- Essay Samples
- College Essay
- Writing Tools
- Writing guide


Creative samples from the experts
↑ Return to Essay Samples
Cause & Effect Essay: Global Warming
Many people moan throughout the winter season. I know I do. I hate shoveling snow and worrying about whether my pipes will freeze. But I understand that snow and cold temperatures are a part of life. But will they be forever? The news about global warming has dire predictions about the future. Global warming is not a scary myth that scientists have made up, but a very real natural condition that is affecting the world more and more each day.
Global warming is, in essence, the gradual warming of the earth’s surface. The Earth’s average temperature is slowly rising, causing shorter and milder winter seasons in various countries around the world. But understanding global warming is nearly impossible without also having a base knowledge of another phenomenon: the Greenhouse Effect. Greenhouse gases are building up in our planet’s atmosphere and are acting like a blanket – trapping in heat that would otherwise be released back out into space. This is why global temperatures are rising.
There are many gases in the Earth’s atmosphere, but many are natural and harmless. CO2, however, is not healthy for the atmosphere. CO2 remains in the atmosphere longer than other gases and traps in heat extremely well. Even a slight increase in CO2 in the atmosphere can cause significant increases in global temperatures. Most CO2 emissions come from the burning of fossil fuels. Cars and other vehicles can produce up to 1.5 billion tons of CO2 annually, and coal-burning power plants can produce 2.5 billion tons. Sadly, the United States is responsible for a great deal of these emissions. And though the U.S. is doing their best to rectify this problem by lowering their emission rates, other countries are doing the opposite.
So what affect does global warming actually have on the environment and human civilization? Does an annual (average) increase in temperature of less than a degree actually transfer to a change in daily life? The answer is: yes. Global warming has been linked to the increase in wildfires and floods. It has been seen as the cause of rising sea levels and stronger hurricanes. Heat waves in Europe in 2003 led to the death of 20,000 people and over a thousand people in India. Also, the Arctic’s polar ice caps are melting at a rate of 9% every decade. Animals, such as polar bears, are losing their habitats and may end up extinct.
There are solutions to global warming, thankfully. Scientists and governments are working together to create ‘greener’ alternatives to daily life. People don’t have to give up their vehicles, but they may decide to choose hybrid cars instead of ones that rely solely on fossil fuels. Wind turbines and other sources of renewable energy can prevent the burning of coal, which is a major contributor to CO2. Global warming is not a problem that cannot be solved, but it is an issue that governments and average people need to be aware of in order to protect the people, animals, and habitats of planet Earth.

Follow Us on Social Media
Get more free essays

Send via email
Most useful resources for students:.
- Free Essays Download
- Writing Tools List
- Proofreading Services
- Universities Rating
Contributors Bio

Find more useful services for students
Free plagiarism check, professional editing, online tutoring, free grammar check.

25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

Essay on Global Warming
- Updated on
- Nov 23, 2023

Being able to write an essay is an integral part of mastering any language. Essays form an integral part of many academic and scholastic exams like the SAT , and UPSC amongst many others. It is a crucial evaluative part of English proficiency tests as well like IELTS , TOEFL , etc. Major essays are meant to emphasize public issues of concern that can have significant consequences on the world. To understand the concept of Global Warming and its causes and effects, we must first examine the many factors that influence the planet’s temperature and what this implies for the world’s future. Here’s an unbiased look at the essay on Global Warming and other essential related topics.
This Blog Includes:
Short essay on global warming and climate change, what are the causes of global warming, solutions for global warming, effects of global warming, essay on global warming paragraph in 100 – 150 words, essay on global warming in 250 words, essay on global warming in 500 words, essay on global warming upsc, climate change and global warming essay, tips to write an essay.
Since the industrial and scientific revolutions, Earth’s resources have been gradually depleted. Furthermore, the start of the world’s population’s exponential expansion is particularly hard on the environment. Simply put, as the population’s need for consumption grows, so does the use of natural resources , as well as the waste generated by that consumption.
Climate change has been one of the most significant long-term consequences of this. Climate change is more than just the rise or fall of global temperatures; it also affects rain cycles, wind patterns, cyclone frequencies, sea levels, and other factors. It has an impact on all major life groupings on the planet.
Also Read: World Population Day
What is Global Warming?
Global warming is the unusually rapid increase in Earth’s average surface temperature over the past century, primarily due to the greenhouse gases released by people burning fossil fuels . The greenhouse gases consist of methane, nitrous oxide, ozone, carbon dioxide, water vapour, and chlorofluorocarbons. The weather prediction has been becoming more complex with every passing year, with seasons more indistinguishable, and the general temperatures hotter. The number of hurricanes, cyclones, droughts, floods, etc., has risen steadily since the onset of the 21st century. The supervillain behind all these changes is Global Warming. The name is quite self-explanatory; it means the rise in the temperature of the Earth.
Also Read: What is a Natural Disaster?
According to recent studies, many scientists believe the following are the primary four causes of global warming:
- Deforestation
- Greenhouse emissions
- Carbon emissions per capita
Extreme global warming is causing natural disasters , which can be seen all around us. One of the causes of global warming is the extreme release of greenhouse gases that become trapped on the earth’s surface, causing the temperature to rise. Similarly, volcanoes contribute to global warming by spewing excessive CO2 into the atmosphere.
The increase in population is one of the major causes of Global Warming. This increase in population also leads to increased air pollution . Automobiles emit a lot of CO2, which remains in the atmosphere. This increase in population is also causing deforestation, which contributes to global warming.
The earth’s surface emits energy into the atmosphere in the form of heat, keeping the balance with the incoming energy. Global warming depletes the ozone layer, bringing about the end of the world. There is a clear indication that increased global warming will result in the extinction of all life on Earth’s surface.
Also Read: Land, Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation, and Wildlife Resources
Of course, industries and multinational conglomerates emit more carbon than the average citizen. Nonetheless, activism and community effort are the only viable ways to slow the worsening effects of global warming. Furthermore, at the state or government level, world leaders must develop concrete plans and step-by-step programmes to ensure that no further harm is done to the environment in general.
Although we are almost too late to slow the rate of global warming, finding the right solution is critical. Everyone, from individuals to governments, must work together to find a solution to Global Warming. Some of the factors to consider are pollution control, population growth, and the use of natural resources.
One very important contribution you can make is to reduce your use of plastic. Plastic is the primary cause of global warming, and recycling it takes years. Another factor to consider is deforestation, which will aid in the control of global warming. More tree planting should be encouraged to green the environment. Certain rules should also govern industrialization. Building industries in green zones that affect plants and species should be prohibited.
Also Read: Essay on Pollution
Global warming is a real problem that many people want to disprove to gain political advantage. However, as global citizens, we must ensure that only the truth is presented in the media.
This decade has seen a significant impact from global warming. The two most common phenomena observed are glacier retreat and arctic shrinkage. Glaciers are rapidly melting. These are clear manifestations of climate change.
Another significant effect of global warming is the rise in sea level. Flooding is occurring in low-lying areas as a result of sea-level rise. Many countries have experienced extreme weather conditions. Every year, we have unusually heavy rain, extreme heat and cold, wildfires, and other natural disasters.
Similarly, as global warming continues, marine life is being severely impacted. This is causing the extinction of marine species as well as other problems. Furthermore, changes are expected in coral reefs, which will face extinction in the coming years. These effects will intensify in the coming years, effectively halting species expansion. Furthermore, humans will eventually feel the negative effects of Global Warming.
Also Read: Concept of Sustainable Development
Sample Essays on Global Warming
Here are some sample essays on Global Warming:
Global Warming is caused by the increase of carbon dioxide levels in the earth’s atmosphere and is a result of human activities that have been causing harm to our environment for the past few centuries now. Global Warming is something that can’t be ignored and steps have to be taken to tackle the situation globally. The average temperature is constantly rising by 1.5 degrees Celsius over the last few years. The best method to prevent future damage to the earth, cutting down more forests should be banned and Afforestation should be encouraged. Start by planting trees near your homes and offices, participate in events, and teach the importance of planting trees. It is impossible to undo the damage but it is possible to stop further harm.
Also Read: Social Forestry
Over a long period, it is observed that the temperature of the earth is increasing. This affected wildlife , animals, humans, and every living organism on earth. Glaciers have been melting, and many countries have started water shortages, flooding, and erosion and all this is because of global warming. No one can be blamed for global warming except for humans. Human activities such as gases released from power plants, transportation, and deforestation have increased gases such as carbon dioxide, CFCs, and other pollutants in the earth’s atmosphere. The main question is how can we control the current situation and build a better world for future generations. It starts with little steps by every individual. Start using cloth bags made from sustainable materials for all shopping purposes, instead of using high-watt lights use energy-efficient bulbs, switch off the electricity, don’t waste water, abolish deforestation and encourage planting more trees. Shift the use of energy from petroleum or other fossil fuels to wind and solar energy. Instead of throwing out the old clothes donate them to someone so that it is recycled. Donate old books, don’t waste paper. Above all, spread awareness about global warming. Every little thing a person does towards saving the earth will contribute in big or small amounts. We must learn that 1% effort is better than no effort. Pledge to take care of Mother Nature and speak up about global warming.
Also Read: Types of Water Pollution
Global warming isn’t a prediction, it is happening! A person denying it or unaware of it is in the most simple terms complicit. Do we have another planet to live on? Unfortunately, we have been bestowed with this one planet only that can sustain life yet over the years we have turned a blind eye to the plight it is in. Global warming is not an abstract concept but a global phenomenon occurring ever so slowly even at this moment. Global Warming is a phenomenon that is occurring every minute resulting in a gradual increase in the Earth’s overall climate. Brought about by greenhouse gases that trap the solar radiation in the atmosphere, global warming can change the entire map of the earth, displacing areas, flooding many countries, and destroying multiple lifeforms. Extreme weather is a direct consequence of global warming but it is not an exhaustive consequence. There are virtually limitless effects of global warming which are all harmful to life on earth. The sea level is increasing by 0.12 inches per year worldwide. This is happening because of the melting of polar ice caps because of global warming. This has increased the frequency of floods in many lowland areas and has caused damage to coral reefs. The Arctic is one of the worst-hit areas affected by global warming. Air quality has been adversely affected and the acidity of the seawater has also increased causing severe damage to marine life forms. Severe natural disasters are brought about by global warming which has had dire effects on life and property. As long as mankind produces greenhouse gases, global warming will continue to accelerate. The consequences are felt at a much smaller scale which will increase to become drastic shortly. The power to save the day lies in the hands of humans, the need is to seize the day. Energy consumption should be reduced on an individual basis. Fuel-efficient cars and other electronics should be encouraged to reduce the wastage of energy sources. This will also improve air quality and reduce the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. Global warming is an evil that can only be defeated when fought together. It is better late than never. If we all take steps today, we will have a much brighter future tomorrow. Global warming is the bane of our existence and various policies have come up worldwide to fight it but that is not enough. The actual difference is made when we work at an individual level to fight it. Understanding its import now is crucial before it becomes an irrevocable mistake. Exterminating global warming is of utmost importance and each one of us is as responsible for it as the next.
Always hear about global warming everywhere, but do we know what it is? The evil of the worst form, global warming is a phenomenon that can affect life more fatally. Global warming refers to the increase in the earth’s temperature as a result of various human activities. The planet is gradually getting hotter and threatening the existence of lifeforms on it. Despite being relentlessly studied and researched, global warming for the majority of the population remains an abstract concept of science. It is this concept that over the years has culminated in making global warming a stark reality and not a concept covered in books. Global warming is not caused by one sole reason that can be curbed. There are multifarious factors that cause global warming most of which are a part of an individual’s daily existence. Burning of fuels for cooking, in vehicles, and for other conventional uses, a large amount of greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide, and methane amongst many others is produced which accelerates global warming. Rampant deforestation also results in global warming as lesser green cover results in an increased presence of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere which is a greenhouse gas. Finding a solution to global warming is of immediate importance. Global warming is a phenomenon that has to be fought unitedly. Planting more trees can be the first step that can be taken toward warding off the severe consequences of global warming. Increasing the green cover will result in regulating the carbon cycle. There should be a shift from using nonrenewable energy to renewable energy such as wind or solar energy which causes less pollution and thereby hinder the acceleration of global warming. Reducing energy needs at an individual level and not wasting energy in any form is the most important step to be taken against global warming. The warning bells are tolling to awaken us from the deep slumber of complacency we have slipped into. Humans can fight against nature and it is high time we acknowledged that. With all our scientific progress and technological inventions, fighting off the negative effects of global warming is implausible. We have to remember that we do not inherit the earth from our ancestors but borrow it from our future generations and the responsibility lies on our shoulders to bequeath them a healthy planet for life to exist.
Also Read: Essay on Disaster Management
One good action in a day is to combat the heat.
Global Warming and Climate Change are two sides of the same coin. Both are interrelated with each other and are two issues of major concern worldwide. Greenhouse gases released such as carbon dioxide, CFCs, and other pollutants in the earth’s atmosphere cause Global Warming which leads to climate change. Black holes have started to form in the ozone layer that protects the earth from harmful ultraviolet rays. Human activities have created climate change and global warming. Industrial waste and fumes are the major contributors to global warming. Another factor affecting is the burning of fossil fuels, deforestation and also one of the reasons for climate change. Global warming has resulted in shrinking mountain glaciers in Antarctica, Greenland, and the Arctic and causing climate change. Switching from the use of fossil fuels to energy sources like wind and solar. When buying any electronic appliance buy the best quality with energy savings stars. Don’t waste water and encourage rainwater harvesting in your community.
Also Read: Essay on Air Pollution
Writing an effective essay needs skills that few people possess and even fewer know how to implement. While writing an essay can be an assiduous task that can be unnerving at times, some key pointers can be inculcated to draft a successful essay. These involve focusing on the structure of the essay, planning it out well, and emphasizing crucial details. Mentioned below are some pointers that can help you write better structure and more thoughtful essays that will get across to your readers:
- Prepare an outline for the essay to ensure continuity and relevance and no break in the structure of the essay
- Decide on a thesis statement that will form the basis of your essay. It will be the point of your essay and help readers understand your contention
- Follow the structure of an introduction, a detailed body followed by a conclusion so that the readers can comprehend the essay in a particular manner without any dissonance.
- Make your beginning catchy and include solutions in your conclusion to make the essay insightful and lucrative to read
- Reread before putting it out and add your flair to the essay to make it more personal and thereby unique and intriguing for readers
Relevant Blogs
Ans. Both natural and man-made factors contribute to global warming. The natural one also contains methane gas, volcanic eruptions, and greenhouse gases. Deforestation , mining , livestock raising, burning fossil fuels, and other man-made causes are next.
Ans. The government and the general public can work together to stop global warming. Trees must be planted more often, and deforestation must be prohibited. Auto usage needs to be curbed, and recycling needs to be promoted.
Ans. Switching to renewable energy sources , adopting sustainable farming, transportation, and energy methods, and conserving water and other natural resources.
We hope this blog gave you an idea about how to write and present an essay on global warming that puts forth your opinions. The skill of writing an essay comes in handy when appearing for standardized language tests . Thinking of taking one soon? Leverage Edu provides the best online test prep for the same via Leverage Live . Register today to know more!
Digvijay Singh
Having 2+ years of experience in educational content writing, withholding a Bachelor's in Physical Education and Sports Science and a strong interest in writing educational content for students enrolled in domestic and foreign study abroad programmes. I believe in offering a distinct viewpoint to the table, to help students deal with the complexities of both domestic and foreign educational systems. Through engaging storytelling and insightful analysis, I aim to inspire my readers to embark on their educational journeys, whether abroad or at home, and to make the most of every learning opportunity that comes their way.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *
This was really a good essay on global warming… There has been used many unic words..and I really liked it!!!Seriously I had been looking for a essay about Global warming just like this…
Thank you for the comment!
I want to learn how to write essay writing so I joined this page.This page is very useful for everyone.
Hi, we are glad that we could help you to write essays. We have a beginner’s guide to write essays ( https://leverageedu.com/blog/essay-writing/ ) and we think this might help you.
It is not good , to have global warming in our earth .So we all have to afforestation program on all the world.
thank you so much
Very educative , helpful and it is really going to strength my English knowledge to structure my essay in future
Thank you for the comment, please follow our newsletter to get more insights on studying abroad and exams!
Global warming is the increase in 𝓽𝓱𝓮 ᴀᴠᴇʀᴀɢᴇ ᴛᴇᴍᴘᴇʀᴀᴛᴜʀᴇs ᴏғ ᴇᴀʀᴛʜ🌎 ᴀᴛᴍᴏsᴘʜᴇʀᴇ

Leaving already?
8 Universities with higher ROI than IITs and IIMs
Grab this one-time opportunity to download this ebook
Connect With Us
25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. take the first step today..

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
September 2024
January 2025
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
Essay on Effects of Global Warming for Students and Children
500+ words essay on effects of global warming.
Global warming refers to climate change that causes an increase in the average of Earth’s temperature. Natural events and human influences are believed to be top contributions towards the increase in average temperatures. Global warming is a rise in the surface and atmospheric temperature of the earth that has changed various life forms on the earth. The issues that ascertain global warming are divided into two broad categories – “natural” and “human influences” of global warming.

Natural Causes of Global Warming
The climate has been continuously changing for centuries. One natural cause of global warming is greenhouse gases. Greenhouse gases are carbon monoxide and sulphur dioxide . It traps the solar rays and prevents them from escaping the surface of the earth.
This causes an increase in the temperature of the earth. Volcanic eruptions are another reason for global warming. A single volcanic eruption can release a great amount of carbon dioxide and ash to the atmosphere. Increased carbon dioxide leads to a rise in the temperature of the earth.
Also, methane gas is another contributor to global warming. Methane is also a greenhouse gas. Methane is twenty times more effective in trapping heat in the atmosphere than carbon dioxide. Usually, methane gas is released from many areas like animal waste, landfill, natural gas, and others.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Human Influences on Global Warming
Human influence has been a very serious issue now as it is contributing more than natural causes of global warming. Since human evolution, the earth has been changing for many years until now and it is still changing because of our modern lifestyle. Human activities include industrial production, burning fossil fuel, mining of minerals, cattle rearing and deforestation.
Industries, transportation such as cars, buses, trucks burn fuel to power machines, which eventually releases carbon dioxide and monoxide from the exhaust, leading to an increase in a temperature rise of Earth’s atmosphere.
Another contributor is mining. During the process of mining, the methane gas trapped below the earth escapes. Rearing cattle also causes the release of methane from manure. Another cause is the most common but most dangerous – deforestation.
Deforestation is a human influence because human have been cutting down trees to produce paper, wood, build houses and more. Trees can absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and their absence can lead to the concentration of such gases.
The Effect of Global Warming
The impact that global warming is causing on earth is extremely serious. There are many hazardous effects that will happen in the future if global warming continues. It includes melting of polar ice caps, leading to an increase in sea level drowning coastlines and slowly submerging continents.
Recent studies by National Snow and Ice Datacenter “if the ice melted today the seas would rise about 230 feet”. Another effect is climate change leading to the extinction of various species. More hurricanes, cyclonic storms, heat waves, drought, and extreme rainfalls will occur causing disaster to humankind.
The solution to Stop Global Warming
We humans need to work together towards the prevention of global warming. To reduce global warming we can contribute by reducing the production and concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. We need to curb usage of gasoline, electricity and other activities including mining and industrialization that cause global warming.
Another way to reduce global warming is through recycling. Recycling can help reduce open burning of garbage by reusing plastic bags, bottles, papers or glass. We need to stop open burning dry leaves or burning garbage. It contributes to releasing carbon dioxide and toxins. Besides, we should reduce deforestation and start planting more trees. Trees will help improve the temperature on earth and prevent drastic climatic change.
From today’s scenario, we can derive that our earth is “sick” and we humans need to “heal” it. Global Warming has already caused many problems for human and we need to prevent disasters of the future. Our generation needs to take care of the earth with immediate effect to safeguard future generations or they will suffer the consequences of global warming.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App


Search the United Nations
- What Is Climate Change
- Myth Busters
- Renewable Energy
- Finance & Justice
- Initiatives
- Sustainable Development Goals
- Paris Agreement
- Climate Ambition Summit 2023
- Climate Conferences
- Press Material
- Communications Tips

Causes and Effects of Climate Change
Fossil fuels – coal, oil and gas – are by far the largest contributor to global climate change, accounting for over 75 per cent of global greenhouse gas emissions and nearly 90 per cent of all carbon dioxide emissions. As greenhouse gas emissions blanket the Earth, they trap the sun’s heat. This leads to global warming and climate change. The world is now warming faster than at any point in recorded history. Warmer temperatures over time are changing weather patterns and disrupting the usual balance of nature. This poses many risks to human beings and all other forms of life on Earth.

Sacred plant helps forge a climate-friendly future in Paraguay

El Niño and climate crisis raise drought fears in Madagascar
The El Niño climate pattern, a naturally occurring phenomenon, can significantly disrupt global weather systems, but the human-made climate emergency is exacerbating the destructive effects.
“Verified for Climate” champions: Communicating science and solutions
Gustavo Figueirôa, biologist and communications director at SOS Pantanal, and Habiba Abdulrahman, eco-fashion educator, introduce themselves as champions for “Verified for Climate,” a joint initiative of the United Nations and Purpose to stand up to climate disinformation and put an end to the narratives of denialism, doomism, and delay.
Facts and figures
- What is climate change?
- Causes and effects
- Myth busters
Cutting emissions
- Explaining net zero
- High-level expert group on net zero
- Checklists for credibility of net-zero pledges
- Greenwashing
- What you can do
Clean energy
- Renewable energy – key to a safer future
- What is renewable energy
- Five ways to speed up the energy transition
- Why invest in renewable energy
- Clean energy stories
- A just transition
Adapting to climate change
- Climate adaptation
- Early warnings for all
- Youth voices
Financing climate action
- Finance and justice
- Loss and damage
- $100 billion commitment
- Why finance climate action
- Biodiversity
- Human Security
International cooperation
- What are Nationally Determined Contributions
- Acceleration Agenda
- Climate Ambition Summit
- Climate conferences (COPs)
- Youth Advisory Group
- Action initiatives
- Secretary-General’s speeches
- Press material
- Fact sheets
- Communications tips
Global Warming 101
Everything you wanted to know about our changing climate but were too afraid to ask.

Temperatures in Beijing rose above 104 degrees Fahrenheit on July 6, 2023.
Jia Tianyong/China News Service/VCG via Getty Images

- Share this page block
What is global warming?
What causes global warming, how is global warming linked to extreme weather, what are the other effects of global warming, where does the united states stand in terms of global-warming contributors, is the united states doing anything to prevent global warming, is global warming too big a problem for me to help tackle.
A: Since the Industrial Revolution, the global annual temperature has increased in total by a little more than 1 degree Celsius, or about 2 degrees Fahrenheit. Between 1880—the year that accurate recordkeeping began—and 1980, it rose on average by 0.07 degrees Celsius (0.13 degrees Fahrenheit) every 10 years. Since 1981, however, the rate of increase has more than doubled: For the last 40 years, we’ve seen the global annual temperature rise by 0.18 degrees Celsius, or 0.32 degrees Fahrenheit, per decade.
The result? A planet that has never been hotter . Nine of the 10 warmest years since 1880 have occurred since 2005—and the 5 warmest years on record have all occurred since 2015. Climate change deniers have argued that there has been a “pause” or a “slowdown” in rising global temperatures, but numerous studies, including a 2018 paper published in the journal Environmental Research Letters , have disproved this claim. The impacts of global warming are already harming people around the world.
Now climate scientists have concluded that we must limit global warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius by 2040 if we are to avoid a future in which everyday life around the world is marked by its worst, most devastating effects: the extreme droughts, wildfires, floods, tropical storms, and other disasters that we refer to collectively as climate change . These effects are felt by all people in one way or another but are experienced most acutely by the underprivileged, the economically marginalized, and people of color, for whom climate change is often a key driver of poverty, displacement, hunger, and social unrest.
A: Global warming occurs when carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) and other air pollutants collect in the atmosphere and absorb sunlight and solar radiation that have bounced off the earth’s surface. Normally this radiation would escape into space, but these pollutants, which can last for years to centuries in the atmosphere, trap the heat and cause the planet to get hotter. These heat-trapping pollutants—specifically carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, water vapor, and synthetic fluorinated gases—are known as greenhouse gases, and their impact is called the greenhouse effect.
Though natural cycles and fluctuations have caused the earth’s climate to change several times over the last 800,000 years, our current era of global warming is directly attributable to human activity—specifically to our burning of fossil fuels such as coal, oil, gasoline, and natural gas, which results in the greenhouse effect. In the United States, the largest source of greenhouse gases is transportation (29 percent), followed closely by electricity production (28 percent) and industrial activity (22 percent). Learn about the natural and human causes of climate change .
Curbing dangerous climate change requires very deep cuts in emissions, as well as the use of alternatives to fossil fuels worldwide. The good news is that countries around the globe have formally committed—as part of the 2015 Paris Climate Agreement —to lower their emissions by setting new standards and crafting new policies to meet or even exceed those standards. The not-so-good news is that we’re not working fast enough. To avoid the worst impacts of climate change, scientists tell us that we need to reduce global carbon emissions by as much as 40 percent by 2030. For that to happen, the global community must take immediate, concrete steps: to decarbonize electricity generation by equitably transitioning from fossil fuel–based production to renewable energy sources like wind and solar; to electrify our cars and trucks; and to maximize energy efficiency in our buildings, appliances, and industries.
A: Scientists agree that the earth’s rising temperatures are fueling longer and hotter heat waves , more frequent droughts , heavier rainfall , and more powerful hurricanes .
In 2015, for example, scientists concluded that a lengthy drought in California—the state’s worst water shortage in 1,200 years —had been intensified by 15 to 20 percent by global warming. They also said the odds of similar droughts happening in the future had roughly doubled over the past century. And in 2016, the National Academies of Science, Engineering, and Medicine announced that we can now confidently attribute some extreme weather events, like heat waves, droughts, and heavy precipitation, directly to climate change.
The earth’s ocean temperatures are getting warmer, too—which means that tropical storms can pick up more energy. In other words, global warming has the ability to turn a category 3 storm into a more dangerous category 4 storm. In fact, scientists have found that the frequency of North Atlantic hurricanes has increased since the early 1980s, as has the number of storms that reach categories 4 and 5. The 2020 Atlantic hurricane season included a record-breaking 30 tropical storms, 6 major hurricanes, and 13 hurricanes altogether. With increased intensity come increased damage and death. The United States saw an unprecedented 22 weather and climate disasters that caused at least a billion dollars’ worth of damage in 2020, but, according to NOAA, 2017 was the costliest on record and among the deadliest as well: Taken together, that year's tropical storms (including Hurricanes Harvey, Irma, and Maria) caused nearly $300 billion in damage and led to more than 3,300 fatalities.
The impacts of global warming are being felt everywhere. Extreme heat waves have caused tens of thousands of deaths around the world in recent years. And in an alarming sign of events to come, Antarctica has lost nearly four trillion metric tons of ice since the 1990s. The rate of loss could speed up if we keep burning fossil fuels at our current pace, some experts say, causing sea levels to rise several meters in the next 50 to 150 years and wreaking havoc on coastal communities worldwide.
A: Each year scientists learn more about the consequences of global warming , and each year we also gain new evidence of its devastating impact on people and the planet. As the heat waves, droughts, and floods associated with climate change become more frequent and more intense, communities suffer and death tolls rise. If we’re unable to reduce our emissions, scientists believe that climate change could lead to the deaths of more than 250,000 people around the globe every year and force 100 million people into poverty by 2030.
Global warming is already taking a toll on the United States. And if we aren’t able to get a handle on our emissions, here’s just a smattering of what we can look forward to:
- Disappearing glaciers, early snowmelt, and severe droughts will cause more dramatic water shortages and continue to increase the risk of wildfires in the American West.
- Rising sea levels will lead to even more coastal flooding on the Eastern Seaboard, especially in Florida, and in other areas such as the Gulf of Mexico.
- Forests, farms, and cities will face troublesome new pests , heat waves, heavy downpours, and increased flooding . All of these can damage or destroy agriculture and fisheries.
- Disruption of habitats such as coral reefs and alpine meadows could drive many plant and animal species to extinction.
- Allergies, asthma, and infectious disease outbreaks will become more common due to increased growth of pollen-producing ragweed , higher levels of air pollution , and the spread of conditions favorable to pathogens and mosquitoes.
Though everyone is affected by climate change, not everyone is affected equally. Indigenous people, people of color, and the economically marginalized are typically hit the hardest. Inequities built into our housing , health care , and labor systems make these communities more vulnerable to the worst impacts of climate change—even though these same communities have done the least to contribute to it.
A: In recent years, China has taken the lead in global-warming pollution , producing about 26 percent of all CO2 emissions. The United States comes in second. Despite making up just 4 percent of the world’s population, our nation produces a sobering 13 percent of all global CO2 emissions—nearly as much as the European Union and India (third and fourth place) combined. And America is still number one, by far, in cumulative emissions over the past 150 years. As a top contributor to global warming, the United States has an obligation to help propel the world to a cleaner, safer, and more equitable future. Our responsibility matters to other countries, and it should matter to us, too.
A: We’ve started. But in order to avoid the worsening effects of climate change, we need to do a lot more—together with other countries—to reduce our dependence on fossil fuels and transition to clean energy sources.
Under the administration of President Donald Trump (a man who falsely referred to global warming as a “hoax”), the United States withdrew from the Paris Climate Agreement, rolled back or eliminated dozens of clean air protections, and opened up federally managed lands, including culturally sacred national monuments, to fossil fuel development. Although President Biden has pledged to get the country back on track, years of inaction during and before the Trump administration—and our increased understanding of global warming’s serious impacts—mean we must accelerate our efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Despite the lack of cooperation from the Trump administration, local and state governments made great strides during this period through efforts like the American Cities Climate Challenge and ongoing collaborations like the Regional Greenhouse Gas Initiative . Meanwhile, industry and business leaders have been working with the public sector, creating and adopting new clean-energy technologies and increasing energy efficiency in buildings, appliances, and industrial processes.
Today the American automotive industry is finding new ways to produce cars and trucks that are more fuel efficient and is committing itself to putting more and more zero-emission electric vehicles on the road. Developers, cities, and community advocates are coming together to make sure that new affordable housing is built with efficiency in mind , reducing energy consumption and lowering electric and heating bills for residents. And renewable energy continues to surge as the costs associated with its production and distribution keep falling. In 2020 renewable energy sources such as wind and solar provided more electricity than coal for the very first time in U.S. history.
President Biden has made action on global warming a high priority. On his first day in office, he recommitted the United States to the Paris Climate Agreement, sending the world community a strong signal that we were determined to join other nations in cutting our carbon pollution to support the shared goal of preventing the average global temperature from rising more than 1.5 degrees Celsius above preindustrial levels. (Scientists say we must stay below a 2-degree increase to avoid catastrophic climate impacts.) And significantly, the president has assembled a climate team of experts and advocates who have been tasked with pursuing action both abroad and at home while furthering the cause of environmental justice and investing in nature-based solutions.
A: No! While we can’t win the fight without large-scale government action at the national level , we also can’t do it without the help of individuals who are willing to use their voices, hold government and industry leaders to account, and make changes in their daily habits.
Wondering how you can be a part of the fight against global warming? Reduce your own carbon footprint by taking a few easy steps: Make conserving energy a part of your daily routine and your decisions as a consumer. When you shop for new appliances like refrigerators, washers, and dryers, look for products with the government’s ENERGY STAR ® label; they meet a higher standard for energy efficiency than the minimum federal requirements. When you buy a car, look for one with the highest gas mileage and lowest emissions. You can also reduce your emissions by taking public transportation or carpooling when possible.
And while new federal and state standards are a step in the right direction, much more needs to be done. Voice your support of climate-friendly and climate change preparedness policies, and tell your representatives that equitably transitioning from dirty fossil fuels to clean power should be a top priority—because it’s vital to building healthy, more secure communities.
You don’t have to go it alone, either. Movements across the country are showing how climate action can build community , be led by those on the front lines of its impacts, and create a future that’s equitable and just for all .
This story was originally published on March 11, 2016 and has been updated with new information and links.
This NRDC.org story is available for online republication by news media outlets or nonprofits under these conditions: The writer(s) must be credited with a byline; you must note prominently that the story was originally published by NRDC.org and link to the original; the story cannot be edited (beyond simple things such as grammar); you can’t resell the story in any form or grant republishing rights to other outlets; you can’t republish our material wholesale or automatically—you need to select stories individually; you can’t republish the photos or graphics on our site without specific permission; you should drop us a note to let us know when you’ve used one of our stories.
Related Stories

Liquefied Natural Gas 101

What’s the Most Energy-Efficient Water Heater?

What Do “Better” Batteries Look Like?
When you sign up, you’ll become a member of NRDC’s Activist Network. We will keep you informed with the latest alerts and progress reports.

Yale Program on Climate Change Communication
- About YPCCC
- Yale Climate Connections
- Student Employment
- For The Media
- Past Events
- YPCCC in the News
- Climate Change in the American Mind (CCAM)
- Publications
- Climate Opinion Maps
- Climate Opinion Factsheets
- Six Americas Super Short Survey (SASSY)
- Resources for Educators
- All Tools & Interactives
- Partner with YPCCC
Home / For Educators: Grades 6-12 / Climate Explained: Introductory Essays About Climate Change Topics
Climate Explained: Introductory Essays About Climate Change Topics
Filed under: backgrounders for educators ,.
Climate Explained, a part of Yale Climate Connections, is an essay collection that addresses an array of climate change questions and topics, including why it’s cold outside if global warming is real, how we know that humans are responsible for global warming, and the relationship between climate change and national security.
More Activities like this

Climate Change Basics: Five Facts, Ten Words
Backgrounders for Educators
To simplify the scientific complexity of climate change, we focus on communicating five key facts about climate change that everyone should know.

Why should we care about climate change?
Having different perspectives about global warming is natural, but the most important thing that anyone should know about climate change is why it matters.

External Resources
Looking for resources to help you and your students build a solid climate change science foundation? We’ve compiled a list of reputable, student-friendly links to help you do just that!
Subscribe to our mailing list
Please select all the ways you would like to hear from Yale Program on Climate Change Communication:
You can unsubscribe at any time by clicking the link in the footer of our emails. For information about our privacy practices, please visit our website.
We use Mailchimp as our marketing platform. By clicking below to subscribe, you acknowledge that your information will be transferred to Mailchimp for processing. Learn more about Mailchimp's privacy practices here.
- Biology Article
- Essay on Global Warming
Essay On Global Warming
Essay on global warming is an important topic for students to understand. The essay brings to light the plight of the environment and the repercussion of anthropogenic activities. Continue reading to discover tips and tricks for writing an engaging and interesting essay on global warming.
Essay On Global Warming in 300 Words
Global warming is a phenomenon where the earth’s average temperature rises due to increased amounts of greenhouse gases. Greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide, methane and ozone trap the incoming radiation from the sun. This effect creates a natural “blanket”, which prevents the heat from escaping back into the atmosphere. This effect is called the greenhouse effect.
Contrary to popular belief, greenhouse gases are not inherently bad. In fact, the greenhouse effect is quite important for life on earth. Without this effect, the sun’s radiation would be reflected back into the atmosphere, freezing the surface and making life impossible. However, when greenhouse gases in excess amounts get trapped, serious repercussions begin to appear. The polar ice caps begin to melt, leading to a rise in sea levels. Furthermore, the greenhouse effect is accelerated when polar ice caps and sea ice melts. This is due to the fact the ice reflects 50% to 70% of the sun’s rays back into space, but without ice, the solar radiation gets absorbed. Seawater reflects only 6% of the sun’s radiation back into space. What’s more frightening is the fact that the poles contain large amounts of carbon dioxide trapped within the ice. If this ice melts, it will significantly contribute to global warming.
A related scenario when this phenomenon goes out of control is the runaway-greenhouse effect. This scenario is essentially similar to an apocalypse, but it is all too real. Though this has never happened in the earth’s entire history, it is speculated to have occurred on Venus. Millions of years ago, Venus was thought to have an atmosphere similar to that of the earth. But due to the runaway greenhouse effect, surface temperatures around the planet began rising.
If this occurs on the earth, the runaway greenhouse effect will lead to many unpleasant scenarios – temperatures will rise hot enough for oceans to evaporate. Once the oceans evaporate, the rocks will start to sublimate under heat. In order to prevent such a scenario, proper measures have to be taken to stop climate change.
More to Read: Learn How Greenhouse Effect works
Tips To Writing the Perfect Essay
Consider adopting the following strategies when writing an essay. These are proven methods of securing more marks in an exam or assignment.
- Begin the essay with an introductory paragraph detailing the history or origin of the given topic.
- Try to reduce the use of jargons. Use sparingly if the topic requires it.
- Ensure that the content is presented in bulleted points wherever appropriate.
- Insert and highlight factual data, such as dates, names and places.
- Remember to break up the content into smaller paragraphs. 100-120 words per paragraph should suffice.
- Always conclude the essay with a closing paragraph.
Explore more essays on biology or other related fields at BYJU’S.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Very helpful Byju’s
this app is very useful
Sample essay on global warming
Very nice and helpful⭐️
Amazing essay
This essay is very helpful to every student Thank you Byjus! 😊😊😊
This one is so helpful and easy to understand. Thank you, Byju’s!
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

ENCYCLOPEDIC ENTRY
Global warming.
The causes, effects, and complexities of global warming are important to understand so that we can fight for the health of our planet.
Earth Science, Climatology
Tennessee Power Plant
Ash spews from a coal-fueled power plant in New Johnsonville, Tennessee, United States.
Photograph by Emory Kristof/ National Geographic

Global warming is the long-term warming of the planet’s overall temperature. Though this warming trend has been going on for a long time, its pace has significantly increased in the last hundred years due to the burning of fossil fuels . As the human population has increased, so has the volume of fossil fuels burned. Fossil fuels include coal, oil, and natural gas, and burning them causes what is known as the “greenhouse effect” in Earth’s atmosphere.
The greenhouse effect is when the sun’s rays penetrate the atmosphere, but when that heat is reflected off the surface cannot escape back into space. Gases produced by the burning of fossil fuels prevent the heat from leaving the atmosphere. These greenhouse gasses are carbon dioxide , chlorofluorocarbons, water vapor , methane , and nitrous oxide . The excess heat in the atmosphere has caused the average global temperature to rise overtime, otherwise known as global warming.
Global warming has presented another issue called climate change. Sometimes these phrases are used interchangeably, however, they are different. Climate change refers to changes in weather patterns and growing seasons around the world. It also refers to sea level rise caused by the expansion of warmer seas and melting ice sheets and glaciers . Global warming causes climate change, which poses a serious threat to life on Earth in the forms of widespread flooding and extreme weather. Scientists continue to study global warming and its impact on Earth.
Media Credits
The audio, illustrations, photos, and videos are credited beneath the media asset, except for promotional images, which generally link to another page that contains the media credit. The Rights Holder for media is the person or group credited.
Production Managers
Program specialists, last updated.
February 21, 2024
User Permissions
For information on user permissions, please read our Terms of Service. If you have questions about how to cite anything on our website in your project or classroom presentation, please contact your teacher. They will best know the preferred format. When you reach out to them, you will need the page title, URL, and the date you accessed the resource.
If a media asset is downloadable, a download button appears in the corner of the media viewer. If no button appears, you cannot download or save the media.
Text on this page is printable and can be used according to our Terms of Service .
Interactives
Any interactives on this page can only be played while you are visiting our website. You cannot download interactives.
Related Resources

- ENVIRONMENT
How global warming is disrupting life on Earth
The signs of global warming are everywhere, and are more complex than just climbing temperatures.
Our planet is getting hotter. Since the Industrial Revolution—an event that spurred the use of fossil fuels in everything from power plants to transportation—Earth has warmed by 1 degree Celsius, about 2 degrees Fahrenheit.
That may sound insignificant, but 2023 was the hottest year on record , and all 10 of the hottest years on record have occurred in the past decade.
Global warming and climate change are often used interchangeably as synonyms, but scientists prefer to use “climate change” when describing the complex shifts now affecting our planet’s weather and climate systems.
Climate change encompasses not only rising average temperatures but also natural disasters, shifting wildlife habitats, rising seas , and a range of other impacts. All of these changes are emerging as humans continue to add heat-trapping greenhouse gases , like carbon dioxide and methane, to the atmosphere.
What causes global warming?
When fossil fuel emissions are pumped into the atmosphere, they change the chemistry of our atmosphere, allowing sunlight to reach the Earth but preventing heat from being released into space. This keeps Earth warm, like a greenhouse, and this warming is known as the greenhouse effect .
Carbon dioxide is the most commonly found greenhouse gas and about 75 percent of all the climate warming pollution in the atmosphere. This gas is a product of producing and burning oil, gas, and coal. About a quarter of Carbon dioxide also results from land cleared for timber or agriculture.
Methane is another common greenhouse gas. Although it makes up only about 16 percent of emissions, it's roughly 25 times more potent than carbon dioxide and dissipates more quickly. That means methane can cause a large spark in warming, but ending methane pollution can also quickly limit the amount of atmospheric warming. Sources of this gas include agriculture (mostly livestock), leaks from oil and gas production, and waste from landfills.
What are the effects of global warming?
One of the most concerning impacts of global warming is the effect warmer temperatures will have on Earth's polar regions and mountain glaciers. The Arctic is warming four times faster than the rest of the planet. This warming reduces critical ice habitat and it disrupts the flow of the jet stream, creating more unpredictable weather patterns around the globe.
( Learn more about the jet stream. )
A warmer planet doesn't just raise temperatures. Precipitation is becoming more extreme as the planet heats. For every degree your thermometer rises, the air holds about seven percent more moisture. This increase in moisture in the atmosphere can produce flash floods, more destructive hurricanes, and even paradoxically, stronger snow storms.
The world's leading scientists regularly gather to review the latest research on how the planet is changing. The results of this review is synthesized in regularly published reports known as the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) reports.
A recent report outlines how disruptive a global rise in temperature can be:
- Coral reefs are now a highly endangered ecosystem. When corals face environmental stress, such as high heat, they expel their colorful algae and turn a ghostly white, an effect known as coral bleaching . In this weakened state, they more easily die.
- Trees are increasingly dying from drought , and this mass mortality is reshaping forest ecosystems.
- Rising temperatures and changing precipitation patterns are making wildfires more common and more widespread. Research shows they're even moving into the eastern U.S. where fires have historically been less common.
- Hurricanes are growing more destructive and dumping more rain, an effect that will result in more damage. Some scientists say we even need to be preparing for Cat 6 storms . (The current ranking system ends at Cat 5.)
How can we limit global warming?
Limiting the rising in global warming is theoretically achievable, but politically, socially, and economically difficult.
Those same sources of greenhouse gas emissions must be limited to reduce warming. For example, oil and gas used to generate electricity or power industrial manufacturing will need to be replaced by net zero emission technology like wind and solar power. Transportation, another major source of emissions, will need to integrate more electric vehicles, public transportation, and innovative urban design, such as safe bike lanes and walkable cities.
( Learn more about solutions to limit global warming. )
One global warming solution that was once considered far fetched is now being taken more seriously: geoengineering. This type of technology relies on manipulating the Earth's atmosphere to physically block the warming rays of the sun or by sucking carbon dioxide straight out of the sky.
Restoring nature may also help limit warming. Trees, oceans, wetlands, and other ecosystems help absorb excess carbon—but when they're lost, so too is their potential to fight climate change.
Ultimately, we'll need to adapt to warming temperatures, building homes to withstand sea level rise for example, or more efficiently cooling homes during heat waves.
Related Topics
- CLIMATE CHANGE
- ENVIRONMENT AND CONSERVATION
- POLAR REGIONS
You May Also Like

Why all life on Earth depends on trees

Life probably exists beyond Earth. So how do we find it?

For Antarctica’s emperor penguins, ‘there is no time left’

Polar bears are trying to adapt to a warming Arctic. It’s not working.

A photographic eulogy for Greenland's departing icebergs
- History & Culture
- Photography
- Environment
- Paid Content
History & Culture
- Mind, Body, Wonder
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Your US State Privacy Rights
- Children's Online Privacy Policy
- Interest-Based Ads
- About Nielsen Measurement
- Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information
- Nat Geo Home
- Attend a Live Event
- Book a Trip
- Inspire Your Kids
- Shop Nat Geo
- Visit the D.C. Museum
- Learn About Our Impact
- Support Our Mission
- Advertise With Us
- Customer Service
- Renew Subscription
- Manage Your Subscription
- Work at Nat Geo
- Sign Up for Our Newsletters
- Contribute to Protect the Planet
Copyright © 1996-2015 National Geographic Society Copyright © 2015-2024 National Geographic Partners, LLC. All rights reserved
- Share full article

The Science of Climate Change Explained: Facts, Evidence and Proof
Definitive answers to the big questions.
Credit... Photo Illustration by Andrea D'Aquino
Supported by
By Julia Rosen
Ms. Rosen is a journalist with a Ph.D. in geology. Her research involved studying ice cores from Greenland and Antarctica to understand past climate changes.
- Published April 19, 2021 Updated Nov. 6, 2021
The science of climate change is more solid and widely agreed upon than you might think. But the scope of the topic, as well as rampant disinformation, can make it hard to separate fact from fiction. Here, we’ve done our best to present you with not only the most accurate scientific information, but also an explanation of how we know it.
How do we know climate change is really happening?
How much agreement is there among scientists about climate change, do we really only have 150 years of climate data how is that enough to tell us about centuries of change, how do we know climate change is caused by humans, since greenhouse gases occur naturally, how do we know they’re causing earth’s temperature to rise, why should we be worried that the planet has warmed 2°f since the 1800s, is climate change a part of the planet’s natural warming and cooling cycles, how do we know global warming is not because of the sun or volcanoes, how can winters and certain places be getting colder if the planet is warming, wildfires and bad weather have always happened. how do we know there’s a connection to climate change, how bad are the effects of climate change going to be, what will it cost to do something about climate change, versus doing nothing.
Climate change is often cast as a prediction made by complicated computer models. But the scientific basis for climate change is much broader, and models are actually only one part of it (and, for what it’s worth, they’re surprisingly accurate ).
For more than a century , scientists have understood the basic physics behind why greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide cause warming. These gases make up just a small fraction of the atmosphere but exert outsized control on Earth’s climate by trapping some of the planet’s heat before it escapes into space. This greenhouse effect is important: It’s why a planet so far from the sun has liquid water and life!
However, during the Industrial Revolution, people started burning coal and other fossil fuels to power factories, smelters and steam engines, which added more greenhouse gases to the atmosphere. Ever since, human activities have been heating the planet.
We know this is true thanks to an overwhelming body of evidence that begins with temperature measurements taken at weather stations and on ships starting in the mid-1800s. Later, scientists began tracking surface temperatures with satellites and looking for clues about climate change in geologic records. Together, these data all tell the same story: Earth is getting hotter.
Average global temperatures have increased by 2.2 degrees Fahrenheit, or 1.2 degrees Celsius, since 1880, with the greatest changes happening in the late 20th century. Land areas have warmed more than the sea surface and the Arctic has warmed the most — by more than 4 degrees Fahrenheit just since the 1960s. Temperature extremes have also shifted. In the United States, daily record highs now outnumber record lows two-to-one.

Where it was cooler or warmer in 2020 compared with the middle of the 20th century

This warming is unprecedented in recent geologic history. A famous illustration, first published in 1998 and often called the hockey-stick graph, shows how temperatures remained fairly flat for centuries (the shaft of the stick) before turning sharply upward (the blade). It’s based on data from tree rings, ice cores and other natural indicators. And the basic picture , which has withstood decades of scrutiny from climate scientists and contrarians alike, shows that Earth is hotter today than it’s been in at least 1,000 years, and probably much longer.
In fact, surface temperatures actually mask the true scale of climate change, because the ocean has absorbed 90 percent of the heat trapped by greenhouse gases . Measurements collected over the last six decades by oceanographic expeditions and networks of floating instruments show that every layer of the ocean is warming up. According to one study , the ocean has absorbed as much heat between 1997 and 2015 as it did in the previous 130 years.
We also know that climate change is happening because we see the effects everywhere. Ice sheets and glaciers are shrinking while sea levels are rising. Arctic sea ice is disappearing. In the spring, snow melts sooner and plants flower earlier. Animals are moving to higher elevations and latitudes to find cooler conditions. And droughts, floods and wildfires have all gotten more extreme. Models predicted many of these changes, but observations show they are now coming to pass.
Back to top .
There’s no denying that scientists love a good, old-fashioned argument. But when it comes to climate change, there is virtually no debate: Numerous studies have found that more than 90 percent of scientists who study Earth’s climate agree that the planet is warming and that humans are the primary cause. Most major scientific bodies, from NASA to the World Meteorological Organization , endorse this view. That’s an astounding level of consensus given the contrarian, competitive nature of the scientific enterprise, where questions like what killed the dinosaurs remain bitterly contested .
Scientific agreement about climate change started to emerge in the late 1980s, when the influence of human-caused warming began to rise above natural climate variability. By 1991, two-thirds of earth and atmospheric scientists surveyed for an early consensus study said that they accepted the idea of anthropogenic global warming. And by 1995, the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, a famously conservative body that periodically takes stock of the state of scientific knowledge, concluded that “the balance of evidence suggests that there is a discernible human influence on global climate.” Currently, more than 97 percent of publishing climate scientists agree on the existence and cause of climate change (as does nearly 60 percent of the general population of the United States).
So where did we get the idea that there’s still debate about climate change? A lot of it came from coordinated messaging campaigns by companies and politicians that opposed climate action. Many pushed the narrative that scientists still hadn’t made up their minds about climate change, even though that was misleading. Frank Luntz, a Republican consultant, explained the rationale in an infamous 2002 memo to conservative lawmakers: “Should the public come to believe that the scientific issues are settled, their views about global warming will change accordingly,” he wrote. Questioning consensus remains a common talking point today, and the 97 percent figure has become something of a lightning rod .
To bolster the falsehood of lingering scientific doubt, some people have pointed to things like the Global Warming Petition Project, which urged the United States government to reject the Kyoto Protocol of 1997, an early international climate agreement. The petition proclaimed that climate change wasn’t happening, and even if it were, it wouldn’t be bad for humanity. Since 1998, more than 30,000 people with science degrees have signed it. However, nearly 90 percent of them studied something other than Earth, atmospheric or environmental science, and the signatories included just 39 climatologists. Most were engineers, doctors, and others whose training had little to do with the physics of the climate system.
A few well-known researchers remain opposed to the scientific consensus. Some, like Willie Soon, a researcher affiliated with the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, have ties to the fossil fuel industry . Others do not, but their assertions have not held up under the weight of evidence. At least one prominent skeptic, the physicist Richard Muller, changed his mind after reassessing historical temperature data as part of the Berkeley Earth project. His team’s findings essentially confirmed the results he had set out to investigate, and he came away firmly convinced that human activities were warming the planet. “Call me a converted skeptic,” he wrote in an Op-Ed for the Times in 2012.
Mr. Luntz, the Republican pollster, has also reversed his position on climate change and now advises politicians on how to motivate climate action.
A final note on uncertainty: Denialists often use it as evidence that climate science isn’t settled. However, in science, uncertainty doesn’t imply a lack of knowledge. Rather, it’s a measure of how well something is known. In the case of climate change, scientists have found a range of possible future changes in temperature, precipitation and other important variables — which will depend largely on how quickly we reduce emissions. But uncertainty does not undermine their confidence that climate change is real and that people are causing it.
Earth’s climate is inherently variable. Some years are hot and others are cold, some decades bring more hurricanes than others, some ancient droughts spanned the better part of centuries. Glacial cycles operate over many millenniums. So how can scientists look at data collected over a relatively short period of time and conclude that humans are warming the planet? The answer is that the instrumental temperature data that we have tells us a lot, but it’s not all we have to go on.
Historical records stretch back to the 1880s (and often before), when people began to regularly measure temperatures at weather stations and on ships as they traversed the world’s oceans. These data show a clear warming trend during the 20th century.

Global average temperature compared with the middle of the 20th century
+0.75°C
–0.25°

Some have questioned whether these records could be skewed, for instance, by the fact that a disproportionate number of weather stations are near cities, which tend to be hotter than surrounding areas as a result of the so-called urban heat island effect. However, researchers regularly correct for these potential biases when reconstructing global temperatures. In addition, warming is corroborated by independent data like satellite observations, which cover the whole planet, and other ways of measuring temperature changes.
Much has also been made of the small dips and pauses that punctuate the rising temperature trend of the last 150 years. But these are just the result of natural climate variability or other human activities that temporarily counteract greenhouse warming. For instance, in the mid-1900s, internal climate dynamics and light-blocking pollution from coal-fired power plants halted global warming for a few decades. (Eventually, rising greenhouse gases and pollution-control laws caused the planet to start heating up again.) Likewise, the so-called warming hiatus of the 2000s was partly a result of natural climate variability that allowed more heat to enter the ocean rather than warm the atmosphere. The years since have been the hottest on record .
Still, could the entire 20th century just be one big natural climate wiggle? To address that question, we can look at other kinds of data that give a longer perspective. Researchers have used geologic records like tree rings, ice cores, corals and sediments that preserve information about prehistoric climates to extend the climate record. The resulting picture of global temperature change is basically flat for centuries, then turns sharply upward over the last 150 years. It has been a target of climate denialists for decades. However, study after study has confirmed the results , which show that the planet hasn’t been this hot in at least 1,000 years, and probably longer.
Scientists have studied past climate changes to understand the factors that can cause the planet to warm or cool. The big ones are changes in solar energy, ocean circulation, volcanic activity and the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. And they have each played a role at times.
For example, 300 years ago, a combination of reduced solar output and increased volcanic activity cooled parts of the planet enough that Londoners regularly ice skated on the Thames . About 12,000 years ago, major changes in Atlantic circulation plunged the Northern Hemisphere into a frigid state. And 56 million years ago, a giant burst of greenhouse gases, from volcanic activity or vast deposits of methane (or both), abruptly warmed the planet by at least 9 degrees Fahrenheit, scrambling the climate, choking the oceans and triggering mass extinctions.
In trying to determine the cause of current climate changes, scientists have looked at all of these factors . The first three have varied a bit over the last few centuries and they have quite likely had modest effects on climate , particularly before 1950. But they cannot account for the planet’s rapidly rising temperature, especially in the second half of the 20th century, when solar output actually declined and volcanic eruptions exerted a cooling effect.
That warming is best explained by rising greenhouse gas concentrations . Greenhouse gases have a powerful effect on climate (see the next question for why). And since the Industrial Revolution, humans have been adding more of them to the atmosphere, primarily by extracting and burning fossil fuels like coal, oil and gas, which releases carbon dioxide.
Bubbles of ancient air trapped in ice show that, before about 1750, the concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere was roughly 280 parts per million. It began to rise slowly and crossed the 300 p.p.m. threshold around 1900. CO2 levels then accelerated as cars and electricity became big parts of modern life, recently topping 420 p.p.m . The concentration of methane, the second most important greenhouse gas, has more than doubled. We’re now emitting carbon much faster than it was released 56 million years ago .

30 billion metric tons
Carbon dioxide emitted worldwide 1850-2017
Rest of world
Other developed
European Union
Developed economies
Other countries
United States

E.U. and U.K.

These rapid increases in greenhouse gases have caused the climate to warm abruptly. In fact, climate models suggest that greenhouse warming can explain virtually all of the temperature change since 1950. According to the most recent report by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, which assesses published scientific literature, natural drivers and internal climate variability can only explain a small fraction of late-20th century warming.
Another study put it this way: The odds of current warming occurring without anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions are less than 1 in 100,000 .
But greenhouse gases aren’t the only climate-altering compounds people put into the air. Burning fossil fuels also produces particulate pollution that reflects sunlight and cools the planet. Scientists estimate that this pollution has masked up to half of the greenhouse warming we would have otherwise experienced.
Greenhouse gases like water vapor and carbon dioxide serve an important role in the climate. Without them, Earth would be far too cold to maintain liquid water and humans would not exist!
Here’s how it works: the planet’s temperature is basically a function of the energy the Earth absorbs from the sun (which heats it up) and the energy Earth emits to space as infrared radiation (which cools it down). Because of their molecular structure, greenhouse gases temporarily absorb some of that outgoing infrared radiation and then re-emit it in all directions, sending some of that energy back toward the surface and heating the planet . Scientists have understood this process since the 1850s .
Greenhouse gas concentrations have varied naturally in the past. Over millions of years, atmospheric CO2 levels have changed depending on how much of the gas volcanoes belched into the air and how much got removed through geologic processes. On time scales of hundreds to thousands of years, concentrations have changed as carbon has cycled between the ocean, soil and air.
Today, however, we are the ones causing CO2 levels to increase at an unprecedented pace by taking ancient carbon from geologic deposits of fossil fuels and putting it into the atmosphere when we burn them. Since 1750, carbon dioxide concentrations have increased by almost 50 percent. Methane and nitrous oxide, other important anthropogenic greenhouse gases that are released mainly by agricultural activities, have also spiked over the last 250 years.
We know based on the physics described above that this should cause the climate to warm. We also see certain telltale “fingerprints” of greenhouse warming. For example, nights are warming even faster than days because greenhouse gases don’t go away when the sun sets. And upper layers of the atmosphere have actually cooled, because more energy is being trapped by greenhouse gases in the lower atmosphere.
We also know that we are the cause of rising greenhouse gas concentrations — and not just because we can measure the CO2 coming out of tailpipes and smokestacks. We can see it in the chemical signature of the carbon in CO2.
Carbon comes in three different masses: 12, 13 and 14. Things made of organic matter (including fossil fuels) tend to have relatively less carbon-13. Volcanoes tend to produce CO2 with relatively more carbon-13. And over the last century, the carbon in atmospheric CO2 has gotten lighter, pointing to an organic source.
We can tell it’s old organic matter by looking for carbon-14, which is radioactive and decays over time. Fossil fuels are too ancient to have any carbon-14 left in them, so if they were behind rising CO2 levels, you would expect the amount of carbon-14 in the atmosphere to drop, which is exactly what the data show .
It’s important to note that water vapor is the most abundant greenhouse gas in the atmosphere. However, it does not cause warming; instead it responds to it . That’s because warmer air holds more moisture, which creates a snowball effect in which human-caused warming allows the atmosphere to hold more water vapor and further amplifies climate change. This so-called feedback cycle has doubled the warming caused by anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions.
A common source of confusion when it comes to climate change is the difference between weather and climate. Weather is the constantly changing set of meteorological conditions that we experience when we step outside, whereas climate is the long-term average of those conditions, usually calculated over a 30-year period. Or, as some say: Weather is your mood and climate is your personality.
So while 2 degrees Fahrenheit doesn’t represent a big change in the weather, it’s a huge change in climate. As we’ve already seen, it’s enough to melt ice and raise sea levels, to shift rainfall patterns around the world and to reorganize ecosystems, sending animals scurrying toward cooler habitats and killing trees by the millions.
It’s also important to remember that two degrees represents the global average, and many parts of the world have already warmed by more than that. For example, land areas have warmed about twice as much as the sea surface. And the Arctic has warmed by about 5 degrees. That’s because the loss of snow and ice at high latitudes allows the ground to absorb more energy, causing additional heating on top of greenhouse warming.
Relatively small long-term changes in climate averages also shift extremes in significant ways. For instance, heat waves have always happened, but they have shattered records in recent years. In June of 2020, a town in Siberia registered temperatures of 100 degrees . And in Australia, meteorologists have added a new color to their weather maps to show areas where temperatures exceed 125 degrees. Rising sea levels have also increased the risk of flooding because of storm surges and high tides. These are the foreshocks of climate change.
And we are in for more changes in the future — up to 9 degrees Fahrenheit of average global warming by the end of the century, in the worst-case scenario . For reference, the difference in global average temperatures between now and the peak of the last ice age, when ice sheets covered large parts of North America and Europe, is about 11 degrees Fahrenheit.
Under the Paris Climate Agreement, which President Biden recently rejoined, countries have agreed to try to limit total warming to between 1.5 and 2 degrees Celsius, or 2.7 and 3.6 degrees Fahrenheit, since preindustrial times. And even this narrow range has huge implications . According to scientific studies, the difference between 2.7 and 3.6 degrees Fahrenheit will very likely mean the difference between coral reefs hanging on or going extinct, and between summer sea ice persisting in the Arctic or disappearing completely. It will also determine how many millions of people suffer from water scarcity and crop failures, and how many are driven from their homes by rising seas. In other words, one degree Fahrenheit makes a world of difference.
Earth’s climate has always changed. Hundreds of millions of years ago, the entire planet froze . Fifty million years ago, alligators lived in what we now call the Arctic . And for the last 2.6 million years, the planet has cycled between ice ages when the planet was up to 11 degrees cooler and ice sheets covered much of North America and Europe, and milder interglacial periods like the one we’re in now.
Climate denialists often point to these natural climate changes as a way to cast doubt on the idea that humans are causing climate to change today. However, that argument rests on a logical fallacy. It’s like “seeing a murdered body and concluding that people have died of natural causes in the past, so the murder victim must also have died of natural causes,” a team of social scientists wrote in The Debunking Handbook , which explains the misinformation strategies behind many climate myths.
Indeed, we know that different mechanisms caused the climate to change in the past. Glacial cycles, for example, were triggered by periodic variations in Earth’s orbit , which take place over tens of thousands of years and change how solar energy gets distributed around the globe and across the seasons.
These orbital variations don’t affect the planet’s temperature much on their own. But they set off a cascade of other changes in the climate system; for instance, growing or melting vast Northern Hemisphere ice sheets and altering ocean circulation. These changes, in turn, affect climate by altering the amount of snow and ice, which reflect sunlight, and by changing greenhouse gas concentrations. This is actually part of how we know that greenhouse gases have the ability to significantly affect Earth’s temperature.
For at least the last 800,000 years , atmospheric CO2 concentrations oscillated between about 180 parts per million during ice ages and about 280 p.p.m. during warmer periods, as carbon moved between oceans, forests, soils and the atmosphere. These changes occurred in lock step with global temperatures, and are a major reason the entire planet warmed and cooled during glacial cycles, not just the frozen poles.
Today, however, CO2 levels have soared to 420 p.p.m. — the highest they’ve been in at least three million years . The concentration of CO2 is also increasing about 100 times faster than it did at the end of the last ice age. This suggests something else is going on, and we know what it is: Since the Industrial Revolution, humans have been burning fossil fuels and releasing greenhouse gases that are heating the planet now (see Question 5 for more details on how we know this, and Questions 4 and 8 for how we know that other natural forces aren’t to blame).
Over the next century or two, societies and ecosystems will experience the consequences of this climate change. But our emissions will have even more lasting geologic impacts: According to some studies, greenhouse gas levels may have already warmed the planet enough to delay the onset of the next glacial cycle for at least an additional 50,000 years.
The sun is the ultimate source of energy in Earth’s climate system, so it’s a natural candidate for causing climate change. And solar activity has certainly changed over time. We know from satellite measurements and other astronomical observations that the sun’s output changes on 11-year cycles. Geologic records and sunspot numbers, which astronomers have tracked for centuries, also show long-term variations in the sun’s activity, including some exceptionally quiet periods in the late 1600s and early 1800s.
We know that, from 1900 until the 1950s, solar irradiance increased. And studies suggest that this had a modest effect on early 20th century climate, explaining up to 10 percent of the warming that’s occurred since the late 1800s. However, in the second half of the century, when the most warming occurred, solar activity actually declined . This disparity is one of the main reasons we know that the sun is not the driving force behind climate change.
Another reason we know that solar activity hasn’t caused recent warming is that, if it had, all the layers of the atmosphere should be heating up. Instead, data show that the upper atmosphere has actually cooled in recent decades — a hallmark of greenhouse warming .
So how about volcanoes? Eruptions cool the planet by injecting ash and aerosol particles into the atmosphere that reflect sunlight. We’ve observed this effect in the years following large eruptions. There are also some notable historical examples, like when Iceland’s Laki volcano erupted in 1783, causing widespread crop failures in Europe and beyond, and the “ year without a summer ,” which followed the 1815 eruption of Mount Tambora in Indonesia.
Since volcanoes mainly act as climate coolers, they can’t really explain recent warming. However, scientists say that they may also have contributed slightly to rising temperatures in the early 20th century. That’s because there were several large eruptions in the late 1800s that cooled the planet, followed by a few decades with no major volcanic events when warming caught up. During the second half of the 20th century, though, several big eruptions occurred as the planet was heating up fast. If anything, they temporarily masked some amount of human-caused warming.
The second way volcanoes can impact climate is by emitting carbon dioxide. This is important on time scales of millions of years — it’s what keeps the planet habitable (see Question 5 for more on the greenhouse effect). But by comparison to modern anthropogenic emissions, even big eruptions like Krakatoa and Mount St. Helens are just a drop in the bucket. After all, they last only a few hours or days, while we burn fossil fuels 24-7. Studies suggest that, today, volcanoes account for 1 to 2 percent of total CO2 emissions.
When a big snowstorm hits the United States, climate denialists can try to cite it as proof that climate change isn’t happening. In 2015, Senator James Inhofe, an Oklahoma Republican, famously lobbed a snowball in the Senate as he denounced climate science. But these events don’t actually disprove climate change.
While there have been some memorable storms in recent years, winters are actually warming across the world. In the United States, average temperatures in December, January and February have increased by about 2.5 degrees this century.
On the flip side, record cold days are becoming less common than record warm days. In the United States, record highs now outnumber record lows two-to-one . And ever-smaller areas of the country experience extremely cold winter temperatures . (The same trends are happening globally.)
So what’s with the blizzards? Weather always varies, so it’s no surprise that we still have severe winter storms even as average temperatures rise. However, some studies suggest that climate change may be to blame. One possibility is that rapid Arctic warming has affected atmospheric circulation, including the fast-flowing, high-altitude air that usually swirls over the North Pole (a.k.a. the Polar Vortex ). Some studies suggest that these changes are bringing more frigid temperatures to lower latitudes and causing weather systems to stall , allowing storms to produce more snowfall. This may explain what we’ve experienced in the U.S. over the past few decades, as well as a wintertime cooling trend in Siberia , although exactly how the Arctic affects global weather remains a topic of ongoing scientific debate .
Climate change may also explain the apparent paradox behind some of the other places on Earth that haven’t warmed much. For instance, a splotch of water in the North Atlantic has cooled in recent years, and scientists say they suspect that may be because ocean circulation is slowing as a result of freshwater streaming off a melting Greenland . If this circulation grinds almost to a halt, as it’s done in the geologic past, it would alter weather patterns around the world.
Not all cold weather stems from some counterintuitive consequence of climate change. But it’s a good reminder that Earth’s climate system is complex and chaotic, so the effects of human-caused changes will play out differently in different places. That’s why “global warming” is a bit of an oversimplification. Instead, some scientists have suggested that the phenomenon of human-caused climate change would more aptly be called “ global weirding .”
Extreme weather and natural disasters are part of life on Earth — just ask the dinosaurs. But there is good evidence that climate change has increased the frequency and severity of certain phenomena like heat waves, droughts and floods. Recent research has also allowed scientists to identify the influence of climate change on specific events.
Let’s start with heat waves . Studies show that stretches of abnormally high temperatures now happen about five times more often than they would without climate change, and they last longer, too. Climate models project that, by the 2040s, heat waves will be about 12 times more frequent. And that’s concerning since extreme heat often causes increased hospitalizations and deaths, particularly among older people and those with underlying health conditions. In the summer of 2003, for example, a heat wave caused an estimated 70,000 excess deaths across Europe. (Human-caused warming amplified the death toll .)
Climate change has also exacerbated droughts , primarily by increasing evaporation. Droughts occur naturally because of random climate variability and factors like whether El Niño or La Niña conditions prevail in the tropical Pacific. But some researchers have found evidence that greenhouse warming has been affecting droughts since even before the Dust Bowl . And it continues to do so today. According to one analysis , the drought that afflicted the American Southwest from 2000 to 2018 was almost 50 percent more severe because of climate change. It was the worst drought the region had experienced in more than 1,000 years.
Rising temperatures have also increased the intensity of heavy precipitation events and the flooding that often follows. For example, studies have found that, because warmer air holds more moisture, Hurricane Harvey, which struck Houston in 2017, dropped between 15 and 40 percent more rainfall than it would have without climate change.
It’s still unclear whether climate change is changing the overall frequency of hurricanes, but it is making them stronger . And warming appears to favor certain kinds of weather patterns, like the “ Midwest Water Hose ” events that caused devastating flooding across the Midwest in 2019 .
It’s important to remember that in most natural disasters, there are multiple factors at play. For instance, the 2019 Midwest floods occurred after a recent cold snap had frozen the ground solid, preventing the soil from absorbing rainwater and increasing runoff into the Missouri and Mississippi Rivers. These waterways have also been reshaped by levees and other forms of river engineering, some of which failed in the floods.
Wildfires are another phenomenon with multiple causes. In many places, fire risk has increased because humans have aggressively fought natural fires and prevented Indigenous peoples from carrying out traditional burning practices. This has allowed fuel to accumulate that makes current fires worse .
However, climate change still plays a major role by heating and drying forests, turning them into tinderboxes. Studies show that warming is the driving factor behind the recent increases in wildfires; one analysis found that climate change is responsible for doubling the area burned across the American West between 1984 and 2015. And researchers say that warming will only make fires bigger and more dangerous in the future.
It depends on how aggressively we act to address climate change. If we continue with business as usual, by the end of the century, it will be too hot to go outside during heat waves in the Middle East and South Asia . Droughts will grip Central America, the Mediterranean and southern Africa. And many island nations and low-lying areas, from Texas to Bangladesh, will be overtaken by rising seas. Conversely, climate change could bring welcome warming and extended growing seasons to the upper Midwest , Canada, the Nordic countries and Russia . Farther north, however, the loss of snow, ice and permafrost will upend the traditions of Indigenous peoples and threaten infrastructure.
It’s complicated, but the underlying message is simple: unchecked climate change will likely exacerbate existing inequalities . At a national level, poorer countries will be hit hardest, even though they have historically emitted only a fraction of the greenhouse gases that cause warming. That’s because many less developed countries tend to be in tropical regions where additional warming will make the climate increasingly intolerable for humans and crops. These nations also often have greater vulnerabilities, like large coastal populations and people living in improvised housing that is easily damaged in storms. And they have fewer resources to adapt, which will require expensive measures like redesigning cities, engineering coastlines and changing how people grow food.
Already, between 1961 and 2000, climate change appears to have harmed the economies of the poorest countries while boosting the fortunes of the wealthiest nations that have done the most to cause the problem, making the global wealth gap 25 percent bigger than it would otherwise have been. Similarly, the Global Climate Risk Index found that lower income countries — like Myanmar, Haiti and Nepal — rank high on the list of nations most affected by extreme weather between 1999 and 2018. Climate change has also contributed to increased human migration, which is expected to increase significantly .
Even within wealthy countries, the poor and marginalized will suffer the most. People with more resources have greater buffers, like air-conditioners to keep their houses cool during dangerous heat waves, and the means to pay the resulting energy bills. They also have an easier time evacuating their homes before disasters, and recovering afterward. Lower income people have fewer of these advantages, and they are also more likely to live in hotter neighborhoods and work outdoors, where they face the brunt of climate change.
These inequalities will play out on an individual, community, and regional level. A 2017 analysis of the U.S. found that, under business as usual, the poorest one-third of counties, which are concentrated in the South, will experience damages totaling as much as 20 percent of gross domestic product, while others, mostly in the northern part of the country, will see modest economic gains. Solomon Hsiang, an economist at University of California, Berkeley, and the lead author of the study, has said that climate change “may result in the largest transfer of wealth from the poor to the rich in the country’s history.”
Even the climate “winners” will not be immune from all climate impacts, though. Desirable locations will face an influx of migrants. And as the coronavirus pandemic has demonstrated, disasters in one place quickly ripple across our globalized economy. For instance, scientists expect climate change to increase the odds of multiple crop failures occurring at the same time in different places, throwing the world into a food crisis .
On top of that, warmer weather is aiding the spread of infectious diseases and the vectors that transmit them, like ticks and mosquitoes . Research has also identified troubling correlations between rising temperatures and increased interpersonal violence , and climate change is widely recognized as a “threat multiplier” that increases the odds of larger conflicts within and between countries. In other words, climate change will bring many changes that no amount of money can stop. What could help is taking action to limit warming.
One of the most common arguments against taking aggressive action to combat climate change is that doing so will kill jobs and cripple the economy. But this implies that there’s an alternative in which we pay nothing for climate change. And unfortunately, there isn’t. In reality, not tackling climate change will cost a lot , and cause enormous human suffering and ecological damage, while transitioning to a greener economy would benefit many people and ecosystems around the world.
Let’s start with how much it will cost to address climate change. To keep warming well below 2 degrees Celsius, the goal of the Paris Climate Agreement, society will have to reach net zero greenhouse gas emissions by the middle of this century. That will require significant investments in things like renewable energy, electric cars and charging infrastructure, not to mention efforts to adapt to hotter temperatures, rising sea-levels and other unavoidable effects of current climate changes. And we’ll have to make changes fast.
Estimates of the cost vary widely. One recent study found that keeping warming to 2 degrees Celsius would require a total investment of between $4 trillion and $60 trillion, with a median estimate of $16 trillion, while keeping warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius could cost between $10 trillion and $100 trillion, with a median estimate of $30 trillion. (For reference, the entire world economy was about $88 trillion in 2019.) Other studies have found that reaching net zero will require annual investments ranging from less than 1.5 percent of global gross domestic product to as much as 4 percent . That’s a lot, but within the range of historical energy investments in countries like the U.S.
Now, let’s consider the costs of unchecked climate change, which will fall hardest on the most vulnerable. These include damage to property and infrastructure from sea-level rise and extreme weather, death and sickness linked to natural disasters, pollution and infectious disease, reduced agricultural yields and lost labor productivity because of rising temperatures, decreased water availability and increased energy costs, and species extinction and habitat destruction. Dr. Hsiang, the U.C. Berkeley economist, describes it as “death by a thousand cuts.”
As a result, climate damages are hard to quantify. Moody’s Analytics estimates that even 2 degrees Celsius of warming will cost the world $69 trillion by 2100, and economists expect the toll to keep rising with the temperature. In a recent survey , economists estimated the cost would equal 5 percent of global G.D.P. at 3 degrees Celsius of warming (our trajectory under current policies) and 10 percent for 5 degrees Celsius. Other research indicates that, if current warming trends continue, global G.D.P. per capita will decrease between 7 percent and 23 percent by the end of the century — an economic blow equivalent to multiple coronavirus pandemics every year. And some fear these are vast underestimates .
Already, studies suggest that climate change has slashed incomes in the poorest countries by as much as 30 percent and reduced global agricultural productivity by 21 percent since 1961. Extreme weather events have also racked up a large bill. In 2020, in the United States alone, climate-related disasters like hurricanes, droughts, and wildfires caused nearly $100 billion in damages to businesses, property and infrastructure, compared to an average of $18 billion per year in the 1980s.
Given the steep price of inaction, many economists say that addressing climate change is a better deal . It’s like that old saying: an ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure. In this case, limiting warming will greatly reduce future damage and inequality caused by climate change. It will also produce so-called co-benefits, like saving one million lives every year by reducing air pollution, and millions more from eating healthier, climate-friendly diets. Some studies even find that meeting the Paris Agreement goals could create jobs and increase global G.D.P . And, of course, reining in climate change will spare many species and ecosystems upon which humans depend — and which many people believe to have their own innate value.
The challenge is that we need to reduce emissions now to avoid damages later, which requires big investments over the next few decades. And the longer we delay, the more we will pay to meet the Paris goals. One recent analysis found that reaching net-zero by 2050 would cost the U.S. almost twice as much if we waited until 2030 instead of acting now. But even if we miss the Paris target, the economics still make a strong case for climate action, because every additional degree of warming will cost us more — in dollars, and in lives.
Veronica Penney contributed reporting.
Illustration photographs by Esther Horvath, Max Whittaker, David Maurice Smith and Talia Herman for The New York Times; Esther Horvath/Alfred-Wegener-Institut
An earlier version of this article misidentified the authors of The Debunking Handbook. It was written by social scientists who study climate communication, not a team of climate scientists.
How we handle corrections
What’s Up in Space and Astronomy
Keep track of things going on in our solar system and all around the universe..
Never miss an eclipse, a meteor shower, a rocket launch or any other 2024 event that’s out of this world with our space and astronomy calendar .
A new set of computer simulations, which take into account the effects of stars moving past our solar system, has effectively made it harder to predict Earth’s future and reconstruct its past.
Dante Lauretta, the planetary scientist who led the OSIRIS-REx mission to retrieve a handful of space dust , discusses his next final frontier.
A nova named T Coronae Borealis lit up the night about 80 years ago. Astronomers say it’s expected to put on another show in the coming months.
Voyager 1, the 46-year-old first craft in interstellar space which flew by Jupiter and Saturn in its youth, may have gone dark .
Is Pluto a planet? And what is a planet, anyway? Test your knowledge here .
Advertisement
The Economic Consequences of Climate Change: An Interview with Nobel Laureate William Nordhaus

William Nordhaus and Lint Barrage (PhD ’13)
What are the economic consequences and opportunities of climate change? How do you integrate economic analysis with the science of climate change?
These questions are at the heart of Nobel laureate William Nordhaus ’s career, and in research released this week in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), he and coauthor Lint Barrage (PhD ’13) present new findings from the updated DICE-2023 model, with major implications for global climate policy.
The DICE model (the Dynamic Integrated model for Climate and the Economy) is one of the first integrated assessment models or IAMs . This approach provides policy-relevant insights into global environmental issues through quantitative descriptions of key processes in human and earth systems. IAMs model the climate problem from end to end, from economy to emissions to atmospheric chemistry to climate dynamics, then on to impacts such as sea-level rise, wildfire, and health impacts, and finally closing the loop by including policies to bend the curve of CO2 emissions. The outputs of these models play a key role in understanding key relationships and formulating efficient policies to slow or reverse the trends.
One important finding is that international climate policy has set ambitious goals but has failed to establish an architecture for implementation…Additionally, we estimate that current policies will lead the global mean temperature increase (above pre-industrial levels) to pass the 1.5 °C target later in this decade, while without major policy changes, the globe will surpass the 2 °C goal of the Paris Accord by mid-century.” - William Nordhaus
The original DICE model was developed and published at Yale in 1992 and is the most widely used climate-change integrated assessment model. The US and other governments employ it to calculate the social cost of carbon, as well as create consistent scenarios and evaluate policies and uncertainties. The new study updates the 2016 DICE model with revised treatments of the carbon cycle, damages, discounting, and also includes results on the Paris Accord and temperature-limited scenarios.

Among the key findings from the new study, the authors note that both current policies and the extended Paris Accord fall far short of limiting global warming to 2 °C. They also highlight the substantial economic stakes at play in global climate policy: in the efficient scenario, where climate change policies maximize economic welfare according to the principles of cost–benefit analysis—they estimate a net present value of economic benefits of around $120 trillion.
Journal Publication

In the Q&A below, author and Nobel laureate William Nordhaus discusses the key findings and implications of this new research.
What are the major new findings today? What are the major surprises?

One important finding is that international climate policy has set ambitious goals but has failed to establish a realistic architecture for implementation. This is seen in the “price of carbon” (or the cost to polluters of emitting CO2 into the atmosphere) that is far below the level necessary to reach international goals. We estimate that a global carbon price of $80 per ton of CO2 would be necessary to reach the goals of the 2015 Paris Accord. Yet, the World Bank estimates that the current global price is only a tiny $3 per ton.
Additionally, we estimate that current policies will lead the global mean temperature increase (above pre-industrial levels) to pass the 1.5 °C target later in this decade, while the globe will surpass the 2 °C goal of the Paris Accord by mid-century without major policy changes. All this might not be a big surprise – perhaps alarm is a better word. Professor Barrage and I emphasize that it is critically important to recognize how countries’ climate policies fall so far short of their rhetoric and goals, and this is borne out by the recent release of DICE 2023.
What does this new study say about the “social cost of carbon”?
This critical measure (“SCC” for short) is the most important single economic concept in the economics of climate change. It designates the current and future damages caused by an additional ton of carbon dioxide emissions or its equivalent. The SCC has become a central tool used in climate change policy, particularly in the determination of regulatory policies that involve greenhouse gas emissions. The SCC has been used by the US government in rules that provide more than $1 trillion in benefits. Integrated models like DICE are essential to the calculation of the SCC and have been used by many governments in their formulation of climate policies.
We estimate that the SCC is around $80 per ton of CO2 in today’s dollars. With about 5 billion tons annually of emissions, this represents a debit of about $400 billion for the US economy (out of a total output of $28 trillion). This is a useful finding because it shows again how inadequate climate policy is because current carbon prices are so far below our estimates of SCC. The figure below shows alternative estimates of the SCC from the publication.
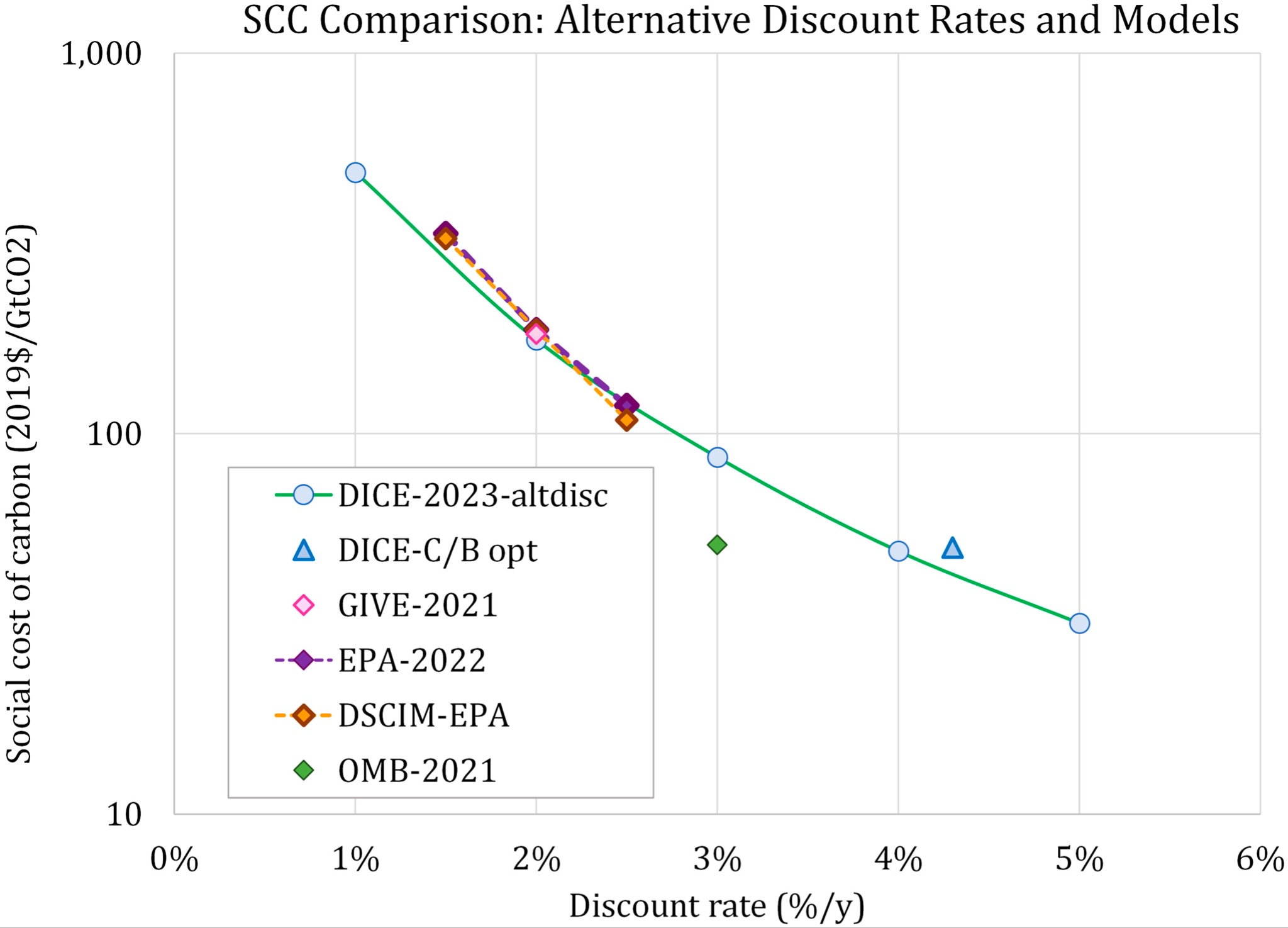
Figure 4 from the article shows the relationship between the social cost of carbon and the discount rate for different scenarios of the DICE-2023 and several other models.
What suggestions for climate policy emerge from your work?
Looking at the landscape of climate policy, we see three necessary aspects of an effective policy.
The first , mentioned above, is that countries need to raise carbon prices sharply to provide appropriate incentives for the private and public sectors to reduce emissions. This cannot be done overnight, obviously, but we need to move forward with this critical step as soon as possible. Here in the United States, there is an unusual opportunity because major tax provisions expire next year, and we face the need to either raise income taxes substantially or find other revenue sources. This would be a good time to replace the scheduled increases in income taxes with taxes on carbon emissions.
The second step is to replace the flawed international architecture on climate policy with a structure with carrots and sticks for incentivizing countries to participate in strong policies. I have called this the “climate club” to suggest a structure of pricing policies along with penalties for countries who do not participate. The flawed structure of current international agreements is a major reason why so little progress has been made to curtail carbon emissions to date.
The final step is to recognize that a policy of decarbonizing our economies will require major new technologies – ones that are only in the laboratories or at small scale – and that these need strong government fiscal support. Examples of such technologies are advanced renewables, negative-emissions technologies, and futuristic technologies such as fusion, advanced nuclear, and superconducting networks.
The most important support would be government subsidies for fundamental and applied research on green energy technologies. It is striking how little governments have recognized the importance of this aspect of climate policy. Major countries today provide only $40 billion of support for green energy R&D. This is less than half of the money that companies in the United States devote to research and development in pharmaceuticals. We do not have a prayer of reaching our climate goals without strong government research support.
These three steps are hardly revolutionary in concept, but they are awesomely challenging politically. They are the best chance for the community of nations to prevent the growing threats to humans and the global environment of rapid climate change.
The modeling behind DICE-2023 sounds like a major enterprise. Are these models complex to code and calculate?
The models themselves are relatively small compared to many scientific studies (you can see some representative code below). But they have a particularly complex structure because they are “optimization models,” which means that they solve for the least-cost or highest-value path of the variables.
If you excuse a little excursion into geekiness, I will explain a bit more. The simplest version of DICE has 1475 variables and 1381 linear and nonlinear constraints.
Solving this problem would not have been remotely possible without modern mathematics, software, and hardware, but today’s PCs can solve it in only 1.3 seconds. One interesting feature is that the solution is so fast and robust because of the development of an algorithm known as “linear programming,” by Yale economist Tjalling Koopmans, for which he won the 1974 Nobel Prize in Economics.
What has been Yale's role in the development of integrated models like DICE?
Yale has been in the forefront of integrated climate-economic modeling for decades. Contributors to earlier DICE-related studies over the years have been Yale scholars such as Robert Mendelsohn and Ken Gillingham at the Environment School and Economics Department faculty such as Tony Smith (Chair of Economics) and Sam Kortum . Yale-derived work has pioneered DICE spinoffs, such as multi-region versions, ones introducing uncertainty, approaches with research and development, and learning by doing.
I would emphasize, however, that each new study and every passing year reveal new complexities and challenges. A world aflame with wildfires, and New Yorkers sheltering from record-setting pollution from Canadian fires, are the surprises that await us in the years ahead if unchecked warming continues.

Climate Change: Evidence and Causes: Update 2020 (2020)
Chapter: conclusion, c onclusion.
This document explains that there are well-understood physical mechanisms by which changes in the amounts of greenhouse gases cause climate changes. It discusses the evidence that the concentrations of these gases in the atmosphere have increased and are still increasing rapidly, that climate change is occurring, and that most of the recent change is almost certainly due to emissions of greenhouse gases caused by human activities. Further climate change is inevitable; if emissions of greenhouse gases continue unabated, future changes will substantially exceed those that have occurred so far. There remains a range of estimates of the magnitude and regional expression of future change, but increases in the extremes of climate that can adversely affect natural ecosystems and human activities and infrastructure are expected.
Citizens and governments can choose among several options (or a mixture of those options) in response to this information: they can change their pattern of energy production and usage in order to limit emissions of greenhouse gases and hence the magnitude of climate changes; they can wait for changes to occur and accept the losses, damage, and suffering that arise; they can adapt to actual and expected changes as much as possible; or they can seek as yet unproven “geoengineering” solutions to counteract some of the climate changes that would otherwise occur. Each of these options has risks, attractions and costs, and what is actually done may be a mixture of these different options. Different nations and communities will vary in their vulnerability and their capacity to adapt. There is an important debate to be had about choices among these options, to decide what is best for each group or nation, and most importantly for the global population as a whole. The options have to be discussed at a global scale because in many cases those communities that are most vulnerable control few of the emissions, either past or future. Our description of the science of climate change, with both its facts and its uncertainties, is offered as a basis to inform that policy debate.
A CKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The following individuals served as the primary writing team for the 2014 and 2020 editions of this document:
- Eric Wolff FRS, (UK lead), University of Cambridge
- Inez Fung (NAS, US lead), University of California, Berkeley
- Brian Hoskins FRS, Grantham Institute for Climate Change
- John F.B. Mitchell FRS, UK Met Office
- Tim Palmer FRS, University of Oxford
- Benjamin Santer (NAS), Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory
- John Shepherd FRS, University of Southampton
- Keith Shine FRS, University of Reading.
- Susan Solomon (NAS), Massachusetts Institute of Technology
- Kevin Trenberth, National Center for Atmospheric Research
- John Walsh, University of Alaska, Fairbanks
- Don Wuebbles, University of Illinois
Staff support for the 2020 revision was provided by Richard Walker, Amanda Purcell, Nancy Huddleston, and Michael Hudson. We offer special thanks to Rebecca Lindsey and NOAA Climate.gov for providing data and figure updates.
The following individuals served as reviewers of the 2014 document in accordance with procedures approved by the Royal Society and the National Academy of Sciences:
- Richard Alley (NAS), Department of Geosciences, Pennsylvania State University
- Alec Broers FRS, Former President of the Royal Academy of Engineering
- Harry Elderfield FRS, Department of Earth Sciences, University of Cambridge
- Joanna Haigh FRS, Professor of Atmospheric Physics, Imperial College London
- Isaac Held (NAS), NOAA Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory
- John Kutzbach (NAS), Center for Climatic Research, University of Wisconsin
- Jerry Meehl, Senior Scientist, National Center for Atmospheric Research
- John Pendry FRS, Imperial College London
- John Pyle FRS, Department of Chemistry, University of Cambridge
- Gavin Schmidt, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center
- Emily Shuckburgh, British Antarctic Survey
- Gabrielle Walker, Journalist
- Andrew Watson FRS, University of East Anglia
The Support for the 2014 Edition was provided by NAS Endowment Funds. We offer sincere thanks to the Ralph J. and Carol M. Cicerone Endowment for NAS Missions for supporting the production of this 2020 Edition.
F OR FURTHER READING
For more detailed discussion of the topics addressed in this document (including references to the underlying original research), see:
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), 2019: Special Report on the Ocean and Cryosphere in a Changing Climate [ https://www.ipcc.ch/srocc ]
- National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine (NASEM), 2019: Negative Emissions Technologies and Reliable Sequestration: A Research Agenda [ https://www.nap.edu/catalog/25259 ]
- Royal Society, 2018: Greenhouse gas removal [ https://raeng.org.uk/greenhousegasremoval ]
- U.S. Global Change Research Program (USGCRP), 2018: Fourth National Climate Assessment Volume II: Impacts, Risks, and Adaptation in the United States [ https://nca2018.globalchange.gov ]
- IPCC, 2018: Global Warming of 1.5°C [ https://www.ipcc.ch/sr15 ]
- USGCRP, 2017: Fourth National Climate Assessment Volume I: Climate Science Special Reports [ https://science2017.globalchange.gov ]
- NASEM, 2016: Attribution of Extreme Weather Events in the Context of Climate Change [ https://www.nap.edu/catalog/21852 ]
- IPCC, 2013: Fifth Assessment Report (AR5) Working Group 1. Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis [ https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar5/wg1 ]
- NRC, 2013: Abrupt Impacts of Climate Change: Anticipating Surprises [ https://www.nap.edu/catalog/18373 ]
- NRC, 2011: Climate Stabilization Targets: Emissions, Concentrations, and Impacts Over Decades to Millennia [ https://www.nap.edu/catalog/12877 ]
- Royal Society 2010: Climate Change: A Summary of the Science [ https://royalsociety.org/topics-policy/publications/2010/climate-change-summary-science ]
- NRC, 2010: America’s Climate Choices: Advancing the Science of Climate Change [ https://www.nap.edu/catalog/12782 ]
Much of the original data underlying the scientific findings discussed here are available at:
- https://data.ucar.edu/
- https://climatedataguide.ucar.edu
- https://iridl.ldeo.columbia.edu
- https://ess-dive.lbl.gov/
- https://www.ncdc.noaa.gov/
- https://www.esrl.noaa.gov/gmd/ccgg/trends/
- http://scrippsco2.ucsd.edu
- http://hahana.soest.hawaii.edu/hot/

Climate change is one of the defining issues of our time. It is now more certain than ever, based on many lines of evidence, that humans are changing Earth's climate. The Royal Society and the US National Academy of Sciences, with their similar missions to promote the use of science to benefit society and to inform critical policy debates, produced the original Climate Change: Evidence and Causes in 2014. It was written and reviewed by a UK-US team of leading climate scientists. This new edition, prepared by the same author team, has been updated with the most recent climate data and scientific analyses, all of which reinforce our understanding of human-caused climate change.
Scientific information is a vital component for society to make informed decisions about how to reduce the magnitude of climate change and how to adapt to its impacts. This booklet serves as a key reference document for decision makers, policy makers, educators, and others seeking authoritative answers about the current state of climate-change science.
Welcome to OpenBook!
You're looking at OpenBook, NAP.edu's online reading room since 1999. Based on feedback from you, our users, we've made some improvements that make it easier than ever to read thousands of publications on our website.
Do you want to take a quick tour of the OpenBook's features?
Show this book's table of contents , where you can jump to any chapter by name.
...or use these buttons to go back to the previous chapter or skip to the next one.
Jump up to the previous page or down to the next one. Also, you can type in a page number and press Enter to go directly to that page in the book.
Switch between the Original Pages , where you can read the report as it appeared in print, and Text Pages for the web version, where you can highlight and search the text.
To search the entire text of this book, type in your search term here and press Enter .
Share a link to this book page on your preferred social network or via email.
View our suggested citation for this chapter.
Ready to take your reading offline? Click here to buy this book in print or download it as a free PDF, if available.
Get Email Updates
Do you enjoy reading reports from the Academies online for free ? Sign up for email notifications and we'll let you know about new publications in your areas of interest when they're released.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Global Warming Essay 6 (2500 words) "Global warming refers to the increase in the temperatures of the global surface causing various effects on the climate of the world," (Spencer, 2003). Changes in climate will include change in the patterns of rainfall, rise in the sea level among other climate changes.
Global warming has several negative impacts on the environment, including rising sea levels, extreme weather events, and biodiversity loss. Rising temperatures cause glaciers and ice sheets to melt, leading to a rise in sea levels. This rise is affecting coastal areas, including low-lying islands and cities such as Miami, New York, and Tokyo.
Modern global warming is the result of an increase in magnitude of the so-called greenhouse effect, a warming of Earth's surface and lower atmosphere caused by the presence of water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxides, and other greenhouse gases. In 2014 the IPCC first reported that concentrations of carbon dioxide, methane, and ...
Global warming has been linked to the increase in wildfires and floods. It has been seen as the cause of rising sea levels and stronger hurricanes. Heat waves in Europe in 2003 led to the death of 20,000 people and over a thousand people in India. Also, the Arctic's polar ice caps are melting at a rate of 9% every decade.
Another cause of global warming is greenhouse gases. Greenhouse gases are carbon monoxide and sulphur dioxide it trap the solar heats rays and prevent it from escaping from the surface of the earth. This has cause the temperature of the earth increase. Volcanic eruptions are another issue that causes global warming.
The most important cause of global warming is greenhouse gases, which trap hot air in the Earth's atmosphere instead of allowing that heat to escape into space. Greenhouse gasses build up in the earth's atmosphere, effectively insulating the planet just as a greenhouse used to grow fruits and vegetables traps heat.
These effects will intensify in the coming years, effectively halting species expansion. Furthermore, humans will eventually feel the negative effects of Global Warming. Also Read: Concept of Sustainable Development. Sample Essays on Global Warming. Here are some sample essays on Global Warming: Essay on Global Warming Paragraph in 100 - 150 ...
500+ Words Essay on Effects of Global Warming. Global warming refers to climate change that causes an increase in the average of Earth's temperature. Natural events and human influences are believed to be top contributions towards the increase in average temperatures. Global warming is a rise in the surface and atmospheric temperature of the ...
A rise in global temperatures can lead to additional changes in the environment, such as rising sea levels. Since an increase in the temperature causes the glaciers and icebergs to melt at a rapid pace, it causes the sea levels to rise. On the Weather: Global Warming causes intense heat waves by significantly increasing the temperature which ...
Fossil fuels - coal, oil and gas - are by far the largest contributor to global climate change, accounting for over 75 per cent of global greenhouse gas emissions and nearly 90 per cent ...
A: Global warming occurs when carbon dioxide (CO 2) and other air pollutants collect in the atmosphere and absorb sunlight and solar radiation that have bounced off the earth's surface. Normally ...
Disclaimer: This is an example of a student written essay. Click here for sample essays written by our professional writers. ... Global Warming Causes And Effects Analysis Environmental Sciences Essay 'Global warming' is one facet of the broader term 'climate change'. It is the increase in the average temperature of the Earth's ...
One of the first things the IPCC concluded is that there are several greenhouse gases responsible for warming, and humans emit them in a variety of ways. Most come from the combustion of fossil ...
global warming, Increase in the global average surface temperature resulting from enhancement of the greenhouse effect, primarily by air pollution.In 2007 the UN Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change forecast that by 2100 global average surface temperatures would increase 3.2-7.2 °F (1.8-4.0 °C), depending on a range of scenarios for greenhouse gas emissions, and stated that it was ...
Climate Explained, a part of Yale Climate Connections, is an essay collection that addresses an array of climate change questions and topics, including why it's cold outside if global warming is real, how we know that humans are responsible for global warming, and the relationship between climate change and national security.
Essay On Global Warming in 300 Words. Global warming is a phenomenon where the earth's average temperature rises due to increased amounts of greenhouse gases. Greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide, methane and ozone trap the incoming radiation from the sun. This effect creates a natural "blanket", which prevents the heat from escaping ...
Global warming is the long-term warming of the planet's overall temperature. Though this warming trend has been going on for a long time, its pace has significantly increased in the last hundred years due to the burning of fossil fuels.As the human population has increased, so has the volume of . fossil fuels burned.. Fossil fuels include coal, oil, and natural gas, and burning them causes ...
Global Warming is caused by many different things. Greenhouse gases, deforestation, and solar activity are three different proven facts that cause global warming. Global warming is not something that is going to disappear; it is only going to get worse if people do not start doing something about it. Don't use plagiarized sources.
What are the effects of global warming? One of the most concerning impacts of global warming is the effect warmer temperatures will have on Earth's polar regions and mountain glaciers. The Arctic ...
Global warming is a process of the Earth's temperature rising, due to radiation from sunlight that is being trapped in the earth by greenhouse gases such as methane and carbon dioxide. The process starts with the greenhouse gases allowing the sunlight to access the Earth; letting the necessary amount in.
Average global temperatures have increased by 2.2 degrees Fahrenheit, or 1.2 degrees Celsius, since 1880, with the greatest changes happening in the late 20th century. Land areas have warmed more ...
Global Warming Causes And Effects Analysis Environmental Sciences Essay. 'Global warming' is one facet of the broader term 'climate change'. It is the increase in the average temperature of the Earth's surface air and oceans from the mid-20th century, and the projected continuation. The Global warming is primarily the consequence of ...
Temperature data showing rapid warming in the past few decades, the latest data going up through 2023. According to NASA, Earth's average surface temperature in 2023 was the warmest on record since recordkeeping began in 1880, continuing a long-term trend of rising global temperatures. On top of that, the 10 most recent years have been the ...
These questions are at the heart of Nobel laureate William Nordhaus's career, and in research released this week in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), he and coauthor Lint Barrage (PhD '13) present new findings from the updated DICE-2023 model, with major implications for global climate policy.
Global Warming Cause and Effect Essay. It is believed people's careless use of fossil fuels are responsible for causing Global warming. Environmentalists say people do not realize the serious effects of their own actions. They continue to waste resources and pollute the air despite all the evidence pointing to the effects of such behavior.
C ONCLUSION. This document explains that there are well-understood physical mechanisms by which changes in the amounts of greenhouse gases cause climate changes. It discusses the evidence that the concentrations of these gases in the atmosphere have increased and are still increasing rapidly, that climate change is occurring, and that most of ...