
Types of Point of View: The Ultimate Guide to First Person and Third Person POV
by Joe Bunting | 72 comments
In my experience as an editor, point of view problems are among the top mistakes I see new writers make, and they instantly erode credibility and reader trust. Point of view isn't easy though, since there are so many to choose from: first person point of view, third person limited, third person omniscient, and second person.
What do those even mean? And how do you choose the right one for your story?
All stories are written from a point of view. However, when point of view goes wrong—and believe me, it goes wrong often—you threaten whatever trust you have with your reader. You also fracture their suspension of disbelief.
However, point of view is simple to master if you use common sense.
This post will define point of view, go over each of the major POVs, explain a few of the POV rules, and then point out the major pitfalls writers make when dealing with that point of view.
Table of Contents
Point of View Definition The 4 Types of Point of View The #1 POV Mistake First Person Point of View Second Person Point of View Third Person Limited Point of View Third Person Omniscient Point of View FAQ: Can you change POV in a Series? Practice Exercise
Point of View Definition
The point of view, or POV, in a story is the narrator's position in the description of events, and comes from the Latin word, punctum visus , which literally means point sight. The point of view is where a writer points the sight of the reader.
Note that point of view also has a second definition.
In a discussion, an argument, or nonfiction writing, a point of view is an opinion about a subject. This is not the type of point of view we're going to focus on in this article (although it is helpful for nonfiction writers, and for more information, I recommend checking out Wikipedia's neutral point of view policy ).
I especially like the German word for POV, which is Gesichtspunkt , translated “face point,” or where your face is pointed. Isn't that a good visual for what's involved in point of view? It's the limited perspective of what you show your reader.
Note too that point of view is sometimes called narrative mode or narrative perspective.
Why Point of View Is So Important
Why does point of view matter so much?
For a fiction writer, point of view filters everything in your story. Everything in your story must come from a point of view.
Which means if you get it wrong, your entire story is damaged.
For example, I've personally read and judged thousands of stories for literary contests, and I've found point of view mistakes in about twenty percent of them. Many of these stories would have placed much higher if only the writers hadn't made the mistakes we're going to talk about soon.
The worst part is these mistakes are easily avoidable if you're aware of them. But before we get into the common point of view mistakes, let's go over each of the four types of narrative perspective.
The Four Types of Point of View
Here are the four primary types of narration in fiction:
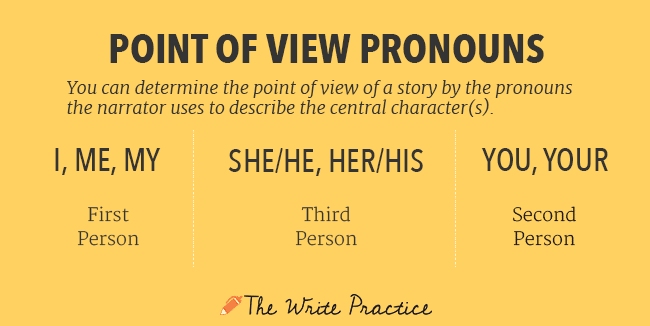
- First person point of view. First person perspective is when “I” am telling the story. The character is in the story, relating his or her experiences directly.
- Second person point of view. The story is told to “you.” This POV is not common in fiction, but it's still good to know (it is common in nonfiction).
- Third person point of view, limited. The story is about “he” or “she.” This is the most common point of view in commercial fiction. The narrator is outside of the story and relating the experiences of a character.
- Third person point of view, omniscient. The story is still about “he” or “she,” but the narrator has full access to the thoughts and experiences of all characters in the story. This is a much broader perspective.
I know you've seen and probably even used most of these point of views.
While these are the only types of POV, there are additional narrative techniques you can use to tell an interesting story. To learn how to use devices like epistolary and framing stories, check out our full narrative devices guide here .
Let's discuss each of the four types, using examples to see how they affect your story. We'll also go over the rules for each type, but first let me explain the big mistake you don't want to make with point of view.
The #1 POV Mistake
Do not begin your story with a first person narrator and then switch to a third person narrator. Do not start with third person limited and then abruptly give your narrator full omniscience. This is the most common type of error I see writers make with POV.
The guideline I learned in my first creative writing class in college is a good one:
Establish the point of view within the first two paragraphs of your story.
And above all, don't change your point of view . If you do, it creates a jarring experience for the reader and you'll threaten your reader's trust. You could even fracture the architecture of your story.
That being said, as long as you're consistent, you can sometimes get away with using multiple POV types. This isn't easy and isn't recommended, but for example, one of my favorite stories, a 7,000 page web serial called Worm , uses two point of views—first person with interludes of third-person limited—very effectively. (By the way, if you're looking for a novel to read over the next two to six months, I highly recommend it—here's the link to read for free online .) The first time the author switched point of views, he nearly lost my trust. However, he kept this dual-POV consistent over 7,000 pages and made it work.
Whatever point of view choices you make, be consistent. Your readers will thank you!
Now, let's go into detail on each of the four narrative perspective types, their best practices, and mistakes to avoid.
First Person Point of View
In first person point of view, the narrator is in the story and telling the events he or she is personally experiencing.
The simplest way to understand first person is that the narrative will use first-person pronouns like I, me, and my.
Here's a first person point of view example from Herman Melville's Moby Dick :
Call me Ishmael. Some years ago—never mind how long precisely—having little or no money in my purse, and nothing particular to interest me on shore, I thought I would sail about a little and see the watery part of the world
First person narrative perspective is one of the most common POVs in fiction. If you haven't read a book in first person point of view, you haven't been reading.
What makes this point of view interesting, and challenging, is that all of the events in the story are filtered through the narrator and explained in his or her own unique narrative voice.
This means first person narrative is both biased and incomplete, but it can also deliver a level of intimacy other POVs can't.
Other first person point of view examples can be found in these popular novels :
- The Sun Also Rises by Ernest Hemingway
- Twilight by Stephenie Meyer
- Ready Player One by Ernest Cline
- The Hunger Games by Suzanne Collins
- The Great Gatsby by F. Scott Fitzgerald
- Jane Eyre by Charlotte Brönte
First Person Narrative is Unique to Writing
There's no such thing as first person in film or theater—although voiceovers and mockumentary interviews like the ones in The Office and Modern Family provide a level of first person narrative in third person perspective film and television.
In fact, the very first novels were written in first person, modeled after popular journals and autobiographies which were first-person stories of nonfiction..
First Person Point of View is Limited
First person narrators are narrated from a single character's perspective at a time. They cannot be everywhere at once and thus cannot get all sides of the story.
They are telling their story, not necessarily the story.
First Person Point of View is Biased
In first person novels, the reader almost always sympathizes with a first person narrator, even if the narrator is an anti-hero with major flaws.
Of course, this is why we love first person narrative, because it's imbued with the character's personality, their unique perspective on the world.
The most extreme use of this bias is called an unreliable narrator. Unreliable narration is a technique used by novelists to surprise the reader by capitalize on the limitations of first person narration to make the narrator's version of events extremely prejudicial to their side and/or highly separated from reality.
You'll notice this form of narration being used when you, as the reader or audience, discover that you can't trust the narrator.
For example, Gillian Flynn's Gone Girl pits two unreliable narrators against one another. Each relates their conflicting version of events, one through typical narration and the other through journal entries. Another example is Fight Club , in which *SPOILER* the narrator has a split personality and imagines another character who drives the plot.
Other Interesting Uses of First Person Narrative:
- The classic novel Heart of Darkness is actually a first person narrative within a first person narrative. The narrator recounts verbatim the story Charles Marlow tells about his trip up the Congo river while they sit at port in England.
- William Faulkner's Absalom, Absalom is told from the first person point of view of Quentin Compson; however, most of the story is a third person account of Thomas Sutpen, his grandfather, as told to Quentin by Rosa Coldfield. Yes, it's just as complicated as it sounds!
- Salman Rushdie's award-winning Midnight's Children is told in first person, but spends most of the first several hundred pages giving a precise third person account of the narrator's ancestors. It's still first person, just a first person narrator telling a story about someone else.
Two Big Mistakes Writers Make with First Person Point of View
When writing in first person, there are two major mistakes writers make :
1. The narrator isn't likable. Your protagonist doesn't have to be a cliché hero. She doesn't even need to be good. However, she must be interesting .
The audience will not stick around for 300 pages listening to a character they don't enjoy. This is one reason why anti-heroes make great first person narrators.
They may not be morally perfect, but they're almost always interesting. (Remember Holden Caulfield in The Catcher in the Rye ?)
2. The narrator tells but doesn't show. The danger with first person is that you could spend too much time in your character's head, explaining what he's thinking and how he feels about the situation.
You're allowed to mention the character's mood, but don't forget that your reader's trust and attention relies on what your character does , not what he thinks about doing.
Second Person Point of View
While not used often in fiction—it is used regularly in nonfiction, song lyrics, and even video games—second person POV is still helpful to understand.
In this point of view, the narrator relates the experiences using second person pronouns like you and your. Thus, you become the protagonist, you carry the plot, and your fate determines the story.
We've written elsewhere about why you should try writing in second person , but in short we like second person because it:
- Pulls the reader into the action of the story
- Makes the story personal
- Surprises the reader
- Stretches your skills as a writer
Here's an example from the breakout bestseller Bright Lights, Big City by Jay Mclnerney (probably the most popular example that uses second person point of view):
You have friends who actually care about you and speak the language of the inner self. You have avoided them of late. Your soul is as disheveled as your apartment, and until you can clean it up a little you don't want to invite anyone inside.
Second person narration isn't used frequently, however there are some notable examples of it.
Some other novels that use second person point of view are:
- Remember the Choose Your Own Adventure series? If you've ever read one of these novels where you get to decide the fate of the character (I always killed my character, unfortunately), you've read second person narrative.
- The Fifth Season by N.K. Jemison
- The opening of The Night Circus by Erin Morgenstern
There are also many experimental novels and short stories that use second person, and writers such as William Faulkner, Nathaniel Hawthorne, and Albert Camus played with the style.
Breaking the fourth wall:
In the plays of William Shakespeare, a character will sometimes turn toward the audience and speak directly to them. In A Midsummer Night's Dream , Puck says:
If we shadows have offended, think but this, and all is mended, that you have but slumbered here while these visions did appear.
This narrative device of speaking directly to the audience or the reader is called breaking the fourth wall (the other three walls being the setting of the story).
To think of it another way, it's a way the writer can briefly use second person in a first or third person narrative.
It's a lot of fun! You should try it.
Third Person Point of View
In third person narration, the narrator is outside of the story and relating the experiences of a character.
The central character is not the narrator. In fact, the narrator is not present in the story at all.
The simplest way to understand third person narration is that it uses third-person pronouns, like he/she, his/hers, they/theirs.
There are two types of this point of view:
Third Person Omniscient
The all-knowing narrator has full access to all the thoughts and experiences of all the characters in the story.
Examples of Third Person Omniscient:
While much less common today, third person omniscient narration was once the predominant type, used by most classic authors. Here are some of the novels using omniscient perspective today.
- War and Peace by Leo Tolstoy
- Middlemarch by George Eliot
- Where the Crawdad's Sing by Delia Owens
- The Old Man and the Sea by Ernest Hemingway
- Still Life by Louise Penny (and all the Inspector Gamache series, which is amazing, by the way)
- Gossip Girl by Cecily von Ziegesar
- Strange the Dreamer by Laini Taylor
- Little Women by Louisa May Alcott
- Crazy Rich Asians by Kevin Kwan (one of my favorites!)
- A Wizard of Earthsea by Ursula Le Guin
- Pride and Prejudice by Jane Austen
- More third person omniscient examples can be found here
Third Person Limited
The narrator has only some, if any, access to the thoughts and experiences of the characters in the story, often just to one character .
Examples of Third Person Limited
Here's an example of a third person limited narrator from Harry Potter and the Sorcerer's Stone by J.K. Rowling:
A breeze ruffled the neat hedges of Privet Drive, which lay silent and tidy under the inky sky, the very last place you would expect astonishing things to happen. Harry Potter rolled over inside his blankets without waking up. One small hand closed on the letter beside him and he slept on, not knowing he was special, not knowing he was famous…. He couldn't know that at this very moment, people meeting in secret all over the country were holding up their glasses and saying in hushed voices: “To Harry Potter—the boy who lived!”
Some other examples of third person limited narration include:
- Game of Thrones s eries by George R.R. Martin (this has an ensemble cast, but Martin stays in one character's point of view at a time, making it a clear example of limited POV with multiple viewpoint characters, which we'll talk about in just a moment)
- For Whom the Bell Tolls by Ernest Hemingway
- The Way of Kings by Brandon Sanderson
- The Da Vinci Code by Dan Brown
- The Girl with the Dragon Tattoo by Stieg Larsson
- Ulysses by James Joyce
- Love in the Time of Cholera by Gabriel Garcia Marquez
- 1984 by George Orwell
- Orphan Train by Christina Baker Kline
- Fates and Furies by Lauren Groff
Should You Use Multiple Viewpoint Characters vs. a Single Perspective?
One feature of third person limited and first person narrative is that you have the option of having multiple viewpoint characters.
A viewpoint character is simply the character whose thoughts the reader has access to. This character become the focus of the perspective during the section of story or the story as a whole.
While it increases the difficulty, you can have multiple viewpoint characters for each narrative. For example, Game of Thrones has more than a dozen viewpoint characters throughout the series. Fifth Season has three viewpoint characters. Most romance novels have at least two viewpoint characters.
The rule is to only focus on one viewpoint character at a time (or else it changes to third person omniscient).
Usually authors with multiple viewpoint characters will change viewpoints every chapter. Some will change after section breaks. However, make sure there is some kind of break before changing so as to prepare the reader for the shift.
Should You Use Third Person Omniscient or Third Person Limited
The distinction between third persons limited and omniscient is messy and somewhat artificial.
Full omniscience in novels is rare—it's almost always limited in some way—if only because the human mind isn't comfortable handling all the thoughts and emotions of multiple people at once.
The most important consideration in third person point of view is this:
How omniscient are you going to be? How deep are you going to go into your character's mind? Will you read their thoughts frequently and deeply at any chance? Or will you rarely, if ever, delve into their emotions?
To see this question in action, imagine a couple having an argument.
Tina wants Fred to go to the store to pickup the cilantro she forgot she needed for the meal she's cooking. Fred is frustrated that she didn't ask him to pick up the cilantro on the way home from the office, before he had changed into his “homey” clothes (AKA boxer shorts).
If the narrator is fully omniscient, do you parse both Fred and Tina's emotions during each back and forth?
“Do you want to eat ? If you do, then you need to get cilantro instead of acting like a lazy pig,” Tina said, thinking, I can't believe I married this jerk. At least back then he had a six pack, not this hairy potbelly . “Figure it out, Tina. I'm sick of rushing to the store every time you forget something,” said Fred. He felt the anger pulsing through his large belly.
Going back and forth between multiple characters' emotions like this can give a reader whiplash, especially if this pattern continued over several pages and with more than two characters. This is an example of an omniscient narrator who perhaps is a little too comfortable explaining the characters' inner workings.
“ Show, don't tell ,” we're told. Sharing all the emotions of all your characters can become distraction. It can even destroy any tension you've built.
Drama requires mystery. If the reader knows each character's emotions all the time, there will be no space for drama.
How do You Handle Third Person Omniscient Well?
The way many editors and many famous authors handle this is to show the thoughts and emotions of only one character per scene (or per chapter).
George R.R. Martin, for example, uses “ point of view characters ,” characters whom he always has full access to understanding. He will write a full chapter from their perspective before switching to the next point of view character.
For the rest of the cast, he stays out of their heads.
This is an effective guideline, if not a strict rule, and it's one I would suggest to any first-time author experimenting with third person narrative. Overall, though, the principle to show, don't tell should be your guide.
The Biggest Third Person Omniscient Point of View Mistake
The biggest mistake I see writers make constantly in third person is head hopping .
When you switch point of view characters too quickly, or dive into the heads of too many characters at once, you could be in danger of what editors call “head hopping.”
When the narrator switches from one character’s thoughts to another’s too quickly, it can jar the reader and break the intimacy with the scene’s main character.
We've written about how you can get away with head hopping elsewhere , but it's a good idea to try to avoid going into more than one character's thoughts per scene or per chapter.
Can You Change POV Between Books In a Series?
What if you're writing a novel series? Can you change point of view or even POV characters between books?
The answer is yes, you can, but whether you should or not is the big question.
In general, it's best to keep your POV consistent within the same series. However, there are many examples of series that have altered perspectives or POV characters between series, either because the character in the previous books has died, for other plot reasons, or simply because of author choice.
For more on this, watch this coaching video where we get into how and why to change POV characters between books in a series:

Which Point of View Will You Use?
Here's a helpful point of view infographic to help you decide which POV to use in your writing:
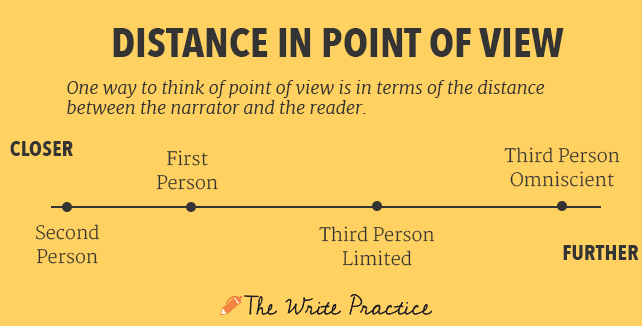
Note that these distances should be thought of as ranges, not precise calculations. A third person narrator could conceivably draw closer to the reader than a first person narrator.
Most importantly, there is no best point of view. All of these points of view are effective in various types of stories.
If you're just getting started, I would encourage you to use either first person or third person limited point of view because they're easy to understand.
However, that shouldn't stop you from experimenting. After all, you'll only get comfortable with other points of view by trying them!
Whatever you choose, be consistent. Avoid the mistakes I mentioned under each point of view.
And above all, have fun!
How about you? Which of the four points of view have you used in your writing? Why did you use it, and what did you like about it? Share in the comments .
Using a point of view you've never used before, write a brief story about a teenager who has just discovered he or she has superpowers.
Make sure to avoid the POV mistakes listed in the article above.
Write for fifteen minutes . When your time is up, post your practice in the Pro Practice Workshop (if you’re not a member yet, you can join here ). And if you post, please be sure to give feedback to your fellow writers.
We can gain just as much value giving feedback as we can writing our own books!
Happy writing!
Joe Bunting
Joe Bunting is an author and the leader of The Write Practice community. He is also the author of the new book Crowdsourcing Paris , a real life adventure story set in France. It was a #1 New Release on Amazon. Follow him on Instagram (@jhbunting).
Want best-seller coaching? Book Joe here.
72 Comments
My book is a memoir so first person is what I chose.
That was my choice for memoir, but am exploring other avenues for better character development.
I hate to be such a nag but isn’t the plural “points of view” and not “point of views”? As in brothers in law and not brother in laws
Joe, excellent post on POV. Probably the best I’ve read. Thanks!
I go for third person deep. In the PoV character’s head, using her unique voice, no author intrusion, no filter words. Am I doing it right? Far from it, but I’ve attended deep writing classes, an it’s easier to pinpoint slips.
Greetings from Greece!
Thanks for sharing this tit bit. I will be looking out for a deep writing class!
When deciding your POV, I strongly believe genre and tense should be considered as well.
Here is my first time ever uploading a “practice.” I chose to try second person, please be kind!
I couldn’t believe it when you called me, waking me from an intense fantasy dream, to tell me that you had been somehow magically transformed overnight into some type of superhero. You cannot blame me if my reaction appeared to be less than awe and more of disbelief and worry for your current state of mind. You will not want me to ask this, but have you started doing drugs? Remember, Freshman Health class, one of the signs to look for was if your friend suddenly changes or acts crazy. Well dude, you are acting more than just a little bit crazy.
Can you really fly? I have been waiting for 15 minutes for you to appear at my bedroom window, and so far nothing. I can envision you, at this very moment, running down the alley and between the houses. You will get to my back gate, jump over, and scurry behind the bushes; all bent over and believing that I can’t see you. When you are sure of your timing and that I have no idea at your mastery, you will jump out and try to convince me that you flew to your location. Please try to remember that I have known you since Kindergarten. Very little about you surprises me anymore, yet you are entertaining.
Although, you did sound different on the phone this morning, you voice had a quality I had never heard before. I would call it confidence. You weren’t trying to convince me that you had a special new talent. You were telling me, informing me.
You need new boots, I know this because I noticed the hole in the bottom of the left one as you slowly descended from the top of my window. Your smile was radiant, your arms crossed confidently across your puffed out chest. You are transformed.
You don’t look peaceful, but you look at peace. Morphine will do that to you. Your flaky, red eyes flutter in your sleep—do you dream, there? “The eyes are the windows to the soul,” so they say; with the curtains drawn, does your gaze turn inward? Do you dream of me amidst the pain, or are you cradled in the gentle embrace of the abyss?
This was your fault, you know; waving that gun in my face, pushing me around; what did you expect?
Certainly not this; no one could have expected this. Dazzling cords of fire springing from the fingertips of your would-be, should-be victim—perhaps it would’ve been wiser to hand over the money—but then, who next? Woudl you have let me go in the first place?
It wasn’t for anything venial, was it? Not for clothes or jewelry—not from what I can tell; you don’t seem the type. But it’s hard to tell. There’s not much left of your clothes, you know.
There’s not much left of you.
They’ll pour maggots over your chest and into your eyes, and flake off the blackness with gentle sponges, and alcohol over everything. That will hurt.
Your hair was so pretty. The doctor says most of it will grow back.
The cops are taking your side, you know. Figures. At least guns don’t burn. I wouldn’t be sticking around if they hadn’t cuffed me to the bed, and set it beside yours—someone in blue has a sick sense of irony.
There are birds fluttering by the windowpane, and whispers of white amidst pastels of blue. Your burns will heal. Mine have only just begun.
Yeah, having superpowers would actually be terrifying. Especially fire. Fire is bad.
I’ve used second-person before, but very rarely, so I went with it, since I’ve used all the points of view you mentioned.
Changing point of view is not only acceptable, it’s quite common. You just italicize it. I don’t know how to do that in a comment, but the general form would be something akin to: He felt around for the plot device. *Damn; I can’t find this thing. Woe is me, I am woe, woe unto me, woe betides me, etc.* He found it. *Huzzah!*
Further, your example for third-person POV includes a sputter of second-person: “the very last place *you* would expect astonishing things to happen.” This is the rhetorical “you,” not an actual pronoun—that is, “you” isn’t referring to anyone—but it still counts.
I think the argument shouldn’t be “never switch POV,” but, rather, “use the turn signal;” that is to say, give the reader an indication that the POV is changing, and why. Italics for brief periods, chapters for changing the individual narrator (you can have lots in one book), etc. Much like turning in traffic, problems generally arise not from the turn, but from the surprise. “Head hopping” is easy to avoid with, for instance, section separators—a vertical space, or a line of three little stars if the space breaks across a page, so that the reader knows a shift is happening. After familiarizing the reader with the mechanism, you can abuse it as much as you want.
Hemingway’s way works too, although I was never a big fan of Hemingway.
P.S. Give away an antique typewriter; brilliant—plenty of nostalgia; tangled ribbons, torn sheets, jammed keys; I can see why you want to inflict it on somebody else!
Wow, that was amazing descriptions. I loved your opening and closing lines as well. You did a great job of setting the dark mood of the story. Very well done.
Great post! It is quite thorough and engaging, and you offered plenty of terrific examples and practical tips.
I tend to write my stories more in the third person POV, I tend to focus on one main character but sometimes try to give some insight on another character’s perspective. The only reason I shy away from first person is because it can be emotionally exhausting to write. The funny thing is my most dramatic story was written in first person (though I did switch between two people) but I felt it would come off stonger in first person rather than third.
I’m not sure I qualify for this practice, because I’ve written in pretty much every POV: My novel is 3rd person deep, my short stories are first person, my articles are second, and my songs cover all of the above plus the others. 🙂 In my book I have several POVs, but I make sure to change the scene completely before changing the person. (Like Jerry Jenkins’/Tim Lahaye’s Left Behind.) I’m not breaking any rules like that, am I? This is a great and informative article that I’ll definitely reference in the future. Thanks for sharing your knowledge!
“Whatsoever ye do, do unto the Glory of God” Reagan
Nice post! Very helpful of keeping them strait. I tend to lean toward first person or third person limited, so I decided to try out second person for the prompt. I also used a dialogue prompt, which is the first line of the story. Here goes nothing!
“The last time I said yes to you, a lot of people died.” You say it low, under your breath, perhaps because you don’t really want him to hear you or perhaps because you don’t want to hear yourself, don’t want to remember that it happened.
“You know,” He reaches out to you, and you pull away, not wanting to touch his hands, hands that could have prevented the deaths of so many, but that have always been so gentle with you. He turns his face to the ground and, you realize, he is just as pained by the memory as you. “You know that I couldn’t have done it.”
“No.” The word comes out all wrong, because of your still upper lip, “You couldn’t have. I knew that then and I know that now.” You lock eyes with him, “Don’t you understand that’s what I’m saying? Don’t you understand that the answer is no?”
“But I can’t…” He grimaces, as though someone has twisted a knife in his gut, “I can’t just let you kill yourself.”
And now it’s your turn to grimace, to feel the pain twisting your stomach into knots. You don’t really know why you do it though. Are you afraid to die? No. That’s not it. You’re afraid for him. For the pain your death will cause him.
“You have to be strong.” You say, “For me.” This time it’s you that reaches out, to lay a hand gently on his shoulder, “You know if I don’t do this, a lot of people will die. Because I know, if I go berserk again, you won’t be able to pull the trigger. And it wouldn’t be fair to ask you to do that anyway. So the answer is no, I won’t let you be my safety net anymore.” His only response is a nod. You slide the hand gently off of his shoulder. That will be your only goodbye. It will be easier that way.
The cup that holds the poison looks normal. Just a regular coffee cup, containing your favorite blend of Colombian roast, and, of course, the substance that will kill you, quickly and painlessly, which is more then you deserve. You are not afraid. You are ready. You pick the cup up off the table and bring it close to your lips but then hesitate, because you see that shining in his eyes, the shining that means he’ll start crying. There is that twisting feeling in your stomach again. Seeing him in pain has always hurt the worst. But you can’t risk it anymore. You can’t let yourself live at the cost of more deaths.
Before you can hesitate, you take a gulp, the coffee burning your throat as it goes down. The room wobbles and you fall, but he catches you, like you knew he would, so that your head doesn’t crack open on the concrete floor.
You are paralyzed, but still conscious, and you know you only have a few seconds before the world grows dark.
He sinks to his knees, cradling you in his arms, like a child. He is no longer holding back his tears. Perhaps because he already thinks you dead.
“I wish,” He says, through sobs and tears and unbecoming bubbles of snot, “I wish you would have said yes.”
He puts his forehead to yours and you feel warm drops of moisture fall on your cheeks. In that moment you, too, wish you had said yes. That things could have been different. That you could have been alive and happy.
But you do not doubt your decision, not in the last seconds that you have breath. Because the last time you said yes to him, a lot of people died and this time, the death tole would be a single, solitary, one.
That was amazing and beautiful and very very emotional. You’ve used second person very effectively! I love it. Did this just come from the top of your head or is there a longer story behind it?
Thanks! It was a sort of top of my head thing. I used this writing prompt and also a dialogue prompt. Also, I’ve been thinking of werwolfs a lot lately for some odd reason (which is what the main character is). The rest of it kinda flowed from there. I’m glad you liked it!
Wonderful story
Not knowing much about POV, I believe I’ve been hedge hopping between them, but appear to prefer Third Person Omniscient, but will have to first discover what that last big word means? Then a re-write may well be called for!
The post is excellent, extending a warm hug of inspiration to the budding writers. I prefer ‘third person omniscient’ POV, with no room for any boredom in my narration.
Peter had his normal “I’m paying attention” look plastered on his face, but his mind was chasing super villains, decimating evil minions with mighty punches that laid ten low at one swipe.
One ear caught, “Good morning, we have a guest speaker this morning, the Rev. Charles Birch, from the 2nd Baptist Church. Rev. Birch will present the creationist side to what we have been studying in the physical sciences. Rev. Birch.”
“Blah … blah … blah,” Peter heard in his public ear but his private ear heard Dr. Daemon spewing his maleficent threats, “Capt. Magnificent, you have no hope of defeating my eco-destroying minions!” On and on it went, Birch preaching “let there be light … the dominion of man over all things … everything in it’s proper order … on the first day God created the second day … and on the third day blah blah blah,” and of course during all of this Dr. Daemon and Capt. Magnificent continued their mighty struggle on the farside of the moon, until Peters public ear heard, “of course the universe can only be 10,000 years old …”
What? What was that his public ear just heard? The Universe is a maximum of 10,000 years old? Peter was now attentive to what the pompous windbag in front of the class was saying.
A single hand raised itself amongst the sea of blank faces.
“Yes, young man?”
“Uh, Rev. Birch, how can the universe be 10,000 years old?”
“Easy uh huh,” Ms. Murphy whispered into the Reverends ear, “yes, Peter, we know the age of the universe from the generations that are recorded in the Bible.”
“But … I was at a dig in Colorado last summer and the rock strata around the fossils …”
“Humph, all conjecture. I believe God made the fossil and the rocks surrounding it ten thousand years ago.”
“All fossils are like that then?”
“Well of course. Given He made the fossils He made the surrounding rock. We only think that it took millions of years.”
Peter’s hand shot up again.
Rev. Birch tried to avoid him, but Peter was a persistent little son of… “Yes?”
“So God’s just a practical joker, creating false evidence to fool the sciences?”
The class was coming out it’s “guest speaker” lethargy, as Peter again had his hand up and spoke before acknowledged, “Does the Bible say what the speed of light is?”
“Well, now I think that has no bearing …”
Susan piped up, adding onto Peter’s question “How can Andromeda be millions of light-years away if the universe is only 10,000 years old?”
“Uh well … Andromeda?”
“No wonder He didn’t have time to save my baby sister if He wasted all that time making fossils look millions of years old,” came a loud, whispered, comment from the back of the room.
Ms. Murphy quickly ushered Rev. Birch from the classroom, and shook his hand in the hall, “Thank you so much for coming. We do appreciate all view points.”
“Who are those kids?” the Reverend asked.
“Oh, the Anderson District Scholars Program. Basically our high school geniuses in sciences and math. It’s required we allow all view points to be presented.”
Interesting. Uh, Gary, how could you have written the story in 15 minutes? Or did you dig up a fossil story you wrote millions of years ago…?
Does it matter?
It took a day and a half to percolate through my gray matter. I then took approximately 15 to 20 minutes to rough it out and get it into Draftin. Then another while, hours, lots of minutes, to get it to where I wanted to post it. Once posted, I’ve gone back and edited it, probably dozens of times, making changes as it has continued to peroclate.
I loved the flashing between reality and a story he is telling himself in his head. That’s me about 90% of the time. lol
I would also just like to add, that all creationists aren’t young earth creationists. There are a lot of different theories. Take the gap theory and theistic evolution for example. Then you have people who take it as a literal six days and others who don’t because of the bible verse that says “a day is like a thousand years and a thousand years is like a day”. Then, there are two different meanings to the word “day” if you look at the translation of the bible from Hebrew to English. So there is argument over which version of the word “day” is being used sense one can be taken literally and the other figuratively. There are literally of books written on these subjects, with Christians arguing amongst themselves over which is right. I have actually meet very few people who think the way the reverend in this story does, especially sense when you go to seminary they teach you how to not look like an idiot in these situations.
I think It’s important to remember when you’re writing Christians (or any group that often gets stereotyped) that they are not stereotypes. I’ve written atheists and it’s really easy just to make them injured people who are angry at God and dissatisfied with life, but that’s just not the reality. A lot of atheists know their stuff and have good reason for their beliefs. The same applies to Christians. If you still want to debunk the Christian in the end, I’m totally cool with it. I would just say, have the Christian have a better argument then “God put the fossils their like that”. Make it harder for your main character to debunk him, create more conflict, and make us cheer him on all the more when he wins.
Just thought that was worth mentioning. All in all, the piece is very well written.
Assumption: Pastors and or reverends have been to seminary. Not true. In the Southern Baptist Convention, at least when I was in the SBC, pastors were not assigned by the convention, nor was any kind of, pre or post graduate, pastoral education required. Pastors were called by the local church, without guidance from the convention, and could easily not even have finished high school. There are many churches that have no affiliation with any established denomination, and therefore call whomever they want as their pastor.
Oh, yes, you handled POV nicely. I’m just the kind of person that will comment on every part of the story. And I’m sorry if the comment was too much, or you didn’t find it helpful. I just tend to say what I think. But for the exercise you did a good job on the POV.
Oh the comment wasn’t too much. After 68 years my hide is pretty tough and criticism I tend to take in a constructive manner and/or with a grain of salt.
But you assumed something in your comment that, in my experience is simply not true. In my experience, the pastors that had graduated college, let alone ever attended seminary were zero. My denomination, at the time, was lucky to have pastors that finished high school.
68 years, wow that’s a lot of time and experience! You have the respect of a young Padawan.
You’re right. I was looking at it from a United Methodist view point (sense that’s the denomination I belong to). Our denomination is pretty strict with schooling and is very organized when it comes to chain of command. I discounted the fact that not all denominations and churches are like mine. My current pastor actually has a PhD and really knows what he’s talking about, so were lucky in that. I’ve also grown up in a home where ignorance isn’t tolerated. We learn about our religion (and everything else we can learn about) and are not victims of blind acceptance.
I’m sorry you had experiences with uneducated pastors. I hope they weren’t all as bad as the one in the story. If they were, then that stinks. And I do realize that there are, sadly, some pastors like the one from your story who don’t have very good arguments when it comes to the science of their faith. But I also hope that people know that all Christians aren’t, to put it frankly, stupid.
Again, assumptions. Christianity was never equated to stupidity, and above all else no attempt to equate uneducated to stupid was ever made. In all those 68 years I have seen incredibly educated people, read that doctorates, that were, above all else, stupid. I have also encountered uneducated people that could best be described as genius.
Birch was, at best, unprepared. His fault, Murphy’s fault, irrelevant, not what I was striving for. It was simply the vehicle used to convey POV switching from character to character. Birch could have been Islamic and quoting the Torah.
I wrote for 20 minutes before I realized it, so here’s what I got.
“Okay, calm down, calm down. You must get a hold of yourself” I murmured frantically to myself, I had to calm down before I blew another hole through the wall, or worse. I sat still on the hard floor, and I still couldn’t believe what had happened, it didn’t make sense at all, but there was evidence of it right before my eyes: a brick wall that now had a wide circle in its middle, still glowing hot from what I had done. Yet it was nothing compared to the silver glow that came from my hands, it felt strange, alien yet oddly comfortable, like I was wearing a glove while sparks coursed throug my arms.
I kept staring at my hands for a long time, trying to find some explanation for what had happened, it couldn’t have been me who did that, I wasn’t that special, I didn’t have some special blood, nor had I gone through any experiment, I didn’t even fit in any origin story of any Super. I was sure of that, I had even taken the tests at the Dome.
“This can’t be happening!” I screamed, letting loose all the emotions I had tried to hold back. “ARGGGHhhh!”
Then, it happened again, the room was bathed again in a silver hue as another silver beam left my hands and destroyed the wall a bit more, leaving behind only one third of what had been an sturdy wall once. That flash had confirmed my fears, this was the reality I had been the one to destroy the wall. I was angry, scared and happy at the same time, these emotions clashing one against the other as I witnessed the destruction I had wrecked in less than 10 minutes.
A grave sound pierced the old room I was in, it sounded like a lament, a sorrowful lament from a strange lonely monster. It only lasted a few seconds, and then, a piece of the roof fell about 5 meters from me. It was followed by another one, and another one bigger than the first two. Soon the whole roof was falling in, and fear once again took a hold of me. I was going to die, I knew I was going to die, buried beneath the rubis of the room.
“I, I don’t want to die” I screamed with all the force of my lungs while I tried to protect my head with my hands, I knew it wasn’t going to be enough, it wasn’t going to be enough if I wanted to live. I want to live. That thought was the last one I had before a surge of power coursed through my body, engulfing my vision in a white blanket before I passed out.
When I woke up, I felt groggy, moving my body was hard, and the air was packed with dust. But I didn’t hurt anywhere, not did I feel like I was buried under something. I slowly made my way to my knees, looking at myself for any sign of injuries, but there was none, in fact except for the dust my clothes were exactly the same as they had been before the fall in.
“This is impossible” I said out loud to no on, but how did this happen? I thought I was done for sure. It was only then that I looked around me and I was shocked for the fifth time that day.
There wasn’t any rubis near me, no for a meter around me. Was that possible? How?
Well done. There are a couple of times where the protagonist is thinking, not speaking. It would help to clarify that like using italics, or at least quoting.
Thanks for the advice- I usually use italics when it comes to thoughts, but I wasn’t sure if they were going to copy that way from writer. So I’ll try to use them next time.
I wrote one short story in the first person POV twenty five years ago. I never tried it again. Since I decided to face my fears, here I go again.
I had just opened my eyes and before I could see clearly, I was standing next to the bed jumping up and down. All of a sudden, i was standing next to the dresser drawer. did I run? I had so much energy. It seemed as if I had four cups of coffee and six energy pills. I looked across the room at the hamper. The hamper was empty and the clothes that were stuffed there were clean and folded. Last night the hamper was full of dirty clothes.. I head a soft voice that sounded like mine. “Esther, you now have super human power. The clothes were washed and folded last night. If you go to the kitchen, there is no longer a pile of dirty dishes. They have all be washed and put away. That’s all I have to say.” “What are you talking about? Who are you?” Suddenly, I was jumping up and down next to my dresser drawer.. I paused and looked into my mirror. I still looked the same. A long braid with a hair pin fastened to the left close to may ear. I did feel energized. At once I felt like I needed or wanted to run. I walked down the stairs toward the front door. The moment that i stepped out. I had dashed down the block, turned to the right and dashed down that block and Paused, standing in right in from of me was me. she looked exactly like me. She had a long braid that was pinned to the side like i did. She was wearing a light tan tee-shirt and black short shorts, blue gym shoes. Just like I am wearing. We both stood there, sweating, jumping up and down as though there were springs.under our shoes. ” Who are you?” ” I just you told you when we were in the house.” Then, she said “I’ll just tell you this much. Let’s race back to the house and up the stairs and stand next to the bed. Whoever get there first wins. “Win what,” “You’ll find out.” she dashed past me to the right. I spun back around so fast that I became dizzy. I dashed down the block and turned left. Before I knew it, I was in the kitchen. Mama was there. I was downstairs sitting at the table with her. “I am impressed. you have fixed breakfast and washed the dishes and I see you have been running.” Thanks mama, I said. Then in my mind and my ear I heard my own voice. There are two Esther. The one who procrastinate and don”t get things done and the one that get things done immediately without being told.. Then mama looked at me and smiled. She never smiles in the morning. but today, she did. She said, well today you cooked the breakfast and washed the dishes without waiting until you got home from school. I like this part of you, Esther. Then, I knew what had happened, KEN Well, there it is. Now, this means that I have used the first person again. I feel okay because, even if it’s terrible. I tried.
My go to POV is 3rd Person, limited.
Oops!! Just realized I completely blew the prompt.
Oh well … back to he drawing board (or computer).
This app helps me understand a lot about the 3d person
The first time it happened took me by surprise. It would anyone wouldn’t it? I was standing in line at the grocery store with my mom. I was tapping my foot to the beat of my own boredom, impatiently waiting for the guy ahead of us to move his cart; which if you ask me he didn’t even need. I added in some finger snaps. 1…2…and…3. The third snap brought with it an echo. When I looked around, I wasn’t in the grocery store anymore. I was in a cave.
I had waited for my eyes to adjust to the dark. The only light that was coming through was a small crack far ahead of me to my left side. I looked down at my feet for a path. Right in front of me the rock I was standing on dropped off into an abyss of black. Behind me stood the edge of the cave. I remember hyperventilating. I was so scared I couldn’t move. I started snapping my fingers again and said out loud, “think, think, think,” matching my snaps to the words in my head. On the third snap, I was back in the grocery store. Police were there talking with my mother. I had been gone a long time.
After that day I tried experimenting with my new formed ability. I started thinking of specific places that I wanted to visit; I wanted to see if I could control it. After a few failed attempts ending up in grungy basements, restaurant cooler storages, and an actor’s cottage, I got a hold of the pattern.
The success of my teleportation was contingent on my ability to breathe evenly. I needed to remain completely calm. When I realized that my ability was never going away, my excitement is what kept me from perfection. Failure after failure brought an increased frustration with myself.
It’s good. You haven’t overdone anything. You’ve shown what happened through your character really well. I particularly like the line “dropped off into an abyss of black.”
This was my attempt at using 2nd person. I rarely use it. Any advice would be appreciated. Thank you 🙂
“Now what can you tell me about God? Anybody? Yes, yes, um Alice?” “Alicia, Miss. God is often described with the three Os. He is omnipotent, all powerful, omnipresent, everywhere and omniscient, all knowing.” You suppress a groan. “Which textbook did she swallow to spew that out?” you whisper to your friend. She giggles quietly. “Shhhh,” she replies. You sigh and put your head on the table. You’ve been stuck in this stuffy classroom for half an hour and you really won’t last for another half. You can practically eat religion in this school.
“Hey you, you, sleepy child,” the teacher says. For a moment you’re confused but then your friend nudges you and you realise the woman is talking to you. ‘Can’t she learn our names?’ you think. “Yes, Miss?” you dare to risk saying. “What can you tell me about God?” she asks. ‘Oh for God’s sake,’ you think before realising the irony. “Um,” you reply. You could almost swear that time was slowing down. Everyone’s eyes turn towards you almost in slow motion before they stop as if frozen. You wish the ground would hurry up and swallow you. It takes you a moment to realise that no one is blinking. “Hello?” you say, hoping you don’t sound like an idiot. Nobody responds. ‘Okay, this is really creepy.’ You poke your friend but she doesn’t move. A bead of sweat trickles down your forehead that has nothing to do with the heat. What is going on? A cold feeling washes over you and you sit back in your seat feeling dizzy. You try to control your breathing but it is rapid and coming in gasps. You glance at the clock only to see that the second hand has stopped moving. Hands clammy, you glare at it willing it to move. Millimetre by millimetre it does. You sigh with relief when everybody’s movement resumes only to find yourself under the scrutiny of 30 pairs of eyes.
“Well?” asks the teacher. Suddenly desperate, you look at the clock and wonder if you can make time go faster.
Who’s point of view;
So there’s this guy, this one guy I never liked, he’s constantly stealing my ideas, getting credit for the success, or if the idea fails, that’s when he throws me under the bus. Oh it’s so aggravating when he takes the words right outta my mouth, when I try to participate in the discussion, he cuts me off, I swear he thinks he knows everything he’s talking about. Oh, yeah and he’s always making an ass out of me, no matter what it is, especially at every work party. This guy thinks he’s so slick, two steps ahead of everyone, but he’s not quick, I know every move he’s gonna make before he makes them. It’s also extremely embarrassing he always seems to wear what I have on, then to hear people say how good he looks, I swear his heads swelling from the compliments. Have you seen him? That car he’s driving, that watch he’s wearing, his house, and kids, and his wife, most people only dream of marrying. He has everything I ever wanted, yet he takes it all for granted, he won’t let anyone else enjoy the spot light, like it’s impossible for him to share it. He never talks to me, which makes it that much more awkward, because I always see him in the bathroom, and every time I wash my hands, there he is, just starring, blocking my reflection. When I try to move, he moves too, it’s so obvious he’s doing it on purpose, but I don’t like drama, quite frankly his demeanor makes me a little nervous. So I just ignore it, I’m starting to wonder if I should report him, but what if the boss thinks I’m jealous? I much rather prefer waiting until the day he quits, or who knows maybe he’ll get fired, I just hope he’s not still here up until the day that I retire.
Until the age of five almost six, I thought everyone could figure out how to walk through walls. The morning my mom was walking me to my first day of school she broke the news to me. Once we reached the first intersection, and we were standing at the corner waiting for the light to change, she first asked me, “Maddy, remember that I mentioned to you every person in the world is unique?” I nodded while I kept my eye on the street light. “and what did I say was so unique about you?” “That I have three freckles on my nose.” “Maddy! Not that but the one thing nobody can tell by looking at you.” I looked up at her and said, “That I am a smart kid and I figured out that walls don’t divide or separate?”
Chapbook 25
Last night I was scared, I had another bad dream I just wanted my mommy there but she was in another room asleep. It was a nightmare, the one I often have, about a monster, who’s over 6ft. He chases me down, grabs me by my hair, thrown me into walls, I don’t know why he’s so angry, he’s even kicked me down the stairs.
I woke up sweating, my eyes filled with tears, and what scared me the most was bruises had appeared. They covered me from head to toe, I couldn’t hide them underneath my clothes. Today I was supposed start my first day of school, but mommy said I couldn’t go.
Back to sleep, I don’t even remember getting ready for bed, I just blacked out, when I woke up a pain filled my head. My dream had some how become real, there was the monster, standing over my body, breathing, and grunting, where is my mommy. Why doesn’t she come and help, why isn’t she protecting me, can’t she hear me if I yell.
Can anyone hear me, why can’t anyone figure it out, I wish my daddy was here, but mommy won’t let him around. When will this nightmare finally end, what will it take for him to leave, one of us dead, or broken and bleeding?
Years have gone by, I’m learning to deal, he’s still in our lives, drinking his meal. He is always mad always drunk, never caring, incapable of feeling love. Beating satisfies a need inside him, one that reminds him he’s alive, he’s in control, that everyone’s beneath him, we do as were told.
My other siblings have dealt with it their own way, my oldest sibling has different personality traits. One minute he’s him, by the next someone else, he swears one day he’ll be free of this hell, and when he does he never wants to see any of us again, he disowns our family, he can’t be my friend. The pain is so much more than anyone should take, it won’t be long from now till one of us breaks.
It finally happened, as I began to prepare my food, cutting up vegetables, trying not to listen to them argue, but low and behold i couldnt ignore the thump, at that very moment I snapped into somebody else.
Someone stronger than who I thought I’d become, with a knife in one hand, and a plan in the other, I made my way to the second floor, and found the that thud was my mother. As the plaster in the wall shaped like her head, I looked for the monster, and seen him covered in red.
Like a bull I charged toward him, digging the knife in his gut, 1,2,3 times ain’t enough. Like the monster he’s always been, courage from his bottle, the pierces in his side didn’t stop him, he was numb from the booze, and like a mad man, he retaliated, nothing could keep him from trying to kill me.
I just woke up from a terrible dream, just to find myself in a worse reality. Laying at the bottom if the stair case, in a puddle of my own blood, flashing lights reassured me help had finally come, but I couldn’t move, my body paralyzed, what had I done? I see my mother screaming she is covered in blood, Then I seen the monster sitting up with tape across his abdomen arms crossed in cuffs, finally he will get what he deserves, but what does this mean or us?
The only girl out of eight kids, the second eldest of the bunch, I thought we stuck together this long, and through such hell, we’d most likely stay together, but only time could tell. If only the words for what’s felt could every truly be spoken, perhaps only then could anyone listening would know just what was dealt, but sometimes you can’t mutter out the words that would allow others to understand what kind of welt gets lashed across a tiny body when beaten with a belt.
Even after hundreds of beatings, thousands of black and blue marks, fractured bones like ribs and wrists, almost on a daily basis. I bet your thinking how the hell does this go on for so long, when a parent allows another adult to enter their home, use them for everything they own, get drunk and stands by as that person takes their angers and frustration out on the innocent lives they should be protecting. When a mother or father chooses a stranger over their own little ducklings. That is how monsters get away with it so long, because an active parent allows it to go on.
The truth is of all the afflictions none bare as much pain as the very thought that a mother could prefer a stranger, a monster, putting her babies in danger, actually acts like she doesn’t see what she did wrong. She won’t acknowledge her errors, and the ultimate worst, the day she would choose another guy over us, again, this guy just another monster, and yet he is her life, treats her like crap, calls her an asset, not as his wife. Let her keep him, and the life she’s made, I have my own daughter now, I will never allow her to grow up this way, I will be nothing like my momster, this is the ultimate promise I make, and would die before I’d ever let it break.
Great piece about a super villain, and how this kind of thing does not happen in a vacuum. Your POV was consistent, first person, but there are places where you need to highlight that these are the thoughts of the protagonist. Italics would work, or even quotes.
I only just came across this site today an I was immediately intrigued. I’ve always been self conscious about my writing but I like the idea of being about to just practice like this and get genuine feedback. Anyway I wrote mine in third person limited, I trying to practice how to use better descriptions without overdoing it and getting to fluffy. Here goes..
I remember the day Melissandra first told me she had superpowers. I would have laughed right then and there if I hadn’t learned to recognize the tension burrowed between her brows. Her pale youthful skin now sagged to that of a woman three times her age. The bags beneath her eyebrows had become so swollen and dark you would have thought she hadn’t slept in weeks. The dark shadows behind her eyes gave way to little life. She hunched over me, her body twitching like little jolts of electricity pulsed through her. In health classes we had often seen videos of the effects of hard drugs on addicts, the way they scratched and clawed, itching to escape their bodies. Could she had gotten herself into hard drugs? No, I definitely would have noticed. This was something worse, as a tenth grader living in the suburbs true terror had never struck me very hard, but the fear that gripped her eyes sent a chill through my spine.
“Mel, is everything okay?” I ask as we push our way through the crowded cafeteria.
Mel leans in close looking over her shoulder with unease checking to see that no one else is listening. She whispers, almost inaudibly.
“I think I have superpowers Suz.”
Laughter roars through my belly, which is quickly stifled by the lifeless expression on her face. I’ve never seen her so afraid.
“I’m sorry, did you say superpowers Mel?” I ask in disbelief.
Her eyes fix on me with a cold hard expression, there’s no laughter in her eyes, no punch line at the end of this story.
She lowers her voice as she begins to explain.
“Last night I went for a climb on Bears Peak. I must of got 150 feet when I lost my footing on the rocks. I was so sure I had all my ropes secured, but as I started to fall nothing caught. In that moment I thought I was going to die. Than, just before my body hit the ground I stopped. My body just suspended, hovering in mid air. It wasn’t long, only a moment, a few seconds at best, but enough time for my body to correct itself and find its footing on the ground.”
I stare at her in bewilderment, she’s not saying what I think she is, is she.
“Suzan!” she exclaims as her eyes show a flicker of light. “Last night I flew.”
I just discovered this site tonight, I like it already. I wrote mine in third person limited.
I remember the day Melissandra first told me she had superpowers. I would have laughed right then and there if I hadn’t learned to recognize the tension burrowed between her brows. Her pale youthful skin now sagged to that of a woman three times her age. The bags beneath her eyes had become so swollen and dark you would have thought she hadn’t slept in weeks. The dark shadows behind her eyes gave way to little life. She hunched over me, her body twitching like little jolts of electricity pulsed through her. In health classes we had often seen videos of the effects of hard drugs on addicts, the way they scratched and clawed, itching to escape their bodies. Could she had gotten herself into hard drugs? No, I definitely would have noticed. This was something worse, as a tenth grader living in the suburbs true terror had never struck me very hard, but the fear that gripped her eyes sent a chill through my spine.
Great article, Joe! I really appreciate the detail you went into. You made the different points of view so clear. The breadth of your knowledge of literature is awesome, and your two graphics were helpful and concise.
Katherine Rebekah, great story! You did the second-person POV seamlessly.
All the best, Deena
Well thanks, Deena. 🙂
My genre is romantic suspense, or romantic thrillers, if you will. I always write third person point of view, omniscient, and steer clear of first person for exactly the reasons you’ve stated above. I find first person too limited and stifling. When I read a novel written in first person I find myself distracted, wondering what the other main character(s) are thinking or feeling. Particuarly in a romance – I don’t want to spend my entire reading experience wondering: Is he feeling the same way way or she on her own here?
Granted, the authors that I habitually read do not typically write in first person, but when they do, I will admit, they’re pretty good at showing me the thoughts and feelings of the other party without actually going into their POV. But, I would say it is a tough thing to accomplish, and only the best writers do.
Any feedback would be nice, thanks!
There are no more villains to fight you. No more evil-doers who wish to challenge your right—the right the people gave you to defend their lives. The monument that watched over the city like an old father is the tribute they built for you. The responsibility that you now stand in. Watching over them. An extraterrestrial guardian.
You look up to see grey clouds swirling, forming some odd shape. You take flight, and burst through the glass pane, as people below begin to chant your name. The clouds merge with one another, swirling in and out of each other. With your vision you can see the faces of the ones you swore to protect, even at the cost of your life. Some are smiles, the faces of those that believe in you—the ones if they could would join you without a second thought. Others had grief-stricken eyes; doubt lined their faces. How could you protect them forever? Surely someone greater than you, stronger than you would destroy everything that you deemed worth saving. Maybe there was someone that could take your place, someone that made all this easier. Hopefully.
No. Your chest bursts out and the veins in your arms feel ready to explode. Your fists clench tighter with each breath. Your eyes narrow. Never will you doubt yourself ever again. A crash of lightning hit a nearby building, signifying your resolve. You charge into the vortex still swallowing the sky. The mass of clouds block your path and out the whirlwind a humanoid shape takes form. You. You face off against yourself. “Of course. A hero’s greatest challenge is his or herself,” you say.
How I hate head-hopping! This is a common mistake my students make – and an easy one that can slip into our drafts. Hence, the importance of revision and beta readers.
Thank you for this thorough discussion of such an important element of story!
The worst limitation I find writing in first person is exactly what Joe pointed out, that you cannot be everywhere at once. I find myself getting frustrated at having to switch POV’s between characters in order to be able to tell the story better and show how different characters are feeling because of certain situations; or in my story’s case: one very sinister character.
But since I’m using my past experiences as a means to write the way I do, I kind of need to stay in first person. It’s both a blessing and a curse.
How interesting that a man who has written a 7000-page story is the author of a bestselling book about writing a short story. 😉
“Tina, what the heck. Put me down.”
“Sorry Charlie, I just ate a spinach salad.”
“Clever, but not humorous. Popeye wouldn’t be so frivolous. What if mom and dad had seen you showing off, or worse, if one of the Dancings is spying on us.”
“You’re no fun, you’re boring and paranoid. Brother or not, I may look for another partner”
“Be my guest. I’ll find someone who takes our mission seriously. Who won’t jeopardize our friends and family out of boredom, and the childish need for attention. Grow up a little. You’re sixteen years old.”
“And, you’re eighteen going on eighty. It’s true what they say about friends and family.”
“Whose they?
“Idiot. They’re the consensus.”
“What does the consensus have to say on the subject?”
“Family is the luck of the draw. Friends are deliberate choices.”
“I’d mention a few of your choices but that won’t get this conversation on track. I, we, need to find out what the Dancings are up to. You need to get close enough to read their daughter’s mind. I’ve got a plan. It could work if you can augment your powers with a dash of maturity.”
My sister Tina and I were abducted a month ago while hiking in the Grand Canyon. If I had the words to describe the aliens or their vessel, I’d share them, but I don’t. They were spirits as much as anything and I may have been sedated somehow. They separated us. Apparently Tina was more qualified for mental and physical superpowers than I was. She can read minds and has the strength of The Hulk. My power is cooler though. My eyes shoot lasers when I squint and concentrate. If it was just a matter of squinting, the neighborhood would be ablaze. My vision is less than perfect. I’ve been squinting for years. Maybe that’s why I got this power? Whatever. If the Dancings are building a dirty bomb in their basement, I may need to set fire to them and their house. Soon maybe. First, I need to know that my suspicions are warranted.
Tina needed to befriend the Dancing’s daughter Tanya, an introvert who spoke to no one at school. If she couldn’t befriend her, Tina at least needed to sit by her at lunch, hopefully to learn something from her thoughts. My sister gets bored easily, so sitting near a person who won’t acknowledge her was going to be a challenge. That’s why I was so irritated with Tina and her circus tricks just now. I’m convinced our neighbors are terrorists. But I can’t just burn their house down. What if somebody died and I was wrong? It was time for my sister to step up and put her powers to good use.
Appreciate the write up Joe. Laura
I am having a lot of difficulty with point of view. For instance, Let’s say you have a Memoir or “Diary” type fiction. You want to it to be from the point of view of the person writing the diary; however, you need your reader to know facts about the characters the speaker interacts with that he couldn’t possible know. (perhaps he just met them, etc.) How can you give the reader information about a person that the speaker deosn’t know yet?
hey, I am in the same boat as you, and I uncovered something called First Person Omniscient, which is– if you are still not away after a year of writing the comment I am replying back to– the character is in first person, still uses “I” and “we” and such, but also knows information about other characters that he/she does not yet know, precisely as what you described in your comment. However, this type of first person is rare, as very few novels and authors decide to use this method. But whatever floats your boat! Hope I helped, even though I am clearly late!
Try second person
One question I have in regards to POV and which to choose, is suppose you’re writing a story about something that’s already happened. The story is being told by the main character in the story, years later after the story is “over” (kind of like in a journal of what happened, how it ended- to a certain point- leaving out what has happened to the main character due to his choices made). But, one of the unique situations is that the main character is not just one person, but a person literally divided into 3 separate selves. He himself is the Present self, the other two are what has already happened (past- alternate choice of reality) and the last one is “what could be if” situation” (future). The main (present) is part of the three, but only knows the whole story after it’s happened and how the other two responded to events as they occurred. How would the story be told in what point of view? Both first and third? I know it probably sounds confusing; so if you’re willing to give me advice and need some clarification I can do that. Thanks.
Amanda stared at herself in the mirror. She lifted her hands and gazed at all of the blood on them. “Why am I not dead?” she asked herself puzzled. “It was a head on collision…with a truck!” she exclaimed to herself in amazement. She turned on her heel and marched to her kitchen and grabbed a large knife. She waved the knife around in the air before placing it on her wrist. “If I can’t make it look like an accident, I guess my parents would have to deal with the fact I wanted to die.” Amanda spat. She winced as the blade dug deep into her delicate flesh and watched her blood flow. But the seconds later it stopped. Blinking, she brought her arm closer to her face and stared at her smooth skin -without a single scratch on it. In disbelief she dropped the knife and ran back into the bathroom and wiped her arm of its blood and confirmed there wasn’t a wound. Desperate, Amanda ran down into the basement and grabbed her father’s rifle. “Heal from this if you can.” Amanda put the point under her chin and pulled the trigger. Everything went black and she felt herself crash to the floor. Moments later, Amanda woke up with a huge headache. “What happened?” she groaned but then gasped when she remembered what she had tried to do. “What is happening to me?!” she cried. “I don’t want to be in this world anymore, let me die!” she screamed. Amanda got up from the floor and shuffled up stairs to take a warm shower. “Maybe drowning would work…”
You forgot deep pov; close third. >:(
Deep POV is still third person limited.
Great write-up! Worth sharing and bookmarking.
As for me, I prefer to write (and read) in either first person or third person limited.
Good article except that the plural of point of view is points of view and NOT point of views! C’mon!
Though I’ve only started writing in earnest this year, POV is a topic that has been pointed out to me again and again concerning my WIP. TODAY, as I go through the comments I received overnight POV is the stumbling block I inadvertently put in my story. I’m consciously employing the third person omniscient POV, but it’s not coming through to my readers. I’ve read this article before and anew and I still don’t get it… I’m doomed.
talented writer, Noddy, mentioned this article . is good read . reread since wanted to make the third person omniscient viewpoint cleaner without head hopping . soon peruse Italo Calvino book written in second person pov to see how a master wrote .
Write two pieces of 750 words. One will be from the point of view of a traveller travelling to a foreign country. The other will be from the point of view of a native of that country who receives that traveller which person do I write form the first person, second person or the third person please help
You know, i had a dream once… I wanted to redo my entire life, I’m getting a divorce from my wife, Scarlett. We have two children, Alex and Maggie, and they’e both seniors in the high school I used to attend. I was driving to Ned’s house one rainy night and saw a man on a bridge. I got out and ran after him. When I got there he jumped, i looked over the edge and then I fell off. I woke up in Ned’s house and looked in the mirror. I was my young self again… I was 17 again.
What about this post is actual, and what part’s a dream? It’s hard to distinguish what dialogue this follows, and what efforts are trying to be accomplished.
Everything about this was my dream… I woke up after i fell and thought, I need some pancakes.
Hi- I’m writing a novel in 3rd omniscient. I struggle with the point of view on a micro level, never dipping into 1st or second person. Here is an example of what I mean is this… ‘While Eunice and Barbara were in the nursery spending a few minutes with the baby boy, Margaret walked away from a group and then grabbed a quick nibble of cheese from the buffet. She continued on to the bar where she picked up a full glass of vodka with a twist of lemon. On her way out the door to the patio, she looked back over her shoulder directly to where Jules stood, as if she had known his position to the inch.’ Does ‘she looked back over her shoulder’ now put the reader in Margaret’s POV???
I could use some advice.
I have a novel focusing on the relationship of two people. This is entirely written in 3rd person limited with occasional internal dialogue.
Initially, this story was focused on one character (A); however, I realised the protagonist was the other character (B). I re-wrote the novel to be inside B’s head, and generally this works *much* better.
Here’s the problem. Although the entire novel is written in 3rd person limited for B, there are several action points within the novel that follows A, not B because there is not much going on with B during this time.
There’s no head hopping or reading of A’s mind in these few scenes, but nothing is happening to B at this point, so narrative-wise, it seems okay to follow A through action (not thought).
So, question 1) because there’s no head hopping, is following A occasionally too distracting for this story? And if so, 2) I’m open to suggestions on how to handle this, because it’s what happens to A in these scenes that changes things.
Very good article. Great examples.
Nice article
Trackbacks/Pingbacks
- Are You Writing From the Right Point of View? - […] Want to know more about POV? See our definitive point of view guide here. […]
- Links To Blog Posts on Writing – September 2015 | Anna Butler - […] Point of View in Writing – Joe Bunting at The Write Practice, with an article that manages to cover…
- Why You Can’t Finish Writing Your Book - […] the Genre? 2. What are the conventions and obligatory scenes for that Genre? 3. What’s the point of view? 4.What are…
- Who’s on First? Exploring Point of View | Dawne Webber - […] I Write in First Person Point of View? @ Editor’s Quill Point of View in Writing @ The Write Practice What…
- Write From The Perspective of a Shoe - […] Seriously, if you want to know everything there is to know about Point Of View, or POV, read Joe’s…
- Last Weeks Writing Links 12/21-12/26 | B. Shaun Smith - […] Point of View in Writing […]
- How to Choose the RIGHT Tense for Your Novel - […] Lights, Big City is notable both for being written in present tense and second-person. While it’s not necessarily something you should use…
- A Matter of Perspective (#0039) | Dominika Lein - […] involving a narrator’s position, then feel free to read these decent articles on the issue; The Write Practice’s Point of…
- Blog – Writer's Thumbprint - […] All of this comes down to POV. The person who did make the movie is telling it from his/her…
- 10 Tips: How to Edit and Improve Your Writing – livewritelovelearn - […] https://thewritepractice.com/point-of-view-guide/ […]
- The Power of Perspective: Understanding Point of View in Creative Writing – The Waterhole - […] to The Write Practice, “Point of View” refers to two things in […]
- Why You Should Consider Writing With an Omniscient Narrator | Creative Writing - […] But before you “stick it to the man” and start drafting your magnum opus in third person omniscient, let’s…
- Point of view guide – LOVE INDIE ROMANCE - […] Point of view guide […]
- POV Rules! - […] https://thewritepractice.com/point-of-view-guide/ […]
- Resources from WW | Elijah - […] Blog Posts: I didn’t read this entire article, but the first third of it seemed very good: https://thewritepractice.com/point-of-view-guide/ These…
- POV | Elijah - […] The Ultimate Point of View Guide: Third Person Omniscient vs. Third Person Limited vs. First Person […]
- Fixing POV Violations - Sun's Golden Ray Publishing - […] Violations (point of view violation). Basically, you have established a point of view for the book (First, Third Close,…
- Bibliography | 網站標題 - […] https://thewritepractice.com/point-of-view-guide/ […]
- Beyond NaNoWriMo: What Do You Do Next? - Story Grid - […] detailed descriptions of the four major types of point of view, read Joe Bunting’s article at The Write Practice.…
- Summer Solstice, New York City by Sharon – Nicholas Hacker's Moorpark College Spring '18 Website - […] [I’m looking at this point-of-view guide from thewritepractice.com to figure out what POV the spea… […]
- Writing Chapter 2: Developing your Opening Hook | Now Novel - […] change of POV: Describe what another character is going through, in an arc linked to the scenario in your…
- How to Publish a Short Story: Write Your First and Second Drafts - […] hopping: Stay in one point of view. There’s not enough time or space in a short to skip […]
- Guest Post - Como Criar Uma Proposta Irresistível - MBFA - […] Tom e perspectiva também usualmente são especificamente analisados. Muitas publicações preferem que você fale em primeira, segunda ou terceira pessoa.…
- Lesson 2: Point Of View – What's right Is Write - […] https://thewritepractice.com/point-of-view-guide/ […]
- How to Write a Book from Multiple Perspectives - […] So if you’re ready for the challenge, here’s how to write a book from multiple perspectives. […]
- How do you develop your plot? – thefictionwritersfriendblog - […] a really good article on Point of View on the Write Practice site. It goes into in more detail…
- Getting to Step 8: Setting the Scenes (Gesichtpunkt) – Short Ramblings - […] your adventure’ books. The other POVs are best suited for my kind of project. (*[2] https://thewritepractice.com/point-of-view-guide/ […]
- P.O.V | The Psychiatrist's Couch - […] https://thewritepractice.com/point-of-view-guide/ […]
- How to Keep Your Point Of View Consistent – by Hannah Green | The Writers College Times - […] Bestselling author Joe Bunting put it best when he said: […]
- How to Leverage Point of View to Power Your Story - […] the purposes of this article, toss out second person and choose between first and third. Each has its strengths…
- How to Leverage Point of View to Power Your Story | rogerpseudonym - […] the purposes of this article, toss out second person and choose between first and third. Each has its strengths…
- Point of View Magic: How to Cast a Spell on Your Readers - […] crucial to understand that EVERY WORD of a story is told through a character’s point of view. If your…
- Henrik Widell – Lektör - […] https://thewritepractice.com/point-of-view-guide/ […]
- Which POV Is Best for Your Story? – Renea Guenther - […] Between Three Different Points of View Writing 101: Choosing the Best Point of View for Your Story The Ultimate…
- Bethany's Best: Writing Point of View & More - Bethany Henry - […] The Ultimate Point of View Guide – The Write Practice […]
- Wie man einen unwiderstehlichen Vorschlag für einen Gastbeitrag macht - […] Perspektive sind dabei auch sehr wichtig. Viele Blogs und Webseiten bevorzugen Artikel, die in der ersten, zweiten oder dritten…
- The Independent – Evila Penonymous - […] Literature reference: [1] […]
- What Is Self-Editing – Writing without Drama - […] https://thewritepractice.com/point-of-view-guide/ […]
- Character Development: Create Characters that Readers Love - […] multiple is a Point of View character. These characters carry the narrative, and in a story told in third…
- What Is an Epilogue? And Is It Okay to Use One in YOUR Book? - […] epilogues that tend to be shorter than other chapters. They are also usually different in tone, point of view,…
- What Is an Epilogue? And Is It Okay to Use One in YOUR Book? – Lederto.com Blog - […] epilogues that tend to be shorter than other chapters. They are also usually different in tone, point of view,…
- 5 Ways to Ruin Your Creative Writing – Books, Literature & Writing - […] Learn more: The Ultimate Point of View Guide: Third Person Omniscient vs. Third Person Limited vs. First Person […]
- What’s the most intriguing writing tip you’ve uncovered from this post? - […] ones is a Point of View character. These characters carry the narrative, and in a story told in third…
- Character Development – Christina's blog - […] ones is a Point of View character. These characters carry the narrative, and in a story told in third…
- Drop a link below if you’ve found anything cool for authors! - […] ones is a Point of View character. These characters carry the narrative, and in a story told in third…
- How to Craft Irresistible Guest Blogging Proposal - […] Tone and perspective are also specifically targeted often. Many publications prefer you speak in the first, second, or third…
- How to Write a Good First Chapter: A Checklist - […] is your story’s point of view? Are you going to choose third person limited, third person omniscient, first person,…
- How to Write a Good First Chapter: A Checklist – Lederto.com Blog - […] is your story’s point of view? Are you going to choose third person limited, third person omniscient, first person,…
- Hit the love button if you like this info! - […] is your story’s point of view? Are you going to choose third person limited, third person omniscient, first person,…
- How will you implement the tips from this post? - […] is your story’s point of view? Are you going to choose third person limited, third person omniscient, first person,…
- Preferred POV and Tense – My Ity Opinion | ItyReadsBooks - […] *Found on The Write Practice […]
- Point of View, or Who’s Telling the Story? – Amanda Down the Rabbit Hole - […] Joe Bunting, “The Ultimate Point of View Guide: Third Person Omniscient vs. Third Person Limited vs. First Person,” https://thewritepractice.com/point-of-view-guide/…
- Mastering Point of View: An In-depth Guide To Better Writing - […] The Ultimate Point of View Guide: Third Person Omniscient vs. Third Person Limited vs. First Person […]
- Welcome to YeahWrite’s Weekly Writing Challenge #484 - YeahWrite - […] sure what that means? Click here. Scroll past the introduction to the First Person banner heading, or read the entire…
- Welcome to YeahWrite’s Weekly Writing Challenge #485 - YeahWrite - […] sure what that means? Click here. Scroll past the introduction to the First Person banner heading, or read the entire…
- Rules and Fiction Writing - LaBine Editorial - […] to dig deeper into POV issues and rules in a later post, but if you’d like to learn more…
- What does mood first ,second and third person mean in literature? - My Literature - […] Point of View in 2022: Third Person Omniscient vs. Third … […]
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Submit Comment
Join over 450,000 readers who are saying YES to practice. You’ll also get a free copy of our eBook 14 Prompts :
Popular Resources
Book Writing Tips & Guides Creativity & Inspiration Tips Writing Prompts Grammar & Vocab Resources Best Book Writing Software ProWritingAid Review Writing Teacher Resources Publisher Rocket Review Scrivener Review Gifts for Writers
Books By Our Writers

Now, Take Your Idea and Write a Book!
Enter your email to get a free 3-step worksheet and start writing your book in just a few minutes.
You've got it! Just us where to send your guide.
Enter your email to get our free 10-step guide to becoming a writer.
Get the POV Cheatsheet for Writers
Enter your email for a free cheatsheet for the top two point of views!
You've got it! Just us where to send your book.
Enter your first name and email to get our free book, 14 Prompts.
The Art of Narrative
Learn to write.

Point of View: The Ultimate Guide
Answer all your questions about how to write in first, second, and third person point of view. Every point of view is covered including how to use tense.
I’ve been staring at my screen for ten minutes trying to come up with a hook that somehow, someway will lead off an article about literary point of view. I’ve come to a definite conclusion: you can’t. To do so would subvert the laws of man, physics and God. It’s impossible. I defy you to try it.
Anyway, let’s talk about POV.
If you’re a beginning writer you might not think much about point of view. But, you should.
All writers should spend significant time considering what POV they’ll use for a story, and why. POV is as important to a story as is your plot , characters , setting , etc.
What is point of view in writing?

Point of view tells your reader who is important in your story. It affects the relationship your reader builds with your characters. And, if done poorly, the point of view can ruin an otherwise perfect story.
You’d like to avoid that, wouldn’t you? Of course! So, for your consideration, I bring to you the ultimate guide to point of view.
(Is it really the ultimate guide to POV? Probably not, but it makes for a good title, right?)
In this article I will explain every type of POV you could possibly use in your writing, and when to use each one. I’ll also answer all your burning questions about POV. You know the ones you’ve always wondered about but didn’t want to ask.
More importantly, I’ll cover some of the common POV mistakes and how to avoid them.
But first, let’s start with the basics-
Point of view is the term used to describe who the author chooses to tell their story. But really, and more importantly, it’s who your reader is engaging with.
When we talk about point of view we’re talking about the narrator. An author might have the main character or a secondary character speak directly to the reader as if you are reading that character’s journal.
Or, the narrator might not be in the story at all, but a voice above the fray who can describe the action of a story.
The narrator may also know certain characters’ thoughts and feelings about the events unfolding. While some POVs will insert the reader directly into the action of the story.
The point is, point of view is an important consideration for any story, and mistakes in POV can ruin a story. So, it’s important to choose your POV carefully and avoid the common pitfalls.
With that said, let’s discuss the different types of POV, why they are used, and the common POV mistakes that you need to avoid.
What are the different types of point of view?
Point of view can be divided into three categories- first person, second person, and third person. Third person point of view can be broken down further into limited, omniscient, and objective.
All POVs can be written either in the past or present tense.
Let’s take a look at each of these individually.
First Person Point of View

What is First Person Point of View?
You’re the reader and the character is telling you the story. You and the character are like old friends; they’re very open with you about their thoughts and feelings. It’s as if you’re reading their journal. Usually, the perspective character is the main character of the story, but not always.
Take, for instance, The Great Gatsby which is written in the first person, but the perspective character is Nick Caraway. Nick takes part in the events of the story and relays them to the reader, but he is not the main character.
However, this is an exception, not the rule. Your point of view character should be the protagonist unless you have a good reason for them not to be.
You’ll know your reading a story in the first person when you see pronouns like I, me, or my. The character is the narrator, so they will be speaking directly to the reader.
How to write First Person Point of View
Writing from a first person point of view is a solid choice if your beginning writer. It’s a straightforward perspective that isn’t too difficult to work with. Choose a character, like your protagonist, and write the story as if they are retelling the events to the reader.
If you choose the first person perspective you’ll need to know your character intimately. You want their personality to remain consistent throughout the narrative. That is unless they’re a dynamic character . Even then, changes in the character will need to have a cause that develops from your plot.
Interview your point of view character. Know their background, what their fears are, and what motivates them. The challenge of the first-person perspective is keeping your character’s voice, actions, and reactions consistent and believable.
In other words, don’t change your character’s personality for the needs of the plot. What does that mean? If your character has been even-keeled and calm throughout the story don’t force them to blow up in anger because you need to inject some tension into a scene.
Know your perspective character, and don’t deviate from the personality that you’ve established, unless that change is earned through the narrative. Your reader will notice otherwise.
When to use First Person Point of View
There are times when using the first person perspective is axiomatic like when writing a memoir or a personal essay. The first person POV is a good choice for writers who are just starting out. The limited nature of first person will help beginning writers avoid some common POV mistakes such as head-hopping. But, more on that later.
Because of its natural limits, the first person is a good choice if there are details of the plot that you want to hide from the reader. Take the example of an unreliable narrator who is lying about the events of the story. Discovering new information a narrator has kept hidden can be an exciting revelation for your reader.
Or, because your writing from the perspective of one character, the reader can discover story details as your character does. This works to great effect in the genres of mystery, horror, and romance. These genres require the character, and reader to work through the details of an event slowly to discover startling truths.
Lastly, the first person POV is a good choice if you’re writing a small, character-driven plot with a limited cast. However, it’s not the best choice for your epic, world-building fantasy.
Example of First Person Point of View
“I couldn’t forgive him or like him, but I saw that what he had done was, to him, entirely justified. It was all very careless and confused. They were careless people, Tom and Daisy—they smashed up things and creatures and then retreated back into their money or their vast carelessness, or whatever it was that kept them together, and let other people clean up the mess they had made.”
― F. Scott Fitzgerald, The Great Gatsby
Learn about first-person point of view here!

What is Second Person Point of View?
You, the reader, are now in the story. You are the protagonist. You’re taking part in the action. Not literally, obviously. Not yet anyway. Until some advances in VR second person will remain figurative.
The writer uses pronouns like you and your. In fiction, this is not a very common practice. But, you will find the second person POV a lot in non-fiction works. Instructional texts like cookbooks are written in second-person. Think, “You’ll need to preheat your oven to 450 degrees. ”
Why isn’t Second Person Point of View popular?
The limitation of the second person perspective is that you’re asking your readers to put themselves directly into the story. This takes considerable suspension of disbelief on their part. And, it may put your reader off as they’re not used to reading this kind of narrative.
The second person point of view tells your reader that they are someone they’re not. That the events of the story are happening to them, the reader. It’s a funky style, let’s be honest. Reserved, mostly, for those “choose your adventure” books we read as children.
However, when executed well, this funkiness is the secret strength of the second-person perspective. What better way to encourage your reader to empathize with a character and experience a new perspective.
While not traditional, a story written in the second-person perspective could be a great way to set your work apart from the pack. But, only if you put in the effort to make it work. Know that an editor will ask the question- “Why did you choose second person POV?” If you don’t have an obvious answer, revealed in the text, this may be a weakness.
When it comes to digital storytelling though, second person POV could be the dominant perspective. Maybe we should start practicing…
Example of Second Person Point of View
“Things happen, people change,’ is what Amanda said. For her that covered it. You wanted an explanation, and ending that would assign blame and dish up justice. You considered violence and you considered reconciliation. But what you are left with is a premonition of the way your life will fade behind you, like a book you have read too quickly, leaving a dwindling trail of images and emotions, until all you can remember is a name.”
― Jay McInerney, Bright Lights, Big City
Third Person Limited Point of View

What is Third Person Limited Point of View?
Take one step above the story. The narrator is no longer in the fray and action. They are on the outside looking in, commenting on the action. The narrator tells the reader what is happening, and what the perspective character is thinking and feeling.
A third person limited perspective means that we are limited (get it?) to a single character at a time. So, it’s like the first person perspective, but rather than a character speaking directly to us, the narrator is telling us what the character is doing, thinking and feeling.
How to write Third Person Limited Point of View
The first thing you want to do is choose a character to limit yourself to. More than likely, this will be your protagonist. You may also switch to another perspective character in your story.
However, don’t switch character perspectives within the confines of a single scene, or even a chapter. In truth, you may want to keep your perspective limited to the same character throughout the narrative.
There are examples of rotating perspective when using third person limited. Authors who do this will change the perspective characters from one character to the next. For clarity, chapters are usually named after the point of view character in that chapter.
How to describe characters in Third Person Limited Point of View
This is a question that comes up when writing from a limited point of view. Character descriptions can be tricky because overtly describing a non-POV character’s emotions would count as a slip in POV. You don’t want that.
Rely on the old adage- show, don’t tell. If a non-POV character is upset then have them slam a door, throw a punch, or break a window. Demonstrate emotion through action, not through adverbs.
Remember that your narration is limited physically, as well. Your narration can’t describe anything the point of view character isn’t able to see, touch, taste, hear or smell directly. The character’s eyes are your window into the world of the story. Keep this in mind when describing the different aspects of your story.
When to use Third Person Limited Point of View
Much like first person point of view, the third person is used when you want to limit the reader’s perspective. Use this POV when you want your readers to spend time with, and become very familiar with a character or cast of characters. When you want your reader to become attached to your protagonist(s). Third person POV is perfect for your character-driven story arcs.
Choose third person POV over first person when your story has several character arcs to explore. An example would be the Harry Potter series. Sure, Harry is important, but we care about Hermione and Ron too.
Also, the third person limited POV works well in mysteries, horrors, and crime stories. This is because you can easily hide information from your reader like you can with first person POV.
Because of its versatility, third person limited is the most popular POV in modern fiction. Readers and editors are used to reading in third person limited POV. In most cases, third person limited POV will be a good choice for your story. .
Example of Third Person Limited Point of View
“For the first time, he heard something that he knew to be music. He heard people singing. Behind him, across vast distances of space and time, from the place he had left, he thought he heard music too. But perhaps, it was only an echo.”
― Lois Lowry, The Giver
Third Person Omniscient Point of View

What is Third Person Omniscient Point of View?
You’re the reader, and the narrator is God. They can give you access to every character’s thoughts and feelings, at the same time. Third person omniscient is like third person limited in that the narrator is separate from the story.
However, the narrator is not limited to one character’s viewpoint when describing the story. The narrator has full knowledge of all the characters and has no preference for any single character. Common pronouns used with third person omniscient are “he,” and “she.”
How to write in Third Person Omniscient Point of View
Third person omniscient can be challenging as you have a lot of characters to keep up with. Each major character will need the same attention from the narrator. It can also be difficult to keep your narrative focused with the POV spread out like this.
Use this perspective to insert your own authorial voice into the narrative. As the narrator, you can comment on the action of the story, or the characters. But, beware that this is not a style of writing that is currently in vogue.
The third person omniscient POV does provide a lot of creative freedom, though. Because of the “God-like” presence of the narrator, you’re not hemmed in by a lot of rules. The author can describe anything that a character is thinking, wearing, doing, seeing, etc.
When to use Third Person Omniscient Point of View
Never. Just kidding, but keep this in mind:
The third person omniscient perspective, while once omnipresent, is not very popular anymore. It’s a good choice if you have a plethora of characters in your story. This is because this perspective gives you the ability to inhabit any character in the story. However, realize this will make developing any single character difficult.
Choose the third person omniscient POV when you have a very strong voice, and you want the narrative commentary to take the center stage of your story.
Example of Third Person Omniscient Point of View
“A man’s at odds to know his mind cause his mind is aught he has to know it with. He can know his heart, but he don’t want to. Rightly so. Best not to look in there. It ain’t the heart of a creature that is bound in the way that God has set for it. You can find meanness in the least of creatures, but when God made man the devil was at his elbow. A creature that can do anything. Make a machine. And a machine to make the machine. And evil that can run itself a thousand years, no need to tend it.”
― Cormac McCarthy, Blood Meridian, or the Evening Redness in the West
Third Person Objective Point of View

What is Third Person Objective Point of View?
In the third person objective POV, the reader does not have access to any character’s thoughts or feelings. The narrator is completely objective.
How and when to use Third Person Objective POV
Again, show don’t tell.
With third person objective, a writer will have to convey all the characters’ emotions through action alone. If you’re a beginning writer try and write at least one story in the third person objective POV. It’s good for practice.
In order to master this POV, a writer must be a keen observer of people in the real world. How do people show their emotions- on their face, in their body language, with words?
How does someone demonstrate they’re angry with their boss? A real person wouldn’t act out dramatically. They wouldn’t flip a table or punch a hole in the drywall (hopefully). Because acting like that would get them fired, probably arrested. They may, instead, make a snide remark, purse their lips, or cross their arms.
The point is, people can be very subtle in how they display their inward feelings. Many people do their best to mask emotions. Others act out for attention. As a writer, you should be able to identify these subtle tells and insert them into your story. Especially if you plan on using the third person objective.
Third person objective POV is also useful in non-fiction. A biographer can’t always comment on the thoughts of feelings of their subject. Especially if the subject has been dead for hundreds of years. In that case, they can only convey a sense of emotion through their subject’s words or actions.
Example of Third Person Objective POV
“When a friend of Abigail and John Adams was killed at Bunker Hill, Abigail’s response was to write a letter to her husband and include these words, “My bursting heart must find vent at my pen.”
― David McCullough, John Adams
Present Tense versus Past Tense in Writing

Most authors choose the past tense when writing fiction. However, some writers choose present tense for their stories. Why? Immediacy is one reason. Like with second person POV, the use of the present tense can pull a reader into a story in a way that feels intimate. They are experiencing the story along with the narrator in real time.
The downside of writing in the present tense is that you’ll be working against the grain. Most stories are told in the past tense, so unless you have a good narrative purpose for using the present tense you should probably avoid it. Without a clear purpose, using the present tense will come off as gimmicky.
But, I’m no expert on this subject and you can find a very informative post on writing in the past tense here .
Example of Present Tense POV
“I can feel Peeta press his forehead into my temple and he asks, ‘So now that you’ve got me, what are you going to do with me?’ I turn into him. ‘Put you somewhere you can’t get hurt.”
― Suzanne Collins, The Hunger Games
Common Point of View mistakes
Head-hopping.

What is head hopping in writing?
Head-hopping is when a writer suddenly changes the viewpoint character without purpose. A story will be narrated from one character’s point of view then that point of view shifts to another character mid-paragraph, or worst mid-sentence.
Head-hopping will leave readers feeling confused and frustrated. It’s a mistake that signals your in the hands of a careless writer. As such, head-hopping should be avoided at all costs.
How to avoid head hopping.
The obvious way to avoid this is to stay in one character’s point of view throughout a story.
If you need to shift perspective wait until a logical point like a scene or chapter break. Think of your character’s viewpoint as a camera lens. The action is being recorded by that single lens. You cannot describe anything that isn’t within the view of that single lens.
When shifting perspective, be sure to establish the change by mentioning the character’s name and something about the setting in your narration. Do this immediately to establish the shift in your reader’s mind.
Here’s an example of how to open a scene that has shifted perspective to a new character:
“Paul glanced at his watch and realized he’d been waiting in the coffee shop for over an hour.”
Who’s the POV character? Paul. Where is he? A coffee shop. What is he doing? Waiting.
Only shift the POV if it serves your narrative. And, establish any shift in POV at the opening of the scene or chapter.
Inconsistent POV

What is an Inconsistent Point of View?
An inconsistent point of view means that the writer is switching point of view throughout the narrative. One scene may be told in the first person and the next scene’s narration switches to the third person omniscient. Like head-hopping, this will confuse your reader.
How to fix Inconsistent Point of View
Choose a point of view and stick to it. If your a first-time writer then the first person is the way to go. The first person point of view limits your opportunities to make mistakes like head-hopping.
Third person limited is the most widely used perspective and one that the modern reader is very comfortable with. Again, like the first person, you’re limited to a single character, and this will ensure a consistent POV.
Familiarize yourself with the rules of each of these POVs. Be mindful of what POV you’ve chosen. If your writing in the third person limited POV, don’t describe something that your POV character couldn’t possibly know.
These mistakes will probably occur in your early drafts and that’s okay. But, planning and outlining is key. As well as purposely choosing your POV. And, most importantly, find good editors! Preferably, fiction writers who are more experienced than you.
Also, don’t shift your point of view unless you have a very good narrative purpose behind the shift. I really can’t say that enough.
Choosing the wrong POV for your story

Choosing the right point of view is vital in effective storytelling. Each POV has its pros and cons. Do you want to tell a story that is an intimate character study? Use the first person. Don’t use the third person omniscient. But, if your book is an epic fantasy that spans multiple worlds or realms, then the third person is the way to go.
POV is also how you tell your reader who is important. If a writer is narrating from a single character’s point of view then the reader will assume that character is important. Using the POV of a character who is not essential to the plot will confuse your reader.
The point is, spend a lot of time thinking about what point of view you’ll use and how it will affect your reader’s experience. This should be part of your pre-writing. POV is not a decision to be taken lightly.
Too many POVs

Using more than one POV character can help give your reader a broad view of your story. It can also be used as a way of slowly revealing important plot points.
I once read a story where the author effectively used POV shifts to explain the same event four times. Each time the new character would have a different perspective on the event, like a game of telephone. It was a clever use of shifting POV.
However, if you’re shifting the POV every chapter or scene for no apparent reason than your reader will get annoyed. POV should indicate an important character. And, shifts in POV should have a narrative purpose behind them.
Choose POV characters for a reason. The reader will feel loyal to a POV character, intuitively. The POV character should have something at stake in the story, or a goal. They should be someone like, oh I don’t know, a protagonist! Or, someone equally important. Who could that be? Hmmm. Maybe, an antagonist ! Don’t give the POV to any old, schlub, though.
Bottom line- don’t waste time using the POV of a character who isn’t important to your narrative. And, make sure that any shifts in POV are done for a specific narrative purpose. An example would be retelling an event of the story from a new perspective that adds new information the reader didn’t already know.
So, that’s everything I can think of when it comes to POV. Still, have questions? Drop them in the comments and I’ll do my best to answer them. Or check out some of these other great resources on POV!
All About Point of View: Which One Should You Choose?
How to Choose Your Novel’s Point of View
Published by John
View all posts by John
6 comments on “Point of View: The Ultimate Guide”
Excellent post!
Thanks, KM!
- Pingback: Exploring Nonlinear Narratives - The Art of Narrative
- Pingback: A Complete Guide to The Hero's Journey (or The Monomyth) - The Art of Narrative
- Pingback: First Person Point of View: What it is & How to use it - The Art of Narrative
- Pingback: Elements of a Story - The Art of Narrative
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Copy and paste this code to display the image on your site
Discover more from The Art of Narrative
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
Get 25% OFF new yearly plans in our Spring Sale
- Features for Creative Writers
- Features for Work
- Features for Higher Education
- Features for Teachers
- Features for Non-Native Speakers
- Learn Blog Grammar Guide Community Events FAQ
- Grammar Guide
Point of View: What Is It? (With 1st, 2nd, 3rd, and 4th POV Examples)

Hannah Yang
One of the most powerful tools in a writer’s toolkit is point of view.
So, what is point of view in literature, and why is it important?
The short answer is that point of view, also called POV, refers to the angle from which a story is told. It includes the specific character who’s telling the story, as well as the way the author filters the story through that character to the reader.
This article will discuss the different points of view you can use in writing, including their strengths, weaknesses, and examples from literature.
What Is Point of View in Writing and Literature?
The importance of point of view, summary of the different points of view, first person point of view, second person point of view, third person point of view, fourth person point of view, what about alternating point of view, conclusion on point of view.
Point of view refers to the perspective through which a story is told.
To understand point of view, try this quick exercise. Imagine you’re telling a story about a well-traveled stranger who enters a small, rural town.
What are all the different perspectives you could tell this story from?
You might tell it from the perspective of the stranger who has never seen this town before and views all of its buildings and streets through fresh eyes.
You might tell it from the collective perspective of the townspeople, who are curious about who this stranger is and why he’s come to this part of the world.
You might even tell it from the perspective of an all-seeing entity, who can see into the minds of both the stranger and the townspeople, all at the same time.
Each of these options centers a different point of view—a different angle for the reader to approach the same story.
Point of view is one of the most important aspects of your story that you must decide before putting pen to paper (or fingers to keyboard). It can have an enormous impact on the tone, style, and even plot of the story.
Each point of view has its own strengths and limitations. In order to choose the right POV, you have to know what you want your story to accomplish.
For example, if you choose first person POV, you’ll be able to immerse the reader in a single character’s voice, humor, and worldview. On the other hand, you also have to show the world with that character’s biases and flawed observations.
The right POV can also completely change the way the story feels. POV is a matter of choice, but one that affects every part of your story or novel.
F. Scott Fitzgerald had to rewrite The Great Gatsby because he initially wrote it in Gatsby’s voice. He decided it would be much more powerful coming from Nick’s more naïve point of view. Imagine that masterpiece with a different point of view—it wouldn’t have the same objective, reliable feeling that it has now.
There are four main points of view that we’ll be discussing in this article: first person, second person, third person (with two subtypes: limited and omniscient), and fourth person.
- First person (“ I pet the cat because I think it looks cute.”)
- Second person (“ You pet the cat because you think it looks cute.”)
- Third person limited (“ She pets the cat because she thinks it looks cute.”) and third person omniscient (“ She pets the cat because she thinks it looks cute. Little does she know, this cat is actually an alien in disguise.”)
- Fourth person (“ We pet the cat because we think it looks cute.”)

Read on to learn the strengths and weaknesses of each of these points of view.
With first person point of view, everything is told intimately from the viewpoint of a character, usually your protagonist. The author uses the first person pronouns I and me to show readers what this character sees and thinks.
First person is the best way to show the story from one person’s point of view because you have an individual person telling you her story directly in her own words. It’s also the easiest way to tell a story that uses a distinct, quirky voice.
The limitations of first person point of view, however, restrict you to only describing what this character sees, thinks, and feels, and sometimes that narrator can be unreliable.
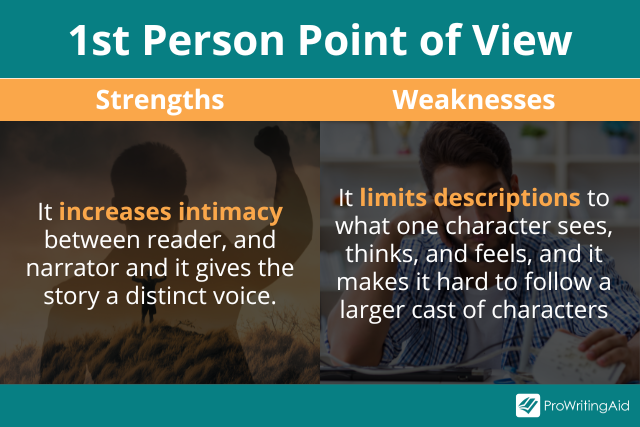
First Person POV Examples
One great example of first person POV is The Bell Jar by Sylvia Plath. The narrator is a flawed character, but we see the world entirely through her eyes, complete with her own faults and sorrows. Here’s a short excerpt:
“I began to think vodka was my drink at last. It didn’t taste like anything, but it went straight down into my stomach like a sword swallowers’ sword and made me feel powerful and godlike.”
Compare that with the intimacy you get when reading Scout’s view of things in Harper Lee’s To Kill a Mockingbird . She speaks with a childlike innocence, giving the reader that same feeling, even if we understand the racism of her town better than she does herself.
“We lived on the main residential street in town—Atticus, Jem and I, plus Calpurnia our cook. Jem and I found our father satisfactory: he played with us, read to us, and treated us with courteous detachment.”
Second person point of view, which uses the pronoun you , is one of the least used POVs in literature because it places the reader in the hot seat and is hard to manage for a full-length novel. It’s used in experimental literature to try out new styles of writing.
In the wrong hands, it just feels gimmicky. But when done well, second person point of view can accomplish a range of wonderful effects.
Second Person POV Examples
“Story of Your Life” by Ted Chiang is a fantastic example of second person POV. It takes the form of a story a mother tells her daughter to explain the circumstances of the daughter’s life. Because the mother is speaking directly to the daughter, the story is imbued with an extra sense of intimacy.
“Right now your dad and I have been married for about two years, living on Ellis Avenue; when we move out you’ll still be too young to remember the house, but we’ll show you pictures of it, tell you stories about it.”
The Fifth Season by N.K. Jemisin is a Hugo-winning fantasy novel that uses many different POVs, including second person. The second person point of view serves to provide a feeling of disorientation, like the protagonist needs to talk to herself to remind herself what’s going on. Here’s a short excerpt from the very beginning of the story:
“You are she. She is you. You are Essun. Remember? The woman whose son is dead.”
Third person point of view uses pronouns like he , she , and it . This POV allows the reader to follow a character, or multiple characters, from a more distanced perspective than first or second person.
Third Person Limited vs Third Person Omniscient
There are two subtypes of third person point of view: limited and omniscient.
In third person limited, the story follows only one character’s viewpoint throughout the entire piece. This means your reader sees only what the third person narrator sees and learns things at the same time the third person narrator does.
You can show what your main character thinks, feels, and sees, which helps close the emotional distance between your reader and the main character.
This is an excellent POV to use when your story focuses on a single character. In many ways, third person limited is quite similar to first person, even though it involves different pronouns.
The drawback with third person limited POV is that you can only follow one character. Showing other characters’ thoughts and feelings is a no-no.
The other type of third person POV is third person omniscient. In this POV, the story is told from the perspective of an omniscient narrator, who can see inside the heads of all the characters in the story.
This is a great POV to use when you have multiple characters, each with their own plot line to follow, and you want your reader to see everything as it unfolds. It’s also useful for imparting universal messages and philosophies, since the narrator can draw conclusions that no character would be able to on its own.
The downside to third person omniscient is that it can be emotionally distant from the story. Because you’re constantly jumping around to different characters and their story arcs, it’s harder for your reader to get as emotionally involved with your characters.

Third Person POV Examples
Examples of the third person limited POV are the Harry Potter novels. The reader sees everything that’s going on, but is limited to Harry’s point of view. We’re surprised when Harry is surprised, and we find out the resolution at the ending when Harry does. Here’s a short excerpt from the seventh book, Harry Potter and the Deathly Hallows:
“Harry sat up and examined the jagged piece on which he had cut himself, seeing nothing but his own bright green eye reflected back at him.”
An excellent example of third person omniscient POV is Victor Hugo’s Les Miserables . The reader sees everything that is happening in the story and gets a vivid lesson in politics and society in France’s history.
“He was cunning, rapacious, indolent and shrewd, and by no means indifferent to maidservants, which was why his wife no longer kept any.”
Fourth person is a newer POV that only recently started to be recognized as a distinct POV. It involves a collective perspective, using the plural pronouns we and us .
This POV allows you to tell a story from the perspective of a group, rather than an individual. Since there’s no singular narrative, this option is great for critiquing larger institutions and social norms. Fourth person is even rarer than second person, but when it’s done well, it can be very powerful.
Fourth Person POV Examples
“A Rose for Emily” by William Faulkner is told from the perspective of an entire town.
“We did not say she was crazy then. We believed she had to do that. We remembered all the young men her father had driven away, and we knew that with nothing left, she would have to cling to that which had robbed her, as people will.”
The Virgin Suicides by Jeffrey Eugenides is told from the perspective of a group of teenage boys.
“They were short, round-buttocked in denim, with roundish cheeks that recalled that same dorsal softness. Whenever we got a glimpse, their faces looked indecently revealed, as though we were used to seeing women in veils.”
You might choose to write a novel or story with multiple different points of view.
Some books have two main characters and switch back and forth between their perspectives—this is very common in the romance genre, for instance. Others rotate between three or more characters.

Alternating POV is a great option if your story features multiple main characters, all of whom play an equally important role in the story. The biggest drawback is that you risk confusing your reader when you switch back and forth.
Make sure your reader knows when you’re switching POVs. One common solution is to include a chapter break each time the perspective changes. Some books change the font for each POV, or even the color of the typeface.
It’s also important to make sure each character has a distinct voice. For example, maybe one character writes with short, brusque sentences, while another writes with long, flowery sentences. Keeping the different POVs distinct is crucial for success.
There you have it—a complete guide to point of view and how to choose the right POV for your story.
Before you start experimenting with point of view, get comfortable with the basics first. Read works by authors who use these different POVs with great success to understand how each POV changes the narrative arc of the story.
Happy writing!
Be confident about grammar
Check every email, essay, or story for grammar mistakes. Fix them before you press send.
Hannah Yang is a speculative fiction writer who writes about all things strange and surreal. Her work has appeared in Analog Science Fiction, Apex Magazine, The Dark, and elsewhere, and two of her stories have been finalists for the Locus Award. Her favorite hobbies include watercolor painting, playing guitar, and rock climbing. You can follow her work on hannahyang.com, or subscribe to her newsletter for publication updates.
Get started with ProWritingAid
Drop us a line or let's stay in touch via :
Point of View in Academic Writing
Writing in 1st, 2nd, and 3rd Person from the George Mason University School of Management
Writing from a specific point of view alters the reader’s perception of what you write. It can be confusing to the reader if you shift the point of view in your writing (meaning starting in the 3rd person, moving to the 2nd person, then switching back to 3rd). Look at this example of switching points of view:
Increasing one’s [3rd person] workload is taxing on both your [2nd person] physical and mental health. Unless someone [3rd person] is in a physically-intensive profession, your [2nd person] body is wasting away while you [2nd person] are working. Additionally, diet [3rd person] also suffers as you [2nd person] spend more time at work. No longer do you [2nd person] have the time to prepare healthy meals at home or even worse, we [1st person] may not have time to eat at all.
After reading this passage, a reader must wonder who is being addressed in the passage. Is it the reader? Is it a general audience? The shifting back and forth confuses the reader. Thus, it is important to maintain the same point of view in your writing.
You should use particular points of view in particular situations. To help you with this, keep these three things in mind:
- Use 1st person to indicate personal experience, evaluation, and/or opinion.
- Use 2nd person to instruct or address the reader.
- Use 3rd person to generalize the experience or situation.
In academic writing, you should write in 3rd person whenever possible. This way, you avoid shifting points of view and confusing the reader.
Here are some examples of the same passage written in the three different points of view. Read them to understand the difference in tone and purpose.
- 1st person, indicating a personal experience I have found increasing my workload is taxing on both my physical and mental health. Unless I am in a physically-intensive profession, my body is wasting away while I work. Additionally, my diet has also suffered as I have spent more time at work. No longer do I have the time to prepare healthy meals at home or even worse; I sometimes do not have time to eat at all.
- 2nd person, instructing the reader Increasing your workload is taxing on both your physical and mental health. Unless you are in a physically-intensive profession, your body is wasting away while you are working. Additionally, your diet also suffers as you spend more time at work. No longer [do you] have the time to prepare healthy meals at home or even worse, you may not have time to eat at all.
- 3rd person, addressing a general situation Increasing workloads tax both physical and mental health. Unless a person is in a physically-intensive profession, a body will waste away with inactivity. Additionally, diet suffers as more time is spent at work as people do not have the time to prepare healthy meals or, even worse, may not have time to eat at all.
Also note the grammatical changes in subjects (“I” vs. “increasing” vs. “increasing workloads”; number (singular vs. plural); and verb tenses (perfect forms in 1st person “have found”; simple be forms in 2nd person “is” and “are”; and simple active forms “tax” in 3rd person).
Writing in the third person creates a more authoritative voice, which is something you want in expository writing. Use 3rd person point of view as the standard although it is possible to use first person when using personal experience as part of the writing. It is not conventional to use second person “you” and sentences and ideas that contain “you” should be rewritten from a different point of view.
Avoiding Metadiscourse or When Not to Use “I”
Metadiscourse is when you are self-referential in your writing. Use of phrases like “I believe” or “I am writing about” or “In the paragraph before where I said” are all referring back to yourself as writer or the act of writing the essay. These bits of metadiscourse tend to be distracting, pulling the reader’s attention from the ideas being discussed to focus instead on the writer and his or her process of writing. Though it is true that every piece of writing is authored and perhaps avoiding any reference to the writer is merely presents an illusion of objectivity, it is nevertheless conventional to avoid such discourse markers. Ideas expressed in your essays are implicitly yours, so you do no need to say “I believe”, “I think”, or “In my opinion.” These are phrases we like to throw into our speech and writing to qualify our ideas, so we don’t sound too forceful or authoritative. However, in your academic writing, you are the expert and you should sound like one. Check out the two examples below to see what a difference metadiscourse makes:
With Metadiscourse Markers A. There are many definitions of the word grassroot and I tried to find where the root of the word started. I found it started in the United States in 1912 by the Progressive Party. One other definition that I discovered on the Internet describes grassroots as designing political processes where the decision making authority is shifted to the organization’s lowest levels rather than being isolated at the top. Grassroots movements are important because I think that democratic power is best exercised when it is vested in the local community rather than in isolated individuals.
Without Metadiscourse Markers B. There are many definitions of the word grassroot and where the root of the word started. It started in the United States in 1912 by the Progressive Party. One other definition on the Internet describes grassroots as designing political processes where the decision making authority is shifted to the organization’s lowest levels rather than being isolated at the top. Grassroots movements are important because democratic power is best exercised when it is vested in the local community rather than in isolated individuals.
As you can see, version B focuses the reader on the subject at hand rather than on the experience of writing it. The elimination of metadiscourse such as “I tried to find” or “I found” or “I discovered/think” makes the writing more smooth and factual rather than based on opinion, a factor that leads to greater credibility as a writer.
Avoiding and Replacing Second Person “You”
Read the following paragraph and rewrite it in order to eliminate the use of 2nd person “you.” You may use choose to substitute another personal pronoun, an indefinite pronoun, or simply address the general situation. Make sure that your indefinite pronouns agree with their antecedents.
Another example of commitment outside of marriage is one that is made when you make a financial decision to obligate yourself to a signed contract. An example of this would be purchasing a new car. Once you have decided to on the car you want, you have to come to an agreement on the terms. You then sign a contract that you are expected to fulfill. If you do not adhere to this formal commitment, you will have to face getting the car repossessed by the company whom you purchased the car from.
How did you do it?
Some of you probably decided to use another personal noun like “he” or “she”, which is a 3rd person point of view. For example, sentence one would say, “ Another example of commitment outside of marriage is one that is made when he or she makes a financial obligation.” Some of you might have substituted a more specific word like “a person” or “ people” or “ a couple,” which is the best thing to do since it now specifies who you really mean when you use the generic “you.”
If you used another personal pronoun, like he or she, that is fine, but you have to clarify who is the “he” or “she”? Pronouns are words that take the place of a person or thing. Pronouns must take an antecedent (the person or thing it stands for) and sometimes you don’t want to specify someone in particular. That’s usually why we end up using the word “you” because we want to imply a general person somewhere out there rather than Stan or Lucy or someone specific. So, another solution is to use an indefinite pronoun.
Indefinite Pronouns
For more practice, go to: http://www.towson.edu/ows/modulepaa.htm
So your paragraph could do something like this:
Another example of commitment outside of marriage is one that is made when someone makes a financial decision to obligate him or herself to a signed contract. An example of this would be purchasing a new car. Once a person have decided on the car he or she wants, he or she has to come to an agreement on the terms.
Now you might find this awkward because you have to keep saying “he or she” and “him and her” which can get unwieldy. Instead, you can make the subject or indefinite pronoun plural:
The couple then sign a contract that they are expected to fulfill. If they do not adhere to this formal commitment, they will have to face getting the car repossessed by the company whom they purchased the car from.
Don’t forget that when you change the subject and it changes from singular to plural or vice versa, then the verb also needs to change form!
Need more practice? Check out the links provided, which contain a review of not only indefinite pronouns but pronouns in general as well as many helpful exercises.

Privacy Policy

Academic Writing: Point of View
If you’re sitting down to write an analytical or research essay (common in the humanities), use the third-person point of view: Achebe argues … or Carter describes her experiences as…
Scientists (including social scientists) tend to use third-person point of view as well, because they depend largely on quantitative research to present their findings or support their opinions: The results indicated…
Occasionally, social scientists and writers in the humanities will use first person to discuss their own experiences while doing research or if writing part of a personal narrative as evidence: After spending a year living with the Upendi, I came to the conclusion that… or Every Christmas we went to the same place, as if our memories could be rekindled…
About Writing: A Guide Copyright © 2015 by Robin Jeffrey is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
- AI in action
- AI in the enterprise
- Humans of AI
Words at work
- Inside Writer
- Content strategy
- Inspiration
– 6 min read
Point of view: a complete guide

Jessica Malnik

Whether you’re writing a blog post, a novel, an academic report, or a simple email to a colleague, you have a decision to make.
What point of view should you use?
Each POV has its benefits, but you’ll need to have an understanding of how they work before you can decide which one is right for your story. That’s why we’ve put together this guide.
Here, we’ll cover everything you need to know about points of view, including what they are, why they’re important, and a breakdown of the three main types. We’ll also include examples of each type of point of view so you can see the differences.
1. What is point of view?
Point of view (POV) applies when you’re talking or writing, but you’ll most likely see it referred to in fiction writing. The point of view you choose will greatly affect the storytelling process and narrative.
Point of view is essentially the perspective from which the story or narrative is being told. It answers the question of “who” is telling the story. Another way to look at it is the position from which someone or something like a scene or narrative, is being observed.
Point of view can be told from three different POVs: first-person, second-person, or third-person. We’ll dive into the specifics of these later in this post, but for now, just know there are three to choose from.

2. Why is POV important?
As mentioned above, the point of view you pick determines how a story unfolds. What do you want your audience to know? Should they “hear” what’s going on inside the heads of the characters, or should they be viewing it from an outsider’s perspective? The point of view you choose determines this.
Point of view can be used as a tool to help express feelings and thoughts. You can use it to reveal someone’s motivations or experiences. Don’t think of it as a box to check in your list of story elements; rather, consider point of view a literary device that can help your story shine.
3. Types of POV
There are three distinct points of view that you should be aware of. Each one has the potential to change the angle of your story. Here’s a bit on each POV so you can understand how they work and know when to use them in your writing.
First-person point of view
If you notice the narrator using first-person pronouns like I , me , mine , or myself , then you’re likely dealing with a story written in the first-person narrative. The first-person point of view helps the reader vicariously live out the story through the eyes of the narrator. When someone tells you a story verbally, they’ll often use this point of view to describe something they’ve witnessed themselves.
In this POV, you may have the protagonist as the main character. Meaning whoever I is — that’s who the story is about. When the protagonist is written in first-person voice, the audience gets an insight into the main character’s mind or thoughts. Sometimes this point of view is achieved through the use of journals, diaries, or letters.
Note that the first-person point of view can be used without making the story entirely about the person speaking. For instance, the narrator may tell the story in the first person, but they aren’t the ones witnessing what’s happening. They may appear to have an omniscient presence in the story or book. The person speaking may also be a minor character or unreliable in their perspective. You should never assume the person speaking in first-person voice knows everything that’s going on.
Second-person point of view
If you notice the storyteller using the pronoun you, then you’re likely reading a second-person account. This isn’t commonly used in fiction, but it can be done. One benefit to using the second-person point of view is that you can pull the reader right into the action. You don’t necessarily have to set a stage.
Keep in mind that, of the three POVs, the second-person point of view can be the most challenging to use for storytelling or fiction. This is mainly because it can feel like a gimmick or repetitive with the use of the word you . However, some stories or formats lend well to the second-person point of view. For instance, if you were writing a how-to story or “choose your own adventure” book, it absolutely makes sense to employ the second-person point of view.
Third-person point of view
If you notice the narrator utilizing pronouns like she , they , he , or it , then you’re probably reading a story written in third-person voice. This POV is often the most commonly used of the three. This is because it gives the writer more flexibility when they don’t have to write from a singular perspective. It essentially broadens the horizons of the story.
However, that’s not always the case. When writing in third-person limited, the point of view does have to be written from one character’s perspective. Often with this POV, that character is the protagonist.
On the other hand, writing in third-person multiple lets the narrator follow the perspectives of more than one character. This is where that flexibility piece plays in. The writer can switch between the different characters in the story. Even less restrictive is third-person omniscient, which allows the author to tell the story from anyone’s point of view.
4. Point of view examples
In this section, we’ll share examples of all three points of view, so you can learn to identify each.
First-person examples
Remember, first-person POV uses these pronouns:
I, my, our, we, me , us
Here are a few examples of what first person looks like:

Second-person examples
Second-person POV relies on the following pronouns:
you, your, yours
Here are some examples of second-person POV in use:

Third-person examples
You’ll see the following pronouns used for third-person POV:
she, they, he, it
Here are a couple examples of third-person POV:

Let’s practice: One fun way to exercise your POV writing skills is to look at a common story and picture it from the three different points of view. Let’s take Cinderella, for example.
First person: I left my glass slipper at the ball last night.
Second person: You see her step out of her glass slipper and leave it at the ball.
Third person: She seemed flustered as she ran away from her glass slipper.
If you’re just getting started with storytelling or writing fiction, it helps to begin with first- or third-person voice. These offer more flexibility and are easier to work with. However, there’s no rule telling you which point of view you have to use. Consider what makes sense for your unique story. But most of all, have fun with it!
Looking for more ways to improve your writing? Start a free trial today.
--> “A wide screen just makes a bad film twice as bad.” -->
May Habib CEO, Writer.com
Here’s what else you should know about Ascending.
More resources

3 expert tips for approaching diversity and inclusion language

Amy Cuevas Schroeder

Your sleeping style guide isn’t good enough

Ashley Coolman
– 13 min read
Planning for uncertainty

Michelle Newblom

- Point of View

Point of View Definition
What is point of view? Here’s a quick and simple definition:
Point of view refers to the perspective that the narrator holds in relation to the events of the story. The three primary points of view are first person , in which the narrator tells a story from their own perspective ("I went to the store"); second person , in which the narrator tells a story about you, the reader or viewer ("You went to the store"); and third person , in which the narrator tells a story about other people ("He went to the store"). Each point of view creates a different experience for the reader, because, in each point of view, different types and amounts of information are available to the reader about the story's events and characters.
Some additional key details about point of view:
- Each different point of view has its own specific qualities that influence the narrative. It's up to the author to choose which point of view is best for narrating the story he or she is writing.
- Second person point of view is extremely rare in literature. The vast majority of stories are written in either the first or third person.
- You may hear "point of view" referred to simply as "perspective." This isn't wrong, it's just another way of referring to the same thing.
The Three "Modes" of Point of View
Stories can be told from one of three main points of view: first person, second person, or third person. Each of the different modes offers an author particular options and benefits, and the point of view that an author chooses will have a tremendous impact on the way that a reader engages with a story.
First Person Point of View
In first person point of view, the narrator tells the story from his or her own perspective. You can easily recognize first person by its use of the pronouns "I" or "We." First person offers the author a great way to give the reader direct access to a particular character's thoughts, emotions, voice, and way of seeing the world—their point of view about the main events of the story. The choice of which character gets to have first person point of view can dramatically change a story, as shown in this simple scenario of a thief snatching a lady's purse
- Thief's POV: "I was desperate for something to eat. Judging by her expensive-looking shoes, I figured she could afford to part with her purse."
- Victim's POV: "He came out of nowhere! Too bad for him, though: I only had five dollars in my bag."
Consider also one of the most famous examples of first person point of view, the very first line of Herman Melville's Moby-Dick :
Call me Ishmael.
Melville uses first person here because he wants to establish a confessional tone for the protagonist. He wants the reader to feel like Ishmael has just sat down next to him on a bar stool, and is about to tell him his life's story. Only first person can have this colloquial and intimate effect. Saying, "His name was Ishmael," for instance, would insert more distance between the reader and the character Ishmael, because the third person narrator would sit between the reader and Ishmael. First person, in this way, can have the effect of connecting the reader directly with the story.
First Person Point of View and the Protagonist
In a story told in the first person, the character who acts as narrator will often also be the protagonist of the story. However, some stories told from the first person do not make the narrator the protagonist:
- First person in which the narrator is the protagonist: In The Catcher in the Rye , the first person narrator Holden Caulfield is the clear protagonist of the story. His voice dominates the story, and the story he tells is his own.
- First person in which the narrator is not the protagonist: The novel The Great Gatsby is narrated by Nick Carraway, but the protagonist of the novel is Jay Gatsby. Nick Carraway tells the story, and the reader is limited to understanding the story through what Nick himself sees, knows, and thinks, but nevertheless the story that Nick tells is not his own but rather Gatsby's.
Second Person Point of View
Second person point of view uses the pronoun "you" to immerse the reader in the experience of being the protagonist. It's important to remember that second person point of view is different from simply addressing the reader. Rather, the second person point of view places the reader "on the playing field" by putting them in the position of the protagonist—the one to whom the action occurs. Few stories are appropriate for such a perspective, but occasionally it is quite successful, as in Jay McInerney's Bright Lights, Big City , a novel in which the reader is taken on a wild night through Manhattan.
Eventually you ascend the stairs to the street. You think of Plato's pilgrims climbing out of the cave, from the shadow world of appearances toward things as they really are, and you wonder if it is possible to change in this life. Being with a philosopher makes you think.
Of the three points of view, second person is the most rarely used, primarily because it doesn't allow the narrator as much freedom as first person and third person, so it's hard to sustain this style of narration for very long.
Third Person Point of View
In third person point of view, the narrator is someone (or some entity) who is not a character in the story being told. Third person point of view uses the pronouns "he," "she," and "they," to refer to all the characters. It is the most common point of view in writing, as it gives the writer a considerable amount of freedom to focus on different people, events, and places without being limited within the consciousness of a single character. Below is an example of dialogue written in third person by Joseph Heller in his novel Catch-22 :
"What are you doing?" Yossarian asked guardedly when he entered the tent, although he saw at once. "There's a leak here," Orr said. "I'm trying to fix it." "Please stop it," said Yossarian. "You're making me nervous."
The exchange above is narrated by a narrator who is outside the interaction between Yossarian and Orr; such distance is the hallmark of third person point of view.
Third Person and Degree of Distance
The third person mode is unique from first and second person in another way as well: third person has different variants. These variants depend on how far removed the narrator is from the events of the story, and how much the narrator knows about each character:
- Third Person Omniscient Point of View: "Third person omniscient" means that the narrator knows all the thoughts and feelings of every character and can dip in and out of the the internal life of anyone, as needed. Omniscient just means "all-knowing." This type of narrator is more god-like than human, in the sense that their perspective is un limited.
- A story like Young Goodman Brown , which follows one character closely and reports on that character's thoughts and feelings (but not the thoughts and feelings of others), is an example of third person limited point of view. This type of story gives the reader the feeling that they are inside one person's head without using first person pronouns like "I."
Alternating Point of View
Many stories are told from alternating points of view—switching between different characters, or even between different modes of storytelling.
- Stories can switch between third person points of view: Many novels switch between different third person points of view. For instance, the chapters of George R.R. Martin's The Song of Ice and Fire books are all named after characters, and each chapter is told from the limited third person point of view of the named character.
- Stories can switch between first person points of view: William Faulkner's novel As I Lay Dying is structurally similar to the Song of Ice and Fire books in the sense that each chapter is named after a character. However, each chapter is told in the first person by the named character. The Darl chapters are told in the first person by Darl, the Cash chapter are narrated by Cash, the Vardamon chapters by Vardamon, and so on.
- Stories can even switch between modes of storytelling: Though less common than other sorts of alternating points of view, some stories can shift not only between different character's points of view, but between actual modes of storytelling. For example, Faulkner's The Sound and the Fury has four parts. The first three parts are all narrated in the first person, with the first part narrated by Benjy, the second part by Quentin, and the third part by Jason. But the fourth part is told in the third person omniscient and follows a bunch of different characters at different times.
Point of View Examples
Every work of literature has a point of view, and so there are essentially endless examples of point of view in literature. The examples below were chosen because they are good examples of the different modes, and in the case of The Metamorphosis the the subtle shift in the nature of the narrator's point of view also shows how an author can play with point of view to suit the themes and ideas of a story.
Third Person Point of View in Kafka's Metamorphosis
A great example of third person point of view in literature is the first line from Kafka's The Metamorphosis .
As Gregor Samsa awoke one morning from uneasy dreams he found himself transformed in his bed into a gigantic insect.
For the remainder of the book, Kafka follows the protagonist, Gregor Samsa, in a limited third person point of view as he struggles to come to terms with his sudden transformation into an insect. For as long as Gregor remains alive, the third person narrator remains limited by Gregor's own consciousness—the story is told in the third person, but the narrator never knows or sees any more than Gregor himself does.
However, in the few pages of the story that continue after Gregor dies, the narrator shifts into a third person omniscient point of view , almost as if Gregor's death has freed the narrator in a way not so dissimilar to how his death tragically relieves a burden on his family.
Point of View in Tolstoy's Anna Karenina
Leo Tolstoy's Anna Karenina is a great example of the omniscient third person point of view. In the novel, the narrator sees and knows all, and moves around between the lives of the different characters, dipping into their internal lives and thoughts, and commenting on the narrative as a whole. In Part 5, Chapter 6, the internal lives of two characters are commented on at once, in the moment of their marriage to one another:
Often and much as they had both heard about the belief that whoever is first to step on the rug will be the head in the family, neither Levin nor Kitty could recall it as they made those few steps. Nor did they hear the loud remarks and disputes that, in the observation of some, he had been the first, or, in the opinion of others, they had stepped on it together.
Point of View in Thoreau's Walden
Henry David Thoreau's transcendental meditations on isolation were based on his actual lived experience. It makes sense, then, that Walden (his account of time spent alone in the woods) is written in the first person point of view :
When I wrote the following pages, or rather the bulk of them, I lived alone, in the woods, a mile away from any neighbor, in a house which I had built myself, on the shore of Walden Pond, in Concord, Massachusetts, and earned my living by the labor of my hands only. I lived there two years and two months. At present I am a sojourner in civilized life again.
What's the Function of Point of View in Literature?
Point of view is the means by which an author relays either one or a multiplicity of perspectives about the events of their story. It is the lens crafted by the writer that allows the reader to see a story or argument unfold. Depending on how much information the writer wants to give the reader, this lens will be constructed differently—or in other words, a different mode of point of view will be chosen:
- If the writer wants the reader to have full access to a particular character's internal life, then they might choose either first person or a closely limited third person point of view.
- If the writer wants the reader to know select bits and pieces about every character, they might choose an omniscient third person point of view.
- If the writer wants the reader to know about the rich internal lives of multiple characters, they might choose an alternating first person point of view.
- Lastly, if the writer wants the reader to feel like they themselves are in the center of the action, they might choose a second person point of view.
Other Helpful Point of View Resources
- The Wikipedia Page on Point of View: An overview of narration with a focus on literary point of view.
- The Dictionary Definition of Point of View: A very basic definition of the term point of view.
- Examples of Second Person: A page with some examples of writing in the less common second person point of view.

- PDFs for all 136 Lit Terms we cover
- Downloads of 1900 LitCharts Lit Guides
- Teacher Editions for every Lit Guide
- Explanations and citation info for 39,983 quotes across 1900 books
- Downloadable (PDF) line-by-line translations of every Shakespeare play
- Protagonist
- Deus Ex Machina
- Dramatic Irony
- Alliteration
- Pathetic Fallacy
- Dynamic Character
- Formal Verse
- Antanaclasis
- Tragic Hero
- Onomatopoeia

Point of View in Academic Writing
Point of view is the perspective from which an essay is written. The following chart lists both the personal pronouns and their possessive forms used with these points of view:
When choosing appropriate point of view for academic or formal writing, consider the type and purpose of the assignment.
First Person
First-person point of view is used to write stories/narratives or examples about personal experiences from your own life. Note the following paragraph:
Several people have made a lasting impression on me . I remember one person in particular who was significant to me . Dr. Smith, my high school English teacher, helped my family and me through a difficult time during my junior year. We appreciated her care, kindness, and financial help after the loss of our home in a devastating fire.
Note : Academic writing often requires us to avoid first-person point of view in favor of third-person point of view, which can be more objective and convincing. Often, students will say, “ I think the author is very convincing.” Taking out I makes a stronger statement or claim: “The author is very convincing.”
Second Person
Second-person point of view, which directly addresses the reader, works well for giving advice or explaining how to do something. A process analysis paper would be a good choice for using the second-person point of view, as shown in this paragraph:
In order to prepare microwave popcorn, you will need a microwave and a box of microwave popcorn which you’ve purchased at a grocery store. First of all, you need to remove the popcorn package from the box and take off the plastic wrap. Next, open your microwave and place the package in the center with the proper side up. Then set your microwave for the suggested number of minutes as stated on the box. Finally, when the popcorn is popped, you’re ready for a great treat.
Note : Academic writing generally avoids second-person point of view in favor of third-person point of view. Second person can be too casual for formal writing, and it can also alienate the reader if the reader does not identify with the idea.
Replacing You
In academic writing, sometimes "you" needs to be replaced with nouns or proper nouns to create more formality or to clarify the idea. Here are some examples:
Third Person
Third-person point of view identifies people by proper noun (a given name such as Shema Ahemed) or noun (such as teachers, students, players, or doctors ) and uses the pronouns they, she, and he . Third person also includes the use of one, everyone, and anyone. Most formal, academic writing uses the third person. Note the use of various third-person nouns and pronouns in the following:
The bosses at the company have decided that employees need a day of in-house training. Times have been scheduled for everyone . Several senior employees will be required to make five-minute presentations. One is not eager to speak in front of others since he’s very shy. Another one , however, is anxious to relate their expertise. The variation in routine should provide an interesting day for all people concerned.
Third Person Pronouns: Gender-Fair Use of Language and Singular “They”
In the past, if you wanted to refer to one unnamed person, you used the masculine pronoun: If a person is strong, he will stand up for himself . Today, you should avoid the automatic use of the masculine pronoun because it is considered sexist language.
Also avoid perpetuating gender stereotypes by assigning a particular gendered pronoun: A doctor should listen to his patients. A nurse should listen to her patients . These examples make assumptions that doctors are men and nurses are women, which is a sexist stereotype.
Instead, use the pronouns they or them to refer to a person whose gender is undisclosed or irrelevant to the context of the usage: If a person is strong, they will stand up for themselves when they believe in something.
Looking to publish? Meet your dream editor, designer and marketer on Reedsy.
Find the perfect editor for your next book
1 million authors trust the professionals on Reedsy. Come meet them.
Guides • Perfecting your Craft
Last updated on Nov 14, 2022
Point of View: The Ultimate Guide to Writing Perspectives
Point of view (POV) is the narrative perspective from which a story is told. It’s the angle from which readers experience the plot, observe the characters’ behavior, and learn about their world. In fiction, there are four types of point of view: first person, second person, third person limited, and third person omniscient.
This guide will look at each point of view, and provide examples to help you understand them better. Let’s dive in.
Which POV is right for your book?
Take our quiz to find out! Takes only 1 minute.
First person
First person narratives are quite common and relatively intuitive to write: it’s how we tell stories in everyday life. Sentences written in first person will use the pronouns I , we , my , and our . For example:
I told my mother that we lost our passports.
First person can create intimacy between the reader and the characters, granting us direct access to their emotions, psyches and inner thoughts. In stories where the protagonist’s internal life is at the fore, you will often find a first-person narrator.

FREE COURSE
Understanding Point of View
Learn to master different POVs and choose the best for your story.
Having a single fixed narrator can limit the scope of a story 一 the reader can only know what the narrator knows. It’s also said that a first person narrator is biased, since they provide a subjective view of the world around them, rather than an objective one. Of course, this isn’t necessarily a bad thing, and intentionally unreliable narrators are fascinating literary creatures in their own right.
Genres that commonly use a first person POV
Young Adult . Introspective coming-of-age narratives often benefit from a first-person narrative that captures the protagonist’s voice and (often mortifying) internal anxieties. Some examples are novels like The Hunger Games by Suzanne Collins , The Fault in Our Stars by John Green , and The Catcher in the Rye by J.D. Salinger.
Science Fiction . In sci-fi novels, a first person perspective can nicely convey the tension and awe associated with exploring unfamiliar environments and technologies. Some examples of this approach include Project Hail Mary by Andy Weir, Flowers for Algernon by Daniel Keyes, and Ready Player One by Ernest Cline.

Memoir . The first person is perfect for memoirs, which allow readers to relive life events with the author. Some pageturners in this genre are Open by Andre Agassi, Educated by Tara Westover, and Becoming by Michelle Obama.
As you might expect, after first person comes…
Second person
Second person narratives are far less common in literature — but not entirely unheard of. The pronouns associated with second person include you , your , and yours , as in:
You instruct the chief of police to bring the prisoner to your office.
Second person POV is all about putting the reader directly in the headspace of a particular character: either the protagonist or a secondary figure. When mishandled, this POV can alienate readers — but when executed well, it can create an intimate reading experience like no other.
Since this POV requires quite a lot of focus for most readers, it’s often suited to shorter, lyrical pieces of writing, like poetry. It can also be used alongside other points of view to provide variety in a longer novel, or to indicate a change of character (see: The Fifth Season by N.K. Jemisin).

GET ACCOUNTABILITY
Meet writing coaches on Reedsy
Industry insiders can help you hone your craft, finish your draft, and get published.
Genres that commonly use a second person POV
Creative Fiction . Short stories, poetry, and screenplays can benefit from the immediacy and intimacy of the second person. Two examples are The Brief Wondrous Life of Oscar Wao by Junot Diaz, or Pants are Optional by Aeris Walker 一 a brilliant piece from Reedsy’s Short Story competition.
Nonfiction . In self-help in particular, the second person can be used to ‘enter the reader's mind’, establish rapport, and guide them through a transformation process. For example, in Eckhart Tolle's The Power of Now many teachings are conveyed through a series of questions and answers written in second person.
Now that you have seen how second person narratives work, let’s meet some third person limited narrators and see how they handle things.
Third person limited
Everyone has read a third person limited narrative, as literature is full of them. This POV uses third-person pronouns such as he , his , she , hers , they , their , to relate the story:
She told him that their assessment of the situation was incorrect.
Third person limited is where the narrator can only reveal the thoughts, feelings, and understanding of a single character at any given time — hence, the reader is “limited” to that perspective. Between chapters, many books wrote in this POV switch from character to character, but you will only hear one perspective at a time. For instance:
“ She couldn't tell if the witness was lying.”

The limited third person POV portrays characters from a bit of distance, and asks the readers to engage and choose who they’re rooting for 一 but this POV poses a challenge for authors when trying to create truly compelling characters . A limited perspective definitely adds intrigue, but writers should bear in mind that being able to tell only one side of the story at a time can limit their ability to reveal important details.
Genres that commonly use a third person limited POV
Romance . A love story always has two sides, and the third person point of view is ideal for authors who wish to convey both. Examples in this genre include Shadow and Bone by Leigh Bardugo, Eleanor & Park by Rainbow Rowell, and The Grand Sophy by Georgette Heyer.
Thriller . In suspense-driven plots the limited third person POV works well, since it’s fun to try and solve a mystery (or mysterious characters) alongside the protagonists. Two examples are Murder on the Orient Express by Agatha Christie, or Nine Perfect Strangers by Moriarty Liane.
A solid story structure will help you maintain a coherent point of view. Build it with our free book development template.

FREE RESOURCE
Get our Book Development Template
Use this template to go from a vague idea to a solid plan for a first draft.
If you’re done with the intimacy of “close” viewpoints, perhaps we can interest you in one final POV — a God’s-eye view of storytelling.
Third person Omniscient
The third person omniscient is as popular as the limited one, and uses the same pronouns. The difference, however, is that the narrator is “all knowing” — meaning that they’re not limited to one character’s perspective, but instead can reveal anything that is happening, has happened, or will happen in the world of the story. For example:
He thought the witness was honest, but she didn't think the same of him .
It’s a popular point of view because it allows a writer to pan out beyond the perspective of a single character, so that new information (beyond the protagonist’s comprehension) can be introduced. At the same time, it heavily relies on the voice and authority of the narrator, and can therefore take some focus away from the character.
Genres that commonly use a third person omniscient POV
Fantasy fiction . In elaborate fantasy worlds, being unencumbered from a character’s personal narrative means that the narrator can provide commentary on the world, or move between characters and locations with the flick of a pen. You’ll see this approach in action in Reaper Man by Terry Pratchett, Howl's Moving Castle by Diana Wynne Jones, and The Chronicles of Narnia by C. S. Lewis.
Literary fiction . An all-encompassing perspective can allow authors to explore different character quirks, but also interpersonal dynamics between characters. Leo Tolstoy does this masterfully in his great classics Anna Karenina and War and Peace .
Now that we have established the basics of the major points of view, let’s dig a little deeper. If you’re ready for a closer look at POV, head over to the next post in this guide to learn more about first person perspective.
5 responses
Aysha says:
19/04/2020 – 19:56
The Book Thief would be considered First Person POV, similar to Arthur Conan Doyle's Sherlock Holmes, right? Thank you for the wonderful information. It gave a lot of insight into choosing which POV would be most suitable for a particular story. Pretty clear-cut.
Sasha Anderson says:
31/05/2020 – 10:41
I sometimes have difficulty telling the difference between third person limited and omniscient. For example, in the quote from I am Legend, the sentence "If he had been more analytical, he might have calculated the approximate time of their arrival" sounds very omniscient to me, because Robert wasn't, and didn't. Is there an easy way to tell that this is limited rather than omniscient, or does it not really matter as long as it reads well?
Lilian says:
18/06/2020 – 05:15
This was a very helpful piece and I hope it's okay to share the link for reference.
↪️ Martin Cavannagh replied:
18/06/2020 – 08:51
Of course! Share away :)
18/06/2020 – 05:44
It deal with the challenges associated with POV in writing. I like that it clearly distinguishes between third person limited POV and third person omniscient POV as most beginner writers are guilty of abrupt and inconsistent interchange in the two leading to head hopping. Greattach piece, I muse confess.
Comments are currently closed.
Join a community of over 1 million authors
Reedsy is more than just a blog. Become a member today to discover how we can help you publish a beautiful book.
Take our 1 minute quiz to find out.

1 million authors trust the professionals on Reedsy. Come meet them.
Enter your email or get started with a social account:

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 5: The Essay
5.5 Your Point of View
In Chapter 4: Summary , you practised clearly explaining your point of view. Your point of view may have agreed with that of your source. Or you may have disagreed. Or you may have had a mixed reaction: agreeing with some of your source’s point of view, while disagreeing with other parts. All of these responses are valid.
Ideally, the reader gets a hint of your point of view in the introductory paragraph, or even the first sentence. For example, to go back to our topic of the Prime Minister’s residential schools apology, you might begin:
In 2008, Prime Minister Stephen Harper made a long overdue apology to all those injured by the residential school system in Canada.
The words “long overdue” give the reader the idea that you disagree with the timing of the apology and that your essay may argue that the apology should have come much earlier.
Review Questions
- See how you can change the reader’s impression of your point of view simply by changing a word. What would the reader think, for example, if in the first introductory sentence above, instead of “long overdue,” you wrote “unnecessary”? How about “damaging”?
- Look at Table 5.4 above. What is the writer’s point of view in each example? Can you predict what each essay will eventually say?
- In the first sentence, agree with a particular point of view.
- In the second version, disagree with the same point of view.
- In the third version, mix your response. Agree with some parts, but disagree with other parts of the point of view.
Points to Consider
- Take out the introduction you wrote for Chapter 5.1 The Introduction . No matter what kind of essay introduction you chose, does it clearly indicate your point of view?
- See if you can change a single word (as you did in question 1 above) or phrase to indicate an entirely different point of view. If you chose to write an introduction to a biographical essay, for example, and your introduction mentioned how much you had learned from the person, you could revise it to say that you have in fact learned only one thing from this person.
Building Blocks of Academic Writing Copyright © 2020 by Carellin Brooks is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

A Writer’s Guide to Point of View
Budding writers often ask me:
“How do I master Point of View?”
The inability to grasp this concept is the most common problem I see in aspiring novelists.
Veteran editor Dave Lambert says, “No decision you make will impact the shape and texture of your story more than your choice of Point of View.”
So let’s straighten it out, shall we?
After you read this post, you’ll know the crucial POV rules and techniques professional writers use (and publishers look for)—and how to apply them to your story .
- What is Point of View?
Things to understand about Point of View before we break it down:
1. Point of View is really two things:
A. The Voice with which you tell your story.
Not to be confused with the tone or sound of your writing (think of that Voice as your writing attitude), this is your choice to tell it in First Person (I), Second Person (you), or Third Person (he, she, or it).
B. Your Perspective Character.
Basically, that answers “Whose story is this?”
2. The cardinal rule of Point of View:
Limit yourself to one Perspective Character per scene, preferably per chapter, ideally per book .
That means no switching POV characters within the same scene, let alone within the same paragraph or sentence.
(Yes, that’s a common amateur mistake, and it results in head-hopping—a giant Point of View no-no I cover in more detail below.)
Point of View is worth stressing over, it’s that important .
Even pros have to remind themselves to avoid sliding into an Omniscient viewpoint.
I avoid that by imagining my Point of View or Perspective Character as my camera—I’m limited to writing only what my character “camera” sees, hears, and knows.
In essence, I’m limited to his or her perspective.
- Breaking Down the Point of View Voices

While POV is limited to one perspective character at a time, each of the three primary voices may be written in the present or past tense.
First Person Point of View
In this POV, the perspective character tells the story.
First Person is the second most common voice in fiction, but I recommend it for many beginning novelists, because it forces you to limit your viewpoint to one Perspective Character—which you should do with all POVs except Omniscient.
My first 13 novels (The Margo Mysteries) were written in first-person past tense.
First Person Examples
The most common use of first-person is past tense.
Herman Melville’s Moby-Dick begins in present tense but immediately switches to past:
Call me Ishmael. Some years ago, never mind how long precisely, having little or no money in my purse and nothing particular to interest me on shore, I thought I would sail about a little and see the watery part of the world.
While I recommend first-person, I think you’d find present tense awkward and difficult to sustain.
On the other hand, The Hunger Games by Suzanne Collins is rendered that way and has become one of the most successful novel series ever.
If you have colossal writing talent and an idea as cosmic as hers, feel free to ignore my counsel and go for it. Here’s how hers begins:
When I wake up, the other side of the bed is cold. My fingers stretch out, seeking Prim’s warmth but finding only the rough canvas cover of the mattress. She must have had bad dreams and climbed in with our mother. Of course, she did. This is the day of reaping.
Second Person Point of View
This point of view uses “you, your” construction, and the narrator makes “you,” the reader, become the protagonist.
Though rare in fiction and far more popular in nonfiction, it’s been said that because it plunges the reader into the action of the story, second person can bring a sense of immediacy to a novel.
I wouldn’t dare attempt it and don’t recommend it.
Second Person Examples
Jay McInerney used second-person present tense in Bright Lights, Big City this way:
You are not the kind of guy who would be at a place like this at this time of the morning. But here you are, and you cannot say that the terrain is entirely unfamiliar, although the details are fuzzy. You are at a nightclub talking to a girl with a shaved head.
You can see how this method forces the reader, in essence, to become a character and how difficult that might be for the writer to sustain for 300 or 400 pages.
Third Person Point of View
Finally, we’ve come to the most commonly used point of view in storytelling — third-person.
Third Person Limited
When written in third-person limited, the story is about he or she/him or her , or the character is mentioned by name.
As with all other POVs besides Omniscient, the writer is limited to one perspective character—your camera.
Everything you write must be seen through that camera: your perspective character’s eyes, ears, and mind.
Third Person Omniscient
Here the story is still about he or she , but the narrator writes from the all-knowing, all-seeing perspective and is not even limited by time.
Because so many of us were raised on the classics with their Omniscient author/narrator, it seems ingrained in us to want to know and tell all about every character onstage and off.
We even want to tell unseen things and things yet unseen. Such miraculous foretellings were often worded like: “Little did our hero know that 20 miles away, what would happen to him the next day was already being planned.”
Writing from that perspective might sound like an advantage, but fiction from an Omniscient viewpoint rarely succeeds in the traditional or indie markets today.
In nonfiction, the Omniscient narrator is common and makes sense, because you’re an expert trying to teach or persuade, and so you adopt a posture of knowing everything and telling everything.
Third Person Examples
Because many readers find third-person present tense weird, you won’t find it in many novels.
It would sound something like this:
Fritz skips out to the garage, fishing in his pocket for his keys. He slips behind the wheel and starts the car.
You can imagine how distracting that would be to the reader if maintained throughout.
By far, the most common choice for modern fiction is third-person past tense.
My perspective character at the start of Left Behind is an airline pilot.
I write it in third-person limited, past tense:
Rayford Steele’s mind was on a woman he had never touched. With his fully loaded 747 on autopilot above the Atlantic en route to a 6 a.m. landing at Heathrow, Rayford had pushed from his mind thoughts of his family.
As I mentioned above, the cardinal rule of POV is to limit yourself to one perspective character per scene, preferably per chapter, ideally per book.
If you’re J.K. Rowling, however, whose bestselling Harry Potter series gloriously breaks this rule, you have my wholehearted permission to ignore this advice.
Head-hopping is the problem .
Here’s an example of what it would have looked like, had I forgotten to limit myself to a single camera (Rayford) as the Perspective Character in Left Behind :
Rayford Steele’s mind was on a woman he had never touched. Meanwhile, his co-pilot was wondering what Rayford was thinking as he gazed out the cockpit window.
See how I slipped out of Rayford’s perspective and into the copilot’s from one sentence to the next?
That’s head hopping—hopping in and out of various characters’ heads.
That takes me from Third Person Limited to Omniscient. And Omniscient narrators are decades out of fashion.
- The Secret to Using Multiple Points of View in the Same Story

In the Left Behind novel series (Tyndale House Publishers), I alternated between as many as five perspective characters per book , but never within the same scene. And I made it crystal clear every time I switched.
I would add an extra space between paragraphs, insert what’s called a typographical dingbat—like this: ###—and fully introduce the new POV character:
Meanwhile, in Los Angeles, Buck Williams sat hunched over his laptop…
In my novel The Valley of the Dry Bones (Worthy Publishing), I employ a single Perspective Character for the entire book.
- Employing The Most Popular Point of View
If you’re a beginning writer , you might assume you must write in the first person, your Perspective Character referring to himself or herself as I .
But third-person limited is the most common choice for contemporary fiction.
Following is an example of how to effectively employ that voice.
A writer asked how he could better describe his character to portray her legalism and self-righteousness.
You can see how this would be easy if written in first person from her standpoint.
But how do we do it in third person limited?
His original:
Mother Clotilde sat at an ornate desk absentmindedly fingering a string of beads encircling her waist as she leafed through a thick leather-bound Bible. She looked like something unearthed at a dig.
Did you catch the POV violation?
Mother Clotilde is the perspective character, but because she’s alone, we can’t really say she “looked like something unearthed at a dig.”
Another character could say that or think that, if we were in that character’s POV. Needless to say, Mother Clotilde would not describe herself that way.
- Which POV Will You Choose?
Choose wisely, because the decision could make the difference between your manuscript landing a contract or being rejected.
Our job as novelists is to pull our readers so deeply into our story that they even forget they’re turning the pages.
Your Point of View choices can make that happen.

Are You Making This #1 Amateur Writing Mistake?

Faith-Based Words and Phrases

What You and I Can Learn From Patricia Raybon

Wait! Before you go...
Here's a FREE copy of my 12-step guide to writing a novel.
Just tell me where to send it:

Enter your email to instantly access my ultimate self-editing checklist.
- How to Cite
- Language & Lit
- Rhyme & Rhythm
- The Rewrite
- Search Glass
How to Write a Point of View Analysis Essay
A point of view analysis essay represents a formal work of writing that focuses its analysis on the point of view of a particular literary composition. An essay that analyzes point of view puts forth some sort of position or an argument. This argument is the essay's thesis statement, and it typically considers the effects that a particular point of view has on different aspects of the narrative.
Point of View
Point of view is the perspective from which the story is told. The first-person narrator relays the story using “I,” showing the reader what he is seeing and experiencing throughout the story. This narrator is typically the main character, but he can also be a supporting character. The third-person narrator relays the story using “he” or “she,” showing the reader a broader perspective. Third-person narration may be limited to a particular character, revealing only his thoughts, actions and/or feelings or omniscient, relaying many characters’ thoughts, actions and/or feelings.
Analyzing Point of View
To write a point of view analysis essay, you should read the literary narrative and take notes on the writer's use of point of view. A writer uses a particular point of view to tell a certain kind of story. Relaying the story from another perspective would make a completely different story. As a result, in analyzing point of view, it is particularly important to pay close attention to the effect that a narrative's point of view has on various aspects of the story and on the story as a whole.
Write Your Essay’s Thesis Statement
Your analysis of a narrative's point of view should be conveyed in one sentence, a thesis statement, which is typically found at the end of your essay's introductory paragraph. The thesis statement should relay your main argument about the writer’s use of point of view and what effect that has on some other aspect of the narrative. For example, you might notice that a first-person perspective might be too limiting because it only presents one character's feelings. As a result, you might conclude that this style of narration gives the story a certain kind of immediacy or tension.
Write the Body of the Essay
Once you have analyzed a narrative’s point of view and developed your thesis statement, you can write the rest of the essay. You should place your thesis statement at the end of your introductory paragraph and use the other paragraphs of the essay to support your thesis. A thesis statement of a point of view analysis essay might be similar to the following example: "In 'Catcher in the Rye,' J.D. Salinger uses first-person point of view to show the unreliability and subjectivity of reality." The body paragraphs of this essay should provide support for this argument by using evidence from the novel to illustrate how the first-person perspective shows unreliability and subjectivity. At the end, you should summarize your main argument and evidence in the conclusion paragraph.
- University of Purdue: Online Writing Lab: Developing Strong Thesis Statements
- University of Toronto: Organizing an Essay
Kate Prudchenko has been a writer and editor for five years, publishing peer-reviewed articles, essays, and book chapters in a variety of publications including Immersive Environments: Future Trends in Education and Contemporary Literary Review India. She has a BA and MS in Mathematics, MA in English/Writing, and is completing a PhD in Education.
Table of Contents
Collaboration, information literacy, writing process, chapter: point of view.
September 10, 2019

Point of View
What Is Point of View? In writing, point of view refers to whether the writing takes on a singular or plural perspective in either 1st person, 2nd person, or 3rd person. First person is the perspective of the writer; 1st person uses words like “I,” “my,” “me,” or “we.” 2nd-person is the perspective of the ...
August 28, 2017
A Synthesis of Professor Perspectives on Using First and Third Person in Academic Writing
For many novice academic writers, the decision of whether to use first-person or third-person voice is determined by several factors. First and third-person refers to the point of view the author adopts, where first-person uses the singular and plural pronouns “I,” “we,” “me,” and “us,” as in “I argue that,” and third-person uses “she,” “he,” “it,” or “they.” Often times, academic writers will identify the subject in the third-person, as in “Stone argues that,” or “The researchers suggest.”
May 3, 2012
Understanding Point-of-View: Wizard Activity
The Beginning of Your Journey
You are writing for a class. You realize that you have no idea what point-of-view is appropriate for this piece of writing. You quickly text a friend but discover that she does not know. Your teacher is currently teaching subject/verb agreement to a nest of talking dragons and is not available. Desperate for help, you head into the forest to the fabled Point-of-View Castle. Dodging past giant spiders, enormous werewolves, and cute little pixies (who are surely up to no good), you arrive at the castle to discover that you can choose from one of three bridges across a moat filled with ravenous alligators. On each bridge stands a wizard who wants to talk to you. All three wear long, flowing robes and have the required gray beards and mystical staffs of power. Each robe has a word written on it. What do you do?
April 25, 2012

Using First Person in an Academic Essay: When is It Okay?
Many times, high school students are told not to use first person (“I,” “we,” “my,” “us,” and so forth) in their essays. As a college student, you should realize that this is a rule that can and should be broken—at the right time, of course.
By now, you’ve probably written a personal essay, memoir, or narrative that used first person. After all, how could you write a personal essay about yourself, for instance, without using the dreaded “I” word?
April 24, 2012
The First Person
The first person—“I,” “me,” “my,” etc.—can be a useful and stylish choice in academic writing, but inexperienced writers need to take care when using it.
There are some genres and assignments for which the first person is natural. For example, personal narratives require frequent use of the first person (see, for example, " Employing Narrative in an Essay ). Profiles, or brief and entertaining looks at prominent people and events, frequently employ the first person. Reviews, such as for movies or restaurants, often utilize the first person as well. Any writing genre that involves the writer’s taste, recollections, or feelings can potentially utilize the first person.
April 19, 2012
Exercise: “We” and “You” in Academic Writing
Look at the following lines and determine how you might revise them so that they remove the pronoun “you” or define the pronoun “we”:
- You can understand what it’s like to have a stack of papers to grade and only two days to do it.
- We now know that cigarettes can cause various types of cancer.
- I would like you to understand that not all students are lazy.
- We believe that gay marriage is not immoral or harmful to the American family; as such, we argue that it should be legalized.
- Doughnuts are really harmful to our health, so we should stop ingesting them.
March 30, 2012
Third-Person Point of View
When is third-person point of view used.
Third person is used when a degree of objectivity is intended, and it is often used in academic documents, such as research and argument papers. This perspective directs the reader’s attention to the subject being presented and discussed. Third person personal pronouns include he, she, it, they, him, her, them, his, her, hers, its, their, and theirs .
Second-Person Point of View
When is second person point of view used.
Second person point of view is often used for giving directions, offering advice, or providing an explanation. This perspective allows the writer to make a connection with his or her audience by focusing on the reader. Second person personal pronouns include you , your , and yours .
Examples of sentences written from the second person point of view:
- You should put your cell phone in the trunk if you want to resist the temptation to use it while you are driving.
- When you write an academic paper, keep in mind that the appearance of your paper can make a positive or negative impression on your reader.
First-Person Point of View
When is first person point of view used.
First person point of view is often used in personal narrative—when the writer is telling a story or relating an experience. This perspective is writer’s point of view, and the writer becomes the focal point. First person personal pronouns include I, we, me, us, my, mine, our, and ours.
Examples of sentences written from the first person point of view:
- I was only seven years old when my family moved to the United States.
- We took a vacation that allowed us to explore our nation from east to west and north to south.
Featured Articles

Academic Writing – How to Write for the Academic Community

Professional Writing – How to Write for the Professional World

Authority – How to Establish Credibility in Speech & Writing
Free IELTS lessons signup

- Academic practice
- General practice
- Task 1 Academic
- Task 1 General
- Task 2 (essay)
IELTS Writing Task 2: discuss both views + give your opinion
In this guide, you'll learn how to answer IELTS writing task 2 questions that ask you to discuss both points of view before giving your opinion . This type of question is often confused with an agree/disagree question or a give your opinion question. In the latter types of questions, you can choose an opinion and generate your arguments. However, for a discuss both views + give opinion question, you have to discuss both points of view impartially before giving your own view.
In this lesson you will see IELTS writing task 2 sample question + model answer and learn:
- how to impartially discuss the points of view
- how to present your own point of view
- how to give a band 9 answer
IELTS question - discuss both views + give opinion
Let's look at an example of IELTS writing task 2 question that asks you to discuss both views and give your opinion:
You should spend about 40 minutes on this task.
It is commonly believed that nowadays main factors that affect a child's development are media, pop culture and friends. A different point of view is that family plays the most significant role.
Discuss both views and give your opinion.
Write at least 250 words.
Generate arguments for each point of view:
First of all, you have to identify the two opinions . These are:
- External factors have more considerable influence on a child's development.
- The family has a greater influence on a child's development.
Next, let's brainstorm for arguments that support each side:
- External factors have a more considerable influence on a child's development.
- Children tend to copy the behaviour of their favourite fictional characters.
- Children spend a lot of time with their peers.
- Technology has an all-pervasive impact on children.
- Parents are always present in the life of a child.
- The younger the children are, the more malleable their character is.
- Parents can set boundaries and have more control over their children.
Choose your point of view:
For our essay, we will agree that although external factors influence the development of a child, parents and family still have the upper hand.
Our reason: A child's choice of friends, books or music depends on the values instilled in them by their parents.
Band 9 answer structure for discuss both views + give opinion essay
Though there are many ways to structure your IELTS essay, we’ll use this time-tested band 9 essay structure:
- Introduction
- Body paragraph 1 – discuss the first opinion
- Body paragraph 2 – discuss the second opinion
- Body paragraph 3 – give your own opinion
It is often held that teachers, peers and the media have a significant influence on the life of children. While some people argue that these factors are predominant in shaping a child's future, others believe that parents impact their offspring in more critical ways. This essay will discuss both these points of view and argue in favour of the latter.

On the one hand, the books children read and the music they listen to form their belief system. In other words, children tend to copy the behaviour of their favourite personality or fictional character. Moreover, when little ones work and play in groups, they are influenced by their peers. Finally, other factors, like the media, prompt children to want things regarded as fashionable. For instance, children demand toys that they see on television.

On the other hand, a child's personality is malleable at a very young age, and parents are always present in their life at this stage. Also, very young children love to imitate. For example, children who come from a dysfunctional family often exhibit behavioural problems at school. An emotionally secure environment at home is critical for the child's confidence. Moreover, parents also teach children about setting boundaries.
In my opinion, children's choice of friends, books or music depends on the values instilled in them by their parents. Therefore, parents hold more substantial sway over their offspring than media, pop culture and friends circle.
In conclusion, the outside world influences the intellectual and social development of children. However, I believe that it is parents who set the stage for these developments by laying a strong foundation from a very young age.
Band 9 answer sample
(273 words)

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
First person point of view. First person perspective is when "I" am telling the story. The character is in the story, relating his or her experiences directly. Second person point of view. The story is told to "you.". This POV is not common in fiction, but it's still good to know (it is common in nonfiction).
In writing, point of view refers to whether the writing takes on a singular or plural perspective in either 1st person, 2nd person, or 3rd person. First person is the perspective of the writer; 1st person uses words like "I," "my," "me," or "we.". 3rd-person is the perspective of a different party who is neither writer nor ...
The first person point of view limits your opportunities to make mistakes like head-hopping. Third person limited is the most widely used perspective and one that the modern reader is very comfortable with. Again, like the first person, you're limited to a single character, and this will ensure a consistent POV.
Second person point of view, which uses the pronoun you, is one of the least used POVs in literature because it places the reader in the hot seat and is hard to manage for a full-length novel. It's used in experimental literature to try out new styles of writing. In the wrong hands, it just feels gimmicky.
In academic writing, you should write in 3rd person whenever possible. This way, you avoid shifting points of view and confusing the reader. Here are some examples of the same passage written in the three different points of view. Read them to understand the difference in tone and purpose. 1st person, indicating a personal experience.
Academic Writing: Point of View. If you're sitting down to write an analytical or research essay (common in the humanities), use the third-person point of view: Achebe argues … or Carter describes her experiences as…. Scientists (including social scientists) tend to use third-person point of view as well, because they depend largely on ...
Point of view can be used as a tool to help express feelings and thoughts. You can use it to reveal someone's motivations or experiences. Don't think of it as a box to check in your list of story elements; rather, consider point of view a literary device that can help your story shine. 3. Types of POV.
While there are numerous ways to employ point of view in fiction, it's good to familiarize yourself with the basics of this literary device. ... Writing Complete Guide to Different Types of Point of View: Examples of Point of View in Writing. Written by MasterClass. Last updated: Sep 1, 2021 • 8 min read.
Point of view refers to the perspective that the narrator holds in relation to the events of the story. The three primary points of view are first person, in which the narrator tells a story from their own perspective ("I went to the store"); second person , in which the narrator tells a story about you, the reader or viewer ("You went to the ...
Third Person. Third-person point of view identifies people by proper noun (a given name such as Shema Ahemed) or noun (such as teachers, students, players, or doctors) and uses the pronouns they, she, and he.Third person also includes the use of one, everyone, and anyone. Most formal, academic writing uses the third person. Note the use of various third-person nouns and pronouns in the following:
Point of view (POV) is the narrative perspective from which a story is told. It's the angle from which readers experience the plot, observe the characters' behavior, and learn about their world. In fiction, there are four types of point of view: first person, second person, third person limited, and third person omniscient.
Write three first sentences of an essay on the topic of future challenges in immigration in Canada. In the first sentence, agree with a particular point of view. In the second version, disagree with the same point of view. In the third version, mix your response. Agree with some parts, but disagree with other parts of the point of view.
Simple phrases to make your point of view essay better. You don't have to use all these phrases in your text. Actually, you shouldn't, because it will not make much sense. These expressions will help you to make your ideas more structured. They will simplify the reading process and add conciseness to your essay. 1.
1. Point of View is really two things: A. The Voice with which you tell your story. Not to be confused with the tone or sound of your writing (think of that Voice as your writing attitude), this is your choice to tell it in First Person (I), Second Person (you), or Third Person (he, she, or it). B.
In academic writing, the use of the third-person pronouns (he/she/it and they/them) neither refer to the writer or the person being addressed. For example, in academic writing one may say "the study from the University of Pennsylvania states that 1 in 5 people have blue eyes.". On the other hand, first-person pronouns (I/me/my and we/us ...
To write a point of view analysis essay, you should read the literary narrative and take notes on the writer's use of point of view. A writer uses a particular point of view to tell a certain kind of story. Relaying the story from another perspective would make a completely different story. As a result, in analyzing point of view, it is ...
1. Avoid obvious tags. In first person, avoid phrases that take the reader out of the character's thoughts—for example, "I thought" or "I felt.". While one of the advantages of first-person writing is knowing what the narrator is thinking, don't get stuck in the character's head.
Point of View The Who's Who of Writing Most students enter their composition classes with at least a basic understanding of point of view, but where ... when you write an essay, your full focus should be on the topic at hand. Unless your audience is directly in front of you (as in a speech) or is the ...
In writing, point of view refers to whether the writing takes on a singular or plural perspective in either 1st person, 2nd person, or 3rd person. First person is the perspective of the writer; 1st person uses words like "I," "my," "me," or "we." 2nd-person is the perspective of the ... August 28, 2017.
This is an ideal choice if you are new to fiction writing, because it allows you to stick with one point of view. Typically, your story will be told from the perspective of your protagonist, or main character. When writing in the 1st person POV, you will use first-person pronouns such as "I," "we," and "me," throughout the story.
Choose your point of view: For our essay, we will agree that although external factors influence the development of a child, parents and family still have the upper hand. Our reason: A child's choice of friends, books or music depends on the values instilled in them by their parents. Band 9 answer structure for discuss both views + give opinion ...
Second, follow these steps on how to write an argumentative essay: Brainstorm: research, free-write, and read samples to choose a debatable topic. Prepare: organize thoughts, craft a thesis, decide on arguments and evidence. Draft: outline an essay, start with an engaging introduction, delve into arguments, and conclude like a boss.