Jun 21, 2023

Proposal Essay Examples: Convincing Ideas for Your Research Paper or Essay
Dive into the power of persuasive writing through captivating proposal essay examples. Explore ideas that inspire, enrich your work, and unlock impactful proposal crafting. Prepare to elevate your writing and leave a lasting impression!
Writing a compelling proposal essay often presents a challenge for many students. A large proportion can't distinguish a research paper proposal from a proposal essay, and even more find difficulty in creating persuasive ideas for their essays. If this situation resonates with you, rest assured you're not alone.
In this extensive guide, we aim to simplify the process of writing a proposal essay. We provide a host of resources such as examples of proposal essays, a carefully constructed outline template, and proven writing techniques. Our guide, honed through years of experience in academic writing, is specifically designed to help you achieve high grades in your proposal essay assignment.
Embark on this journey with us to uncover the nuances of crafting an excellent proposal essay. Armed with the correct resources and guidance, you will transition from uncertainty to confidence, ready to produce an impressive proposal essay. Let's start delving into the craft of writing an engaging proposal essay.
What is a Proposal Essay?
An essay proposal is a document that outlines the content and purpose of your proposed essay. Whereas a thesis conveys the central concept of your study, an essay proposal summarizes the intent and substance of a specific essay.
A proposal essay also serves as a detailed plan of action addressing a particular problem. The writer identifies a problem, suggests a solution, and provides evidence to persuade the reader to agree with the proposed solution or idea. In essence, your role as a writer is to convince the reader that your concept is exceptional and that they should support its execution.
These essays function as a strategic tool, enabling you to sell an idea, belief, or yourself in a manner that not only piques the reader's interest but also convinces them of your capability to bring the proposed plan to fruition. Although proposal essays are frequently associated with business and economics disciplines, they extend beyond these fields.
Proposal essays fundamentally promote critical thinking and problem-solving skills among students. They allow you to venture beyond the structured academic syllabus and engage with real-world issues that require innovative solutions. Writing a proposal essay, therefore, is an opportunity to demonstrate your analytical acumen and your capacity to think creatively.
How to Write a Proposal Essay
Writing a compelling proposal essay requires careful planning, thorough research, and meticulous execution. Here are the steps to ensure your proposal essay stands out:
1. Understand Your Audience: Begin by identifying your target audience. Who are they, and what is their role in the context of your proposal? What are their needs, concerns, or interests? Understanding your audience's perspectives helps in tailoring your message, increasing the chances of your proposal being accepted.
2. Research Thoroughly: Deep and broad research is crucial. Even if you're well-versed with the topic, there is always more to learn. Look at what experts in the field have said and how your proposal aligns or diverges from their views. This research will not only fortify your arguments but also make your essay more credible and authoritative.
3. Create a Detailed Plan: Once you've completed your research, start to structure your essay. Begin with an introduction where you present the problem or issue. Then, propose your solution in the body paragraphs, where each paragraph should focus on a single point or argument, supported by evidence. Finally, wrap up your proposal in the conclusion by summarizing your key points and reinforcing the significance of your solution.
4. Write Your First Draft: Start writing your essay based on the plan you have created. Be clear and concise, avoid jargon, and make sure your arguments are logically constructed and easy to follow.
5. Revise and Edit: After completing your first draft, it's important to revisit it with a critical eye. Look for areas where your argument can be strengthened, check for coherence and flow, correct grammatical errors, and ensure your language is clear and precise. It may be helpful to have others review your work for a fresh perspective.
6. Proofread: Once you're satisfied with the content of your essay, proofread it one final time to catch any minor mistakes or inconsistencies. Remember, a polished essay demonstrates your diligence and commitment to quality.
By following these steps, you can create a persuasive, well-structured proposal essay that effectively communicates your idea and its value.
Structure of a Proposal Essay
Writing a proposal essay requires a specific structure that enables you to present your idea clearly and persuasively. Here's an overview of the necessary elements:
1. Introduction: Your introduction sets the stage for your proposal. It should include a captivating hook that draws readers in, and a clear thesis statement that summarizes your proposal. For Example: A feasible approach to decreasing the alarming mortality rate among young mothers is by equipping parents with necessary skills to support their teenage daughters who become pregnant.
2. Problem Statement: After the introduction, delve deeper into the problem your proposal aims to solve. Describe its nature, roots, and implications. Clarify why it's critical to address this problem, how it affects your readers, and what benefits solving it would bring.
3. Proposal Statement: In this section, elucidate your proposal in detail. Describe the solution you've come up with, highlighting both its benefits and potential drawbacks. Ensure you present your idea as the optimal solution to the problem at hand.
4. Implementation Plan: Next, explain how you plan to execute your proposal. This should be a clear and comprehensive guide demonstrating the practicability of your solution. Identify potential obstacles that might arise during implementation and include steps to overcome them. Discuss why your approach is unique and why previous attempts to solve the problem have failed.
5. Expected Outcome: Here, discuss the positive results you expect from the implementation of your proposal. Provide a clear, concise picture of the improvements and advantages your solution will bring. 6. Evaluation: In this section, provide an estimate of the resources, including time, money, and expertise, necessary to implement your proposal. Discuss its feasibility within the current situation and address possible objections or criticisms from those who might disagree with your proposal.
7. Timeline and Required Resources: Clearly specify the resources required to implement your proposal, such as manpower, funds, and equipment. Include a timeline if possible, giving a chronological order of the steps to be taken.
8. Conclusion: Summarize the key points of your essay and reaffirm the significance of your proposal. This is your final opportunity to convince your readers, so end with a powerful call to action.
Avoid introducing new ideas in the conclusion, as it can confuse readers and may unnecessarily elongate your essay. Stick to wrapping up what you've already presented and reemphasizing its importance.
Proposal Essay Examples
In the following section, we present a collection of Proposal Essay Examples. These essays serve as excellent references for those looking to understand the structure and content of a compelling proposal.
Each one addresses a unique and important topic, provides an insightful problem statement, proposes thoughtful solutions, and concludes by summarizing the main points. These examples illustrate the effective strategies used in proposal writing to engage readers and convincingly present an argument.
Let's delve into these intriguing examples to inspire and enhance your proposal writing skills.
1. Reducing Plastic Waste: A Proposal for Action
Introduction:
With the escalating global environmental crisis, the specter of plastic waste looms large. Forecasts from the United Nations indicate that, failing to reduce plastic waste, we'll have more plastic than fish in the oceans by 2050. This proposal aims to present tangible solutions to this predicament.
Problem Statement:
The unchecked production and disposal of plastic products significantly contribute to plastic waste, endangering the environment and marine life. Given the lifespan of plastic waste—lasting centuries—it's crucial to devise an effective solution to curb plastic production.
Suggested measures to combat plastic waste include:
Government-imposed ban on single-use plastic items, such as straws, cups, and cutlery.
Government incentives encouraging the use of reusable products.
Awareness campaigns conducted by the government and NGOs about the environmental impact of plastic waste.
Investments in improved waste management systems for the proper handling of plastic waste.
Conclusion:
Reducing plastic waste is an urgent priority. By implementing the proposed measures, we can alleviate the issue, protect our environment and marine life, and build a more sustainable future.
2. Dangers of Texting While Driving
Despite countless warnings and campaigns, texting while driving remains a widespread, dangerous habit. This essay investigates the perils of this behavior and proposes measures to mitigate it.
Texting while driving constitutes a severe distraction, often leading to road accidents. Studies even rank it as more dangerous than drunk driving, as it considerably delays a driver's reaction time.
To address this peril, the following steps are suggested:
Launching educational programs and campaigns to inform drivers about the risks of texting while driving.
Implementing stricter penalties for drivers caught in the act.
Promoting technologies that restrict texting while driving.
Texting while driving is a lethal habit that warrants immediate attention. By raising awareness, enforcing stricter rules, and employing technology, we can significantly cut down road accidents due to distracted driving.
3. The Causes of Homelessness
Homelessness, affecting millions worldwide, is a complex and pressing social issue. This essay explores the causes behind homelessness and suggests viable solutions.
Causes of Homelessness:
Poverty, mental illness, addiction, and family breakdowns constitute the four primary triggers of homelessness.
To alleviate homelessness, the following steps are suggested:
Stimulate the supply of affordable housing by offering financial incentives to developers and reducing zoning restrictions.
Facilitate access to mental health services, addiction treatment, and support services for individuals and families experiencing homelessness.
Alleviate poverty by raising the minimum wage, providing job training, and enhancing access to education and healthcare.
Addressing homelessness calls for a comprehensive and coordinated effort. By implementing the proposed measures, we can significantly reduce homelessness, emphasizing our collective responsibility to extend support to those grappling with this issue.
Final Words
In conclusion, crafting a persuasive proposal essay involves thoughtful planning, in-depth research, and adept writing techniques. With Jenni.ai's cutting-edge AI tools at your disposal, this process becomes simpler, enabling you to create standout proposal essays. Take this opportunity to enhance your writing skills and leave an enduring impression on your audience. Experience the transformative capabilities of Jenni.ai today!
Try Jenni for free today
Create your first piece of content with Jenni today and never look back

How to Write a Proposal Essay/Argument

It is common for students to be assigned to a proposal essay assignment. Although many can write it based on the essay prompt, 4 out of 10 students find it hard to complete a proposal argument essay. Out of the ten requests we receive requiring our experts to help write proposal essays, four students appear to be confused between a proposal essay and a research proposal.
Not anymore because in this article, our senior research proposal writers put together their wits and insights to help you understand how to write a high-quality and effective proposal essay. We also provide a succinct sample and outline to help you do so quickly. This is a cheat sheet to scoring the best grades because we have tips and tricks that will make you ace your proposal essay.
What is a proposal essay?
As the name suggests, a proposal essay or paper is a type of academic paper that proposes an idea by providing evidence intended to convince the reader why an idea is good or bad.
It is sometimes referred to as a proposal argument essay, written if there is a problem to fix or a change to be made.
For instance, instead of just arguing that cigarette smoking affects health, it would be prudent to make a good argument on why there is a need to reduce the number of teenagers who are becoming cigarette addicts.
Even though proposals are written in business, economics, and management fields, they are also written by students, scientists, and other professional domains.
A proposal essay:
- Convinces the reader to adopt a given or proposes idea/change
- Shows the mastery of the concepts in a given field
- It makes a case for the implementation of an idea or change process
- Confirms the feasibility, practicality, and applicability of a program, idea, or change
Things to do/know before beginning
The pre-writing stage is the most critical part as it defines how smooth the entire writing process would be. Before typing or penning down the first sentence or even sitting down to write your proposal, there are certain mandatory rituals that you need to observe.
Primarily referred to as the proposal essay planning stage, here are the five steps to take:
1. Profile your target audience
A proposal essay or proposal argument aims to convince your audience that an idea is feasible, relevant, and practical. It might also persuade the readers that an idea is not worth pursuing.
As such, you need to have a deep understanding of your target audience. Are they business people or academics? What is their level of knowledge of the issue? What do you want to inform them about and why? Will they buy your suggestion? What is the best approach?
Understanding and profiling your audience helps you set the scope and tone of the proposal essay. For instance, when writing for the management and business people, proposing an idea with financial benefits could win their trust and time. On the other hand, when writing for healthcare workers, presenting strategies to improve patient quality, healthcare workers� wellbeing, and access to care could be relevant.
When you understand the people, who will read your proposal, you can quickly structure it better to draw their attention right from the start.
You need to consider what you need the audience to understand from your proposal. As well, you have to provide them with some facts that will help in decision-making. It also helps to choose a preferred style that will impress the readers.
It is about knowing what you are writing for to make them acknowledge the gist of the proposal. In the academic contexts, the audience is a professor, teaching assistant, associate professor, or instructor/lecturer. In this case, stick to the proposal essay prompt.
2. Define your research problem
With the audience in mind, you need to show that you understand the problem. One way of doing so is to highlight or state your situation so that your audience know the idea in the proposal.
This stage helps you win the trust of the readers. It also enables you to create an impression that you are knowledgeable about the issues at hand. Support your arguments with facts, references, and credible views to establish your identity/ethos.
Where necessary, ensure that you clarify and offer enough proof. Make sure to state the problem and why you feel it needs to be solved. It is the same aspect that appears in the introduction of a problem-solution essay .
When writing your problem statement section, ask yourself:
- What is the main issue? Use statistics, facts, and examples
- Who is affected by the issue? Who are the stakeholders?
- What has been done before?
- Why are previous/conventional solutions not working?
- Why will your innovative idea/solution works?
- How urgent is the problem or solution required?
- What are other researchers saying about the problem?
In sum, you need to prove that you have thoroughly researched and assessed the issue. Your problem statement must display your knowledge about the topic.
3. Research and gather sources
After outlining the problem, you now need to research how to solve it. Use secondary and primary sources to support your claims/proposal. As you persuade your readers, ensure that you report on what has worked and what has failed.
As you do so, ensure that your proposed solution is well-backed with evidence from credible and relevant scholarly literature.
As a rule of thumb, stick to research articles written five years ago unless otherwise instructed by the professor/instructor to use older sources.
4. Write your proposal outline
With the problem statement and the sources backing your proposal in place, it is now time to explain your answer.
You now have the problem, and you should strive to solve it. Before writing the proposal essay outline , ensure that you have read the request for proposal (RFP) prompt or template.
An outline helps you structure your proposal, find means of convincing difficult readers and coherently lay the sections. It also helps brainstorm excellent ideas and approaches then organizing them into a comprehensive and structured proposal format. We will present a sample outline later in this article.
5. Proceed to write the essay
After having the skeleton of your proposal, it is now time to write your first draft by filling in the various parts. Once you are done, revise the draft as much as possible or enlist for proofreading and editing before turning in the final draft.
Sections of a Proposal Essay/Argument
We have summarized the main parts of a proposal essay in this section. Note that the sections might differ depending on the preferred elements by your university or college. In this regard, some parts might be added or omitted. When writing, you can alter the body of your proposal to meet your needs.
1. Title Page
This is for you if you are wondering how to title your proposal essay. Like the dissertation, theses, or research papers, the proposal essay has a title page that includes:
- The title of your proposal essay, e.g., Rethinking Recycling: Why Reusing Needs to Be User Friendly.
- Your full official names
- The name of your professor/instructor/lecturer
- Name of your school and department
Depending on your college or university, or department, the title page could differ. There are also institutions with pre-written/designed title pages sent alongside the instructions. The bottom line is that you need to read the assignment prompt or the RFP file carefully.
2. Introduction
Your introduction is the entry point to your essay. Like any other essay introduction , the proposal essay introduction gives a brief background of the proposal. It introduces the subject to your audience (s).
As it is the most crucial section, it needs to be well written. You can begin it using a hook, mostly facts, statistics, or statements. It should also have a topic sentence that introduces the readers to a topic. Ensure that it has a relevant topic that entices the audience on why they should care about the particular topic.
The introduction then has a thesis statement that contains the proposal you are making for solving a problem. In a proposal essay, the thesis should clearly state the proposition . An example of a good thesis statement when writing a proposal essay on teenage pregnancy could sound like:
Although teenage pregnancy is considered a taboo topic, educating parents on how to take care of the teenage girls with pregnancy could reduce the high mortality rate of teen mothers.
If you were to write a proposal essay on childhood obesity, a good thesis statement could read:
Childhood obesity is a menace affecting society, creating public health pressure and needs to be solved through proper school-based health promotion activities that involve the parents.
Another example of a good thesis statement for a proposal essay on depression is:
Depression has claimed the lives of many people and needs to be addressed through multi-professional collaboration among teachers, healthcare workers, media core, governments, and employers.
Again, your thesis statement should highlight the problem and the solutions that you are proposing. It narrows down to knowing your audience so that your introduction emphasizes the benefits of the proposal to this specific audience.
4. Problem statement
Even though you have already stated the problem in your introduction paragraph, you need to expound on the problem. Explain why there is a need to solve the issue. Here, your aim is to invite the readers to understand the core of your proposal. State the aims of your proposal and declare the importance of the topic in this section.
The section helps you to assert the issue. The section defines and expounds on the specific issue, the sources, and the consequences.
You also need to highlight why the issue needs to be solved and how solving it impacts the reader. Instead of using moral principles or universal pleas to feelings, think of what is important to your reader.
5. Proposal/Statement of purpose
After broadly defining your problem in the first paragraph of the body of your proposal essay, you now need to state the purpose of the essay. The section is exclusively meant to discuss the proposal that you are making.
Take your time to explore the advantages and disadvantages of your proposed solutions, change, or ideas. It can be a few sentences long if it is a shorter proposal or a few paragraphs if it is a long proposal.
6. Action Plan
After highlighting the proposed solutions, changes, or ideas, it is now time to write the plan of action. Here your focus is on the implementation of the ideas or solutions.
You need to show the audience that the solutions or changes are practical, feasible, relevant, and desirable.
When writing this section, you need to convince the readers that your proposal is a good idea over other available option. Furthermore, you must provide a detailed explanation about the implementation of the solutions or changes. Ensure that you anticipate the potential barriers or challenges during the implementation phase because every proposal must highlight the challenges and how to overcome them.
As you do so, also look at the viability, relevance, practicality, and desirability of your proposal. Will it work? What has prevented past solutions from working? What is different about your proposal?
7. Desired Outcomes
As the name suggests, this is the section of the essay that you anticipate the outcomes of your proposal. It is your chance to make everything you have been writing about clear.
8. Evaluation
When writing the evaluation phase, you need to consider the cost and resource implications of your proposed idea or change. Is the idea feasible compared to what is there currently? As well, you need to include the contrary opinions of the dissenting voices over the proposed solutions. Assure the audience that despite the challenges, the proposed solution will work.
9. Resources Required and timeline
Explain the resources such as skills, finances, time, and equipment that are required to implement your change, solutions, or ideas.
10. Conclusion
Your conclusion needs to emphasize your proposal and leave your audience with a call to action. State your proposal, call to action, and why the audience must consider your suggestions.
Never include new information in your conclusion, as that would extend the word count as you try to expound on the new topic and further confuse your already settled/convinced audience.
11. Works cited/references/bibliography
Any academic paper, white paper, or professional paper must have citations. We use citations to avoid plagiarism by mentioning those we read their work while writing our own. Depending on your chosen format: APA, MLA, Harvard, or Chicago format, the title can be references, bibliography, or works cited. Works cited is exclusively for MLA, while references can be used for both APA and Harvard. In Chicago format, you will title the consulted resources as Bibliography. In Harvard format, you can use either references or a reference list. Remember, a bibliography includes all the relevant sources you read, even those not cited in the paper.
Sample Proposal Essay Paper (in image format)
Below is a proposal argumentative essay on climate change, focusing on recycling courtesy of Excelsior Online Writing Lab .
Note that the sections are not titled. However, the paragraphs have been organized around our suggested parts.

Proposal Essay Structure: Video
Here is a video that explains the structure of a proposal argument
Final Words
Now that you�ve learnt how to write a proposal essay, you can conquer this type of assignment without a doubt. However, if you are stuck, you can hire an essay writer to write one for you.
Related Reading: Good persuasive speech topics.
We are known as the best website that writes essays for any level . Our professional writers are experts and masters in writing any type of essay. So, if you just hate writing essays, we can take over the process from you. We can edit and proofread your essay, polish your essay, and write you an essay outline.
Now that you have read this visit our blog for more college essay ideas . Be kind to share with friends as well.
Here are some commonly asked questions about the process of writing a quality proposal essay or proposal argument. You can send your questions, and we will answer them to enlighten our readers.
What is the format for a proposal essay?
Here are the main parts of a proposal essay:
- Introduction ( hook , background, thesis statement (proposal))
- Problem statement
- Statement of purpose/proposal declaration
- Plan of action
- Resources require
- References/works cited
What makes a good proposal essay?
A good proposal essay proposes an idea and offers evidence or arguments to convince the readers about the goodness or badness of the idea. A good one:
- Has all claims well-supported
- It is organized into paragraphs
- It does not have filler words
- Uses relevant and recent credible/scholarly sources
- Cites all the sources, especially quotes, to avoid plagiarism
- Uses formal language to present ideas
- Has well-balanced, coherent, clear, explained, and concise paragraphs
- Every paragraph stick to an idea
- Has a thesis statement that stands out
- Begins with a good hook
How do you write a proposal essay?
Here are the steps that are taken to write one:
- Read the proposal prompt
- Select a good topic or area that interests you
- Research on the issue you want to solve
- Write an outline for your proposal
- Write the first draft of your proposal
- Polish, edit, and re-read your proposal
- Submit the proposal essay through Canvas, Turnitin, SafeAssign, DropBox, or any platform as suggested by the instructor
- Enjoy your grades
Is the proposal essay similar to the research proposal paper?
No. while a proposal essay leaves the audience with a call to action, a research proposal paper highlights the strategies and steps a researcher will take to conduct research, just like a thesis and dissertation proposal. A proposal essay tackles an issue by suggesting change, ideas, or solutions based on the available information from scholarly literature.
It ends with the audience making the decision. On the other hand, a research proposal ends with the researcher conducting a study followed by writing a final research paper, term paper, dissertation, or thesis that details recommendations, suggestions, and conclusions.
What are the topics for proposal essays?
Suppose you need a good proposal essay topic; you need to think of areas such as healthcare, homelessness, world hunger, poverty, abortion, climate change, vaping, human and organ trafficking, and mental health.
You can also brainstorm topics relating to gun violence, gun control, election fraud, drink driving, teenage pregnancy, police brutality, pollution, COVID-19, cyberbullying, and cigarette smoking. The bottom line is to choose an exciting topic with credible scholarly articles and details.
Does a proposal essay need an annotated bibliography?
Unless otherwise stated on your essay prompt, including the reference as per the sample above is enough.
Does a proposal essay require research questions?
No, unlike the research proposal, a proposal argument or proposal essay does not require research questions since no research is being conducted. The purpose of such essays is to propose a solution, more like the problem solution essay.

Gradecrest is a professional writing service that provides original model papers. We offer personalized services along with research materials for assistance purposes only. All the materials from our website should be used with proper references. See our Terms of Use Page for proper details.

Home — Essay Types — Proposal Essay
Proposal Essay Examples
Exploring proposal essay topics opens up a realm of possibilities for addressing various issues and challenges, ranging from practical business plans to cutting-edge engineering solutions. These topics serve as the foundation for constructing well-reasoned proposals, demonstrating the thoughtfulness and ingenuity of the writer. Whether you are delving into Economics, Business Management, Engineering, or any other field, proposal essay topics provide the canvas upon which your innovative ideas can be sketched and evaluated.
Proposal Essay Ideas and Topics
The realm of proposal essays is vast and encompasses a multitude of ideas and topics across various disciplines. Here are a few proposal essay ideas and topics, along with some proposal essay examples, to inspire your own academic exploration:
- Environmental Sustainability : Propose initiatives to combat climate change and promote sustainable practices in urban areas.
- Education Reform: Offer innovative solutions to enhance the quality of primary and secondary education, addressing challenges such as remote learning and educational inequality.
- Healthcare Access: Propose policies to improve access to healthcare services, especially in underserved communities.
- Business Strategies: Suggest strategies for small businesses to thrive in the digital age, adapting to evolving market trends and consumer behaviors.
- Technological Advancements: Explore proposals for ethical and sustainable technological advancements, focusing on areas like renewable energy sources or artificial intelligence ethics.
Proposal Argument Essay Topics
Proposal argument essay topics encompass a wide range of issues and ideas that can be explored and debated. These topics typically revolve around proposing a solution or course of action to address a specific problem or challenge. Here are some proposal argument essay topics to consider:
- Implementing Stricter Gun Control Laws to Reduce Gun Violence
- Promoting Sustainable Agriculture and Reducing Food Waste
- Reforming the Criminal Justice System to Focus on Rehabilitation
- Addressing the Student Loan Debt Crisis with Debt Forgiveness Programs
- Combating Climate Change through Renewable Energy Initiatives
- Improving Mental Health Support and Services in Schools
- The Impact of Technological Advancements
- Promoting Gender Equality in the Workplace through Pay Equity Measures
- Enhancing Cybersecurity Measures to Protect Personal Data
- Combating Childhood Obesity through Healthier School Lunch Programs
When considering a topic for your proposal argument essay, it's essential to choose one that aligns with your interests and allows you to present persuasive arguments supported by compelling evidence and reasoning.
Topic Proposal Essay Example
You might explore the benefits of implementing community policing programs as a solution to improve trust, transparency, and cooperation between the police and the community—a topic proposal essay example that addresses real-world issues and proposes practical solutions for positive change.
These proposal argument essay topics cover a wide range of social, political, environmental, and economic issues, providing ample opportunities for in-depth research and critical analysis. Select a topic that resonates with your passion and enables you to construct a convincing argument for your proposed solution.
In conclusion, a proposal essay is a valuable genre of academic writing that allows students to delve into critical issues, propose solutions, and support their ideas with sound research and evidence. It serves as a platform for innovative thinking and problem-solving across various academic disciplines.
What is a Proposal Essay
A proposal essay is a type of academic writing where the author presents a problem and proposes a solution or course of action to address that problem. This type of essay is often assigned in college courses, and its primary goal is to persuade the reader or audience that the proposed solution is viable, effective, and well-reasoned. To better understand how to craft a proposal essay, it can be helpful to explore proposal essay examples , which you can find on our essays base.
Proposal essays can cover a wide range of topics, from social and environmental issues to business and policy proposals. They are a valuable exercise in critical thinking, research, and persuasive writing, as they require the author to analyze a problem, develop a well-considered solution, and present it convincingly to an audience. These essays are commonly assigned in college courses to assess students’ ability to think critically and propose practical solutions to real-world problems.
Proposal and personal narrative essays are distinct in their purpose, structure, and content. A proposal essay aims to persuade the reader to accept a proposed solution to a problem or support a specific course of action. It typically includes an introduction presenting the issue, a statement of the proposed solution, evidence supporting the proposal, and a conclusion summarizing the argument. On the other hand, a personal narrative essay recounts a personal experience or event and reflects on its significance. It often involves vivid storytelling, introspection, and conveying emotions to engage the reader and convey a deeper understanding of the narrator’s journey.
How to Write Proposal Essay and Tips for Success
Navigating the world of proposal essays can be a daunting task, especially when faced with a vast array of potential topics. The key to success lies in understanding how to craft a proposal essay that not only captures the attention of your professor and audience but also persuades them to take action. When writing a proposal essay , consider these essential steps and tips to create a compelling and persuasive piece of academic writing.
Much like a research outline, a proposal essay delves into an event or argument, providing compelling reasons for why a particular action should be taken or why a certain social event may not be beneficial. The structure of your proposal will largely depend on your chosen topic and objectives. For instance, financial reports may necessitate the inclusion of statistical data, while fashion studies may require a different approach to essay writing. When learning how to write a proposal essay , it’s crucial to tailor your approach to your specific subject matter. The overarching goal is to present a clear and convincing piece of evidence right from the introduction.
By incorporating insights and exploring proposal essay examples , you can confidently craft compelling proposals that leave a lasting impact.
How to Write Proposal Essay Introduction
The introduction of a proposal essay plays a crucial role in engaging the reader and setting the stage for the proposal’s main arguments. It typically begins with a hook or attention-grabbing statement to draw the reader in. Here’s a proposal essay introduction example :
“Imagine a community where families struggle to put food on the table, where children go to bed hungry each night. This is the harsh reality faced by many residents in our town. In this proposal essay, we will address the pressing issue of food insecurity in our community and present a viable solution that can make a significant difference—the establishment of a community food bank. This proposal aims to not only alleviate hunger but also foster a sense of unity and support among our residents. In the following sections, we will explore the reasons behind food insecurity, the benefits of the proposed food bank, and the steps needed for its successful implementation.”
This introduction effectively grabs the reader’s attention by highlighting a pressing issue and presenting the proposed solution, setting the stage for the essay’s main arguments and supporting evidence.
Structuring Your Proposal Essay
At its core, a proposal essay is similar to a research outline, where you will discuss an event or argument and provide compelling reasons for why a particular action should be taken or why a certain social event may not be beneficial. The structure of your proposal will largely depend on your chosen topic and objectives. For instance, financial reports may necessitate the inclusion of statistical data, while fashion studies may require a different approach to essay writing. Regardless of the topic, the overarching goal is to present a clear and convincing piece of evidence right from the introduction.
- Introduction with a hook sentence.
- Thesis statement .
- Three body paragraphs where you set your objectives by explaining your proposal with the statistical data, surveys, and other facts.
- Conclusion . It must be kept brief as you work on your topic. The major part should be taken from your proposal’s justification.
- A literature review.
To craft a proposal essay, consider these essential elements:
- A captivating introduction : Grab the reader’s attention from the outset by highlighting the significance of your topic and why it warrants consideration.
- A well-defined problem statement: Clearly articulate the issue or challenge that your proposal aims to address.
- A compelling solution: Propose a well-thought-out solution to the identified problem, ensuring its feasibility and effectiveness.
- Supporting evidence: Substantiate your proposal with relevant data, research findings, or expert opinions.
- A persuasive conclusion: Reiterate the significance of your proposal and its potential impact, leaving a lasting impression on the reader.
7 Most Common Proposal Essay Mistakes to Avoid
Addressing these common mistakes will significantly improve the quality and effectiveness of your proposal essay.
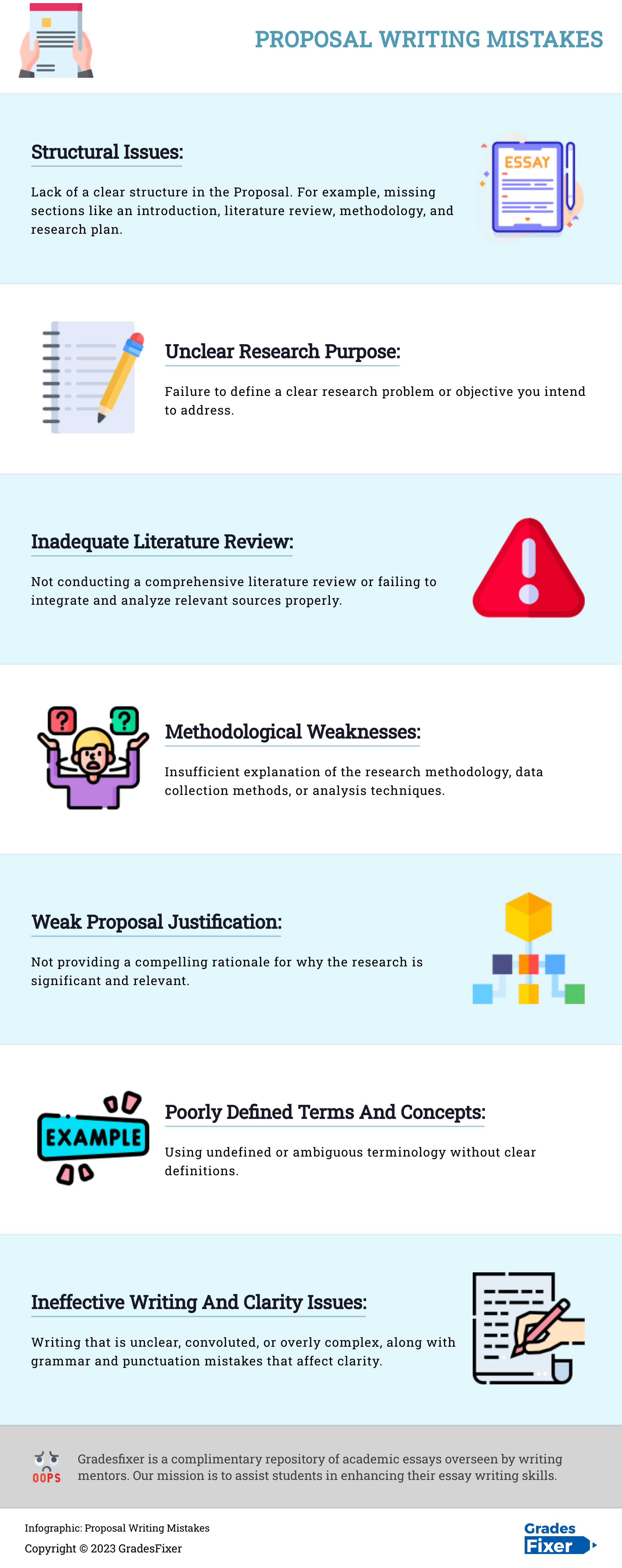
Examples of a Proposal Essays
To further enhance your understanding, let’s delve into a few examples of proposal essays :
- Example 1 : Advocating for a Greener Campus
Propose the implementation of sustainable practices on campus, such as energy-efficient lighting, recycling programs, and composting initiatives.
- Example 2: Addressing the Issue of Homelessness
Advocate for the establishment of a community shelter or propose a volunteer program to assist the homeless population.
- Example 3 : Promoting Healthy Eating Habits
Suggest the introduction of healthier food options in school cafeterias or advocate for nutrition education programs.
Remember : Tailor your proposal essay to the specific requirements of your assignment and ensure it aligns with your chosen topic.
How to Write a Proposal Argument Essay
Writing a proposal argument essay involves a structured approach to presenting your ideas, arguments, and proposed solutions to a specific issue or problem. Here are the key steps to follow when learning how to write a proposal argument essay :
- Choose a Relevant Topic
- Research Extensively
- Identify Your Audience
- Craft a Strong Thesis Statement
- Outline Your Essay
- Write a Compelling Introduction
- Present Your Arguments
- Address Counterarguments
- Propose Solutions
- Conclude Effectively
- Revise and Edit
- Cite Sources
- Seek Feedback
Remember that a well-written proposal argument essay presents a clear problem, provides compelling evidence, and offers practical solutions while considering the needs and perspectives of the audience.
Key Differences Between Proposal Argument Essays and Proposal Essays
The key difference between proposal argument essays and proposal essays is that proposal argument essays argue for why their proposal is the best one, while proposal essays do not. Proposal argument essays are also typically more persuasive than proposal essays.
Proposal argument essay examples :
- An essay that proposes a new law to reduce gun violence.
- An essay that proposes a new program to help homeless people find housing.
- An essay that proposes a new marketing strategy for a business.
Proposal essay examples:
- An essay that proposes a new curriculum for a school.
- An essay that proposes a new event for a community.
- An essay that proposes a new product or service for a company.
Which Type of Essay Should You Write?
The type of essay that you should write depends on your assignment and your audience. If you are writing an essay for a class, your professor will likely tell you which type of essay to write. If you are writing an essay for a professional audience, you should choose the type of essay that will be most effective in persuading your audience to support your proposal.
Both proposal argument essays and proposal essays can be effective ways to communicate your ideas and persuade others to support your cause. When choosing which type of essay to write, it is important to consider your assignment, your audience, and the purpose of your essay.
General Essay Proposal Examples
Proposal essay writing checklist.
Instead of offering a classic structure template that won’t relate to your course topic, you must follow our free checklist that will provide you with much better assistance as you compare your paper to what we have:
- Your objectives are included in the first sentence in the introduction. (It should also be reflected in your hook sentence and the title of your proposal.)
- You provide a background of a problem in the introduction.
- Your proposal has a brief literature review that will be used as the supporting data.
- Your proposal essay explains why your objectives will be met. (It’s the heart of your proposal. Use an explanatory tone as you apply analysis.)
- Your tone is persuading by turning to quotes and the evidence.
- Your conclusion is brief and simply re-states your thesis ideas.
Take your time to explore various proposal essay examples to see how much scope you should use when discussing some argument. Keep your tone unbiased when you provide information that represents what’s being common sense. Refer to your course and talk things out with your academic advisor to ensure that your proposal essay’s theme has been fully understood.
Explore also analytical essay writing tips. They are dissecting the intricacies of this essay type. Analytical essays differ from proposals in their approach to analysis and argumentation. While both essays types require critical thinking, analytical essays emphasize interpretation and examination over persuasion and advocacy.
Transforming Traditional Business: An Electronic Business Proposal
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, businesses must adapt and embrace electronic business (e-business) strategies to remain competitive and thrive. This proposal outlines the key elements and benefits of implementing e-business practices and technologies within our organization, paving the way for a more efficient, customer-centric,…
Prioritizing Early Intervention for Children’s Mental Health
As the prevalence of mental health disorders continues to rise, it is essential to prioritize early intervention in addressing mental health issues in children. Mental health problems can have long-term consequences on a child’s emotional, social, and physical development, making early intervention crucial in preventing…
Opening a Coffee Shop in Downtown: A Comprehensive Business Proposal
The coffee culture has been booming in recent years, and it is no surprise that coffee shops are popping up everywhere. Downtown areas are a hub for businesses, and opening a coffee shop in a downtown area can be a great idea. A coffee shop…
Gun Control: An Essential Step in Reducing Gun Violence
Introduction Gun control is a topic that has been debated for decades in the United States. The issue is a complex one that involves balancing the right to bear arms with the need to protect public safety. In the wake of numerous mass shootings and…
Get professional help in 5 minutes

Community Service Project: Improving Education for Low-Income Families
Introduction Education is a fundamental right that every individual should have access to, yet many low-income families struggle to provide adequate education for their children. The purpose of this community service project proposal essay is to address this issue and provide a solution that will…
An Examination of Abortion and its Health Implications on Women
Introduction Abortion is a controversial issue that has remained a topic of heated debate in the United States and other parts of the world. It is a medical procedure that involves terminating a pregnancy before the fetus is viable. While some people believe that women…
Air Pollution: Causes, Effects, and Proposed Solutions
Air pollution is a significant global problem that affects the health of millions of people, damages the environment, and costs billions of dollars. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), outdoor air pollution causes around 4.2 million premature deaths worldwide every year. Moreover, air pollution…
A Proposed Policy for a Campus-Based Food Cooperative
College students face many challenges in their academic journeys, including time management, financial constraints, and mental health problems. One of the most significant challenges is the lack of access to affordable and healthy food options. Many college students, especially those from low-income backgrounds, struggle to…
A Tax on High-Calorie Foods: A Solution to the Global Obesity Epidemic
According to the World Health Organization, in 2016, more than 1.9 billion adults were overweight, of which around 650 million were obese. In the United States alone, more than 42% of the population is considered obese. This epidemic not only has significant health consequences but…
A Proposal Paper on Texting and Driving
Texting and driving refer to the practice of sending or reading text messages while operating a vehicle. This dangerous behavior has become increasingly prevalent, especially among young drivers, and has been shown to have severe consequences. According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA),…
What is a proposal essay?
It is an idea with a list of facts that help the readers see why a particular suggestion is good or bad. The proposal essay topics are limitless. They can deal with education and propound the benefits of distance learning or turn to technology and research the woes of video games. Good proposal essay examples should provide evidence and a list of arguments.
How to write a proposal essay?
A good paper proposal example should include a brief explanation of why you have chosen the topic with a clear thesis statement. The key is to introduce your idea and explain why you think it matters. Check out our essay proposal example to see how it turns to trusted evidence and lists reliable references or similar research on the subject.
What is the primary purpose of a proposal essay?
The primary purpose of a proposal essay is to advocate for a specific idea, solution, or change and provide convincing arguments and evidence to persuade the reader of its feasibility and importance.
How should I choose a proposal essay topic?
Choose a proposal essay topic that you are passionate about and that addresses a real problem or issue. Consider topics that interest you and are relevant to your audience or community.
What is the difference between a proposal essay and a research paper?
While both involve research and writing, a proposal essay focuses on advocating for a specific idea or solution, whereas a research paper typically presents findings and analysis of existing research on a broader topic.
Are proposal essays used outside of academic settings?
Yes, proposal essays are used in various professional and real-world settings, such as business proposals, grant applications, and policy recommendations, in addition to academic assignments.
The most popular topics for Proposal Essay
- Business Ethics
- Teenage Pregnancy
- Drunk Driving
- Climate Change
- Plastic Bags
- Animal Testing
- Illegal Immigration
- Deforestation
- Consumerism
- Discrimination
Students also browse
- Research Essay
- Satire Essay
- Exploratory Essay
- Memoir Essay
- Personal Narrative Essay
- Argumentative Essay
- Evaluation Essay
- Persuasive Essay
- Rhetorical Analysis Essay
- Cause and Effect Essays
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
Proposal Essay Examples
A proposal essay is a description of a future project. It pursues two purposes: to convince the reader that the research or business deserves attention and to test the plan’s viability. Because while writing this essay, you may encounter unsurpassable problems that will require you to change the topic.
How to write a paper proposal and what to include in it? The answer largely depends on the topic and the tutor’s requirements. But in any case, it should comprise a literature overview, the methods to be used, and the predicted results.
This website section features proposal essay examples for different study levels and disciplines. Feel free to use them for reference or inspiration.
503 Best Proposal Essay Examples
Employee engagement and retention: sustainability topic.
- Subjects: Business Employees Management
Creating a Safe and Non-toxic Environment
- Subjects: Business Employee Relationships
Equipping Children With Guns for Public Consideration
- Subjects: Society's Imperfections Sociology
Adverse Childhood Experiences With Incarcerated Parents
- Subjects: Child Psychology Psychology
Post-Operational Care in Diabetic Bariatric Surgery
- Subjects: Health & Medicine Healthcare Research
The Representation of Saudi Women in the Media
- Subjects: Gender Inequality Sociology
Stress Management Through Transcendental Meditation
- Subjects: Alternative Medicine Health & Medicine
Indoors Adventure Program
- Subjects: Architecture Design
Risks and Limitations Facing Organizations in International Diversification
- Subjects: Business Risk Management
Problems With Relying on Work of Auditors in Other Countries
- Subjects: Business Business Controversies
The Effectiveness of Financial and Accounting Software Tools
- Subjects: Applications Tech & Engineering
Environmental Assessment
- Subjects: Environment Environmental Studies
Expansion Plan of the Retail Store
- Subjects: Business Marketing Project
Copyright Issues in Libya
- Subjects: Intellectual Property Law
Fiduciary Duties: Review
- Subjects: Business & Corporate Law Law
Prevention as the Future of Managed Health Care
- Subjects: Administration and Regulation Health & Medicine
Aging as Social Problem in North American Society
- Words: 1018
Criminologist Advisor as Profession
- Subjects: Criminology Law
Roles of Organizations in the Recruitment of Nurses in Saudi Arabia
- Subjects: Health & Medicine Nursing
Managing Natural Resources: Recycling
- Subjects: Environment Recycling
Index Funds Mersus Actively-Managed Funds
- Subjects: Business Financial Management
Mother’s Perception on Childhood Obesity in Libya
- Subjects: Health & Medicine Pediatrics
How Acupuncture Can Help Patients With Migraines
The celebrity obsessed culture: marketing of colleges.
- Subjects: Advertising Entertainment & Media
The Functional Statement of the Asset Management Department
- Subjects: Business Management
Strategy: The Benchmarking Program
- Subjects: Business Strategy
Brand: An Exceptional Food Experience
- Subjects: Brand Management Business
MRSA: Executive Summary
Emotional intelligence in nursing study by winship, health promotion and smoking cessation.
- Subjects: Family, Life & Experiences Lifestyle
Social Media Applications in the Workplace
- Subjects: Entertainment & Media Social Media Issues
Financial Risk Management in Islamic Banking
Bond evaluation types, methods, and factors.
- Subjects: Economic Concepts Economics
Preventing Painful IV Sticks in Children
Prescribing rights for nurse practitioners in the state of georgia.
- Words: 1087
Business Transactions With Costco Business Case
- Subjects: Business Case Study
The Importance of Teamwork With Limited Resources
The lockout and one-punch laws.
- Subjects: Drug and Alcohol Addiction Sociology
Network Topology Supporting Different Quantity of Employees
- Subjects: Computer Science Tech & Engineering
Implementation of Menu Labeling
- Subjects: Diet & Nutrition Food Safety
COVID-19 Awareness in Different Levels of Dental Students
- Subjects: Health & Medicine Public Health
Ban Key Single-Use Plastic Products
- Subjects: Environment Human Impact
The Development of New Leadership Needs
- Subjects: Business Leadership Styles
Windows vs Google. New Operating System as the Key to Success
- Subjects: Programming Tech & Engineering
The Modern-Day Global Economy
- Subjects: Economic Development Economics
The Popularity of Outsourcing
Witch-hunt in europe during the middle ages.
- Subjects: History Medieval History
- Words: 1032
Home Life and Individuals With Asperger’s Syndrome
- Subjects: Diagnostics Health & Medicine
Poem Concerning the American Revolutionary War
- Subjects: Literature Poems
Investigating Zeolites to Separate Hydrogen from Syngas in a Pressure Swing Adsorption
- Subjects: Chemistry Sciences
Chinese Economy: The Impact of the Novel Coronavirus
- Subjects: Economic Theories Economics
Information Technology: The Impact of Paperless
- Subjects: Tech & Engineering Technology Effect
Agricultural Sector: The Use of Drones
- Subjects: Other Technology Tech & Engineering
The Tracking Device for BEA19 Technologies Ltd: Opportunities
- Subjects: Sports Sports Science
Policy Alternatives to Control and Prevent the Spread of Schistosomiasis
- Words: 1026
Racial Issues of “Lemonade” by Beyoncé
- Subjects: Art Singers
The Success of Homeschooling and How the Program Can Be Increased
- Subjects: Education Education System
Sunrise Life Skills Software Business
- Subjects: Project Management Tech & Engineering
- Words: 1092
Social Distancing: Communication With Patients Families
- Subjects: Epidemiology Health & Medicine
Recreation Hub as a Way to Combat Sedentary Lifestyle
The state project al-mazunah free zone.
- Subjects: Economics Investment
Sick Leave Exposition: Interview Regulation
- Subjects: Communications Sociology
Business Plan For the Rock T-Shirt Brand
Economic development in saudi arabia: unemployment amongst young saudi generation.
- Subjects: Sciences Scientific Method
Treasured Objects in Beowulf, Milton’s Paradise Lost, and Pope’s “Rape of the Lock”
Plato’s “method of division”.
- Subjects: Philosophers Philosophy
The Teachers Service Commission
- Subjects: Education Teacher Career
The Law and Application of Corporate Sustainability in Saudi Arabia
Resolute energy corporation: project plan template, prayer’s impact on individuals and their health, interactive whiteboard use during a meeting.
- Subjects: Business Business Communication
Student Learning in Traditional Setting vs. Career Academies
- Subjects: Approach to Learning Education
Ella Fitzgerald, the Jazz Singer
Cardiovascular diseases and saudi male patients aged 40 – 65 years.
- Subjects: Cardiology Health & Medicine
The Self-Conscious Song in the Opera, the Return of Ulysses to His Homeland
- Subjects: Art Musicians
The Future of Customer Satisfaction Based on Saudi Corporations Social Marketing Programs
- Subjects: Business Marketing

Physical and Psychological Trauma in Women
Saudi primary school science teachers’ beliefs: teaching new curriculum.
- Subjects: Curriculum Development Education
Businesses Restructuring By Delivery and Payment Plan of Goods in Kuwait
- Subjects: Economics Trade
The Gap Between Managers and Employees in Saudi Arabia
A model for defining relationships between variables.
- Subjects: Human Rights Sociology
The Concept of Network Security Information
- Subjects: Computer Security Tech & Engineering
Northern Illinois University Analysis
Key performance indicators for risk management, investigation of the day-to-day life of culture.
- Subjects: Cultural Studies Culture
- Words: 1083
Sustainable Development Solutions in Organisations
- Subjects: Business Entrepreneurship
Artificial and Automated: Innovation in Marketing
- Subjects: Business Marketing Communication
Contacting Clients for Their Satisfaction
New business and blueprint for the business, global movement “education for all”, the g4 reforming the united nations security council.
- Subjects: International Relations Politics & Government
Special Education Professional Development Needs of Teachers in Saudi Arabia Assessment
- Subjects: Education Pedagogical Approaches
IT Executives Role in Successful E-transformation in the UAE
- Subjects: Cyber Security Tech & Engineering
Narrative Approach to Explore the Moral Residue Problem
- Subjects: Philosophical Concept Philosophy
Total Quality Management: A Viable Solution for Zayed University
- Subjects: Education Education Theories
The Positive Effects Proactive Maintenance on Asset Sustainability
Rightfoods, inc. sales problems.
- Subjects: Business Company Analysis
Approaches for Firms to Integrate Inexperienced Graduates
The problem of aging, and the needs of aging employees, renewable energy resources in qatar.
- Subjects: Environment Environmental Management
10 Years of Government Excellence Program
- Subjects: Politics & Government Public Administration Activity
Studying Abroad and Improving the Outcomes of Students’ Career Development
- Subjects: Education Education Abroad
Green Supply Chain With ISO 14001 and 9001 in Australian Hospitals
Sales plan for computer equipment, a leading government strategy in abu dhabi.
- Subjects: Government Politics & Government
Realism in Girlfriends Directed by Claudia Weill
- Subjects: Entertainment & Media Movies
Educational Leadership: Data Analysis
Arts and crafts festival event.
- Subjects: Entertainment & Media Events
Civil Union: Legal Recognition of Same-Sex Couples’ Marriages
- Words: 2045
Granite City Building Inspectors: Service Crime
- Subjects: Criminal Investigation Law
New Jersey’s Charter and Public Schools’ Impact
Everyday communication surrounding climate change.
- Subjects: Climate Change Environment
Advanced Practice Nursing Framework
Ethics in sport industry and role of equipment.
- Subjects: Ethics Sociology
Human Security and Collapse of the Soviet Union
- Subjects: Political Ideologies Politics & Government
Human Environmental Security as a Global Challenge
- Subjects: Ecology Environment
Various Issues Surrounding the Concept of Lawful Humanitarian
Deciphering the best start-up fundraising ways, mobile health promotion unit project, kfc restaurant project plan.
6.5 Writing Process: Creating a Proposal
Learning outcomes.
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Describe the elements of the rhetorical situation for your proposal.
- Apply prewriting strategies to discover a problem to write about.
- Gather and synthesize information from appropriate sources.
- Draft a thesis statement and create an organizational plan.
- Compose a proposal that develops your ideas and integrates evidence from sources.
- Implement strategies for drafting, peer reviewing, and revising.
Sometimes writing a paper comes easily, but more often writers work hard to generate ideas and evidence, organize their thoughts, draft, and revise. Experienced writers do their work in multiple steps, and most engage in a recursive process that involves thinking and rethinking, writing and rewriting, and repeating steps multiple times as their ideas develop and sharpen. In broad strokes, most writers go through the following steps to achieve a polished piece of writing:
- Planning and Organization . Your proposal will come together more easily if you spend time at the start considering the rhetorical situation, understanding your assignment, gathering ideas and evidence, drafting a thesis statement, and creating an organizational plan.
- Drafting . When you have a good grasp of the problem and solution you are going to write about and how you will organize your proposal, you are ready to draft.
- Review . With a first draft in hand, make time to get feedback from others. Depending on the structure of your class, you may receive feedback from your instructor or your classmates. You can also work with a tutor in the writing center on your campus, or you can ask someone else you trust, such as a friend, roommate, or family member, to read your writing critically and give honest feedback.
- Revising . After reviewing feedback from your readers, plan to revise. Focus on their comments: Is your thesis clear? Do you need to make organizational changes to the proposal? Do you need to explain or connect your ideas more clearly?
Considering the Rhetorical Situation
Like other kinds of writing projects, a proposal starts with assessing the rhetorical situation —the circumstance in which a writer communicates with an audience of readers about a subject. As a proposal writer, you make choices based on the purpose for your writing, the audience who will read it, the genre , and the expectations of the community and culture in which you are working. The brainstorming questions in Table 6.1 can help you begin:
Summary of Assignment
Write a proposal that discusses a problem you want to learn more about and that recommends a solution. The problem you choose must be a current problem, even though it may have been a problem for many years. The problem must also affect many people, and it must have an actual solution or solutions that you can learn about through research. In other words, the problem cannot be unique to you, and the solution you recommend cannot be one you only imagine; both the problem and the solution must be grounded in reality.
One way to get ideas about a problem to write about is to read a high-quality newspaper, website, or social media account for a week. Read widely on whatever platform you choose so that you learn what people are saying, what a newspaper’s editorial board is taking a stand on, what opinion writers are making cases for in op-eds, and what community members are commenting on. You’ll begin to get a handle on problems in your community or state that people care about. If you read a paper or website with a national or international audience, you’ll learn about problems that affect people in other places.
You will need to consult and cite at least five reliable sources. They can be scholarly, but they do not have to be. They must be credible, trustworthy, and unbiased. Possible sources include articles from reputable newspapers, magazines, and academic and professional journals; reputable websites; government sources; and visual sources. Depending on your topic, you may want to conduct a survey, an interview, or an experiment. See Research Process: Accessing and Recording Information and Annotated Bibliography: Gathering, Evaluating, and Documenting Sources for information about creating and finding sources. Your proposal can include a visual or media source if it provides appropriate, relevant evidence.
Another Lens. Another way to approach a proposal assignment is to consider problems that affect you directly and affect others. Perhaps you are concerned about running up student loan debt. Or perhaps you worry about how to pay your rent while earning minimum wage. These concerns are valid and affect many college students around the United States. Another way is to think about problems that affect others. Perhaps students in your class or on your campus have backgrounds and experiences that differ from yours— what problems or challenges might they have encountered during their time in college that you don’t know about?
As you think about the purpose and audience for your proposal, think again about the rhetorical situation, specifically about the audience you want to reach and the mode of presentation best suited to them and your purpose. For example, say you’re dissatisfied with the process for electing student leaders on your campus. If your purpose is to identify the problems in the process and propose a change, then your audience would include other students, the group or committee that oversees student elections, and perhaps others. To reach other students who might also be dissatisfied, you might write an article, editorial, or letter for the campus newspaper, social media page, or website, depending on how students on your campus get news. In addition, you might organize a meeting of other students to get their input on the problem. To reach the decision makers, which may include elected students, faculty, and administrators, you might need to prepare an oral presentation and a slide deck.
Below in Figure 6.7 are three slides from Shawn Krukowski’s proposal that he adapted for a presentation: the title slide, a slide on one aspect of the problem, and a slide introducing one of the proposed solutions.
Quick Launch: Finding a Problem to Write About
A proposal must address a real-life problem and present one or more workable solutions. Usually, problems worth writing about are not easily solved; if they were, they would no longer be considered problems. Indeed, problems in proposals are often complex, and solutions are often complicated and involve trade-offs. Sometimes people disagree about whether the problem is a problem at all and whether any proposed solutions are viable solutions.
Exploring a Problem
One way to generate ideas about a problem is to brainstorm. To explore a topic for your proposal, use a graphic organizer like Table 6.2 to write responses to the following statements and questions:
For example, perhaps you’re considering a career in information technology, and you’re taking an IT class. You might be interested in exploring the problem of data breaches. A data breach is a real-world problem with possible solutions, so it passes the first test of being an actual problem with possible solutions. Your responses to the questions above might look something like those in Table 6.3 :
Narrowing and Focusing
Many problems for a proposal can be too broad to tackle in a single paper. For example, the sample above reveals that data breaches are indeed a problem but that several aspects can be explored. If you tried to cover all the aspects, you would be left writing general paragraphs with little specific information. The topic needs to be narrowed and focused.
The data breaches example above could be narrowed to the following problems—and possibly even more. Note that the questions start to zero in on possible solutions, too. In your own writing, as you brainstorm, try placing subtopics you discover into their own categories and asking more questions, as shown in Table 6.4 .
Sample Proposal Topics
The following broad topics are potentially suitable as a start for a proposal. Choose one of these or one of your own, and ask the exploring questions. Then look at your responses, and ask focusing questions. Continue to focus until you have a specific problem that you can discuss in sufficient depth and offer a concrete solution or solutions.
- Health fields: cost of medical and dental care for uninsured people, management of chronic conditions and diseases, infection control, vaccinations, access to mental health care, drug use and addiction, sports injuries, workplace safety
- Education: gaps in academic achievement, curriculum, recruitment and retention of staff and/or students, buildings and grounds, graduation rates, cocurricular activities
- Environment: forest management and fires, hurricanes and other extreme storms, water and air pollution, sustainable development, invasive species, waste management, recycling and composting, community gardening
- Engineering and computer science: robotics, vehicles and transportation, digital divide, online privacy, misinformation and misbehavior on social media, video games
- Business and manufacturing: quality improvement, process improvement, cost control, communication, social media, pay equity, fundraising, sourcing of materials, net-zero energy processes, workplace safety
- Policy and politics: public institutions, such as public schools, libraries, transportation systems, and parks; taxes, fees, and services; donations to political campaigns; healthcare, such as Medicare and Medicaid; social security; unemployment insurance; services for active military and veterans; immigration policy
- Society and culture: social media and free speech; inequality in housing, employment, education, and more; cancel culture; bullying; wealth and poverty; support for the arts; athletes and sports; disparities related to race, sex, gender identity and expression, age, and/or ability
Gathering Information
Proposals are rooted in information and evidence; therefore, most proposal assignments require you to conduct research. Depending on your assignment, you may need to do formal research, an activity that involves finding sources and evaluating them for reliability, reading them carefully and taking notes, and citing all words you quote and ideas you borrow. See Research Process: Accessing and Recording Information and Annotated Bibliography: Gathering, Evaluating, and Documenting Sources for detailed instruction on conducting research. If you are proposing a solution to a problem in your local community or on your campus, you may need to conduct primary research as well, such as a survey or interviews with people who live or work there.
Whether you conduct in-depth research or do background reading, keep track of the ideas that come to you and the information you learn. You can write or dictate notes using an app on your phone or computer, or you can jot notes in a journal if you prefer pen and paper. Then, when you are ready to begin to organize what you have learned, you will have a record of your thoughts and information. Always track the source of the information you gather, whether from your reading or a person you interviewed, so that you can return to that source if you need more information and can credit the source in your paper.
Kinds of Evidence
You will use evidence to demonstrate that the problem is real and worthy of being solved and that your recommended solution is workable. Choose evidence for your proposal that is rooted in facts. In addition, choose evidence that best supports the angle you take on your topic and meets your instructor’s requirements. Cite all evidence you use from a source. Consider the following kinds of evidence and examples of each:
Definition : an explanation of a key word, idea, or concept.
The Personal Data Notification & Protection Act of 2017 defines a security breach as “a compromise of the security, confidentiality, or integrity of, or the loss of, computerized data that results in… (i) the unauthorized acquisition of sensitive personally identifiable information; or (ii) access to sensitive personally identifiable information that is for an unauthorized purpose, or in excess of authorization.”
Example : an illustration of an idea or concept.
Every month, university staff members receive a fake phishing email from the IT department. The goal is to train employees of the university to be critical readers of every email they receive.
Expert opinion : a statement by a professional whose opinion is respected in the field.
In The Sixth Extinction , science writer Elizabeth Kolbert observes that humans are making the choice about “which evolutionary pathways will remain and open and which will be forever closed” (268).
Fact : information that is true and can be proven correct or accurate. Statements of fact are built on evidence and data.
In March and April of 2020, 43 states in the United States issued orders directing residents to stay home except for essential activities.
Interview : a person-to-person, phone, or remote conversation that involves an interviewer posing questions to another person or group of people.
During an interview, I asked about parents’ decisions to vaccinate their children. One pediatrician said, “The majority of parents see the benefits of immunizations for their children and for public health. For those who don’t, I talk to them and try to understand why they feel the way they do.”
Quotation : the exact words of an author or speaker.
According to the Federal Aviation Administration, SpaceX was required to conduct a “comprehensive review of the company’s safety culture, operational decision-making, and process discipline,” in addition to investigating the crash of its prototype spacecraft (Chang).
Statistics : numerical fact or item of data.
According to the Environmental Protection Agency, more than 40 million tons of food waste were generated in 2017, comprising 15.2% of all trash sent to landfills (DeSilver).
Survey : a structured interview in which respondents are all asked the same questions and their answers are tabulated and interpreted. Surveys reveal attitudes, beliefs, or habits of the general public or segments of the population.
In a survey of adults conducted in July 2020, 64 percent of respondents said that social media have a mostly negative effect on American society (Auxier).
- Visuals and other media : graphs, figures, tables, photographs, diagrams, charts, maps, videos, audio recordings, etc.
Thesis and Organization
Drafting a thesis.
When you have a solid grasp of the problem and solution, try drafting a thesis . A thesis is the main idea that you will convey in your proposal and to which all the paragraphs in the paper should relate. In a proposal, you will likely express this main idea in a thesis statement of one or two sentences toward the end of the introduction.
For example, in the thesis statement Shawn Krukowski wrote for his proposal on climate change, he identifies the problem and previews the solutions he presents:
student sample text What is needed to slow climate change is unified action in two key areas—mitigation and adaptation—spurred by government leadership in the United States and a global commitment to addressing the problem immediately. end student sample text
Here is another example that identifies a problem and multiple solutions:
student sample text The number of women employed in the IT field is decreasing every year, a trend that can be changed with a multifaceted approach that includes initiatives in middle schools, high schools, and colleges; active recruitment; mentoring programs; and flexible work arrangements. end student sample text
After you draft a thesis statement, ask these questions and revise it as needed:
- Is it engaging? A thesis for a proposal should pique readers’ interest in the problem and possible solutions.
- Is it precise and specific? If you are interested in curbing the spread of invasive plant species, for example, your thesis should indicate which environment the plant or plants are invading and that you are proposing ways to stop the spread.
Organizing Your Ideas
A proposal has a recognizable shape, starting with an introduction, followed by discussions of the problem, possible solutions, potential objections to the solutions, and a conclusion with a recommendation. A graphic organizer like Table 6.5 can help you organize your ideas and evidence.
Drafting a Proposal
With a tentative thesis, an organization plan, and evidence, you are ready to begin drafting your proposal. For this assignment, you will discuss a problem, present possible solutions, address objections to the solutions, and conclude with a recommendation.
Introduction
You may choose to write the introduction first, last, or midway through the drafting process. Whenever you choose to write it, use it to draw readers in. Make the proposal topic clear, and be concise. End the introduction with your thesis statement.
Opening a proposal with an overview of your topic is a reliable strategy, as shown in the following student-written example on women working in IT. The thesis statement, which appeared earlier in this section, is underlined:
student sample text People who work in the information technology (IT) field often start their careers fixing computers and other electronic devices for others. Through experience and education, an IT worker’s career path can branch out to specialize in everything from programming new software to setting up and maintaining networks. The IT field is growing because of the constant development of technology, and the demand for employees also is growing. underline Yet the number of women employed in the IT field is decreasing every year, a trend that can be changed with a multifaceted approach that includes initiatives in middle schools, high schools, and colleges; active recruitment; mentoring programs; and flexible work arrangements end underline . end student sample text
Body Paragraphs: Problem, Solutions, Objections
The body paragraphs of your proposal should present the problem, the solution or solutions, and potential objections to the proposed solution(s). As you write these paragraphs, consider using the point , evidence , and analysis pattern:
- The point is the central idea of the paragraph, usually given in a topic sentence stated in your own words at or toward beginning of the paragraph.
- With the evidence you provide, you develop the paragraph and support the point given in the topic sentence. Include details, examples, quotations, paraphrases, and summaries from sources. In your sentences and paragraphs, synthesize the evidence you give by showing the connections between sources. See Position Argument: Practicing the Art of Rhetoric and Argumentative Research: Enhancing the Art of Rhetoric with Evidence for more information on quoting, summarizing, paraphrasing, and synthesizing.
- The analysis comes at the end of the paragraph. In your own words, draw a conclusion about the evidence you have provided and relate it to the topic sentence.
The paragraphs that follow show the point-evidence-analysis pattern in practice.
Body Paragraphs: Problem
Follow the introduction with a discussion of the problem. Using paragraph structure, define the problem and discuss it, drawing on evidence from your sources. This paragraph (or paragraphs) should answer these questions: What is the problem? Why is this a problem? The following example, from the proposal on women working in IT, answers the first question:
student sample text The information technology (IT) field is continuously expanding, with many more positions available than workers to fill them. In fact, the pool of IT professionals was so small that in 2001, Congress raised the visa limit in an effort to fill the gap with employees from overseas (Varma, 2002). And yet the number of women represented in the occupation is decreasing. From 1990 to 2020, the percentage of women in IT declined from 31 percent to 25 percent, even though women make up 47 percent of all employed adults in the United States. According to White (2021), only 19 percent of women pursue a computer science major in college, compared to 27 percent in 1997. Of those women who graduated with a computer science degree, 38 percent are working in the field compared to 56 percent of men, a statistic that indicates women are not staying in the field. Although gender diversity supposedly is valued in the workplace, the underrepresentation of women in IT is clearly a problem. end student sample text
The writer then goes on to answer the second question: Why is this a problem? The writer discusses stereotypes, lack of encouragement and role models, workplace culture, pay, and prospects for advancement (not shown here).
Body Paragraphs: Solutions
After presenting and explaining the problem, use specific information from the sources you consulted to present the solution or solutions you have discovered through your research. If you are proposing more than one solution, present them one at a time, using headings as appropriate.
The solutions section will likely be the longest part of your proposal. Below are two paragraphs from the proposal about women working in IT. Note how the first paragraph introduces the solutions and how the second paragraph uses evidence to develop the first proposed solution. Also note the informative boldface headings.
student sample text The following suggestions are ways to encourage women to enter IT and build their careers, with the eventual goal of achieving gender balance in the field. The solutions discussed include encouraging interest in computer technology among girls in middle school and high school, actively recruiting college-age women to study IT, and within the field, mentoring women and expanding workplace flexibility to improve retention. end student sample text
student sample text The National Center for Women & Information Technology (NCWIT) is an organization that encourages girls in middle school and high school to explore their interest in IT. One program, the NCWIT’s Aspirations in Computing, supports women in high school by showing them that they can succeed in technology and introducing them to other students with similar interests. The same program matches middle-school girls with female high-school and college students and awards scholarships for computing and programming competitions. In addition, internships and IT courses in middle school and high school provide opportunities to learn what a career in IT entails, with or without a degree in IT. Opportunities like these give girls and women support and a sense of belonging. end student sample text
The paragraphs that follow (not shown here) continue the discussion of the possible solutions.
Body Paragraphs: Objections
Depending on the problem and solution, consider the objections readers may raise, and explain why your proposal is necessary and worthwhile. For example, the proposal on women in IT does not discuss objections because few people would object to the writer’s proposal. Shawn Krukowski, however, in his proposal on climate change, includes a section on objections to taking action. He focuses the discussion on people who deny that climate change is a problem. Would you do the same? Consider whether this section of Shawn’s proposal might have been stronger had he addressed objections to the solutions he proposed—mitigation and adaptation—instead of objections to the problem.
student sample text Despite scientific evidence, some people and groups deny that climate change is real or, if they admit it exists, insist it is not a valid concern. Those who think climate change is not a problem point to Earth’s millennia-long history of changing climate as evidence that life has always persisted. Most of the change, however, predates human civilization, which has benefited from thousands of years of stable climate. The rapid change since the Industrial Revolution is unprecedented in human history. end student sample text
student sample text Those who deny climate change or its dangers seek primarily to relax or remove pollution standards and regulations in order to protect, or maximize profit from, their industries. To date, their lobbying has been successful. For example, the world’s fossil-fuel industry received $5.3 trillion in 2015 alone, while the U.S. wind-energy industry received $12.3 billion in subsidies between 2000 and 2020 (Green America, 2020). end student sample text
Conclusion and Recommendation
The conclusion and recommendation section of your proposal is the part in which you interpret your findings and make a recommendation or give a call to action. At this point, focus on the solution that will best solve the problem, suggesting or summarizing specific actions.
Below is the recommendation section from the proposal about women in IT. In the full conclusion (not shown here), the writer summarizes the main points of the proposal. In the recommendation paragraph that follows, the writer calls for specific actions:
student sample text Many researchers have studied why few women choose IT as a career and why some decide to leave the field. Although the numbers cannot be improved immediately, the following changes in school and the workplace could recruit and retain more women in IT: end student sample text
- Include technology education courses and formal IT programs in middle- and high-school curricula to give girls and young women opportunities to develop an interest at an early age.
- Develop internship and mentor programs in high schools and colleges to combat stereotyping and encourage women to enter the field.
- Develop and encourage workplace mentor programs, flexible work options, and open communication for professional growth and retention.
student sample text With time and effort, these actions may result in more women seeing themselves in long-term IT careers. end student sample text
References or Works Cited Page
Including any data you gathered through primary research, such as a survey you created and administered, interviews you conducted, or observational notes you took, you must cite the sources you consulted. These sources appear in the text of your proposal and in a bibliography at the end. The paragraphs in the previous section, including Shawn Krukowski’s proposal, use APA documentation style. For more on documenting sources, see Index and Guide to Documentation , MLA Documentation and Format , and APA Documentation and Format .
Abstract or Executive Summary
An abstract (or executive summary) summarizes your proposal. The purpose is to present information briefly and economically so that readers can decide whether they want to read further. Include your main points, but not the evidence.
Although an abstract or executive summary comes first in a proposal, it is advisable to write it after you have completed your proposal and are certain of your main points. The example below is the abstract from the proposal about women in IT.
student sample text The purpose of this proposal is to raise awareness of the small number of women working in the information technology (IT) field, to examine the factors that contribute to discouraging women from entering IT, and to propose ways to draw women into the field and retain them. Although the IT field is growing, the number of women employed within it remains low. Women may be reluctant to pursue a career in IT because of stereotypes, few role models, and lack of encouragement. Women who have already established a career in IT report leaving the field for these reasons, as well as family responsibilities and lack of advancement. There are several potential ways to raise the number of women in IT. Encouraging interest in computer technology among girls in middle school and high school, recruiting college-age women to study IT, mentoring young professional women, and improving workplace flexibility will, over time, break down stereotypes and increase the number of women in the IT field. end student sample text
Peer Review: Getting Feedback from Readers
With a complete draft in hand, you may engage in peer review with your classmates, giving feedback to each other about the strengths and weaknesses of your drafts. For peer review within a class, your instructor may provide a list of questions or a form for you to complete as you work together.
Conferencing in Writing Groups
Other people can provide feedback on your writing beside your classmates. If you have an on-campus writing center, it is well worth your time to make an online or in-person appointment with a tutor at any point in your writing process. You will get valuable comments and improve your ability to review your own writing.
Another way to get fresh eyes on your writing is to ask a friend or family member to read your draft. To get useful feedback, provide a list of questions or a form such as the one shown in Table 6.6 for them to complete as they read.
Revising Your Proposal
A strong college paper is rarely written in a single draft, so build in time to revise your work. Take time with the comments you receive from your readers, and read your own work with a critical eye.
Responding to Reviewers’ Feedback
When you receive feedback from readers—whether from your instructor, your classmates, a writing tutor, or someone else—read each comment carefully to understand what the reader is communicating. Do your best not to become defensive, and be open to suggestions for improvement. Remind yourself that your readers are trying to help. As someone who hasn’t thought about your proposal as much as you have, a new reader can often see strengths and weaknesses that you cannot. Analyze each response, and decide whether acting on a suggestion will make your writing better. Remember that you remain the author, and you make the final call on your writing.
As you read, keep track of the comments your readers make. Pay special attention to strengths and weaknesses that more than one reader identifies. Use that information to improve later assignments as well as your proposal.
Revising on Your Own
The following revising strategies can help you read your draft critically and carefully:
- Read your draft aloud. Read the entire text from the beginning slowly and carefully, marking spots that need revision. Reading in this way allows you to see areas that need clarification, explanation, or development that you may have missed when you wrote the first draft. You can also have someone read your draft aloud to you.
- Make a paragraph outline. The most common unit of thought in writing is the paragraph, a group of sentences set off from other groups because they focus on a single idea. Writing a paragraph outline creates a map of your whole paper that can help you determine whether the organization is effective or needs changing. Number each paragraph and write a phrase describing its topic or focus. Check that each paragraph has a topic sentence that states the main idea of the paragraph.
- Test your evidence. Check whether each piece of evidence is factual and supports the main idea of the paragraph. Check that each piece of evidence is introduced, woven into your sentences, and cited.
- Listen for your voice. In most college papers, your language should sound like a real person. If your instructor requires a formal style for the assignment, the language should be objective and in third-person point of view .
- Let go if you need to. View change as good. Learn to let go of words, sentences, paragraphs, and maybe even your entire first draft. Sometimes the best way to revise is to start fresh. The knowledge you have built in writing a first draft will serve you well if you need to start over.
- Create a new file for each revision. Each time you revise a draft, save the new version with a new file name so that you don’t lose your previous work. That way, you can return to an earlier version of your draft if you are not happy with the revision.
- Edit and proofread. When you are satisfied with the overall shape of your paper, reread it once again to check for sentence-level errors in grammar, punctuation, spelling, and source citations.
Taking It Public: Publishing or Presenting Your Proposal
Publishing is a final step in the writing process. You may want to consider publishing your full proposal in your campus newspaper (or rewriting it as a letter to the editor) if your topic is related to your school. Or you may want to present it to an organization or committee on campus that can help you make your solution a reality. If your topic is related to the community in which you live, consider submitting your proposal to the local newspaper or presenting it at a city council meeting. (Note that if you decide to present your proposal orally, you’ll need to figure out in advance the procedure for speaking or getting on a meeting agenda.) If your topic is more general and involves substantial research, consider submitting your proposal to one of these journals that publish undergraduate research work in all fields:
- American Journal of Undergraduate Research
- Midwest Journal of Undergraduate Research
- PURSUE Undergraduate Research Journal
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/writing-guide/pages/1-unit-introduction
- Authors: Michelle Bachelor Robinson, Maria Jerskey, featuring Toby Fulwiler
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Writing Guide with Handbook
- Publication date: Dec 21, 2021
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/writing-guide/pages/1-unit-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/writing-guide/pages/6-5-writing-process-creating-a-proposal
© Dec 19, 2023 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
Essay Introduction Examples
#scribendiinc
Written by Scribendi
Always have a road map for an essay introduction . Having a strong essay introduction structure is critical to a successful paper. It sets the tone for the reader and interests them in your work. It also tells them what the essay is about and why they should read it at all.
It shouldn't leave the reader confused with a cliffhanger at the end. Instead, it should generate interest and guide the reader to Chapter One. Using the right parts of an essay introduction can help with this.
Check out an effective essay introduction structure below. It’s a road map for writing an essay—just like the parts of essay introductions are road maps for readers.
Essay Introduction Structure
Attention-grabbing start
Outline of argument
Thesis statement
Some academics find the beginning the most difficult part of writing an essay , so our editors have created some examples of good essay introductions to guide you. Let's take a look at the samples below to see how the essay introduction structures come together.
If you are unsure about your paper, our essay editors would love to give you some feedback on how to write an essay introduction.
[1] According to Paul Ratsmith, the tenuous but nonetheless important relationship between pumpkins and rats is little understood: "While I've always been fascinated by this natural kinship, the connection between pumpkins and rats has been the subject of few, if any, other studies" (2008). [2] Ratsmith has been studying this connection, something he coined "pumpkinology," since the early 1990s. He is most well known for documenting the three years he spent living in the wild among pumpkins and rats. [3] Though it is a topic of little recent interest, the relationship has been noted in several ancient texts and seems to have been well understood by the Romans. Critics of Ratsmith have cited poor science and questionable methodology when dismissing his results, going so far as to call pumpkinology "rubbish" (de Vil, 2009), "stupid" (Claw, 2010), and "quite possibly made up" (Igthorn, 2009). [4] Despite these criticisms, there does appear to be a strong correlation between pumpkin patches and rat populations, with Ratsmith documenting numerous pumpkin–rat colonies across North America, leading to the conclusion that pumpkins and rats are indeed "nature's best friends" (2008).
Let's break down this example of a good essay introduction structure. The beginning hooks our attention from the get-go in section one. This is because it piques our curiosity. What is this strange relationship? Why has no one studied it? Then, section two gives us context for the topic. Ratsmith is an expert in a controversial field: pumpkinology. It's the study of the connection between pumpkins and rats.
The second half of the paragraph also demonstrates why this is a good essay introduction example. Section three gives us the main argument: the topic is rarely studied because critics think Ratsmith's work is "rubbish," but the relationship between pumpkins and rats has ancient roots. Then section four gives us the thesis statement: Ratsmith's work has some merit.
The parts of an essay introduction help us chart a course through the topic. We know the paper will take us on a journey. It's all because the author practiced how to write an essay introduction.
Let’s take a look at another example of a good essay introduction.
[1] Societies have long believed that if a black cat crosses one's path, one might have bad luck—but it wasn't until King Charles I's black cat died that the ruler's bad luck began (Pemberton, 2018). [2] Indeed, for centuries, black cats have been seen as the familiars of witches—as demonic associates of Satan who disrespect authority (Yuko, 2021). Yet, they have also been associated with good luck, from England's rulers to long-distance sailors (Cole, 2021). [3] This essay shows how outdated the bad luck superstition really is. It provides a comprehensive history of the belief and then provides proof that this superstition has no place in today's modern society. [4] It argues that despite the prevailing belief that animals cause bad luck, black cats often bring what seems to be "good luck" and deserve a new reputation.
This example of a good essay introduction pulls us in right away. This is because section one provides an interesting fact about King Charles I. What is the story there, and what bad luck did he experience after his cat passed away? Then, section two provides us with general information about the current status of black cats. We understand the context of the essay and why the topic is controversial.
Section three then gives us a road map that leads us through the main arguments. Finally, section four gives us the essay's thesis: "black cats often bring what seems to be 'good luck' and deserve a new reputation."
Still feeling unsure about how to write an essay introduction? Here's another example using the essay introduction structure we discussed earlier.
[1] When the Lutz family moved into a new house in Amityville, New York, they found themselves terrorized by a vengeful ghost (Labianca, 2021). Since then, their famous tale has been debunked by scientists and the family themselves (Smith, 2005). [2] Yet ghost stories have gripped human consciousness for centuries (History, 2009). Scientists, researchers, and theorists alike have argued whether ghosts are simply figments of the imagination or real things that go bump in the night. In considering this question, many scientists have stated that ghosts may actually exist. [3] Lindley (2017) believes the answer may be in the quantum world, which "just doesn’t work the way the world around us works," but "we don’t really have the concepts to deal with it." Scientific studies on the existence of ghosts date back hundreds of years (History, 2009), and technology has undergone a vast evolution since then (Lamey, 2018). State-of-the-art tools and concepts can now reveal more about ghosts than we've ever known (Kane, 2015). [4] This essay uses these tools to provide definitive proof of the existence of ghosts in the quantum realm.
This example of a good essay introduction uses a slightly different strategy than the others. To hook the reader, it begins with an interesting anecdote related to the topic. That pulls us in, making us wonder what really happened to the Lutzs. Then, section two provides us with some background information about the topic to help us understand. Many people believe ghosts aren't real, but some scientists think they are.
This immediately flows into section three, which charts a course through the main arguments the essay will make. Finally, it ends with the essay's thesis: there is definitive proof of the existence of ghosts in the quantum realm. It all works because the author used the parts of an essay introduction well.
For attention-grabbing introductions, an understanding of essay introduction structure and how to write an essay introduction is required.
Our essay introduction examples showing the parts of an essay introduction will help you craft the beginning paragraph you need to start your writing journey on the right foot.
If you'd like more personalized attention to your essay, consider sending it for Essay Editing by Scribendi. We can help you ensure that your essay starts off strong.
Image source: Prostock-studio/Elements.envato.com
Let’s Get Your Essay Ready to Wow an Audience
Hire one of our expert editors , or get a free sample, about the author.

Scribendi's in-house editors work with writers from all over the globe to perfect their writing. They know that no piece of writing is complete without a professional edit, and they love to see a good piece of writing transformed into a great one. Scribendi's in-house editors are unrivaled in both experience and education, having collectively edited millions of words and obtained numerous degrees. They love consuming caffeinated beverages, reading books of various genres, and relaxing in quiet, dimly lit spaces.
Have You Read?
"The Complete Beginner's Guide to Academic Writing"
Related Posts

Essay Writing: Traffic Signals for the Reader

How to Write a Great Thesis Statement

How to Write a Persuasive Essay

MLA Formatting and MLA Style: An Introduction
Upload your file(s) so we can calculate your word count, or enter your word count manually.
We will also recommend a service based on the file(s) you upload.
English is not my first language. I need English editing and proofreading so that I sound like a native speaker.
I need to have my journal article, dissertation, or term paper edited and proofread, or I need help with an admissions essay or proposal.
I have a novel, manuscript, play, or ebook. I need editing, copy editing, proofreading, a critique of my work, or a query package.
I need editing and proofreading for my white papers, reports, manuals, press releases, marketing materials, and other business documents.
I need to have my essay, project, assignment, or term paper edited and proofread.
I want to sound professional and to get hired. I have a resume, letter, email, or personal document that I need to have edited and proofread.
Prices include your personal % discount.
Prices include % sales tax ( ).

- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » How To Write A Proposal – Step By Step Guide [With Template]
How To Write A Proposal – Step By Step Guide [With Template]
Table of Contents

How To Write A Proposal
Writing a Proposal involves several key steps to effectively communicate your ideas and intentions to a target audience. Here’s a detailed breakdown of each step:
Identify the Purpose and Audience
- Clearly define the purpose of your proposal: What problem are you addressing, what solution are you proposing, or what goal are you aiming to achieve?
- Identify your target audience: Who will be reading your proposal? Consider their background, interests, and any specific requirements they may have.
Conduct Research
- Gather relevant information: Conduct thorough research to support your proposal. This may involve studying existing literature, analyzing data, or conducting surveys/interviews to gather necessary facts and evidence.
- Understand the context: Familiarize yourself with the current situation or problem you’re addressing. Identify any relevant trends, challenges, or opportunities that may impact your proposal.
Develop an Outline
- Create a clear and logical structure: Divide your proposal into sections or headings that will guide your readers through the content.
- Introduction: Provide a concise overview of the problem, its significance, and the proposed solution.
- Background/Context: Offer relevant background information and context to help the readers understand the situation.
- Objectives/Goals: Clearly state the objectives or goals of your proposal.
- Methodology/Approach: Describe the approach or methodology you will use to address the problem.
- Timeline/Schedule: Present a detailed timeline or schedule outlining the key milestones or activities.
- Budget/Resources: Specify the financial and other resources required to implement your proposal.
- Evaluation/Success Metrics: Explain how you will measure the success or effectiveness of your proposal.
- Conclusion: Summarize the main points and restate the benefits of your proposal.
Write the Proposal
- Grab attention: Start with a compelling opening statement or a brief story that hooks the reader.
- Clearly state the problem: Clearly define the problem or issue you are addressing and explain its significance.
- Present your proposal: Introduce your proposed solution, project, or idea and explain why it is the best approach.
- State the objectives/goals: Clearly articulate the specific objectives or goals your proposal aims to achieve.
- Provide supporting information: Present evidence, data, or examples to support your claims and justify your proposal.
- Explain the methodology: Describe in detail the approach, methods, or strategies you will use to implement your proposal.
- Address potential concerns: Anticipate and address any potential objections or challenges the readers may have and provide counterarguments or mitigation strategies.
- Recap the main points: Summarize the key points you’ve discussed in the proposal.
- Reinforce the benefits: Emphasize the positive outcomes, benefits, or impact your proposal will have.
- Call to action: Clearly state what action you want the readers to take, such as approving the proposal, providing funding, or collaborating with you.
Review and Revise
- Proofread for clarity and coherence: Check for grammar, spelling, and punctuation errors.
- Ensure a logical flow: Read through your proposal to ensure the ideas are presented in a logical order and are easy to follow.
- Revise and refine: Fine-tune your proposal to make it concise, persuasive, and compelling.
Add Supplementary Materials
- Attach relevant documents: Include any supporting materials that strengthen your proposal, such as research findings, charts, graphs, or testimonials.
- Appendices: Add any additional information that might be useful but not essential to the main body of the proposal.
Formatting and Presentation
- Follow the guidelines: Adhere to any specific formatting guidelines provided by the organization or institution to which you are submitting the proposal.
- Use a professional tone and language: Ensure that your proposal is written in a clear, concise, and professional manner.
- Use headings and subheadings: Organize your proposal with clear headings and subheadings to improve readability.
- Pay attention to design: Use appropriate fonts, font sizes, and formatting styles to make your proposal visually appealing.
- Include a cover page: Create a cover page that includes the title of your proposal, your name or organization, the date, and any other required information.
Seek Feedback
- Share your proposal with trusted colleagues or mentors and ask for their feedback. Consider their suggestions for improvement and incorporate them into your proposal if necessary.
Finalize and Submit
- Make any final revisions based on the feedback received.
- Ensure that all required sections, attachments, and documentation are included.
- Double-check for any formatting, grammar, or spelling errors.
- Submit your proposal within the designated deadline and according to the submission guidelines provided.
Proposal Format
The format of a proposal can vary depending on the specific requirements of the organization or institution you are submitting it to. However, here is a general proposal format that you can follow:
1. Title Page:
- Include the title of your proposal, your name or organization’s name, the date, and any other relevant information specified by the guidelines.
2. Executive Summary:
- Provide a concise overview of your proposal, highlighting the key points and objectives.
- Summarize the problem, proposed solution, and anticipated benefits.
- Keep it brief and engaging, as this section is often read first and should capture the reader’s attention.
3. Introduction:
- State the problem or issue you are addressing and its significance.
- Provide background information to help the reader understand the context and importance of the problem.
- Clearly state the purpose and objectives of your proposal.
4. Problem Statement:
- Describe the problem in detail, highlighting its impact and consequences.
- Use data, statistics, or examples to support your claims and demonstrate the need for a solution.
5. Proposed Solution or Project Description:
- Explain your proposed solution or project in a clear and detailed manner.
- Describe how your solution addresses the problem and why it is the most effective approach.
- Include information on the methods, strategies, or activities you will undertake to implement your solution.
- Highlight any unique features, innovations, or advantages of your proposal.
6. Methodology:
- Provide a step-by-step explanation of the methodology or approach you will use to implement your proposal.
- Include a timeline or schedule that outlines the key milestones, tasks, and deliverables.
- Clearly describe the resources, personnel, or expertise required for each phase of the project.
7. Evaluation and Success Metrics:
- Explain how you will measure the success or effectiveness of your proposal.
- Identify specific metrics, indicators, or evaluation methods that will be used.
- Describe how you will track progress, gather feedback, and make adjustments as needed.
- Present a detailed budget that outlines the financial resources required for your proposal.
- Include all relevant costs, such as personnel, materials, equipment, and any other expenses.
- Provide a justification for each item in the budget.
9. Conclusion:
- Summarize the main points of your proposal.
- Reiterate the benefits and positive outcomes of implementing your proposal.
- Emphasize the value and impact it will have on the organization or community.
10. Appendices:
- Include any additional supporting materials, such as research findings, charts, graphs, or testimonials.
- Attach any relevant documents that provide further information but are not essential to the main body of the proposal.
Proposal Template
Here’s a basic proposal template that you can use as a starting point for creating your own proposal:
Dear [Recipient’s Name],
I am writing to submit a proposal for [briefly state the purpose of the proposal and its significance]. This proposal outlines a comprehensive solution to address [describe the problem or issue] and presents an actionable plan to achieve the desired objectives.
Thank you for considering this proposal. I believe that implementing this solution will significantly contribute to [organization’s or community’s goals]. I am available to discuss the proposal in more detail at your convenience. Please feel free to contact me at [your email address or phone number].
Yours sincerely,
Note: This template is a starting point and should be customized to meet the specific requirements and guidelines provided by the organization or institution to which you are submitting the proposal.
Proposal Sample
Here’s a sample proposal to give you an idea of how it could be structured and written:
Subject : Proposal for Implementation of Environmental Education Program
I am pleased to submit this proposal for your consideration, outlining a comprehensive plan for the implementation of an Environmental Education Program. This program aims to address the critical need for environmental awareness and education among the community, with the objective of fostering a sense of responsibility and sustainability.
Executive Summary: Our proposed Environmental Education Program is designed to provide engaging and interactive educational opportunities for individuals of all ages. By combining classroom learning, hands-on activities, and community engagement, we aim to create a long-lasting impact on environmental conservation practices and attitudes.
Introduction: The state of our environment is facing significant challenges, including climate change, habitat loss, and pollution. It is essential to equip individuals with the knowledge and skills to understand these issues and take action. This proposal seeks to bridge the gap in environmental education and inspire a sense of environmental stewardship among the community.
Problem Statement: The lack of environmental education programs has resulted in limited awareness and understanding of environmental issues. As a result, individuals are less likely to adopt sustainable practices or actively contribute to conservation efforts. Our program aims to address this gap and empower individuals to become environmentally conscious and responsible citizens.
Proposed Solution or Project Description: Our Environmental Education Program will comprise a range of activities, including workshops, field trips, and community initiatives. We will collaborate with local schools, community centers, and environmental organizations to ensure broad participation and maximum impact. By incorporating interactive learning experiences, such as nature walks, recycling drives, and eco-craft sessions, we aim to make environmental education engaging and enjoyable.
Methodology: Our program will be structured into modules that cover key environmental themes, such as biodiversity, climate change, waste management, and sustainable living. Each module will include a mix of classroom sessions, hands-on activities, and practical field experiences. We will also leverage technology, such as educational apps and online resources, to enhance learning outcomes.
Evaluation and Success Metrics: We will employ a combination of quantitative and qualitative measures to evaluate the effectiveness of the program. Pre- and post-assessments will gauge knowledge gain, while surveys and feedback forms will assess participant satisfaction and behavior change. We will also track the number of community engagement activities and the adoption of sustainable practices as indicators of success.
Budget: Please find attached a detailed budget breakdown for the implementation of the Environmental Education Program. The budget covers personnel costs, materials and supplies, transportation, and outreach expenses. We have ensured cost-effectiveness while maintaining the quality and impact of the program.
Conclusion: By implementing this Environmental Education Program, we have the opportunity to make a significant difference in our community’s environmental consciousness and practices. We are confident that this program will foster a generation of individuals who are passionate about protecting our environment and taking sustainable actions. We look forward to discussing the proposal further and working together to make a positive impact.
Thank you for your time and consideration. Should you have any questions or require additional information, please do not hesitate to contact me at [your email address or phone number].
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Grant Proposal – Example, Template and Guide

How To Write A Business Proposal – Step-by-Step...

Business Proposal – Templates, Examples and Guide

How To Write A Research Proposal – Step-by-Step...

Proposal – Types, Examples, and Writing Guide

How to choose an Appropriate Method for Research?
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Research paper
Writing a Research Paper Introduction | Step-by-Step Guide
Published on September 24, 2022 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on March 27, 2023.

The introduction to a research paper is where you set up your topic and approach for the reader. It has several key goals:
- Present your topic and get the reader interested
- Provide background or summarize existing research
- Position your own approach
- Detail your specific research problem and problem statement
- Give an overview of the paper’s structure
The introduction looks slightly different depending on whether your paper presents the results of original empirical research or constructs an argument by engaging with a variety of sources.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Step 1: introduce your topic, step 2: describe the background, step 3: establish your research problem, step 4: specify your objective(s), step 5: map out your paper, research paper introduction examples, frequently asked questions about the research paper introduction.
The first job of the introduction is to tell the reader what your topic is and why it’s interesting or important. This is generally accomplished with a strong opening hook.
The hook is a striking opening sentence that clearly conveys the relevance of your topic. Think of an interesting fact or statistic, a strong statement, a question, or a brief anecdote that will get the reader wondering about your topic.
For example, the following could be an effective hook for an argumentative paper about the environmental impact of cattle farming:
A more empirical paper investigating the relationship of Instagram use with body image issues in adolescent girls might use the following hook:
Don’t feel that your hook necessarily has to be deeply impressive or creative. Clarity and relevance are still more important than catchiness. The key thing is to guide the reader into your topic and situate your ideas.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
This part of the introduction differs depending on what approach your paper is taking.
In a more argumentative paper, you’ll explore some general background here. In a more empirical paper, this is the place to review previous research and establish how yours fits in.
Argumentative paper: Background information
After you’ve caught your reader’s attention, specify a bit more, providing context and narrowing down your topic.
Provide only the most relevant background information. The introduction isn’t the place to get too in-depth; if more background is essential to your paper, it can appear in the body .
Empirical paper: Describing previous research
For a paper describing original research, you’ll instead provide an overview of the most relevant research that has already been conducted. This is a sort of miniature literature review —a sketch of the current state of research into your topic, boiled down to a few sentences.
This should be informed by genuine engagement with the literature. Your search can be less extensive than in a full literature review, but a clear sense of the relevant research is crucial to inform your own work.
Begin by establishing the kinds of research that have been done, and end with limitations or gaps in the research that you intend to respond to.
The next step is to clarify how your own research fits in and what problem it addresses.
Argumentative paper: Emphasize importance
In an argumentative research paper, you can simply state the problem you intend to discuss, and what is original or important about your argument.
Empirical paper: Relate to the literature
In an empirical research paper, try to lead into the problem on the basis of your discussion of the literature. Think in terms of these questions:
- What research gap is your work intended to fill?
- What limitations in previous work does it address?
- What contribution to knowledge does it make?
You can make the connection between your problem and the existing research using phrases like the following.
Now you’ll get into the specifics of what you intend to find out or express in your research paper.
The way you frame your research objectives varies. An argumentative paper presents a thesis statement, while an empirical paper generally poses a research question (sometimes with a hypothesis as to the answer).
Argumentative paper: Thesis statement
The thesis statement expresses the position that the rest of the paper will present evidence and arguments for. It can be presented in one or two sentences, and should state your position clearly and directly, without providing specific arguments for it at this point.
Empirical paper: Research question and hypothesis
The research question is the question you want to answer in an empirical research paper.
Present your research question clearly and directly, with a minimum of discussion at this point. The rest of the paper will be taken up with discussing and investigating this question; here you just need to express it.
A research question can be framed either directly or indirectly.
- This study set out to answer the following question: What effects does daily use of Instagram have on the prevalence of body image issues among adolescent girls?
- We investigated the effects of daily Instagram use on the prevalence of body image issues among adolescent girls.
If your research involved testing hypotheses , these should be stated along with your research question. They are usually presented in the past tense, since the hypothesis will already have been tested by the time you are writing up your paper.
For example, the following hypothesis might respond to the research question above:
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing - try for free!
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Try for free
The final part of the introduction is often dedicated to a brief overview of the rest of the paper.
In a paper structured using the standard scientific “introduction, methods, results, discussion” format, this isn’t always necessary. But if your paper is structured in a less predictable way, it’s important to describe the shape of it for the reader.
If included, the overview should be concise, direct, and written in the present tense.
- This paper will first discuss several examples of survey-based research into adolescent social media use, then will go on to …
- This paper first discusses several examples of survey-based research into adolescent social media use, then goes on to …
Full examples of research paper introductions are shown in the tabs below: one for an argumentative paper, the other for an empirical paper.
- Argumentative paper
- Empirical paper
Are cows responsible for climate change? A recent study (RIVM, 2019) shows that cattle farmers account for two thirds of agricultural nitrogen emissions in the Netherlands. These emissions result from nitrogen in manure, which can degrade into ammonia and enter the atmosphere. The study’s calculations show that agriculture is the main source of nitrogen pollution, accounting for 46% of the country’s total emissions. By comparison, road traffic and households are responsible for 6.1% each, the industrial sector for 1%. While efforts are being made to mitigate these emissions, policymakers are reluctant to reckon with the scale of the problem. The approach presented here is a radical one, but commensurate with the issue. This paper argues that the Dutch government must stimulate and subsidize livestock farmers, especially cattle farmers, to transition to sustainable vegetable farming. It first establishes the inadequacy of current mitigation measures, then discusses the various advantages of the results proposed, and finally addresses potential objections to the plan on economic grounds.
The rise of social media has been accompanied by a sharp increase in the prevalence of body image issues among women and girls. This correlation has received significant academic attention: Various empirical studies have been conducted into Facebook usage among adolescent girls (Tiggermann & Slater, 2013; Meier & Gray, 2014). These studies have consistently found that the visual and interactive aspects of the platform have the greatest influence on body image issues. Despite this, highly visual social media (HVSM) such as Instagram have yet to be robustly researched. This paper sets out to address this research gap. We investigated the effects of daily Instagram use on the prevalence of body image issues among adolescent girls. It was hypothesized that daily Instagram use would be associated with an increase in body image concerns and a decrease in self-esteem ratings.
The introduction of a research paper includes several key elements:
- A hook to catch the reader’s interest
- Relevant background on the topic
- Details of your research problem
and your problem statement
- A thesis statement or research question
- Sometimes an overview of the paper
Don’t feel that you have to write the introduction first. The introduction is often one of the last parts of the research paper you’ll write, along with the conclusion.
This is because it can be easier to introduce your paper once you’ve already written the body ; you may not have the clearest idea of your arguments until you’ve written them, and things can change during the writing process .
The way you present your research problem in your introduction varies depending on the nature of your research paper . A research paper that presents a sustained argument will usually encapsulate this argument in a thesis statement .
A research paper designed to present the results of empirical research tends to present a research question that it seeks to answer. It may also include a hypothesis —a prediction that will be confirmed or disproved by your research.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, March 27). Writing a Research Paper Introduction | Step-by-Step Guide. Scribbr. Retrieved April 8, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/research-paper/research-paper-introduction/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, writing strong research questions | criteria & examples, writing a research paper conclusion | step-by-step guide, research paper format | apa, mla, & chicago templates, what is your plagiarism score.
- EssayBasics.com
- Pay For Essay
- Write My Essay
- Homework Writing Help
- Essay Editing Service
- Thesis Writing Help
- Write My College Essay
- Do My Essay
- Term Paper Writing Service
- Coursework Writing Service
- Write My Research Paper
- Assignment Writing Help
- Essay Writing Help
- Call Now! (USA) Login Order now
- EssayBasics.com Call Now! (USA) Order now
- Writing Guides
How To Write A Proposal Essay In 2023?
Also Read: Best Cheap Essay Writing Service , Cheap Essays Online , Online Essay Service
Table of Contents
How To Write A Proposal Essay (Writing Guide)
- How to start a proposal essay
- How to write body for a proposal essay
- How to conclude a proposal essay
- Outline example
Briefly, a proposal essay is an essay which puts forward an original idea, and then defends it through the use of well-backed up research and personal opinion combined to try and persuade whoever is reading it of the advantages\disadvantages of the idea.
Proposals are mainly found in three fields: education (it is a good way to teach and learn critical thinking), business (as a way of showing why particular moves would be a bad idea, or a good one, respectively), and economics, for much the same reason. This of course does not mean that they are limited to these areas – proposal essay writing is something which can be useful for many fields.
How to Start a Proposal Essay
Much of the work which goes into a good proposal essay is done ahead of time; as the following paragraphs will show, being able to persuade others of your point of view is as much to do with the quality of the research being done, and the ways in which you pitch your argument as it does with the writing style. Writing is (it should go without saying) important, but it can only do so much.
Knowing the audience for your work is incredibly important – the audience will determine the overall tone of the paper, as well as possibly influence the types of sources which can and should be used to back up the arguments made in the paper itself. For example, if the paper is aimed at business people, then arguments should revolve around the financial benefits or drawbacks of the situation being proposed. Alternatively, academics should be tackled by using strictly academic sources and previous academic theories , whether to agree with them or disagree.
Don’t skip over the research. This is the most important part of the process, even more so than having polished writing; less than stellar writing and good research will stand up to scrutiny far more easily than perfect writing and a lack of research will. Good research also makes it more likely that the essay will fulfill its purpose in persuading other people to the point of view it discusses.
Before writing the essay, start by creating a list of your ideas, and forming them into an outline . This outline does not need to be fixed, but it will you to organize your thoughts and the essay so that they both flow coherently in the writing.
An introduction in an essay is how you introduce the topic to whoever is reading. Not only is it the place to lay out the arguments which you will be relying on throughout the essay, but also gives space for any necessary history or important people to be mentioned and discussed before the actual essay begins. The introduction is possibly one of the most important parts of the essay, as it sets up what is to come, and begins the work of persuading people of a particular point of view by convincing them to read on. Outside of an educational setting, proposal essays are generally only written as a means of solving a problem or showing one potential way to solve a problem. Therefore, they highlight the problem which they are attempting to solve within the introduction itself, so as to ensure that the audience understands.

Related: Why Order Essay Writing Service
How to Write the Main Part of a Proposal Essay
An outline will be featured at the end of this article, which will show the relevant parts of a proposal essay – note that depending on the context, some parts may need to be taken out or rearranged to better suit what it is trying to convey.
The Proposal
The proposal should act as a statement of purpose, something which explains the purpose behind writing the essay. It can be anything from a few lines long to an entire paragraph – it depends on the length of the essay itself – but it should contain the problem\opinion\topic which is under discussion, and an explanation of why it is worth debating.
Body Paragraph One – First Argument
This is the paragraph where you lay out your first argument for or against the proposal. Make sure that the writing is good, clear, and doesn’t go off into unnecessary tangents. Similarly, make sure that everything is referenced properly, and prepare to back up every argument (including any follow-up arguments) with well-checked facts.
Body Paragraph Two – Second Argument
This should be the same as above, except with an entirely new argument.
Body Paragraph Three – Third (Opposing) Argument
Again, this should be the same as above, although many people use it as a means of expressing an opposing opinion to the one they hold. It is entirely up to the writer as to how to use this paragraph, though it should be noted that devoting time to debunking the more common arguments or opposing opinions in the essay will tell the audience that the research into the problem has been thorough and well-done.
How to Conclude a Proposal Essay
The conclusion should not be a simple re-statement of the introduction, with all of the relevant history and essay points, but it should contain some elements of it all. You should include just enough to serve as a reminder of why the proposal was deemed appropriate in the first place, without any in-depth knowledge of the introduction. The main arguments being made in your proposal should also be reiterated. Once this is done, there are two ways in which a proposal essay can be ended, and it depends on what type of proposal essay was being written. If the proposal essay was written in an educational setting, then the conclusion should wrap up all the research done and deliver the final conclusion, along with any last pieces of information which might be appropriate at this stage. The other kind of proposal essay, the one did in a professional setting, should have several more strands to it.
For people who are giving a professional proposal essay : state the goal of the proposal, just to ensure that everybody who reads the essay knows what it is handling, and then focus on why the proposal will work, with reference to any previous moves in this direction, or any potential assets to the proposal which would particularly suit your audience.
Outline Example
- It should be banned because it goes against the family-friendly nature of the paper
- It should be banned because it is overall degrading, and outdated
- It should not be banned because the women gave their consent to be photographed that way.
- Proposal – page three is something that should be banned because it is an outdated feature of the newspaper which blatantly goes against the nature of the paper as stated by its publishers. It has no place in a society that claims to view men and women as equal.
- Body paragraph one – the Sun claims that it is family-friendly, so what message is the topless woman sending to the family, and specifically, to children? It teaches boys that women should be related to sex objects, it teaches girls that they should be okay with being related to a sex object.
- Body paragraph two – women are supposed to be seen as equals in our society, but there are no corresponding naked men features, so the topless women become one more part of our ‘sex-sells’ culture. This is degrading to women who want to be more than that.
- Body paragraph three – the women in question are presumably over the age of consent and therefore chose to be photographed like this. Is it not degrading to take their choice away from them?
- Reiterate the proposal
- Go over the main arguments
- Come to an overall conclusion.

Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Research process
- How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
Published on 30 October 2022 by Shona McCombes and Tegan George. Revised on 13 June 2023.
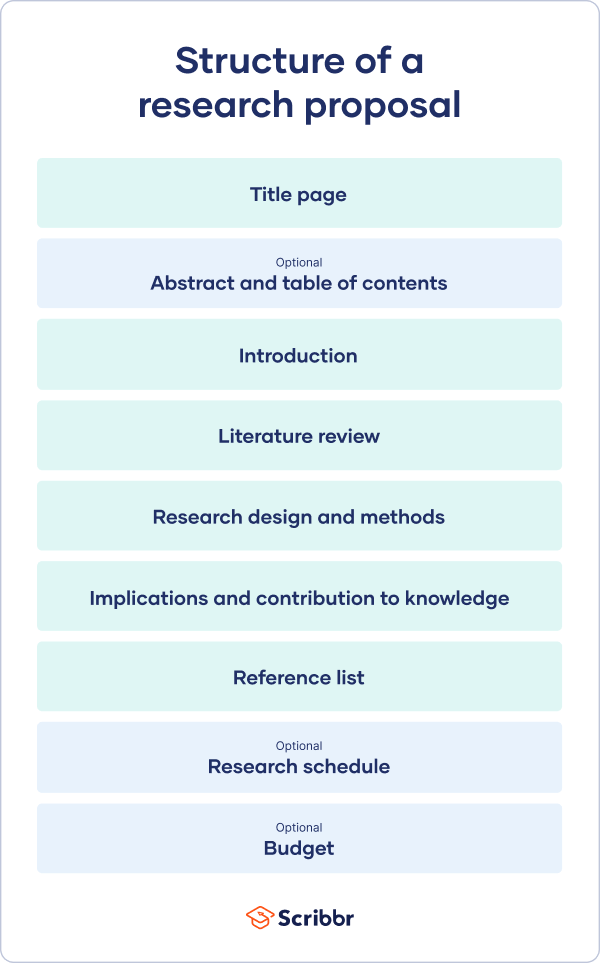
A research proposal describes what you will investigate, why it’s important, and how you will conduct your research.
The format of a research proposal varies between fields, but most proposals will contain at least these elements:
Introduction
Literature review.
- Research design
Reference list
While the sections may vary, the overall objective is always the same. A research proposal serves as a blueprint and guide for your research plan, helping you get organised and feel confident in the path forward you choose to take.
Table of contents
Research proposal purpose, research proposal examples, research design and methods, contribution to knowledge, research schedule, frequently asked questions.
Academics often have to write research proposals to get funding for their projects. As a student, you might have to write a research proposal as part of a grad school application , or prior to starting your thesis or dissertation .
In addition to helping you figure out what your research can look like, a proposal can also serve to demonstrate why your project is worth pursuing to a funder, educational institution, or supervisor.
Research proposal length
The length of a research proposal can vary quite a bit. A bachelor’s or master’s thesis proposal can be just a few pages, while proposals for PhD dissertations or research funding are usually much longer and more detailed. Your supervisor can help you determine the best length for your work.
One trick to get started is to think of your proposal’s structure as a shorter version of your thesis or dissertation , only without the results , conclusion and discussion sections.
Download our research proposal template
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We’ve included a few for you below.
- Example research proposal #1: ‘A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management’
- Example research proposal #2: ‘ Medical Students as Mediators of Change in Tobacco Use’
Like your dissertation or thesis, the proposal will usually have a title page that includes:
- The proposed title of your project
- Your supervisor’s name
- Your institution and department
The first part of your proposal is the initial pitch for your project. Make sure it succinctly explains what you want to do and why.
Your introduction should:
- Introduce your topic
- Give necessary background and context
- Outline your problem statement and research questions
To guide your introduction , include information about:
- Who could have an interest in the topic (e.g., scientists, policymakers)
- How much is already known about the topic
- What is missing from this current knowledge
- What new insights your research will contribute
- Why you believe this research is worth doing
As you get started, it’s important to demonstrate that you’re familiar with the most important research on your topic. A strong literature review shows your reader that your project has a solid foundation in existing knowledge or theory. It also shows that you’re not simply repeating what other people have already done or said, but rather using existing research as a jumping-off point for your own.
In this section, share exactly how your project will contribute to ongoing conversations in the field by:
- Comparing and contrasting the main theories, methods, and debates
- Examining the strengths and weaknesses of different approaches
- Explaining how will you build on, challenge, or synthesise prior scholarship
Following the literature review, restate your main objectives . This brings the focus back to your own project. Next, your research design or methodology section will describe your overall approach, and the practical steps you will take to answer your research questions.
To finish your proposal on a strong note, explore the potential implications of your research for your field. Emphasise again what you aim to contribute and why it matters.
For example, your results might have implications for:
- Improving best practices
- Informing policymaking decisions
- Strengthening a theory or model
- Challenging popular or scientific beliefs
- Creating a basis for future research
Last but not least, your research proposal must include correct citations for every source you have used, compiled in a reference list . To create citations quickly and easily, you can use our free APA citation generator .
Some institutions or funders require a detailed timeline of the project, asking you to forecast what you will do at each stage and how long it may take. While not always required, be sure to check the requirements of your project.
Here’s an example schedule to help you get started. You can also download a template at the button below.
Download our research schedule template
If you are applying for research funding, chances are you will have to include a detailed budget. This shows your estimates of how much each part of your project will cost.
Make sure to check what type of costs the funding body will agree to cover. For each item, include:
- Cost : exactly how much money do you need?
- Justification : why is this cost necessary to complete the research?
- Source : how did you calculate the amount?
To determine your budget, think about:
- Travel costs : do you need to go somewhere to collect your data? How will you get there, and how much time will you need? What will you do there (e.g., interviews, archival research)?
- Materials : do you need access to any tools or technologies?
- Help : do you need to hire any research assistants for the project? What will they do, and how much will you pay them?
Once you’ve decided on your research objectives , you need to explain them in your paper, at the end of your problem statement.
Keep your research objectives clear and concise, and use appropriate verbs to accurately convey the work that you will carry out for each one.
I will compare …
A research aim is a broad statement indicating the general purpose of your research project. It should appear in your introduction at the end of your problem statement , before your research objectives.
Research objectives are more specific than your research aim. They indicate the specific ways you’ll address the overarching aim.
A PhD, which is short for philosophiae doctor (doctor of philosophy in Latin), is the highest university degree that can be obtained. In a PhD, students spend 3–5 years writing a dissertation , which aims to make a significant, original contribution to current knowledge.
A PhD is intended to prepare students for a career as a researcher, whether that be in academia, the public sector, or the private sector.
A master’s is a 1- or 2-year graduate degree that can prepare you for a variety of careers.
All master’s involve graduate-level coursework. Some are research-intensive and intend to prepare students for further study in a PhD; these usually require their students to write a master’s thesis . Others focus on professional training for a specific career.
Critical thinking refers to the ability to evaluate information and to be aware of biases or assumptions, including your own.
Like information literacy , it involves evaluating arguments, identifying and solving problems in an objective and systematic way, and clearly communicating your ideas.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. & George, T. (2023, June 13). How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved 8 April 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/the-research-process/research-proposal-explained/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, what is a research methodology | steps & tips, what is a literature review | guide, template, & examples, how to write a results section | tips & examples.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Sample Academic Proposals

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Media File: Sample Academic Proposals
This resource is enhanced by an Acrobat PDF file. Download the free Acrobat Reader
Select the Sample Academic Proposals PDF in the Media box above to download this file and read examples of proposals for conferences, journals, and book chapters.
Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature
How to Write a Research Paper Introduction (with Examples)

The research paper introduction section, along with the Title and Abstract, can be considered the face of any research paper. The following article is intended to guide you in organizing and writing the research paper introduction for a quality academic article or dissertation.
The research paper introduction aims to present the topic to the reader. A study will only be accepted for publishing if you can ascertain that the available literature cannot answer your research question. So it is important to ensure that you have read important studies on that particular topic, especially those within the last five to ten years, and that they are properly referenced in this section. 1 What should be included in the research paper introduction is decided by what you want to tell readers about the reason behind the research and how you plan to fill the knowledge gap. The best research paper introduction provides a systemic review of existing work and demonstrates additional work that needs to be done. It needs to be brief, captivating, and well-referenced; a well-drafted research paper introduction will help the researcher win half the battle.
The introduction for a research paper is where you set up your topic and approach for the reader. It has several key goals:
- Present your research topic
- Capture reader interest
- Summarize existing research
- Position your own approach
- Define your specific research problem and problem statement
- Highlight the novelty and contributions of the study
- Give an overview of the paper’s structure
The research paper introduction can vary in size and structure depending on whether your paper presents the results of original empirical research or is a review paper. Some research paper introduction examples are only half a page while others are a few pages long. In many cases, the introduction will be shorter than all of the other sections of your paper; its length depends on the size of your paper as a whole.
- Break through writer’s block. Write your research paper introduction with Paperpal Copilot
Table of Contents
What is the introduction for a research paper, why is the introduction important in a research paper, craft a compelling introduction section with paperpal. try now, 1. introduce the research topic:, 2. determine a research niche:, 3. place your research within the research niche:, craft accurate research paper introductions with paperpal. start writing now, frequently asked questions on research paper introduction, key points to remember.
The introduction in a research paper is placed at the beginning to guide the reader from a broad subject area to the specific topic that your research addresses. They present the following information to the reader
- Scope: The topic covered in the research paper
- Context: Background of your topic
- Importance: Why your research matters in that particular area of research and the industry problem that can be targeted
The research paper introduction conveys a lot of information and can be considered an essential roadmap for the rest of your paper. A good introduction for a research paper is important for the following reasons:
- It stimulates your reader’s interest: A good introduction section can make your readers want to read your paper by capturing their interest. It informs the reader what they are going to learn and helps determine if the topic is of interest to them.
- It helps the reader understand the research background: Without a clear introduction, your readers may feel confused and even struggle when reading your paper. A good research paper introduction will prepare them for the in-depth research to come. It provides you the opportunity to engage with the readers and demonstrate your knowledge and authority on the specific topic.
- It explains why your research paper is worth reading: Your introduction can convey a lot of information to your readers. It introduces the topic, why the topic is important, and how you plan to proceed with your research.
- It helps guide the reader through the rest of the paper: The research paper introduction gives the reader a sense of the nature of the information that will support your arguments and the general organization of the paragraphs that will follow. It offers an overview of what to expect when reading the main body of your paper.
What are the parts of introduction in the research?
A good research paper introduction section should comprise three main elements: 2
- What is known: This sets the stage for your research. It informs the readers of what is known on the subject.
- What is lacking: This is aimed at justifying the reason for carrying out your research. This could involve investigating a new concept or method or building upon previous research.
- What you aim to do: This part briefly states the objectives of your research and its major contributions. Your detailed hypothesis will also form a part of this section.
How to write a research paper introduction?
The first step in writing the research paper introduction is to inform the reader what your topic is and why it’s interesting or important. This is generally accomplished with a strong opening statement. The second step involves establishing the kinds of research that have been done and ending with limitations or gaps in the research that you intend to address. Finally, the research paper introduction clarifies how your own research fits in and what problem it addresses. If your research involved testing hypotheses, these should be stated along with your research question. The hypothesis should be presented in the past tense since it will have been tested by the time you are writing the research paper introduction.
The following key points, with examples, can guide you when writing the research paper introduction section:
- Highlight the importance of the research field or topic
- Describe the background of the topic
- Present an overview of current research on the topic
Example: The inclusion of experiential and competency-based learning has benefitted electronics engineering education. Industry partnerships provide an excellent alternative for students wanting to engage in solving real-world challenges. Industry-academia participation has grown in recent years due to the need for skilled engineers with practical training and specialized expertise. However, from the educational perspective, many activities are needed to incorporate sustainable development goals into the university curricula and consolidate learning innovation in universities.
- Reveal a gap in existing research or oppose an existing assumption
- Formulate the research question
Example: There have been plausible efforts to integrate educational activities in higher education electronics engineering programs. However, very few studies have considered using educational research methods for performance evaluation of competency-based higher engineering education, with a focus on technical and or transversal skills. To remedy the current need for evaluating competencies in STEM fields and providing sustainable development goals in engineering education, in this study, a comparison was drawn between study groups without and with industry partners.
- State the purpose of your study
- Highlight the key characteristics of your study
- Describe important results
- Highlight the novelty of the study.
- Offer a brief overview of the structure of the paper.
Example: The study evaluates the main competency needed in the applied electronics course, which is a fundamental core subject for many electronics engineering undergraduate programs. We compared two groups, without and with an industrial partner, that offered real-world projects to solve during the semester. This comparison can help determine significant differences in both groups in terms of developing subject competency and achieving sustainable development goals.
Write a Research Paper Introduction in Minutes with Paperpal
Paperpal Copilot is a generative AI-powered academic writing assistant. It’s trained on millions of published scholarly articles and over 20 years of STM experience. Paperpal Copilot helps authors write better and faster with:
- Real-time writing suggestions
- In-depth checks for language and grammar correction
- Paraphrasing to add variety, ensure academic tone, and trim text to meet journal limits
With Paperpal Copilot, create a research paper introduction effortlessly. In this step-by-step guide, we’ll walk you through how Paperpal transforms your initial ideas into a polished and publication-ready introduction.

How to use Paperpal to write the Introduction section
Step 1: Sign up on Paperpal and click on the Copilot feature, under this choose Outlines > Research Article > Introduction
Step 2: Add your unstructured notes or initial draft, whether in English or another language, to Paperpal, which is to be used as the base for your content.
Step 3: Fill in the specifics, such as your field of study, brief description or details you want to include, which will help the AI generate the outline for your Introduction.
Step 4: Use this outline and sentence suggestions to develop your content, adding citations where needed and modifying it to align with your specific research focus.
Step 5: Turn to Paperpal’s granular language checks to refine your content, tailor it to reflect your personal writing style, and ensure it effectively conveys your message.
You can use the same process to develop each section of your article, and finally your research paper in half the time and without any of the stress.
The purpose of the research paper introduction is to introduce the reader to the problem definition, justify the need for the study, and describe the main theme of the study. The aim is to gain the reader’s attention by providing them with necessary background information and establishing the main purpose and direction of the research.
The length of the research paper introduction can vary across journals and disciplines. While there are no strict word limits for writing the research paper introduction, an ideal length would be one page, with a maximum of 400 words over 1-4 paragraphs. Generally, it is one of the shorter sections of the paper as the reader is assumed to have at least a reasonable knowledge about the topic. 2 For example, for a study evaluating the role of building design in ensuring fire safety, there is no need to discuss definitions and nature of fire in the introduction; you could start by commenting upon the existing practices for fire safety and how your study will add to the existing knowledge and practice.
When deciding what to include in the research paper introduction, the rest of the paper should also be considered. The aim is to introduce the reader smoothly to the topic and facilitate an easy read without much dependency on external sources. 3 Below is a list of elements you can include to prepare a research paper introduction outline and follow it when you are writing the research paper introduction. Topic introduction: This can include key definitions and a brief history of the topic. Research context and background: Offer the readers some general information and then narrow it down to specific aspects. Details of the research you conducted: A brief literature review can be included to support your arguments or line of thought. Rationale for the study: This establishes the relevance of your study and establishes its importance. Importance of your research: The main contributions are highlighted to help establish the novelty of your study Research hypothesis: Introduce your research question and propose an expected outcome. Organization of the paper: Include a short paragraph of 3-4 sentences that highlights your plan for the entire paper
Cite only works that are most relevant to your topic; as a general rule, you can include one to three. Note that readers want to see evidence of original thinking. So it is better to avoid using too many references as it does not leave much room for your personal standpoint to shine through. Citations in your research paper introduction support the key points, and the number of citations depend on the subject matter and the point discussed. If the research paper introduction is too long or overflowing with citations, it is better to cite a few review articles rather than the individual articles summarized in the review. A good point to remember when citing research papers in the introduction section is to include at least one-third of the references in the introduction.
The literature review plays a significant role in the research paper introduction section. A good literature review accomplishes the following: Introduces the topic – Establishes the study’s significance – Provides an overview of the relevant literature – Provides context for the study using literature – Identifies knowledge gaps However, remember to avoid making the following mistakes when writing a research paper introduction: Do not use studies from the literature review to aggressively support your research Avoid direct quoting Do not allow literature review to be the focus of this section. Instead, the literature review should only aid in setting a foundation for the manuscript.
Remember the following key points for writing a good research paper introduction: 4
- Avoid stuffing too much general information: Avoid including what an average reader would know and include only that information related to the problem being addressed in the research paper introduction. For example, when describing a comparative study of non-traditional methods for mechanical design optimization, information related to the traditional methods and differences between traditional and non-traditional methods would not be relevant. In this case, the introduction for the research paper should begin with the state-of-the-art non-traditional methods and methods to evaluate the efficiency of newly developed algorithms.
- Avoid packing too many references: Cite only the required works in your research paper introduction. The other works can be included in the discussion section to strengthen your findings.
- Avoid extensive criticism of previous studies: Avoid being overly critical of earlier studies while setting the rationale for your study. A better place for this would be the Discussion section, where you can highlight the advantages of your method.
- Avoid describing conclusions of the study: When writing a research paper introduction remember not to include the findings of your study. The aim is to let the readers know what question is being answered. The actual answer should only be given in the Results and Discussion section.
To summarize, the research paper introduction section should be brief yet informative. It should convince the reader the need to conduct the study and motivate him to read further. If you’re feeling stuck or unsure, choose trusted AI academic writing assistants like Paperpal to effortlessly craft your research paper introduction and other sections of your research article.
1. Jawaid, S. A., & Jawaid, M. (2019). How to write introduction and discussion. Saudi Journal of Anaesthesia, 13(Suppl 1), S18.
2. Dewan, P., & Gupta, P. (2016). Writing the title, abstract and introduction: Looks matter!. Indian pediatrics, 53, 235-241.
3. Cetin, S., & Hackam, D. J. (2005). An approach to the writing of a scientific Manuscript1. Journal of Surgical Research, 128(2), 165-167.
4. Bavdekar, S. B. (2015). Writing introduction: Laying the foundations of a research paper. Journal of the Association of Physicians of India, 63(7), 44-6.
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- Scientific Writing Style Guides Explained
- 5 Reasons for Rejection After Peer Review
- Ethical Research Practices For Research with Human Subjects
- 8 Most Effective Ways to Increase Motivation for Thesis Writing
Practice vs. Practise: Learn the Difference
Academic paraphrasing: why paperpal’s rewrite should be your first choice , you may also like, ai in education: it’s time to change the..., is it ethical to use ai-generated abstracts without..., what are journal guidelines on using generative ai..., quillbot review: features, pricing, and free alternatives, what is an academic paper types and elements , should you use ai tools like chatgpt for..., publish research papers: 9 steps for successful publications , what are the different types of research papers, how to make translating academic papers less challenging, self-plagiarism in research: what it is and how....

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

7.6.1: Annotated Sample Proposal Argument
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 92716
Media Alternative
Listen to an audio version of this page (12 min, 39 sec):
Format note: This version is accessible to screen reader users. Refer to these tips for reading our annotated sample arguments with a screen reader . For a more traditional visual format, see the PDF version of "Why We Should Open Our Borders."
Laurent Wenjun Jiang
Prof. Natalie Peterkin
July 25, 2020
Why We Should Open Our Borders
Refugees, inequalities, economic instabilities...the fact that we are bombarded by news on those topics every day is proof that we live in a world with lots of problems, and many of us suffer as a consequence. Nations have tried a variety of solutions, but the reality has not improved. Yet there exists a single easy measure that could solve almost all of the problems mentioned above: an open-border policy. The current border and immigration practices, including border controls and detention centers, are unjustified and counterproductive. (Note: The first body paragraph gives background on the problem, opportunity, or situation.) This paper discusses the refugee problem, the history of open-border policy, the refutations for the current border policies on philosophical and moral grounds, and the arguments why this open-border policy will work economically.
Refugees are a problem of worldwide concern. Recently the biggest wave of refugees came from Syria, which witnessed an eight-year-long civil war. In an interview, a Syrian refugee expresses deep sorrows regarding the loss of her home: “My brothers, sisters, uncles, neighbors, streets, the bread ovens, schools, children going to schools ...we miss all of that, everything in Syria is precious to us” she says, with tears hovering in her eyes (Firpo). She also exposes the terrible living conditions there: “[W]e didn’t run away, Syria has become uninhabitable. Not even animals could live there. No power, no running water, no safety, and no security. You don’t know who to fight...even when you lock yourself away, you’re not safe...I was most scared of seeing my children die right in front of me” (Firpo). (Note: Moving refugee testimonies serve as evidence supporting the claim that their situation is one of great urgency.) As heart-breaking as it sounds, we should also know that this is only the tip of the iceberg: Gerhard Hoffstaedter, an anthropologist at the University of Queensland, states that there are around 70 million displaced people in developing countries, which is the highest recorded number since the 1950s, causing the United Nations to call this world issue “a crisis.” The leading nations in the world do not offer enough support to displaced people living in abject conditions. Refugees at the U.S.-Mexico border and in Southeast Asia and Australia are constantly kept in detention centers. Many nations do not comply with the provisions signed in the 1951 Refugee Convention and the succeeding 1967 Protocol; they treat the refugees only as those in passive need of simply humanitarian aids (Hoffstaedter). In this crisis, it is our common responsibility as members of an international community to help those who are in need.
Historically, the large-scale control of the mobility of people is a relatively new phenomenon worldwide. (Note: This body paragraph starts with a definition argument to show that the current trend is new. This argument later becomes support for the idea that open borders are possible.) In the modern era, border signifies “ever more restrictive immigration policies” at the same time grants “greater freedom of mobility to capital and commodities”, as defined in the editorial “Why No Borders.” This creates a contradictory ideology that could cause potential harm to those who need to migrate (Anderson, et al.). John Maynard Keynes dates the beginning of this process only back to World War I in the early 20th century. However, this trend did not become widespread until after World War II. According to a historical outline created by Christof Van Mol and Helga de Valk, due to the booming in the industrial production in northwestern Europe in the 1950s, the local workers were increasingly educated and gradually became whitecollar employers, leaving vacancies in blue-collar occupations (Mol and Valk).
Thus, those countries started recruiting immigrants from other parts of Europe and even North Africa: for example, Germany and France started seasonal working programs to attract immigrants (Mol and Valk). Because of the lack of job opportunities in the other parts of Europe and North Africa and the need for workers in the industrializing countries in Northern and Western Europe, “international migration was generally viewed positively because of its economic benefits, from the perspective of both the sending and the receiving countries'' (Mol and Valk). This early migration pattern within Europe provides the basic model for the European Union that builds on the fundamental ideology of the free movements of goods and human resources. In recent days, the European Union has become one of the biggest multinational organizations, which can also serve as a successful example of this open-border ideology, at least on a regional scale.
Borders do not satisfy the needs of contemporary societies. From both philosophical and moral perspectives, restrictive border policies are not justified. First of all, borders divide and subjugate people. The editorial “Why No Borders” describes the border as being“thoroughly ideological” (Anderson, et al.). The authors argue that because border policies try to categorize people into “desirable and non-desirable” according to their skills, race, or social status, etc., they thus create an interplay between “subjects and subjectivities,” placing people into “new types of power relationship” (Anderson, et al.). This is what is identified as the ultimate cause of the divisions and inequalities between people.
Some fear that competition from immigrants would cause a reduction in the wages of local workers (Caplan). (Note: In this body paragraph, the author attempts to disprove the counterargument about a downside of open borders for local workers.) This is not an uncalled-for worry, but it is also a misunderstanding of the nature of the open-border policy. Nick Srnicek reasons that this kind of competition has already existed under the current trend of globalization, where workers in developed countries are already competing against those in developing countries that have cheaper labor. He argues, “Workers in rich countries are already losing, as companies eliminate good jobs and move their factories and offices elsewhere” (Srnicek). The border serves companies by making workers in the developing world stay where wages are low. Thus, “companies can freely exploit” cheap labor. In this sense, workers on both sides will be better off under an open-border policy (Srnicek). A recent study from the University of Wisconsin-Madison investigating the economic implications of immigration between rich and poor countries concluded that the benefits of an open-border policy far outweigh the cons and that “the real wage effects are small” (Kennan).
Although an open border could lead to minor reductions in the wages of local workers in developed countries, there is a simple solution. Since the labor market follows the economic law of supply, work supply and wages are inversely related, meaning that the lower the supply of labor, the more wages rise. (Note: This paragraph could be seen as a limit and a rebuttal because the open border would need to be combined with changes to labor laws in order to avoid a possible bad effect.) Nick Srnicek proposes, “a shortening of the workweek...would reduce the amount of work supplied, spread the work out more equally among everyone and give more power to workers ... more free time to everyone” (Srnicek). Thus, although the open-border policy is not perfect, its downside is easy to address. (Note: The author does not investigate how much time, money, and will an open border policy would need; the argument remains mostly theoretical because it doesn’t address feasibility.)
As an expatriate myself, I can truly relate to this type of thinking. Due to a variety of the political, economic, and social limitations that I came across in my home country, I was not able to achieve self-actualization. In pursuit of a better education and a more free living environment, I went abroad and finally arrived in this country a few years ago. It was not until then that I gained a vision of my future. Now I am working in hopes that one day the vision could become reality. Sometimes I cannot help wondering what could happen if I was not so lucky to be where I am today. But at the same time, I am also conscious of the fact that there are also millions of people out there who cannot even conceive of what it is like to actualize their lives. (Note: The conclusion humanizes the possible benefits of the proposed solution.) I am sure that one of the mothers who escaped her war-torn home country with her family has the sole hope to witness her children growing up in a happy and free place, just like any mother in the world. I am sure that there is one little girl whose family fled her country in desperation who once studied so hard in school, dreaming of becoming the greatest scientist in the world. I am also sure that there is a young boy who survived persecutions and wishes to become a politician one day to make the world a better place for the downtrodden. Because of borders, these children can only dream of the things that many of us take for granted every day. We, as human beings, might be losing a great mother, great scientist, great politician, or just a great person who simply wishes for a better world. But everything could be otherwise. Change requires nothing but a minimal effort. With open borders, we can help people achieve their dreams.
Works Cited
Hoffstaedter, Gerhard. “There Are 70 Million Refugees in the World. Here Are 5 Solutions to the Problem.” The Conversation , 24 Mar. 2020, theconversation.com/there-are-70-million-refugees-in-the-world-here-are-5- solutions-to-the-problem-118920.
Anderson, Sharma. “Editorial: Why No Borders?” Refuge , vol. 26, no. 2, 2009, pp.5+. Centre for Refugee Studies, York University. Accessed July 26, 2020.
D, D. “Keynes, J. M., The economic consequences of the peace.” Ekonomisk tidskrift, vol. 22, no. 1, Basil Blackwell Ltd., etc, Jan. 1920, p. 15–. Accessed July 26, 2020.
Srnicek, Nick. “The US$100 Trillion Case for Open Borders.” The Conversation , 18 Feb. 2020, theconversation.com/the-us-100-trillion-case-for-open-borders-72595.
Caplan, Bryan. "Why Should We Restrict Immigration?" Cato Journal , vol. 32, no. 1, 2012, pp. 5-24. ProQuest , https://libris.mtsac.edu/login?url=https://search- proquest-com.libris.mtsac.edu/docview/921128626?accountid=12611.Accessed July 26, 2020.
Kennan, John. “Open Borders in the European Union and Beyond: Migration Flows and Labor Market Implications.” NBER Working Paper Series, 2017, www.nber.org/papers/w23048.pdf.
Firpo, Matthew K., director. Refuge . 2016. The Refuge Project, www.refugeproject.co/watch.
Van Mol, Cristof, and Helga de Valk. “Migration and Immigrants in Europe: A Historical and Demographic Perspective.” Integration Processes and Policies in Europe , edited by Blanca Garcés-Mascareñas and Rinus Penninx, 2016, IMISCOE Research Series, pp. 33-55.
Attribution
This sample essay was written by Laurent Wenjun Jiang and edited and annotated by Natalie Peterkin. Licensed CC BY-NC 4.0 .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
7. Preparations Made. Show the audience that you know what you are doing. The more prepared you look the better your chances are to get the proposal passed (or get a better grade if it is for a class). 8. Conclusion. Do not restate your introduction here if you choose to mention the "history" of a certain proposal.
Research proposal examples. Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We've included a few for you below. Example research proposal #1: "A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management".
For Example: A feasible approach to decreasing the alarming mortality rate among young mothers is by equipping parents with necessary skills to support their teenage daughters who become pregnant. 2. Problem Statement: After the introduction, delve deeper into the problem your proposal aims to solve.
Here is an example proposal essay outline for a topic on reducing plastic waste in a community: I. Introduction ... A proposal essay typically includes an introduction, background information, a problem statement, a proposed solution, an implementation plan, and a conclusion. It should also be well-supported by evidence and address potential ...
Primarily referred to as the proposal essay planning stage, here are the five steps to take: 1. Profile your target audience. A proposal essay or proposal argument aims to convince your audience that an idea is feasible, relevant, and practical. It might also persuade the readers that an idea is not worth pursuing.
Here's a proposal essay introduction example: "Imagine a community where families struggle to put food on the table, where children go to bed hungry each night. This is the harsh reality faced by many residents in our town. In this proposal essay, we will address the pressing issue of food insecurity in our community and present a viable ...
Table of contents. Step 1: Hook your reader. Step 2: Give background information. Step 3: Present your thesis statement. Step 4: Map your essay's structure. Step 5: Check and revise. More examples of essay introductions. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about the essay introduction.
The good examples of proposal essay should. Have a clear topic - this should be identical or similar to the essay question asked by the university/college. Show the writer's passion for the subject - when writing essays, the writer's zeal and excitement are always evident.
A proposal essay is a description of a future project. It pursues two purposes: to convince the reader that the research or business deserves attention and to test the plan's viability. Because while writing this essay, you may encounter unsurpassable problems that will require you to change the topic.
Whenever you choose to write it, use it to draw readers in. Make the proposal topic clear, and be concise. End the introduction with your thesis statement. Opening a proposal with an overview of your topic is a reliable strategy, as shown in the following student-written example on women working in IT.
Academic Proposals. ... Introduction. An important part of the work completed in academia is sharing our scholarship with others. ... (Larsen 6) as well as one sample chapter to showcase the style and quality of your writing. You should also include the resources you need for the completion of the book and a biographical statement ("About the ...
Here are the key takeaways for how to write essay introduction: 3. Hook the Reader: Start with an engaging hook to grab the reader's attention. This could be a compelling question, a surprising fact, a relevant quote, or an anecdote. Provide Background: Give a brief overview of the topic, setting the context and stage for the discussion.
Example 3. [1] When the Lutz family moved into a new house in Amityville, New York, they found themselves terrorized by a vengeful ghost (Labianca, 2021). Since then, their famous tale has been debunked by scientists and the family themselves (Smith, 2005). [2]
Develop an Outline. Create a clear and logical structure: Divide your proposal into sections or headings that will guide your readers through the content. Consider the typical structure of a proposal: Introduction: Provide a concise overview of the problem, its significance, and the proposed solution. Background/Context: Offer relevant ...
Writing an effective research proposal is essential to acquire funding for your research. The introduction, being the first part of your proposal, must provide the funders a clear understanding of what you plan to do. A well written introduction will help make a compelling case for your research proposal.
Table of contents. Step 1: Introduce your topic. Step 2: Describe the background. Step 3: Establish your research problem. Step 4: Specify your objective (s) Step 5: Map out your paper. Research paper introduction examples. Frequently asked questions about the research paper introduction.
Outline example; Briefly, a proposal essay is an essay which puts forward an original idea, and then defends it through the use of well-backed up research and personal opinion combined to try and persuade whoever is reading it of the advantages\disadvantages of the idea. ... Outline Example. Introduction - page three should be banned. Page ...
Research proposal examples. Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We've included a few for you below. Example research proposal #1: 'A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management'.
Select the Sample Academic Proposals PDF in the Media box above to download this file and read examples of proposals for conferences, journals, and book chapters.
Sample Proposal Argument. Now that you have had the chance to learn about writing a proposal argument, it's time to see what one might look like. Below, you'll see a sample proposal argumentative essay written using APA 7 th edition formatting guidelines. Click the image below to open a PDF of the sample paper. Previous. Next.
Define your specific research problem and problem statement. Highlight the novelty and contributions of the study. Give an overview of the paper's structure. The research paper introduction can vary in size and structure depending on whether your paper presents the results of original empirical research or is a review paper.
Attribution. This sample essay was written by Laurent Wenjun Jiang and edited and annotated by Natalie Peterkin. Licensed CC BY-NC 4.0 . 7.6.1: Annotated Sample Proposal Argument is shared under a CC BY-NC 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by LibreTexts.