How to Write and Structure a Persuasive Speech
- Homework Tips
- Learning Styles & Skills
- Study Methods
- Time Management
- Private School
- College Admissions
- College Life
- Graduate School
- Business School
- Distance Learning
- M.Ed., Education Administration, University of Georgia
- B.A., History, Armstrong State University
The purpose of a persuasive speech is to convince your audience to agree with an idea or opinion that you present. First, you'll need to choose a side on a controversial topic, then you will write a speech to explain your position, and convince the audience to agree with you.
You can produce an effective persuasive speech if you structure your argument as a solution to a problem. Your first job as a speaker is to convince your audience that a particular problem is important to them, and then you must convince them that you have the solution to make things better.
Note: You don't have to address a real problem. Any need can work as the problem. For example, you could consider the lack of a pet, the need to wash one's hands, or the need to pick a particular sport to play as the "problem."
As an example, let's imagine that you have chosen "Getting Up Early" as your persuasion topic. Your goal will be to persuade classmates to get themselves out of bed an hour earlier every morning. In this instance, the problem could be summed up as "morning chaos."
A standard speech format has an introduction with a great hook statement, three main points, and a summary. Your persuasive speech will be a tailored version of this format.
Before you write the text of your speech, you should sketch an outline that includes your hook statement and three main points.

Writing the Text
The introduction of your speech must be compelling because your audience will make up their minds within a few minutes whether or not they are interested in your topic.
Before you write the full body you should come up with a greeting. Your greeting can be as simple as "Good morning everyone. My name is Frank."
After your greeting, you will offer a hook to capture attention. A hook sentence for the "morning chaos" speech could be a question:
- How many times have you been late for school?
- Does your day begin with shouts and arguments?
- Have you ever missed the bus?
Or your hook could be a statistic or surprising statement:
- More than 50 percent of high school students skip breakfast because they just don't have time to eat.
- Tardy kids drop out of school more often than punctual kids.
Once you have the attention of your audience, follow through to define the topic/problem and introduce your solution. Here's an example of what you might have so far:
Good afternoon, class. Some of you know me, but some of you may not. My name is Frank Godfrey, and I have a question for you. Does your day begin with shouts and arguments? Do you go to school in a bad mood because you've been yelled at, or because you argued with your parent? The chaos you experience in the morning can bring you down and affect your performance at school.
Add the solution:
You can improve your mood and your school performance by adding more time to your morning schedule. You can accomplish this by setting your alarm clock to go off one hour earlier.
Your next task will be to write the body, which will contain the three main points you've come up with to argue your position. Each point will be followed by supporting evidence or anecdotes, and each body paragraph will need to end with a transition statement that leads to the next segment. Here is a sample of three main statements:
- Bad moods caused by morning chaos will affect your workday performance.
- If you skip breakfast to buy time, you're making a harmful health decision.
- (Ending on a cheerful note) You'll enjoy a boost to your self-esteem when you reduce the morning chaos.
After you write three body paragraphs with strong transition statements that make your speech flow, you are ready to work on your summary.
Your summary will re-emphasize your argument and restate your points in slightly different language. This can be a little tricky. You don't want to sound repetitive but will need to repeat what you have said. Find a way to reword the same main points.
Finally, you must make sure to write a clear final sentence or passage to keep yourself from stammering at the end or fading off in an awkward moment. A few examples of graceful exits:
- We all like to sleep. It's hard to get up some mornings, but rest assured that the reward is well worth the effort.
- If you follow these guidelines and make the effort to get up a little bit earlier every day, you'll reap rewards in your home life and on your report card.
Tips for Writing Your Speech
- Don't be confrontational in your argument. You don't need to put down the other side; just convince your audience that your position is correct by using positive assertions.
- Use simple statistics. Don't overwhelm your audience with confusing numbers.
- Don't complicate your speech by going outside the standard "three points" format. While it might seem simplistic, it is a tried and true method for presenting to an audience who is listening as opposed to reading.
- How to Write a Persuasive Essay
- 5 Tips on How to Write a Speech Essay
- Tips on How to Write an Argumentative Essay
- Writing an Opinion Essay
- How To Write an Essay
- 5 Steps to Writing a Position Paper
- How to Structure an Essay
- Ethos, Logos, Pathos for Persuasion
- What Is Expository Writing?
- Audience Analysis in Speech and Composition
- Definition and Examples of Analysis in Composition
- 100 Persuasive Speech Topics for Students
- What an Essay Is and How to Write One
- How to Write a Good Thesis Statement
- How to Write a Graduation Speech as Valedictorian
- How to Write a Letter of Complaint
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- Communication Skills
- Public Speaking
- Speechwriting
How to Write a Persuasive Speech
Last Updated: December 10, 2023 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Patrick Muñoz . Patrick is an internationally recognized Voice & Speech Coach, focusing on public speaking, vocal power, accent and dialects, accent reduction, voiceover, acting and speech therapy. He has worked with clients such as Penelope Cruz, Eva Longoria, and Roselyn Sanchez. He was voted LA's Favorite Voice and Dialect Coach by BACKSTAGE, is the voice and speech coach for Disney and Turner Classic Movies, and is a member of Voice and Speech Trainers Association. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 1,523,586 times.
A persuasive speech is a speech intended to convince the audience to do something. Whether you want to get people to vote, stop littering, or change their minds about an important issue, persuasive speeches are an effective way to sway an audience. There are many elements that go into a successful persuasive speech. But, with some preparation and practice, you can deliver a powerful speech.
Preparing to Write

- Especially if your topic is a controversial one, it's a good idea to know the arguments on all sides of the issue. [1] X Research source Whatever argument you are making, you'll be more persuasive if you can address the views of the opposing side.
- Spend some time reading books or articles about your topic. You can go to the library and ask a librarian for help finding books, or just go online and find some articles. Make sure to use reliable sources, like major news organizations, or academic books or articles.
- Opinion-oriented sources, like editorials, talk radio, or partisan cable news, can be valuable for finding out what other people think about your topic. But, don't rely on them as your only source of information. They can be very biased. If you use them at all, make sure to read a variety of viewpoints on the matter, not just one side.

- For example, if your topic is recycling, it's important to know a lot about recycling. But, your speech will need to reflect exactly what you hope the audience will do. Are you trying to get people to vote in favor of a citywide recycling program? Or are you trying to convince them to sort out their glass and cans and put them in a separate bin? These will be different speeches, so having the goal spelled out early will help you craft your message.

- An audience that knows little about your topic will need more background information and simpler language. An audience made up of experts on the topic would likely find such a simple speech boring.
- Likewise, an audience that already supports your view on a topic will be easier to persuade to take some action. You won't need to convince them you are right, but only that they need to do something. By contrast, an audience that does not agree with you will need persuasion to even consider your point of view.
- For example, imagine you want to convince your audience to support a city-wide recycling program. If they already think recycling is important, you only need to convince them of the value of this specific program. But, if they don't care about recycling or oppose it, you will need to first convince them that recycling is worthwhile.

- Ethos. These are appeals to the audience's ethics or morals. For example: "Recycling is the right thing to do. Wasting our limited resources steals from future generations, which is immoral."
- Pathos. These are appeals to the audience's emotions. For example: "Think of the animals that lose their homes every day because of trees being chopped down. If we recycled more, we could save these beautiful forests."
- Logos. These are appeals to the audiences logic or intellect. For example: "We know that there is a limited supply of natural resources. We can make this supply last longer by recycling."
- You can rely on any one or some combination.

- The number of points you can make to support your position will be determined by how much time you have to speak.
- As a rule of thumb, three to four supporting points is usually a good number. [2] X Research source
- For example, in the speech about recycling, your three main points might be: 1. Recycling saves resources, 2. Recycling reduces the amount of garbage, and 3. Recycling is cost-effective.
Writing your Speech

- An attention grabber. This could be a statement (or sometimes a visual) that gets your audience's attention. It can be a good idea to be a little startling or dramatic at the opening of your speech. For example, you might start with information (or pictures) showing how a nearby landfill is nearly full to capacity.
- A link to the audience. This is a means of showing that you have something in common with the audience. Show that you have a similar background or share an emotional connection of some kind. This will really depend on knowing your audience. For example, if you are a parent, speaking to other parents, you might emphasize the concern for your own children's future. If you share a common interest or ideological position with your audience, you can emphasize that.
- Your credentials. This is a means of showing that you are knowledgeable or an authority on the topic of the speech. Highlight the research you've done on your topic. If you have any personal or professional experience with the topic, be sure to emphasize that, too. In the recycling example, you might say "I've invested many hours studying the recycling issue and the types of programs available in other cities."
- Your goal. Explain to the audience what you hope the speech will accomplish. For example: "I hope by the end of my talk that you will agree that we need a city wide recycling program."
- A road map. Finally, tell the audience what the main points of the speech will be. For example, "I believe we must start a recycling program for these three reasons...."

- Arrange these points logically. Don't jump from one point to the next, and then back again. Instead, complete an argument, then move on to another that flows logically from it. [4] X Research source
- Use credible sources from your research to back the points you are making. Even if your point is more emotional (pathos), introducing some factual information will make your argument stronger. For example "Each year, 40,000 acres of beautiful forests are destroyed to make paper, according to a study from the American Recycling Institute."
- Use real life examples that the audience can relate to. Even an argument based on facts and logic (logos) should relate to the audience's lives and interests. For example: "In these hard economic times, I know many of you are afraid that a recycling program will mean a costly increase in taxes. But, the city of Springfield started a program like this one three years ago. So far they've seen an increase in revenue as a result of the program. Many residents have seen a decrease in their taxes as a result."

- Make sure that you describe opposing views fairly and objectively. Consider whether someone who actually holds that view would approve of the way you are describing their position. If you aren't sure, find someone who thinks that way and ask!
- For example, you would not want to say: "opponents of recycling just don't care if we waste our precious resources, or our money." That's not a fair description of their opinion.
- Instead, you might say: "opponents of recycling are concerned that the cost might be much higher than just using new materials," and then go on to offer an argument about why recycling might be the more cost-effective option.

- Don't just restate, verbatim, what you've already said. Instead, use this as an opportunity to reinforce the way your main points support your call to action. For example: "To sum up, I've shown you (points a, b, and c). These three undeniable facts point to a city-wide recycling program as the most sensible and ethical step we can take in helping create a more sustainable future. Please, join me in voting 'yes' on this program in November."
Delivering your Speech

- Try practicing in front of a mirror, so that you can see how you are delivering the speech. This can help you notice your facial expressions and body language. These can help or hinder your ability to get your message across.
- For example, you might notice you are slouching, or that that you fidget with your collar. These actions suggest to an audience that you aren't confident.
- Better still, record yourself with a video camera and watch the tape afterwards. This can help you see (and hear) where your delivery needs improvement. [5] X Research source It has the benefit of providing audio, and also won't distract you as much as a mirror when you're speaking.
- Once you've practiced on your own a few times, try giving the speech to a small group of friends or family members. Ask for their feedback on your message and delivery.

- Generally speaking, this will mean dressing professionally. But, the degree of formality will vary. A speech to a film club to convince them to show your film won't require the same degree of formality as speaking to the executives of a movie distribution company. For the executives, you would want to wear a suit. For the film club, that might be overdoing it.

- Be friendly and make eye contact with the audience.
- Move around, where appropriate, but don't fidget or pick at your clothes or hair.
- Don't read the speech. It's okay to use a few notes to keep yourself on track, but your speech should be mostly memorized.
- Roll with the punches. If you make a mistake, don't let it derail your whole speech. This might be an opportunity to use a little humor. Then, move on.

- For example, if you want them to contact the mayor, demanding a recycling program, don't just ask them to do it. Give them stamped, addressed envelopes to send a letter, or cards with the mayor's phone number and email address. If you do this, many more people are likely to follow through.
Patrick Muñoz
Speak from your heart and connect with your audience. Look them in the eyes and really talk to them. Make sure you're comfortable delivering your speech and that you use a warm, confident tone.
Sample Template

Community Q&A
- Look around at the audience, making eye contact, especially during pauses in your speech. If you're feeling nervous about this, pick out a single person in the audience and pretend you are speaking only to them. After a little while, pick someone else, and repeat. [6] X Research source Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- Speak forward, projecting your voice toward the audience with confidence. Do not speak down toward the floor. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- Try to cite sources for statistics and use credible, non-biased sources. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

- Avoid being confrontational, when possible. Don't be sarcastic or mocking when discussing viewpoints other than your own. This can be alienating to your audience, even those who may agree with you. Thanks Helpful 55 Not Helpful 17
- Don't be pompous or arrogant during your speech. Be humble, and be open to questions, suggestions, and feedback. Thanks Helpful 1 Not Helpful 1
You Might Also Like

- ↑ http://grammar.yourdictionary.com/style-and-usage/steps-for-writing-a-persuasive-speech.html
- ↑ http://www.best-speech-topics.com/writing-a-persuasive-speech.html
- ↑ https://www.speechanddebate.org/wp-content/uploads/Tips-for-Writing-a-Persuasive-Speech.pdf
- ↑ https://www.comm.pitt.edu/structuring-speech
- ↑ https://www.leonardoenglish.com/blog/recording-yourself-in-english
- ↑ https://www.zenbusiness.com/blog/eyecontact/
About This Article

To write a persuasive speech, start with a strong opening that will make your reader want to pay attention, including an attention grabber, your credentials, the essay's goal, and a road map for the essay. Next, offer persuasive evidence or reasons why the reader should support your viewpoint. Arrange these points logically, use credible sources, and employ some real life examples. Additionally, address counter-arguments to show that you’re looking at the topic from all sides. Finally, conclude by clearly letting the audience know how to put your ideas into action. To learn how to involve your audience when you deliver your speech, keep reading. Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Evan Murphree
Feb 8, 2022
Did this article help you?
Dianka Pradhan
Jun 28, 2019
Brittany Grech
Mar 27, 2017
Mavis Agyeiwaa Kyei
Oct 27, 2020
Jun 5, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter
6 Tips for Writing a Persuasive Speech (On Any Topic)

B y far, the best way to learn how to write speeches is to read the great ones, from Pericles’ Funeral Oration, to Dr. King’s Mountaintop speech, to Faulkner’s Nobel acceptance address. But if you’re looking for some quick tips, here are a few things to bear in mind next time you’re asked to give a speech:
1. Write like you talk. There is no First Law of Speechwriting, but if there were, it would probably be something like this: a speech is meant to be spoken, not read. That simple (and obvious) fact has a few important (and less obvious) implications. Use short words. Write short sentences. Avoid awkward constructions that might cause a speaker to stumble. Tip: Read the speech aloud as you’re writing. If you do it enough, you’ll start hearing the words when you type them.
2. Tell a story . I once wrote speeches for a governor whose aide told me: speechwriting is about slinging soundbites together. That approach is a recipe for writing neither good speeches nor good soundbites. Whenever we sat down to discuss a speech for the first time, President Obama would ask us: What’s the story we’re trying to tell? Like any good story, a speech has its own narrative arc. For the President, it’s usually a slow warm-up, a substantive middle, and an inspirational end. That’s his style. Tell your story in whatever way feels natural. Tip: A good story can be a lot more powerful than the most compelling facts and statistics.
3. Structure matters . It’s usually harder to figure out the right structure for a speech – the order of the points to make – than the words themselves. The order of those points matters because an argument that’s clear and logical is more likely to be persuasive. There is a reason that some of America’s greatest speechwriters – from Lincoln to JFK’s speechwriter Ted Sorensen to President Obama himself – studied the law, a profession that values the ability to make a logical argument. Tip: Lists (like this one) are one way to impose a structure on a speech.
4. Be concise. It is said that Woodrow Wilson once gave the following reply to a speaking request: “If you’d like me to speak for five minutes, I’ll need a month to prepare. If you’d like me to speak for 20 minutes, I’ll need two weeks. But if you’d like me to speak for an hour, I’m ready right now.” As Wilson knew, it’s harder to be concise than verbose. But the best way to make a point is concisely, as Churchill did when he announced during a wartime address: “The news from France is very bad.” Next time you think you can’t afford to cut that paragraph you love, remember: the Gettysburg Address, perhaps the greatest speech in American history, is fewer than 300 words. Tip: Challenge yourself to cut as many words as possible from each sentence without losing the line’s meaning.
5. Be authentic. If you’ve ever given a speech, you’ve probably been told, “Just speak from the heart.” It’s not very helpful writing advice, but that doesn’t mean it’s wrong. Once, when we were writing President Obama’s 2008 Democratic Convention address, we got stuck on a certain section of the speech. The President advised us: Think about the moment we’re in, think about what the country is going through, and write something that feels true. It was a helpful reminder to stop focusing on polls and soundbites and simply say something we believed in as simply as we could. Tip: Sharing a personal story can help you find your voice and build a connection with the audience.
6. Don’t just speak – say something. When Michelangelo was tasked with painting the Sistine Chapel, he considered it a thankless job. He would have much rather spent his time sculpting than painting. But he used the occasion to paint perhaps the most revered fresco in history. So, the next time you’re asked to speak, don’t just write a speech, write a great one. A speech’s greatness has as much to do with its values as anything else. No one remembers the speeches of segregationists, though there were no doubt eloquent preachers spewing hate in the days of Jim Crow. No one remembers Hitler’s speeches, though few would dispute his oratorical prowess. Of course, Hitler, like the segregationists, lost. But it’s also because hope will always be more compelling than hate. It’s no accident that the best-known, best-loved speech in history – the Sermon on the Mount – is an articulation of humanity’s highest ideals. Tip: Before sitting down to write, get inspired by reading great speeches from collections like William Safire’s “Lend Me Your Ears.”
Adam Frankel is VP, External Affairs at Andela . Previously, he was Special Assistant and Senior Speechwriter to President Barack Obama.
More Must-Reads From TIME
- Jane Fonda Champions Climate Action for Every Generation
- Biden’s Campaign Is In Trouble. Will the Turnaround Plan Work?
- Why We're Spending So Much Money Now
- The Financial Influencers Women Actually Want to Listen To
- Breaker Sunny Choi Is Heading to Paris
- Why TV Can’t Stop Making Silly Shows About Lady Journalists
- The Case for Wearing Shoes in the House
- Want Weekly Recs on What to Watch, Read, and More? Sign Up for Worth Your Time
Contact us at [email protected]
You May Also Like
A Comprehensive Guide to Writing a Persuasive Speech
Hrideep barot.
- Speech Writing

The term Persuasion means the efforts to change the attitudes or opinions of others through various means.
It is present everywhere: election campaigns, salesmen trying to sell goods by giving offers, public health campaigns to quit smoking or to wear masks in the public spaces, or even at the workplace; when an employee tries to persuade others to agree to their point in a meeting.
How do they manage to convince us so subtly? You guessed it right! They engage in what is called Persuasive Speech.
Persuasive Speech is a category of speech that attempts to influence the listener’s beliefs, attitudes, thoughts, and ultimately, behavior.
They are used in all contexts and situations . It can be informal , a teenager attempting to convince his or her parents for a sleepover at a friend’s house.
It can also be formal , President or Prime Minister urging the citizens to abide by the new norms.
But not to confuse these with informative speeches! These also aim to inform the audience about a particular topic or event, but they lack any attempt at persuasion.
The most typical setting where this kind of speech is practiced is in schools and colleges.
An effective speech combines both the features of an informative and persuasive speech for a better takeaway from an audience’s point of view.
However, writing and giving a persuasive speech are different in the sense that you as a speaker have limited time to call people to action.
Also, according to the context or situation, you may not be able to meet your audience several times, unlike TV ads, which the audience sees repeatedly and hence believes the credibility of the product.
So, how to write and deliver an effective persuasive speech?
How to start a persuasive speech? What are the steps of writing a persuasive speech? What are some of the tricks and tips of persuasion?
Read along till the end to explore the different dimensions and avenues of the science of giving a persuasive speech.
THINGS TO KEEP IN MIND BEFORE WRITING A PERSUASIVE SPEECH
1. get your topic right, passion and genuine interest in your topic.
It is very important that you as a speaker are interested in the chosen topic and in the subsequent arguments you are about to put forward. If you are not interested in what you are saying, then how will the audience feel the same?
Passion towards the topic is one of the key requirements for a successful speech as your audience will see how passionate and concerned you are towards the issue and will infer you as a genuine and credible person.
The audience too will get in the mood and connect to you on an emotional level, empathizing with you; as a result of which will understand your point of view and are likely to agree to your argument.
Consider this example: your friend is overflowing with joy- is happy, smiling, and bubbling with enthusiasm.
Before even asking the reason behind being so happy, you “catch the mood”; i.e., you notice that your mood has been boosted as a result of seeing your friend happy.
Why does it happen so? The reason is that we are influenced by other people’s moods and emotions.
It also means that our mood affects people around us, which is the reason why speaking with emotions and passion is used by many successful public speakers.
Another reason is that other’s emotions give an insight into how one should feel and react. We interpret other’s reactions as a source of information about how we should feel.
So, if someone shows a lot of anxiety or excitement while speaking, we conclude that the issue is very important and we should do something about it, and end up feeling similar reactions.
Meaningful and thought-provoking
Choose a topic that is meaningful to you and your audience. It should be thought-provoking and leave the audience thinking about the points put forward in your speech.
Topics that are personally or nationally relevant and are in the talks at the moment are good subjects to start with.
If you choose a controversial topic like “should euthanasia be legalized?”, or” is our nation democratic?”, it will leave a dramatic impact on your audience.
However, be considerate in choosing a sensitive topic, since it can leave a negative impression on your listeners. But if worded in a neutral and unbiased manner, it can work wonders.
Also, refrain from choosing sensitive topics like the reality of religion, sexuality, etc.
2. Research your topic thoroughly

Research on persuasion conducted by Hovland, Janis, and Kelley states that credible communicators are more persuasive than those who are seen as lacking expertise.
Even if you are not an expert in the field of your topic, mentioning information that is backed by research or stating an expert’s opinion on the issue will make you appear as a knowledgeable and credible person.
How to go about researching? Many people think that just googling about a topic and inferring 2-3 articles will be enough. But this is not so.
For writing and giving an effective speech, thorough research is crucial for you as a speaker to be prepared and confident.
Try to find as many relevant points as possible, even if it is against your viewpoint. If you can explain why the opposite viewpoint is not correct, it will give the audience both sides to an argument and will make decision-making easier.
Also, give credit to the source of your points during your speech, by mentioning the original site, author, or expert, so the audience will know that these are reliable points and not just your opinion, and will be more ready to believe them since they come from an authority.
Other sources for obtaining data for research are libraries and bookstores, magazines, newspapers, google scholar, research journals, etc.
Analyze your audience
Know who comprises your audience so that you can alter your speech to meet their requirements.
Demographics like age group, gender ratio, the language with which they are comfortable, their knowledge about the topic, the region and community to which they belong; are all important factors to be considered before writing your speech.
Ask yourself these questions before sitting down to write:
Is the topic of argument significant to them? Why is it significant? Would it make sense to them? Is it even relevant to them?
In the end, the speech is about the audience and not you. Hence, make efforts to know your audience.
This can be done by surveying your audience way before the day of giving your speech. Short polls and registration forms are an effective way to know your audience.
They ensure confidentiality and maintain anonymity, eliminating social desirability bias on part of the audience, and will likely receive honest answers.
OUTLINE OF A PERSUASIVE SPEECH
Most speeches follow the pattern of Introduction, Body and Conclusion.
However, persuasive speeches have a slightly different pathway.
INTRODUCTION
BODY OR SUPPORTING STATEMENTS( ATLEAST 3 ARGUMENTS)
CONCLUSION OR A CALL TO ACTION
1. INTRODUCTION
Grab attention of your audience.

The first few lines spoken by a speaker are the deciding factor that can make or break a speech.
Hence, if you nail the introduction, half of the task has already been done, and you can rest assured.
No one likes to be silent unless you are an introvert. But the audience expects that the speaker will go on stage and speak. But what if the speaker just goes and remains silent?
Chances are high that the audience will be in anticipation of what you are about to speak and their sole focus will be on you.
This sets the stage.
Use quotes that are relevant and provocative to set the tone of your speech. It will determine the mood of your audience and get them ready to receive information.
An example can be “The only impossible journey is the one you never begin” and then state who gave it, in this case, Tony Robbins, an American author.
Use what-if scenarios
Another way to start your speech is by using what-if scenarios and phrases like “suppose if your home submerges in water one day due to global warming…”.
This will make them the center of attention and at the same time grabbing their attention.
Use personal anecdotes
Same works with personal experiences and stories.
Everyone loves listening to first-hand experiences or a good and interesting story. If you are not a great storyteller, visual images and videos will come to your rescue.
After you have successfully grabbed and hooked your audience, the next and last step of the introduction is introducing your thesis statement.
What is a thesis statement?
It introduces the topic to your audience and is one of the central elements of any persuasive speech.
It is usually brief, not more than 3 sentences, and gives the crux of your speech outline.
How to make a thesis statement?
Firstly, research all possible opinions and views about your topic. See which opinion you connect with, and try to summarize them.
After you do this, you will get a clear idea of what side you are on and this will become your thesis statement.
However, the thesis should answer the question “why” and “how”.
So, for instance, if you choose to speak on the topic of the necessity of higher education, your thesis statement could be something like this:
Although attending university and getting a degree is essential for overall development, not every student must be pushed to join immediately after graduating from school.
And then you can structure your speech containing the reasons why every student should not be rushed into joining a university.
3. BODY OF THE SPEECH
The body contains the actual reasons to support your thesis.
Ideally, the body should contain at least 3 reasons to support your argument.
So, for the above-mentioned thesis, you can support it with possible alternatives, which will become your supporting statements.
The option of a gap year to relax and decide future goals, gaining work experience and then joining the university for financial reasons, or even joining college after 25 or 35 years.
These become your supporting reasons and answers the question “why”.
Each reason has to be resourcefully elaborated, with explaining why you support and why the other or anti-thesis is not practical.
At this point, you have the option of targeting your audience’s ethos, pathos, or logos.
Ethos is the ethical side of the argument. It targets morals and puts forth the right thing or should be.
This technique is highly used in the advertising industry.
Ever wondered why celebrities, experts, and renowned personalities are usually cast as brand ambassadors.?
The reason: they are liked by the masses and exhibit credibility and trust.
Advertisers endorse their products via a celebrity to try to show that the product is reliable and ethical.
The same scenario is seen in persuasive speeches. If the speaker is well-informed and provides information that is backed by research, chances are high that the audience will follow it.
Pathos targets the emotional feelings of the audience.
This is usually done by narrating a tragic or horrifying anecdote and leaves the listener moved by using an emotional appeal to call people to action.
The common emotions targeted by the speaker include the feeling of joy, love, sadness, anger, pity, and loneliness.
All these emotions are best expressed in stories or personal experiences.
Stories give life to your argument, making the audience more involved in the matter and arousing sympathy and empathy.
Visuals and documentaries are other mediums through which a speaker can attract the audience’s emotions.
What was your reaction after watching an emotional documentary? Did you not want to do something about the problem right away?
Emotions have the power to move people to action.
The last technique is using logos, i.e., logic. This includes giving facts and practical aspects of why this is to be done or why such a thing is the most practical.
It is also called the “logical appeal”.
This can be done by giving inductive or deductive reasoning.
Inductive reasoning involves the speaker taking a specific example or case study and then generalizing or drawing conclusions from it.
For instance, a speaker tells a case study of a student who went into depression as the child wasn’t able to cope with back-to-back stress.
This problem will be generalized and concluded that gap year is crucial for any child to cope with and be ready for the challenges in a university.
On the other hand, deductive reasoning involves analyzing general assumptions and theories and then arriving at a logical conclusion.
So, in this case, the speaker can give statistics of the percentage of university students feeling drained due to past exams and how many felt that they needed a break.
This general data will then be personalized to conclude how there is a need for every student to have a leisure break to refresh their mind and avoid having burned out.
Using any of these 3 techniques, coupled with elaborate anecdotes and supporting evidence, at the same time encountering counterarguments will make the body of your speech more effective.
4. CONCLUSION
Make sure to spend some time thinking through your conclusion, as this is the part that your audience will remember the most and is hence, the key takeaway of your entire speech.
Keep it brief, and avoid being too repetitive.
It should provide the audience with a summary of the points put across in the body, at the same time calling people to action or suggesting a possible solution and the next step to be taken.
Remember that this is your last chance to convince, hence make sure to make it impactful.
Include one to two relevant power or motivational quotes, and end by thanking the audience for being patient and listening till the end.
Watch this clip for a better understanding.
TIPS AND TRICKS OF PERSUASION
Start strong.
A general pattern among influential speeches is this: all start with a powerful and impactful example, be it statistics about the issue, using influential and meaning statements and quotes, or asking a rhetorical question at the beginning of their speech.
Why do they do this? It demonstrates credibility and creates a good impression- increasing their chance of persuading the audience.
Hence, start in such a manner that will hook the audience to your speech and people would be curious to know what you are about to say or how will you end it.
Keep your introduction short
Keep your introduction short, and not more than 10-15% of your speech.
If your speech is 2000 words, then your introduction should be a maximum of 200-250 words.
Or if you are presenting for 10 minutes, your introduction should be a maximum of 2 minutes. This will give you time to state your main points and help you manage your time effectively.
Be clear and concise
Use the correct vocabulary to fit in, at the same time making sure to state them clearly, without beating around the bush.
This will make the message efficient and impactful.
Answer the question “why”
Answer the question “why” before giving solutions or “how”.
Tell them why is there a need to change. Then give them all sides of the point.
It is important to state what is wrong and not just what ought to be or what is right, in an unopinionated tone.
Unless and until people don’t know the other side of things, they simply will not change.
Suggest solutions
Once you have stated the problem, you imply or hint at the solution.
Never state solutions, suggest them; leaving the decision up to the audience.
You can hint at solutions: “don’t you think it is a good idea to…?” or “is it wrong to say that…?”, instead of just stating solutions.
Use power phrases
Certain power-phrases come in handy, which can make the audience take action.
Using the power phrase “because” is very impactful in winning and convincing others.
This phrase justifies the action associated with it and gives us an understanding of why is it correct.
For instance, the phrase “can you give me a bite of your food?” does not imply attitude change.
But using “may I have a bite of your food because I haven’t eaten breakfast?” is more impactful and the person will likely end up sharing food if you use this power- phrase, because it is justifying your request.
Another power-phrase is “I understand, but…”.
This involves you agreeing with the opposite side of the argument and then stating your side or your point of view.
This will encourage your audience to think from the other side of the spectrum and are likely to consider your argument put forth in the speech.
Use power words
Use power words like ‘incredible’, ‘fascinating’, ‘unquestionable’, ‘most important’, ‘strongly recommend’ in your speech to provoke your audience into awe.
Watch this video of some of the common but effective words that can be used in a persuasive speech.
Give an emotional appeal
Like mentioned earlier as one of the techniques of persuasion called pathos, targeting emotions like joy, surprise, fear, anticipation, anger, sadness, or disgust gives your speech an emotional appeal, and more feel to your content, rather than just neutrally stating facts and reasons.
Hence, to keep your audience engaged and not get bored, use emotions while speaking.
Make use of the non=verbal elements
Actions speak louder than words, and they create a huge difference if used effectively.
There is so much else to a speech than just words.
Non-verbal elements include everything apart from your words.
Maintaining eye contact, matching your body language with your words for effective transmission of the message including how you express your emotions, making use of the visual signs and symbols via a PPT are all important parts of any speech.
Check your paralanguage i.e., your voice intonation, pitch, speed, effective pauses, stressing on certain words to create an impact.
Doing all of these will make your speech more real and effective, and will persuade your audience into taking action.
Give real-life examples
Speak facts and avoid giving opinions.
However, just mentioning hard statistical facts will take you nowhere, as there is a chance that people may not believe the data, based on the possibility of them recollecting exceptions.
Hence, back up your statistics with real-life examples of situations.
Also, consider using precise numerical data.
For example, using “5487 people die due to road accidents every day”, instead of “approximately 5500 people”.
Have no personal stake
You can lose credibility if the audience feels that you have a personal stake in it.
Suppose that you are speaking for the idea of using reusable plastic products, and you say that you are from a company that sells those goods.
People are likely to perceive your argument as promoting self-interest and will not be ready to change their opinion about reusable plastic products.
Consequently, if you argue against your self-interest, your audience will see you as the most credible.
So, if you say that you are working in a plastics manufacturing company and have a statistical record of the pollution caused by it; and then promote reusable plastic as an alternative to stop pollution and save the environment, people are likely to accept your point of argument.
The you attitude
Shift your focus to the audience, and chances are high that they are likely to relate the issue to themselves and are most likely to change.
Hence, use the “you attitude” i.e., shifting focus to the listener and giving them what they want to hear and then making subtle additions to what you want them to hear.
Make a good first impression
The first impression is indeed the last. This is the reason why image consultancy is such a growing sector.
A good first impression works wonders on the people around you, including the audience, and makes your work of convincing a lot easier.
Avoid appearing shabby, ill-mannered, and refrain from using uncourteous and biased language.
Doing these will reverse the effect you want from the audience and will drive them away from your opinion.
HOW TO MAKE A GOOD FIRST IMPRESSION?
If you are the type who gets nervous easily and have fear of public speaking, practice till you excel in your task.
I used to dread speaking in front of people, and partly still do.
Earlier, unless and until someone called my name to state my opinion or start with the presentation, I didn’t even raise my hand to say that I have an opinion or I am left to present on the topic.
I had to do something about this problem. So, I made a plan.
2 weeks before the presentation, I wrote the script and read it over and over again.
After reading multiple times, I imagined my room to be the classroom and practiced in front of a mirror.
The main thing I was concerned about was keeping my head clear on the day of my presentation. And that’s what happened.
Since my mind was clear and relaxed, and I had practiced my speech over and over again, presenting came more naturally and confidently.
You might ask what is the purpose of impression management?
Impressions are used for Ingratiation i.e., getting others to like us so that they will be more than willing to accept or agree to your point.
If you like someone, you are drawn towards them and are likely to agree on what they agree or say.
TIP- Try to come early to the venue, and dress appropriately to the needs of the occasion. And don’t forget to smile!
PERSUASIVE SPEECH EXAMPLES
1. wendy troxel – why school should start later for teens.
Almost all the important elements of a persuasive speech are found in this TED talk by Wendy Troxel.
Take a closer look at how she starts her introduction in the form of a real-life personal story, and how she makes it relevant to the audience.
Humor is used to hook the audience’s attention and in turn their interest.
She is also likely to be perceived as credible, as she introduces herself as a sleep researcher, and is speaking on the topic of sleep.
Thesis of how early school timings deprive teenagers of their sleep and its effects is introduced subtly.
The speaker supports her statements with facts, answers the question “why” and most importantly, presents both sides of an argument; effects of less to lack of sleep and its consequences and the effects of appropriate and more sleep on teenagers.
The use of non-verbal elements throughout the speech adds value and richness to the speech, making it more engaging.
The use of Pathos as a persuasive technique appeals to the audience’s emotions; at the same time backing the argument with Logos, by giving scientific reasons and research findings to support the argument.
Lastly, the speech is meaningful, relevant, and thought-provoking to the audience, who are mostly parents and teenagers.
2. Crystal Robello- Being an introvert is a good thing
In this example, Crystal Robello starts by giving personal experiences of being an introvert and the prejudices faced.
Notice how even without much statistics the speech is made persuasive by using Ethos as a technique; and how credibility is achieved by mentioning leaders who are introverts.
3. Greta Thunberg- School strike for climate
One of my favorite speeches is the above speech by Greta Thunberg.
She uses all the techniques; pathos, ethos and logos.
Also notice how the speaker speaks with emotions, and uses body and paralanguage efficiently to create a dramatic impact on the audience.
Her genuine interest is clearly reflected in the speech, which makes the audience listen with a level of concern towards the topic, climate change.
To sum up, we looked at the things to keep in mind before writing a speech and also became familiar with the general outline or the structure of a persuasive speech.
We also looked at some of the tips and tricks of persuasion, and lastly, got introduced to 3 amazing persuasive speech examples.
So, now that you know everything about persuasion, rest assured and keep the above-mentioned things in mind before starting your next speech!
Also, check out related posts:
Enroll in our transformative 1:1 Coaching Program
Schedule a call with our expert communication coach to know if this program would be the right fit for you

Interrupted while Speaking: 8 Ways to Prevent and Manage Interruptions

Speak English Like a Pro at the Workplace

Talk Smart: Strategies for Efficient and Impactful Communication

- [email protected]
- +91 98203 57888
Get our latest tips and tricks in your inbox always
Copyright © 2023 Frantically Speaking All rights reserved
Kindly drop your contact details so that we can arrange call back
Select Country Afghanistan Albania Algeria AmericanSamoa Andorra Angola Anguilla Antigua and Barbuda Argentina Armenia Aruba Australia Austria Azerbaijan Bahamas Bahrain Bangladesh Barbados Belarus Belgium Belize Benin Bermuda Bhutan Bosnia and Herzegovina Botswana Brazil British Indian Ocean Territory Bulgaria Burkina Faso Burundi Cambodia Cameroon Canada Cape Verde Cayman Islands Central African Republic Chad Chile China Christmas Island Colombia Comoros Congo Cook Islands Costa Rica Croatia Cuba Cyprus Czech Republic Denmark Djibouti Dominica Dominican Republic Ecuador Egypt El Salvador Equatorial Guinea Eritrea Estonia Ethiopia Faroe Islands Fiji Finland France French Guiana French Polynesia Gabon Gambia Georgia Germany Ghana Gibraltar Greece Greenland Grenada Guadeloupe Guam Guatemala Guinea Guinea-Bissau Guyana Haiti Honduras Hungary Iceland India Indonesia Iraq Ireland Israel Italy Jamaica Japan Jordan Kazakhstan Kenya Kiribati Kuwait Kyrgyzstan Latvia Lebanon Lesotho Liberia Liechtenstein Lithuania Luxembourg Madagascar Malawi Malaysia Maldives Mali Malta Marshall Islands Martinique Mauritania Mauritius Mayotte Mexico Monaco Mongolia Montenegro Montserrat Morocco Myanmar Namibia Nauru Nepal Netherlands Netherlands Antilles New Caledonia New Zealand Nicaragua Niger Nigeria Niue Norfolk Island Northern Mariana Islands Norway Oman Pakistan Palau Panama Papua New Guinea Paraguay Peru Philippines Poland Portugal Puerto Rico Qatar Romania Rwanda Samoa San Marino Saudi Arabia Senegal Serbia Seychelles Sierra Leone Singapore Slovakia Slovenia Solomon Islands South Africa South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands Spain Sri Lanka Sudan Suriname Swaziland Sweden Switzerland Tajikistan Thailand Togo Tokelau Tonga Trinidad and Tobago Tunisia Turkey Turkmenistan Turks and Caicos Islands Tuvalu Uganda Ukraine United Arab Emirates United Kingdom United States Uruguay Uzbekistan Vanuatu Wallis and Futuna Yemen Zambia Zimbabwe land Islands Antarctica Bolivia, Plurinational State of Brunei Darussalam Cocos (Keeling) Islands Congo, The Democratic Republic of the Cote d'Ivoire Falkland Islands (Malvinas) Guernsey Holy See (Vatican City State) Hong Kong Iran, Islamic Republic of Isle of Man Jersey Korea, Democratic People's Republic of Korea, Republic of Lao People's Democratic Republic Libyan Arab Jamahiriya Macao Macedonia, The Former Yugoslav Republic of Micronesia, Federated States of Moldova, Republic of Mozambique Palestinian Territory, Occupied Pitcairn Réunion Russia Saint Barthélemy Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan Da Cunha Saint Kitts and Nevis Saint Lucia Saint Martin Saint Pierre and Miquelon Saint Vincent and the Grenadines Sao Tome and Principe Somalia Svalbard and Jan Mayen Syrian Arab Republic Taiwan, Province of China Tanzania, United Republic of Timor-Leste Venezuela, Bolivarian Republic of Viet Nam Virgin Islands, British Virgin Islands, U.S.
Rhetoric: The Art of Persuasive Writing and Public Speaking
Gain critical communication skills.
This Harvard online course introduces learners to the art of persuasive writing and speaking and teaches how to construct and defend compelling arguments.

What You'll Learn
We are living in a contentious time in history. Fundamental disagreements on critical political issues make it essential to learn how to make an argument and analyze the arguments of others. This ability will help you engage in civil discourse and make effective changes in society. Even outside the political sphere, conveying a convincing message can benefit you throughout your personal, public, and professional lives.
We will be using selected addresses from prominent twentieth-century Americans—including Martin Luther King Jr., John F. Kennedy, Margaret Chase Smith, Ronald Reagan, and more—to explore and analyze rhetorical structure and style. Through this analysis, you will learn how speakers and writers persuade an audience to adopt their point of view.
Built around Harvard Professor James Engell’s on-campus course, “Elements of Rhetoric,” this course will help you analyze and apply rhetorical structure and style, appreciate the relevance of persuasive communication in your own life, and understand how to persuade and recognize when someone is trying to persuade you. You will be inspired to share your viewpoint and discover the most powerful ways to convince others to champion your cause. Join us to find your voice!
The course will be delivered via edX and connect learners around the world. By the end of the course, participants will be able to:
- When and how to employ a variety of rhetorical devices in writing and speaking
- How to differentiate between argument and rhetorical technique
- How to write a persuasive opinion editorial and short speech
- How to evaluate the strength of an argument
- How to identify logical fallacies in arguments
Course Outline
- Define the term "rhetoric."
- Articulate the importance of effective communication
- Summarize the history of rhetorical study, from the ancient Greeks to the modern-day
- Identify the parts of discourse
- Define the three modes of appeal
- Identify tropes and schemes, and explain their use in composition
- Compose an opinion editorial on a topic of your choice
- Analyze Martin Luther King, Jr.’s “I Have a Dream…” speech
- Define inductive reasoning and some of its associated topics
- Identify instances of inductive reasoning in writing and speech
- Define deductive reasoning and some of its associated topics
- Identify instances of deductive reasoning in writing and speech
- Recognize and evaluate the strength of an argument's refutation
- Apply the elements of rhetoric you have learned so far into the final draft of your op-ed
- Analyze Sarah Brady’s Democratic National Convention Keynote Speech
- Analyze Charlton Heston’s speech on the Second Amendment
- Define “inductive reasoning” and some of its associated topics
- Define “deductive reasoning” and some of its associated topics
- Recognize and evaluate the strength of an argument’s refutation
- Apply the elements of rhetoric you have learned so far in the final draft of your op-ed
- Describe the origins of the practice of oratory
- Recognize ways in which orators tailor their writing for the spoken word
- Describe techniques for effective public speaking, both prepared and extemporaneous
- Brainstorm ideas for your own short speech
- Analyze Joseph McCarthy’s “Enemies Within” speech
- Analyze Margaret Chase Smith’s "A Declaration of Conscience" speech
- Identify the modes of appeal and the logical reasoning of the featured speeches
- Identify both common and special topics used in these speeches, like cause and effect, testimony, justice and injustice, and comparison, and begin to recognize their use in other speeches
- Identify examples from these speeches of logical fallacies including the either/or fallacy, the fallacy of affirming the consequent, the argument ad hominem, the argument ad populum, begging the question, the complex question, and the use of imprecise language
- Discuss the importance of winning and keeping an audience’s trust and the pros and cons of attempting to tear down their confidence in an opponent
- Define for yourself the definition of "extremist rhetoric," debate its use as a political tool
- Consider the moral responsibilities of those who would seek to persuade others through language
- Discuss how the audience and the desired tone for a speech can influence diction (word choice)
- Compare the effects of using passive vs. active voice, and first-person vs. other tenses in a speech
- Discuss the effectiveness of the use of symbolism in writing and speech
- Define hyperbole, antimetabole, and polysyndeton, and identify when these devices might be appropriate and useful in terms of persuasion
- Describe techniques for connecting with your audience, including storytelling and drawing on shared experience
Your Instructor
James Engell is Gurney Professor of English and Professor of Comparative Literature, also a member of the Committee on the Study of Religion, and a faculty associate of the Harvard University Center for the Environment. He has also directed dissertations in American Studies, as well as Romance Languages & Literatures (French).
Education: B.A. 1973, Ph.D. 1978 Harvard
Interests: Romantic, Eighteenth-Century, and Restoration British Literature; Comparative Romanticism; Criticism and Critical Theory; Rhetoric; Environmental Studies; History and Economics of Higher Education
Selected Works: The Call of Classical Literature in the Romantic Age (2017, ed. with K. P. Van Anglen) and contributor, "The Other Classic: Hebrew Shapes British and American Literature and Culture." William Wordsworth's Prelude (1805), edited from the manuscripts and fully illustrated in color (2016, ed. with Michael D. Raymond). Environment: An Interdisciplinary Anthology (2008, ed. with Adelson, Ranalli, and Van Anglen). Saving Higher Education in the Age of Money (2005, with Anthony Dangerfield). The Committed Word: Literature and Public Values (1999). Coleridge: The Early Family Letters (1994, ed.). Forming the Critical Mind (1989). Johnson and His Age (1984, ed. and contributor). Biographia Literaria for the Collected Coleridge (1983, ed. with W. Jackson Bate). The Creative Imagination: Enlightenment to Romanticism (1981).
Ways to take this course
When you enroll in this course, you will have the option of pursuing a Verified Certificate or Auditing the Course.
A Verified Certificate costs $209 and provides unlimited access to full course materials, activities, tests, and forums. At the end of the course, learners who earn a passing grade can receive a certificate.
Alternatively, learners can Audit the course for free and have access to select course material, activities, tests, and forums. Please note that this track does not offer a certificate for learners who earn a passing grade.
Related Courses
Exercising leadership: foundational principles.
The crises of our time generate enormous adaptive challenges for our families, organizations, communities, and societies. The need for leadership that can mobilize people to meet these challenges and improve life is critical.
Leadership: Creating Public Value
Learn how to face and meet today’s challenges and design a public value proposition that is both actionable and value creating.
Remote Work Revolution for Everyone
In Remote Work Revolution for Everyone, you will learn how to build trust, increase productivity, use digital tools intelligently, and remain fully aligned with your remote team.
Persuasive Speech
Making Persuasive Speech Writing Easy: Steps and Tips

People also read
Good Persuasive Speech Topics & Ideas for Debaters
Top Motivational Speech Topics and Ideas
16 Best Persuasive Speech Examples for Students
Persuasive Speech Outline - Samples, Format, and Writing Tips
3 Basic Types of Persuasive Speeches
Having trouble writing a persuasive speech? You're not alone.
Many students and aspiring orators find themselves wrestling with the complexities of persuasive speech composition.
But fear not! Our comprehensive guide is here to assist you at every step of the way. With practical steps, illustrative examples, and invaluable tips, we'll help you hone your persuasive speech writing skills.
So, keep reading!
- 1. What is a Persuasive Speech
- 2. Parts of A Persuasive Speech
- 3. How to Write A Persuasive Speech
- 4. Persuasive Speech Examples
- 5. Persuasive Speech Topics
- 6. Tips For Writing A Good Persuasive Speech
What is a Persuasive Speech
A persuasive speech is a type of speech in which the speaker aims to influence the thoughts, opinions, or actions of the audience.
It involves presenting a viewpoint on a specific topic and providing compelling arguments and evidence to convince the listeners. The speaker's objective is to bring about a change in the audience's beliefs, attitudes, or behaviors.
The speaker uses a range of rhetorical techniques, including the persuasive appeals of ethos, pathos, and logos .
- Ethos pertains to the speaker's credibility and character. It involves establishing trust and authority, which makes the audience more receptive to the speaker's message.
- Pathos involves appealing to the emotions and feelings of the audience. It aims to create a strong emotional connection and empathy, making the audience more inclined to take action.
- Logos is about using logic and reason to construct a persuasive argument. It relies on evidence, facts, and clear reasoning to support the speaker's viewpoint.
Parts of A Persuasive Speech
In a persuasive speech, the core sections typically include:
Introduction
The introduction is your opportunity to capture your audience's attention. Start with an engaging hook or attention-grabber.
Provide some background information on the topic to contextualize your argument.
Main Points
Your speech should have two to four main points, each supporting your main argument. Each main point should be a distinct argument that reinforces your overall position.
These arguments serve as the core structure of your speech and should be well-researched and logically presented.
Supporting evidence, examples, or statistics should be included for each main point to bolster your argument and make it more persuasive.
Transitions
Smooth transitions are essential in maintaining the coherence and flow of your speech.
Transitions may be as simple as a sentence or phrase that connects one point to the next, ensuring your speech flows logically.
Counterarguments
Recognizing and addressing potential counterarguments or opposing viewpoints is a sign of a well-rounded and well-researched argument. Devote a section of your outline to these counter arguments, acknowledging them in a fair and unbiased manner.
Then, provide a well-reasoned response to refute these opposing views, demonstrating the strength and credibility of your own position.
The conclusion is where you wrap up your speech by summarizing your main points and restating your thesis.
This reinforces your central argument and leaves a lasting impression on your audience. A strong conclusion should provide a clear sense of closure, emphasizing the key takeaways from your speech.

Call to Action
Consider including a call to action in your conclusion to motivate your audience to take a specific step or support your cause.
This step adds a practical and actionable element to your persuasive speech, encouraging your audience to apply what they've learned.
Closing Remarks
End your speech with a memorable statement that leaves a final impression. You can use a powerful quote, a thought-provoking statement, or a call for reflection.
Additionally, thank your audience for their time and attention, fostering a sense of appreciation and respect for their presence.
An outlines guides you through the process of crafting a persuasive message and making a successful persuasive speech. Certain steps can vary according to whichever type of persuasive speech you’re working on.
How to Write A Persuasive Speech
Writing a persuasive speech is a structured process that makes your message compelling and effective in conveying ideas to the audience.
Here's a step-by-step guide to help you craft a persuasive speech:
Step 1: Choose a Persuasive Topic
Selecting the right topic is the foundation of a persuasive speech. Look for subjects that you are passionate about and that resonate with your audience. Moreover, an effective persuasive topic is one that can be debated or has varying viewpoints.
Your chosen topic should be relevant to your audience's interests, beliefs, and concerns. For instance, if you're addressing university students, consider what issues are important to them.
Let's say you choose "The Importance of Mental Health Awareness on Campus" as your topic. This topic is relevant, given the high levels of stress and mental health challenges that college students often face.
Step 2: Research Your Topic
To create a compelling persuasive speech, thorough research is essential.
Gather information, data, and evidence that support your arguments and help you establish credibility as a speaker.
For the topic of mental health awareness, research may include finding statistics on mental health issues among college students. Look for academic studies that discuss the impact of mental health on academic performance.
Step 3: Know Your Audience
Understanding your audience is crucial. Consider their attitudes, beliefs, values, and concerns related to your chosen topic.
For a college student audience, it's essential to comprehend their experiences and viewpoints on mental health. By acknowledging their existing knowledge and attitudes, you can tailor your speech to resonate more effectively with them.
Step 4: Organize Your Speech
Like any speech, persuasive speech should follow a logical structure.
Start with a compelling opening, which may include a relevant story, a surprising fact, or a thought-provoking question. Clearly state your main argument here. In the case of mental health awareness, it could be something like,
"Promoting mental health awareness on campus is essential for the well-being and success of college students."
Create a speech outline, which could be structured around the problems, solutions, and a call to action regarding mental health on campus. A speech outline is a blueprint which helps in delivering your persuasive speech in a logically fluent way and convincing your audience.
Here is a sample speech outline:
Step 5: Craft Persuasive Arguments
In the body of your speech, you'll present persuasive arguments to support your thesis.
In the "Understanding the Problem" section, talk about rising student stress, mental health stigma, and their impact on academic performance.
Use evidence and examples to back up each argument. Cite specific statistics or sharing stories of students who have faced these challenges.
Step 6: Use Rhetorical Devices
To make your persuasive speech more engaging and relatable to your audience, it's essential to employ rhetorical devices effectively.
These devices add depth and emotional resonance to your message. Some key rhetorical devices to consider include metaphors, anecdotes, and emotional appeals.
Personal stories or anecdotes about mental health issues can create a connection with your audience and evoke empathy.
Step 7: Address Counterarguments
It's important to acknowledge potential counterarguments in your speech. This shows that you've considered multiple perspectives. Acknowledging and refuting opposing views enhances the strength and credibility of your own point of view.
A potential argument could be that mental health awareness is too costly for universities. You can counter this by presenting cost-effective solutions that have been implemented successfully at other institutions.
Step 8: Call to Action
Conclude your speech with a compelling call to action. Encourage your audience to take specific steps to support your cause.
For instance, you could encourage them to participate in mental health awareness campaigns on campus, or advocate for improved mental health services in the university community.
Step 9: Revise and Practice
After writing your speech, revise it for clarity, coherence, and impact.
Practice your delivery multiple times to enhance your confidence and effectiveness as a speaker.
Persuasive Speech Examples
Here are some persuasive speech examples for helping you:
Persuasive Speech Examples For Students
Persuasive Speech Topics For College Students
Want to consult a few more examples? Check out these persuasive speech examples to help you get more ideas!
Persuasive Speech Topics
A good persuasive speech topic is one that grabs your audience's attention and stirs their thoughts.
To choose the right topic, it should be something you truly care about and that's important to your audience members. It's also essential that there are different opinions on the topic because it creates room for a meaningful discussion.
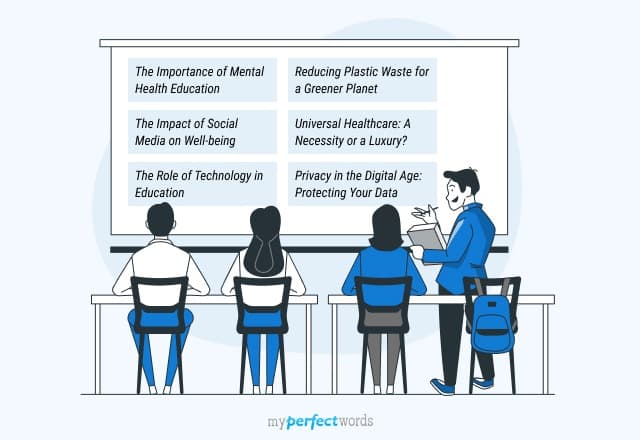
Here are some persuasive speech ideas:
Funny Persuasive Speech Topics
- Why cats are secretly plotting to take over the world.
- The importance of having a designated pizza night every week.
- How to survive a zombie apocalypse with just your wits and a backpack of snacks.
- The merits of watching cute animal videos during work hours.
- Why we should replace final exams with rap battles.
- The best excuses for being late to class (that actually work).
- How to annoy your roommates without getting caught.
- The compelling case for declaring "National Pajama Day."
- The benefits of talking to your houseplants and why they're great listeners.
- Why coffee should be classified as a daily essential nutrient.
Unique Persuasive Speech Topics
- The impact of social media on our sense of self-worth and well-being.
- The need for implementing mindfulness and meditation in schools.
- The benefits of fostering a community garden in every neighborhood.
- Why we should prioritize space exploration and colonizing other planets.
- The importance of teaching coding and programming in elementary schools.
- The ethical implications of gene editing and designer babies.
- Promoting eco-friendly travel options and reducing the environmental impact of tourism.
- The benefits of a four-day workweek for improved productivity and work-life balance.
- The need for teaching financial literacy in high schools.
- The impact of virtual reality on therapy and mental health treatment.
Can’t pick a topic? View this extensive list of persuasive speech topics on different themes!
Tips For Writing A Good Persuasive Speech
Creating and giving a strong persuasive speech involves different steps. Here are some tips for both writing and delivering your speech effectively:
- Learn what your audience cares about and shape your message accordingly.
- Back your points with credible data, facts, expert views, or real-life stories.
- Utilize credibility, emotions, and logic in a way that appeals to the audience.
- Share relatable anecdotes to connect with your audience.
- Time your speech to fit the allotted duration for maximum impact.
- Make good eye contact to connect with your audience and display confidence.
- Maintain open and confident body language; avoid nervous habits.
To sum it up, you've learned the steps and important tips for making a strong persuasive speech. You have the tools to choose the right topic, use evidence effectively, and engage your audience.
But if you ever need help or find it tough, remember you can hire our professional essay writing service . We're here to assist you in creating a persuasive speech that makes an impact.
Our experienced writers have a proven track record in creating impactful speeches. So, just buy speech and receive top quality results!

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Cathy has been been working as an author on our platform for over five years now. She has a Masters degree in mass communication and is well-versed in the art of writing. Cathy is a professional who takes her work seriously and is widely appreciated by clients for her excellent writing skills.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading
What are your chances of acceptance?
Calculate for all schools, your chance of acceptance.
Your chancing factors
Extracurriculars.
112 Persuasive Speech Topics That Are Actually Engaging
What’s covered:, how to pick an awesome persuasive speech topic, 112 engaging persuasive speech topics, tips for preparing your persuasive speech.
Writing a stellar persuasive speech requires a carefully crafted argument that will resonate with your audience to sway them to your side. This feat can be challenging to accomplish, but an engaging, thought-provoking speech topic is an excellent place to start.
When it comes time to select a topic for your persuasive speech, you may feel overwhelmed by all the options to choose from—or your brain may be drawing a completely blank slate. If you’re having trouble thinking of the perfect topic, don’t worry. We’re here to help!
In this post, we’re sharing how to choose the perfect persuasive speech topic and tips to prepare for your speech. Plus, you’ll find 112 persuasive speech topics that you can take directly from us or use as creative inspiration for your own ideas!
Choose Something You’re Passionate About
It’s much easier to write, research, and deliver a speech about a cause you care about. Even if it’s challenging to find a topic that completely sparks your interest, try to choose a topic that aligns with your passions.
However, keep in mind that not everyone has the same interests as you. Try to choose a general topic to grab the attention of the majority of your audience, but one that’s specific enough to keep them engaged.
For example, suppose you’re giving a persuasive speech about book censorship. In that case, it’s probably too niche to talk about why “To Kill a Mockingbird” shouldn’t be censored (even if it’s your favorite book), and it’s too broad to talk about media censorship in general.
Steer Clear of Cliches
Have you already heard a persuasive speech topic presented dozens of times? If so, it’s probably not an excellent choice for your speech—even if it’s an issue you’re incredibly passionate about.
Although polarizing topics like abortion and climate control are important to discuss, they aren’t great persuasive speech topics. Most people have already formed an opinion on these topics, which will either cause them to tune out or have a negative impression of your speech.
Instead, choose topics that are fresh, unique, and new. If your audience has never heard your idea presented before, they will be more open to your argument and engaged in your speech.
Have a Clear Side of Opposition
For a persuasive speech to be engaging, there must be a clear side of opposition. To help determine the arguability of your topic, ask yourself: “If I presented my viewpoint on this topic to a group of peers, would someone disagree with me?” If the answer is yes, then you’ve chosen a great topic!
Now that we’ve laid the groundwork for what it takes to choose a great persuasive speech topic, here are over one hundred options for you to choose from.
- Should high school athletes get tested for steroids?
- Should schools be required to have physical education courses?
- Should sports grades in school depend on things like athletic ability?
- What sport should be added to or removed from the Olympics?
- Should college athletes be able to make money off of their merchandise?
- Should sports teams be able to recruit young athletes without a college degree?
- Should we consider video gamers as professional athletes?
- Is cheerleading considered a sport?
- Should parents allow their kids to play contact sports?
- Should professional female athletes be paid the same as professional male athletes?
- Should college be free at the undergraduate level?
- Is the traditional college experience obsolete?
- Should you choose a major based on your interests or your potential salary?
- Should high school students have to meet a required number of service hours before graduating?
- Should teachers earn more or less based on how their students perform on standardized tests?
- Are private high schools more effective than public high schools?
- Should there be a minimum number of attendance days required to graduate?
- Are GPAs harmful or helpful?
- Should schools be required to teach about standardized testing?
- Should Greek Life be banned in the United States?
- Should schools offer science classes explicitly about mental health?
- Should students be able to bring their cell phones to school?
- Should all public restrooms be all-gender?
- Should undocumented immigrants have the same employment and education opportunities as citizens?
- Should everyone be paid a living wage regardless of their employment status?
- Should supremacist groups be able to hold public events?
- Should guns be allowed in public places?
- Should the national drinking age be lowered?
- Should prisoners be allowed to vote?
- Should the government raise or lower the retirement age?
- Should the government be able to control the population?
- Is the death penalty ethical?
Environment
- Should stores charge customers for plastic bags?
- Should breeding animals (dogs, cats, etc.) be illegal?
- Is it okay to have exotic animals as pets?
- Should people be fined for not recycling?
- Should compost bins become mandatory for restaurants?
- Should electric vehicles have their own transportation infrastructure?
- Would heavier fining policies reduce corporations’ emissions?
- Should hunting be encouraged or illegal?
- Should reusable diapers replace disposable diapers?
Science & Technology
- Is paper media more reliable than digital news sources?
- Should automated/self-driving cars be legalized?
- Should schools be required to provide laptops to all students?
- Should software companies be able to have pre-downloaded programs and applications on devices?
- Should drones be allowed in military warfare?
- Should scientists invest more or less money into cancer research?
- Should cloning be illegal?
- Should societies colonize other planets?
- Should there be legal oversight over the development of technology?
Social Media
- Should there be an age limit on social media?
- Should cyberbullying have the same repercussions as in-person bullying?
- Are online relationships as valuable as in-person relationships?
- Does “cancel culture” have a positive or negative impact on societies?
- Are social media platforms reliable information or news sources?
- Should social media be censored?
- Does social media create an unrealistic standard of beauty?
- Is regular social media usage damaging to real-life interactions?
- Is social media distorting democracy?
- How many branches of government should there be?
- Who is the best/worst president of all time?
- How long should judges serve in the U.S. Supreme Court?
- Should a more significant portion of the U.S. budget be contributed towards education?
- Should the government invest in rapid transcontinental transportation infrastructure?
- Should airport screening be more or less stringent?
- Should the electoral college be dismantled?
- Should the U.S. have open borders?
- Should the government spend more or less money on space exploration?
- Should students sing Christmas carols, say the pledge of allegiance, or perform other tangentially religious activities?
- Should nuns and priests become genderless roles?
- Should schools and other public buildings have prayer rooms?
- Should animal sacrifice be legal if it occurs in a religious context?
- Should countries be allowed to impose a national religion on their citizens?
- Should the church be separated from the state?
- Does freedom of religion positively or negatively affect societies?
Parenting & Family
- Is it better to have children at a younger or older age?
- Is it better for children to go to daycare or stay home with their parents?
- Does birth order affect personality?
- Should parents or the school system teach their kids about sex?
- Are family traditions important?
- Should parents smoke or drink around young children?
- Should “spanking” children be illegal?
- Should parents use swear words in front of their children?
- Should parents allow their children to play violent video games?
Entertainment
- Should all actors be paid the same regardless of gender or ethnicity?
- Should all award shows be based on popular vote?
- Who should be responsible for paying taxes on prize money, the game show staff or the contestants?
- Should movies and television shows have ethnicity and gender quotas?
- Should newspapers and magazines move to a completely online format?
- Should streaming services like Netflix and Hulu be free for students?
- Is the movie rating system still effective?
- Should celebrities have more privacy rights?
Arts & Humanities
- Are libraries becoming obsolete?
- Should all schools have mandatory art or music courses in their curriculum?
- Should offensive language be censored from classic literary works?
- Is it ethical for museums to keep indigenous artifacts?
- Should digital designs be considered an art form?
- Should abstract art be considered an art form?
- Is music therapy effective?
- Should tattoos be regarded as “professional dress” for work?
- Should schools place greater emphasis on the arts programs?
- Should euthanasia be allowed in hospitals and other clinical settings?
- Should the government support and implement universal healthcare?
- Would obesity rates lower if the government intervened to make healthy foods more affordable?
- Should teenagers be given access to birth control pills without parental consent?
- Should food allergies be considered a disease?
- Should health insurance cover homeopathic medicine?
- Is using painkillers healthy?
- Should genetically modified foods be banned?
- Should there be a tax on unhealthy foods?
- Should tobacco products be banned from the country?
- Should the birth control pill be free for everyone?
If you need more help brainstorming topics, especially those that are personalized to your interests, you can use CollegeVine’s free AI tutor, Ivy . Ivy can help you come up with original persuasive speech ideas, and she can also help with the rest of your homework, from math to languages.
Do Your Research
A great persuasive speech is supported with plenty of well-researched facts and evidence. So before you begin the writing process, research both sides of the topic you’re presenting in-depth to gain a well-rounded perspective of the topic.
Understand Your Audience
It’s critical to understand your audience to deliver a great persuasive speech. After all, you are trying to convince them that your viewpoint is correct. Before writing your speech, consider the facts and information that your audience may already know, and think about the beliefs and concerns they may have about your topic. Then, address these concerns in your speech, and be mindful to include fresh, new information.
Have Someone Read Your Speech
Once you have finished writing your speech, have someone read it to check for areas of strength and improvement. You can use CollegeVine’s free essay review tool to get feedback on your speech from a peer!
Practice Makes Perfect
After completing your final draft, the key to success is to practice. Present your speech out loud in front of a mirror, your family, friends, and basically, anyone who will listen. Not only will the feedback of others help you to make your speech better, but you’ll become more confident in your presentation skills and may even be able to commit your speech to memory.
Hopefully, these ideas have inspired you to write a powerful, unique persuasive speech. With the perfect topic, plenty of practice, and a boost of self-confidence, we know you’ll impress your audience with a remarkable speech!
Related CollegeVine Blog Posts

Rhetoric: The Art of Persuasive Writing and Public Speaking
Gain critical communication skills in writing and public speaking with this introduction to American political rhetoric.

Associated Schools

Harvard Faculty of Arts & Sciences
What you'll learn.
When and how to employ a variety of rhetorical devices in writing and speaking
How to differentiate between argument and rhetorical technique
How to write a persuasive opinion editorial and short speech
How to evaluate the strength of an argument
How to identify logical fallacies in arguments
Course description
We are living in a contentious time in history. Fundamental disagreements on critical political issues make it essential to learn how to make an argument and analyze the arguments of others. This ability will help you engage in civil discourse and make effective changes in society. Even outside the political sphere, conveying a convincing message can benefit you throughout your personal, public, and professional lives.
This course is an introduction to the theory and practice of rhetoric, the art of persuasive writing and speech. In it, you will learn to construct and defend compelling arguments, an essential skill in many settings. We will be using selected addresses from prominent twentieth-century Americans — including Martin Luther King Jr., John F. Kennedy, Margaret Chase Smith, Ronald Reagan, and more — to explore and analyze rhetorical structure and style. Through this analysis, you will learn how speakers and writers persuade an audience to adopt their point of view.
Built around Harvard Professor James Engell’s on-campus course, “Elements of Rhetoric,” this course will help you analyze and apply rhetorical structure and style, appreciate the relevance of persuasive communication in your own life, and understand how to persuade and recognize when someone is trying to persuade you. You will be inspired to share your viewpoint and discover the most powerful ways to convince others to champion your cause. Join us to find your voice!
Course Outline
Introduction to Rhetoric
- Define the term "rhetoric."
- Articulate the importance of effective communication.
- Summarize the history of rhetorical study, from the ancient Greeks to the modern-day.
- Identify the parts of discourse.
- Define the three modes of appeal.
- Identify tropes and schemes, and explain their use in composition.
- Compose an opinion editorial on a topic of your choice.
Civil Rights - Martin Luther King, Jr.
- Analyze Martin Luther King, Jr.’s “I Have a Dream…” speech
- Define inductive reasoning and some of its associated topics
- Identify instances of inductive reasoning in writing and speech
- Define deductive reasoning and some of its associated topics
- Identify instances of deductive reasoning in writing and speech
- Recognize and evaluate the strength of an argument's refutation
- Apply the elements of rhetoric you have learned so far into the final draft of your op-ed
Gun Control - Sarah Brady and Charlton Heston
- Analyze Sarah Brady’s Democratic National Convention Keynote Speech.
- Analyze Charlton Heston’s speech on the Second Amendment.
- Define “inductive reasoning” and some of its associated topics
- Define “deductive reasoning” and some of its associated topics
- Recognize and evaluate the strength of an argument’s refutation
- Apply the elements of rhetoric you have learned so far in the final draft of your op-ed
Introduction to Oratory
- Describe the origins of the practice of oratory.
- Recognize ways in which orators tailor their writing for the spoken word.
- Describe techniques for effective public speaking, both prepared and extemporaneous.
- Brainstorm ideas for your own short speech.
The Red Scare - Joseph McCarthy and Margaret Chase Smith
- Analyze Joseph McCarthy’s “Enemies Within” speech.
- Analyze Margaret Chase Smith’s "A Declaration of Conscience" speech.
- Identify the modes of appeal and the logical reasoning of the featured speeches.
- Identify both common and special topics used in these speeches, like cause and effect, testimony, justice and injustice, and comparison, and begin to recognize their use in other speeches.
- Identify examples from these speeches of logical fallacies including the either/or fallacy, the fallacy of affirming the consequent, the argument ad hominem, the argument ad populum, begging the question, the complex question, and the use of imprecise language.
- Discuss the importance of winning and keeping an audience’s trust and the pros and cons of attempting to tear down their confidence in an opponent.
- Define for yourself the definition of "extremist rhetoric," debate its use as a political tool.
- Consider the moral responsibilities of those who would seek to persuade others through language.
Presidential Rhetoric - John F. Kennedy and Ronald Reagan
- Discuss how the audience and the desired tone for a speech can influence diction (word choice).
- Compare the effects of using passive vs. active voice, and first-person vs. other tenses in a speech.
- Discuss the effectiveness of the use of symbolism in writing and speech.
- Define hyperbole, antimetabole, and polysyndeton, and identify when these devices might be appropriate and useful in terms of persuasion.
- Describe techniques for connecting with your audience, including storytelling and drawing on shared experience.
Instructors

James Engell
You may also like.

Effective Writing for Health Care
This Harvard Medical School one-year, application-based certificate program is designed to help clinicians, researchers and allied health professionals achieve their writing career goals.

Modern Masterpieces of World Literature
Examine how great modern writers capture the intricacies of our globalized world and how their works circulate within that world to find their own audiences.
Masterpieces of World Literature
Embark on a global journey to explore the past, present, and future of world literature.
How to Write a Persuasive Speech | Tips for Crafting an Effective One in 2023
Leah Nguyen • 04 Oct 2023 • 6 min read
A persuasive speech doesn’t make you talk till your throat’s dry.
In today’s discussion, we’ll break down the proven formula successful orators use to move minds and hearts.
Whether you’re running for office, pitching new product, or advocating for an important cause, let’s check out how to write a persuasive speech .
Table of Contents
What is a persuasive speech, #1. research the subject, #2. cut down the fluff, #3. craft a persuasive speech structure, #4. tell a story, short persuasive speech examples, persuasive speech topics, bottom line, frequently asked questions, tips for audience engagement.
- Eye Contact in Communication
- Persuasive Speech Outline

Start in seconds.
Get free templates for your next interactive presentation. Sign up for free and take what you want from the template library!
Have you ever been truly moved by a speaker who had you hanging on their every word? Who took you on such an inspiring journey that you left wanting to take action? Those are the hallmarks of a master persuader at work.
A persuasive speech is a type of public speaking designed to literally change minds and motivate behaviour. It’s part communication magic, part psychology hack – and with the right tools, anyone can learn to do it.
At its core, a persuasive speech aims to convince an audience of a specific idea or course of action by appealing to both logic and emotion. It lays out clear arguments while also tapping into passions and values.

A successful persuasive structure will introduce the topic, outline key points, address counterarguments, and conclude with a memorable call to action. Visual aids, stories, rhetorical devices and enthusiastic delivery all enhance the experience.
Although meant to be convincing, quality persuaders never resort to manipulation. Rather, they present solid facts with empathy and honour other perspectives along the journey.
From campaign speeches to PTA fundraisers , the ability to strategically rally support around a viewpoint through oration alone is a talent worth cultivating. So whether you aspire to inspire social change or simply motivate mindsets in your circle, adding persuasion to your public speaking playbook is sure to magnify your impact.
How to Write a Persuasive Speech
Crafting the perfect persuasive address requires thoughtful planning. But fear not, with the right framework you’ll be well on your way to masterfully motivating any audience.

They say knowing is half the battle. When you’re doing research on the topic, you’ll unconsciously remember every detail and information along the way. And because of that, smooth information will flow out of your mouth before you know it.
Get familiarised with reputational research papers, peer-reviewed journals and expert opinions to craft a concrete foundation for your speech. They also present different views and counterarguments so you can address them on the day.
You can map each point with a respective counterargument using a mind-mapping tool for a structured and more organised approach.

This is no time to flex your wealth of ultra-complicated technical words. The idea of a persuasive speech is to get your point across verbally.
Make it sound natural so that you have no trouble spewing it out loud and your tongue doesn’t linger trying to pronounce something like anthropomorphism.
Avoid lengthy constructions that cause you to stumble. Chop the sentences down to short and concise pieces of information.
See this example:
- It could be said that in light of the presently existing circumstances which are currently surrounding us at this moment in time, there may potentially exist certain conditions that might feasibly be conducive toward potentially providing an optimum environment for potentially achieving desired outcomes.
Sounds unnecessarily long and complex, isn’t it? You can just bring this down to something like this:
- The current circumstances could create conditions conducive to achieving desired outcomes.
The clearer version gets the same point across in a more direct and succinct way by removing extra words, simplifying the phrasing and structure, and using more active rather than passive construction.

The general outline for a speech needs to be clear and logical. Here are some tips on how to craft one:
- Start with a compelling hook. Capture attention instantly with a surprising stat, intriguing anecdote or open question. Pique curiosity about the issue.
- Clearly state your thesis up front. Distil your central argument and goal into a concise, memorable statement. Paint the picture of what you aim to achieve.
- Support your thesis with well-chosen facts. Cite respected sources and data-driven evidence to rationally reinforce key talking points. Appeal to logic as well as emotion.
- Anticipate objections and address counterarguments respectfully. Show you understand opposing viewpoints yet position why yours is most sound.
- Weave in illustrative stories and examples. Relate concepts to people’s lives through a compelling narrative. Paint a vivid mental image they’ll never forget.
- Close powerfully with a call to action. Inspire audiences to take a specific next step that furthers your cause. Motivate minds and spark an enduring commitment to your vision.

While logic and facts are important, truly moving an audience to act requires connecting on a deeper human level through emotion.
Persuasive speeches that only present dry statistics and reasoning, no matter how sound, will fail to inspire.
To craft a speech that sways hearts as well as minds, strategically incorporate stories, anecdotes and value-based language tailored to your listeners.
Describe how the issue personally impacts real people in a way the audience can relate to and feel empathetic towards. Share a short, engaging narrative that puts a vivid face to the topic.
Appeal to your crowd’s core beliefs and priorities by framing your argument in terms of principles they cherish such as justice, empathy or progress.
Tap into emotions like pride, hope or outrage to energise their conviction to support your solution. With targeted emotional insights paired with rational appeals, you’ll guide your audience along a far more persuasive journey of the heart and soul.

Here are examples of short persuasive speeches. A convincing one should have a specific purpose, as well as central arguments built on it.
Persuasive Speech Example 1: Title: Why Recycling Should Be Mandatory Specific Purpose: To persuade my audience that recycling should be required by law in all communities. Central Idea: Recycling helps the environment, conserves natural resources and saves money; therefore, all communities should pass laws to mandate recycling programs.
Persuasive Speech Example 2: Title: Why Social Media Is Detrimental to Teen Mental Health Specific Purpose: To persuade parents to monitor and limit their teen’s social media usage. Central Idea: Excessive social media use has been linked to increased anxiety, depression and loneliness in teens by promoting social comparison and FOMO. Implementing reasonable limits can help protect mental well-being.
Persuasive Speech Example 3: Title: Why School Lunches Need Improvement Specific Purpose: To persuade the PTA to lobby for healthier cafeteria food options. Central Idea: The current lunch offerings at our school are often overly processed and lack nutrients, leading to obesity risks. Upgrading to fresher, whole foods will boost student health and focus.

Practising a chosen speech topic can increase your persuasion skills tremendously. Here are some topics to kickstart:
- Year-round schooling, later start times, homework policies, funding for arts/sports, dress codes
- Immigration reform, gun control laws, LGBTQ+ rights, abortion, marijuana legalisation
- Sugar/food taxes, banning plastic straws, GMO labelling, smoking bans, green energy initiatives
- Social media regulations, driverless cars, surveillance laws, video game restrictions
- Minimum wage increases, universal basic income, trade policies, taxes
- Prison/sentencing reform, police use of force, drug decriminalisation, private prisons
- Foreign aid, refugees/asylum, trade agreements, military budget
- Gender roles, body positivity, social media/TV influence, work-life balance
- Free will vs. determinism, ethical consumption, technology’s impact, social justice
- Ratings systems, content restrictions, media bias, streaming vs. cable
In closing, an effective persuasive speech has the power to inspire change and bring people together behind important causes. If you understand audience psychology and craft your message strategically with passion and precision, you too can sway minds on issues you care about.
How do I start a persuasive speech?
Start your persuasive speech with a startling statistic, fact or emotional story to hook the audience instantly.
What makes a good persuasive speech?
A good persuasive speech often comprises logic, emotion and credibility. Satisfying all three criteria will enhance your argument.
Leah Nguyen
Words that convert, stories that stick. I turn complex ideas into engaging narratives - helping audiences learn, remember, and take action.
More from AhaSlides


Improve your practice.
Enhance your soft skills with a range of award-winning courses.
75 Persuasive Speech Topics and Ideas
October 4, 2018 - Gini Beqiri
To write a captivating and persuasive speech you must first decide on a topic that will engage, inform and also persuade the audience. We have discussed how to choose a topic and we have provided a list of speech ideas covering a wide range of categories.
What is persuasive speech?
The aim of a persuasive speech is to inform, educate and convince or motivate an audience to do something. You are essentially trying to sway the audience to adopt your own viewpoint.
The best persuasive speech topics are thought-provoking, daring and have a clear opinion. You should speak about something you are knowledgeable about and can argue your opinion for, as well as objectively discuss counter-arguments.
How to choose a topic for your speech
It’s not easy picking a topic for your speech as there are many options so consider the following factors when deciding.
Familiarity
Topics that you’re familiar with will make it easier to prepare for the speech.
It’s best if you decide on a topic in which you have a genuine interest in because you’ll be doing lots of research on it and if it’s something you enjoy the process will be significantly easier and more enjoyable. The audience will also see this enthusiasm when you’re presenting which will make the speech more persuasive.
The audience’s interest
The audience must care about the topic. You don’t want to lose their attention so choose something you think they’ll be interested in hearing about.
Consider choosing a topic that allows you to be more descriptive because this allows the audience to visualize which consequently helps persuade them.
Not overdone
When people have heard about a topic repeatedly they’re less likely to listen to you as it doesn’t interest them anymore. Avoid cliché or overdone topics as it’s difficult to maintain your audience’s attention because they feel like they’ve heard it all before.
An exception to this would be if you had new viewpoints or new facts to share. If this is the case then ensure you clarify early in your speech that you have unique views or information on the topic.
Emotional topics
Emotions are motivators so the audience is more likely to be persuaded and act on your requests if you present an emotional topic.
People like hearing about issues that affect them or their community, country etc. They find these topics more relatable which means they find them more interesting. Look at local issues and news to discover these topics.
Desired outcome
What do you want your audience to do as a result of your speech? Use this as a guide to choosing your topic, for example, maybe you want people to recycle more so you present a speech on the effect of microplastics in the ocean.

Persuasive speech topics
Lots of timely persuasive topics can be found using social media, the radio, TV and newspapers. We have compiled a list of 75 persuasive speech topic ideas covering a wide range of categories.
Some of the topics also fall into other categories and we have posed the topics as questions so they can be easily adapted into statements to suit your own viewpoint.
- Should pets be adopted rather than bought from a breeder?
- Should wild animals be tamed?
- Should people be allowed to own exotic animals like monkeys?
- Should all zoos and aquariums be closed?
Arts/Culture
- Should art and music therapy be covered by health insurance?
- Should graffiti be considered art?
- Should all students be required to learn an instrument in school?
- Should automobile drivers be required to take a test every three years?
- Are sports cars dangerous?
- Should bicycles share the roads with cars?
- Should bicycle riders be required by law to always wear helmets?
Business and economy
- Do introverts make great leaders?
- Does owning a business leave you feeling isolated?
- What is to blame for the rise in energy prices?
- Does hiring cheaper foreign employees hurt the economy?
- Should interns be paid for their work?
- Should employees receive bonuses for walking or biking to work?
- Should tipping in restaurants be mandatory?
- Should boys and girls should be taught in separate classrooms?
- Should schools include meditation breaks during the day?
- Should students be allowed to have their mobile phones with them during school?
- Should teachers have to pass a test every decade to renew their certifications?
- Should online teaching be given equal importance as the regular form of teaching?
- Is higher education over-rated?
- What are the best ways to stop bullying?
- Should people with more than one DUI lose their drivers’ licenses?
- Should prostitution be legalised?
- Should guns be illegal in the US?
- Should cannabis be legalised for medical reasons?
- Is equality a myth?
- Does what is “right” and “wrong” change from generation to generation?
- Is there never a good enough reason to declare war?
- Should governments tax sugary drinks and use the revenue for public health?
- Has cosmetic surgery risen to a level that exceeds good sense?
- Is the fast-food industry legally accountable for obesity?
- Should school cafeterias only offer healthy food options?
- Is acupuncture a valid medical technique?
- Should assisted suicide be legal?
- Does consuming meat affect health?
- Is dieting a good way to lose weight?
Law and politics
- Should voting be made compulsory?
- Should the President (or similar position) be allowed to serve more than two terms?
- Would poverty reduce by fixing housing?
- Should drug addicts be sent for treatment in hospitals instead of prisons?
- Would it be fair for the government to detain suspected terrorists without proper trial?
- Is torture acceptable when used for national security?
- Should celebrities who break the law receive stiffer penalties?
- Should the government completely ban all cigarettes and tobacco products
- Is it wrong for the media to promote a certain beauty standard?
- Is the media responsible for the moral degradation of teenagers?
- Should advertising be aimed at children?
- Has freedom of press gone too far?
- Should prayer be allowed in public schools?
- Does religion have a place in government?
- How do cults differ from religion?
Science and the environment
- Should recycling be mandatory?
- Should genetically modified foods be sold in supermarkets?
- Should parents be allowed to choose the sex of their unborn children?
- Should selling plastic bags be completely banned in shops?
- Should smoking in public places be banned?
- Should professional female athletes be paid the same as male athletes in the same sport?
- Should doping be allowed in professional sports?
- Should schools be required to teach all students how to swim?
- How does parental pressure affect young athletes?
- Will technology reduce or increase human employment opportunities?
- What age should children be allowed to have mobile phones?
- Should libraries be replaced with unlimited access to e-books?
- Should we recognize Bitcoin as a legal currency?
- Should bloggers and vloggers be treated as journalists and punished for indiscretions?
- Has technology helped connect people or isolate them?
- Should mobile phone use in public places be regulated?
- Do violent video games make people more violent?
World peace
- What is the safest country in the world?
- Is planetary nuclear disarmament possible?
- Is the idea of peace on earth naive?
These topics are just suggestions so you need to assess whether they would be suitable for your particular audience. You can easily adapt the topics to suit your interests and audience, for example, you could substitute “meat” in the topic “Does consuming meat affect health?” for many possibilities, such as “processed foods”, “mainly vegan food”, “dairy” and so on.
After choosing your topic
After you’ve chosen your topic it’s important to do the following:
- Research thoroughly
- Think about all of the different viewpoints
- Tailor to your audience – discussing your topic with others is a helpful way to gain an understanding of your audience.
- How involved are you with this topic – are you a key character?
- Have you contributed to this area, perhaps through blogs, books, papers and products.
- How qualified are you to speak on this topic?
- Do you have personal experience in it? How many years?
- How long have you been interested in the area?
While it may be difficult to choose from such a variety of persuasive speech topics, think about which of the above you have the most knowledge of and can argue your opinion on.
For advice about how to deliver your persuasive speech, check out our blog Persuasive Speech Outline and Ideas .
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Student Opinion
310 Prompts for Argumentative Writing
Questions on everything from mental health and sports to video games and dating. Which ones inspire you to take a stand?

By Natalie Proulx
Does social media harm young people’s mental health? Do video games deserve the bad rap they often get? Should parents track their children? Who is the greatest athlete of all time?
Every school day, we publish new questions for students based on the news of the day, including prompts, like these, that inspire persuasive writing.
Below, we’ve rounded up over 300 of those argumentative prompts, organized by topic, all in one place. They cover everything from parenting and schools to music and social media. Each one, drawn from our Student Opinion column , links to a free New York Times article as well as additional subquestions that can help you think more deeply about it.
You can use these prompts however you like, whether to inspire an entry for our new Open Letter Contest , to hone your persuasive writing skills or simply to share your opinions on the issues of today. So scroll through the list below and see which ones inspire you to take a stand.
If you enjoy these questions, know that you can find all of our argumentative writing prompts, as they publish, here . Students 13 and up from anywhere in the world are invited to comment.
Argumentative Prompt Topics
Technology and social media, college, work and money, health and relationships, gender and race, arts and entertainment, parenting and childhood, government and politics, animals, science and time.
Social Media
1. Does Social Media Harm Young People’s Mental Health? 2. How Much Should Speech Be Moderated on Social Media? 3. Should the United States Ban TikTok? 4. How Young Is Too Young to Use Social Media? 5. Should Kids Be Social Media Influencers? 6. What Should Be Done to Protect Children Online? 7. Should There Be Separate Social Media Apps for Children? 8. Are You a Fan of ‘School Accounts’ on Social Media? 9. Will Social Media Help or Hurt Your College and Career Goals? 10. Is It Ever OK to Use Strangers as Content for Social Media?
Phones and Devices
11. Should More Teenagers Ditch Their Smartphones? 12. Should the Adults in Your Life Be Worried by How Much You Use Your Phone? 13. Should Phones Ever Be a Part of Family or Holiday Gatherings? 14. What Are Your Texting Dos and Don’ts? 15. Does Grammar Still Matter in the Age of Twitter? 16. Is Your Phone Love Hurting Your Relationships? 17. Should Texting While Driving Be Treated Like Drunken Driving? 18. How Young Is Too Young for an Apple Watch?
The Internet
19. Do Memes Make the Internet a Better Place? 20. How Excited Are You About the Metaverse? 21. Should Websites Force Users to Prove How Old They Are? 22. What Is the Best Way to Stop Abusive Language Online? 23. How Do You Feel About Cancel Culture? 24. Does Online Public Shaming Prevent Us From Being Able to Grow and Change? 25. Do You Think Online Conspiracy Theories Can Be Dangerous? 26. Does Technology Make Us More Alone?
School Discipline and Attendance
27. Should Schools Ban Cellphones? 28. How Should Schools Hold Students Accountable for Hurting Others? 29. What Are Your Thoughts on Uniforms and Strict Dress Codes? 30. Should Schools Test Their Students for Nicotine and Drug Use? 31. How Can Schools Engage Students Who Are at Risk of Dropping Out? 32. Should Students Be Allowed to Miss School for Mental Health Reasons? 33. Should Your School Day Start Later? 34. Should There Still Be Snow Days? 35. Do Kids Need Recess? 36. Should Students Be Punished for Not Having Lunch Money?
School Quality and Effectiveness
37. How Do You Think American Education Could Be Improved? 38. Do Schools Need to Do More to Hold Students Accountable? 39. Are Straight A’s Always a Good Thing? 40. Should Students Have the Same Teachers Year After Year? 41. Do Teachers Assign Too Much Homework? 42. Should We Get Rid of Homework? 43. Should We Eliminate Gifted and Talented Programs? 44. Is It Time to Get Rid of Timed Tests? 45. What Role Should Textbooks Play in Education? 46. How Should Senior Year in High School Be Spent? 47. Does Your School Need More Money? 48. Do School Employees Deserve More Respect — and Pay? 49. Should Public Preschool Be a Right for All Children?
Teaching and Learning
50. Do You Think We Need to Change the Way Math Is Taught? 51. Should Financial Literacy Be a Required Course in School? 52. Should Schools Teach Students Kitchen and Household Skills? 53. Do We Need Better Music Education? 54. What Are the Most Important Things Students Should Learn in School? 55. What Is the Purpose of Teaching U.S. History? 56. Do Schools Need to Do More to Support Visual Thinkers? 57. Is School a Place for Self-Expression? 58. Should Media Literacy Be a Required Course in School? 59. Can Empathy Be Taught? Should Schools Try to Help Us Feel One Another’s Pain? 60. Should Schools Teach You How to Be Happy? 61. Should All Schools Teach Cursive? 62. Should Kids Still Learn to Tell Time? 63. How Important Is Knowing a Foreign Language
Technology in School
64. How Should Schools Respond to ChatGPT? 65. Does Learning to Be a Good Writer Still Matter in the Age of A.I.? 66. Is Online Learning Effective? 67. Should Students Be Monitored When Taking Online Tests? 68. Should Schools Be Able to Discipline Students for What They Say on Social Media? 69. Can Social Media Be a Tool for Learning and Growth in Schools? 70. Should Facial Recognition Technology Be Used in Schools? 71. Is Live-Streaming Classrooms a Good Idea? 72. Should Teachers and Professors Ban Student Use of Laptops in Class? 73. Are the Web Filters at Your School Too Restrictive?
Education Politics
74. Do You Feel Your School and Teachers Welcome Both Conservative and Liberal Points of View? 75. Should Students Learn About Climate Change in School? 76. Should Teachers Provide Trigger Warnings for ‘Traumatic Content’? 77. Should Teachers Be Allowed to Wear Political Symbols? 78. What Do You Think About Efforts to Ban Books From School Libraries? 79. What Is Your Reaction to the Growing Fight Over What Young People Can Read? 80. What Do You Think About the Controversy Surrounding the New A.P. Course on African American Studies? 81. Should Schools or Employers Be Allowed to Tell People How They Should Wear Their Hair? 82. Does Prayer Have Any Place in Public Schools? 83. Should Schools Be Allowed to Censor Student Newspapers?
College Admissions
84. Should Colleges Consider Standardized Tests in Admissions? 85. Should Students Let ChatGPT Help Them Write Their College Essays? 86. What Is Your Reaction to the End of Race-Based Affirmative Action in College Admissions? 87. Are Early-Decision Programs Unfair? Should Colleges Do Away With Them? 88. Is the College Admissions Process Fair? 89. How Much Do You Think It Matters Where You Go to College? 90. Should Everyone Go to College? 91. Should College Be Free? 92. Is Student Debt Worth It? 93. Should High Schools Post Their Annual College Lists?
Campus Life
94. What Should Free Speech Look Like on Campus? 95. Should Greek Life on College Campuses Come to an End? 96. Should Universities Work to Curtail Student Drinking? 97. How Should the Problem of Sexual Assault on Campuses Be Addressed? 98. Are Lavish Amenities on College Campuses Useful or Frivolous? 99. Should ‘Despised Dissenters’ Be Allowed to Speak on College Campuses? 100. Should Emotional Support Animals Be Allowed on College Campuses?
Jobs and Careers
101. Is High School a Good Time to Train for a Career? 102. Is There Such a Thing as a ‘Useless’ College Major? 103. Should All High School Students Have Part-Time Jobs? 104. Should National Service Be Required for All Young Americans? 105. Is It OK to Use Family Connections to Get a Job?
Money and Business
106. Do You Think the American Dream Is Real? 107. Should All Young People Learn How to Invest in the Stock Market? 108. Should We All Go Cashless? 109. When Should You Tip? 110. Should We End the Practice of Tipping? 111. Are You a Crypto Optimist or Skeptic? 112. Do Celebrities and Influencers Make You Want to Buy What They’re Selling? 113. Is $1 Billion Too Much Money for Any One Person to Have? 114. Are C.E.O.s Paid Too Much? 115. Is It Immoral to Increase the Price of Goods During a Crisis? 116. What Should Stores Do With Unsold Goods? 117. Is There a ‘Right Way’ to Be a Tourist? 118. Who Should We Honor on Our Money?
Mental Health
119. Is Teen Mental Health in a State of Crisis? 120. ‘Love-Bombing.’ ‘Gaslighting.’ ‘Victim.’ Is ‘Trauma Talk’ Overused? 121. Does Achieving Success Always Include Being Happy? 122. Is Struggle Essential to Happiness? 123. Should Schools Teach Mindfulness? 124. How Can We Bring an End to the ‘Epidemic of Loneliness’? 125. Does Every Country Need a ‘Loneliness Minister’? 126. What Ideas Do You Have to Bring Your Community Closer Together? 127. Are Emotional-Support Animals a Scam? 128. Is It OK to Laugh During Dark Times?
Dating and Relationships
129. Who Should Pay for Dates? 130. Do Marriage Proposals Still Have a Place in Today’s Society? 131. Should Your Significant Other Be Your Best Friend? 132. How Do You Think Technology Affects Dating?
Physical Health
133. Should Governments Do More to Discourage People From Smoking and Vaping? 134. How Should Adults Talk to Kids About Drugs? 135. Can Laziness Be a Good Thing? 136. Should There Be Requirements for Teens Who Want to Ride E-Bikes? 137. What Advice Should Parents and Counselors Give Teenagers About Sexting? 138. Should All Children Be Vaccinated? 139. Do We Worry Too Much About Germs?
140. Is It Becoming More Acceptable for Men and Boys to Cry? 141. Is It Harder for Men and Boys to Make and Keep Friends? 142. Should Award Shows Eliminate Gendered Categories? 143. Should There Be More Gender Options on Identification Documents? 144. Justice Ginsburg Fought for Gender Equality. How Close Are We to Achieving That Goal? 145. What Should #MeToo Mean for Teenage Boys? 146. What Is Hard About Being a Boy? 147. Should There Be More Boy Dolls? 148. Is Single-Sex Education Still Useful? 149. Are Beauty Pageants Still Relevant? 150. Should Period Products Be Free? 151. What Are Your Thoughts on Last Names? 152. What Rules Should Apply to Transgender Athletes When They Compete? 153. What Is Your Reaction to the Recent Wave of Legislation That Seeks to Regulate the Lives of Transgender Youths? 154. What Do You Wish Lawmakers Knew About How Anti-L.G.B.T.Q. Legislation Affects Teenagers?
Identity, Race and Ethnicity
155. How Should Schools Respond to Racist Jokes? 156. How Should Parents Teach Their Children About Race and Racism? 157. What Is Your Reaction to Efforts to Limit Teaching on Race in Schools? 158. How Should Racial Slurs in Literature Be Handled in the Classroom? 159. Should Confederate Statues Be Removed or Remain in Place? 160. Should We Rename Schools Named for Historical Figures With Ties to Racism, Sexism or Slavery? 161. How Should We Remember the Problematic Actions of the Nation’s Founders? 162. Does the United States Owe Reparations to the Descendants of Enslaved People? 163. What Can History Teach Us About Resilience? 164. Should All Americans Receive Anti-Bias Education? 165. Is Fear of ‘The Other’ Poisoning Public Life? 166. What Stereotypical Characters Make You Cringe? 167. When Talking About Identity, How Much Do Words Matter? 168. How Useful Is It to Be Multilingual?
TV and Movies
169. Is True Crime As a Form of Entertainment Ethical? 170. Should Old TV Shows Be Brought Back? 171. Does Reality TV Deserve Its Bad Rap? 172. How Closely Should Actors’ Identities Reflect the Roles They Play? 173. In the Age of Digital Streaming, Are Movie Theaters Still Relevant? 174. Do We Need More Female Superheroes? 175. Is Hollywood Becoming More Diverse? 176. When Does Lying in Comedy Cross a Line? 177. How Do You Feel About ‘Nepotism Babies’?
Music and Video Games
178. Will A.I. Replace Pop Stars? 179. If Two Songs Sound Alike, Is It Stealing? 180. Should Musicians Be Allowed to Copy or Borrow From Other Artists? 181. How Do You Feel About Censored Music? 182. What Are the Greatest Songs of All Time? 183. Do Video Games Deserve the Bad Rap They Often Get? 184. Should There Be Limits on How Much Time Young People Spend Playing Video Games? 185. Should More Parents Play Video Games With Their Kids?
186. Are A.I.-Generated Pictures Art? 187. What Work of Art Should Your Friends Fall in Love With? 188. If Artwork Offends People, Should It Be Removed? 189. Should Museums Return Looted Artifacts to Their Countries of Origin? 190. Should Art Come With Trigger Warnings? 191. Is the Digital Era Improving or Ruining the Experience of Art? 192. Are Museums Still Important in the Digital Age? 193. Can You Separate Art From the Artist? 194. Are There Subjects That Should Be Off-Limits to Artists, or to Certain Artists in Particular? 195. Should Graffiti Be Protected?
Books and Literature
196. Is Listening to a Book Just as Good as Reading It? 197. Should Classic Children’s Books Be Updated for Today’s Young Readers? 198. Should White Writers Translate a Black Author’s Work? 199. Is There Any Benefit to Reading Books You Hate? 200. Should Libraries Get Rid of Late Fees?
201. What’s the Best — and Worst — Part of Being a Sports Fan? 202. Who Is the GOAT? 203. Do Women’s Sports Deserve More Attention? 204. What Should Be Done About the Gender Pay Gap in Sports? 205. Should Girls and Boys Sports Teams Compete in the Same League? 206. Should More Sports Be Coed? 207. College Athletes Can Now Be Paid. But Not All of Them Are Seeing Money. Is That Fair? 208. Should High School-Age Basketball Players Be Able to Get Paid? 209. Are Some Youth Sports Too Intense? 210. Are Youth Sports Too Competitive? 211. Is It Bad Sportsmanship to Run Up the Score in Youth Sports? 212. Is It Ethical to Be a Football Fan? 213. Does the N.F.L. Have a Race Problem? 214. What New Rules Would Improve Your Favorite Sport? 215. What Sports Deserve More Hype? 216. How Should We Punish Sports Cheaters? 217. Should Technology in Sports Be Limited? 218. Does Better Sports Equipment Unfairly Improve Athletic Ability? 219. Is It Offensive for Sports Teams and Their Fans to Use Native American Names, Imagery and Gestures? 220. Is It Selfish to Pursue Risky Sports Like Extreme Mountain Climbing? 221. Should Cheerleading Be an Olympic Sport?

Related Writing Prompt
222. Should Parents Ever Be Held Responsible for the Harmful Actions of Their Children? 223. Where Is the Line Between Helping a Child Become More Resilient and Pushing Them Too Hard? 224. Should Parents Give Children More Responsibility at Younger Ages? 225. Should Parents Tell Children the Truth About Santa? 226. Should Parents Weigh in on Their Kids’ Dating Lives? 227. Should Parents Track Their Children? 228. How Should Parents Support a Student Who Has Fallen Behind in School? 229. Do Parents Ever Cross a Line by Helping Too Much With Schoolwork? 230. What’s the Best Way to Discipline Children? 231. What Are Your Thoughts on ‘Snowplow Parents’? 232. Should Stay-at-Home Parents Be Paid? 233. Should Parents Bribe Their Children?
Childhood and Growing Up
234. Is It Harder to Grow Up in the 21st Century Than It Was in the Past? 235. Is Childhood Today Over-Supervised? 236. When Do You Become an Adult? 237. Who Should Decide Whether a Teenager Can Get a Tattoo or Piercing? 238. Do We Give Children Too Many Trophies? 239. What Can Older Generations Learn From Gen Z? 240. What Is the Worst Toy Ever?
Legislation and Policy
241. Should the Death Penalty Be Abolished? 242. Should Marijuana Be Legal? 243. Should the United States Decriminalize the Possession of Drugs? 244. What Is Your Reaction to the State of Abortion Rights? 245. Should the Government Cancel Student Debt? 246. Should Public Transit Be Free? 247. Should There Be More Public Restrooms? 248. Should the U.S. Be Doing More to Prevent Child Poverty? 249. Should the Government Provide a Guaranteed Income for Families With Children? 250. Should Law Enforcement Be Able to Use DNA Data From Genealogy Websites for Criminal Investigations?
Gun Violence
251. Are You Concerned About Violence in America? 252. How Should Americans Deal With the Problem of Gun Violence? 253. What Should Lawmakers Do About Guns and Gun Violence? 254. Should the U.S. Ban Military-Style Semiautomatic Weapons? 255. Should Teachers Be Armed With Guns?
Voting and Elections
256. How Much Faith Do You Have in the U.S. Political System? 257. Is the Electoral College a Problem? Does It Need to Be Fixed? 258. Does Everyone Have a Responsibility to Vote? 259. Should We All Be Able to Vote by Mail? 260. Should There Be a Minimum Voting Age? 261. Should the Voting Age Be Lowered to 16? 262. Should Ex-Felons Have the Right to Vote? 263. Are Presidential Debates Helpful to Voters? Or Should They Be Scrapped?
Freedoms and Rights
264. How Important Is Freedom of the Press? 265. Why Does the Right to Protest Matter? 266. Does the U.S. Constitution Need an Equal Rights Amendment? 267. Do You Care Who Sits on the Supreme Court? Should We Care? 268. Should You Have a Right to Be Rude? 269. Should Prisons Offer Incarcerated People Education Opportunities?
Civic Participation
270. Are You Optimistic About the State of the World? 271. If You Could Take On One Problem Facing Our World, What Would It Be? 272. If You Were Mayor, What Problems Facing Your Community Would You Tackle? 273. Do You Think Teenagers Can Make a Difference in the World? 274. Do You Think It Is Important for Teenagers to Participate in Political Activism? 275. Is Your Generation Doing Its Part to Strengthen Our Democracy? 276. How Is Your Generation Changing Politics? 277. Why Is It Important for People With Different Political Beliefs to Talk to Each Other? 278. Are We Being Bad Citizens If We Don’t Keep Up With the News? 279. Why Do Bystanders Sometimes Fail to Help When They See Someone in Danger? 280. When Is It OK to Be a Snitch? 281. Should Reporters Ever Help the People They Are Covering? 282. Should Celebrities Weigh In on Politics? 283. Should Athletes Speak Out On Social and Political Issues? 284. Should Corporations Take Political Stands? 285. What Do You Think the Role of the First Lady — or First Spouse — Should Be Today?
286. Is Animal Testing Ever Justified? 287. What Is Our Responsibility to Lab Animals? 288. What Are Your Thoughts About Hunting Animals? 289. Should We Be Concerned With Where We Get Our Pets? 290. What Do You Think of Pet Weddings? 291. Is It Wrong to Focus on Animal Welfare When Humans Are Suffering? 292. Should We Bring Back Animals From Extinction? 293. Are Zoos Immoral? 294. Do Bugs Deserve More Respect?
Environment and Science
295. What Role Should Young People Play in the Fight Against Climate Change? 296. Should We Be More Optimistic About Efforts to Combat Climate Change? 297. How Far Is Too Far in the Fight Against Climate Change? 298. Should Plastic Bags Be Banned Everywhere? 299. Is It Ethical to Create Genetically Edited Humans? 300. Should We Still Be Sending Astronauts to Space? 301. Do You Think Pluto Should Be a Planet? 302. Should We Treat Robots Like People?
Time and Seasons
303. What Is the Best Month of the Year? What Is the Worst? 304. Would Life Be Better Without Time Zones? 305. Do You Think It Is Time to Get Rid of Daylight Saving Time? 306. When Do Holiday Decorations Go From Festive to Excessive? 307. Should We Rethink Thanksgiving? 308. When Does a Halloween Costume Cross the Line? 309. Should School Be a Place to Celebrate Halloween? 310. Should the Week Be Four Days Instead of Five?
Students 13 and older in the United States and Britain, and 16 and older elsewhere, are invited to comment. All comments are moderated by the Learning Network staff, but please keep in mind that once your comment is accepted, it will be made public and may appear in print.
Find more Student Opinion questions here. Teachers, check out this guide to learn how you can incorporate these prompts into your classroom.
Natalie Proulx joined The Learning Network as a staff editor in 2017 after working as an English language arts teacher and curriculum writer. More about Natalie Proulx

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The purpose of a persuasive speech is to convince your audience to agree with an idea or opinion that you present. First, you'll need to choose a side on a controversial topic, then you will write a speech to explain your position, and convince the audience to agree with you. You can produce an effective persuasive speech if you structure your ...
How to write a persuasive speech. Incorporate the following steps when writing a persuasive speech: Step 1 - Identify the type of persuasive speech (factual, value, or policy) that will help accomplish the goal of the presentation. Step 2 - Select a good persuasive speech topic to accomplish the goal and choose a position. How to write a persuasive speech
Tips for Writing a Persuasive Speech Putting together a three-minute speech can be daunting—especially if you've never written one before! The key to effective communication lies in a well organized, clearly articulated, and thoroughly researched and sourced argument. The following outlines the basic format of a persuasive speech, but ...
Persuasive Speech Outline, with Examples. A persuasive speech is a speech that is given with the intention of convincing the audience to believe or do something. This could be virtually anything - voting, organ donation, recycling, and so on. A successful persuasive speech effectively convinces the audience to your point of view, providing ...
To write a persuasive speech, start with a strong opening that will make your reader want to pay attention, including an attention grabber, your credentials, the essay's goal, and a road map for the essay. Next, offer persuasive evidence or reasons why the reader should support your viewpoint. Arrange these points logically, use credible ...
Use short words. Write short sentences. Avoid awkward constructions that might cause a speaker to stumble. Tip: Read the speech aloud as you're writing. If you do it enough, you'll start ...
Step 2: After the Story, Now, Give Your Advice. When most people write a persuasive presentation, they start with their opinion. Again, this makes the listener want to play Devil's advocate. By starting with the example, we give the listener a simple way to agree with us.
Persuasive Speech is a category of speech that attempts to influence the listener's beliefs, attitudes, thoughts, and ultimately, behavior. They are used in all contexts and situations. It can be informal, a teenager attempting to convince his or her parents for a sleepover at a friend's house. It can also be formal, President or Prime ...
11 Tips for a persuasive speech. Now that you know which persuasive speech style suits you best, we are ready to write our persuasive speech. Here are our eleven tips and tricks: Credibility. Do not slack when it comes to research. People will automatically be drawn to someone who can establish credibility on stage.
Once you've chosen your persuasive speech topic (our list of 110 riveting persuasive speech ideas is coming next!) and completed your research on the subject, you'll begin the writing process. Use this step-by-step approach to produce an outstanding speech that easily persuades your audience to adopt your viewpoint.
Not sure where to start with writing a persuasive speech? With these six steps, learn how to write a persuasive speech easily and captivate your audience.
Through this analysis, you will learn how speakers and writers persuade an audience to adopt their point of view. Built around Harvard Professor James Engell's on-campus course, "Elements of Rhetoric," this course will help you analyze and apply rhetorical structure and style, appreciate the relevance of persuasive communication in your ...
When writing a persuasive speech, you want to make it seem like you're speaking directly to each and every audience member. As Richard Greene explains, "I want to get every single person to feel that they're having a direct connection and direct communication with me.". Asking questions is a great way to get your audience engaged ...
Persuasive Speech Writing Examples. Many persuasive speeches are political in nature, often addressing subjects like human rights. Here are some of history's most well-known persuasive writing examples in the form of speeches. I Have a Dream by Dr. Martin Luther King Jr.
Writing a persuasive speech is a structured process that makes your message compelling and effective in conveying ideas to the audience. Here's a step-by-step guide to help you craft a persuasive speech: Step 1: Choose a Persuasive Topic. Selecting the right topic is the foundation of a persuasive speech. Look for subjects that you are ...
Start your persuasive speech with a strong introduction, grabbing the attention of your audience. This can be emotional, shocking, or funny - as long as it is powerful. After you have your audience's attention, you should clearly introduce the topic of your speech. You now need to distil your research into a few key arguments.
112 Engaging Persuasive Speech Topics. Tips for Preparing Your Persuasive Speech. Writing a stellar persuasive speech requires a carefully crafted argument that will resonate with your audience to sway them to your side. This feat can be challenging to accomplish, but an engaging, thought-provoking speech topic is an excellent place to start.
This ability will help you engage in civil discourse and make effective changes in society. Even outside the political sphere, conveying a convincing message can benefit you throughout your personal, public, and professional lives. This course is an introduction to the theory and practice of rhetoric, the art of persuasive writing and speech.
You can map each point with a respective counterargument using a mind-mapping tool for a structured and more organised approach. #2. Cut down the fluff. How to write a persuasive speech. This is no time to flex your wealth of ultra-complicated technical words. The idea of a persuasive speech is to get your point across verbally.
Policy persuasive speeches are often used in political or advocacy settings, where the speaker seeks to influence the audience's actions or decisions on a particular issue or policy. Example: Proposing a ban on single-use plastics to reduce environmental pollution and promote sustainable practices. Writing a persuasive speech: step-by-step guide
The aim of a persuasive speech is to inform, educate and convince or motivate an audience to do something. You are essentially trying to sway the audience to adopt your own viewpoint. The best persuasive speech topics are thought-provoking, daring and have a clear opinion. You should speak about something you are knowledgeable about and can ...
Tips for Writing and Structuring a Persuasive Speech That Captivates Your Audience. 1. Use thorough analysis: Before you start writing your speech, take the time to thoroughly analyze your topic. Understand the problem, cause, and potential solutions, and gather relevant evidence and references.
Every school day, we publish new questions for students based on the news of the day, including prompts, like these, that inspire persuasive writing. Below, we've rounded up over 300 of those ...