What is CAT6 Ethernet? The Complete Guide

Navigation What is CAT6? CAT6: Features and Specifications CAT6 vs. CAT6a CAT5 vs. CAT6 CAT6: Applications & Use Cases Conclusion CAT6 FAQ
Navigating through the myriad of Ethernet cable types and connectivity options can often seem daunting, especially when setting up a network for optimal performance. Among the most common questions that arise in this realm are the differences between various cable categories like CAT5 and CAT6, the usage of RJ45 connectors, and the choice between wired and wireless options such as WiFi. This article aims to shed light on these topics, demystifying the technical specifications and providing clear answers to frequently asked questions regarding CAT6 cables.
Whether you're setting up a home network, upgrading your business infrastructure, or simply looking to understand the benefits of CAT6 over its predecessors and wireless connections, this guide will serve as your comprehensive resource. Let's dive into the world of CAT6 and explore how it compares to other networking standards, ensuring you have all the necessary information to make informed decisions about your networking needs.

What is CAT6?
Category 6, better known as CAT6, represented a significant advancement in the Ethernet cabling industry when it was developed in 2002. Introduced to address the needs of modern networking environments, CAT6 was designed to facilitate faster data transmission speeds, minimize crosstalk (the transmission of signals between adjacent wires), and provide a robust solution for both residential and commercial network setups.
At its core, CAT6 includes four pairs of copper wire, much like its predecessor CAT5e, but it differs significantly in its capacity for performance. Where CAT5e cables provide up to 1 gigabit per second (Gbps) performance, CAT6 cables are engineered to operate at double that capacity, reaching speeds up to 2 Gbps under ideal conditions. When considering the operation of networks over longer distances, CAT6 maintains a higher quality of connection, supporting 10 Gbps speeds up to 55 meters compared to CAT5e’s markedly reduced efficiency over similar stretches.
The physical differences don’t end with the internal wiring. CAT6 cables are often better shielded than their earlier counterparts, a feature that translates to significantly reduced crosstalk and better overall network performance. This shielding varies, with some CAT6 cables incorporating a central spine that helps to reduce crosstalk further.
As a result of these advancements, CAT6 has become a popular choice for a range of applications. It is favored for professional data centers, office buildings, and other environments where high-speed internet service is critical. Moreover, as smart home technologies and other internet-dependent devices become more common, CAT6 is increasingly recommended for residential installations to future-proof home networks.
CAT6: Features and Specifications
Delving deeper into CAT6’s features and specifications reveals why it has become the go-to choice for networking needs. Beyond the basic capability of supporting data rates of 1 Gbps to 10 Gbps and maintaining these speeds over up to 55 meters, CAT6 cables are engineered to operate efficiently at a frequency of up to 250 MHz—twice that of CAT5e cables. This enhanced frequency capability is key to supporting faster data transmission and accommodating bandwidth-intensive applications without degradation in signal quality.
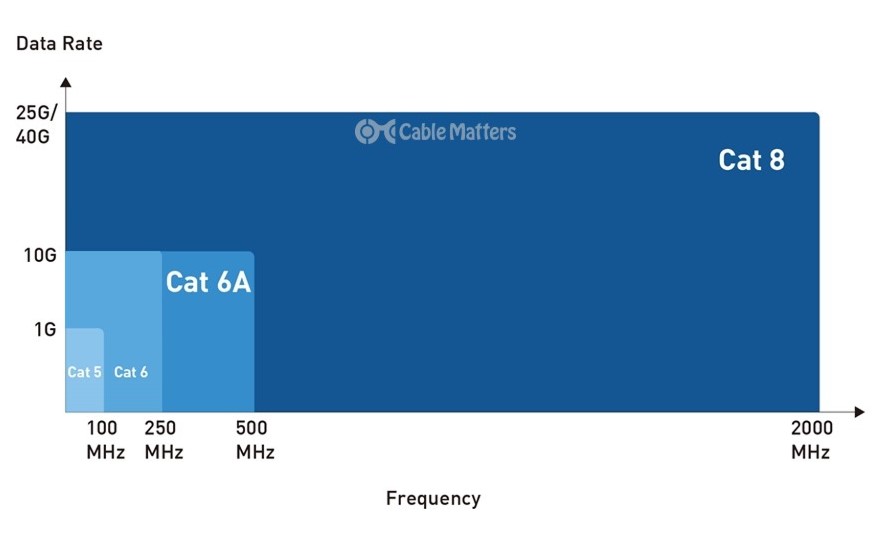
The specifications for CAT6 cables are not merely about speed and frequency; they also encompass stricter physical construction standards. The tighter winding of CAT6’s copper wires and the optional use of plastic cross-separation within the cabling work together to minimize internal crosstalk. Furthermore, to combat external interference, some CAT6 cables feature improved shielding around the wires or even individual pairs, an aspect that becomes crucial in environments with significant electromagnetic interference.
Considering these enhanced performance specifications, it’s no wonder CAT6 is recommended for applications where network reliability, speed, and bandwidth are critical. From professional data centers requiring the utmost in data transfer efficiency and reliability to commercial installations where network performance can impact business operations, CAT6 provides a future-proof solution.
Additionally, for residential users, the difference made by CAT6 can be noticeable in everyday internet use. With the increasing presence of high-definition streaming services, gaming, and smart home devices—all of which demand robust and speedy connections—CAT6 offers a significantly improved user experience compared to older cable categories.
CAT6 vs. CAT6a
In the landscape of Ethernet cabling, the distinction between CAT6 and CAT6a is critical for those looking to optimize network performance. CAT6a, or Category 6 augmented, represents an evolution of the CAT6 standard, offering enhanced capabilities designed to meet the demands of high-speed networks more effectively.
One of the most significant upgrades CAT6a brings to the table is its doubling of operational frequency to 500 MHz, compared to CAT6's 250 MHz. This increase permits more robust data transfer rates and extends the cable's maximum effective distance for 10 Gbps networking to 100 meters, without sacrificing speed or reliability. Such attributes make CAT6a an ideal candidate for expansive network settings where both distance and data integrity are paramount.
Addressing the challenges of electromagnetic interference (EMI), CAT6a introduces more stringent specifications for crosstalk and noise suppression. This is achieved through the use of thicker wire gauges and enhanced shielding techniques, such as S/FTP or F/UTP, which encase individual wire pairs or the entire cable, respectively. These improvements significantly mitigate potential signal degradation due to external noise, thus ensuring a clearer signal transmission across the network.
However, the benefits of CAT6a come with certain considerations, notably in installation. The cable's increased diameter and stiffness might pose challenges in tight conduits or crowded cable paths, potentially impacting installation logistics and costs.
Despite these installation nuances, opting for CAT6a could be considered a strategic network infrastructure investment. Its superior performance not only caters to today's high-speed connectivity demands but also positions networks to seamlessly accommodate future technological advancements. Therefore, for enterprises that anticipate growth in bandwidth needs or operate in EMI-prone environments, CAT6a presents a future-proof solution that balances current performance requirements with long-term scalability.
CAT5 vs. CAT6
The differences between CAT5 and CAT6 Ethernet cables are substantial, with CAT6 outpacing CAT5 cables in various performance parameters. A highlight of CAT6 cables includes their provision of greater bandwidth, faster data transfer rates, and better handling of crosstalk and interference.
Though originally designed in the mid-90s, CAT5 cables, specifically the later variant CAT5e (Category 5 Enhanced), continued to be employed in many networking contexts for their straightforwardness and cost-effectiveness. They had adequate specifications for many personal and small business networks—supporting frequencies up to 100 MHz and data transfer speeds up to 1 Gbps over 100 meters.
However, as the demands on networks have grown in speed and complexity—supported by developments such as high-definition streaming, online gaming, cloud technology, and complex data transfers—the capabilities of CAT5e cables have increasingly struggled to meet users' needs. This is where CAT6 cables make their mark.
CAT6 cables double the bandwidth of CAT5e, supporting frequencies up to 250 MHz. When it comes to data transfer speeds, CAT6 does not necessarily increase the rate (still offering 1 Gbps over 100 meters), but where CAT6 truly shines is in its capacity to handle 10 Gbps over shorter distances (up to 55 meters), a feat CAT5e cannot accomplish.
Besides, CAT6 presents tighter specifications for cross-talk reduction. Significantly, CAT6 cables often feature more substantial shielding and tight twisting of the internal pairs of wires, minimizing interference from both within the cable (crosstalk) and from external sources.
Given the advancements CAT6 brings, it offers benefits for any networking environment. Its superior performance in high-demand applications, resistance to interference, and increasing affordability make it an attractive upgrade option even for smaller-scale or home networks.
CAT6: Applications & Use Cases
CAT6 cables have seen wide adoption in diverse industries due to their performance capabilities. Let's discuss the areas where CAT6 shines in particular because of its unique features and specifications.
One of the most notable applications for CAT6 cabling is in data centers. These demanding environments require high-speed data transfer and reliable connections to support immense amounts of data traveling between servers and endpoints. With its ability to handle 10 Gbps up to 55 meters and 1 Gbps over longer distances (up to 100 meters), CAT6 is an excellent choice for these applications. Its shielding mechanisms also help ensure reliable performance in an environment often packed with numerous signal sources.
Beyond data centers, CAT6 is prevalent in office environments. With businesses relying heavily on digital technologies, having a network infrastructure that supports high-speed, high-bandwidth, and high-reliability connections is non-negotiable. Whether it’s to support VoIP telephony, cloud services, large-scale file transfers, or conferencing platforms, CAT6 is the standard for new installations.
Enabled by its high-frequency abilities, CAT6 is also gaining traction in audio and video applications. It can support IPTV, video conferencing, and other streaming media services, providing clear, lag-free delivery.
For residential use, CAT6 is becoming increasingly popular for modern home networks. Its ability to support superior data speeds and minimize interference is crucial with the rise of smart home technologies, HD and 4K streaming, online gaming, and working or learning-from-home scenarios.
CAT6 represents a significant leap in Ethernet cabling standards. Designed for today’s high-speed, high-data network environments, CAT6 offers greater bandwidth and faster data transfer rates than CAT5e for a marginally higher cost.
But CAT6 cables don’t just promise better speed and bandwidth. They are robustly constructed to reduce signal interference—both from within the cable and from other sources in the environment. This makes them an attractive choice for data-heavy businesses and individuals alike, offering reliable connections that can handle the demands of modern apps and devices.
Choosing to invest in CAT6 cabling can thus provide significant long-term benefits. Such an investment ensures a network of future-proofed infrastructure, able to accommodate the continued growth in demand for bandwidth and speed in the digital era. Whether you're a large enterprise, a small business, or looking to optimize your home network, CAT6 cables should be the go-to choice for your networking needs.
Can I plug a Cat6 cable into a Cat5 jack?
Absolutely. CAT6 cables are backward compatible. This means that even though CAT6 cables are equipped to handle higher speeds and volumes of data, they can be plugged into older CAT5 or CAT5e jacks and ports. But remember, the speed at which data can be transferred will be limited to the capabilities of the slower CAT5/CAT5e components in such cases.
Is Cat5 faster than Cat6?
No. CAT6 surpasses CAT5e in terms of both data transfer speed and its frequency rate. While CAT5e can support speeds up to 1 Gbps at a frequency of 100 MHz, CAT6 can support 1 Gbps at a frequency double that of CAT5e (250 MHz). Moreover, unlike CAT5e, CAT6 can manage 10 Gbps speeds at shorter distances.
Is Cat6 better than WiFi?
CAT6 provides a faster, more stable, and secure connection than WiFi. Wired connections like CAT6 allow for higher-speed data transfers, fewer interruptions from interference, and added security that WiFi cannot match. However, the convenience and flexibility of a wireless WiFi connection make it the preferred option for devices like smartphones and tablets. For tasks that require high-speed, reliable connections—such as gaming, streaming in HD/4K, or big data transfers—CAT6 is often the better choice.
What is the difference between RJ45 and Cat6?
RJ45 and CAT6 refer to different aspects of networking. RJ45 is a type of connector that is used to connect a networking cable to a network port on a computer, router, switch, or another network device. On the other hand, CAT6 (Category 6) is a standard for network cables that provide higher data rates and frequencies compared to its predecessors like CAT5 and CAT5e. Simply put, RJ45 connectors are used to plug CAT6 cables into network devices; CAT6 describes the specifications of the cable itself.
Related Products

[UL Listed] Cat 6 UTP CM Rated 24 AWG Stranded Bulk Cable in Blue - 500ft
Cable Matters [UL Listed] Cat 6 UTP CM Rated 24 AWG Stranded Bulk Cable in Blue - 500ft

Cat6 Snagless Ethernet Patch Cable
Cable Matters Cat 6 Snagless Network Patch Cable offers universal connectivity to computers and network components, such as routers, switch and other network devices.

Cat6A Snagless Shielded (SSTP/SFTP) Ethernet Patch Cable
Cable Matters Cat 6A Snagless Shielded S/FTP Ethernet Patch Cable provides superior performance for video streaming in harsh environments.
Related posts

How to Wire a Keystone Jack
Learn how to wire keystone jacks to expand your home or office network. Learn about the best tools and techniques by Cable Matters.

Ethernet Cable Types: Cat5e to Cat8 Explained
Delve into our blog post 'Ethernet Cable Types: Cat5e to Cat8 Explained'. Learn key differences, benefits, and applications for optimal networking solutions.

Best Ethernet Cable for PS5
Discover the ultimate gaming upgrade with our guide on the best Ethernet cable for PS5. From performance benefits to top recommendations, enhance your gaming experience now!
Add comment
Cancel reply to comment
5+7-THREE = The captcha value you provided is incorrect.
This website uses cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website. Learn More
- Get Great Eclipse Photos with Your Phone
- The Best Noise-Canceling Headphones to Buy
Cat 6 Ethernet Cables Explained
The standard is slowly replacing Cat 5 and Cat 5e networking cables
- Massachusetts Institute of Technology
- University of Illinois
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/headshot-00415ba557444a8a9b6bb139498b97c5.jpg)
- The Wireless Connection
- Routers & Firewalls
- Network Hubs
- Installing & Upgrading
- Wi-Fi & Wireless
Category 6 is an Ethernet cable standard defined by the Electronic Industries Association and Telecommunications Industry Association. Cat 6 is the sixth generation of twisted pair Ethernet cabling that is used in home and business networks. Cat 6 cabling is backward compatible with the Cat 5 and Cat 5e standards that preceded it.
How CAT 6 Cable Works
Category 6 cables support Gigabit Ethernet data rates of 1 gigabit per second . These cables can accommodate 10 Gigabit Ethernet connections over a limited distance—commonly about 180 feet for a single cable. Cat 6 cable contains four pairs of copper wire and uses all the pairs for signaling to obtain its high level of performance.
Other basic facts about Cat 6 cables include:
- The ends of a Cat 6 cable use the same RJ-45 standard connector as previous generations of Ethernet cables.
- The cable is identified as Cat 6 by printed text along the insulation sheath.
- An enhanced version of Cat 6, called Cat 6a, supports up to 10 Gbps speeds at greater distances.
Cat 6 vs. Cat 6a
The Category 6 Augmented cable standard, or Cat 6a, was created to further improve the performance of Cat 6 Ethernet cables. Using Cat 6a enables 10 Gigabit Ethernet data rates over a single cable run up to 328 feet. Cat 6 supports 10 Gigabit Ethernet only up to 164 feet of cable length. With the higher performance, Cat 6a cables generally cost more than Cat 6 and are slightly thicker. Cat 6a still uses the standard RJ-45 connectors.
What is an Ethernet Cable?
Cat 6 vs. cat 5e.
The history of cable design for Ethernet networks resulted in two separate efforts to improve on the previous generation Category 5 cable standard. One eventually became Cat 6. The other, called Category 5 Enhanced, was standardized earlier.
Cat 5e lacks some of the technical improvements that went into Cat 6, but it supports Gigabit Ethernet installations at a lower cost. Like Cat 6, Cat 5e uses a four wire-pair signaling scheme to achieve its data throughput rates. In contrast, Cat 5 cables contain four wire-pairs but only use two of the pairs.
Because it became available on the market sooner and offered acceptable performance for Gigabit Ethernet at a more affordable price point, Cat 5e became a popular choice for wired Ethernet installations. This value proposition, along with the relatively slow transition of the industry to 10 Gigabit Ethernet, significantly slowed the adoption of Cat 6.
Cat 6 costs more than Cat 5e, so many buyers choose Cat 5e over Cat 6. Eventually, as 10 Gigabit Ethernet speeds become more widely available, people may need to upgrade to Cat 6 or Cat 6a to take full advantage of these higher speeds.
Limitations of Cat 6
As with all other types of twisted pair EIA/TIA cabling, individual Cat 6 cable runs are limited to a maximum recommended length of 328 feet for nominal connection speeds. Cat 6 cabling supports 10 Gigabit Ethernet connections, but not at this full distance.
Get the Latest Tech News Delivered Every Day
- The Story Behind CAT5 Cables and Category 5 Ethernet
- What Is Gigabit Ethernet?
- Running Ethernet Cables Outdoors
- Introduction to Network Cables
- Introduction to Ethernet Network Technology
- What Is a Crossover Cable?
- Ethernet Cables, How They Work and How to Choose the Right One
- The Best Wireless Printer Adapters of 2024
- The Best Wi-Fi Range Extenders of 2024
- The Best Wireless Routers of 2024
- How to Connect HDMI Over Long Distances
- What Is a Patch Cable?
- The Best Cable Modem/Router Combos of 2024
- How Fast Is Ethernet Networking?
- The Fundamentals of an Ethernet LAN, Explained
- The Best Routers Under $50 of 2024
- Create Account
- Free shipping on every order*
- 30-day returns
- Help Center
Payment methods accepted
Bulk Ethernet Cable
- Above Ground
- Direct Burial
- Cat5e-350MHz
- Cat6-550MHz
- Cat6A-750MHz
Terminations
- RJ45 Connectors
- Keystone Jacks
- Strain Relief Boots
- Replacement Parts
Patch Cables
- Cat6 28AWG Unshielded
Unsure what Ethernet cable you need? Look no further than our Ethernet Cable Finder. Answer a couple of questions and let trueBOT guide you to the perfect cable for any situation. Still have questions? Check out our in-depth blogs, insightful white papers, and instructional videos on all things Ethernet cable and low voltage supplies.

Read: The Difference Between Cat6 vs Cat6A Ethernet Cable

Understand: Selecting the Correct Outdoor Ethernet Cable
Bulk Coax Cable
- Dual Shield
- Quad Shield
Coaxial Cable Connectors
- RG6 Compression F Connectors
- Compressing
Time to find coaxial cable and connectors for your install? Well, you are in the right spot! Check out our in-depth blogs, white papers, and instructional videos about everything going on in the low voltage industry and one of the best sources for coaxial information. Have questions? Our networking experts have the answers! Check out our Cable Academy. for more information.
Read: The Difference Between Dual Shield vs Quad Shield Coaxial Cable
Understand: How To: Universal RG6 Compression F Connector on Quad Shield Coaxial Cable
Fiber Patch Cables
- OS2 Simplex
Bulk Distribution Fiber
- 1 Fiber 6PK
Pre-Terminated Fiber
- Multimode Armored
- Singlemode Armored
Fiber Optic expertise at your fingertips. Looking to deepen your understanding of fiber optic technology? Look no further than trueCABLE's Cable Academy. Our extensive collection of blogs, masterfully crafted by industry experts, offers a wealth of invaluable insights into the world of fiber optic cabling. Have questions? Our networking experts have the answers. Check out our Cable Academy. for more information.
Read: Fiber Optic Splicing: Examining the Factors that Affect Splice Performance

Understand: Using Fiber Optics to Extend Your Ethernet Network Beyond Copper's Limits
Accessories
- Hook and Loop Straps
- Copper Strips
- Cable Caddy
- Cable Pulling Lubricant
- Wall Plates
Patch Panels
- Shielded Ethernet Patch Panel Bond & Ground Extension Wire Adapter
Effortless cable management. Learn how we do it. Low-voltage tools and accessories should keep your networking installations clean and organized. trueCABLE has a variety of high quality cable management tools, accessories and informative blogs for all your installation needs. Check out our Cable Academy today and expand your knowledge.
Read: Copper Fabric Strips for Bonding Shielded Ethernet Cable

Understand: When Aliens Attack! Avoiding Ethernet Alien Crosstalk

Cat6 Ethernet Cable: Which Ethernet Cables to Buy for Your Application
Written by Dave Harris, trueCABLE Technical Specialist, BICSI INST1 Certified and Don Schultz, trueCABLE Technical Manager, BICSI INSTC/INSTCF Certified and Fluke Networks Cable Test Technician
Continuing with our three-part series comparing the characteristics of Cat5e, Cat6 and Cat6A Ethernet cable, trueCABLE is exploring the benefits of Cat6. Knowing which cable to buy can save time and make your installation process simpler. We’re weighing performance versus cost to help you identify your best investment for the near future. Our experts at trueCABLE will explain how to choose an Ethernet cable and which one is best for your needs. Read on to learn more about the Cat6 Ethernet cable types.
What applications run on Cat6 Ethernet cables?
So, what is a Cat6 Ethernet Cable ? Cat6 Ethernet cable is a cost-effective option for smart home installations, enterprise networks and electronic labs. It has more stringent performance specifications to enable higher speeds and more robust data transfer yet still keep an eye on a price point. With the potential for faster speeds, greater bandwidth, and less crosstalk, Cat6 cable has dominated enterprise and home networks as the cable of choice, but is being quickly supplanted by Cat6A for new installations. Though slightly more costly than Cat5e , Cat6 cable can operate at higher network speeds and is a good fit for the wave of Power over Ethernet (PoE) technologies currently on the market, especially given that solid copper Cat6 structured cabling often uses 23 AWG copper conductors. Thicker copper equals higher current carrying capacity and better heat dissipation. Cat5e normally uses 24 AWG conductors (higher numbers are thinner gauges).
How is Cat6 different from Cat5e?
Cat6 Ethernet cable, which is a more conservatively priced option than Cat6A , supports speeds up to 10 gigabits per second (Gbps) at shorter distances of 165 feet or less. At the maximum channel length of 100 meters (328 feet) this is reduced to 5 gigabits per second (Gbp/s). Cat6 meets modern expectations for massive data transfer applications in deployments such as data centers, government websites, hospitals, and school systems.
Cat6 cable offers:
- More tightly wound wire pairs than Cat5e
- Typically a center spline
- Thicker copper conductors
- Thicker cable jacket compared to Cat5e
These features combine to provide higher performance and better resistance to interior cable noise, also known as crosstalk. Thicker cable jackets also help protect against cable-to-cable (alien) crosstalk (ANEXT), which starts becoming an issue at higher frequencies.
Interesting historical reference point: Cat5 (no “e”) Ethernet (long since deprecated) was the cabling widely used at the time 1000BASE-T was introduced and was designed to support 100 Mbp/s but had trouble reaching 1 Gbp/s. Cat5e was considered a “stop gap” measure to handle 1 Gbp/s networking until a better cable came along. The “better cable” that came along was Cat6. However, as manufacturing techniques improved over time Cat5e greatly improved while Cat6 was in development and Cat5e is still viable and in use today. Therefore, Cat6 never actually replaced Cat5e and now both are ANSI/TIA 568 recognized options. Cat6 has been called upon to do more over time as well.

Cat6 is still available at a budget friendly price point for larger installs and yet retains the possibility for future installation compatibility with switches that support IoT technology in-home or in the workplace.
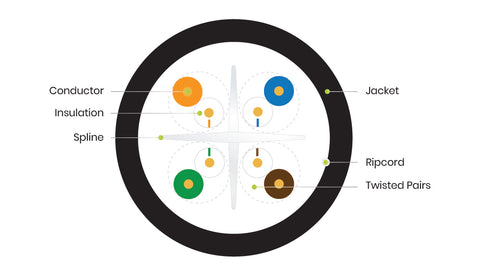
Cross-section diagram of Category 6 unshielded Ethernet cable
How is Cat6 different from Cat6A?
Cat6A supports double the bandwidth frequency as Cat6 cable and can support 10 Gigabit Ethernet at 100 meters (328 feet). At these speeds Cat6 cabling can only transmit up to 55 meters (165 feet or less) under ideal conditions--but more often is limited to 120 feet in installations with significant ANEXT (large cable bundles) . Cat6A cables must be built to even higher performance specifications and often possess construction techniques that improve upon signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of the original Cat6. Cat6, per the ANSI/TIA 568-2.D specification, supports 250 MHz bandwidth frequency and 5 Gbp/s transmission speed at 328 feet (100 meters). Cat6A cable must support bandwidth frequencies at 500 MHz and support 10 Gigabit speed to the maximum length that any Ethernet cable can be run (100 meters or 328 feet). The ANSI/TIA Cat5e bandwidth specification is only 100 MHz, and can support speeds of up to 2.5 Gbp/s transmission to the same distances.
Cost per foot
Now, you may be wondering, how much does Ethernet cable cost? The price you pay for Cat6 cable depends on several things. Shielding is more expensive but opens the possibilities for a broader range of deployments. Plenum cable is usually more expensive than riser cable. Bulk quantities are also budget friendly. Cat6 cable is more expensive than Cat5e, but less expensive than Cat6A.
Jacket ratings
Both shielded and unshielded Cat6 cable come in every type of jacket rating. Outdoor rated (direct burial) Cat6 Ethernet cable has limited resistance to combustion but is designed for outdoor deployment. The linear low density polyethylene (LLDPE) jacket provides protection from the ultraviolet (UV) radiation in sunlight, and is much more resistant to water and severe weather than indoor cable. Riser rated Cat6 Ethernet cable has some fire resistance and is designed to be used within the interiors of buildings, except for plenum spaces. A ”plenum space” is part of a building that is involved in air handling. Plenum spaces are often encountered above suspended ceilings or below raised floors. Plenum rated Cat6 Ethernet cable is more fire resistant and designed to be used in the plenum spaces of buildings due to low toxicity smoke emitted if it actually burns.
For more information on cable jacket ratings, please read Facts About Ethernet Cable Jacket Ratings.
Maximum supported bandwidth at a given distance
Cat6 (802.3bz IEEE) can achieve 5 Gbp/s for up to 100 meters when deploying NBASE-T switching technologies such as 5GBASE-T. Cat6 and Cat5e both run at 1 Gbps at 328 feet without NBASE-T technology. As mentioned above, for shorter distance runs, Cat6 can support up to 10 Gbps speed to distances up to 165 feet. This is typically in environments where large data transfer is desirable, like hospitals, school districts and data centers, but where deployment of Cat6A (or replacement of current Cat6 cabling) would be cost prohibitive and 10 Gigabit speeds are not needed past that distance. It should be noted that 120 feet is the ANSI/TIA stated distance limit for 10 Gigabit transmission on Cat6 Ethernet cable under typical alien (cable to cable) crosstalk conditions but may be increased to 165 feet on a case by case basis depending on the installation environment. In any event, each installation is different and performance test results should be certified by qualified professionals to the ANSI/TIA 568-2.D specification with documented results.
Shielded Cable
Cat6 cable is available both with and without shielding. In certain installation environments, cable with one or more internal metallic shields is required. If the installation space presents electromagnetic interference such as that from AC power cables, motors, and transformers, shielded cable might be necessary. Also, if static charge can build up on the cable jacket, such as from air movement, then shielded cable will be needed. You can read more about shielded cable in our Cable Academy blog, “Shielded vs. Unshielded Cable.” Keep in mind that shielded Ethernet cable of any Category presents increased installation complexity and challenges due to weight, more restrictive bend radius limitations, and the requirement to bond the cable shield to ground.
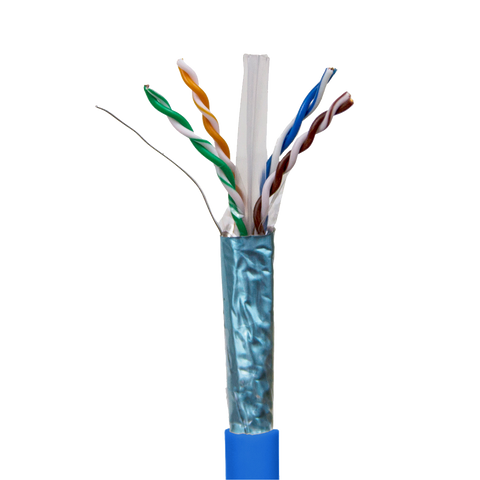
Category 6 shielded Ethernet cable
Shielding terminology
The following acronyms are used to identify common types of Ethernet cable:
- U/UTP = Unshielded completely
- F/UTP = Overall foil shield, individual twisted pairs unshielded
- S/FTP = Overall screen braid shield, individual twisted pairs are foil shielded
- U/FTP = Unshielded overall, but individual twisted pairs are foil shielded
- SF/FTP = Overall screen braid AND foil shield, plus individual twisted pairs are foil shielded
There’s much more about shielding terminology in our blog, “ Ethernet Cable Shielding Types .”
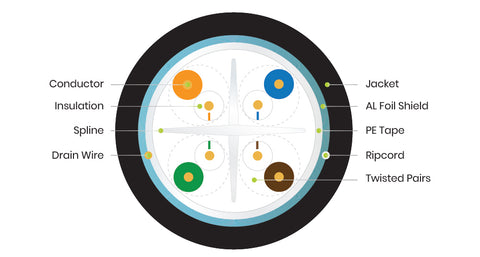
Cross-section diagram of Category 6 shielded Ethernet cable
Shielded termination hardware
To take full advantage of the benefits of shielded cable, be sure to use shielded termination hardware. The entire length of your cable installation is otherwise vulnerable to electromagnetic interference (EMI), including the ends. RJ45 plug termination on Cat6 cable may present a challenge as opposed to Cat5e due to the thickness of the cable, especially when the Cat6 cable is shielded. Conductor insulation diameter is an important metric for matching certain connectors to the correct cable. You can read more about hardware selection in our blog, “Choosing the Right Termination - Keystone Jack vs RJ45 Connector vs Field Termination Plug.”
Common bulk lengths sold (boxes versus reels)
Cat6 Ethernet cable may be purchased in lengths of 1,000 and 500 feet. Unshielded Cat6 Riser and Unshielded Cat6 Plenum are available in handy pull boxes. Want to learn more about how to know which Ethernet cable to buy?
Read the other articles in this series:
Cat6A Ethernet Cable: Know Which Ethernet Cables to Buy for Your Application Cat5e Ethernet Cable: Know Which Ethernet Cables to Buy for Your Application
So, why Cat6?
Quite frankly, Cat6 is extremely versatile. Often more than enough for home use, and typically “just enough” for business use, Cat6 cable is less expensive. Each installation is unique, and cable selection is more than “simply buy the faster cable”. Sometimes the fastest option is less desirable due to factors such as budget and ease of installation along with current and future needs. In installations that only require relatively short cable runs, Cat6 is often the most economical choice.
HAPPY NETWORKING!!
trueCABLE presents the information on our website, including the “Cable Academy” blog and live chat support, as a service to our customers and other visitors to our website subject to our website terms and conditions. While the information on this website is about data networking and electrical issues, it is not professional advice and any reliance on such material is at your own risk.
Improve Your Home WiFi: When to Use Extenders vs Access Points for Signal Issues
Basic Components of a Fiber Optic Cable
Q&A: Tracing Ethernet's Journey and What's Next
Stay connected.
Want 5% off your next order? Join our email newsletter below and text CABLE to 970-516-4986 to sign up for texts.
- Ethernet Cable
- Coax Cables
- Fiber Optic
- Cable Management
- Cable Academy
- Meet the Team
- Quality Certifications
- Shipping Policy
- Exclusive Discounts
- Headquarters Kansas City, MO
- 800.719.8277 [email protected]
© Copyright trueCABLE Inc. All Rights Reserved.
- Terms and Conditions
- Privacy Policy

We are having issues with Support Ticket Submissions. Please use the "Let's Chat" or call 1-877-297-6937 to connect with support while we resolve this issue.
— What is Cat 6 (Cat6)?
Filter by Topic
- Software (31)
- Power Inverters (9)
- FTTx Telecom (8)
- Power Adapters (6)
- Warranties (6)
- USB Hubs (5)
- USB Chargers (3)
- Notices (2)
- Travel Adapters (1)
What is Cat 6 (Cat6)?
FAQ Category: Cables
Category 6 cable, commonly referred to as Cat 6 (Cat6), is a standardized cable for Gigabit Ethernet and other network physical layers. It is backward compatible with the Category 5/5e cable standards.
Compared with Cat 5 and Cat 5e, Cat 6 features more protection for crosstalk and system noise. The Cat 6 cable standard also provides performance of up to 250 MHz and is suitable for 10BASE-T, 100BASE-TX (Fast Ethernet), 1000BASE-T/1000BASE-TX (Gigabit Ethernet), and 10GBASE-T (10-Gigabit Ethernet).
Category 6 cable can be identified by the printing on the side of the cable.
- Was this Helpful ?
- Yes No
Related Posts
Products interests, industry interests.
CyberPower Systems values your privacy and your information will never be rented or sold. Information provided will be used for CyberPower's internal use only. View our Privacy Policy .
© 2024 Cyber Power Systems (USA), Inc. CyberPower is a registered trademark and brand of Cyber Power Systems (USA), Inc. All rights reserved.
- Terms & Conditions
- Privacy Policy
- Do not sell my personal information (CCPA)
- What is Cat 5 (Cat5)?
- Differences Between Cable Types | CyberPower
Cat 6 (short for "Category 6") is an Ethernet standard. It operates at 250 MHz and supports data transfer rates of 10 Gbps . The maximum speed of Cat 6 is 10x faster than the previous standard, Cat 5e .
From the outside, Cat 6 cables look identical to Cat 5 and Cat 5e cables. They use the same RJ45 connectors and are backward-compatible with Cat 5/5e Ethernet networks. Internally, Cat 6 cables retain the same "twisted pair" wiring scheme with eight internal wires. The primary difference between Cat 6 and Cat 5 is that Cat 6 operates at 250 MHz, while Cat 5 and 5e operate at 100 MHz. The higher frequency enables Cat 6 cables to transfer data more quickly.
Cat 6 vs Cat 6a
Similar to Cat 5, Cat 6 has a variant with performance improvements. The variant is called Cat 6a (rather than Cat 6e). Cat 6a operates at 500 MHz, twice the frequency of Cat 6, but supports the same maximum data transfer rate of 10 Gbps. The difference is that Cat 6 can only transmit data at 10 Gbps for 55 meters (180 feet), while Cat 6a supports 10 Gbps for 100 meters (328 feet). A Cat 6 cable will still work over 55 meters, but the speed may decline.
While Cat 5e was the most popular Ethernet standard for nearly two decades, many modern LANs now use Cat 6 or Cat 6a cables. Even if the network equipment does not support 10 Gbps transfer speeds, Cat 6 cable is necessary to transfer data over 1 Gbps. Cat 6 cables are usually more expensive than Cat 5/5e cables, but re-running new Ethernet lines can be time-consuming and costly. Therefore, it is typically worth the extra expense to future-proof a network with faster Ethernet cables.
NOTE: Most Ethernet cables have the type of standard printed on the outer jacket.
Test Your Knowledge
In what year did Apple release the first "Apple silicon" processor?
Tech Factor
Related terms, cat 6 images.

The Tech Terms Computer Dictionary
The definition of Cat 6 on this page is an original definition written by the TechTerms.com team . If you would like to reference this page or cite this definition, please use the green citation links above.
The goal of TechTerms.com is to explain computer terminology in a way that is easy to understand. We strive for simplicity and accuracy with every definition we publish. If you have feedback about this definition or would like to suggest a new technical term, please contact us .
Sign up for the free TechTerms Newsletter
You can unsubscribe or change your frequency setting at any time using the links available in each email. Questions? Please contact us .
We just sent you an email to confirm your email address. Once you confirm your address, you will begin to receive the newsletter.
If you have any questions, please contact us .
The Tech Edvocate
- Advertisement
- Home Page Five (No Sidebar)
- Home Page Four
- Home Page Three
- Home Page Two
- Icons [No Sidebar]
- Left Sidbear Page
- Lynch Educational Consulting
- My Speaking Page
- Newsletter Sign Up Confirmation
- Newsletter Unsubscription
- Page Example
- Privacy Policy
- Protected Content
- Request a Product Review
- Shortcodes Examples
- Terms and Conditions
- The Edvocate
- The Tech Edvocate Product Guide
- Write For Us
- Dr. Lynch’s Personal Website
- The Edvocate Podcast
- Assistive Technology
- Child Development Tech
- Early Childhood & K-12 EdTech
- EdTech Futures
- EdTech News
- EdTech Policy & Reform
- EdTech Startups & Businesses
- Higher Education EdTech
- Online Learning & eLearning
- Parent & Family Tech
- Personalized Learning
- Product Reviews
- Tech Edvocate Awards
- School Ratings
How to Pack for a Water Park
4 simple ways to lower calcium in blood, how to detect embezzlement, 4 ways to transfer euros to a us bank account, 3 ways to be a cheerleader, how to make rice cakes: 12 steps, how to sing happy birthday: 13 steps, how to do toe raises: 9 steps, 3 ways to connect the ipod to itunes, how to say please in french: 7 steps, what is a category 6 cable (cat 6 cable).

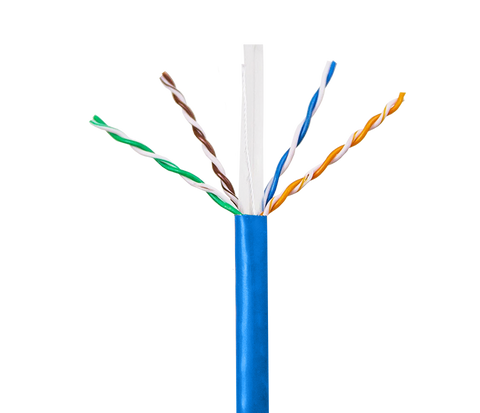
Category 6 cable, also known as Cat 6 cable, is a type of twisted pair cable that is designed for carrying high-speed data and networking signals. It is an upgrade from the older Category 5 (Cat 5) cable, and it offers higher bandwidth and a lower noise-to-signal ratio.
Cat 6 cable contains four pairs of twisted copper wires, each with its own insulation. The pairs are typically color-coded and twisted together to minimize crosstalk and interference. The cable is wrapped in a protective jacket, which can be either PVC or plenum-rated for use in air-handling spaces.
One of the primary advantages of Cat 6 cable is its ability to transmit data at speeds of up to 10 Gigabits per second (Gbps). This makes it ideal for use in high-performance networks, such as data centers and server rooms, where fast and reliable connectivity is essential. Cat 6 cable is also backwards-compatible with older Cat 5 and Cat 5e cables, allowing it to be used in a variety of different networking environments.
In addition to its high-speed capabilities, Cat 6 cable also features advanced shielding and isolation against electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI). This is accomplished through various design features, such as tighter twists in the wire pairs, improved insulation materials, and enhanced cable jacket shielding.
While Cat 6 cable is more expensive than older Cat 5 and Cat 5e cables, its improved performance and reliability make it a worthwhile investment for businesses and organizations that rely on high-speed networking. It is also becoming increasingly popular in residential settings, where homeowners are looking for faster and more reliable internet connections for streaming video, gaming, and other bandwidth-intensive activities.
In conclusion, Cat 6 cable is a high-performance data and networking cable that offers faster speeds and better interference protection than its predecessors. Whether you are building a server room, upgrading your office network, or simply looking for faster internet speeds, Cat 6 cable is an excellent choice that will provide reliable, high-speed connectivity for years to come.
What is a Candidate Key?
Strategies that students can use to start ....
Matthew Lynch
Related articles more from author.

How to Turn Off Motion Control on Nintendo Switch

How to Unlock Android Phone’s Safe Folder

Buying a Refurbished Mac? Things You Need to Know

What Is Windows Core OS?
What Are PopSockets? Reasons Why You Should Consider Buying One

Create A Multi-Camera CCTV System With Raspberry Pi and motionEyeOS

- Support Center
- Download Center
- App & Client
- Shop Refurbished
- Track Order

- Sign up Log in
Cat 6 vs. Cat 6a: The Full Comparison Guide
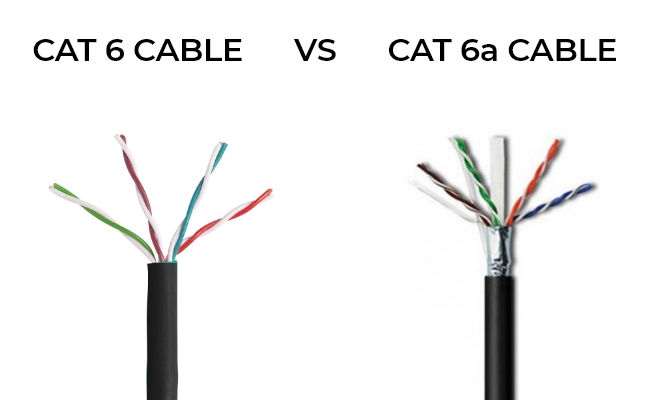
In the network, the type of Ethernet cable you choose can make a substantial difference in your connection quality and data transmission speeds. Cat 6 (Category 6) and Cat 6a (Category 6a) cables are two stalwarts in the networking cables, each with its own strengths and capabilities. Before establishing or upgrading your network infrastructure, it's crucial to understand the distinctions between these two cable options.
Cat 6 vs. Cat 6a Ethernet Cables: Key Differences
Basic of cat 6 and cat 6a ethernet cables, types of cat6 and cat 6a cables, cat 6 vs. cat 6a: which cable should you choose, the similarity of cat 6 and cat 6a.
- Cat5 vs. Cat 6 vs. Cat 6a vs. Cat 7: What's the Difference?
Both cables provide impressive performance at a cost-effective price point. However, Cat6a holds the edge with its ability to deliver faster data rates over extended distances and superior crosstalk shielding. It's worth noting that Cat6, while slightly more budget-friendly, still offers enhanced performance for shorter distances.
Speed and bandwidth
Cat 6 cables support data transfer speeds of up to 10 gigabits per second (Gbps) over a maximum distance of 100 meters (approximately 328 feet). They have a bandwidth of 250 MHz. While, Cat 6a cables are designed to handle data transfer speeds of up to 10 Gbps over a longer distance, up to 100 meters (approximately 328 feet). They have a significantly higher bandwidth of 500 MHz.
Cat 6 cables commonly feature U/FTP (Unshielded with Foil Twisted Pair) or F/UTP (Foiled Twisted Pair) configurations, which provide a layer of overall foil shielding. Some Cat 6 cables may not have individual pair shielding, relying primarily on the foil shielding for EMI protection.
Cat 6a cables often incorporate more robust shielding options, such as S/FTP (Shielded with Foil Twisted Pair) or F/FTP (Foiled Twisted Pair) configurations. In addition to the overall foil shield, Cat 6a cables usually have individual pair shielding, offering enhanced protection against electromagnetic interference and crosstalk.
Cable thickness
Cat 6 cables are typically thinner and more flexible than Cat 6a cables, which can make them easier to work with in tight spaces or when bending around corners.
Due to their high-quality materials, Cat6a cables come at a higher cost than Cat6 cables. Moreover, upgrading a network to Cat6a entails cable replacement and adopting higher-performance switches and other network infrastructure components.
Patch panels for servers
In practical terms, there are no significant distinctions between Cat6 and Cat6a patch panels. However, it's important to note that the larger dimensions of Cat6a cables and their resulting increased minimum bend radius can alter the installation demands, cable handling procedures, and considerations for pathway and space design.
Comparison table
Here is a comparison table of cat 6 and cat 6a:
After knowing the key differences of cat 6 and cat 6a, let's explore their details.
What is cat 6 Ethernet Cables?
Cat 6 is a standardized twisted-pair Ethernet cable that employs the familiar 8P8C connector, also known as RJ45, on both ends. This design ensures backward compatibility with earlier Ethernet cable standards like Cat 5e, Cat 5, and their predecessors.
Despite this compatibility, Cat 6 stands out for its elevated performance capabilities, accommodating speeds of up to 10 Gbps across distances spanning up to 55 meters. It's noteworthy that beyond this 55-meter length and up to the standard Ethernet maximum of 100 meters, the data rate aligns with Cat 5e, capping at 1 Gbps.
Furthermore, the cost-effectiveness and widespread availability of Cat 6 cables contribute to their prominence as a favored choice for networks in residential settings and small to medium-sized businesses.
What is cat 6a Ethernet Cables?
Cat 6a cables build upon the advantages of Category 6 cables while elevating their capabilities through enhanced performance and superior shielding. These cables can support higher frequencies, rendering them adept at handling elevated data rates across extended distances. With a rating of 10 Gbps over 100 meters, Cat 6a cables excel in delivering improved performance due to upgraded shielding and decreased crosstalk among the cable's twisted pairs.
Cat 6a cables prove particularly advantageous in scenarios demanding dependable, high-speed connectivity. These encompass applications like data centers, enterprise networks, and settings where the imperative is to curtail interference and signal attenuation.
Broadly speaking, Cat6 and Cat6a cables can be classified into two main categories: shielded and unshielded. Shielded cables typically incorporate an outer shielding layer around individual twisted pairs or all pairs collectively. Depending on the intended usage, varying degrees of shielding are available to cater to diverse applications.
U/UTP: Commonly known as UTP, this is the prevailing and widely embraced cable type. Comprising four twisted pairs, UTP lacks a shielding structure. Despite this, it features symmetrical pairs and a balanced design that aids in mitigating NEXT (Near-End Crosstalk).
F/UTP: F/UTP indicates a cable with four unshielded twisted pairs enveloped by an overarching outer foil shield. This shielding mechanism provides a degree of protection against interference.
U/FTP : U/FTP does not boast external shielding, but each twisted pair possesses an individual foil screen. This arrangement serves to deter crosstalk interference.
F/FTP: F/FTP incorporates four foil-shielded twisted pairs, fortified by an external foil shield. This design enhances the shielding for improved signal integrity.
S/FTP: S/FTP combines the shielding prowess of four foil-shielded twisted pairs with an overall outer braid screen. This robust shielding structure bolsters protection against external interference.
SF/FTP: Offering the utmost safeguarding against interference, SF/FTP boasts a dual-layer defense. It features both braid and foil shielding in conjunction with foiled twisted pairs, ensuring comprehensive protection for the cable.
Let's explore some scenarios in which you might choose either Cat 6 or Cat 6a Ethernet cables based on specific networking needs.
Home network with standard usage
If you're setting up a basic home network for everyday internet browsing, streaming, and occasional online gaming, Cat 6 cables are likely sufficient. They offer 1 Gbps speeds, which are more than enough for standard household activities. Cat 6 cables are also thinner and more flexible, making them easier to install around your home.
Large office or data center
In environments where a significant amount of data needs to be transmitted quickly and without interruption, Cat 6a is preferable. Cat 6a's 10 Gbps speeds and enhanced shielding help prevent crosstalk and interference, making it suitable for data centers, larger offices, and professional settings.
Future-Proofing for network upgrades
If you're planning for future network upgrades or want to ensure your cabling infrastructure remains relevant for years, Cat 6a is the better choice. It supports higher bandwidth, making it more suitable for handling new technologies and increased data demands.
While Cat 6 and Cat 6a possess distinct features that set them apart, notable similarities form the common ground upon which their capabilities are built.
RJ45 connectors
An RJ45 connector, also known as an 8P8C connector, is the universal interface for Ethernet cables. Both Cat 6 and Cat 6A cables utilize this familiar connector type, ensuring compatibility with a wide range of networking devices and equipment.
Maximum data rate
Both cable types share the same maximum data rate of 10 Gbps (gigabits per second). This means that whether you opt for Cat 6 or Cat 6A, you're assured of their capability to handle high-speed data transfer, making them suitable for various applications.
Backward compatibility
Both Cat 6 and Cat 6a cables are designed with backward compatibility in mind. They can be seamlessly integrated into existing networks that use earlier Ethernet standards, such as Cat 5 and Cat 5e. This feature ensures a smooth transition when upgrading network components.
Twisted pair design
Both Cat 6 and Cat 6a cables are built upon the foundation of a twisted pair design. This entails four pairs of copper wires, each individually insulated and twisted together. This design minimizes electromagnetic interference and crosstalk, improving signal integrity and data transmission quality.
Cat5 vs. Cat 6 vs. Cat 6a vs. Cat 7: What's the Difference?
Besides Cat 6 and Cat 6a, someone may be interested in Cat 5 and Cat 7. Let's explore their distinctions.
What is Cat5?
Cat 5 is typically the baseline standard for hosting VoIP services. The numeric designation signifies the cable's data-handling capabilities, with Cat 5 supporting a maximum speed of 10/100 Mbps and a bandwidth of up to 100 MHz.
What is Cat7?
Cat 7 Ethernet cables are distinct within the Ethernet cable landscape. Notably, they are not recognized by industry-standard organizations such as TIA or the EIA.
Despite this, Cat 7 cables offer remarkable capabilities, surpassing Cat 6A in terms of bandwidth with an impressive 600MHz capacity. They also introduced support for 10Gbps Ethernet speeds several years ahead of Cat 6A's approval.
However, what sets them apart is their utilization of TERA GG45 connectors instead of the more common 8P8C connectors. While Cat 7 cables can still work with 8P8C connectors, this unconventional choice in connectors made them less suitable for standard network installations.
Comparison between Cat5 vs. Cat 6 vs. Cat6a vs. Cat7
1. is cat6a worth it over cat6.
If you're building a new network or upgrading an existing one and anticipate the need for higher speeds and longer cable runs, Cat6a is a worthwhile investment. However, if Cat6 can meet your current requirements and cost is a significant concern, Cat6 may still be a viable option. Ultimately, the decision should be based on your specific networking needs and budget.
2. What are the disadvantages of Cat6a cable?
One drawback is its cost. Cat6a cables are generally more expensive than Cat6 cables due to their thicker and more intricate design. This can make them less cost-effective for smaller-scale installations or budgets prioritizing cost savings.
Another disadvantage is their increased bulkiness. Cat6a cables are thicker and less flexible than Cat6 cables, which can make them more challenging to install in tight spaces or through conduits.
3. What is the life expectancy of Cat6a?
Under normal conditions and proper installation, Cat6a cables are designed to have a lifespan of up to 10-15 years or even longer.

4. Is it worth upgrading from Cat5e to Cat6a?
Upgrading from Cat5e to Cat6a can be a worthwhile investment if you require higher bandwidth, plan for future-proofing your network, need to cover longer cable distances, or operate in environments with potential interference issues.
Cat6a provides significantly better performance, supports faster data transfer rates, and offers improved resistance to crosstalk and electromagnetic interference. If your network demands 10 Gigabit Ethernet (10GbE) or higher speeds, Cat6a is a suitable choice.
Whether you choose Cat 6 or Cat 6a, it's essential to ensure proper installation and maintenance to maximize their performance. Investing in quality cables, connectors, and professional installation will help you make the most of your network infrastructure, regardless of the category you select.
If you like this article and find it helpful, share it with your friends. Got something to say about ethernet cables? Make sure you leave a comment below!
- Reolink Argus Track Review: Digging Deep
- 16MP Security Camera: Upgrade to High-Resolution Protection
- Does WiFi 6 Penetrate Walls Better?
- Is 4K Worth It? All You Need to Know
Be in the Know
Security insights & offers right into your inbox
All Comments Are Welcome
Yucy, as a proficient editor in Reolink, specializes in the field of home security. Her expertise lies in providing insightful information regarding the latest advancements in security systems, surveillance technologies, and safety measures. Comment and discuss with her!
Shopping Cart:
- --> need help? Call --> need help? --> Theme FAQs --> blog --> Compare ( 0 ) -->