
- Wind Energy Technologies Office
- Wind Energy Career Map
- Key Activities in Wind Energy
- WETO Budget
- WETO Organization & Contacts
- Atmosphere to Electrons
- Distributed Wind
- Environmental Impacts & Siting
- Next-Generation Wind Technology
- Demonstration
- Floating Offshore Wind Shot
- Market Acceleration
- R&D Consortium
- Renewable Systems Integration
- Resource Assessment & Characterization
- Testing & Certification
- Drivetrains
- Infrastructure & Logistics
- Wind Turbine Radar Interference
- Wind Turbine Sustainability
- Workforce Development & Education
- History of Wind Energy
- How Distributed Wind Works
- How Wind Turbines Work
- WINDExchange
- Small Wind Systems FAQs
- WETO Peer Reviews
- Wind Energy FAQs
- Wind Energy Market Reports
- Wind Energy Projects Map
- Related Opportunities
- Wind Energy Technologies Office Updates
- Wind R&D Newsletter
Wind energy offers many advantages, which explains why it's one of the fastest-growing energy sources in the world. To further expand wind energy’s capabilities and community benefits, researchers are working to address technical and socio-economic challenges in support of a decarbonized electricity future.
Learn more about ongoing research to take advantage of these benefits and tackle wind energy challenges.

Advantages of Wind Power
- Wind power creates good-paying jobs. There are over 125,000 people working in the U.S. wind industry across all 50 states, and that number continues to grow. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics , wind turbine service technicians are the fastest growing U.S. job of the decade. Offering career opportunities ranging from blade fabricator to asset manager, the wind industry has the potential to support hundreds of thousands of more jobs by 2050.
- Wind power is a domestic resource that enables U.S. economic growth. In 2022, wind turbines operating in all 50 states generated more than 10% of the net total of the country’s energy . That same year, investments in new wind projects added $20 billion to the U.S. economy.
- Wind power is a clean and renewable energy source. Wind turbines harness energy from the wind using mechanical power to spin a generator and create electricity. Not only is wind an abundant and inexhaustible resource, but it also provides electricity without burning any fuel or polluting the air. Wind energy in the United States helps avoid 336 million metric tons of carbon dioxide emissions annually —equivalent to the emissions from 73 million cars.
- Wind power benefits local communities. Wind projects deliver an estimated $2 billion in state and local tax payments and land-lease payments each year. Communities that develop wind energy can use the extra revenue to put towards school budgets, reduce the tax burden on homeowners, and address local infrastructure projects.
- Wind power is cost-effective. Land-based, utility-scale wind turbines provide one of the lowest-priced energy sources available today. Furthermore, wind energy’s cost competitiveness continues to improve with advances in the science and technology of wind energy.
- Wind turbines work in different settings. Wind energy generation fits well in agricultural and multi-use working landscapes. Wind energy is easily integrated in rural or remote areas, such as farms and ranches or coastal and island communities, where high-quality wind resources are often found.
Challenges of Wind Power
- Wind power must compete with other low-cost energy sources. When comparing the cost of energy associated with new power plants , wind and solar projects are now more economically competitive than gas, geothermal, coal, or nuclear facilities. However, wind projects may not be cost-competitive in some locations that are not windy enough. Next-generation technology , manufacturing improvements , and a better understanding of wind plant physics can help bring costs down even more.
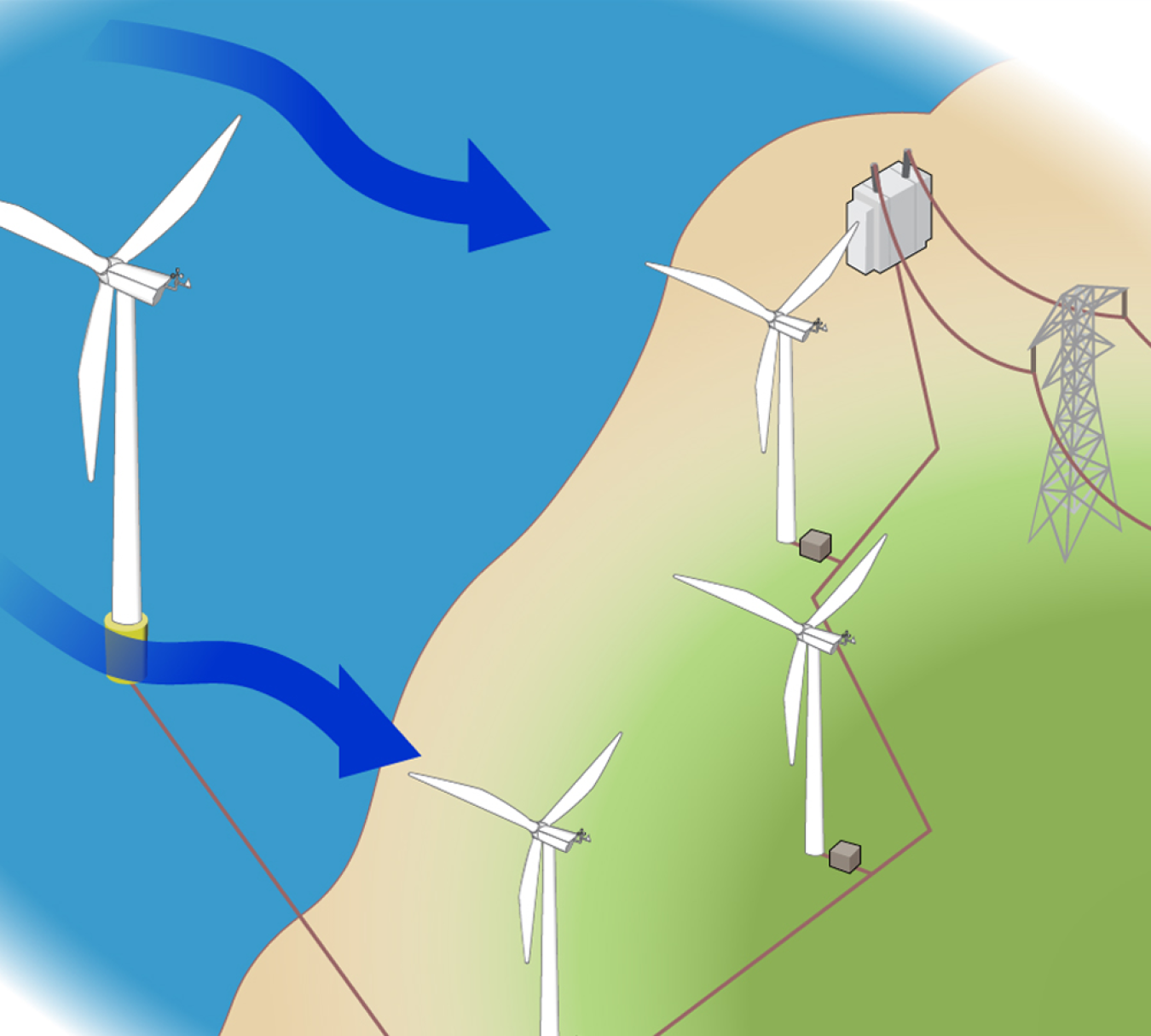
- Ideal wind sites are often in remote locations. Installation challenges must be overcome to bring electricity from wind farms to urban areas, where it is needed to meet demand. Upgrading the nation’s transmission network to connect areas with abundant wind resources to population centers could significantly reduce the costs of expanding land-based wind energy. In addition, offshore wind energy transmission and grid interconnection capabilities are improving.
- Turbines produce noise and alter visual aesthetics. Wind farms have different impacts on the environment compared to conventional power plants, but similar concerns exist over both the noise produced by the turbine blades and the visual impacts on the landscape .
- Wind plants can impact local wildlife. Although wind projects rank lower than other energy developments in terms of wildlife impacts, research is still needed to minimize wind-wildlife interactions . Advancements in technologies, properly siting wind plants, and ongoing environmental research are working to reduce the impact of wind turbines on wildlife.

What Is the Future of Wind Energy?
This article was reviewed by a member of Caltech's Faculty .
Humans have used windmills to capture the force of the wind as mechanical energy for more than 1,300 years . Unlike early windmills, however, modern wind turbines use generators and other components to convert energy from the spinning blades into a smooth flow of AC electricity.
In the video below, Resnick Sustainability Institute researcher John Dabiri discusses the future of wind energy technology.
How much of global electricity demand is met by wind energy?
Wind energy is a small but fast-growing fraction of electricity production. It accounts for 5 percent of global electricity production and 8 percent of the U.S. electricity supply.
Globally, wind energy capacity surpasses 743 gigawatts , which is more than is available from grid-connected solar energy and about half as much as hydropower can provide. Nearly three-quarters of that 651 gigawatts comes from wind farms in five countries: China, the U.S., Germany, India, and Spain. Wind energy capacity in the Americas has tripled over the past decade.
In the U.S., wind is now a dominant renewable energy source , with enough wind turbines to generate more than 100 million watts, or megawatts, of electricity, equivalent to the consumption of about 29 million average homes.
The cost of wind energy has plummeted over the past decade. In the U.S., it is cost-competitive with natural gas and solar power.
Wind energy and solar energy complement each other, because wind is often strongest after the sun has heated the ground for a time. Warm air rises from the most heated areas, leaving a void where other air can rush in, which produces horizontal wind currents . We can draw on solar energy during the earlier parts of the day and turn to wind energy in the evening and night. Wind energy has added value in areas that are too cloudy or dark for strong solar energy production, especially at higher latitudes.
How big are wind turbines and how much electricity can they generate?
Typical utility-scale land-based wind turbines are about 250 feet tall and have an average capacity of 2.55 megawatts, each producing enough electricity for hundreds of homes. While land-based wind farms may be remote, most are easy to access and connect to existing power grids.
Smaller turbines, often used in distributed systems that generate power for local use rather than for sale, average about 100 feet tall and produce between 5 and 100 kilowatts.
One type of offshore wind turbine currently in development stands 853 feet tall, four-fifths the height of the Eiffel Tower, and can produce 13 megawatts of power. Adjusted for variations in wind, that is enough to consistently power thousands of homes. While tall offshore turbines lack some of the advantages of land-based wind farms, use of them is burgeoning because they can capture the energy of powerful, reliable winds high in the air near coastlines, where most of the largest cities in the world are located.
What are some potential future wind technologies other than turbines?
Engineers are in the early stages of creating airborne wind turbines , in which the components are either floated by a gas like helium or use their own aerodynamics to stay high in the air, where wind is stronger. These systems are being considered for offshore use, where it is expensive and difficult to install conventional wind turbines on tall towers.
Trees, which can withstand gale forces and yet move in response to breezes from any direction, also are inspiring new ideas for wind energy technology. Engineers speculate about making artificial wind-harvesting trees . That would require new materials and devices that could convert energy from a tree's complex movements into the steady rotation that traditional generators need. The prize is wind energy harvested closer to the ground with smaller, less obtrusive technologies and in places with complex airflows, such as cities.
What are the challenges of using wind energy?
Extreme winds challenge turbine designers. Engineers have to create systems that will start generating energy at relatively low wind speeds and also can survive extremely strong winds. A strong gale contains 1,000 times more power than a light breeze, and engineers don't yet know how to design electrical generators or turbine blades that can efficiently capture such a broad range of input wind power. To be safe, turbines may be overbuilt to withstand winds they will not experience at many sites, driving up costs and material use. One potential solution is the use of long-term weather forecasting and AI to better predict the wind resources at individual locations and inform designs for turbines that suit those sites.
Climate change will bring more incidents of unusual weather, including potential changes in wind patterns . Wind farms may help mitigate some of the harmful effects of climate change. For example, turbines in cold regions are routinely winterized to keep working in icy weather when other systems may fail, and studies have demonstrated that offshore wind farms may reduce the damage caused by hurricanes . A more challenging situation will arise if wind patterns shift significantly. The financing for wind energy projects depends critically on the ability to predict wind resources at specific sites decades into the future. One potential way to mitigate unexpected, climate-change-related losses or gains of wind is to flexibly add and remove groups of smaller turbines, such as vertical-axis wind turbines , within existing large-scale wind farms.
Wind farms do have environmental impacts . The most well-known is harm to wildlife, including birds and bats . Studies are informing wind farm siting and management practices that minimize harm to wildlife , and Audubon, a bird conservation group, now supports well-planned wind farms. The construction and maintenance of wind farms involves energy-intensive activities such as trucking, road-building, concrete production, and steel construction. Also, while towers can be recycled, turbine blades are not easily recyclable. In hopes of developing low-to-zero-waste wind farms, scientists aim to design new reuse and disposal strategies , and recyclable plastic turbine blades. Studies show that wind energy's carbon footprint is quickly offset by the electricity it generates and is among the lowest of any energy source .
Dive Deeper

Wind Vision: A New Era for Wind Power in the United States

Caltech Energy 10 to Develop the Roadmap for 50% Reduction in Emissions by 2030

Tweaking Turbine Angles Squeezes More Power Out of Wind Farms
Wind Energy: Advantages and Disadvantages
Dallas lloyd december 11, 2014, submitted as coursework for ph240 , stanford university, fall 2014, wind energy: what is it.
To obtain wind power, the kinetic energy of wind is used to create mechanical power. A generator converts this power into electricity so that it may be used for the benefit of mankind. Recently, different types of electricity generation have been a frequent topic of debate amongst experts. Surely, wind energy is one of the frontrunners of the technological breakthroughs that might lead to more efficient energy production. At a glance, the future of wind energy seems promising. This may be the case, but there are also some disadvantages that must be considered.
The advantages of wind energy are more apparent than the disadvantages. The main advantages include an unlimited, free, renewable resource (the wind itself), economic value, maintenance cost, and placement of wind harvesting facilities. First and foremost, wind is an unlimited, free, renewable resource. Wind is a natural occurrence and harvesting the kinetic energy of wind doesn't affect currents or wind cycles in any way. Next, harvesting wind power is a clean, non-polluting way to generate electricity. Unlike other types of power plants, it emits no air pollutants or greenhouse gases. The wind turbines harmlessly generate electricity from wind passing by. Wind energy is far more ecofriendly than the burning of fossil fuels for electricity. Currently, the United States, along with other countries, remains dependent on fossil fuels imported from unstable and unreliable nations. [1] Strains on supply (of fossil fuels) are likely to increase the prices of fossil fuel resources and leave the US economy exposed to international market volatility. Wind power has the ability to free the US from the figurative economic bondage of fossil fuels. Once turbines and energy centers have been installed, the cost of maintaining turbines and generating wind power is next to nothing. Another advantage of wind power is the ability to place turbines wherever necessary. After performing research and finding areas that have adequate wind, experts may place the turbines in desired areas. These areas are usually unpopulated (offshore wind turbines, for example). [1] In fact, offshore winds tend to blow harder and more uniformly than on land, providing the potential for increased electricity generation and smoother, steadier operation than land-based wind power systems. Fig. 1 shows offshore wind turbines harvesting energy.
Disadvantages
The two major disadvantages of wind power include initial cost and technology immaturity. Firstly, constructing turbines and wind facilities is extremely expensive. The second disadvantage is technology immaturity. [1] High cost of energy can, in part, be addressed directly with technology innovations that increase reliability and energy output and lower system capital expenses. Offshore wind energy produces more energy than onshore wind energy, but costs much more to establish. The primary costs of wind turbines include construction and maintenance. [1] New technology is needed to lower costs, increase reliability and energy production, solve regional deployment issues, expand the resource area, develop infrastructure and manufacturing facilities, and mitigate known environmental impacts. Therefore, one may argue that implementation of wind energy must be delayed until technological advancements are made. Other disadvantages include:
Aesthetic impact: Many people are concerned with the visual effects that wind turbines have on the beautiful scenery of nature. They believe that giant wind turbines distract viewers from the beautiful surroundings. Fig. 2 shows just how big wind turbines can be.
Wildlife: Wind turbines may be dangerous to flying animals. Many birds and bats have been killed by flying into the rotors. Experts are now conducting research to learn more about the effects that wind turbines have on marine habitats.
Remoteness of location: Although this may be an advantage (placing wind turbines in desolate areas, far away from people), it may also be a disadvantage. The cost of travel and maintenance on the turbines increases and is time consuming. Offshore wind turbines require boats and can be dangerous to manage.
Noise: Some wind turbines tend to generate a lot of noise which can be unpleasant
Safety at Sea: In the darkness/at night it may be difficult for incoming boats to see wind turbines thus leading to collisions.
© Dallas Lloyd. The author grants permission to copy, distribute and display this work in unaltered form, with attribution to the author, for noncommercial purposes only. All other rights, including commercial rights, are reserved to the author.
[1] W. Musial and B. Ram, "Large-Scale Offshore Wind Power in the United States," U.S. National Renewable Energy Laboratory, NREL/TP-500-40745 , September 2010.
Wind Energy
The facts and advantages of wind energy—and why we’re turning to turbines to power our clean energy future.
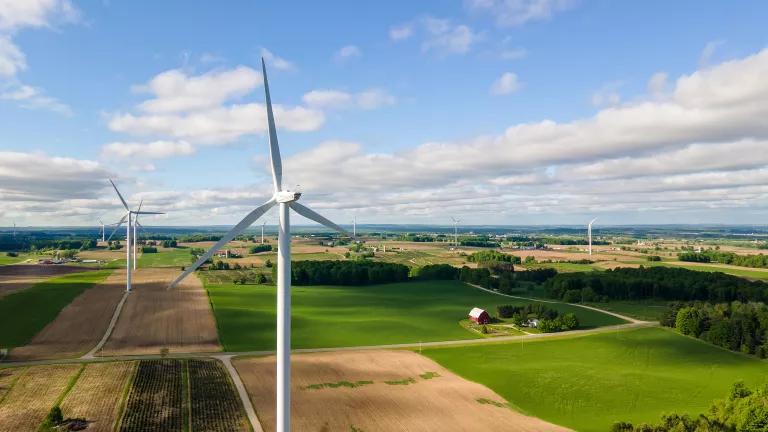

Turbines at Heritage Sustainable Energy's Stoney Corners Wind Farm in McBain, Michigan
Shutterstock

- Share this page block
For thousands of years, humans have recognized the potential of harnessing the wind: propelling ships, pumping water, and even sawing wood. Today, modern wind power and other forms of renewable energy are the fastest-growing energy sources in the world, with wind making up about 10 percent of total energy production in the United States. Read on to learn more about how declining costs and enticing climate, health, and economic benefits are helping wind energy soar.
What is wind energy?
How does wind energy work, what are wind farms, advantages of wind energy, challenges with wind energy, wind energy growth in the united states.
Let’s start with some basics. Wind is the movement of air caused by pressure differences in the earth’s atmosphere, which is caused by the uneven heating of the earth’s surface from the sun. Because of earth’s irregular surface, the slight tilt of the planet, and its rotation, different areas heat up at different rates. As warmer air expands and rises, it creates a pressure imbalance with the nearby cooler air, which then rushes in to fill that space. That’s the wind! The greater the pressure difference, the stronger the wind: like an untied balloon blowing out air.
Generating wind energy is all about kinetic energy, aka the energy of motion. Anything that moves—a person walking, a dog running, a book falling—has kinetic energy. A wind turbine takes the kinetic energy of wind and turns it into electrical energy. (Be careful not to confuse wind turbines with the iconic windmill, which was invented over a thousand years ago and was primarily used to mill grain, not generate electricity.)
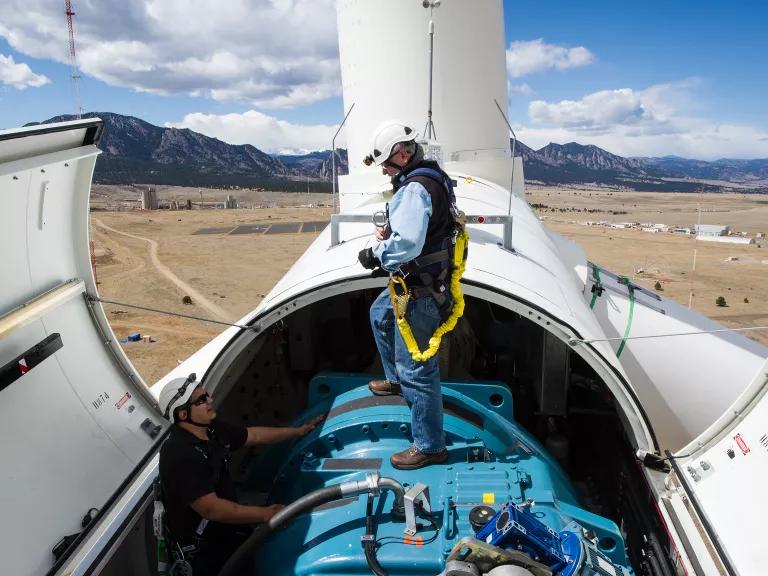

The nacelle of a Siemens 2.3 megawatt wind turbine at NREL's National Wind Technology Center (NWTC) in Colorado
Dennis Schroeder/NREL, 24548
How do wind turbines work?
The most common type of turbine used in the United States today are horizontal-axis wind turbines, which have two to three long, flat propeller blades that face the direction of the wind. Less common are vertical-axis wind turbines, which have blades that look like the beaters in a mixer and don’t have to face the wind to capture energy. This latter type is not as efficient at producing electricity.
Each wind turbine contains a set of propeller blades attached to a rotor at the very top of the turbine tower. Connected to the rotor is a nacelle—a box-like covering that contains a shaft and a generator. The kinetic energy is transformed into electricity by a chain of churning: the wind spins the blades, which also spins the rotor, which then turns the shaft, which spins the generator. The electricity produced by the generator flows down the turbine tower and through a transformer to be converted to the right voltage to be transmitted to our power grid. This entire process produces no air pollution, unlike fossil fuel–powered plants, which have to burn through polluting coal, oil, or gas to create the steam that turns the gears to create electricity.
The bigger the wind turbine, the more energy it can produce. Turbines are also tall because wind blows more consistently and faces less resistance higher up in the air. Longer blades can catch more available wind, even in places that are relatively less windy. There is a wide range in turbine sizes but the average land-based turbine installed in 2022 was 321 feet tall, with propeller blades that are 429 feet in diameter.
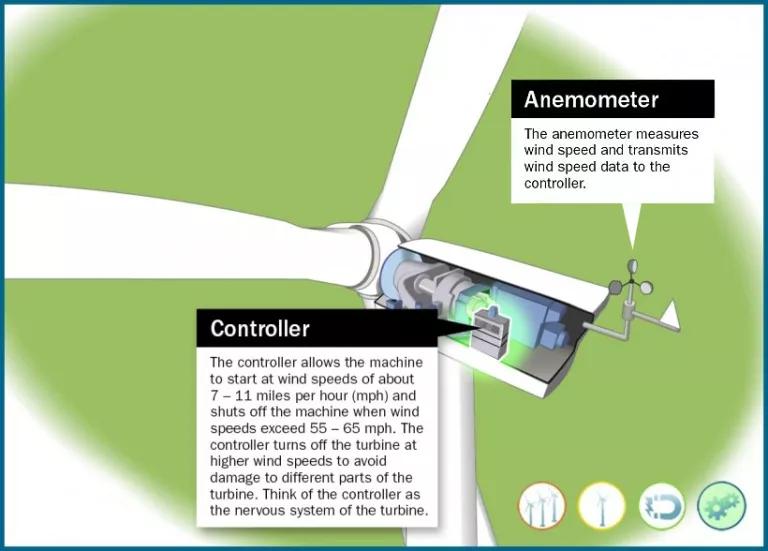
U.S. Department of Energy
Other key components of a turbine include the anemometer and the controller. The anemometer measures wind speed and sends the data to the controller, which turns the turbine on when the wind has reached the minimum speed of 7–11 miles per hour. The controller turns the turbine off if wind speeds are too high to avoid damaging the blades, around 55 miles per hour.
According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration, the average output of a new commercial wind turbine is 843,000 kilowatt-hours of electricity per month. The average U.S. home uses about 893 kilowatt-hours of electricity a month, so a single commercial wind turbine could power nearly 1,000 homes. (By comparison, to power just one home for a month would take more than 1,000 pounds of coal and 6,600 cubic feet of gas .)
Wind farms—essentially, groups of wind turbines—are often located on agricultural lands and in rural areas. Most are owned by independent power producers that sell the electricity to utilities and consumers.
Deciding where to place a wind farm is an essential part of the development process. For starters, a farm should be sited away from large trees and buildings, which might block or slow the wind. Some are built adjacent to communities in remote areas where importing fuel might be expensive. Others are planned in more populated areas with high energy needs. The good news is that wind farms can be developed both on land and over water. There are three key types.
- Land-based wind energy projects: Sometimes referred to as onshore wind, these range in size, with as few as two or three turbines. The average U.S. utility-scale wind farm has 50; the country’s largest (and the third largest in the world) is the Alta Wind Energy Center in California, with 600 turbines. For those located on farmland (as is common in parts of the Midwest), crop rows can be planted and livestock may graze between the turbines, as when landowners choose to host wind developments in exchange for annual payments from power companies.
- Distributed wind energy projects: These are also land-based but operate on a small scale, with capacity that is usually under a megawatt. Instead of generating wholesale energy for a utility, a distributed wind project is on the customer’s side of the meter. It might include just one or a few turbines to serve local needs, like powering a water pump on a farm or electrifying a home.
- Offshore wind farms: Turbines built over water are larger than those on land (up to double the size), allowing them to better catch the strong coastal winds. They can either be anchored onto shallow seafloor, in which case they’re called fixed-bottom wind turbines, or installed on a floating platform in deeper waters. A small floating turbine might power an offshore research facility. A larger farm could supply mainland communities, with the electricity transported via cables to the power grid on land.
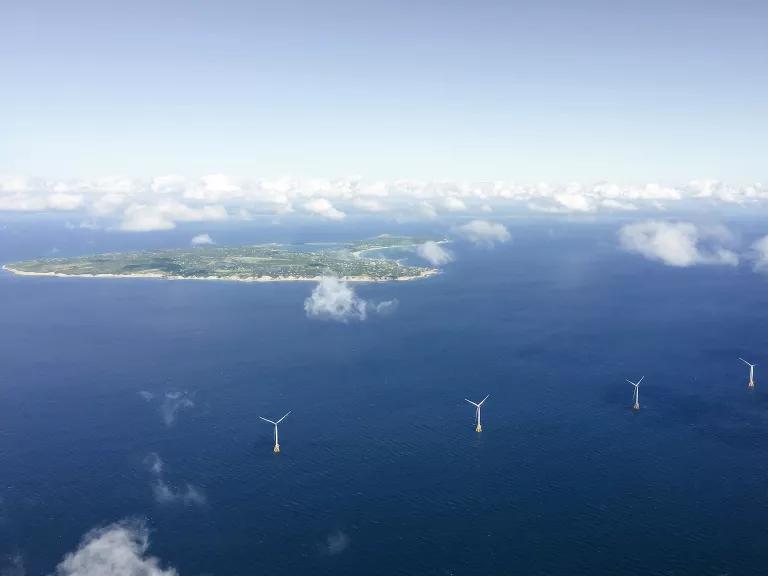

Block Island Wind Farm in the Atlantic Ocean, 3.8 miles from Block Island, Rhode Island
Courtesy of GE
With the clean energy transition comes a windfall of benefits.
Health benefits
Wind energy’s health benefits aren’t about what it produces, but what it doesn’t: air pollution. Long-term investments into clean energy mean we can rely less on power plants that burn coal, oil, and gas, which generate pollutants linked to respiratory and cardiovascular damage , as well as environmental harms. For instance, coal-fired power plants generate 35 percent of mercury emissions in the United States, as well as two-thirds of our sulfur dioxide emissions (which contribute to acid rain) and the vast majority of harmful particulate matter in our air.
Climate benefits
Electricity production accounts for 25 percent of the United States’ greenhouse gas emissions. That’s because we still rely on burning fossil fuels, mostly coal and gas, for 60 percent of the nation’s power supply. As we grapple with the escalating impacts of the climate crisis , we absolutely must end our dependence on fossil fuels by increasing sources of clean energy, like wind.
Cheap energy
Wind energy has rapidly become one of the cheapest energy sources in the country—dropping by 74 percent since 2008 to reach a record low in 2018. (Supply chain issues have recently caused prices to tick up somewhat.) Consumers stand to benefit even more from new investments in the industry. For example, as engineers develop taller towers and bigger blades, turbines can produce power with lower average wind speeds. As efficiency improves and fewer materials are required, operation and installation costs will decrease.
Job creation and economic growth
As the wind industry expands, job opportunities are growing along with it. As of 2022, wind power employs just above 125,000 people , who manufacture, operate, and maintain turbines across the country. According to the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE), there are more than 500 U.S. manufacturing facilities for components, such as blades, towers, and generators. The DOE also estimates there could be up to 600,000 jobs within the wind industry by 2050.
As bright as the future of wind may be, like with any industry, there are challenges to developing and operating wind projects.
Weather and location dependency
Wind is generated everywhere on earth. It’s abundant and inexhaustible—but also variable and uncontrollable. And we need strong, sustained winds to generate reliable electricity. Weather variability makes it harder for communities, especially in low-wind regions, to depend on wind power for all of their energy needs. In the United States, the areas where wind resources are most plentiful may be far from the biggest energy consumers, like densely populated cities.
One major, overdue solution: Update the U.S. power grid . As the nation takes steps to modernize its grid infrastructure, increasing the capacity of the existing grid, incorporating more distributed energy sources, and building new transmission lines will go a long way toward ushering in the clean energy future we need. In fact, in times of record-breaking heat and electricity demand, new wind energy resources have helped save our grid more than once. And when we can connect wind resources across different regions—to capture wind blowing in one area while it’s slowing down in another—we’ll boost resilience even more.
Another solution is battery storage , which can capture excess energy generated by renewable projects and discharge it when it’s needed. Battery storage can increase flexibility and prevent blackouts, especially when it’s combined with improving wind technology, forecasting, and transmission . It also helps to have other renewable sources like solar—since the sun may be shining when the wind isn’t blowing, and vice versa.
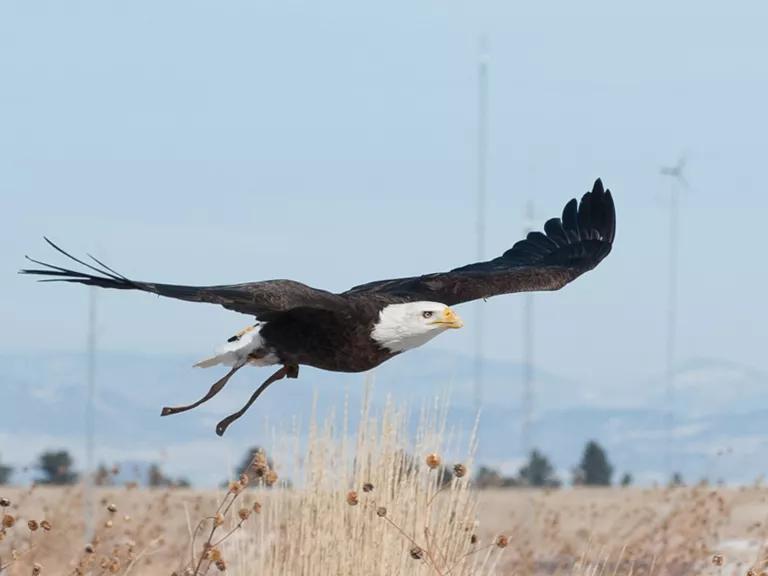

Eagles, trainers, and a veterinarian participated in research to help the U.S. Department of Energy's National Renewable Energy Laboratory develop a radar and visual systems that prevent bird strikes with wind turbines.
Dennis Schroeder/NREL
Wildlife impacts
Many people, including the experts at NRDC, are working to ensure that we develop wind in a way that takes into account the well-being of wildlife and delicate marine ecosystems, which face risks as the industry grows. At the same time, fossil fuels are no friend to wildlife: Tens of millions of animals are killed indirectly each year by fossil fuel projects that destroy habitats, pollute the air, and contaminate water. And climate change, caused largely by the extraction and burning of fossil fuels, will do even more harm.
One of the biggest concerns with wind is the potential risk of birds and bats colliding with propeller blades, especially during migration. Thankfully, efforts are being made to minimize harm. For instance, in February 2024, the U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service released a permitting rule that requires wind projects to be demonstrably low risk to bald and golden eagles. The DOE has also committed to studying potential conflicts between wind and wildlife.
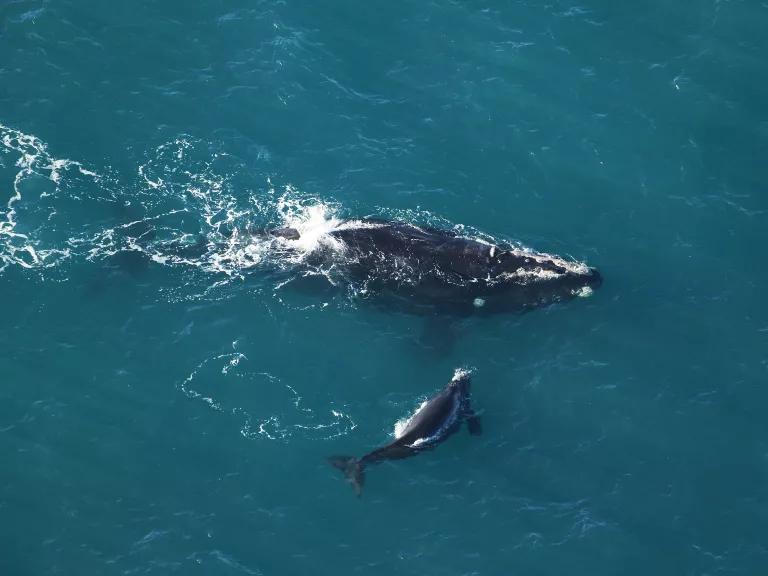

Endangered North Atlantic right whales’ habitat overlaps with virtually all of the offshore wind areas being developed and planned for off the East Coast of the United States.
Clearwater Marine Aquarium Research Institute & USACE, NOAA permit #20556-01, CC BY-NC-ND 4.0
Hazards specific to offshore wind farms might include collision risks with construction and maintenance vessels, as well as disruptive noise during the surveying and construction of a wind farm, which can interfere with the communication between marine mammals. But with proper planning, these impacts can be minimized. NRDC serves on the board of the Renewable Energy Wildlife Institute , which supports research on these solutions, and as far back as 2012, NRDC has collaborated with wind developers to create guidelines that protect marine ecosystems during planning phases. This includes having construction and operations boats move slowly through the water to reduce the risk of whale strikes, monitoring when whales are nearby so loud construction noises don’t disturb them, employing tools that reduce sound impacts, and avoiding construction when whales are feeding or migrating through the area.
Transportation and shipping
As technology evolves and turbine parts get larger, transportation and installation become more challenging. For instance, a port could be equipped for deliveries of large turbine parts, but if the roads out to the designated site are not wide enough, the parts can’t reach their destination. Companies are looking into how to build flexible blades that can be transported more easily and methods to produce the parts right on-site at wind farms.
A common talking point for wind energy skeptics is that the tall towers are too much of an eyesore, especially against a natural landscape. Despite critics’ best efforts, however, public opinion on wind and solar energy has remained positive, with around 75 percent of U.S. adults in support of expanding wind farms. For the vast majority of people, solving the climate crisis is worth altering the view.
Climate misinformation
There’s a lot of climate misinformation out there, and clean energy doesn’t get a pass. Despite what some social media posts may suggest, turbines do not pose a risk to human health. More than 100 peer-reviewed studies about wind energy have concluded that there are no health harms from things like infrasound (low frequency sounds that cannot be audibly heard), shadow flickers (when the blades pass over the sun and cause a quick flicker), or electromagnetic field emissions.
Most land-based wind farms in operation today are located along the West Coast and across the Great Plains in the Midwest, where developers have found strong, consistent winds. Just five states generated half of the country’s wind power in 2022: Texas, Oklahoma, Iowa, Kansas, and Illinois.
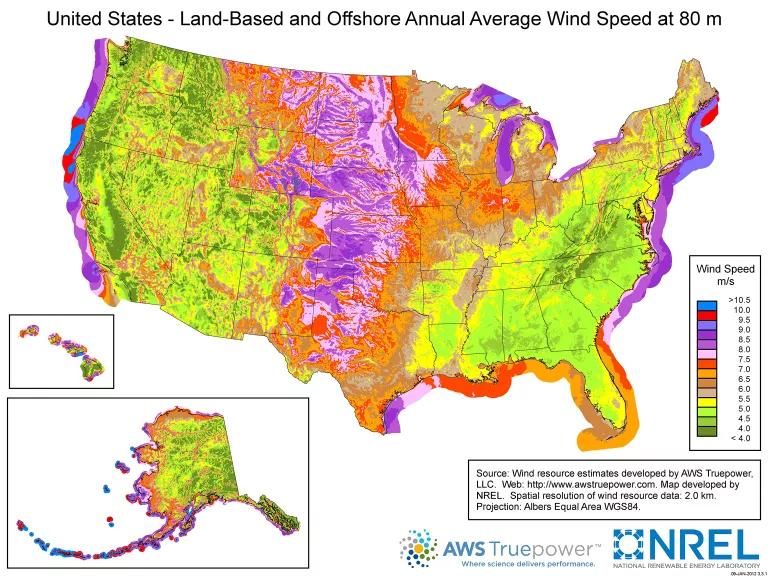
Map of U.S. wind capacity.
NREL/U.S. Department of Energy
Wind energy development is spreading to other parts of the country—both onshore and off—thanks to decreasing costs and the new policies and renewable energy standards that many states are using to combat climate change. Rock Port, Missouri, was the first town in the country to build a community-scale project that has the capacity to generate all of the city’s electricity needs from wind. The project’s four wind turbines are capable of generating 5 megawatts of power—double the amount that the community of 1,200 residents usually needs. When they have excess power, they’re even able to sell it to the state’s power pool.
Some states that once balked at introducing wind farms into their coal-dependent economies have felt the winds shift, if you will, and are now investing in renewable energy projects. (Looking at you, Wyoming .) Unfortunately, high interest rates and supply chain issues have slowed this progress in some places.
Right now, the United States has three completed offshore wind farms: the Block Island farm in Rhode Island’s waters; the Coastal Virginia Offshore Wind pilot project; and the South Fork Wind farm off Long Island, New York, which has the capacity to generate 130 megawatts of energy, enough to power 70,000 homes, with 12 turbines. Many more wind farms are in development, including the 800-megawatt Vineyard Wind 1, which is already generating electricity near Massachusetts. In fact, more than 7 gigawatts of offshore wind projects, supplying power to seven states, are expected to be operational within the next three years.
A much-needed boost for U.S. wind energy came from the Inflation Reduction Act . Government incentives, including tax credits and funding for planning and analysis, have spurred greater private investment. That means more renewable energy, more new jobs, and more action on climate. And that’s a future we’d like to breeze toward.
This NRDC.org story is available for online republication by news media outlets or nonprofits under these conditions: The writer(s) must be credited with a byline; you must note prominently that the story was originally published by NRDC.org and link to the original; the story cannot be edited (beyond simple things such as grammar); you can’t resell the story in any form or grant republishing rights to other outlets; you can’t republish our material wholesale or automatically—you need to select stories individually; you can’t republish the photos or graphics on our site without specific permission; you should drop us a note to let us know when you’ve used one of our stories.
We need climate action to be a top priority in Washington.
Tell President Biden and Congress to slash climate pollution and reduce our dependence on fossil fuels.

Urge President Biden and Congress to make equitable climate action a top priority in 2024
Related stories.

What’s the Most Energy-Efficient Water Heater?

How to Ditch the Biggest Fossil Fuel Offenders in Your Life

Easy Ways to Save Energy at Home
When you sign up, you’ll become a member of NRDC’s Activist Network. We will keep you informed with the latest alerts and progress reports.

- Wind Energy Advantages and Disadvantages
- Energy 101: Resources to Help Understand Energy
- Energy Innovation
Wind energy advantages and disadvantages are important considerations when making decisions about energy with the environment in mind. A cleaner future will involve a mix of energy sources, including those that are renewable like wind power.
Wind is produced as the sun heats the earth unevenly due to the earth’s rotation and geographic features. Warm air rises to create low-pressure areas, while cold air sinks to create high-pressure areas. Air molecules typically move from high pressure areas to low ones, creating the phenomenon we experience as wind.
Harnessing wind as energy is an idea that is thousands of years old. Because it does not involve burning limited fossil fuels and because using wind energy does not decrease the amount of wind, it is considered a renewable energy source. While there are wind power advantages and disadvantages, wind energy has a valuable role to play in a climate-friendly power grid.
Advantages of Wind Energy

In considering wind power pros and cons, the advantages of wind energy are many. These are the reasons for investing in wind power generating capacity.
1. Wind is a type of clean energy
First off, how does wind energy work? It starts with a turbine that the wind turns as it blows. The wind’s kinetic energy turns a generator in the structure that creates electricity. Modern wind turbines are extremely efficient at turning even light breezes into electricity.
One of the advantages of wind energy is that it is clean energy , meaning that it doesn’t emit greenhouse gasses when generating electricity. Your carbon footprint is the total of all gasses, like carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide, that result from burning fossil fuels. If you can burn less fossil fuel for energy, replacing it with clean, renewable energy like from wind, you reduce your carbon footprint .
2. Wind is a renewable energy source
Another advantage of wind energy is that it is renewable energy. It comes from wind, which is a naturally occurring resource that doesn’t get used up. How is green energy different from renewable energy? In addition to coming from an unlimited resource, it does not produce greenhouse gasses. In these ways, wind energy is similar to solar energy .
3. Wind power has a low operating cost
Because wind power is a renewable energy source , there is no ongoing expense to acquire fuel. Once the wind turbine is installed, the only real cost is maintenance. As the world decarbonizes electricity generation in the future, wind is a clean, renewable, and low-cost option.
4. Wind turbines save space
Another factor in the wind power pros and cons equation is the fact that it is space efficient and fits well with other land uses. Wind turbines can be spread across fields with enough space between them to be productive. Because they are elevated off the ground the space below them is open to other uses, like farming.
5. Wind power generation promotes domestic economic growth
Harnessing wind power is economically beneficial beyond wind energy being inexpensive to produce. It relies on a local resource and creates local jobs . Investment in wind power is growing. In the last 10 years, wind generation capacity has increased 30 percent. Utility-scale wind plants across 41 states have created more than 100,000 jobs in the U.S.
Disadvantages of Wind Energy
We must consider both wind energy advantages and disadvantages when weighing the benefits of this renewable energy source. Indeed, there are disadvantages to wind power.
1. Wind turbines can be dangerous to some wildlife
Wind turbines can be fatal to wildlife. Birds and bats collide with them and turbines interfere with bat sonar navigation. Certain species with low reproductive rates are more impacted, as are migratory birds, but researchers are investigating innovative ways to reduce the danger to wildlife.
2. Wind turbines can be noisy
Wind turbines create both aerodynamic noise of the blades slicing through the air and mechanical noise of the power generating machinery in them. The noise can affect wildlife but is generally not a factor unless you are standing nearby.
3. Wind power is limited by location
Wind power won’t work everywhere. You need areas where wind blows strong and steady to make the investment worthwhile. Even with ideal locations in coastal areas, hills, and open fields where the wind is especially strong, it doesn’t blow all the time. Energy generation slows or stops when the wind slows or stops, a concept known as “intermittency.”
Learn More about Wind Energy from Constellation
As you make your home more sustainable , consider the residential renewable plans available in many areas, including wind energy plans. You can compare renewable energy rates and choose the option that best fit your needs. With an appreciation of wind energy advantages and disadvantages, you can make choices that benefit the environment.
Zip Code is not valid
Wind Power Pros & Cons: Advantages, Disadvantages of Wind Energy
Pop quiz: what is the most prevalent source of renewable electricity in the u.s. today hint: the answer might blow you away. wind power is on the rise thanks to its many advantages and benefits—both economical and environmental..

Topics covered
What is wind energy.
- Advantages of wind energy
- Disadvantages of wind energy
How much energy does a wind turbine produce?
Is wind energy expensive, does wind energy cause pollution, the future of wind energy.
In 2020, renewables accounted for more total electricity generation than coal for the first time on record. In other words, the renewable revolution is well underway. And paving the path?
Wind power.
Wind is currently the most widespread renewable electricity source in the U.S., accounting for 8% of all renewable electricity generation —more than hydro, solar, and biomass. That number is projected to continue to grow in the coming years.
We tend to hear a lot about the benefits of solar. For good reason: the solar industry is booming and for many homeowners, solar is more suitable and accessible than other renewable sources like hydro, geothermal, and wind.
But wind has played and will continue to play a crucial role in paving the way toward a collective clean energy future. Below, we’re diving into the pros and cons of wind energy to fully understand why the outlook is promising.
Relative to other renewables, how wind energy works is actually fairly straightforward.
In fact, if you’ve ever seen a wind turbine, then you have a sense of what wind energy is. Quite simply, wind energy refers to electricity created from the wind.
Wind power is generated via massive wind turbines that collect the kinetic energy of the wind through rotor blades. When the wind blows, it turns the blades of a turbine which captures the aerodynamic force of the wind and uses it to power a generator that produces electricity. That electricity is then sent through wires—in the case of residential wind turbines , directly to a home—or to the electric grid where it is then redistributed by utilities to homes and businesses across the U.S.
Like many renewables, wind is a variable energy source, meaning it only produces energy intermittently (when the wind is blowing) rather than on demand. Still, one large turbine can produce a lot of energy every year. In fact, an average-sized wind turbine can produce enough electricity to power a home for a whole month in just under 100 minutes of operation.
What are the advantages of wind energy?
Like all renewables, wind energy claims a variety of advantages not only over fossil fuels , but also over other renewable energy sources. Here are some of the biggest benefits of wind power.
It’s clean, sustainable, and abundant
Wind energy is a clean energy source—the electricity it generates is free of greenhouse gas emissions. Once a turbine is built, it can entirely be powered by the wind, meaning it doesn’t have any emissions. And all the energy that it generates can be distributed across the electric grid, greening the overall electric supply. Moreover, wind is an abundant energy source, enabling it to provide substantial power supply to the electric grid. Although wind energy cannot be generated on demand, it can still generate enough electricity to power thousands of homes, businesses, and communities across the country every year.
It’s cost effective
Another major benefit of wind energy is that it’s highly cost effective. While wind turbines can be relatively expensive to install, they can easily make up that upfront investment due to their low maintenance and operation costs. Wind’s levelized cost of energy (LCOE) is lower than many other renewables and significantly lower than coal and gas. Wind costs just an average of $0.01-0.02 per kilo-watt hour generated. These low costs are not just good for investors looking to invest in the wind industry, but they’re also helping to lower the cost of energy for residents too.
The price for wind energy continues to decrease as technology improves
As technology improves, the cost of wind is dropping. A 2019 study found that the cost of onshore wind had dropped by 27% since 2013, and that trend is anticipated to continue. In fact, this is a trend that is widely common across the entire renewables industry. In 2021, renewables officially became the cheapest energy source on earth. In many markets, it’s now cheaper to build and operate a new wind or solar farm today than it is to continue to operate an already existing coal plant. This drop in price is largely due to improvements in technology which have lowered installation costs as well as operation and maintenance costs.
Turbines are an efficient use of land
Although wind turbines are massive, they take up a relatively small amount of land space. It’s entirely possible to build a wind turbine on a farm and still maintain the agricultural value of that land.
Helps to revitalize rural economies and supports agriculture
Installing wind turbines has become popular in agricultural regions of the country as a way to receive consistent income every year. Wind turbines provide a steady stream of income that can help farmers navigate the unpredictability of farming. As droughts, floods, tariffs, and fluctuating prices have become commonplace for farmers in recent years, wind energy has allowed farmers to persevere through the uncertainty. Wind energy has also helped boost the tax base in rural regions which has helped revitalize the economy in those areas, helping to fund things like new schools and new public work facilities. Installing wind turbines has also helped create jobs in these economies.
What are the disadvantages of wind energy?
It’s a variable energy source (it needs wind to work).
One of the major disadvantages of wind energy is that it is a variable energy source, meaning it cannot be generated on demand. Wind farms are dependent on wind blowing, which means on their own, wind farms are not a suitable solution for a sustainable and reliable energy grid. That being said, energy storage technology continues to improve and become more cost-effective, which is helping to stabilize energy supply and demand. For the time being, electrical grids require additional sources of power to supplement the times where energy demand is high, and the wind isn’t blowing.
Not the most aesthetically pleasing
Some people don’t like seeing turbines in the landscape. Their big rotors take up a lot of space and many claim that they’re an eyesore. Another major complaint when it comes to wind turbines has to do with the flickering shadow they cast as their blades rotate. This flickering shadow can be disturbing to both people and animals.
Turbines can be loud In addition to potentially being an eyesore
wind turbines are also fairly loud. As the rotors get spinning, they produce a lot of residual noise which can be disturbing to locals who live nearby wind farms. It’s important that wind farms are carefully designed and properly spaced out from residential homes to ensure that noise isn’t a major issue.
Construction can cause local disturbances
Once installed, wind turbines have a fairly small footprint on land. However, the process of installing wind turbines can be disruptive. Constructing wind turbines requires heavy equipment and lots of space due to the sheer size and weight of the turbines. This can be especially disruptive for farms that are hoping to grow crops around their wind turbines. The good news is that most of this disruption can be mitigated and repaired once the turbine is up and running.
Can negatively impact local wildlife if not carefully designed
Wind turbines have been shown to be disruptive to some wildlife, particularly bats and birds and even some plants. Constructing wind turbines can have adverse effects on land that can affect the wildlife that previously lived in those areas. Offshore wind turbines also can potentially have a negative impact on sea-environments, disrupting fish habitat.
Your wind energy questions, answered
The amount of energy that a wind turbine can produce depends on several factors including the size of the rotors, the type of wind turbine, and, of course, the amount of wind that’s blowing. Newer designs with larger, more aerodynamic rotors will generate more energy when the wind is blowing than smaller, less efficient turbines. Offshore turbines typically generate more energy than onshore turbines, partly because the wind is more consistent at sea versus on land.
According to the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS), the average wind turbine in the U.S. produces around 400,000 kWhs of electricity per month when operating at 33% capacity. This is enough energy to power 450 homes with the average monthly electricity usage (893 kWhs). The output is calculated at 33% because wind turbines typically cannot convert 100% of the kinetic energy they harness into electricity—they operate at around 30-50% of their power efficiency rating.
The most efficient wind turbine on the market is called a three-blade horizontal-axis wind turbine (three-blade HAWT). Hundreds of thousands of these turbines have been deployed across the world. In addition to having very efficient blades, these turbines are also controlled by computers to face the optimal direction to harness the power of the wind, no matter what direction it is blowing. As technology advances, wind turbines are getting more efficient, able to convert wind into electricity more effectively.
One of the major pros of wind energy is that it is relatively cheap to produce. While it can be expensive to build and install both onshore and offshore wind turbines, the maintenance and operation costs of generating wind energy is remarkably cheap.
In 2019, the average cost of building and operating a new solar farm was roughly $0.053 per kilowatt-hour, with the range varying depending on the region between $0.051 and $0.099 according to the Internation Renewable Energy Agency . These prices have dropped by 44%-78% across different regions and markets since 2010, and that trend is expected to continue as technology improves and operation costs decline. Just the cost of installing onshore wind turbines has decreased by hundreds of dollars per kilowatt-hour since 2013. Offshore wind is typically a bit more expensive per kilowatt-hour due to the higher cost of building these turbines.
Generating wind energy is emissions-free and has a relatively low impact on the environment in comparison to other energy sources. In almost all cases, operating a wind farm does not contribute to pollution and helps to reduce carbon emissions by mitigating the need for coal and gas plants to generate electricity.
The only major emissions and pollutants generated from wind energy come from the manufacturing and construction of the turbine. That being said, the overall environmental footprint of manufacturing, building, installing, and operating a wind turbine is considered to be low. Once erected, they even take up very little ground space, and the habitat that was disrupted during the construction process can be revitalized.

The future of wind energy is bright. Many experts predict that wind energy will be an abundant and affordable source of energy by 2050. As technology advances, the cost of installing and operating wind turbines will continue to decrease. At the same time, wind turbines will also become more efficient, allowing them to convert more wind power into usable electricity. This means more affordable, cleaner electricity for homeowners and businesses.
Additionally, technological and scientific advancements can mitigate some of wind energy’s current disadvantages. Tech innovations have already led to new wind turbine designs that are less unsightly and, in some cases, can even capture wind indirectly in ways outside of the wind blowing—such as from the air displaced by a driving a car.
The benefits of the wind industry extend beyond just increasing the amount of renewable energy generated across the electrical grid too. The wind industry is predicted to generate 600,000 manufacturing, maintenance, and installation jobs by 2050. Wind energy also helps stabilize energy prices, and as wind becomes more popular and prevalent, it should help reduce the occurrences of rate spikes and volatile electricity prices. In summary, wind is well-positioned to play a crucial role in our renewable energy revolution.


Get matched to a local solar farm and save on your electricity costs.
- Clean energy
- Wind energy
- The top pros and cons of...
The top pros and cons of wind energy
- Share to LinkedIn
- Share to Facebook
- Jacob Marsh
As subject matter experts, we provide only objective information. We design every article to provide you with deeply-researched, factual, useful information so that you can make informed home electrification and financial decisions. We have:
Sourced the majority of our data from hundreds of thousands of quotes through our own marketplace.
Incorporated third-party data and information from primary sources, government agencies, educational institutions, peer-reviewed research, or well-researched nonprofit organizations.
Built our own database and rating system for solar equipment, including solar panels, inverters, and batteries.
We won't charge you anything to get quotes through our marketplace. Instead, installers and other service providers pay us a small fee to participate after we vet them for reliability and suitability. To learn more, read about how we make money and our Editorial Guidelines .
)
Wind energy refers to any form of mechanical energy that is generated from wind or some other naturally occurring airflow. There are advantages and disadvantages to any type of energy source, and wind energy is no different. In this article, we'll review some of the top pros and cons of generating electricity from wind turbines.
- 100% free to use, 100% online
- Access the lowest prices from installers near you
- Unbiased Energy Advisors ready to help
Top pros and cons of wind energy
Wind energy is one of the most common types of renewable energy in the U.S. today and also happens to be one of our fastest-growing sources of electricity. However, while there are a number of environmental benefits to using wind energy, there are some downsides. Here are a few of the top pros and cons:
Pros and cons of wind energy
On the pros side, wind is a clean, renewable energy source and is one of the most cost-effective sources of electricity. On the cons side, wind turbines can be noisy and unappealing aesthetically and can sometimes adversely impact the physical environment around them. Similar to solar power, wind power is also intermittent, meaning that turbines are reliant on weather and therefore aren't capable of generating electricity 24/7.
Below, we'll explore these pros and cons in further detail.
Advantages of wind energy
Wind energy is clean and renewable.
Unlike coal, natural gas, or oil, generating electricity from wind doesn't result in greenhouse gas emissions. While there are some environmental considerations that come with building large wind farms, once operational, wind turbines themselves don't require burning any fossil fuels to operate.
Additionally, wind energy is entirely renewable and will never run out. In opposition to traditional fossil fuel resources that replenish very slowly, wind naturally occurs in our atmosphere, and we don't have to worry about supply issues in the future.
Wind energy is a job creator
In terms of job creation, the wind energy sector is the fastest-growing in the United States. There are more than 100,000 workers in the field, with the potential to support more than 600,000 in the coming years.
Wind energy has low operating costs
Regarding upfront costs, wind farms or individual turbines can be expensive to install. However, once up and running, operating costs are relatively low; their fuel (wind) is free, and the turbines don't require too much maintenance over the course of their lifetime.
Wind energy is space-efficient
Cumulatively, wind farms can take up a lot of land space; however, the actual turbines and equipment don't use up much real estate. This means that land used for wind turbines can often also be used for other purposes, such as farming.
Disadvantages of wind energy
Wind energy is intermittent.
A wind turbine's effectiveness in generating electricity depends on the weather; thus, it can be difficult to predict exactly how much electricity a wind turbine will generate over time. If wind speeds are too low on any given day, the turbine's rotor won't spin.
This means wind energy isn't always available for dispatch in times of peak electricity demand. In order to use wind energy exclusively, wind turbines need to be paired with some sort of energy storage technology.
Wind energy causes noise and visual pollution
One of the biggest downsides of wind energy is the noise and visual pollution. Wind turbines can be noisy when operating due to both the mechanical operation and the wind vortex created when the blades are rotating. Additionally, because wind turbines need to be built up high enough to capture a good amount of wind, the turbines can often interrupt otherwise scenic landscapes, such as mountain ranges, lakes, oceans, and more.
Wind turbines have some negative impacts on their surrounding environment
A wind turbine's blades are very large and rotate at very high speeds. Unfortunately, their blades can harm and kill species that fly into them, like birds and bats. The construction of wind farms can also disrupt the natural habitats of local species if not conducted sustainably. However, these problems can be solved to some extent with technological advancements and properly-siting wind farms.
Wind energy is remote
Wind energy requires transmission. In many cases, turbines and generation sites may be located quite far from the population centers where electricity is needed. Therefore, transmission lines are an additional piece of infrastructure that must be built for this form of energy generation to be successful.
Create your own clean energy with solar panels.
Enjoy the benefits of solar without rooftop panels.
Explore heat pumps, the latest in clean heating & cooling technology.
See solar prices near you.
Enter your zip code to find out what typical solar installations cost in your neighborhood.
- Our offerings
- Community solar
- Heating & cooling
- Backup power
- EV charging
- For your business
- Other energy options
- Solar calculator
- Solar rebates
- Help center
- Home solar guide
- Market intel
- Refer a friend
- Mission & values
- How it works
- Editorial guidelines
- Work with us
- Solar & HVAC installers
- Corporate partnerships
- Community programs
- Utility programs
ENERGYSAGE is a registered trademark and the EnergySage logo is a trademark of EnergySage, Inc. Other trademarks are the property of either EnergySage, Inc. or our licensors and are used with permission.
© Copyright 2009-2024 EnergySage, Inc. All rights reserved.
Learn more about our success working with the U.S. Department of Energy.
ENCYCLOPEDIC ENTRY
Wind energy.
Scientists and engineers are using energy from the wind to generate electricity. Wind energy, or wind power, is created using a wind turbine.
Earth Science, Climatology
As renewable energy technology continues to advance and grow in popularity, wind farms like this one have become an increasingly common sight along hills, fields, or even offshore in the ocean.
Photograph by inga spence / Alamy Stock Photo

Anything that moves has kinetic energy , and scientists and engineers are using the wind’s kinetic energy to generate electricity. Wind energy , or wind power , is created using a wind turbine , a device that channels the power of the wind to generate electricity.
The wind blows the blades of the turbine , which are attached to a rotor. The rotor then spins a generator to create electricity. There are two types of wind turbines : the horizontal - axis wind turbines (HAWTs) and vertical - axis wind turbines (VAWTs). HAWTs are the most common type of wind turbine . They usually have two or three long, thin blades that look like an airplane propeller. The blades are positioned so that they face directly into the wind. VAWTs have shorter, wider curved blades that resemble the beaters used in an electric mixer.
Small, individual wind turbines can produce 100 kilowatts of power, enough to power a home. Small wind turbines are also used for places like water pumping stations. Slightly larger wind turbines sit on towers that are as tall as 80 meters (260 feet) and have rotor blades that extend approximately 40 meters (130 feet) long. These turbines can generate 1.8 megawatts of power. Even larger wind turbines can be found perched on towers that stand 240 meters (787 feet) tall have rotor blades more than 162 meters (531 feet) long. These large turbines can generate anywhere from 4.8 to 9.5 megawatts of power.
Once the electricity is generated, it can be used, connected to the electrical grid, or stored for future use. The United States Department of Energy is working with the National Laboratories to develop and improve technologies, such as batteries and pumped-storage hydropower so that they can be used to store excess wind energy. Companies like General Electric install batteries along with their wind turbines so that as the electricity is generated from wind energy, it can be stored right away.
According to the U.S. Geological Survey, there are 57,000 wind turbines in the United States, both on land and offshore. Wind turbines can be standalone structures, or they can be clustered together in what is known as a wind farm . While one turbine can generate enough electricity to support the energy needs of a single home, a wind farm can generate far more electricity, enough to power thousands of homes. Wind farms are usually located on top of a mountain or in an otherwise windy place in order to take advantage of natural winds.
The largest offshore wind farm in the world is called the Walney Extension. This wind farm is located in the Irish Sea approximately 19 kilometers (11 miles) west of the northwest coast of England. The Walney Extension covers a massive area of 149 square kilometers (56 square miles), which makes the wind farm bigger than the city of San Francisco, California, or the island of Manhattan in New York. The grid of 87 wind turbines stands 195 meters (640 feet) tall, making these offshore wind turbines some of the largest wind turbines in the world. The Walney Extension has the potential to generate 659 megawatts of power, which is enough to supply 600,000 homes in the United Kingdom with electricity.
Media Credits
The audio, illustrations, photos, and videos are credited beneath the media asset, except for promotional images, which generally link to another page that contains the media credit. The Rights Holder for media is the person or group credited.
Production Managers
Program specialists, last updated.
October 19, 2023
User Permissions
For information on user permissions, please read our Terms of Service. If you have questions about how to cite anything on our website in your project or classroom presentation, please contact your teacher. They will best know the preferred format. When you reach out to them, you will need the page title, URL, and the date you accessed the resource.
If a media asset is downloadable, a download button appears in the corner of the media viewer. If no button appears, you cannot download or save the media.
Text on this page is printable and can be used according to our Terms of Service .
Interactives
Any interactives on this page can only be played while you are visiting our website. You cannot download interactives.
Related Resources
{{ currentSearchSuggestions.title }}
- {{ lang.text }}
{{ currentMenugamenu.label }}
{{ currentMenugamenu.desc }}
- currentSubMenugamenuIndex ? 1 : 0" @click=" onMegamenuItemClick( $event, index, item, currentMenugamenu.track + ':' + item.track ) " @keydown.space.stop.prevent=" onMegamenuItemClick( $event, index, item, currentMenugamenu.track + ':' + item.track ) "> {{ item.label }}
{{ currentSubMenugamenu.label }}
{{ currentSubMenugamenu.desc }}
{{ card.title }}
{{ currentsubmenugamenu.numbers.title }}, all the benefits of wind power.
Wind power is a technologically mature source of energy with enormous potential. Increasingly competitive, it takes up less land because it extends vertically, requires minimal maintenance and integrates perfectly with the circular economy model.

Essay on Wind Energy
Students are often asked to write an essay on Wind Energy in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Wind Energy
Introduction to wind energy.
Wind energy is a form of renewable energy produced by wind turbines. These are large structures that capture the wind’s power and convert it into electricity.
How Wind Energy Works
Wind turbines use blades to collect the wind’s kinetic energy. The wind turns the blades, which spin a shaft connected to a generator, creating electricity.
Advantages of Wind Energy
Wind energy is sustainable and doesn’t release harmful emissions. It’s a great way to reduce our reliance on fossil fuels, helping to combat climate change.
In conclusion, wind energy is a valuable, renewable source of power with many benefits for our planet.
Also check:
- 10 Lines on Wind Energy
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Wind Energy
- Paragraph on Wind Energy
250 Words Essay on Wind Energy
Wind energy, a renewable source of power, has been harnessed by humans for centuries. Today, it plays a pivotal role in the global energy landscape, offering a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels.
The Science Behind Wind Energy
Wind energy is derived from the natural movement of air across the Earth’s surface. When heated by the sun, air rises and cooler air rushes in to replace it, creating wind. Wind turbines capture this kinetic energy and convert it into electricity. The larger the turbine and the faster the wind speed, the more electricity is produced.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Wind energy is a clean, renewable source of power that produces no greenhouse gas emissions during operation. Moreover, wind turbines take up less space than the average power station, making them less detrimental to the environment. The sustainability of wind energy makes it a key player in the fight against climate change.
Economic Implications
The initial investment for wind energy infrastructure can be high. However, the long-term benefits include low operational costs and a stable power source not subject to fuel market fluctuations. As technology advances, the cost of wind energy continues to decrease, making it an increasingly viable economic choice.
Conclusion: The Future of Wind Energy
Wind energy is poised to play a significant role in the future of global energy production. As we strive for a more sustainable future, harnessing the power of the wind is a practical and necessary step. With advancements in technology and increased investment, the potential of wind energy is limitless.
500 Words Essay on Wind Energy
Wind energy, a form of renewable energy, harnesses the power of the wind to generate electricity. It is an increasingly significant part of the global renewable energy landscape and plays a fundamental role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
The science behind wind energy is simple yet powerful. Wind turbines capture the wind’s kinetic energy and convert it into electrical power. The blades of a wind turbine rotate when hit by the wind, which then drives an electric generator to produce electricity. The stronger the wind, the more electricity is generated.
Wind energy offers a multitude of benefits. Firstly, it is a renewable resource, meaning it is inexhaustible and can be replenished naturally. This contrasts with fossil fuels, which are finite and harmful to the environment.
Secondly, wind energy is clean and does not emit any greenhouse gases during operation, contributing to the fight against climate change. It also requires no water for operation, thus conserving water resources.
Lastly, wind energy can be a significant job creator. The design, manufacturing, installation, and maintenance of wind turbines require a diverse range of skills, thus creating employment opportunities.
Challenges and Solutions
Despite its advantages, wind energy also faces challenges. Wind is an intermittent source of energy, and wind turbines produce electricity only when the wind blows. This intermittency can be mitigated by pairing wind farms with energy storage systems or other forms of renewable energy like solar power.
Another challenge is the environmental impact of wind turbines, including noise pollution and the potential harm to wildlife, particularly birds. However, advances in technology are mitigating these issues. For example, newer turbines are quieter and designed to minimize harm to birds.
The Future of Wind Energy
The future of wind energy is promising. With advancements in technology and increasing investment, wind energy’s efficiency and affordability continue to improve. Offshore wind farms, which can harness stronger and more consistent winds, are expected to play a significant role in the future energy mix.
Furthermore, the integration of wind energy with other renewable energy sources and storage technologies will enhance grid reliability and resilience. This will allow for a higher penetration of wind energy into the energy system, contributing to a sustainable and carbon-neutral future.
In conclusion, wind energy is a crucial component of the global renewable energy portfolio, offering a clean, renewable, and increasingly cost-effective solution to our energy needs. While there are challenges to overcome, the future of wind energy is bright, promising a sustainable and carbon-neutral energy future.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
- Essay on Save Energy
- Essay on One Step Towards Green and Clean Energy
- Essay on Importance of Energy Conservation
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Home Essay Examples Environment Wind Energy
Renewable Energy: Advantages And Disadvantages Of Wind Energy
- Category Environment
- Subcategory Environmental Sustainability
- Topic Solar Energy , Wind Energy

Introduction:
It is indisputable that electricity has completely revolutionised modern society. By creating a better and more efficient lifestyle, electricity has now been embedded in all facets of our day to day lives, to which we now rely on it heavily. With the perpetual growth and advances in technology globally, it is palpable that the demand for energy is increasing significantly as a direct result of our modern day requirements. Can we continue to meet this demand? Currently, the most well-established energy source is obtained through the thermal decomposition of naturally obtained fossil fuels (coal, oil, natural gasses etc). While this may be a relatively consistent means of generating energy in our current day, our exponential growth in population and demand for electricity has meant that our once abundant supply of fossil fuels has been heavily depleted and risks being completely exhausted.
Essentially, this is due to the millions of years that the fossils take to fully replenish in conjunction with the superfluous amounts of fossil fuels we burn daily to meet our energy demands. At the current rates of production, it is projected that oil will run out in 53 years, natural gas in 54 years, and coal in 110 years. To add to the negative foreseeable future of the non-renewable energy source in fossil fuels, comprehensive studies have shown that the process yields substantial amounts of carbon dioxide into the air. As a result, ‘global warming’ and ‘acid rain’ are promoted, which has an exceedingly severe effect on the environment.
Our writers can write you a new plagiarism-free essay on any topic
Essentially, the continuous depletion of fossil fuels in combination with the harsh environmental repercussions has sent mankind into a search for an alternative to solve this global enigma. With such adversity surrounding the non-renewable energy scheme, the idea of ‘renewable energy’has been introduced. This energy comes from natural sources (wind, solar, hydro, geothermal heat etc) that are restored on a more prompt timescale. Despite the inconsistent nature and intermittency issues of renewables, we have seen consistent inflation in the number of renewable systems as the effectiveness increases by the day. Ultimately, this report will perlustrate the viability of wind as an adequate energy source for the future social and economic development of the world.
Wind Energy:
Wind is essentially an intricate form of energy that is evident due to solar energy, the variation in land and water formations, and the continuous rotation of the earth. As a result of these factors, there are considerable variations in atmospheric pressure around the world. When a difference in atmospheric pressure exists, air moves from the higher to the lower pressure area, resulting in winds with a diverse range of speeds. Across different regions, wind patterns can be established which helps to outline the areas with consistent high wind zones.
Basically, wind turbines are used to convert the kinetic energy in wind into other sources of usable electricity. Windfarms operate under a relatively simple concept, but have become more sophisticated as technology has been enhanced to increase the yield of usable energy. As wind hits the turbine, simple airfoil technology allows the propeller to rotate around the rotor. These rotator blades have the ability to be adjusted depending on the wind speed. This is in order to find the best pitch and maximise energy output. Because the turbines turn at such a low velocity (due to noise constraints and mechanical problems), the gearbox (located in the nacelle) converts the lower speed rotation of the drive shaft into high-speed rotations using a planetary gear set arrangement. Consequently, the electricity that is produced is transferred through the cables to the base where a step-up transformer is situated. This energy can then be transmitted to a power grid that it used to distribute the electricity accordingly.
Advantages of Wind Energy:
Wind Energy is one of the most eco-friendly energy sources available in this current day. Most non-renewable energy sources need to be burnt which releases carbon dioxide and methane into the atmosphere. After comprehensive studies, it has been confirmed that these greenhouse gases contribute to global warming and acid rain. On the other hand, wind turbines produce no harmful emissions and therefore do not impact the earth, water table or the quality of the air we breathe. Wind-generated electricity relies solely on the presence of wind. Since there is always an imbalance of thermal input, there is no way in which an atmospheric ‘equilibrium’ could be obtained that completely terminates wind. Hence, wind is both completely renewable and sustainable, which means that it is a consistent form of energy that could provide electricity for the foreseeable future. The wind energy industry has flourished since wind turbines became commercially available. As a result of this, copious amounts of people have been provided with a stable job and workplace.
According to data released by the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), the wind power industry employed 1.15 million people in the manufacturing, installation, maintenance and energy consultation regarding wind-powered electricity. For rural communities (where wind farms are normally situated) this has relieved a lot of money- related stress that comes with trying to make a living. Not only has this led to economic growth by minimising poverty, but it has also created a better quality of life for developing nations. Land-based utility-scale wind is one of the lowest priced renewable energy technologies available to this day. Depending on the wind resource and project financing of the particular wind farm, it normally costs between four and six cents per kilowatt hour. Electricity derived from wind farms is then sold at a fixed price. This fact in conjunction with the idea that its fuel is ‘free’ means that wind energy alleviates price inconsistency that is often associated with fossil fuels. The worldwide potential for wind power is prodigious. Multiple research teams have also been able to establish an amazing development; More than 400 terawatts of power could be generated from surface winds and more than 1800 terawatts could be extracted from atmospheric winds. Comparatively, people globally use about 1800 terawatts of power. Ultimately, it is important to understand that these amounts are immensely bigger than our current and projected global energy demands. Because this also provides an alternate form of creating energy for all countries, it gives a sense of freedom from the political volatility of oil and gas from other countries.
Disadvantages of Wind Energy:
It is inevitable that wind fluctates. Although wind energy is sustainable and will never ‘run out’, wind is inconsistent as patterns change considerably over the course of the day. As a result, wind energy is not considered as an effective base load energy source. This effectively means that other sources are required to be used in tandem with turbines to assure we meet our high and continuously increasing energy demands. Although costs are reducing over time, wind turbines still require large financial investments to cover the installation and maintenance costs. Because high wind sites are normally stationed in rural areas, this also means that more money, time and effort is required to build the turbines and distribute electricity into the urban areas that are more energy dense. One of the most common disadvantages of wind energy is the noise and aesthetic pollution that is at the forefront of public objection. Because of the outright size of wind farms, they are often considered as a large detriment to the landscape – which is what we are essentially trying to preserve when using renewable systems.
Additionally, it can be noted that people living in close proximity to windfarms often complain about the noise leading to physiological distress and hearing loss. The most common wind turbine consists of 116-ft blades atop a 212-ft tower for a total height of 328 feet. Overall, the blades cover a vertical airspace of just under an acre. Because this area is so substantial, wind turbines pose a significant threat to wildlife. For example, with more than 6,700 turbines in Ontario, over 16,000 birds and between 26,000 and 93,000 bats are killed each year in that province alone. Although these numbers are insignificant compared to other manmade structures, wind farms still contribute to mortality rates among birds/bats and will continue to increase as wind farms become more popular. Another key point of contention against wind farms is that they require much larger amounts of land to match the same amount of electricity that a typical fossil fuel system would generate. This is an important downgrade of their ‘eco friendly’ motto that is often conveniently ignored. While wind turbines have been known to have been a successful economic investment, it may not be the most effective use of land as alternative uses of the land (ie. farming animals/crops) may be more profitable.
We have 98 writers available online to start working on your essay just NOW!
Related Topics
Related essays.
By clicking "Send essay" you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
By clicking "Receive essay" you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
We can edit this one and make it plagiarism-free in no time
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
Home — Essay Samples — Environment — Wind Energy — Application And Advantages Of Wind Energy In South Africa
Application and Advantages of Wind Energy in South Africa
- Categories: South Africa Wind Energy
About this sample

Words: 2407 |
13 min read
Published: Oct 25, 2021
Words: 2407 | Pages: 5 | 13 min read
Table of contents
Introduction, feasibility in south africa, advantages of wind power.

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Verified writer
- Expert in: Geography & Travel Environment

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
1 pages / 572 words
1 pages / 291 words
6 pages / 3053 words
1 pages / 335 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Wind Energy
The debate over the use of wind power as a sustainable energy source has become increasingly contentious in recent years. Proponents argue that wind power is a clean and renewable alternative to fossil fuels, while opponents [...]
A wind farm is a collection of wind turbines that generate electricity by harnessing the power of wind. These turbines are typically installed in areas with strong and consistent winds, such as onshore and offshore locations. [...]
Wind power, a renewable and clean source of energy, has gained increasing attention and significance in recent years as the world strives to reduce its reliance on fossil fuels and combat climate change. This essay explores the [...]
Wind energy, simply put, is the process of harnessing the power of the wind to generate electricity. It is a renewable and clean source of energy that holds immense importance in our efforts to combat climate change and [...]
India is presently ranked fourth in the worldwide wind energy installation list, with an estimated capability of approximately 1271 MW installed on 28 February 2001, a figure behind Germany, Denmark and the US. The Worldwatch [...]
Over the last few decades, concerns have been raised on whether renewable energy is green and beneficial, especially during this period when there are heightened efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Several bills have [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
Wind Energy, Its Advantages and Disadvantages Research Paper
Wind energy, wind as a cost effective source of energy, saves forests and form of sustainable development parameter, uses of wind energy, disadvantages of using wind energy, wind energy as the less known used source of energy, works cited.
Globalization and technological advancement has contributed towards an increase in the number of industries in the world. In the process of production, fuel is required to run some machines; however, this fuel is a major source of pollution to the environment.
Fossil fuels, for example, emit gases (when burnt) that are harmful to human beings and the environment at large. Kyoto protocol, which is aimed at reducing the amount of gases emitted in the atmosphere, noted that among the major emitters of green house gases is burning of fossil fuels.
To sustain production of goods and services to feed the world populations, there is need to have reliable sources of energy. Reliable sources of energy need to be renewable; they include wind energy, solar energy and hydro-energy; wind energy is a dependable source of energy although it remains the least used among the available renewable sources of energy (Burton 1-23). This paper discusses wind energy; it will look into how the energy is produced, its cost effectiveness advantage and disadvantages of using the energy.
Wind is moving air; it is caused by non-uniform distribution of heat due to solar energy in different regions, which causes movement of hot from relatively hot places to cold areas. It blows from area of high pressure to areas of low pressure. Wind has a potential of producing approximately 100 billion watts per year of power.
The technology involved in wind energy is converting kinetic energy into electric energy. Wind has kinetic energy, which rotates turbines for electricity generation. When wind is “harvested”, it can be used to produce electricity energy to be used in industries, home and in offices.
How wind energy is produced
Wind power is derived from using the kinetic energy that wind has as it blows on the earth’s service, wind is air moving from one area to another; when in movement it has some energy.
Along the way of the wind, Wind turbines are set up; the turbines are rotated by the moving air; then convert the kinetic energy in the wind to mechanical energy, the mechanical power produced at this stage can be used for various purposes that include grinding grain or pumping water. Furthermore, the energy can be converted into electricity power by the use of generator or dynamos, after the conversion, it can then be used to provide energy to homes, offices and factories.
When compared with other sources of energy, wind energy is relatively cheap in maintaining the structures. To put up a wind energy generator, it uses a lot of money and resources; but to maintain the plant is cheap. This makes the net cost lower. The cost of electricity from wind is the cheapest in the world and thus companies and people can utilize the important product at an affordable cost. From an indirect approach, the following is the cost effectiveness of wind energy:
It is a renewable source of energy
The energy can be used today and in the future without reducing. The energy comes from natural occurring, which can be tapped to produce energy; the energy can be used repeatedly without limiting the potential that it has. It is also considered as clean technology since it emits minimal green house gasses. Examples of other renewable energy sources are sun, tides and waterpower. Non-renewable sources of energy on the other hand are sources of energy whose use depletes the level of utility that can be derived by future generation.
Wind energy leads to minimal or no pollution of the atmosphere, it is considered as a clean source of energy. Using of wind energy reduces emission of carbon to the environment; carbon is one of the green house emissions that lead to global warming.
Some industries and households use firewood as their source of energy; when this happens, they lead to deforestation. Deforestation has lead to numerous challenges to human nature. They include the occurrence of hot spots; a natural depleted environment that has been of great use by the people characterizes a hotspot but through the very people’s action, they have overexploited the natural setting and leaving it to affect them negatively.
It is characterized by exceptional levels of plant endemism. Sustainable development is about caring for the present generation and not limiting future generation of use of available resources. When using wind energy people do not need to cut trees, this is good for a good life on earth.
When using fuel like firewood, then trees is cut, when the forests are destroyed then large amounts of carbon dioxide, which is the main green house gas, are released into the atmosphere, which increases global warming. Urbanization and industrialization have also played a major role in deforestation where some industries like the paper factories use wood directly from forests to make paper.
Wind energy can be used in industries and in homes for various purposes; it is a reliable source of energy for heating, lightening and running of machinery. In manufacturing of goods and services, it is considered as one of the input costs incurred. This is in terms of lightening the factory, running of manufacturing and administrative machines and heating.
In homes wind energy is used for lightening, running of electrical equipments like television, electric fans and electric heaters among others. It assister in making life better as people can connect to the outside world through various equipments like computers, phones, radio and telegrams which are run by electric power.
Of late, the energy has been tapped in transport industry where it is used in electric tramways, railways, and new development of electrically charged motor vehicles.
Though the energy can be relied upon, it is not available across all parts of the world. Some areas do not have adequate supply of wind to be used to drive turbines and get the moving air energy good enough for generation of energy.
Secondly, wind energy like any other energy cannot be stored (although technology has come-up with methods of storing energy like batteries although they are only short term) ; it is used as it is produced thus the reliability of the energy is hampered by its very nature. The lack of storability means that it is possible to have some time that is needed yet the wind is not blowing.
Thirdly some places that wind pass through need to be left bare for an effective generation of energy, for instance when a massive land is used to generate wind energy, then plants like trees cannot be planted in the area, thus hampers other developmental and use of land purposes.
When the energy hampers the use of land for agriculture and planting of vegetation, it is seen to be interfering with efforts to conserve the environment. The environment needs to be protected to give live hood to humanity. Some of the big sizes of land used when the energy is produced can be used for other purposes that might be more beneficial than generation of energy (Hermann-Josef and Jyotirmay 12-56).
When a plant for generation the energy is made, it uses a big part of land that could be used for another thing like farming; this is not good for the community around there.
Although wind energy is cheap and can be used for various uses, the energy is less common to other sources like water, solar and tidal energy. The main reason for this is the distribution of wind patterns and their movement, not all places have adequate amount of wind that can be used for generation of economical energy. This makes governments, firms and individuals not fully interested in tapping the energy.
When blowing on a large volume of land, it passes through property of different people and governing bodies, when the land is put on another use, they the project of wind energy tapping is hampered. The movement of wind varies with time and seasons, for this reason, depending with wind energy cannot guarantee that the supply of energy will be throughout the year. This discourages energy developers to depend with the energy fully (Wald).
Burton, Tony. Wind energy: handbook . New Jersey: John Wiley and Sons, 2001.Print.
Hermann-Josef, Wagner, and JyotirmayMathur. Introduction to wind energy systems: basics, technology and operation . Boston: Springer, 2009.Print.
Wald, Matthew. Wind Farms May Not Lower Air Pollution, Study Suggests. New York Times, 4 May 2007. Web.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2023, December 5). Wind Energy, Its Advantages and Disadvantages. https://ivypanda.com/essays/wind-energy-2/
"Wind Energy, Its Advantages and Disadvantages." IvyPanda , 5 Dec. 2023, ivypanda.com/essays/wind-energy-2/.
IvyPanda . (2023) 'Wind Energy, Its Advantages and Disadvantages'. 5 December.
IvyPanda . 2023. "Wind Energy, Its Advantages and Disadvantages." December 5, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/wind-energy-2/.
1. IvyPanda . "Wind Energy, Its Advantages and Disadvantages." December 5, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/wind-energy-2/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Wind Energy, Its Advantages and Disadvantages." December 5, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/wind-energy-2/.
- Lightening Solution for a Green Building
- Wind Energy: The Use of Wind Turbines
- Hydro Energy Advantages and Disadvantages
- The Relationship Between the Kinetic Energy of Motion and the Force
- Sliding Friction: Static and Kinetic Friction
- Kinetic Xbox 360 by the Microsoft
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Wind Energy
- Conceptual Chemistry. Wind Turbine vs. Coal Energy
- The Uses and Working of Aircraft Turbines
- Turbine Windmills: Annotated Bibliography
- Trend Analysis: Water Scarcity Issue
- Radiation in the Workplace
- Water and Water Pollution in Point of Economics’ View
- Public Awareness of Climate Changes and Carbon Footprints
- The Benefits of Renewable and Non-Renewable Energy
Adaptive Model Predictive Control for Articulated Steering Vehicles 2024-01-5042
Vehicles equipped with articulated steering systems have advantages such as low energy consumption, simple structure, and excellent maneuverability. However, due to the specific characteristics of the system, these vehicles often face challenges in terms of lateral stability. Addressing this issue, this paper leverages the precise and independently controllable wheel torques of a hub motor-driven vehicle. First, an equivalent double-slider model is selected as the dynamic control model, and the control object is rationalized. Subsequently, based on the model predictive control method and considering control accuracy and robustness, a weight-variable adaptive model predictive control approach is proposed. This method addresses the optimization challenges of multiple systems, constraints, and objectives, achieving adaptive control of stability, maneuverability, tire slip ratio, and articulation angle along with individual wheel torques during the entire steering process of the vehicle. Finally, the effectiveness of the controller is validated through hardware-in-the-loop testing, and the data indicates that the proposed adaptive model predictive controller significantly enhances the vehicle’s handling stability.
SAE MOBILUS
Subscribers can view annotate, and download all of SAE's content. Learn More »
Access SAE MOBILUS »

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Wind energy in the United States helps avoid 336 million metric tons of carbon dioxide emissions annually. (link is external) —equivalent to the emissions from 73 million cars. Wind power benefits local communities. Wind projects deliver an estimated $2 billion. (link is external) in state and local tax payments and land-lease payments each year.
Wind energy is a small but fast-growing fraction of electricity production. It accounts for 5 percent of global electricity production and 8 percent of the U.S. electricity supply. Globally, wind energy capacity surpasses 743 gigawatts, which is more than is available from grid-connected solar energy and about half as much as hydropower can ...
The two major disadvantages of wind power include initial cost and technology immaturity. Firstly, constructing turbines and wind facilities is extremely expensive. The second disadvantage is technology immaturity. [1] High cost of energy can, in part, be addressed directly with technology innovations that increase reliability and energy output ...
Wind power is renewable energy. Wind energy makes up about 10 percent of U.S. energy production. Find out the facts and advantages of wind power and how it works.
The advantages of wind energy are inexhaustible. Let us now have a look at the negative aspects of wind energy. There are a number of disadvantages that can be associated with wind energy. Firstly, wind energy competes with the conventional sources of power in terms of cost. The competitiveness of a wind plant generating power is highly ...
3. Wind power has a low operating cost. Because wind power is a renewable energy source, there is no ongoing expense to acquire fuel. Once the wind turbine is installed, the only real cost is maintenance. As the world decarbonizes electricity generation in the future, wind is a clean, renewable, and low-cost option. 4.
This essay explores wind energy to identify various aspects of this energy source. These aspects include the advantages, disadvantages and the general view of energy from academic and professional perspectives. Main Body. ... Despite the many advantages of wind energy with regard to costs and prevention of climate change, there are several ...
Advantages of wind energy. Disadvantages of wind energy. Clean, sustainable and abundant. Variable energy source (needs wind to work) Cost-effective. Not the most aesthetically appealing. Price continues to drop. Turbines can be loud. Turbines are an efficient use of land.
Wind energy is one of the most common types of renewable energy in the U.S. today and also happens to be one of our fastest-growing sources of electricity. However, while there are a number of environmental benefits to using wind energy, there are some downsides. Here are a few of the top pros and cons: Pros and cons of wind energy
Anything that moves has kinetic energy, and scientists and engineers are using the wind's kinetic energy to generate electricity. Wind energy, or wind power, is created using a wind turbine, a device that channels the power of the wind to generate electricity.. The wind blows the blades of the turbine, which are attached to a rotor.The rotor then spins a generator to create electricity.
Wind energy is classified as a renewable source of energy since it can be considered to be unlimited. This paper is an exploration of the advantages and disadvantages of wind energy. Wind power can be credited for its production of clean energy. Therefore, unlike some other sources of energy, wind energy does not pollute the environment.
Wind Energy: A Review Paper. Atul Kumar Muhammad Zafar Ullah Khan Bishwajeet Pandey. M S College, University of Management & Gyancity Rese arch Lab, 1 Motihari, India Technology, Sialkot Campus ...
In short, today wind power has all the necessary prerequisites to play a leading role in the global energy transitionand the shift towards using green energy sources. Many of the benefits of wind power are common to other renewables. First of all is its role in combatting climate change: exploiting wind power means reducing the use of fossil ...
The use of wind power as a source of energy is associated with many benefits compared to other sources of energy. Following is a summary of some of the most common advantages of wind energy. Wind Energy is Free, Pure and Renewable. One main advantage of wind energy over all the other forms of energy is that it is free, clean and renewable.
1. Renewable and Clean Energy: One of the main advantages of wind power is that it is a renewable energy source. Wind is a natural resource that is abundant and will not deplete over time, unlike finite fossil fuels. Additionally, wind power generation produces no greenhouse gas emissions, making it a cleaner option for combating climate change ...
250 Words Essay on Wind Energy Introduction to Wind Energy. Wind energy, a renewable source of power, has been harnessed by humans for centuries. Today, it plays a pivotal role in the global energy landscape, offering a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels. ... Despite its advantages, wind energy also faces challenges. Wind is an ...
Wind energy, simply put, is the process of harnessing the power of the wind to generate electricity. It is a renewable and clean source of energy that holds immense importance in our efforts to combat climate change and transition to a more sustainable future. With the looming threat of global warming and the depletion of finite fossil fuels ...
View our collection of wind energy essays. Find inspiration for topics, titles, outlines, & craft impactful wind energy papers. Read our wind energy papers today! ... Advantages of Wind Power Despite the claims of opponents, the reality is that the use of wind power is a viable resource. A good example of this can be seen with Denmark (who ...
Wind Energy as Forms of Sustainable Energy Sources. T he only costs to be met in producing wind energy is the cost of equipment for harnessing wind, wind turbines for converting the energy and photovoltaic panels for storing energy. We will write. a custom essay specifically for you by our professional experts.
Ultimately, this report will perlustrate the viability of wind as an adequate energy source for the future social and economic development of the world. Wind Energy: Wind is essentially an intricate form of energy that is evident due to solar energy, the variation in land and water formations, and the continuous rotation of the earth.
The advantages are : Sea wind provides greater wind speeds. Less turbulence provides long life. Lower visual intrusion. Environmental Impacts We have both positive and negative impacts to the use of wind energy .But, with their future applications, positive sides will out way its negative sides. 1. Benefits of electricity generation by wind energy
Wind energy essay. Long time ago, ancient mariners used sails to capture the wind and explore the world. Farmers once used windmills to grind their grains and pump water. Today, more and more people are using wind turbines to wring electricity from the breeze. Over the past decade, wind turbine use has increased at more than 25 percent a year.
Contrasting the energy supplied by fossil fuels such as coal, wind power (also referred to as Wind Energy) is a form of energy that is a non-polluting and renewable form of energy. For adequate energy to be generated through wind power, wind turbines with generators are built to function with assistance from prevailing winds within an area.
Wind as a Cost effective source of energy. When compared with other sources of energy, wind energy is relatively cheap in maintaining the structures. To put up a wind energy generator, it uses a lot of money and resources; but to maintain the plant is cheap. This makes the net cost lower.
Abstract. In order to effectively solve the shortcomings of traditional express cabinets such as limited service places and seasonal power supply obstacles, this paper studies an off-grid express cabinet using wind-solar complementary principle, which is mainly composed of near-ground and low-speed wind power generation device, solar photovoltaic battery pack, controller, battery pack and DC load.
Adaptive Model Predictive Control for Articulated Steering Vehicles. 2024-01-5042. Vehicles equipped with articulated steering systems have advantages such as low energy consumption, simple structure, and excellent maneuverability. However, due to the specific characteristics of the system, these vehicles often face challenges in terms of ...