Advanced Microeconomics with calculus
Why ace micro.
Essential skills at your own pace

You're in control
Wherever you want, whenever you want.
- Choose what you need to practice
- Available anytime
- Available anywhere
Straight to the point
Important concepts step by step.
- Content curated by a specialist
- Complex stuff in bite-size chunks
Unlimited practice
More practice than in any book.
- Millions of questions
- Detailed answers
- All that for free
These are all the topics available right now
Consumer Behavior
- Budget Constraint
- Marginal Rate of Transformation
- Utility Function
- Indifference Curve
- Marginal Utility
- Marginal Rate of Substitution
- Utility Maximization
- Consumer Demand
Firm Behavior
- Production Function
- Returns to Scale
- Short-Run Production
- Marginal Product of Labor
- Marginal Product of Capital
- Marginal Rate of Technical Substitution
- Marginal Rate of Technical Transformation
- Long-Run Cost Minimization
Perfect Competition
- Price Elasticity of Demand
- Inverse Demand
- Consumer Surplus
- Price Elasticity of Supply
- Inverse Supply
- Producer Surplus
- Equilibrium
Market Distortions
- Price Floor
- Price Ceiling
- Tax on Consumers
- Tax on Producers
- Marginal Revenue
- Marginal Cost
- Profit Maximization
- Best Response Functions
- Cournot Equilibrium
- Stackelberg Equilibrium
Game Theory
- Payoff Matrix
- Best Response
- Pure Strategy Nash Equilibrium
- Expected Payoff
- Mixed Strategy Nash Equilibrium
HIGH SCHOOL
- ACT Tutoring
- SAT Tutoring
- PSAT Tutoring
- ASPIRE Tutoring
- SHSAT Tutoring
- STAAR Tutoring
GRADUATE SCHOOL
- MCAT Tutoring
- GRE Tutoring
- LSAT Tutoring
- GMAT Tutoring
- AIMS Tutoring
- HSPT Tutoring
- ISAT Tutoring
- SSAT Tutoring
Search 50+ Tests
Loading Page
math tutoring
- Elementary Math
- Pre-Calculus
- Trigonometry
science tutoring
Foreign languages.
- Mandarin Chinese
elementary tutoring
- Computer Science
Search 350+ Subjects
- Video Overview
- Tutor Selection Process
- Online Tutoring
- Mobile Tutoring
- Instant Tutoring
- How We Operate
- Our Guarantee
- Impact of Tutoring
- Reviews & Testimonials
- Media Coverage
- About Varsity Tutors
FREE AP Microeconomics Practice Tests
All ap microeconomics resources, free ap microeconomics diagnostic tests, ap microeconomics diagnostic test 1, ap microeconomics diagnostic test 2, ap microeconomics diagnostic test 3.
Our free AP Microeconomics Practice Tests are each a selection of 10 to 12 questions, which will give you a cross-section of topics from the Microeconomics section of the official AP. You might think of them as little quizzes, which you can use to hone your skills. Before Test Day What is the AP Microeconomics exam? In general, the AP program provides students who are academically well-prepared to engage in college-level studies while still in high school. Each course is modeled on a comparable college course. Successfully demonstrating your mastery of the coursework can earn you college credit, advanced placement, or both. The AP Microeconomics course aims to provide the student with a similar learning experience to a typical college introductory course in microeconomics. More detail regarding the content covered is below. What topics or subject areas does the AP Microeconomics exam cover? The following are the four major topic areas a student should learn in an AP Microeconomics course that will be tested on the exam. Next to the topic title is the approximate percentage of the multiple choice section of the exam devoted to each area. Basic Economic Concepts (8-14%) Including scarcity, opportunity cost, and different economic systems The Nature and Function of Product Markets (55-70%) Including supply and demand, consumer choice theory, and firm behavior Factor Markets (10-18%) Including decisions in the market for labor and capital Market Failure and the Role of Government (12-18%) Including externalities, public goods, and public policy How is the AP Microeconomics exam structured? Each exam includes a 70-minute, 60-question multiple choice section and a 60-minute free response section. The free response section will include two shorter essays and one longer one. The 60 minutes for the free response period begins with a 10 minute reading period. During this time students should read the questions, sketch graphs, makes notes, and plan answers. The final score is weighted 2/3 to the multiple choice section and 1/3 to the free response. How much does it cost to take the AP Microeconomics exam? It currently costs $89 for each AP exam. There is a fee reduction available, the primary criteria for which is being enrolled in or eligible for the Free or Reduced Price Lunch Program. The details may vary by state and the amount of the fee reduction is still being finalized by the College Board for 2014. When can I take the AP Microeconomics exam? In 2014, the exam is offered on Thursday, May 15. How should I study for the AP Microeconomics exam? Don’t wait for the test date to be near to start preparing. Review the material from your AP course early on to reinforce what you are learning. Sample multiple choice and free response questions are available for practice. You should try to closely replicate test conditions, taking a practice exam in a timed, distraction-free setting at least once before you take the actual exam. Begin your review by taking a free Full-Length AP Microeconomics Practice Test. Each complete test spans the entire range of topics you may encounter on the real exam. These longer form tests also gives you the chance to see how you pace yourself and get familiar with the test’s length and scope. Just like the one for the shorter practice tests, the results pages for the complete practice tests include extensive explanations and additional information relevant to each question. The free online practice tests for AP Microeconomics can also help you to fine-tune your review plan. They’ll show you which concepts you know, and those you’ll want to spend a little time on. You can take advantage of any of the other Learning Tools to review as you work toward test day, and check your progress by taking another Full-Length AP Microeconomics Practice Test. Use these practice tests to get a sense of how you might do on the AP Microeconomics exam. Each test covers a variety of subjects found on the AP Microeconomics exam. You can use this tool to help identify specific subjects for review, allowing you to focus your studying and improve your understanding of AP Microeconomics. You can also use Varsity Tutors’ other free AP Microeconomics resources to help you study, such as free AP Microeconomics Diagnostic Tests, free AP Microeconomics Flashcards, and free AP Microeconomics Questions of the Day. Our free AP Microeconomics resources are written by teachers, professors, content specialists, and tutors. Explanations are given for each question, so if you miss a question, you can find out where you went wrong. On Test Day What should I bring to the AP Microeconomics exam? A number 2 pencil is required for the multiple choice section. The free response section is required to be written in black or blue ink. Students should bring several pens and pencils. Students may also bring a watch in case they cannot easily see the clock in the room of the test. Are calculators allowed on the AP Microeconomics exam? No, calculators of any kind are not permitted. Should I guess if I don’t know an answer on the AP Microeconomics exam? Yes, points are not deducted for incorrect answers or given out for unanswered questions on the AP exam; however, as a general test-taking strategy, you should try to eliminate one or more answers you are confident are incorrect. Budget your time wisely, remembering you have a little more than one minute per multiple choice question. If you are stuck and cannot eliminate any wrong answers, feel free to guess and move onto other questions, coming back only if you have time. How should I answer the free response questions on the AP Microeconomics exam? Keep your answers clear and concise. Long paragraphs and even complete sentence responses are not always necessary. Pay close attention to the wording of the prompts. “Show” means use a diagram to illustrate your answer. “Explain” means to take the reader through all the steps in a line of economic reasoning. “Identify” means a specific answer that doesn’t require additional elaboration. “Calculate” means use math to end up at a specific numerical response, showing your steps along the way. After Test Day How soon after the AP Microeconomics exam can I see my score? Scores will be available online in July, regardless of the date you took the exam. You must have an online College Board account to access scores. Students will no longer receive a paper copy of scores through the mail. How do I send my AP Microeconomics exam score to colleges? On exam day you can elect one college to send your score to for free. Sending your score to additional colleges can be done online through the College Board service or by sending a written request to AP Services. The fee is $15 for regular processing, $25 for rush.

Free AP Microeconomics Practice Tests
Practice tests by concept, competition practice test, perfectly competitive markets practice test, perfectly competitive labor markets practice test, perfectly competitive output markets practice test, government policies practice test, effect on socially optimum levels practice test, marginal revenue product of labor mrp practice test, microeconomics graphs practice test, positive externalities graphs practice test, socially optimum equilibrium quantity practice test, side-by-side graphs practice test, long-run business equilibrium practice test, quantity equilibrium practice test, long-run market equilibrium practice test, price equilibrium practice test, output practice test, price practice test, short-run earnings practice test, practice quizzes, ap microeconomics problem set 15, ap microeconomics problem set 14, ap microeconomics problem set 13, ap microeconomics problem set 12, ap microeconomics problem set 11, ap microeconomics problem set 10, ap microeconomics problem set 8, ap microeconomics problem set 7, ap microeconomics problem set 6, ap microeconomics problem set 5, ap microeconomics problem set 4, ap microeconomics problem set 2, ap microeconomics problem set 1.

AP® Microeconomics
Basic economic concepts, short answer, comparative and absolute advantage: tulips and cheese, utility-maximization for crispitos and pizza, supply and demand, long answer, supply and demand: elasticity and utility-maximization, supply and demand: cookies and milk, supply and demand: single serve coffee capsules, utility-maximization and elasticity: coffee and tea, production, cost, and the perfect competition model, perfect competition: cattle market, imperfect competition, game theory: airlines, monopoly: holiday movies, monopoly: short run equilibrium for self-driving cars, monopoly: small town hospital, game theory: restaurants, factor markets, factor market: perfectly competitive labor market for backpacks, monopsony: automobile factory, perfectly competitive factor market for tires, market failure and the role of government, market failures and government intervention, externalities: mosquito treatments, externalities: paper mills.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Book Title: Intermediate Microeconomics: Interactive Question Bank
Author: Zhen He

Book Description: This open resource question bank provides problem sets for students of Intermediate Microeconomics. Questions are also created using H5P, which will allow students to check their understanding of theories efficiently. This question bank can be a supplementary resource for instructors to create interactive quizzes, assignments, exams, and discussion questions. Problem sets are related to the following topics: demand and supply, consumer theory, theory of firm and production, price and output determination under competition and monopoly, and market power analysis.
Book Information
Intermediate Microeconomics: Interactive Question Bank Copyright © 2021 by Zhen He is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Microeconomics
Very Short Questions and Answers - Introduction Micro Economics | Economics Class 11 - Commerce PDF Download
Q.2. Draw a production possibility curve and mark the following situations: (a) under utilization of resources (b) full employment of resources (c) growth of resources Ans. Every point on PP curve like ABCDEF indicates full employment and efficient uses of resources. Any point below or inside PP curve like G underutilization of resources. Any point above PP curves like H indicates growth of resources.
Production Possibility Curve And Opportunity Cost It refers to a curve which shows the various production possibilities that can be produced with given resources and technology. Production Possibilities
If the economy devotes all its resources to the production of commodity B, it can produce 15 units but then the production of commodity A will be zero. There can be a number of production possibilities of commodity A & B. If we want to produce more commodity B, we have to reduce the output of commodity A & vice versa. Shape of PP curve and marginal opportunity cost. 1. PP curve is a downward sloping curve. In a full employment economy, more of one goods can be obtained only by giving up the production of other goods. It is not possible to increase the production of both of them with the given resources. 2. The shape of the production possibility curve is concave to the origin. The opportunity cost for a commodity is the amount of other commodity that has been foregone in order to produce the first. The marginal opportunity cost of a particular good along the PPC is defined as the amount sacrificed of the other good per unit increase in the production of the good in question.
Example: Suppose a doctor having a private clinic in Delhi is earning Rs. 5lakhs annually. There are two other alternatives for him. (i) Joining a Govt. hospital in Bangalore earning Rs. 4 lakhs annually. (ii) Opening a clinic in his home town in Mysore and earning 3 lakhs annually.
The opportunity cost will be joining Govt. hospital in Bangalore. Increasing marginal opportunity cost implies that PPC is concave. Shift in PPC
(i) Upward shift
- When there is improvement in technology.
- Increase in resources.
(ii) Downward shift
When Resources depletes
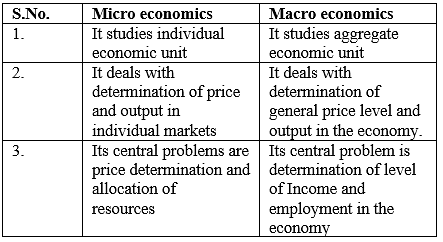
3. Distinguish between micro economics and macroeconomics.
Top Courses for Commerce
Faqs on very short questions and answers - introduction micro economics - economics class 11 - commerce, very short questions and answers - introduction micro economics | economics class 11 - commerce, previous year questions with solutions, past year papers, semester notes, study material, mock tests for examination, viva questions, objective type questions, sample paper, shortcuts and tricks, practice quizzes, video lectures, important questions, extra questions.

Very Short Questions and Answers - Introduction Micro Economics Free PDF Download
Importance of very short questions and answers - introduction micro economics, very short questions and answers - introduction micro economics notes, very short questions and answers - introduction micro economics commerce, study very short questions and answers - introduction micro economics on the app, welcome back, create your account for free.
Forgot Password
Unattempted tests, change country.
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
Microeconomics
Course: microeconomics > unit 1, introduction to economics.
- Scarcity and rivalry
- Four factors of production
- Economic models
- Normative and positive statements
- Lesson summary: Scarcity, choice, and opportunity costs
Want to join the conversation?
- Upvote Button navigates to signup page
- Downvote Button navigates to signup page
- Flag Button navigates to signup page

Video transcript
- Create A Quiz
- Relationship
- Personality
- Harry Potter
- Online Exam
- Entertainment
- Training Maker
- Survey Maker
- Brain Games
- ProProfs.com
Microeconomics Quizzes, Questions & Answers
Top trending quizzes.
Popular Topics
Recent quizzes.
« Previous 1 2 Next »
Popular Quizzes
- List of Commerce Articles
- Important Questions Class 11 Economics Part B Unit 1
Important Questions Class 11 Economics Part B Unit 1- Introduction to Micro Economics
Important Questions with Answers for CBSE Class 11 Economics Part B Unit 1 – Introduction to Micro Economics, which is outlined by expert Economics teachers from the latest version of CBSE (NCERT) books.
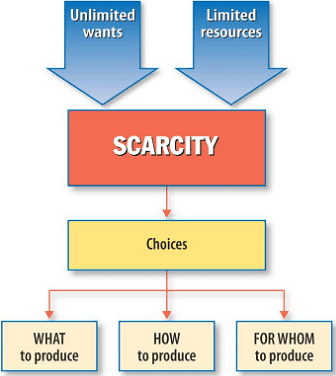
What are the three central problems of Economy?
The three central problems of Economy are:
- What to Produce
- How to Produce
- For whom to Produce
Give two examples of Micro and Macro Economy.
Two examples of Micro economy are individual supply and individual demand and two examples of Macro economy are aggregate supply and aggregate demand.
Define Scarcity.
Scarcity refers to the deficit of resources as compared to the demand.
A growth of resources in an economy is shown in PP by.
(a) Leftward Shift
(b) Unchanged PPC
(c) Rightward Shift
(d) None of the above
What is another name for opportunity cost in economics?
(a) Economic problem
(b) Marginal Cost
(c) Total Cost
(d) Economic Cost
The central economy in market research is solved by.
(a) Demand for goods
(b) Supply of goods
(c) Planning authority
(d) Market mechanism
Is the subject of the Jute industry studied in a macroeconomy?
(d) Can’t say
What is the Production Possibility Frontier?
Production Possibility Frontier is the curve that depicts the maximum output possibility for two combination goods that are produced when the resources are fixed at a given period of time.
Define marginal rate of transformation.
Marginal Rate of Production MRT is the ratio of a particular product sacrificed to manufacture another product. MRT= ▲y / ▲x
Question 10
From the scheduled PP evaluate MRT of good X.
Question 11
The primary assumption about resources while drawing a PPC is
(a) Resources are limited
(b) Resources depend on the kind of products produced
(c) Resources can be put to a particular use
(d) Resources are constant and given
Question 12
Which of the following is a statement of normative nature in economics
(a) Economics is a study of choices /alternatives
(b)The government should be concerned with how to reduce unemployment
(c) According to the estimate, in spite of severe shortage, more than 10% of houses in Indian cities are vacant
(d) Accommodation of refugees is posing a big problem for Europe
Question 13
What are the three central problems of an economy?
Answer: The three central problems of an economy are (a) What to produce? (b) How to produce (c) For whom to produce?
Question 14
What is the opportunity cost?
Opportunity Cost is the next best alternative foregone.
Question 15
What do you mean by economising of resources?
Economizing means making the best of the available resources.
Question 16
Define Normative Economics.
Normative Economics is a theory that understands what an actual economy should be under ideal circumstances as compared to what it actually is. It is mostly based on judgmental analysis and a statement ‘what ought to be’.
Question 17
What does the problem for whom to produce refer to?
The problem for whom to produce refers to a particular section of people who will consume the end product. Here, the problem of choices arises because the manufacturers are unable to produce each product in huge quantity to satisfy everybody’s need.
So, the consumers have to make choices between which product is more important to them, so the limited resources can be distributed rationally.
Question 18
What does the opportunity cost mean? Explain with a numerical example.
Opportunity Cost is something when an individual has to give up something to achieve or acquire something else. In microeconomy, the opportunity cost is also known as alternative cost and it is also used in calculating cost benefits or analysing a project in terms of best alternative while making a choice.
For example, Dev has three career offers to choose from. Job X has a salary offer of Rs 60000, job Y offer is Rs. 70000 and job Z offer is Rs. 80000. So, in this case, out of three offers, Dev has to choose what is best for him. If Dev opts for job offer Z the next best alternative not chosen is job offer Y and thus the opportunity cost is Rs 70000.
Question 19
What is the difference between the planned economy and market economy?
Planned Economy – A planned economy has one person or a group who takes a decision on production, investment, pricing and distribution, etc, and produces products and services that are pre-planned. The planned economy is a centrally planned economy and the decisions are basically taken by the government.
In other words, the planned economy is also known as a command economy because everybody has to follow one person, his command and guidelines. The aim of the planned economy is to increase production by making sure that everything required is manufactured and that everyone’s requirements are fulfilled.
Most assets are controlled and owned by the state.
Market Economy- A market economy is controlled by external authority and may have one individual who might decide what to produce, whom to produce, and how to get the things done. This type of economy keeps changing according to the demand and supply and taste of a consumer. The main issue in the economy is that a company might refuse to manufacture goods if it’s unprofitable for them. Most assets are controlled and owned privately.
A few differences between the planned economy and market economy are as follows.
- The planned economy operates according to the structure planned by the government. Whereas, the market economy operates based on market demand.
- Decisions on production, investment, pricing, and distribution, etc are taken by the government whereas in the market economy it is in the free market.
- A planned economy doesn’t identify consumer needs, supply and shortages. Whereas, in a market economy, demand and supply are based on those factors.
Question 20
Explain the central problem of the choices of products to be produced.
The basic economic activities are based on the production, allocation and distribution of goods and services. These are the major problems in the economy and other difficulties revolve around them. Allocation of goods and services relates to a problem of assigning the inadequate supplies in such a way that it fulfills the requirements of maximum number of consumers.
As the demand for the insufficient goods is more than that of the supply it is important to utilize it in the most effective way. In other words, an economy allocates its goods and resources and picks from a different possible package of goods (what to produce), selects from various ways of production (how to produce), and therefore decides who will utilize the product (for whom to produce).
Stay tuned to BYJU’S for more CBSE Class 11 Economics Important Questions, question papers, sample papers, syllabus and Commerce notifications.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
Scarcity means human wants for goods and services exceed the available supply. Supply is limited because resources are limited. Demand, however, is virtually unlimited. Whatever the supply, it seems human nature to want more.
100 people / 10 people per ham = a maximum of 10 hams per month if all residents produce ham. Since consumption is limited by production, the maximum number of hams residents could consume per month is 10.
She is very productive at her consulting job, but not very productive growing vegetables. Time spent consulting would produce far more income than it what she could save growing her vegetables using the same amount of time. So on purely economic grounds, it makes more sense for her to maximize her income by applying her labor to what she does best (i.e. specialization of labor).
The engineer is better at computer science than at painting. Thus, his time is better spent working for pay at his job and paying a painter to paint his house. Of course, this assumes he does not paint his house for fun!
There are many physical systems that would work, for example, the study of planets (micro) in the solar system (macro), or solar systems (micro) in the galaxy (macro).
Draw a box outside the original circular flow to represent the foreign country. Draw an arrow from the foreign country to firms, to represents imports. Draw an arrow in the reverse direction representing payments for imports. Draw an arrow from firms to the foreign country to represent exports. Draw an arrow in the reverse direction to represent payments for imports.
There are many such problems. Consider the AIDS epidemic. Why are so few AIDS patients in Africa and Southeast Asia treated with the same drugs that are effective in the United States and Europe? It is because neither those patients nor the countries in which they live have the resources to purchase the same drugs.
Public enterprise means the factors of production (resources and businesses) are owned and operated by the government.
The United States is a large country economically speaking, so it has less need to trade internationally than the other countries mentioned. (This is the same reason that France and Italy have lower ratios than Belgium or Sweden.) One additional reason is that each of the other countries is a member of the European Union, where trade between members occurs without barriers to trade, like tariffs and quotas.
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/principles-microeconomics-2e/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Steven A. Greenlaw, David Shapiro
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Principles of Microeconomics 2e
- Publication date: Sep 15, 2017
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/principles-microeconomics-2e/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/principles-microeconomics-2e/pages/chapter-1
© Jun 15, 2022 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Learn Microeconomics Concepts With Our Practice Exams, Study Guides & Videos. All The Learning Tools You Need In One Place. Start Earning Better Grades Today.
Microeconomics Short Answer Questions. Why the Marginal Cost (MC) curve intersects the Average Variable Cost (AVC) and Average Total Cost (ATC) curves at their minimum? Click the card to flip 👆. The reason for this is that the marginal cost is part of the average total cost. Therefore, a change in the marginal cost of making the next unit of ...
Use graphs to answer these questions. 2. Substitutes and complements. Good A and good B are related to each other, either being substitutes or comple-ments. Now the price of good B rises. Illustrate the impact on the market for good A (with graphs) if. A and B are substitutes; A and B are complements. Minimum price.
Download free-response questions from past exams along with scoring guidelines, sample responses from exam takers, and scoring distributions. If you are using assistive technology and need help accessing these PDFs in another format, contact Services for Students with Disabilities at 212-713-8333 or by email at [email protected]. The ...
Introduction to Demand and Supply; 3.1 Demand, Supply, and Equilibrium in Markets for Goods and Services; 3.2 Shifts in Demand and Supply for Goods and Services; 3.3 Changes in Equilibrium Price and Quantity: The Four-Step Process; 3.4 Price Ceilings and Price Floors; 3.5 Demand, Supply, and Efficiency; Key Terms; Key Concepts and Summary; Self-Check Questions; Review Questions
Sample Question 1: Two Short Questions. (Questions taken from: 2015 and 2007 AP® Microeconomics Exams) Allotted time: 25 minutes (plus 5 minutes to submit) The graph below shows the market for widgets. The government is considering intervening in this market. (a) Calculate the total producer surplus at the market equilibrium price and quantity.
Bite-size lessons in Microeconomics with millions of questions and answers with calculus. Ace Micro; ... Short-Run Production; Isoquant; Marginal Product of Labor; ... Millions of questions; Detailed answers; All that for free; Start now! These are all the topics available right now.
Microeconomics. 9 units · 44 skills. Unit 1. Basic economic concepts. Unit 2. Supply, demand, and market equilibrium. Unit 3. Elasticity. ... Test your understanding of Basic economic concepts with these NaN questions. Start test. Our mission is to provide a free, world-class education to anyone, anywhere. Khan Academy is a 501(c)(3) nonprofit ...
All AP Microeconomics Resources. Our free AP Microeconomics Practice Tests are each a selection of 10 to 12 questions, which will give you a cross-section of topics from the Microeconomics section of the official AP. You might think of them as little quizzes, which you can use to hone your skills.
Original free-response prompts for AP® Microeconomics that mimic the questions found on the real exam. Our expert authors also provide an exemplary response for each AP free response question so students can better understand what AP graders look for. ... Short Answer. 3 questions. Supply and Demand: Cookies and Milk. 4.B, MKT-3, MKT-3.E, MKT ...
Name at least one aspect of micro economics that touches on operation or fiscal stratification. View Answer. Demand curves are derived while holding constant: a) income and tastes. b) income, tastes, and the price of the good. c) tastes and the price of other goods. d) income, tastes, and the price of oth... View Answer.
a. Someone publicly donates to a charity using Facebook. b. A bonus is offered to the employee with best results at the end of the quarter. c. A child is allowed to play with his toys only after finishing his homework. d. After an increase in shoplifting, a store installs hidden cameras. 3.
Get exam information and free-response questions with sample answers you can use to practice for the AP Microeconomics Exam. ... The AP Microeconomics Exam will test your understanding of the economic concepts covered in the course, as well as your ability to define economic principles and models; explain given economic outcomes; determine ...
Book Description: This open resource question bank provides problem sets for students of Intermediate Microeconomics. Questions are also created using H5P, which will allow students to check their understanding of theories efficiently. This question bank can be a supplementary resource for instructors to create interactive quizzes, assignments, exams, and discussion questions.
Full syllabus notes, lecture and questions for Very Short Questions and Answers - Introduction Micro Economics - Economics Class 11 - Commerce ... Ans. Microeconomics is a branch of economics that focuses on the study of individual decision-making units such as households, firms, and industries. ...
ECO101 (Fall 2021) Microeconomics Prof. Freitas eco101h1f l301, l401: principles of microeconomics midterm fall 2021 university of toronto, faculty of arts and. Skip to document. University; ... Short Answer Questions. Consider the perfectly competitive market for student summer internships. Quantity Q is number of internships.
Introduction to economics. In this video, we introduce the field of economics using quotes from the person that many consider to be the "father" of economics: Adam Smith. Topics include the definition of economics, microeconomics, and macroeconomics as a field and the role of assumptions in economic decisionmaking. Created by Sal Khan.
7.2 Production in the Short Run; 7.3 Costs in the Short Run; 7.4 Production in the Long Run; 7.5 Costs in the Long Run; ... essentially unwinding the process described in the answer to question 1. In the long-run equilibrium, all firms in monopolistically competitive markets will earn zero economic profits. ... Principles of Microeconomics 3e ...
Microeconomics Quizzes, Questions & Answers. Our newest quiz is about that part of economics that studies the behavior of individuals and small players on the market. If you've studied it in college then there is no way you cannot get to the bottom of it. Our questions will not be impossible to answer but you will need to remember some of ...
Answer: Two examples of Micro economy are individual supply and individual demand and two examples of Macro economy are aggregate supply and aggregate demand. Question 3. Define Scarcity. Answer: Scarcity refers to the deficit of resources as compared to the demand. Question 4.
Self-Check Questions; Review Questions; Critical Thinking Questions; ... 7.2 Production in the Short Run; 7.3 Costs in the Short Run; 7.4 Production in the Long Run; 7.5 Costs in the Long Run; ... Principles of Microeconomics 2e Publication date: Sep 15, 2017 Location: Houston, Texas Book URL ...
Sophia Microeconomics; Question; Subject: General Management. Anonymous Student. 4 days ago. 14. Profit maximization and shutting down in the short run. The following graph plots daily cost curves for a firm operating in the competitive market for rompers. Using the following table, for each price level, calculate the optimal quantity of units ...