this type, the computer system of the person is hacked to get personal
information. In many countries, including India, hacking is a punishable act.
It is quite different from ethical hacking. In normal hacking, illegal use
different types of software to enter the system of the target person. Hacker is
then able to monitor every activity done by the person.
This Cybercrime is about violating copyright and downloading music or movies. In
India, many movies before their releases are leaked on the movie download
sites. In other words , theft is also called privacy, which can bring a huge
loss to the organization.
Cyber Stalking
It is online harassment by an individual or a group of people. Normally, these
stalkers target an individual and harass online. There are many cases of
cyberstalking in India, resulting in the target person ending up taking
Malicious Software
These are computer-based cybercrimes where virus-based software is installed in the
target people or organization computers. This is to damage the system and
corrupt the data of the target.
Laws Related to Cybercrime
In India, there are many cybercrime laws enacted to stop this threat. Be it for
the individual or the organization; these laws help to either bring down the
number of cases or eliminate these digital crimes.
Apart from these laws, as an individual, you also need to take steps to stop these
crimes. Like, not providing your login details, installing trust anti-virus
software and keeping your online profile private can help to act against such
Cybercrime is a significant threat that can bring huge loss to the individual and the
organization. It is essential to follow basic online rules to ensure the safety
of self and the organization.
Benefits of Cyber Crime Essay in English provided by Vedantu
The essay on cybercrime provided by Vedantu is prepared by highly qualified teachers which makes it a reliable source of information. This information could be utilized for a variety of reasons. Being a reliable piece of information the essay will benefit everyone curious to know about the topic.
Following are the highlights of its benefits:
Reliable information
Adaptive to the context
Precise language
Fulfills the requirements of the students for english exam questions
Comprehensive and analytical. The article digs in the depth of the issue and analyzes it through a 360 degree perspective.
The essay could also be used by the students for preparing themselves for the essay question in the English paper. This essay is an excellent guide to understand what the examiner is looking for in the exam. Moreover, the topic of cybercrime is quite a recurrent one in the exam. So the students use this essay to deal with the same topic.
The Essay on Cyber Crime is an excellent guide on averting any possibilities of a cyber attack. On today's date, one is mostly on the internet for a variety of reasons. It becomes essential for one to know important tips that can keep one safe from cyberbullies, thieves, or blackmailers. It is also important for one to understand the right course of actions to be taken in an eventuality of such an incident.
Download the cybercrime essay for students in English on the Vedantu website.

FAQs on Cyber Crime Essay
1. How Does Cybercrime Work?
Group of people or an individual commits most of these cyber-crimes. These criminals use a systematic process to hack and commit these acts. These criminal communities share strategies and tools to launch attacks. Some of the cybercrime techniques
Fast Flux - In this method, the hacker moves data quickly among computers in a botnet, making it challenging to find the right source.
Social Engineering - This method includes using lies and manipulation to trick people into revealing their personal information.
Skimmers - This involves installing a skimming tool in an ATM and stealing the information. You may find such skimming devices in ATMs.
There are some digital criminals targeting organizations to steal personal information.
2. How Cybercrime Affects Society?
Cybercrime can hugely affect society. In 2018, the US faced a loss of $600 billion. As consumers are increasingly allowing technologies to get into their lives, cyber attackers are getting better access. Some of the essential information available are-
Personal health data, sleep schedules, and geo-locations Shopping history, account information, and passive conversations noticed voice-controlled devices, Private conversations on social media accounts.
Your entire life is now available on social media, making it vulnerable to hack or cyber-attack. Attackers use different techniques including- installing malware, virus, phishing, cyberstalking, etc. These can certainly bring loss of lives and data for individuals and organizations. For society, this is a significant loss in the long run. One needs to be very careful when presenting himself socially.
3. How to stay secure in times of cybercrime?
Cybercrime is a real threat posing to society. It is the 21st-century version of theft and blackmailing. There are certain ways one should adopt to prevent any possibilities of cybercrime. Do not disclose the banking details to random people or fill the CVV of your debit or credit cards on an unknown and unverified website. Keep your passwords always discrete. The camera of the laptop should always be covered.
4. Where can I get a cybercrime essay?
One can find a good quality cyber crime essay on Vedantu's website. The essay which is prepared by the expert teachers describes everything that one needs to know about cybercrime. It is the one-stop solution for all your requirements on the topic. Their essay is available in PDF format on the website and could be downloaded on any device. One downloaded essay could be used in offline mode too. If one finds it feasible, the printout of the PDF could also be taken out.
50 Latest Cyber crime IELTS Topics
- Unlimited Essay Checks: Practice and perfect your skills.
- Detailed Error Analysis: Spot every mistake.
- In-Built Grammar Checker: Say no to grammatical errors.
- Personalized Suggestions: Know how to boost your score.
- Progress Tracking: View your checked essay history.
- Still thinking? We have a 14-day money-back guarantee. Take a leap of faith!
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Springer Nature - PMC COVID-19 Collection

Cybercrime: Victimization, Perpetration, and Techniques
James hawdon.
Virginia Tech, Blacksburg, VA USA
The creation of the World Wide Web revolutionized communication. At the turn of the twenty-first century, roughly 413 million people used the internet (Roser & Ortiz-Ospina, 2015 ). A mere 21 years later, nearly 4.7 billion people, or about 60% of the world’s population, actively use the internet (We Are Social, & DataReportal, & Hootsuite, 2021 ). The pace of innovation in information technology, from the introduction of email in the 1960s to the rise of multiple social media platforms in the early 2000s to the rise of the Internet of Things (Iot) and 5 g, has been astonishing. It is now almost inconceivable to imagine life without access to the internet. Yet the IT revolution, like all technological revolutions, has been a dual-edge sword. Indeed, the internet’s many benefits and drawbacks have been discussed in numerous forums, and these discussions will undoubtedly continue as long as we remain dependent on this technology. This special edition of the American Journal of Criminal Justice contributes to those discussions by considering one of the drawbacks: cybercime.
Cybercrime, or the use of computer technology or online networks to commit crimes, ranges from fraud and identity theft to threats and intimidation. Cybercrime and its many manifestations has clearly increased over the past 20 years. For example, cybercrime costs increased from approximately $3 trillion in 2015 to more than $6 trillion in 2021, and these are expected to increase to over $10.5 trillion by 2025 (Morgan, 2020 ). In the U.S. alone, approximately 23 percent of households experience some sort of cybercrime annually (Reinhart, 2018 ; Hawdon et al., 2020 ). Indeed, in the same way that larceny characterized the twentieth century, cybercrime is characterizing the twenty-first century (Albanese, 2005 ). And these facts just reflect the economic costs of cybercrime and do not account for the non-monetary harms caused by cyberviolence. Cyberstalking, online sexual exploitation, cyber-harassment and bullying, threats of violence, and online violent extremism are also commonly committed acts of cyberviolence (FBI, 2021 ).
In many ways, it is unsurprising that cybercrime has increased in recent years. As technology becomes more sophisticated, so do cybercriminals, and cybercriminals now target individuals, businesses, healthcare facilities, educational institutions, and governments. As more people engage in an ever-increasing variety of online activities and more businesses conduct their affairs online, it is predictable that there would be a rise in cybercrime. To use the familiar language of Routine Activity Theory (Cohen & Felson, 1979 ), we have a lot more suitable targets in insufficiently guarded space being victimized by an increasing number motivated offenders. It is also unsurprising that there is a growing body of literature dedicated to cybercrime as scholars scramble to understand the ever-evolving phenomena. Entire journals are now dedicated to its study, and new academic disciplines have been created to try to prevent it. While our understanding of cybercrime has accumulated quickly and impressively, there is so much about cybercrime that we still do not know. This special issue of the A merican Journal of Criminal Justice offers nine new articles to help fill that knowledge gap.
The articles included in this issue reflect three broad areas of cybercrime research: cybercrime victimization, cybercrime perpetration, and techniques and facilitators of cybercrime. While there is some overlap, the issue includes three papers focused on each of these three areas.
The first area covered in the special issue focuses on cybercrime victimization. This area has generated the most research to date. In part because victims of cybercrime are relatively easy to find, considerable research has been conducted on cybervictimization across a variety of cybercrimes. Three of the articles in this special issue focus on cybervictimization, and they add to the literature in interesting ways by providing cross-national perspectives, building on theoretical traditions, or providing systematic summaries of the state of field at this time.
The first article in this section by Michelle Wright and a team of colleagues investigates how adolescent from China, Cyprus, the Czech Republic, India, Japan, and the United States explain being a victim of cyberbully. The investigation compares if how adolescents explain victimization varies by setting (private vs. public), medium (offline vs cyber), and severity and if cultural differences alter these relationships. Their findings suggest the need for prevention and intervention efforts to consider the role of setting, medium, severity, and cultural values if they are to be successful.
The second paper focusing on victimization builds on the frequent finding that problematic social media use is associated with negative life experiences and provides empirical support for a theoretical link between problematic social media use and cybervictimization. The analysis, conducted by colleagues Eetu Marttila, Aki Koivula, and Pekka Räsänen, is framed in Routine Activity Theory/Lifestyle-Exposure Theory. The results indicate that not only is problematic social media use strongly correlated with cybervictimization in a between-subject analysis, but within-subject analyses also reveal that problematic social media use has a cumulative effect on victimization.
The third paper bridges research on cybercrime victimization and cybercrime perpetration and provides a glimpse at the state of knowledge about a specific form of cyberviolence. Catherine Marcum and George Higgins conduct a systematic review of literature investigating both offending and victimization of cyberstalking, cyberdating abuse, and interpersonal electronic surveillance. Using a number of electronic databases, the authors focus on 31 studies to identify correlates of involvement in these cybercrimes. Victims are disproportionately female. Other correlates of victimization include overall social media use, risky online behavior, and negative external factors such as being attached to abusive peers. Correlates of perpetration provide support for a number of leading criminological theories as perpetrators tend to have low levels of self-control, associate with delinquent peers, and have low levels of parental supervision. As more research is conducted, there is a great need for more systematic literature reviews so we can begin to better refine our understanding and identify the theoretical approaches that provide the most insight into the world of cybercrime.
There are another three articles included in this special issue that focus on cybercrime perpetration. All three articles test traditional criminological theories and find support for them. In the first, Adam Bossler uses Sykes and Matza’s ( 1957 ) techniques of neutralization to examine the effects of techniques of neutralization on college students’ willingness to commit cybercrime, specifically hacking websites to deface them or compromise foreign and domestic financial and government targets. An overall techniques of neutralization scale significantly predicts being willing to commit cyberattacks even after controlling for other relevant factors. In addition to the theoretical implications of finding strong support for Sykes and Matza’s framework, the findings also have implications for situational crime prevention efforts aimed at removing excuses for offenders.
In another article focusing on perpetration, Thomas Dearden and Katalin Parti use a national online sample of 1,109 participants and find strong support for social learning theory as measures of both online and offline social learning correlate with a measure of cyber-offending. However, the authors also argue that self-control will interact with social learning variables to further influence the likelihood of cyber-offending. Overall, they find that both social learning and self-control, individually and as an interaction, are good predictors of cyber-offending.
In the final article dedicated to investigating the perpetration of cybercrime, Ashley Reichelmann and Matthew Costello use a nationally representative sample to explore how various dimensions of American national identity relate to producing online hate materials. The analysis reveals that higher levels of salience and public self-regard are weakly related to producing online hate. However, the findings suggest that understanding the nuances of “what it means to be American” is important for fully understanding the phenomenon of cyberhate, especially in this polarizing time when what it means to “be American” is frequently questioned.
Another three articles deal with perpetrating cybercrimes or “pseudo-cybercrimes,” but their focus is on how these crimes are committed. That is, the investigations deal with using the Dark Web or the surface web to make illegal or pseudo-legal purchases of illegal or quasi-legal substances. In the first paper in the section, Eric Jardine provides a crime script for purchasing drugs on the Dark Web. The script involves four generic stages (i.e. Informational Accumulation; Account Formation; Market Exchange; Delivery/Receipt) and provides an opportunity to review known law enforcement interventions that have effectively targeted each stage of the script to reduce the use of these online markets. The paper highlights numerous steps that law enforcement could take to effectively reduce the illegal selling and purchasing of drugs on the Dark Web.
Next, Robert Perdue engages in green criminology and focuses on the illegal trade of endangered species. Noting that regulating this trade is a critical, and very difficult, challenge for conservationists and law enforcement agents, Perdue examines the role the Internet plays in critically endangered plant transactions, but instead of focusing on the Dark Web, he investigates eBay to understand the extent to which such trades occur in plain sight. He finds that nearly a third of the critically endangered plant species examined were for sale in some form on eBay. Yet, despite the evidence that there is a high degree of open trading in these species, the complexity of the international legal frameworks regulating these transactions makes it difficult to ascertain their legality. Nevertheless, at least a subset of these sales are probably unlawful.
Finally, J. Mitchell Miller and Holly Ventura Miller provide insight into the computer-facilitated gray market of pseudo-legal marijuana sales in Los Vegas, Nevada. The ethnographic study reveals how various cannabis products are illegally diverted from legal markets to the gray market, and how brokers use the Internet in clever ways to advertise their products and services to a public that is likely unaware that they are engaging in illegal activities by skirting the regulations and tight control of the legal market.
Taken together, these three papers highlight the tremendous difficulties with regulating e-commerce. While the Dark Web provides an environment to conduct illegal transactions with minimal risk, it turns out that the Dark Web may be unnecessary for many illegal cyber-purchases. Given the surface web is convenient, widely available, and scarcely policed, many cybercriminals simply commit their crimes in the open. Using the language of Routine Activity Theory again, the internet—Dark or Surface—is an environment largely devoid of capable guardians.
As a whole, I believe these nine papers speak to the current state and future promise of cybercriminology. Currently, we are building a large body of empirical studies that speak to patterns of victimization and perpetration. With respect to victimization, we have learned a lot about who is likely to be victimized and how the patterns of victimization vary by type of cybercrime. We also have a good understanding of the activities that increase the likelihood of victimization, the emotional and financial costs of being a victim, and how people view victims depending on the setting and type of victimization. The body of evidence supporting a slightly modified version of Routine Activity Theory/Lifestyle-Exposure Theory is increasingly impressive, and the papers by Marttila, Koivula, and Räsänen as well as the article by Marcum and Higgins offer additional support for aspects of this theoretical approach.
Similarly, our understanding of cybercrime perpetration has expanded exponentially in recent years. While finding samples of cybercriminals is always a challenge, the growing body of evidence suggests that the behavior of cybercriminals is largely explained by the same set of factors that can account for the behavior of more traditional criminals. That is, cybercriminals tend to have low levels of self and social control, are largely unsupervised, experience strains, and learn the how, when, and why of their crimes from their associates. The papers in this issue offer additional support for techniques of neutralization, social learning theory, and self-control theory. While there are nuanced differences in how some criminogenic factors play out in the virtual and offline worlds, our existing theories appear to be robust as many of our theories apply to both online and offline criminal behavior. A number of the differences that exist largely relate to the asynchronous nature of many online interactions. The fact that online interactions can occur synchronously as well as asynchronously expands our networks and provide additional opportunities for others beyond our immediate environment to influence us and for us to commit crimes. The full ramifications of these changes in social networks, criminogenic forces, and criminal opportunities are not understood; however, we understand these far better today than we did even just a few years ago.
We also have a far greater understanding of the techniques of committing cybercrimes. We know considerably more about the use of the Dark Web to find and purchase illegal goods and services, and we have learned that the Surface Web plays a significant role in computer-dependent crimes. Moreover, as the article by Miller and Miller highlights, information technology has helped blur the line between legal, pseudo-legal, and illegal behaviors. What work in this area really highlights is how difficult it is to monitor and police the internet. While there is certainly social control exercised on the internet, there are limits to the effectiveness of this control (see Hawdon et al., 2017 ). Yet, by understanding the patterns of victimization, the underlying causes of perpetration, and the techniques that facilitate cybercrime, we become better armed in designing strategies to prevent it, defend against it, mitigate its adverse effects, and prosecute those who commit it. All of the articles included in this issue further that understanding.
The Special Issue
The process of selecting the articles for this special issue was perhaps unusual but also rather intensive. The process began by me inviting a group of scholars to submit manuscripts for the special issue. I selected these scholars because I knew of their work and was confident they would submit quality papers that covered a wide range of topics in the area of cybercrime. After discussing their planned submissions with the authors to assure there would be good topic coverage, the authors submitted their paper. An anonymous scholar and I reviewed these initial submissions (the anonymous scholar served as a typical double-blind reviewer). Each contributing author also reviewed one or two of the included articles. Authors then revised their work based on the reviewers’ comments and resubmitted the papers. Each contributing author was then asked to read all nine revised papers. Then, the authors and I took advantage of the brief pause in the COVID-19 pandemic and gathered for a two-day workshop in Asheville, North Carolina as part of the Center for Peace Studies and Violence Prevention’s annual research workshop program. The lone exception to this was our Finnish colleagues who were unable to get a special visa to visit the U.S. at that time. These colleagues joined the workshop via Zoom. The authors/workshop participants then discussed and provided feedback on all of the articles. The authors then made final revisions to their papers based on these discussions. Thus, these papers have been through three rounds of revisions. As the editor of the special edition, I am proud of the finished product.
is a professor of sociology and Director of the Center for Peace Studies and Violence Prevention at Virginia Tech. Dr. Hawdon’s research focuses on how communities influence the causes and consequences of violence. He is currently researching how online communities influence online hate, extremism, political polarization, and cybercrime. Since 2013, he and his colleagues have collected multiple waves of data on online hate speech and extremism in the Finland, France, Germany, Poland, Spain, the United Kingdom, and the United States. His recent work has been funded by the National Institute of Justice, the National Science Foundation, and The Commonwealth Cyber Initiative. He has published eight books and over 130 articles, books chapters, and technical reports.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
- Albanese JS. Fraud: The characteristic crime of the 21st Century. Trends in Organized Crime. 2005; 8 :5–16. doi: 10.1007/s12117-005-1033-9. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cohen LE, Felson M. Social change and crime rate trends: A routine activity approach. American Sociological Review. 1979; 44 (4):588–608. doi: 10.2307/2094589. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Federal Bureau of Investigation . 2020 Internet crime report. U.S. Government Printing Office; 2021. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hawdon J, Costello C, Ratliff T, Hall L, Middleton J. Conflict management styles and cybervictimization: An extension of routine activity theory. Sociological Spectrum. 2017; 37 (4):250–266. doi: 10.1080/02732173.2017.1334608. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hawdon J, Parti K, Dearden TE. Cybercrime in America amid COVID-19: The initial results from a natural experiment. American Journal of Criminal Justice. 2020; 45 :546–562. doi: 10.1007/s12103-020-09534-4. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Morgan, S. (2020). Cybercrime to cost the World $10.5 Trillion Annually by 2025. Cybercrime Magazine , November 13, 2020. https://cybersecurityventures.com/hackerpocalypse-cybercrime-report-2016/
- Reinhart, R. J. (2018). One in four Americans have experienced cybercrime. Gallup Politics . https://news.gallup.com/poll/245336/one-four-americans-experienced-cybercrime.aspx
- Roser, M. H. R. & Ortiz-Ospina, E. (2015). "Internet". Published online at OurWorldInData.org. Retrieved from: ' https://ourworldindata.org/internet ' [Online Resource]
- Sykes GM, Matza D. Techniques of neutralization: A theory of delinquency. American Sociological Review. 1957; 22 (6):664–670. doi: 10.2307/2089195. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- We Are Social, & DataReportal, & Hootsuite. (2021). Global digital population as of January 2021 (in billions) [Graph]. In Statista . Retrieved September 24, 2021, from https://www.statista.com/statistics/617136/digital-population-worldwide/
- Kaspersky Premium
- Kaspersky Plus
- Kaspersky Standard
- Kaspersky Safe Kids
- Kaspersky Password Manager
- Renew Licence
- Trials & Downloads
- Small Business
- Medium Business
- Find a reseller
- Find a distributor
- Partnership with Kaspersky
- Get to know us
- Company overview
- Transparency
- Corporate News
- Awards & Recognitions
- Top 3 Rankings
- Press center
- Sponsorships
- Policy blog
What is cybercrime? How to protect yourself

What is cybercrime?
Cybercrime is criminal activity that either targets or uses a computer, a computer network or a networked device. Most cybercrime is committed by cybercriminals or hackers who want to make money. However, occasionally cybercrime aims to damage computers or networks for reasons other than profit. These could be political or personal.
Cybercrime can be carried out by individuals or organizations. Some cybercriminals are organized, use advanced techniques and are highly technically skilled. Others are novice hackers.
What are the types of cybercrime?
Types of cybercrime include:
- Email and internet fraud.
- Identity fraud (where personal information is stolen and used).
- Theft of financial or card payment data.
- Theft and sale of corporate data.
- Cyberextortion (demanding money to prevent a threatened attack).
- Ransomware attacks (a type of cyberextortion).
- Cryptojacking (where hackers mine cryptocurrency using resources they do not own).
- Cyberespionage (where hackers access government or company data).
- Interfering with systems in a way that compromises a network.
- Infringing copyright.
- Illegal gambling.
- Selling illegal items online.
- Soliciting, producing, or possessing child pornography.
Cybercrime involves one or both of the following:
- Criminal activity targeting computers using viruses and other types of malware .
- Criminal activity using computers to commit other crimes.
Cybercriminals that target computers may infect them with malware to damage devices or stop them working. They may also use malware to delete or steal data. Or cybercriminals may stop users from using a website or network or prevent a business providing a software service to its customers, which is called a Denial-of-Service (DoS) attack.
Cybercrime that uses computers to commit other crimes may involve using computers or networks to spread malware, illegal information or illegal images.
Cybercriminals are often doing both at once. They may target computers with viruses first and then use them to spread malware to other machines or throughout a network. Some jurisdictions recognize a third category of cybercrime which is where a computer is used as an accessory to crime. An example of this is using a computer to store stolen data.

Examples of cybercrime
Here are some famous examples of different types of cybercrime attack used by cybercriminals:
1. Malware attacks
A malware attack is where a computer system or network is infected with a computer virus or other type of malware. A computer compromised by malware could be used by cybercriminals for several purposes. These include stealing confidential data, using the computer to carry out other criminal acts, or causing damage to data.
A famous example of a malware attack was the WannaCry ransomware attack, a global cybercrime committed in May 2017. WannaCry is a type of ransomware, malware used to extort money by holding the victim’s data or device to ransom. The ransomware targeted a vulnerability in computers running Microsoft Windows.
When the WannaCry ransomware attack hit, 230,000 computers were affected across 150 countries. Users were locked out of their files and sent a message demanding that they pay a Bitcoin ransom to regain access.
Worldwide, the WannaCry cybercrime is estimated to have caused $4 billion in financial losses. To this day, the attack stands out for its sheer size and impact.
2. Phishing
A phishing campaign is when spam emails, or other forms of communication, are sent with the intention of tricking recipients into doing something that undermines their security. Phishing campaign messages may contain infected attachments or links to malicious sites, or they may ask the receiver to respond with confidential information.
A famous example of a phishing scam took place during the World Cup in 2018. According to our report, 2018 Fraud World Cup , the World Cup phishing scam involved emails that were sent to football fans. These spam emails tried to entice fans with fake free trips to Moscow, where the World Cup was being hosted. People who opened and clicked on the links contained in these emails had their personal data stolen.
Another type of phishing campaign is known as spear-phishing . These are targeted phishing campaigns which try to trick specific individuals into jeopardizing the security of the organization they work for.
Unlike mass phishing campaigns, which are very general in style, spear-phishing messages are typically crafted to look like messages from a trusted source. For example, they are made to look like they have come from the CEO or the IT manager. They may not contain any visual clues that they are fake.
3. Distributed DoS attacks
Distributed DoS attacks (DDoS) are a type of cybercrime attack that cybercriminals use to bring down a system or network. Sometimes connected IoT (Internet of Things) devices are used to launch DDoS attacks.
A DDoS attack overwhelms a system by using one of the standard communication protocols it uses to spam the system with connection requests. Cybercriminals who are carrying out cyberextortion may use the threat of a DDoS attack to demand money. Alternatively, a DDoS may be used as a distraction tactic while another type of cybercrime takes place.
A famous example of this type of attack is the 2017 DDoS attack on the UK National Lottery website . This brought the lottery’s website and mobile app offline, preventing UK citizens from playing. The reason behind the attack remains unknown, however, it is suspected that the attack was an attempt to blackmail the National Lottery.

Impact of cybercrime
Generally, cybercrime is on the rise. According to Accenture’s State of Cybersecurity Resilience 2021 report , security attacks increased 31% from 2020 to 2021. The number of attacks per company increased from 206 to 270 year on year. Attacks on companies affect individuals too since many of them store sensitive data and personal information from customers.
A single attack – whether it’s a data breach, malware, ransomware or DDoS attack - costs companies of all sizes an average of $200,000, and many affected companies go out of business within six months of the attack, according to insurance company Hiscox .
Javelin Strategy & Research published an Identity Fraud Study in 2021 which found that identity fraud losses for the year totalled $56 billion.
For both individuals and companies, the impact of cybercrime can be profound – primarily financial damage, but also loss of trust and reputational damage.
How to report a cybercrime
If you need to report a cybercrime in India, you can find useful information on The Indian Express , where they provide useful tips and advice on how to report cybercrime.
Bangladesh:
For reporting a cybercrime in Bangladesh you can contact the Bangladesh Police . Bangladesh Police has a Cyber Crime Help Desk where victims can report the incident and seek assistance. The Dhaka Tribune also offers useful advice on how to file a report.
You can find information about how to report cybercrime in the UAE on this official website here .
File a report with the Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3) as soon as possible. Visit ic3.gov for more information.
Contact Action Fraud as soon as possible – find out more on their website here.
- How to protect yourself against cybercrime
Given its prevalence, you may be wondering how to stop cybercrime? Here are some sensible tips to protect your computer and your personal data from cybercrime:
1. Keep software and operating system updated
Keeping your software and operating system up to date ensures that you benefit from the latest security patches to protect your computer.
2. Use anti-virus software and keep it updated
Using anti-virus or a comprehensive internet security solution like Kaspersky Premium is a smart way to protect your system from attacks. Anti-virus software allows you to scan, detect and remove threats before they become a problem. Having this protection in place helps to protect your computer and your data from cybercrime, giving you piece of mind. Keep your antivirus updated to receive the best level of protection.
3. Use strong passwords
Be sure to use strong passwords that people will not guess and do not record them anywhere. Or use a reputable password manager to generate strong passwords randomly to make this easier.
4. Never open attachments in spam emails
A classic way that computers get infected by malware attacks and other forms of cybercrime is via email attachments in spam emails. Never open an attachment from a sender you do not know.
5. Do not click on links in spam emails or untrusted websites
Another way people become victims of cybercrime is by clicking on links in spam emails or other messages, or unfamiliar websites. Avoid doing this to stay safe online.
6. Do not give out personal information unless secure
Never give out personal data over the phone or via email unless you are completely sure the line or email is secure. Make certain that you are speaking to the person you think you are.
7. Contact companies directly about suspicious requests
If you are asked for personal information or data from a company who has called you, hang up. Call them back using the number on their official website to ensure you are speaking to them and not a cybercriminal. Ideally, use a different phone because cybercriminals can hold the line open. When you think you’ve re-dialed, they can pretend to be from the bank or other organization that you think you are speaking to.
8. Be mindful of which website URLs you visit
Keep an eye on the URLs you are clicking on. Do they look legitimate? Avoid clicking on links with unfamiliar or URLs that look like spam. If your internet security product includes functionality to secure online transactions, ensure it is enabled before carrying out financial transactions online.
9. Keep an eye on your bank statements
Spotting that you have become a victim of cybercrime quickly is important. Keep an eye on your bank statements and query any unfamiliar transactions with the bank. The bank can investigate whether they are fraudulent.
A good antivirus will protect you from the threat of cybercrime. Learn more about Kaspersky Premium.
Further reading:
- How to protect your data online by using a password manager
- What to do if you’ve been a victim of a phishing attack
- Ransomware protection: how to keep your data safe in 2024
Related videos:
Related articles
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
UPSC Coaching, Study Materials, and Mock Exams
Enroll in ClearIAS UPSC Coaching Join Now Log In
Call us: +91-9605741000
Cybercrime – Definition, Types, and Reporting
Last updated on March 11, 2024 by Alex Andrews George

Computers, mobile phones, and the internet have changed modern life. They provide us with many benefits.
However, information technology also makes us vulnerable to a wide range of threats. These threats may result in financial loss or damage to our reputation.
A minor lapse in managing our digital lives can open the door to cybercriminals. So it is extremely important to know how to prevent us from cybercrimes.
Table of Contents
What is cybercrime?
A Cybercrime is a crime involving computers and networks.
The computer may have been used in the execution of a crime or it may be the target.
Definition of Cyber Crime
Cybercrime may be defined as “Any unlawful act where computer or communication device or computer network is used to commit or facilitate the commission of a crime”.
Learn more from: ClearIAS Study Materials
Two Main Types of Cybercrimes
Most cybercrime falls under two main categories:
- Criminal activity that targets computers.
- Criminal activity that uses computers.
Cybercrime that targets computers often involves malware like viruses.
Cybercrime that uses computers to commit other crimes may involve using computers to spread malware, illegal information or illegal images.
List of Cybercrimes: Examples
Cybercrimes include monetary crimes as well as non-monetary offences. The crimes result in damage to persons, computers, or governments.
1. Child Pornography OR Child sexually abusive material (CSAM)
Child sexually abusive material (CSAM) refers to a material containing sexual images in any form, of a child who is abused or sexually exploited. Section 67 (B) of the IT Act states that “it is punishable for publishing or transmitting of material depicting children in the sexually explicit act, etc. in electronic form.
2. Cyber Bullying
A form of harassment or bullying inflicted through the use of electronic or communication devices such as computers, mobile phones, laptops, etc.
3. Cyber Stalking
Cyberstalking is the use of electronic communication by a person to follow a person, or attempts to contact a person to foster personal interaction repeatedly despite a clear indication of disinterest by such person; or monitors the internet, email or any other form of electronic communication commits the offence of stalking.
4. Cyber Grooming
Cyber Grooming is when a person builds an online relationship with a young person and tricks or pressures him/ her into doing a sexual act.
5. Online Job Fraud
Online Job Fraud is an attempt to defraud people who are in need of employment by giving them false hope/ promise of better employment with higher wages.
6. Online Sextortion
Online Sextortion occurs when someone threatens to distribute private and sensitive material using an electronic medium if he/ she doesn’t provide images of a sexual nature, sexual favours, or money.
7. Phishing
Phishing is a type of fraud that involves stealing personal information such as Customer ID, IPIN, Credit/Debit Card number, Card expiry date, CVV number, etc. through emails that appear to be from a legitimate source.
Vishing is an attempt where fraudsters try to seek personal information like Customer ID, Net Banking password, ATM PIN, OTP, Card expiry date, CVV etc. through a phone call.
9. Smishing
Smishing is a type of fraud that uses mobile phone text messages to lure victims into calling back on a fraudulent phone number, visiting fraudulent websites or downloading malicious content via phone or web.
10. Sexting
Sexting is an act of sending sexually explicit digital images, videos, text messages, or emails, usually by cell phone.
11. SIM Swap Scam
SIM Swap Scam occurs when fraudsters manage to get a new SIM card issued against a registered mobile number fraudulently through the mobile service provider. With the help of this new SIM card, they get One Time Password (OTP) and alerts, required for making financial transactions through the victim’s bank account. Getting a new SIM card against a registered mobile number fraudulently is known as SIM Swap.
12. Credit Card Fraud or Debit Card Fraud
Credit card (or debit card) fraud involves the unauthorized use of another’s credit or debit card information for the purpose of purchases or withdrawing funds from it.
13. Impersonation and identity theft
Impersonation and identity theft is an act of fraudulently or dishonestly making use of the electronic signature, password or any other unique identification feature of any other person.
14. Spamming
Spamming occurs when someone receives an unsolicited commercial message sent via email, SMS, MMS and any other similar electronic messaging media. They may try to persuade the recipient to buy a product or service, or visit a website where he can make purchases, or they may attempt to trick him/ her into divulging bank account or credit card details.
15. Ransomware
Ransomware is a type of computer malware that encrypts the files, storage media on communication devices like desktops, Laptops, Mobile phones etc., holding data/information as a hostage. The victim is asked to pay the demanded ransom to get his device decrypts
16. Viruses, Worms, and Trojans
A computer virus is a program written to enter your computer and damage/alter your files/data and replicate itself.
Worms are malicious programs that make copies of themselves again and again on the local drive, network shares, etc.
A Trojan horse is not a virus. It is a destructive program that looks like a genuine application. Unlike viruses, Trojan horses do not replicate themselves but they can be just as destructive. Trojans open a backdoor entry to your computer which gives malicious users/programs access to your system, allowing confidential and personal information to be theft.
17. Data Breach
A data breach is an incident in which information is accessed without authorization.
18. Denial of Services (DoS) attack
A denial of Services (DoS) attack is an attack intended for denying access to computer resources without the permission of the owner or any other person who is in charge of a computer, computer system or computer network.
A Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack is an attempt to make an online service unavailable by overwhelming it with traffic from multiple sources.
19. Website Defacement
Website Defacement is an attack intended to change the visual appearance of a website and/ or make it dysfunctional. The attacker may post indecent, hostile and obscene images, messages, videos, etc.
20. Cyber-Squatting
Cyber-Squatting is an act of registering, trafficking in or using a domain name with an intent to profit from the goodwill of a trademark belonging to someone else.
21. Pharming
Pharming is a cyber-attack aiming to redirect a website’s traffic to another, bogus website.
22. Cryptojacking
Cryptojacking is the unauthorized use of computing resources to mine cryptocurrencies.
23. Online Drug Trafficking
Online Drug Trafficking is a crime of selling, transporting, or illegally importing unlawful controlled substances, such as heroin, cocaine, marijuana, or other illegal drugs using electronic means.
24. Espionage
Espionage is the act or practice of obtaining data and information without the permission and knowledge of the owner.
How to file a Cybercrime complaint online in India?
A cybercrime complaint can be filed using the National Crime Reporting Portal of India .
Website link is – https://cybercrime.gov.in/
National Cyber Crime Reporting Portal of India
This portal is an initiative of the Government of India to facilitate victims/ complainants to report cybercrime complaints online.
This portal caters for all types of cybercrime complaints including complaints pertaining to
- online Child Pornography (CP),
- Child Sexual Abuse Material (CSAM),
- sexually explicit content such as Rape/Gang Rape (CP/RGR) content and
- other cybercrimes such as mobile crimes, online and social media crimes, online financial frauds, ransomware, hacking, cryptocurrency crimes and online cyber trafficking.
The portal also provides an option of reporting an anonymous complaint about reporting online Child Pornography (CP) or sexually explicit content such as Rape/Gang Rape (RGR) content.
Cybercrime Helpline Number
The Cyber Crime Helpline Number is 155260.
Indian Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-IN or ICERT)
The Indian Computer Emergency Response Team ( CERT-IN or ICERT ) is an office within the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology of the Government of India.
CERT-In is the national nodal agency for responding to computer security incidents as and when they occur. CERT-In is operational since January 2004.
CERT-In has been designated to serve as the national agency to perform the following functions in the area of cyber security:
- Collection, analysis and dissemination of information on cyber incidents.
- Forecast and alerts of cyber security incidents.
- Emergency measures for handling cyber security incidents.
- Coordination of cyber incident response activities.
- Issue guidelines, advisories, vulnerability notes and whitepapers relating to information security practices, procedures, prevention, response and reporting of cyber incidents.
- Such other functions relating to cyber security may be prescribed.
CERT-IN has overlapping responsibilities with other agencies such as National Critical Information Infrastructure Protection Centre (NCIIPC) .
Cyber Laws in India
Information Technology Act 2000 (IT Act 2000) is the main law connected with cyber security in India.
Indian Penal Code, 1860 is also used to book criminals connected with cybercrimes.
India also has a cyber security policy .
Read: eSIM: All you need to know

Take a Test: Analyse Your Progress
Aim IAS, IPS, or IFS?

About Alex Andrews George
Alex Andrews George is a mentor, author, and social entrepreneur. Alex is the founder of ClearIAS and one of the expert Civil Service Exam Trainers in India.
He is the author of many best-seller books like 'Important Judgments that transformed India' and 'Important Acts that transformed India'.
A trusted mentor and pioneer in online training , Alex's guidance, strategies, study-materials, and mock-exams have helped many aspirants to become IAS, IPS, and IFS officers.
Reader Interactions
December 4, 2021 at 12:15 pm
How can one enroll for the mains course
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Don’t lose out without playing the right game!
Follow the ClearIAS Prelims cum Mains (PCM) Integrated Approach.
Join ClearIAS PCM Course Now
UPSC Online Preparation
- Union Public Service Commission (UPSC)
- Indian Administrative Service (IAS)
- Indian Police Service (IPS)
- IAS Exam Eligibility
- UPSC Free Study Materials
- UPSC Exam Guidance
- UPSC Prelims Test Series
- UPSC Syllabus
- UPSC Online
- UPSC Prelims
- UPSC Interview
- UPSC Toppers
- UPSC Previous Year Qns
- UPSC Age Calculator
- UPSC Calendar 2024
- About ClearIAS
- ClearIAS Programs
- ClearIAS Fee Structure
- IAS Coaching
- UPSC Coaching
- UPSC Online Coaching
- ClearIAS Blog
- Important Updates
- Announcements
- Book Review
- ClearIAS App
- Work with us
- Advertise with us
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions
- Talk to Your Mentor
Featured on

and many more...

- All Lessons
- business english
- comprehension
- culture & tips
- expressions
- pronunciation
Learn English with the News: Cyber Crime
Test your understanding of this English lesson
107 comments.
Thanks Rebecca.
English is changing constantly especially with advent of high tech gadgets, not to mention the Internet. It is good to be familiar with all this vocabulary to understand current news related to cyber crimes.
Just one question Rebecca, does the term cybernaut exist?
What does it refer to?
Thanks a lot for this vocabulary lesson.
Correction: . . . with THE advent of . . .
Hi Dear friends i am new in this Group so i am kindly requested every one please help me in learning English I want to improve my English.
thanks from all you
I got 7 correct out of 9. Recently I have thought we should remain vigilant for fraud (especially my daughter). ‘Vigilant’ and ‘heist’ were my new words. Thank you, Rebecca :)
You were close to get the higher mark Happy04, but keep in mind that making mistakes help us learn more.
You see? I made a mistake:
“. . . you were close to get the highEST mark…”
I’ve learned from it!
There has to be ‘Like’ link for your comments, Regino.
Thank you, Regino. I will keep in mind :)
Thank you Rebecca! You gave us an information about cyber crime. We have to pay attention when we use the internet. I realized again that importance.
Cool video! Thanks!
Thanks Rebecca, I have received nice score from the first test.
thanks for this beautiful comment
Nice lesson i have learned many vocabulary … thanks Rebecca and do more lesson like this about different topics to improve our english ..we really appreciate that :)
In internet there are many kind of “frauds”. I think the worse are the ones that involve the sphere of emotions. Thanks Rebecca, very useful words!
thank you very much Rebecca.
very good lesson many thanks rebecca
very good lessonI think the worse are the ones that involve the sphere of emotions. many thanks rebecca
Thanks, Rebecca your clases are great. Do you know a web site where I can speak english and improve my pronunciation. Regards
Very well discussed, and I got it all!
good morning
Thanks Rebecca for Lesson.
from where i can get video lecture.
thnks Rebicca!!
Thanks Rebecca.:P
Hi Rebecca.thanks for ur great effort to teach us EN. May i ask you or your colleagues a favor? could you have a lesson about differences between these words?? i’m really confused Riot-Rally-Outcry and Revolt Thnak you in advance
Thanks for the idea. I will pass it on. All the best to you.
It’s the first time I’m writing you, because it’s a little time i’m studyng English online on my own without any help from nobody person. I’m listening and looking all the lesson of this site, but understanding all the tachers form me it’s difficult, anyway you’re the best teacher I’m able to understand better. Therefore I thank you for all my improvements I got in this period of time. Thanks Rebecca for your utility words. regards
Each engid lesson will help you in a different way and step by step you will certainly improve. You have a very good attitude towards learning and I’m sure that will help you reach your goal. My best wishes to you.
what ENGVID Rebecca?
Wonderful lesson, I always learn English by reading a newspapers online and listening to BBC radio. Thank you very much Rebecca for your helpful lessons.
Reading and listening to the news is an excellent way to improve your English. Good for you. I am sure you will pick up lots of useful, advanced vocabulary that way. My best wishes to you.
Thank you Rebecca! I live in California and last year in November when lots of credit card numbers were stolen from Target store, I was one of those people who used their credit card during those dates in one of these stores in California but thank God I luckily wasn’t affected. :) When I heard about this at the news, I was scared. :( I went to my bank and reported and they changed my credit card number right away.
Thank you teacher,it’s very intrestingi got new vocabularies,and new cotexts.
It is a good job for me. I got 9 correct out of 9 The first time I have got 100 % Thank you Rebecca. I would like to practiec speak english more. please anyone add me :Skype is ukrit_2011 Thanks for all
Congratulations! Keep watching and you will definitely improve. All the best.
Quite nice lesson. Thank you.
Thank you Rebecca. I always learn something new. I got 8 out of 9.
thank you teacher i got 7/9 it’s not bad i think
useful lesson 6/9 thanks
thank you miss rebecca………. got 9 out of nine……… thanks again….
Good for building up vocabulary.
9/9 In this case, the hackers target, was the target himself. Hohoho Christmas time.
Haha. Good one. All the best to you, Jorge.
i love lesson
if we can learn for skype then more
Thanks a lot.
thanks rebeca
really useful! many thanks
you’re something else rebecca
It is very easy quiz
Thank you so much, Rebecca.
thanks rebecca
Thank you very much , personally I like your lesson and you are great teacher.
Although I got 9correct out of 9,,I didn’t understand many words or it’s just very difficult to me and I didn’t get the explaining!!! I have not enjoyed with the lesson :/
Thanks Rebecca, I got all right . I really appreciate this lesson.
Thanks so much this lesson . This very helpful , for me . ^^
I like it. Keep it up
Interesting! Very well explained. Thank you.
Thanks for the lesson!
Thanks to all of you for your feedback. It really helps us to hear from you. I admire your desire to improve and being here and watching these lessons proves that you are serious about improving. I really wish you all the best.
Thanks, my nice pedagog, I got 89% without watching the lesson.
Oh! Thank you so much. It’s really helpful for me. :)
EXCELENT ! Thanks Thanks Thanks.
100% Excelent!!!!
thank you so much Rebecca.
Thank you, Rebecca.
Awsome video Rabecca
i got 8 correct out of nine.my new words were heist, breach,vigilant and fraud. Thanks Rebbeca
I got 8 correct out of 9. thanks a lot. You are a brilliant teacher
it is useful vocabulary ,thanks Rebecca…
THANK YOU FOR YOUR LESSON!
Dear Rebecca, You remind us that, by studying the news everyday, we can reach our target : to improve our English. Best regards.
Like this one. Thahk you again.
yes; I do it; 10 correct out of 10. Thanks teacher.
It is very useful lesson. Thanks Rebecca.
your lesson is very clerarly. thank you rebecca
Thank you Rebeca…you are awesome!
Thank you so much, teacher! I liked how you took the information from the paragraph, :) See you later!
9/9. thank u
Hello everybody! does anyone want to improve speaking english skills by skype? lets help each other :) (my skype: master_serg555)
Excellent ! How attractive ! These vocabularies are wonderful. Thanks a lot. Please go on this way !
Thank you ,i really like the way you teach and it helps me a lot
thanx my dear teacher … but would u please make more lessons on this topic i.e the language that’s spoken or written in the news ..
thank you so much Rebeca . it’s very useful of private tuition we can not forget you’re own efforts . I’m pleasure withe and feeling provided myself to the ward of success .
Hello, Rebecca! Thank you for your lesson! Could you explain the difference between report and alert? Thank you!
I really appreciate your help
watch the lesson 3 times then i got to know the mean,thanks Rebecca
What cyber means
It means having to do with the Internet or computers. Some other examples: cyberbullying means bullying done over the Internet; cyberpunk is a genre of science fiction.
9 out of 9 Very good lesson long ago I was looking for a lesson like this, since I used to watch CNN News and many times I didn’t understand the terms, I would like to watch much more videos like these, thanks anyhow Rebecca. You’re awesome.
Somebody to practice speaking my skype:(+57 3217502267)
I got 100%!
yes 9 out of 9 great video
You got 9 correct out of 9.
thanks a lot…
thank you very much Rebecca
Yes,thanks Rebecca.
Thank you 9of 9?
the cyber crimes are popular today, these crimes may have a political or military aims or just to steal info. and money like in payment card heist. information is very important in now days because all companies need it to deliver their advertisements to there target customers.
if there is a mistake in the above sentence please correct it to me
Thank you v.much! good style of giving information. but if you’d added some picters, or even some sort of moving pictures (flash for example) iy would be a revolution. thanks again!
Cyber security is required to get protected from cyber attacks. Stay safe
about engVid
Learn English for free with 2045 video lessons by experienced teachers. Classes cover English grammar, vocabulary, pronunciation, IELTS, TOEFL, and more. Join millions of English learners worldwide who are improving every day with engVid.
- 2-Intermediate
- Privacy Policy
© 2024 LearnVid Inc.
Key strategies for building cyber resilience in 2024

Cyber resilience is an essential approach for safeguarding digital assets. Image: Getty Images/iStockphoto
.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo{-webkit-transition:all 0.15s ease-out;transition:all 0.15s ease-out;cursor:pointer;-webkit-text-decoration:none;text-decoration:none;outline:none;color:inherit;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:hover,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-hover]{-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:focus,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-focus]{box-shadow:0 0 0 3px rgba(168,203,251,0.5);} Deryck Mitchelson
.chakra .wef-9dduvl{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-9dduvl{font-size:1.125rem;}} Explore and monitor how .chakra .wef-15eoq1r{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-size:1.25rem;color:#F7DB5E;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-15eoq1r{font-size:1.125rem;}} Cybersecurity is affecting economies, industries and global issues

.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;color:#2846F8;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{font-size:1.125rem;}} Get involved with our crowdsourced digital platform to deliver impact at scale
Stay up to date:, cybersecurity.
- Cyber threats are a not a matter of 'if' but 'when', making cyber resilience an essential approach for organizations to safeguard digital assets.
- Resilience is about being prepared for an inevitable cybersecurity breach and recognizing that every system has potential potential vulnerabilities.
- Here's why taking a proactive approach to cybersecurity can build resilience that addresses both today's threats and the challenges of tomorrow.
Cyber resilience is more than just a buzzword in the security industry; it is an essential approach to safeguarding digital assets in an era where cyber threats are not a matter of “if” but “when”.
According to Check Point’s 2024 Cyber Security Report , 2023 experienced a 90% increase in publicly extorted victims of ransomware attacks. Security is one thing, but resilience extends beyond the traditional defensive perimeter.
It encompasses the ability of an organization to maintain its core functions – not just in the face of attacks but also during recovery from them. It is about being prepared for the inevitable breach, and recognizing that every system, no matter how robust, has potential vulnerabilities.

About 4 in 10 (39%) of global businesses say they aren’t resilient enough to handle a sophisticated cyberattack, and as attack methods evolve and increasingly utilize artificial intelligence, the actual figure is likely to be much higher.
Some businesses may think they are well prepared if they have a secure perimeter, but resilience is less about the first line of defence, and more about how well businesses can absorb risk and cope with mounting threats. Fending off one attack does not equal resilience.
The essence of cyber resilience lies in its dual focus. On one hand, it involves fortifying operations against constant attacks, ensuring business continuity under what can be considered “normal” cyber warfare conditions.
Have you read?
Iot security: we are keeping consumers safe from cyber threats, how to rebuild trust after a cybersecurity breach.
On the other, it demands a robust strategy for post-breach scenarios. This means having a plan that goes beyond mere recovery, one that adapts and evolves in response to the incident. Such a strategy acknowledges that the digital landscape is a dynamic battlefield, where threats evolve and so must defences.
The role of leadership in cyber resilience
Leadership plays a pivotal role in shaping an organization's approach to cyber resilience. It's not just about having a technically sound cybersecurity team; it's about fostering a culture where cyber resilience is ingrained in every decision and action. This starts at the top, with board members and executives who don't just passively endorse cybersecurity strategies but actively engage with them.
Effective leaders understand that cybersecurity is not a siloed IT issue but a critical business function that impacts every aspect of the organization. They ensure that cybersecurity discussions are not relegated to the IT department alone but are a regular feature of boardroom conversations.
Moreover, leaders in this field recognize the importance of being proactive rather than reactive. They don't wait for an incident to occur to appreciate the value of a resilient cybersecurity posture. Instead, they invest in continuous education, staying abreast of emerging threats and adapting their strategies accordingly.
This proactive stance involves not only understanding the technicalities of cyber threats but also appreciating their potential business impact. By doing so, they can make informed decisions about where to allocate resources, how to develop their teams and when to implement new technologies or strategies, ensuring that the organization's cyber resilience is always a step ahead of potential threats.
Technological and human elements of cyber resilience
When it comes to resilience, technology and human expertise must work in tandem. While advanced technological solutions like AI and machine learning are indispensable in identifying and responding to threats swiftly, the human element remains irreplaceable.
This synergy is crucial; technology can provide the tools and automation necessary for efficient threat detection and response, but it is the human insight that contextualizes and interprets these threats within the unique framework of each organization. Staff training, capacity management and a keen understanding of the organization's specific risk landscape are as vital as the technology deployed to protect it.
AI and cybersecurity: How to navigate the risks and opportunities
What does 2024 have in store for the world of cybersecurity?
The human aspect also extends to fostering a security-aware culture within the organization. This involves regular training and awareness programmes to ensure that all employees, not just the IT staff, understand the role they play in maintaining cybersecurity.
Overall, it's about creating an environment where cybersecurity is everyone's responsibility, and where employees are equipped to recognize and report potential threats. Such an approach not only strengthens the organization's defence against external threats but also helps in mitigating risks posed by insider threats, whether intentional or accidental.
Frameworks and strategies for enhanced resilience
Adopting comprehensive frameworks and strategies is also essential for building a robust cyber resilience infrastructure. Frameworks like NIST2 and MITRE offer structured approaches, guiding organizations through the complexities of cybersecurity and resilience.
In the US, the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) provides comprehensive guidelines and frameworks for cybersecurity, including the widely recognized NIST Cybersecurity Framework . This framework offers a flexible approach to managing cybersecurity risks, emphasizing the importance of identifying, protecting, detecting, responding, and recovering from cyber incidents.
MITRE, on the other hand, is known for its MITRE ATT&CK framework , a globally accessible knowledge base of adversary tactics and techniques based on real-world observations. This framework is used as a foundation for the development of specific threat models and methodologies in the cybersecurity community, helping organizations to understand and prepare for potential attack scenarios.
Both frameworks help in identifying vulnerabilities, setting priorities and implementing measures that go beyond conventional defence mechanisms. They encourage a holistic view of cybersecurity, encompassing not just technical defences but also aspects like risk management, incident response and recovery strategies.
By aligning with such frameworks, organizations can develop a more nuanced understanding of their cybersecurity position, enabling them to anticipate, withstand, and recover from adverse cyber events more effectively. This strategic alignment ensures that cybersecurity efforts are not just about meeting compliance standards but are tailored to the specific needs and challenges of the organization, thereby enhancing overall resilience.
Futureproofing against emerging cyber threats
Safeguarding against emerging threats is a critical component of cyber resilience. This requires organizations to stay vigilant and adaptive, anticipating not just current threats but also preparing for future challenges.
The rise of sophisticated AI-driven attacks, for instance, necessitates a forward-thinking approach where defence mechanisms are continuously updated and refined. Organizations must also consider the broader geopolitical landscape, which can influence the nature and frequency of cyber threats.
The World Economic Forum's Centre for Cybersecurity at the forefront of addressing global cybersecurity challenges and making the digital world safer for everyone.
Our goal is to enable secure and resilient digital and technological advancements for both individuals and organizations. As an independent and impartial platform, the Centre brings together a diverse range of experts from public and private sectors. We focus on elevating cybersecurity as a key strategic priority and drive collaborative initiatives worldwide to respond effectively to the most pressing security threats in the digital realm.
Learn more about our impact:
- Cybersecurity training: In collaboration with Salesforce, Fortinet and the Global Cyber Alliance, we are providing free training to the next generation of cybersecurity experts . To date, we have trained more than 122,000 people worldwide.
- Cyber resilience: Working with more than 170 partners, our centre is playing a pivotal role in enhancing cyber resilience across multiple industries: oil and gas , electricity , manufacturing and aviation .
Want to know more about our centre’s impact or get involved? Contact us .
By integrating advanced technologies, continuous learning and strategic planning, organizations can develop a resilience posture that not only addresses today's threats but is also agile enough to adapt to the unknown challenges of tomorrow.
This proactive approach to cybersecurity ensures that organizations are not just responding to threats, but are always a step ahead, ready to counteract and mitigate the risks in this dynamic digital era.
Don't miss any update on this topic
Create a free account and access your personalized content collection with our latest publications and analyses.
License and Republishing
World Economic Forum articles may be republished in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International Public License, and in accordance with our Terms of Use.
The views expressed in this article are those of the author alone and not the World Economic Forum.
The Agenda .chakra .wef-n7bacu{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-weight:400;} Weekly
A weekly update of the most important issues driving the global agenda
.chakra .wef-1dtnjt5{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;} More on Cybersecurity .chakra .wef-17xejub{-webkit-flex:1;-ms-flex:1;flex:1;justify-self:stretch;-webkit-align-self:stretch;-ms-flex-item-align:stretch;align-self:stretch;} .chakra .wef-nr1rr4{display:-webkit-inline-box;display:-webkit-inline-flex;display:-ms-inline-flexbox;display:inline-flex;white-space:normal;vertical-align:middle;text-transform:uppercase;font-size:0.75rem;border-radius:0.25rem;font-weight:700;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;line-height:1.2;-webkit-letter-spacing:1.25px;-moz-letter-spacing:1.25px;-ms-letter-spacing:1.25px;letter-spacing:1.25px;background:none;padding:0px;color:#B3B3B3;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;box-decoration-break:clone;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;}@media screen and (min-width:37.5rem){.chakra .wef-nr1rr4{font-size:0.875rem;}}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-nr1rr4{font-size:1rem;}} See all

China outlines new plans for industrial cybersecurity - and other cybersecurity news to know this month
Akshay Joshi
March 21, 2024

3 trends set to drive cyberattacks and ransomware in 2024
Scott Sayce
February 22, 2024

'Operation Cronos' seizes major cybercrime group – and other cybersecurity news to know this month
February 21, 2024

LockBit: How an international operation seized control of ‘the world’s most harmful cybercrime group’
Kate Whiting

How to secure the modern cyber supply chain and surge in third-party risks amid AI automation
Anna Sarnek
February 19, 2024

Aleksandr Yampolskiy
February 15, 2024
- Mobile Site
- Staff Directory
- Advertise with Ars
Filter by topic
- Biz & IT
- Gaming & Culture
Front page layout
2023 Exchange breach —
Microsoft blamed for “a cascade of security failures” in exchange breach report, summer 2023 intrusion pinned to corporate culture, "avoidable errors.".
Kevin Purdy - Apr 3, 2024 6:51 pm UTC

A federal Cyber Safety Review Board has issued its report on what led to last summer's capture of hundreds of thousands of emails by Chinese hackers from cloud customers, including federal agencies. It cites "a cascade of security failures at Microsoft" and finds that "Microsoft's security culture was inadequate" and needs to adjust to a "new normal" of cloud provider targeting.
The report , mandated by President Biden in the wake of the far-reaching intrusion, details the steps that Microsoft took before, during, and after the breach and in each case finds critical failure. The breach was "preventable," even though it cites Microsoft as not knowing precisely how Storm-0558, a "hacking group assessed to be affiliated with the People's Republic of China," got in.
"Throughout this review, the board identified a series of Microsoft operational and strategic decisions that collectively points to a corporate culture that deprioritized both enterprise security investments and rigorous risk management," the report reads.
The report notes that Microsoft "fully cooperated with the Board's review." A Microsoft spokesperson issued a statement regarding the report. " We appreciate the work of the CSRB to investigate the impact of well-resourced nation state threat actors who operate continuously and without meaningful deterrence," the statement reads. "As we announced in our Secure Future Initiative , recent events have demonstrated a need to adopt a new culture of engineering security in our own networks ." Along with hardening its systems and implementing more sensors and logs to "detect and repel the cyber-armies of our adversaries," Microsoft said it would "review the final report for additional recommendations."
“Inaccurate public statements” and unsolved mysteries
The Cyber Safety Review Board (CSRB), formed two years ago, is composed of government and industry officials, from entities including the Departments of Homeland Security, Justice, and Defense, the NSA, FBI, and others. Microsoft provides cloud-based services, including Exchange and Azure, to numerous government agencies, including consulates.
Further Reading
Congress and government agencies called on Microsoft to offer far more disclosure , and others, including Tenable's CEO, offered even harsher assessments . In September, the company met them partway. It was an engineer's account that was hacked , Microsoft claimed, giving attackers access to a supposedly locked-down workstation, the consumer signing key, and, crucially, access to crash dumps moved into a debugging environment. A "race condition" prevented a mechanism that strips out signing keys and other sensitive data from crash dumps from functioning. Furthermore, "human errors" allowed for an expired signing key to be used in forging tokens for modern enterprise offerings.
Those kinds of unrevealing, withholding public statements were cited by the CSRB in its finding of Microsoft's failures. The report cites "Microsoft’s decision not to correct, in a timely manner, its inaccurate public statements about this incident, including a corporate statement that Microsoft believed it had determined the likely root cause of the intrusion when in fact, it still has not." It also notes that Microsoft did not update its September 2023 blog post about the invasion cause until March 2024, "as the Board was concluding its review and only after the Board’s repeated questioning about Microsoft’s plans to issue a correction." (The updated blog post notes that Microsoft has "not found a crash dump containing the impacted key material.")
reader comments
Channel ars technica.
Special Features
Vendor voice.
World's second-largest eyeglass lens-maker blinded by infosec incident
Japan's hoya also makes components for chips, displays, and hard disks, and has spent four days groping for a fix.
If ever there was an incident that brings the need for good infosec into sharp focus, this is the one: Japan's Hoya – a maker of eyeglass and contact lenses, plus kit used to make semiconductor manufacturing, flat panel displays, and hard disk drives – has halted some production and sales activity after experiencing an attack on its IT systems.
The official view of what happened is blurry. On April 1 the optics conglomerate advised that its Tokyo HQ and several business units had "experienced an IT system incident."
A Thursday update [PDF] told a darker story.
"In the morning of March 30, 2024, we discovered a discrepancy in system behavior at one of our overseas offices and confirmed that a system failure had occurred," the update opens.
Compromised kit was isolated, forensic specialists hired, and the corporation has promised it "will take measures to restore the systems necessary for production and sales activities and to resume the supply system of products to customers as soon as possible."
Hoya currently has no insight into whether "confidential or personal information held by the Company has been compromised or accessed by third parties" and warned that "full analysis is expected to take a considerable number of days."
Note that the statement doesn't offer an estimate for remediation or restoration.
- Execs in Japan busted for winning dev bids then outsourcing to North Koreans
Simulation reveals all Japanese will have the same surname by 2531
- Japan's NTT and NEC reckon they can boost optical network capacities 12x
- Toyota admits its engines are overrated – by its own power testing software
The business also had mixed news for investors.
"The impact of this matter on our business performance is not known at this time, but we will promptly disclose the impact of this matter on our business performance, if any, as soon as it arises," its Thursday statement reads.
The value of Hoya shares has fallen five percent this week.
It is unclear which facilities are impacted by this incident, and which supply chains may be disrupted. Hoya's Japanese consumer business, Vision Care, on Tuesday apologised for disruptions to deliveries.
Hoya joins fellow Japanese entities NTT , LINE , Fujitsu , and space agency JAXA on the list of recently compromised outfits. ®
Narrower topics
- Advanced persistent threat
- Application Delivery Controller
- Authentication
- Common Vulnerability Scoring System
- Cybersecurity
- Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency
- Cybersecurity Information Sharing Act
- Data Breach
- Data Protection
- Digital certificate
- Identity Theft
- Incident response
- Kenna Security
- Palo Alto Networks
- Quantum key distribution
- Remote Access Trojan
- RSA Conference
- Surveillance
- Trusted Platform Module
- Vulnerability
Broader topics
Send us news
Other stories you might like
Us government excoriates microsoft for 'avoidable errors' but keeps paying for its products, microsoft slammed for lax security that led to china's cyber-raid on exchange online, a different view from the edge.
Malicious xz backdoor reveals fragility of open source
Rust developers at google are twice as productive as c++ teams, us critical infrastructure cyberattack reporting rules inch closer to reality, feds finally decide to do something about years-old ss7 spy holes in phone networks, feds probe alleged classified us govt data theft and leak, apple's gofetch silicon security fail was down to an obsession with speed, rubrik files to go public following alliance with microsoft, nearly 1m medical records feared stolen from city of hope cancer centers.
- Advertise with us
Our Websites
- The Next Platform
- Blocks and Files
Your Privacy
- Cookies Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Ts & Cs

Copyright. All rights reserved © 1998–2024

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Types of cybercrime. Cybercrime ranges across a spectrum of activities. At one end are crimes that involve fundamental breaches of personal or corporate privacy, such as assaults on the integrity of information held in digital depositories and the use of illegally obtained digital information to harass, harm, or blackmail a firm or individual. These new cybercapabilities have caused intense ...
116 CyberCrime Topics & Essay Samples. Updated: Mar 2nd, 2024. 9 min. If you are writing a cybercrime essay, our team prepared this article just for you. Here, you will find 115 unique topics for any type of paper. We will write. a custom essay specifically for you by our professional experts. 809 writers online.
500 Words Essay on Cyber Crime. Cybercrime is a type of crime in which illegal activities are carried out online or using computers. Cybercrime comes in a variety of forms which involves harassing online users. Cybercrime is the most serious and rapidly expanding type of crime in this day and age. Any person's life may be negatively impacted ...
The 1s and 0s behind cyber warfare. Chris Domas is a cybersecurity researcher, operating on what's become a new front of war, "cyber." In this engaging talk, he shows how researchers use pattern recognition and reverse engineering (and pull a few all-nighters) to understand a chunk of binary code whose purpose and contents they don't know.
Cybercrime is criminal activity that either targets or uses a computer, a computer network or a networked device. Most cybercrime is committed by cybercriminals or hackers who want to make money. However, occasionally cybercrime aims to damage computers or networks for reasons other than profit. These could be political or personal.
Cybercrime encompasses a wide range of criminal activities that are carried out using digital devices and/or networks. These crimes involve the use of technology to commit fraud, identity theft, data breaches, computer viruses, scams, and expanded upon in other malicious acts. Cybercriminals exploit vulnerabilities in computer systems and ...
Cybercrime is a type of criminal activity that involves the use of computers and the Internet . It represents the perpetuation of previous criminal activities in the digital age, as well as novel illicit behaviors that became possible with the advance of technology. What this means is that the type of criminal behavior associated with ...
Cybercrime. Cybercrime is an evolving form of transnational crime. The complex nature of the crime as one that takes place in the border-less realm of cyberspace is compounded by the increasing involvement of organized crime groups. Perpetrators of cybercrime and their victims can be located in different regions, and its effects can ripple ...
500+ Words Essay on Cyber Crime. Cyber Crime Essay- Everybody thinks that only stealing someone's private data is Cyber Crime.But in defining terms we can say that 'Cyber Crime refers to the use of an electronic device (computer, laptop, etc.) for stealing someone's data or trying to harm them using a computer.
There are 4 modules in this course. This course introduces fundamental notions of cybercrime. Namely, what cybercrime is, the main questions surrounding cybercrime, how cybercrime can be defined, and how it can be studied. You will learn about the difficulties in measuring the occurrence, the frequency and the impact of cybercrime, and build a ...
The UK now has around 1.25 million "infected" computers. And the average number of PCs across the world sending out spam emails every month shot up to 10 million last year, more than double the 4.2 million in 2006, which was double the 2.1 million in 2005. Cyber crime has become a multi-billion-pound, international criminal, industry including ...
In this view, students must have information on cyber crime and stay prepared to tackle such topics in the essay question in the English paper. Introduction. Cybercrime is a dangerous attack a company or an individual may face. There are many cases where the cyber attack has brought massive loss to the company and individuals due to the data ...
The ways in which cyber crime is evolving include: Higher damages: Cyber attacks are becoming more damaging to their victims in terms of financial, legal, and reputational risk. Greater sophistication: Criminals can leverage new technologies and exploit new vulnerabilities, allowing for more sophisticated attacks.
50 Latest Cyber crime IELTS Topics. Get a band score and detailed report instantly. Check your IELTS essays right now! Many people today worried about cyber crime . Cause and solution discuss. In many countries, paying for things using mobile phone apps is becoming increasingly common.
Introduction. Online fraud involves using the internet to trick someone into giving away their money or data and takes many forms. It is regarded by some as a highly profitable and relatively low ...
The articles included in this issue reflect three broad areas of cybercrime research: cybercrime victimization, cybercrime perpetration, and techniques and facilitators of cybercrime. While there is some overlap, the issue includes three papers focused on each of these three areas. The first area covered in the special issue focuses on ...
Long and Short Essays on Cyber Crime for Students and Kids in English. We are providing students with essay samples on an extended essay of 500 words and a short piece of 150 words on the topic Cyber Crime for reference. Long Essay on Cyber Crime 500 Words in English. Long Essay on Cyber Crime is usually given to classes 7, 8, 9, and 10.
Cybercrime is criminal activity that either targets or uses a computer, a computer network or a networked device. Most cybercrime is committed by cybercriminals or hackers who want to make money. However, occasionally cybercrime aims to damage computers or networks for reasons other than profit. These could be political or personal.
Although it is universally agreed that cybercrime exists, there is no universal definition of what it means (Holt and Bossler, 2014; Kshetri, 2010; Wall, 2017a).Terms including cybercrime, cyber-crime, computer crime, cloud-crime and computer misuse are often used interchangeably and can refer to any internet- or computer-related criminal activity (Goodman and Brenner, 2002).
Cryptojacking is the unauthorized use of computing resources to mine cryptocurrencies. 23. Online Drug Trafficking. Online Drug Trafficking is a crime of selling, transporting, or illegally importing unlawful controlled substances, such as heroin, cocaine, marijuana, or other illegal drugs using electronic means.
Whats a security breach, cyber heist, or identity theft? Learn the modern vocabulary of crime with this essential English News lesson. Find out how cyber criminals affected 70 million customers, what problems they caused, and how to protect yourself. Understanding this English vocabulary and these dangers can help keep you safer in todays world.
Cyber threats are a not a matter of 'if' but 'when', making cyber resilience an essential approach for organizations to safeguard digital assets. Resilience is about being prepared for an inevitable cybersecurity breach and recognizing that every system has potential potential vulnerabilities.
The Cyber Safety Review Board (CSRB), formed two years ago, is composed of government and industry officials, from entities including the Departments of Homeland Security, Justice, and Defense ...
Microsoft made that promise last year after its shoddy security practices allowed Chinese cyber spies to compromise tens of thousands of email accounts belonging to government officials. Washington's Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency's Cyber Safety Review Board (CSRB) this week lashed Redmond for a "cascade" of "avoidable errors ...
The seven suspected members of APT31 charged by the United States on Monday are: Ni Gaobin, 38; Weng Ming, 37; Cheng Feng, 34; Peng Yaowen, 38; Sun Xiaohui, 38; Xiong Wang, 35; and Zhao Guangzong, 38. Gaobin and Guangzong were the pair sanctioned by the UK and US regarding Wuhan Xiaoruizhi. All are believed to reside in the People's Republic of China, so there's a slim-to-zero chance of them ...
To facilitate adoption of the CRA provisions, these requirements need to be translated into the form of harmonised standards, with which manufacturers can comply. In support of the standardisation effort, this study attempt to identify the most relevant existing cybersecurity standards for each CRA requirement, analyses the coverage already offered on the intended scope of the requirement and ...
Topics. Security Security. All Security Cyber-crime Patches Research CSO. Off-Prem Off-Prem. All Off-Prem Edge + IoT Channel PaaS + IaaS SaaS. On-Prem ... Cyber-crime 5 Apr 2024 | 18. Microsoft slammed for lax security that led to China's cyber-raid on Exchange Online. CISA calls for 'fundamental, security-focused reforms' to happen ASAP ...