Home — Essay Samples — Social Issues — Child Labour — The Pros And Cons Of Child Labor In The Globalized World

The Pros and Cons of Child Labor in The Globalized World
- Categories: Child Labour Slavery in The World
About this sample

Words: 1062 |
Published: Dec 16, 2021
Words: 1062 | Pages: 2 | 6 min read
Table of contents
Introduction, disadvantages and advantages of child labor.
- Reduced Industrial Actions
- Working Children Help to Support their Families
- Child Labor Helps Children to Become Independent and Mature Fast
- Exploitation and Mistreatment
- Growth in Illegal Businesses
- Child Labor Denies Children an Opportunity to Exploit their Potentials
- Hazardous Working Environments Exposes Children to Health Risks

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Prof. Kifaru
Verified writer
- Expert in: Social Issues History

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
6 pages / 2775 words
1 pages / 557 words
2 pages / 1011 words
1 pages / 484 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online

Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Child Labour
Introduction to child labor as a significant issue Mention of childhood as an important period of learning and development Introduction to the argumentative essay on child labor Prevalence of child labor in [...]
Sook, E. (2014). Child labor in cocoa production: Assessment across countries. The Review of International Organizations, 9(3), 387-413.Wickramasinghe, D. (2016). Environmental and social issues in cocoa production: An overview. [...]
Balzac, Honoré de. 'Behind every fortune there is a crime.' Famous Quotes Magazine.Mistrati, Miki. The Dark Side of Chocolate. Directed by Miki Mistrati.Nestlé. 'Corporate Responsibility and Sustainability.' Nestlé Annual [...]
The term forced labor is often associated with historical atrocities, but unfortunately, it remains a pervasive issue in the modern world. This essay delves into the complex and distressing phenomenon of forced labor, examining [...]
Child labour, a pervasive issue affecting millions of children worldwide, robs them of their basic rights, education, and the joys of childhood. This essay on how to stop child labour will delve into the intricate problem of [...]
Nike, should we Boycott? Did you know that Nike workers have the worst working conditions? According to Portland Business Journal Most factors owned by nike are held in Vietnam, and not surprisingly they make the lowest wages [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Ind Psychiatry J
- v.27(1); Jan-Jun 2018
Challenges and perspectives of child labor
Amir radfar.
College of Graduate Health Studies, A.T. Still University, Mesa, Arizona, USA
Seyed Ahmad Ahmadi Asgharzadeh
1 Faculty of Medicine, Babol University of Medical Sciences, Babol, Iran
Fernando Quesada
2 Department of Medicine, Universidad de El Salvador, San Salvador, El Salvador
Irina Filip
3 Department of Psychiatry, Kaiser Permanente, Fontana, California, USA
Child labor is one of the oldest problems in our society and still an ongoing issue. During the time, child labor evolved from working in agriculture or small handicraft workshops to being forced into work in factories in the urban setting as a result of the industrial revolution. Children were very profitable assets since their pay was very low, were less likely to strike, and were easy to be manipulated. Socioeconomic disparities and lack of access to education are among others contributing to the child labor. Religious and cultural beliefs can be misguiding and concealing in delineating the limits of child labor. Child labor prevents physical, intellectual, and emotional development of children. To date, there is no international agreement to fully enforced child labor. This public health issue demands a multidisciplinary approach from the education of children and their families to development of comprehensive child labor laws and regulations.
INTRODUCTION AND HISTORICAL FACTS
Child labor is an old problem well rooted in human history. Children were exploited to various extents during different periods of time. The problem was common in poor and developing countries. In the 1800's, child labor was part of economic life and industrial growth. Children less than 14 years old worked in agriculture, factories, mining, and as street vendors.[ 1 ] Children from poor families were expected to participate to the family income, and sometimes they worked in dangerous conditions in 12-hour shifts.[ 1 ]
In the 1900's, in England, more than a quarter of poor families lost their children to diseases and death, endangering their extra financial support.[ 1 ] Boys worked in glass factories in high heat in three shifts because the furnaces were kept fired all the time to increase productivity, while girls were forced into prostitution. In 1910, it was estimated that more than two million children in the United States were working.[ 1 ]
With the increase of education, economy, and the emergence of labor laws, child labor decreased. However, child labor is still a widespread problem in many parts of the world in developed and developing countries. With the development of agriculture, children were again forced to be employed mostly by the families rather than factories. The main cause of child labor is the lack of schools and poverty.[ 2 ]
Per International Labor Organization (ILO, 2002), in the world, there are 211 million children laborers, 73 million under 10 years of age, 126 million children work in the worst forms of child labor, and more than 8 million are kept as slaves for domestic work, in trafficking, armed conflict, prostitution, and pornography. More than 20,000 children die yearly due to work-related accidents. Nearly, one-third of the world's children work in Africa.[ 3 ] Countries such as India have made efforts to tackle the worst forms of child labor. Despite this, 56.4% of children aged 5–14 work in agriculture and 33.1% work in industry.[ 4 ] Indian children are forced into labor to pay family debt. They work sometimes in hazardous environments, being forced into commercial sexual exploitation, human trafficking, or forcibly recruited or kidnapped to be part of terrorist groups.[ 4 ]
Child labor is morally and ethically unacceptable. United Nations Children's Fund (UNICEF) was the first international body that signed in 1989 the Convention on the Rights of the Children. It is for the first time in history when children are seen as humans with rights rather than economic assets of their parents. Child labor was defined as labor that harms the health of the children and deprives them of education rights. This law does not exclude children that work for their families.
ETHICAL FACETS OF CHILD LABOR
Child labor has many facets from the ethical point of view. Autonomy, beneficence, justice, nonmaleficence, privacy, and veracity are endangered during child labor.[ 5 ] Utilitarianists would support the idea of child labor as long as they are the sole providers for the family and without their income, the family would not survive and as long as the labor is voluntarily provided. The ends justify the means. Forced child labor is unethical because it is against the autonomy of the children. The consent of the working child is mostly manipulated by the parents. To give consent, a child needs to understand the situation, the consequences, and voluntarily agree to work. Children of young age, who have a less than fully competent capacity, can assent to an action by getting involved in the decision-making process. Children fall easy victims to unfair job conditions, and they do not have the power to stand-up against mistreatments.[ 6 ] The maleficence of this act has long-term physical, psychological, behavioral, and societal consequences. Even if they are lacking the competency of making informed decisions, they are considered individuals with autonomy that should be protected and safeguarded.[ 6 ]
Child labor is more common in developing countries where more than 90% of children live.[ 3 ] Child labor in developing countries affects 211 million children.[ 3 ] The continent with the highest child employment rate is Asia with 61%, followed by Africa and Latin America. Nearly 41% of the children in Africa are below 14 years old, followed by Asia with 22% and Latin America 17%.[ 3 ] India has made progress in reducing the child labor. However, more than 4 million children in India between 5 and 14 years old work more than 6 hours a day, while about 2 million children aged 5–14 work 3–6 months in a year.[ 4 ]
CULTURAL BELIEFS AND CHILD LABOR
Cultural beliefs have an important role in encouraging child labor. In developing countries, people believe that work has a constructive effect on character building and increases skill development in children. There is a tradition in these families, where children follow the parents' footsteps and learn the job from an early age. Some cultural beliefs may contribute to the misguided concept that a girl's education is not as important as a boy's education, and therefore, girls are pushed into child labor as providers of domestic services.[ 7 ] In India, not putting a child to work means the family would not make enough income to sustain their living. Sociocultural aspects such as the cast system, discrimination, and cultural biases against girls contribute to child labor.[ 4 ]
RELIGION AND CHILD LABOR
It is generally accepted that parents have the fundamental right to educate and raise their children. Parents almost always try to act in the child's best interest at the best of their knowledge and beliefs. In doing so, they are reasonably motivated by their intellectual growth, social development, and at times by spiritual salvation. Oftentimes, parents seek guidance in religion to shape the upbringing of their children and to enhance their progress. Hard work is among others, an important religious value to instill from a young age.
Krolikowski found that Christian children were the least likely to work, while Muslim children, children with no religion, and children affiliated with a traditional African religion were more likely to work than Christians.[ 8 ] The 40% higher incidence of child labor among Indian Muslims compared with Indian Hindus is due perhaps to the impoverishment of Muslim community.[ 4 ] Amish people's life is also regulated by religious values. They believe that work and faith bring people closer to God.[ 9 ] Amish children are initiated from childhood into apprenticeship to learn the trade, and beyond eighth grade, they have to provide like an adult for the community. Education of children beyond eighth grade is considered a threat to the community values. The U. S. labor laws forbid children less than 16 years of age to work in hazardous places such as sawmill or woodworking. However, in 2004 an exception was made by the United States Department of Labor, who approved an amendment that allows Amish children between 14 and 18 years old to work.[ 10 ]
POLICIES AND CHILD LABOR
Child labor is rooted in poverty, income insecurity, social injustice, lack of public services, and lack of political will.[ 7 ] Working children are deprived from a proper physical and mental development. The millennium development goals (MDGs), issued in 2001 to implement the Millennium Declaration, set up commitments for poverty reduction, education, and women's empowerment. Persistence of poverty is the major cause of labor. However, child labor also causes poverty because it deprives the children from education and from a normal physical and mental development hampering a prosperous life as adults. The first MDG in addressing poverty is the elimination of child labor.[ 11 ]
The International Program on the Elimination of Child Labor (IPEC) was created by ILO in 1992 to progressively eliminate child labor. The priority addresses the worst forms of child labor such as slavery, prostitution, drug trafficking, and recruitment of children in armed conflicts.[ 12 ] IPEC is working with stakeholders from many countries to increase strengths and promote the fight against child labor. IPEC engage with multiple organizations, international and governmental bodies, community-based organizations, religious groups, private plural form businesses, children and their families.
Policy reform was promoted through country-based programs. The capacity building of institutions has been increased to better understand the obstacles and increase the ability of obtaining sustainable measures. These measures were meant to decrease child labor and bring children back in schools. In all these processes, statistical data were collected at the worldwide level, methodologies were set in place, and guidelines were created.
The Child Labor Platform was created as a business-led initiative by ILO in 2012, to identify the obstacles of the implementation of ILO conventions at the community level and to come up with solutions. This platform is a win-win situation for all parties involved: stakeholders as well children and their families. This platform offers training, research, and specialized tools to member companies, so they can carry out activities against child labor. Eliminating child labor is part of the corporates' social responsibility in line with their values and is what the society expects from them. This platform provides information how to get involved and how to find businesses that work collaboratively with the communities to solve the problem. Training and knowledge is a real value added for companies.[ 12 ] The Indian Government implemented a national project deemed to assist population to eradicate child labor, and set in place enforcements of criminal and labor law.[ 4 ]
ARGUMENTS FAVORING CHILD LABOR
Despite all these international and national measures against child labor, there are arguments in favor of child labor. Some argue that poor families would be even poorer without the supplemental financial contribution of children. Lack of money will deprive them of the basic needs of food and shelter which will decrease their survival rate. In addition, an increase in poverty would make children even more susceptible to exploitation.
The supporters of these ideas argue that the benefit of creating a safe workplace and allowing children to work is helpful in certain situations. They also emphasize that child work is not child labor as long as it does not interfere with schooling and children have safe workplace conditions with a limited number of hours per day.[ 13 ]
STAKEHOLDERS’ ROLE AND CHILD LABOR
The stakeholders most directly affected are the children and their families. Children are working at the expense of their education and normal mental development. Education is important not only for the intellectual development but also for the empowerment and acquisition of new skills for adult life. The health of children is endangered by work in hazardous conditions, abuse, exhaustion, malnutrition, or exposure to toxic materials. The psychological harm leads to behavioral problems later on in life.[ 14 ]
Despite the implementation of laws and measurements at the international level, child labor still persists, and it is caused by the same factors as 100 years ago. There is a need to address poverty and access to education. To date, there is no international agreement to define child labor. Every country has different laws and regulations regarding the minimum age for starting working based on the type of labor. The lack of international consensus on child labor makes the limits of child labor very unclear.[ 15 ]
Therefore, it is mandatory to create international policies that adopt a holistic approach to free quality education for all children, including labor children from poor families. Education should be continued beyond the primary school level and should be done in a formal setting. Studies show that nonformal education is a necessary but not a sufficient prerequisite for permanently withdrawing children from work.[ 15 ] The public educational system should be expanded to accommodate laborer children who still do not have access to school. More schools should be built, more teachers should be trained, and more educational materials should be available. A special attention should be given to children living in exceptional geographical conditions and mobility should be provided at the cost of the community. Children who dropped out of school should receive adequate guidance and support, and a smooth reentry should be facilitated. The development of schools in the rural areas would decrease the load of children in urban schools. This will allow parents to accommodate children's needs without having to migrate in big cities.
Another phenomenon that should be addressed is the social exclusion. Children engaged in the worst forms of child labor come from the lowest strata of the society. International Labor Organization launched a project on Indigen and tribal people, who are the most targeted by social exclusion. This project promotes their rights and encourages building capacity among their community.[ 15 ] Proper enforcement of child labor policies and the focus on education can break the cycle of poverty that drives the children into labor.
Child labor is a public health issue with negative outcomes that demands special attention. A multidisciplinary approach is needed to tackle child labor issues. Per ILO, poverty is a major single cause behind child labor. Lack of affordable schools and affordable education is another major factor to force children to work. Certain cultural beliefs rationalize this practice and encourage child labor as character building and skill development for children. Some cultural traditions encourage child labor as footsteps to their parents' jobs. Socioeconomic disparities, poor governance, and poor implementation of international agreements are among major causes of child labor. Macroeconomic factors also encourage child labor by the growth of low pay informal economy. Child labor prevents the normal well-being including physical, intellectual, and emotional psychosocial development of children. This public health issue cannot be eliminated by only enforcement of child labor laws and regulations. Any comprehensive policies should engulf a holistic approach on the education of children and their families, investment in early childhood development programs, establishing public education task forces in rural areas, implementing policies with focus on increasing adult wages, and discouraging consumers to buy products made by forced child labor. As such, ethical practice requires protection of all rights of children and protective policies and procedures which support the provisions of ILO's standards.
Financial support and sponsorship
Conflicts of interest.
There are no conflicts of interest.
Acknowledgment
The authors wish to thank the University Writing Center at A.T. Still University for assistance with this manuscript.

- High contrast
- Press Centre
Search UNICEF
- Child labour
Nearly 1 in 10 children are subjected to child labour worldwide, with some forced into hazardous work through trafficking.

Economic hardship exacts a toll on millions of families worldwide – and in some places, it comes at the price of a child’s safety.
Roughly 160 million children were subjected to child labour at the beginning of 2020, with 9 million additional children at risk due to the impact of COVID-19. This accounts for nearly 1 in 10 children worldwide. Almost half of them are in hazardous work that directly endangers their health and development.
Children may be driven into work for various reasons. Most often, child labour occurs when families face financial challenges or uncertainty – whether due to poverty, sudden illness of a caregiver, or job loss of a primary wage earner.
The consequences are staggering. Child labour can result in extreme bodily and mental harm, and even death. It can lead to slavery and sexual or economic exploitation. And in nearly every case, it cuts children off from schooling and health care, restricting their fundamental rights.
Migrant and refugee children – many of whom have been uprooted by conflict, disaster or poverty – also risk being forced into work and even trafficked, especially if they are migrating alone or taking irregular routes with their families.
Trafficked children are often subjected to violence, abuse and other human rights violations. For girls, the threat of sexual exploitation looms large, while boys may be exploited by armed forces or groups .
Whatever the cause, child labour compounds social inequality and discrimination. Unlike activities that help children develop, such as contributing to light housework or taking on a job during school holidays, child labour limits access to education and harms a child’s physical, mental and social growth. Especially for girls, the “triple burden” of school, work and household chores heightens their risk of falling behind, making them even more vulnerable to poverty and exclusion.

UNICEF works to prevent and respond to child labour, especially by strengthening the social service workforce . Social service workers play a key role in recognizing, preventing and managing risks that can lead to child labour. Our efforts develop and support the workforce to respond to potential situations of child labour through case management and social protection services, including early identification, registration and interim rehabilitation and referral services.
We also focus on strengthening parenting and community education initiatives to address harmful social norms that perpetuate child labour, while partnering with national and local governments to prevent violence, exploitation and abuse.
With the International Labour Organization (ILO), we help to collect data that make child labour visible to decision makers. These efforts complement our work to strengthen birth registration systems, ensuring that all children possess birth certificates that prove they are under the legal age to work.
Children removed from labour must also be safely returned to school or training. UNICEF supports increased access to quality education and provides comprehensive social services to keep children protected and with their families.
To address child trafficking, we work with United Nations partners and the European Union on initiatives that reach 13 countries across Africa, Asia, Eastern Europe and Latin America.
Learn more about child labour

COVID-19 and child labour
A time of crisis, a time to act

Child labour and responsible business conduct
Guidance to businesses, policy makers and other stakeholders to advance progress towards SDG Target 8.7 on eradicating child labour by 2025
UNICEF Executive Director Catherine Russell's remarks at the World Day Against Child Labour High-Level Side Event

Charting the course
Embedding children's rights in responsible business conduct
Related resources
Unicef humanitarian practice: covid-19 technical guidance, child labour: global estimates 2020, trends and the road forward, child labour: unicef data, inter-agency coordination group against trafficking in persons, unicef child protection advocacy brief: child labour, iom handbook for protection and assistance for migrants vulnerable to violence, exploitation and abuse, guidelines to strengthen the social service workforce for child protection.
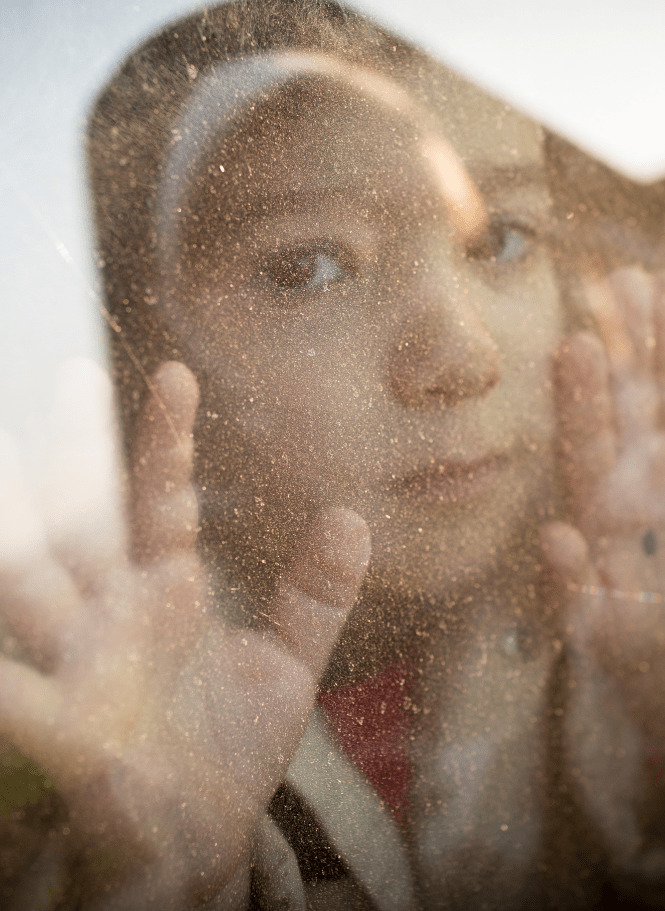

What is Child Labor?
Child labor is the exploitation of children through any form of work that deprives them of their childhood, interferes with their ability to attend regular schools, and is mentally, physically, socially, or morally harmful.
This global issue encompasses a wide range of tasks and activities that subject children to conditions that impede their well-being, hinder their development, and undermine their fundamental rights.
The term extends to situations where children are engaged in work that is dangerous, prevents them from accessing education, or involves excessive hours and labor that is detrimental to their physical and mental health.
- Child labor statistics
The global landscape of child labor is alarming, with an estimated 160 million children, comprising 63 million girls and 97 million boys, engaged in various forms of labor worldwide. Disturbingly, almost one in ten children globally is affected by this issue.
A significant concern is the hazardous work that nearly half of these children, totaling 79 million, are involved in, posing direct threats to their health, safety, and moral development.
Recent data from a report by the International Labour Organization (ILO) and UNICEF, published in June 2021, reveals a troubling increase of 8.4 million child laborers in the last four years, and an additional 9 million children are at risk due to the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic.
The age distribution is particularly concerning, with children aged 5 to 11 constituting 48% of all child laborers, emphasizing the vulnerability of the youngest demographic.
Although there was a notable reduction of 94 million child laborers between 2000 and 2016, progress has slowed in recent years. Regional disparities are evident, with Africa having the highest percentage (one-fifth) and the highest absolute number (92 million) of children in child labor.
The agricultural sector remains a significant contributor, accounting for 70% of all child labor cases, involving a staggering 112 million children. These statistics underscore the urgent need for global efforts to address child labor, safeguard children’s rights, and ensure their well-being and access to education.
- Forms of Child Labor
Child labor takes various forms, impacting millions of children globally. The notable forms include:
1. Slavery or Similar Practices:
Involves the ownership of individuals, treating them as property, and forcing them to work without any control over their circumstances. Slaves are often held against their will and lack the freedom to refuse work.
2. Child Trafficking:
The illegal trading of children involves activities such as buying, selling, and moving children for labor or sexual exploitation. Trafficked children may be coerced or forced into various forms of work against their will.
3. Forced Recruitment into Armed Conflict:
Children are compelled or coerced into participating in armed conflicts, serving in roles such as soldiers, scouts, cooks, guards, or messengers. This is a blatant violation of human rights law.
4. Prostitution and Pornography:
Exploitation of children for sexual purposes includes engaging them in prostitution or involving them in the production of pornographic material. This form of child labor exposes children to significant physical and psychological harm.
5. Drug Production and Trafficking or Other Illegal Acts:
Children are involved in the production and trafficking of drugs or engaged in other illegal activities. This often exposes them to dangerous conditions, addiction, and the risk of criminal repercussions.
6. Debt Bondage:
Forced labor where individuals or families work to pay off debts that cannot be settled with money or goods. Often, this creates a cycle of perpetual enslavement, especially when the debt-holder has no intention of lifting the debt.
7. Hazardous Work that Can Cause Injury or Moral Corruption:
Involves engaging children in work that poses risks to their health, safety, or morals. This could include physically demanding or dangerous work that interferes with their normal development.
8. Involvement in Illicit Activities:
Children may be exploited for various criminal activities, such as theft, burglary, drug production, and trafficking. Organized crime gangs can groom and exploit children, exposing them to addiction and other risks.
9. Agricultural Labor:
Child labor is concentrated in agriculture, with children engaged in farming, fishing, livestock, forestry, and aquaculture. Poverty often drives children into agricultural labor, and any work that interferes with schooling or harms their health is considered exploitation.
10. Mining:
Thousands of children globally work in mines, extracting materials like cobalt, salt, gold, and mica. Conditions in mines are often harsh, with long hours, exposure to toxic substances, and inadequate safety measures.
11. Factory Work:
Children may be exploited in factories where they face poor ventilation, exposure to toxic materials, and hazardous machinery. Instances of child labor have been reported in various industries, including meatpacking plants.
12. Domestic Work:
Involves various tasks and services within households. Exploitation occurs when children work at ages younger than legal limits, face hazardous conditions, or when their domestic work interferes with education. Domestic work exploitation is sometimes “hidden” as children are expected to contribute to the household.
These forms of child labor not only endanger the immediate well-being of children but also hinder their long-term development and perpetuate cycles of poverty.
- Causes of Child Labor
Child labor can be attributed to various factors, and experts highlight several key causes:
1. Poverty:
Poverty is identified as the primary force driving children into the workplace. Families facing economic hardships often resort to child labor as a means of supplementing household income.
2. Unhealthy Family Life and Economic Deprivation:
Challenging domestic situations, such as instability, domestic violence, or neglect, may lead families to involve their children in work for coping or survival.
3. Lack of Access to Quality Education:
Limited access to quality education, including barriers like school fees and uniform costs, contributes to low literacy rates and diminishes opportunities for children.
4. Poor Governance and Inadequate Implementation of International Agreements:
Ineffective governance, weak regulatory frameworks, and corruption create an environment where exploitative labor practices can persist. Inadequate implementation of international agreements against child labor further hampers progress.
5. Conflicts & Mass Migration:
Regions affected by conflicts and mass migration experience increased vulnerability to child labor due to economic instability, breakdown of social structures, and displacement of families.
6. Limited Economic Resources:
Families in poverty often view children as economic assets, compelling them to seek additional income streams through child labor.
7. Limited Understanding of Child Labor:
Cultural beliefs and social norms that view work as character-building may contribute to families not fully understanding the dangers of child labor.
8. Natural Disasters & Climate Change:
Rural families dependent on farming may send their children to work when crops are destroyed due to climate changes, contributing to economic struggles.
9. Lack of Funding for Education:
Insufficient funding for educational projects in various regions limits access to quality education, especially in conflict zones.
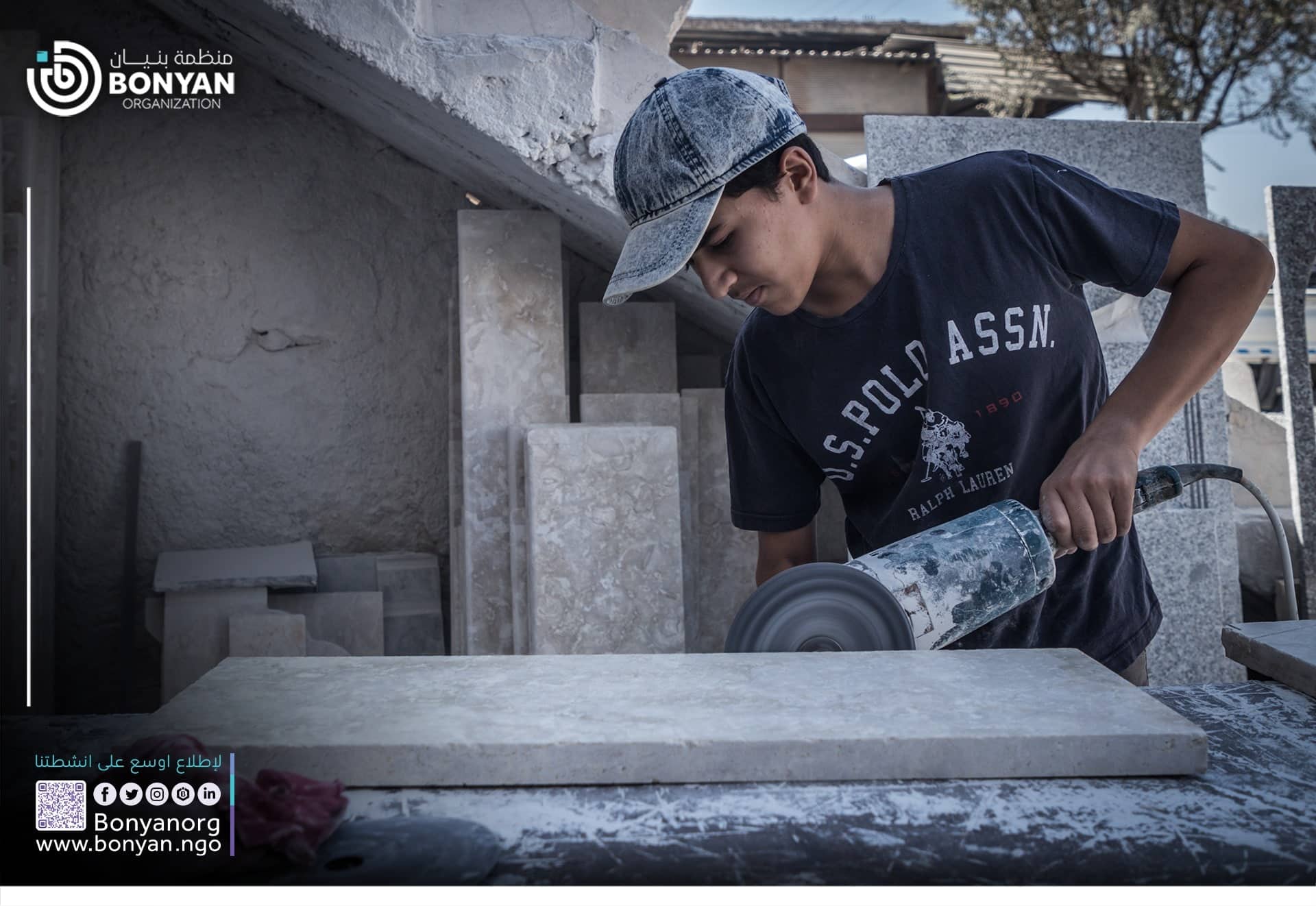

Effects of Child Labor
- Physical Effects
Malnutrition:
- Working children often face insufficient access to a balanced and nutritious diet.
- Inadequate nutrition can lead to stunted growth, weakness, and vulnerability to illnesses.
Exposure to Hazardous Conditions:
- In agriculture, children may handle toxic fertilizers and pesticides, posing risks to their respiratory and overall health.
- In mining, exposure to explosives and poisonous chemicals, coupled with the danger of mine collapses, increases the likelihood of severe injuries or fatalities.
Physical and Verbal Abuse:
- Child labor victims may endure physical abuse through harsh working conditions, leading to injuries such as cuts, bruises, and fractures.
- Verbal abuse can contribute to emotional trauma, affecting a child’s self-esteem and mental well-being.
- Mental Health Effects
Adverse Mental Health Outcomes:
- Children engaged in labor face the stress of adult responsibilities, leading to an increased risk of mental health issues.
- Hazardous work conditions can result in chronic stress, anxiety disorders, and long-term psychological consequences.
Destructive Habits:
- Coping mechanisms, such as smoking, alcoholism, or drug abuse, may arise as a response to the emotional and psychological stress of child labor.
- These habits further exacerbate health risks and can persist into adulthood.
Emotional and Relationship Difficulties:
- Exposure to abusive environments during child labor contributes to long-lasting emotional difficulties, including challenges in forming trusting and healthy relationships.
- Victims may struggle with self-esteem, hindering personal development.
- Long-term Consequences
Long-term Health Consequences:
- The physical toll of child labor may lead to chronic health conditions that persist into adulthood, affecting overall quality of life.
- Early exposure to hazardous substances can result in long-term health issues, such as respiratory diseases and neurological disorders.
- Societal Impact
Cycle of Poverty:
- Families trapped in the cycle of child labor may prioritize immediate income over investing in education, perpetuating a cycle of poverty.
- Lack of education limits future opportunities, reinforcing socio-economic disparities.
Hindrance to Social Development:
- The prevalence of child labor creates a workforce with limited skills and education, hindering a nation’s overall social and economic development.
- A less educated and skilled workforce may struggle to contribute effectively to technological advancements and economic growth.
Jeopardizing Community Well-being:
- Ignoring child labor jeopardizes the well-being of communities, as these children are not just the future but integral members of society today.
- Failure to address child labor weakens community bonds and resilience, as a significant portion of the population faces physical, mental, and socio-economic challenges.
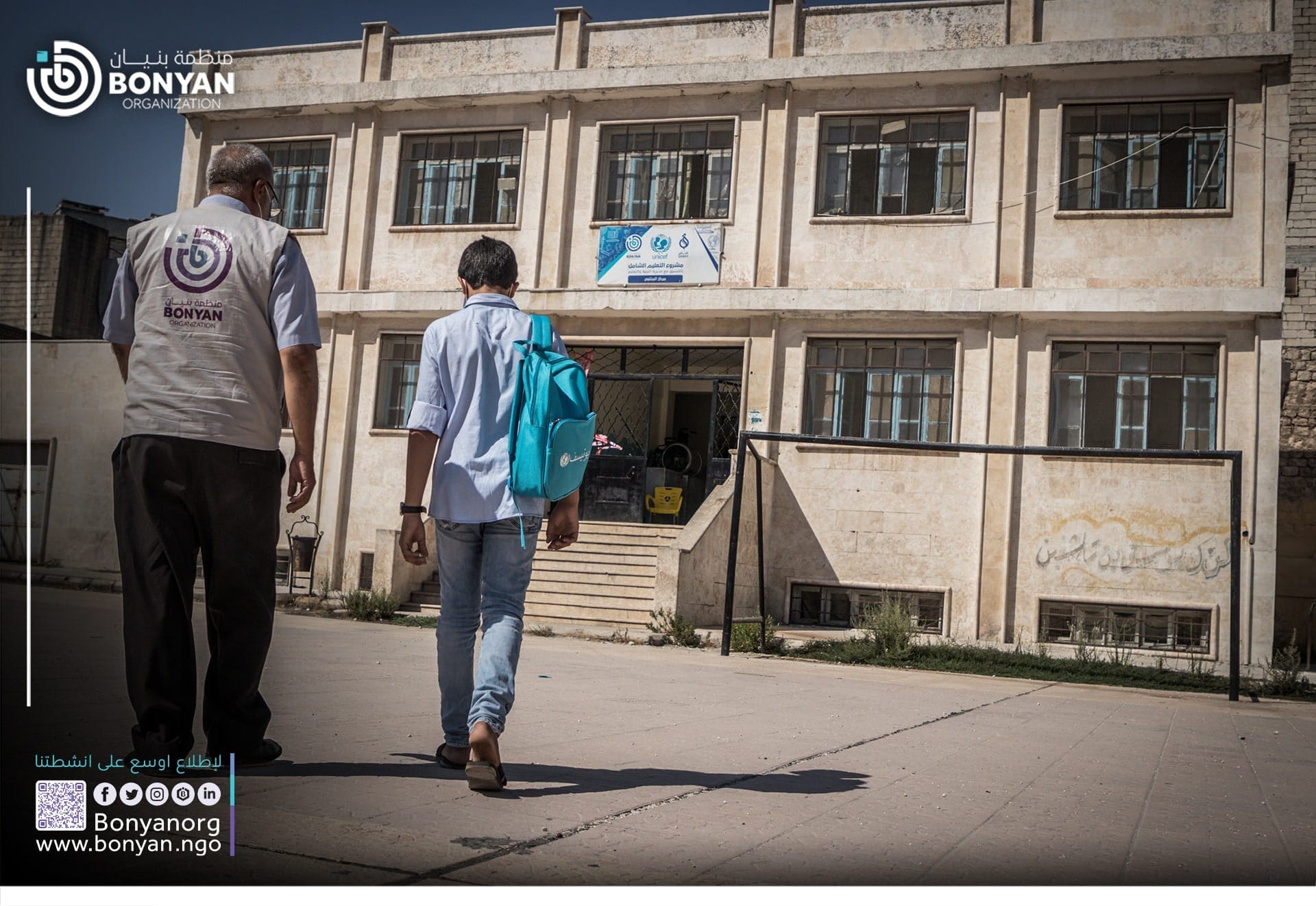

- How to stop child labor
Stopping child labor requires a multi-faceted and comprehensive approach:
1. Education :
Promote and improve accessibility, quantity, and quality of education to discourage child labor.
2. Awareness:
- Educate individuals about child labor issues.
- Engage with businesses to encourage responsible practices in supply chains.
3. Fair Trade Practices:
Support fair trade products and companies committed to ethical production.
4. Government and Civil Society Involvement:
- Advocate for strong government policies against child labor.
- Collaborate with civil society organizations to implement effective measures.
5. Living Wage:
Work towards paying a living wage to address poverty, a significant driver of child labor.
6. Discourage Employment of Children:
Sensitize trade organizations and discourage the employment of children in various settings.
7. Financial Support:
Contribute to reputable organizations working globally to protect children from labor and exploitation.
8. Child Sponsorship:
Sponsor a child to support their education and overall well-being.
9. Ethical Investments:
Assess the ethical impact of investments to discourage support for companies exploiting child labor.
10. Certification Initiatives:
Advocate for a universal labeling initiative certifying products free from child labor.
By combining these strategies, individuals, businesses, governments, and civil society can collectively work towards eradicating child labor and building a fair, just, and compassionate society.
- Bonyan Organization’s Efforts to End Child Labor
At Bonyan, we embark on a heartfelt mission to eliminate child labor, recognizing the profound impact it has on the lives of vulnerable children.
Our commitment extends across various initiatives designed to break the cycle of exploitation and provide meaningful alternatives. Through our education programs , we strive to empower refugee children with the invaluable gift of knowledge, redirecting their paths away from labor and towards a brighter future.
Our social empowerment endeavors aim to uplift entire communities, addressing the root causes that perpetuate child labor. Bonyan’s pioneering Early Recovery and Livelihood (ERL) Program serves as a catalyst for change, offering financial support, vocational training, and employment opportunities to alleviate economic pressures that often force children into labor.
We take pride in our holistic approach, seamlessly integrating education activities with our ERL Program , providing families with comprehensive support through vocational training and seed funds. As active contributors to policy development, we work tirelessly towards systemic changes that safeguard children from exploitative labor practices.
Donate to end child labor
Join Bonyan in our relentless pursuit to end child labor. Together, let’s create a world where every child is free to learn, dream, and thrive.
Stand with Bonyan. End Child Labor Today!

- WARMTH FOR SYRIA & PALESTINE: A CALL FROM HEART TO HEART

- Bright Futures, One Child at a Time

- Football for Peace with Bonyan
- Build Classrooms for Syrian Kids
- What is Meant by Child Labor?
Child labor is defined as work that denies children of their childhood, their potential, and their dignity.
- What are the root causes of child labor?
Root causes include poverty, lack of access to quality education, poor access to decent work, and limited understanding of child labor.
- How can child labor be addressed at its root?
Addressing the root cause of child labor involves tackling poverty. One effective strategy is to pay adult workers decent wages, enabling them to support their families without relying on child labor.
- What are The Problems of Child Labor?
Psychological and physical damage. Deprivation of education. Sexual exploitation. Child marriage. Begging and gangs that exploit children.
- What are the consequences of child labor?
Child labor can lead to extreme bodily and mental harm, slavery, and sexual or economic exploitation. In nearly every case, it deprives children of their childhood and fundamental rights.
- How can we combat child labor?
Strategies to combat child labor involve promoting education, raising awareness, supporting fair trade practices, advocating for government policies, and working towards paying living wages.
- Child Labour (ILO-Ankara)
Essay on Child Labour for Students and Children
500+ words essay on child labour.
Child labour is a term you might have heard about in news or movies. It refers to a crime where children are forced to work from a very early age. It is like expecting kids to perform responsibilities like working and fending for themselves. There are certain policies which have put restrictions and limitations on children working.

The average age for a child to be appropriate to work is considered fifteen years and more. Children falling below this age limit won’t be allowed to indulge in any type of work forcefully. Why is that so? Because child labour takes away the kids opportunity of having a normal childhood, a proper education , and physical and mental well-being. In some countries, it is illegal but still, it’s a far way from being completely eradicated.
Causes of Child Labour
Child Labour happens due to a number of reasons. While some of the reasons may be common in some countries, there are some reasons which are specific in particular areas and regions. When we look at what is causing child labour, we will be able to fight it better.
Firstly, it happens in countries that have a lot of poverty and unemployment . When the families won’t have enough earning, they put the children of the family to work so they can have enough money to survive. Similarly, if the adults of the family are unemployed, the younger ones have to work in their place.

Moreover, when people do not have access to the education they will ultimately put their children to work. The uneducated only care about a short term result which is why they put children to work so they can survive their present.
Furthermore, the money-saving attitude of various industries is a major cause of child labour. They hire children because they pay them lesser for the same work as an adult. As children work more than adults and also at fewer wages, they prefer children. They can easily influence and manipulate them. They only see their profit and this is why they engage children in factories.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Eradication of Child Labour
If we wish to eradicate child labour, we need to formulate some very effective solutions which will save our children. It will also enhance the future of any country dealing with these social issues . To begin with, one can create a number of unions that solely work to prevent child labour. It should help the children indulging in this work and punishing those who make them do it.
Furthermore, we need to keep the parents in the loop so as to teach them the importance of education. If we make education free and the people aware, we will be able to educate more and more children who won’t have to do child labour. Moreover, making people aware of the harmful consequences of child labour is a must.
In addition, family control measures must also be taken. This will reduce the family’s burden so when you have lesser mouths to feed, the parents will be enough to work for them, instead of the children. In fact, every family must be promised a minimum income by the government to survive.
In short, the government and people must come together. Employment opportunities must be given to people in abundance so they can earn their livelihood instead of putting their kids to work. The children are the future of our country; we cannot expect them to maintain the economic conditions of their families instead of having a normal childhood.
{ “@context”: “https://schema.org”, “@type”: “FAQPage”, “mainEntity”: [{ “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “What causes child labour?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”: “Child Labour is caused by many factors. The most important one is poverty and illiteracy. When people barely make ends meet, they put their children to work so they can have food two times a day.”} }, { “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “How can we prevent child labour?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”:”Strict measures can prevent child labour. Unions should be made to monitor the activities of child labour. Education must be made free to enroll more and more kids in school. We must also abolish child trafficking completely to save the children.”} }] }
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App


Missing Texas Woman’s Dog Discovered Alone 9 Days Following Her Mysterious Disappearance: Family Concerned Over Uncharacteristic Behavior

Oklahoma Resident Apprehended Following Alleged Attempted Theft of Balenciaga Shoes

Emergency Dispatch Report Captures The Moment Baltimore’s Key Bridge Collapsed Due To A Cargo Incident

- Lifesaving Discoveries: How Important Clinical Research Shapes Medicine

- Planning On Transferring Colleges? 7 Strategies For A Seamless School Swap

From Concept To Completion: 7 Essential Steps In Successful Project Management


Pros And Cons Of Child Labor
Currently, about 250 million children in the world are engaged in one form of work or the other. Over 150 million of this population are working in very dangerous conditions. Also, every year, over1 million of the children who are working will be vulnerable and be victims of human trafficking.
What Exactly Is Child Labor?
Child labor refers to any form of work or physical activity that can deprive a child of his or her childhood. Such activities are activities that are unfavorable to both the physical and mental health of the children involved and also activities that deter their normal development.
As we are all aware, child labor is a much talked about and thought about topic, and both the pros and cons of child labor are considered. Yes, while child labor has its negatives, it also has its positives
A lot of people who live in the western developed world will see child labor as a taboo, and consider it a problem. Some countries also try to lessen this form of labor in other countries with laws and sanctions, and these countries also try to help curb or reduce the use of this form of labor with funding and education.
A lot of international organizations also consider child labor to be exploitative. Child labor has also been used throughout most of the past, but now that universal schooling has been adopted, this form of labor has become a bad practice and by most standards, no longer practiced, at least it is no longer a thing in developed countries.
Economic Benefits Of Child Labor
Of course, the most obvious benefit of working is economic. In countries where poverty is extreme or there is severe economic crisis, children’s work is needed if they want to survive. This is obvious to everyone.
In cases like this, work becomes too much and usually dangerous, and children’s agency becomes so constrained; dangerous child labor is a sign that something is very wrong.
In this case, intervention is needed to reduce the poverty and provide the material needs. Besides relieving severe poverty, child labor can provide improvements to the quality of life for the children and their families.
Psycho-Social Benefits Of Child Labor
Children love to take pride in the work they do when they successfully take part in the work activities. Most of us have witnessed, firsthand how work foster self-esteem in a child, especially if that child is otherwise marginalized.
Work helps children’s individual psychological development and their social relationships. Social relationships helps to improve well-being in short and long term .
Educational Benefits Of Child Labor

Apart from having economic and psycho-social benefits, child labor can have value for learning. It can confer educational benefits on children.
Education outside formal institutions can be gotten from the work children do to survive. Education is not all about formal schooling. Although it includes formal schooling in the modern world, it goes beyond that. Children learn a lot from the work they do – they learn how to interact with people, they learn the culture into which they were born, and work can also teach the certain skills.
Studies show that children street workers pick up the mathematical skills necessary for their day-to-day business. Other studies said they also picked up their communication skills which help them progress into more remunerative forms of work.
Cons Of Child Labor
The tasks these children are made to carry out are usually very difficult and the working conditions are very harsh, which creates a lot of problems for them such as malnutrition, premature aging, depression, drug dependency, and lots more.
These child laborers have no protection, from underprivileged backgrounds, minority groups, or taken forcefully from their parents. Their employers do anything they think is needed to make the children completely irrelevant, therefore, they able to exercise a total control over them. These child laborers work in humiliating conditions, their employers not minding all the principles and fundamental rights of the children.
Also, children who works will not have access to a normal education and will be destined to become an illiterate in their adult life, with no possibility to grow their professional and social life.
Child labor, in some cases also endangers the children’s dignity and morals, especially when they are sexually exploited, in cases such as prostitution and child pornography.
Children who work will also be more exposed to malnutrition. Child laborers are usually exposed to physical, mental, and sexual violence.
Children who work start working at a very young age. If they start working at such young age, they are stripped off their childhood. These children have no experience normal children have, as they are doing things that are meant for adults.
The organizations that employ child labor usually abuse them illegally if the children are not working up to the expected standards.
Why Do We Still Have Child Labor?

There are so many explainable reasons that despite its obvious negative impacts, child labor is still being practiced in some parts of the world.
The reason we still have child labor are;
Everyone considers poverty as the main reason children work at jobs they shouldn’t be working at, considering their ages. These children work because their parents can’t afford their needs , so they have to work to add to the family income or provide unpaid labor.
Child Labor is very cheap and obedient
The wages these children are paid is very low, and this is why employers like to take advantage of child labor. Some of this children even work without getting paid as domestic workers, Employers also find that they can control children more than they can control adults.
Child workers, unlike their older counterparts, are very unlikely to start protests or form trade unions. Children are also easily intimidated by adults. Their employers can force them into submission when these children depend on them for food, accommodation, and even emotional support.
In so many parts of the world, some parents beat their children and it is not considered improper, so employers of child labor take advantage of the fact that the public accepts corporal punishment and they beat their younger employees as a means of controlling them.
Inadequate laws
Even though is so many countries across the world , there are national laws that state that children who are below the age of 1 should not be allowed to work, the law is usually not respected. Over 13 countries signed an international convention that says children should not be allowed to work full-time before they reach the age of 14 0r 15.
However, in some of the nations that signed this convention, laws on child labor are confusing or vague and not obeyed. Employers of child labor usually have one reason or another to justify young children working for them.
Additionally, some countries do not have a constant birth registration system, so a lot of their citizens do not have birth certificates. Children’s ages can’t be known for sure and without proper documentation, these children may not be allowed to have access to state services such as schools.
Role of education
Not taking part in educational activities and attending school has a role to play in child labor. In a lot of countries, education is not free, and parents of these children have to pay for their children to be able to attend school. They also need money to buy books and their school uniform. This can be so much money for poor families and they cannot afford it.
How Can We Stop Child Labor?
There are so many ways by which we can put an end to child labor. No matter how little our effort is, we can discourage this bad practice.
Negative feedback and from consumers and bad publicity are not friends of all companies. They avoid this like a plague. No organization wants to be accused of employing child laborers because they know it will affect their profit when consumers stop buying their products.
You as a consumer can stop buying products of companies that employ child labor. A lot of websites give information on brands and companies that employ child labor, so you can do your research.
In countries where citizens don’t have access to free education and enough basic amenities, child labor is guaranteed to be a thing, so it is the role of the government to see to it that their citizens do not lack all these social amenities and their right to education.
You May Like These Articles As Well:
Can you join the army with depression history?
Pickled Garlic Health Benefits You Must Know
How College Students Can Maintain a Balanced Lifestyle
You may also like

Exploring Yourself: What Is Past Life Regression Therapy?

15 Fun And Unique Corporate Event Ideas For 2024
Recent posts, popular posts.

OSM Worldwide: Simplifying Logistics With Comprehensive Tracking Services

Manhunt Underway For Suspect In Targeted Walmart Shooting, Victim Left In Critical State In Memphis
Empowering San Francisco’s Green Future: Premier EV Charger Installation And Expert Electricians

Blake Lively Expresses Mortification After Kate Middleton Reveals Cancer Battle, Amid Criticism of ‘Photoshop Fails’ Comment

Search Search
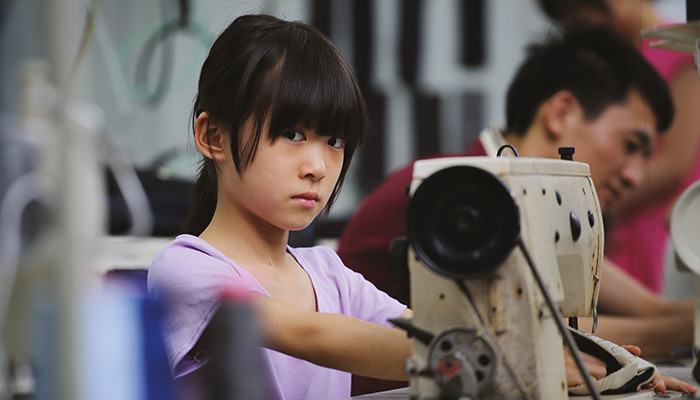
Five Reasons Why Eradicating Child Labor Is Crucial For Education

11 Jun 2016
Photo by AsiaInspection.
June 12, 2016, marks the World Day Against Child Labor, and this year, child labor in supply chain is in focus. With over 168 million child laborers worldwide, this problem still remains grave. In addition to the disadvantages faced by many workers in poorer countries, such as hazardous working conditions, long hours, lack of mandated leave, etc., child laborers are denied a fundamental human right: the right to education.
In the daily work of AsiaInspection (AI), a global product safety, quality, and compliance provider, child labor is a critical factor in any social audit carried out for AI’s clients. Any indication of underage workers being present at a factory is enough to give a social audit a failing grade, and label the factory as non-compliant.
However, for any brand that discovers their supplier has been compromised, simply choosing a different factory may not the best solution. A more constructive way forward is to work with the factory to ensure that child laborers are put back in school.
In investigating child labor, AI’s process is not limited to identifying and reporting the problem. Coordinating their efforts with the brand, AI’s social auditors ensure the child laborer’s safety and create an environment in which they feel comfortable discussing their honest views on work and education. With an understanding of the underage worker’s family and economic situation, AI and the brand engage the help of NGOs to improve it.
The most common reason for child and underage labor is the family’s need for an extra provider. Because of this, one of the best ways to handle the problem is ensuring education for the child while securing the income they used to bring to their family. Some brands put pressure on their suppliers to replace the child laborer with an adult member of their family, or to pay the child’s salary while they receive their education.
People often restrict their idea of child labor to very young children. However, workers in their early teens are equally vulnerable, and their being underage is not always immediately apparent. The International Labour Organization sets the minimum working age at 15, and rules that no-one under 18 should be involved in hazardous work.
Another key aspect of the definition of child labor by the ILO is “work that deprives children of the opportunity to attend school.” Indeed, child labor is incompatible with education, and here are five reasons why:
- Child labor is a barrier to education access and enrollment
Even in communities where schools are available, child labor is often perceived as the best use of the children’s time. Recent studies confirm that child labor is negatively correlated with school enrolment and delays school entry. For example, in Cambodia, a child is 17% less likely to enter school at the enrolment age. Child labor also increases drop-out rates, as poverty forces many children out of schools and into paying jobs.
- Child labor is a barrier to learning
In countries where child labor is common, children who combine work and school are disadvantaged compared to children in full-time education. Limited time and exhaustion from work greatly impairs their participation, and they are much less likely to receive the full benefits of the education available to them. A 2014 study of sixty countries showed that working children face an attendance disadvantage of 10% to 30% compared to their non-working counterparts (Policy Paper: Out-of-school Children and Child Labor. Global March Against Child Labour, 2014). Statistically, working children have lower test scores, poorer attendance rates, and are more likely to repeat grades.
- Child labor traps children in poverty
Entering the workforce too early diminishes a child’s lifetime earning potential. Child laborers have very limited ability to take advantage of educational opportunities that would help them receive better-paying jobs as adults. As a result, someone who started working as a child may remain in a low-paying and hazardous job for the rest of their life, failing to improve their own economic position and that of their future family.
- Child labor has consequences for the next generation
As a logical consequence of the above reason, child labor can perpetuate inter-generational cycles of poverty. Parents who entered the workforce early at the expense of schooling are more likely to compel their children to do the same: for economic reasons, as well as due to the acquired expectation that turning their child into an earner is more important than giving them an education.
- Education and child labor are co-dependent challenges
Without access to quality and free education, many families and children themselves will view work as the better option – if the benefits of education aren’t obvious, or school tuition is not affordable. However, simply offering good education options is not enough to tackle all child labor problems. Economic incentives must be offered for children to stay in school instead of dropping out early, and awareness of the importance of education must be raised among all family members.
While child labor is a deeply entrenched, multidimensional problem that requires complex solution, one thing remains clear. As long as child labor exists, universal primary education cannot happen, and simultaneously, until all children have access to free and quality education, child labor will persist.

“Cutting ties with a non-compliant supplier can help a brand’s reputation, but will contribute little to the bigger picture, at AI, we aim to work together with brands, supplies, and NGOs to ensure education for children and secure their future.” – Sébastien Breteau, CEO, AsiaInspection.
1 http://globalmarch.org/sites/default/files/Policy-Paper.pdf
Sample details
- Views: 2,501
Related Topics
- Conversation
- Grandmother
- Interpersonal Relationship
- Family Tradition
- Family planning
- Family therapy
- Responsibility
- Family History
- Importance of family
Child Labor: Advantages and Disadvantages
Child labor has both advantages and disadvantages. On one hand, it can provide much-needed financial support for poor families and allow factory workers to pay children less and get their work done for free. However, the disadvantages of child labor include the fact that children are often not mentally or physically prepared for it, leading to illiteracy and exposure to hazardous materials. Child labor also contributes to social issues by making adults feel ashamed for not being able to support their families. Despite the fact that 20 million children work today, child labor should be banned as it takes away children’s rights and prevents them from pursuing education and their own interests.
There are some pros of child labor like children providing money for their families, and factory workers earning more money and having less time to woo ark. Since the children were already poor and could not get an education, working help d provide a little more for their families. The factory workers got an advantage out of chill d labor because they paid the children a lot less and practically got there work done f or free.
Some disadvantages of child labor are that the child is not mentally or physics prepared for it. Children being involved in child labor at a young age are perm neatly considered illiterate since they cannot go to school nor have any type of educe action. Many kids employed in hazardous industries are sometimes afflicted with tubercular sis and many other diseases. They are being exposed to dangerous stuff like making crackers, match boxes, etc.
While children are getting jobs in factories and supporting t heir families, many adults are ashamed because they can’t support their family, w which causes social issues. Child labor has been known around the world and still goes on doubTABLE 2 0 million children work today, they don’t go to school and have little/ no time to play. Although many children have the opportunity to go to school for free and still have jobs by a certain age.
Child labor can be seen as a good thing for some people, but I think it should be banned. It is not fair to the kids because they don’t get to do what t hey want, they carry stones in their hands instead of books. Their rights are being taken away from them as they are forced into labor. Children should be TABLE to do whatever the eye want, child labor is a horrible thing and should not continue.
Cite this page
https://graduateway.com/essay-child-labor-advantages-and-disadvantages-ideas/
You can get a custom paper by one of our expert writers
- Dispute Resolution
- Extended family
- Appreciation
Check more samples on your topics
Child labor as per international labor organization.
Child Labour
Child labor as per International Labor Organization is defined as “work that deprives children of their childhood, their potential and their dignity, and that is also harmful to their physical and mental development.” It also refers to types of work that deprive them of getting an education and, in the most extreme cases it involves
Knights of Labor and the American Federation of Labor
The labor unions, including the Knights of Labor and the American Federation of Labor, were founded in the 19th century with the aim of supporting workers. Nonetheless, their actions had unforeseen outcomes that hindered their public acceptance. Rather than effectively aiding workers, these unions incited conflicts, harm, and even violence between workers and business owners.
History of Labor Union and Labor Relations
ABSTRACT Broadly speaking, labor relations may refer to any transaction between employer and employees with regards to certain employment conditions. More frequently, however, labor relations refer to communication between management and a workforce that has been previously unionized, or has the probability to become unionized (Investor Glossary). Whereas, as labor union is an alliance of employees recognized
Child Labor In The Philippines Research
Introduction All people were born with rights. Childs are people excessively; so, kids besides have rights. These rights are violated through kid labour. Child labour is defined as, the employment of a kid in a concern or industry particularly in misdemeanor of province or federal legislative acts forbiding the employment of kids under a specified age. Obviously,
Child Labor in Nike
Nikkei quickly established an international presence, beginning with their entry into the Canadian market in 1972. Today, Nikkei has a presence in ore than 1 60 countries and has recently introduced its Global Growth Strategy, targeting revenues of 527 billion by the end of 2015. However, these levels of noTABLE success are undeniably accompanied by
Child Labor 2 Research Paper 2
“ The kids are the hereafter of our nation. ” This celebrated line of Dr. Jose Rizal has gained prominence particularly among policy shapers in their quest to develop and implement Torahs and plans that will impel the entire development of a state ’ s 1000000s of kids. I personally agree with Rizal ’ s
Child Labor and Human Rights Essay
After World War II, the UN of General Assembly adopted the Universal Declaration of Human Rights. World leaders joined together in order to ensure that each and every human being was guaranteed equal rights. Equal rights basically, in short, ensures that there is no legal preferential treatment to anyone regardless of sex, gender, race, ethnicity,
Children In Bangladesh: Child Labor And Poverty
Child Labor
Bangladesh, to the east of India on the Bay of Bengal, is a South Asian country marked by lush greenery and many waterways. The population of Bangladesh is 163 million. There are 51.3 million children (ages 0-14 years) living in Bangladesh, of which 24.9 million are girls and 26.4 million are boys. Bangladesh is a
The Influence of the Industrial Revolution to the Rise of Child Labor
Coal mining came along in 1700; coal mining was an easy process in the early days as it was inexpensive and easy as coal was close to the surface. 2 types of coal mines existed before the industrial revolution had begun. The drift and bell mines, both were small and produced large quantity of solid

Hi, my name is Amy 👋
In case you can't find a relevant example, our professional writers are ready to help you write a unique paper. Just talk to our smart assistant Amy and she'll connect you with the best match.

- भाषा : हिंदी
- Classroom Courses
- Our Selections
- Student Login
- About NEXT IAS
- Director’s Desk
- Advisory Panel
- Faculty Panel
- General Studies Courses
- Optional Courses
- Interview Guidance Program
- Postal Courses
- Test Series
- Current Affairs
- Student Portal

- Pre Cum Mains Foundation Courses
- GS + CSAT Pre cum Main Foundation Course
- GS Pre cum Main Foundation Course
- GS + CSAT + Optional
- GS + Optional
- Prelims Courses
- Current Affairs Course for CSE 2025
- CSAT Course
- Current Affairs for Prelims (CAP)-2024
- Mains Courses
- Mains Advance Course (MAC)
- Essay Course Cum Test Series
- First Step — NCERT Based Course
- Optional Foundation Courses
- Mathematics
- Anthropology
- Political Science and International Relations (PSIR)
- Optional Advance Courses (Optional Through Questions)
- Civil Engineering
- Electrical Engineering
- Mechanical Engineering
- Interview Guidance Programme / Personality Test Training Program
- GS + CSAT Postal Courses
- Current Affairs Magazine – Annual Subscription
- GS+CSAT Postal Study Course
- First Step Postal Course
- Postal Study Course for Optional Subjects
- Prelims Test Series for CSE 2024 (Offline/Online)
- General Studies
- GS Mains Test Series for CSE 2024
- Mains Test Series (Optional)
- Paarth PSIR
- PSIR Answer Writing Program
- PSIR PRO Plus Test Series
- Mathematics Year Long Test Series (MYTS) 2024
- Indian Economic Services
- Anubhav (All India Open Mock Test)
- Prelims (GS + CSAT)
- Headlines of the Day
- Daily Current Affairs
- Editorial Analysis
- Monthly MCQ Compilation
- Monthly Current Affairs Magazine
- Previous Year Papers
- Down to Earth
- Kurukshetra
- Union Budget
- Economic Survey
- NIOS Study Material
- Social Justice
Child Labour in India: Causes, Consequences and Solutions

Child Labour means when children are made to work in a way that takes away their childhood, potential, and self-respect.
- It includes work that is dangerous or harmful to children’s physical, mental, social, or moral well-being.
- It also includes work that stops them from going to school, either by not allowing them to attend or by forcing them to leave early.
Whether a particular type of work is considered child Labour depends on factors like the child’s age, the kind and hours of work, the conditions in which it takes place, and the rules set by each country. The definition may vary from country to country and even within different industries within a country.
Facts and Statistics of Child Labour in India
- Total child population (5-14 years) in India: 259.6 million (Census 2011).
- Working children in India: 10.1 million (3.9% of the total child population) as “main workers” or “marginal workers.”
- Out-of-school children in India: more than 42.7 million.
- Child Labour decreased in India by 2.6 million between 2001 and 2011.
- The decline is more visible in rural areas, while the number of child workers increased in urban areas, indicating a growing demand for child workers in menial jobs.
Causes of Child Labour
There are many other factors that contribute to the problem, such as social norms, cultural beliefs, and discrimination.
Consequences of Child Labour
The consequences faced have a far-reaching impact on the child, society, and the nation as a whole:
Solutions to the Issue of Child Labour in India
Addressing the issue of child Labour in India requires a comprehensive approach involving various stakeholders.
- Strengthening Legislative Framework: Enforce and strengthen existing laws, such as the Child Labour (Prohibition and Regulation) Act, to ensure comprehensive protection for children and stricter penalties for offenders. Amendments should align with international standards.
- Access to Quality Education: Ensure universal access to free and quality education for all children. Implement and enforce the Right to Education Act, focusing on reducing dropout rates and increasing enrollment in schools.
- Poverty Alleviation: Tackle the root causes of child Labour by implementing poverty alleviation programs, providing economic support to families living in poverty, and promoting livelihood opportunities for parents.
- Awareness and Sensitization: Conduct widespread awareness campaigns targeting parents, communities, and employers about the detrimental effects of child Labour on children’s physical, mental, and educational development.
- Rehabilitation and Social Protection: Develop and implement comprehensive rehabilitation programs for rescued child laborers, including access to education, vocational training, healthcare, and psychological support. Establish social protection schemes for vulnerable families to prevent children from entering the Labour force.
- International Cooperation: Collaborate with international organizations, such as the International Labour Organization (ILO) and UNICEF, to access expertise, technical assistance, and financial resources to combat child Labour effectively.
- Empowering Local Communities: Involve local communities, including parents, teachers, and community leaders, in preventing child Labour. Empower them to identify and report cases of child Labour and provide support for rehabilitation and reintegration efforts.
It is important to recognize that addressing child Labour is a complex and multifaceted issue that requires sustained efforts, collaboration, and the commitment of all stakeholders to create lasting change.
Addressing and eliminating child Labour is crucial for the well-being of children, the progress of society, and the sustainable development of a nation. It requires concerted efforts, comprehensive policies, and the active involvement of various stakeholders to ensure the protection of children’s rights and their holistic development.
How Many Children are Presently Working as Labour in India?
There are around 10.1 million (3.9% of the total child population) as “main workers” or “marginal workers.”
What is the Major Reason for Child Labour in India?
The major reason for child Labour in India is poverty. Families living in poverty often resort to child Labour as a means of survival, as children can be paid less and are more vulnerable to exploitation.
What are the 10 Causes of Child Labour?
The 10 causes of child Labour include poverty, lack of access to education, limited enforcement of child Labour laws, cultural attitudes and norms, armed conflict, discrimination, inadequate social protection, migration, globalization, and demand for cheap Labour.
RELATED ARTICLES MORE FROM AUTHOR
International women’s day 2024: history, theme, celebrations & significance, child trafficking in india: facts, causes, global initiatives, indian laws and solutions, food security in india: challenges and opportunities, anti-conversion laws: issue, controversy & criticism, leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Featured Post

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Disadvantages Of Child Labour. 1831 Words8 Pages. Burra (2005) has tried to redefine the concept of child 'work' and 'labor'. She has also tried to find out the difference between these two concepts. According to the author, any activities which interrupt the growth of children is harmful and should be banned, irrespective of whether it ...
Child Labor Helps Children to Become Independent and Mature Fast. Most children that engage in paid labor do so because of poverty at home, though others may be lured through cheap money. Children forced into child labor by poor conditions at home learn to be responsible for taking care of their families (Radfar 3).
Child labor is an old problem well rooted in human history. Children were exploited to various extents during different periods of time. The problem was common in poor and developing countries. In the 1800's, child labor was part of economic life and industrial growth. Children less than 14 years old worked in agriculture, factories, mining ...
Child labour is a very real problem in the world today, and although it is declining, progress is happening at a slow and unequal pace. Child labour by the International Labour Organization is defined as "work that deprives children of their childhood, their potential and their dignity, and that is harmful to physical and mental development (Diallo, Etienne, & Mehran, 2013, p. 2)."
Economic hardship exacts a toll on millions of families worldwide - and in some places, it comes at the price of a child's safety. Roughly 160 million children were subjected to child labour at the beginning of 2020, with 9 million additional children at risk due to the impact of COVID-19. This accounts for nearly 1 in 10 children worldwide.
Forms of Child Labor. Child labor takes various forms, impacting millions of children globally. The notable forms include: 1. Slavery or Similar Practices: Involves the ownership of individuals, treating them as property, and forcing them to work without any control over their circumstances.
500+ Words Essay on Child Labour. Child labour is a term you might have heard about in news or movies. It refers to a crime where children are forced to work from a very early age. It is like expecting kids to perform responsibilities like working and fending for themselves. There are certain policies which have put restrictions and limitations ...
Sustainable Development Goal target 8.7 aims to eradicate child labour in all its forms by 2025. Ten years before this deadline, the objective is far from being achieved since in 2016, about one ...
child labor is harmful to children's development underpins both the theoretical literature and the policy debate. For example, from the policy perspective, there is a general ... All of these papers examine the correlation, rather than the causal relationship, between child labor and schooling. As we discuss in detail below, there are many ...
In 2008, there were approximately 215 million child labourers, aged 5-17, in the world. According to the International Labour Organization, the number of child labourers globally fell by 3% from the years of 2004-2008 which is slower in comparison to the 2000-2004 period that had an 11% decrease (Diallo, Etienne, & Mehran, 2013).There has also been a 15% decrease in the number of girls in ...
Cons Of Child Labor. The tasks these children are made to carry out are usually very difficult and the working conditions are very harsh, which creates a lot of problems for them such as malnutrition, premature aging, depression, drug dependency, and lots more. These child laborers have no protection, from underprivileged backgrounds, minority ...
Child labor was a major issue in our nation's history, from its founding through the early decades of the twentieth century. In 1900, United States census records counted at least 1.75 million children who were "gainful workers," (that is, worked for pay), comprising six percent of the nation's workforce.
In this essay, I will examine both aspects of an argument and give my opinion on the subject. On the one hand, participation in paid labour by children is frequently deemed unacceptable. Children who engage in paid work may be deprived of their childhood and education, and they may be susceptible to exploitation and maltreatment.
Causes And Disadvantages Of Child Labour. 1480 Words6 Pages. Introduction As defined by the ILO/Inter-Parliamentary Union (2002) child labour is: "work that is mentally, physically, socially or morally dangerous and harmful to children; and interferes with their schooling by depriving them of the opportunity to attend school; by obliging them ...
The disadvantages of child labor include: susceptibility to abuse, low pay rates, hazardous working conditions and illegal work, such as drug trafficking, child prostitution and human trafficking. Additionally, the educational development of child laborers is often stunted by the limited access to school time and other educational opportunities. According to the ILO conference report of 1996 ...
2- He overworks or gives over time to Labor. 3- He works due to the psychological, social, and materialistic pressure. 4- He becomes ready to Labor on a very low pay. Today, Pakistan is ranked 3rd in the countries with most child force. In Pakistan children aged 5-14 are above 40 million.
Child Labour Theory, policy and evidence. January 2001. Saqib Jafarey. Sajal Lahiri. The purpose of this paper is to pull together the emerging theoretical and empirical literature on the ...
June 12, 2016, marks the World Day Against Child Labor, and this year, child labor in supply chain is in focus. With over 168 million child laborers worldwide, this problem still remains grave. In addition to the disadvantages faced by many workers in poorer countries, such as hazardous working conditions, long hours, lack of mandated leave ...
March 7, 2022 by Prasanna. Debate on Child Labour: The term "child labour" is often defined as work that deprives children of their childhood, their potential, and their dignity, and that is harmful to physical and mental development. It refers to work that is mentally, physically, socially, or morally dangerous and harmful to children.
The factory workers got an advantage out of chill d labor because they paid the children a lot less and practically got there work done f or free. Some disadvantages of child labor are that the child is not mentally or physics prepared for it. Children being involved in child labor at a young age are perm neatly considered illiterate since they ...
The 10 causes of child Labour include poverty, lack of access to education, limited enforcement of child Labour laws, cultural attitudes and norms, armed conflict, discrimination, inadequate social protection, migration, globalization, and demand for cheap Labour. child labor in India. Understand the causes, consequences, and explore effective ...