Custom Essay, Term Paper & Research paper writing services
- testimonials
Toll Free: +1 (888) 354-4744
Email: [email protected]

Writing custom essays & research papers since 2008
The ultimate guide on how to write a memo essay.

Memos, short form for memorandums, are common types of communication, especially in business settings. In practice, people use memos to provide directives, answer questions and provide information. It is a brief message from a person, department, or company to another. So, when you are faced with a memo essay type of assignment, how do you go about it?
This post is a comprehensive guide on how to write a memo essay to help you become a pro writer. We will also provide you with the definition of a memo, sample, writing tips, and answer the question: “What is memo format?”
What is a Memo?
Before diving into the mechanics of writing a memo essay, it is important to start with the basics.
A memo is a short written notice usually done by management of an organization to address a specific issue.
Memos can be classified into several groups:
- Directive memos.
- Status memos.
- Field report memos.
- Response memos.
- Suggestion memos.
In an academic setting, a memo is a form of academic assignment used to help students hone their communication skills. You will need these skills later when you work in companies or government departments.
How to Write a Good Memo Essay
The secret to writing a great memo is ensuring you are as clear as possible. In many cases, memos are written to address specific issues. Therefore, your selection of words, sentences, and the message should be as clear as possible. Here are some useful tips to help you write a top-notch memo style paper.
- Keep the memo short: If you make the memo lengthy, it will become tiresome, and the message might not be delivered as anticipated. Therefore, summarize the memo as much as possible without omitting any detail.
- Make sure to use simple English: The goal of a memo is to ensure that even if the target audience takes a single glance, the message will be delivered. Therefore, avoid jargon and complex sentences.
- Use captivating heading for the memo: An attractive heading will easily attract the audience. For example, you can bold the heading or use a highly reflective color.
- Avoid grammar and sentence errors: Like any other type of academic writing, you need to ensure that your memo does not have errors such as typos, clichés, and running sentences. Therefore, make sure to proofread the memo essay so that the grammar is okay and message clear.
- Hone your skills: To be able to write a good memo, it is important to practice your writing skills as much as possible. Therefore, make sure to check and follow another top memo essay example to see how experts do it.
Memorandum Essay Format
When you write a memo and post on a board, what distinguishes it from others is its format. As you sit down to craft your memo, it is crucial also to learn how to write a memo format. So here is one of the best formats for writing your memo:
The heading comes at the top of the page and should be done in bold letters. You should use the header to give the document identity.
- Recipient address
Below the header, you should provide the address of the recipient. Make sure to be official and write a specific name or group of people targeted by the memo.
After writing the sender details, you should indicate the sender. Ensure to write your name as well as your position in the organization.
The date of the memo should come immediately below the sender’s details. Note that this highlights when the memo was sent and should help to distinguish it from other memos on the notice board.
The title follows the date and helps to indicate what the memo is about. By simply looking at the title, readers can have an idea of what the memo is talking about. Make sure to align the heading content to the left and use the right spacing.
When it comes to the body of the memo, you should try to keep it short by sticking to the main point. Here are some useful points to help you write the body of a memo essay:
- Think about your readers. These are the people you are the addressee in the memo. Once you understand the targeted readers, make sure to use the right language that suits them.
- Go straight to the point. After deciding the goal of writing the memo, leave out salutations, and go directly to the point.
- Provide a small background about the issue at hand. Once you address the problem under consideration, offer some reasons for the implementation of your recommendations. This can be in the form of bullets or numbers.
- Close the memo with a summary. This is a summary of the points you have brought out in the memo. Make the summary as positive as possible.
- Lastly, sign the memo to make it look official.
Memorandum Essay Example
To provide you with a clearer picture of how to write a memo paper, take a closer look at the memo paper example below. Note how the header content is arranged and spaced.
MEMORANDUM To: All Students Pursuing Accounting Courses at the University. From: The Dean, School of Business, Date: January 7, 2020. Subject: Submission of Your Final Project. It has come to my notice that most of you are yet to submit the final year projects, which is very important at this juncture because it determines if you are going to graduate this year or not. In the past, I have seen this problem, and students came crying after discovering that they are missing from the graduation list. Note that your project accounts for 40% of the final grade and, therefore, should be taken seriously. On this note, the department has put a deadline of March 20, 2020. Students who will not have submitted their projects by the close of the deadline will have to wait for another full academic year before being able to graduate. You are advised to submit your project on time. We do not want you to suffer when graduation finally comes. Thanks in Advance Yours sincerely, Sign……. The Dean
When to Seek Writing Assistance
Using the above guide and sample, go ahead and start working on your memo. However, if you are finding it hard to craft the essay, do not hesitate to seek assistance. Often, students find it hard to write a memo format paper because of the following reasons:
- Tight deadlines.
- Poor writing skills.
- Complex topics.
- Other engagements.
No matter the reason making you feel nervous or stressed about memo essay, you should know that a helping hand is only a click away. Professional writing assistance is offered by experts who understand how to write a memo for a research paper and guarantee you top grades. You can never go wrong with expert writers.
- Improve Productivity & Efficiency
- Mastering Task Batching
- Monthly Budget Templates
- Top Down Vs. Bottom Up
- Weekly Schedule Templates
- Kaizen Principles
- Opportunity Mapping
- Strategic-Goals
- Strategy Mapping
- T Chart Guide
- Business Continuity Plan
- Developing Your MVP
- Incident Management
- Needs Assessment Process
- Product Development From Ideation to Launch
- Visualizing Competitive Landscape
- Communication Plan
- Graphic Organizer Creator
- Fault Tree Software
- Bowman's Strategy Clock Template
- Decision Matrix Template
- Communities of Practice
- Goal Setting for 2024
- Meeting Templates
- Meetings Participation
- Microsoft Teams Brainstorming
- Retrospective Guide
- Skip Level Meetings
- Visual Documentation Guide
- Weekly Meetings
- Affinity Diagrams
- Business Plan Presentation
- Post-Mortem Meetings
- Team Building Activities
- WBS Templates
- Online Whiteboard Tool
- Communications Plan Template
- Idea Board Online
- Meeting Minutes Template
- Genograms in Social Work Practice
- How to Conduct a Genogram Interview
- How to Make a Genogram
- Genogram Questions
- Genograms in Client Counseling
- Understanding Ecomaps
- Visual Research Data Analysis Methods
- House of Quality Template
- Customer Problem Statement Template
- Competitive Analysis Template
- Creating Operations Manual
- Knowledge Base
- Folder Structure Diagram
- Online Checklist Maker
- Lean Canvas Template
- Instructional Design Examples
- Genogram Maker
- Work From Home Guide
- Strategic Planning
- Employee Engagement Action Plan
- Huddle Board
- One-on-One Meeting Template
- Story Map Graphic Organizers
- Introduction to Your Workspace
- Managing Workspaces and Folders
- Adding Text
- Collaborative Content Management
- Creating and Editing Tables
- Adding Notes
- Introduction to Diagramming
- Using Shapes
- Using Freehand Tool
- Adding Images to the Canvas
- Accessing the Contextual Toolbar
- Using Connectors
- Working with Tables
- Working with Templates
- Working with Frames
- Using Notes
- Access Controls
- Exporting a Workspace
- Real-Time Collaboration
- Notifications
- Meet Creately VIZ
- Unleashing the Power of Collaborative Brainstorming
- Uncovering the potential of Retros for all teams
- Collaborative Apps in Microsoft Teams
- Hiring a Great Fit for Your Team
- Project Management Made Easy
- Cross-Corporate Information Radiators
- Creately 4.0 - Product Walkthrough
- What's New
How to Write a Memo: Templates and Examples

What is a Memo?
A memo, short for memorandum, is a type of written communication used in business or academic settings. Unlike informal emails or verbal announcements, memos are not prone to ambiguity or misunderstanding. They are meant to deliver messages that are direct and to the point, leaving no room for doubt or confusion. Memos can be written for various purposes, such as:
Creating a record of key decisions and policies.
Communicating a consistent and coherent message to a large audience within the company.
Keeping all team members updated and aligned on current projects and progress.
Requesting approval or authorization for a decision.
Announcing a meeting or an event.
Sharing important news or achievements.
Why We Use Memos
Memos are an important part of the internal communication system of any organization. They help to inform and update colleagues on various topics, from policy changes to project updates. Here’s how memos help to communicate clearly and briefly:
Brevity: Memos are concise and focused. They only include the most relevant information, making sure that the message is received and acted on quickly and effectively.
Authority: The structured format of a memo gives it a sense of authority and formality, which is often needed for official communications within a company.
Documentation: Memos create a written record of communication, which can be used for clarification or during audits, making them useful for accountability and historical reference.
Memos are especially useful in situations where email might be too informal or when a permanent record of communication is required. They are suitable for instructions, procedures, and announcements that need attention and retention. In the fast-paced environment that product managers work in, the ability to easily create, customize, and share memos can improve team coordination and project management.
Types of Memos
There are different types of memos depending on the purpose and the audience.
- Informative memo: This type of memo provides information about a topic, such as a new policy, a change in procedure, or an upcoming event. The goal of an informative memo is to inform the readers and explain the rationale behind the information.

- Directive memo: This type of memo gives instructions or directions to the readers, such as how to complete a task, follow a rule, or comply with a requirement. The goal of a directive memo is to persuade the readers and provide clear and specific guidance.
- Request memo: This type of memo asks the readers to do something, such as approve a proposal, grant a permission, or provide a resource. The goal of a request memo is to convince the readers and justify the request.
- Response memo: This type of memo answers a question, addresses a concern, or provides feedback to the readers, such as responding to an inquiry, resolving an issue, or evaluating a performance. The goal of a response memo is to satisfy the readers and demonstrate competence.
How to Write a Memo in Five Steps
Regardless of the type, memos should be concise, clear, courteous, and coherent. Memos should also follow a standard format that includes a heading, an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. Memos should be written in a professional tone that reflects the relationship between the writer and the reader. Here are some steps to follow when writing a memo:
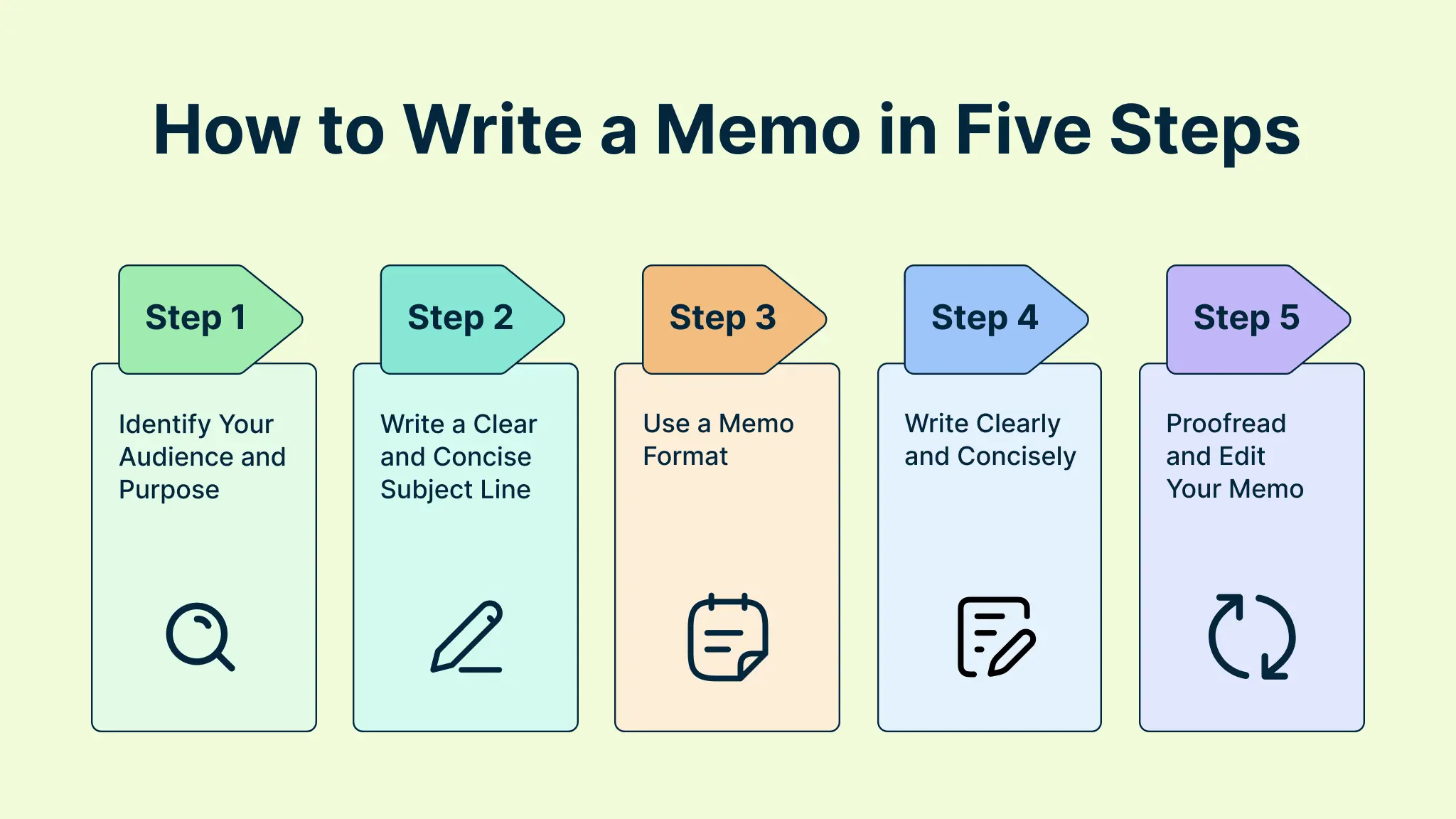
Step 1 - Identify Your Audience and Purpose
Before you start writing, think about who will read your memo and what you want them to do or know. This will help you tailor your tone, language, and content to suit their needs and expectations.
Step 2 - Write a Clear and Concise Subject Line
The subject line is the first thing that the recipients will see, so make it interesting and relevant. It should summarize the main point of your memo and capture the attention of the reader.
Step 3 - Use a Memo Format
Use a standard memo format. A memo typically consists of four parts:
Heading: Date, recipients, subject, and reference.
Opening: Purpose of the memo in a concise statement.
Context: Background information relevant to the message.
Closing: Summary and next steps or call to action.
When it comes to design, choose fonts and colors that reflect your organization’s branding for a professional look. A clean, readable font like Arial or Times New Roman is often preferred. For colors, stick to a simple palette that doesn’t distract from the content. Remember, the goal is to communicate effectively, not to showcase design skills.
Step 4 - Write Clearly and Concisely
Use simple, direct, and active language to express your ideas. Avoid jargon, slang, or unnecessary words that may confuse or distract the reader. Use bullet points, lists, headings, and white space to organize your information and make it easy to scan. Keep your sentences and paragraphs short and focused.
Step 5 - Proofread and Edit Your Memo
Before you send your memo, check it for spelling, grammar, punctuation, and formatting errors. Make sure your memo is consistent, accurate, and complete. Ask someone else to review your memo if possible and get their feedback.
Tips to Write Professional Memos
Organize your content: Use headings, bullet points, and white space to structure your memo and make it easy to scan and understand.
Attach relevant documents: If you need to provide additional information or evidence, attach them to your memo and refer to them in the body. Use descriptive file names and labels for your attachments.
Follow up: After sending your memo, follow up with your recipients to ensure they have received it and understood it. If you need a response or feedback, set a deadline and remind them politely.
Review previous memos: If you are writing a memo on a similar topic or to the same audience as before, review previous memos to ensure consistency and avoid duplication.
Mistakes to Avoid When Writing Memos
Not using appropriate language. Make sure your memo does not include slang, jargon, acronyms, or abbreviations that may confuse or offend the reader.
Using an accusatory tone: A memo should use formal, polite, and respectful language that suits the context and the relationship between the sender and the receiver. It should also not use emotional, aggressive, or sarcastic tone that may undermine the credibility or professionalism of the sender.
Adding unnecessary details, jargon, and repetition. Use short sentences and paragraphs, and get to the point quickly.
How Creately Helps You to Write a Good Memo
Creately offers real-time collaboration and an infinite canvas, which can simplify the memo creation process, ensuring that the message is not only clear and brief but also visual. With Creately, you can:
Choose from a variety of memo templates that suit different purposes and situations
Customize your memo with your own logo, colors, fonts, and images
Add comments, notes, links, attachments, and icons to enhance your memo
Collaborate with your team members in real-time and get their input
Store and organize your memo in folders accessible by specific teams or the entire organization
Export your memo as a PDF, PNG, or JPEG file and share it with your recipients
Join over thousands of organizations that use Creately to brainstorm, plan, analyze, and execute their projects successfully.
FAQs About Writing Memos
More related articles.

Hansani has a background in journalism and marketing communications. She loves reading and writing about tech innovations. She enjoys writing poetry, travelling and photography.

How it works
Transform your enterprise with the scalable mindsets, skills, & behavior change that drive performance.
Explore how BetterUp connects to your core business systems.
We pair AI with the latest in human-centered coaching to drive powerful, lasting learning and behavior change.
Build leaders that accelerate team performance and engagement.
Unlock performance potential at scale with AI-powered curated growth journeys.
Build resilience, well-being and agility to drive performance across your entire enterprise.
Transform your business, starting with your sales leaders.
Unlock business impact from the top with executive coaching.
Foster a culture of inclusion and belonging.
Accelerate the performance and potential of your agencies and employees.
See how innovative organizations use BetterUp to build a thriving workforce.
Discover how BetterUp measurably impacts key business outcomes for organizations like yours.
A demo is the first step to transforming your business. Meet with us to develop a plan for attaining your goals.

- What is coaching?
Learn how 1:1 coaching works, who its for, and if it's right for you.
Accelerate your personal and professional growth with the expert guidance of a BetterUp Coach.
Types of Coaching
Navigate career transitions, accelerate your professional growth, and achieve your career goals with expert coaching.
Enhance your communication skills for better personal and professional relationships, with tailored coaching that focuses on your needs.
Find balance, resilience, and well-being in all areas of your life with holistic coaching designed to empower you.
Discover your perfect match : Take our 5-minute assessment and let us pair you with one of our top Coaches tailored just for you.

Best practices, research, and tools to fuel individual and business growth.
View on-demand BetterUp events and learn about upcoming live discussions.
The latest insights and ideas for building a high-performing workplace.
- BetterUp Briefing
The online magazine that helps you understand tomorrow's workforce trends, today.
Innovative research featured in peer-reviewed journals, press, and more.
Founded in 2022 to deepen the understanding of the intersection of well-being, purpose, and performance
We're on a mission to help everyone live with clarity, purpose, and passion.
Join us and create impactful change.
Read the buzz about BetterUp.
Meet the leadership that's passionate about empowering your workforce.

For Business
For Individuals
How to write a memo: 8 steps with examples

Elevate your communication skills
Unlock the power of clear and persuasive communication. Our coaches can guide you to build strong relationships and succeed in both personal and professional life.
Jump to section
What’s a memorandum?
How to write a business memo in 8 steps, when to write a memo, 5 examples of memos, unleashing the power of effective memos.
Whether you’re planning a meeting or working on a project with dozens of moving parts, effective communication is the key to success.
But it’s hard to keep everyone in the loop all the time. You can’t always host a 1:1 meeting or talk to coworkers face-to-face when new information arises. Sometimes, all you need is a short notification that alerts everyone at the same time — and does so quickly.
Memos provide a streamlined channel for internal communication. In a short space, you can share vital information with clarity and impact. Here’s the step-by-step process of how to write a memo with specific examples, from crafting a compelling header to including action plans and timelines.
A memorandum, also known as a memo, is a concise written message that quickly and efficiently shares vital information. This could come in the form of an email, Slack announcement, or a piece of paper on a bulletin board, depending on the workplace.
A well-structured memo offers lots of information in a short space. It does everything from announcing changes in company policy to providing vital project updates, all without wasting readers’ time. Anyone can write an email, but memo-writing is a learned skill that takes time to truly perfect.
To create a succinct and comprehensive memo, formatting is key. Just like a professional email , every piece of information plays a role in making the memo easily digestible and actionable — from subject line to salutation .
Here’s a step-by-step approach to ensure your messages are both effective and clear:
1. Start with a header
To set the stage, always start with a comprehensive header. The header should include the date and the general subject, along with who the memo is to and from. These elements offer context and ensure that readers quickly grasp the basic premise, aiding quick decision-making about the action they need to take.
2. Craft a clear objective statement
The first paragraph of your memo should directly express its purpose in an objective statement or problem statement . This not only helps the recipients understand the memo's relevance, but also ensures they grasp its intent swiftly.
Think of a cover letter . The first line is usually something like “I am writing to…” A memo should have the same clarity so readers immediately know what they’re looking at and why.

3. Provide a comprehensive body paragraph
The body of the memo is where you'll develop your main points, so it should be as comprehensive as possible despite the short space. Always start with critical details as early as possible, then move towards less significant but still pertinent information.
To enhance readability, structure the body using bullet points or numbered lists. And remember to stay away from unnecessary jargon that may confuse your readers. A memo’s goal is brevity, so make sure it’s easy to understand.
4. Provide background information
If your memo references previous events, circumstances, or memos, include a brief background section. This provides context, orients your readers, and ties your current communication to past events or actions, offering a holistic understanding of the situation at hand.
5. Include action items and timelines
Memos often need to include a call to action that tells readers what to do next, whether that’s to acknowledge receipt or find a meeting room ASAP. Clearly define the steps they need to take, identify the parties responsible, and specify the deadlines for these tasks.
By doing so, you encourage accountability and create a shared understanding of expectations, fostering a more organized and efficient work environment .

6. Add a summary
If your memo tackles a complex issue or is particularly lengthy, add a short conclusion to summarize the most important points. In the absence of face-to-face cues, reiterating the main points through a brief summary reinforces the essential elements of your message, aiding comprehension.
7. Include your contact information
As hard as you may try, communication isn’t always clear. People might have questions about what to do next, and failing to provide a clear path toward those answers could add unnecessary hurdles.
To avoid this, always add your contact information at the end of your memo, whether that’s your desk location or your Slack handle. This lets your colleagues reach out if they have questions or need further clarification on any points.
8. Add attachments if necessary
If you reference other documents, graphs, or materials, either attach them or provide accessible links. This ensures that your readers have all the resources at their disposal to fully understand and act upon the memo. Linking out also keeps you from adding too much information to the memo itself.
According to Gallup’s 2022 State of the Global Workplace Report, 41% of employees wish they could change their company’s engagement or culture . And communication falls into that category. Meetings, emails, and effective memos all support the interactions that uplift strong culture .
Knowing when to write a memo helps you choose the right type of communication for the situation and avoid information silos . Here are some scenarios where memos shine:
Inform about company policies or changes: If your organization is undergoing changes in policies, procedures, or strategies, a memo is an excellent way to update staff. It ensures uniform understanding and gives everyone the chance to ask questions as soon as possible, saving time and stunting the spread of misinformation.
Raise awareness about an issue: If a significant issue is impacting your organization's functioning, a memo brings it to everyone's attention. In this situation, a memo is also vital for overall engagement and the employee experience because it keeps people in the loop on important issues and reinforces the value of their contributions.
Provide updates on a project: Memos are a great tool for informing stakeholders about a project's progress, timeline adjustments, or resource requirements. Informing everyone of all the project's deadlines and ongoing developments prevents roadblocks and helps projects run smoothly.
Make a request: A memo effectively communicates formal requests, including those for resources, approvals, or feedback . By clearly articulating the reasons and potential benefits of your request, a memo acts as a persuasive tool for support or approval. It can also anticipate and address possible questions.
Recognize employee achievement: Memos are also a method for acknowledging outstanding employee performance a nd achievements like a promotion . This has the multipurpose effect of expressing recognition for hard work while emphasizing company values , boosting morale , and fostering a positive work environment.

To help you better visualize how to write a good memo, here are five memo examples for different situations:
1. Change in policy memo
This example not only outlines changes in company policy, but also explains the reasons behind the change. It encourages questions and tells readers exactly where to go for more information, offering transparency and support.
To: [person or department name]
From: [person or department name]
Date: [insert date]
Subject: [subject] Policy Change
I'm writing to inform you of an important update regarding [policy]. Effective [date], we will be implementing changes to [specific details of the policy changes].
The purpose of this change is to [explain the rationale behind the change and its benefits]. We believe that these adjustments will contribute to [goal].
Please take the time to review the attached document outlining the updated policy in detail. Should you have any questions or concerns, feel free to reach out to [contact person or department].
Thank you for your attention to this matter.
Best regards,
2. Project update memo
An update memo keeps everyone informed about a project's progress, any changes to the original plan, or any challenges along the way. This ongoing communication helps preempt problems and ensures everyone is working towards the same goals.
Subject: [project name] Update
Here’s an update on the progress of [project name]. Here are the key developments since our last update:
- [a summary of tasks and milestones]
- [any challenges or issues and how they were resolved]
- [any adjustments to the project timeline or scope, if applicable]
Overall, we’re making steady progress and remain on track to meet our goals. Please stay vigilant and continue to give your best effort to ensure the successful completion of this project.
If you have any questions or need further clarification, please don't hesitate to reach out to me. Let's keep up the excellent work!
3. Issue alert memo
This type of memo raises awareness about a specific issue affecting the company, a department, or a specific project. Besides highlighting the problem, it may also suggest potential steps to address it, encouraging proactive problem-solving within the organization.
Subject: [subject] Issue
I'm writing to bring your attention to an issue with [subject]. It has come to our attention that [describe the issue and its impact on the company or employees].
We understand the potential challenges that this may pose and are actively working on resolving the situation. In the meantime, we encourage everyone to [provide any necessary instructions or precautions].
Rest assured that we’re taking this matter seriously, and we will keep you updated on any progress or further instructions. If you have any insights or suggestions related to this issue, please share them with [contact person or department].
Thank you for your understanding and cooperation.

4. Request memo
A request memo formalizes a need for resources, feedback, or approval. By clearly outlining the reasons behind the request, you effectively communicate the need for these items and the impact they could have on the team.
Subject: [specific request]
Hi [person or department name],
I hope this message finds you well. I'm writing to formally request [specific request]. This is because [provide a concise explanation of the request, including its importance and potential benefits for the company].
I’ve attached a detailed proposal outlining the specifics of the request, including [details, supporting data, and relevant information].
Should you have any questions or require further information, please don't hesitate to reach out to me. I appreciate your attention.
5. Employee recognition memo
According to data from Gallup, employees who don’t experience enough recognition are twice as likely to say they’ll quit in the next year .
A memo is a quick way to give kudos and celebrate an employee's achievement or contribution to the company. Not only does it express appreciation for hard work , but it also boosts morale and fosters a healthy environment for everyone.
Subject: Quick kudos
Let’s all take a moment to appreciate [employee name] from [department/team]’s exceptional performance and dedication. They have consistently demonstrated [specific achievements, qualities, or contributions].
Their hard work and commitment to excellence have been truly remarkable and deserving of recognition. [employee name]’s efforts reflect positively on the entire team and contribute to our overall success as a company.
Please join me in congratulating [employee name] for their outstanding achievement. We appreciate their continued dedication and professionalism. Let's celebrate this milestone and continue to inspire and support one another in our respective roles.
Warmest congratulations once again!
Mastering how to write a memo is an essential skill in the corporate world because it lets you convey a message with clarity and simplicity.
Whether you're drafting a project update or learning how to write a memo to your boss, you can become a better communicator and break down silos. Never underestimate the power of a well-structured and purposeful memo.
Elizabeth Perry
Content Marketing Manager, ACC
How improving your concentration helps your memory
Learn what process mapping is and how to create one (+ examples), what is lateral thinking 7 techniques to encourage creative ideas, how to make a daily schedule: tips and examples, get smart about your goals at work and start seeing results, how to prioritize tasks: 7 tips to perfect your workflow, curious wanting to learn more is key to career success, how to introduce yourself in an interview: examples & tips, learn to let it go: how to deal with career disappointment, similar articles, encouraging explicit knowledge sharing throughout your workforce, how to write an exciting promotion announcement, how to write an executive summary in 10 steps, write thank you letters after interviews to stand out as job applicant, 8 tips on how to write a professional email (with examples), write an intro email to a new team to start your job on the right foot, tips for how to write a linkedin summary and examples, how to send a reminder email that’s professional and effective, how to write a follow-up email 2 weeks after an interview, stay connected with betterup, get our newsletter, event invites, plus product insights and research..
3100 E 5th Street, Suite 350 Austin, TX 78702
- Platform Overview
- Integrations
- Powered by AI
- BetterUp Lead
- BetterUp Manage™
- BetterUp Care™
- Sales Performance
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Case Studies
- Why BetterUp?
- About Coaching
- Find your Coach
- Career Coaching
- Communication Coaching
- Life Coaching
- News and Press
- Leadership Team
- Become a BetterUp Coach
- BetterUp Labs
- Center for Purpose & Performance
- Leadership Training
- Business Coaching
- Contact Support
- Contact Sales
- Privacy Policy
- Acceptable Use Policy
- Trust & Security
- Cookie Preferences

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

6.10: Memorandum explaining how to write a memo
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 86310
MYTHIC UNIVERSITY ONLINE
DATE : August 9, 2008 TO : Users of Style for Students Online FROM : Joe Schall SUBJECT : Writing Memos for your Classes
This memo provides you with tips on writing memos for your classes, with special attention to a memo’s audience, format, organization, content, tone, and style. Because my advice comes in the form of a memo, you can use this document as a model for writing your own memos.
The Audience for a Memo
It is useful to begin by considering that a memo is essentially a one-on-one communication between writer and reader. Although a memo may be written to a group of people or with various audiences in mind, usually it is a highly goal-oriented communication between two people who need to share information. When you write a memo to a professor in the classroom setting, you are much like the employee who has been assigned to investigate a problem and report back to a supervisor. Therefore, you are expected to provide concrete information, even information that the supervisor might already know, in a form that clarifies ideas and puts them into context. Finally, a memo enjoys a broader context than an essay; hence, you might refer to other related memos as you write, or you might respond to specific requests made by the audience in your text, in effect, carrying on a professional conversation.
Typical Memo Format
The overall format of a memo can be broken down into the heading, the body, and the closing notations. What follows is a brief description of each component.
The Heading The heading has two parts: part one includes two centered lines at the top of page 1, identifying the name of the company or institution on the first line, with the word “memorandum” on the second line; part two includes the “DATE,” “TO,” “FROM,” and “SUBJECT” lines at the left margin, filled in appropriately.
The Body The body of the memo follows the Introduction, and it is usually presented in single-spaced paragraphs with a line skipped between each paragraph. The first lines of new paragraphs can appear at the left margin or they can be indented five spaces.
The Closing Notations The closing notations, used to identify such things as attachments, appear at the left margin two lines below the text of the final paragraph. By simply typing the word “Attachment” as a closing notation, you automatically refer the reader to any attachment, such as a map, a set of calculations, spreadsheets, or a References page.
How Memos are Organized
The general organization of a memo mirrors that of an essay: an introduction, followed by body paragraphs, followed by a conclusion. However, the first paragraph of a memo is typically used as a forecasting device. Note how the opening paragraph of this memo defines the memo’s function and reflects its organization. It is sensible to open memos for your classes in the same way, first directly stating the memo’s purpose, then setting forth the organization and noting how the memo can be used.
Organization in the body of a memo is typically characterized by the use of section headings and short paragraphs. Paragraphs should not be too bulky—five or six per page is usually ideal. On the sentence level, you should take full advantage of the same organizational tools that you employ when you write an essay: meaningful topic sentences; carefully selected transition words; focused section headings; indented blocks of cited text; a bulleted series of examples; powerful punctuation marks such as the colon, semicolon, and dash.
Selection and Citation of Content
A memo’s content, of course, is guided by the assignment and the research required. It is important to remember as you present the content that selectivity and relevance matter greatly. Your job is to select and present the most pertinent, most current information available to you. Do not hesitate, of course, to let your memo’s content be heavily informed by your research, but also provide your own interpretation and organization of this research.
As in any essay, you must document the sources of your information so that your reader could find the original source of the information if desired. If your memo uses sources, provide the bibliographic information related to your sources on a References page as an attachment at the end of the memo—just as I have in this memo.
A Memo’s Tone and Style
Memos for your classes require a highly informative and straightforward tone, but allow for a slightly informal style compared to essays. As in this memo, “I” and “you” are handy because they provide a straightforward way of communicating, but you must be careful not to overuse these terms. Stylish prose is key to good memo writing, and you should not hesitate to use active, interpretive adverbs and verbs and concrete, carefully chosen adjectives and nouns.
A memo need not be written in a dry, dull fashion; rather, it should emulate the same stylistic standards that good prose has always embraced. These standards are summed up neatly in the popular style guide, The Elements Of Style, as follows:
A sentence should contain no unnecessary words, a paragraph no unnecessary sentences, for the same reason that a drawing should have no unnecessary lines and a machine no unnecessary parts (Strunk and White 1979).
As this quote suggests, good prose can achieve elegance by its clarity, efficiency, and sense of purpose.
The conclusion of a memo should not simply provide a summary of the memo’s entire contents, but it should be a true conclusion—that is, an articulated conviction arrived at on the basis of the evidence presented. The closing paragraph is the place to spell out the bottom line to the reader. Therefore, I close with my bottom line about writing memos for your classes:
- Study and use standard memo format to present your text;
- Use internal organizational tools such as section headings, topic sentences, transition words, and powerful punctuation marks to enhance the flow of ideas;
- Write with the same clarity, grace, and efficiency expected of you in any essay.
Strunk, William Jr and White, E.B., 1979: The Elements of Style. Macmillan Publishing Company, Inc., New York, 92 pp.
- Style For Students Online. Authored by : Joe Schall. Provided by : The Pennsylvania State University. Located at : https://www.e-education.psu.edu/styleforstudents/ . Project : Penn State's College of Earth and Mineral Sciences' OER Initiative. License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
Module 4: Written Correspondence
Memorandum explaining how to write a memo, mythic university online.
DATE : August 9, 2008 TO : Users of Style for Students Online FROM : Joe Schall SUBJECT : Writing Memos for your Classes
This memo provides you with tips on writing memos for your classes, with special attention to a memo’s audience, format, organization, content, tone, and style. Because my advice comes in the form of a memo, you can use this document as a model for writing your own memos.
The Audience for a Memo
It is useful to begin by considering that a memo is essentially a one-on-one communication between writer and reader. Although a memo may be written to a group of people or with various audiences in mind, usually it is a highly goal-oriented communication between two people who need to share information. When you write a memo to a professor in the classroom setting, you are much like the employee who has been assigned to investigate a problem and report back to a supervisor. Therefore, you are expected to provide concrete information, even information that the supervisor might already know, in a form that clarifies ideas and puts them into context. Finally, a memo enjoys a broader context than an essay; hence, you might refer to other related memos as you write, or you might respond to specific requests made by the audience in your text, in effect, carrying on a professional conversation.
Typical Memo Format
The overall format of a memo can be broken down into the heading, the body, and the closing notations. What follows is a brief description of each component.
The Heading The heading has two parts: part one includes two centered lines at the top of page 1, identifying the name of the company or institution on the first line, with the word “memorandum” on the second line; part two includes the “DATE,” “TO,” “FROM,” and “SUBJECT” lines at the left margin, filled in appropriately.
The Body The body of the memo follows the Introduction, and it is usually presented in single-spaced paragraphs with a line skipped between each paragraph. The first lines of new paragraphs can appear at the left margin or they can be indented five spaces.
The Closing Notations The closing notations, used to identify such things as attachments, appear at the left margin two lines below the text of the final paragraph. By simply typing the word “Attachment” as a closing notation, you automatically refer the reader to any attachment, such as a map, a set of calculations, spreadsheets, or a References page.
How Memos are Organized
The general organization of a memo mirrors that of an essay: an introduction, followed by body paragraphs, followed by a conclusion. However, the first paragraph of a memo is typically used as a forecasting device. Note how the opening paragraph of this memo defines the memo’s function and reflects its organization. It is sensible to open memos for your classes in the same way, first directly stating the memo’s purpose, then setting forth the organization and noting how the memo can be used.
Organization in the body of a memo is typically characterized by the use of section headings and short paragraphs. Paragraphs should not be too bulky—five or six per page is usually ideal. On the sentence level, you should take full advantage of the same organizational tools that you employ when you write an essay: meaningful topic sentences; carefully selected transition words; focused section headings; indented blocks of cited text; a bulleted series of examples; powerful punctuation marks such as the colon, semicolon, and dash.
Selection and Citation of Content
A memo’s content, of course, is guided by the assignment and the research required. It is important to remember as you present the content that selectivity and relevance matter greatly. Your job is to select and present the most pertinent, most current information available to you. Do not hesitate, of course, to let your memo’s content be heavily informed by your research, but also provide your own interpretation and organization of this research.
As in any essay, you must document the sources of your information so that your reader could find the original source of the information if desired. If your memo uses sources, provide the bibliographic information related to your sources on a References page as an attachment at the end of the memo—just as I have in this memo.
A Memo’s Tone and Style
Memos for your classes require a highly informative and straightforward tone, but allow for a slightly informal style compared to essays. As in this memo, “I” and “you” are handy because they provide a straightforward way of communicating, but you must be careful not to overuse these terms. Stylish prose is key to good memo writing, and you should not hesitate to use active, interpretive adverbs and verbs and concrete, carefully chosen adjectives and nouns.
A memo need not be written in a dry, dull fashion; rather, it should emulate the same stylistic standards that good prose has always embraced. These standards are summed up neatly in the popular style guide, The Elements Of Style, as follows:
A sentence should contain no unnecessary words, a paragraph no unnecessary sentences, for the same reason that a drawing should have no unnecessary lines and a machine no unnecessary parts (Strunk and White 1979).
As this quote suggests, good prose can achieve elegance by its clarity, efficiency, and sense of purpose.
The conclusion of a memo should not simply provide a summary of the memo’s entire contents, but it should be a true conclusion—that is, an articulated conviction arrived at on the basis of the evidence presented. The closing paragraph is the place to spell out the bottom line to the reader. Therefore, I close with my bottom line about writing memos for your classes:
- Study and use standard memo format to present your text;
- Use internal organizational tools such as section headings, topic sentences, transition words, and powerful punctuation marks to enhance the flow of ideas;
- Write with the same clarity, grace, and efficiency expected of you in any essay.
Strunk, William Jr and White, E.B., 1979: The Elements of Style. Macmillan Publishing Company, Inc., New York, 92 pp.
- Style For Students Online. Authored by : Joe Schall. Provided by : The Pennsylvania State University. Located at : https://www.e-education.psu.edu/styleforstudents/ . Project : Penn State's College of Earth and Mineral Sciences' OER Initiative. License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike

Privacy Policy
- FRONT MATTER
- TABLE OF CONTENTS
In many courses, you are asked to submit your writing in memo form, and in some cases your assignments are given to you as memos. This not only gives you practice in writing a professional document, it invites you to see your writing as purposeful and aimed at a particular audience. A detailed instructional memo about memo writing—a "metamemo," if you will—follows.
DATE : August 9, 2008 TO : Users of Style for Students Online FROM : Joe Schall SUBJECT : Writing Memos for your Classes
This memo provides you with tips on writing memos for your classes, with special attention to a memo’s audience, format, organization, content, tone, and style. Because my advice comes in the form of a memo, you can use this document as a model for writing your own memos.
The Audience for a Memo It is useful to begin by considering that a memo is essentially a one-on-one communication between writer and reader. Although a memo may be written to a group of people or with various audiences in mind, usually it is a highly goal-oriented communication between two people who need to share information. When you write a memo to a professor in the classroom setting, you are much like the employee who has been assigned to investigate a problem and report back to a supervisor. Therefore, you are expected to provide concrete information, even information that the supervisor might already know, in a form that clarifies ideas and puts them into context. Finally, a memo enjoys a broader context than an essay; hence, you might refer to other related memos as you write, or you might respond to specific requests made by the audience in your text, in effect, carrying on a professional conversation.
Typical Memo Format The overall format of a memo can be broken down into the heading, the body, and the closing notations. What follows is a brief description of each component.
The Heading The heading has two parts: part one includes two centered lines at the top of page 1, identifying the name of the company or institution on the first line, with the word "memorandum" on the second line; part two includes the "DATE," "TO," "FROM," and "SUBJECT" lines at the left margin, filled in appropriately.
The Body The body of the memo follows the Introduction, and it is usually presented in single-spaced paragraphs with a line skipped between each paragraph. The first lines of new paragraphs can appear at the left margin or they can be indented five spaces.
The Closing Notations The closing notations, used to identify such things as attachments, appear at the left margin two lines below the text of the final paragraph. By simply typing the word "Attachment" as a closing notation, you automatically refer the reader to any attachment, such as a map, a set of calculations, spreadsheets, or a References page.
How Memos are Organized The general organization of a memo mirrors that of an essay: an introduction, followed by body paragraphs, followed by a conclusion. However, the first paragraph of a memo is typically used as a forecasting device. Note how the opening paragraph of this memo defines the memo’s function and reflects its organization. It is sensible to open memos for your classes in the same way, first directly stating the memo’s purpose, then setting forth the organization and noting how the memo can be used.
Organization in the body of a memo is typically characterized by the use of section headings and short paragraphs. Paragraphs should not be too bulky—five or six per page is usually ideal. On the sentence level, you should take full advantage of the same organizational tools that you employ when you write an essay: meaningful topic sentences; carefully selected transition words; focused section headings; indented blocks of cited text; a bulleted series of examples; powerful punctuation marks such as the colon, semicolon, and dash.
Selection and Citation of Content A memo’s content, of course, is guided by the assignment and the research required. It is important to remember as you present the content that selectivity and relevance matter greatly. Your job is to select and present the most pertinent, most current information available to you. Do not hesitate, of course, to let your memo’s content be heavily informed by your research, but also provide your own interpretation and organization of this research.
As in any essay, you must document the sources of your information so that your reader could find the original source of the information if desired. If your memo uses sources, provide the bibliographic information related to your sources on a References page as an attachment at the end of the memo—just as I have in this memo.
A Memo’s Tone and Style Memos for your classes require a highly informative and straightforward tone, but allow for a slightly informal style compared to essays. As in this memo, "I" and "you" are handy because they provide a straightforward way of communicating, but you must be careful not to overuse these terms. Stylish prose is key to good memo writing, and you should not hesitate to use active, interpretive adverbs and verbs and concrete, carefully chosen adjectives and nouns.
A memo need not be written in a dry, dull fashion; rather, it should emulate the same stylistic standards that good prose has always embraced. These standards are summed up neatly in the popular style guide, The Elements Of Style, as follows:
A sentence should contain no unnecessary words, a paragraph no unnecessary sentences, for the same reason that a drawing should have no unnecessary lines and a machine no unnecessary parts (Strunk and White 1979).
As this quote suggests, good prose can achieve elegance by its clarity, efficiency, and sense of purpose.
Conclusion The conclusion of a memo should not simply provide a summary of the memo’s entire contents, but it should be a true conclusion—that is, an articulated conviction arrived at on the basis of the evidence presented. The closing paragraph is the place to spell out the bottom line to the reader. Therefore, I close with my bottom line about writing memos for your classes:
- Study and use standard memo format to present your text;
- Use internal organizational tools such as section headings, topic sentences, transition words, and powerful punctuation marks to enhance the flow of ideas;
- Write with the same clarity, grace, and efficiency expected of you in any essay.
Strunk, William Jr and White, E.B., 1979: The Elements of Style. Macmillan Publishing Company, Inc., New York, 92 pp.
For more information on memo writing, chase down these two websites:
Advice on writing memos from the Writing Center at Rennselaer Polytechnic Institute
Advice on memo writing from The Ohio University College of Business
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Finance and Business
- Business Skills
- Business Writing
- Business Letters
How to Write a Memo
Last Updated: November 30, 2023 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Mary Erickson, PhD . Mary Erickson is a Visiting Assistant Professor at Western Washington University. Mary received her PhD in Communication and Society from the University of Oregon in 2011. She is a member of the Modern Language Association, the National Communication Association, and the Society for Cinema and Media Studies. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 6,667,665 times.
Memos are a great way to communicate big decisions or policy changes to your employees or colleagues. It’s important that you take the time to craft a good memo so your message comes across how you want it to.
Things You Should Know
- Write a clear heading. Then, add 2-3 sentences to introduce the problem or issue and state your proposed solution.
- Specify any actions the recipients need to take and conclude with a summary restating the next steps.
- Review and proofread the memo carefully before you send it out.
Sample Memos

Writing the Memo’s Heading

- Double space between this line and the next line of the heading.

- If you are sending a memo to the entire staff, you might write: “TO: All Employees.”

- For example, instead of writing, “Ants,” for the subject, be more specific by writing, “Ant Problem in the Office.”

- A sample heading would look like: TO: Name and job title of the recipient FROM: Your name and job title DATE: Complete date when the memo was written SUBJECT: (or RE:) What the memo is about (highlighted in some way)
- When constructing the heading, be sure to double space between sections and align the text.
- You may choose to add a line below the heading that goes all the way across the page. This will separate the heading from the body of the memo.
Writing the Body of the Memo

- Think about your audience’s priorities and concerns are.
- Try to anticipate any questions your readers might have. Brainstorm some content for the memo, such as examples, evidence, or other information that will persuade them.
- Considering the audience also allows you to be sensitive to including any information or sentiments that are inappropriate for your readers.

- As a general guideline, the opening should take up about one paragraph.

- If it’s relevant, continue your memo by stating why the policy is being implemented. For example, you might write: “The county government voted to require all employees in the county to receive a $15/hour minimum wage.”

- Feel free to include graphics, lists, or charts, especially in longer memos. Just be sure they are truly relevant and persuasive.
- For longer memos, consider writing short headings that clarify the content of each category. For example, instead of stating "Policies," write "New policies regarding part-time employees." Be specific and brief in every heading so that the basic point of your memo is apparent to the reader right away.

- For example, you might write, “All employees must use the new accounting system by June 1, 2015.”
- This can also include some evidence to back up your recommendations.

- You might write, "I will be glad to discuss these recommendations with you later on and follow through on any decisions you make."
- You might end with something like, “We are excited about the expansion of this product line. We’re confident that this will grow our business and make this company a more sustainable business.”
- This should generally be one to two sentences in length.
Finalizing the Memo

- Use block style paragraphs. Double space between paragraphs. Do not indent each paragraph.

- Review for spelling, grammar, and content errors. Pay particular attention to names, dates, or numbers.
- Check that it is not excessively long, and cut out any extraneous material.

- If you are creating a digital document (to use for emailing, for example), you might want to create your own letterhead in a Word document that has your company logo and basic contact information. Use this as your memo template for every memo you send out.

- If you send your memo via email, you might want to format your email in HTML . Alternately, you can save your memo as a PDF and attach it to your email.
Using Memo Templates

- Download the template that best fits your needs.
- Be sure to read the terms of use before using any templates from a web source.

- It’s a good idea to use the latest version of Microsoft Word in order to ensure that you will not run into any unforeseen software problems and that the template will operate as it was designed to function. If you are operating on an older version of Microsoft Word, simply update your software before downloading any templates.

- Maintain the template’s formatting. This will ensure that your paragraph alignment is proper and you have the correct margins and font size.
- If necessary, you can even customize the memo to use a table. This is sometimes a good idea, especially if using a bullet list or something similar makes the memo look too crowded or difficult to read.
- Make sure that you have deleted any words that were already in the template. Also, carefully proofread your memo before sending it.

Community Q&A

- Don't give too many whys. It's important to explain why you want something done, but don't overdo it. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- Memos should be always brief. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 1

You Might Also Like

- ↑ http://www.fsb.muohio.edu/heitgedl/Memo%20writing%20tips%20ACC333%20SP06.pdf
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/subject_specific_writing/professional_technical_writing/memos/parts_of_a_memo.html
- ↑ https://openoregon.pressbooks.pub/lbcctechwriting/chapter/4-2-memos/
- ↑ https://www.indeed.com/career-advice/career-development/memo-format
- ↑ https://www.grammarly.com/blog/how-to-write-memo/
- ↑ https://writingcenter.uagc.edu/writing-business-memo

About This Article

The best way to write a memo is to start with a 1-paragraph introduction that explains what’s happening or what you want people to do and why. Then, write a body that includes more background information and evidence that supports the decision you’re notifying people about. If people need to take action, make it clear what they need to do and when. Conclude your memo with a friendly summary that reiterates why you think the decision is for the best. For more advice from our reviewer, like how to write a memo heading and sign a memo, read on! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Stephanie Morelock
Apr 27, 2017
Did this article help you?
Ayodeji Adisa
Aug 15, 2021
Christiana Lyonga
Jul 15, 2016
Ndako Dauda
Nov 17, 2021
Oct 26, 2018

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter
Faculty at Illinois State University
The Writer’s Memo
For background and details on the Writer’s Memo, see Jeffrey Sommers’s “Behind the Paper: Using the Student-Teacher Memo,” College Composition and Communication 39.1 (Feb. 1988): 77-80.
Rationale for Writer’s Memo
- Encourages a feeling of agency and responsibility on the part of writers with regard to their work
- Requires writers to set the agenda for response to their work
- Optimizes the efforts of writers’ respondents by helping them focus on those points most important to writers
- Requires writers to assess their own work critically
- Requires writers to assess their own work appreciatively
- Requires writers to develop awareness of writing processes, both those they have used and those they haven’t used
How to use the Writer’s Memo
Any time you prepare a draft for response, compose a Writer’s Memo and post it alongside (or attach it to) the draft.
Quick-Start Guide to the Writer’s Memo
Please read the rest of this document to learn the full story on the Writer’s Memo. Meanwhile, this is an acceptable start on what a Writer’s Memo needs to include:
- What you did so far (describe your key writing processes to this point)
- What you like about the current draft (specific strength[s])
- What you want from your readers (two or three specific and well-developed questions and/or points of focus)
- What you plan to do with this piece in the future (revisions, purposes, audiences, forums for publication, etc.)
What to include in your Writer’s Memo (I have bolded what I find to be the most important elements):
- Standard memo headings: To, From, Date, Re
- Briefly state topic, angle, purpose, audience, and any other rhetorical considerations that will help to orient and focus your reader. If the piece you are submitting fulfills a particular assignment, state clearly which assignment it fulfills. (1 brief ¶)
- Briefly discuss your key writing processes on this piece up to this point: What interesting things have happened so far? Unexpected turns? Discoveries? Frustrations? Urgent needs for resources? Satisfactions? (1 brief ¶)
- What do you like best about this piece in its current form? (1 sentence)
- Where are you headed with this piece? What do you plan to work on next? (1 sentence)
- Statement on recycling: Explain whether and how you have done or will do work on this project in some other class or other setting. If, for example, you have submitted or will submit a related project for course credit in a course other than this one, you must say so. [This item is mainly relevant and necessary for the course instructor. It is not necessary for Writer’s Memos addressed to peers.] (1 sentence)
- Questions and/or points for focus. Indicate two or three specific aspects of your piece on which you want your reader to focus her/his responses. Research? Style? Tone? Pace? Organization? Ideas? Lead? Conclusion? Humor? Emotion? Other aspects? (1 sentence for each point)
- If there is a specific approach to response that you find helpful, request it of your readers. For example, some people benefit from a balance of affirmation and challenges or suggestions. Other people prefer to receive only bracingly critical responses. Others revise best when their readers offer them lots of questions and/or pointers toward what additional possibilities they see for the piece.
- Designate in what form you want to receive your readers’ responses: in a written memo, in a conference or meeting, or in an audio recording (mp3 file).
Other tips (and requirements) for submitting your written work
- Write page numbers in the top right corner of your draft (if you are submitting actual paper draft; not necessary for electronic submissions)
- Include a Works Cited section if you cite published works
How to Write a Memo
Good communication is important for success in any job. Today, most written communication within a company happens over email. But depending on your position within the company you work for, you may be expected to send out memorandums from time to time. Memos may seem like an old school form of communication, but they still have their uses.
So, what is a memo, and how do you write one?
What Is It?
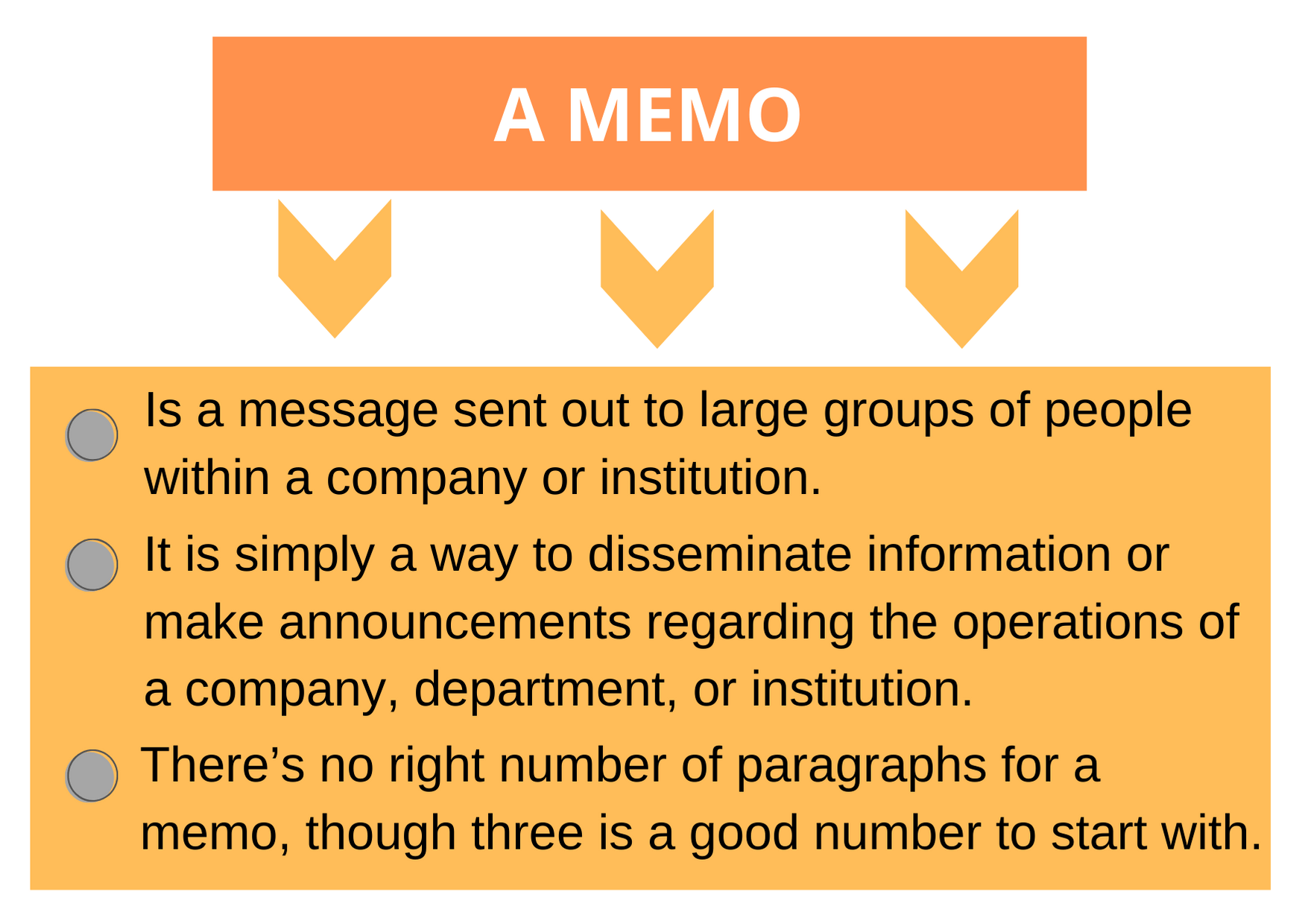
Memorandums (often referred to as memos) are messages sent out to large groups of people within a company or institution. They are most often sent by management, though employees may need to send them as well. Memos are used for internal business or communication. They are not meant to be read by people outside the company.
Memos are simply a way to disseminate information or make announcements. Today, they are typically sent out over email, though they may also be posted to bulletin boards around the office or distributed in the mailroom. More formal than standard emails, they don’t necessarily require a response, though a call to action may be included. To help you differentiate between emails and memos, try thinking of standard emails as a conversation—you send one expecting a reply—and a memo as an announcement put out over email.
When to Write It
First things first, check to see if your company has rules about writing memos. Many companies have guidelines regarding when it is appropriate and how to format them.
Generally speaking, anytime you have an announcement to make regarding the operations of a company, department, or institution, you can do so through a memo.
This could include but is not limited to:
- Changes to management
- Changes to daily operations
- Changes in clientele going forward
- Changes in business hours
- Quarterly or yearly earnings reports
- Responses to major legislation or national events
Memos can even be used for simple things like reminding everyone that passwords reset on a certain date or announcing the company holiday party.
They are used most often as a way to communicate information, not to foster conversation. If you are looking for a conversation, a standard email is a better way to achieve that.

How to Write a Memorandum
All memorandums start with a standard header that looks like this:
This is the opening of your memo. You do not include a personal salutation after this like you would in an email or letter. Begin with a heading, in larger font size than the rest of your text, that says “memorandum.” After that, fill in the rest of the information: who the memo is to, from, the date, and the subject of the memo.
Including this information makes it clear to the recipient that this is a memo, not a standard email. It also provides all the pertinent information upfront, making it clear what the memo is going to be about and who was meant to receive it. This way, anyone who may have received the memo by mistake can safely disregard it.
2. First paragraph
The first paragraph of your memo should clearly establish why you are writing the memo. Make the announcement you need to make or state the problem you are addressing. Keep this paragraph short and to the point. Think of it as your thesis statement, the support, and evidence for which will come in subsequent paragraphs.
3. Second paragraph
Use your second paragraph to provide context for your announcement. If you are announcing changes in management, explain why the changes are necessary and when you can reasonably expect the changes to be complete. Be as transparent as you can. Fostering a good workplace environment relies on clear and open communication. If you are announcing quarterly sales figures, this would be the place to include any relevant data, including charts, graphs, or lists. Always provide citations for the data and facts included in your memorandum.
4. Third paragraph
This is where you close your memo. If you expect your employees or coworkers to take a specific action in response to the memo, such as signing up to bring chips to the office party or resetting their password, include that here. Be specific about what you need people to do; don’t leave any room for creative interpretation. You may also indicate when further information on the subject discussed in the memo will be available, if applicable. Don’t forget to thank people for taking the time out of their busy day to read your memo.
There’s no right number of paragraphs for a memo, though three is a good number to start with. If you need more space than that to effectively communicate on the issue, take more space. If you find that your memo is quickly becoming longer than two pages, stop and consider whether a memo is the right way to get the information across.
Tips and Tricks for Professional Memorandums
Follow company guidelines. Many companies have internal standards for written communication. If your company has a memo template, use it. If they provide a style guide, follow it.
Use a template. If you are unsure about how to format your memo, and your company doesn’t provide guidelines, there are many templates available online that you can use.
Choose your audience carefully. Not every memo needs to go out company-wide. Share the information only with the people who need it. This avoids cluttering your coworker’s and employee’s inboxes with unnecessary emails, which is something we can all get behind.
Know your audience. This is good advice for anything you write. Know the people you are writing it for. Don’t write over their heads, and don’t provide more information than they want or need. Anticipate questions your audience may have about your announcement and answer as many as you can in the memo itself.
Keep it short. Memos are usually no longer than one page. However, there are situations in which longer memos may be required. Use your discretion while keeping it as short as possible. This shows your readers that you value their time, and you are not going to take it up unnecessarily. If you find your memo quickly becoming unwieldy, the information you need to convey may be better suited to an email, report, or meeting.
Stay on topic. Avoid including information not pertinent to your subject. Memos aren’t the place to chat and catch people up on the office gossip. Write what needs to be said, no more, no less. If you want to encourage your coworkers to read more information on the subject of the memo, include a link to other materials that they can peruse at their leisure.
Be specific. Include relevant dates and facts when you have them, so your coworkers and employees have ready access to accurate information. Avoid hypotheticals when possible.
Be professional. You may adopt a more casual tone in emails with your workplace BFF, but memorandums are official workplace documents. Your tone and word choice should reflect that. Write in complete sentences with a tone appropriate for a professional setting.
Be mindful of the calendar. If you are sending out a memo announcing the observance of a holiday, a mandatory meeting, or anything that is time-sensitive, send the memo out at least one week in advance of the relevant date. Do your coworkers and employees the courtesy of allowing them to adjust their schedules and plans accordingly.
Use subheadings. Subheadings are especially helpful if your memo is on the longer side. This will help your readers find the information they need easily. It also appeals to those who are skimmers rather than readers. And let’s face it, there will always be at least one person who skims official communication instead of reading it completely.
Use white space to your advantage. Avoid the wall of text look by writing short paragraphs and using numbered lists and bullet points when appropriate. People are more likely to read something all the way through if it is pleasing to look at.
Proofread. There’s no better way to undercut everything you’ve written than to have it riddled with errors. Take the time to proofread your memo before you send it out. If you have the time, wait to do the proofreading until the day after you write the memo. You are likely to catch more errors with fresh eyes than you are at the end of a long day. Ask a coworker to take a look as well if you can. The chances are high that they will find a stray comma or misspelling that you missed.
If you want to write a great memo, remember to keep things professional, short, and to the point. Say exactly what you need to say and include facts and additional information on the topic as necessary. Follow your company’s guidelines or a simple template and you can’t go wrong. Before you know it, you’ll be a memo writing expert.
EssayTigers brings you the best in custom paper writing! EssayTigers brings you the best in custom paper writing!
To get started, simply place an order and provide the details!
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
The Beginner's Guide to Writing an Essay | Steps & Examples
An academic essay is a focused piece of writing that develops an idea or argument using evidence, analysis, and interpretation.
There are many types of essays you might write as a student. The content and length of an essay depends on your level, subject of study, and course requirements. However, most essays at university level are argumentative — they aim to persuade the reader of a particular position or perspective on a topic.
The essay writing process consists of three main stages:
- Preparation: Decide on your topic, do your research, and create an essay outline.
- Writing : Set out your argument in the introduction, develop it with evidence in the main body, and wrap it up with a conclusion.
- Revision: Check your essay on the content, organization, grammar, spelling, and formatting of your essay.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Essay writing process, preparation for writing an essay, writing the introduction, writing the main body, writing the conclusion, essay checklist, lecture slides, frequently asked questions about writing an essay.
The writing process of preparation, writing, and revisions applies to every essay or paper, but the time and effort spent on each stage depends on the type of essay .
For example, if you’ve been assigned a five-paragraph expository essay for a high school class, you’ll probably spend the most time on the writing stage; for a college-level argumentative essay , on the other hand, you’ll need to spend more time researching your topic and developing an original argument before you start writing.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Before you start writing, you should make sure you have a clear idea of what you want to say and how you’re going to say it. There are a few key steps you can follow to make sure you’re prepared:
- Understand your assignment: What is the goal of this essay? What is the length and deadline of the assignment? Is there anything you need to clarify with your teacher or professor?
- Define a topic: If you’re allowed to choose your own topic , try to pick something that you already know a bit about and that will hold your interest.
- Do your research: Read primary and secondary sources and take notes to help you work out your position and angle on the topic. You’ll use these as evidence for your points.
- Come up with a thesis: The thesis is the central point or argument that you want to make. A clear thesis is essential for a focused essay—you should keep referring back to it as you write.
- Create an outline: Map out the rough structure of your essay in an outline . This makes it easier to start writing and keeps you on track as you go.
Once you’ve got a clear idea of what you want to discuss, in what order, and what evidence you’ll use, you’re ready to start writing.
The introduction sets the tone for your essay. It should grab the reader’s interest and inform them of what to expect. The introduction generally comprises 10–20% of the text.
1. Hook your reader
The first sentence of the introduction should pique your reader’s interest and curiosity. This sentence is sometimes called the hook. It might be an intriguing question, a surprising fact, or a bold statement emphasizing the relevance of the topic.
Let’s say we’re writing an essay about the development of Braille (the raised-dot reading and writing system used by visually impaired people). Our hook can make a strong statement about the topic:
The invention of Braille was a major turning point in the history of disability.
2. Provide background on your topic
Next, it’s important to give context that will help your reader understand your argument. This might involve providing background information, giving an overview of important academic work or debates on the topic, and explaining difficult terms. Don’t provide too much detail in the introduction—you can elaborate in the body of your essay.
3. Present the thesis statement
Next, you should formulate your thesis statement— the central argument you’re going to make. The thesis statement provides focus and signals your position on the topic. It is usually one or two sentences long. The thesis statement for our essay on Braille could look like this:
As the first writing system designed for blind people’s needs, Braille was a groundbreaking new accessibility tool. It not only provided practical benefits, but also helped change the cultural status of blindness.
4. Map the structure
In longer essays, you can end the introduction by briefly describing what will be covered in each part of the essay. This guides the reader through your structure and gives a preview of how your argument will develop.
The invention of Braille marked a major turning point in the history of disability. The writing system of raised dots used by blind and visually impaired people was developed by Louis Braille in nineteenth-century France. In a society that did not value disabled people in general, blindness was particularly stigmatized, and lack of access to reading and writing was a significant barrier to social participation. The idea of tactile reading was not entirely new, but existing methods based on sighted systems were difficult to learn and use. As the first writing system designed for blind people’s needs, Braille was a groundbreaking new accessibility tool. It not only provided practical benefits, but also helped change the cultural status of blindness. This essay begins by discussing the situation of blind people in nineteenth-century Europe. It then describes the invention of Braille and the gradual process of its acceptance within blind education. Subsequently, it explores the wide-ranging effects of this invention on blind people’s social and cultural lives.
Write your essay introduction
The body of your essay is where you make arguments supporting your thesis, provide evidence, and develop your ideas. Its purpose is to present, interpret, and analyze the information and sources you have gathered to support your argument.
Length of the body text
The length of the body depends on the type of essay. On average, the body comprises 60–80% of your essay. For a high school essay, this could be just three paragraphs, but for a graduate school essay of 6,000 words, the body could take up 8–10 pages.
Paragraph structure
To give your essay a clear structure , it is important to organize it into paragraphs . Each paragraph should be centered around one main point or idea.
That idea is introduced in a topic sentence . The topic sentence should generally lead on from the previous paragraph and introduce the point to be made in this paragraph. Transition words can be used to create clear connections between sentences.
After the topic sentence, present evidence such as data, examples, or quotes from relevant sources. Be sure to interpret and explain the evidence, and show how it helps develop your overall argument.
Lack of access to reading and writing put blind people at a serious disadvantage in nineteenth-century society. Text was one of the primary methods through which people engaged with culture, communicated with others, and accessed information; without a well-developed reading system that did not rely on sight, blind people were excluded from social participation (Weygand, 2009). While disabled people in general suffered from discrimination, blindness was widely viewed as the worst disability, and it was commonly believed that blind people were incapable of pursuing a profession or improving themselves through culture (Weygand, 2009). This demonstrates the importance of reading and writing to social status at the time: without access to text, it was considered impossible to fully participate in society. Blind people were excluded from the sighted world, but also entirely dependent on sighted people for information and education.
See the full essay example
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
The conclusion is the final paragraph of an essay. It should generally take up no more than 10–15% of the text . A strong essay conclusion :
- Returns to your thesis
- Ties together your main points
- Shows why your argument matters
A great conclusion should finish with a memorable or impactful sentence that leaves the reader with a strong final impression.
What not to include in a conclusion
To make your essay’s conclusion as strong as possible, there are a few things you should avoid. The most common mistakes are:
- Including new arguments or evidence
- Undermining your arguments (e.g. “This is just one approach of many”)
- Using concluding phrases like “To sum up…” or “In conclusion…”
Braille paved the way for dramatic cultural changes in the way blind people were treated and the opportunities available to them. Louis Braille’s innovation was to reimagine existing reading systems from a blind perspective, and the success of this invention required sighted teachers to adapt to their students’ reality instead of the other way around. In this sense, Braille helped drive broader social changes in the status of blindness. New accessibility tools provide practical advantages to those who need them, but they can also change the perspectives and attitudes of those who do not.
Write your essay conclusion
Checklist: Essay
My essay follows the requirements of the assignment (topic and length ).
My introduction sparks the reader’s interest and provides any necessary background information on the topic.
My introduction contains a thesis statement that states the focus and position of the essay.
I use paragraphs to structure the essay.
I use topic sentences to introduce each paragraph.
Each paragraph has a single focus and a clear connection to the thesis statement.
I make clear transitions between paragraphs and ideas.
My conclusion doesn’t just repeat my points, but draws connections between arguments.
I don’t introduce new arguments or evidence in the conclusion.
I have given an in-text citation for every quote or piece of information I got from another source.
I have included a reference page at the end of my essay, listing full details of all my sources.
My citations and references are correctly formatted according to the required citation style .
My essay has an interesting and informative title.
I have followed all formatting guidelines (e.g. font, page numbers, line spacing).
Your essay meets all the most important requirements. Our editors can give it a final check to help you submit with confidence.
Open Google Slides Download PowerPoint
An essay is a focused piece of writing that explains, argues, describes, or narrates.
In high school, you may have to write many different types of essays to develop your writing skills.
Academic essays at college level are usually argumentative : you develop a clear thesis about your topic and make a case for your position using evidence, analysis and interpretation.
The structure of an essay is divided into an introduction that presents your topic and thesis statement , a body containing your in-depth analysis and arguments, and a conclusion wrapping up your ideas.
The structure of the body is flexible, but you should always spend some time thinking about how you can organize your essay to best serve your ideas.
Your essay introduction should include three main things, in this order:
- An opening hook to catch the reader’s attention.
- Relevant background information that the reader needs to know.
- A thesis statement that presents your main point or argument.
The length of each part depends on the length and complexity of your essay .
A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your paper or essay . Everything else you write should relate to this key idea.
The thesis statement is essential in any academic essay or research paper for two main reasons:
- It gives your writing direction and focus.
- It gives the reader a concise summary of your main point.
Without a clear thesis statement, an essay can end up rambling and unfocused, leaving your reader unsure of exactly what you want to say.
A topic sentence is a sentence that expresses the main point of a paragraph . Everything else in the paragraph should relate to the topic sentence.
At college level, you must properly cite your sources in all essays , research papers , and other academic texts (except exams and in-class exercises).
Add a citation whenever you quote , paraphrase , or summarize information or ideas from a source. You should also give full source details in a bibliography or reference list at the end of your text.
The exact format of your citations depends on which citation style you are instructed to use. The most common styles are APA , MLA , and Chicago .
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked.
- How long is an essay? Guidelines for different types of essay
- How to write an essay introduction | 4 steps & examples
- How to conclude an essay | Interactive example
More interesting articles
- Checklist for academic essays | Is your essay ready to submit?
- Comparing and contrasting in an essay | Tips & examples
- Example of a great essay | Explanations, tips & tricks
- Generate topic ideas for an essay or paper | Tips & techniques
- How to revise an essay in 3 simple steps
- How to structure an essay: Templates and tips
- How to write a descriptive essay | Example & tips
- How to write a literary analysis essay | A step-by-step guide
- How to write a narrative essay | Example & tips
- How to write a rhetorical analysis | Key concepts & examples
- How to Write a Thesis Statement | 4 Steps & Examples
- How to write an argumentative essay | Examples & tips
- How to write an essay outline | Guidelines & examples
- How to write an expository essay
- How to write the body of an essay | Drafting & redrafting
- Kinds of argumentative academic essays and their purposes
- Organizational tips for academic essays
- The four main types of essay | Quick guide with examples
- Transition sentences | Tips & examples for clear writing
"I thought AI Proofreading was useless but.."
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
Memo Examples
#scribendiinc
Written by Scribendi
Like most forms of writing, memos come with so many rules, instructions, and suggestions that it's easy to forget a few. Since we've already addressed the dos and don'ts of how to write a memo , let's take a moment to look at these rules in practice using the below memorandum examples.
Features of a Memo
While reading over these memo writing examples, pay special attention to the key features of a memo. ask yourself the following questions:.
- Is it addressed to the right audience?
- Does the subject line accurately convey its contents?
- Does it anticipate and address potential objections?
- Is it formatted clearly and consistently?
Learn from Our Memo Format Example
When considering memo writing examples, pay close attention to the structure.
- The opening paragraph should restate the memo's purpose indicated in the subject line.
- Notice also how each of our memo examples' subsequent paragraphs build on this opening statement and explain the memo's purpose in detail.
- Unnecessary information should be removed, and word choice should remain straightforward and professional.
If you are unsure what to include and what to omit from your memo, send it to Scribendi's five-star proofreading service .
For an example of standard memo writing format, read on.
Memo Example 1: A General Office Memo
To: All Staff
From: The Manager
Date: May 27, 2021
Subject: Inappropriate use of time on Google Doodle games
It has come to my attention that many in the office have been spending time on the Google home page microgames. This memo is a reminder to use your work hours for work.
According to a recent article, the estimated daily cost of people collectively playing these games instead of working is over $120 million—which is calculated based on the daily average increased time spent on the Google home page (36 seconds).
If these estimates are applied to our 600 office employees, this results in a nearly $700 weekly loss.
This is a conservative estimate considering the extensive discussions that occur about beating the office's current high score. The extra cost quickly adds up.
Of course, we don't want you to view our organization as a place of drudgery and draconian rules. I encourage a fun and competitive environment, and I recognize that we certainly won't be profitable if you are unhappy or dissatisfied with your jobs. This is just a reminder to be careful with your use of company time.
The Manager
Wright, Tony. (2010). The Tragic Cost of Google Pac-Man – 4.82 million hours . Retrieved May 26, 2010 from: https://blog.rescuetime.com/the-tragic-cost-of-google-pac-man-4-82-million-hours/
Memo Example 2: A Departmental Memo
To: Computer Programming Division
From: Vice President Lumbergh
Date: February 19, 2021
Subject: Attaching cover sheets to TPS reports
This is to remind the division that, starting today, we are now filing all Testing Procedure Specification (TPS) reports with new cover sheets.
The reason for this change is simple. In addition to a new format, the cover sheets provide a summary of the report as well as the updated legal copy. The new cover sheets also include Initech's new logo.
Though this change may initially seem like a headache and an extra step, it is necessary to include the new cover sheets due to their updated information. Failing to do so will result in a confusing and inaccurate product being delivered to our customers.
Please be sure to follow this new procedure.
Best regards,
Vice President Lumbergh
Memo Example 3: A Memo Example to Students
To: All First-Year Psychology Students
From: Professor Jenkins
Date: October 23, 2021
Subject: Update to this week's assignment
Dear Students,
This is to let you know there is a mistake in the reading list for this week.
The literature list you all received is from last year and is outdated. We have since made changes, and these changes are outlined below.
Instead of reading Chapters 1–3 of The Science of Psychology , and Chapters 6–8 of Neurobiology , read Chapters 2–3 of The Science of Psychology and Chapters 5–8 of Neurobiology .
Please be sure to follow these new instructions.
Professor Jenkins
By following these memorandum examples and our memo writing format and addressing your audience in clear, concise language, you'll make your correspondence more effective.
If you're short for time or would like an expert to review your memo, try Scribendi's proofreading service .
Polish Your Writing with Professional Proofreading
Try our business proofreading service , or get a free sample, about the author.

Scribendi's in-house editors work with writers from all over the globe to perfect their writing. They know that no piece of writing is complete without a professional edit, and they love to see a good piece of writing transformed into a great one. Scribendi's in-house editors are unrivaled in both experience and education, having collectively edited millions of words and obtained numerous degrees. They love consuming caffeinated beverages, reading books of various genres, and relaxing in quiet, dimly lit spaces.
Have You Read?
"The Complete Beginner's Guide to Academic Writing"
Related Posts

10 Reasons to Hire a Professional Editor

How to Write a Formal Letter: Professional Letter Format & Examples

How to Write a Memo
Upload your file(s) so we can calculate your word count, or enter your word count manually.
We will also recommend a service based on the file(s) you upload.
English is not my first language. I need English editing and proofreading so that I sound like a native speaker.
I need to have my journal article, dissertation, or term paper edited and proofread, or I need help with an admissions essay or proposal.
I have a novel, manuscript, play, or ebook. I need editing, copy editing, proofreading, a critique of my work, or a query package.
I need editing and proofreading for my white papers, reports, manuals, press releases, marketing materials, and other business documents.
I need to have my essay, project, assignment, or term paper edited and proofread.
I want to sound professional and to get hired. I have a resume, letter, email, or personal document that I need to have edited and proofread.
Prices include your personal % discount.
Prices include % sales tax ( ).

Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
This handout will help you solve your memo-writing problems by discussing what a memo is, describing the parts of memos, and providing examples and explanations that will make your memos more effective.
The format of a memo follows the general guidelines of business writing. A memo is usually a page or two long, single spaced and left justified. Instead of using indentations to show new paragraphs, skip a line between sentences. Business materials should be concise and easy to read. Therefore it is beneficial to use headings and lists to help the reader pinpoint certain information.
Add Headings: You can help your reader understand your memo better by using headings for the summary and the discussion segments that follow it. Write headings that are short but clarify the content of the segment. For example, instead of using "Summary" for your heading, try "New Advertising Recommendations," which is much more specific. The major headings you choose are the ones that should be incorporated in your purpose-statement in the opening paragraph.
Use Lists: For easy reading, put important points or details into lists rather than paragraphs when possible. This will draw the readers' attention to the section and help the audience remember the information better. Using lists will help you be concise when writing a memo.
Sections: The sections of the memo should be allocated in the following manner:
- Header: 1/8 of the memo
- Opening, Context and Task: 1/4 of the memo
- Summary, Discussion Segment: 1/2 of the memo
- Closing Segment, Necessary Attachments: 1/8 of the memo
This is a suggested distribution of the material to make writing memos easier. Not all memos will be the same, and the structure can change as you see necessary. Different organizations may have different formatting procedures, so be flexible in adapting your writing skills.

- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
How to Write a Personal Essay for Your College Application

What does it take to land in the “accept” (instead of “reject”) pile?
How can you write an essay that helps advance you in the eyes of the admissions officers and makes a real impression? Here are some tips to get you started.
- Start early. Do not leave it until the last minute. Give yourself time when you don’t have other homework or extracurriculars hanging over your head to work on the essay.
- Keep the focus narrow. Your essay does not have to cover a massive, earth-shattering event. Some people in their teens haven’t experienced a major life event. Some people have. Either way, it’s okay.
- Be yourself. Whether writing about a painful experience or a more simple experience, use the narrative to be vulnerable and honest about who you are. Use words you would normally use. Trust your voice and the fact that your story is interesting enough in that no one else has lived it.
- Be creative. “Show, don’t tell,” and that applies here — to an extent. The best essays typically do both. You can help your reader see and feel what you are describing by using some figurative language throughout your piece.
- Make a point. As you finish your final body paragraphs ask yourself “So what?” This will help you hone in on how to end your essay in a way that elevates it into a story about an insight or discovery you made about yourself, rather than just being about an experience you had.
Where your work meets your life. See more from Ascend here .
We’ve all heard about the dreaded “college essay,” the bane of every high school senior’s existence. This daunting element of the college application is something that can create angst for even the most accomplished students.
- AA Amy Allen is a writer, educator, and lifelong learner. Her freelance writing business, All of the Write Words , focuses on providing high school students with one-on-one feedback to guide them through the college application process and with crafting a thoughtful personal essay. A dedicated poet, Amy’s work has also been published in several journals including Pine Row Press , Months to Years, and Atlanta Review .
Partner Center
Is a robot writing your kids’ essays? We asked educators to weigh in on the growing role of AI in classrooms.
R emember writing essays in high school? Chances are you had to look up stuff in an encyclopedia — an actual one, not Wikipedia — or else connect to AOL via a modem bigger than your parents’ Taurus station wagon.
Now, of course, there’s artificial intelligence. According to new research from Pew, about 1 in 5 US teens who’ve heard of ChatGPT have used it for schoolwork. Kids in upper grades are more apt to have used the chatbot: About a quarter of 11th- and 12th-graders who know about ChatGPT have tried it.
For the uninitiated, ChatGPT arrived on the scene in late 2022, and educators continue to grapple with the ethics surrounding its growing popularity. Essentially, it generates free, human-like responses based on commands. (I’m sure this sentence will look antiquated in about six months, like when people described the internet as the “information superhighway.”)
I used ChatGPT to plug in this prompt: “Write an essay on ‘The Scarlet Letter.’” Within moments, ChatGPT created an essay as thorough as anything I’d labored over in AP English.
Is this cheating? Is it just part of our strange new world? I talked to several educators about what they’re seeing in classrooms and how they’re monitoring it. Before you berate your child over how you wrote essays with a No. 2 pencil, here are some things to consider.
Adapting to new technology isn’t immoral. “We have to recalibrate our sense of what’s acceptable. There was a time when every teacher said: ‘Oh, it’s cheating to use Wikipedia.’ And guess what? We got used to it, we decided it’s reputable enough, and we cite Wikipedia all the time,” says Noah Giansiracusa, an associate math professor at Bentley University who hosts the podcast “ AI in Academia: Navigating the Future .”
“There’s a calibration period where a technology is new and untested. It’s good to be cautious and to treat it with trepidation. Then, over time, the norms kind of adapt,” he says — just like new-fangled graphing calculators or the internet in days of yore.
“I think the current conversation around AI should not be centered on an issue with plagiarism. It should be centered on how AI will alter methods for learning and expressing oneself. ‘Catching’ students who use fully AI-generated products ... implies a ‘gotcha’ atmosphere,” says Jim Nagle, a history teacher at Bedford High School. “Since AI is already a huge part of our day-to-day lives, it’s no surprise our students are making it a part of their academic tool kit. Teachers and students should be at the forefront of discussions about responsible and ethical use.”
Teachers and parents could use AI to think about education at a higher level. Really, learning is about more than regurgitating information — or it should be, anyway. But regurgitation is what AI does best.
“If our system is just for students to write a bunch of essays and then grade the results? Something’s missing. We need to really talk about their purpose and what they’re getting out of this, and maybe think about different forms of assignments and grading,” Giansiracusa says.
After all, while AI aggregates and organizes ideas, the quality of its responses depends on the users’ prompts. Instead of recoiling from it, use it as a conversation-starter.
“What parents and teachers can do is to start the conversation with kids: ‘What are we trying to learn here? Is it even something that ChatGPT could answer? Why did your assignment not convince you that you need to do this thinking on your own when a tool can do it for you?’” says Houman Harouni , a lecturer on education at the Harvard Graduate School of Education.
Harouni urges parents to read an essay written by ChatGPT alongside their student. Was it good? What could be done better? Did it feel like a short cut?
“What they’re going to remember is that you had that conversation with them; that someone thought, at some point in their lives, that taking a shortcut is not the best way ... especially if you do it with the tool right in front of you, because you have something real to talk about,” he says.
Harouni hopes teachers think about its implications, too. Consider math: So much grunt work has been eliminated by calculators and computers. Yet kids are still tested as in days of old, when perhaps they could expand their learning to be assessed in ways that are more personal and human-centric, leaving the rote stuff to AI.
“We could take this moment of confusion and loss of certainty seriously, at least in some small pockets, and start thinking about what a different kind of school would look like. Five years from now, we might have the beginnings of some very interesting exploration. Five years from now, you and I might be talking about schools wherein teaching and learning is happening in a very self-directed way, in a way that’s more based on … igniting the kid’s interest and seeing where they go and supporting them to go deeper and to go wider,” Harouni says.
Teachers have the chance to offer assignments with more intentionality.
“Really think about the purpose of the assignments. Don’t just think of the outcome and the deliverable: ‘I need a student to produce a document.’ Why are we getting students to write? Why are we doing all these things in the first place? If teachers are more mindful, and maybe parents can also be more mindful, I think it pushes us away from this dangerous trap of thinking about in terms of ‘cheating,’ which, to me, is a really slippery path,” Giansiracusa says.
AI can boost confidence and reduce procrastination. Sometimes, a robot can do something better than a human, such as writing a dreaded resume and cover letter. And that’s OK; it’s useful, even.
“Often, students avoid applying to internships because they’re just overwhelmed at the thought of writing a cover letter, or they’re afraid their resume isn’t good enough. I think that tools like this can help them feel more confident. They may be more likely to do it sooner and have more organized and better applications,” says Kristin Casasanto, director of post-graduate planning at Olin College of Engineering.
Casasanto says that AI is also useful for de-stressing during interview prep.
“Students can use generative AI to plug in a job description and say, ‘Come up with a list of interview questions based on the job description,’ which will give them an idea of what may be asked, and they can even then say, ‘Here’s my resume. Give me answers to these questions based on my skills and experience.’ They’re going to really build their confidence around that,” Casasanto says.
Plus, when students use AI for basics, it frees up more time to meet with career counselors about substantive issues.
“It will help us as far as scalability. … Career services staff can then utilize our personal time in much more meaningful ways with students,” Casasanto says.
We need to remember: These kids grew up during a pandemic. We can’t expect kids to resist technology when they’ve been forced to learn in new ways since COVID hit.
“Now we’re seeing pandemic-era high school students come into college. They’ve been channeled through Google Classroom their whole career,” says Katherine Jewell, a history professor at Fitchburg State University.
“They need to have technology management and information literacy built into the curriculum,” Jewell says.
Jewell recently graded a paper on the history of college sports. It was obvious which papers were written by AI: They didn’t address the question. In her syllabus, Jewell defines plagiarism as “any attempt by a student to represent the work of another, including computers, as their own.”
This means that AI qualifies, but she also has an open mind, given students’ circumstances.
“My students want to do the right thing, for the most part. They don’t want to get away with stuff. I understand why they turned to these tools; I really do. I try to reassure them that I’m here to help them learn systems. I’m focusing much more on the learning process. I incentivize them to improve, and I acknowledge: ‘You don’t know how to do this the first time out of the gate,’” Jewell says. “I try to incentivize them so that they’re improving their confidence in their abilities, so they don’t feel the need to turn to these tools.”
Understand the forces that make kids resort to AI in the first place . Clubs, sports, homework: Kids are busy and under pressure. Why not do what’s easy?
“Kids are so overscheduled in their day-to-day lives. I think there’s so much enormous pressure on these kids, whether it’s self-inflicted, parent-inflicted, or school-culture inflicted. It’s on them to maximize their schedule. They’ve learned that AI can be a way to take an assignment that would take five hours and cut it down to one,” says a teacher at a competitive high school outside Boston who asked to remain anonymous.
Recently, this teacher says, “I got papers back that were just so robotic and so cold. I had to tell [students]: ‘I understand that you tried to use a tool to help you. I’m not going to penalize you, but what I am going to penalize you for is that you didn’t actually answer the prompt.”
Afterward, more students felt safe to come forward to say they’d used AI. This teacher hopes that age restrictions become implemented for these programs, similar to apps such as Snapchat. Educationally and developmentally, they say, high-schoolers are still finding their voice — a voice that could be easily thwarted by a robot.
“Part of high school writing is to figure out who you are, and what is your voice as a writer. And I think, developmentally, that takes all of high school to figure out,” they say.
And AI can’t replicate voice and personality — for now, at least.

Is a robot writing your kids’ essays? We asked educators to weigh in on the growing role of AI in classrooms.
Educators weigh in on the growing role of ai and chatgpt in classrooms..

Remember writing essays in high school? Chances are you had to look up stuff in an encyclopedia — an actual one, not Wikipedia — or else connect to AOL via a modem bigger than your parents’ Taurus station wagon.
Now, of course, there’s artificial intelligence. According to new research from Pew, about 1 in 5 US teens who’ve heard of ChatGPT have used it for schoolwork. Kids in upper grades are more apt to have used the chatbot: About a quarter of 11th- and 12th-graders who know about ChatGPT have tried it.
For the uninitiated, ChatGPT arrived on the scene in late 2022, and educators continue to grapple with the ethics surrounding its growing popularity. Essentially, it generates free, human-like responses based on commands. (I’m sure this sentence will look antiquated in about six months, like when people described the internet as the “information superhighway.”)
Advertisement
I used ChatGPT to plug in this prompt: “Write an essay on ‘The Scarlet Letter.’” Within moments, ChatGPT created an essay as thorough as anything I’d labored over in AP English.
Is this cheating? Is it just part of our strange new world? I talked to several educators about what they’re seeing in classrooms and how they’re monitoring it. Before you berate your child over how you wrote essays with a No. 2 pencil, here are some things to consider.
Adapting to new technology isn’t immoral. “We have to recalibrate our sense of what’s acceptable. There was a time when every teacher said: ‘Oh, it’s cheating to use Wikipedia.’ And guess what? We got used to it, we decided it’s reputable enough, and we cite Wikipedia all the time,” says Noah Giansiracusa, an associate math professor at Bentley University who hosts the podcast “ AI in Academia: Navigating the Future .”
“There’s a calibration period where a technology is new and untested. It’s good to be cautious and to treat it with trepidation. Then, over time, the norms kind of adapt,” he says — just like new-fangled graphing calculators or the internet in days of yore.
“I think the current conversation around AI should not be centered on an issue with plagiarism. It should be centered on how AI will alter methods for learning and expressing oneself. ‘Catching’ students who use fully AI-generated products ... implies a ‘gotcha’ atmosphere,” says Jim Nagle, a history teacher at Bedford High School. “Since AI is already a huge part of our day-to-day lives, it’s no surprise our students are making it a part of their academic tool kit. Teachers and students should be at the forefront of discussions about responsible and ethical use.”

Teachers and parents could use AI to think about education at a higher level. Really, learning is about more than regurgitating information — or it should be, anyway. But regurgitation is what AI does best.
“If our system is just for students to write a bunch of essays and then grade the results? Something’s missing. We need to really talk about their purpose and what they’re getting out of this, and maybe think about different forms of assignments and grading,” Giansiracusa says.
After all, while AI aggregates and organizes ideas, the quality of its responses depends on the users’ prompts. Instead of recoiling from it, use it as a conversation-starter.
“What parents and teachers can do is to start the conversation with kids: ‘What are we trying to learn here? Is it even something that ChatGPT could answer? Why did your assignment not convince you that you need to do this thinking on your own when a tool can do it for you?’” says Houman Harouni , a lecturer on education at the Harvard Graduate School of Education.
Harouni urges parents to read an essay written by ChatGPT alongside their student. Was it good? What could be done better? Did it feel like a short cut?
“What they’re going to remember is that you had that conversation with them; that someone thought, at some point in their lives, that taking a shortcut is not the best way ... especially if you do it with the tool right in front of you, because you have something real to talk about,” he says.
Harouni hopes teachers think about its implications, too. Consider math: So much grunt work has been eliminated by calculators and computers. Yet kids are still tested as in days of old, when perhaps they could expand their learning to be assessed in ways that are more personal and human-centric, leaving the rote stuff to AI.
“We could take this moment of confusion and loss of certainty seriously, at least in some small pockets, and start thinking about what a different kind of school would look like. Five years from now, we might have the beginnings of some very interesting exploration. Five years from now, you and I might be talking about schools wherein teaching and learning is happening in a very self-directed way, in a way that’s more based on … igniting the kid’s interest and seeing where they go and supporting them to go deeper and to go wider,” Harouni says.
Teachers have the chance to offer assignments with more intentionality.
“Really think about the purpose of the assignments. Don’t just think of the outcome and the deliverable: ‘I need a student to produce a document.’ Why are we getting students to write? Why are we doing all these things in the first place? If teachers are more mindful, and maybe parents can also be more mindful, I think it pushes us away from this dangerous trap of thinking about in terms of ‘cheating,’ which, to me, is a really slippery path,” Giansiracusa says.
AI can boost confidence and reduce procrastination. Sometimes, a robot can do something better than a human, such as writing a dreaded resume and cover letter. And that’s OK; it’s useful, even.
“Often, students avoid applying to internships because they’re just overwhelmed at the thought of writing a cover letter, or they’re afraid their resume isn’t good enough. I think that tools like this can help them feel more confident. They may be more likely to do it sooner and have more organized and better applications,” says Kristin Casasanto, director of post-graduate planning at Olin College of Engineering.
Casasanto says that AI is also useful for de-stressing during interview prep.
“Students can use generative AI to plug in a job description and say, ‘Come up with a list of interview questions based on the job description,’ which will give them an idea of what may be asked, and they can even then say, ‘Here’s my resume. Give me answers to these questions based on my skills and experience.’ They’re going to really build their confidence around that,” Casasanto says.
Plus, when students use AI for basics, it frees up more time to meet with career counselors about substantive issues.
“It will help us as far as scalability. … Career services staff can then utilize our personal time in much more meaningful ways with students,” Casasanto says.
We need to remember: These kids grew up during a pandemic. We can’t expect kids to resist technology when they’ve been forced to learn in new ways since COVID hit.
“Now we’re seeing pandemic-era high school students come into college. They’ve been channeled through Google Classroom their whole career,” says Katherine Jewell, a history professor at Fitchburg State University.
“They need to have technology management and information literacy built into the curriculum,” Jewell says.
Jewell recently graded a paper on the history of college sports. It was obvious which papers were written by AI: They didn’t address the question. In her syllabus, Jewell defines plagiarism as “any attempt by a student to represent the work of another, including computers, as their own.”
This means that AI qualifies, but she also has an open mind, given students’ circumstances.
“My students want to do the right thing, for the most part. They don’t want to get away with stuff. I understand why they turned to these tools; I really do. I try to reassure them that I’m here to help them learn systems. I’m focusing much more on the learning process. I incentivize them to improve, and I acknowledge: ‘You don’t know how to do this the first time out of the gate,’” Jewell says. “I try to incentivize them so that they’re improving their confidence in their abilities, so they don’t feel the need to turn to these tools.”
Understand the forces that make kids resort to AI in the first place . Clubs, sports, homework: Kids are busy and under pressure. Why not do what’s easy?
“Kids are so overscheduled in their day-to-day lives. I think there’s so much enormous pressure on these kids, whether it’s self-inflicted, parent-inflicted, or school-culture inflicted. It’s on them to maximize their schedule. They’ve learned that AI can be a way to take an assignment that would take five hours and cut it down to one,” says a teacher at a competitive high school outside Boston who asked to remain anonymous.
Recently, this teacher says, “I got papers back that were just so robotic and so cold. I had to tell [students]: ‘I understand that you tried to use a tool to help you. I’m not going to penalize you, but what I am going to penalize you for is that you didn’t actually answer the prompt.”
Afterward, more students felt safe to come forward to say they’d used AI. This teacher hopes that age restrictions become implemented for these programs, similar to apps such as Snapchat. Educationally and developmentally, they say, high-schoolers are still finding their voice — a voice that could be easily thwarted by a robot.
“Part of high school writing is to figure out who you are, and what is your voice as a writer. And I think, developmentally, that takes all of high school to figure out,” they say.
And AI can’t replicate voice and personality — for now, at least.
Kara Baskin can be reached at [email protected] . Follow her @kcbaskin .
AI Internal Memo Announcement Generator
Start generating internal memo announcement for free below.
If you need help, please refer to the detailed step-by-step instructions entitled below.
Write about
Generate internal memo announcement in these simple steps.
Enter topic
Select language, tone and word count
Click on the Generate button
Introducing WriteCream’s Instant AI Internal Memo Announcement Generator: Crafting Memos with a Single Click
The AI Internal Memo Announcement Generator by Writecream is a user-friendly tool designed to streamline the process of creating internal memos and announcements within organizations. With just one click, users can generate professional and polished internal communications effortlessly.
How It Works:
- Input Details: Enter the necessary information such as the memo title, recipient list, and main message into the designated fields.
- Generate Email: Click on the “Generate” button to instantly create a professionally formatted internal memo or announcement based on the provided details.
- Review and Customize: Review the generated memo for accuracy and clarity. Customize any sections as needed to ensure the message is tailored to the intended audience.
- Copy and Use: Once satisfied with the content, simply copy the generated memo and distribute it via email, internal communication platforms, or any other preferred channels.
Key Features:
- Efficiency: Generate internal memos and announcements with just one click, saving valuable time and effort.
- Customization: Tailor the content to suit specific needs and ensure messages are aligned with company culture and branding.
- Professionalism: Produce polished and well-crafted communications that reflect positively on the organization.
- Accessibility: Access the tool from anywhere with an internet connection, making it convenient for users on the go.
The AI Internal Memo Announcement Generator simplifies the process of creating internal communications, empowering users to deliver clear, concise, and professional messages with minimal effort. By leveraging this tool, organizations can enhance internal communication practices and ensure important information reaches employees in a timely and effective manner.
Create content in minutes, not weeks.
© Copyright 2024 Writecream | All Rights Reserved
Wait! Before you go...
Sign up to get 10,000 words per month for free, please enter your name and email below:.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Writing Professional Memos, Fall 2019. 1 of 4 Writing Professional Memos ... Introduction: Similar to an introduction of an essay, an introduction in a memo states the purpose of a memo by providing the context of the issue/event and the proposed solution/call to action. In other words, it provides a short overview of what the rest of the
How to Write a Good Memo Essay. The secret to writing a great memo is ensuring you are as clear as possible. In many cases, memos are written to address specific issues. Therefore, your selection of words, sentences, and the message should be as clear as possible. Here are some useful tips to help you write a top-notch memo style paper.
Step 3 - Use a Memo Format. Use a standard memo format. A memo typically consists of four parts: Heading: Date, recipients, subject, and reference. Opening: Purpose of the memo in a concise statement. Context: Background information relevant to the message. Closing: Summary and next steps or call to action.
Sample Memo. TO: Kelly Anderson, Marketing Executive. FROM: Jonathon Fitzgerald, Market Research Assistant. DATE: June 14, 2007. SUBJECT: Fall Clothes Line Promotion. Market research and analysis show that the proposed advertising media for the new fall lines need to be reprioritized and changed. Findings from focus groups and surveys have made ...
6. Add a summary. If your memo tackles a complex issue or is particularly lengthy, add a short conclusion to summarize the most important points. In the absence of face-to-face cues, reiterating the main points through a brief summary reinforces the essential elements of your message, aiding comprehension. 7.
In your first sentence, restate the subject of the memo in sentence form. The opening paragraph should flow easily from the subject line. Like a thesis statement, it should clearly state the intent of the memo, while setting the tone for the rest of the memo. Overall, the first paragraph should explain exactly what your memo is going to be about.
Nevertheless, the memo-writing genre holds standard conventions that can guide your writing. Developing an acute sense of audience and purpose awareness, which parts to include, and general formatting guidelines will aid your composition of a successful memo. Reading sample memos can also help clarify the rules of the genre. Resources
Identify Your Audience: Understand who the memo is for and tailor your language and content accordingly . Write the Heading: Include "To," "From," "Date," and "Subject.". Be clear and concise, especially in the subject line . Opening Statement: Begin with a brief summary of the memo's purpose.
The Heading. The heading has two parts: part one includes two centered lines at the top of page 1, identifying the name of the company or institution on the first line, with the word "memorandum" on the second line; part two includes the "DATE," "TO," "FROM," and "SUBJECT" lines at the left margin, filled in appropriately ...
The heading has two parts: part one includes two centered lines at the top of page 1, identifying the name of the company or institution on the first line, with the word "memorandum" on the second line; part two includes the "DATE," "TO," "FROM," and "SUBJECT" lines at the left margin, filled in appropriately. The Body.
SUBJECT : Writing Memos for your Classes. This memo provides you with tips on writing memos for your classes, with special attention to a memo's audience, format, organization, content, tone, and style. Because my advice comes in the form of a memo, you can use this document as a model for writing your own memos. The Audience for a Memo
simple and understandable. Unlike other forms of writing, such as research essays, where your audience is an instructor expecting a complex piece of writing, memos tend to have simple and concise language. In a memo, your audience is almost always in a workplace environment as opposed to a scholarly one.
Opening Segment. The purpose of a memo is usually found in the opening paragraph and includes: the purpose of the memo, the context and problem, and the specific assignment or task. Before indulging the reader with details and the context, give the reader a brief overview of what the memo will be about. Choosing how specific your introduction ...
Writing the Memo's Heading. Download Article. 1. Type "MEMORANDUM" at the top of the page. State that this document is a memorandum at the outset. Label the page "MEMORANDUM" 1.5 inches (3.8 cm) from the top of the page. Put the word in bold on the first line.
Rationale for Writer's Memo. Encourages a feeling of agency and responsibility on the part of writers with regard to their work. Requires writers to set the agenda for response to their work. Optimizes the efforts of writers' respondents by helping them focus on those points most important to writers. Requires writers to assess their own ...
The first paragraph of your memo should clearly establish why you are writing the memo. Make the announcement you need to make or state the problem you are addressing. Keep this paragraph short and to the point. Think of it as your thesis statement, the support, and evidence for which will come in subsequent paragraphs.
Come up with a thesis. Create an essay outline. Write the introduction. Write the main body, organized into paragraphs. Write the conclusion. Evaluate the overall organization. Revise the content of each paragraph. Proofread your essay or use a Grammar Checker for language errors. Use a plagiarism checker.
If you are unsure what to include and what to omit from your memo, send it to Scribendi's five-star proofreading service. For an example of standard memo writing format, read on. Memo Example 1: A General Office Memo. MEMORANDUM. To: All Staff. From: The Manager. Date: May 27, 2021. Subject: Inappropriate use of time on Google Doodle games ...
Format. The format of a memo follows the general guidelines of business writing. A memo is usually a page or two long, single spaced and left justified. Instead of using indentations to show new paragraphs, skip a line between sentences. Business materials should be concise and easy to read.
Here are some tips to get you started. Start early. Do not leave it until the last minute. Give yourself time when you don't have other homework or extracurriculars hanging over your head to ...
Kara Baskin used ChatGPT to plug in this prompt: "Write an essay on 'The Scarlet Letter.'" Within moments, the software created an essay as thorough as anything she'd labored over in AP ...
Kara Baskin used ChatGPT to plug in this prompt: "Write an essay on 'The Scarlet Letter.'" Within moments, the software created an essay as thorough as anything she'd labored over in AP ...
1. Input Your Topic: Simply provide the tool with your essay topic or prompt. Whether it's a literary analysis, historical overview, or scientific exploration, the Instant Essay Typer can handle a diverse range of subjects. 2. Click to Generate: Once you've entered your topic, click the "Generate Essay" button.