Frontiers for Young Minds

- Download PDF

How Does Social Context Influence Our Brain and Behavior?
When we interact with others, the context in which our actions take place plays a major role in our behavior. This means that our understanding of objects, words, emotions, and social cues may differ depending on where we encounter them. Here, we explain how context affects daily mental processes, ranging from how people see things to how they behave with others. Then, we present the social context network model. This model explains how people process contextual cues when they interact, through the activity of the frontal, temporal, and insular brain regions. Next, we show that when those brain areas are affected by some diseases, patients find it hard to process contextual cues. Finally, we describe new ways to explore social behavior through brain recordings in daily situations.
Introduction
Everything you do is influenced by the situation in which you do it. The situation that surrounds an action is called its context. In fact, analyzing context is crucial for social interaction and even, in some cases, for survival. Imagine you see a man in fear: your reaction depends on his facial expression (e.g., raised eyebrows, wide-open eyes) and also on the context of the situation. The context can be external (is there something frightening around?) or internal (am I calm or am I also scared?). Such contextual cues are crucial to your understanding of any situation.
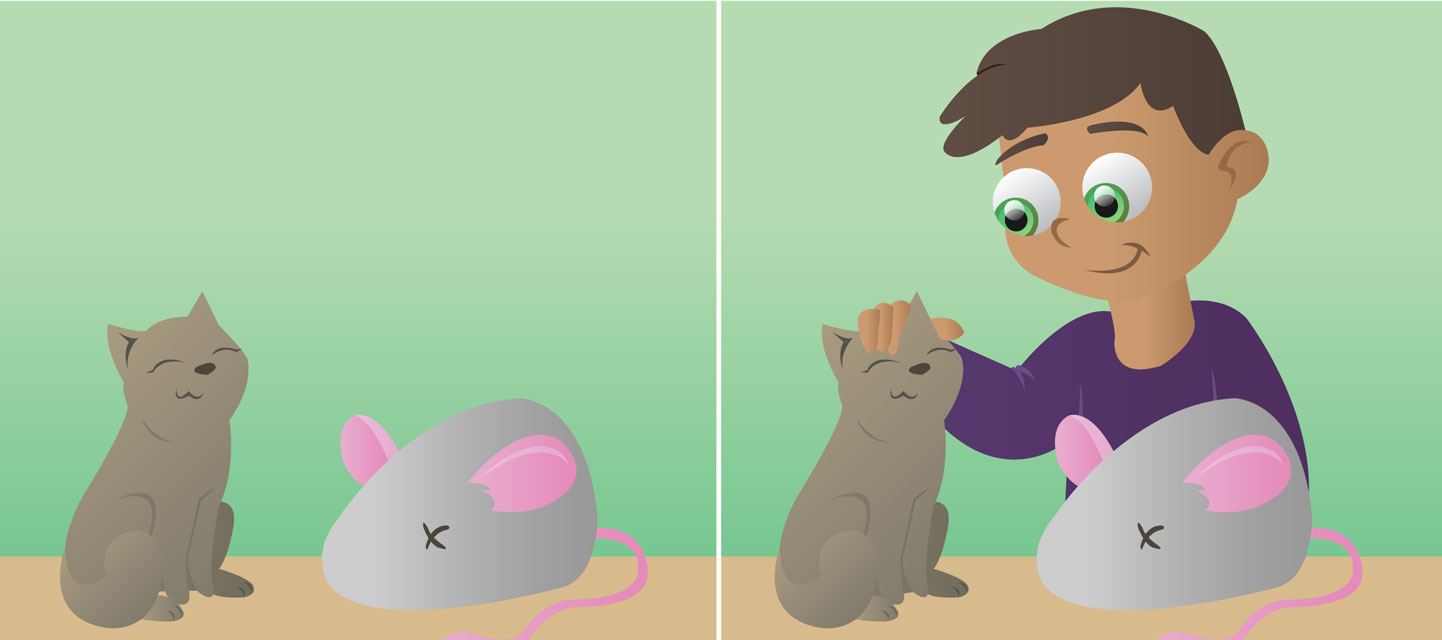
Context shapes all processes in your brain, from visual perception to social interactions [ 1 ]. Your mind is never isolated from the world around you. The specific meaning of an object, word, emotion, or social event depends on context ( Figure 1 ). Context may be evident or subtle, real or imagined, conscious or unconscious. Simple optical illusions demonstrate the importance of context ( Figures 1A,B ). In the Ebbinghaus illusion ( Figure 1A ), rings of circles surround two central circles. The central circles are the same size, but one appears to be smaller than the other. This is so because the surrounding circles provide a context. This context affects your perception of the size of the central circles. Quite interesting, right? Likewise, in the Cafe Wall Illusion ( Figure 1B ), context affects your perception of the lines’ orientation. The lines are parallel, but you see them as convergent or divergent. You can try focusing on the middle line of the figure and check it with a ruler. Contextual cues also help you recognize objects in a scene [ 2 ]. For instance, it can be easier to recognize letters when they are in the context of a word. Thus, you can see the same array of lines as either an H or an A ( Figure 1C ). Certainly, you did not read that phrase as “TAE CHT”, correct? Lastly, contextual cues are also important for social interaction. For instance, visual scenes, voices, bodies, other faces, and words shape how you perceive emotions in a face [ 3 ]. If you see Figure 1D in isolation, the woman may look furious. But look again, this time at Figure 1E . Here you see an ecstatic Serena Williams after she secured the top tennis ranking. This shows that recognizing emotions depends on additional information that is not present in the face itself.

- Figure 1 - Contextual affects how you see things.
- A,B. The visual context affects how you see shapes. C. Context also plays an important role in object recognition. Context-related objects are easier to recognize. “THE CAT” is a good example of contextual effects in letter recognition (reproduced with permission from Chun [ 2 ]). D,E. Context also affects how you recognize an emotion [by Hanson K. Joseph (Own work), CC BY-SA 4.0 ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0 ), via Wikimedia Commons].
Contextual cues also help you make sense of other situations. What is appropriate in one place may not be appropriate in another. Making jokes is OK when studying with your friends, but not OK during the actual exam. Also, context affects how you feel when you see something happening to another person. Picture someone being beaten on the street. If the person being beaten is your best friend, would you react in the same way as if he were a stranger? The reason why you probably answered “no” is that your empathy may be influenced by context. Context will determine whether you jump in to help or run away in fear. In sum, social situations are shaped by contextual factors that affect how you feel and act.
Contextual cues are important for interpreting social situations. Yet, they have been largely ignored in the world of science. To fill this gap, our group proposed the social context network model [ 1 ]. This model describes a brain network that integrates contextual information during social processes. This brain network combines the activity of several different areas of the brain, namely frontal, temporal, and insular brain areas ( Figure 2 ). It is true that many other brain areas are involved in processing contextual information. For instance, the context of an object that you can see affects processes in the vision areas of your brain [ 4 ]. However, the network proposed by our model includes the main areas involved in social context processing. Even contextual visual recognition involves activity of temporal and frontal regions included in our model [ 5 ].
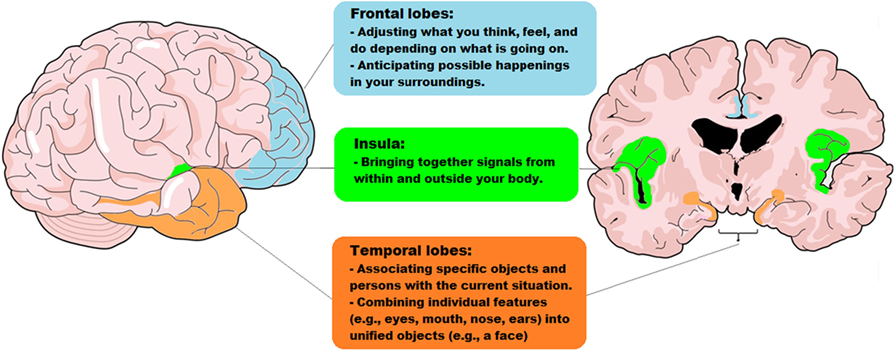
- Figure 2 - The parts of the brain that work together, in the social context network model.
- This model proposes that social contextual cues are processed by a network of specific brain regions. This network is made up of frontal (light blue), temporal (orange), and insular (green) brain regions and the connections between these regions.
How Does Your Brain Process Contextual Cues in Social Scenarios?
To interpret context in social settings, your brain relies on a network of brain regions, including the frontal, temporal, and insular regions. Figure 2 shows the frontal regions in light blue. These regions help you update contextual information when you focus on something (say, the traffic light as you are walking down the street). That information helps you anticipate what might happen next, based on your previous experiences. If there is a change in what you are seeing (as you keep walking down the street, a mean-looking Doberman appears), the frontal regions will activate and update predictions (“this may be dangerous!”). These predictions will be influenced by the context (“oh, the dog is on a leash”) and your previous experience (“yeah, but once I was attacked by a dog and it was very bad!”). If a person’s frontal regions are damaged, he/she will find it difficult to recognize the influence of context. Thus, the Doberman may not be perceived as a threat, even if this person has been attacked by other dogs before! The main role of the frontal regions is to predict the meaning of actions by analyzing the contextual events that surround the actions.
Figure 2 shows the insular regions, also called the insula, in green. The insula combines signals from within and outside your body. The insula receives signals about what is going on in your guts, heart, and lungs. It also supports your ability to experience emotions. Even the butterflies you sometimes feel in your stomach depend on brain activity! This information is combined with contextual cues from outside your body. So, when you see that the Doberman breaks loose from its owner, you can perceive that your heart begins to beat faster (an internal body signal). Then, your brain combines the external contextual cues (“the Doberman is loose!”) with your body signals, leading you to feel fear. Patients with damage to their insular regions are not so good at tracking their inner body signals and combining them with their emotions. The insula is critical for giving emotional value to an event.
Lastly, Figure 2 shows the temporal regions marked with orange. The temporal regions associate the object or person you are focusing on with the context. Memory plays a major role here. For instance, when the Doberman breaks loose, you look at his owner and realize that it is the kind man you met last week at the pet shop. Also, the temporal regions link contextual information with information from the frontal and insular regions. This system supports your knowledge that Dobermans can attack people, prompting you to seek protection.
To summarize, combining what you experience with the social context relies on a brain network that includes the frontal, insular, and temporal regions. Thanks to this network, we can interpret all sorts of social events. The frontal areas adjust and update what you think, feel, and do depending on present and past happenings. These areas also predict possible events in your surroundings. The insula combines signals from within and outside your body to produce a specific feeling. The temporal regions associate objects and persons with the current situation. So, all the parts of the social context network model work together to combine contextual information when you are in social settings.
When Context Cannot be Processed
Our model helps to explain findings from patients with brain damage. These patients have difficulties processing contextual cues. For instance, people with autism find it hard to make eye contact and interact with others. They may show repetitive behaviors (e.g., constantly lining up toy cars) or excessive interest in a topic. They may also behave inappropriately and have trouble adjusting to school, home, or work. People with autism may fail to recognize emotions in others’ faces. Their empathy may also be reduced. One of our studies [ 6 ] showed that these problems are linked to a decreased ability to process contextual information. Persons with autism and healthy subjects performed tasks involving different social skills. Autistic people did poorly in tasks that relied on contextual cues—for instance, detecting a person’s emotion based on his gestures or voice tone. But, autistic people did well in tasks that didn’t require analyzing context, for example tasks that could be completed by following very general rules (for example, “never touch a stranger on the street”). Thus, the social problems that we often see in autistic people might result from difficulty in processing contextual cues.
Another disease that may result from problems processing contextual information is called behavioral variant frontotemporal dementia . Patients with this disease exhibit changes in personality and in the way they interact with others, after about age 60. They may do improper things in public. Like people with autism, they may not show empathy or may not recognize emotions easily. Also, they find it hard to deal with the details of context needed to understand social events. All these changes may reflect general problems processing social context information. These problems may be caused by damage to the brain network described above.
Our model can also explain patients with damage to the frontal lobes or those who have conditions such as schizophrenia or bipolar disorder [ 7 ]. Schizophrenia is a mental disorder characterized by atypical social cognition and inability to distinguish between real and imagined world (as in the case of hallucinations). Similar but milder problems appear in patients with bipolar disorder, which is another psychiatric condition mainly characterized by oscillating periods of depression and periods of elevated mood (called hypomania or mania).
In sum, the problems with social behavior seen in many diseases are probably linked to poor context processing after damage to certain brain areas, as proposed by our model ( Figure 2 ). Future research should explore how correct this model is, adding more data about the processes and regions it describes.
New Techniques to Assess Social Behavior and Contextual Processing
The results mentioned above are important for scientists and doctors. However, they have a great limitation. They do not reflect how people behave in daily life! Most of the research findings came from tasks in a laboratory, in which a person responded to pictures or videos. These tasks do not really represent how we act every day in our lives. Social life is much more complicated than sitting at a desk and pressing buttons when you see images on a computer, right? Research based on such tasks doesn’t reflect real social situations. In daily life, people interact in contexts that constantly change.
Fortunately, new methods allow scientists to assess real-life interactions. Hyperscanning is one of these methods. Hyperscanning allows measurement of the brain activity of two or more people while they perform activities together. For example, each subject can lie inside a separate scanner (a large tube containing powerful magnets). This scanner can detect changes in blood flow in the brain while the two people interact. This approach is used, for example, to study the brains of a mother and her child while they are looking at each other’s faces ( Figure 3A ).
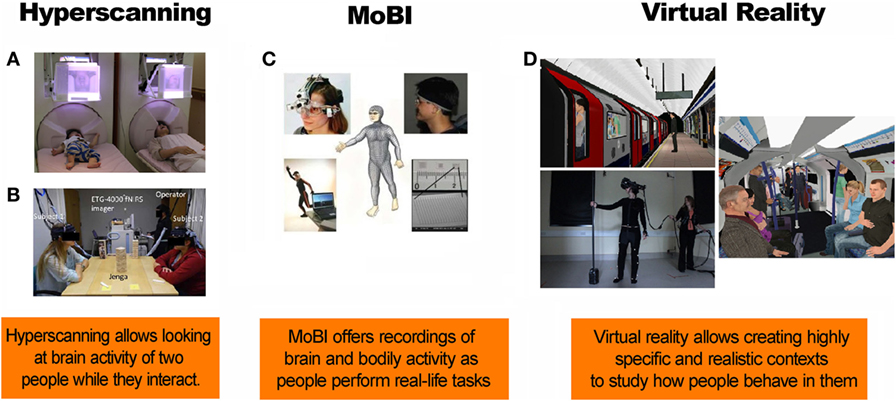
- Figure 3 - New techniques to study processing of contextual cues.
- A. A mother and her infant look at each others’ facial expression while their brain activity is recorded (reproduced with permission from Masayuki et al. [ 8 ]). B. Hyperscanning of people interacting with each other during a game of Jenga (reproduced with permission from Liu et al. [ 9 ]). C. A new method of studying brain activity, called mobile brain/body imaging (MoBI) (reproduced with permission from Makeig et al. [ 10 ]). D. Virtual reality simulations of a virtual train at the station and a virtual train carriage (reproduced with permission from Freeman et al. [ 11 ]).
Hyperscanning can also be done using electroencephalogram equipment. Electroencephalography measures the electrical activity of the brain. Special sensors called electrodes are attached to the head. They are hooked by wires to a computer which records the brain’s electrical activity. Figure 3B shows an example of the use of electroencephalogram hyperscanning. This method has been used to measure the brain activity in two individuals while they are playing Jenga. Future research should apply this technique to study the processing of social contextual cues.
One limitation of hyperscanning is that it typically requires participants to remain still. However, real-life interactions involve many bodily actions. Fortunately, a new method called mobile brain/body imaging (MoBI, Figure 3C ) allows the measurement of brain activity and bodily actions while people interact in natural settings.
Another interesting approach is to use virtual reality . This technique involves fake situations. However, it puts people in different situations that require social interaction. This is closer to real life than the tasks used in most laboratories. As an example, consider Figure 3D . This shows a virtual reality experiment in which participants traveled through an underground tube station in London. Our understanding of the way context impacts social behavior could be expanded in future virtual reality studies.
In sum, future research should use new methods for measuring real-life interactions. This type of research could be very important for doctors to understand what happens to the processing of social context cues in various brain injuries or diseases. These realistic tasks are more sensitive than most of the laboratory tasks that are usually used for the assessment of patients with brain disorders.
Empathy : ↑ The ability to feel what another person is feeling, that is, to “place yourself in that person’s shoes.”
Autism : ↑ A general term for a group of complex disorders of brain development. These disorders are characterized by repetitive behaviors, as well as different levels of difficulty with social interaction and both verbal and non-verbal communications.
Behavioral Variant Frontotemporal Dementia : ↑ A brain disease characterized by progressive changes in personality and loss of empathy. Patients experience difficulty in regulating their behavior, and this often results in socially inappropriate actions. Patients typically start to show symptoms around age 60.
Hyperscanning : ↑ A novel technique to measure brain activity simultaneously from two people.
Virtual Reality : ↑ Computer technologies that use software to generate realistic images, sounds, and other sensations that replicate a real environment. This technique uses specialized display screens or projectors to simulate the user’s physical presence in this environment, enabling him or her to interact with the virtual space and any objects depicted there.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by grants from CONICYT/FONDECYT Regular (1170010), FONDAP 15150012, and the INECO Foundation.
[1] ↑ Ibanez, A., and Manes, F. 2012. Contextual social cognition and the behavioral variant of frontotemporal dementia. Neurology 78(17):1354–62. doi:10.1212/WNL.0b013e3182518375
[2] ↑ Chun, M. M. 2000. Contextual cueing of visual attention. Trends Cogn. Sci. 4(5):170–8. doi:10.1016/S1364-6613(00)01476-5
[3] ↑ Barrett, L. F., Mesquita, B., and Gendron, M. 2011. Context in emotion perception. Curr. Direct Psychol. Sci. 20(5):286–90. doi:10.1177/0963721411422522
[4] ↑ Beck, D. M., and Kastner, S. 2005. Stimulus context modulates competition in human extrastriate cortex. Nat. Neurosci. 8(8):1110–6. doi:10.1038/nn1501
[5] ↑ Bar, M. 2004. Visual objects in context. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 5(8):617–29. doi:10.1038/nrn1476
[6] ↑ Baez, S., and Ibanez, A. 2014. The effects of context processing on social cognition impairments in adults with Asperger’s syndrome. Front. Neurosci. 8:270. doi:10.3389/fnins.2014.00270
[7] ↑ Baez, S, Garcia, A. M., and Ibanez, A. 2016. The Social Context Network Model in psychiatric and neurological diseases. Curr. Top. Behav. Neurosci. 30:379–96. doi:10.1007/7854_2016_443
[8] ↑ Masayuki, H., Takashi, I., Mitsuru, K., Tomoya, K., Hirotoshi, H., Yuko, Y., and Minoru, A. 2014. Hyperscanning MEG for understanding mother-child cerebral interactions. Front Hum Neurosci 8:118. doi:10.3389/fnhum.2014.00118
[9] ↑ Liu, N., Mok, C., Witt, E. E., Pradhan, A. H., Chen, J. E., and Reiss, A. L. 2016. NIRS-based hyperscanning reveals inter-brain neural synchronization during cooperative Jenga game with face-to-face communication. Front Hum Neurosci 10:82. doi:10.3389/fnhum.2016.00082
[10] ↑ Makeig, S., Gramann, K., Jung, T.-P., Sejnowski, T. J., and Poizner, H. 2009. Linking brain, mind and behavior: The promise of mobile brain/body imaging (MoBI). Int J Psychophys 73:985–1000
[11] ↑ Evans, N., Lister, R., Antley, A., Dunn, G., and Slater, M. 2014. Height, social comparison, and paranoia: An immersive virtual reality experimental study. Psych Res 218(3):348–52. doi:10.1016/j.psychres.2013.12.014

Social Context
‘Social Context’ refers to the immediate physical and social setting in which people live or in which something happens or develops. This includes the culture that the individual was educated or lives in, and the people and institutions with whom they interact. Social context influences and, to some extent, determines thought, feeling, and action. It ranges from a brief interaction with a stranger to broad societal and cultural forces.
Understanding Social Context
To grasp the concept of social context, we must delve into its components and the influence it exerts on individuals and societies.
Social context can be broken down into various elements, including cultural norms, social structures (like family or community), and the specific situation in which an individual finds themselves.
Influence on Behavior and Perceptions
Social context significantly impacts individual behavior, perceptions, and interactions. It can shape an individual’s values, beliefs, and expectations.
The Role in Different Fields
Social context plays a pivotal role across various disciplines, from psychology to sociology and beyond.
In Psychology
In psychology, social context is used to understand individual behavior in social situations and the influences of societal norms and structures.
In Sociology
Sociologists study social context to comprehend societal patterns, trends, and structures, helping them understand social phenomena and changes over time.
Understanding the social context offers valuable insights into various aspects of life and society.
Enhances Communication
By understanding the social context of a situation, we can communicate more effectively, considering cultural norms, values, and expectations.
Guides Policy and Decision-Making
Social context is crucial in informing policy-making, ensuring that decisions consider societal norms, values, and structures.
To further illuminate the concept, let’s consider some examples of social context.
Example 1: Educational Settings
The social context of a classroom— including its cultural norms, student-teacher dynamics, and broader school environment— can influence students’ learning and engagement.
Example 2: Online Communities
Online communities, like those on social media platforms, have their unique social contexts that impact user behavior, interactions, and content creation.
Recognizing and Analyzing Social Context
Being able to recognize and analyze social context is a valuable skill. Here are some tips to help.
Be Observant
Pay attention to the physical and social environment, the individuals involved, and the cultural and societal norms at play.
Keep an Open Mind
Maintain an open mind and be sensitive to cultural differences, acknowledging that social context can differ greatly between societies and groups.
In essence, social context is a crucial factor that shapes our behaviors, interactions, perceptions, and the world around us. By understanding and considering social context, we can communicate more effectively, make informed decisions, and appreciate the complexity and diversity of human societies.
Home — Essay Samples — Literature — Things Fall Apart — Sharing Social Context A Literary Analysis
Sharing Social Context a Literary Analysis
- Categories: 1984 Things Fall Apart
About this sample

Words: 825 |
Published: Mar 14, 2024
Words: 825 | Pages: 2 | 5 min read

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Prof Ernest (PhD)
Verified writer
- Expert in: Literature

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
3 pages / 986 words
2 pages / 864 words
2 pages / 877 words
2 pages / 887 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Things Fall Apart
Chinua Achebe’s novel is a gripping portrayal of the tumultuous changes that occurred in Nigeria during the late 19th century. The novel follows the life of Okonkwo, a respected leader in the Igbo community, as he grapples with [...]
In Chinua Achebe's Things Fall Apart, the character Ekwefi is introduced as the second wife of the protagonist Okonkwo. Ekwefi's story is one of loss and tragedy, as she suffers multiple miscarriages and the tragic loss of her [...]
In Chinua Achebe's novel, "Things Fall Apart," the story of Okonkwo, a proud and powerful Igbo leader in pre-colonial Nigeria, unfolds against the backdrop of cultural clash and colonial invasion. As the title suggests, the [...]
Irony is an essential tool used by authors to enhance the themes and messages of their works. Chinua Achebe's Things Fall Apart is an exemplary novel that employs irony to convey the themes of the novel effectively. This essay [...]
In Chinua Achebe's groundbreaking novel, "Things Fall Apart," the character of Nwoye undergoes a profound transformation that mirrors the larger themes of the story. Through the careful analysis of Nwoye's quotes throughout the [...]
From the very title of this historical fiction novel, Things Fall Apart, composed by Chinua Achebe, it foreshadows the tragedy which is triggered by the tragic hero. Defined by Aristotle, an ancient Greek philosopher, a tragic [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
17 Read the Room! Navigating Social Contexts and Written Texts
Sarah Seeley; Kelly Xu; and Matthew Chen
This chapter is a collaboration between a professor (Sarah Seeley) and two former students (Kelly Xu and Matthew Chen). [1] We begin with a discussion of a key concept: the discourse community. In doing so, we illustrate why it is necessary to examine the social side of communication. This is an invitation for readers to think about the fact that academic communication practices are structured in ways that are actually quite similar to the more familiar communication practices they use on a daily basis. We offer readers a framework for understanding how the social assumptions associated with familiar communicative contexts may be useful in understanding new or unfamiliar contexts.
We use the social media platform TikTok as an extended example as we explore the various criteria that define a discourse community. Xu and Chen then offer examples of how people become competent communicators within the context of new new-to-them scientific discourse communities. They cover topics including learning a “hidden” lexicon, building confidence and independence, and navigating tacit power hierarchies. These experiences reinforce the fact that effective communication requires contextual awareness and that understanding social norms is essential for developing that awareness.
Navigating new communicative contexts can be tricky. This is true of enrolling at a new school, starting a new job, or joining a new friend group. In each case, we need to start by “reading the room.” This means identifying the values and circumstances that shape the new social context so we can communicate confidently and appropriately. But, as we know, what it means to speak or write “appropriately” is not the same in all social contexts. While it may seem like a stretch to compare the task of writing a lab report and that of writing a text message, each context equally requires us to examine what counts as “appropriate.” This chapter offers you tools and examples that should help you examine and respond to the social circumstances that characterize unfamiliar contexts in your own life.
To help guide the process of “reading” whatever “room” you may find yourself in, we will begin with a discussion of an important concept: the discourse community. We will use the social media platform TikTok as an example as we explore the various criteria that define a discourse community. We will then move on to offer two narrative-based examples of how college students have navigated the social challenges involved with becoming productive members of new-to-them scientific discourse communities. Kelly Xu will detail her experiences as a biology student interning at a cancer research institution, and Matthew Chen will discuss his experiences of being a mechanical engineering student doing research in an ecology laboratory. We juxtapose these scientific examples with the TikTok example because we want you, the reader, to understand that academic communication practices are structured in ways that are actually quite similar to the more familiar communication practices you use on a daily basis.
The Discourse Community
Being new to “the room” is an inevitable experience. This happens whenever we start a new class or accept a new job. We have to learn the language and expectations required to succeed in the new situation. The discourse community concept will help you examine, understand, and thus succeed in those new situations. The linguist John Swales first developed a list of criteria for defining discourse communities in his book Genre Analysis (1990). In a more recent (2017) article, he revised these criteria because he wanted to account for the changing nature of communication in our contemporary world. In the following list, we are paraphrasing an article published in the journal Composition Forum , where Swales suggests that discourse communities are defined by the following eight criteria:
- broadly agreed upon sets of goals
- ways of communicating within the group
- member participation that provides information, feedback, and initiates action
- the use of specific formats (genres) for communicating within the group
- the use of specific vocabulary (lexis) for communicating within the group
- a core group of experienced members
- the sense that certain things can be left unsaid
- horizons of expectation
In the next section, we will have a closer look at each of these criteria.
How Can These Criteria be Used to Understand TikTok?
At the time of this writing, TikTok is consistently in the news for its role in circulating conspiracy theories and cultivating extremism (Ovide; Clayton). The community is receiving increasing amounts of attention, and, with the mobile app having been downloaded more than 2 billion times, it offers a timely case study: can TikTok “tick” all the boxes in Swales’ list (Brown; Leskin)?
First, Swales suggests that a discourse community is defined by a broadly agreed upon set of goals. Can we say this is true of the TikTok community as a whole? Probably not. Like most others of its kind, this platform is made up of distinctive interest communities (more on this in a moment). Such divisions make it hard to say that the community is defined by shared goals. For example, it is difficult to claim that the dancer Charli D’Amelio shares the same goals as the people behind the far-right extremist accounts. It is similarly difficult to claim that #CottageCore creators like @speckledhijabi or users posting to #BlackLivesMatter share the same goals as content creators who are cancelled for their use of racist slurs (Jennings). Within this vast social landscape, the only agreed upon goals are very, very broad: producing, circulating, and accessing new and quickly consumable content. As we know, that could mean nearly anything.
What about ways of communicating and participating within the community? Here is where we move onto firmer ground. All social media platforms offer methods for group communication and participation. From rotating trends to “likes” and hashtags, TikTok seems to tick boxes two and three on Swales’ list.
How about specific formats and vocabulary? Tick, tick. TikTok is defined by short video content sharing. Creators can loop or otherwise string together shorter clips to circulate “larger” videos that are up to 60 seconds long. In this way, TikTok builds on the short video format, or genre, that was a staple of its predecessor Musical.ly. Of course, this genre has also been popularized by Vine’s 6 second videos (R.I.P.), and we can also see short form video content sharing in other places, like 15-second Instagram Reels.
Now, does TikTok have a core group of experienced members? Well, yes and no. We cannot answer this question without circling back to our discussion of the first criterion. Recall, we had trouble saying that the TikTok community, as a whole , shares any specific goals. Building on this, we can say that there are experienced or core members, but that they are clustered across different “pockets” of the community. These clusters can be mapped across one important divide: Alt TikTok vs. Straight TikTok. Within these very large categories, content is characterized by wildly different goals and values. So, while there are core members within “sub-communities” across, for example, Alt TikTok, individual users also retain the freedom to shape genres and vocabulary in individualistic and grassroots ways (Sung).
Swales’s seventh criterion relates to the fact that, within a given community, certain things can be left unsaid. Drawing on the work of the linguist Alton Becker, Swales calls this “silential relations.” To understand this concept, we could think about the building abbreviations and program acronyms that are used on our respective campuses. For example, as members of our own campus-based discourse community, we, the writers, know exactly what “COMM+D” means, so we don’t need to spell out the Center for Global Communication and Design. We’re sure there are similar acronyms and abbreviations that define your campus community. We could also think about “silential relations” in terms of slang. From platform-wide slang like “story time” and “duet” to the slang that characterizes TikTok’s niche communities, this box is ticked.
The final criterion relates to something Swales calls a “horizon of expectation.” As he puts it, a discourse community “develops horizons of expectation, defined rhythms of activity, a sense of its history, and value systems for what is good and less good work” (Swales, “Concept”). There are a lot of considerations bundled here. Linking back to the idea that TikTok users generally aim to produce, circulate, and access new and quickly consumable content, we can see, once again, that the TikTok community as a whole is too large to be meaningfully examined in terms of some of these criteria. Numerous histories, value systems, and associated social expectations are observable across TikTok at any given moment. For example, at the time of this writing, the TikTok site indicates that videos categorized under #BLM have received a collective 12.3 billion views. On the other hand, TikTok also had to issue an apology in June 2020 over allegations of censoring this very hashtag (Harris). In other words, TikTok is comprised of a myriad of “rooms” that may need to be “read” quite differently.
As a new(ish) member of a university community, you may be interested to know that, like TikTok, the academic community as a whole is also too large to be meaningfully examined as a singular discourse community. What counts as “good” writing or “successful” communication is going to vary widely across the classes you take in different disciplines. This is because disciplinary goals, genres, languages, and expectations all vary. We must always read the room and respond accordingly. Now that we’ve explored how the discourse community criteria can (and cannot) help us understand TikTok, Kelly Xu and Matthew Chen will apply the same ideas in their stories of learning social norms and gaining authority as new members of scientific discourse communities.
The Lab Experience: Free Trial vs. Full Membership (Kelly)
After interning at a medical oncology lab for two summers, I have experienced being a member, an outsider, and everything in between. In what follows, I will reflect on these experiences using the discourse community framework. As you likely know from your own experiences, the conceptual boundaries of any community are most evident to anyone who is new. Simply not understanding the tacit rules, structure, and lexis of a community can make one feel ostracized as an outsider to the “in group.” In the case I’m about to describe, I entered the lab community as an intern who had minor publications and one year of undergraduate education under my belt. I was certainly under-qualified, and I felt daunted before I even stepped foot in the lab.
In lab settings, educational qualifications underlie all power structures. In other settings, positions may be malleable and accommodating based on pertinent experience, but in the lab, power is clearly defined by education and publication status. The Principal Investigator holds the most authority, followed by MD/PhDs and post-doctoral students, then doctoral students, followed by lab technicians, and finally undergraduate interns. We will also see how this same type of hierarchy structures other lab contexts in the next section, but for now, we should keep in mind: no amount of seniority as an undergraduate can ever allow for a “promotion” to the level of a PI.
Upon receiving my internship offer, I felt like I was infiltrating the company, rather than earning my position. Although I owned a company ID and looked like any other lab member, there were clearly invisible borders that I needed to breach to become an integrated member of the community. I was a long way from understanding the means of participating and communicating that were seemingly obvious to core members of the community. For example, even menial tasks like picking up mice revealed the fact that I was still an outsider. My mentor often said that mice perceive their handler’s emotions and react correspondingly. While she confidently grabbed the base of their tails with ease and they would immediately stop squirming, my hesitant grip allowed the mice to wriggle out with ease.
Lab-specific lexis, or vocabulary, also proved to have a learning curve. I was fascinated by the secret language of abbreviations and terminology that researchers commanded so fluently. I took fastidious notes on the aliases we used for reagents, the tiny modifications made to procedures, etc. But I found that even self-proclaimed mastery of the genres and lexis of this community were insufficient for me to establish a place in the lab. Though I rehearsed the words I heard my colleagues use so expertly, they felt ill-fitting and improper when I used them in practice, akin to a child wearing an oversized suit. More precisely, I didn’t (yet) feel I had the right to use such mature terminology because I still had so little experience. I now realize that the attribute I lacked and yearned for so distinctly was authority. Since gaining authority is a multi-faceted task, I want to discuss two components of this process: autonomy and reputation.
From where I sit now, I see my first summer interning as a “training period” wherein I lacked the agency to plan my own schedule or act without supervision. To put it in Swales’ terms, I could not yet participate independently or initiate my own action. While my days were rigidly structured and scheduled by my mentor, I looked upon the independence of my lab peers with admiration. They were so familiar with the intervals of time they needed to complete aspects of their projects that they could come into work at any time and leave at their leisure. Whereas I was paid hourly and expected to work 9-5, their jobs seem so much more integrated into their lifestyles and tailored to their personal work ethic. Perhaps more importantly, they were confident enough in their skills to complete tasks within a time window they allotted themselves. Circling back to Swales’ criteria, it is clear that my peers were self-sufficient enough that they were able to recognize and participate in the rhythms of work that support overarching lab goals. Meanwhile, I was given a generous margin of error in everything I did, from booking lab machines times to pipetting reagents from a mastermix. I had to gain my own footing and learn to function as an individual before I could participate as a member of the community and contribute towards its goals.
For an undergraduate with little formal lab training, there is only so much autonomy you can attain since most procedures must be learned under supervision. However, I would like to argue that I did make some progress towards attaining autonomy. At first, I repeatedly executed the same protocol under strict observation. After verifying that I could successfully replicate one protocol, I was invited to apply the same skills (e.g. pipetting or making a gel) to other protocols without supervision. I repeated this process until I was gradually trusted to learn new protocols entirely on my own. Though I still felt restricted by the structure of the lab hierarchy, I came to appreciate these small landmarks of independence as they reminded me of the progress I was making. The better I understood the goals, actions, and lexis of the community, the more my autonomy increased. Hence, personal growth and increased familiarity are the keys to establishing an autonomous position within any discourse community. Whereas my earliest days in the lab felt like a stressful lab practical, I felt like a valuable partner by the end.
I was often scared of asking questions during the first year of my internship. Not only did I lack the confidence to ask a question, but I lacked the basic understanding needed to even form a question. At meetings, I would often stay quiet. This was out of fear that I would ask about something that had already been clearly explained or that I had misinterpreted a figure. Even during my second year, after having completed two rigorous 4000-level biology courses, I still found it challenging to interpret the specifics of my colleagues’ experiments. This, of course, was because I was still developing an understanding of my colleagues’ goals, and I was still in the process of mastering their genres. During the typical lab day, I felt like a nuisance asking what I thought were overly simplistic questions. In fact, I would ask questions in a “bottom-up” manner. I started with asking my undergraduate peers and then worked my way up the ladder if needed because I didn’t want to damage my reputation by annoying the higher-ups. In doing so, I was actually internalizing and taking action within the social structure of the lab.
This social work eventually started to pay off. Another lab member actually consulted me for advice on executing an assay that I commonly performed. I was shocked and honored. This was a recognition of my proficiency and knowledge, and I was elated that, despite my position in the academic hierarchy, my work and reputation preceded me. I had established my colleague’s respect, which went a long way toward making me feel like I was establishing my own authority. Afterwards, I proudly listed “PCR” as a lab skill on my resume; I finally felt confident enough in my technique to claim that I specialized in it. I no longer felt like I was a child donning an ill-fitting lab coat, but began to believe in my own credibility. Thus, practice with the genres and lexis of the lab allowed me to gain confidence as a researcher.
Finally, I took the ultimate test of trust and reputation: the dreaded lab meeting. Lab meetings are notoriously difficult because one is required to present their research progress to-date. In addition, rigorous follow-up questions test your knowledge of every detail of your project and (potentially) highlight every oversight. For example, it was insufficient for me to just know the names of the cell lines I was growing. I also needed to know why they were chosen and be able to discuss the levels of expression for multiple genes in each. To put it in Swales’ terms, the lab meeting is a demonstration of member participation: you provide information, receive feedback, and action is initiated. Though it was incredibly daunting, I was proud to work with my mentor to create the slides I would present as well as field questions from the audience. By being held to the same scrutiny and high standards as my peers, I really felt like I was no longer just an undergraduate intern but recognized as a true researcher.
One of the most important ways to gain membership within a new discourse community is to cultivate your confidence and a sense of belonging. While this involves rather gradual changes in perception, it is something we can all take control of as individual communicators. Ultimately, though, becoming integrated into a discourse community is a more nuanced process than a simple list of criteria might indicate. Learning vocabulary and techniques is merely the beginning of fitting into a discourse community. This is true in the same way that reading a book can’t replace having the actual experience being described. However, the novice communicator can make the integration process less daunting by setting more attainable goals. We can proudly reflect on the landmarks we achieve. In my case, this meant presenting with my mentor during a lab meeting or pausing to feel gratified after a peer had asked me for advice. Upon concluding my two-year internship, I finally felt like I earned a place in my lab community. I have moved beyond the free trial into the highest level of membership I can afford for now.
From Robots to Frog Guts: An Engineer in Ecologist’s Clothes (Matthew)
Going into my second semester of college, I found myself wanting to do something apart from my regimented engineering classes, so I decided to join an ecology lab. My routine of experimenting with circuits and fixing up machines was no more. Instead, I was experimenting with snails and fixing lunch for frogs. Some may ask why I would do this. Through countless hours spent hiking, mountain biking, and camping, the environment has become significant to me. That said, I quickly realized the vast difference between my personal environmental interests and the ecological knowledge these researchers possessed. Similar to the situation described in the previous section, I had some work to do! In order to establish myself within this discourse community, I had to accomplish three main tasks: adapting to their way of communicating, understanding their professional motives, and building their trust. Progressively meeting these goals allowed me to integrate myself into the ecology community in increasingly meaningful ways.
Throughout that first semester, I picked dead invertebrates from a slushy mixture of dirt and sand for eight hours a week. As we saw in the previous section, mundane tasks often serve as a foundation for adjusting to new environments. After weeks spent alone in a windowless lab, churning through one Petri dish of smudge after another, a post-doc invited me to their weekly “journal discussions.” I accepted the invitation immediately and found out later that these meetings were a venue for discussing ecology and environmental science papers.
Going into my first journal meeting, I felt that my contributions were going to be pointless. At first, this fear was confirmed. While the graduate students and postdocs shared their thoughts, I was frantically Googling on my laptop in an attempt to understand them. Though I had read the entire paper front to back, I hadn’t grasped the context behind it. These ecologists came to these discussions with years of experience conducting, writing up, and publishing experiments. Thinking in terms of Swales’ criteria, these years of experience furnished them with a context for understanding the goals of ecological research, for critiquing such research, for decoding ecology genres, and for using ecology vocabulary. I had had none of that.
However, after attending a few of the discussions, I started to understand more. For example, I realized that no one says “standard artificial media 5-salt culture water.” This phrase is ridiculously long and thus shortened to SAM-5S water. Here, we can see the concept of silential relations at play, yet understanding what should be said and what can remain unsaid required more than just learning word definitions. It also required me to understand the ideas within a larger context. For example, through talking with a grad student, I learned the context surrounding the issue of pseudoreplication, which is a situation where one would artificially inflate their sample size by sampling multiple times from a single source. She explained how she would avoid this by setting up 50 individual pools of water with the experimental chemicals and animals. Thus, the experiment would generate true statistical significance, which would make it publishable, thus serving one of the main goals of this discourse community.
In addition, I realized that the journal discussions were always guided by a series of standard questions. Where and when was the paper published? What is the significance of the results? Do they make sense? Are there any discrepancies? Recognizing the format of the discussions and learning more about ecology and scientific genres, I was able to understand the goals of the lab and the context behind their experiments. After attending several journal discussions, I became comfortable speaking my thoughts to the group. I began relating the paper we were discussing to the current research being done in the lab, and making these connections allowed me to get a deeper understanding of the life of an ecologist. Doing this, my comments and questions began sparking a more in-depth discussion, rather than a dead-end conversation. I no longer needed to stress about what to say next or worry about the discussion becoming awkward. Thinking in Swales’ terms, this is when I started to internalize one facet of the community’s horizon of expectations: the value system that defines meaningful (and not-so-meaningful) commentary and critique.
On another occasion, a postdoc started passionately exclaiming how the figures in a paper were way too confusing and complex. This showed me how undoubtedly passionate they are about their work, and how they meticulously critique the textual artifacts that make up their scientific community. It was also relieving to know how even the most experienced in the lab sometimes found figures difficult to interpret too, with the difference being that they are able to back up their critiques with an onslaught of evidence. With each passing journal discussion, I was increasingly able to relate to the ecologists’ work and get to know them better. This is how I started to break free of that “new person” feeling.
While these journal discussions expanded my knowledge of ecology, I also gained insight into how the scientific research community communicates and circulates information. Put differently, these are the actions encompassed by Swales’ second and third criteria. As opposed to engineering, the scientific method for demonstrating results is quite textual. This differs from the more physical nature of engineering, as while I am resizing the fit of a 3D model, the ecologists are meticulously rewriting their manuscripts so as to appease reviewer two. In noting this realization about textual vs. material communication, we can circle back to Swales’ first and fourth criteria. Here we see members of engineering and ecology discourse communities using very different research genres, or formats, to achieve very different goals. And, to put it in more day-to-day terms, I learned that emailing busy ecologists is a nuanced task. These messages had to be short and to the point if I wanted to receive a response in the same week!
At the end of the fall semester working in the lab, I’d learned how these ecologists communicate, how they characterize their passions and goals, and how I fit into the community. These successes paved the way for my next opportunity: a summer internship position. Shifting into the new role, I would continue the work of picking dead invertebrates out of wet dirt. Then, after three weeks, a grad student asked me if I wanted to catch snails from a pond. I was so excited to finally work with an organism that was alive . A little slow, but alive, nonetheless. I picked each snail out from the pond so gently, like they were the last one on earth, and I brought them back to the lab for the graduate student. Upon examining the snails and realizing they were all alive, she told me “good job.” This very brief interaction demonstrated that she regarded snail collection as the most basic of tasks, while I perceived it to be more involved and sophisticated. Essentially, I was the ecologists’ coffee boy, but instead of delivering coffee, I delivered snails!
Nevertheless, after having success with retrieving snails, I was able to communicate to my co-workers that I am capable of successfully carrying out more complex tasks. After around two weeks of snail work, I advanced to a more complex (and quicker!) organism: frogs. I began transporting live (jumping!) frogs from outdoor experiments into the lab. Given the strong possibility that I might lose a frog, or a data point in the eyes of a PhD student, I worked alongside another person. After a week as a member of the frog-catching duo, I was told I could catch them on my own. I was no longer the undergrad who picks dead worms from dirt. I had become the undergrad who catches live frogs out of kiddie pools!
In addition, I started to realize subtleties in the way my colleagues worked, and I developed my own daily routines. I was finally gaining some of that autonomy Kelly Xu discusses in the previous section. For example, each morning I would organize the glassware, check-up on the live animals, collect specific animals, and touch base with the director. At the close of each day, I would start washing glassware and check our chemical inventory. Initially, I did not do any of those things; it was only after talking to them over lunch each day that I came to recognize my colleagues’ workloads and time constraints. So, when I was given a menial task like washing dishes, I worked it into my routine and continued to do it each day, thus freeing up crucial time for my colleagues. By demonstrating that I shared the ecologists’ goals and viewpoints, I was able to gain their trust and integrate myself into their discourse community.
Regardless of the discourse community, gaining membership and authority involves recognizing the social context that surrounds communication. It demands that we read the room. In doing so, we can gain trust through demonstrating our awareness of a community’s goals, genres, and language. As we have seen through our explorations of social media and scientific discourse communities, understanding situated social norms is essential for developing that awareness. Effective communication always requires contextual awareness. This is the social side of communication. In order to understand and be understood, one must learn to read the room. We hope that our examples and discussions have illustrated the intellectual and emotional components of being a novice communicator. Further, we hope you now have the tools to embrace this novice status. It is inevitable that we will all wander into a new room from time to time. Once we cross a new threshold, it is up to us to find knowledge and power there.
Works Cited
Barbaro, Michael. “Cancel Culture, Part 1: Where It Came From.” The Daily , The New York Times, 10 Aug. 2020. The New York Times, https://www.nytimes.com/2020/08/10/podcasts/the-daily/cancel-culture.html . Accessed 10 Aug. 2020.
Becker, Alton L. Beyond Translation: Essays Toward a Modern Philology . University of Michigan Press, 1995.
Brown, Dalvin. “Survey Finds More Than Half of All Americans Back Potential Ban on TikTok.” USA Today , 12 Aug. 2020, https://www.usatoday.com/story/tech/2020/08/12/harris-poll-survey-americans-tiktok-ban/3353051001/ . Accessed 12 Aug. 2020.
Clayton, James. “TikTok’s Boogaloo Extremism Problem.” BBC News , 2 July 2020, https://www.bbc.com/news/technology-53269361 . Accessed 9 Aug. 2020.
Geertz, Clifford. Local Knowledge: Further Essays in Interpretive Anthropology . Basic Books, 1983.
Gumperz, John J. “The Speech Community.” International Encyclopedia of the Social Sciences , edited by David L. Sills and Robert K. Merton, Macmillan, 1968, pp. 381-86.
—. Language in Social Groups . Stanford University Press, 1971. Harris, Margot.
“TikTok Apologized for the Glitch Affecting the ‘Black Lives Matter’ Hashtag After Accusations of Censorship: ‘We Know This Came at a Painful Time.’” Insider , 1 June 2020, https://www.insider.com/tiktok-apologizes-for-blm-hashtag-glitch-after-censorship-allegations-2020-6 . Accessed 6 Aug. 2020.
Jennings, Rebecca. “This Week in TikTok: The Racism Scandal Among the App’s Top Creators.” Vox , 28 April 2020, https://www.vox.com/the-goods/2020/4/28/21239065/emmuhlu-n-word-mattia-polibio-chase-hudson-tiktok . Accessed 6 Aug. 2020.
Johns, Ann M. “Discourse Communities and Communities of Practice: Membership, Conflict, and Diversity.” Text, Role, and Context: Developing Academic Literacies , Cambridge University Press, 1997, pp. 51-70.
Leskin, Paige. “TikTok Surpasses 2 Billion Downloads and Sets a Record for App Installs in a Single Quarter.” Business Insider , 30 April 2020, https://www.businessinsider.com/tiktok-app-2-billion-downloads-record-setting-q1-sensor-tower-2020-4 . Accessed 9 Aug. 2020.
Luu, Chi. “Cancel Culture is Chaotic Good.” JSTOR Daily , 18 Dec. 2019, https://daily.jstor.org/cancel-culture-is-chaotic-good/ . Accessed 10 Aug. 2020.
Ovide, Shira. “A TikTok Twist on ‘PizzaGate.’” The New York Times , 29 June 2020, https://www.nytimes.com/2020/06/29/technology/pizzagate-tiktok.html . Accessed 9 Aug. 2020.
Rectenwald, Michael and Lisa Carl. Academic Writing, Real World Topics . Broadview Press, 2015.
Sung, Morgan. “The Stark Divide Between ‘Straight TikTok’ and ‘Alt TikTok.’” Mashable , 21 June 2020, https://mashable.com/article/alt-tiktok-straight-tiktok-queer-punk/ . Accessed 9 Aug. 2020.
Swales, John M. Genre Analysis: English in Academic and Research Settings . Cambridge University Press, 1990.
—. “The Concept of Discourse Community: Some Recent Personal History.” Composition Forum , vol. 37, 2017, https://compositionforum.com/issue/37/swales-retrospective.php .
Teacher Resources for Read the Room! Navigating Social Contexts and Written Texts
Overview and teaching strategies.
John Swales’s discourse community framework has been widely anthologized. It is, of course, something he has updated over time ( Genre ; “Concept”). It also builds on prior work in linguistic anthropology (Gumperz “Speech”; Language ), and it is often understood as being adjacent or complementary to other frameworks relating to the social nature of communication (Geertz; Johns). We raise these points because they offer a good context for how one might teach this chapter in a way that makes the discourse community concept plausible for students who are new(ish) members of academic discourse communities. Learning to read the room is only truly helpful if one can also understand a broader lay of the land, so to speak.
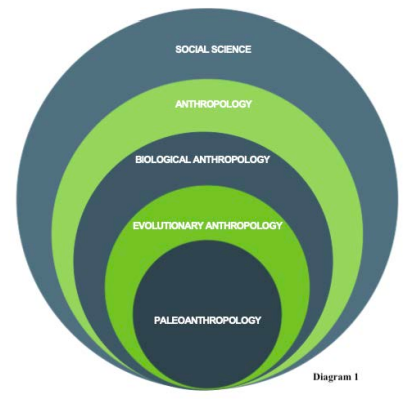
Scholars (in any discipline) develop ideas that retain varying amounts of power and authority over time. They do this within their discourse communities. Because this is an academic context, it means they do so within disciplines and sub-disciplines, which are “rooms” of differing sizes that students may need to learn how to “read.” For example, we could visualize disciplinary relationships as a series of nesting circles. The largest category in figure 1, social science, encompasses many distinct disciplines: anthropology, sociology, political science, etc. The diagram further maps out one tiny corner of the anthropological knowledge-making terrain. What’s more, we could have just as easily selected the biological sciences or the humanities and displayed a similarly small slice of disciplinary relationships within, for example, ecology or media studies.
Our overarching point is this: the smallest subset of academic inquiry pictured within our diagram—paleoanthropology—is a discourse community. It may share features with the larger social science or anthropology discourse communities, but we can still expect that it will have its own unique features. Paleoanthropology is, in effect, its own room, and ought to be read as such. Yet, one can still learn to understand it by applying what they know from inhabiting other rooms: adjacent academic disciplines and subdisciplines, or different workplace or media communities. Similarly, the TikTok section of our chapter offers a pop cultural framework for illustrating how far Swales’ criteria can (and cannot) stretch as we attempt to read a room. We believe this social media discussion can productively set the stage for parallel in-class discussions about academic knowledge production and the boundaries of academic discourse communities.
Tracing the history of an idea—when it appeared, where, and how it’s been used or expanded—is only possible when we can map out these kinds of disciplinary relationships. The powerful ideas tend to be cited, developed, and expanded on by other scholars within and across disciplinary discourse communities. The migration of Swales’ framework out of linguistics and into writing studies is a good example. In order to truly understand an idea, students must go outside of the content to examine the context of its production. These are very important skills. This is especially true for speakers and writers—like your students—who are in the process of becoming members of new academic discourse communities. As we illustrate in our chapter, this novice status is an inevitable social condition.
This chapter may be assigned during a unit focused on discourse communities, but it also presents ideas and prompts discussion that may be productive for transitioning into a unit on conducting academic research and narrowing research questions. In support of these goals, we offer two class activities. The first is specifically focused on helping students develop their understanding of the discourse community concept. The second is more a method for integrating oneself into an academic discourse community— particularly those associated with the humanities and social sciences.
Discourse Communities and Power Struggles: Examining Cancel Culture
This first activity was created for use during class time, so the podcast (audio and transcript options linked below) should be assigned in advance. At that point, class time could be loosely structured in “think, pair, share” terms.
As we know, there are core members within social media “subcommunities,” but individual users also retain the freedom to shape genres and vocabulary in individualistic and grassroots ways. This freedom can be seen across social media outlets, for example: upvoting on Reddit or the general phenomenon of cancel culture.
Today, we will examine cancel culture. The rise of this phenomenon draws attention to an important question on the social media discourse community landscape: How is power distributed? How are people scrambling to redistribute it? What are the implications of our own participation in these power structures?
You listened to (or read) an episode of The Daily called “Cancel Culture, Part 1: Where It Came From” (Barbaro). In it, host Michael Barbaro explores what it means to be canceled and how the whole thing began. Take five minutes to recall the episode, review any notes you made, or skim the transcript. Once you’re up to speed, we will form groups and engage with the discussion questions outlined below. I’ll pop in to hear some of your ideas individually, but you should regard the small group discussion as a platform for contributing to a full class discussion when we come back together toward the end of class.
Discussion Questions
Please begin by reading all the questions that follow. Decide whether you’d like to focus your discussion on Cluster 1 or Cluster 2. Once you make that choice, you should be thinking in discourse community terms. In other words, how might the discourse community concept help us to wade through this messiness and create situational answers to these questions? For example, what can genre and vocabulary tell us about any of these definitions or applications of cancel culture? Are terms like “liberal” or “young person” narrow enough for analyzing cancel culture? Are all “young people” members of the same discourse communities? Recall Swales’ concept of silential relations. How does a sense that certain things can be left unsaid support (or thwart) the politicization or weaponization of cancel culture?
Barbaro presents speech snippets where both Barack Obama and Donald Trump discuss cancel culture. How can cancel culture be labeled as “bad” in two ways that are so very different? Is “canceling” to be avoided because it’s impolite or some kind of cop-out as Obama seems to suggest? Is it to be criticized because the “liberals” are weaponizing it, as Trump suggests? Is it even possible to analyze this phenomenon apolitically?
All types of people exhibit socially unacceptable behavior, whether they are relatively powerful or relatively powerless. Given this, how can we make a distinction between canceling a celebrity and canceling an “average” citizen? How should personal security and loss of income factor into this distinction? Should we even draw a line here? Where does it seem to be drawn currently? In whose minds? Should it be re-drawn?
The Synthesis Grid
The Synthesis Grid activity, as adapted from Rectenwald and Carl, may be enacted during class or used as a formal assignment. It can be productive to assign students to submit a synthesis grid as a supporting document that accompanies, for example, a discourse community analysis, a genre analysis, or a researched argument.
What Is Synthesis?
Synthesis is an important writing practice. It is an especially important rhetorical strategy for learning to write in academic contexts. When writers offer a synthesis, they are combining, blending, or weaving related ideas from different sources.
What Is the Value of a Synthesis Grid?
Producing a synthesis grid offers you an opportunity to take notes in a structured way so you deepen your understanding of a particular topic or question. In effect, a synthesis grid is a material artifact of your research process. It is a record of all the reading and thinking you’ve done as a part of your writing process. Since writing can’t proceed without reading and thinking, it can feel particularly satisfying to document all this “behind the scenes” work. Then, you want to apply that “behind the scenes” work in your writing. For example, offering a synthesis within an academic argument is a very common (and effective!) method for establishing credibility.
How Do You Create a Synthesis Grid?
- You want to begin by settling on a particular topic or concept that will be the subject of your grid. For example, perhaps you want to write about cancel culture. This is a complex and controversial phenomenon with its own history, so starting a synthesis grid may help you to solidify your own ideas on the subject.
- Once you have your topic, you need to locate three or four pieces of writing that deal with the topic. Keeping with the cancel cultruel example, I might decide to start with a podcast transcript—Barbaro—and an article—Luu—then build my grid from there.
- Once you have the topic and some reading material, you want to create the “shell” of the grid. This involves making a series of rows that correspond to the number of readings you want to include. This also involves making a series of columns that correspond to the sub-topics you are interest in learning more about. See table 1 for an example.
- Once you’ve created the shell, you want to continuously add your notes as you move through readings related to your topic. Keep in mind that you won’t know all the sub-topics when you begin this activity. You will fill them in as you learn more. For example, perhaps you were interested in the redistribution of power ot start with, theyn you noticed that writers were often discussing the politicization of cancel culture. That’s a good indicator that you might want to add a column for politicization. Perhaps you then realize many writers are discussing the history of the phenomenom or how the pandemic has shaped the phenomenon. Perhaps you notice many writers discussing a specific social implication—for example, the negativity or destructiveness that is often attributed to cancel culture. If so, you should similarly follow such cues to add additional columns to your grid.
How Do You Use a Synthesis Grid?
Recall, the value of the grid is two-fold. It allows you to document the “backstage” work of reading and thinking, and it assists you in pulling the ideas you developed into the “foreground.” What follows is a sample synthesis that could be derived from this grid (even in though it’s still a work in progress). We can see how the ideas presented by Barbaro and Luu might be woven together to set up a line of inquiry in Table 2.
A Sample Synthesis
While cancel culture may appear to be a relatively new phenomenon, people have long been mobilizing against perceived injustice both on and offline. Both Michael Barbaro and Chi Luu have recently discussed this phenomenon and how it relates to internet language and culture at large. Barbaro and Luu each present the perceived positives and negatives surrounding cancel culture. Barbaro’s podcast episode was released more than six months after Luu’s article was published, and it draws on the words and experiences of politicians, celebrities, and everyday racists as a method for exploring the complexities of this phenomenon. One major question within all of this is how to differentiate between the “cancelation” of a relatively powerful person versus that of a relatively powerless person.
Connecting the Synthesis Grid to the Discourse Community Concept
As we suggest in our chapter, learning to mobilize the discourse community concept is an important method for “reading the room.” Learning how, for example, vocabulary or genre is shaped by social expectations sets student-writers up to understand writing as an audience-driven act. And, learning to map the epistemological landscape of a social debate similarly sets student-writers up to understand academic writing in terms of situated social exigencies.
- This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0) and is subject to the Writing Spaces Terms of Use. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ , email [email protected] , or send a letter to Creative Commons, PO Box 1866, Mountain View, CA 94042, USA. To view the Writing Spaces Terms of Use, visit http://writingspaces.org/terms-of-use . ↵
Read the Room! Navigating Social Contexts and Written Texts Copyright © 2021 by Sarah Seeley; Kelly Xu; and Matthew Chen is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
VCE Study Tips
English Language

Private Tutoring

Only one more step to getting your FREE text response mini-guide!
Simply fill in the form below, and the download will start straight away
The importance of Context in Literature
June 2, 2016

Want insider tips? Sign up here!
Go ahead and tilt your mobile the right way (portrait). the kool kids don't use landscape....
Literature is probably one of your hardest VCE subjects. If it’s not, then go you! (please tell me your secrets).
However, if you’re anything like me, then you probably look a bit like this when you begin considering the overall meaning of a text, the author’s views and values, and how any three passages in the text create the meaning.
When I became awash with confusion, like our old pal Ryan Renolds, the first thing I did (after eating a whole block of chocolate), was ensure I understood the context of the text. Without a clear understanding of the context of your text, you cannot fully comprehend the views and values of the author, nor the overall meaning of a text (it’s also part of the criteria for literary perspectives)!
So if you want to be feeling like this after you write a piece for literature:
Consider the following:
AUTHOR’S CONTEXT VS. READER’S CONTEXT
Austen was hunched over her small writing desk in the village of Chawton during England’s Georgian era as she wrote Persuasion. You are more likely reading it in a cozy bed, listening to Taylor Swift and half considering what you’re going to watch on Netflix later. Remember, your current social and cultural context can have a great influence on how you read a text, so it’s always important to imagine the author’s own context – whether this be very similar, or very different from the context of their text. It’s as easy as a Google search!
For a more in-depth look into how authorial intent and context is important in VCE English, read Context and Authorial Intention in VCE English .
SOCIAL CONTEXT
The social context of a text is the way in which the features of the society it is set in impact on its meaning. There are two aspects to social context: the kind of society in which the characters live, and the one in which the author’s text was produced.
Charlotte Brontë’s Jane Eyre was set in the same social context she herself lived in. It was one in which women were seen as the lesser sex, there was a great divide between the wealthy and lower class, and strict class boundaries were enforced. All of these societal features are key in determining Brontë’s views on the importance of social inclusion, and her championing of the strength of women. Or just listen to Phoebe:
HISTORICAL CONTEXTS
The historical context of a text is entangled with its social context, as underlying norms and convention are historically specific. The historical context is important to note especially when large changes have occurred between the time the work was produced, and our current day, so it is not assessed by our own concerns alone.
Aeschylus’ Agamemnon was first performed in 458BC, in Ancient Greece, a time vastly different from our own. Therefore, it is important to be aware of how the play was delivered, at the festival of Dionysus as part of a trilogy. Also have an understanding of the myths surrounding the Trojan War as well as those surrounding Agamemnon, Cassandra and Clytemnestra.
CULTURAL CONTEXTS
Culture refers to a particular ‘way of life’, involving religion, race and nationality, as well as things like food, dress code and manners. Furthermore, culture can relate to art, music, writing and literature itself. Cultural context, which is similarly linked with social, historical and ideological context, is especially important to note if the author is attempting to make a comment on an aspect of culture, or the clash of two cultures.
Cross cultural contact between an Indigenous tribe in Western Australia, and the British colonizers of this land, is explored by Kim Scott in his novel That Deadman Dance. He reveals aspects of culture largely unknown to current members of Australian society, as well as explores whether assimilation can be seen as a harmonious sign of friendship, or an intrusive loss of culture. The evolution, damage and protection of culture is an important context in this novel, and has a large bearing on the overall meaning of the text, as well as Scott’s views and values.
IDEOLOGICAL CONTEXTS
Ideology refers to the systems of beliefs and ideas that underpin our attitudes and behavior. Such ideology may be valued by society as a whole, or be the basis of conflict. Ideology is a context that is in many ways ‘invisible’. This is because our own is largely internalized and normalized, we act accordingly to our assumptions and social norms.
Many texts explore ideological context, either challenging or championing it. In his play Who’s Afraid of Virginia Woolf? Edward Albee challenged perceptions at the time of the family unit, portraying a couple that symbolizes the immense dissatisfaction caused by idealistic portrayals of marriage, and the fallacies of the American Dream. He illuminates how George and Martha escape from meaningless by creating fantasies and illusions, but how these eventually lead to the breakdown of their mental health.
So next time you’re struggling to get started on a literature piece, remember to think deeply about the different aspects of your text’s context!
Get our FREE VCE English Text Response mini-guide
Now quite sure how to nail your text response essays? Then download our free mini-guide, where we break down the art of writing the perfect text-response essay into three comprehensive steps. Click below to get your own copy today!

Access a FREE sample of our Literature study guide
- Focused on Developing Interpretations and Close Analysis , both of which you need for your exam
- Covering what it means to ‘interpret a text’, how to breakdown critical essays, different Close Analysis structures and more
- Includes sample A+ essays with EVERY essay annotated and broken down on HOW and WHY past authors achieved A+
- Essays written by multiple authors all scoring 40+ so you can learn different strategies and implement the advice that resonates with you most
%20(2).jpg)
Theme vs. Motif vs. Symbol
Themes, motifs and symbols are different kinds of narrative elements - they’re parts of a story that help to shape its overall effect. However, even though they’re words we use all the time in our English studies, it isn’t always easy to tell the difference!
This post will take you through some definitions , give you some examples and show you how you can use them in essays too. Let’s start with the broadest of the three…
What Is a Theme?
A theme is an idea or a subject that an author wants to explore. Themes appear throughout a work, and they’re often abstract ideas rather than concrete images that you can explicitly identify. Themes usually appear in interactions: for example, a parent reuniting with a child might evoke the theme of parenthood or family, an experience of discrimination might evoke the theme of prejudice or racism, a character facing a difficult choice might evoke the theme of morality or conflict, and so on. As you might be able to see, themes can require us to read between the lines because they are usually implied.
What Is a Motif?
A motif is something a bit more specific. Rather than an abstract idea, we’re looking for a concrete object (usually physical items, but also potentially sounds, places, actions, situations or phrases) that returns time and time again throughout a text. This repetition of motifs helps to create structure for a text - it can tether parts of the story to or around a central image. Because motifs are often linked to a theme , they can also serve as a reminder of that theme’s importance. For example, if the central theme was family or parenthood, the author might create a bird’s nest outside a character’s room; as we watch the bird and the chicks grow throughout the text, parallels are also drawn back to the theme.
What Is a Symbol?
You can think of symbols as motifs minus the repetition . It’s the more default word we use when referring to an object that represents an idea, and unlike a motif, symbols only need to appear once to have an impact. They can simply tell us more about a character or situation in that instant, at that specific time, rather than being a parallel or recurring throughout a text. However, they’re still identified in a similar way to motifs: symbols are also concrete objects and they’re still connected to themes.
Examples of Themes, Motifs and Symbols
Here are some text-specific examples for a closer look at these terms:

Check out our Macbeth , Rear Window and The Great Gatsby blog posts for more on these texts. If you’re studying other texts, have a look at our list of text guides in The Ultimate Guide to Text Response .
Identifying and Using Themes
Themes usually come across in interactions , and a possible first step to identifying them is thinking about if an interaction is good or bad, and why. For example:
In Rear Window , one of the neighbours berates everyone else for failing to notice their dog’s death.
This is a bad interaction because:
- a dog dying is never any good
- it tells us that none of these neighbours are looking out for or really care about each other
- someone may have killed the dog
The theme we might identify here is duty. The film might suggest that we have a duty to look out for our neighbours (without sacrificing their privacy) or to do our part to keep the neighbourhood safe from potential criminals.
Another example might be:
In The Great Gatsby , the Sloanes invite Gatsby over for dinner without really meaning it.
- it tells us how nasty the Sloanes are
- Gatsby still seems to be a misfit despite his wealth
- Tom is at best complicit in the Sloanes’ insincerity
The themes here might be society, wealth and class . This interaction shows us where these characters really stand with regard to these categories or ideas. Because he is ‘new money’, Gatsby cannot understand or fit in with the cruel and disingenuous customs of ‘old money’.
Most interactions in a text will fit into a theme somewhere, somehow - that’s why it’s been included in the story! Try to identify the themes as you go , or maintain lists of interactions and events for different themes. Because themes are so broad, they’re useful for guiding your understanding of a text, particularly as you’re reading it. They also provide a great foundation for essay planning since you can draw on events across the text to explore a certain theme.
Identifying and Using Motifs & Symbols
While themes can generally appear in texts without the author needing to make too much of an effort, motifs and symbols have to be used really consciously . A lot of interactions might just be natural to the plot, but the author has to take extra care to insert a symbol or motif into the story.
To identify either, pay attention to objects that might feel unusual or even unnecessary to the scene at first - from the examples above, Gatsby showing Daisy his shirts might seem like a strange detail to include, but it’s actually an important symbol in that moment. Then, you go into the brainstorming of what the object could represent - in this case, Gatsby’s newfound wealth. Symbols in particular often appear at turning points : the relationship between two characters might take a turn, an important sacrifice might be made or perhaps someone crosses a point of no return - all of these are potential plot points for the author to include symbols. For motifs , look more for repetition . If we’re always coming back to an image or an object, like Daisy’s green light or Lisa Fremont’s dresses, then it’s likely that image or object has significance.
Symbols and motifs can be more subtle than themes, but they will also help to set your essay apart if you find a way to include them. You’d usually include them as a piece of evidence (with or without a quote) and analyse what they tell us about a theme. For example:
On the surface, Gatsby appears to be financially successful. Over several years, he has acquired many material belongings in order to demonstrate his great wealth. For example, Fitzgerald includes a scene featuring Gatsby tossing his many ‘beautiful’ shirts onto Daisy, who sobs as she admires them. This display of wealth represents the superficial natures of both characters, who prize material belongings over the substance of their relationship.
You don’t need a quote that’s too long or overpowering ; just capture the essence of the symbol or motif and focus on what it represents. This is a really good way to show examiners how you’ve thought about a text’s construction, and the choices an author has made on what to include and why. To learn more about text construction, have a read of What Is Metalanguage?
So…you’ve just begun the school year and you’re feeling pretty excited about English. You’re determined to put aside all distractions this year and to only focus on studying, studying and studying. But…the minute you sit down at your desk, you find that your mind goes completely blank and that you are left only with one dreadful question: What now?
If this sounds all too familiar to you, you are definitely not alone. English can often make you feel like you don’t even know where to start. So, here is a quick guide that can help you to plan out your year, to break free from procrastination and to find some sparks of motivation when you feel like there is simply no road ahead.
Step 1: Read Your Text !
This may seem like the most obvious step, but it can make all the difference when done thoughtfully and thoroughly. One thing that VCAA English examiners always look for when reading text responses is in-depth knowledge and understanding of the text, and the best way to develop and gain this knowledge is to read, read, and read again! Try to treat your text like a blank map, full of unexplored territories and winding roads that are there for you to uncover each time you read the text.
When you read your text for the first time, look out for the major roads and landmarks; the setting and premise, the plot, the characters, the broad ideas, the authorial voice and style etc. Once you’ve gotten a good grasp of the major elements of your text, read it again, and focus on adding more detail to your map; fleshing out characters, understanding their motives, understanding the author’s purpose, and underlining key quotations and particular passages that encompass a broader idea. If you’re a forgetful person like me, you might find it helpful to note down some key observations as you go and to create a summary you can always refer back to throughout the year.
Step 2: Read Around Your Text
While reading and rereading your text will definitely help you to know your text in and out, in order to fully tick the box of knowledge and understanding, it is also important to read around the text; to understand the context of when and why the text was written, for whom it was written, and the impact the text has had on both its original audience and its audience today. Especially for texts that are rooted in history, like The Women of Troy or Rear Window , understanding context and background information is essential in understanding the text itself. After all, Rear Window just wouldn’t be Rear Window if it weren’t for the McCarthyistic attitudes that were so prevalent at the time, and The Women of Troy would have been a far more different play had it not been written during wartime. Each text is a product of both its creator and its time, so make the effort to research the writer, playwright or filmmaker , and the historical, cultural, social and political context of your text.
When doing your research, it can be helpful to use a set of questions like the one below as a guideline, to ensure that the information you’re finding is always relevant.
- Who is the writer/playwright/filmmaker?
- Who is the audience?
- When/where was your text written?
- When/where is your text set?
- Why was your text written?
- What is the style/genre of your text?
Step 3: Study Your Text
Here’s where it gets a bit more difficult. Now that you’ve drawn out your map, and dotted it with various landmarks, rivers and roads, it is time to actually use your map to go somewhere; to make use of all the knowledge and background information you have gathered so that you can begin to analyse and dissect your text in greater detail. Studying a subject with as large of a cohort as VCE English can oftentimes mean that ideas are recycled and exams are repetitive, so in order to distinguish yourself from the pack, try to look for ways to craft your own original path ; a view of the text that is distinctly your own, instead of following others. The best way to do this is to do a bit of thinking at home; to create your own original set of notes and observations and to spend time analysing each section of your text in greater detail than you may have done in class.
Constructing a notes table like the one below can help you greatly in sorting and fleshing out your ideas, and, when done consistently throughout the year, can save a lot of time and effort when it comes to studying for the exam!
The Women of Troy Notes Table:
%20(1).png)
Step 4: Target Your Study to Your SAC
So...you’ve made it all the way to your SAC. You may be feeling nervous at this point, even a little burnt out, but there is no need to worry. Studying for your SAC simply requires a bit of adjusting to your normal studying routine; changing it up so that instead of simply brainstorming ideas, you’re actually using these ideas in topic sentences, and instead of collating a list of quotes, you’re embedding these quotes into a practice paragraph. These are all examples of targeted study: taking all the information you’ve gathered on your text, all the notes you’ve made, and all the work you’ve done in class, and putting it into practice.
Targeted study could be done in the form of an essay plan, or unpacking an essay question
As an example, I've unpacked an essay prompt below using LSG’s THINK and EXECUTE strategy , a technique to help you write better VCE essays. If you’re unfamiliar with this strategy, then check it out in How To Write A Killer Text Response .
Within the THINK strategy, we have 3 steps, or ABC. These ABC components are:
Step 1: A nalyse Step 2: B rainstorm Step 3: C reate a Plan
The Prompt:
‘I ask you not to hate me. With the greatest reluctance / I must tell you the news…’ Euripides softens the brutality of the Greeks’ behaviour through his characterisation of Talthybius.
Step 1: Analyse
- This is an example of a quote-based prompt ( learn about the 5 different prompt types here )
- Bold keywords from the prompt: ‘I ask you not to hate me . With the greatest reluctance / I must tell you the news…’ Euripides softens the brutality of the Greeks’ behaviour through his characterisation of Talthybius.
- To what extent do you agree? This part is asking me to adopt a specific viewpoint, whether you agree, disagree or are somewhere in between.
Step 2: Brainstorm
Unpack the keywords in the topic:
- 'not to hate me' , 'greatest reluctance' – Talthybius’ desire to be liked, his understanding of the actions of Greeks
- Softens the brutality – Talthybius serves as the opposing force to the Greeks’ brutal behaviour, makes the Greeks more sympathetic
- Characterisation – Talthybius’ personality, behaviour, actions, language
Step 3: Create a Plan
Contention: While Talthybius is used by Euripides to evoke some sympathy for the Greeks, ultimately, he serves to exacerbate the cruelty of the Greeks’ actions and the devastating consequences of their fall from a civilised, sacred people to a bestial, impulse-driven group of men.
Paragraph 1: Certainly, amongst his peers which are excoriated by Euripides for their cruel, unfeeling behaviour, Talthybius is depicted to be the most humane of the Greeks due to his conflicted nature, evoking sympathy amongst the audience, and reinstating some humanity to the Greeks’ otherwise sullied reputation.
Targeted study could also be done in the form of unpacking quotes, and analysing their significance
We can also use the ABC steps here. For example:
'Like the mother bird to her plundered nest, my song has become a scream'
Step 1: Analyse
Demonstrates the dehumanisation of the Trojan women, and the heinous, beastly actions of the Greek men, who, like their 'war machine' description, have subverted all that is natural to become violent, and all that is beautiful to become grotesque
Step 2: Brainstorm
- 'Mother bird' - animal imagery, maternalistic
- 'My song has become a scream' - demonstrates devastation, contrast between melody to dissonance
Embed the quote into a sentence, e.g.:
Euripides’ description of Hecuba as a 'mother bird' at her 'plundered nest' demonstrates the innately maternal nature of her character through animal imagery, while also emphasising the vulnerability of the Trojan women, who have been reduced to defenceless prey as a result of the Greeks’ predatory and beastly behaviour.
Planning essays and breaking down prompts/quotes are extremely time-efficient ways to approach your texts and SACs. Rather than slaving away for hours and hours writing full essays, these simpler forms of targeted study can and will save you the burnout and will get you feeling confident faster.
Only move on to writing a full practice essay or some practice paragraphs once you feel you have a good in-depth understanding of how to plan an essay and once you have already naturally memorised some important quotes that you can use in your essay ( learn how to embed your quotes like a boss here ). Remember, quality over quantity, so spend your time before your SAC revising thoughtfully and carefully, targeting your revision, and taking things slowly, rather than robotically churning out essay after essay.
Step 5: Embrace the Exam!
The end of every VCE English journey is the highly anticipated, dreaded and feared English exam. Now, while you may be reading those words with a horror movie soundtrack playing in your mind, the English exam, despite being a gruelling 3 hours of essay-writing, really isn’t as horrific as it sounds. Preparing for it is also much less intense than you might think it to be, because essentially, from the very first time you read your text, you will have already begun preparing for the exam. All that is left to do before the English exam is to polish up on some of your weaknesses identified in your SACs, to look over all the notes and information you have gathered throughout the year, to freshen up on essay writing and essay planning , and to do a couple of practices, so that you can feel as ready as you can for the real thing.
In particular, I found that in the leadup to my English exam, studying with my friends and peers was not only a welcome stress reliever, but a really good way to expand my own knowledge by helping others and being helped myself. Having your peers review your essays and helping to give feedback on theirs is always an excellent way to improve your own essay-writing skills, and, a great way to provide good constructive criticism is to follow the GIQ rule (I’m not sure if this is a real rule…but it works!)
- What was GOOD about the piece? e.g. Your sentences flow really well, and you embed quotes into sentences phenomenally!
- What could be IMPROVED? e.g. Perhaps adding a couple of sentences elaborating on this idea could make your essay even better!
- What QUESTIONS do you have about the piece? e.g. I don’t really understand this sentence, what were you trying to say here?
Hopefully, these tips will be able to help you out throughout the year in staying motivated and feeling okay about English! Remember, this is just here as a guide to help you, and not a strict regimen to follow, because everyone studies differently, and has different goals in English.
However, now that you have a clearer pathway and plan for learning your texts in-depth, what’s next? Well, it’s pretty important that you learn about the different areas of study so that you understand how you’ll actually apply all of your new-found text knowledge to each of your SACs and the exam. Our Ultimate Guide to Text Response and Ultimate Guide to Comparative give you a full rundown of what is required in these two areas of study (where you will have to learn specific texts) so I would highly recommend having a read!
Written expression is often overlooked in our essays. Often, if we are made aware of clunky or awkward expression, we are also not quite sure how to go about improving it. Although sophisticated and pertinent ideas serve as the foundation of a successful essay, how we construct our sentences and express these ideas may be what distinguishes a good essay from a great essay.
These differences can be rather subtle, but the small things can and do matter.
1) USE YOUR VOCAL CHORDS
(to read out loud, not sing… unless you really want to)
Take your essay and read it out loud. Let your own conscience guide you in terms of whether a particular sentence flows well, is complete and makes sense. Keep your eye out for these small errors in particular: Grammar: Does your sentence actually make sense? Let’s have a look at an example: Although Funder suggests that the act of telling one’s story, especially one of victimisation, can catalyse the internal confrontation and healing required to move on.
(This is not grammatically correct! This is because this example only contains a subordinate clause and is lacking a main clause.)
But wait… what is this ‘subordinate clause’ and ‘main clause’?
A clause includes a subject and a verb .
Melissa ate an apple.After Wendy ate an apple.
What is the difference between the two clauses above?
‘Melissa ate an apple’ makes grammatical sense on its own. This is what we call a main clause (or an independent clause). On the other hand, ‘ After Wendy ate an apple’ is an incomplete sentence as it does not make sense. What happened after Wendy ate her apple? This is the information that is missing from the latter clause, making this a subordinate clause (or a dependent clause).
So now let’s try again…
Although Funder suggests that the act of telling one’s story, especially one of victimisation, can catalyse the internal confrontation and healing required to move on, ultimately, these individuals can never be truly free from the past that has irrevocably defined them.
(Hooray! This is a complete sentence now.)
Spelling : Are the title of the text, the author or director’s name, characters’ names, publisher’s name, etc. all spelt correctly (and capitalised, underlined, and italicised appropriately)?
Did you use the correct there, their and they’re? How about it’s and its? (and so on).
Sentence length: Did that sentence just go on for 5 lines on a page and you are out of breath now? You can most probably split that overloaded sentence into two or more sentences that make much more sense. Check whether you have a clear subject in your sentence. If you have three different ideas in one sentence, give each idea its own opportunity (ie. sentence) to shine. The opposite also applies: if it is for a very short sentence, did that sentence pack enough content or analysis?
One spelling error or half-finished sentence in an essay will not severely affect your mark, but they can easily add up if they occur often enough. Consequently, this will distract the reader from engaging with your ideas fully and thus disrupt the flow of your essay.
By being aware of these aspects, you are now able to easily fix them and boost your writing.
2) BE SUBTLE
Try not to be casual or overt in your writing as it can be quite jarring to read and unfortunately give readers a potentially negative impression of your piece.
Try not to use phrases such as:
- In my opinion… (You do not need it as your entire essay should be your implicit opinion!)
- This quote shows that… (Embed the quote and link to its implication instead)
- This technique is designed to… (Identify the technique and be specific, especially in Language Analysis)
- I think that…, I believe… (Avoid using first person in a formal essay. Use of first person in creative writing is fine though if required)
They are redundant and do not add much to your ideas and analysis. Try omitting them and see whether that helps your sentence flow better and seem more formal.
3) LINK ‘EM UP
Sentences that seem disjointed or a clear connection can make it difficult for your teacher or the assessor to join the dots between an idea and an implication or consequence. Use linking words as they are fantastic for explicitly showing the reader how your ideas are related and thus allow your writing to proceed smoothly.
Therefore, hence, thus, thereby, consequently, subsequently, in addition, additionally, furthermore, moreover, on the other hand, on the contrary, however, henceforth, and so on… The list is endless!
4) ADD OOMPH (through vocabulary)
In general, having a wide vocabulary will allow you to express your ideas and analysis more accurately as you are likely to have access to a precise word that can capture the essence of your idea. Make a vocabulary list for a particular text or for Language Analysis (such as tone words) and aim to use varied language to convey yourself well.
If you’d like to see a list of sentence starters and essay phrases to help you get a headstart on expanding your vocabulary, check out this blog .
Focus on verbs and expanding your list of synonyms for words such as shows, demonstrates, highlights, emphasises, suggests and so on. An individual, character, author or director may not only be conveying but also denigrating or remonstrating or bolstering or glorifying or insinuating . Adding precision to your writing through careful vocabulary choice will distinguish your writing and also add complexity.
BEWARE! There is a fine line to tread with sophisticated vocabulary - do not overload your writing as you can risk writing convoluted sentences that hinder the reader’s ability to understand your piece. Also make sure that you understand the nuances of each synonym and that they are used in the correct context! (They are synonyms after all - not the same word!)
If you are debating whether to use a word, ask yourself: do you know what it means?
If yes: Go for it!
If no: Do not use it until you know what it means.
Reading sample essays, The Age Text Talks, reviews and more of the texts you are currently studying will expose you to not only a multitude of interpretations of your text, but also to different sentence structures, writing styles or vocabulary that you could incorporate into your own writing.
I would also highly recommend that you read outside of the texts you are studying if you have time, whether that may be novels by the same author or even newspapers. Your written expression will only benefit from this exposure as the ways you can express yourself through writing continue to increase upon seeing others’ eloquence.
6) GET WRITING
If you do not write, you will never be able to improve your written expression. Put pen to paper (or hands to keyboard) and start constructing that essay. You can only fix your writing once you have writing to fix.
Let's all be honest here, Year 12 is endlessly tiring. Literature, for all its greatness, can also be endlessly tiring. Along with 3-4 other subjects, sometimes the idea of writing a practice piece, deeply analyzing the language of your text, or doing research into the context, views and values of the author are things you really, really don’t feel like doing.
Although these things are necessary and important, they’re also often difficult, taxing, and possibly not that interesting. Not too long before the Literature exam, my friend and I were texting, both feeling immense stress and guilt because we felt we hadn’t studied enough for the exam, but equally tired and unable to write any practice pieces. I’m sure many of you are very familiar with the paradox of not spending time studying because you are instead spending that time worrying about not studying.
However, there’s really no need to suddenly feel full of stress and anxiety when you have no motivation to do such work for Literature, that’s just wasted energy! Instead, accept that you’re going to have a little break from the serious stuff, and use that energy instead to improve your understanding and knowledge of your text (part of the exam criteria!!).
My friend and I decided we’d meet for coffee, and try and just discuss our exam texts together (Who’s Afraid of Virginia Woolf and Dark Roots).
‘Bring paper and the books’ she texted me ‘I’ve got an idea’. And that idea was...
VCE Literature Charades
How to play:1. Find a friend2. Think a concept, character, quote, theme, literary device or anything really from one of your texts3. Forget about your dignity4. Act it out until your friend guesses5. Swap and repeat.And once people started to stare as we theatrically mimed things like ‘metaphor’ and ‘the albatross’ we decided to tone it down a little bit, leading to the invention of...
VCE Literature Pictionary
How to play:1. Find a friend2. Think of a concept, character, quote, theme, literary device (you get the idea)3. Keep your dignity intact!4. Start drawing the idea until your friend eventually guesses (warning: could lead to many failed attempts at drawing ‘foreshadowing’)5. Swap and repeat.
So I know this seems ridiculous but I swear, without even realizing it you’re getting to know your text so much better. There’ll be that moment in the exam room when all you’re thinking is ‘what on earth is that quote’, and suddenly you’ll remember how you’re friend fell off her chair trying to mime it. Either way, it’s a much more valuable use of time than worrying about not studying, especially because you’ll spend most of the time laughing.
If you’re alone, and you really don’t feel like studying for literature, but you still kind of have to study for literature… don’t despair! Find a place in your house where you wont be disturbed (or disturb anyone) and pretend you’re running an information session on your text. I used to record endless minutes of myself rambling about all different facets of my text, with no comprehensible structure, just trying to say and explain everything I knew about it. I would delete them almost straight away, but trust me, taking on the role of a teacher can be very fun, and when no ones watching, you can really just go for it. Things are much more likely to stay in your memory when you’ve explained them aloud, so you’ll be super prepared for your SACS!
Of course, it is beyond important to make sure you write as many practice pieces as you think you need to, and to work on tasks that may at times be ‘boring’, but if you want to avoid burning out try making studying a little fun!
Introduction
Arguably one of the greatest modern playwrights of our time, Tennessee Williams produced some of the best post-war 1950’s American plays that have now engrained themselves as classics. After the conclusion of the second world war, America was pervaded with hypermasculinity, deep levels of insecurity and a desperate need to regain the pre-war success of the 1920s. During the 1950s, the United States began to regain its economic success and spirits were high as ever; however, this may only have been ostensible. Beneath the surface of such success lurked unshaken expectations on both men and women and deep-rooted bigotry.
In this article, we will get to know how these concepts are explored in ‘Cat on a Hot Tin Roof’ and examine why this text is important in the context of Lit Perspectives and Close Analysis.
Characters Analysis
Brick is too numb to feel much of anything any more; he is a drunk and cold shell of what he once was. Since the death of his friend Skipper, Brick has retreated into solitude and emotional aloofness, and the only emotions that he can express are disgust and boredom. The other characters can only coax an emotional response out of him when they mention Skipper
Maggie is a traditional 1950’s beauty, she is lively, gorgeous and has a deeply sexual presence. She spends the majority of the play trying to get Brick to sleep with her- both to satisfy her own needs, and to allow her to conceive a baby. This which would guarantee her share of the Pollitt family wealth.
Big Daddy, like Brick, gets a lot of undeserved attention and love; this is because he sits upon the Pollitt wealth he built. He worked hard for economic success, and now he wants to enjoy it. He is uninterested in Big Mama and treats her with little affection or respect.
She is an older version of Maggie - more dramatic, needier, having let herself go. She loves her husband unconditionally despite his cruelty and indifference to her. Like Big Daddy, she cannot help but prefer Brick to Gooper because he is so much like Big Daddy.
Brick’s older brother but has lived in his shadow since the day he was born. While Brick got the attention with looks and football, Gooper married into society and became a successful lawyer. But the unfair attention and focus on Brick has made Gooper vengeful and petty, and so it is out of both greed and spite that he actively campaigns for control of Big Daddy’s estate.
Gooper’s wife who has all of his greed and sourness, without any of his justifying history. She taunts Maggie’s lack of motherhood by parading her plethora of children around the house.
Concepts and Concerns
TIP: Concepts and concerns should form the basis of your analysis whether you are doing a close analysis or a literary perspectives essay!
MENDACITY VS TRUTH
The central tension in the play is underscored by mendacity, lying and deception. The repressed truth is constantly on the verge of being unleashed and it is the “inadmissible thing” that pervades the family. The two primary sources of mendacious repression are Brick’s homosexual desires and Big Daddy’s imminent death from cancer. Ironically, it is these two who value integrity and honesty the most.
When Big Daddy finally finds out the truth about his impending death he exclaims: “By all the goddam lies and liars that I have had to put up with, and all the goddam hypocrisy that I lived with all these forty years that we(big mama) been living together”
In a final moment of existential dread and disgust, Brick resignedly claims that “mendacity is a system that we live in. Liquor is one way out and death is another”. These are the fates that are destined for Brick and Big Daddy respectively.
The truth (if there can be such a thing) is that both Brick and Big Daddy are loved so ardently by their partners, but they blinded by their dishonesty to themselves. It is because Brick cannot come to terms with his own sexuality and Big Daddy cannot fathom his inevitable death that lies, and deceit is perpetuated in the text.
MASCULINITY AND HOMOSEXUALITY
Williams himself was gay and lived in a society that constantly repressed and shamed it as a deeply sinful practice and associated it with failed masculinity. Thus, he explores the deep turmoils of homosexuality in the 1950s and its implications on manliness, bigotry and society.
Whilst not stated explicitly, it is implied that Skipper confessed his love to Brick; whilst Brick felt the same way, he knew this would not be accepted by society. Consequently, he shuts Skipper down and later that night, Skipper commits suicide. Brick cannot admit the truth to himself because in his mind “purity” and “homosexuality” are mutually exclusive, due to his own internalized homophobia and even when Big Daddy makes Brick face his desires and the guilt that pervades him; he cannot escape the bigoted societal norms imbued within him
Williams paints an image of distress, pain and grief caused by the prevailing homophobia of the 1950s. Brick is crippled both by his failure as a man and his failure to be true to himself.
THE AMERICAN DREAM
Back in the 1950s, the American Dream was the dream that everyone was expected to aspire for was much more conservative. It included a traditional family with a stay at home mother, hard-working and masculine father, 2-3 children, a home and money, lots of it!
The Pollitt family truly embodied the American Dream. With their self-made fortune, successful sons (though Brick is now a mess) and even grandchildren. In many aspects, Gooper and Mae fulfil the expectations of the American Dream much more than Brick and Maggie do; they have children, success and ambition. They attempt to use this to their advantage in their bid to win over Big Daddy’s estate but even that fails to sway Big Daddy’s favouritism for Brick.
Brick is as resigned and aloof to the idea of wealth and tradition as he is to his wife Maggie. His repressed homosexuality already divorces him from the ingrained social expectation of the American Dream and it disappoints him to pretend to desire the same things his brother Gooper does. This, ironically, only makes him more favoured by his parents.
In a world of strict expectations and immovable bigotry, there is no room for homosexuality, and this disappoints no one more than Brick himself. In his world, the very essence of his being contradicts the dream that everyone is taught to value. Williams asks readers to consider the consequences of such restrictive beliefs, he questions the American dream at a fundamental level by asking: so why do we all have to want the same thing?
MOTHERHOOD AND FEMININITY
What does it mean to be a woman? For Mae, that means being a loving housewife and being able to bear children. In the petty feud for Big Daddy’s will, she insults Maggie’s childless state, she is less of a woman because of it. Of course, the reason Maggie cannot have children is that Brick is unwilling to sleep with her. Again, even though Mae has provided Big Daddy and Big Mama with a plethora of grandchildren, they still prefer Maggie’s young and sensual energy.
Williams attempts to undermine the characteristics that were supposed to define women as feminine through Maggie. Moreover, women were supposed to be passive players in the family, to do their husbands bidding and to be polite and proper at all times. Maggie is none of these things. She is unapologetically sexual, unwaveringly ambitious in her pursuit of the Pollitt family wealth and determined to cement herself as Brick’s partner although she knows of his homosexual desires. In a society where women were not supposed to have dreams let alone pursue them, Maggie is a “cat on a hot tin roof”, chasing her dreams with careless disregard of established hetero norms.
Literary Perspectives
Now we get into the tricky stuff! This is one part of your exam and is the Unit 4 Outcome 1 SAC so it’s important that you get a competent grasp of the task! TIP: Follow this link to get an overview of the literary perspectives task (I’m thinking of linking the ultimate lit perspectives guide here, let me know what you think)
Some prevalent perspectives should jump out at you immediately just by looking at the Concepts and Concerns. Remember that you don’t have to choose just one perspective, it’s more important that you develop an overall interpretation of the text and incorporate the buzzwords that reflect your perspective. Use your perspective/interpretation as a lens to the concepts and concerns mentioned above as a springboard for your analysis
Now we get into the tricky stuff! This is one part of your exam and is the Unit 4 Outcome 1 SAC so you must get a competent grasp of the task! TIP: Follow this link to get an overview of the literary perspectives task (I’m thinking of linking the ultimate lit perspectives guide here, let me know what you think)
Here are some general perspectives that you might want to think about:
Think about the role the women in this text play and how they are portrayed. You have three vastly different women who all reflect the social standards that defined the 1950s in varying degrees.
Maggie does not seem to care much about what Brick wants as much as she cares about her own needs proven when she attempts to force him to do things he doesn’t care much for (pretending he remembered Big Daddy’s birthday or sleeping with her). She stands in diametric opposition to Big Mama and Mae who are both stereotypical women of their times, always forgoing their own desires for their husbands’. In this sense, our sympathy for Maggie only confirms Williams’ notion that women should be able to freely chase their ambitions and break free of restrictive stereotypes.
These societal standards that reinforce traditional gender roles, heterosexuality and the pervasive male gaze form what literary critics call heteronormativity. This is a key notion in feminism and extends this perspective to more than just an analysis of women in society. It also asks us to question how these hetero norms may influence overarching definitions of masculinity. We can see how these hetero norms have forced Brick into an empty cripple whose only clutch is alcohol and the “click” of peace he drinks for.
TIP: Heteronormativity can also be linked to Marxism as it forms part of the superstructure (institutions and culture considered to result from and reflect the economic system underlying society) that perpetuates the belief that men must be the breadwinner to support their housewives and children. In other words, if you are not supporting your family financially, you are not considered a true man.
Some might argue that the central conflict in the play comes down to who will inherent Big Daddy’s wealth after his death and is only inflamed by Brick’s repressed sexuality. The American Dream is literally underscored by the chasing of money!
Consider how the class impacts the tension in the story. Because of their high social status, Brick’s sexuality is only more scandalous. Funnily enough, despite the fact that Maggie knows he does not love her, she could not care less. As I’ve probably hammered in enough by now, she has more regard for the money than Brick (though she does love him). Furthermore, Gooper’s job as a lawyer, in his mind, only further cements him claim to the Pollitt family throne because it pays well and is highly respected.
Psychoanalysis
Pain, trauma, guilt, desire, gaze and the unconscious. All these things come into play when thinking about psychoanalysis. Popularised by Sigmund Freud who believed (and I’m simplifying here) that psychological theories and techniques could help people better understand their unconscious thoughts, feelings and desires. This is turn, would help them explain their behaviours.
The best way to start a psychoanalysis of ‘Cat on a Hot Tin Roof’ is to think about what each character wants, how they are behaving and how their past might influence this. Brick’s homosexuality and the guilt he feels at Skipper’s death is a great place to start. This is also a great way to integrate to touch on other perspectives if you think about the ways in which heteronormativity or social status may have influenced his decisions back then.
Close Analysis
TIP: Just because it’s close analysis, doesn’t mean you can forego an overall interpretation!! Remember the Concepts and Concerns of the author! Here is a link to help you out with more general close analysis advice (again same idea as previous section, to
Some might argue that the central conflict in the play comes down to who will inherit Big Daddy’s wealth after his death and is only inflamed by Brick’s repressed sexuality. The American Dream is underscored by the chasing of money!
Consider how the class impacts the tension in the story. Because of their high social status, Brick’s sexuality is only more scandalous. Funnily enough, even though Maggie knows he does not love her, she could not care less. As I’ve probably hammered in enough by now, she has more regard for the money than Brick (though she does love him). Furthermore, Gooper’s job as a lawyer, in his mind, only further cements him claim to the Pollitt family throne because it pays well and is highly respected.
The best way to start psychoanalysis of ‘Cat on a Hot Tin Roof’ is to think about what each character wants, how they are behaving and how their past might influence this. Brick’s homosexuality and the guilt he feels at Skipper’s death is a great place to start. This is also a great way to integrate to touch on other perspectives if you think about how heteronormativity or social status may have influenced his decisions back then.
TIP: Just because it’s close analysis, doesn’t mean you can forego an overall interpretation!! Remember the Concepts and Concerns of the author! Here is a link to help you out with more general close analysis advice (again same idea as the previous section, to link the ultimate guides)
The close analysis essentially wants you to analyse the nitty-gritty of your text. Demonstrate to VCAA that you understand how language creates meaning and can support the overarching values of the author. Questions of form, structure, language devices and literary techniques all come in to play when thinking about how Tennessee Williams created meaning in the play. Think of yourself as a detective who must find the most forensic examples in supporting your overall perspective. Here are a few things you might want to consider when closely analysing ‘Cat on a Hot Tin Roof’.
The Form – Play
The Play as a form is one of the most distinct types. It is a show for an audience and does not have as much intimacy as a novel. It has stage directions that the audience does not see and even minute punctuation that must be portrayed by actors. It is important that you can demonstrate you understand this!
Different stage directions will impact the audience in a multitude of ways. For example, Williams had detailed ‘Notes for the Designer’ that closely depicted the setting and atmosphere of the play. In it, he detailed the story of “Jack Straw and Peter Ochello, a pair of old bachelors” who were rumoured to be gay. This instantly establishes homosexuality as a backdrop of the play, it is woven into the setting.
Or you might want to analyse the stage directions that constantly punctuate Brick’s dialogue; every time he speaks it is “absently”, “dreamily” or “vaguely”, which further emphasises his cool and aloof nature. This is in contrast to when he speaks about Skipper in which he suddenly becomes defensive; his dialogue graduates from resigned one-liners to profuse emotional rants.
Structure – The Acts, the Setting, characters, timeframe
Whilst the form of a play is unique in itself, there are certain aspects of ‘Cat on a Hot Tin Roof’ that differentiates it from others.
For example, the play in its entirety occurs within one day. This emphasises the extent to which the Pollitt family had already been teetering on the edge of unleashing the secrets of the family. The confirmation of Big Daddy’s death only opens this up further and unwinds the atmosphere of secrecy, denial and mendacity in merely a few hours.
This is only heightened by the fact that the entire play occurs in one room, the “bed-sitting-room” of the plantation home. Therefore, no matter how hard the family tries to escape the truth, the claustrophobia created by having so many of them in one room together acts as a catalyst for the truth to be revealed.
Also, consider how these characters are established! What has been said explicitly and what has been alluded to. For example, it is never explicitly said that Brick is gay or that Big Daddy will die (to his face at least). In some ways, despite the fact that everyone knows the truth, it is still a truth too difficult to bear and speaking it out loud will only confirm what they have been in denial about for so long.
This blog is part of a series of blogs breaking down the 2023-2027 VCE Literature Study design. For in-depth takes on the study design and the new AoS (Developing Interpretations) check out The Ultimate Guide to VCE Literature and A Guide to Developing Interpretations .
Here, we’ll take a deep look into the SAC for Unit 3.2: Developing Interpretations. We’ll be using Margaret Atwood’s 1996 Alias Grace to demonstrate parts A and B of the SAC criteria so you can see the thinking process behind developing interpretations.
The SAC has two parts:
- Part A: An initial interpretation of the text’s views and values within its historical, social and cultural context.
- Part B: A written response that compares/interweaves and analyses an initial interpretation with a subsequent interpretation, using a key moment from the text.
Your teacher may decide to do them in two separate SACs, Part A after considering the text, and Part B after considering the supplementary reading. Or they may do them together, having you analyse a passage and answer a question just based on your own understanding of the text, and then continuing that analysis by adding the supplementary reading.
Understanding Context
Part A of the Developing Interpretations SAC task involves the text’s 'historical, social and cultural context’, so it is imperative we have an understanding of firstly, the author and their world, and the text and its world.
Alias Grace was published in 1996, close enough to our modern times that we can consider it contemporary literature. On the surface, there is not much to link it directly to the big global events of the 1990s - like the Gulf Wars, the Monica Lewinsky scandal or the uncertainty of the new millennium. Margaret Atwood is Canadian, and the events of Alias Grace also take place in Canada; any criticism of government or cultural issues in the text can then be considered criticisms of Canadian culture, but may also be of Western or Anglo societies at large. It’s also worth keeping in mind Atwood’s track record as a feminist activist who became famous for the feminist intentions in texts like The Handmaid’s Tale (1985) and Cat’s Eye (1988).
The world of Alias Grace is about 150 years prior to the text’s publication. The murder that put Grace in prison occurred in 1843, and Grace died sometime around 1873. Feminism as a socio-political movement did not exist at this time, so any ‘feminist bent’ that Grace or Mary Whitney display is the result of independent dissatisfaction, not the influence of wider cultural forces. The role of psychology is strong in Alias Grace and in the afterword, Atwood notes the increasing academic interest in the mind and subconscious. Whilst we could venture into the specific who’s who of 1850s new world psychological history, it is most important to recognise that there were disparate ideas of how memory is formed and recalled, and that defiant or mentally ill women were often stigmatised and categorised as 'insane', when we would now acknowledge the range of mental health diagnoses and traumatic backgrounds that would better explain certain behaviours. Note also that mental health institutions were tools of a patriarchal system that viewed the internment of women as a means of control over women, regardless of mental illness, leading to the regular and indiscriminate use of procedures like lobotomy or Electro-Convulsive Therapy (ECT) to keep women 'in check'.
Part A of the SAC: An Initial Interpretation
When forming an interpretation of the text, it is necessary to first decide two things. Firstly, you need to recognise the author’s intention and what you think are the primary views and values . Then, you need to find aspects of the text that support your understanding of the text’s primary meaning.
Of all the concepts and ideas in Alias Grace , two are particularly pertinent and stick out to me as a reader. One is memory , the other is sexuality . There are of course other ideas, but these two were the big ones I noted reading the text. Thinking about what you find interesting or core to the text will help you to form an initial interpretation. Once you have the initial ideas, try to expand them into full sentences. To use memory as our example:
Atwood explores the fallibility and role of memory in our understandings of ourselves and our actions, in particular, noting how people subconsciously decide which memories to keep or forget.
See how meaty this sentence is? Even if I can’t quite touch on all of these ideas in a full essay, I have so much I can talk about that it basically makes it impossible to fall short. Now, I want some aspects of the text that help provide through-lines. By this, I mean that I want a smaller part of the text that helps to exemplify my interpretation and that, preferably, would be evident in a passage analysis. I’m someone who finds structure really interesting in texts, so I look at things like form, genre and plot very closely. Alias Grace is really interesting for its use of ‘primary source’ quotes at the start of sections, as well as the fact it has basically no quotation marks to delineate dialogue. Moreover, the fact that Grace’s narration is first-person and that Jordan’s narration is third-person provides ripe territory for analysis. I need to link this to memory, and put it in a sentence:
Atwood’s use of Grace’s first-person narration without quoted dialogue, thus structuring the plot around her speech and remembering, provides a long-form case study in how the psychological process of remembering helps provide understandings of the self.
So, just based on my understanding of the context (1850s psychology and its impact on women) and the world of the text, I am able to determine my initial interpretation: that Alias Grace is about memory and forgetting in the face of trauma and an indeterminate sense of self. This idea is displayed in the structure of the text which relies heavily on displaying thought processes.
Part B of the SAC: The Supplementary Reading
The supplementary reading can be a number of pieces of writing given to you by your teacher. This could be something written by your teacher, an explainer of a literary theory (like Marxism or feminism), or as I’ll be using here, an academic article. Check out our blog on Developing Interpretations which goes into how to read academic articles.
The article I’ve chosen is Margaret Rogerson’s ‘Reading the Patchworks in Alias Grace’ (1998). At the core of Rogerson’s argument is that the recurring motif of sewing and patchwork is a significant indicator of Grace’s identity and her self-expression and that Atwood uses the symbolism of various quilting patterns to reflect the ambiguity of Grace’s character and our understanding of her (since quilting symbols are heavily subjective). Just based on this brief summary of Rogerson’s interpretation, we can start to see how it is somewhat at odds with my initial interpretation (from Part A) - Rogerson isn’t as concerned with memory and psychology, nor am I concerned with symbolism because I focus on structures and narrative.
Rogerson’s article doesn’t necessarily disagree with my interpretation, in fact, both exist alongside each other quite nicely. I would phrase Rogerson’s interpretation as 'running parallel' to my own because they don’t always touch on the same ideas. Recognising where the supplementary reading sits in relation to your own interpretation is important because it helps to break down how to respond to its position and enhance your own interpretation. Try to place it on a scale of ‘total disagreement’ to ‘total agreement’. It will probably be somewhere in the middle.
Self-Reflection and Reinterpretation
Now that I’ve read my supplementary reading and placed it in relation to my initial interpretation, I need to ask myself a few questions, and be honest with myself:
- What new information have I learnt from the reading?
- What ideas/themes/motifs did I initially ignore?
- How do these new ideas and pieces of information challenge my interpretation?
- How do these new ideas and pieces of information support my interpretation?
- Can I find links between the seemingly challenging aspects of the reading and link them to my initial interpretation?
- Can I link specific aspects of my initial interpretation to the theories and ideas presented in the supplementary reading?
Rogerson’s article contained a lot of ideas and information that I had previously glossed over. Significantly, I learnt that 'quilt patterns [...] appear with their names as section headings throughout the text' (p. 8), a theme I hadn’t noticed. Moreover, Rogerson explains the literary and political significance of quilting and patchwork symbolism, drawing attention to the role it played in women’s lives and the inaccessibility of this symbolism to men.
Do these new ideas challenge my interpretation? Not really. Do they fully support my interpretation? Not really, BUT, they do provide a new way of thinking about my initial interpretation. I can link the quilting symbolism to the idea of Grace’s narrative style because Rogerson emphasises that when Grace discusses quilting, she is discussing her own life. In addition, Rogerson notes that 'sections of the novel [are] separate patterns that are to be fitted into a whole quilt' (p. 8) so that 'the reader becomes a quilt maker in the process of interpreting the text' (p.9). The concept of the physical book being a ‘quilt’ supports and extends on my understanding of structure, thus allowing me to further investigate how that structure functions.
The notion of the reader as a ‘quilt maker’ interpreting the text also allows me to consider something else I have ignored in my initial interpretation: self-presentation. I initially took for granted Grace’s investigation into her own mind, and that her novel-length yarn reflects the burgeoning field of psychology. Rogerson emphasises through the quilting work, however, that Grace’s motivations are entirely ambiguous to Jordan, the reader and others, so we have to try to decide if she is actually remembering events, or simply telling a story. At the end of the text, Grace makes her own quilt using cloth given to her or taken from the women of her past, Rogerson posing the question 'does the quilt represent memory, amnesia, or madness?' (p. 21). The result, therefore, is that my initial interpretation does make sense, but with some important new additions to be made.
Atwood’s Alias Grace investigates how individuals relate to their memories through the use of Grace Marks’ speech and interactions with medical psychology, which intend to force her to remember (1). This process of remembering, however, is simultaneously hindered and deepened by Grace’s presentation of self, which wonders into utter performativity, amnesia, and potentially disingenuous motivations for her continued speech (2). Rogerson emphasises Grace’s relationship with the language of patchwork and how this relationship influences her narrative style and remembering, and thus the reader’s ability to fit separate patterns 'into a whole quilt' (p. 8) (3).
This interpretation is significantly more chunky, but that’s because I’m trying to make the nuance of the argument incredibly clear. The first sentence (1) is a reworded version of my initial interpretation with slightly less detail. The second sentence (2) is an elaboration of my previous interpretation that includes ideas gleaned from Rogerson’s article. The final sentence (3) is a brief summary of Rogerson’s method that introduces her work as well as some extra details about Grace’s story-telling and the analysis of readers’ responses.
The key to developing interpretations is self-reflection. Constantly question why you think the things you do, and it will force you to reconsider your interpretation. The supplementary reading is to provide you with a way to self-reflect and another interpretation to respond to. I strongly encourage those looking to do exceptionally in developing interpretations to read widely and around the text you’ve been set. Some of those texts for Alias Grace are in the resources section below.
Further Resources
Rogerson, Margaret. ‘Reading the Patchworks in Alias Grace’ The Journal of Commonwealth Literature 33 (1998): 5-22. https://doi.org/10.1177/002200949803300102
The Ultimate Guide to VCE Literature
VCE Literature Study Design (2023-2027): A Guide to Developing Interpretations
For Alias Grace
Margaret Atwood’s other texts including: Cat’s Eye , The Handmaid’s Tale , and Oryx and Crake.
Glaspell, Susan. Trifles . 1916. Available here. A play cited in Rogerson’s article, featuring an accused murderess and a quilt. Sound familiar?
Freud, Sigmund. The Interpretation of Dreams . 1899. Available Via Gutenburg A very dense text on the psychoanalysis of dreams. Useful for its discussions of symbolism as a signifier of psychology
Atwood cites a number of texts in her acknowledgements (p. 543), the most interesting appear as follows:
Moodie, Susanna. Life in the Clearings . 1853
Crabtree, Adam. From Mesmer to Freud: Magnetic Sleep and the Roots of Psychological Healing . 1993.
Brandon, Ruth. The Passion for the Occult in the Nineteenth and Twentieth Centuries . 1983.
Studying both English and Literature in VCE is an interesting undertaking, and I’ve heard very mixed opinions about whether or not it’s a good idea. For me it was a no-brainer; I’d always loved English so why wouldn’t I take advantage of the opportunity to study two English-based subjects? Looking back on my VCE experience now, and comparing my experience of studying each subject, I can see that they are each very different. However, if you’re going to study both, don’t expect that each subject will unfold in isolation, because your work in one of these subjects will undoubtedly impact upon your work in the other - even if, like me, you complete them in different years. So if you enjoy English I would 100% endorse studying both VCE English and VCE Literature, but being an English-nerd I still think there are benefits to analysing the process of studying this dynamic-duo back to back.
The Content
At the beginning, I assumed that Literature and English would be fairly similar in terms of studying and writing. It’s all about reading books and writing essays, right? Well, whilst this is essentially true, it turns out that the process for each subject is quite different. I studied year 12 Literature first, completing it in 2017 as a year 11 student, and as my only unit 3/4 subject for that year it was the focus of a lot of my time, energy, and creativity. What I loved about VCE Literature from the beginning was the departure from formula; the impetus to “dive right in” as my teacher always used to say. Instead of worrying about how many sentences your introductions and conclusions have to be, in Literature you can simply get straight into the analysis and see how far it takes you. So, if you’re the kind of person who needs to stick to that body paragraph structure acronym that has always served you so well, then when you first start studying Literature it might be a challenge to loosen up. Or, if you’re like me and can’t shake the compulsion to write paragraphs that take up double-sided sheets of paper, you might find this subject to be a welcome respite from some of the restrictions of English tasks.
Although English is often viewed as the more ‘basic’ of the two, in many ways I found it more difficult once I hit year 12. Having just finished VCE Literature, shifting my focus back to English definitely wasn’t as seamless as I might have expected. In comparison to my Literature essays where I would base paragraphs around in-depth analysis of a few of Gaskell’s sentences, my English text responses felt stunted and forced – English isn’t really compatible with tangents, and so it was difficult to train myself to be expressive whilst also being concise. In my opinion, the most daunting of the year 12 VCE English SACs is the comparative, and this is where my lack of flow was most evident. Being accustomed to delving into complex discussion of the details of my Literature texts, it seemed impossible to provide insightful analysis of two texts simultaneously, whilst also comparing them to each other and also keeping my essays well structured. My first comparative practices sounded somewhat awkward when I read over them, and I just felt like I never really knew what I was trying to get across. This provoked me to be frustrated with myself, and then my frustration distracted me from writing, and then my essays read even more contrived; you get the idea.
So, how do you push past this sense of friction between the study of English and the study of Literature? Well, I think the best way to reconcile the conflicting approaches is to realise that each subject brings out different strengths, but these strengths can be applied to either type of study. Yes to a certain extent English is supposed to be formulaic, but you can use the analysis skills you learn in Literature to enhance your English text responses and give your work a point of difference. On the flip side, the structure you work with in English can be applied to Literature to ensure that your essays always exhibit direction and purpose, even if they encompass a broader range of discussion. Once I realised that I didn’t have to discard all of my Literature skills and start writing my English work exactly the same as everybody else, I began to develop a more fluid, balanced writing style that enhanced all of my English tasks – even the comparative.
Let’s start with the obvious comparisons between the English exam and the Literature exam. Firstly, the English exam encompasses three essays in three hours (with 15 minutes reading time), whilst Literature is only two essays in two hours. The English exams tasks include a text response to a prompt, a comparative text response to a prompt, and a language analysis. The Literature exam involves a passage analysis, and a text response to a prompt influenced by a literary perspective. Where in the English exam you are given a choice of prompts for each text choice, whereas for both sections of the Literature exam only one choice is available for each text. Whilst both exams involve some supplied material, in Literature this material is a passage from one of the set texts, however for the language analysis section of the English exam this is completely unseen material created by the VCAA. For me, this felt like a very significant difference, because there is no familiar material (i.e. passages from the texts) to rely on in the English exam; if you get lost you can’t latch on to anything except what you have memorised.
Personally, I think that the study strategies I utilised for each exam were fairly similar, although obviously geared towards different tasks. I took in depth notes on my texts, planned essays, memorised quotations and explored their significance, timed my practice essays etc. My actual approach to each exam was also similar, for example I made sure to allocate one hour for each different task and did all of my planning mentally during reading time. So although obviously everyone’s study and exam techniques are different, this shows that your own personal strategies that you develop can be applied to both the Literature and the English exams. However, despite the continuity in this sense I still found myself feeling very different coming out of my English exam than I had leaving my Literature exam the year before. Where after the Literature exam I had been content with the knowledge that I had showcased the best version of my abilities, after the English exam I felt much more unsure and ready to believe the worst about the outcome. This particular comparison is of course specific to every individual person, however I think it could have something to do with the knowledge that most VCE students study English and the difficulty in believing that your work could stand out from the work of 40,000 others.
The Results
In the end, I achieved very different results from these two subjects, with English being my highest study score and Literature being one of my 10% contributions. It seems to be a general consensus (or at least it was at my school) that it is more difficult to crack the high 40s in Literature than in English, and whether this is true or not it definitely impacted my expectations of my results each subject. However, that said, after being slightly disappointed with my Literature results in year 11 I was not overly optimistic about doing much better in English. When talking about this with my Literature teacher, she told me to “remember that English is marked very differently to Lit, so don’t think you can’t get a 50” and I think this is very solid advice. Whilst you might feel you were equally skilled at both subjects, this doesn’t mean you will receive equally ‘good’ results’, but don’t let this disparity discourage you because, as we have discussed throughout this post, when it comes to Literature and English one size does not fit all.
The idea of critical lenses in literary perspective essays can often be tough to fully grasp. Is sticking to just one ok? Are there enough examples in the text to support a purely feminist viewpoint? Or a Marxist one? What about post-colonialism? Sometimes it’s difficult to find a clear through line, especially when the concepts you’re attempting to discuss are so complex.
Luckily when it comes to Shakespearean texts, Twelfth Night in particular, a lot of people throughout history have already studied these ideas and critical lenses, and there are many more resources out there for you to utilize than you might think.
Thus, we are faced with the extremely helpful nature of published critical readings. These critical essays are pieces often published by university professors or scholars which offer an in-depth analysis and examination of a given text. While much of the language is complicated and a bit overwrought at times, the content within the essays can give you helpful ideas and can help you gather a repertoire of vocabulary and evidence for your own literary perspectives essay. In fact, if you type in “Twelfth Night critical readings” into your google search tab, there will be pages of valuable content at your disposal.
Literary perspectives
For instance, the critical essay Rethinking Sexuality and Class in Twelfth Night by Nancy Lindhiem, gives insight into both the Marxist and the queer lens.
Here is an extract from Lindhiem’s reading in which she discusses the idea of “androgyny” and sexuality (noted specifically in the bolded words):
“While Viola is barely male except in attire, the dual aspect of Sebastian’s androgyny is carefully explored. The Elizabethan audience’s first, external, impression – he looks like his sister! – is reinforced ‘internally’ in his conversation with Antonio. His exquisite sensitivity to the quality of his friend’s feelings and the obligation it lays upon him might well be seen as a woman’s trait. ”
After reading Lindhiem’s discussion of the “androgynous” twins within the play and how this displays a disparity between gender identity, this student then decided to expand on in a similar idea in a part of their paragraph below (queer lens). In the first part of the sentence, the student outlines the idea of androgyny (shown in bold) specific to the character of Viola. Later on, the student also explores the idea of different behaviours contributing to certain gender traits much like Lindhiem’s notation of it in the above paragraph (shown in bold in the last sentence), however concludes on a broader outline of sexuality as a whole, rather than focussing on just female traits.
Viola’s mediatory role between Olivia and Orsino’s households, coupled with her androgynous performance as a woman playing a man (adding further confusion to the Elizabethan stage convention of a male actors playing women on stage) evokes a form of genderbending and identity perplexity that pervades the play’s dramatic trajectory and opens up what is possible, if not overtly permissible, on a spectrum of sexuality.
Another way of making use of these critical readings is to draw from some of their sophisticated vocabulary. The following is an example of how a student was able to adjust and expand her vocabulary specific to their chosen lens by reading critical essays.
After studying a couple of feminist and queer critical essays to Twelfth Night , the student highlighted some repetitive language and terms used within the essays, and was able to use them within their own essay.
Casey Charles’ Theatre Journal exert Gender Trouble in Twelfth Night uses the phrasing
“ the phenomenon of love itself operates as a mechanism that destabilizes gender binarism and its concomitant hierarchies”.
The student went on to use the term gender binarism in one of her essay’s sentences:
In all, Twelfth Night delineates the true fluidity within gender binarisms as well as the way in which societal structures are enforced and reiterated…
Alternatively, the critical essay Gender Ambiguity and Desire in Twelfth Night by Maria Del Rosario Arias Doblas makes use of the terms “homoerotic” and “heterosexual” throughout its text - “homoeroticism residing in theatrical transvestitism… and homosexual allusions and so on pervade the play to create the “most highly intricate misunderstandings”’ - thus outlining the type of high-level language specific to a queer reading of the play that the student was able to implement in their own work:
In fact, Shakespeare oscillates between reinforcing patriarchal ideology and heterosexual language, and the deconstruction of such romantic ideals, simultaneously closeting and disclosing the queer possibilities typical to conservative societies that use violence to repress homosociality and police the safe expression of homosexual exploration within heterosexual norms.
As you can see, the student’s language is now specified to the type of lens they are using in their literary perspectives essay, and is also of a high register.
External or Contextual references
Another benefit of going through critical readings is the external or contextual references they make. An example of this is in Rethinking Sexuality and Class in Twelfth Night by Nancy Lindhiem, where the author makes reference to Narcissus, a character from Metamorphoses – a Latin narrative poem from 8 AD:
“For all the likelihood that both Olivia and Sebastian are seduced by a visual perception, we probably feel that Olivia succumbs mainly to Cesario’s way with words.9 Several critics have commented on the allusion to Ovid’s Echo in Cesario’s ‘babbling gossip of the air’ (1.5.277)”
Noticing this reference as a motif in many other critical readings too, this student decided to insert it into their own essay here:
These central relationships therefore reapply the idea of self-reflexivity while blurring the structured boundaries of identity stability, central to the Narcissus myth of which Echo from Ovid’s Metamorphosis forms a part ; “a very echo to the seat/ where love is throned” invokes a doubling motif, as well as the troubling foundation of representation over reality.
See how the student was able to discuss it in their own way? Referencing external texts in your literary perspectives essay can prove very useful if done once or twice, as it demonstrates that you are able to apply the values within the chosen text to wider elements of society and culture.
Getting started
One of the most efficient ways of going through these sorts of essays (which are often quite elaborate and at times difficult to understand fully) is to print them out, grab a highlighter and pen and skim through as much as possible. Highlight words, terms or phrases which spark your intrigue, or ones you feel you may be able to manipulate as evidence to support your own essay.
Overall, reading as many of these expert-written critical essays as possible can be extremely beneficial in developing a greater understanding of the critical lenses, the ideals and context of the Elizabethan theatre, and the way both dialogue and staging can be used as evidence in your own essays.
The more you know about the play, the more you’ll be able to write about it. So, get reading!
Links to the readings:
Rethinking Sexuality and Class in Twelfth Night, Nancy Lindheim
Gender Ambiguity and Desire in Twelfth Night, Maria Del Rosario Arias Doblas
Gender Trouble in Twelfth Night, Casey Charles
“Once upon a time…”
The fairy tale of Cinderella is a well-known, well-loved and well-ingrained story that was always told to me as a bedtime story. Who could forget the mean-spirited stepsisters who punished and ruined Cinderella’s life to no end? According to the dark Brothers Grimm version, the stepsisters mutilated their feet by cutting off their heels and toes to fit into the infamous shoe, and their eyes were pecked away by birds until they were blinded! It’s definitely one way to send a message to children… don’t be bullies or you’ll be punished. Which is exactly what the Brothers Grimm’s views and values were. Their construction of their fairy tale to send a message of what they viewed as ‘good’ or ‘bad’ is simplistically shown through the writers’ choice in determining the characters’ fate. The evil stepsisters are punished, while Cinderella receives happiness and riches because she remained kind and pure. A clear and very simple example of how texts reflect the beliefs, world views and ethics of the author, which is essentially the author’s views and values!
What are the views and values of a text?
Writers use literature to criticise or endorse social conditions, expressing their own opinions and viewpoints of the world they live in. It is important to remember that each piece of literature is a deliberate construction. Every decision a writer makes reflects their views and values about their culture, morality, politics, gender, class, history or religion. This is implicit within the style and content of the text, rather than in overt statements. This means that the writer’s views and values are always open to interpretation, and possibly even controversial. This is what you (as an astute literature student) must do – interpret the relationship between your text and the ideas it explores and examines, endorses or challenges in the writer’s society.
How do I start?
Consider the following tips:
- What does the writer question and critique with their own society? What does this say about the writer’s own views and the values that uphold?
- For example, “Jane Austen in Persuasion recognises the binding social conventions of the 19th century as superficial, where they value wealth and status of the utmost priority. She satirises such frivolous values through the microcosmic analysis of the Elliot family.”
- The writer’s affirming or critical treatment of individual characters can be a significant clue to what values they approve or disapprove of. What fate do the characters have? Who does the writer punish or reward by the end of the text?
- Which characters challenge and critique the social conventions of the day?
- Look at the writer’s use of language:
- Characterisation
- Plot structure
- Description
- In other words …what are the possible meanings generated by the writer’s choices?
- Recognition and use of metalanguage for literary techniques is crucial because you are responding to a work of literature. Within literature ideas, views and values and issues do not exist in a vacuum. They arise out of the writer’s style and create meaning .
- How do the writer’s choices make meaning?
- How are the writer’s choices intended to affect the reader’s perception of social values?
- Weave views and values throughout your close analysis essays, rather than superficially adding a few lines at the conclusion of the essay to indicate the writer’s concerns.
- Using the writer’s name frequently will also assist in creating a mindset of analysing the writer’s commentary on society.
Below are some examples from an examiner report of successful and insightful responses reflecting the views and values of the writer:
(Another tip is to go through examiner’s reports and take note of high quality responses, even if they are not the text you’re studying)
When contrasted with the stark, blunt tone of Caesar throughout the play ‘You may see, Lepidus, and henceforth know...’ the richness of Shakespeare’s poetry with regard to his ‘couple so famous’ denotes how the playwright himself ultimately values the heroic age to which his protagonists belong over the machinations of the rising imperial Rome.
It is the word ‘natural’ here through which Mansfield crafts a sharp irony that invites us to rate Edna’s obsession with her own performance.... It is this satiric impulse that also leaps to the fore through the image of Edna, ‘clasping the black book in her fingers as though it were a missal’...the poignant economy of Mansfield’s characteristic style explores her views on the fragility of the human condition .
‘In Cold Blood’ provides a challenging exploration of the value placed on human life. The seemingly pointless murders undermine every concept of morality that reigns in Middle America, the ‘Bible Belt’, as well as the wider community. Capote insinuates his personal abhorrence of the death penalty and the disregard of mental illness in the justice system .
Why are views and values important in literature, and especially for close analysis?
Every year, the examiner reports emphasise how the best close analysis responses were ones that “showed how the text endorsed and reflected the views and values of the writer and were able to weave an understanding of these through the essay” (2013 VCAA Lit examiner report). By analysing HOW the text critiques, challenges or endorses the accepted values of the society in the text, you are demonstrating an understanding of the social and cultural context of the text, thus acknowledging the multifaceted layers that exist within literature. You are identifying the writer’s commentary of humanity through your own interpretation. Bring some insight into your essays!
When it comes to VCE Literature, ‘Literary Perspectives’ is a major component of your learning and exams. If you’re studying any of the Shakespearian texts, the idea of using different ‘lenses’ to interpret 400-year-old plays seems silly and is a difficult task to approach. So today, I’m writing a plan for a Literary Perspectives essay on Shakespeare’s Othello . The question we are looking at is:
In Shakespeare’s Othello, Venetian society is depicted as unwelcoming to the ‘Other’. To what extent do you agree?
Breaking-it-Down
So what does this question mean? Well let’s first look at the keywords, and what each means.
“Venetian Society” -This is the group of people depicted in Othello . Whilst some characters like Cassio and Othello are from other city-states, they adhere to the norms and traditions of the Venetians, who live in Venice, Italy.
“Unwelcoming” - In my essay, I consider “unwelcoming” to be active discrimination against people, with the intent of alienating them from society at large, but this is open to interpretation.
“The Other” -This is a technical term from a few different literary perspectives. On a broad level, the Other is a person or group of people who are viewed as the ‘enemy’ or different from the dominant culture.
These keywords are essentially what you have to include in terms of knowledge. But, what is the question? Our essay topic says “To what extent do you agree?”. You can choose to agree, or not at all, or be somewhere in the middle. Any of these options consider the extent of Venice’s welcomeness, but you have to use evidence, and uniquely, a literary perspective.
My Approach
Before I even choose my contention, now is the time to decide which perspective to use for my essay. A few apply to the question and Othello , but I can only have one. Using Feminism you could argue that the women of the play are ‘Othered,’ but because they lack lots of meaningful dialogue I think it would be hard to uncover enough evidence. Marxism would also be good and would argue the working-class is othered. The issue with Marxist interpretations of Othello , however, is that there are almost no lower-class characters. Marxist theorists also regularly adopt feminist and postcolonial language, meaning I could appear as though I used multiple perspectives. I think Postcolonialism is the ideal perspective. The term “Other” was coined by postcolonial theorists, and Othello’s race and place in Venetian society give me the ability to flex my understanding of postcolonialism.
So, now that I know I am writing from a postcolonial perspective, I can come up with a contention. First of all, who is the Other, according to postcolonialism? In Othello, it is quite clearly Othello himself, who is from North Africa, and is constantly the victim of racism, which begins to answer my second question; is Othello welcomed by Venetian Society? Well, it’s complicated, he’s an army commander and woos a Venetian woman, but he constantly has to prove himself worthy of these things. As a result, my contention will be somewhere in between complete agreement and complete disagreement with the question.
The othered characters in Othello are orientalised by most members of Venetian society, and must constantly prove their material worth to maintain their agency. Despite this, the women of the play act as a foil to the racism and distrust of society.
Postcolonialism
Postcolonial theory has roots in a more modern context than Shakespeare. The colonialism of the 19th century and the decolonisation of the 20th century lead to colonised people reevaluating their lives and the role of the European colonists on a global, social, and psychological scale. When writing from a postcolonial lens, you should try to focus on some key areas. The most significant is the relationship between the colonised and the coloniser. How do they interact? What do they think of each other? The next area is the psychology of colonialism. One useful theorist here is Frantz Fanon, a psychologist living during the French colonisation of Algier. His text The Wretched of the Earth stated the ways that colonised Africans were mentally oppressed, viewing themselves as less than human. This is important when discussing the Other because ‘other’ represents the dehumanisation of Native lives which caused such psychological distress. A term I used in my contention should also be explained: orientalism. This term was coined by Edward Said and it explores the way the Other is viewed by the West. To ‘orientalise’ something is to portray it as something wholly different to European cultures, and exaggerate these differences. It results in non-Europeans being viewed as ‘backwards’ or ‘savage’ and justifies racist stereotypes. Other useful Postcolonial terms include: the Subaltern, who are the groups completely outside the margins of society, or people who lack any freedom; and Agency is the ability to act out of free-will and have a degree of power.
With my contention and some useful postcolonial terms, I can now plan each paragraph. I am doing three, but it is possible to do four or more. I follow TEEL (Topic, explanation, evidence, link) structure quite closely, and have given simple but punchy topic sentences for each paragraph. When structuring the essay as a whole, I try to make sure each paragraph builds off of the previous argument, almost like a staircase leading to my conclusion.
1. Othello is treated as an outsider and is a victim of racism and orientalisation due to his cultural background, constantly reminded that he is not fully Venetian.
My goal in this paragraph is to agree with the question. My explanation has to show that Othello isn’t welcome in Venetian society, highlighting that his blackness and European views of the Moors fits Edward Said’s theory of orientalism. I will mainly rely on Iago’s perception of Othello, and Iago as a symbol of Venice’s intoleration towards the Other.
Evidence of his culture being viewed as ‘backwards’ or fundamentally different from Venice will support this point. Iago’s first monologue (1.1.8-33) displays his intolerance to outsiders, specifically referring to Othello as “the Moor”, rather than by his name. Roderigo also displays a racist attitude, calling Othello “the thick-lips” (1.1.71). You should try to choose linguistically significant evidence. For example, Iago’s metaphor of a “black ram is tupping [Brabantio’s] white ewe” (1.1.96-7) provokes imagery of the devil (black ram) defiling a symbol of purity (a white ewe).
To link this paragraph, refer to the use of orientalism as a method of othering that turns people against Othello, and intends to keep him separate (unwelcome) from society.
2. Despite Iago’s representation of an intolerant Venice, Othello displays a pathway for the Other to prove themselves in Venetian society, although this proof is constantly reevaluated by the dominant culture.
In this argument I’m going against my previous paragraph, saying that Othello is welcome, but on a case-by-case basis. My explanation will include an analysis of how Othello is othered and orientalised, but still displays agency and has a role of authority in Venice. Othello is trusted, but it is a very loose trust that relies on Othello’s continued adherence to society’s rules. To use postcolonial language, Othello is the Other, but he is not a subaltern; he has been given a place at the coloniser’s table. But despite viewing himself as a permanent part of this table, the colonisers are always ready to remove his seat.
I could use Brabantio as evidence of this, as he had “loved [Othello” (1.3.145) but quickly begins to refer to his “sooty bosom” (1.2.85) and “foul charms” (1.2.88) when he thinks Othello has overstepped his place in Venetian society by marrying a white woman. Even though Othello has proven himself as a General, the senate makes him answer for accusations based on racism and stigma. Once Othello begins to fall for Iago’s trap of jealousy, Lodovico questions the faith placed in Othello, claiming “I am deceived in him” (4.2.310).
Therefore, despite being allowed a place within the Governmental structures of Venice, Othello’s agency is constantly at risk, being welcomed for his proven talents, but distrusted for his ‘Otherness’.
3. Although Venetian society at large is unwelcoming to Othello, either through racism or distrust, Desdemona represents an attitude of acceptance towards the Other.
This argument looks at a different aspect of the question; who is the Other welcomed by? Besides Othello, Othered characters are the women and Cassio, who is from Florence. Despite not fitting into the key areas of postcolonial thought, women still have a place in this analysis, as a subcategory of the native’s relationship with the coloniser. How does a group that is discriminated against in their own society treat someone else who is discriminated against? Well, we see in Othello that the women treat him quite well.
Desdemona is the obvious source of evidence for this. Her adoration of Othello transcends his colour and she accepts him as part of her Venetian world. She is unswayed by the racist commentary on Othello from those around her, such as Emilia, and instead represents the welcoming of the Other on a personal, although not societal level.
Thus, Desdemona in her own Otherness and orderliness acts a foil to Iago’s disorder and discrimination. As a discriminated against woman, she represents the acceptance of the other in Venetian society, and the unbridled trust of Othello that the men of Venice lack.
Your conclusion should include a restatement of your arguments and your contention but also look at them in another way. I usually go through my points and how they relate to each other and my contention in a logical step-by-step way, each point building on the other to reach my contention. Point 1 leads to point 2, which leads to point 3, and combined, makes my contention.
Hopefully, this brief guide to literary perspectives in Othello , focusing on postcolonialism, acts as a starting point for your studies. It’s about understanding the beliefs of the lens and then using this to form an argument. It certainly isn’t easy, so I encourage you to read around and practice this writing style as much as possible.
Recommended Resources
On shakespeare.
How to Approach Shakespeare-Studying Shakespeare for the First time
Post-colonialism in Shakespearean Work by Alina Popa (2013)
On Postcolonialism
Literary Perspectives 101
List of Postcolonial Terms
Definition of Postcolonialism
Benefits of Critical Essays for Literary Perspectives Essays
The Wretched of the Earth by Frantz Fanon (2001), Penguin Modern Classics, Great Britain.
Orientalism by Edward W. Said (2003), Penguin Modern Classics, Great Britain.
Updated for the new 2023-2027 Study Design!
AoS 1: Adaptations and Transformations
Aos 2: developing interpretations.
- AoS 1: Creative Responses to Texts

AoS 2: Close Analysis
This is your ultimate guide to everything you need to know to get started with VCE Literature. We will be covering all the sections within Units 3 and 4, and have included resources that will help improve your skills and make you stand out from the rest of your cohort!
Scope of Study
Here's what the VCAA study design states...
'The study of VCE Literature fosters students’ enjoyment and appreciation of the artistic and aesthetic merits of stories and storytelling, and enables students to participate more fully in the cultural conversations that take place around them. By reading and exploring a diverse range of established and emerging literary works, students become increasingly empowered to discuss texts. As both readers and writers, students extend their creativity and high-order thinking to express and develop their critical and creative voices.'
'Throughout this study, students deepen their awareness of the historical, social and cultural influences that shape texts and their understanding of themselves as readers. Students expand their frameworks for exploring literature by considering literary forms and features, engaging with language, and refining their insight into authorial choices. Students immerse themselves in challenging fiction and non-fiction texts , discovering and experimenting with a variety of interpretations in order to develop their own responses.'
...but don't worry if the above is vague, we'll take you through exactly what you need to know for Year 12 Literature! Let's get into it!
In Unit 3, students consider how meaning is created through form, and how different interpretations may be developed out of a singular text. First, students understand how writers adapt and transform texts, and how their interpretation of the text impacts this transformation into a different form. Secondly, students use another text to develop their own interpretations of a text with regard to its context , and views and values . Unit 3 School-Assessed Coursework is worth 25 per cent of your total study score!
This task is designed for you to critically analyse and actively engage with the text, understanding its nuances inside and out in order to decipher its meaning. Be individual in comparing and contrasting the two texts – avoid the obvious similarities/differences everyone in your class will also notice. It is the insightful analysis of the subtleties of how meaning is altered that will help you stand out!
Here are some important aspects to consider and questions to ask yourself while tackling this SAC:
- Identify the unique conventions in the construction of the original text
- Now do Step 1 with the adapted/transformed text
- How do the two text forms differ ? How are they the same ? The most crucial step is what meaning can be derived from the similarities and differences? How does the meaning change?
- Note additions and omissions (and even silences)
- Historical context and setting
- How does the change in form impact you as the reader/viewer ?
- Incorporate pertinent quotations from both forms of text to substantiate and support your ideas and key points.
Most importantly, share your original interpretation of what meaning and significance you can extract from the text, and how you believe it changes once the form alters.
Also ask yourself these questions:
- What makes the text in its original form interesting or unique?
- Is that quality captured in its adaptation/transformation?
For more detailed explanations on these 7 aspects, you might want to check out Adaptations and Transformations Lit SAC: A How To Guide.
Developing interpretations is an AoS that focuses on investigating the meaning and messages in texts, as evidenced by the text itself, it’s author and their context . As per the study design:
'Students first develop their own interpretations of a set text, analysing how ideas, views and values are presented in a text, and the ways these are endorsed, challenged and/or marginalised through literary forms, features and language. These student interpretations should consider the historical, social and cultural context in which a text is written and set. Students also consider their own views and values as readers.'
Following this, you investigate a supplementary reading which will offer another interpretation of the text, which may enrich or challenge your interpretation by agreeing or disagreeing with your interpretation. Using this supplementary reading, you reconsider your initial interpretation and apply your new understanding of the text to key moments.
The SAC for Developing Interpretations is a little bit weird. It’s worth 50% of unit 3 (or 25% of your total study score), but is split into two parts:
Your teacher might do the two parts together, or separately. In any case, Part B will include the use of a passage from the set text that you must engage with. How does the passage help you to interpret the text, and how does that interpretation agree or disagree with the interpretation presented in the supplementary reading?
The most difficult part of the SAC for this AoS is balancing your interpretation, the textual evidence, and the alternative interpretation of the supplementary reading. It is vital that if you are doing Literature this year, that you know your 3.2 text like the back of your hand, and that you practice writing loads and loads. It is also worth trying to make your interpretation incredibly specific, so that you can go in-depth into one idea, rather than simply skimming over 3 or 4 big ideas.
For more on Developing Interpretations, you might want to check out VCE Literature Study Design (2023-2027): A Guide to Developing Interpretations which explains in detail what the new AoS is about and what you need to do.
And, if you're studying Alias Grace you'll find our Developing Interpretations SAC Guide on interpreting Alias Grace especially helpful.
Unit 4: Interpreting Texts
Aos 1: creative response & reflective commentary.
The most important part of this task is that you must have a highly convincing connection between the original text and your creative response .
There must be a tangible relationship present, through an in-depth understanding of the original text’s features. These features include characterisation (what motivates these characters), setting, context, narrative structure, tone and writing/film style.
You can establish this relationship by:
- Adopting or resisting the same genre as the original text
- Adopting or resisting the author’s writing/language style
- Adopting or resisting the text’s point of view
- Adopting or resisting the original setting, narrative structure or tone
- Writing through a peripheral character’s perspective
- Developing a prologue, epilogue or another chapter/scene
- Rewriting a key event/scene from another character’s point of view: Does this highlight how important narrative perspective is?
- Recontextualising the original text
For detailed explanations on how to establish these relationships, read "Creative Response To Text" Ideas .
The VCAA Literature Study Design also determines that students must submit a ‘close analysis of a key passage’. This aspect of the assessment counts for 20 of the 60 marks available for the Create Response outcome. The study design elaborates that students must produce:
‘A close analysis of a key passage from the original text, which includes reflections on connections between the creative response and the original text.’
In short, VCAA wants you to not only analyse the original text and use it as the basis for your Creative Response, they want you to be able to closely analyse a section of the original text, and link it to and reflect upon your creative response. This is different from previous years and the same task in English, the Reflective Commentary. You must use the skills of close analysis in this task. To include these things, look to the key knowledge and skills outlined in the study design.
Key Knowledge:
- Understanding of the point of view, context and form of the original text
- The ways the literary form, features and language convey the ideas of the original text
- Techniques used to create, recreate or adapt a text and how they represent particular views and values
Key Skills:
- Discuss elements of construction, context, point of view and form particular to the text, and apply understanding of these in a creative response
- Analyse closely the literary form, features and language of a text
- Reflect on how language choices and literary features from the original text are used in their adaptation
As you write, ensure you are discussing how the author uses point of view, context, form, elements of construction and stylistic features in their text. It is imperative that you describe how you have similarly used such device in your creative response. Ensure that you also discuss how you are involving the ideas and themes of the text in your creative piece, and how you are discussing them further, or exploring them in greater depth. Obviously only talk about those that are relevant to your creative response!
To read a sample Reflective Commentary, check out Elly's blog post on how to Score 10/10 On The Reflective Commentary
From the VCAA study design:
'In this area of study students focus on a detailed scrutiny of the language, style, concerns and construction of texts. Students attend closely to textual details to examine the ways specific passages in a text contribute to their overall understanding of the whole text. Students consider literary forms, features and language, and the views and values of the text. They write expressively to develop a close analysis, using detailed references to the text.'
In plain words, your teacher (and eventually examiner in the end of year exam) will give you 3 passages from your text. You'll be asked to read each of these passages, identify key ideas or themes present in each of the passages, and write an essay in response.
Writing the Introduction
Introductions are an excellent way to showcase your ability to provide an insight into your personal “reading” of the text, interpret the passages and allow you an avenue through which to begin your discussion of the material.
When constructing introductions, it is important to note that the VCAA Literature Exam Criteria is as follows:
- Understanding of the text demonstrated in a relevant and plausible interpretation
- Ability to write expressively and coherently to present an interpretation
- Understanding of how views and values may be suggested in the text
- Analysis of how key passages and/or moments in the text contribute to an interpretation
- Analysis of the features of a text and how they contribute to an interpretation
- Analysis and close reading of textual details to support a coherent and detailed interpretation of the text
- Considering these points, your introduction should feature these 2 elements: your personal reading of the text and your interpretation of the passages.
- In terms of structure, try to begin with a sentence or two explaining your personal reading of the text. The key to doing so in a manner befitting Close Analysis however, is to utilise quotes from the passages to supplement your assertion.
Head over to Jarrod's blog to read a sample introduction: VCE Literature Close Analysis: Introduction
Extra Resources
Views and Values
VCE Literature Essay Approaches - Not a Language Analysis
What is Authorial Intent in VCE English and Why Is It Important?
The Importance of Context in Literature
Study Techniques: How To Approach a Text That You Hate
Why Genre Matters in VCE Literature: An Analysis of Dracula
Developing Interpretations SAC Guide: Interpreting Alias Grace
How genre works.
We’re not supposed to judge a book based on its cover, but for some reason, we just can’t help it. Sure, we may not be able to tell if we’re going to enjoy the book, nor can we tell what exactly it’s about, but we can tell the tone, set our expectations, and most importantly, guess at the genre. Look at these three book covers and note how they perfectly show their genres - Sci-Fi, Horror and Life Drama, respectively.

Genre is a way of categorising media. We split books, film and music into genres in order to better talk about them and because humans have a strange desire to sort and categorise things. Within whatever medium, genres display certain structures, characters and tropes that audiences expect from that genre . Audiences like to be able to tell the genre of a text because it’s comfortable. If I go to see a superhero movie I expect wacky costumes, cliche dialogue and a final battle scene that the heroes win - were these expectations not to be met, I would likely be a little bit peeved off.
But why should you care about genre in VCE Literature? It’s not on the study design?
Well, not explicitly. In each AoS of the study design, you must engage with ‘the ways the literary forms, features and language of texts affect the making of meaning’ , and/or ‘the ideas of a text and the ways in which they are presented’ . Genres are a feature of texts and are one of the ways that a text will present its ideas. Horror is the most notable example of a genre that uses its tropes to send a message - It Follows is a horror where the monster stands in for sexually transmitted disease, Carrie uses horror to show the horrors of high school, Frankenstein is a criticism of those who would ‘play god’. In the Literature study design, the horror genre is represented by Bram Stoker’s 1897 masterpiece, Dracula.
For an overview of the Literature study design, check out The Ultimate Guide to VCE Literature .
Dracula + The Gothic
I invite you to think hard about the horror films you’ve seen and to try to place Dracula into our modern view of horror. It’s hard to put Stoker’s vampire on the same stage as the Babadook , Annabelle or even the ‘70s slasher craze. This gives us an incredible opportunity to consider how audiences engaged and continue to engage with genres. In order to analyse genre, it is essential to recognise what the audience’s expectations were of a genre, and how the author has utilised those expectations for their own ends. Let’s consider Dracula in context .
Dracula is a horror novel. But, we usually don’t think about those uptight Victorians reading texts that were designed expressly to scare. The Victorian era was actually one of the golden ages of horror literature though. But, it is distinctly different from our modern understandings of horror as defined by trailblazers like Stephen King. So, why is it different? It is here we must consider the sub-genre. If you have read anything about Dracula , you’ll note that it is referred to as a ‘gothic horror’ . The gothic genre of literature encapsulates some of the 19th century and certainly the Victorian period’s (1837-1901) best literature. Dracula of course belongs to this group, but it blows up around 1818 with Mary Shelly’s Frankenstein . Edgar Allen Poe, with his short stories and poetry, is widely lauded as the ‘Father of American Gothic’, with ‘The Fall of the House of Usher’ published in 1839. Note the dates here. Stoker published Dracula in 1897, a good 79 years after Frankenstein began haunting readers. Which means he had an established and large genre to work with. So, how did Stoker use the gothic in Dracula?
Tropes of the Gothic
1) the gothic monster.
The vampire myth used by Stoker is turned into the quintessential gothic monster. Dracula existed in the Victorian mind alongside Frankestein’s monster, Mr. Hyde, and Poe’s mixture of humans made monstrous and surreal monsters like that in ‘The Masque of the Red Death’. The defining feature of the gothic monster is its role in the story as a representation of something wrong with society, whether it’s increasingly amoral medicinal science, human greed or perverted desire.
2) The Creepy Castle
The creepy castle doesn’t have to be a castle. It can be a mansion, a university or the graveyards of London. The important thing is that the setting of the gothic novel should always be - by default - terrifying and evoke a sense of danger. You can never get comfortable in Dracula’s castle, nor in Seward’s asylum, and neither can the characters.
3) Damsel/s in Distress
For sure an outdated trope, but a constant in the gothic. It’s a quick and simple way to show that the innocence of young women is threatened by a malignant force. In Dracula , look to Mina, Lucy and Mrs. Westenra. But what happens when the damsel saves herself?
4) Omens, Portents, Visions
Visions in dreams? Random wild animals escaping from ships? Ships docking with a completely dead crew? Random changes in the weather? You might be dealing with a gothic villain, or going mad. In either case, Renfield, Dracula, Mina and Jonothan all deal with portents and visions.
And This Is Important Because…
Stoker has followed the predominant tropes of the gothic horror genre. Why is this important for our analysis of Dracula ? The ways in which authors use genre and other stylistic elements like form, voice or plot relate directly to their intentions. If we investigate the particular aspects of Stoker’s use of the gothic, we may better understand the views and values that he is promoting. For instance, let’s take Dracula as the gothic monster. Since the gothic monster is always a way to reflect society back onto itself, how is Stoker doing that? A feminist analysis might take Dracula as a reflection of sexual deviancy, which then ties into his constant threat towards women. A post-colonial analysis might question the foreignness of Dracula, and view him as a part of the intrusiveness of foreigners in English society. Either way, you’re touching on a view or value presented by Stoker, and tying it to an aspect of the gothic genre in a way that conveniently also touches on characterisation.
Let’s complicate things a little more. The ‘Damsel in Distress’ trope is clearly evident in Dracula , but what view or value is Stoker commenting on by its inclusion? The simplest answer is that, by showing that women cannot save themselves, Stoker is saying that women are inherently weak and need to be saved by men. But this answer isn’t sufficient for a number of reasons. Firstly, what are the women weak to? Is it a physical mismatch between the women and Dracula, keeping in mind that Dracula is also stronger than the novel’s men? Or is it a symbolic weakness to some aspect of Dracula’s character, be it sexuality or magic? Secondly, and more importantly, are all the women victimised by Dracula the same? Well, obviously not.
It could very well be argued that Stoker is subverting the ‘Damsel in Distress’ trope by actually giving us a woman who is able to be her own saviour (which is actually becoming a trope in itself nowadays!). The dichotomy between Lucy and Mina is a crucial aspect of the text, and the way that Mina’s character doesn’t quite fit into the ‘Damsel in Distress’ archetype is a major interpretative dilemma. By considering the genre tropes, Lucy is clearly a ‘Damsel in Distress’ who cannot save herself and is unduly victimised by Dracula. It can be argued that her implicit promiscuousness is punished through her murder, but in whatever case, she is distressed and must be saved. Mina, however, has an entirely different view of her distresses. Not only does Mina take on a caring role towards Jonothan - in which Jonothan becomes a ‘Master in Distress’ - she actively supports the attempts to save her and kill Dracula. By compiling the journals, letters and newspaper clippings into the epistolary that we the audience are reading, and using herself as a window into Dracula’s mind through their psychic connection, Mina proves to be a means by which to save herself from her distress. So, the question of what Stoker actually thinks about women is still quite open: Lucy is seemingly punished for her character flaws, which indicates a misogynist view of women’s sexuality, but Mina is praised for her use of masculine qualities like leadership and stoicism. Is Stoker saying women should be more masculine? Less masculine and more traditionally feminine? This entire discussion revolves around how and why the ‘Damsel in Distress’ trope is being followed or subverted.
Using Genre in VCE
Whilst a genre-based analysis (or a structural analysis) can be a fantastic way to open up discussion and leads to important questions about views and values , the way I have presented it may appear to be another useless and long-winded thing you have to try to shove into an essay when you already have to balance so much in Literature! Fear not, because there are a couple of really easy ways to fit genre into essays without taking up loads of space.
Option one is to use a genre trope as the basis of a paragraph. If your essay contention is that…
‘Stoker presents the dangers of foreign immigration to England at the height of its colonial empire’
…then you can easily write a paragraph discussing that…
‘Stoker employs the gothic trope of a supernatural monster in Dracula, using this vampire as a stand-in for foreigners in England’.
This paragraph would discuss Dracula’s characterisation, and the settings of Transylvania and London, whilst investigating Stoker’s views on England’s colonialism and race. In a Developing Interpretations or Close Analysis essay, you’ve just touched on several key criteria, including the author’s views and values , your own credible interpretation of the text and how the text presents its messaging (through characterisation and setting). You can do all these things without mentioning genre, but by explicitly using the language of genre analysis you are likely separating yourself from the student next to you - who had a similar idea but described it in a less interesting way. This is the utility of understanding genre, it gives you the words and concepts necessary to improve your writing and interpretation. The ‘Gothic monster’ is an easy way to describe an otherwise GIANT concept.
Another way is to add it to other analyses in passing. Instead of saying “ Dracula presents Lucy and Mina as foils to demonstrate the ways in which modern women’s promiscuity is ultimately harmful”, you can say “the presentation of Lucy and Mina as two ‘damsels in distress’ in dichotomy with each other demonstrates the differing ways in which Victorian women could doom or save themselves” . The latter sentence has not significantly changed the content of the first, still referring to the women’s opposition to each other, but by phrasing it with ‘damsels in distress’ I leave open the possibility of discussing not just Lucy’s promiscuity, but also Mina’s conservative womanhood.
Finally, you need not even mention genre or its tropes in the essay, just use it as a thinking tool. If you go back through the previous section of this blog, you’ll see just how many questions I am asking about the tropes and ideas I am discussing. By using the trope as a jumping-off point for a series of questions, I can develop a nuanced understanding of multiple views and values and the ways in which they interconnect. Take a trope like the ‘creepy castle’ and ask:
“Why would Stoker put Dracula manor in the text?”
“Because it sets up the ‘otherness’ of Dracula.”
“Why do we need to know that Dracula is the other?”
“Because he represents a supernatural foreignness that we need to be scared of.”
“Okay, but why is it right at the start, why is it from Jonothan’s perspective?”
All of these questions offer ways of breaking down the text and they will naturally lead to questions about structure, characterisation and views and values. In doing this, you can start to come up with ways to turn those questions, or the order of those questions into an essay structure. Moreso, this type of questioning is what your teacher, tutors and top-tier Literature students are doing. It is a constant process of asking, answering, reconsidering, reasking and synthesising. And genre is an easy way to start the process.
Get exclusive weekly advice from Lisa, only available via email.
Power-up your learning with free essay topics, downloadable word banks, and updates on the latest VCE strategies.
latest articles
Check out our latest thought leadership on enterprise innovation., vce english unit 3, area of study 2: creating texts - what is it.

Breaking Down Themes & Key Quotes in The Erratics by Vicki Laveau-Harvie

Keep in touch
Have questions? Get in touch with us here - we usually reply in 24 business hours.
Unfortunately, we won't be able to answer any emails here requesting personal help with your study or homework here!

Copyright © Lisa's Study Guides. All Rights Reserved. The VCAA does not endorse and is not affiliated with Lisa's Study Guides or vcestudyguides.com. The VCAA provides the only official, up to date versions of VCAA publications and information about courses including the VCE. VCE® is a registered trademark of the VCAA.
03 9028 5603 Call us: Monday to Friday between 3pm - 6pm or leave us a message and we'll call you back! Address: Level 2 Little Collins St Melbourne 3000 VIC

- Scriptwriting
What is Context — Definition and Examples for Writers
C ontext has the ability to change the meaning of a story and how we view its characters — but what is context? We’re going to answer that question by looking at examples from The Office, In Cold Blood and more. We’ll also look at some tips and tricks for how you can effectively implement this necessary element in your own stories. By the end, you’ll know why context is so important and how to apply it in a variety of different ways. But before we jump into our examples, let’s define context.
Content vs Context Definition
What does context mean.
Whether we realize it or not, context is all around us. It is the fundamental way we come to understand people, situations and ideas. Everything that we think, say, see, hear, and do is a response to the external stimuli of the world.
And how we regard that stimuli is largely in response to the context it’s presented to us in. For more on this idea, check out the video from the University of Auckland below.
What is Context? By University of Auckland
So you’re probably thinking, “Okay that’s fine and good and all, but what is context? Surely the meaning can’t be so vague.” Well, it is and it isn’t.
But by understanding the essential aspects of the term, we’re better prepared to apply it in meaningful ways. So without further ado, let’s dive into a formal context definition.
CONTEXT DEFINITION
What is context.
Context is the facets of a situation, fictional or non-fictional, that inspire feelings, thoughts and beliefs of groups and individuals. It is the background information that allows people to make informed decisions. Most of the time, the view of a person on a subject will be made in response to the presented context. In storytelling, it is everything that surrounds the characters and plot to give both a particular perspective. No story takes place without contextual information and elements.
Characteristics of Context:
- Information that’s presented to us
- Used in an argumentative sense
- Biased/subjective form of education
ContextUal Information
Context clues : in and out of context.
In terms of storytelling, there are only two kinds of context: narrative and non-narrative. The former gives us information on the story and the latter gives us information on everything outside of the story.
Narrative types of context include:
Narrative context is everything that explains “what’s going on” in a story. Take a comedy series like The Office for example: there are a lot of moments in the show that wouldn’t make sense without contextual information — and there just so happens to be a video that explores The Office “out of context.”
What Does Context Mean in The Office?
Even the most ardent fans of The Office may find themselves asking, “what in the world is going on?” when presented with these clips out of context. On social media channels, moments from film and television are often presented like this — like this screen grab from The Good Place .

Context Definition and Examples
In a sense, out of context moments have become a type of humor in and of themselves. But it’s important that we also consider how information outside of the narrative may influence our feelings on the story.
Non-narrative types of context include:
Non-narrative context is everything outside the story that influences our thoughts and opinions on the subject matter. Take Truman Capote’s In Cold Blood for example: when we learn of the circumstances outside of the subject matter, it’s impossible for us to feel the same way about the story.
In Cold Blood is an investigative novel about the murder of a family of four in Holcomb, Kansas. Capote started writing about the murders in earnest before expanding his research into a full-fledged novel — the end result speaks for itself — not only is Capote’s prose considered some of the greatest of all-time, but it also pioneered true-crime writing.
But when In Cold Blood is viewed through the context of the man who wrote it, the setting it took place in, and the precedence of its writing, the meaning is liable to change. The two convicted murderers in the novel, Perry Smith and Dick Hickock, were interviewed by Capote through the writing process.
Their testimony is admitted in the novel, but filtered by Capote. So, for us to say their testimonies are veracious would be irresponsible, considering the context through which it was written.
Elsewhere, critics argue that we can only judge a piece of art based on the merit of the art itself, not the context it was created in. French literary theorist Roland Barthes said that “text” can only speak for itself and that the thoughts and feelings of the author should have no impact on its merit. For more on this “The Death of the Author” theory, watch the video below.
Exploring Context Clues • Lindsay Ellis on ‘The Death of the Author’
In recent years, many fans have criticized J.K. Rowling’s Harry Potter books in light of her political views. Some critics argue that her views change the meaning of the novels. Others argue that her views should have no impact. Alas, there’s no “right” answer, but it’s important to consider how context, both inside and outside of a story, can influence readers.
Context Clues Set the Stage
How to use context as exposition.
There’s a word in screenwriting that most screenwriters shutter to hear… and that word is exposition . Ah yes, the dreaded exposition — or explanatory description — has been known to sink more than a few good scripts. So, how do screenwriters use exposition effectively? Well, it starts with a need for context. When I say need, I mean the story would have no impact without it.
We imported the On the Waterfront screenplay into StudioBinder’s screenwriting software to look at an iconic scene where context is the primary force behind exposition.
In this scene, Terry details how Charley and Johnny abandoned him. This backstory, or exposition, adds the necessary context needed to make Terry’s exclamation, “I coulda’ been a contender!” impactful.
Click the link below to read the scene.

What is Context? • Read the On the Waterfront Screenplay
This explanatory description establishes a context in which we’re able to see that Terry has endured “years of abuse.” The context is further executed as Terry laments the actions of his best friends. Think of it this way: proper exposition should act like a tea-kettle; each relevant detail making the kettle hotter and hotter — or more contextual and more contextual — until — the tension is released… and whoosh, the conflict is resolved.
How to Add Context Clues
Tips for incorporating context.
Context plays a huge role in guiding the attention and emotional attachment of the audience. Say a character does something really bad, like kill another character. Our natural inclination is to vilify them, but if their actions are given context, we might view their actions as heroic.
Take Ridley Scott’s Gladiator for example: when Maximus kills Commodus, we view him as the hero. Let’s take a look at how this scene plays out:
Context Examples in Gladiator
In context, Maximus’ actions are justified. Commodus killed Maximus’ family and rigged the fight against him. As such, it makes sense that we root for his death. Here are some tips for how to incorporate context in your own works:
- Create empathy for your protagonist
- Vilify your antagonist
- Maximize conflict
- Develop themes
- Callback to prior events
By utilizing these strategies, you’ll create narrative continuity. Context relies on the impact of the past, so you should be mindful of the character’s pasts at all times when writing.
What is a Plot?
Context may be what informs our understanding of a story’s events, but it would mean nothing if there weren’t events to be informed of. Plot refers to the events and actions that take place within a story — and it’s an essential aspect of every narrative. In this next article, we look at how plot is used in Die Hard to connect narrative threads from beginning to end!
Up Next: Plot Definition and Examples →
Write and produce your scripts all in one place..
Write and collaborate on your scripts FREE . Create script breakdowns, sides, schedules, storyboards, call sheets and more.
- Pricing & Plans
- Product Updates
- Featured On
- StudioBinder Partners
- The Ultimate Guide to Call Sheets (with FREE Call Sheet Template)
- How to Break Down a Script (with FREE Script Breakdown Sheet)
- The Only Shot List Template You Need — with Free Download
- Managing Your Film Budget Cashflow & PO Log (Free Template)
- A Better Film Crew List Template Booking Sheet
- Best Storyboard Softwares (with free Storyboard Templates)
- Movie Magic Scheduling
- Gorilla Software
- Storyboard That
A visual medium requires visual methods. Master the art of visual storytelling with our FREE video series on directing and filmmaking techniques.
We’re in a golden age of TV writing and development. More and more people are flocking to the small screen to find daily entertainment. So how can you break put from the pack and get your idea onto the small screen? We’re here to help.
- Making It: From Pre-Production to Screen
- What is a Light Meter — Understanding the Photographer's Tool
- What is Metonymy — Definition, Examples & How to Use It
- What is a Short Story — The Art of Brevity in Literature
- What is an Action Hero — Best Examples & Defining Traits
- What is a Movie Spoiler — Types, Ethics & Rules Explained
- 1 Pinterest

8 Tips For Writing A Social Justice Essay
Social justice covers a variety of issues involving race, gender, age, sexual orientation, income equality and much more. How do you write an essay on a social justice issue that’s engaging, informative and memorable? Here are eight tips you should take to heart when writing:
When writing a social justice essay, you should brainstorm for ideas, sharpen your focus, identify your purpose, find a story, use a variety of sources, define your terms, provide specific evidence and acknowledge opposing views.
#1. Brainstorm creatively
Before you start writing your social justice essay, you need a topic. Don’t hesitate to look far and wide for inspiration. Read other social justice essays, look at recent news stories, watch movies and talk to people who are also interested in social justice. At this stage, don’t worry about the “trendiness” of your idea or whether a lot of people are already writing about it. Your topic will evolve in response to your research and the arguments you develop. At the brainstorming stage, you’re focused on generating as many ideas as possible, thinking outside the box and identifying what interests you the most. Take a free online course to get a better understanding of social justice.
You can take a creative brainstorming approach! A blog on Hubspot offers 15 creative ideas such as storyboarding, which involves laying out ideas in a narrative form with terms, images and other elements. You can also try freewriting, which is when you choose something you’re interested in. Next, write down everything you already know, what you need to know but don’t already, why the topic matters and anything else that comes to mind. Freewriting is a good exercise because it helps you decide if there’s any substance to a topic or if it’s clear there’s not enough material for a full essay.
#2. Sharpen your topic’s focus
The best essays narrow on a specific social justice topic and sharpen its focus, so it says something meaningful and interesting. This is often challenging, but wrestling with what exactly you want your essay to say is worth the effort. Why? An essay with a narrow, sharp focus has a clearer message. You’re also able to dig deeper into your topic and provide better analysis. If your topic is too broad, you’re forced to skim the surface, which produces a less interesting essay.
How do you sharpen your essay’s focus? Grace Fleming provides several tips on ThoughtCatalog . First, you can tell your topic is too broad if it can be summarized in just 1-2 words. As an example, “health inequity” is way too broad. Fleming suggests applying the questions, “Who, what, where, when, why and how,” to your topic to narrow it down. So, instead of just “health inequity,” you might end up with something like “The impact of health inequity in maternal healthcare systems on Indigenous women.” Your topic’s focus may shift or narrow even further depending on the research you find.
Writing a human rights topic research paper? Here are five of the most useful tips .
#3. Identify your purpose
As you unearth your topic and narrow its focus, it’s important to think about what you want your essay to accomplish. If you’re only thinking about your essay as an assignment, you’ll most likely end up with a product that’s unfocused or unclear. Vague sentiments like “Everyone is writing about social justice” and “Social justice is important” are also not going to produce an essay with a clear purpose. Why are you writing this essay? Are you wanting to raise awareness of a topic that’s been historically ignored? Or do you want to inspire people to take action and change something by giving them concrete how-to strategies? Identifying your purpose as soon as possible directs your research, your essay structure and how you style your writing.
If you’re not sure how to find your purpose, think about who you’re writing for. An essay written for a university class has a different audience than an essay written for a social justice organization’s social media page. If there are specific instructions for your essay (professors often have requirements they’re looking for), always follow them closely. Once you’ve identified your purpose, keep it at the front of your mind. You’ll produce an essay that’s clear, focused and effective.
#4. Find a human story
The best social justice essays don’t only provide compelling arguments and accurate statistics; they show your topic’s real-world impact. Harvard’s Kennedy School’s communications program describes this process as “finding a character.” It’s especially useful when you’re writing something persuasive. Whatever your topic, try to find the human stories behind the ideas and the data. How you do that depends on the nature of your essay. As an example, if you’re writing something more academic, focusing too much on the emotional side of a story may not be appropriate. However, if you’re writing an essay for an NGO’s fundraising campaign, focusing on a few people’s stories helps your reader connect to the topic more deeply.
How do you choose what stories to feature? Harvard suggests choosing someone you have access to either through your research or as an interview subject. If you get the opportunity to interview people, make sure you ask interesting questions that dig beneath the surface. Your subject has a unique perspective; you want to find the information and stories only they can provide.
#5. Rely on a variety of sources
Depending on your essay’s purpose and audience, there might be certain sources you’re required to use. In a piece for Inside Higher Ed, Stephanie Y. Evans describes how her students must use at least 10 source types in their final paper assignment. Most of the time, you’ll have a lot of freedom when it comes to research and choosing your sources. For best results, you want to use a wide variety. There are a few reasons why. The first is that a variety of sources gives you more material for your essay. You’ll access different perspectives you wouldn’t have found if you stuck to just a few books or papers. Reading more sources also helps you ensure your information is accurate; you’re fact-checking sources against one another. Expanding your research helps you address bias, as well. If you rely only on sources that reflect your existing views, your essay will be much less interesting.
While we’re talking about sources, let’s touch on citations. If you’re writing an essay for school, your teacher will most likely tell you what citation method they want you to use. There are several depending on the discipline. As an example, in the United States, social science disciplines like sociology and education tend to use the American Psychological Association (APA) style. Some places are very rigid about citation styles, while others are more relaxed. If you’re writing an essay where your citation won’t be checked, you still need to give credit to any ideas, thoughts, or research that’s not yours. Proper citation builds trust with your reader and boosts your credibility.
Here are more tips on writing a human rights essay!
#6. Define your key terms
To make your essay as clear and effective as possible, you want every reader on the same page right at the beginning. Defining your key terms is an important step. As Ian Johnston writes, creating an effective argument requires “the establishment of clear, precise, and effective definitions for key terms in the arguments.” You may have to adapt an existing definition or write your own. Johnston offers principles such as adjusting a definition based on the knowledge of who you’re writing for, focusing on what a term is and not just on its effects, and expanding a definition so it covers everything a reader needs to know.
How do you decide which terms are important in your essay? First, never assume a reader understands a term because it’s “obvious.” The most obvious terms are often the ones that need the clearest definitions. If your reader doesn’t know exactly what you’re talking about when you use a term like “health equity,” your essay won’t be as effective. In general, you want to define any terms relevant to your topic, terms that are used frequently and terms with distinct meanings in the context of your essay.
#7. Provide specific evidence and examples
Social justice issues are grounded in reality, so an essay should reflect that. Don’t spend your whole paper being philosophical or hypothetical. As an example, let’s say you’re writing an essay about desertification in Mali. Don’t discuss desertification as an abstract concept. Include real statistics and case studies on desertification in Mali, who it’s affecting the most and what is being done about it. For every argument you make, present supporting evidence and examples.
The strength of your evidence determines the strength of your arguments. How do you find strong evidence? Cite This For Me lists a handful of examples , such as studies, statistics, quotes from subject matter experts and/or reports, and case studies. Good evidence also needs to be accurate and in support of your argument. Depending on your essay topic, how current a piece of evidence is also matters. If you’re not relying on the most current evidence available, it can weaken your overall argument. Evidence should also be as specific as possible to your topic. Referring back to our desertification in Mali essay, that means locating examples of how desertification affects people in Mali , not in Chad or Russia.
Academic essay writing requires specific skills. Here’s an online introductory course on academic writing .
#8. Acknowledge your critics
Not every social justice essay requires an acknowledgment of opposing viewpoints, but addressing critics can strengthen your essay. How? It lets you confront your critics head-on and refute their arguments. It also shows you’ve researched your topic from every angle and you’re willing to be open-minded. Some people worry that introducing counterarguments will weaken the essay, but when you do the work to truly dissect your critic’s views and reaffirm your own, it makes your essay stronger.
The University of Pittsburgh offers a four-step strategy for refuting an argument. First, you need to identify the claim you’re responding to. This is often the trickiest part. Some writers misrepresent the claims of their critics to make them easier to refute, but that’s an intellectually dishonest method. Do your best to understand what exactly the opposing argument is claiming. Next, make your claim. You might need to provide specific evidence, which you may or may not have already included in your essay. Depending on the claim, your own thoughts may be a strong enough argument. Lastly, summarize what your claim implies about your critics, so your reader is left with a clear understanding of why your argument is the stronger one.
You may also like

Apply now: Essex Human Rights Summer School (Fully Online)

17 International Organizations Offering Early-Career Opportunities

Gender Rights Jobs: Our Short Guide

Free MOOC on Children’s Right to Education in Armed Conflict

9 Online Courses on Leading Diverse Teams

40 Top-Rated Social Issues Courses to Study in 2024

10 Courses to Prepare for Your Human Rights Job

Register now: Global Institute of Human Rights Certificate Program

The UN Immersion Programme Is Open for Applications!

The UN Young Leaders Online Training Programme is Open for Applications!

NGO Jobs: Our Short Guide

Apply now: UN Post Graduate Diploma in Global Health Procurement and Supply Chain Management
About the author, emmaline soken-huberty.
Emmaline Soken-Huberty is a freelance writer based in Portland, Oregon. She started to become interested in human rights while attending college, eventually getting a concentration in human rights and humanitarianism. LGBTQ+ rights, women’s rights, and climate change are of special concern to her. In her spare time, she can be found reading or enjoying Oregon’s natural beauty with her husband and dog.
Social Enterprise in Context Essay
Social enterprise, the impact of social enterprises on the society, major achievements of social enterprises, challenges faced by the social enterprises, the social economy in relation to social enterprise, critics associated with social enterprises, recommendations.
According to Price (2008, pp 1), “social enterprises are businesses with primary social objectives whose surpluses are principally reinvested for that purpose in business or in the community, rather that being driven by the need to maximize profit for shareholders and owners.”
Social enterprise is mainly associated with non-profit organizations, mainly privately owned, which sell goods and services with an aim of yielding a return on investments, with the accumulated profits being ploughed back into the business or they are directed to social purposes.
The profits of these organizations are not maximized to benefit the shareholders. In addition, social enterprises may be developed with an aim of fulfilling needs that are rare, such as providing employment to the less fortunate communities and the disadvantaged individuals. Such groups of people include the disabled, low education candidates, and ex-offenders, among others.
These social enterprises also operate in the less attractive locations for other businesses; such places include locations with low level of education, rural areas, and social housing areas among others.
Social enterprise activities mainly revolve around the developing of countries, and they include recycling, renewable energy, and fair trade. Social enterprise mainly aims at the social challenges of poverty, unemployment, disablement, and underdevelopment, which may occur in some locations and communities; they address such challenges via aid and social work (Kerlin, 2009, pp xiii).
Just like other businesses, social enterprises compete in the market, but the difference comes in where profits made are reinvested in social activities. Social enterprises are also viewed as a response that is innovative and is directed into funding socio activities by the non-profit organization (Nyssens, et al, 2006, pp 4).
According to Kerlin (2006, pp 249), social enterprises are characterized by the continuity of producing goods and services, the aim to benefit the community, low amount paid in terms of work, the initiative to take up risks, and the limitation of profit distribution.
Kerlin (2009, pp 6) further explains these characteristics; first, the continuity of producing and selling of goods and services, with the social enterprises being known for their productivity of goods and services. Secondary, high degree of autonomy involves their creation by a group on individuals who govern these enterprises and they are not controlled by the government; hence, they make their own decision.
Thirdly, the important level of economic risk allows their employees to determine their financial stability by how well they secure sufficient resources. In addition, the minimum amount of work that is paid shows that most of their workers are volunteering while only a small portion of them are fully employed.
Their aim to benefit the community entails serving of specific people in a community and promoting social responsibility.
Moreover, these enterprises represent an initiative formed by a group of people with the same aims and objectives, while the decision-making process involves voting, thus incorporating all ideas of the stakeholders. Lastly, the limited issue of profit distribution requires that profits be distributed on limited basis with the aim of minimizing profit maximization motive.
Despite social enterprises playing a major role in the employment of the less-advantaged groups, in some countries like the United Kingdom, it lacks full control of this factor. According to survey, only 2% of the United Kingdom population is employed by the social enterprises. However, this could be due to the fact that the social enterprises pay less as compared to the public sectors.
Nevertheless, these enterprises contribute greatly to the marginalized communities and groups of people (Teasdale, 2010 pp. 95). Teasdale (2010, pp 101) further explains that social enterprises can be of various purposes including providing a social space for the marginalized groups of people such that they are able to develop bonds with others who have a similar situation as theirs.
An example of supported housing enterprise is in the United Kingdom whereby the enterprise accommodated those who suffered from bipolar, as one of the victim shared that he feels much safer at the center other than in the community as he is always harassed and he had no close friends.
When he compares his life in the supported housing enterprise, where he is able to make friends and bond, he feels much safer since there are people with similar situation as his who love and understand him. Hence, this enterprise is a perfect example of a social enterprise from the marginalized groups of people.
Individuals are excluded from activities in the community but are included socially in a group. For instance, a person who has relied on the state’s benefit for some time and then he is finally excluded from such benefits, but within a community enterprise, he is not excluded and was involved even in decision making. Such a person will feel less isolated in the community enterprise as compared to his country.
These enterprises have an aim of creating a paying employment, this is evidence in the case of community times a social enterprise in the United Kingdom that provided employment with a salary to the management team of the organization. Social enterprises involve hierarchy decision-making, tending to fill in, in terms of goods and services, where the state has failed.
Therefore, it is evident that a social enterprise is business aimed at changing the society for the common good. An evident case is that of China, where, despite the social entrepreneurs investing in two projects, they never aimed at profit maximizing, but rather, on strategies that focused on the community (Gunn and Durkin, 2010, pp67).
Social enterprises mainly focus on social responsibility; this is evident when they take up the role of rehabilitating offenders, in which they change the lives of such people for the benefit of the society, since the rate of crime will reduce.
According to Myers and Stocks (2010 pp 267), “the social economy encompasses a range of non-profit and social enterprise organizations that put people before profits, by solving social needs rather than amassing financial profits.” This statement makes it clear that social enterprises sacrifice their private aims and objectives and focus on social needs of the communities.
According to newstatesman (2002, pp ii), social enterprises are seen as organizations that are neither answerable to the government nor have an aim of profit maximization.
This article further explains that the social enterprises are mainly concerned with quality of life of the common people, which involves health, conducive environment, and opportunities for a better education among others. This is summarized by newstatesman (2002, pp. vii) by stating that, “social enterprises are hybrids mixing social values and goals with commercial practices.”
This is evident as they prove to be unconstitutional, as their main driving force are social goals, which include provision of education, support to the incapable families and childcare support; however, to attain such goals, they have to participate and compete in the market through selling their goods and services.
An example can be extracted from the furniture resource centre located in Liverpool, which has a workforce of one hundred and fifty repairing and selling furniture. This business not only sells its products, but it creates a common good to the society by providing employment.
The main aim why the social enterprises make profits is to attain independence and avoid relying on government for support. They therefore focus on communities and customers who have been shunned away by the government.
According to Munoz (2010 pp 59), Tommy Hutchinson made an impact on the society and on social entrepreneurs when he implemented an online social network company named i-genius which operates in over 90 countries.
The network is involved in collaboration of social entrepreneurs and non-governmental organizations; this way, the social enterprises can make international impacts through this website. Using internet, social enterprise is deemed to grow, as the internet creates social collaboration.
According to Leadbeater (2007), the social entrepreneurs had no name ten years ago, but today they are recognized due to their effort to accommodate the written off and laid-off people from schools and workplaces. He further explains that this sector has provided over 40milion employment opportunities and 200 million volunteers worldwide.
For instance, in the United Kingdom, the government created a legal entity, which is the community interest company aimed at incorporating those enterprises that direct their profits to social activities. Social Corporation’s main role is to enhance social entrepreneurship, which entails smoothening the way for employment of the deprived groups and promote training and education (Thomas, 2004, pp 251).
It is evident that a social enterprise consists of corporate social responsibility in its operations, in which social responsibility is the commitment of an organization to improve the well-being of a deprived community via business and social practices; such practices may range from health care to education (Kotler and Lee, 2005, pp 3).
Organizations are expected to impact the society and the communities positively with their activities that are directed towards the welfare of the society and further assume responsibility (Sims, 2003 43).
Therefore, corporate social responsibility entitles one to being a steward of the society’s needs; therefore, it is clear that the social enterprises engage fully in social responsibility unlike other organization who engage partially to the community’s responsibilities.
According to Munoz (2010, pp 30), social enterprises are striving to reach out to the international communities; this is evident in regard to the green work organization which has aided countries like Sudan, Ghana and Sierra Leone among others.
This has left a positive effect worldwide and promoted social responsibility. Social entrepreneurship arise from social enterprise; its main aim being the provision of solutions and aid to social problems facing the society (OECD, 2010 pp 188).
According to Kerlin (2009 pp 76), social enterprises in South Asia have been a major aid to the Asian poverty problem which affects approximately 50% of the Asian population. The corrupt government rarely focuses on eradicating poverty; rather, it enhances unequal distribution of resources.
However, social enterprises have focused on poverty eradication and creating jobs in Asia. One example of such an enterprise is the La Frutera Corporation whose operation involves a banana plantation and work with an aim of improving the quality of lives in the Philippines.
The Maireang farmer’s group involves the poor and landless farmers in Thailand and engages them in the processing of rubber, hence increasing the farmers’ income. According to Yunus (2007 pp, 3), poverty around the world is usually uneven, such that, some communities suffer more than others do.
Relying on the government can be frustrating sometimes; this is because it is slow in acting, hence leading to the emergence of non-profit organizations mainly concerned with the welfare of the needy and desperate. However, theses charitable organizations rely on donations and if the donations cease, they are incapable of assisting the needy.
The author adds that in countries like Bangladesh, where social needs are on high demand, when there are no sufficient donors, some social needs are not catered for at all.
According to Kerlin (2007, pp 77), some of the social enterprise like the entrepreneurs school of Asia promotes entrepreneurial education in which students are molded into becoming social entrepreneurs who focus on profit in business, as well as social impact to the needy communities. The mirror foundation in Thailand enhances education to the remote areas.
According to Kerlin (2006, pp 259), social enterprises face challenges just like other organizations and businesses. For instance, in the United States, social enterprises challenges have been identified that include, “exclusion of specific groups, the weakening of civil society and lack of government involvement” (Kerlin, 2006, pp 259).
The author further explains that social enterprises may be leading to the rising rate of exclusion of the marginalized groups.
For instance, in the United States, members of the enterprise are required to pay a certain fee, however, some of the poor beneficiaries cannot afford to pay, hence being excluded from receiving any benefits. Secondly, some of the social enterprises generate a lot of profits, thus they concentrate more on their clients rather that on the social responsibility for the communities.
Thirdly, social enterprises are seen as a potential risk to the civil society in that, these organizations might abandon some programs such as the volunteer programs due to the demand in other practices. These enterprises may also stop relying on donations and volunteers, hence diminishing the aims of promoting social capital.
According to Kerlin (2006, pp259), Western Europe faces the challenge of limited number of services that are supported by the enterprises as compared to the United States, hence, these social enterprises end up being underutilized. According to Leadbeater (2007), many social entrepreneurs run small firms hence limiting the spread of such schemes. Some lack managerial skills, which are relevant in the growth of an organization.
According to Ducci et al (2002 pp 79), social enterprises faced a number of challenges in France, among them being the incapability of creating an organization with many stakeholders, the difficulty in engaging in economic activities for the social enterprises, and the impossibility of the social enterprise to acquire capital.
According to Marks and Hunter (N.d, pp 7), social firms aimed at reaching out to the needy such as education and health care face a range of queries when it comes to their stability, continuity and their sustainability due to the uncertainties that face them.
When a non-profit organization seeks to establish itself, it is faced by a major challenge of distraction from the charitable objective, such that the organization may end up operating like a normal business by loosing focus of its main mission, which is charity (Crutchfield and Grant, 2008, pp 74).
Social economy is referred to as a part of the economy that is not public or private; it consists of non-profitable organizations inclusive of volunteers whose activities are aimed at a community benefit, for instance, for the deprived groups in the society.
The social economy mainly consists of three sub-sectors; the voluntary sector which consists of organizations that govern themselves and do not rely on the government, operate without a profit maximization motive and involve in volunteer work mostly. Such organizations may include charities.
The second sector is the community sector in which these organizations depend on voluntary and do not pay for these efforts, as they are small support groups. Third is the social enterprise sector that involves businesses whose objectives are to support the community and not on maximizing profits for its shareholders (Social Economy, 2011).
In Northern Ireland, the social economy employs approximately 48,000 workers, while in the European Union, a total of 10 million people are employed. This sector can be differentiated from other sectors through its non-profit aim, the low wages and the voluntary services, its involvement with the community and its reinvestment in profits as opposed to sharing it out to the stakeholders.
Nevertheless, the social sector outweighs other organizations through the following advantages;
- they are normally situated near their customers, and hence respond fast to their clients needs.
- They have the capability of reaching out to the deprived groups in the society.
- Due to their charitable work, they attract many charitable organization and volunteers who come to their aid in terms of money and labor.
- Since their existence, they have contributed to social capital in the country (Social Economy, 2011).
The main aim of the social economy enterprises is to provide a quality life to individuals and the economy at large; hence, they aim at promoting mutuality, equal opportunities, worth employment opportunities, co-operation, and social benefits to the communities among others.
In addition, these social economy enterprises operate under the influence of social aims, which vary from training, job creation, and provision of services among others.
Secondly, they are involved in the production of goods and services in the competing market, hence benefiting the communities through the acquired profits. Therefore, social economy consists of the charitable sector, non-profit sector, and the voluntary sector (Uluorta, 2009, pp14).
According to newstatesman (2002, pp iii), “social enterprises are seen as a government device to open avenues for local authorities to contract out services such a childcare, leisure and transport.”
However, social enterprises are a savior to many as they take up the “left overs” from the government, such as, the laid off employees, neglected citizens and the marginalized communities, thus remodeling them to being better off. According to Leadbeater (2007), social entrepreneurship is seen as a fake idea and that has developed to its capability to adapt and due to its ambiguous nature.
Social enterprises that are successful should aim at promoting productivity and competition in the operating environment. They should also be able to create wealth socially and promote co-operation and cohesiveness in the community. Social enterprise should work towards developing a new way of operating in terms of delivering of goods and services.
Nevertheless, social entrepreneurs should ensure that their enterprise is leaving a positive impact on the community by enhancing their mode of living. A social enterprise should be aimed at developing the potential of the deprived groups, either by providing employment to them or training them into managing their own businesses.
In addition, an effective social enterprise should be competitive in order to enable its survival in the market by attracting several customers. Finally, social enterprises should enhance delivery of public services by collaborating with the government in areas such as health sector, recycling, adoption, and transportation among others; therefore, social entrepreneurship should be promoted in all countries.
Social enterprises are key players to social responsibility worldwide; therefore, this sector should be supported by the government with no strings attached. This way, they can continue enjoying their independence and at the same time have enough funds to support the less fortunate in society. Social enterprises lead to social entrepreneurship, which aims at providing innovative solutions to unsolved problems in a society.
Hence, it is more concerned in alleviating problems other than maximizing profits. Therefore, with social entrepreneurship in place, deprived communities and marginalized groups are well catered for and have a place to call home.
The social enterprise topic seems like a narrow subject, but it has really challenged me due to its depth and content, hence leaving me thirsting for more knowledge. It is however, an important discussion with a variety of references and during my assignment, I have learnt also on matters that seemed confusing at first.
Having acquired this sufficient knowledge, I am in a better position to tackle and understand any matters related to social enterprises.
Crutchfield, L. and Grant, H. (2008). Forces for good: the six practices of high-impact nonprofits . NJ: John Wiley and Sons Publishers.
Ducci, G. et al. (2002). The social enterprise in Europe. International journal of mental health, Vol. 31 Issue 3, p76, 16p. Web.
Gunn, R. and Durkin, C. (2010). Social Entrepreneurship: A Skills Approach . NY: The Policy Press Publisher.
Kerlin, J. (2006). Social Enterprise in the United States and Europe: Understanding and Learning from the Differences. Voluntas: International Journal of Voluntary & Nonprofit Organizations, Vol. 17, Issue 3, p246-263. Web.
Kerlin, J. (2009). Social Enterprise: A Global Comparison. Civil Society: Historical and Contemporary Perspectives . NY: UPNE Publishers.
Kotler, P. and Lee, N. (2005). Corporate social responsibility: doing the most good for your company and your cause . NJ: John Wiley and Sons Publisher.
Leadbeater, C. (2007). Mainstreaming of the mavericks; the social entrepreneurship movement has come of age, writes Charles Leadbeater . What now? Web.
Marks, L. and Hunter, D. Social enterprises and the NHS: changing patterns of ownership and accountability. Web.
Munoz, M. (2010). International Social Entrepreneurship: Pathways to Personal and Corporate Impact. NY: Business Expert Press Publishers.
Myers, J. and Stocks, J. (2010). Fostering the Common Good: The Portrayal of the Social Economy in Secondary Business and Economics Textbooks. Journal of social studies research, Vol 34, issue 2. University of Pittsburgh. Web.
Newstatesman. (2002). social enterprise . Web.
Nyssens, M. et al. (2006). Social Enterprise At the crossroads of market, public policies and civil society. London: Taylor & Francis publishers. Web.
OECD. (2010). OECD Studies on SMEs and Entrepreneurship SMEs, Entrepreneurship and Innovation. Paris: OECD Publishing.
Price, M. (2008). Social enterprise: what it is and why it matters. Wales: Fflan Publishers.
Sims, R. (2003 ). Ethics and corporate social responsibility: why giants fall . CT: Greenwood Publishing Group.
Social Economy. (2011). Business for community benefits . Web.
Teasdale, S. (2010 ). How Can Social Enterprise Address Disadvantage? Evidence from an Inner City Community . Journal of non-profit & public sector marketing, Vol. 22, Issue 2, pp. 89-107. Taylor & Francis publishers. Web.
Thomas, A. (2004). The Rise of Social Cooperatives in Italy. International journal of voluntary and non-profit organization, Vol. 15, Issue 3. Web.
Uluorta, H. (2009). The social economy: working alternatives in a globalizing era. Volume 17 of rethinking globalizations. London: Taylor & Francis Publisher.
Yunus, M. (2007). Creating a world without poverty. Social business and the future of capitalism. NY: Public affairs publisher united states.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2020, January 31). Social Enterprise in Context. https://ivypanda.com/essays/social-enterprise-in-context-essay/
"Social Enterprise in Context." IvyPanda , 31 Jan. 2020, ivypanda.com/essays/social-enterprise-in-context-essay/.
IvyPanda . (2020) 'Social Enterprise in Context'. 31 January.
IvyPanda . 2020. "Social Enterprise in Context." January 31, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/social-enterprise-in-context-essay/.
1. IvyPanda . "Social Enterprise in Context." January 31, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/social-enterprise-in-context-essay/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Social Enterprise in Context." January 31, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/social-enterprise-in-context-essay/.
- Non-Profit Organization: Donors and Volunteers
- Independent Entrepreneurship, Intrapreneurship, and Social Entrepreneurship
- Managing Non-Profit Organizations in Australia
- Management in Entrepreneurship
- Social Entrepreneurship in the New York City
- Volunteer Management Process
- Volunteers Recruitment and Managment
- Social entrepreneurship: What Everyone Needs to Know by Bornstein and Davis
- Non-Profit Organisations Management
- Volunteer Management Practices and Retention of Volunteers
- Sustainability Analysis: British Airways
- Chinese and Indian Clothing Industries
- The Situation Analysis Term Project of T-Mobile
- Organisational Issues at Lufthansa Airlines
- Report on a Social Business Opportunity

Understanding Writing Situations
Many of us think of writing as a solitary activity -- something done when we're alone in a quiet place. Yet most of our writing, like other forms of communication -- texting conversations, emails, classroom discussions, meetings, and presentations -- is an intensely social activity. In this guide, you can learn more about the situations in which writers and readers find themselves and the physical, social, cultural, and historical contexts that shape them.
Reading and Writing as Social Acts
Writing is hard work, and it's usually done in a quiet place, away from others. It might seem odd to hear it called a "social act." However, most experienced writers and writing teachers call it just that.
If you think about it carefully, you'll realize that, with a few exceptions (diaries, travel journals, your notes app, and grocery lists among them), most writing activities are intensely social. Even relatively simple writing activities, such as taking a texting message, sending email, or sending a tweet, involve conveying a message to another person as clearly as possible. The writer of a two-word texting message, for instance, ought to consider whether the person reading the message will understand that "call Gail" means call Gail Garcia and not Gail Evans or Gail Chen.
More complex writing activities, such as writing a business proposal or a progress report, require writers to think much more carefully about how their readers will react to what they've written. A memo to a manager outlining reasons why a promotion and a raise are good ideas is clearly shaped by a writer's concerns about his or her readers. Even decisions made by writers of poems, short stories, novels, and plays are affected by what readers know and how they are likely to react.
In much the same way, readers are engaged in a social act. Knowing that you wrote a particular text message, they will contemplate what you most likely meant by the words "call Gail." A manager, reading a memo requesting a promotion and a raise, will take into account his or her perceptions of the writer and what the writer most likely meant by a phrase such as "or else." Similarly, readers of documents ranging from marketing plans to lyric poems to personal letters will read between the lines of those documents based on their knowledge (or the lack thereof) of the writer. Their interpretation of a document, as a result, will be based at least to some degree on something other than the words themselves.
Reading and Writing as Conversation
In some ways, writers' and readers' interactions with each other are like conversations at a party. You've probably wandered around a party, listening in briefly on conversations until you find one you want to join. What you hear in a conversation is filtered through your interests and experiences. And what you say is shaped by a particular purpose (to entertain or inform someone, to ask a question, or perhaps to interest someone in getting together with you at a later time). If you're like most people, you try to avoid repeating things that have already been said and you try to stay on the subject. To do this, you listen to a conversation before adding to it.
This is one of the ways in which writing is most like a conversation. Just as you do at a party, you want to listen (or read) long enough to know what's been said, what people are discussing at the moment, and what they might welcome as a relevant contribution. In other words, you want to be accountable to what's been going on before you add to the conversation (see Accountability, below).
In addition, members of a conversation typically try to create responses that offer something of value to their readers -- something new or interesting, something that helps move the conversation forward (see Value, below). Your decisions about what you might add to a conversation will be based not only on what you've listened to -- or, in the case of writing, what you've read -- but also on your understanding of the needs, interests, values, and beliefs of other members of the conversation (see Considering Your Readers, below).
For these reasons, the relationships between readers and writers can become quite complex. Just as writers compose documents for a wide range of purposes, readers read for a variety of reasons. The degree to which writers can accomplish their purposes depends in large part on the extent to which their document can influence readers to behave or think in certain ways. The degree to which readers find a document useful depends on the extent to which it is consistent with their interests and needs. The document, as a result, becomes the key point of contact between readers and writers - who might live in different times, be separated by thousands of miles, and/or bring radically different experiences to their writing and reading of the document.
Accountability in Writing
Accountability is a key concept in writing, and particularly so in academic writing and research writing. It would be embarrassing to repeat what someone had just said before you joined a conversation. It would be even more embarrassing to be accused of stealing someone's ideas because you hadn't bothered to read what they'd written about an issue. Knowing what's been written about an issue - being an accountable member of a conversation - is the first step toward becoming an effective writer.
Contributing Something of Value
Contributing something of value to a conversation is centrally important in most writing projects. Simply changing the dates on last year's product marketing plan isn't likely to get you a promotion, nor is it likely that summarizing the current state of debate on an environmental policy issue will elicit more than yawns from people who have been closely following the issue. Just as you'll be ignored or even shut down if you make an irrelevant comment at a party, your writing will be ignored if it fails to offer something of value to your readers.
Considering Your Readers
Considering your readers involves attempting to understand what they bring to the conversation -- their knowledge of the issue, their needs and interests, and their values and beliefs. If you are writing a feature article about an Olympic slalom racer for Ski magazine, for example, you'll annoy your readers if you spend a lot of time defining the terms cap skis and sidecut instead of talking about training techniques and race strategies. On the other hand, if you're writing for Parade magazine, a national publication included in many Sunday newspapers, many of your readers (who will be much less familiar with skiing and ski technology than the readers of Ski magazine) are likely to be annoyed if you fail to define those terms. Similarly, providing a detailed history of the Internet will win you little favor from readers of a technical manual for Web server software, but will be of great value to readers of a book covering the development of the World Wide Web.
In a written conversation, you'll have much more time to consider how your readers will react to what you write. As you draft your contribution to the conversation, consider not only how well it will match your readers' knowledge, but also their needs, interests, values, and beliefs. Consider as well their reasons -- or purposes -- for reading what you'll write.
A Social Model of Writing
Models are useful tools for discussing complex concepts. The model discussed in this guide considers the relationships among writers, readers, and texts. Although it can't fully predict the complexities of a specific writing situation, they can help writers understand the general principles that shape those situations.
This model is based on three observations. First, a text may serve as the only point of contact between a reader and writer, particularly when writers are separated by time and distance. Second, texts cannot pass "meaning" transparently and perfectly from writer to reader. Writers seldom write exactly what they mean and readers seldom interpret a writer's words exactly as the writer intended. Third, the factors that affect the attempts of writers and readers to share an understanding of a text include not only their respective purposes, influences, and understanding of each other, but also the physical, social, cultural, and historical contexts in which reading and writing take place.
This model of the writing situation is based on five key questions:
What is the Writer's Purpose?
Every writer has a purpose for writing. In fact, most writers have multiple purposes . A student writing an essay for a class might want to accomplish several things, including completing the particular assignment as required, learning something new, improving writing skills, convincing others to adopt a particular point of view about an issue, and getting a good grade. An employee working on a project st
atus report for a business might want to convey key information to his or her superiors, earn a manager's approval, perform well enough to earn a promotion, and gain valuable experience in project management. Understanding a writer's purposes can help you understand one of the most important aspects of the writing situation. Among other factors, identifying a writer's purposes can help you understand the writer's decisions about the content, structure, and design of a document.
As a writer, understanding your purposes can help you in virtually every aspect of your writing process. Knowing what you want to accomplish will help you select your topic, consider your readers' needs and interests, and choose appropriate evidence to support your points. It will also help you with decisions regarding tone, style, and document design.
What Influences Writers?
Writers will be influenced by a number of factors as they compose a document. Their interests (what they'd like to do) and their needs (what they must do) will affect their decision about choosing a particular topic, the points they make in that document, and the evidence they use to support their points.
Writers' values and beliefs will also influence their document. Writers are likely to choose examples and evidence that reflects their particular perspective on a topic. They will also affect the way they relate to their readers -- whether they adopt a friendly tone, for example.
Writers' knowledge of a particular topic will also affect their work on a document. When writers know a great deal about a topic, they might find it easier to locate appropriate evidence. When writers know relatively little about a topic, in contrast, they'll need to spend much more time searching for, evaluating, and critically reading sources.
Writers--and the writing situations in which they find themselves--are seldom free of requirements and limitations . Requirements are typically associated with an academic or workplace assignment. Common requirements include: length (in words or pages), due date, number and/or type of sources that can be used, organization and format (such as whether to include a title page, works cited list, and so on), documentation style (such as MLA or APA), and intermediate drafts. In addition to these requirements, writers are likely to face certain limitations, such as lack of access to information and lack of time to work on a project.
Reflecting on the requirements and limitations faced by a particular writer can help you understand why particular decisions were made. As a writer, reflecting on your requirements and limitations can help you decide whether a particular decision-such as choice of topic or the inclusion of evidence from a particular type of source-will help or hurt your chances of accomplishing your purposes.
In contrast to requirements and limitations, opportunities expand the possibilities for a writer. Among many other possibilities, opportunities include access to a specialized or particularly good library, personal experience with and knowledge about a topic, access to people who are experts on a particular topic, and access to hardware or software that can help you produce your document (such as desktop publishing software, a good color printer, and Web development software).
What is the Reader's Purpose?
Like writers, readers have purposes. Most readers don't read something unless they see some sort of benefit in doing so. Perhaps they want to be entertained; perhaps they want to learn something new; perhaps they need to review someone's work in order to write a report or assign a grade. Understanding the purposes readers bring to a document can help you anticipate how they will react to a particular document.
As a writer, understanding the purposes of your readers can help you create a more effective document. If you are working on a writing assignment for a class, for example, one of your most important readers will be your instructor. But your instructor will not necessarily be the only reader of your document. Other readers might include your classmates, people who have a professional or personal interest in your topic, or, should your research project be published in print or online, the readers of a particular magazine, journal, or Website. If you are writing in a business or professional setting, your readers might include your supervisor, his or her supervisors, customers, or other people associated with the organization. In addition, it's possible that your readers will include the writers of sources you might use in your document-writers who share your interest in your topic and who might want to respond to what you will eventually write.
What Influences the Reader?
Readers will be influenced by a number of factors as they read a document. Their interest in a particular topic will affect their decision to read -- or not read -- a given document. Similarly, their needs will also affect their willingness to read a document.
Reader's values and beliefs will also influence their reading of a document. Writers who do not take their readers' values and beliefs into account might miss an opportunity to create a more convincing, useful, or acceptable document. Worse, they might offend their readers -- and increase the chances that their readers will not finish the document.
Readers' knowledge of a particular topic will also affect their reading of a document. When writers assume that readers know more about a topic than they actually do, they can create a document that is difficult to understand. When they assume their readers know less than they actually do, they risk creating documents that repeat information readers already know. In both cases, readers are likely to stop reading the document.
What do Writers and Readers Know about Each Other?
One of the most important factors affecting the writing situation is writers' and readers' representations of each other. When writers understand their readers well -- that is, when they know a fair amount about their readers' purposes and influences -- they're likely to create more successful documents. Similarly, when readers have an accurate understanding of the writer -- his or her purpose, needs, interests, values, beliefs, and knowledge of a topic, among other things -- they are likely to be more successful at interpreting the document in a way that the writer intended.
In many cases, the lack of an accurate representation of readers will result in a "poorly written" document -- that is, a document that doesn't help either the writers or the readers. As you consider writing your document, reflect carefully on what you know about your readers. If you know relatively little about them, or if you're missing important information (such as an understanding of why they would want to read your document or what they would hope to gain from it), consider spending some time learning about them. It will be time well spent.
What is the Context?
The remaining elements of this model of writing as a social activity deal with the setting in which the writing takes place.
Physical context refers to the context in which writers and readers interact with a text. Writers compose texts in a variety of physical settings that can affect what and how they write. For instance, a writer might not be able to do his or her best work in a crowded library or in a noisy corporate cubicle. Similarly, readers might react differently to a text depending on where they read it. Whether a document is read on a crowded bus or train, for instance, rather than in a quiet office, might affect how a reader feels about the text. Even factors such as the lighting available to a reader or the quality of the printer and paper used to create a document can affect the reading of a document.
The community - or social context - to which readers and writers belong can also affect the reading and writing of a document. Writers and readers from the same or similar communities are more likely to communicate effectively with each other via a document than writers and readers who come from different communities. Readers familiar with specific political and social issues, for example, are less likely to expect a writer to define those issues in detail. For instance, readers familiar with violence in American secondary schools will not need to be educated about the issue - they will already know the key points. This reduces the amount of time and effort writers need to devote to providing background information about the issue. Rather than going into detail about the causes and effects of school violence, writers can spend more time developing other aspects of a document.
Cultural context refers to a larger set of similarities and differences among readers. For instance, readers from the American Midwest might find it easier to understand the allusions and metaphors used in a document written by someone from Oregon than those in a document written by someone from Peru or Sri Lanka. Similarly, modern teenagers might find it easier to follow what's being said in a document written one month ago by a high school senior in Milwaukee than a document written in 1897 by a retired railroad engineer from Saskatchewan.
The Role of Context in Shaping Purpose and Constructing Meaning
At best, any model of a writing situation will be inexact. The value of the model discussed in this guide, however, lies not in its attempt to be exact, but in its attempt to call writers' and readers' attention to the factors that can shape their interactions with texts - and, through texts, with each other. Of critical importance in this model is the role played by context-physical, social, and cultural-in shaping the decisions writers make as they compose a text and that readers make as they construct meaning from a text. For writers, context shapes -- some might argue that it actually causes -- the purposes for writing. Moreover, context affects the opportunities, requirements, and limitations that affect the choices writers make as they compose their documents. For readers, context shapes their attempt to construct meaning as they read. Physical context can enhance or diminish their ability to read the document. Social context can affect the extent to which writers and readers share common experiences and expectations about a text. Cultural context will affect the fundamental assumptions, beliefs, and aspirations that they bring to the reading of a text.
It might be tempting to consider the elements of this model -- purposes, influences, representations of readers and writers, and the various levels of context -- as relatively distinct. But the most effective use of this model of writing as a social activity lies in recognizing that these elements are intimately related with each other. As you consider the role that text plays in the attempts of writers and readers to create shared meaning through text, remember that no single element of the model can stand completely separate from the others.
Mangialetti, Tony & Mike Palmquist. (2022). Understanding Writing Situations. Writing@CSU . Colorado State University. https://writing.colostate.edu/guides/guide.cfm?guideid=3
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Write a Short Essay
Last Updated: January 17, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Christopher Taylor, PhD . Christopher Taylor is an Adjunct Assistant Professor of English at Austin Community College in Texas. He received his PhD in English Literature and Medieval Studies from the University of Texas at Austin in 2014. There are 12 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 111,067 times.
Essay writing is a common assignment in high school or college courses, especially within the humanities. You’ll also be asked to write essays for college admissions and scholarships. In a short essay (250-500 words), you will need to provide an introduction with a thesis, a body, and a conclusion, as you would with a longer essay. Depending on the essay requirements, you may also need to do academic or online research to find sources to back up your claims.
Picking a Topic and Gathering Research
- If you have any questions about the topic, ask your instructor. If your essay doesn't respond to the prompt, you likely won't receive full credit.

- If you're writing an essay for an in-class test or for an application, tailor the essay to the given prompt and topic. Quickly brainstorm a few ideas; for example, think of positive things you can say about yourself for a college-entrance essay.
- For example, the topic “depression in American literature” is far too broad. Narrow down your topic to something like “Willie Loman’s depression in Death of a Salesman .”
- Or, you could write about a narrow topic like “the increase in the USA’s national debt in the 1950s” rather than a broad topic like “the American economy in the 20th century.”

- Depending on the field in which you’re writing the essay—e.g., hard sciences, sociology, humanities, etc.—your instructor will direct you towards appropriate databases. For example, if you’re writing a high-school or college-level essay for your English class, visit online literary databases like JSTOR, LION, and the MLA Bibliography.
- If you're writing the essay for a college or graduate-school application, it's unlikely that you'll need to include any secondary sources.
- If you're writing a timed or in-class essay, you may not be able to find research articles. But, still do draw information from texts and sources you've studied both in and out of class, and build from points made in any provided reading passages.

- If you’re writing about current events or journalism topics, read articles from well-known news sites like CNN or the BBC.
- Avoid citing unreliable websites like blogs or any sites that have a clear bias about the topic they’re reporting on.
Composing the Essay

- If you write the essay without outlining, the essay will be poorly organized.

- This thesis statement is far too weak: “ Death of a Salesman shows the difficulty of living in America after WWII.”
- Instead, hone your thesis to something like: “Arthur Miller uses Death of a Salesman to show that the American Dream is materialist and impractical.”

- So, avoid beginning the paragraph by writing something like, “Since the beginning of time, all people have been consumed with the desire for their father’s approval.”
- Instead, write something like, “In the play Death of a Salesman , Willie Loman’s sons compete for their father’s approval through various masculine displays."
- Then, you can say, "To examine this topic, I will perform a close reading of several key passages of the play and present analyses by noted Arthur Miller scholars."

- In a short essay, the conclusion should do nothing more than briefly restate your main claim and remind readers of the evidence you provided.

- So, take the example about Death of a Salesman . The first body paragraph could discuss the ways in which Willie’s sons try to impress him.
- The second body paragraph could dive into Willie’s hopelessness and despair, and the third paragraph could discuss how Miller uses his characters to show the flaws in their understanding of the American Dream.

- Always cite your sources so you avoid charges of plagiarism. Check with your instructor (or the essay prompt) and find out what citation style you should use.
- For example, if you’re summarizing the inflation of the American dollar during the 1930s, provide 2 or 3 years and inflation-rate percentages. Don’t provide a full-paragraph summary of the economic decline.
- If you're writing an in-class essay and don't have time to perform any research, you don't need to incorporate outside sources. But, it will impress your teacher if you quote from a reading passage or bring up pertinent knowledge you may have gained during the class.

- If no one agrees to read the essay, read over your own first draft and look for errors or spots where you could clarify your meaning. Reading the essay out loud often helps, as you’ll be able to hear sentences that aren’t quite coherent.
- This step does not apply to essays written during a timed or in-class exam, as you won't be able to ask peers to read your work.

- It’s always a mistake to submit an unrevised first draft, whether for a grade, for admissions, or for a scholarship essay.
- However, if you're writing an essay for a timed exam, it's okay if you don't have enough time to combine multiple drafts before the time runs out.
Condensing Your Essay

- So, if you’re writing about Death of a Salesman , an article about symbolism in Arthur Miller’s plays would be useful. But, an article about the average cost of Midwestern hotels in the 1940s would be irrelevant.
- If you’re writing a scholarship essay, double-check the instructions to clarify what types of sources you’re allowed to use.

- A common cliche you might find in an essay is a statement like, "I'm the hardest working student at my school."
- For example, this sentence is too verbose: “I have been a relentlessly stellar student throughout my entire high school career since I am a seriously dedicated reader and thoroughly apply myself to every assignment I receive in class.”
- Shortened, it could read: “I was a stellar student throughout my high school career since I was a dedicated reader and applied myself to every assignment I received.”

- Avoid writing something like, “Willie Loman can be seen as having achieved little through his life because he is not respected by his sons and is not valued by his co-workers.”
- Instead, write, “Arthur Miller shows readers that Willie’s life accomplishments have amounted to little. Willie’s sons do not look up to him, and his co-workers treat him without respect.”

- For example, if you’re trying to prove that WWII pulled the USA out of the Great Depression, focus strictly on an economic argument.
- Avoid bringing in other, less convincing topics. For example, don’t dedicate a paragraph to discussing how much it cost the USA to build fighter jets in 1944.
Short Essay Template and Example

Expert Q&A
- When composing the text of your essay, resist the temptation to pull words from a thesaurus in an attempt to sound academic or intelligent. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- If your high school or college has an online or in-person writing center, schedule an appointment. Taking advantage of this type of service can improve your essay and help you recognize structural or grammatical problems you would not have noticed otherwise. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/common_writing_assignments/research_papers/choosing_a_topic.html
- ↑ https://monroecollege.libguides.com/c.php?g=589208&p=4072926
- ↑ https://www.utep.edu/extendeduniversity/utepconnect/blog/march-2017/4-ways-to-differentiate-a-good-source-from-a-bad-source.html
- ↑ https://www.grammarly.com/blog/essay-outline/
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/thesis-statements/
- ↑ https://libguides.newcastle.edu.au/how-to-write-an-essay/essay-introduction
- ↑ https://lsa.umich.edu/sweetland/undergraduates/writing-guides/how-do-i-write-an-intro--conclusion----body-paragraph.html
- ↑ https://mlpp.pressbooks.pub/writingsuccess/chapter/8-3-drafting/
- ↑ https://www.trentu.ca/academicskills/how-guides/how-write-university/how-approach-any-assignment/writing-english-essay/using-secondary
- ↑ https://patch.com/michigan/berkley/bp--how-to-shorten-your-college-essay-without-ruining-it
- ↑ https://writing.wisc.edu/handbook/style/ccs_activevoice/
- ↑ https://wordcounter.net/blog/2016/01/26/101025_how-to-reduce-essay-word-count.html
About This Article

- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
D. L. Smith
Sep 9, 2019
Did this article help you?

Aug 15, 2023

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Develop the tech skills you need for work and life
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Assignments
- Annotated Bibliography
- Analyzing a Scholarly Journal Article
- Group Presentations
- Dealing with Nervousness
- Using Visual Aids
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
- Types of Structured Group Activities
- Group Project Survival Skills
- Leading a Class Discussion
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Works
- Writing a Case Analysis Paper
- Writing a Case Study
- About Informed Consent
- Writing Field Notes
- Writing a Policy Memo
- Writing a Reflective Paper
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Generative AI and Writing
- Acknowledgments
Reflective writing is a process of identifying, questioning, and critically evaluating course-based learning opportunities, integrated with your own observations, experiences, impressions, beliefs, assumptions, or biases, and which describes how this process stimulated new or creative understanding about the content of the course.
A reflective paper describes and explains in an introspective, first person narrative, your reactions and feelings about either a specific element of the class [e.g., a required reading; a film shown in class] or more generally how you experienced learning throughout the course. Reflective writing assignments can be in the form of a single paper, essays, portfolios, journals, diaries, or blogs. In some cases, your professor may include a reflective writing assignment as a way to obtain student feedback that helps improve the course, either in the moment or for when the class is taught again.
How to Write a Reflection Paper . Academic Skills, Trent University; Writing a Reflection Paper . Writing Center, Lewis University; Critical Reflection . Writing and Communication Centre, University of Waterloo; Tsingos-Lucas et al. "Using Reflective Writing as a Predictor of Academic Success in Different Assessment Formats." American Journal of Pharmaceutical Education 81 (2017): Article 8.
Benefits of Reflective Writing Assignments
As the term implies, a reflective paper involves looking inward at oneself in contemplating and bringing meaning to the relationship between course content and the acquisition of new knowledge . Educational research [Bolton, 2010; Ryan, 2011; Tsingos-Lucas et al., 2017] demonstrates that assigning reflective writing tasks enhances learning because it challenges students to confront their own assumptions, biases, and belief systems around what is being taught in class and, in so doing, stimulate student’s decisions, actions, attitudes, and understanding about themselves as learners and in relation to having mastery over their learning. Reflection assignments are also an opportunity to write in a first person narrative about elements of the course, such as the required readings, separate from the exegetic and analytical prose of academic research papers.
Reflection writing often serves multiple purposes simultaneously. In no particular order, here are some of reasons why professors assign reflection papers:
- Enhances learning from previous knowledge and experience in order to improve future decision-making and reasoning in practice . Reflective writing in the applied social sciences enhances decision-making skills and academic performance in ways that can inform professional practice. The act of reflective writing creates self-awareness and understanding of others. This is particularly important in clinical and service-oriented professional settings.
- Allows students to make sense of classroom content and overall learning experiences in relation to oneself, others, and the conditions that shaped the content and classroom experiences . Reflective writing places you within the course content in ways that can deepen your understanding of the material. Because reflective thinking can help reveal hidden biases, it can help you critically interrogate moments when you do not like or agree with discussions, readings, or other aspects of the course.
- Increases awareness of one’s cognitive abilities and the evidence for these attributes . Reflective writing can break down personal doubts about yourself as a learner and highlight specific abilities that may have been hidden or suppressed due to prior assumptions about the strength of your academic abilities [e.g., reading comprehension; problem-solving skills]. Reflective writing, therefore, can have a positive affective [i.e., emotional] impact on your sense of self-worth.
- Applying theoretical knowledge and frameworks to real experiences . Reflective writing can help build a bridge of relevancy between theoretical knowledge and the real world. In so doing, this form of writing can lead to a better understanding of underlying theories and their analytical properties applied to professional practice.
- Reveals shortcomings that the reader will identify . Evidence suggests that reflective writing can uncover your own shortcomings as a learner, thereby, creating opportunities to anticipate the responses of your professor may have about the quality of your coursework. This can be particularly productive if the reflective paper is written before final submission of an assignment.
- Helps students identify their tacit [a.k.a., implicit] knowledge and possible gaps in that knowledge . Tacit knowledge refers to ways of knowing rooted in lived experience, insight, and intuition rather than formal, codified, categorical, or explicit knowledge. In so doing, reflective writing can stimulate students to question their beliefs about a research problem or an element of the course content beyond positivist modes of understanding and representation.
- Encourages students to actively monitor their learning processes over a period of time . On-going reflective writing in journals or blogs, for example, can help you maintain or adapt learning strategies in other contexts. The regular, purposeful act of reflection can facilitate continuous deep thinking about the course content as it evolves and changes throughout the term. This, in turn, can increase your overall confidence as a learner.
- Relates a student’s personal experience to a wider perspective . Reflection papers can help you see the big picture associated with the content of a course by forcing you to think about the connections between scholarly content and your lived experiences outside of school. It can provide a macro-level understanding of one’s own experiences in relation to the specifics of what is being taught.
- If reflective writing is shared, students can exchange stories about their learning experiences, thereby, creating an opportunity to reevaluate their original assumptions or perspectives . In most cases, reflective writing is only viewed by your professor in order to ensure candid feedback from students. However, occasionally, reflective writing is shared and openly discussed in class. During these discussions, new or different perspectives and alternative approaches to solving problems can be generated that would otherwise be hidden. Sharing student's reflections can also reveal collective patterns of thought and emotions about a particular element of the course.
Bolton, Gillie. Reflective Practice: Writing and Professional Development . London: Sage, 2010; Chang, Bo. "Reflection in Learning." Online Learning 23 (2019), 95-110; Cavilla, Derek. "The Effects of Student Reflection on Academic Performance and Motivation." Sage Open 7 (July-September 2017): 1–13; Culbert, Patrick. “Better Teaching? You Can Write On It “ Liberal Education (February 2022); McCabe, Gavin and Tobias Thejll-Madsen. The Reflection Toolkit . University of Edinburgh; The Purpose of Reflection . Introductory Composition at Purdue University; Practice-based and Reflective Learning . Study Advice Study Guides, University of Reading; Ryan, Mary. "Improving Reflective Writing in Higher Education: A Social Semiotic Perspective." Teaching in Higher Education 16 (2011): 99-111; Tsingos-Lucas et al. "Using Reflective Writing as a Predictor of Academic Success in Different Assessment Formats." American Journal of Pharmaceutical Education 81 (2017): Article 8; What Benefits Might Reflective Writing Have for My Students? Writing Across the Curriculum Clearinghouse; Rykkje, Linda. "The Tacit Care Knowledge in Reflective Writing: A Practical Wisdom." International Practice Development Journal 7 (September 2017): Article 5; Using Reflective Writing to Deepen Student Learning . Center for Writing, University of Minnesota.
How to Approach Writing a Reflection Paper
Thinking About Reflective Thinking
Educational theorists have developed numerous models of reflective thinking that your professor may use to frame a reflective writing assignment. These models can help you systematically interpret your learning experiences, thereby ensuring that you ask the right questions and have a clear understanding of what should be covered. A model can also represent the overall structure of a reflective paper. Each model establishes a different approach to reflection and will require you to think about your writing differently. If you are unclear how to fit your writing within a particular reflective model, seek clarification from your professor. There are generally two types of reflective writing assignments, each approached in slightly different ways.
1. Reflective Thinking about Course Readings
This type of reflective writing focuses on thoughtfully thinking about the course readings that underpin how most students acquire new knowledge and understanding about the subject of a course. Reflecting on course readings is often assigned in freshmen-level, interdisciplinary courses where the required readings examine topics viewed from multiple perspectives and, as such, provide different ways of analyzing a topic, issue, event, or phenomenon. The purpose of reflective thinking about course readings in the social and behavioral sciences is to elicit your opinions, beliefs, and feelings about the research and its significance. This type of writing can provide an opportunity to break down key assumptions you may have and, in so doing, reveal potential biases in how you interpret the scholarship.
If you are assigned to reflect on course readings, consider the following methods of analysis as prompts that can help you get started :
- Examine carefully the main introductory elements of the reading, including the purpose of the study, the theoretical framework being used to test assumptions, and the research questions being addressed. Think about what ideas stood out to you. Why did they? Were these ideas new to you or familiar in some way based on your own lived experiences or prior knowledge?
- Develop your ideas around the readings by asking yourself, what do I know about this topic? Where does my existing knowledge about this topic come from? What are the observations or experiences in my life that influence my understanding of the topic? Do I agree or disagree with the main arguments, recommended course of actions, or conclusions made by the author(s)? Why do I feel this way and what is the basis of these feelings?
- Make connections between the text and your own beliefs, opinions, or feelings by considering questions like, how do the readings reinforce my existing ideas or assumptions? How the readings challenge these ideas or assumptions? How does this text help me to better understand this topic or research in ways that motivate me to learn more about this area of study?
2. Reflective Thinking about Course Experiences
This type of reflective writing asks you to critically reflect on locating yourself at the conceptual intersection of theory and practice. The purpose of experiential reflection is to evaluate theories or disciplinary-based analytical models based on your introspective assessment of the relationship between hypothetical thinking and practical reality; it offers a way to consider how your own knowledge and skills fit within professional practice. This type of writing also provides an opportunity to evaluate your decisions and actions, as well as how you managed your subsequent successes and failures, within a specific theoretical framework. As a result, abstract concepts can crystallize and become more relevant to you when considered within your own experiences. This can help you formulate plans for self-improvement as you learn.
If you are assigned to reflect on your experiences, consider the following questions as prompts to help you get started :
- Contextualize your reflection in relation to the overarching purpose of the course by asking yourself, what did you hope to learn from this course? What were the learning objectives for the course and how did I fit within each of them? How did these goals relate to the main themes or concepts of the course?
- Analyze how you experienced the course by asking yourself, what did I learn from this experience? What did I learn about myself? About working in this area of research and study? About how the course relates to my place in society? What assumptions about the course were supported or refuted?
- Think introspectively about the ways you experienced learning during the course by asking yourself, did your learning experiences align with the goals or concepts of the course? Why or why do you not feel this way? What was successful and why do you believe this? What would you do differently and why is this important? How will you prepare for a future experience in this area of study?
NOTE: If you are assigned to write a journal or other type of on-going reflection exercise, a helpful approach is to reflect on your reflections by re-reading what you have already written. In other words, review your previous entries as a way to contextualize your feelings, opinions, or beliefs regarding your overall learning experiences. Over time, this can also help reveal hidden patterns or themes related to how you processed your learning experiences. Consider concluding your reflective journal with a summary of how you felt about your learning experiences at critical junctures throughout the course, then use these to write about how you grew as a student learner and how the act of reflecting helped you gain new understanding about the subject of the course and its content.
ANOTHER NOTE: Regardless of whether you write a reflection paper or a journal, do not focus your writing on the past. The act of reflection is intended to think introspectively about previous learning experiences. However, reflective thinking should document the ways in which you progressed in obtaining new insights and understandings about your growth as a learner that can be carried forward in subsequent coursework or in future professional practice. Your writing should reflect a furtherance of increasing personal autonomy and confidence gained from understanding more about yourself as a learner.
Structure and Writing Style
There are no strict academic rules for writing a reflective paper. Reflective writing may be assigned in any class taught in the social and behavioral sciences and, therefore, requirements for the assignment can vary depending on disciplinary-based models of inquiry and learning. The organization of content can also depend on what your professor wants you to write about or based on the type of reflective model used to frame the writing assignment. Despite these possible variations, below is a basic approach to organizing and writing a good reflective paper, followed by a list of problems to avoid.
Pre-flection
In most cases, it's helpful to begin by thinking about your learning experiences and outline what you want to focus on before you begin to write the paper. This can help you organize your thoughts around what was most important to you and what experiences [good or bad] had the most impact on your learning. As described by the University of Waterloo Writing and Communication Centre, preparing to write a reflective paper involves a process of self-analysis that can help organize your thoughts around significant moments of in-class knowledge discovery.
- Using a thesis statement as a guide, note what experiences or course content stood out to you , then place these within the context of your observations, reactions, feelings, and opinions. This will help you develop a rough outline of key moments during the course that reflect your growth as a learner. To identify these moments, pose these questions to yourself: What happened? What was my reaction? What were my expectations and how were they different from what transpired? What did I learn?
- Critically think about your learning experiences and the course content . This will help you develop a deeper, more nuanced understanding about why these moments were significant or relevant to you. Use the ideas you formulated during the first stage of reflecting to help you think through these moments from both an academic and personal perspective. From an academic perspective, contemplate how the experience enhanced your understanding of a concept, theory, or skill. Ask yourself, did the experience confirm my previous understanding or challenge it in some way. As a result, did this highlight strengths or gaps in your current knowledge? From a personal perspective, think introspectively about why these experiences mattered, if previous expectations or assumptions were confirmed or refuted, and if this surprised, confused, or unnerved you in some way.
- Analyze how these experiences and your reactions to them will shape your future thinking and behavior . Reflection implies looking back, but the most important act of reflective writing is considering how beliefs, assumptions, opinions, and feelings were transformed in ways that better prepare you as a learner in the future. Note how this reflective analysis can lead to actions you will take as a result of your experiences, what you will do differently, and how you will apply what you learned in other courses or in professional practice.
Basic Structure and Writing Style
Reflective Background and Context
The first part of your reflection paper should briefly provide background and context in relation to the content or experiences that stood out to you. Highlight the settings, summarize the key readings, or narrate the experiences in relation to the course objectives. Provide background that sets the stage for your reflection. You do not need to go into great detail, but you should provide enough information for the reader to understand what sources of learning you are writing about [e.g., course readings, field experience, guest lecture, class discussions] and why they were important. This section should end with an explanatory thesis statement that expresses the central ideas of your paper and what you want the readers to know, believe, or understand after they finish reading your paper.
Reflective Interpretation
Drawing from your reflective analysis, this is where you can be personal, critical, and creative in expressing how you felt about the course content and learning experiences and how they influenced or altered your feelings, beliefs, assumptions, or biases about the subject of the course. This section is also where you explore the meaning of these experiences in the context of the course and how you gained an awareness of the connections between these moments and your own prior knowledge.
Guided by your thesis statement, a helpful approach is to interpret your learning throughout the course with a series of specific examples drawn from the course content and your learning experiences. These examples should be arranged in sequential order that illustrate your growth as a learner. Reflecting on each example can be done by: 1) introducing a theme or moment that was meaningful to you, 2) describing your previous position about the learning moment and what you thought about it, 3) explaining how your perspective was challenged and/or changed and why, and 4) introspectively stating your current or new feelings, opinions, or beliefs about that experience in class.
It is important to include specific examples drawn from the course and placed within the context of your assumptions, thoughts, opinions, and feelings. A reflective narrative without specific examples does not provide an effective way for the reader to understand the relationship between the course content and how you grew as a learner.
Reflective Conclusions
The conclusion of your reflective paper should provide a summary of your thoughts, feelings, or opinions regarding what you learned about yourself as a result of taking the course. Here are several ways you can frame your conclusions based on the examples you interpreted and reflected on what they meant to you. Each example would need to be tied to the basic theme [thesis statement] of your reflective background section.
- Your reflective conclusions can be described in relation to any expectations you had before taking the class [e.g., “I expected the readings to not be relevant to my own experiences growing up in a rural community, but the research actually helped me see that the challenges of developing my identity as a child of immigrants was not that unusual...”].
- Your reflective conclusions can explain how what you learned about yourself will change your actions in the future [e.g., “During a discussion in class about the challenges of helping homeless people, I realized that many of these people hate living on the street but lack the ability to see a way out. This made me realize that I wanted to take more classes in psychology...”].
- Your reflective conclusions can describe major insights you experienced a critical junctures during the course and how these moments enhanced how you see yourself as a student learner [e.g., "The guest speaker from the Head Start program made me realize why I wanted to pursue a career in elementary education..."].
- Your reflective conclusions can reconfigure or reframe how you will approach professional practice and your understanding of your future career aspirations [e.g.,, "The course changed my perceptions about seeking a career in business finance because it made me realize I want to be more engaged in customer service..."]
- Your reflective conclusions can explore any learning you derived from the act of reflecting itself [e.g., “Reflecting on the course readings that described how minority students perceive campus activities helped me identify my own biases about the benefits of those activities in acclimating to campus life...”].
NOTE: The length of a reflective paper in the social sciences is usually less than a traditional research paper. However, don’t assume that writing a reflective paper is easier than writing a research paper. A well-conceived critical reflection paper often requires as much time and effort as a research paper because you must purposeful engage in thinking about your learning in ways that you may not be comfortable with or used to. This is particular true while preparing to write because reflective papers are not as structured as a traditional research paper and, therefore, you have to think deliberately about how you want to organize the paper and what elements of the course you want to reflect upon.
ANOTHER NOTE: Do not limit yourself to using only text in reflecting on your learning. If you believe it would be helpful, consider using creative modes of thought or expression such as, illustrations, photographs, or material objects that reflects an experience related to the subject of the course that was important to you [e.g., like a ticket stub to a renowned speaker on campus]. Whatever non-textual element you include, be sure to describe the object's relevance to your personal relationship to the course content.
Problems to Avoid
A reflective paper is not a “mind dump” . Reflective papers document your personal and emotional experiences and, therefore, they do not conform to rigid structures, or schema, to organize information. However, the paper should not be a disjointed, stream-of-consciousness narrative. Reflective papers are still academic pieces of writing that require organized thought, that use academic language and tone , and that apply intellectually-driven critical thinking to the course content and your learning experiences and their significance.
A reflective paper is not a research paper . If you are asked to reflect on a course reading, the reflection will obviously include some description of the research. However, the goal of reflective writing is not to present extraneous ideas to the reader or to "educate" them about the course. The goal is to share a story about your relationship with the learning objectives of the course. Therefore, unlike research papers, you are expected to write from a first person point of view which includes an introspective examination of your own opinions, feelings, and personal assumptions.
A reflection paper is not a book review . Descriptions of the course readings using your own words is not a reflective paper. Reflective writing should focus on how you understood the implications of and were challenged by the course in relation to your own lived experiences or personal assumptions, combined with explanations of how you grew as a student learner based on this internal dialogue. Remember that you are the central object of the paper, not the research materials.
A reflective paper is not an all-inclusive meditation. Do not try to cover everything. The scope of your paper should be well-defined and limited to your specific opinions, feelings, and beliefs about what you determine to be the most significant content of the course and in relation to the learning that took place. Reflections should be detailed enough to covey what you think is important, but your thoughts should be expressed concisely and coherently [as is true for any academic writing assignment].
Critical Reflection . Writing and Communication Centre, University of Waterloo; Critical Reflection: Journals, Opinions, & Reactions . University Writing Center, Texas A&M University; Connor-Greene, Patricia A. “Making Connections: Evaluating the Effectiveness of Journal Writing in Enhancing Student Learning.” Teaching of Psychology 27 (2000): 44-46; Good vs. Bad Reflection Papers , Franklin University; Dyment, Janet E. and Timothy S. O’Connell. "The Quality of Reflection in Student Journals: A Review of Limiting and Enabling Factors." Innovative Higher Education 35 (2010): 233-244: How to Write a Reflection Paper . Academic Skills, Trent University; Amelia TaraJane House. Reflection Paper . Cordia Harrington Center for Excellence, University of Arkansas; Ramlal, Alana, and Désirée S. Augustin. “Engaging Students in Reflective Writing: An Action Research Project.” Educational Action Research 28 (2020): 518-533; Writing a Reflection Paper . Writing Center, Lewis University; McGuire, Lisa, Kathy Lay, and Jon Peters. “Pedagogy of Reflective Writing in Professional Education.” Journal of the Scholarship of Teaching and Learning (2009): 93-107; Critical Reflection . Writing and Communication Centre, University of Waterloo; How Do I Write Reflectively? Academic Skills Toolkit, University of New South Wales Sydney; Reflective Writing . Skills@Library. University of Leeds; Walling, Anne, Johanna Shapiro, and Terry Ast. “What Makes a Good Reflective Paper?” Family Medicine 45 (2013): 7-12; Williams, Kate, Mary Woolliams, and Jane Spiro. Reflective Writing . 2nd edition. London: Red Globe Press, 2020; Yeh, Hui-Chin, Shih-hsien Yang, Jo Shan Fu, and Yen-Chen Shih. “Developing College Students’ Critical Thinking through Reflective Writing.” Higher Education Research and Development (2022): 1-16.
Writing Tip
Focus on Reflecting, Not on Describing
Minimal time and effort should be spent describing the course content you are asked to reflect upon. The purpose of a reflection assignment is to introspectively contemplate your reactions to and feeling about an element of the course. D eflecting the focus away from your own feelings by concentrating on describing the course content can happen particularly if "talking about yourself" [i.e., reflecting] makes you uncomfortable or it is intimidating. However, the intent of reflective writing is to overcome these inhibitions so as to maximize the benefits of introspectively assessing your learning experiences. Keep in mind that, if it is relevant, your feelings of discomfort could be a part of how you critically reflect on any challenges you had during the course [e.g., you realize this discomfort inhibited your willingness to ask questions during class, it fed into your propensity to procrastinate, or it made it difficult participating in groups].
Writing a Reflection Paper . Writing Center, Lewis University; Reflection Paper . Cordia Harrington Center for Excellence, University of Arkansas.
Another Writing Tip
Helpful Videos about Reflective Writing
These two short videos succinctly describe how to approach a reflective writing assignment. They are produced by the Academic Skills department at the University of Melbourne and the Skills Team of the University of Hull, respectively.
- << Previous: Writing a Policy Memo
- Next: Writing a Research Proposal >>
- Last Updated: Mar 6, 2024 1:00 PM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/assignments
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to structure an essay: Templates and tips
How to Structure an Essay | Tips & Templates
Published on September 18, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on July 23, 2023.
The basic structure of an essay always consists of an introduction , a body , and a conclusion . But for many students, the most difficult part of structuring an essay is deciding how to organize information within the body.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
The basics of essay structure, chronological structure, compare-and-contrast structure, problems-methods-solutions structure, signposting to clarify your structure, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about essay structure.
There are two main things to keep in mind when working on your essay structure: making sure to include the right information in each part, and deciding how you’ll organize the information within the body.
Parts of an essay
The three parts that make up all essays are described in the table below.
Order of information
You’ll also have to consider how to present information within the body. There are a few general principles that can guide you here.
The first is that your argument should move from the simplest claim to the most complex . The body of a good argumentative essay often begins with simple and widely accepted claims, and then moves towards more complex and contentious ones.
For example, you might begin by describing a generally accepted philosophical concept, and then apply it to a new topic. The grounding in the general concept will allow the reader to understand your unique application of it.
The second principle is that background information should appear towards the beginning of your essay . General background is presented in the introduction. If you have additional background to present, this information will usually come at the start of the body.
The third principle is that everything in your essay should be relevant to the thesis . Ask yourself whether each piece of information advances your argument or provides necessary background. And make sure that the text clearly expresses each piece of information’s relevance.
The sections below present several organizational templates for essays: the chronological approach, the compare-and-contrast approach, and the problems-methods-solutions approach.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

The chronological approach (sometimes called the cause-and-effect approach) is probably the simplest way to structure an essay. It just means discussing events in the order in which they occurred, discussing how they are related (i.e. the cause and effect involved) as you go.
A chronological approach can be useful when your essay is about a series of events. Don’t rule out other approaches, though—even when the chronological approach is the obvious one, you might be able to bring out more with a different structure.
Explore the tabs below to see a general template and a specific example outline from an essay on the invention of the printing press.
- Thesis statement
- Discussion of event/period
- Consequences
- Importance of topic
- Strong closing statement
- Claim that the printing press marks the end of the Middle Ages
- Background on the low levels of literacy before the printing press
- Thesis statement: The invention of the printing press increased circulation of information in Europe, paving the way for the Reformation
- High levels of illiteracy in medieval Europe
- Literacy and thus knowledge and education were mainly the domain of religious and political elites
- Consequence: this discouraged political and religious change
- Invention of the printing press in 1440 by Johannes Gutenberg
- Implications of the new technology for book production
- Consequence: Rapid spread of the technology and the printing of the Gutenberg Bible
- Trend for translating the Bible into vernacular languages during the years following the printing press’s invention
- Luther’s own translation of the Bible during the Reformation
- Consequence: The large-scale effects the Reformation would have on religion and politics
- Summarize the history described
- Stress the significance of the printing press to the events of this period
Essays with two or more main subjects are often structured around comparing and contrasting . For example, a literary analysis essay might compare two different texts, and an argumentative essay might compare the strengths of different arguments.
There are two main ways of structuring a compare-and-contrast essay: the alternating method, and the block method.
Alternating
In the alternating method, each paragraph compares your subjects in terms of a specific point of comparison. These points of comparison are therefore what defines each paragraph.
The tabs below show a general template for this structure, and a specific example for an essay comparing and contrasting distance learning with traditional classroom learning.
- Synthesis of arguments
- Topical relevance of distance learning in lockdown
- Increasing prevalence of distance learning over the last decade
- Thesis statement: While distance learning has certain advantages, it introduces multiple new accessibility issues that must be addressed for it to be as effective as classroom learning
- Classroom learning: Ease of identifying difficulties and privately discussing them
- Distance learning: Difficulty of noticing and unobtrusively helping
- Classroom learning: Difficulties accessing the classroom (disability, distance travelled from home)
- Distance learning: Difficulties with online work (lack of tech literacy, unreliable connection, distractions)
- Classroom learning: Tends to encourage personal engagement among students and with teacher, more relaxed social environment
- Distance learning: Greater ability to reach out to teacher privately
- Sum up, emphasize that distance learning introduces more difficulties than it solves
- Stress the importance of addressing issues with distance learning as it becomes increasingly common
- Distance learning may prove to be the future, but it still has a long way to go
In the block method, each subject is covered all in one go, potentially across multiple paragraphs. For example, you might write two paragraphs about your first subject and then two about your second subject, making comparisons back to the first.
The tabs again show a general template, followed by another essay on distance learning, this time with the body structured in blocks.
- Point 1 (compare)
- Point 2 (compare)
- Point 3 (compare)
- Point 4 (compare)
- Advantages: Flexibility, accessibility
- Disadvantages: Discomfort, challenges for those with poor internet or tech literacy
- Advantages: Potential for teacher to discuss issues with a student in a separate private call
- Disadvantages: Difficulty of identifying struggling students and aiding them unobtrusively, lack of personal interaction among students
- Advantages: More accessible to those with low tech literacy, equality of all sharing one learning environment
- Disadvantages: Students must live close enough to attend, commutes may vary, classrooms not always accessible for disabled students
- Advantages: Ease of picking up on signs a student is struggling, more personal interaction among students
- Disadvantages: May be harder for students to approach teacher privately in person to raise issues
An essay that concerns a specific problem (practical or theoretical) may be structured according to the problems-methods-solutions approach.
This is just what it sounds like: You define the problem, characterize a method or theory that may solve it, and finally analyze the problem, using this method or theory to arrive at a solution. If the problem is theoretical, the solution might be the analysis you present in the essay itself; otherwise, you might just present a proposed solution.
The tabs below show a template for this structure and an example outline for an essay about the problem of fake news.
- Introduce the problem
- Provide background
- Describe your approach to solving it
- Define the problem precisely
- Describe why it’s important
- Indicate previous approaches to the problem
- Present your new approach, and why it’s better
- Apply the new method or theory to the problem
- Indicate the solution you arrive at by doing so
- Assess (potential or actual) effectiveness of solution
- Describe the implications
- Problem: The growth of “fake news” online
- Prevalence of polarized/conspiracy-focused news sources online
- Thesis statement: Rather than attempting to stamp out online fake news through social media moderation, an effective approach to combating it must work with educational institutions to improve media literacy
- Definition: Deliberate disinformation designed to spread virally online
- Popularization of the term, growth of the phenomenon
- Previous approaches: Labeling and moderation on social media platforms
- Critique: This approach feeds conspiracies; the real solution is to improve media literacy so users can better identify fake news
- Greater emphasis should be placed on media literacy education in schools
- This allows people to assess news sources independently, rather than just being told which ones to trust
- This is a long-term solution but could be highly effective
- It would require significant organization and investment, but would equip people to judge news sources more effectively
- Rather than trying to contain the spread of fake news, we must teach the next generation not to fall for it
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Signposting means guiding the reader through your essay with language that describes or hints at the structure of what follows. It can help you clarify your structure for yourself as well as helping your reader follow your ideas.
The essay overview
In longer essays whose body is split into multiple named sections, the introduction often ends with an overview of the rest of the essay. This gives a brief description of the main idea or argument of each section.
The overview allows the reader to immediately understand what will be covered in the essay and in what order. Though it describes what comes later in the text, it is generally written in the present tense . The following example is from a literary analysis essay on Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein .
Transitions
Transition words and phrases are used throughout all good essays to link together different ideas. They help guide the reader through your text, and an essay that uses them effectively will be much easier to follow.
Various different relationships can be expressed by transition words, as shown in this example.
Because Hitler failed to respond to the British ultimatum, France and the UK declared war on Germany. Although it was an outcome the Allies had hoped to avoid, they were prepared to back up their ultimatum in order to combat the existential threat posed by the Third Reich.
Transition sentences may be included to transition between different paragraphs or sections of an essay. A good transition sentence moves the reader on to the next topic while indicating how it relates to the previous one.
… Distance learning, then, seems to improve accessibility in some ways while representing a step backwards in others.
However , considering the issue of personal interaction among students presents a different picture.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
The structure of an essay is divided into an introduction that presents your topic and thesis statement , a body containing your in-depth analysis and arguments, and a conclusion wrapping up your ideas.
The structure of the body is flexible, but you should always spend some time thinking about how you can organize your essay to best serve your ideas.
An essay isn’t just a loose collection of facts and ideas. Instead, it should be centered on an overarching argument (summarized in your thesis statement ) that every part of the essay relates to.
The way you structure your essay is crucial to presenting your argument coherently. A well-structured essay helps your reader follow the logic of your ideas and understand your overall point.
Comparisons in essays are generally structured in one of two ways:
- The alternating method, where you compare your subjects side by side according to one specific aspect at a time.
- The block method, where you cover each subject separately in its entirety.
It’s also possible to combine both methods, for example by writing a full paragraph on each of your topics and then a final paragraph contrasting the two according to a specific metric.
You should try to follow your outline as you write your essay . However, if your ideas change or it becomes clear that your structure could be better, it’s okay to depart from your essay outline . Just make sure you know why you’re doing so.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, July 23). How to Structure an Essay | Tips & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved April 1, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/essay-structure/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, comparing and contrasting in an essay | tips & examples, how to write the body of an essay | drafting & redrafting, transition sentences | tips & examples for clear writing, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
$2,000 No Essay Scholarship
Help cover the cost of college without writing a single essay!
Niche is giving one student $2,000 to put toward tuition, housing, books or other college expenses — no essay required.
Apply below for your chance to win so you can focus on your education, not your finances. Good luck!
Min 7 characters
By proceeding you acknowledge and agree to our Privacy Policy and Terms of Use .
By proceeding you acknowledge and agree to our Privacy Policy and Terms of Use and Scholarship Rules .
Who Can Apply
All high school and college students, as well as anyone looking to attend college or graduate school in the next year. Please note: Not everyone is eligible for this scholarship. Niche sponsored scholarships and sweepstakes are for people with US citizenship or a valid Visa/US passport only. Read the scholarship rules for full eligibility requirements.
How It Works
The $2,000 “No Essay” Scholarship is an easy scholarship with no essay required! Only one entry allowed per person. The winner will be determined by random drawing and then contacted directly and announced in Niche's email newsletter and on the Scholarship Winners page.
About Niche scholarships
We believe cost shouldn’t keep anyone from pursuing a higher education, so we connect students with thousands of scholarships — many of which don’t require an essay — to help them afford college. In 2023 alone, we offered over $285,000 in Niche scholarships. Read more about Niche scholarships here or visit our FAQs .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Context shapes all processes in your brain, from visual perception to social interactions [ 1 ]. Your mind is never isolated from the world around you. The specific meaning of an object, word, emotion, or social event depends on context ( Figure 1 ). Context may be evident or subtle, real or imagined, conscious or unconscious.
Definition. 'Social Context' refers to the immediate physical and social setting in which people live or in which something happens or develops. This includes the culture that the individual was educated or lives in, and the people and institutions with whom they interact. Social context influences and, to some extent, determines thought ...
In this literary analysis, we will delve into the concept of sharing social context and how it influences the way in which stories are told and received. By examining the connections between literature and society, we will uncover the underlying messages and meanings that authors convey through their works. Through the exploration of various ...
While it may seem like a stretch to compare the task of writing a lab report and that of writing a text message, each context equally requires us to examine what counts as "appropriate." This chapter offers you tools and examples that should help you examine and respond to the social circumstances that characterize unfamiliar contexts in ...
The social context of a text is the way in which the features of the society it is set in impact on its meaning. There are two aspects to social context: the kind of society in which the characters live, and the one in which the author's text was produced. Charlotte Brontë's Jane Eyre was set in the same social context she herself lived in.
Whether we realize it or not, context is all around us. It is the fundamental way we come to understand people, situations and ideas. Everything that we think, say, see, hear, and do is a response to the external stimuli of the world. And how we regard that stimuli is largely in response to the context it's presented to us in.
Here are a few examples: 1. Historical context: Providing the time period and its current events can inform the general mood of the era, setting the stage for the tone of your piece of writing and creating an understanding of the society at the time. Historical context can inform the atmosphere for your audience, giving them context for how ...
Here are eight tips you should take to heart when writing: When writing a social justice essay, you should brainstorm for ideas, sharpen your focus, identify your purpose, find a story, use a variety of sources, define your terms, provide specific evidence and acknowledge opposing views. #1. Brainstorm creatively.
Conformity to socialization is the way a person tends to have the same behaviors of a group of people he or she is attached to. Conformity and obedience to authority in socialization is responsible in shaping or bringing up a morally upright person. The impacts of this can have diverse influences on a individuals in the ways of his/her living.
Table of contents. Step 1: Hook your reader. Step 2: Give background information. Step 3: Present your thesis statement. Step 4: Map your essay's structure. Step 5: Check and revise. More examples of essay introductions. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about the essay introduction.
Learn More. Social enterprise is mainly associated with non-profit organizations, mainly privately owned, which sell goods and services with an aim of yielding a return on investments, with the accumulated profits being ploughed back into the business or they are directed to social purposes. The profits of these organizations are not maximized ...
Q Write a short essay on how social contexts surrounding a person can contribute to his or her upbringing, beliefs and ove. Answered over 90d ago. ... Then, we present the social context network model. Step-by-step explanation. Processes in your brain, from visual perception to social interactions . Your mind is never isolated from the world ...
What is the Context? The remaining elements of this model of writing as a social activity deal with the setting in which the writing takes place. Physical context refers to the context in which writers and readers interact with a text. Writers compose texts in a variety of physical settings that can affect what and how they write.
The purpose of commentary is not simply to report things but to give readers a way to make sense of them. A commentary will help you write critically about a topic and will help you analyze this topic within a larger societal context.1. Following the models of well-known American authors John Steinbeck, Joan Didion, James Baldwin, and the other ...
Five-paragraph themes, stipulating three main points regardless of topic or argument, constituted the focus of expository writing instruction in most secondary schools. Postsecondary writing ...
Composing the Essay. Download Article. 1. Create an outline for the short essay. Before you begin writing the essay, use an outline to plan out what you want to say in each of your paragraphs. Number your paragraphs 1-3 and jot down a phrase or sentence that sums up the major point you want to make in that paragraph.
The essay writing process consists of three main stages: Preparation: Decide on your topic, do your research, and create an essay outline. Writing: Set out your argument in the introduction, develop it with evidence in the main body, and wrap it up with a conclusion. Revision: Check your essay on the content, organization, grammar, spelling ...
This essay begins by discussing the situation of blind people in nineteenth-century Europe. It then describes the invention of Braille and the gradual process of its acceptance within blind education. Subsequently, it explores the wide-ranging effects of this invention on blind people's social and cultural lives.
The discussion section is often considered the most important part of your research paper because it: Most effectively demonstrates your ability as a researcher to think critically about an issue, to develop creative solutions to problems based upon a logical synthesis of the findings, and to formulate a deeper, more profound understanding of the research problem under investigation;
Reflective writing assignments can be in the form of a single paper, essays, portfolios, journals, diaries, or blogs. In some cases, your professor may include a reflective writing assignment as a way to obtain student feedback that helps improve the course, either in the moment or for when the class is taught again.
The basic structure of an essay always consists of an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. But for many students, the most difficult part of structuring an essay is deciding how to organize information within the body. This article provides useful templates and tips to help you outline your essay, make decisions about your structure, and ...
Write a short essay on how social contexts surroundings a person can contribute to his or her up bringing,beliefs, and overall quality of life - 8595525 ... Understanding the social context of a given place requires researchers to endeavor to comprehend and interpret meaning through the eyes of those who live there rather than through the eyes ...
March 31, 2024. Help cover the cost of college without writing a single essay! Niche is giving one student $2,000 to put toward tuition, housing, books or other college expenses — no essay required. Apply below for your chance to win so you can focus on your education, not your finances. Good luck!