Trending Post : 12 Powerful Discussion Strategies to Engage Students


10 of the Best Literary Analysis Activities to Elevate Thinking
Inside this Post: Ready to elevate your literary analysis lessons? This post is full of engaging and effective activities to help students master literary analysis topics.
Literary analysis has become the beating heart of English classes around the world. When students read a text, we want them to peel back the layers one by one, appreciating the deeper meaning that lies within each sentence. As English teachers, many of us connect with texts easily and persevere through complex literature naturally. For our students, this process is not always as enjoyable.
In this post, you’ll find suggestions for elevating thinking with middle and high school students. These ideas can be used with paired or individual texts and can be differentiated to reach a variety of learners.
Engaging and Effective Literary Analysis Activities
Literary analysis elements are best when they are engaging and elevate thinking without frustrating students. I’ve played around with different approaches, and these are the key elements that resonate most with students.

1. Thinking Aloud
One of the best feelings as a teacher is knowing you have an entire class full of teenagers engaged. It’s amazing how every single student in a classroom is in tune with think alouds. Something about making thinking transparent challenges students of all readiness levels. With literary analysis lessons, I love providing think alouds with the whole class. Whether we do this via face to face instruction or by creating a short video for virtual classrooms, we have to model our thinking.
Here’s an example with “All the world’s a stage” from William Shakespeare’s As You Like It …
This speech, at first, seems complicated. But, Shakespeare is talking about the world being a stage, and I think there is something deeper to what he is saying. Let’s go back again and look for clues. The men and women are players on the stage. He writes that they have their exits and entrances. I’m trying to visualize that in my head now. The world is a stage, the people are actors, and when they walk on and off the stage, that is their theatrical entrance and exit. Now that I understand he is using this speech as an extended metaphor, I wonder why would Shakespeare is choosing to compare these two things?
When modeling literary analysis, we can break down our thought process. If we write a written response, we can scaffold by color coding our thoughts in order to highlight the necessary critical thinking steps.
- First, acknowledge what is confusing or uncertain about the text. What might we be missing as readers?
- Second, make observations.
- Third, apply reading strategies (in this case, I used visualizing).
- Last, teach students to ask questions that probe at the deeper meaning and reason for the writing.
2. Graphic Organizers
Graphic organizers are one of my go-to strategies for elevating thinking . We can use them to differentiate and to guide students as we work in small groups. I like to keep a variety of literary analysis graphic organizers for any text on hand so that I can be responsive. If students show a need to work on analyzing a specific literary element – characterization, plot, theme, conflict, etcetera – I use a graphic organizer as we read a text or excerpt together, modeling my thinking. Then, students can practice using the same organizer in small groups, partners, or independently.
Literary analysis consists of asking a bunch of questions to lead students to deeper thinking, and graphic organizers are a bridge that walks students down that path of purposeful questioning.
Grab this print and digital literary analysis graphic organizer for analyzing song lyrics – one of secondary students’ favorite texts to pick apart!
Nothing grabs a student’s attention like an image! Visuals are amazing tools for introducing literary analysis skills. I always begin my literary analysis unit with pictures. Using an image, we can quickly show students how to differentiate between summarizing and analyzing . Then, we can walk them through the steps of acknowledging what we might be missing, making observations, applying reading strategies, and questioning for deeper meaning.
Consider using images from a variety of sources. We can try historical images, political cartoons, famous paintings, graphic novels, wordless picture books, advertisements, or even just regular photographs.
I even work this type of analytical thinking into my vocabulary activities ! Students get used to interpreting photos and using textual evidence to support their thinking.

4. One Pagers
One pagers are one of my favorite literary analysis activities. In order to make them meaningful, I incorporate scaffolding . So, students have access to standards-aligned goals and questions that prompt their responses to the text. Choice helps as well. We can allow students to choose digital or traditional , response angles, and even texts.
In terms of literary analysis benefits, we can really focus on asking students to cite textual evidence to track a universal theme. While doing so, students can draw conclusions about how literary elements work together or how they provide tension to impact a reader’s overall takeaway.
5. Colorful Charts
Mood and tone can be tricky for students to analyze. So that they can understand the difference between them but also so that they see how mood and tone work in tandem, I began using an equalizer metaphor . Students can use color and amplification to analyze how mood and tone change throughout a literary work. By creating a visual representation, there’s a direct connection between the mood and the storyline.
How does setting impact mood , and how does mood impact the conflict in the story?
For instance, the quiet beauty of the Capulet garden sets the stage for a romantic balcony scene, but the noisy bustle of the lewd fighting in the Verona streets helps to define the conflict and tension between the two feuding families.
With tone , how does the author’s word choice and sentence structure in each section convey his or her attitude in the work?
As we study the amplification of tone in the play Romeo and Juliet , we see a consistent change from light-hearted comedy to an intensely poetic and tragic seriousness. Over the course of the play, one might say that Shakespeare’s juxtaposition creates an overall sympathetic tone toward the star-crossed lovers.

6. Get Moving
One of the issues when it comes to citing evidence in a literary analysis essay is finding relevant support. Sometimes, it seems like the lines students select from literature are completely disconnected from what they are writing. That may be because they don’t truly understand how their thesis connects to their main points or how their main points connect to the evidence. For some students, there are too many degrees of separation!
A kinesthetic option to address this issue involves Post-Its (or colored text boxes if you are doing this digitally) and a t-chart. At the top of the paper (use big paper or a white board if you can do this together in the classroom!), write the analytical point. What conclusion can students draw about characters, setting, or another literary element that would support their thesis statement?
Under that, label the T-Chart as “Relevant” and “Off Topic.” Then, you have some options.
BASIC: You identify support for students in advance and have them sort the support based on its relevance. Could they use it to analyze the text, or is it off topic?
ADVANCE: Ask students to find examples of relevant and off-topic lines from the text.
A MIXTURE: Provide students with a handful of lines they can sort into relevant and off-topic categories, and then ask them to find a couple more examples on their own.
To increase the engagement factor, use some washi tape on the floor in the shape of whatever makes the most sense – a character outline for analyzing character, a house for analyzing setting, a circle for analyzing a universal theme. Then, have students stick their Post-It notes inside or outside of the shape. Inside indicates that the evidence is relevant, and outside means it’s off-topic.
7. Children’s Books
We don’t always think to use picture books with older students , but they are one of my absolute favorite ways to scaffold literary analysis! Because picture books are short, we can cover an entire (and often complex) story in a short period of time. And, we can continually refer back to that text throughout the school year. Because picture books are accessible for all students, they will remember sharing the story together, and you can really make significant strides with whole-class discussions and small group lessons.
Try using picture books to teach Notice and Note signposts, language, aesthetics, and theme . One of my favorite ways to use picture books is teaching students to analyze how dialogue impacts decisions, propels action, and develops characters. For example, in the book Elbow Grease , the protagonist is motivated to participate in a race for which he is the underdog simply because some crass comments from his friends make him angry. This really is the turning point in the story, which makes it convenient to analyze how dialogue can lead to decisions and actions that change the course of a storyline.
8. Short Films
For a thousand and one reasons, I adore short films. They’re short (obvious, I know), which makes them ideal for modeling and mini lessons. Plus, they are visually captivating and apply to a wide age range. And, generally, they hold quite a bit of depth and leave room for a variety of interpretations.
During first quarter with ninth graders, I built in a yearly routine of watching short films during our literary analysis unit and having students complete their first full analytical essay. It’s fun. I can model using a short film I enjoy. Then, I get to read a wide range of responses from students who choose different texts. To scaffold for struggling writers, I suggest a few short films I am very familiar with; this way, I can guide them if they get stuck or confused.
You can also build in short films by using them with poetry for paired text analysis .

9. Reading Strategies
One of the building blocks of literary analysis is having a good foundation in apply reading strategies. It’s fun to model what readers do. We can show students how analyzing texts and re-reading for deeper meaning helps us with writing and then ask students to practice those skills.
For instance, when students begin to understand that authors have a purposeful craft that impacts their reading experience, it empowers them to pick that craft apart, studying the nuances of what makes it work. And, it gives them an advantage as authors themselves. They may think, I remember how the author’s purposeful use of short, staccato sentences and onomatopoeias increased the suspense during that scene. Maybe I should use those techniques in this part of my story to add an emotional element for my readers.
These are some of the graphic organizers I’ve used to scaffold reading strategy work with the whole class, and then students can transfer those skills to small group or independent practice, using the same organizer if necessary.
10. Social Media Activities
Social media is everywhere. We might as well use it as a relevant option for analyzing literature! One of my favorites is booksnaps , and I tie in Snapchat by having them take a photo of part of the text they want to analyze. Then, they add interpretations, images, and text as well as a caption with a more detailed analysis. I call these Snap-a-Books. I also created a Spot-a-Book analysis option, reminiscent of Spotify playlists. Students can create playlists relevant to character analysis, setting analysis, conflict analysis, and more!
And, that’s ten! I hope you’ve found some meaningful literary analysis activities to spark creative, critical thinking in your classroom.

Get the latest in your inbox!
- My Storyboards
TWIST Graphic Organizer
TWIST Analysis Graphic Organizers
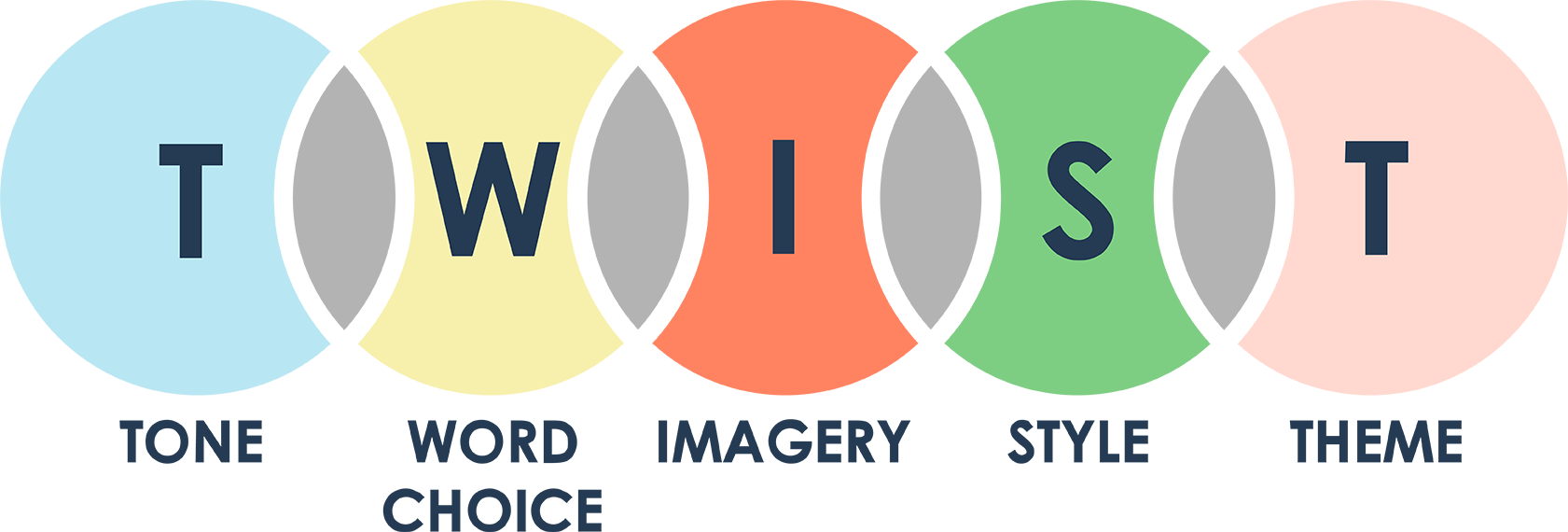
A growing trend in ELA has been the incorporation of vertical teaming strategies in classrooms. These strategies include a number of acronyms, analogous to “PEMDAS”, but for English class. This “order of operations” helps students through a prose analysis by suggesting to them what and where they should start when interpreting a section of literature.
With the TWIST method, students are asked to look for and analyze the following terms: tone, word choice, imagery and detail, style, and theme. When completing a TWIST, students may use a paragraph or even a few pages, looking at each of these items systematically, both sequentially and as they relate to each other. For example, when examining tone and word choice, students should find a correlation between the two. The graphic above illustrates how each part of the TWIST should be connected, as each element overlaps with those adjacent to it.
TWIST Helps You Answer the Following Questions:
- How do great writers create a tone that a reader can feel through their work?
- What are the parts of literature, and how can we learn to analyze its meaning?
- How do literary elements affect a reader's understanding of a work of literature?
Breaking Down TWIST
Before reading, it is a good idea to introduce students to the steps of TWIST and go over any terms that may be new to them.
The general character or attitude of a place, piece of writing, situation, etc. Tone words should always be adjectives and convey one of the following attitudes: Positive, Negative, Humorous (Ironic/Sarcastic), Sorrowful (Fearful, Worried), or Neutral.
- Quarrelsome
- Threatening
- Pessimistic
- Questioning
- Reminiscent
Word Choice
The author’s use of specific and accurate words, to “show” the reader rather than to “tell” them. Adjectives are extremely descriptive, and nouns are very particular. When looking for word choice, students will notice ‘clusters’ of words that evoke the same meaning or tone.
Imagery and Detail
Imagery is visually descriptive or figurative language in a literary work. For this element, students want to look at the use of onomatopoeia, alliteration, similes, metaphors, hyperbole, analogies, personification, and euphemisms. These are all details that the author will use to give a sense of emotion to the reader. Very descriptive, figurative language paints a picture in readers’ minds, making this term exceedingly important for students to examine.
Literary style refers to the way that the author uses words – the author’s vocabulary, sentence structure, figurative language, and sentence arrangement. The way an author presents the information determines the way in which the reader interprets it. The wording itself lends insight into the emotions or concepts the author wants convey with the scene, setting, or characters.
Types of Literary Styles
- Descriptive
- Persuasive or Argumentative
- Journalistic
The subject of a piece of writing, usually the author's thoughts on a specific topic. When looking at theme, students should use the other parts of the TWIST to piece together information about the author's intentions. By looking at the tone and imagery, it makes it possible to pinpoint the topic. From there, students will need to infer the author's thoughts on it. Using imagery and style will help them uncover the attitude of the author on the topic.
Related Activities
Check out these TWIST activities from our guides on "O Captain! My Captain!" , "Caged Bird" , and "If" .
TWIST Analysis Lesson Plan
This lesson will overview the TWIST model of interpreting prose and assist students in learning how to use this systematic method of hypothesis and discovery. This will lead students to understand the deeper meanings contained in the text by completing a prose analysis.
Grade Level: 6-12
Time: 45-minute class meeting.
Although, this lesson can be used for multiple grade levels, below are examples of the Common Core State Standards for Grades 9-10. Please see your Common Core State Standards for the correct grade-appropriate strands.
- ELA-Literacy.RL.9-10.1 : Cite strong and thorough textual evidence to support analysis of what the text says explicitly as well as inferences drawn from the text
- ELA-Literacy.RL.9-10.2 : Determine a theme or central idea of a text and analyze in detail its development over the course of the text, including how it emerges and is shaped and refined by specific details; provide an objective summary of the text
- ELA-Literacy.RL.9-10.4 : Determine the meaning of words and phrases as they are used in the text, including figurative and connotative meanings; analyze the cumulative impact of specific word choices on meaning and tone (e.g., how the language evokes a sense of time and place; how it sets a formal or informal tone)
Students will be able to read and explain the elements of prose using the TWIST method on a segment of a literary work.
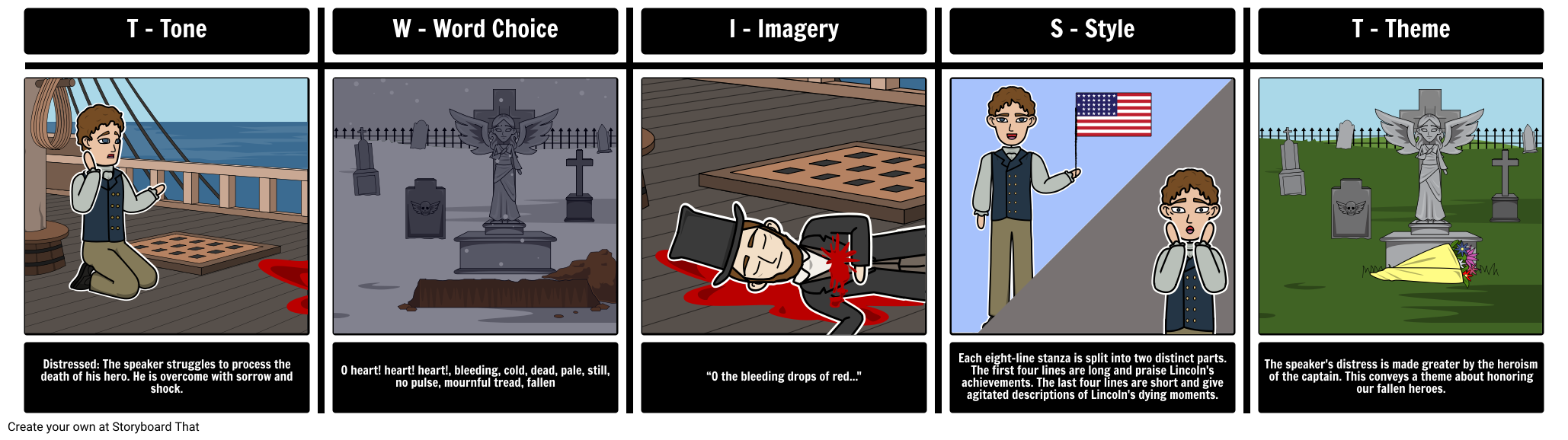
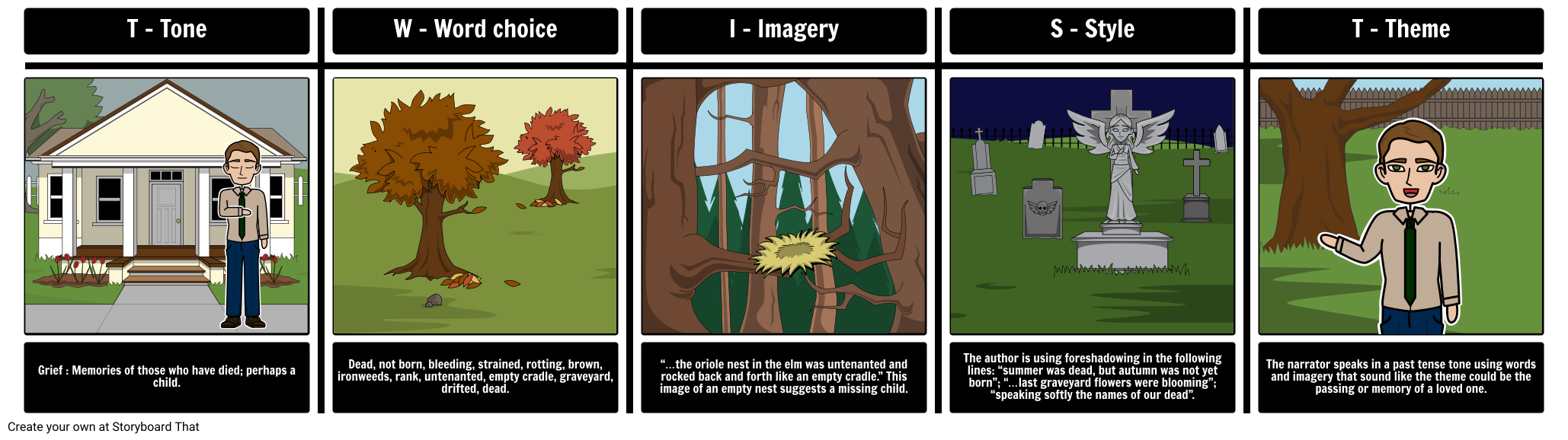
TWIST Example for “The Scarlet Ibis”
Using the first paragraph of “The Scarlet Ibis”, students can depict, explain, and predict what will happen in the story, while getting a good idea of the author’s voice in a prose analysis.
It was in the clove of seasons, summer was dead but autumn had not yet been born, that the ibis lit in the bleeding tree. The flower garden was stained with rotting brown magnolia petals and ironweeds grew rank amid the purple phlox. The five o'clocks by the chimney still marked time, but the oriole nest in the elm was untenanted and rocked back and forth like an empty cradle. The last graveyard flowers were blooming, and their smell drifted across the cotton field and through every room of our house, speaking softly the names of our dead. "The Scarlet Ibis" James Hurst
Grief: Memories of those who have died; perhaps a child.
W - WORD CHOICE
Dead, not born, bleeding, strained, rotting, brown, ironweeds, rank, untenanted, empty cradle, graveyard, drifted, dead.
I - IMAGERY
“…the oriole nest in the elm was untenanted and rocked back and forth like an empty cradle.”: Image of an empty nest.
The author is using foreshadowing in the following lines: “summer was dead, but autumn was not yet born”; “…last graveyard flowers were blooming”; “speaking softly the names of our dead”.
The narrator speaks in a past tense tone using words and imagery that sound like the theme could be the passing or memory of a loved one.
After Reading
If this is your first time doing TWIST with your classes a great idea is to ask students to try filling out the worksheet individually then pair them up, or put them into groups, to create a poster. As you do these more often, you can challenge students by asking that they do it individually.
Once they have finished their worksheet and it has been checked, students can begin to create their storyboard of the prose analysis. Afterwards, you can have students present their storyboards and findings to the class! Just check out our article on how to present a storyboard!
TWIST Example
How to Apply TWIST Analysis to Non-Fiction Texts
Introduce the twist analysis framework.
Explain the TWIST acronym, which stands for Tone, Word Choice, Imagery, Style, and Theme. Emphasize that TWIST analysis can be applied to non-fiction texts to uncover the author's purpose, persuasive techniques, and underlying messages.
Select Relevant Nonfiction Texts
Choose non-fiction texts that are suitable for analysis using the TWIST framework. Consider texts such as speeches, articles, essays, opinion pieces, or informational texts that convey a clear message or argument.
Analyze Tone and Author's Purpose
Guide students to identify the tone of the non-fiction text and determine the author's purpose or intended audience. Encourage students to consider the emotions, attitudes, or persuasive techniques used by the author to convey their message.
Examine Word Choice and Persuasive Techniques
Explore the word choice and vocabulary used in the non-fiction text. Help students analyze how specific words or phrases contribute to the author's argument, evoke emotions, or shape the overall tone of the text.
Analyze Imagery and Rhetorical Devices
Encourage students to identify and analyze any visual or sensory imagery used in the non-fiction text. Discuss the impact of rhetorical devices such as metaphors, similes, or vivid descriptions in conveying the author's message or enhancing the persuasive nature of the text.
Identify Style and Central Theme
Discuss the author's writing style and any distinctive features that contribute to the effectiveness of the non-fiction text. Guide students to identify the central theme or main idea conveyed by the author and analyze how the other TWIST elements contribute to the development of the theme.
Frequently Asked Questions about TWIST Graphic Organizers
What are some common issues that may arise when using twist graphic organisers for literary analysis.
Some common issues that may arise include oversimplification of complex ideas or events, overlooking important details or nuances, and not providing enough guidance or structure for students who may struggle with visual representation. It is important to balance the need for creativity and expression with the need for accuracy and comprehension. It's also important to acknowledge and include other elements for analysis and not just those covered by the TWIST acronym such as point of view and drama.
How is a TWIST storyboard useful in literary analysis?
TWIST is an acronym for tone, word choice, imagery, style, and theme. A TWIST storyboard can be a useful tool since it gives students an opportunity to look at the elements included in a piece of literature and analyze them both systematically and sequentially as well as how they relate to the other literary elements underpinning the literary work. They are useful since they help students better understand and analyze a story by visually representing key elements and facilitating discussions about the literary elements you want to highlight. They are a good starting point for writing assignments or presentations.

Are there other literature-related acronyms that can be useful in lessons and made into storyboard cards?
Yes, there are other acronyms like TWIST applicable in literature analysis and can be made into storyboard cards as lesson aids. Examples include TP-CASTT - title, paraphrase, connotation, attitude, shift, title (again), and theme. TP-CASTT is traditionally used with poetry but can be applied to other types of literature, including short stories and chapters in novels. SMELL - sender, message, evidence, logic, and language for analyzing rhetoric.
What are some common issues that may arise when creating storyboards for literary analysis?
Some common issues that may arise include oversimplification of complex ideas or events, overlooking important details or nuances, and not providing enough guidance or structure for students who may struggle with visual representation. It is important to balance the need for creativity and expression with the need for accuracy and comprehension. Additionally, special considerations should be made for students with special needs, such as providing additional visual aids or modifying the storyboard format to accommodate individual needs. For example, some students may benefit from simplified visual representations or larger font sizes.
Try 1 Month For
30 Day Money Back Guarantee New Customers Only Full Price After Introductory Offer
Learn more about our Department, School, and District packages
- 30 Day Money Back Guarantee
- New Customers Only
- Full Price After Introductory Offer
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to write a literary analysis essay | A step-by-step guide
How to Write a Literary Analysis Essay | A Step-by-Step Guide
Published on January 30, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on August 14, 2023.
Literary analysis means closely studying a text, interpreting its meanings, and exploring why the author made certain choices. It can be applied to novels, short stories, plays, poems, or any other form of literary writing.
A literary analysis essay is not a rhetorical analysis , nor is it just a summary of the plot or a book review. Instead, it is a type of argumentative essay where you need to analyze elements such as the language, perspective, and structure of the text, and explain how the author uses literary devices to create effects and convey ideas.
Before beginning a literary analysis essay, it’s essential to carefully read the text and c ome up with a thesis statement to keep your essay focused. As you write, follow the standard structure of an academic essay :
- An introduction that tells the reader what your essay will focus on.
- A main body, divided into paragraphs , that builds an argument using evidence from the text.
- A conclusion that clearly states the main point that you have shown with your analysis.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Step 1: reading the text and identifying literary devices, step 2: coming up with a thesis, step 3: writing a title and introduction, step 4: writing the body of the essay, step 5: writing a conclusion, other interesting articles.
The first step is to carefully read the text(s) and take initial notes. As you read, pay attention to the things that are most intriguing, surprising, or even confusing in the writing—these are things you can dig into in your analysis.
Your goal in literary analysis is not simply to explain the events described in the text, but to analyze the writing itself and discuss how the text works on a deeper level. Primarily, you’re looking out for literary devices —textual elements that writers use to convey meaning and create effects. If you’re comparing and contrasting multiple texts, you can also look for connections between different texts.
To get started with your analysis, there are several key areas that you can focus on. As you analyze each aspect of the text, try to think about how they all relate to each other. You can use highlights or notes to keep track of important passages and quotes.
Language choices
Consider what style of language the author uses. Are the sentences short and simple or more complex and poetic?
What word choices stand out as interesting or unusual? Are words used figuratively to mean something other than their literal definition? Figurative language includes things like metaphor (e.g. “her eyes were oceans”) and simile (e.g. “her eyes were like oceans”).
Also keep an eye out for imagery in the text—recurring images that create a certain atmosphere or symbolize something important. Remember that language is used in literary texts to say more than it means on the surface.
Narrative voice
Ask yourself:
- Who is telling the story?
- How are they telling it?
Is it a first-person narrator (“I”) who is personally involved in the story, or a third-person narrator who tells us about the characters from a distance?
Consider the narrator’s perspective . Is the narrator omniscient (where they know everything about all the characters and events), or do they only have partial knowledge? Are they an unreliable narrator who we are not supposed to take at face value? Authors often hint that their narrator might be giving us a distorted or dishonest version of events.
The tone of the text is also worth considering. Is the story intended to be comic, tragic, or something else? Are usually serious topics treated as funny, or vice versa ? Is the story realistic or fantastical (or somewhere in between)?
Consider how the text is structured, and how the structure relates to the story being told.
- Novels are often divided into chapters and parts.
- Poems are divided into lines, stanzas, and sometime cantos.
- Plays are divided into scenes and acts.
Think about why the author chose to divide the different parts of the text in the way they did.
There are also less formal structural elements to take into account. Does the story unfold in chronological order, or does it jump back and forth in time? Does it begin in medias res —in the middle of the action? Does the plot advance towards a clearly defined climax?
With poetry, consider how the rhyme and meter shape your understanding of the text and your impression of the tone. Try reading the poem aloud to get a sense of this.
In a play, you might consider how relationships between characters are built up through different scenes, and how the setting relates to the action. Watch out for dramatic irony , where the audience knows some detail that the characters don’t, creating a double meaning in their words, thoughts, or actions.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Your thesis in a literary analysis essay is the point you want to make about the text. It’s the core argument that gives your essay direction and prevents it from just being a collection of random observations about a text.
If you’re given a prompt for your essay, your thesis must answer or relate to the prompt. For example:
Essay question example
Is Franz Kafka’s “Before the Law” a religious parable?
Your thesis statement should be an answer to this question—not a simple yes or no, but a statement of why this is or isn’t the case:
Thesis statement example
Franz Kafka’s “Before the Law” is not a religious parable, but a story about bureaucratic alienation.
Sometimes you’ll be given freedom to choose your own topic; in this case, you’ll have to come up with an original thesis. Consider what stood out to you in the text; ask yourself questions about the elements that interested you, and consider how you might answer them.
Your thesis should be something arguable—that is, something that you think is true about the text, but which is not a simple matter of fact. It must be complex enough to develop through evidence and arguments across the course of your essay.
Say you’re analyzing the novel Frankenstein . You could start by asking yourself:
Your initial answer might be a surface-level description:
The character Frankenstein is portrayed negatively in Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein .
However, this statement is too simple to be an interesting thesis. After reading the text and analyzing its narrative voice and structure, you can develop the answer into a more nuanced and arguable thesis statement:
Mary Shelley uses shifting narrative perspectives to portray Frankenstein in an increasingly negative light as the novel goes on. While he initially appears to be a naive but sympathetic idealist, after the creature’s narrative Frankenstein begins to resemble—even in his own telling—the thoughtlessly cruel figure the creature represents him as.
Remember that you can revise your thesis statement throughout the writing process , so it doesn’t need to be perfectly formulated at this stage. The aim is to keep you focused as you analyze the text.
Finding textual evidence
To support your thesis statement, your essay will build an argument using textual evidence —specific parts of the text that demonstrate your point. This evidence is quoted and analyzed throughout your essay to explain your argument to the reader.
It can be useful to comb through the text in search of relevant quotations before you start writing. You might not end up using everything you find, and you may have to return to the text for more evidence as you write, but collecting textual evidence from the beginning will help you to structure your arguments and assess whether they’re convincing.
To start your literary analysis paper, you’ll need two things: a good title, and an introduction.
Your title should clearly indicate what your analysis will focus on. It usually contains the name of the author and text(s) you’re analyzing. Keep it as concise and engaging as possible.
A common approach to the title is to use a relevant quote from the text, followed by a colon and then the rest of your title.
If you struggle to come up with a good title at first, don’t worry—this will be easier once you’ve begun writing the essay and have a better sense of your arguments.
“Fearful symmetry” : The violence of creation in William Blake’s “The Tyger”
The introduction
The essay introduction provides a quick overview of where your argument is going. It should include your thesis statement and a summary of the essay’s structure.
A typical structure for an introduction is to begin with a general statement about the text and author, using this to lead into your thesis statement. You might refer to a commonly held idea about the text and show how your thesis will contradict it, or zoom in on a particular device you intend to focus on.
Then you can end with a brief indication of what’s coming up in the main body of the essay. This is called signposting. It will be more elaborate in longer essays, but in a short five-paragraph essay structure, it shouldn’t be more than one sentence.
Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein is often read as a crude cautionary tale about the dangers of scientific advancement unrestrained by ethical considerations. In this reading, protagonist Victor Frankenstein is a stable representation of the callous ambition of modern science throughout the novel. This essay, however, argues that far from providing a stable image of the character, Shelley uses shifting narrative perspectives to portray Frankenstein in an increasingly negative light as the novel goes on. While he initially appears to be a naive but sympathetic idealist, after the creature’s narrative Frankenstein begins to resemble—even in his own telling—the thoughtlessly cruel figure the creature represents him as. This essay begins by exploring the positive portrayal of Frankenstein in the first volume, then moves on to the creature’s perception of him, and finally discusses the third volume’s narrative shift toward viewing Frankenstein as the creature views him.
Some students prefer to write the introduction later in the process, and it’s not a bad idea. After all, you’ll have a clearer idea of the overall shape of your arguments once you’ve begun writing them!
If you do write the introduction first, you should still return to it later to make sure it lines up with what you ended up writing, and edit as necessary.
The body of your essay is everything between the introduction and conclusion. It contains your arguments and the textual evidence that supports them.
Paragraph structure
A typical structure for a high school literary analysis essay consists of five paragraphs : the three paragraphs of the body, plus the introduction and conclusion.
Each paragraph in the main body should focus on one topic. In the five-paragraph model, try to divide your argument into three main areas of analysis, all linked to your thesis. Don’t try to include everything you can think of to say about the text—only analysis that drives your argument.
In longer essays, the same principle applies on a broader scale. For example, you might have two or three sections in your main body, each with multiple paragraphs. Within these sections, you still want to begin new paragraphs at logical moments—a turn in the argument or the introduction of a new idea.
Robert’s first encounter with Gil-Martin suggests something of his sinister power. Robert feels “a sort of invisible power that drew me towards him.” He identifies the moment of their meeting as “the beginning of a series of adventures which has puzzled myself, and will puzzle the world when I am no more in it” (p. 89). Gil-Martin’s “invisible power” seems to be at work even at this distance from the moment described; before continuing the story, Robert feels compelled to anticipate at length what readers will make of his narrative after his approaching death. With this interjection, Hogg emphasizes the fatal influence Gil-Martin exercises from his first appearance.
Topic sentences
To keep your points focused, it’s important to use a topic sentence at the beginning of each paragraph.
A good topic sentence allows a reader to see at a glance what the paragraph is about. It can introduce a new line of argument and connect or contrast it with the previous paragraph. Transition words like “however” or “moreover” are useful for creating smooth transitions:
… The story’s focus, therefore, is not upon the divine revelation that may be waiting beyond the door, but upon the mundane process of aging undergone by the man as he waits.
Nevertheless, the “radiance” that appears to stream from the door is typically treated as religious symbolism.
This topic sentence signals that the paragraph will address the question of religious symbolism, while the linking word “nevertheless” points out a contrast with the previous paragraph’s conclusion.
Using textual evidence
A key part of literary analysis is backing up your arguments with relevant evidence from the text. This involves introducing quotes from the text and explaining their significance to your point.
It’s important to contextualize quotes and explain why you’re using them; they should be properly introduced and analyzed, not treated as self-explanatory:
It isn’t always necessary to use a quote. Quoting is useful when you’re discussing the author’s language, but sometimes you’ll have to refer to plot points or structural elements that can’t be captured in a short quote.
In these cases, it’s more appropriate to paraphrase or summarize parts of the text—that is, to describe the relevant part in your own words:
The conclusion of your analysis shouldn’t introduce any new quotations or arguments. Instead, it’s about wrapping up the essay. Here, you summarize your key points and try to emphasize their significance to the reader.
A good way to approach this is to briefly summarize your key arguments, and then stress the conclusion they’ve led you to, highlighting the new perspective your thesis provides on the text as a whole:
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
By tracing the depiction of Frankenstein through the novel’s three volumes, I have demonstrated how the narrative structure shifts our perception of the character. While the Frankenstein of the first volume is depicted as having innocent intentions, the second and third volumes—first in the creature’s accusatory voice, and then in his own voice—increasingly undermine him, causing him to appear alternately ridiculous and vindictive. Far from the one-dimensional villain he is often taken to be, the character of Frankenstein is compelling because of the dynamic narrative frame in which he is placed. In this frame, Frankenstein’s narrative self-presentation responds to the images of him we see from others’ perspectives. This conclusion sheds new light on the novel, foregrounding Shelley’s unique layering of narrative perspectives and its importance for the depiction of character.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, August 14). How to Write a Literary Analysis Essay | A Step-by-Step Guide. Scribbr. Retrieved March 27, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/literary-analysis/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, how to write a thesis statement | 4 steps & examples, academic paragraph structure | step-by-step guide & examples, how to write a narrative essay | example & tips, unlimited academic ai-proofreading.
✔ Document error-free in 5minutes ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
Using Graphic Organizers for Writing Essays, Summaries and Research
Ask any student – essay writing is one of the most despised tasks of their educational career. Perhaps there is so much displeasure associated with the task because it’s perceived as too linear – there isn’t enough visual and creative appeal. But if you use graphic organizer for writing essays then you can make writing enjoyable – or at least less terrible.
Not only enjoyable but graphic organizers (or diagrams) can make the writing process a snap. They’ll help you think outside the box, draw conclusions you wouldn’t normally observe, and make the entire process faster and more efficient.
Why Use Graphic Organizers for Writing
The phrase “graphic organizer” is just a fancy way of saying “diagram” or “visual aid.” Basically, they are a visual representation of the information you’ve acquired in the research process. There are quite a few reasons why you should use them when writing essays or summaries.
- Helps you visualize your research and how elements connect with each other
- Enhance your essays, summaries and research papers with visual elements
- Track correlations between your thoughts, observations, facts or general ideas
When it comes to essay writing, the most common graphic organizers are webs, mind maps, and concept maps .
Using Webs for Brainstorming
Webbing is a great way to see how various topics are interrelated. This graphic organizer is particularly useful during the brainstorming step of the writing process.
A web can sometimes get a bit messy. Usually, there are lots of arrows to connect overlapping ideas. However, even with lines crisscrossing every which way, it is still a great way to visualize your thoughts. If you’re using an online diagramming software like Creately you can overcome some of this because we automatically arrange the object for you.
Once you’ve created a map to document all your ideas and establish connections, you can easily transition to other forms of diagramming to better organize the information.
For example if you’re writing a research paper about the food web of the Australian bushes you can start creating a food web diagram similar to the one below. This way you can easily visualize the web while writing the paper. This is a simple example but graphic organizers become even more important when the subject gets complex.
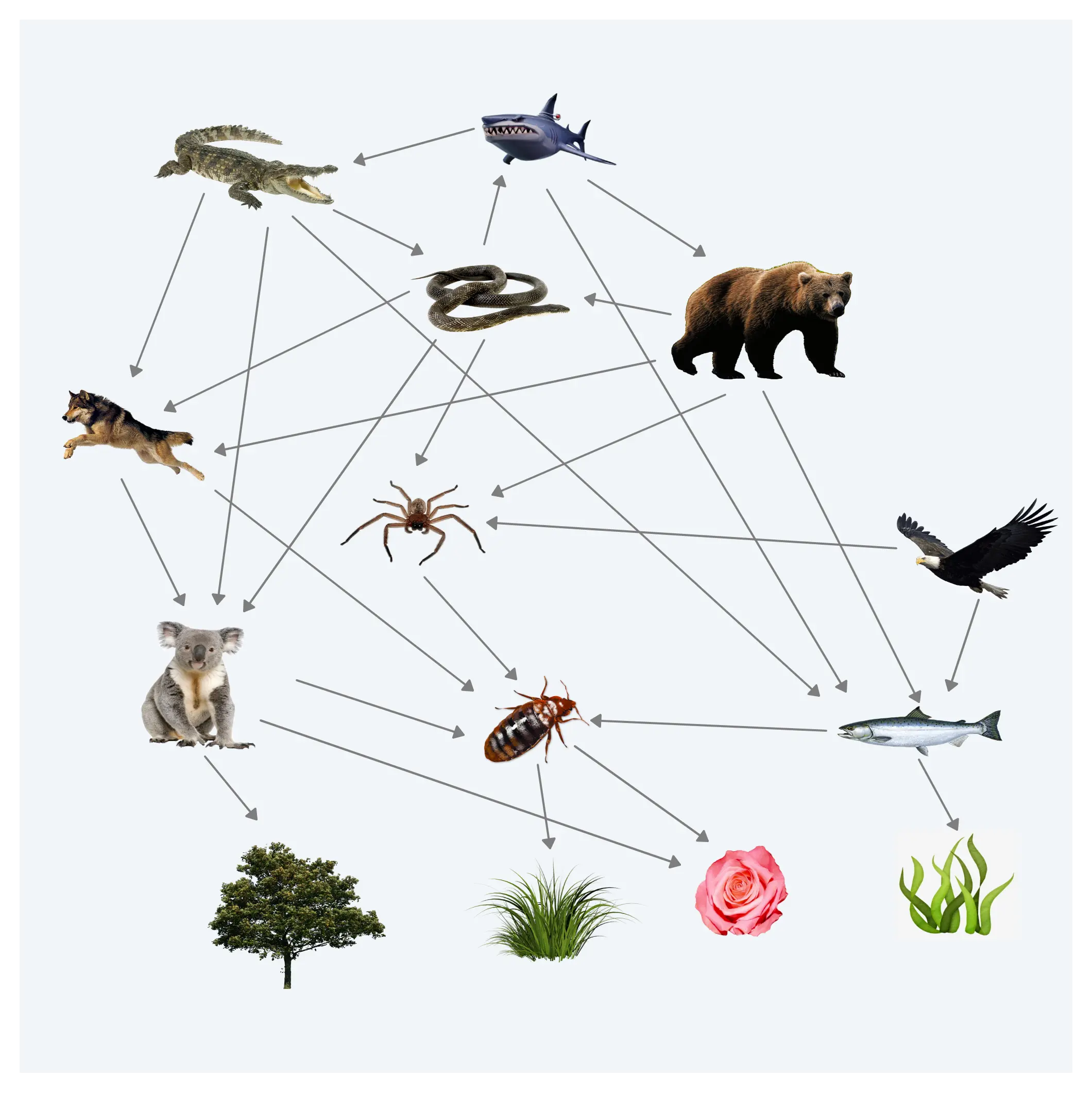
Although simple this example shows the importance of using graphic organizers for writing summaries. A comprehensive diagram pretty much does the summation for you.
Using Mind Maps as Graphic Organizers
Mind maps are a great way to depict a hierarchy. What is hierarchical organization ? The concept is simple: a singular topic dominates with each subsequent idea decreasing in importance.
Usually, the mind map starts with the thesis (or main idea) at the center. From there, you can branch out with your supporting evidence.
Use this process to replace your traditional note taking technique – note cards, outlines, whatever. You’ll quickly realize a mind map is a great way to formulate the structure of your essay. The thing to note here is that the nature of the mind maps force you think about sub topics and how to organize your ideas. And once the ideas are organized writing the essay become very easy.
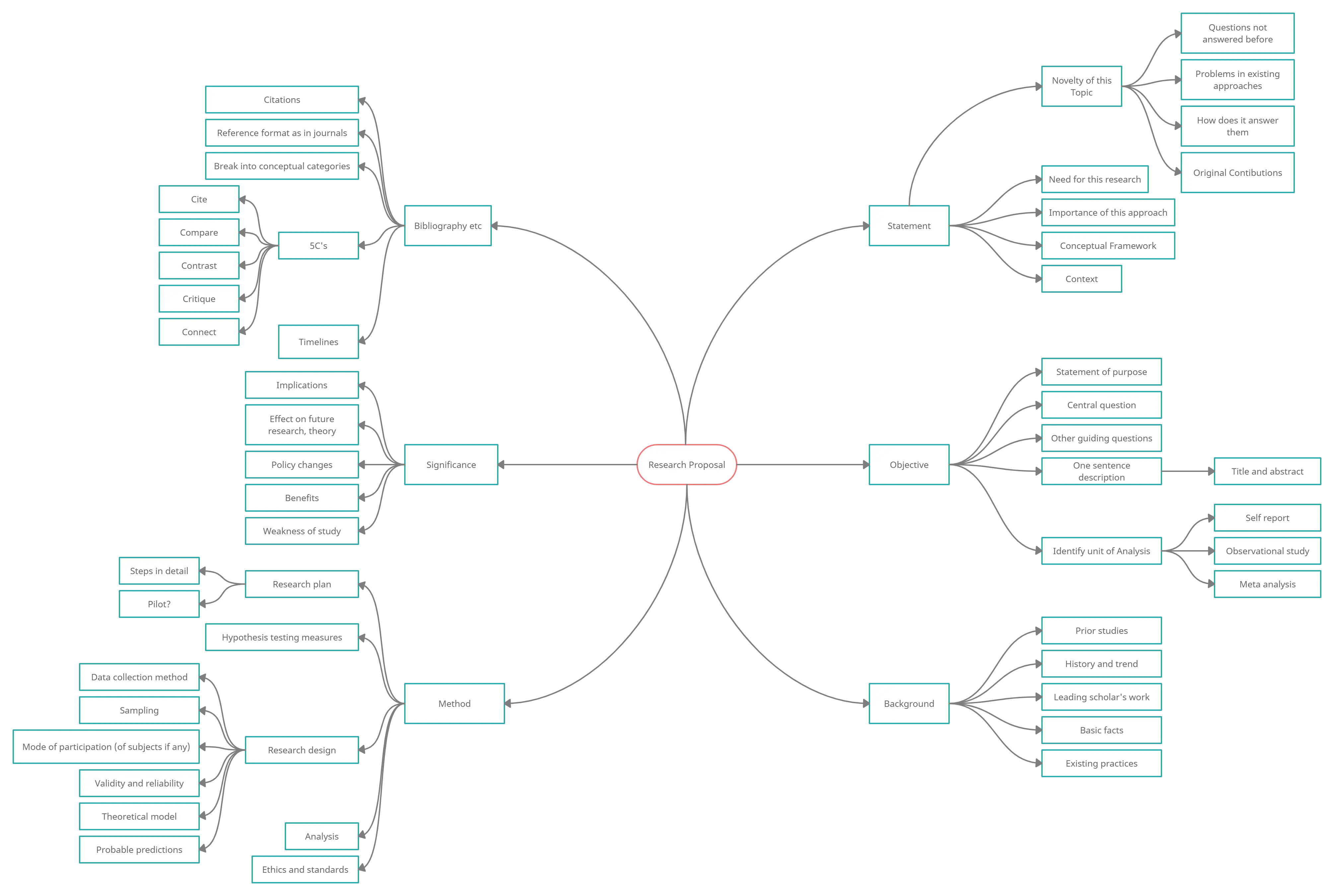
Above is a mind map of a research proposal. Click on it to see the full image or you can see the fully editable template via this link . As you can see in this mind map the difference areas of the research proposal is highlighted. Similarly when your writing the research paper you can use a mind map to break it down to sub topics. We have more mind map templates for you to get started.
Concept Maps
A concept map will help you visualize the connection between ideas. You can easily see cause and effect – how one concept leads to another. Often times, concept mapping includes the use of short words or phrases to depict the budding relationship between these concepts.
If you look closely you can see that its very similar to a mind map. But a concept maps gives more of a free reign compares to the rigid topic structure of a mind map. I’d say it’s the perfect graphic organizer for writing research papers where you have the license to explore.
By creating a concept map , you can also see how a broad subject can be narrowed down into specific ideas. This is a great way to counter writers block. Often, we look at the big picture and fail to see the specifics that lead to it. Identifying contributing factors and supporting evidence is difficult. But with a concept map, you can easily see how the smaller parts add up to the whole.
Why Bother With Graphic Organizers?
If you already detest the writing process, adding another step might seem insane. However, there really are several advantages of using them. If you haven’t already accepted the benefits of each individual diagram style, here are some more perks of graphic organizers in general:
- Quality essays are based on detail. No one is going to accept your opinions and reasoning just because you say so. You’ll need proof. And organizing that proof will require attention to detail. Graphic organizers can help you see that detail and how it contributes to the overall concept.
- Graphic organizers are flexible. You don’t need one of those giant pink erasers. You don’t need to restructure your outline. All you have to do is draw a few arrows and bam – the relationship has totally changed.
- No matter what you are writing about, a graphic organizer can help. They can be used to structure an essay on the Great Wall, theoretical physics, or Spanish speaking countries.
- If you write an outline, can you easily see how point A influences point X? Probably not. But if little thought bubble A is sitting out there all by itself, you can visualize the way it ties into point R, T and X.
- Some of us find it difficult to put our opinions, thoughts, and ideas into writing. However, communicating our feelings with little doodles and sketches is far less threatening.
- As a writer, our brain often feels like a 2-year-old’s toy box – a big jumbled mess. Taking that mess and putting it onto paper with some semblance of organization is challenging. Rather than trying to take your thoughts from total chaos to a perfectly structured list, just try to get them out of your brain and onto paper in the form of a diagram.
- A graphic organizer helps you establish validity and relevance. You can easily nix the ideas that don’t support or enhance your thesis.
The next time you are faced with a writing project, take a few minutes to explore the efficiency of graphic organizers. You can find a wealth of templates here.
Have you ever used a graphic organizer to structure an essay? How did it go? Do you have a diagram suggestion for the writing process that wasn’t mentioned here? Let us know!
Join over thousands of organizations that use Creately to brainstorm, plan, analyze, and execute their projects successfully.
More Related Articles
These are awesome guest posts contributed by our users and technology enthusiasts. Do you have something interesting to share? Want to get exposed to a massive tech audience? Check out our Guest Posting Guidelines to how to proceed.

How to Use Graphic Organizers to Write Better Essays
Lucid Content
Reading time: about 6 min
If you’re a student, there’s no way around the inevitable: You’re going to have to write essays. Lots of essays. In fact, the five-paragraph essay is so fundamental to the high school curriculum that it’s still used on the ACTs, and knowing how to recognize the organizational structure of essays will help you score higher on the SATs.
Even though it seems like a chore, knowing how to organize and write an essay can have a lasting effect on your life, from getting into a better college to scoring a better job to performing better in that job long after your high school days are over.
Here’s a secret: Using graphic organizers for writing essays can help you write better essays faster. (And don’t count yourself out if you’re an educator—you can offer these tools to help your students succeed.) We’ll show you exactly how to do it.
Why use graphic organizers
When ACT graders or teachers are looking your essay, they’re looking for very specific criteria; essentially, they’re looking at how well you’ve organized your thoughts. Many students don’t take the time to outline their essay structure before writing, and that always means a lower score on a test and a lower grade on the essay in class.
Using a writing template can feel like an unnecessary step in an already complicated process. If you need extra motivation to implement these organizers into your writing routine, consider all of their benefits. Graphic organizers can help you:
- Save time by showing you where each piece of the essay “lives.”
- Have more productive brainstorming sessions, either by yourself or with a group.
- Make connections between ideas and create a more cohesive argument.
- Pinpoint holes in your arguments and either adjust the thesis or find supporting statements.
- Keep track of your research.
- Organize your thoughts and come to interesting, more compelling conclusions.
- Stay in the right direction when you feel lost in a sea of words.
- Manage anxiety by converting the fear of a blank assignment into an action plan with a clear map.
With all those benefits, it’s hard to ignore how useful and vital graphic organizers are to writing. And once you’ve become adept at organizing your thoughts for something like a school essay, you’ll find that skill carries with you throughout your life, whether you’re trying to become a more intelligent debater to negotiate prices. It goes beyond just the essay to becoming a better thinker. And it starts with a simple template.
We’ll walk you through several use cases for graphic organizers and provide templates for you to download and fill in when you’re ready to write.
Brainstorming graphic organizers
Brainstorming is important, not only to come up with ideas for topics but to determine what information you need to include in the essay once you’ve determined your topic. Though many think of brainstorming as just freeflow thinking, brainstorming is most productive when you work within specific parameters.
That’s why essay brainstorming graphic organizers are useful, whether you’re using one to brainstorm on your own or you’re working with a group.
In Lucidchart, our mind map shapes and templates double as brainstorming graphic organizers. Start with an essay prompt as your central shape and then fill in the shapes that branch off your prompt with topic ideas. Alternatively, you can add your selected topic to the center and start brainstorming the different ideas you need to cover in your paper.
When the template is filled in, you’ll have a clear starting point for your essay or research paper.
Research paper graphic organizers
Nothing paralyzes students with fear quite like a research paper. These long-form papers require—as the name implies—quite a bit of research, and their purpose is to teach students how to look for valid sources to support their arguments.
But keeping track of all those sources and tying them into your argument can be tricky. That’s where a research paper graphic organizer can be a student’s greatest ally.

This template lays out the writing process itself. After you come up with a general topic, like “the disappearance of honey bees,” fill in the “Research Paper Topic” box.
Then, start looking for reputable sources (Wikipedia doesn’t count) and use the five sources boxes to hold the most relevant quotes and statistics you find. Using those quotes and statistics, you can then fill out a thesis statement that is supported by the research.
Then, you’ll be able to focus your paragraphs on a single topic each that supports the thesis statement and your overarching argument. After you’ve filled out the template, the backbone of the research paper is complete: All that’s left to do is fill in the spaces between sources and arguments.
5-paragraph essay graphic organizer
When it comes to writing the five-paragraph essay, writing diagrams are key. By using graphic organizers for writing, you’re no longer staring at a giant blank piece of paper with no idea how or where to begin. Your graphic organizer is your map.
Although using writing diagrams may seem time-consuming, the fact is that taking the time to fill a graphic organizer in before writing actually saves time. If there’s a problem with the argument, it will show up on the diagram, or if there’s not enough evidence to support your argument, you’ll know before you’ve wasted time writing the paper. And, as we said before, even if your writing is terrible, if your argument is sound, you’ll still score a decent grade.
Try this 5-paragraph essay template to get you started.

Don’t feel pressured to come up with a compelling title right away. Instead, it’s more important that you come up with a thesis statement that can be supported by three solid arguments. Fill in that thesis statement and your arguments. Then, for each argument, figure out three supporting details to support your case.
That’s it! You’ve got the most essential parts of your 5-paragraph essay completed.
Now, come up with an introduction that sets the stage for your argument and a conclusion that wraps up and restates your thesis and supporting arguments in a compelling way. Now you have a solid plan for your paper and can approach it with confidence.
If you’d like a more linear graphic that exactly follows the structure of the 5-paragraph, use the writing template below and follow the same process.

Visuals, such as graphic organizers for writing, can help you better understand concepts, think creatively, and collaborate with your classmates—and there are plenty of other templates where these came from.
Lucidchart offers hundreds of templates to help you through your studies, including timelines, Venn diagrams, word maps, and more. Sign up for Lucidchart and upgrade to an Educational account for free.
Resources for teachers
Providing graphic resources to students is essential; after all, many of your students will be visual learners, so while you may beautifully explain how the process works, there will be some who won’t understand until they see a template of the essay itself.
Lucidchart has many resources for teachers, from lesson plans to writing templates. While you’re teaching your students how to write essays or research papers, it’s useful to print out the templates and fill them out together (even using a completed template as a separate assignment with a separate grade) so that your students can get a feel for properly filling out graphic organizers before attempting it on their own.
Lucidchart, a cloud-based intelligent diagramming application, is a core component of Lucid Software's Visual Collaboration Suite. This intuitive, cloud-based solution empowers teams to collaborate in real-time to build flowcharts, mockups, UML diagrams, customer journey maps, and more. Lucidchart propels teams forward to build the future faster. Lucid is proud to serve top businesses around the world, including customers such as Google, GE, and NBC Universal, and 99% of the Fortune 500. Lucid partners with industry leaders, including Google, Atlassian, and Microsoft. Since its founding, Lucid has received numerous awards for its products, business, and workplace culture. For more information, visit lucidchart.com.
Related articles

Check out how Annika, a recent English graduate of the University of Michigan, used mind mapping in Lucidchart to develop her honors thesis.
Bring your bright ideas to life.
or continue with

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Use this graphic organizer to plan your analytical/persuasive essay. The introduction should start with a broad statement and end with your thesis statement, which “zooms in” on the points you will explore in more depth. The body paragraphs must contain evidence to support your thesis. (The number of body paragraphs coincides with the ...
2. Graphic Organizers. Graphic organizers are one of my go-to strategies for elevating thinking. We can use them to differentiate and to guide students as we work in small groups. I like to keep a variety of literary analysis graphic organizers for any text on hand so that I can be responsive.
Examples include TP-CASTT - title, paraphrase, connotation, attitude, shift, title (again), and theme. TP-CASTT is traditionally used with poetry but can be applied to other types of literature, including short stories and chapters in novels. SMELL - sender, message, evidence, logic, and language for analyzing rhetoric.
Graphic Organizer (Five Paragraph Essay) Overall Essay Planner: Use this page of the graphic organizer to plan what your overall essay will be about (your claim) and what reasons you have to show that your claim is true. These reasons will be the basis for your body paragraphs. Intro Paragraph: What is your claim?
Discovering Evidence for a Literary Analysis Essay, Fall 2014. 2 of 6. meaning of a literary work. This handout focuses on how to write an explication essay because explication is the foundation for literary analysis, whether the essay be a critical argument or an explication. Literary analysis begins with a study of form and effect.
Table of contents. Step 1: Reading the text and identifying literary devices. Step 2: Coming up with a thesis. Step 3: Writing a title and introduction. Step 4: Writing the body of the essay. Step 5: Writing a conclusion. Other interesting articles.
Literary Thesis Essay Graphic Organizer C. Rush 3/2009 2 Introductory Paragraph Thesis statement: Your answer to the essential question posed in the original assignment. _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ Ideas you will address in the body of the essay: This is sometimes referred to as the map or blueprint of the body. Your key points, arguments
Writing a Literary or Textual Analysis Paragraph. Make sure to address all the following topics in your analysis paragraphs (i.e. the paragraphs you are writing for your Process Piece). Take notes on this sheet to help you prepare your paragraph, but the final version should not be in notes or bullet points—it should read like a paragraph ...
Helps you visualize your research and how elements connect with each other. Enhance your essays, summaries and research papers with visual elements. Track correlations between your thoughts, observations, facts or general ideas. When it comes to essay writing, the most common graphic organizers are webs, mind maps, and concept maps.
In Lucidchart, our mind map shapes and templates double as brainstorming graphic organizers. Start with an essay prompt as your central shape and then fill in the shapes that branch off your prompt with topic ideas. Alternatively, you can add your selected topic to the center and start brainstorming the different ideas you need to cover in your ...