- Key Differences
Know the Differences & Comparisons

Difference Between Article and Essay

An article is nothing but a piece of writing commonly found in newspapers or websites which contain fact-based information on a specific topic. It is published with the aim of making the reader aware of something and keeping them up to date.
An essay is a literary work, which often discusses ideas, experiences and concepts in a clear and coherent way. It reflects the author’s personal view, knowledge and research on a specific topic.
Content: Article Vs Essay
Comparison chart, definition of article.
An ‘article’ can be described as any form of written information which is produced either in a printed or electronic form, in newspaper, magazine, journal or website. It aims at spreading news, results of surveys, academic analysis or debates.
An article targets a large group of people, in order to fascinate the readers and engage them. Hence, it should be such that to retain the interest of the readers.
It discusses stories, reports and describes news, present balanced argument, express opinion, provides facts, offers advice, compares and contrast etc. in a formal or informal manner, depending upon the type of audience.
For writing an article one needs to perform a thorough research on the matter, so as to provide original and authentic information to the readers.
Components of Article
- Title : An article contains a noticeable title which should be intriguing and should not be very long and descriptive. However, it should be such that which suggests the theme or issue of the information provided.
- Introduction : The introduction part must clearly define the topic, by giving a brief overview of the situation or event.
- Body : An introduction is followed by the main body which presents the complete information or news, in an elaborative way, to let the reader know about the exact situation.
- Conclusion : The article ends with a conclusion, which sums up the entire topic with a recommendation or comment.
Definition of Essay
An essay is just a formal and comprehensive piece of literature, in which a particular topic is discussed thoroughly. It usually highlights the writer’s outlook, knowledge and experiences on that particular topic. It is a short literary work, which elucidates, argues and analyzes a specific topic.
The word essay is originated from the Latin term ‘exagium’ which means ‘presentation of a case’. Hence, writing an essay means to state the reasons or causes of something, or why something should be done or should be the case, which validates a particular viewpoint, analysis, experience, stories, facts or interpretation.
An essay is written with the intent to convince or inform the reader about something. Further, for writing an essay one needs to have good knowledge of the subject to explain the concept, thoroughly. If not so, the writer will end up repeating the same points again and again.
Components of the Essay
- Title : It should be a succinct statement of the proposition.
- Introduction : The introduction section of the essay, should be so interesting which instantly grabs the attention of the reader and makes them read the essay further. Hence, one can start with a quote to make it more thought-provoking.
- Body : In the main body of the essay, evidence or reasons in support of the writer’s ideas or arguments are provided. One should make sure that there is a sync in the paragraphs of the main body, as well as they, should maintain a logical flow.
- Conclusion : In this part, the writer wraps up all the points in a summarized and simplified manner.
Key Differences Between Article and Essay
Upcoming points will discuss the difference between article and essay:
- An article refers to a written work, published in newspapers, journals, website, magazines etc, containing news or information, in a specific format. On the other hand, an essay is a continuous piece of writing, written with the aim of convincing the reader with the argument or merely informing the reader about the fact.
- An article is objective in the sense that it is based on facts and evidence, and simply describes the topic or narrate the event. As against, an essay is subjective, because it is based on fact or research-based opinion or outlook of a person on a specific topic. It analyses, argues and criticizes the topic.
- The tone used in an article is conversational, so as to make the article easy to understand and also keeping the interest of the reader intact. On the contrary, an essay uses educational and analytical tone.
- An article may contain headings, which makes it attractive and readable. In contrast, an essay does not have any headings, sections or bullet points, however, it is a coherent and organized form of writing.
- An article is always written with a definite objective, which is to inform or make the readers aware of something. Further, it is written to cater to a specific niche of audience. Conversely, an essay is written in response to a particular assertion or question. Moreover, it is not written with a specific group of readers in mind.
- An article is often supported by photographs, charts, statistics, graphs and tables. As opposed, an essay is not supported by any photographs, charts, or graphs.
- Citations and references are a must in case of an essay, whereas there is no such requirement in case of an article.
By and large, an article is meant to inform the reader about something, through news, featured stories, product descriptions, reports, etc. On the flip side, an essay offers an analysis of a particular topic, while reflecting a detailed account of a person’s view on it.
You Might Also Like:

Anna H. Smith says
November 15, 2020 at 6:21 pm
Great! Thank you for explaining the difference between an article and an academic essay so eloquently. Your information is so detailed and very helpful. it’s very educative, Thanks for sharing.
Sunita Singh says
December 12, 2020 at 7:11 am
Thank you! That’s quite helpful.
Saba Zia says
March 8, 2021 at 12:33 am
Great job!! Thank u for sharing this explanation and detailed difference between essay and article. It is really helpful.
Khushi Chaudhary says
February 7, 2021 at 2:38 pm
Thank you so much! It is really very easy to understand & helpful for my test.
Dury Frizza says
July 25, 2022 at 8:18 pm
Thanks a lot for sharing such a clear and easily understood explanation!!!!.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
The Difference Between an Article and an Essay
- An Introduction to Punctuation
- Ph.D., Rhetoric and English, University of Georgia
- M.A., Modern English and American Literature, University of Leicester
- B.A., English, State University of New York
In composition studies , an article is a short work of nonfiction that typically appears in a magazine or newspaper or on a website. Unlike essays , which often highlight the subjective impressions of the author (or narrator ), articles are commonly written from an objective point of view . Articles include news items, feature stories, reports , profiles , instructions, product descriptions, and other informative pieces of writing.
What Sets Articles Apart From Essays
Though both articles and essays are types of nonfiction writing, they differ in many ways. Here are some features and qualities of articles that differentiate them from essays.
Subject and Theme in Articles
"A useful exercise is to look at some good articles and name the broader subject and the particular aspect each treats. You will find that the subject always deals with a partial aspect examined from some viewpoint; it is never a crammed condensation of the whole.
"...Observe that there are two essential elements of an article: subject and theme . The subject is what the article is about: the issue, event, or person it deals with. (Again, an article must cover only an aspect of a whole.) The theme is what the author wants to say about the subject—what he brings to the subject." (Ayn Rand, The Art of Nonfiction: A Guide for Writers and Readers , ed. by Robert Mayhew. Plume, 2001)
"An article is not everything that's true. It's every important thing that's true." (Gary Provost, Beyond Style: Mastering the Finer Points of Writing . Writer's Digest Books, 1988)
Article Structure
"There are five ways to structure your article . They are:
- The inverted pyramid - The double helix - The chronological double-helix - The chronological report - The storytelling model
Think about how you read a newspaper: you scan the captions and then read the first paragraph or two to get the gist of the article and then read further if you want to know more of the details. That's the inverted pyramid style of writing used by journalists, in which what's important comes first. The double-helix also presents facts in order of importance but it alternates between two separate sets of information. For example, suppose you are writing an article about the two national political conventions. You'll first present Fact 1 about the Democratic convention, then Fact 2 about the Republicans, then Fact 2 about the Democrats, Fact 2 about the Republicans, and so on. The chronological double-helix begins like the double helix but once the important facts from each set of information have been presented, it then goes off to relay the events in chronological order...
"The chronological report is the most straightforward structure to follow since it is written in the order in which the events occurred. The final structure is the storytelling model, which utilizes some of the techniques of fiction writing, so you would want to bring the reader into the story right away even if it means beginning in the middle or even near the end and then filling in the facts as the story unfolds." (Richard D. Bank, The Everything Guide to Writing Nonfiction . Adams Media, 2010)
Opening Sentence of an Article
"The most important sentence in any article is the first one. If it doesn't induce the reader to proceed to the second sentence, your article is dead. And if the second sentence doesn't induce him to continue to the third sentence, it's equally dead. Of such a progression of sentences, each tugging the reader forward until he is hooked, a writer constructs that fateful unit, the ' lead .'" (William Zinsser, On Writing Well: The Classic Guide to Writing Nonfiction , 7th ed. HarperCollins, 2006)
Articles and Media
"More and more, article content written for printed media is also appearing on digital devices (often as an edited version of a longer article) for readers who have short attention spans due to time constraints or their device's small screen. As a result, digital publishers are seeking audio versions of content that is significantly condensed and written in conversational style. Often, content writers must now submit their articles with the understanding they will appear in several media formats." (Roger W. Nielsen, Writing Content: Mastering Magazine and Online Writing . R.W. Nielsen, 2009)
Writer's Voice in Articles and Essays
"Given the confusion of genre minglings and overlaps, what finally distinguishes an essay from an article may just be the author's gumption, the extent to which personal voice , vision, and style are the prime movers and shapers, even though the authorial 'I' may be only a remote energy, nowhere visible but everywhere present. ('We commonly do not remember,' Thoreau wrote in the opening paragraphs of Walden , 'that it is, after all, always the first person that is speaking.')" (Justin Kaplan, quoted by Robert Atwan in The Best American Essays, College Edition , 2nd ed. Houghton Mifflin, 1998)
- How to Write a News Article That's Effective
- What Are the Different Types and Characteristics of Essays?
- What Is Expository Writing?
- Definition and Examples of Paragraphing in Essays
- What Is a Synopsis and How Do You Write One?
- How To Write an Essay
- Paragraph Length in Compositions and Reports
- Learn to Write News Stories
- Unity in Composition
- Writing a Lead or Lede to an Article
- How to Structure an Essay
- How to Write Your Graduate School Admissions Essay
- AP English Exam: 101 Key Terms
- How to Write a Great Book Report
- Writers on Writing: The Art of Paragraphing
- Definition and Examples of Analysis in Composition

The Difference between an Essay and an Article
Imagine opening your favorite entertainment magazine or your local newspaper and finding a collection of essays. How long, in that case, would the money you spend on magazines and newspapers be considered part of your entertainment budget?

Articles can be informative and not all of them are entertaining. However, it's more likely to find articles in magazines that offer entertainment for readers than an essay.
The most notable difference between an essay and an article is the tone. Essays traditionally are subjective pieces of formal writing that offers an analysis of a specific topic. In other words, an essay writer studies, researches, and forms a factually-based opinion on the topic in order to inform others about their ideas.
An article is traditionally objective instead of subjective. Writing an article doesn't always require that an opinion to be formed and expressed, and there's no requirement that an analysis be offered about the information being presented.
Scroll through a copy of Cosmopolitan, National Geographic, and today's edition of your local newspaper, and you'll get a sense of how articles can be structured in numerous different ways. Some include headings and subheadings along with accompanying photos to paint a picture for the reader to form their own thoughts and opinions about the subject of an article.
Essays, however, have more strict guidelines on structure depending on which type of essay a writer has chosen. Traditionally, readers will see an introductory paragraph that presents a thesis statement, body paragraphs with topic sentences that relate back to and flesh out the thesis, and a conclusion with the author's take on the information presented.
Entertainment Factor
While narrative essays can tell entertaining stories, it is articles that are most often included in magazines and newspapers to keep their subscribers informed and reading.
It's up to the writer of an article what message they want to convey. Sometimes that message is informative and sometimes it's humorous. For an essay writer, it's all about learning as much as possible about a topic, forming an opinion, and describing how they came to that opinion and why.
You're not likely to find essays in entertainment magazines. A person seeking in-depth information on a subject is going to seek out an essay, while a person looking for an entertaining piece of writing that allows them to draw their own conclusions will be more likely to seek out an article.

What’s The Difference Between An Article, A Paper, And An Essay? (Detailed Analysis)
Categories Culture

School and college life revolves around different types of writing, including opinion articles, review articles, research papers, and essays. Each of these has a different length, structure, and level of research.
You can write articles on various topics and niches if you gather enough information. It is possible to format an interview into an article so that it can be published in a magazine or online publication.
A paper, on the other hand, is longer than an essay or article, and one must follow a specific sequence. There is an abstract at the beginning, followed by a paragraph, a conclusion, and citations at the end.
There are a few paragraphs in the essay, all of which should be transitioned smoothly. The purpose of the essay is to persuade the reader through your logic and ideas. Different types of essays require different thoughts and writing processes.
This article is all about differentiating between an article, paper, and essay, so if it interests you, stick around while we explore these topics. Let’s get into it .
Page Contents
What Is An Article?
Articles are read by thousands of people around the globe and are generally written to educate people about something they’re unaware of. They are either published on an online website, magazine, or newspaper.
In the article, the writer expresses his or her perspective on a certain topic. The articles, mainly, are written to make people aware of a particular topic.

What Is A Paper?
The purpose of writing a research paper is to fill the gaps other authors left while writing on a similar topic.
There’s a structure that one must follow while writing a paper . Before writing a paper, make sure you’ve read the relevant papers.
Another important step is knowing your audience. It’s worth noting that the papers have a different outline of the paper than the essay or article.

Structure of the Paper
- Introduction
- Literature review
- Methodology
- References
Steps To Write A Paper
- First of all, you need to pick a topic that you’re interested in. Choosing a topic you’re not interested in is never a good idea.
- Read at least five relevant papers. There’s no need to read the papers thoroughly; you should only go through the abstract part, the introduction paragraph, and the conclusion.
- Write down the findings and gaps that you can work on. Most of your writing covers areas that other papers do not cover.
- The paper always starts with an introduction. Your thesis statement also goes here.
- Since the body part of a paper is almost 8 to 12 pages, you can add as many paragraphs as you want.
- In the end, you conclude your findings and give references to the sources.
What Is An Essay?
The word essay originates from the Latin word ‘exagium’ which refers to the presentation of the case .
An essay is all about giving a verdict on the issue after looking at all sides of the topic with an open mind. However, you need to consider all the evidence .
Essay writing comes with tremendous benefits. It builds a habit of looking at topics from various angles. Additionally, you get an opportunity to express your opinion after thorough research.
There are three parts to the essay: the introduction, the body, and the conclusion.
Introduction
One has to catch the reader’s attention from the first line of the introduction. The purpose of this is to arouse curiosity, which then leads your readers to read more.
In the introduction section, you give a little bit of an overview of the topic you’re writing about. It gives readers an insight into what’s coming next .
This would prevent most people from reading the bottom of your essay. Therefore, it’s really important to keep your audience hooked and curious.
Starting the introduction with some statistics or research findings is the best way to accomplish this. The most important thing to write in the introduction is the thesis statement.
When writing a paragraph in the body section, it’s important to keep sentences linked with each other. They must be coherent.
There should also be backing to your ideas from some relevant studies or sources. The best way to do this is by citing quotations, statistics, and research papers.
Additionally, you should never include irrelevant data in your essay.
The conclusion part includes a summary of the whole essay. You also write your findings or main points in this section of the essay.
Is the Article Different From The Essay?
There is always a thesis statement in an essay, along with reliable sources supporting the argument whereas an article solely represents your idea or opinion.
You’ll see very few articles that are written to persuade someone, while essays are only meant to persuade the readers.

The tone and the structure of the article are indeed different from the essay. The articles are written in simple English, so users of all ages will be able to understand them.
The length of both pieces of writing also differs. There is no limit to the word count when writing an article. An essay can be as long as a page or as short as a paragraph.
It is recommended that an essay be between 1500 and 2000 words in length.
Articles, Papers, and Essays: Differences and Similarities
- Articles, papers, and essays have different purposes in academic and professional writing.
- Articles inform readers on diverse topics. They engagingly present the author’s viewpoint. They’re often found in magazines or online platforms.
- Research papers have sections like abstracts, introductions, reviews, methodologies, findings, and conclusions. They aim to fill gaps in the literature .
- Essays look at different sides of a topic. They give a conclusion backed by facts and careful thinking.
- Articles can be long or short and can be written in many different ways. Papers need a lot of research and must sound serious and smart. Essays use smart arguments to convince people.
- These are different types of writing with different lengths, tones, and reasons for writing. Essays try to convince people of something. Papers are written to share information. Articles give people information that’s easy to understand.
- Knowing these differences is crucial. It helps you communicate well especially when you’re doing school or college work.
- There are different types of academic writing. Each type has its purpose. They each have different ways to make things easy to understand.
- When you get the little details of these types of writing, it makes it easier to understand how they work. This helps both in school and at work.
Other Articles
- Spear and a Lance-What is the difference?
- The Difference Between A High-res Flac 24/96+ and A Normal Uncompressed 16-bit CD
- What’s the Difference Between Tin Foil and Aluminum?

Comparing and Contrasting
What this handout is about.
This handout will help you first to determine whether a particular assignment is asking for comparison/contrast and then to generate a list of similarities and differences, decide which similarities and differences to focus on, and organize your paper so that it will be clear and effective. It will also explain how you can (and why you should) develop a thesis that goes beyond “Thing A and Thing B are similar in many ways but different in others.”
Introduction
In your career as a student, you’ll encounter many different kinds of writing assignments, each with its own requirements. One of the most common is the comparison/contrast essay, in which you focus on the ways in which certain things or ideas—usually two of them—are similar to (this is the comparison) and/or different from (this is the contrast) one another. By assigning such essays, your instructors are encouraging you to make connections between texts or ideas, engage in critical thinking, and go beyond mere description or summary to generate interesting analysis: when you reflect on similarities and differences, you gain a deeper understanding of the items you are comparing, their relationship to each other, and what is most important about them.
Recognizing comparison/contrast in assignments
Some assignments use words—like compare, contrast, similarities, and differences—that make it easy for you to see that they are asking you to compare and/or contrast. Here are a few hypothetical examples:
- Compare and contrast Frye’s and Bartky’s accounts of oppression.
- Compare WWI to WWII, identifying similarities in the causes, development, and outcomes of the wars.
- Contrast Wordsworth and Coleridge; what are the major differences in their poetry?
Notice that some topics ask only for comparison, others only for contrast, and others for both.
But it’s not always so easy to tell whether an assignment is asking you to include comparison/contrast. And in some cases, comparison/contrast is only part of the essay—you begin by comparing and/or contrasting two or more things and then use what you’ve learned to construct an argument or evaluation. Consider these examples, noticing the language that is used to ask for the comparison/contrast and whether the comparison/contrast is only one part of a larger assignment:
- Choose a particular idea or theme, such as romantic love, death, or nature, and consider how it is treated in two Romantic poems.
- How do the different authors we have studied so far define and describe oppression?
- Compare Frye’s and Bartky’s accounts of oppression. What does each imply about women’s collusion in their own oppression? Which is more accurate?
- In the texts we’ve studied, soldiers who served in different wars offer differing accounts of their experiences and feelings both during and after the fighting. What commonalities are there in these accounts? What factors do you think are responsible for their differences?
You may want to check out our handout on understanding assignments for additional tips.
Using comparison/contrast for all kinds of writing projects
Sometimes you may want to use comparison/contrast techniques in your own pre-writing work to get ideas that you can later use for an argument, even if comparison/contrast isn’t an official requirement for the paper you’re writing. For example, if you wanted to argue that Frye’s account of oppression is better than both de Beauvoir’s and Bartky’s, comparing and contrasting the main arguments of those three authors might help you construct your evaluation—even though the topic may not have asked for comparison/contrast and the lists of similarities and differences you generate may not appear anywhere in the final draft of your paper.
Discovering similarities and differences
Making a Venn diagram or a chart can help you quickly and efficiently compare and contrast two or more things or ideas. To make a Venn diagram, simply draw some overlapping circles, one circle for each item you’re considering. In the central area where they overlap, list the traits the two items have in common. Assign each one of the areas that doesn’t overlap; in those areas, you can list the traits that make the things different. Here’s a very simple example, using two pizza places:
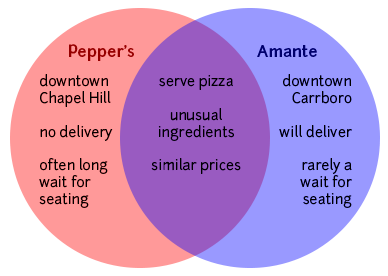
To make a chart, figure out what criteria you want to focus on in comparing the items. Along the left side of the page, list each of the criteria. Across the top, list the names of the items. You should then have a box per item for each criterion; you can fill the boxes in and then survey what you’ve discovered.
Here’s an example, this time using three pizza places:
As you generate points of comparison, consider the purpose and content of the assignment and the focus of the class. What do you think the professor wants you to learn by doing this comparison/contrast? How does it fit with what you have been studying so far and with the other assignments in the course? Are there any clues about what to focus on in the assignment itself?
Here are some general questions about different types of things you might have to compare. These are by no means complete or definitive lists; they’re just here to give you some ideas—you can generate your own questions for these and other types of comparison. You may want to begin by using the questions reporters traditionally ask: Who? What? Where? When? Why? How? If you’re talking about objects, you might also consider general properties like size, shape, color, sound, weight, taste, texture, smell, number, duration, and location.
Two historical periods or events
- When did they occur—do you know the date(s) and duration? What happened or changed during each? Why are they significant?
- What kinds of work did people do? What kinds of relationships did they have? What did they value?
- What kinds of governments were there? Who were important people involved?
- What caused events in these periods, and what consequences did they have later on?
Two ideas or theories
- What are they about?
- Did they originate at some particular time?
- Who created them? Who uses or defends them?
- What is the central focus, claim, or goal of each? What conclusions do they offer?
- How are they applied to situations/people/things/etc.?
- Which seems more plausible to you, and why? How broad is their scope?
- What kind of evidence is usually offered for them?
Two pieces of writing or art
- What are their titles? What do they describe or depict?
- What is their tone or mood? What is their form?
- Who created them? When were they created? Why do you think they were created as they were? What themes do they address?
- Do you think one is of higher quality or greater merit than the other(s)—and if so, why?
- For writing: what plot, characterization, setting, theme, tone, and type of narration are used?
- Where are they from? How old are they? What is the gender, race, class, etc. of each?
- What, if anything, are they known for? Do they have any relationship to each other?
- What are they like? What did/do they do? What do they believe? Why are they interesting?
- What stands out most about each of them?
Deciding what to focus on
By now you have probably generated a huge list of similarities and differences—congratulations! Next you must decide which of them are interesting, important, and relevant enough to be included in your paper. Ask yourself these questions:
- What’s relevant to the assignment?
- What’s relevant to the course?
- What’s interesting and informative?
- What matters to the argument you are going to make?
- What’s basic or central (and needs to be mentioned even if obvious)?
- Overall, what’s more important—the similarities or the differences?
Suppose that you are writing a paper comparing two novels. For most literature classes, the fact that they both use Caslon type (a kind of typeface, like the fonts you may use in your writing) is not going to be relevant, nor is the fact that one of them has a few illustrations and the other has none; literature classes are more likely to focus on subjects like characterization, plot, setting, the writer’s style and intentions, language, central themes, and so forth. However, if you were writing a paper for a class on typesetting or on how illustrations are used to enhance novels, the typeface and presence or absence of illustrations might be absolutely critical to include in your final paper.
Sometimes a particular point of comparison or contrast might be relevant but not terribly revealing or interesting. For example, if you are writing a paper about Wordsworth’s “Tintern Abbey” and Coleridge’s “Frost at Midnight,” pointing out that they both have nature as a central theme is relevant (comparisons of poetry often talk about themes) but not terribly interesting; your class has probably already had many discussions about the Romantic poets’ fondness for nature. Talking about the different ways nature is depicted or the different aspects of nature that are emphasized might be more interesting and show a more sophisticated understanding of the poems.
Your thesis
The thesis of your comparison/contrast paper is very important: it can help you create a focused argument and give your reader a road map so they don’t get lost in the sea of points you are about to make. As in any paper, you will want to replace vague reports of your general topic (for example, “This paper will compare and contrast two pizza places,” or “Pepper’s and Amante are similar in some ways and different in others,” or “Pepper’s and Amante are similar in many ways, but they have one major difference”) with something more detailed and specific. For example, you might say, “Pepper’s and Amante have similar prices and ingredients, but their atmospheres and willingness to deliver set them apart.”
Be careful, though—although this thesis is fairly specific and does propose a simple argument (that atmosphere and delivery make the two pizza places different), your instructor will often be looking for a bit more analysis. In this case, the obvious question is “So what? Why should anyone care that Pepper’s and Amante are different in this way?” One might also wonder why the writer chose those two particular pizza places to compare—why not Papa John’s, Dominos, or Pizza Hut? Again, thinking about the context the class provides may help you answer such questions and make a stronger argument. Here’s a revision of the thesis mentioned earlier:
Pepper’s and Amante both offer a greater variety of ingredients than other Chapel Hill/Carrboro pizza places (and than any of the national chains), but the funky, lively atmosphere at Pepper’s makes it a better place to give visiting friends and family a taste of local culture.
You may find our handout on constructing thesis statements useful at this stage.
Organizing your paper
There are many different ways to organize a comparison/contrast essay. Here are two:
Subject-by-subject
Begin by saying everything you have to say about the first subject you are discussing, then move on and make all the points you want to make about the second subject (and after that, the third, and so on, if you’re comparing/contrasting more than two things). If the paper is short, you might be able to fit all of your points about each item into a single paragraph, but it’s more likely that you’d have several paragraphs per item. Using our pizza place comparison/contrast as an example, after the introduction, you might have a paragraph about the ingredients available at Pepper’s, a paragraph about its location, and a paragraph about its ambience. Then you’d have three similar paragraphs about Amante, followed by your conclusion.
The danger of this subject-by-subject organization is that your paper will simply be a list of points: a certain number of points (in my example, three) about one subject, then a certain number of points about another. This is usually not what college instructors are looking for in a paper—generally they want you to compare or contrast two or more things very directly, rather than just listing the traits the things have and leaving it up to the reader to reflect on how those traits are similar or different and why those similarities or differences matter. Thus, if you use the subject-by-subject form, you will probably want to have a very strong, analytical thesis and at least one body paragraph that ties all of your different points together.
A subject-by-subject structure can be a logical choice if you are writing what is sometimes called a “lens” comparison, in which you use one subject or item (which isn’t really your main topic) to better understand another item (which is). For example, you might be asked to compare a poem you’ve already covered thoroughly in class with one you are reading on your own. It might make sense to give a brief summary of your main ideas about the first poem (this would be your first subject, the “lens”), and then spend most of your paper discussing how those points are similar to or different from your ideas about the second.
Point-by-point
Rather than addressing things one subject at a time, you may wish to talk about one point of comparison at a time. There are two main ways this might play out, depending on how much you have to say about each of the things you are comparing. If you have just a little, you might, in a single paragraph, discuss how a certain point of comparison/contrast relates to all the items you are discussing. For example, I might describe, in one paragraph, what the prices are like at both Pepper’s and Amante; in the next paragraph, I might compare the ingredients available; in a third, I might contrast the atmospheres of the two restaurants.
If I had a bit more to say about the items I was comparing/contrasting, I might devote a whole paragraph to how each point relates to each item. For example, I might have a whole paragraph about the clientele at Pepper’s, followed by a whole paragraph about the clientele at Amante; then I would move on and do two more paragraphs discussing my next point of comparison/contrast—like the ingredients available at each restaurant.
There are no hard and fast rules about organizing a comparison/contrast paper, of course. Just be sure that your reader can easily tell what’s going on! Be aware, too, of the placement of your different points. If you are writing a comparison/contrast in service of an argument, keep in mind that the last point you make is the one you are leaving your reader with. For example, if I am trying to argue that Amante is better than Pepper’s, I should end with a contrast that leaves Amante sounding good, rather than with a point of comparison that I have to admit makes Pepper’s look better. If you’ve decided that the differences between the items you’re comparing/contrasting are most important, you’ll want to end with the differences—and vice versa, if the similarities seem most important to you.
Our handout on organization can help you write good topic sentences and transitions and make sure that you have a good overall structure in place for your paper.
Cue words and other tips
To help your reader keep track of where you are in the comparison/contrast, you’ll want to be sure that your transitions and topic sentences are especially strong. Your thesis should already have given the reader an idea of the points you’ll be making and the organization you’ll be using, but you can help them out with some extra cues. The following words may be helpful to you in signaling your intentions:
- like, similar to, also, unlike, similarly, in the same way, likewise, again, compared to, in contrast, in like manner, contrasted with, on the contrary, however, although, yet, even though, still, but, nevertheless, conversely, at the same time, regardless, despite, while, on the one hand … on the other hand.
For example, you might have a topic sentence like one of these:
- Compared to Pepper’s, Amante is quiet.
- Like Amante, Pepper’s offers fresh garlic as a topping.
- Despite their different locations (downtown Chapel Hill and downtown Carrboro), Pepper’s and Amante are both fairly easy to get to.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift

Difference Between Article and Essay
College writing is divided into two types: articles and essays. Despite a few resemblances, they also have significant distinctions respectively to each other. These disparities are premised on layout, intention, and information. Prior to delving into the distinction between those assignments, we should first examine their meanings. Continue reading to understand all terminology and ideas on how to approach creative writing.

- 1 General Definitions
- 2 Key Rules of an Article
- 3 The Concept of an Essay
- 4 Bottom Line
General Definitions
Most essay examples are seen as written paperwork that explains, examines, and validates a specific topic. They have a predefined word limit and basic structure. This is why many students look for 100% free essays online to get the best grades. On the contrary, an article is a text that is published alongside other posts in a magazine or other periodicals. The primary distinction between our assignments is that the former is written to spread awareness regarding a particular idea. Whereas the latter is drafted in answer to an inquiry or assertion.
The tonality shown in the article is engaging. It makes the text simple to grasp while also maintaining the attention of the audience. You have to prepare detailed information explaining each aspect of the mentioned topic. On the other hand, an essay employs an academic and intellectual style. Despite the official manner, you must include your opinions here. It is crucial to disclose these to open the issue for discussion. No wonder these are so prominent in education.
Key Rules of an Article
This editorial is a form of reporting that appears alongside other posts in a journal, reviews, or other press. It follows a factual and documentary composing pattern. Media, dictionaries, webpages, advertisements, and other blogs also may contain these writings. The layout and information of this text may differ depending on the origin. An opinion column, evaluation, showcase post, university paperwork, and so on are all examples of articles.
Yet, the primary objective of this writing stays unchanged. You have to educate the viewers regarding the relevant themes. Some other prominent factor of such publications is that they generally adhere to a header and sub-header template. This method allows people to comprehend the ideas discussed in the article quickly. This composition can also differ in terms of the kind of data it displays.
These pieces of evidence are generally portrayed objectively. The author’s goal here is to characterize the subject rather than convince the audience to accept his viewpoint. Quotations and bibliography are not required here. Photos, diagrams, and infographics are frequently included to accompany the article summarizer better.
The Concept of an Essay
This assignment is a type of literature in which you classify, assess, and appraise a specific subject or problem. It is a quick, precise type of communication that includes an opening, a body with a few supporting chapters, and a summary. Here you should give an overview, support an assertion, analyze a problem, or expound on a theory. Understand that this text must be a collection of statistical data, evidence, and the author’s thoughts and viewpoints.
An essay can be classified into different categories. Those include storylike, explanatory, convincing, adversarial, interpretive types, and so on. The intent and material of the document can vary depending on the kind you choose. For instance, if you are composing a literary piece , you should focus on the format and the storyline that will pique the viewers’ curiosity. But, you must be more responsible if you are drafting a confrontational or convincing thesis. Provide solid data and evidence to back up your assertion.
Additionally, essays do not follow headings and subheadings. You have all the right not to use images here. Besides, you should keep it contextual since you analyze and critique an issue. Remember to prepare a reference list with appropriate quotations. Another tip is to check for the required word limit for your work. Keep that in mind when composing the text since it can affect your marks at school.
Bottom Line
As a student, you may feel overwhelmed with the wide variety of paperwork you have to do. Be sure to spend some time choosing the perfect essay format. You can always ask for help from your supervisor or friends. Learning the established rules of writing will bring you success in the long run. All pupils strive to get the best grades possible. So, best of luck!

Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Comparing and contrasting in an essay | Tips & examples
Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay | Tips & Examples
Published on August 6, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on July 23, 2023.
Comparing and contrasting is an important skill in academic writing . It involves taking two or more subjects and analyzing the differences and similarities between them.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
When should i compare and contrast, making effective comparisons, comparing and contrasting as a brainstorming tool, structuring your comparisons, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about comparing and contrasting.
Many assignments will invite you to make comparisons quite explicitly, as in these prompts.
- Compare the treatment of the theme of beauty in the poetry of William Wordsworth and John Keats.
- Compare and contrast in-class and distance learning. What are the advantages and disadvantages of each approach?
Some other prompts may not directly ask you to compare and contrast, but present you with a topic where comparing and contrasting could be a good approach.
One way to approach this essay might be to contrast the situation before the Great Depression with the situation during it, to highlight how large a difference it made.
Comparing and contrasting is also used in all kinds of academic contexts where it’s not explicitly prompted. For example, a literature review involves comparing and contrasting different studies on your topic, and an argumentative essay may involve weighing up the pros and cons of different arguments.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
As the name suggests, comparing and contrasting is about identifying both similarities and differences. You might focus on contrasting quite different subjects or comparing subjects with a lot in common—but there must be some grounds for comparison in the first place.
For example, you might contrast French society before and after the French Revolution; you’d likely find many differences, but there would be a valid basis for comparison. However, if you contrasted pre-revolutionary France with Han-dynasty China, your reader might wonder why you chose to compare these two societies.
This is why it’s important to clarify the point of your comparisons by writing a focused thesis statement . Every element of an essay should serve your central argument in some way. Consider what you’re trying to accomplish with any comparisons you make, and be sure to make this clear to the reader.
Comparing and contrasting can be a useful tool to help organize your thoughts before you begin writing any type of academic text. You might use it to compare different theories and approaches you’ve encountered in your preliminary research, for example.
Let’s say your research involves the competing psychological approaches of behaviorism and cognitive psychology. You might make a table to summarize the key differences between them.
Or say you’re writing about the major global conflicts of the twentieth century. You might visualize the key similarities and differences in a Venn diagram.
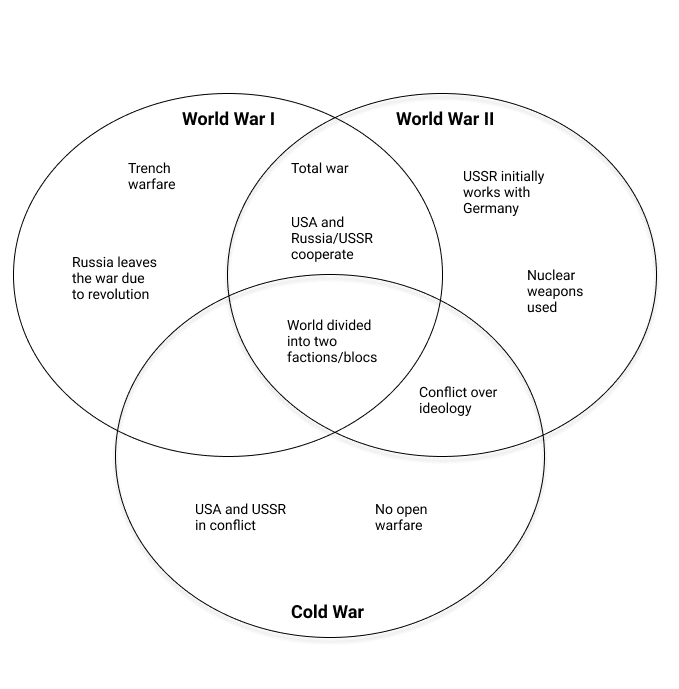
These visualizations wouldn’t make it into your actual writing, so they don’t have to be very formal in terms of phrasing or presentation. The point of comparing and contrasting at this stage is to help you organize and shape your ideas to aid you in structuring your arguments.
When comparing and contrasting in an essay, there are two main ways to structure your comparisons: the alternating method and the block method.
The alternating method
In the alternating method, you structure your text according to what aspect you’re comparing. You cover both your subjects side by side in terms of a specific point of comparison. Your text is structured like this:
Mouse over the example paragraph below to see how this approach works.
One challenge teachers face is identifying and assisting students who are struggling without disrupting the rest of the class. In a traditional classroom environment, the teacher can easily identify when a student is struggling based on their demeanor in class or simply by regularly checking on students during exercises. They can then offer assistance quietly during the exercise or discuss it further after class. Meanwhile, in a Zoom-based class, the lack of physical presence makes it more difficult to pay attention to individual students’ responses and notice frustrations, and there is less flexibility to speak with students privately to offer assistance. In this case, therefore, the traditional classroom environment holds the advantage, although it appears likely that aiding students in a virtual classroom environment will become easier as the technology, and teachers’ familiarity with it, improves.
The block method
In the block method, you cover each of the overall subjects you’re comparing in a block. You say everything you have to say about your first subject, then discuss your second subject, making comparisons and contrasts back to the things you’ve already said about the first. Your text is structured like this:
- Point of comparison A
- Point of comparison B
The most commonly cited advantage of distance learning is the flexibility and accessibility it offers. Rather than being required to travel to a specific location every week (and to live near enough to feasibly do so), students can participate from anywhere with an internet connection. This allows not only for a wider geographical spread of students but for the possibility of studying while travelling. However, distance learning presents its own accessibility challenges; not all students have a stable internet connection and a computer or other device with which to participate in online classes, and less technologically literate students and teachers may struggle with the technical aspects of class participation. Furthermore, discomfort and distractions can hinder an individual student’s ability to engage with the class from home, creating divergent learning experiences for different students. Distance learning, then, seems to improve accessibility in some ways while representing a step backwards in others.
Note that these two methods can be combined; these two example paragraphs could both be part of the same essay, but it’s wise to use an essay outline to plan out which approach you’re taking in each paragraph.

Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
Some essay prompts include the keywords “compare” and/or “contrast.” In these cases, an essay structured around comparing and contrasting is the appropriate response.
Comparing and contrasting is also a useful approach in all kinds of academic writing : You might compare different studies in a literature review , weigh up different arguments in an argumentative essay , or consider different theoretical approaches in a theoretical framework .
Your subjects might be very different or quite similar, but it’s important that there be meaningful grounds for comparison . You can probably describe many differences between a cat and a bicycle, but there isn’t really any connection between them to justify the comparison.
You’ll have to write a thesis statement explaining the central point you want to make in your essay , so be sure to know in advance what connects your subjects and makes them worth comparing.
Comparisons in essays are generally structured in one of two ways:
- The alternating method, where you compare your subjects side by side according to one specific aspect at a time.
- The block method, where you cover each subject separately in its entirety.
It’s also possible to combine both methods, for example by writing a full paragraph on each of your topics and then a final paragraph contrasting the two according to a specific metric.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, July 23). Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay | Tips & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 2, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/compare-and-contrast/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, how to write an expository essay, how to write an argumentative essay | examples & tips, academic paragraph structure | step-by-step guide & examples, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”

What’s The Difference Between An Article A Paper And An Essay
Table of Contents
When it comes to writing, you may wonder what the difference is between an essay, article, and paper. Even the most experienced writers sometimes confuse these terms, but once you understand what they represent, you’ll be able to choose which kind of writing suits your purposes best. With a little help from an essay writer service, you can be certain that each one of your pieces of writing will be polished and ready to impress upon completion.
Introduction
There are three main types of academic writing: essays, articles, and papers. While these categories are similar, there are some major differences. This post will help you identify what separates these terms from one another. Here’s a quick breakdown of each type of academic writing.
Essay vs. Article vs. Paper
Why are they different? What’s in a title? We hear them used all of the time interchangeably in different contexts, but what makes these three so different from one another? To understand how essay writing differs from articles and papers, we need to look at how each differs from another. So let’s get started by exploring some of their main differences: Essay vs. Article vs. Paper – Key Differences 1. Length 2. Subject Matter 3. Author 4. Purpose 5. Audience.
Essays are typically 1–3 pages long. Articles vary in length but run longer than essays. Papers typically range from 10 to 15 pages or more. It’s important to note that essay writer services have very different writing styles. Some writers write with a conversational tone, while others use a formal style for essays and articles. The best way to figure out which type of writing fits your needs is by looking at samples of their work or asking them about their process.
The three types of writing are intended for different purposes. The purpose is often reflected in both length and tone. For example, a paper is generally longer than an essay or an article because it must be more comprehensive. It also tends to be more formal because it’s intended to be read by experts in a particular field (e.g., doctors reading a medical journal). On the other hand, an essay is usually shorter than a paper because it doesn’t have to cover as much ground and can take a more casual tone since it’s not necessarily directed at experts. Finally, articles tend to fall between essays and papers in terms of length, formality, and audience (i.e., they’re generally shorter than papers but longer than essays).
The difference between essays, articles, and papers can be found in the audience. In other words, you will write them for different people and in different situations. If you need to explain something (from a textbook or another piece of writing) or if you are explaining a procedure to someone new to that topic, then your best bet would be to write an essay. Alternatively, if your purpose is simply to inform someone about something they might find interesting, articles would do just fine. Finally, if you want to share some information with a large group of people with similar interests, then a paper would be your choice. So which one should you choose? It depends on what exactly it is that you want to achieve with your writing.
Subject Matter
There are a few distinct differences in subject matter for these different types of written work. Essays should be focused and concise; articles cover a broader scope. For example, if you were writing about gun control in America from a historical standpoint, your essay would focus on one distinct period throughout American history (likely before modern times), while your articles could each look at a different time during which gun laws were passed, enacted or changed. Papers are similar to essays in that they have a narrow focus, but papers typically take on more of an academic tone than essays do. Papers may also have footnotes, bibliographies, and other citations within them. It’s important to note that there isn’t always a clear distinction between essay and paper; some papers can even read like essays!
Unlike essays and articles, papers do not focus on a single topic. Papers are meant to convey complex information that may have been derived from numerous sources of information. Papers are also typically longer than essays or articles, ranging from five to more than 20 pages in length. This makes papers a relatively demanding form of academic writing. While essays often focus on personal reflections or observations, papers delve into specific topics with objective research findings drawn from secondary sources such as newspapers, journals, or books. An essay writer can be anyone who writes essays for money. An essay writer can be someone who has experience working with students in high school, college, or university-level institutions.
Join the thousands who have sharpened their business writing skills with our award winning courses.
Copyright © 2024 Businesswritingblog.com.

- Walden University
- Faculty Portal
Writing a Paper: Comparing & Contrasting
A compare and contrast paper discusses the similarities and differences between two or more topics. The paper should contain an introduction with a thesis statement, a body where the comparisons and contrasts are discussed, and a conclusion.
Address Both Similarities and Differences
Because this is a compare and contrast paper, both the similarities and differences should be discussed. This will require analysis on your part, as some topics will appear to be quite similar, and you will have to work to find the differing elements.
Make Sure You Have a Clear Thesis Statement
Just like any other essay, a compare and contrast essay needs a thesis statement. The thesis statement should not only tell your reader what you will do, but it should also address the purpose and importance of comparing and contrasting the material.
Use Clear Transitions
Transitions are important in compare and contrast essays, where you will be moving frequently between different topics or perspectives.
- Examples of transitions and phrases for comparisons: as well, similar to, consistent with, likewise, too
- Examples of transitions and phrases for contrasts: on the other hand, however, although, differs, conversely, rather than.
For more information, check out our transitions page.
Structure Your Paper
Consider how you will present the information. You could present all of the similarities first and then present all of the differences. Or you could go point by point and show the similarity and difference of one point, then the similarity and difference for another point, and so on.
Include Analysis
It is tempting to just provide summary for this type of paper, but analysis will show the importance of the comparisons and contrasts. For instance, if you are comparing two articles on the topic of the nursing shortage, help us understand what this will achieve. Did you find consensus between the articles that will support a certain action step for people in the field? Did you find discrepancies between the two that point to the need for further investigation?
Make Analogous Comparisons
When drawing comparisons or making contrasts, be sure you are dealing with similar aspects of each item. To use an old cliché, are you comparing apples to apples?
- Example of poor comparisons: Kubista studied the effects of a later start time on high school students, but Cook used a mixed methods approach. (This example does not compare similar items. It is not a clear contrast because the sentence does not discuss the same element of the articles. It is like comparing apples to oranges.)
- Example of analogous comparisons: Cook used a mixed methods approach, whereas Kubista used only quantitative methods. (Here, methods are clearly being compared, allowing the reader to understand the distinction.
Related Webinar
Didn't find what you need? Search our website or email us .
Read our website accessibility and accommodation statement .
- Previous Page: Developing Arguments
- Next Page: Avoiding Logical Fallacies
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.
- School Guide
- English Grammar Free Course
- English Grammar Tutorial
- Parts of Speech
- Figure of Speech
- Tenses Chart
- Essay Writing
- Email Writing
- NCERT English Solutions
- English Difference Between
- SSC CGL English Syllabus
- SBI PO English Syllabus
- SBI Clerk English Syllabus
- IBPS PO English Syllabus
- IBPS CLERK English Syllabus
- Get vs Got | Difference Between Get and Got
- Job vs Work | Difference between Job and Work
- Lady vs Girl | Difference Between Lady and Girl
- Difference Between Which and That
- Into vs In To | Difference Between into and in to
- Difference Between Dessert and Desert
- Difference Between Altogether and All Together
- Difference Between Everyone and Everybody
- Difference Between Like and As
- Much vs More | Difference between Much and More
- Lightening vs Lightning | Difference Between Lightening and Lightning
- Difference Between brought and bought
- Difference Between Bear and Bare
- Will vs. Would
- Difference Between Single and Double Quotes
- Difference between May and Might | May vs Might
- Difference Between Concrete and Abstract Nouns
- Difference Between These and Those
- Difference between Till and Until
Difference Between Article and Essay
Articles and essays are both common forms of written communication that are utilized in a variety of sectors of study and vocations. Their goal, organization, and writing style, however, differ.

Articles are pieces of text that are published in a newspaper, magazine, journal, or website, either in print or electronically. It is intended for a big audience. It is founded on surveys, research, data, and analysis, among other things. Articles can be short or somewhat more than 1500 words. It is written with a certain goal in mind and teaches the readers about an idea.
Articles inform readers and keep them up to date by appearing in newspapers, magazines, encyclopedias, and, increasingly, websites. Let us use an example to better understand what an article is. Assume that in a research center, a scientist discovered any new notions and published a brief essay in a popular magazine, so that individuals in the same area found it useful and were also informed about a new thing.
Examples of articles include news articles, feature articles, and opinion pieces.
An essay is a formal and comprehensive piece of literature that describes a particular issue or topic analyzed and discussed. It refers to a short piece of writing on a particular subject. Mainly students in their academics are asked to write essays on some topics as a response to a question or proposition. It does not have a specific readership in mind.
Through essays, the writer or narrator expresses his or her personal views or opinion on a particular topic or a question and it is based on an educational and analytical tone. Let’s take an example and understand what is essay clearly suppose a school student has an exam and in the question paper he has been asked to write something explaining about Floods in India which is an example of an essay.
Examples of essays include academic essays, personal essays, and argumentative essays.
Tabular Differences between Article and Essay:
Conclusion:.
In summary, articles and essays are two different forms of written communication that serve different purposes. Articles are used to provide information about a particular topic, while essays are used to express personal opinions or persuade the reader to take a certain course of action. Understanding the differences between the two can help you choose the appropriate format for your writing task.
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.

- English-difference-between
- SSC/Banking
- 10 Best Todoist Alternatives in 2024 (Free)
- How to Get Spotify Premium Free Forever on iOS/Android
- Yahoo Acquires Instagram Co-Founders' AI News Platform Artifact
- OpenAI Introduces DALL-E Editor Interface
- Top 10 R Project Ideas for Beginners in 2024
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
Get in touch with us
Are you sure you want to logout?
Please select your grade.
- Earth and space

Article Writing – Differences Between Essay and Article
Writing an article, differences between essay writing and article writing.

Article – It is a piece of writing usually intended for publication in a newspaper, magazine, or on the internet (blog)
Objectives of Article Writing
- Describe an experience, person, event, or place
- Present an unbiased opinion on a topic with a balanced argument –Example
- Video games – Boon or Bane
- Compare and contrast -It is usually between two situations/scenarios /two particular areas. Example – Football Vs. Cricket sport –Changing trends
- Provide information about a problem. Offer suggestions to solve an issue/ a problem. Example -Conservation of wildlife
Three W’s -Starting Point
- What – Objective of the article
- Where – Medium used – Newspaper/Magazine/Website
- Who – Intended readers – specific groups such as students, teenagers, or adults
Language (to be used in article)– Formal, semi-formal, or informal as per the intended readers. Informal is usually used in blogs (online). Formal in school magazines and semi-formal in magazines and newspapers mostly.
Length – Lengthy for magazine articles: 4-6 paragraphs
Newspaper and online blog articles are concise with a less number of paragraphs. Depending on the topic -3-5 paragraphs

Format (Structure) of Writing An Article
- Heading Or Title
- Catchy to draw the attention of the readers
- Not more than five to six words
- Main theme/topic of the article to be stated in an attractive manner.
Tips To Write Catchy Headings
- Use numbers
- Appealing adjectives to connect emotionally with readers
Effortless, Fun, Incredible, Essential, Absolute
- Clear indication to what readers will gain
Reasons, Principles, Facts, Lessons, Ideas, Ways
- Use trigger words – Why, How, When
Example – If a topic is ‘bathing dogs at home’- ‘Why I love Bathing Dogs’/ 10 Unbelievable Ways of Bathing Dogs
- By line –Comes below the title. By line states the name of the writer. It can be written, not mandatorily.
- Introduction – First Paragraph
- Begin with proverb/ phrase or a quote related to the topic/main theme to make it interesting
- Reader comprehends the main theme
- Core of the topic – What, where, and when about the topic should be included in the introductory paragraph
Example – Natural calamities – What, where it occurs, and when can be introduced
- Body –Second/ Third/Fourth Paragraphs
- Engage readers with details – Why and how of the topic. Add facts and reports .
- Readers relate to the magnitude of the topic/ problem.
- Argument points – Agreement and disagreement
- Conclusion – Last Paragraph
- Give suggestions to solve the problem
- Show the change or progression toward the solution
- Conclude with a thought provoking statement/quote directing towards the future.
Steps to Be Followed for Article Writing
- Remember 3 Ws
- Select a topic
- Research the topic- It should be from credential sources –websites/ journals/ newspapers . Facts need to be presented. Data- percentage or ratio
- Write the article as per the standard format
- Edit the article for any errors- Punctuation and Grammar
- Proofread the article to recheck and review.
- Add images and infographics related to the topic. Infographic – Visual representation of data through graphs, pie-chart, etc.

Related topics

Exploring the World of Adjectives: Types, Usage, and Examples
What are Parts of Speech? Parts of speech determine words’ grammatical and semantic position in a sentence. Activity time The parts of speech are nouns, adverbs, conjunctions, pronouns, interjections, adjectives, articles, prepositions, and verbs. Identify the parts of speech of the underlined words in the following sentences. White- Adjective Big- Adjective Exciting- Adjectives New- […]

Memoir Writing: Basic Elements, Structures, and Types
Memoir: A memoir is a narrative written from an author’s perspective about a particular facet of his/her own life. ‘Memoir’ word comes from the French word ‘memoire’, which means ‘memory’ or ‘reminiscence’. Example Night: Elie Wiesel gives an account of how he survived his teenage years at Auschwitz and Buchenwald concentration camps during World War […]
Identification of Main Idea in Fiction and Non-fiction
Every story or paragraph or non-fictional text has at least one main idea. The MAIN IDEA is what the text is mostly about. (It is backed up or supported by SUPPORTING DETAILS) Before discussing how to find the main idea, we shall first look at TOPIC. Can you define a topic? A topic can be […]

Writing an Article: Structure and Essential Tips
What is an article? Structure of Article Writing : Title : Draw the attention of readers with an attractive title and indicate the main topic of the article Introduction : Attract the reader’s attention with a sentence that gives a general presentation of the topic. Main Body : Between these sentences, the body should do […]

Other topics
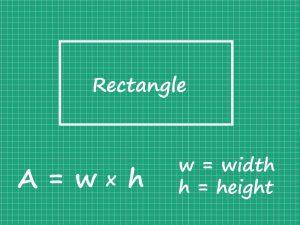
How to Find the Area of Rectangle?

How to Solve Right Triangles?

Ways to Simplify Algebraic Expressions

To revisit this article, visit My Profile, then View saved stories .
- Backchannel
- Newsletters
- WIRED Insider
- WIRED Consulting
Estelle Erasmus
How to Resist the Temptation of AI When Writing

Whether you're a student, a journalist, or a business professional, knowing how to do high-quality research and writing using trustworthy data and sources, without giving in to the temptation of AI or ChatGPT , is a skill worth developing.
As I detail in my book Writing That Gets Noticed , locating credible databases and sources and accurately vetting information can be the difference between turning a story around quickly or getting stuck with outdated information.
For example, several years ago the editor of Parents.com asked for a hot-take reaction to country singer Carrie Underwood saying that, because she was 35, she had missed her chance at having another baby. Since I had written about getting pregnant in my forties, I knew that as long as I updated my facts and figures, and included supportive and relevant peer-reviewed research, I could pull off this story. And I did.
The story ran later that day , and it led to other assignments. Here are some tips I’ve learned that you should consider mastering before you turn to automated tools like generative AI to handle your writing work for you.
Identify experts, peer-reviewed research study authors, and sources who can speak with authority—and ideally, offer easily understood sound bites or statistics on the topic of your work. Great sources include professors at major universities and media spokespeople at associations and organizations.
For example, writer and author William Dameron pinned his recent essay in HuffPost Personal around a statistic from the American Heart Association on how LGBTQ people experience higher rates of heart disease based on discrimination. Although he first found the link in a secondary source (an article in The New York Times ), he made sure that he checked the primary source: the original study that the American Heart Association gleaned the statistic from. He verified the information, as should any writer, because anytime a statistic is cited in a secondary source, errors can be introduced.
Jen Malia, author of The Infinity Rainbow Club series of children’s books (whom I recently interviewed on my podcast ), recently wrote a piece about dinosaur-bone hunting for Business Insider , which she covers in her book Violet and the Jurassic Land Exhibit.
After a visit to the Carnegie Museum of Natural History in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, Malia, whose books are set in Philadelphia, found multiple resources online and on the museum site that gave her the history of the Bone Wars , information on the exhibits she saw, and the scientific names of the dinosaurs she was inspired by. She also used the Library of Congress’ website, which offers digital collections and links to the Library of Congress Newspaper Collection.
Malia is a fan of searching for additional resources and citable documents with Google Scholar . “If I find that a secondary source mentions a newspaper article, I’m going to go to the original newspaper article, instead of just stopping there and quoting,” she says.
Julian Chokkattu

Brenda Stolyar

Adrienne So
Your local public library is a great source of free information, journals, and databases (even ones that generally require a subscription and include embargoed research). For example, your search should include everything from health databases ( Sage Journals , Scopus , PubMed) to databases for academic sources and journalism ( American Periodical Series Online , Statista , Academic Search Premier ) and databases for news, trends, market research, and polls (t he Harris Poll , Pew Research Center , Newsbank , ProPublica ).
Even if you find a study or paper that you can’t access in one of those databases, consider reaching out to the study’s lead author or researcher. In many cases, they’re happy to discuss their work and may even share the study with you directly and offer to talk about their research.
For journalist Paulette Perhach’s article on ADHD in The New York Times, she used Epic Research to see “dual team studies.” That's when two independent teams address the same topic or question, and ideally come to the same conclusions. She recommends locating research and experts via key associations for your topic. She also likes searching via Google Scholar but advises filtering it for studies and research in recent years to avoid using old data. She suggests keeping your links and research organized. “Always be ready to be peer-reviewed yourself,” Perhach says.
When you are looking for information for a story or project, you might be inclined to start with a regular Google search. But keep in mind that the internet is full of false information, and websites that look trustworthy can sometimes turn out to be businesses or companies with a vested interest in you taking their word as objective fact without additional scrutiny. Regardless of your writing project, unreliable or biased sources are a great way to torpedo your work—and any hope of future work.
Author Bobbi Rebell researched her book Launching Financial Grownups using the IRS’ website . “I might say that you can contribute a certain amount to a 401K, but it might be outdated because those numbers are always changing, and it’s important to be accurate,” she says. “AI and ChatGPT can be great for idea generation,” says Rebell, “but you have to be careful. If you are using an article someone was quoted in, you don’t know if they were misquoted or quoted out of context.”
If you use AI and ChatGPT for sourcing, you not only risk introducing errors, you risk introducing plagiarism—there is a reason OpenAI, the company behind ChatGPT, is being sued for downloading information from all those books.
Audrey Clare Farley, who writes historical nonfiction, has used a plethora of sites for historical research, including Women Also Know History , which allows searches by expertise or area of study, and JSTOR , a digital library database that offers a number of free downloads a month. She also uses Chronicling America , a project from the Library of Congress which gathers old newspapers to show how a historical event was reported, and Newspapers.com (which you can access via free trial but requires a subscription after seven days).
When it comes to finding experts, Farley cautions against choosing the loudest voices on social media platforms. “They might not necessarily be the most authoritative. I vet them by checking if they have a history of publication on the topic, and/or educational credentials.”
When vetting an expert, look for these red flags:
- You can’t find their work published or cited anywhere.
- They were published in an obscure journal.
- Their research is funded by a company, not a university, or they are the spokesperson for the company they are doing research for. (This makes them a public relations vehicle and not an appropriate source for journalism.)
And finally, the best endings for virtually any writing, whether it’s an essay, a research paper, an academic report, or a piece of investigative journalism, circle back to the beginning of the piece, and show your reader the transformation or the journey the piece has presented in perspective.
As always, your goal should be strong writing supported by research that makes an impact without cutting corners. Only then can you explore tools that might make the job a little easier, for instance by generating subheads or discovering a concept you might be missing—because then you'll have the experience and skills to see whether it's harming or helping your work.
You Might Also Like …
In your inbox: Introducing Politics Lab , your guide to election season
Google used her to tout diversity. Now she’s suing for discrimination
Our in-house physics whiz explains how heat pumps work
The big questions the Pentagon’s new UFO report fails to answer
AirPods Pro or AirPods Max? These are the best Apple buds for your ears

Michael Calore

Reece Rogers

Boone Ashworth
WIRED COUPONS

Dyson promo code: 20% off all purchases + free shipping

GoPro Promo Code: 15% off Cameras and Accessories

Up to +30% Off with your Samsung promo code

10% Off Everything w/ Dell Coupon Code

New customers Get 25% off w/ this Vistaprint coupon

Newegg Coupon: Take up to 60% Off monitors, PCs & more

Who will Trump pick as his running mate? In 2024, the ‘Veepstakes’ are higher than usual
Adjunct Senior Fellow, School of Global, Urban and Social Studies, RMIT University
Disclosure statement
Emma Shortis is Senior Researcher in International and Security Affairs at the Australia Institute, an independent think tank.
RMIT University provides funding as a strategic partner of The Conversation AU.
View all partners
Being second in line for leadership of the most powerful country in the world is not an easy job. But for Mike Pence, vice president under Donald Trump, things were even harder than usual.
As insurrectionists descended on the US Capitol on January 6, 2021, they had a specific target in mind – the outgoing vice president. They built a wooden gallows, and called out for him by name: “Hang Mike Pence! Hang Mike Pence!”
As the extensive congressional hearings into the insurrection later documented, the threats were not hollow. One informant told FBI investigators that “if given the chance”, certain far-right insurrectionists would have tried to kill him. Pence escaped with his life, but only just .
The insurrectionists, as a federal investigation alleges, were drawn to the Capitol by Trump, who had just lost the 2020 election to Joe Biden. They were after Trump’s VP because, as one later claimed, he had “ betrayed ” Trump by not refusing to certify the election results.
The job of vice president of the United States is not a normal one at the best of times. The person chosen to run alongside Trump in this year’s election will no doubt be keeping Pence’s experience in mind. It will likely be someone who can convincingly pledge undying loyalty to Trump. The former president – and his supporters – will expect nothing less.
Speculation over who that person might be is heating up, and Trump, as usual, is relishing drawing out the process in order to gain as much attention as possible. So, who – and how – will he choose?

Making race a priority
A vice presidential candidate is usually chosen based on a political calculation. For instance, the running mate can be seen to offset a presidential nominee’s weaknesses (be they real or perceived).
The relatively young northerner John F. Kennedy, for example, chose the much more politically experienced southerner, Lyndon B. Johnson. Barack Obama, running to be the first Black president, similarly chose the older and more experienced – and reassuringly white – Biden.
In his first run, Trump settled on Pence to offset his perceived weakness with evangelical voters – a critical mobilising base to any Republican candidate.
Read more: Why 'wokeness' has become the latest battlefront for white conservatives in America
Viewed through this lens, the commonly accepted wisdom is that Trump has both a race and a woman problem, and that he should choose a VP candidate who can address at least one of those concerns.
In the first category, the leading candidates appear to be two men who ran against Trump for this year’s nomination – Tim Scott and Vivek Ramaswamy.
Scott – a South Carolinian that Bloomberg has dubbed “Trump’s New Black Best Friend” – is the only Black Republican in the Senate. He has certainly indicated he is keen for the job, professing his love for Trump and recently announcing his engagement (being single is generally regarded as a political liability ).
During the Republican campaign for the presidential nomination, Ramaswamy had presented himself as the newer, shinier Trump. In one memorable moment in the debates, he was first to raise his hand when the candidates were asked who would still support Trump if he is convicted of a crime. Ramaswamy also quickly endorsed Trump when he dropped out.
Trump would no doubt be pleased with such public professions of loyalty. But there is no indication Trump considers race to be a problem for his candidacy – in fact, quite the opposite.
Trump has been leaning in to increasingly extreme racist rhetoric. If he thought race mattered to his chances, he would likely be behaving differently. Trump’s political rise began with his racist “birther” conspiracies about Obama. It is not a stretch to suggest many of his supporters would baulk at a ticket that wasn’t entirely white.
Why a conservative woman might make sense
In the second category, the accepted wisdom is that Trump’s “ woman problem ” is a direct result of the signature achievement of his administration: the appointment of three conservative justices to the Supreme Court, which subsequently led to the overturning of Roe v Wade.
As Biden put it recently , candidates underestimate the political and electoral power of women at their peril.
Among the leading women Republican VP candidates are Elise Stefanik, a congresswoman from New York, and Kristi Noem, the governor of South Dakota.
The fact both are considered leading candidates reveals the political calculations behind Trump’s possible selection. While Trump has flip-flopped on abortion restrictions himself, both Stefanik and Noem have extremely conservative positions on reproductive rights.
And given what we know about Trump’s views on women, it seems likely his judgement would be almost entirely aesthetic. There is a very specific political reason why Noem has grown out her hair and gotten new teeth.
Congresswomen Marjorie Taylor Green is often added to this list, but may have slimmer chances. While she literally wears her Trump loyalty on her head , she attracts a lot of attention. And Trump does not much like to share the spotlight.
It’s also entirely possible Trump will go with a wildcard candidate. He is increasingly resentful of what we could loosely characterise as “establishment” political advice designed to curb his worst instincts. His campaign is now almost entirely based on a desire for revenge and retribution against the people he believes held him back.
There has never been a reason to believe Trump will follow conventional political wisdom.
The stakes are higher than usual
Given the cult of personality that has developed around Trump, some argue his choice of running mate is unlikely to shift many votes. As a result, it doesn’t actually matter all that much.
Other keen watchers of American politics, though, argue the opposite. Given the advanced ages of both Trump and Biden, the VP pick is more important than usual, not least because of the higher-than-normal chance this person could be elevated to the Oval Office at some point.
Read more: Biden and Trump, though old, are both likely to survive to the end of the next president's term, demographers explain
In Trump’s case, some argue that if he wins, he will be a “lame duck” president from day one since it would be his second term in office. So, all eyes will be on his VP as the presumptive nominee for 2028.
This glosses over the very real questions about the continuity of constitutional law under a second Trump presidency, and ignores the noises Trump supporters are already making about trying to remove presidential term limits. It also assumes that, like Pence, Trump’s next VP would choose to put their own political future or American democracy above being an enthusiastic supporter of Trump’s authoritarianism. This is unlikely.
Like everything this time around, the stakes are higher than usual.
- Donald Trump
- Vice President
- 2024 US presidential election
- Vivek Ramaswamy

Communications and Events Officer

Lecturer (Hindi-Urdu)

Director, Defence and Security

Opportunities with the new CIEHF

School of Social Sciences – Public Policy and International Relations opportunities
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
David Brooks
What Would You Have Israel Do to Defend Itself?

By David Brooks
Opinion Columnist
There seems to be a broad consensus atop the Democratic Party about the war in Gaza, structured around two propositions. First, after the attacks of Oct. 7, Israel has the right to defend itself and defeat Hamas. Second, the way Israel is doing this is “over the top,” in President Biden’s words. The vast numbers of dead and starving children are gut wrenching, the devastation is overwhelming, and it’s hard not to see it all as indiscriminate.
Which leads to an obvious question: If the current Israeli military approach is inhumane, what’s the alternative? Is there a better military strategy Israel can use to defeat Hamas without a civilian blood bath? In recent weeks, I’ve been talking with security and urban warfare experts and others studying Israel’s approach to the conflict and scouring foreign policy and security journals in search of such ideas.
The thorniest reality that comes up is that this war is like few others because the crucial theater is underground. Before the war, Israelis estimated Hamas had dug around 100 miles of tunnels. Hamas leaders claimed they had a much more expansive network, and it turns out they were telling the truth. The current Israeli estimates range from 350 to about 500 miles of tunnels. The tunnel network, according to Israel, is where Hamas lives, holds hostages, stores weapons, builds missiles and moves from place to place. By some Israeli estimates, building these tunnels cost the Gazan people about a billion dollars, which could have gone to building schools and starting companies.
Hamas built many of its most important military and strategic facilities under hospitals, schools and so on. Its server farm, for example, was built under the offices of the U.N. relief agency in Gaza City, according to the Israeli military.
Daphne Richemond-Barak, the author of “Underground Warfare,” writes in Foreign Policy magazine: “Never in the history of tunnel warfare has a defender been able to spend months in such confined spaces. The digging itself, the innovative ways Hamas has made use of the tunnels and the group’s survival underground for this long have been unprecedented.”
In other words, in this war, Hamas is often underground, the Israelis are often aboveground, and Hamas seeks to position civilians directly between them. As Barry Posen, a professor at the security studies program at M.I.T., has written , Hamas’s strategy could be “described as ‘human camouflage’ and more ruthlessly as ‘human ammunition.’” Hamas’s goal is to maximize the number of Palestinians who die and in that way build international pressure until Israel is forced to end the war before Hamas is wiped out. Hamas’s survival depends on support in the court of international opinion and on making this war as bloody as possible for civilians, until Israel relents.
The Israelis have not found an easy way to clear and destroy the tunnels. Currently, Israel Defense Forces units clear the ground around a tunnel entrance and then, Richemond-Barak writes, they send in robots, drones and dogs to detect explosives and enemy combatants. Then units trained in underground warfare pour in. She writes: “It has become clear that Israel cannot possibly detect or map the entirety of Hamas’s tunnel network. For Israel to persuasively declare victory, in my view, it must destroy at least two-thirds of Hamas’s known underground infrastructure.”
This is slow, dangerous and destructive work. Israel rained destruction down on Gaza, especially early in the war. Because very few buildings can withstand gigantic explosions beneath them, this method involves a lot of wreckage, compounding the damage brought by tens of thousands of airstrikes. In part because of the tunnels, Israel has caused more destruction in Gaza than Syria did in Aleppo and more than Russia did in Mariupol, according to an Associated Press analysis .
John Spencer is the chair of urban warfare studies at the Modern War Institute at West Point, served two tours in Iraq and has made two visits to Gaza during the current war to observe operations there. He told me that Israel has done far more to protect civilians than the United States did in Afghanistan and Iraq. Spencer reports that Israel has warned civilians when and where it is about to begin operations and published an online map showing which areas to leave. It has sent out millions of pamphlets, texts and recorded calls warning civilians of coming operations. It has conducted four-hour daily pauses to allow civilians to leave combat areas. It has dropped speakers that blast out instructions about when to leave and where to go. These measures, Spencer told me, have telegraphed where the I.D.F. is going to move next and “have prolonged the war, to be honest.”
The measures are real, but in addition, Israel has cut off power in Gaza, making it hard for Palestinians to gain access to their phones and information and, most important, the evacuation orders published by Israel. Israel has also destroyed a vast majority of Gaza’s cellphone towers and on occasion bombed civilians in so-called safe areas and safe routes. For civilians, the urban battlefield is unbelievably nightmarish. They are caught between a nation enraged by Oct. 7 and using overwhelming and often reckless force and a terrorist group that has structured the battlefield to maximize the number of innocent dead.
So to step back: What do we make of the current Israeli strategy? Judged purely on a tactical level, there’s a strong argument that the I.D.F. has been remarkably effective against Hamas forces. I’ve learned to be suspicious of precise numbers tossed about in this war, but the I.D.F. claims to have killed over 13,000 of the roughly 30,000 Hamas troops. It has disrupted three-quarters of Hamas’s battalions so that they are no longer effective fighting units. It has also killed two of five brigade commanders and 19 of 24 battalion commanders. As of January, U.S. officials estimated that Israel had damaged or made inoperable 20 to 40 percent of the tunnels. Many Israelis believe the aggressive onslaught has begun to restore Israel’s deterrent power. (Readers should know that I have a son who served in the I.D.F. from 2014 to 2016; he’s been back home in the States since then.)
But on a larger political and strategic level, you’d have to conclude that the Israeli strategy has real problems. Global public opinion is moving decisively against Israel. The key shift is in Washington. Historically pro-Israeli Democrats like Biden and Senator Chuck Schumer are now pounding the current Israeli government with criticism. Biden wants Israel to call off its invasion of the final Hamas strongholds in the south. Israel is now risking a rupture with its closest ally and its only reliable friend on the U.N. Security Council. If Israel is going to defend itself from Iran, it needs strong alliances, and Israel is steadily losing those friends. Furthermore, Israeli tactics may be reducing Gaza to an ungovernable hellscape that will require further Israeli occupation and produce more terrorist groups for years.
Hamas’s strategy is pure evil, but it is based on an understanding of how the events on the ground will play out in the political world. The key weakness of the Israeli strategy has always been that it is aimed at defeating Hamas militarily without addressing Palestinian grievances and without paying enough attention to the wider consequences. As the leaders of Hamas watch Washington grow more critical of Jerusalem, they must know their strategy is working.
So we’re back to the original question: Is there a way to defeat Hamas with far fewer civilian deaths? Is there a way to fight the war that won’t leave Israel isolated?
One alternative strategy is that Israel should conduct a much more limited campaign. Fight Hamas, but with less intensity. To some degree, Israel has already made this adjustment. In January, Israel announced it was shifting to a smaller, more surgical strategy; U.S. officials estimated at the time that Israel had reduced the number of Israeli troops in northern Gaza to fewer than half of the 50,000 who were there in December.
The first problem with going further in this direction is that Israel may not be left with enough force to defeat Hamas. Even by Israel’s figures, most Hamas fighters are still out there. Will surgical operations be enough to defeat an enemy of this size? A similar strategy followed by America in Afghanistan doesn’t exactly inspire confidence.
A second problem is that the light footprint approach leaves power vacuums. This allows Hamas units to reconstitute themselves in areas Israel has already taken. As the United States learned in Iraq, if troop levels get too low, the horrors of war turn into the horrors of anarchy.
Another alternative strategy is targeted assassinations. Instead of continuing with a massive invasion, just focus on the Hamas fighters responsible for the Oct. 7 attack, the way Israel took down the terrorists who perpetrated the attack on Israeli Olympians in Munich in 1972.
The difference is that the attack on Israelis at Munich was a small-scale terrorist assault. Oct. 7 was a comprehensive invasion by an opposing army. Trying to assassinate perpetrators of that number would not look all that different from the current military approach. As Raphael Cohen, the director of the strategy and doctrine program at the RAND Corporation, notes : “In practical terms, killing or capturing those responsible for Oct. 7 means either thousands or potentially tens of thousands of airstrikes or raids dispersed throughout the Gaza Strip. Raids conducted on that scale are no longer a limited, targeted operation. It’s a full-blown war.”
Furthermore, Hamas’s fighters are hard to find, even the most notorious leaders. It took a decade for the United States to find Osama bin Laden, and Israel hasn’t had great success with eliminating key Hamas figures. In recent years, Israel tried to kill Mohammed Deif, the commander of Hamas’s military wing, seven times , without success.
The political costs of this kind of strategy might be even worse than the political costs of the current effort. Turkey, a Hamas supporter, has made it especially clear that Israel would pay a very heavy price if it went after Hamas leaders there.
A third alternative is a counterinsurgency strategy, of the kind that the United States used during the surge in Iraq. This is a less intense approach than the kind of massive invasion we’ve seen and would focus on going after insurgent cells and rebuilding the destroyed areas to build trust with the local population. The problem is that this works only after you’ve defeated the old regime and have a new host government you can work with. Israel is still trying to defeat the remaining Hamas battalions in places like Rafah. This kind of counterinsurgency approach would be an amendment to the current Israeli strategy, not a replacement.
Critics of the counterinsurgency approach point out that Gaza is not Iraq. If Israel tried to clear, hold and build new secure communities in classic counterinsurgency fashion, those new communities wouldn’t look like safe zones to the Palestinians. They would look like detention camps. Furthermore, if Israel settles on this strategy, it had better be prepared for a long war. One study of 71 counterinsurgency campaigns found that the median length of those conflicts was 10 years. Finally, the case for a full counterinsurgency approach would be stronger if that strategy had led to American victories in Afghanistan and Iraq, which it did not.
A fourth alternative is that Israel should just stop. It should settle for what it has achieved and not finish the job by invading Rafah and the southern areas of Gaza, or it should send in just small strike teams.
This is now the official Biden position. The national security adviser, Jake Sullivan, has argued that Israel can destroy Hamas in Gaza without a large invasion but “ by other means ” (which he did not elaborate on). The United States has asked Israel to send a delegation to Washington to discuss alternative Rafah strategies, which is good. The problem is that, first, there seems to be a budding disagreement over how much of Hamas needs to be destroyed to declare victory and, second, the I.D.F. estimates that there are 5,000 to 8,000 Hamas fighters in Rafah. Defeating an army that size would take thousands of airstrikes and raids. If you try to shrink the incursion, the math just doesn’t add up. As an Israeli war cabinet member, Benny Gantz, reportedly told U.S. officials, “Finishing the war without demilitarizing Rafah is like sending in firefighters to put out 80 percent of a fire.”
If this war ends with a large chunk of Hamas in place, it would be a long-term disaster for the region. Victorious, Hamas would dominate whatever government was formed to govern Gaza. Hamas would rebuild its military to continue its efforts to exterminate the Jewish state, delivering on its promise to launch more and more attacks like that of Oct. 7. Israel would have to impose an even more severe blockade than the one that it imposed before, this time to keep out the steel, concrete and other materials that Hamas uses to build tunnels and munitions, but that Gazans would need to rebuild their homes.
If Hamas survives this war intact, it would be harder for the global community to invest in rebuilding Gaza. It would be impossible to begin a peace process. As the veteran Middle East observers Robert Satloff and Dennis Ross wrote in American Purpose, “Any talk of a postwar political process is meaningless without Israel battlefield success: There can be no serious discussion of a two-state solution or any other political objective with Hamas either still governing Gaza or commanding a coherent military force.”
So where are we? I’m left with the tragic conclusion that there is no magical alternative military strategy. As Cohen wrote in Foreign Policy: “If the international community wants Israel to change strategies in Gaza, then it should offer a viable alternative strategy to Israel’s announced goal of destroying Hamas in the strip. And right now, that alternate strategy simply does not exist.”
The lack of viable alternatives leaves me with the further conclusion that Israel must ultimately confront Hamas leaders and forces in Rafah rather than leave it as a Hamas beachhead. For now, a cease-fire may be in the offing in Gaza, which is crucial for the release of more hostages.
Israel can use that time to put in place the humanitarian relief plan that Israeli security officials are now, at long last, proposing (but that the country’s prime minister, Benjamin Netanyahu, has not agreed to so far). Israel would also have to undertake a full-scale civilian evacuation of Rafah before any military operation and then try to take out as much of Hamas as possible with as few civilian casualties as possible. Given the horrors of this kind of tunnel-based urban warfare, this will be a painful time and painfully difficult. But absent some new alternative strategy, Biden is wrong to stop Israel from confronting the Hamas threat in southern Gaza.
Finally, like pretty much every expert I consulted, I’m also left with the conclusion that Israel has to completely rethink and change the humanitarian and political side of this operation. Israel needs to supplement its military strategy with an equally powerful Palestinian welfare strategy.
Israel’s core problems today are not mostly the fault of the I.D.F. or its self-defense strategy. Israel’s core problems flow from the growing callousness with which many of its people have viewed the Palestinians over the past decades, magnified exponentially by the trauma it has just suffered. Today, an emotionally shattered Israeli people see through the prism of Oct. 7. They feel existentially insecure, facing enemies on seven fronts — Gaza, West Bank, Lebanon, Syria, Iraq, Yemen and Iran. As Ross has noted , many often don’t see a distinction between Hamas and the Palestinians. Over 80 percent of West Bank Palestinians told pollsters they supported the Oct. 7 attack.
As the columnist Anshel Pfeffer wrote in the Israeli paper Haaretz, “The very idea that Israel needed to take any responsibility whatsoever for the place from which those who had murdered, raped and pillaged had emerged was seen as a moral abomination.”
Pfeffer continued that because of this attitude, “the government’s policy on humanitarian supplies to Gaza is a combination of vengeance, ignorance and incompetence.” He quoted unnamed I.D.F. officials who acknowledged that of course Israel is responsible for the welfare of the people in the area it controls but that the civilian leaders refuse to confront this.
On occasions when Israel has responded to world pressure and shifted policy, it has done so in secret, with no discussion in the cabinet.
An officer whose duties specifically include addressing the needs of civilians told Pfeffer that he didn’t have much to do except for some odd jobs.
Israel is failing to lay the groundwork for some sort of better Palestinian future — to its own detriment. The security experts I spoke with acknowledge that providing humanitarian aid will be hard. As Cohen told me: “If the Israeli military takes over distributing humanitarian aid to Gaza, they will likely lose soldiers in the process. And so Israelis are asking why should their boys die providing aid to someone who wants to kill them. So the United States needs to convince Israel that this is the morally and strategically right thing to do.”
For her book “How Terrorism Ends,” the Carnegie Mellon scholar Audrey Kurth Cronin looked at about 460 terrorist groups to investigate how they were defeated. Trying to beat them with military force alone rarely works. The root causes have to be addressed. As the retired general David Petraeus reminded his audience recently at the New Orleans Book Festival, “Over time, hearts and minds still matter.”
Israel also has to offer the world a vision for Gaza’s recovery, and it has to do it right now. Ross argues that after the war is over, the core logic of the peace has to be demilitarization in exchange for reconstruction. In an essay in Foreign Affairs, he sketches out a comprehensive rebuilding effort, bringing in nations and agencies from all over the world, so Gaza doesn’t become a failed state or remain under Hamas control.
Is any of this realistic given the vicious enmity now ripping through the region? Well, many peace breakthroughs of the past decades happened after one side suffered a crushing defeat. Egypt established ties with Israel after it was thoroughly defeated in the Yom Kippur War. When Israel attacked Hezbollah in southern Lebanon in 2006, the world was outraged. But after the fighting stopped, some Lebanese concluded that Hezbollah had dragged them into a bloody, unnecessary conflict. The Hezbollah leader, Hassan Nasrallah, was forced to acknowledge his error, saying he didn’t know Israel would react so violently. The Lebanese border stabilized. Israel’s over-the-top responses have sometimes served as effective deterrents and prevented further bloodshed.
Israel and the Palestinians have both just suffered shattering defeats. Maybe in the next few years they will do some difficult rethinking, and a new vision of the future will come into view. But that can happen only after Hamas is fully defeated as a military and governing force.
The Times is committed to publishing a diversity of letters to the editor. We’d like to hear what you think about this or any of our articles. Here are some tips . And here’s our email: [email protected] .
Follow The New York Times Opinion section on Facebook , Instagram , TikTok , WhatsApp , X and Threads .
David Brooks has been a columnist with The Times since 2003. He is the author, most recently, of “How to Know a Person: The Art of Seeing Others Deeply and Being Deeply Seen.” @ nytdavidbrooks

COMMENTS
An article may contain headings, which makes it attractive and readable. In contrast, an essay does not have any headings, sections or bullet points, however, it is a coherent and organized form of writing. An article is always written with a definite objective, which is to inform or make the readers aware of something.
The Difference Between an Article and an Essay. In composition studies, an article is a short work of nonfiction that typically appears in a magazine or newspaper or on a website. Unlike essays, which often highlight the subjective impressions of the author (or narrator ), articles are commonly written from an objective point of view.
One common mistake is using "article" when you actually mean "essay.". While both terms refer to written pieces, they have different purposes and structures. An article is a written work that provides information on a topic, while an essay is a more formal piece of writing that presents an argument or point of view.
Both articles and essays are forms of writing used for communication in many fields. Basically, that makes them somewhat similar and confusing. However, these two genres also have very distinct differences. "The term 'article' is used for the academic field, where it's a scientific sub-genre, and for the journalistic field, where it's ...
Article. Essay. 1. An article is a bit of writing intended to be shared in a magazine, newspaper, or other type of publication. An essay is a composition which belongs to a specific issue, or topic. 2. Articles tend to be objective. Essays tend to be subjective.
The most notable difference between an essay and an article is the tone. Essays traditionally are subjective pieces of formal writing that offers an analysis of a specific topic. In other words, an essay writer studies, researches, and forms a factually-based opinion on the topic in order to inform others about their ideas. An article is ...
The tone and the structure of the article are indeed different from the essay. The articles are written in simple English, so users of all ages will be able to understand them. The length of both pieces of writing also differs. There is no limit to the word count when writing an article. An essay can be as long as a page or as short as a paragraph.
An essay is a focused piece of writing designed to inform or persuade. There are many different types of essay, but they are often defined in four categories: argumentative, expository, narrative, and descriptive essays. Argumentative and expository essays are focused on conveying information and making clear points, while narrative and ...
An essay is a piece of writing that describes, analyzes and evaluates a particular topic whereas an article is a piece of writing that is included with others in a newspaper or other publications. The main difference between article and essay is that an article is written to inform the readers about some concept whereas an essay is usually ...
The point is, in different situations of communication and in a different context, article, paper and essay can be interchangeable notions. For example, experimental sciences tend to use words 'article' and 'paper' for pieces of writing that non-experimental sciences would call exactly the opposite names.
An essay is a focused piece of writing that explains, argues, describes, or narrates. In high school, you may have to write many different types of essays to develop your writing skills. Academic essays at college level are usually argumentative: you develop a clear thesis about your topic and make a case for your position using evidence ...
By assigning such essays, your instructors are encouraging you to make connections between texts or ideas, engage in critical thinking, and go beyond mere description or summary to generate interesting analysis: when you reflect on similarities and differences, you gain a deeper understanding of the items you are comparing, their relationship ...
6. Compare and contrast essay: A compare and contrast essay places two things side-by-side and points out the similarities and differences between them, usually to illustrate a larger point. In general, compare and contrast essays have body paragraphs that are organized in two main sections: a comparison section, and a contrast section. 7.
College writing is divided into two types: articles and essays. Despite a few resemblances, they also have significant distinctions respectively to each other. These disparities are premised on layout, intention, and information. Prior to delving into the distinction between those assignments, we should first examine their meanings.
Hi, the differences are based on the format, purpose and content. An article is a piece of writing that can be found in magazines, encyclopedias, websites, newspapers or other publications; the ...
The block method. In the block method, you cover each of the overall subjects you're comparing in a block. You say everything you have to say about your first subject, then discuss your second subject, making comparisons and contrasts back to the things you've already said about the first. Your text is structured like this: Subject 1.
Writers learn different strategies for articulating the implications of an argument—why it matters—and putting ideas in conversation with others by finding, reading, and incorporating ... In my writing classes, every time I asked students to write an essay on Hamlet, I wrote one myself—to get a sense of the steps they were going through and
Essays are typically 1-3 pages long. Articles vary in length but run longer than essays. Papers typically range from 10 to 15 pages or more. It's important to note that essay writer services have very different writing styles. Some writers write with a conversational tone, while others use a formal style for essays and articles.
Use Clear Transitions. Transitions are important in compare and contrast essays, where you will be moving frequently between different topics or perspectives. Examples of transitions and phrases for comparisons: as well, similar to, consistent with, likewise, too. Examples of transitions and phrases for contrasts: on the other hand, however ...
Tabular Differences between Article and Essay: Article. Essay. Written on a specific topic. Expresses the author's opinion on a particular topic. Informative in nature. Persuasive in nature. Usually published in a magazine, newspaper, or website. Can be published in various formats, such as a book or academic journal.
Writing an Article Differences Between Essay Writing and Article Writing. Article - It is a piece of writing usually intended for publication in a newspaper, magazine, or on the internet (blog) Objectives of Article Writing. Describe an experience, person, event, or place; Present an unbiased opinion on a topic with a balanced argument -Example
Start with a topic sentence introducing the subjects. Address each topic separately, listing all relevant points. Block 1: Discuss all the main points about the first topic. Present one aspect of the first topic. Provide evidence and analysis. Transition to the next aspect of the first topic. Block 2: Continue creating blocks for each topic you ...
Follow these tips to produce stronger writing that stands out on the web even in the age of AI and ChatGPT. Whether you're a student, a journalist, or a business professional, knowing how to do ...
A.I.-Generated Garbage Is Polluting Our Culture. Mr. Hoel is a neuroscientist and novelist and the author of The Intrinsic Perspective newsletter. Increasingly, mounds of synthetic A.I.-generated ...
Jonathan A. Greenblatt. New York. The writer is C.E.O. and national director of the Anti-Defamation League. To the Editor: I am an American Jew who can be both liberal regarding American politics ...
The person chosen to run alongside Trump in this year's election will no doubt be keeping Pence's experience in mind. It will likely be someone who can convincingly pledge undying loyalty to ...
(The essay-writing businesspeople are probably using these, too, so you're better off eliminating the middleman and using them on your own.) The best AI essay-helper tools.
By David Brooks. Opinion Columnist. There seems to be a broad consensus atop the Democratic Party about the war in Gaza, structured around two propositions. First, after the attacks of Oct. 7 ...