Looking to publish? Meet your dream editor, designer and marketer on Reedsy.
Find the perfect editor for your next book
1 million authors trust the professionals on Reedsy. Come meet them.
Guides • Perfecting your Craft
Last updated on Jul 24, 2023

15 Examples of Great Dialogue (And Why They Work So Well)
Great dialogue is hard to pin down, but you know it when you hear or see it. In the earlier parts of this guide, we showed you some well-known tips and rules for writing dialogue. In this section, we'll show you those rules in action with 15 examples of great dialogue, breaking down exactly why they work so well.
1. Barbara Kingsolver, Unsheltered
In the opening of Barbara Kingsolver’s Unsheltered, we meet Willa Knox, a middle-aged and newly unemployed writer who has just inherited a ramshackle house.
“The simplest thing would be to tear it down,” the man said. “The house is a shambles.” She took this news as a blood-rush to the ears: a roar of peasant ancestors with rocks in their fists, facing the evictor. But this man was a contractor. Willa had called him here and she could send him away. She waited out her panic while he stood looking at her shambles, appearing to nurse some satisfaction from his diagnosis. She picked out words. “It’s not a living thing. You can’t just pronounce it dead. Anything that goes wrong with a structure can be replaced with another structure. Am I right?” “Correct. What I am saying is that the structure needing to be replaced is all of it. I’m sorry. Your foundation is nonexistent.”
Alfred Hitchcock once described drama as "life with the boring bits cut out." In this passage, Kingsolver cuts out the boring parts of Willa's conversation with her contractor and brings us right to the tensest, most interesting part of the conversation.
By entering their conversation late , the reader is spared every tedious detail of their interaction.
Instead of a blow-by-blow account of their negotiations (what she needs done, when he’s free, how she’ll be paying), we’re dropped right into the emotional heart of the discussion. The novel opens with the narrator learning that the home she cherishes can’t be salvaged.
By starting off in the middle of (relatively obscure) dialogue, it takes a moment for the reader to orient themselves in the story and figure out who is speaking, and what they’re speaking about. This disorientation almost mirrors Willa’s own reaction to the bad news, as her expectations for a new life in her new home are swiftly undermined.

FREE COURSE
How to Write Believable Dialogue
Master the art of dialogue in 10 five-minute lessons.
2. Jane Austen, Pride and Prejudice
In the first piece of dialogue in Pride and Prejudice , we meet Mr and Mrs Bennet, as Mrs Bennet attempts to draw her husband into a conversation about neighborhood gossip.
“My dear Mr. Bennet,” said his lady to him one day, “have you heard that Netherfield Park is let at last?” Mr. Bennet replied that he had not. “But it is,” returned she; “for Mrs. Long has just been here, and she told me all about it.” Mr. Bennet made no answer. “Do you not want to know who has taken it?” cried his wife impatiently. “You want to tell me, and I have no objection to hearing it.” This was invitation enough. “Why, my dear, you must know, Mrs. Long says that Netherfield is taken by a young man of large fortune from the north of England; that he came down on Monday in a chaise and four to see the place, and was so much delighted with it, that he agreed with Mr. Morris immediately; that he is to take possession before Michaelmas, and some of his servants are to be in the house by the end of next week.”
Austen’s dialogue is always witty, subtle, and packed with character. This extract from Pride and Prejudice is a great example of dialogue being used to develop character relationships .
We instantly learn everything we need to know about the dynamic between Mr and Mrs Bennet’s from their first interaction: she’s chatty, and he’s the beleaguered listener who has learned to entertain her idle gossip, if only for his own sake (hence “you want to tell me, and I have no objection to hearing it”).

There is even a clear difference between the two characters visually on the page: Mr Bennet responds in short sentences, in simple indirect speech, or not at all, but this is “invitation enough” for Mrs Bennet to launch into a rambling and extended response, dominating the conversation in text just as she does audibly.
The fact that Austen manages to imbue her dialogue with so much character-building realism means we hardly notice the amount of crucial plot exposition she has packed in here. This heavily expository dialogue could be a drag to get through, but Austen’s colorful characterization means she slips it under the radar with ease, forwarding both our understanding of these people and the world they live in simultaneously.
3. Naomi Alderman, The Power

In The Power , young women around the world suddenly find themselves capable of generating and controlling electricity. In this passage, between two boys and a girl who just used those powers to light her cigarette.
Kyle gestures with his chin and says, “Heard a bunch of guys killed a girl in Nebraska last week for doing that.” “For smoking? Harsh.” Hunter says, “Half the kids in school know you can do it.” “So what?” Hunter says, “Your dad could use you in his factory. Save money on electricity.” “He’s not my dad.” She makes the silver flicker at the ends of her fingers again. The boys watch.
Alderman here uses a show, don’t tell approach to expositional dialogue. Within this short exchange, we discover a lot about Allie, her personal circumstances, and the developing situation elsewhere. We learn that women are being punished harshly for their powers; that Allie is expected to be ashamed of those powers and keep them a secret, but doesn’t seem to care to do so; that her father is successful in industry; and that she has a difficult relationship with him. Using dialogue in this way prevents info-dumping backstory all at once, and instead helps us learn about the novel’s world in a natural way.

Show, Don't Tell
Master the golden rule of writing in 10 five-minute lessons.
4. Kazuo Ishiguro, Never Let Me Go
Here, friends Tommy and Kathy have a conversation after Tommy has had a meltdown. After being bullied by a group of boys, he has been stomping around in the mud, the precise reaction they were hoping to evoke from him.
“Tommy,” I said, quite sternly. “There’s mud all over your shirt.” “So what?” he mumbled. But even as he said this, he looked down and noticed the brown specks, and only just stopped himself crying out in alarm. Then I saw the surprise register on his face that I should know about his feelings for the polo shirt. “It’s nothing to worry about.” I said, before the silence got humiliating for him. “It’ll come off. If you can’t get it off yourself, just take it to Miss Jody.” He went on examining his shirt, then said grumpily, “It’s nothing to do with you anyway.”
This episode from Never Let Me Go highlights the power of interspersing action beats within dialogue. These action beats work in several ways to add depth to what would otherwise be a very simple and fairly nondescript exchange. Firstly, they draw attention to the polo shirt, and highlight its potential significance in the plot. Secondly, they help to further define Kathy’s relationship with Tommy.
We learn through Tommy’s surprised reaction that he didn’t think Kathy knew how much he loved his seemingly generic polo shirt. This moment of recognition allows us to see that she cares for him and understands him more deeply than even he realized. Kathy breaking the silence before it can “humiliate” Tommy further emphasizes her consideration for him. While the dialogue alone might make us think Kathy is downplaying his concerns with pragmatic advice, it is the action beats that tell the true story here.

5. J R R Tolkien, The Hobbit
The eponymous hobbit Bilbo is engaged in a game of riddles with the strange creature Gollum.
"What have I got in my pocket?" he said aloud. He was talking to himself, but Gollum thought it was a riddle, and he was frightfully upset. "Not fair! not fair!" he hissed. "It isn't fair, my precious, is it, to ask us what it's got in its nassty little pocketses?" Bilbo seeing what had happened and having nothing better to ask stuck to his question. "What have I got in my pocket?" he said louder. "S-s-s-s-s," hissed Gollum. "It must give us three guesseses, my precious, three guesseses." "Very well! Guess away!" said Bilbo. "Handses!" said Gollum. "Wrong," said Bilbo, who had luckily just taken his hand out again. "Guess again!" "S-s-s-s-s," said Gollum, more upset than ever.
Tolkein’s dialogue for Gollum is a masterclass in creating distinct character voices . By using a repeated catchphrase (“my precious”) and unconventional spelling and grammar to reflect his unusual speech pattern, Tolkien creates an idiosyncratic, unique (and iconic) speech for Gollum. This vivid approach to formatting dialogue, which is almost a transliteration of Gollum's sounds, allows readers to imagine his speech pattern and practically hear it aloud.
We wouldn’t recommend using this extreme level of idiosyncrasy too often in your writing — it can get wearing for readers after a while, and Tolkien deploys it sparingly, as Gollum’s appearances are limited to a handful of scenes. However, you can use Tolkien’s approach as inspiration to create (slightly more subtle) quirks of speech for your own characters.
6. F Scott Fitzgerald, The Great Gatsby

The narrator, Nick has just done his new neighbour Gatsby a favor by inviting his beloved Daisy over to tea. Perhaps in return, Gatsby then attempts to make a shady business proposition.
“There’s another little thing,” he said uncertainly, and hesitated. “Would you rather put it off for a few days?” I asked. “Oh, it isn’t about that. At least —” He fumbled with a series of beginnings. “Why, I thought — why, look here, old sport, you don’t make much money, do you?” “Not very much.” This seemed to reassure him and he continued more confidently. “I thought you didn’t, if you’ll pardon my — you see, I carry on a little business on the side, a little side line, if you understand. And I thought that if you don’t make very much — You’re selling bonds, aren’t you, old sport?” “Trying to.”
This dialogue from The Great Gatsby is a great example of how to make dialogue sound natural. Gatsby tripping over his own words (even interrupting himself , as marked by the em-dashes) not only makes his nerves and awkwardness palpable but also mimics real speech. Just as real people often falter and make false starts when they’re speaking off the cuff, Gatsby too flounders, giving us insight into his self-doubt; his speech isn’t polished and perfect, and neither is he despite all his efforts to appear so.
Fitzgerald also creates a distinctive voice for Gatsby by littering his speech with the character's signature term of endearment, “old sport”. We don’t even really need dialogue markers to know who’s speaking here — a sign of very strong characterization through dialogue.

7. Arthur Conan Doyle, A Study in Scarlet
In this first meeting between the two heroes of Conan Doyle’s Sherlock Holmes stories, Sherlock Holmes and John Watson, John is introduced to Sherlock while the latter is hard at work in the lab.
“How are you?” he said cordially, gripping my hand with a strength for which I should hardly have given him credit. “You have been in Afghanistan, I perceive.” “How on earth did you know that?” I asked in astonishment. “Never mind,” said he, chuckling to himself. “The question now is about hemoglobin. No doubt you see the significance of this discovery of mine?” “It is interesting, chemically, no doubt,” I answered, “but practically— ” “Why, man, it is the most practical medico-legal discovery for years. Don’t you see that it gives us an infallible test for blood stains. Come over here now!” He seized me by the coat-sleeve in his eagerness, and drew me over to the table at which he had been working. “Let us have some fresh blood,” he said, digging a long bodkin into his finger, and drawing off the resulting drop of blood in a chemical pipette. “Now, I add this small quantity of blood to a litre of water. You perceive that the resulting mixture has the appearance of pure water. The proportion of blood cannot be more than one in a million. I have no doubt, however, that we shall be able to obtain the characteristic reaction.” As he spoke, he threw into the vessel a few white crystals, and then added some drops of a transparent fluid. In an instant the contents assumed a dull mahogany colour, and a brownish dust was precipitated to the bottom of the glass jar. “Ha! ha!” he cried, clapping his hands, and looking as delighted as a child with a new toy. “What do you think of that?”
This passage uses a number of the key techniques for writing naturalistic and exciting dialogue, including characters speaking over one another and the interspersal of action beats.
Sherlock cutting off Watson to launch into a monologue about his blood experiment shows immediately where Sherlock’s interest lies — not in small talk, or the person he is speaking to, but in his own pursuits, just like earlier in the conversation when he refuses to explain anything to John and is instead self-absorbedly “chuckling to himself”. This helps establish their initial rapport (or lack thereof) very quickly.
Breaking up that monologue with snippets of him undertaking the forensic tests allows us to experience the full force of his enthusiasm over it without having to read an uninterrupted speech about the ins and outs of a science experiment.

Starting to think you might like to read some Sherlock? Check out our guide to the Sherlock Holmes canon !
8. Brandon Taylor, Real Life
Here, our protagonist Wallace is questioned by Ramon, a friend-of-a-friend, over the fact that he is considering leaving his PhD program.
Wallace hums. “I mean, I wouldn’t say that I want to leave, but I’ve thought about it, sure.” “Why would you do that? I mean, the prospects for… black people, you know?” “What are the prospects for black people?” Wallace asks, though he knows he will be considered the aggressor for this question.
Brandon Taylor’s Real Life is drawn from the author’s own experiences as a queer Black man, attempting to navigate the unwelcoming world of academia, navigating the world of academia, and so it’s no surprise that his dialogue rings so true to life — it’s one of the reasons the novel is one of our picks for must-read books by Black authors .
This episode is part of a pattern where Wallace is casually cornered and questioned by people who never question for a moment whether they have the right to ambush him or criticize his choices. The use of indirect dialogue at the end shows us this is a well-trodden path for Wallace: he has had this same conversation several times, and can pre-empt the exact outcome.
This scene is also a great example of the dramatic significance of people choosing not to speak. The exchange happens in front of a big group, but — despite their apparent discomfort — nobody speaks up to defend Wallace, or to criticize Ramon’s patronizing microaggressions. Their silence is deafening, and we get a glimpse of Ramon’s isolation due to the complacency of others, all due to what is not said in this dialogue example.
9. Ernest Hemingway, Hills Like White Elephants

In this short story, an unnamed man and a young woman discuss whether or not they should terminate a pregnancy while sitting on a train platform.
“Well,” the man said, “if you don’t want to you don’t have to. I wouldn’t have you do it if you didn’t want to. But I know it’s perfectly simple.” “And you really want to?” “I think it’s the best thing to do. But I don’t want you to do it if you really don’t want to.” “And if I do it you’ll be happy and things will be like they were and you’ll love me?” “I love you now. You know I love you.” “I know. But if I do it, then it will be nice again if I say things are like white elephants, and you’ll like it?” “I’ll love it. I love it now but I just can’t think about it. You know how I get when I worry.” “If I do it you won’t ever worry?” “I won’t worry about that because it’s perfectly simple.”
This example of dialogue from Hemingway’s short story Hills Like White Elephants moves at quite a clip. The conversation quickly bounces back and forth between the speakers, and the call-and-response format of the woman asking and the man answering is effective because it establishes a clear dynamic between the two speakers: the woman is the one seeking reassurance and trying to understand the man’s feelings, while he is the one who is ultimately in control of the situation.
Note the sparing use of dialogue markers: this minimalist approach keeps the dialogue brisk, and we can still easily understand who is who due to the use of a new paragraph when the speaker changes .
Like this classic author’s style? Head over to our selection of the 11 best Ernest Hemingway books .
10. Madeline Miller, Circe
In Madeline Miller’s retelling of Greek myth, we witness a conversation between the mythical enchantress Circe and Telemachus (son of Odysseus).
“You do not grieve for your father?” “I do. I grieve that I never met the father everyone told me I had.” I narrowed my eyes. “Explain.” “I am no storyteller.” “I am not asking for a story. You have come to my island. You owe me truth.” A moment passed, and then he nodded. “You will have it.”
This short and punchy exchange hits on a lot of the stylistic points we’ve covered so far. The conversation is a taut tennis match between the two speakers as they volley back and forth with short but impactful sentences, and unnecessary dialogue tags have been shaved off . It also highlights Circe’s imperious attitude, a result of her divine status. Her use of short, snappy declaratives and imperatives demonstrates that she’s used to getting her own way and feels no need to mince her words.
11. Andre Aciman, Call Me By Your Name
This is an early conversation between seventeen-year-old Elio and his family’s handsome new student lodger, Oliver.
What did one do around here? Nothing. Wait for summer to end. What did one do in the winter, then? I smiled at the answer I was about to give. He got the gist and said, “Don’t tell me: wait for summer to come, right?” I liked having my mind read. He’d pick up on dinner drudgery sooner than those before him. “Actually, in the winter the place gets very gray and dark. We come for Christmas. Otherwise it’s a ghost town.” “And what else do you do here at Christmas besides roast chestnuts and drink eggnog?” He was teasing. I offered the same smile as before. He understood, said nothing, we laughed. He asked what I did. I played tennis. Swam. Went out at night. Jogged. Transcribed music. Read. He said he jogged too. Early in the morning. Where did one jog around here? Along the promenade, mostly. I could show him if he wanted. It hit me in the face just when I was starting to like him again: “Later, maybe.”
Dialogue is one of the most crucial aspects of writing romance — what’s a literary relationship without some flirty lines? Here, however, Aciman gives us a great example of efficient dialogue. By removing unnecessary dialogue and instead summarizing with narration, he’s able to confer the gist of the conversation without slowing down the pace unnecessarily. Instead, the emphasis is left on what’s unsaid, the developing romantic subtext.
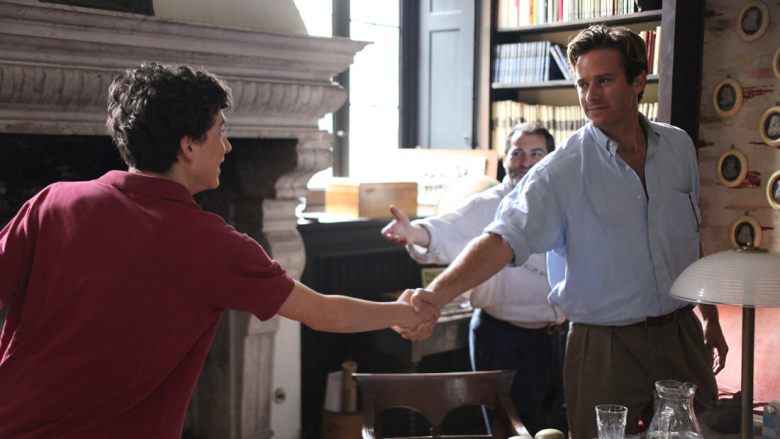

Furthermore, the fact that we receive this scene in half-reported snippets rather than as an uninterrupted transcript emphasizes the fact that this is Elio’s own recollection of the story, as the manipulation of the dialogue in this way serves to mimic the nostalgic haziness of memory.

Understanding Point of View
Learn to master different POVs and choose the best for your story.
12. George Eliot, Middlemarch

Two of Eliot’s characters, Mary and Rosamond, are out shopping,
When she and Rosamond happened both to be reflected in the glass, she said laughingly — “What a brown patch I am by the side of you, Rosy! You are the most unbecoming companion.” “Oh no! No one thinks of your appearance, you are so sensible and useful, Mary. Beauty is of very little consequence in reality,” said Rosamond, turning her head towards Mary, but with eyes swerving towards the new view of her neck in the glass. “You mean my beauty,” said Mary, rather sardonically. Rosamond thought, “Poor Mary, she takes the kindest things ill.” Aloud she said, “What have you been doing lately?” “I? Oh, minding the house — pouring out syrup — pretending to be amiable and contented — learning to have a bad opinion of everybody.”
This excerpt, a conversation between the level-headed Mary and vain Rosamond, is an example of dialogue that develops character relationships naturally. Action descriptors allow us to understand what is really happening in the conversation.
Whilst the speech alone might lead us to believe Rosamond is honestly (if clumsily) engaging with her friend, the description of her simultaneously gazing at herself in a mirror gives us insight not only into her vanity, but also into the fact that she is not really engaged in her conversation with Mary at all.
The use of internal dialogue cut into the conversation (here formatted with quotation marks rather than the usual italics ) lets us know what Rosamond is actually thinking, and the contrast between this and what she says aloud is telling. The fact that we know she privately realizes she has offended Mary, but quickly continues the conversation rather than apologizing, is emphatic of her character. We get to know Rosamond very well within this short passage, which is a hallmark of effective character-driven dialogue.
13. John Steinbeck, The Winter of our Discontent
Here, Mary (speaking first) reacts to her husband Ethan’s attempts to discuss his previous experiences as a disciplined soldier, his struggles in subsequent life, and his feeling of impending change.
“You’re trying to tell me something.” “Sadly enough, I am. And it sounds in my ears like an apology. I hope it is not.” “I’m going to set out lunch.”
Steinbeck’s Winter of our Discontent is an acute study of alienation and miscommunication, and this exchange exemplifies the ways in which characters can fail to communicate, even when they’re speaking. The pair speaking here are trapped in a dysfunctional marriage which leaves Ethan feeling isolated, and part of his loneliness comes from the accumulation of exchanges such as this one. Whenever he tries to communicate meaningfully with his wife, she shuts the conversation down with a complete non sequitur.

We expect Mary’s “you’re trying to tell me something” to be followed by a revelation, but Ethan is not forthcoming in his response, and Mary then exits the conversation entirely. Nothing is communicated, and the jarring and frustrating effect of having our expectations subverted goes a long way in mirroring Ethan’s own frustration.
Just like Ethan and Mary, we receive no emotional pay-off, and this passage of characters talking past one another doesn’t further the plot as we hope it might, but instead gives us insight into the extent of these characters’ estrangement.
14. Bret Easton Ellis , Less Than Zero
The disillusioned main character of Bret Easton Ellis’ debut novel, Clay, here catches up with a college friend, Daniel, whom he hasn’t seen in a while.
He keeps rubbing his mouth and when I realize that he’s not going to answer me, I ask him what he’s been doing. “Been doing?” “Yeah.” “Hanging out.” “Hanging out where?” “Where? Around.”
Less Than Zero is an elegy to conversation, and this dialogue is an example of the many vacuous exchanges the protagonist engages in, seemingly just to fill time. The whole book is deliberately unpoetic and flat, and depicts the lives of disaffected youths in 1980s LA. Their misguided attempts to fill the emptiness within them with drink and drugs are ultimately fruitless, and it shows in their conversations: in truth, they have nothing to say to one another at all.
This utterly meaningless exchange would elsewhere be considered dead weight to a story. Here, rather than being fat in need of trimming, the empty conversation is instead thematically resonant.
15. Daphne du Maurier, Rebecca

The young narrator of du Maurier’s classic gothic novel here has a strained conversation with Robert, one of the young staff members at her new husband’s home, the unwelcoming Manderley.
“Has Mr. de Winter been in?” I said. “Yes, Madam,” said Robert; “he came in just after two, and had a quick lunch, and then went out again. He asked for you and Frith said he thought you must have gone down to see the ship.” “Did he say when he would be back again?” I asked. “No, Madam.” “Perhaps he went to the beach another way,” I said; “I may have missed him.” “Yes, Madam,” said Robert. I looked at the cold meat and the salad. I felt empty but not hungry. I did not want cold meat now. “Will you be taking lunch?” said Robert. “No,” I said, “No, you might bring me some tea, Robert, in the library. Nothing like cakes or scones. Just tea and bread and butter.” “Yes, Madam.”
We’re including this one in our dialogue examples list to show you the power of everything Du Maurier doesn’t do: rather than cycling through a ton of fancy synonyms for “said”, she opts for spare dialogue and tags.
This interaction's cold, sparse tone complements the lack of warmth the protagonist feels in the moment depicted here. By keeping the dialogue tags simple , the author ratchets up the tension — without any distracting flourishes taking the reader out of the scene. The subtext of the conversation is able to simmer under the surface, and we aren’t beaten over the head with any stage direction extras.
The inclusion of three sentences of internal dialogue in the middle of the dialogue (“I looked at the cold meat and the salad. I felt empty but not hungry. I did not want cold meat now.”) is also a masterful touch. What could have been a single sentence is stretched into three, creating a massive pregnant pause before Robert continues speaking, without having to explicitly signpost one. Manipulating the pace of dialogue in this way and manufacturing meaningful silence is a great way of adding depth to a scene.
Phew! We've been through a lot of dialogue, from first meetings to idle chit-chat to confrontations, and we hope these dialogue examples have been helpful in illustrating some of the most common techniques.
If you’re looking for more pointers on creating believable and effective dialogue, be sure to check out our course on writing dialogue. Or, if you find you learn better through examples, you can look at our list of 100 books to read before you die — it’s packed full of expert storytellers who’ve honed the art of dialogue.
Join a community of over 1 million authors
Reedsy is more than just a blog. Become a member today to discover how we can help you publish a beautiful book.
We have an app for that
Build a writing routine with our free writing app.

1 million authors trust the professionals on Reedsy. Come meet them.
Enter your email or get started with a social account:
- Features for Creative Writers
- Features for Work
- Features for Higher Education
- Features for Teachers
- Features for Non-Native Speakers
- Learn Blog Grammar Guide Community Events FAQ
- Grammar Guide
How to Write Dialogue: 7 Great Tips for Writers (With Examples)

Hannah Yang

Great dialogue serves multiple purposes. It moves your plot forward. It develops your characters and it makes the story more engaging.
It’s not easy to do all these things at once, but when you master the art of writing dialogue, readers won’t be able to put your book down.
In this article, we will teach you the rules for writing dialogue and share our top dialogue tips that will make your story sing.
Dialogue Rules
How to format dialogue, 7 tips for writing dialogue in a story or book, dialogue examples.
Before we look at tips for writing powerful dialogue, let’s start with an overview of basic dialogue rules.
- Start a new paragraph each time there’s a new speaker. Whenever a new character begins to speak, you should give them their own paragraph. This rule makes it easier for the reader to follow the conversation.
- Keep all speech between quotation marks . Everything that a character says should go between quotation marks, including the final punctuation marks. For example, periods and commas should always come before the final quotation mark, not after.
- Don’t use end quotations for paragraphs within long speeches. If a single character speaks for such a long time that you break their speech up into multiple paragraphs, you should omit the quotation marks at the end of each paragraph until they stop talking. The final quotation mark indicates that their speech is over.
- Use single quotes when a character quotes someone else. Whenever you have a quote within a quote, you should use single quotation marks (e.g. She said, “He had me at ‘hello.’”)
- Dialogue tags are optional. A dialogue tag is anything that indicates which character is speaking and how, such as “she said,” “he whispered,” or “I shouted.” You can use dialogue tags if you want to give the reader more information about who’s speaking, but you can also choose to omit them if you want the dialogue to flow more naturally. We’ll be discussing more about this rule in our tips below.
Let’s walk through some examples of how to format dialogue .
The simplest formatting option is to write a line of speech without a dialogue tag. In this case, the entire line of speech goes within the quotation marks, including the period at the end.
- Example: “I think I need a nap.”
Another common formatting option is to write a single line of speech that ends with a dialogue tag.
Here, you should separate the speech from the dialogue tag with a comma, which should go inside the quotation marks.
- Example: “I think I need a nap,” Maria said.

You can also write a line of speech that starts with a dialogue tag. Again, you separate the dialogue tag with a comma, but this time, the comma goes outside the quotation marks.
- Example: Maria said, “I think I need a nap.”
As an alternative to a simple dialogue tag, you can write a line of speech accompanied by an action beat. In this case, you should use a period rather than a comma, because the action beat is a full sentence.
- Example: Maria sat down on the bed. “I think I need a nap.”
Finally, you can choose to include an action beat while the character is talking.
In this case, you would use em-dashes to separate the action from the dialogue, to indicate that the action happens without a pause in the speech.
- Example: “I think I need”—Maria sat down on the bed—“a nap.”
Now that we’ve covered the basics, we can move on to the more nuanced aspects of writing dialogue.
Here are our seven favorite tips for writing strong, powerful dialogue that will keep your readers engaged.
Tip #1: Create Character Voices
Dialogue is a great way to reveal your characters. What your characters say, and how they say it, can tell us so much about what kind of people they are.
Some characters are witty and gregarious. Others are timid and unobtrusive.
Speech patterns vary drastically from person to person.
To make someone stop talking to them, one character might say “I would rather not talk about this right now,” while another might say, “Shut your mouth before I shut it for you.”
When you’re writing dialogue, think about your character’s education level, personality, and interests.
- What kind of slang do they use?
- Do they prefer long or short sentences?
- Do they ask questions or make assertions?
Each character should have their own voice.
Ideally, you want to write dialogue that lets your reader identify the person speaking at any point in your story just by looking at what’s between the quotation marks.
Tip #2: Write Realistic Dialogue
Good dialogue should sound natural. Listen to how people talk in real life and try to replicate it on the page when you write dialogue.
Don’t be afraid to break the rules of grammar, or to use an occasional exclamation point to punctuate dialogue.
It’s okay to use contractions , sentence fragments , and run-on sentences , even if you wouldn’t use them in other parts of the story.
This doesn’t mean that realistic dialogue should sound exactly like the way people speak in the real world.
If you’ve ever read a court transcript, you know that real-life speech is riddled with “ums” and “ahs” and repeated words and phrases. A few paragraphs of this might put your readers to sleep.
Compelling dialogue should sound like a real conversation, while still being wittier, smoother, and better worded than real speech.
Tip #3: Simplify Your Dialogue Tags
A dialogue tag is anything that tells the reader which character is talking within that same paragraph, such as “she said” or “I asked.”
When you’re writing dialogue, remember that simple dialogue tags are the most effective .
Often, you can omit dialogue tags after the conversation has started flowing, especially if only two characters are participating.
The reader will be able to keep up with who’s speaking as long as you start a new paragraph each time the speaker changes.
When you do need to use a dialogue tag, a simple “he said” or “she said” will do the trick.
Our brains generally skip over the word “said” when we’re reading, while other dialogue tags are a distraction.

A common mistake beginner writers make is to avoid using the word “said.”
Characters in amateur novels tend to mutter, whisper, declare, or chuckle at every line of dialogue. This feels overblown and distracts from the actual story.
Another common mistake is to attach an adverb to the word “said.” Characters in amateur novels rarely just say things—they have to say things loudly, quietly, cheerfully, or angrily.
If you’re writing great dialogue, readers should be able to figure out whether your character is cheerful or angry from what’s within the quotation marks.
The only exception to this rule is if the dialogue tag contradicts the dialogue itself. For example, consider this sentence:
- “You’ve ruined my life,” she said angrily.
The word “angrily” is redundant here because the words inside the quotation marks already imply that the character is speaking angrily.
In contrast, consider this sentence:
- “You’ve ruined my life,” she said thoughtfully.
Here, the word “thoughtfully” is well-placed because it contrasts with what we might otherwise assume. It adds an additional nuance to the sentence inside the quotation marks.

You can use the ProWritingAid dialogue check when you write dialogue to make sure your dialogue tags are pulling their weight and aren’t distracting readers from the main storyline.
Sign up for your free ProWritingAid account to check your dialogue tags today.
Tip #4: Balance Speech with Action
When you’re writing dialogue, you can use action beats —descriptions of body language or physical action—to show what each character is doing throughout the conversation.
Learning how to write action beats is an important component of learning how to write dialogue.
Good dialogue becomes even more interesting when the characters are doing something active at the same time.
You can watch people in real life, or even characters in movies, to see what kinds of body language they have. Some pick at their fingernails. Some pace the room. Some tap their feet on the floor.

Including physical action when writing dialogue can have multiple benefits:
- It changes the pace of your dialogue and makes the rhythm more interesting
- It prevents “white room syndrome,” which is when a scene feels like it’s happening in a white room because it’s all dialogue and no description
- It shows the reader who’s speaking without using speaker tags
You can decide how often to include physical descriptions in each scene. All dialogue has an ebb and flow to it, and you can use beats to control the pace of your dialogue scenes.
If you want a lot of tension in your scene, you can use fewer action beats to let the dialogue ping-pong back and forth.
If you want a slower scene, you can write dialogue that includes long, detailed action beats to help the reader relax.
You should start a separate sentence, or even a new paragraph, for each of these longer beats.

Tip #5: Write Conversations with Subtext
Every conversation has subtext , because we rarely say exactly what we mean. The best dialogue should include both what is said and what is not said.
I once had a roommate who cared a lot about the tidiness of our apartment, but would never say it outright. We soon figured out that whenever she said something like “I might bring some friends over tonight,” what she meant was “Please wash your dishes, because there are no clean plates left for my friends to use.”

When you’re writing dialogue, it’s important to think about what’s not being said. Even pleasant conversations can hide a lot beneath the surface.
Is one character secretly mad at the other?
Is one secretly in love with the other?
Is one thinking about tomorrow’s math test and only pretending to pay attention to what the other person is saying?
Personally, I find it really hard to use subtext when I write dialogue from scratch.
In my first drafts I let my characters say what they really mean. Then, when I’m editing, I go back and figure out how to convey the same information through subtext instead.
Tip #6: Show, Don’t Tell
When I was in high school, I once wrote a story in which the protagonist’s mother tells her: “As you know, Susan, your dad left us when you were five.”
I’ve learned a lot about the writing craft since high school, but it doesn’t take a brilliant writer to figure out that this is not something any mother would say to her daughter in real life.

The reason I wrote that line of dialogue was because I wanted to tell the reader when Susan last saw her father, but I didn’t do it in a realistic way.
Don’t shoehorn information into your characters’ conversations if they’re not likely to say it to each other.
One useful trick is to have your characters get into an argument.
You can convey a lot of information about a topic through their conflicting opinions, without making it sound like either of the characters is saying things for the reader’s benefit.
Here’s one way my high school self could have conveyed the same information in a more realistic way in just a few lines:
Susan: “Why didn’t you tell me Dad was leaving? Why didn’t you let me say goodbye?”
Mom: “You were only five. I wanted to protect you.”
Tip #7: Keep Your Dialogue Concise
Dialogue tends to flow out easily when you’re drafting your story, so in the editing process, you’ll need to be ruthless. Cut anything that doesn’t move the story forward.
Try not to write dialogue that feels like small talk.
You can eliminate most hellos and goodbyes, or summarize them instead of showing them. Readers don’t want to waste their time reading dialogue that they hear every day.
In addition, try not to write dialogue with too many trigger phrases, which are questions that trigger the next line of dialogue, such as:
- “And then what?”
- “What do you mean?”
It’s tempting to slip these in when you’re writing dialogue because they keep the conversation flowing. I still catch myself doing this from time to time.
Remember that you don’t need three lines of dialogue when one line could accomplish the same thing.
Let’s look at some dialogue examples from successful novels that follow each of our seven tips.
Dialogue Example #1: How to Create Character Voice
Let’s start with an example of a character with a distinct voice from Harry Potter and the Chamber of Secrets by J.K. Rowling.
“What happened, Harry? What happened? Is he ill? But you can cure him, can’t you?” Colin had run down from his seat and was now dancing alongside them as they left the field. Ron gave a huge heave and more slugs dribbled down his front. “Oooh,” said Colin, fascinated and raising his camera. “Can you hold him still, Harry?”
Most readers could figure out that this was Colin Creevey speaking, even if his name hadn’t been mentioned in the passage.
This is because Colin Creevey is the only character who speaks with such extreme enthusiasm, even at a time when Ron is belching slugs.
This snippet of written dialogue does a great job of showing us Colin’s personality and how much he worships his hero Harry.
Dialogue Example #2: How to Write Realistic Dialogue
Here’s an example of how to write dialogue that feels realistic from A Thousand Splendid Suns by Khaled Hosseini.
“As much as I love this land, some days I think about leaving it,” Babi said. “Where to?” “Anyplace where it’s easy to forget. Pakistan first, I suppose. For a year, maybe two. Wait for our paperwork to get processed.” “And then?” “And then, well, it is a big world. Maybe America. Somewhere near the sea. Like California.”
Notice the punctuation and grammar that these two characters use when they speak.
There are many sentence fragments in this conversation like, “Anyplace where it’s easy to forget.” and “Somewhere near the sea.”
Babi often omits the verbs from his sentences, just like people do in real life. He speaks in short fragments instead of long, flowing paragraphs.
This dialogue shows who Babi is and feels similar to the way a real person would talk, while still remaining concise.

Dialogue Example #3: How to Simplify Your Dialogue Tags
Here’s an example of effective dialogue tags in Rebecca by Daphne du Maurier.
In this passage, the narrator’s been caught exploring the forbidden west wing of her new husband’s house, and she’s trying to make excuses for being there.
“I lost my way,” I said, “I was trying to find my room.” “You have come to the opposite side of the house,” she said; “this is the west wing.” “Yes, I know,” I said. “Did you go into any of the rooms?” she asked me. “No,” I said. “No, I just opened a door, I did not go in. Everything was dark, covered up in dust sheets. I’m sorry. I did not mean to disturb anything. I expect you like to keep all this shut up.” “If you wish to open up the rooms I will have it done,” she said; “you have only to tell me. The rooms are all furnished, and can be used.” “Oh, no,” I said. “No. I did not mean you to think that.”
In this passage, the only dialogue tags Du Maurier uses are “I said,” “she said,” and “she asked.”
Even so, you can feel the narrator’s dread and nervousness. Her emotions are conveyed through what she actually says, rather than through the dialogue tags.
This is a splendid example of evocative speech that doesn’t need fancy dialogue tags to make it come to life.
Dialogue Example #4: How to Balance Speech with Action
Let’s look at a passage from The Princess Bride by William Goldman, where dialogue is melded with physical action.
With a smile the hunchback pushed the knife harder against Buttercup’s throat. It was about to bring blood. “If you wish her dead, by all means keep moving," Vizzini said. The man in black froze. “Better,” Vizzini nodded. No sound now beneath the moonlight. “I understand completely what you are trying to do,” the Sicilian said finally, “and I want it quite clear that I resent your behavior. You are trying to kidnap what I have rightfully stolen, and I think it quite ungentlemanly.” “Let me explain,” the man in black began, starting to edge forward. “You’re killing her!” the Sicilian screamed, shoving harder with the knife. A drop of blood appeared now at Buttercup’s throat, red against white.
In this passage, William Goldman brings our attention seamlessly from the action to the dialogue and back again.
This makes the scene twice as interesting, because we’re paying attention not just to what Vizzini and the man in black are saying, but also to what they’re doing.
This is a great way to keep tension high and move the plot forward.
Dialogue Example #5: How to Write Conversations with Subtext
This example from Ender’s Game by Orson Scott Card shows how to write dialogue with subtext.
Here is the scene when Ender and his sister Valentine are reunited for the first time, after Ender’s spent most of his childhood away from home training to be a soldier.
Ender didn’t wave when she walked down the hill toward him, didn’t smile when she stepped onto the floating boat slip. But she knew that he was glad to see her, knew it because of the way his eyes never left her face. “You’re bigger than I remembered,” she said stupidly. “You too,” he said. “I also remembered that you were beautiful.” “Memory does play tricks on us.” “No. Your face is the same, but I don’t remember what beautiful means anymore. Come on. Let’s go out into the lake.”
In this scene, we can tell that Valentine missed her brother terribly, and that Ender went through a lot of trauma at Battle School, without either of them saying it outright.
The conversation could have started with Valentine saying “I missed you,” but instead, she goes for a subtler opening: “You’re bigger than I remembered.”
Similarly, Ender could say “You have no idea what I’ve been through,” but instead he says, “I don’t remember what beautiful means anymore.”
We can deduce what each of these characters is thinking and feeling from what they say and from what they leave unsaid.
Dialogue Example #6: How to Show, Not Tell
Let’s look at an example from The Name of the Wind by Patrick Rothfuss. This scene is the story’s first introduction of the ancient creatures called the Chandrian.
“I didn’t know the Chandrian were demons,” the boy said. “I’d heard—” “They ain’t demons,” Jake said firmly. “They were the first six people to refuse Tehlu’s choice of the path, and he cursed them to wander the corners—” “Are you telling this story, Jacob Walker?” Cob said sharply. “Cause if you are, I’ll just let you get on with it.” The two men glared at each other for a long moment. Eventually Jake looked away, muttering something that could, conceivably, have been an apology. Cob turned back to the boy. “That’s the mystery of the Chandrian,” he explained. “Where do they come from? Where do they go after they’ve done their bloody deeds? Are they men who sold their souls? Demons? Spirits? No one knows.” Cob shot Jake a profoundly disdainful look. “Though every half-wit claims he knows...”
The three characters taking part in this conversation all know what the Chandrian are.
Imagine if Cob had said “As we all know, the Chandrian are mysterious demon-spirits.” We would feel like he was talking to us, not to the two other characters.
Instead, Rothfuss has all three characters try to explain their own understanding of what the Chandrian are, and then shoot each other’s explanations down.
When Cob reprimands Jake for interrupting him and then calls him a half-wit for claiming to know what he’s talking about, it feels like a realistic interaction.
This is a clever way for Rothfuss to introduce the Chandrian in a believable way.

Dialogue Example #7: How to Keep Your Dialogue Concise
Here’s an example of concise dialogue from The Catcher in the Rye by J.D. Salinger.
“Do you blame me for flunking you, boy?” he said. “No, sir! I certainly don’t,” I said. I wished to hell he’d stop calling me “boy” all the time. He tried chucking my exam paper on the bed when he was through with it. Only, he missed again, naturally. I had to get up again and pick it up and put it on top of the Atlantic Monthly. It’s boring to do that every two minutes. “What would you have done in my place?” he said. “Tell the truth, boy.” Well, you could see he really felt pretty lousy about flunking me. So I shot the bull for a while. I told him I was a real moron, and all that stuff. I told him how I would’ve done exactly the same thing if I’d been in his place, and how most people didn’t appreciate how tough it is being a teacher. That kind of stuff. The old bull.
Here, the last paragraph diverges from the prior ones. After the teacher says “Tell the truth, boy,” the rest of the conversation is summarized, rather than shown.
The summary of what the narrator says in the last paragraph—“I told him I was a real moron, and all that stuff”—serves to hammer home that this is the type of “old bull” that the narrator has fed to his teachers over and over before.
It doesn’t need to be shown because it’s not important to the narrator—it’s just “all that stuff.”
Salinger could have written out the entire conversation in dialogue, but instead he kept the dialogue concise.
Final Words
Now you know how to write clear, effective dialogue! Start with the basic rules for dialogue and try implementing the more advanced tips as you go.
What are your favorite dialogue tips? Let us know in the comments below.
Do you know how to craft memorable, compelling characters? Download this free book now:

Creating Legends: How to Craft Characters Readers Adore… or Despise!
This guide is for all the writers out there who want to create compelling, engaging, relatable characters that readers will adore… or despise., learn how to invent characters based on actions, motives, and their past..
Be confident about grammar
Check every email, essay, or story for grammar mistakes. Fix them before you press send.
Hannah Yang is a speculative fiction writer who writes about all things strange and surreal. Her work has appeared in Analog Science Fiction, Apex Magazine, The Dark, and elsewhere, and two of her stories have been finalists for the Locus Award. Her favorite hobbies include watercolor painting, playing guitar, and rock climbing. You can follow her work on hannahyang.com, or subscribe to her newsletter for publication updates.
Get started with ProWritingAid
Drop us a line or let's stay in touch via :

- Scriptwriting
How to Write Dialogue — Examples, Tips & Techniques
E very screenwriter wants to write quippy, smart dialogue that makes the page sparkle and keeps the actors inspired. But how do you do it? There are dozens, if not hundreds, of lists and guides that provide useful tips for how to write dialogue in a story. In this post, we’ll look at dialogue writing examples, examine a few tried-and-true methods for how to write good dialogue, and provide you with all the best dialogue writing tips.
Watch: Anatomy of a Screenplay
Subscribe for more filmmaking videos like this.
How to Write Dialogue Format
1. study dialogue writing.
A good first step is to look to accomplished writers to see how they became skilled at how to write dialogue . But we have to know what we’re looking for. You can start by reading some dialogue examples from different mediums or practice with some dialogue prompts .
Writer-director Quentin Tarantino is as famous for his dialogue as he is for breaking the rules of screenwriting. Sure, to be able to craft dialogue that is so compelling it becomes a set piece unto itself, a la Tarantino, may be a good aesthetic model.
But trying to emulate his more stream-of-consciousness approach to dialogue writing may prove disorienting. Check out our video below and see if you notice anything that stands out about his approach to writing dialogue.
Tarantino Dialogue • Subscribe on YouTube
Though Tarantino doesn’t necessarily write according to plotted out script templates, and he probably doesn't adhere to proper dialogue format all the time. His creative choices might be largely unconscious, and his secret weapon in how to write a good dialogue may be his well-developed characters.
He knows who his characters are and what they want, and the characters’ desires shape his dialogue writing.
And as we will see when we look at other screenwriters’ methods, character is everything in how to write dialogue in a script.
Tarantino on set
As the old adage goes, learning the rules in order to break them can make you a stronger writer – and in this case, we want to look at some of the best writing dialogue rules.
Writing from a structure can help make sure you don’t lose the thread of your story by getting too caught up in crafting clever, flashy dialogue that doesn’t connect to anything.
And, a good structure can provide the perimeters for your writing to flow within, so you don’t have to pause to remember fifteen different rules of how to do dialogue!
How to Write a Good Dialogue
2. make your character's wants clear.
In a post about how to approach how to write dialogue it may seem contradictory to say this, but a good rule for dialogue writing in a scene is to write the dialogue last.
After building out the other elements of your story (your arcs, acts, scenes, and story beats) you will have a better sense of how each scene connects to the larger unfolding of the story and, most importantly, what each character wants in a given scene.
You may not need a “how to write good dialogue format” if you always keep in mind your larger story arc, how each scene drives the story forward, and what character motivations are in every scene.
An iconic dialogue scene from The Social Network
A good starting place in thinking about how to write dialogue in a script is to remember that in a screenplay, dialogue is not mere conversation. It always serves a larger purpose, which is to move the story forward.
The function of dialogue can be broken down into three purposes: exposition , characterization , or action. If we’re always clear on the larger purpose of a scene and we know each character’s motivations, we know what our dialogue is “doing” in that scene.
When we know what a character wants, we don’t have to worry as much about how to write dialogue because the motivations of the characters drive what they say. See our post on story beats to dig into story beats, which help illuminate what each character wants, and when they want it.
Functions of Dialogue
Exposition (to relay important information to other characters)
Characterization (to flesh out who a character is and what they want)
Action (to make decisions, reveal what they’re going to do)
The famous diner scene from Nora Ephron’s When Harry Met Sally is an excellent example of both exposition and characterization, critical components of how to write dialogue between two characters. Here's a breakdown we did of the iconic When Harry Met Sally screenplay .
The ongoing question of the film, and of Harry and Sally’s relationship, is whether heterosexual women and heterosexual men can really be platonic friends. Every other character in the film and their issues (the friend in an affair with a married man, the friends who are in a happy couple and getting married) all support the driving dilemma of the film: the desire to partner and escape the presumed suffering of dating.
Take a look at the scene:
When Harry Met Sally
Underneath this question of whether men and women can be friends is the subtext that they may ultimately end up together after all. The overriding question of the film is, after knowing each other, “how come they haven’t already?” The diner scene teases out the idea of sexual tension in a supposedly platonic friendship, raising the stakes.
Here's a breakdown of subtext.
The Art of Subtext • Subscribe on YouTube
Remember, though the scene depicts Harry and Sally having a conversation in a diner, the words they are speaking are not mere “conversation” – it is dialogue written to sound like a natural conversation. There is a difference.
Each word in Ephron’s dialogue writing has a purpose. Sally says she is upset about how Harry treats the women he dates and that she’s glad she never dated him (underscoring the ongoing conflict of the film).
Harry defends himself, saying he doesn’t hear any of them complaining (alluding to how he wouldn’t disappoint her, either). When Sally suggests the women he dates might be faking orgasm, Harry doesn’t believe her.
This prompts her to fake an orgasm right there in the diner to make her point (ratcheting up the primary conflict, while also providing some comic relief).
You can read the scene, which we imported into StudioBinder’s screenwriting software , below:
When Harry Met Sally script
This scene works so well because it serves a crystal clear purpose in driving the story forward.
Great dialogue writing examples always drive the plot from one scene to the next. You may not like plotting out your story beats, thinking about story arcs in a methodological way, or approaching how to write dialogue between two characters systematically at all.
Just remember, most professional screenwriters do, and Writing Dialogue rules might be an instance where it is worth learning the rules in order to break them. Check out more great dinner scenes to inspire how to tackle this awkward but important type of scene!
How to Write Dinner Dialogue • Subscribe on YouTube
How to write dialogue in a script , 3. give your dialogue purpose.
Finally, we’ve come to our favorite part. The lines. Famed playwright and screenwriter David Mamet says great dialogue boils down to this one concept:

“Nobody says anything unless they want something.”
— David Mamet
This handy motto is one of the best dialogue writing tips, if not the only one you need. This principle encapsulates what many other rules of dialogue writing are getting at. What they want also may not be spoken aloud, which is where writing internal dialogue comes in handy.
The advice to use as few words as possible, to cut the fat, to arrive late and leave early, to write with subtext in mind, to show rather than tell – all of those goals can be met by keeping the focus on what the characters want.

David Mamet at work
If they don’t want anything, they don’t need to say anything. If you have a clear idea of who your characters are, and what the function of each scene is in the story, then your characters' agendas, conflicts, and obstacles, and their manner of speaking to express themselves, can come forward more naturally.
If you know what your characters want, you may find that you know how to write dialogue in a story very naturally!
And yet, there is a caveat here: Screenwriter Karl Iglesias warns that it can be easy to have the character saying what you , the writer, want, not what they , the character, want.
Below is a playlist from our 4 Endings video series where we look at how "wants and needs" play out in a screenplay.
Wants vs. Needs • Watch the entire playlist
Because what you , the writer, want them to do is of course to carry some part of the story for you. So another important tool to put in your toolbox of dialogue writing tips is to always zoom in on the character , and stay tuned into what they want at any given point in the story.
Check out the last scene from Mamet’s Glengarry Glen Ross , a film based on the screenplay, also by Mamet, and a gold standard of excellent movie dialogue.
Mamet’s principle that each character has to show what they want is demonstrated brilliantly in the final scene. At the beginning of the film, everyone at a New York City real estate office learns all but the top two salesmen will be fired in two weeks.
Levene (Jack Lemmon) is a salesman who wants to keep his job and survive. In the final scene, Williamson (Kevin Spacey) accuses Levene of stealing leads from the office. By this final scene, what Levene wants has shifted. Now he wants to convince Williamson of his innocence.
Take a look:

Final Scene from Glengarry Glen Ross, 1992
Dialogue writing examples , 4. edit and focus the dialogue.
Now it’s time to sculpt the general arc of your story into form – and the minimalist principles of how to write dialogue in a story can help bring your vision to life.
You want to cast a harsh light on your text in order to whittle down everything you’ve written. Make sure every last word really needs to be there. You want to yank anything that gets in the way of telling the great story you want to tell. That way, the lines will be focused, compelling, and inspire great actors to want to bring them to life.
Remember: We’re not yanking lines if they’re not sparkly or punchy enough, we’re yanking them if they don’t serve a purpose.
Even the cutest remark can actually be clutter, and even the more mundane lines can play a vital role by elucidating our character’s motives, the conflict they’ve encountered, and where the story is going next. The more dialogue writing examples you read, the more you’ll see how the characters’ motivations are driving not only what is said, but how it is said.
Related Posts
- 22 Essential Screenwriting Tips →
- What is a Story Beat in a Screenplay? →
- FREE: Search StudioBinder’s Database of Film & TV Screenplays →
Another approach for how to write great dialogue in a script is to read through every line of the script aloud to make sure it flows naturally.
You could also try putting your hand or a piece of paper of the names of the characters. Can you tell who is saying what?
If each character doesn’t have a discernible way of speaking, revisit your character development and really define who this person is, what they want, and all their quirks and characteristics. Then revamp their lines to make all of that come to the forefront in each line. And when in doubt, revisit dialogue writing examples from your favorite movies and shows to get the juices flowing.
Another tip for how to properly write dialogue is to scan your script for “dialogue dumps.” The best way to avoid “As you know, Bob…” information dumps in your dialogue is to let the characters bat pieces of information back and forth. Check out our video on exposition below:
How to write good exposition • Subscribe on YouTube
Let them reveal bits of it over time, scattered throughout a scene like breadcrumbs. Let them argue about it, challenge what each other knows. Do they already know it, or are they wrestling with it?
Assess your dialogue to make sure what you’re trying to accomplish with a line of dialogue couldn’t better be said with an action, an adjustment to scene or setting, a facial expression, or some other nonverbal detail.
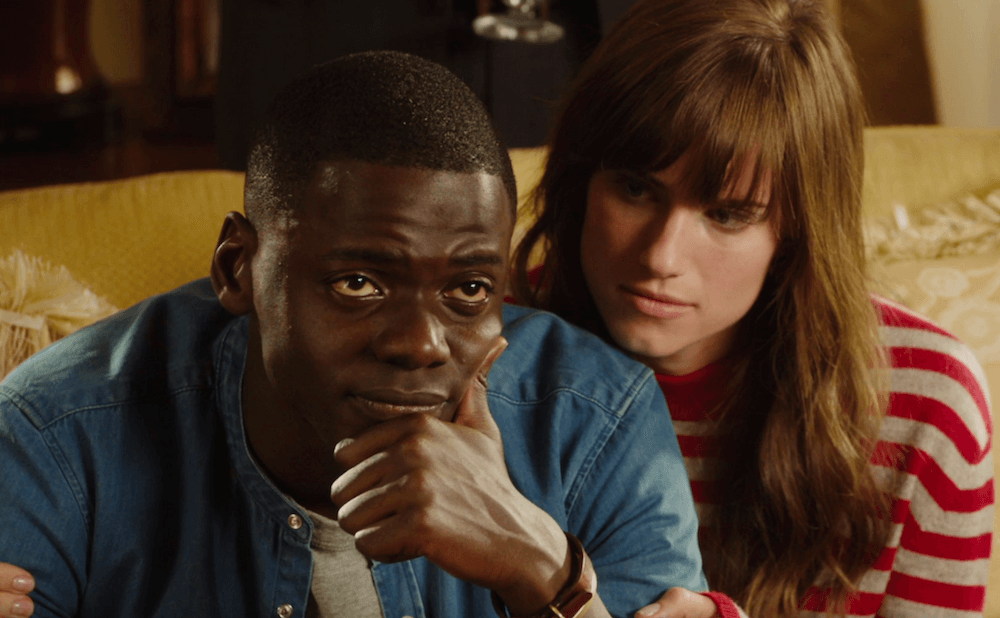
The “Good to See Another Brother” scene from Get Out is a great example of keeping the dialogue minimal and letting facial expression, costume, and tone convey the information:

Get Out screenplay
At this point in the story, Chris still thinks he is simply one of the few black people in his white girlfriend’s upper middle class white family and their social circle.
We, the audience, still might think we’re watching a rom com that conveys only a mild awareness of race, somewhere off in the background of the story. But in this scene, race starts moving forward as a central plot point.
Chris approaches Andre, because he wants to feel a sense of connection in an isolating environment. In order to convey layers of social anxiety and racial tension, all that Jordan Peele needs is the line, “It’s good to see another brother around here.”
Throughout the film, Peele exemplifies how spreading information out like bread crumbs can help build tension and curiosity about a scene.
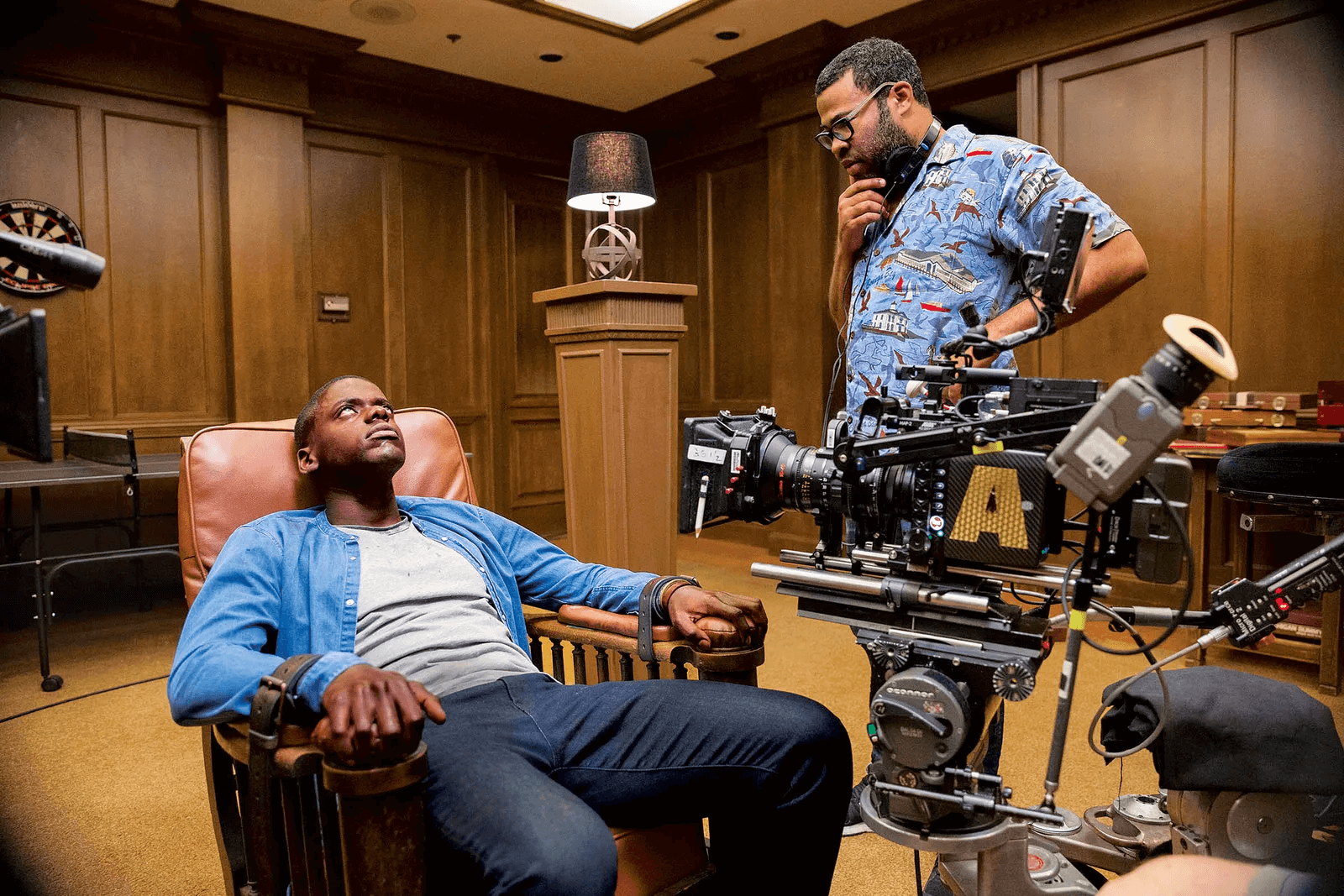
Jordan Peele on the set of Get Out
Look at how much room Peele leaves in the script to describe how Andre’s character should convey his response (“soft-spoken,” “no trace of an urban dialect”). This helps load every word in the scene with more weight and purpose. When Andre does speak, his words are few.
He has visibly changed his style and manner of speaking since Chris first saw him, he won’t say much, and has a glazed over expression on his face. All of this raises the stakes: What is going on here?

Get Out still
In order to learn how to write dialogue, one of the most important writing dialogue rules is to stay in touch with where your characters are in the story at all times.
Building your story, your character arcs, and your story beats before writing can help provide a structure that will give your writing a container in which to flow. Developing compelling characters and making sure that every bit of dialogue real estate on the page is devoted to serving a function in your screenplay can help streamline the whole dialogue writing process.
But regardless of which method you use, if anything, just remember the Mamet Motto: “Nobody says anything unless they want something.”
Up Next
How to introduce your characters.
Writing great dialogue is the icing on the cake of a great story. The importance of building out your story and really being clear on where we’re going, who wants what, and what the conflicts and motivations are the foundation beneath all the other writing dialogue rules. But having solid character descriptions is only the first step. You also have to give each one a great entrance. Check out our post to get some tips on how each compelling, amazing character you write can make their grand entrance.
Up Next: Introducing Characters →
Write and produce your scripts all in one place..
Write and collaborate on your scripts FREE . Create script breakdowns, sides, schedules, storyboards, call sheets and more.
Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- Pricing & Plans
- Product Updates
- Featured On
- StudioBinder Partners
- The Ultimate Guide to Call Sheets (with FREE Call Sheet Template)
- How to Break Down a Script (with FREE Script Breakdown Sheet)
- The Only Shot List Template You Need — with Free Download
- Managing Your Film Budget Cashflow & PO Log (Free Template)
- A Better Film Crew List Template Booking Sheet
- Best Storyboard Softwares (with free Storyboard Templates)
- Movie Magic Scheduling
- Gorilla Software
- Storyboard That
A visual medium requires visual methods. Master the art of visual storytelling with our FREE video series on directing and filmmaking techniques.
We’re in a golden age of TV writing and development. More and more people are flocking to the small screen to find daily entertainment. So how can you break put from the pack and get your idea onto the small screen? We’re here to help.
- Making It: From Pre-Production to Screen
- What is Film Distribution — The Ultimate Guide for Filmmakers
- What is a Fable — Definition, Examples & Characteristics
- Whiplash Script PDF Download — Plot, Characters and Theme
- What Is a Talking Head — Definition and Examples
- What is Blue Comedy — Definitions, Examples and Impact
- 0 Pinterest

A Complete Guide To Writing Dialogue
One of the writer’s most effective tools is dialogue. A story with little or no conversation between characters can sometimes make the eyelids flicker. Too much may leave the reader breathless. Writing dialogue is tough and a skill that takes time to master.
However, there are plenty of useful tips, tools and methods to help you learn how to write dialogue in a story and how to format it too.
And for your benefit, you can find them all in this comprehensive guide.
Below, you can find the definition of dialogue, tags and formatting guidelines and a discussion on the different ways characters speak and converse.
And you can also find plenty of illuminating dialogue examples to help you gain a clear understanding of the mechanics and how you can apply it to our own writing.
You can jump through this guide by clicking below:
Choose A Chapter
What is dialogue, how to format dialogue.
- Should I Use ‘Said’ And Asked?
How To Write Dialogue Between Two Characters
How to write dialogue readers love, how to write internal dialogue, an exercise on how to write dialogue in a story, good dialogue examples from fiction, technical writing tip – how does dialogue impact the pacing of a story, how do you edit dialogue, more guides on creative writing.
Dialogue is defined as a conversation between two or more characters , particularly in the context of a book, film or play.
Specific to writing, dialogue is the conversation between characters.
A n author may use dialogue to provide the reader with new information about characters or the plot, delivered in a more natural way. They may also utilise it to speed up the pace of the story.
As we’ll see below, there seems to be one pervading guideline when it comes to writing great dialogue and that is clarity reigns supreme.
What Is Internal Dialogue?
Internal dialogue is that which happens within a character’s mind . This can sometimes be reflected in fiction with the use of italics. For example:
I hope they don’t come down here, Mycah thought.
Internal dialogue is a great way of delving deeper into a character’s mind and perspective and is a powerful weapon when it comes to characterization. We explore it in more detail below.
Writers have different stylistic preferences when it comes to dialogue. Below, we’ll take a look at some of the best practices and common literary conventions, such as the use of a dialogue tag and quotation marks.
Using Quotation Marks
If sticking to the principle of clarity reigns supreme, then for me, using double quotation marks is the most effective way of communicating dialogue.
They’re universally recognised as a means of conveying dialogue, and they stand out more on the page in contrast to single quotation marks. There are more reasons for using them, however, and that involves a criqute of the single quotation mark.
Writing Dialogue With Single Quotation Marks
This does come down to a matter of style.
The best format I’ve found, and by best I mean the approach readers find clearest, is to use speech marks (“) as opposed to a single apostrophe (‘).
If, for instance, a character is speaking and quotes someone else, single quotation marks can be used within the speech marks, therefore avoiding any confusion, for example:
“I can’t believe she called me ‘an ungrateful cow.’ She’s got some nerve.”
Format Dialogue On A Single Line
Another helpful approach to help maintain clarity is to begin a piece of dialogue on a new line whenever a new character speaks. For instance:
“Who was at the door?” Nick asked. “A couple of Mormons,” Sarah said.
Adding Dialogue Tags
Dialogue tags are simply a piece of prose that follows a piece of speech that identifies who spoke. You can see it in the example above featuring Nick and Sarah.
You can use a dialogue tag in lots of useful ways. For example body language.
If a character reacts to something another character says or does, to maintain clarity, pop the reaction on a new line, followed by dialogue. So for example:
“We’re all sold out,” Dan said. Jim sighed. “Have you not got any in the back?”
Do You Always Need To Use Dialogue Tags?
Something I’ve noticed some of my favourite writers doing—James Barclay and George R.R. Martin, in particular—is, when possible, avoid using an attribution altogether. Less is more, as they say. If just a couple of people are talking, it may already be clear from the voices and language of the characters who exactly is speaking.
Again, to aid clarity, if there are a number of people involved in a conversation, it helps to use an attribution whenever a different character speaks. Nobody wants to waste time re-reading passages to check who’s speaking. I don’t enjoy it and I’m sure others don’t either.
Repetitive use of attribution may grate on a reader. It can suggest a lack of trust in them to follow the story. It helps when editing to look for moments where it’s unclear who’s speaking and if necessary add an attribution.
A brief point on the styles of attribution. If you read a lot, you may notice some writers prefer the order “John said,” and some prefer “said John”. Sanderson is of the view that the character’s name should come first because that’s the most important bit of information to the reader. But the likes of Tolkien adopted the latter version. It’s all personal preference. Why not mix and match?
Should I Use “Said” And “Asked”?
When it comes to the questions I often see asked on how to write dialogue, this is perhaps the most common.
An attribution, also known as an identifier or tag, is the part of the sentence that follows a piece of dialogue. For example: “John said.” In his creative writing lectures, Brandon Sanderson shares a few useful tips.
- Try to place the attribution as early as possible to help make it clear in the reader’s mind who is speaking. This can be done mid-sentence, such as: “I don’t fancy that,” Milo said. “What else do you have?” Breaking away like this works well if a character is going to be speaking for a few lines or paragraphs. You can also use an attribution before the dialogue, though there’s something about this that I find jarring. Used sparingly it works well, but too often just seems annoying and archaic. It’s all personal preference though.
- Try using beats, but not too many. What’s a beat? A beat is a reaction to something said or done. So for example facial expressions like frowning, smiling, narrowing of the eyes, biting of the lip, and hand gestures such as pointing, clenching fists, and fidgeting. And then you’ve got physical movements, like pacing up and down, smashing a glass, punching a wall.
- Don’t worry about using ‘said’ and ‘asked’. To the reader, these words are almost invisible. What they care about is who exactly is speaking.
- When a character first speaks refer to them by name, but after that, it’s fine to refer to them as he or she, provided they’re still the one speaking. It’s even desirable to use the pronoun; repeating a name over and over can irritate a reader.
Remember the overarching principle for when it comes to writing dialogue: clarity reigns supreme. Using ‘said’ and ‘asked’ is often the clearest way of getting your point across.
What To Use Instead Of Said In Dialogue
Remember, there’s no problem with using the word ‘said’ after a piece of dialogue. But if you find when reading your piece aloud that the repeated use jars, especially in a dialogue-rich scene, you may want to mix things up.
Using words other than ‘said’ can help to characterize too—everybody reacts differently to things and those reactions reveal a lot about a person.
So, here’s a list of twenty words that you can use instead of ‘said’ when writing dialogue:
- Pointed out
- Interrupted
So, let’s take a look at how to write dialogue between two characters. If you’d rather have a visual explainer, check out this informative video below.
A useful distinction to make is between everyday dialogue and the dialogue we find in fiction.
The chatter we hear in real life is full of rambling, repetitive sentences, grumbles, grunts, ‘erms’ and ‘ahs’, with answers to questions filled with echoes (repeating a part of the question posed, e.g. “How are you?” asked A. “How am I?” B answered).
When we think of the dialogue we read in books, it contains little of the things we find in these everyday exchanges. According to Sol Stein, there’s a reason for this—it’s boring to read.
If it holds no relevance to the story, we don’t care if a character’s cat prefers to eat at your neighbour’s house instead of your own, or if they think their nail job isn’t worth the money they paid, or if they think the window cleaner isn’t cleaning their windows. There are some snippets we overhear on the street that are interesting—an unusual name, a section of a story we want to know more about. Rare diamonds in a mine miles deep. I’ve fallen into the trap of trying to achieve realistic dialogue and it makes for drawn-out scenes and boring exchanges.
According to Stein, dialogue ought not to be a recording of actual speech, but rather a semblance of it.
What is this semblance of dialogue why should we try and achieve it?
So, how do we write good dialogue?
When we scrutinise a person as they’re talking (all the boring stuff aside) we discover a lot about their character: who they are, what they believe in, and sometimes, if they reveal them, their motives. We glean all this from word choice, sentence structure, choice of topic, their behaviour as they say something.

It’s these little details we as writers must dig for, so when it comes to writing our own dialogue, we can use them to help characterise our own characters and, if possible, develop the plot. The key to mastering dialogue , according to Stein, is to factor in both characterisation and plot.
How do we do it? Let’s look at some dialogue writing examples:
Milford: How are you? Belle: How am I? I’m fine. How are you? Milford: Well thanks. And the family? Belle: Great
I had to stop myself from stabbing my eyes out with my pen. This example is mundane, riddled with echoes, and gives us no imagery about the characters involved. How about this version?
Milford: How are you? Belle: Oh, I’m sorry, didn’t see you there. Milford: Is this a bad time? Belle: No, no. Absolutely not.
See the difference? Milford asks Belle a question, which Belle doesn’t answer. This is an example of oblique dialogue . It’s indirect, evasive, and creates conflict.
It’s a great tool for when it comes to looking at how to write dialogue in a story using different approaches. Our character is not getting answers. Oblique language helps to reveal a bit about the characters and the plot, namely that Belle could be a bit shifty and up to something unsavoury.
Writing Realistic Dialogue
When it comes to knowing how to write natural dialogue, the question to ask yourself is whether or not this style is going to fit your story.
Natural dialogue suits some stories wonderfully. However, it can also work against your story, maybe confusing things for your readers or making it too difficult to read.
When it comes to writing natural dialogue, it’s important to bear in mind the principles discussed here. Give your conversations purpose, make them oblique or intriguing, and don’t give information up cheaply.
You can achieve this in a natural or more casual or informal style.
If you’re looking for more visual tips and advice on writing dialogue, check out this excellent video below:
Say It Aloud
When you’ve written a piece of dialogue, one of the best and simplest techniques to check how it works is to say it out loud.
In doing so you’ll get a sense of how natural it is or whether it jars, or even if it’s cringy or cliche—we’ve all been there.
If you don’t feel comfortable speaking it aloud, you can use a Text to Voice function, like on a website like Natural Readers which allows you to paste in text and then have it read it back to you (it’s free).
Add Slang From Your World
An effective way to write good dialogue that not only characterizes and drives the plot but adds to your world, is to use slang or world-specific references. This can be particularly useful in the fantasy and sci-fi genres .
For example, in my novel Pariah’s Lament , I refer to the world in place of phrases that refer to our own. So instead of “What in the world was that?” I’d say something like “What in Tervia was that?”
Small Talk And Hellos And Goodbyes
As a general rule, there’s no need to include small talk, hellos and goodbyes. The reader isn’t really too bothered about these niceties. They just want to get to the action, the conflict.
You can brush over things like small talk and hellos with short descriptions in your prose writing . For instance:
Stef and John stepped into the room. A sea of smiling faces welcomed them and before they knew it, they were shaking hands and embracing. “I wasn’t expecting such a warm welcome,” Stef said. “It’s like they have no idea what we’ve done,” John replied. “Maybe they don’t.” “Or maybe they do, and it’s all a ruse.” Stef looked at him a moment, thoughtful. “You’re getting paranoid.”
See here how the hellos were glided by and we’re straight into more interesting dialogue? You can also cut back on the odd superfluous dialogue tag too if it doesn’t add to your story.
Give Your Characters Their Own Voice
A character’s voice is an important factor in dialogue. Nobody speaks in the same way. Some people have lisps, some people say their ‘r’s’ like ‘w’s’, some people don’t enunciate properly, say words differently, speak in accents, and have a nasal twang. There are so many variables.
Introducing these features to some or all of your characters can help to make them more memorable and distinct.
How To Write Dialogue For A Drunk Character
When we’re writing our stories it’s likely that some of our characters may become intoxicated with alcohol or drugs. This creates the question in a writer’s mind, how do you write dialogue for a drunk character?
We can fall into the trap of spelling out the words that they try to say, factoring in the slurs, the missed words and the mispronunciations. The problem this can create is that it can go against our overarching principle of clarity reigns supreme.
Dialogue that’s too difficult to read can cause frustration in the reader. They may get fed up and stop reading altogether—the last thing we want.
The best technique is to provide a description of how the person is talking. Describe how they slur their words, how certain letters sound in their drunken state and so on. Including body language in this will help a great deal too. You can then write dialogue in a more natural and understandable way.
The same applies to the likes of writing stuttering in dialogue. It can be very frustrating for a person to listen to a person with a stutter. To include it in your writing can cause problems too. So again one of the best solutions is to describe the stutter first and then write dialogue naturally.
Hopefully, these tips will help you with how to write dialogue for our intoxicated characters.
An Author May Use Dialogue To Provide The Reader With Information, But Don’t Info Dump
An author may use dialogue to provide the reader with useful information. However, if done incorrectly it can have a negative effect.
In his book The First Five Pages , Noah Lukeman says that one of his biggest reasons for rejecting a manuscript is the use of informative dialogue. In other words, using dialogue as a means for conveying information, or info-dumping . He says it suggests the writer is lazy, too unimaginative to convey the information in a subtler way. If you’d like to learn more about avoiding info dumps, check out my guide on natural worldbuilding .
Sometimes dialogue will give us no information at all. Sometimes snippets. Often if you overhear a conversation between two people you’ll find you understand little of what they discuss. It’s the little details they reveal that are most interesting. Take the example of someone mentioning they went to the hospital. The person they’re with may know why they went, but you don’t. Give the reader pieces of the giant puzzle and leave them wanting more.
Lukeman suggests a few solutions to mend instances of informative dialogue. One is to highlight pieces of dialogue that merely convey information and do not reveal or suggest the character’s personality or wants. Break them apart and find a way to let them trickle into the story.
Understanding how to write internal dialogue can prove a key weapon in your writing arsenal.
This style of dialogue can be employed effectively in scenes or stories focused on lone characters. It can break up the monotony of long paragraphs of exposition, which provides welcome relief to readers. Unlike other forms, you don’t need to use a dialogue tag as such.
There are a couple of common ways that you can employ internal dialogue in writing:
- The first option is to italicise the comments made by your character internally. For example: “A door downstairs slammed shut. It’s not windy tonight. How the hell could that have happened?” The main idea here is that the italicised words make it clear to the reader that this is internal dialogue.
- Another option is to write internal dialogue as you would normal dialogue, with speech marks. The difference is what follows that passage of conversation. Usually, it’s something like, “I really do need to get that fixed,” Halle thought to herself. Here, you simply identify that the dialogue was spoken in the mind and not aloud.
As for which is best for how to write effective dialogue for internal thoughts, it’s all a matter of style. However, my personal preference is using italics. To me, it’s just clearer to readers, and that’s the main aim. So that is how to write internal dialogue.
As a little exercise, try and think of some oblique responses to the following line. I’ll give you an example to start. Remember to factor in Stein’s key ingredients— characterisation and plot:
Exercise: “You’re the most beautiful woman I’ve ever seen.”
Example: “Did you say the same thing to that blonde girl behind the bar?”
In this example of how to write dialogue, we get a response that avoids answering the statement. She could quite easily turn around and say “Thank you,” but that’s boring. Instead, we’re wondering about this man and what he’s about, and a bit more about the woman too, namely that she’s observant.
Let’s take a look at some good dialogue examples from some of the finest pieces of fiction to grave our bookshelves:
Dialogue Example #1 “The Silence of the Lambs” by Thomas Harris
“Good morning, Dr. Lecter. How are you feeling?”
“Better than your last visit, Clarice. Shall I have a chair brought in for you?”
“No thank you, I’d rather stand.”
“Please, sit. That’s better. You know, you remind me of someone. A young man I met long ago. He was a student like yourself, with a quick mind and a charming smile. I wonder what became of him.”
“I don’t know, Dr. Lecter. I’m here to ask you about Buffalo Bill.”
Dialogue Example #2 “The Catcher in the Rye” by J.D. Salinger
“You’re lucky. You’re really lucky. You know that, don’t you?” I said.
“Don’t worry about me,” Sally said. “I’ll be all right. I’m serious.”
“I know you will,” I said. “That’s why I’d like to talk to you for just a minute. This is no kidding. You’re going to have to have yourself a grand time this summer. Especially this summer. Have yourself a real need. Because you’re going to go to a lot of parties, and some of them are going to be quite grim, and you’re going to need that need.”
“I know I will,” Sally said. “Don’t worry about me.”
“I know you will,” I said. “But do it anyway. Do it for me. Okay?”
Dialogue Example #3 “To Kill a Mockingbird” by Harper Lee
“Atticus, are we going to win it?”
“No, honey.”
“Then why-”
“Simply because we were licked a hundred years before we started is no reason for us not to try to win,” Atticus said.
One of the most important things to know when it comes to looking at dialogue is the impact it has on pacing.
Dialogue has a knack for increasing the pace and moving the story forward. Readers can find themselves tearing through pages laden with dialogue. As if with all tools of the craft, it pays to know how best to use it. Literary agent Noah Lukeman said a writer must learn how to use restraint when it comes to dialogue, “to sustain suspense and let a scene unfold slowly.”
Again, it’s all a matter of preference.
It’s one thing to know how to write dialogue, it’s another to know how to edit it.
For sound editing advice a good person to turn to is a master editor. In his book on the craft of writing, Sol Stein provides a very helpful checklist when going over passages of conversation:
- What is the purpose of this exchange? Does it begin or heighten an existing conflict, for example?
- Does it stimulate curiosity in the reader?
- Does it create tension?
- What is the outcome of the exchange? Builds to a climax, or a turn of events in the story, or a change in relationship with the speakers?
- Has the correct dialogue tag been used for each character, one that enhances the tale.
One additional step Stein recommends is reading dialogue aloud in a monotone expression. Listen to the meaning of the words in your exchanges.
“What counts is not what is said but the effect of what it means… The reader takes from fiction the meaning of words. And above all, they take the emotion that meaning generates.”
So these are a few things that I’ve found helpful when it comes to writing dialogue. As we’ve seen, an author may use dialogue to provide the reader with interesting information, delivered in a compelling and intriguing way.
Perhaps the most important advice I’ve taken away from them all is to always maintain clarity while using obliqueness to give dialogue that snappy, enticing edge. It’s easier said than done, mind.
Before I leave you, I wanted to point you in the direction of some other guides I think you may find useful.
- Great Examples Of The 5 Senses In Writing
- Men Writing Women
- How To Avoid Duplicate Content Issues – if you need help with plagiarism or making your content unique, head here
- How To Plot A Story
- More Dialogue Writing Examples from Florida Gulf Coast University, with useful advice on making the best use of a dialogue tag
For more writing tips and guides , head here. Or you can find lots of links on all types of creative writing topics on my home page . Thanks for reading this guide on how to write dialogue that readers will love.
- Recent Posts
- 5 Tips to Help Your Child Learn and Succeed at Primary School - February 26, 2024
- The Advantages Of Using An AI Essay Typer Alternative - February 14, 2024
- Advice On Getting Help With Your Homework - January 26, 2024
8 thoughts on “A Complete Guide To Writing Dialogue”
I think crafting one’s own “book on writing” is a great exercise for any writer, regardless of whether or not they want to publish it. The act itself is a great way to organize one’s thoughts and ideas about writing, and compare one’s existing ideas to those one may encounter through others (books, blogs, interviews, etc.). I don’t know if mine will ever be fit for publication, but I find it very helpful to write such things down, instead of worrying about whether or not I’ll remember it.
Definitely! That’s one of the main reasons I’m doing it. We’ve got nothing to lose!
Mmm. And writing it out, organizing it, really helps us retain it afterwards. I feel like I rarely need to consult my notes, but the act of writing them out really helps.
Pingback: A Fantasy Writers’ Handbook by Richie Billing @Magpie_Richie #Spotlight #BookPromo – Chat About Books
Pingback: Great Examples Of The 5 Senses In Writing | Richie Billing
Pingback: How To Edit A Novel - Richie Billing
Pingback: What Is Foreshadowing In A Story? [Definition and Examples] - Richie Billing
Pingback: The Best Show Don't Tell Examples For Writers - Richie Billing
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
Notify me of new posts by email.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .

No thanks, close this box
Writing dialogue: Complete guide to storied speech
Writing dialogue is an important skill to develop so that characters’ speech is imbued with voice and advances the story. Learn more in this complete guide to dialogue writing and formatting, with examples.
- Post author By Jordan
- 37 Comments on Writing dialogue: Complete guide to storied speech

This guide to writing dialogue is all about using speech and conversation in storytelling to make your characters’ voices drive plot, tension and drama. Use the links to jump to the dialogue-writing topic you want to learn more about right now.
What is dialogue? Key terms
Dialogue in writing is conversation between two or more people/animated voices (animated voices because it could be speech between a person and an inanimate object they personify, for example, an imaginary or supernatural voice, and so forth).
Dialogue can be compared to:
- A tennis or fencing match: Speakers may spar, score points, volley arguments or statements (and rebuttals to them) back and forth
- A dance: One speaker says one line, the other replies, and sometimes one person may lead, at other times, the other leads
- Pieces in a puzzle coming together: What different characters say may build up a gradual picture, for example an idea of the persona of a character who has not yet appeared in a story scene but has been spoken about by others
- Music: sometimes there is harmony (working together), other times discord (strife, heated conversation or disagreement)
Key terms in writing dialogue
There are several terms in dialogue worth knowing as they crop up often in discussing this element of writing craft:
Active listening: Dialogue is (usually) responsive
When somebody is engaged in ‘active listening’, they aren’t just waiting for their turn to speak. In a true conversation, people hear one another, respond.
There may be instances where your dialogue’s subtext or context (more on these below) calls for characters not to actively listen to one another, of course. There may be cause for them to interrupt, speak over, speak at cross purposes.
In these cases, it should be contextually or otherwise clear why characters aren’t properly responding to each other’s speech (the dialogue should not read or sound like random non sequiturs, each person’s utterances totally disconnected for no clear reason).
Context for dialogue
Effective dialogue involves its context. For example, in a frenzied car chase, the squeal of tires may drown out the exchange here or there. Speech and action in this context may reflect rapid decision-making, keeping pace.
In the middle of a bank heist, people may be curt, decisive (of course, inept thieves could wax lyrical and by talking too much make rookie mistakes).
Either way, context will inform how readers make sense of your dialogue, and helps to fill dialogue with tone and mood . Nobody whispers to each other standing next to Niagara falls (if they want to be heard).
Subtext and dialogue
Subtext in dialogue is the underlying meaning, motivation or feeling behind the words characters speak.
For example, a boss starts a casual conversation with a new employee but the subtext is that they’re having regrets at hiring the person and trying to come to a decision on whether to terminate in the trial period. The subtext will inform what language they will use (and this language would be different to someone ecstatic with their employee’s performance).
Subtext adds depth and complexity to dialogue, strata of the said and unsaid.
Purpose in dialogue
Why is the information you are writing in a scene given as dialogue? Knowing the purpose of dialogue (and writing dialogue that feels purpose-driven) is useful to ensure that every spoken line counts. In a stage play, dialogue and action are the two drivers of story.
In narrative fiction, you also get to use narration to convey meaning. A story where all character information is conveyed through narration may read oddly voiceless, impersonal. Dialogue makes your characters pause, take a breath, like real flesh and blood.
Recommended reading
Learn more about writing conversations that feel real and draw on cause and effect, call and response:
- Context and subtext in dialogue: Creating layered speech
- How to make dialogue in writing carry your story
- 7 dialogue rules for writing fantastic conversations
To the top ↑
I write plays because writing dialogue is the only respectable way of contradicting yourself. I put a position, rebut it, refute the rebuttal, and rebut the refutation. Tom Stoppard

GET YOUR FREE GUIDE TO SCENE STRUCTURE
Read a guide to writing scenes with purpose that move your story forward.
Why dialogue matters
Why do most stories benefit from liberal use of dialogue?
1. Dialogue brings characters and their differences to life
In dialogue, you could show a character’s personality in a handful of words. Here, for example, Dostoyevsky creates the sense of a decisive doctor, used to dealing with uncertain, anxious patients in The Double :
‘Krestyan Ivanovich … I …’ ‘Hm,’ interrupted the doctor, ‘what I’m telling you is that you need to radically change your whole lifestyle and in a sense you must completely transform your character.’ (Krestyan Ivanovich particularly emphasized the word ‘transform’ and paused for a moment with an extremely significant look.) Fyodor Dostoyevsky, The Double , trans. Ronald Wilks (1846, 2009), p. 11
There is an immediate sense of power dynamic (and differential) – the hesitating patient and his decisive doctor.
2. Dialogue splits up exposition into varied parts
If all the revelation of your characters and world is in long, wall-of-text narration, it becomes slightly draining to read.
Dialogue lifts us out of a ‘this happened, then that’ sense of explanation and throws us into the immediate – sound striking the eardrum. Tweet This
3. Dialogue advances a story
Characters may tell each other things that reveal – or shift – goals, motivations, conflicts. ‘But first, I must tell you Mr Bond…’ A villain may say too much, a lover, too little (or vice versa).
4. Conversation builds relationships
Some of the most beautiful relationships (or the most ugly) emerge through what people say to one another.
Ed’s note: As an undergraduate in English Literature, I attended a lecture on Pride and Prejudice where the lecturer illustrated how Lizzie and Darcy’s love is established through the grammar of their language and how it shifts. At one point, Darcy says, ‘You are loved by me’ – a different structure to the standard ‘I love you’ that places the subject first, in a way that reads as full of care.
We detect attraction and resentment in the language people use with one another. A conversation about the weather may imply feelings – it comes down to tone, address, mood, agreement and disagreement.
5. Dialogue brings humor, levity and persona to stories
Dialogue is often a vehicle for comedy. It’s a crucial part of how to write a funny story .
You can narrate that a character has grown wealthy and fallen out of touch with their humble origins. But in Dickens’ Great Expectations, when a character named ‘Trabb’s boy’, the tailor’s son, follows the main character Pip down the street mimicking him and saying, ‘Don’t know ya!’ after Pip is left wealth, it’s a brilliant and funny illustration of how people change (and perceive and react to changes in others).
Pip seems ‘too good for’ others now that he has wealth, and three words convey Trabb’s boy’s contempt with sly humor. Three words (paired with action, the following and mimicking) convey complex social dynamics and feelings.
Why else do you think dialogue matters? Tell us in the comments.
Learn more about writing dialogue that drives stories:

10 dialogue tips to hook readers
Hook readers into your story with dialogue that catches their attention.

- Writing movement and action in dialogue: 6 tips
How can movement and action make your dialogue more immersive? Find out.
Dialogue is the place that books are most alive and forge the most direct connection with readers. It is also where we as writers discover our characters and allow them to become real. Laini Taylor
How to format dialogue
Speech marks or quotation marks, and where do the line breaks go? Read on for how to format dialogue, common differences between UK and US formatting styles, and more:
Why do we format dialogue? Clarity, ease and flow
Try to write an exchange in dialogue all as block paragraph text and it becomes a nightmare trying to keep track of who says what:
“You’re late,” she said. “But I didn’t say what time I was coming.” “I don’t care, I’ve been waiting half an hour.” There was an awkward silence for a few seconds. “Well don’t say anything, whatever.”
It’s not clear from the above dialogue without line breaks and with no attribution for the last spoken sentence who says what at all times.
This is much easier to read because line breaks signal when the speaker changes:
It’s much easier to follow the back and forth (and because only two characters are present, the dialogue does not need excess attribution of who says what thanks to the line breaks clarifying this).
How to format dialogue in stories: 8 tips
To make sure it’s clear who’s speaking, when it changes, and when speech begins and ends (and narration or description interrupts):
1. Use quotation or speech marks to show when speech starts and stops
If a character is still speaking, don’t close speech marks prematurely.
2. Start a new line each time the speaker changes
Although it is common practice to use an indent for each change of speaker, make sure to use paragraph formatting in your word processor rather than the tab button as this can make indentation too large or wonky (using paragraph-wide settings is most precise).

3. Decide how you’ll format dialogue (and stick with it)
Speech marks with double quotations like the example from Colleen Hoover above (“) are more commonly used in the US, single quotation marks (‘) in books published in the UK.
Some contemporary novels don’t use speech marks at all, using an em dash at the start of a line or presenting dialogue another way. Whichever approach you use, consistency is key.
Example: Using single quotation marks to indicate speech

4. Always use a comma if there is an attributing tag
If dialogue is attributed using a tag such as ‘she said’ (read more on dialogue tags below), use a comma and not a period/full stop. For example:
“Writing dialogue is harder than I thought.” She said. ❌ “Writing dialogue is harder than I thought,” she said. ✔️
Remember: the tag continues the sentence.
5. Split long monologue over multiple paragraphs
What if the same character is speaking for a long time in dialogue?
To format this, the convention is to open speech marks for each new paragraph without closing speech marks for the previous one, until the speaker is finished talking.
Example: Dialogue where one speaker continues over paragraphs
“First I want to thank you all for being here on our special day. It does take a village (but you can put down the pitchforks, take off the creepy masks, and relax a little, guys, it’s not that kind of village) … Er eheh… OK I’m firing my joke writers.
“But in all seriousness, I couldn’t have chosen a better bride…zilla.”
6. Use the appropriate dialogue punctuation
If a speaker pauses, put it in with a comma or something longer such as a semicolon. This is where it helps to read dialogue out loud as you will hear where there is a natural pause that needs punctuating. Colons have an announcing effect. Example: “OK, here’s the kicker: The guard changes every forty-five minutes.”
If there is a question or exclamation, use the appropriate speech mark (that includes the occasional special effect, such as an interrobang (!?).
7. Write interruption or other changes in dialogue’s flow clearly
Ellipses are effective in showing a character trailing off or pausing to think for longer, mid-dialogue.
“Oh yes, I remember, it was … whatshername.”
There are several ways to show interruption. You could:
- Use an em-dash just after cut-off speech. Example: “If you’d just let me fini—”
- Use parentheses to show self-interruption. Example: “If you’d just let me finish what I was (actually, it’s fine, carry on).”
8. Format narration interrupting dialogue clearly
If you want to describe a character’s manner, movement, expression mid-dialogue, remember to use a comma before and resume dialogue without capitalization (unless the word is a proper noun):
“I can’t believe you said that,” John said, shaking his head, “and with absolutely zero remorse, too.”
Read more on how to ensure your dialogue reads clearly, including how to write ensemble dialogue with multiple characters present:
- Writing dialogue between multiple characters
Nothing teaches you as much about dialogue as listening to it. Judy Blume
Effective vs weak dialogue
Why does some dialogue scintillate, stir interest, while other dialogue reads like talking heads saying nothing of great impact in an inky void? There are several hallmarks of effective and less effective dialogue:
What makes dialogue effective:
- An authentic sense of voice. Do characters sound like cipher’s for an author’s pretension (this may be true to a specific stylistic choice, though) or like real people talking?
- Purpose-driven dialogue. Each line of dialogue should have identifiable purpose, whether it’s establishing character, advancing the story, building tone and mood, or dialogue serves another purpose.
- Aptness for type (or explicable ‘against type’ voice). Avoid confusing your reader by having a five-year old speak like a fifty-year-old (unless there’s a plot-given or other explicable reason for this anomaly).
- Varied structure. If every sentence is clipped or brusque, or every sentence is long and meandering, the eye (and ear) may tire. Switch it up if possible.
- Natural language. Contractions (e.g. ‘it’s’ for ‘it is’) and other ways people naturally speak (colloquial language or slang) lend further authenticity to voice.
- Conflict and tension . ‘As you know, Bob’ info dumps and happy people in happy land don’t make dialogue exciting (but tension, disagreement, doubt – sparks of contradiction – do).
- Movement and gesture. A gesture may change the entire meaning of a spoken phrase (a shrug, turn, sitting down, standing up, waving arms, and so on).
- Subtext and inference. What a character is truly thinking or feeling might not match up perfectly with what they’re saying. People lie, omit, embellish, and so forth.
What can weaken dialogue in fiction?
Dialogue in stories may feel bland or confusing (or too over the top and melodramatic) when:
- It’s all one note. If every utterance is an exclamation (with an exclamation mark), that gets old fast. Use special effects like salt – just enough to enhance the conversation.
- Connection is absent. Your reader may be confused if what characters reply to each other seems as though they’re having two different conversations (unless there is contextual explanation, e.g. both are hard of hearing).
- The scenery stays outside. If your characters are having an argument in the kitchen, does someone bang a pot, slam a drawer? Bring in surrounds.
- There is no differentiation. If everyone has the exact same vocabulary, mannerisms, and pattern of speech, characters start to become clone-like, like so many Agent Smiths.
- Excessive or bizarre tags. Characters shouldn’t honk or trumpet speech too often. Favor tags that you can say or express (no, “What!” she flabbergasted’). Leave out tags entirely if context tells your reader who speaks (and content of speech gives tone/mood).
- Excessive dialect or accent. At best excessive dialect or accent may read distracting, at worst, like hurtful stereotype or caricature.
- Adverbs clutter speech. Instead of overusing ‘she says softly’, leave space for the silence to come through.
- Dialogue dumps information. ‘As you know, Bob’ is a phrase used for dialogue where characters tell each other things both already know solely for the reader’s benefit. Find ways to make the retelling new/fresh, find what Bob doesn’t yet know and needs to be told.
Keep reading about ways to make dialogue characterful and engaging:
- Dialogue words: Other words for ‘said’ (and what to avoid)
- How to write accents and dialects: 6 tips
- Realistic dialogue: Creating characters’ speech patterns

Pay $0 for writing insights and how to’s
Be first to know whenever we publish and get bonus videos and the latest Now Novel news.
Dialogue devices for characterful speech
There are several dialogue devices that help to advance stories and create a sense of movement, tension and change:
Dialogue tags and action tags
What are dialogue tags and action tags?
Dialogue tag: The words added after dialogue that attribute who has spoken (and often the mood, emotion, or volume of speech).
“You might want that tattoo, but I know all your secrets and your twenty-first is coming up and don’t think for a second I’m above making an awkward speech,” mom warned.
“Shh!” he hissed in a half-whisper. “This freaking place is haunted.”
Action tag: Indicates the speaker’s movements or gestures in dialogue. This can be used to attribute speech and make dialogue livelier.
“You might want that tattoo, but …” Mom leaned over theatrically as though to confide something important. “I know all your secrets and […]’
Movement and gesture
Movement and gesture may punctuate dialogue, immersing the reader in a scene further.
‘Then go,’ said Mrs Williams, handing him the buckets and the coil of rope. ‘Swim,’ she said maliciously. She knew he was afraid of the sea. He carried his fear coiled and tangled in him like other boys carry twine and string in their crumb-filled pockets. Peter Carey, Oscar and Lucinda (1988), p. 16
Interruption
Interruption is a useful device in dialogue for argument, dramatic scenes with high stakes where characters are speaking over one another, and so forth.
“I could have killed you.” “Or I could have killed you,” Percy said. Jason shrugged. “If there’d been an ocean in Kansas, maybe.” “I don’t need an ocean—” “Boys,” Annabeth interrupted, “I’m sure you both would’ve been wonderful at killing each other. But right now, you need some rest.” Rick Riordan, The Mark of Athena (2012).
Conflict and suspense
Conflict and suspense in dialogue keep the reader intrigued. Characters may argue, refuse to speak, tell a fib the reader may know to be untrue, or otherwise stir tension.
“What’s this for?” Tessie asked suspiciously. “What do you mean, what is it for?” “It’s not my birthday. It’s not our anniversary. So why are you giving me a present?” “Do I have to have a reason to give you a present? Go on, open it.” Tessie crumpled up one corner of her mouth, unconvinced. Jeffrey Eugenides, Middlesex (2002), p. 10.
Read more on devices in dialogue, including dialogue tags vs action tags and how to create tension:
- 421 ways to say said? Simplify dialogue instead
- Dialogue 101: Using dialogue tags vs action tags
- Writing tense dialogue: 5 ways to add arresting tension
I never say ‘She says softly.’ If it’s not already soft, you know, I have to leave a lot of space around it so a reader can hear that it’s soft. Toni Morrison
Dialogue examples that work
Read examples of dialogue that works from a cross-selection of genres including fantasy, romance, science fiction, thriller, historical, contemporary and more:
1. Fantasy dialogue example ( A Game of Thrones )
Note how George R. R. Martin weaves in setting to create mood between utterances in this exchange from the prologue to A Game of Thrones :
“We should start back,” Gared urged as the woods began to grow dark around them. “The wildlings are dead.” “Do the dead frighten you?” Ser Waymar Royce asked with just the hint of a smile. Gared did not rise to the bait. He was an old man, past fifty, and he had seen the lordlings come and go. “Dead is dead,” he said. “We have no business with the dead.” George R. R. Martin, A Game of Thrones (1996).
2. Historical romance dialogue example ( The Duke and I )
Julia Quinn begins the first chapter in the first of her popular Regency-set romance novels with a typical Regency setting – a drawing room (and drama in letters):
“Oooooooooohhhhhhhhhh!” Violet Bridgerton crumped the single-page newspaper into a ball and hurled it across the elegant drawing room. Her daughter Daphne wisely made no comment and pretended to be engrossed in her embroidery. “Did you read what she said?” Violet demanded. “Did you?” Julia Quinn, The Duke and I (2000).
3. Mystery dialogue example ( The Murder of Roger Ackroyd )
Dame Agatha Christie’s The Murder of Roger Ackroyd is often voted one of her best detective novels. In the first chapter already, conversation turns to death and the topic of who knows what about whom (and how):
My sister’s nose, which is long and thin, quivered a little at the tip, as it always does when she is interested or excited over anything. “Well?” she demanded. “A bad business. Nothing to be done. Must have died in her sleep.” “I know, said my sister again. This time I was annoyed. “You can’t know,” I snapped. “I didn’t know myself until I got there and I haven’t mentioned it to a soul yet. If that girl Annie knows, she must be a clairvoyant.” Agatha Christie, The Murder of Roger Ackroyd (1926)
4. Science fiction dialogue example ( Hyperion )
Dan Simmons’ Hyperion which won a Hugo Award was hailed as ‘The book that reinvented Space Opera’. Note the weaving in of dialogue between human and machine in the prologue:
‘We need your help,’ said Meina Gladstone. ‘It is essential that the secrets of the Time Tombs and Shrike be uncovered. This pilgrimage may be our last chance. If the Ousters conquer Hyperion, their agent must be eliminated and the Time Tombs sealed at all cost. The fate of the Hegemony may depend upon it.’ The transmission ended except for the pulse of rendezvous coordinates. ‘Response?’ asked the ship’s computer. Dan Simmons, Hyperion (1989).
5. Psychological thriller dialogue example ( Sharp Objects )
Notice how in Gillian Flynn’s debut Sharp Objects how even a simple conversation between reporter Camille Preaker and her editor at the St. Louis Chronicle who sends her back to her hometown on assignment is laced with a sense of tension and avoidance:
“Tell me about Wind Gap.” Curry held the tip of a ballpoint pen at his grizzled chin. I could picture the tiny prick of blue it would leave among the stubble. “It’s at the very bottom of Missouri, in the boot heel. Spitting distance from Tennessee and Arkansas,” I said, hustling for my facts. Curry loved to drill reporters on any topics he deemed pertinent – the number of murders in Chicago last year, the demographics for Cook County, or, for some reason, the story of my hometown, a topic I preferred to avoid. Gillian Flynn, Sharp Objects (2006).
6. Humor dialogue example ( Lessons in Chemistry )
See here how Bonnie Garmus weaves together humorous dialogue and character description to create the portrait of a man who does not have much luck in love:
“I can’t believe you’re having trouble,” his Cambridge teammates would tell him. “Girls love rowers.” Which wasn’t true. “And even though you’re an American, you’re not bad looking.” Which was also not true. Part of the problem was Calvin’s posture. He was six feet four inches tall, lanky and long, but he slouched to the right – probably a by-product of always rowing stroke side. Bonnie Garmus, Lessons in Chemistry (2022).
7. Historical/fantasy dialogue example ( The Invisible Life of Addie LaRue )
V.E. Schwab creates a sense of early, 17th Century times in this conversation about prayer and witches’ fates in her historical fantasy novel that involves immortality and contemporary romance:
“How do you talk to them?” she asks. “The old gods. Do you call them by name?” Estele straightens, joints cracking like dry sticks. If she’s surprised by the question, it doesn’t show. “They have no names.” “Is there a spell?” Estele gives her a pointed look. “Spells are for witches, and witches are too often burned.” V.E. Schwab, The Invisible Life of Addie LaRue (2020).
8. Literary fiction dialogue example ( Home )
Toni Morrison is a master of capturing the authentic ring of a real human voice. See the difference between the Reverend and his wife who dismisses his jaundiced view of the world as ‘foolishness’ in this dialogue example:
“You from down the street? At that hospital?” Frank nodded while stamping his feet and trying to rub life back into his fingers. Reverend Locke grunted. “Have a seat,” he said, then, shaking his head, added, “You lucky, Mr. Money. They sell a lot of bodies out of there.” “Bodies?” Frank sank down on the sofa, only vaguely caring or wondering what the man was talking about. “Uh-huh. To the medical school.” “They sell dead bodies? What for?” “Well, you know, doctors need to work on the dead poor so they can help the live rich.” “John, stop.” Jean Locke came down the stairs, tightening the belt of her robe. “That’s just foolishness.” Toni Morrison, Home (2012).
What is a favorite section of dialogue from a book in your favorite genre? Share in the comments below.
Join The Process for weekly feedback on dialogue and other writing, webinars on dialogue writing and other writing craft topic, and structured writing tools to brainstorm and develop your story.
Now Novel has been invaluable in helping me learn about the craft of novel writing. The feedback has been encouraging, insightful and useful. I’m sure I wouldn’t have got as far as I have without the support of Jordan and the writers in the groups. Highly recommend to anyone seeking help, support or encouragement with their first or next novel. – Oliver
Recommended Reading
Read further examples of effective dialogue:
- Dialogue writing examples from top books vs AI (2023)
- Writing conversations using setting (examples)
- 5 types of dialogue your novel needs
Related Posts:
- Realistic dialogue: Creating characters' speech patterns
- Writing process: From discovery to done (complete guide)
- Tags dialogue examples , dialogue tags , how to write dialogue
Jordan is a writer, editor, community manager and product developer. He received his BA Honours in English Literature and his undergraduate in English Literature and Music from the University of Cape Town.
37 replies on “Writing dialogue: Complete guide to storied speech”
Thank you for this! I notice these are all first person narratives; could you do something also with stories told in third person?
It’s a pleasure! Happily. While not on dialogue specifically, you might find this post on starting a story in third person helpful: https://www.nownovel.com/blog/how-to-start-a-novel-in-third-person/
“Very illuminating,” I said.
Thanks, Rob!
thanks this really helped
I’m thrilled to hear that, Randolyn. Thank you for the feedback.
As Rob said, very illuminating!
Do you have any recommendations on books with similar dialogue? Or should I give Tartt’s whole bibliography a go?
Thanks for the insight! Dialogue is one of my worker points in writing and I aim to correct that.
Hi Marco! It’s a pleasure. Tartt’s writing is very punchy, but there are many authors who write fantastic dialogue. Another great one is Toni Morrison – she’s a great master of every element of story, from exposition to dialogue to description and more.
Good luck, with focus I’m sure it’ll improve to the level you want it to be quickly.
This was immensely helpful. I’ve always handed dialogue fairly well, I think, but these tips will help me clean it up and use it to move the story forward, rather than just using it as page filler.
That’s great to hear, Brianna. I hope your current WIP is coming along well 🙂
yes helpfull
Hi Umer, thank you for the feedback. Good luck with your story!
Hello this is a nice example…….
Thanks, Joel!
This is truly helpful. Thanks!
I’m glad to hear that, April. It’s a pleasure! I hope you’re writing great dialogue.
I am doing a class project on figurative language and i need examples but short ones do you have any i could use
This was surprisingly helpful. I’m so glad I came across this website. Writing dialogue has always been something I’ve had difficulty doing, but these tips have significantly improved my dialogue writing. Thank you so much.
We’re glad to hear that, Prakhar! Keep writing 🙂
it is really usefull to me madam thank u so much
I’m glad to hear that, Manjunatha. Have a great weekend!
Thanks, Nathan, I’m glad to hear that.
kinda helpful to me 😀
I got my 18,5 mark from this Amazing ?
Fantastic, Chihab – do give yourself some of the credit! Well done.
Very useful to me… Thanks !!☺☺
It’s a pleasure, thank you for reading our articles and taking the time to share your feedback ?
[…] some dialogue writing tips at the following blog and evaluate them with some fellow […]
I want to know about the rule of using open quotation mark at the end of the dialogue 1 ‘We are not allowed to-‘
Hi Jagadishkk, thank you for sharing your question. From the example you’ve written, do you mean using interruption at the end of a line of dialogue? The way you’ve written that example is correct, you would usually use a dash with the interrupting person’s dialogue appearing immediately below on a new line (with indentation if indenting changes of speaker as is a common formatting style choice).
Hi I want you to help me with dialogue first draft
Hi Peggy, you can get constructive feedback from our community in our writing groups, they’re free to join. You can sign up here .
What is a favorite section of dialogue from a book in your favorite genre? Here is one of mine from “Bring up the bodies” by H. Mantel.
“Majesty, the Muscovites has taken three hundred miles of Polish territory. They say fifty thousand men are dead.” “Oh,” Henry says. “I hope they spare the libraries. The scholars. There are very fine scholars in Poland.” “Mm? Hope so too.”
Tells us something about Henry VIII — he “doesn’t give a hoot” about libraries and scholars in Poland or dead men.
Hi Nara, thanks so much for sharing that dialogue example. I like that Henry VIII seems preoccupied or disinterested in his responses, the simplicity of monosyllabic words and even how Mantel has him drop the subject ‘I’ to make it read more cursory, saying the bare minimum. He was probably too busy marrying and remarrying (and beheading) 🙂
Hey Jordan,
fantastic article, thank you very much – it helped me a lot, especially because i am translating my German Novel into English right now! However there is still an open question to me:
Here is an example/ little excerpt of my novel, which I already translated but kept the original German Formatting. I am asking myself if the colon can stay like this ( Then she said: ) or do I have to replace it with a comma ( Then she said, ) and begin with the dialogue in the next line. Here is the example ->>
After my mother echoed Michael’s exact words, she looked at me with a fixed gaze for several seconds. Then she said: “Do you understand now, Jordan, why I opened my eyes so wide just now?” “Yes… I feel as if he is here right now, Mother. I know him, but I don‘t know where…” “But now I really want to ask you, were you aware of his words, Jordan?”
I really hope you can help me with this little question. Thank you in advance 🙂
Greetings from Germany Yannic
Hi Yannic, thank you for your kind feedback, I’m glad you found this guide to dialogue helpful. One can use a colon or a comma to precede quoted speech. Technically, it is usual to only use a colon if the introductory words form an independent clause or the quotation is a complete sentence. Because the mother’s words fit this rule, a colon is totally acceptable in this case.
Good luck with your translation, that is quite the undertaking.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Pin It on Pinterest

Nathaniel Tower
Juggling writing and life
How to Write Dialogue with Good and Bad Dialogue Examples
Last Updated on January 28, 2023 by Nathaniel Tower
If you want to be a great storyteller, you have to know how to write dialogue.
I’m about to make a shocking confession: sometimes when I’m reading a book, I’ll start skimming. And when I skim, I often will pass quickly through large blocks of narrative in search of dialogue. Thankfully, the dialogue will usually get me back on track.
As a reader, I love reading dialogue. As a writer, I tend to overuse it at times, particularly during a first draft. Nonetheless, I love writing dialogue because it’s where the characters can really shine and help the story become more powerful.
Don’t get me wrong. Narration can be just as powerful. But dialogue is often far more memorable and makes your story more relatable for your readers. And that’s why it’s essential for writers to understand how to write great dialogue.

The two sides of writing dialogue
There are two primary aspects to writing effective and compelling dialogue:
- The technical side – This is the boring but essential stuff like proper conventions, punctuation, etc.
- The execution – This is the fun stuff. Here I’m talking about the actual words the characters say. In order to effectively execute, you need to make it real, engaging, compelling, impactful, etc.
The second is much harder to do, but if you don’t get the first point down first, it won’t matter how brilliant the dialogue is.
So let’s get the technical side out of the way. Here’s what you need to know:
Dialogue goes in quotation marks
Feel free to fight me on this one. I know it’s experimental and hip to leave out the quotation marks. But let me tell you this: 9 out of 10 times, this creates a lousy and confusing experience for the reader. There’s a really good reason why we put dialogue in quotation marks: it makes it clear someone is talking.
I’ve yet to hear a good reason why quotation marks should be omitted. If you want to write your story without them, make sure you have a damn good reason beyond, “Hey, I just want to do something different.”
Punctuating dialogue is easy (and proper capitalization isn’t hard either)
It really shouldn’t be that hard, but I see writers screw this up all the time. Of course, the ones who can’t punctuate dialogue properly also tend to write terrible dialogue, but maybe that’s just because they are so confused about the conventions.
Okay, we’re going to have to break this one into some sub-rules, and I’m going to have to use a lot of examples.
Punctuation goes inside the closing quotation mark. This includes commas, periods, exclamation points, and question marks. Yes, there are times when certain punctuation can go outside of a quotation mark, but when you are talking about dialogue, put it inside. Here are some examples:
- Sally said, “I’m really excited!”
- Sally said, “You should always put punctuation inside the quotation marks.”
- Sally asked, “Are you seriously going to omit quotation marks in your dialogue?”
- “Let’s write some dialogue,” said Sally.
- “Do you like the dialogue I have written?” asked Sally.
Capitalize the beginning of a quotation. Whenever you are starting a quotation, the first letter is always capitalized regardless of whether or not it’s the start of the sentence. Note the second example below. If the dialogue is interrupted with narration and then continued within the same sentence, you should not capitalize the second string of dialogue. Examples:
- Sally gazed upon the glistening dew and said, “Properly punctuated dialogue is a beautiful thing.”
- “Don’t you think,” Sally began, “that writing dialogue can be a beautiful thing?”
Don’t capitalize the first word outside of the quotation unless it’s a proper noun or a new sentence. This is true regardless of the punctuation mark in the quotation. I’ve already shown a couple examples of this above, but let’s look again:
- “I love writing dialogue!” she shouted at the top of her lungs.
- “Don’t you love the way dialogue looks on paper?” she asked.
- “This is a beautiful sentence,” said Sally.
That wasn’t too hard, right? If you can remember those three basic rules, then you’ll be in great shape and both your readers and your characters will thank you.
Start a new paragraph when a new speaker is talking
Remember the first rule about using quotation marks? We did that to make it easier on our readers. And that’s why we’re going to start a new paragraph when a new speaker is talking. Once again, it can be cool and experimental to have a really long paragraph with a bunch of speakers confined within, but it pretty much always sucks.
Look, I’m not a prude when it comes to experimentation in writing. There’s just certain things that aren’t worth experimenting with. Omitting quotation marks or jamming multiple speakers into a single paragraph doesn’t make your story more meaningful. It just makes it harder to read.
Here’s an example of this in action:
“I’m not sure how to write dialogue,” Johnny said to Sally.
Sally looked Johnny in the eyes and smiled. “It’s really not that hard,” she said as she touched his cheek.
“That’s easy for you to say. You’ve been doing it for years. You have three published books. I’m a nobody.”
“We all start as nobodies.”
Johnny laughed. “You can say that again.”
See how easy it is to tell who is speaking? And see how much more meaning comes out of every bit of dialogue when it’s given the proper room to breathe. Even this relatively meaningless exchange is vastly improved by the pacing created through paragraphing.
So those are the basics from the technical side. Not too hard, right?
Now we have to get into the other, much more complex side of how to write great dialogue. Let’s start simple:
Don’t use a thesaurus to find synonyms for “said”
People say things. They don’t emote, whinny, sigh, or express them. It’s okay to use “said” most of the time. It’s not acceptable to find a different synonym every time someone talks.
At some point, someone started teaching people they shouldn’t use “said” as part of a dialogue tag. Whoever started that trend was wrong. I’d love to blame it on the anti-quotation mark movement, but it’s a separate epidemic led by a different group of people.
When you use different verbs in your dialogue tags, you are taking away the significance of the dialogue and putting it onto the tag instead. Put another way, the words of your characters lose impact and you as the writer become an intrusive narrator who doesn’t trust your characters.
It’s also okay to forego the dialogue tags completely in favor of actions outside of speech.
Example: Sally grabbed her pen. “I love writing dialogue.”
It’s obvious that Sally is speaking even though we didn’t explicitly say she said it. We can also imagine how she’s saying it based on what she is saying as well as the context around it. We don’t need to be told whether she shouted, exclaimed, or whispered it. The fact that she grabbed her pen and said she loves writing dialogue tells us all we need to know.
And don’t even think about using an adverb to tell the read how it was said. If Sally said it boldly, then you better make that clear by her actions and the other characters’ reactions.

Make dialogue real (but not too real)
Dialogue is a great opportunity to make your characters relatable and real. To do so, they need to sound like real people. Here are some helpful tips to accomplish that:
- People speak in contractions and use slang/informal language when they talk. Your dialogue should reflect this. Don’t make your dialogue sound like an academic essay.
- People don’t say each other’s names very often when they are addressing each other. Don’t make your characters frequently spit out the other person’s name.
- People don’t usually speak in huge blocks of text when they are having a conversation. Make your dialogue short and to the point.
- People don’t describe their actions as they are doing them. That’s what narration is for.
- People do occasionally use filler words, such as “like,” “umm,” and a few others. Sprinkle these in as appropriate, but don’t overdo them. Think of how insufferable it is to listen to someone who says “like” a lot. Reading it a lot is even worse.
At the same time, you shouldn’t try too hard to emulate speech patterns. This is particularly true when it comes to writing dialects. Unless you are an exceptional writer with a masterful comprehension of a specific dialect, you’re going to butcher it when you try to write it.
Your dialogue doesn’t need to be a perfect representation of speech patterns, accents, and dialects. Just make it seem real and make it easy for your readers to comprehend.
Make dialogue meaningful, but don’t force it
No one wants to read filler. Every word in your story or novel should be important, especially the dialogue.
When I say that, I mean it should be important for the flow and meaning of the story. That certainly doesn’t mean every word and every line of dialogue has to be brilliant and memorable. People say plenty of non-brilliant things. Let your characters be themselves. Don’t stuff your dialogue so full of memorable one-liners that it comes across as inauthentic.
Meaningful dialogue will do the following:
- Reveal important things about your characters’ personalities and actions
- Help the plot move forward in a natural way
- Make your characters feel like real people
- Hint at subtleties that are deeper than what the characters are actually speaking about in the moment
Although we can think of many famous quotes from literature and movies that are dialogue, remember there are infinitely more character quotes that mean absolutely nothing out of context. Your job as a writer isn’t to make every single line profound. It’s to tell a meaningful, engaging story that will resonate with your audience.
Bad dialogue examples – What to avoid when writing dialogue
Here are four visual and text examples of bad dialogue. Whatever you do, don’t write dialogue like this:
Don’t use dialogue to describe everything
“Look at that,” he stated.
“What?” he asked.
“The thing I am pointing at,” he replied.
“What are you pointing at?” he asked.
“The glowing orange sunset piercing through those marshmallow clouds in the sky blue sky,” he said while pointing.
“Oh. Why didn’t you say that in the first place rather than just pointing at the sky,” he said.
If you are trying to describe things, use narration. People don’t do this in real life.
Don’t use dialogue to convey actions

“I am going to kill you,” he said to the other guy.
“That isn’t a nice thing to say,” the other guy said back.
“No, I mean I am about to take action to kill you for real,” the first guy said.
“No, please don’t. My arms are now raised in fear as my body quivers,” the guy who was being threatened said.
“I am removing a knife from my leather sheath. Now I am plunging it into your face. Oh, look at all the blood coming out of you,” the killing guy said.
“Oh, I am in so much pain. Listing to my cries of agony as I am dying,” the dying guy said.
Once again, actions should be conveyed in the narration, not the dialogue. No one describes exactly what they are doing as they do it.
Don’t use dialogue that’s too formal or rigid
“Is it not a beautiful day?” the guy on the stump said.
“Why yes, I am sharing your feelings at this moment,” the other guy said.
“I did not know you were capable of sharing,” the guy who was no longer on the stump said.
“There is much about me which you do not know,” the second guy said.
“Shall we discuss it over a delicious meal?” the first guy said.
“Unfortunately, I do not have the time to make such arrangements. Let us just agree to agree,” the non-stump guy said.
These don’t sound like humans. Make your characters talk like real people.
Don’t use dialogue that tries too hard to sound real

“‘Sup, man,” the one guy said.
“Nadda whole lot,” guy #2 stated.
“Sweet. Wanna go do somethin’,” first guy said.
“Yeah, that would be like sweet,” said #2.
“Awesome. Lemme grab some stuff and we can bounce,” said #1.
“Ummm, sounds super tight. What we doin’?” replied #2.
“Whatevers,” said #1 non-chalantly.
“That’s chill,” said the other insufferable moron.
These also don’t sound like humans. They sound like insufferable morons. I hope your characters aren’t like this.
Also, make sure your dialogue doesn’t overuse profanity , which can be a turnoff for many readers.
Of course, these are extreme examples of bad dialogue, but they should give you the idea of how bad dialogue can derail your writing.
A special thank you to my good friend and exceptional writer April Bradley for creating the images above.
Further reading on how to write dialogue
It’s impossible to teach someone how to be an expert at writing dialogue in a single blog post. In order to really master this skill, you need to read and practice. Here are some sources for you:
- The Bartleby Snopes Dialogue Contest – This was a short story contest I hosted for 9 years. The basic premise was that stories could only consist of dialogue. Check out the winners to see how dialogue can effectively drive plot and character.
- Hemingway’s “Hills Like White Elephants” – If you haven’t read this story before, then read it before you ever write another line of dialogue. The way Hemingway moves the story forward and subtly reveals everything about the characters through short, authentic dialogue is essentially a master class on writing dialogue.
There are plenty of other resources out there for writing great dialogue, but I don’t want to overwhelm you. Besides, it’s time for you to go try it yourself.
How to Write Dialogue FAQ
What is dialogue.
When we refer to dialogue in writing, we are referring to the speech of characters. Whether it’s one person talking to him/herself, two people talking back and forth, or a whole group of people chatting, you have dialogue.
How do you write dialogue?
Writing dialogue requires both technical formatting and natural execution. When writing dialogue, make sure you use quotation marks and also make it clear who is speaking. Dialogue should be written in a natural way that feels realistic without being forced. Don’t try too hard to write like people talk, but make sure you the speech isn’t too formal either.
Should dialogue go in quotation marks?
Generally speaking, dialogue should always go in quotation marks. Some experimental writing does not use quotation marks, but this can make it difficult for your reader to follow along. If you are going to write dialogue without quotation marks, make sure you have a good reason for doing so.
Where does punctuation go in dialogue?
When writing dialogue, punctuation should always go inside the quotation marks.
Should you capitalize the beginning of a quotation?
Yes, you should always capitalize the first letter of a quotation, even when the quotation starts in the middle of the sentence.
Should you start a new paragraph for dialogue?
You don’t need to start a new paragraph unless there is a change in speaker. Every time you have a new speaker, you should start a new paragraph to make it clear that someone new is speaking. However, you don't need to start a new paragraph if the speaker's dialogue fits within the context of the current paragraph.
What is a dialogue tag?
A dialogue tag is a form of narration in which you indicate who is speaking. You don’t always need a dialogue tag, but it can be helpful to make speech clear. A dialogue tag can come before or after the quote.
Is it okay to use said in dialogue tags?
It’s perfectly acceptable to use said in your dialogue tags. In fact, many writers and readers prefer said to synonyms for said. It’s also generally frowned upon to use adverbs in dialogue tags. You should be able to convey how someone is saying something through the dialogue itself.
As always, please share your thoughts, comments, and questions about writing dialogue in the comments. And don’t forget to share this post on all your favorite channels.

Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
4 thoughts on “ How to Write Dialogue with Good and Bad Dialogue Examples ”
Excellent tips! I’m agree with you about no quote marks. I once read a book that didn’t have them and it was so frustrating. Turned me off wanting to read anything else by that author.
While I agree with using contractions and some slang, it’s possible for writers to overdo it. I’ve seen attempts to portray us “country folk” as Okies from the Great Depression. Shockingly enough, a lot of us speak with decent grammar. It’s important to spend time with people in order to avoid crassly stereotyping the characters.
Very useful tips thanks! But it makes me wonder on the one of the ‘DON’T’s – which says, don’t make it too formal/rigid. Don’t you think it also depends on the character? I know it’s not often but it can happen. I’ve read books or seen movies in which the character is, for example, a stiff, super formal lady with a royal British background. She really spoke so cold, distant and ‘official’ like you’re reading academic report.
This is a great point. Ultimately, the dialogue should fit the character – and it should tell us more about the character. As with any writing rules, there are always exceptions!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Privacy overview.
This Playwright Explains How to Write Great Dialogue
by Guest Blogger | 27 comments
You’ve hit that point in the writing process. You’ve had that story or poem germinating in your head for a long time. You know the characters backward and forward from their biggest dreams to their pickiest pet peeves. Now all that’s needed to move the piece forward is for them to speak—and for you to write their dialogue—except the words aren’t coming. They are standing there tongue-tied and silent. How do you find your characters’ voices? How do you write dialogue that sings?

Photo by Graham (creative commons). Adapted by The Write Practice.
I’m lucky in this case. I know now that I’m good at dialogue. This is a very a good thing considering I’m a playwright. But even after I’d written my first two plays, I didn’t count dialogue as one of my strengths. It was just what the form called for and that’s what my first two big writing projects had to be: plays.
Then a couple of years ago I wrote a short story for a fiction workshop. When we started the discussion on my story, the other students started giggling. “What?” I asked, nervous to be diving back into fiction again.
“We knew this one was your’s before we started reading,” they said.
How? Because of the pages of dialogue.
In my fiction class, this embarrassed me at first. I don’t like boiling scriptwriting down to fiction hold everything but the speaking parts. But, as I began to get requests from fiction buddies and even some poets about how to craft good dialogue I realized that there is some truth behind the power of dialogue in playwriting.
Good Stories Have Great Dialogue
Without engaging dialogue, a stage play usually dies. It sounds stilted and it falls prey to the same trap that catches many an amateur writer of any genre: telling, and not showing .
“I’m angry at you, can’t you tell?”
“Can’t you see that I’m trying to convince you to get out of this room?”
(Really obvious examples, I know, but it’s surprising how easy statements like these slip in when you’re more focused on plot than form.)
How to Write Effective Dialogue
Great playwrights (or fiction writers or poets or creative nonfiction authors, for that matter) can do a lot with just words. Read the prologue to Henry V if you’re not sure why William Shakespeare is such a big deal centuries later.
No audience will give its full attention to a play whose dialogue is stilted. —George Wellwarth ( tweet that )
Great writers don’t simply write to move the plot forward or describe every detail in order to create a vivid world for the audience on stage. They create that world through just a few details and, more importantly, through dialogue combined with action.
An Essential DON'T When Writing Dialogue
Great writers also don’t record verbatim what people say in everyday conversation; verbatim theatre is a genre in its own right but it takes a lot of work to gather enough material to create a worthwhile production.
Why? We stammer, stutter, leave sentences half-finished, jabber about boring tidbits, and fill the time with meaningless small talk.
Try recording the next conversation you hear on the bus or street corner. Your hand might start to cramp with all the “Um” and “Ah” before you reach the meat of their dialogue.
Want to Write Great Dialogue? Here's a Tip from Acting
Learn from the process actors use to get into their character. When the actor (or editor) gets a manuscript, the first thing they will ask is “ What does this character want? What is the obstacle blocking him or her?”
As he or she reads through your dialogue, the actor will then note how your character tries to convey, protect, share, or fight for what he or she wants and when this tactic changes.
Your language can be poetic and lyrical or blunt and straightforward, but if there isn’t a clear desire behind it, then there’s no reason for it to be spoken and, therefore, it shouldn’t be dialogue.
Would you consider yourself good at writing dialogue? Share in the comments section .
Create two characters with opposing desires. For example, a mother and daughter are fighting. The mother wants her daughter to stay at an in-state college or university. The daughter wants to go as far away as possible.
Write their argument but here’s the trick: don’t take sides. As the writer, you equally defend and fight for both characters’ main objectives. Use your best tactics to play for both teams and see where this leads you.
Write for at least fifteen minutes . When you’re finished, post your practice in the comments section . And if you post, be sure to leave feedback for a few other practitioners.
Happy dialoguing!
Guest Blogger
This article is by a guest blogger. Would you like to write for The Write Practice? Check out our guest post guidelines .

27 Comments
This was a good practice. I wrote a dialogue for 15 minutes, but I don’t think it’s exactly right if it were part of a book. It would have to be tightened up and given better direction. I would have to have a better idea of where I was going with it. But, FWIW, this is the dialogue I came up with in 15 minutes. It doesn’t have an ending, per se, because I quit when the alarm went off. Here goes:
“Mom, I don’t want to go to the U of M. Or anything local. I want to go away, far away. As far as possible. Oxford, if I could get in.”
“But why? Do you hate us so much?”
“Don’t be stupid.”
“Katie, you know that we have savings for your college education. But not enough to send you half way across the world. We’ll have to take out additional loans just to send you to the local University.”
“Oh, because of course I couldn’t get any scholarships. Have you noticed my grades, mother? And my extra curriculars?”
“Of course, but that’s not the kind of thing you can just count on. You can count on us. Your parents.”
“It’s not your education. I’m going to be 18. A grown up. I’m glad for your help, but it’s time for me to make it on my own, you know? Do the things I want to do.”
“Turning 18 isn’t some magic date, Katie. It doesn’t magically endow you with anything except the legal right to vote and sign contracts. And be legally responsible for your life. But it doesn’t suddenly change who you are.”
“And who is that?”
“Our daughter! I’m not going to suddenly stop caring about you, taking care of you. I’m not going to just leave you out in the cold because of this magic number you’ve hit in years.”
“I’m not asking you to do that. I just think college is a time for me to spread my wings. I know, corny. But seriously, I’ve been in this same small town for all my life. Everybody and everything I know is here. There’s a whole world out there, and I want to become a part of it.”
“I understand that, believe me, I do. I had the same kind of dreams when I was your age.”
“That’s the perfect example of why I should go, Mom. Look what happened to you. You went to the local university. You found dad, got married, had us kids, and never left your home town. I don’t want to end up like that.”
“My life hasn’t exactly been a misery, you know.”
“Of course, I understand that, Mom. I’m just saying it’s not the life I want. I want to go places, do things, meet people totally different from anyone I’ve ever known. I want to have a lover who barely speaks English and let him show me his world.”
“Katie!”
“Oh, please, Mom. Don’t be all prude on me. I want to live. And learn.”
“So we’ve been holding you back. From living. You know, we’ve worked pretty hard to give you all sorts of opportunities. You went on every band trip, every year. You went to Paris with your French class, for God’s sake. Oh, please don’t tell me you were sleeping with French men while you were there.”
“Mom, I was only 16. Of course not. But if I go there for college, then I could if I wanted to.”
“Is that what this is about? You want to have sex with foreigners?”
“No, Mom, that is not what this is about. This is about my life. My future. Bottom line, are you saying you won’t support me if I choose to go to a college in another country?”
“No, Katie, I’m not saying that. Your college fund is for your college education. I just… I can’t picture not seeing you for months at a time. You’re my first child. I’m not ready to let you go so far away.”
“That’s not really fair to me, though, is it?”
“I don’t know what to do here. I mean, do I really let you decide?”
Ah the perils of letting go, I have been tempted to be that mom…I chuckled at the French guy idea 🙂 I could tell the dialog was developing the more you wrote. I love how the free writing helps get the ideas out. thanks for being brave and posting.
I agree with Jennifer. Thanks for posting. I agree it would have to be tightened up to be part of something larger. My main question when I read it is: what started the argument? Did a piece of mail come about applying to an out of state college that the mom found before her daughter got home? Bones of the scene like that could quickly tighten it up and make it more specific.
I enjoyed this. It had a depth that was building. I mean, I was captivated and I chuckled not only because the whole french guy bit was funny, but it’s not a far difference from how mothers would really respond. It had a realistic quality, but an artistic style.
“Jason, for the last time, put the toilet seat down when you leave the bathroom!”
“Okay! I know! You don’t have to scream at me!”
“I’m not screaming! I’ve told you-”
“Yes you are! You’re shouting at me! Screaming in that pissy voice you get when you’re mad!”
“It’s not pissy! I’m sick of telling you over, and over, and over to do things! You don’t do anything in this house! All you do is sit in that chair and drink beer. That’s it.”
“What about you? You don’t have a job! We’re living off of my disability!”
“We could be better off if you didn’t spend half of it on alcohol! Oh, don’t give me that look.”
“What look?”
“You know what it is. The I-am-completely-innocent-you’re-lying look.”
“I don’t spend half our money on alcohol! You’re being melodramatic, and you are making my head hurt, and you are screaming at me. What happened, Abigail? What did I do that suddenly turned you into this screaming bitch?”
“You changed, John.”
“After what?”
“After Haley died. You haven’t been the same since. You drink, you stopped painting, you quiet your job, and now all you do is sit and wallow in misery.”
“You just let it go like it was nothing. The day after the funeral you were fine. You didn’t cry, didn’t get nightmares, weren’t consumed with wondering if you had a part in it.”
“She’s gone, John. And she’s not coming back. You have got to let it go.”
“She’s our daughter. How the hell am I supposed to let that go? I let her go to that party. I let her stay. Then she was killed in that accident. So tell me, how am I supposed to let that go?”
That is very strong emotional scene. Thanks for sharing!
This is great Lauren, You really had me caught up in what was first just an annoying complaint building to the root of the issue. It gave a “surprise” effect. I appreciate your example of carrying the emotions to a climax. This helps me see how dialogue can work by itself.
Starting with the small and then ramping up to the real reason behind the dialogue was great. But I do wonder: how long ago did this accident happen? Is it still really raw? Are they okay at this point in their grief to talk about it? What would they both already know that they don’t even have to say out loud–because they are married and grieving over the same dead child? Great premise though. You found a great argument and followed it to an interesting, rich place.
Definitely agree with Maggie, starting with the small and almost petty arguments nearly always hides a bigger, deeply-seated reason to argue and you led to that very well! It felt like a natural crescendo. Not so sure about the little bits of telling in the dialogue where surely, Abigail would know what he means – like “Then she was killed in that accident” or, “You changed/ After what” just so you can lead to your “after Haley died” bit. Maybe try to weave in some more mystery for the reader and introduce her death very implicitly as both parties would know exactly what they are talking about…
The build up was really great. I never thought of having dialogue unfold like a plot, which is the impression I get when reading your dialogue here. I definitely learned some things reading this piece.
Very good at being objective and not picking sides. I like that.
“Do we have to go outside today? It’s like freezing out.”
Mother glances at her whiney daughter Sydney and states bluntly “it is 50 degrees and sunny. We only need to go outside to pick the tomatoes. If you co-operate it will take all of five minutes then you can get back to you warm blanket and book. What are you reading anyway?”
“If you ever cared to pay attention to what I like, you would know that I am not reading anything right now. I am writing my newest short story. I announced that at breakfast today. If you paid a semblance of attention to me you would have known that.”
“Well maybe if you stopped running your mouth all the time than I would pay attention to you. And maybe you shouldn’t be so hypocritical yourself. You had to ask me three times yesterday when the family reunion would be. Not that you care about seeing you grandparents again.”
“Mo-om,” Sydney whines “you know that I love my grandparents but I don’t know them, like at all. They keep treating me like I’m five. I am nearly eighteen! When will people treat me like an adult? It’s like you guys don’t realize that I’m growing up. I do have some of my own ideas and such.”
“I know that sweetheart, but it is hard for us to see you grown up. We ‘old people’ can remember when you were knee high to a grasshopper. To imagine you grown up after so few years…it is disconcerting. When did you grow up?”
“I grew up one day while you were at work. You are never home anymore and Dad is gone. If you could be bothered to spend any time at home then you would know that I am growing up. Did you even know that I made first honors this quarter at school? Would you even care if you knew?”
“Is that what this attitude is about? You think I intentionally stay at work and work long hours to avoid you? Well little missy I can assure you that that isn’t true. Not one little bit. I have to work long hours to keep you in clothes and shoes. It is expensive to buy you all of the latest technology and brands.”
Great start. It looks like you got to the real reason behind the argument near the end there–that the parents are working and never there. That could give you more to explore.
I like the characters, especially of the teenager. The small argument builds and builds and we begin to see layers of who they are and what they really want. I saw what Sydney wanted more than what her mother wanted. My assumption is that the mother wants her daughter to stay young and listen to her. Overall, really nice read.
“Are you seriously going to sit there and act like you didn’t hear me?” “Pretty much.” He said staring at his computer screen. “So, you don’t have anything to say to the fact that I’m leaving? Our marriage is ending? No questions, comments or concerns? Maybe that’s why it’s come to this you arrogant jerk.” “What is it you want me to say, Lexy? Arrogant? If anyone here is arrogant, it’s you. You don’t care what I need or want as long as I don’t get in the way of your “career”. Look, whatever. You just can’t stand that I’m not crying and begging you not to leave. If you want to leave, leave.”
His responses are great. What is he looking at on the computer? Could that enter the conversation? Would he even say too much to her or would he be entirely distracted by the computer?
“Jazz, I was…”
“No, please, me first!”
Laurent had shaved his beard, he looked just like the night of New Year’s Eve.
“I have to tell you something and I know… I know it’s way too late but…”
“Jazz!” Laurent grabbed her shoulders.
“I am so sorry, I haven’t been your friend.. I haven’t, I just wanted you all to myself and…”
“Jazz!” Reiterated Laurent with a smile. “I’m coming with you!”
“I turned it down. I’m coming with you.”
Speechless, she wiped her eyes and swallowed dry.
“You… You did what?” she mumbled, struggling to process Laurent’s words.
“It’s no big deal” he shrugged, “I’ll apply again next year!”
She burst into tears. It was now or never. She pulled out the letter from her pocket and handed it to him. A perplexed look on his face, Laurent unfolded the paper.
“What is…” he mumbled, his eyes scanning the page, confusion quickly turning into shock.
“Jazz… Where did you find this?”
She took a deep breath and explained everything. How she’d spent three hours fumbling in the dark and found the letter. How she’d kept it to herself and known all along that he had been accepted into Harvard, how she was so afraid of losing him and how she couldn’t lie any more.
Laurent heard her out until she had nothing more left to say and then silence settled in. All around them, congratulations were being offered, screams of joy and pride, students sighing and tapping each other on the back, satisfied and hopeful for the future.
“I was just your marionette…” he finally muttered, his eyebrows frowning like she’d never seen them before. “You manipulated me at your ease…”
“Laurent please… I was just…”
“I thought you were my friend! I fell in love with you for god’s sake! With your kindness, your compassion, your devotion and…” His voice was rising and a few heads turned to eavesdrop on their conversation.
“I never meant to hurt you, I just couldn’t…”
“You just couldn’t what? You couldn’t let me go but you did well enough watching me struggle for five months? You watched me, Jazz! You knew how important this was to me and I had to live every day not even knowing if I’d gotten in or not!” He crumpled the letter and threw it on the floor. “And you know why I didn’t know? Because I was waiting to open it with you, to share this moment with you!”
Jazz’s eyes were filling with tears, she begged him for forgiveness but all he granted her with was a cold, livid look.
“Let me just ask you one thing. Did it ever occur to you what could’ve happened if I hadn’t received the second letter? Did it…” He froze mid-sentence. “Oh my god… I turned it down… I turned it down to be with you, because I cared about you, I was ready to give up my future for you…”
Jazz could barely catch her breath. Her mind was a maze and there was no way out. She was trapped, surrounded by high walls and no view of the sky. The barrage in her eyes had broken and water was now spilling out with force, blurring her vision. She tried holding Laurent’s hand but all her apologies were met with rejection.
“Enjoy the ball. I’ve got a phone call to make”, he said and stormed out with further a due, leaving Jazz feeling sorry for herself.
I enjoyed this post a lot and I spent maybe an extra 10min on the practice. Plus, I’ll probably be editing and correcting myself as a I am typing my work. Dialogue is somethings I’ve been wanting to work with. The argument is hopefully self-explanatory of their opposing sides.
Jack is walking back into the cell where his friend Louie has stood at attention. Jack watches the guards walk away and then walks up to Louie.
“I just talked with my contact. Get ready because in about 30 minutes the plan will be—”
“No! Stop! Just call it off!”
“C’mon! We’ve been through this, Louie. You aren’t meant to be here.”
“Tell that to the man I killed.”
“It was self-defense.”
“That doesn’t make the blood on my hands any less red.” Staring at his own hands.
“That guy was a fucking idiot to hold that gun up to you. He was trigger happy, not you.”
“No, he was a security guard doing his job and I shot him.”
“From where I was standing, he had it coming.”
“His face is imprinted on my brain, Jack. Don’t you know what that means?! I can’t escape what I’ve done. I can’t escape this fate.”
“Why are you doing this? I got arrested just to put this whole operation into the works. For you! Dammit! Do you here me, Louie? You are an innocent man.”
“What if he had kids?”
“You have kids! You have a wife. A life! And it’s not in here.”
“I can’t face them. Not any of them. If I stay here, maybe I can atone for my sins.”
“No. You’re coming with me, Louie.”
“I deserve to be here.”
Jack grabs louie by the collar and forces him against the wall.
“You listen to me. In a few minutes, we will follow the escape plan and leave this hell. The fresh air may do you some good and help you think straight.”
“I won’t follow you.”
“I promised Mary I would bring her husband home. She needs you.”
Louie struggling.
“No. Shut up! I need to—”
“If I have to, I will bring you by force. You hear me?”
“Guards! Guards!”
Jack punches the wall in anger.
“Fuck you, Louie! FUCK YOU!”
This is intense. I really get the feelings of each character clearly. I could take either side, though being a law abiding citizen, leaned towards the not escaping side. 🙂 But as far as in a story, both sides were presented as equally valid, and I flipped back and forth between who I agreed with. Excellent.
“I got it!” she said, waving the letter in her hand above her head.
Mary turned from her desk and smiled a smile her daughter recognized with a sinking heart.
“Mom, it’s a full scholarship!” Carry said, her smile now gone.
“That’s great, baby” She held out her hand and Carry sprang into her mother’s bedroom to hand the acceptance letter over.
Carry watched her mother’s eyes reading each word with great care. Then the eyes rose from the letter to her daughter’s hopeful face.
Mary took a deep breath, handed the letter back in silence.
“What? Why aren’t you happy for me?”
“Because New York City is five thousand miles away.”
“Oh, please, really? That’s your answer? It’s one of the best dern schools in the whole dern nation!”
“Carry, honey, you grew up on this farm. What do you know about taking subways and taxi cabs, and–”
“You want me to spend my life in this little—“
“I want you to just think for a second. How are you going to like living in a city of nine trillion people?” Do you have any idea how expensive New York is?”
“Mom, I am not going to marry a goddamn farmer, and end up…”
“Don’t you cuss!” Marry said.
They stared at each other in a long moment of silence.
“You are not going to end up like what?”
“I am going to New York!”
“You are going to do as your father and I—“
“Elworth? You want me to go to Elworth, and what? What… study home eck? I hate it here!” Carry turned then and ran from the room, slowing just enough to slam the door behind her.
The End…
Jinx stared straight ahead with her hands clasped behind her back. Soldiers waited in patient lines around her — each perfect replicas in posture, attitude and buzz cuts. Well, except for her, of course. She wouldn’t let anyone come near her with a razor.
“What’s this about, then?” Sergeant Jules demanded.
She glanced down at him with a frown. “How would I know?”
“Just thought you might have some inside info.”
Jinx rolled her eyes to the ceiling, her lips compressing. So Pearce hadn’t been kidding about the rumours. When had that started? And why?
“No, Jules. I know as much as you do.”
She scanned the crowd again. Where was Pearce? Vanbuuren had summoned him hours ago.
Jules interrupted her train of thought. “Hey, what you doing tonight?”
“Tonight. What you doing?”
“Sleeping.”
“Before that.”
“Between eating and sleeping.”
She glared at him. “Why?”
“Thought you might be up for a little… you know… rough and tumble.” Jules glanced up at her, eyebrows hopping suggestively. She tightened the grip on her wrist and inhaled through her nose.
“Jules. The only action you’re ever going to get from me is when I take you to the surface and kick the living shit—”
“Do you have something to share, Sergeant Jinx?”
Her head snapped forward. A sea of faces turned back to look at her. General Standers had arrived. He was paused halfway up the stairs to the dais, eyebrows lifted in enquiry. A blush raced up her neck. She shook her head and he nodded, resuming his journey.
Beside her, Jules snickered.
“It was enough last year, and the year before. “ Ace pushed away his bowl, frowning. “You want to buy a cow or something?”
“No—” Ray bit off what he’d been going to say.
His father took a breath that strained his shirt even further. Ace flinched, expecting a button to come flying off any second.
“We need a big haul, because it’s going to be your buy-in.”
Silence sank down between them. Ace blinked and rose to his feet. Ray surged forward, grabbing his wrist. He dragged Ace down until his stomach touched the top of his soup bowl.
Ace had to force his words through gritted teeth. “I—won’t—do—it.”
“You seem to think you have some sort of choice.” His father’s arm muscles twitched as Ace tried to retract his wrist, but he might as well have been trying to lift a car over his head. “You don’t.”
“Of course—”
Ray stabbed at the tabletop with his index finger. “While you live here, under my roof, eating my food, you follow my rules.” Muscles corded his father’s neck.
“I refuse to work for that piece of shit tyrant—”
“You earn three tokens a week, Ace. Three.” Ray held up three fingers.
Did his father think he’d lost the ability to count?
“What if something happens to me? Huh? How the hell are you going to take care of your mother?” Ray demanded.
“I didn’t know she needed—”
Ray’s fist slammed down on the table, rattling the crockery and cutlery. Ace was surprised there wasn’t a crack in the thick wood. When he looked up, his father’s face was ashen.
“How dare you?” his father hissed. “She’s your mother, Ace. You know what they’ll do if she can’t pay rent.” Ray’s grip tightened, squeezed the bones in Ace’s wrist together. “You know what they’ll do to her.”
Ace tried to keep anger from his voice. “You’re hurting me.”
“I should be doing a lot worse, you ungrateful—”
“What the hell are you two doing?” Selena demanded.
They spun around to stare at her. She stood in the doorway, soap suds on her hands, her fair skin mottled red. “I said talk, not tear out each other’s throats!”
Ray hastily released Ace. They both sank down in their chairs. Ray cleared his throat as he arranged the crockery. Ace wiped at his shirt where a few spots of soup dampened the cloth.
His mother tipped her head toward Ace, staring at Ray. “Have you asked him yet?”
“I was trying—” Ray began.
Selena lifted her eyebrows and Ray stopped talking. She turned to Ace, her damp hands clutching her waist.
“Your father wants to know if you’re interested in joining the military.”
“No,” Ace said. His shoulders began to crawl. His father was no doubt subjecting him to a level ten death stare.
“Well, there we go. Now Ace, help me—”
“Ace is going.” Ray’s chair skittered out behind him and crashed into the wall. Selena jerked at the sound.
His mother gave her head a small shake. “My love, I—”
“Selena. I have spoken.”
Ace turned back to his mother. His shoulders sank at her suddenly wide-eyed expression.
“My love, we should talk—”
“I have spoken,” Ray repeated.
Ace slowly got to his feet, in case any sudden movements would trigger physical violence. Ray watched him, his hands curling up into huge fists. He tried a calm, reasonable tone on his father.
“Pa, there’s a reason why—”
Ray growled. Ace stopped talking and took a small step back.
“I don’t care about your petty excuses, Ace. So what if the Leider’s corrupt? So is everyone else in this life. So what if he uses money to control us? I can’t live without it. Neither can you. Neither can your mother.”
“Of course you can—”
“I don’t care about your pathetic excuses. Because that’s all they are. Excuses.”
“Ray…” Selena’s soft voice had no effect on his father.
“Enough is enough, Ace. I’ve been scavenging every day of my life to find enough food for this family. Every single day I’m up there.” Ray stabbed at the ceiling. “Gone for days, weeks, trying to keep this family going. Every day since the two of you were born—”
Selena gasped. Ace’s chest tightened, his breathing growing quick.
“For you—” Ray started again, his lips quivering. He broke eye contact with Ace when he looked at Selena. “For your mother.”
Selena ran from the kitchen. Her muffled sobs grew faint as she moved down the hallway. Ray sat down heavily. Sadness etched deep shadows in his face, ageing him.
I like this one the best. I feel their emotions and the communication seems more real…interruptions a lot like real people communicate and much nonverbal communications. I’m just trying to learn to write dialogue but I am reading many books on it and writing a fantasy novel. Good job!
It sounded fun so I tried this exercise. I did have trouble defending both sides at the same time. Maybe it’s how my brain works, but I had to sympathize with Joan first and then go back and help Tom make his point:
“Joan, look at me. I want you to see the real me.”
“You mean look out into the darkness? And give you the faint impression that I am looking at you? Seeing you? Caring about you? I can’t see you, Tom. I can’t care about anything you say, you know that.”
“I know, but still, I am talking to you so at least listen. I want you to be happy, I really do. I want to be happy, and I want you to be happy.”
“No. You are selfish. You want me all to yourself. You haven’t even known me that long. And you’re not listening to me when I say this is over, which means you don’t actually care about my happiness, you just want to hear what you want to hear. You should let me go.”
“I guess I’m not ready to. Maybe I’m hoping you would change your mind. Maybe I’m hoping there is this one secret tiny thing I could say or do that made you reconsider. A magic key to unlocking our relationship.”
“What relationship? You have some abstract idea in your head about the sort of person I am, that is really just an image of the sort of person you wish I were. You don’t know anything about me.”
“Yes I do. I do. I think I do.”
“You think you do. That’s the problem. Please, Tom, let me go.”
“I have. I just wanted to talk to you again. Even if you are only a memory.”
“I know, Tom. Any time.”
“How could you be so selfish!” “Selfish?! Mom it’s MY education” “Well it’s our money and I won’t have you using it to follow some girl off to college when we could be sending you to U of M” “She isn’t just some girl mom we’ve been together for years” “See! You don’t even care about what college it is all you care about is her” “It’s a good college! It has a well rounded engineering program and great connections” “As great as U of M?” “No, but it is a good compromise between what I want” “A good compromise! I haven’t even had a say in the matter” “That’s because it isn’t your decision to make!” “Well I’m sorry that I care about you” “It’s not as if I’m leaving the country mom I’m only going to be a couple states away” “I just don’t think you will end up happy” “Just because you and dad didn’t work out doesn’t mean me and Jenny won’t” “Don’t you compare our marriage to you and your girlfriend who’ve barely known each other for three years” “It’s the same principle” “Would you marry her?” “Mom we’re getting off topic the point is I’m an adult now and I’m going to do what I want and that includes getting the education I want” “Then you can pay for it” “Fine!” “Fine”
“Do like Moses, let my people go.”
“I’m atheist. Your people have homework to do.”
“Please Mother. I’m practically begging you. I’ll be home by eight; I promise.”
“There are things you need to learn in life Crystal. You may hate me now but later you’ll see.”
“See what? The only thing I’m trying to see is a movie and you won’t let me go.”
“Responsibility is more important than flaunting your stuff to boys.”
“You gave it to me to flaunt.”
“Don’t get smart with me kid. And besides, Grandmother spent a lot of time making us that lovely antique couch in there. Watch a movie here; much better than the stuffy theater anyway.”
“Whatever- just- whatever. I’m so done.”
“Tears? Really? Over that boy?”
“That boy actually respects me.”
“Goodness child. All I’m saying is finish your homework. There will be other days. Save your money for God’s sake.”
“What do you mean?”
“Has he paid for you once? Your father did so much-”
“Oh my God. You tried to use Dad against me. Wow I’m in shock right now. I’m leaving, not even because I want to but for the sake of our crumbling household.”
“I CAN’T BE LIKE HIM DAMNIT!”
“I NEVER WANTED YOU TO.”
Dad and Daughter
Daughter: Why don’t you trust me? I haven’t given you a single reason not to trust me since my last screw up!
Dad: This isn’t up for discussion, I’ve already told you no.
Daughter: This isn’t fair! I made one mistake and I have to suffer for it, but my sister makes the same mistake I had and she gets no punishment.
Dad: This isn’t about your sister, this is about you. You know what you did and now you must endure the consequences.
Daughter: How can I earn your trust back if you don’t give me an opportunity to it back. I’m going to school, I get decent grades – I am home every day and do nothing but take the garbage out. I’m doing everything you’ve asked of me and beyond. I’m not perfect dad, but neither are you.
Dad: Enough! I have told you my say so this discussion is over, don’t bring it back up again. Go to your room young lady!
Daughter: No.
Dad: What did you just say?
Daughter: I said no. I’m not leaving til you see my side of things. I was stupid and reckless, but you’re not the only one giving me a hard time about my mistake. I’m beating myself up every day because I didn’t listen to you. But I’ve learned to forgive myself so I can move one. It’d be best if you did the same. But Dad I can’t move in if you don’t let me.
Dad: Don’t you think I want to move on? I want to but I can’t, because after everything you and that boy did and all the stuff that happened after, just thinking about it makes me angry. I can’t trust my own daughter to hang out with anyone but her family because if I let her go out the whole time I’m going to be thinking that she’s lying to me about where she’s at, whom she’s with and what she’s doing, I can’t let you be a teen because you wanted to be an adult and you decided to make the grown up decision to have sex and you ended up pregnant! But no only that both you and that boy game your word that you would do that, but you went behind my back and did it anyway. But not only that I ended up having to pick up the mess that boy left you in. And while my daughter is still mending a broken heart and grieving over a loss that BOY! Is running around Scott free making the same promise to another girl’s father, while I’m here making sure my own daughter doesn’t kill herself because of some selfish kid! It’s not that I don’t trust you – I just don’t trust anyone else with your well-being anymore, other than your mother and myself.
Daughter: Dad you can’t protect me forever, I know your intentions aren’t anything but pure. But Daddy I’m going to get hurt no matter how hard you try, you can’t baby proof the world. You can’t teach me and guide me all you want but that doesn’t mean I won’t run into bad people along the road. You can let go now Daddy, just let go.
Trackbacks/Pingbacks
- This Playwright Explains How to Write Great Dialogue – THE WRITE PRACTICE | likeaudreychicblog - […] This Playwright Explains How to Write Great Dialogue. […]
- 10 Writing Resources: Drafting - Alyssa Hollingsworth - […] 5. This Playwright Explains How to Write Great Dialogue […]
- Write Along Radio | 7 Tips for Improving Dialogue - […] This Playwright Explains How to Write Great Dialogue […]
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Submit Comment
Join over 450,000 readers who are saying YES to practice. You’ll also get a free copy of our eBook 14 Prompts :
Popular Resources
Book Writing Tips & Guides Creativity & Inspiration Tips Writing Prompts Grammar & Vocab Resources Best Book Writing Software ProWritingAid Review Writing Teacher Resources Publisher Rocket Review Scrivener Review Gifts for Writers
Books By Our Writers

You've got it! Just us where to send your guide.
Enter your email to get our free 10-step guide to becoming a writer.
You've got it! Just us where to send your book.
Enter your first name and email to get our free book, 14 Prompts.
Want to Get Published?
Enter your email to get our free interactive checklist to writing and publishing a book.
Improve your writing in one of the largest and most successful writing groups online
Join our writing community!
How to Write Dialogue: Rules, Examples, and 8 Tips for Engaging Dialogue

by Fija Callaghan
You’ll often hear fiction writers talking about “character-driven stories”—stories where the strengths, weaknesses, and aspirations of the central cast of characters stay with us long after the book is closed. But what drives character, and how do we create characters that leave long-lasting impressions?
The answer lies in dialogue : the device used by our characters to communicate with each other. Powerful dialogue can elevate a story and subtly reveal important information, but poorly written dialogue can send your work straight to the slush bin. Let’s look at what dialogue is in writing, how to properly format dialogue, and how to make your characters’ dialogue the best it can be.
What is dialogue in a story?
Dialogue is the verbal exchange between two or more characters. In most fiction, the exchange is in the form of a spoken conversation. However, conversations in a story can also be things like letters, text messages, telepathy, or even sign language. Any moment where two characters speak or connect with each other through their choice of words, they’re engaging in dialogue.

Why does dialogue matter in a story?
We use dialogue in a story to reveal new information about the plot, characters, and story world. Great dialogue is essential to character development and helps move the plot forward in a story.
Writing good dialogue is a great way to sneak exposition into your story without stating it overtly to the reader; you can also use tools like dialect and diction in your dialogue to communicate more detail about your characters.

Through a character’s dialogue, we can learn about their motivations, relationships, and understanding of the world around them.
A character won’t always say what they mean (more on dialogue subtext below), but everything they say will serve some larger purpose in the story. If your dialogue is well-written, the reader will absorb this information without even realizing it. If your dialogue is clunky, however, it will stand out and pull your reader away from your story.

Rules for writing dialogue
Before we get into how to make your dialogue realistic and engaging, let’s make sure you’ve got the basics down: how to properly format dialogue in a story. We’ll look at how to punctuate dialogue, how to write dialogue correctly when using a question mark or exclamation point, and some helpful dialogue writing examples.
Here are the need-to-know rules for formatting dialogue in writing.
Enclose lines of dialogue in double quotation marks
This is the most essential rule in basic dialogue punctuation. When you write dialogue in North American English, a spoken line will have a set of double quotation marks around it. Here’s a simple dialogue example:
“Were you at the party last night?”
Any punctuation such as periods, question marks, and exclamation marks will also go inside the quotation marks. The quotation marks give a visual clue to the reader that this line is spoken out loud.

In European or British English, however, you’ll often see single quotation marks being used instead of double quotation marks. All the other rules stay the same.
Enclose nested dialogue in single quotation marks
Nested dialogue is when one line of dialogue happens inside another line of dialogue—when someone is verbally quoting someone else. In North American English, you’d use single quotation marks to identify where the new dialogue line starts and stops, like this:
“And then, do you know what he said to me? Right to my face, he said, ‘I stayed home all night.’ As if I didn’t even see him.”
The double and single quotation marks give the reader clues as to who’s speaking. In European or British English, the quotation marks would be reversed; you’d use single quotation marks on the outside, and double quotation marks on the inside.
Every speaker gets a new paragraph
Every time you switch to a new speaker, you end the line where it is and start a new line. Here are some dialogue examples to show you how it looks:
“Were you at the party last night?” “No, I stayed home all night.”
The same is true if the new “speaker” is only in focus because of their action. You can think of the paragraphs like camera angles, each one focusing on a different person:
“Were you at the party last night?” “No, I stayed home all night.” She raised a single, threatening eyebrow. “Yeah, I wasn’t feeling that well, so I just stayed in and watched Netflix instead.”
If you kept the action on the same line as the dialogue, it would get confusing and make it look like she was the one saying it. Giving each character a new paragraph keeps the speakers clear and distinct.
Use em-dashes when dialogue gets cut short
If your character begins to speak but is interrupted, you’ll break off their line of dialogue with an em-dash, like this:
“Yeah, I wasn’t feeling that well, so I just stayed in and—” “Is that really what happened?”
Be careful with this one, because many word processors will treat your em-dash like the beginning of a new sentence and attach your closing quotation marks backwards:
“Yeah, I wasn’t feeling that well, so I just stayed in and—“
You may need to keep an eye out and adjust as you go along.
In this dialogue example, the new speaker doesn’t lead with an em-dash; they just start speaking like normal. The only time you’ll ever open a line of dialogue with an em-dash is if the speaker who’s been cut off continues with what they were saying:
“Yeah, I wasn’t feeling that well, so I just stayed in and—” “Is that really what happened?” “—watched Netflix instead. Yes, that’s what happened.”
This shows the reader that there’s actually only one line of dialogue, but it’s been cut in the middle by another speaker.
Each line of dialogue is indented
Every time you give your speaker a new paragraph, it’s indented from the left-hand side. Many word processors will do this automatically. The only exception is if your dialogue is opening your story or a new section of your story, such as a chapter; these will always start at the far left margin of the page, whether they’re dialogue or narration.

Long speeches don’t use use closing quotation marks until the end
Most writers favor shorter lines of dialogue in their writing, but sometimes you might need to give your character a longer one—for instance, if the character speaking is giving a speech or telling a story. In these cases, you might choose to break up their speech into shorter paragraphs the way you would if you were writing regular narrative.
However, here the punctuation gets a bit weird. You’ll begin the character’s dialogue with a double quotation mark, like normal. But you won’t use a double quotation mark at the end of the paragraph, because they haven’t finished speaking yet. But! You’ll use another opening quotation mark at the beginning of the subsequent paragraph. This means that you may use several opening double quotation marks for your character’s speech, but only ever one closing quotation mark.
If your character is telling a story that involves people talking, remember to use single quotation marks for your dialogue-within-dialogue as we looked at above.
Sometimes these dialogue formatting rules are easier to catch later on, during the editing process. When you’re writing, worry less about using the exact dialogue punctuation and more about writing great dialogue that supports your character development and moves the story forward.
How to use dialogue tags
Dialogue tags help identify the speaker. They’re especially important if you have a group of people all talking together, and it can get pretty confusing for the reader trying to keep everybody straight. If you’re using a speech tag after your line of dialogue—he said, she said, and so forth—you’ll end your sentence with a comma, like this:
“No, I stayed home all night,” he said.
But if you’re using an action to identify the person speaking instead, you’ll punctuate the sentence like normal and start a new sentence to describe the action taking place:
“No, I stayed home all night.” He looked down at his feet.
The dialogue tags and action tags always follow in the same paragraph. When you move your story lens to a new person, you’ll switch to a new paragraph. Each line where a new person speaks propels the story forward.
When to use capitals in dialogue tags
You may have noticed in the two examples above that one dialogue tag begins with a lowercase letter, and one—which is technically called an action tag—begins with a capital letter. Confusing? The rules are simple once you get a little practice.
When you use a dialogue tag like “he said,” “she said,” “he whispered,” or “she shouted,” you’re using these as modifiers to your sentence—dressing it up with a little clarity. They’re an extension of the sentence the person was speaking. That’s why you separate them with a comma and keep going.
With an action tag , you’re ending one sentence and beginning a whole new one. Each sentence represents two distinct moments in the story. That’s why you end the first sentence with a period, and then open the next one with a capital letter.
If you’re not sure, try reading them out loud:
“No, I stayed home all night,” he said. “No, I stayed home all night.” He looked down at his feet.
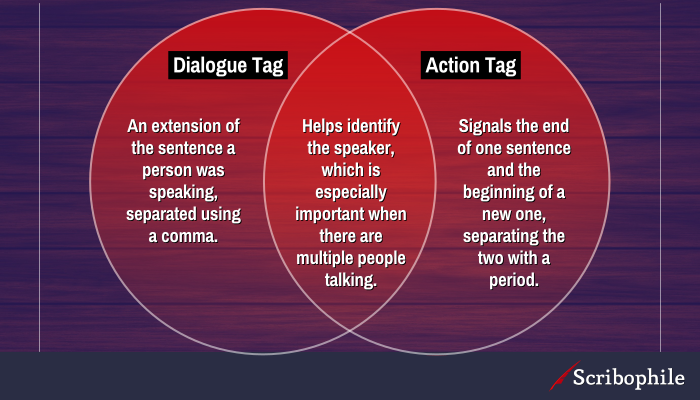
Since you can’t hear quotation marks out loud, the way you say them will show you if they’re one sentence or two. In the first example, you can hear how the sentence keeps going after the dialogue ends. In the second example, you can hear how one sentence comes to a full stop and another one begins.
But what if your dialogue tag comes before the dialogue, instead of after? In this case, the dialogue is always capitalized because the speaker is beginning a new sentence:
He said, “No, I stayed home all night.” He looked down at his feet. “No, I stayed home all night.”
You’ll still use a comma after the dialogue tag and a period after the action tag, just like if you’d separate them if you were putting your tag at the end.
If you’re not sure, ask yourself if your leading tag sounds like a full sentence or a partial sentence. If it sounds like a partial sentence, it gets a comma. If it reads like a full sentence that stands on its own, it gets a period.
External vs. internal dialogue
All of the dialogue we’ve looked at so far is external dialogue, which is directed from one character to another. The other type of dialogue is internal dialogue, or inner dialogue, where a character is talking to themselves. You’ll use this when you want to show what a character is thinking, but other characters can’t hear.
Usually, internal dialogue will be written in italics to distinguish it from the rest of the text. That shows the reader that the line is happening inside the character’s head. For example:
It’s not a big deal, she thought. It’s just a new school. It’ll be fine. I’ll be fine.
Here you can see that the dialogue tag is used in the same way, just as if it was a line of external dialogue. However, “she thought” is written in regular text because it’s not a part of what the character is thinking. This helps keep everything clear for the reader.

In your story, you can play with using contrasting internal and external dialogue to show that what your characters say isn’t always what they mean. You may also choose to use this internal dialogue formatting if you’re writing dialogue between two or more characters that isn’t spoken out loud—for instance, telepathically or by sign language.
8 tips for creating engaging dialogue in a story
Now that you’ve mastered the mechanics of how to write dialogue, let’s look at how to create convincing, compelling dialogue that will elevate your story.
1. Listen to people talk
To write convincingly about people, you’ll first need to know something about them. The work of great writers is often characterized by their insight into humanity; you read them and think, “Yes, this is exactly what people are like.” You can begin accumulating your own insight by listening to what real people say to each other.
You can go to any public place where people are likely to gather and converse: cafés, art galleries, political events, dimly lit pubs, bookshops. Record snippets of conversation, pay attention to how people’s voices change as they move from speaking to one person to another, try to imagine what it is they’re not saying, the words simmering just under the surface.
By listening to stories unfold in real time, you’ll have a better idea of how to recreate them in your writing—and inspiration for some new stories, too.
2. Give each spoken line a purpose
Here is something that actors have drilled into their heads from their first day at drama school, and writers would do well to remember it too: every single line of dialogue has a hidden motivation. Every time your character speaks, they’re trying to achieve something, either overtly or covertly.
Small talk is rare in fiction, because it doesn’t advance the plot or reveal something about your characters. The exception is when your characters are using their small talk for a specific purpose, such as to put off talking about the real issue, to disarm someone, or to pretend they belong somewhere they don’t.
When writing your own dialogue, ask yourself what the line accomplishes in the story. If you come up blank, it probably doesn’t need to be there. Words need to earn their place on the page.

3. Embrace subtext
In real life, we rarely say exactly what we really mean. The reality of polite society is that we’ve evolved to speak in circles around our true intentions, afraid of the consequences of speaking our mind. Your characters will be no different. If your protagonist is trying to tell their best friend they’re in love with them, for instance, they’ll come up with about fifty different ways to say it before speaking the deceptively simple words themselves.
To write better dialogue, try exploring different ways of moving your characters around what’s really being said, layering text and subtext side by side. The reader will love picking apart the conversation between your characters and deducing what’s really happening underneath (incidentally, this is also the place where fan fiction is born).
4. Keep names to a minimum
You may notice that on television, in moments of great upheaval, the characters will communicate exactly how important the moment is by saying each other’s names in dramatic bursts of anger/passion/fear/heartbreak/shock. In real life, we say each other’s names very rarely; saying someone’s name out loud can actually be a surprisingly intimate experience.
Names may be a necessary evil right at the beginning of your story so your reader knows who’s who, but after you’ve established your cast, try to include names in dialogue only when it makes sense to do so. If you’re not sure, try reading the dialogue out loud to see if it sounds like something someone would actually say (we’ll talk more about reading out loud below).
5. Prune unnecessary words
This is one area where reality and story differ. In life, dialogue is full of filler words: “Um, uh, well, so yeah, then I was like, erm, huh?” You may have noticed this when you practiced listening to dialogue, above. We won’t say there’s never a place for these words in fiction, but like all words in storytelling, they need to earn their place. You might find filler words an effective tool for showing something about one particular character, or about one particular moment, but you’ll generally find that you use them a lot less than people really do in everyday speech.
When you’re reviewing your characters’ dialogue, remember the hint above: each line needs a purpose. It’s the same for each word. Keep only the ones that contribute something to the story.
6. Vary word choices and rhythms
The greatest dialogue examples in writing use distinctive character voices; each character sounds a little bit different, because they have their own personality.
This can be tricky to master, but an easy way to get started is to look at the word choice and rhythm for each character. You might have one character use longer words and run-on sentences, while another uses smaller words and simple, single-clause sentences. You might have one lean on colloquial regional dialect, where another sounds more cosmopolitan. Play around with different ways to develop characters and give each one their own voice.

7. Be consistent for each character
When you do find a solid, believable voice for your character, make sure that it stays consistent throughout your entire story. It’s easy to set a story aside for a while, then return to it and forget some of the work you did in distinguishing your characters’ dialogue. You might find it helpful to write down some notes about the way each character speaks so you can refer back to it later.
The exception, of course, is if your character’s speech pattern goes through a transformation over the course of the story, like Audrey Hepburn in My Fair Lady . In this case, you can use your character’s distinctive voice to communicate a major change. But as with all things in writing, make sure that it comes from intention and not from forgetfulness.
8. Read your dialogue out loud
After you’ve written a scene between two or more characters, you can take the dialogue for a trial run by speaking it out loud. Ask yourself, does the dialogue sound realistic? Are there any moments where it drags or feels forced? Does the voice feel natural for each character? You’ll often find there are snags you miss in your writing that only become apparent when read out loud. Bonus: this is great practice for when you become rich and famous and do live readings at bookshops.
3 mistakes to avoid when writing dialogue
Easy, right? But there are also a few pitfalls that new writers often encounter when writing dialogue that can drag down an otherwise compelling story. Here are the things to watch out for when crafting your story dialogue.
1. Too much exposition
Exposition is one of the more demanding literary devices , and one of the ones most likely to trip up new writers. Dialogue is a good place to sneak in some information about your story—but subtlety is essential. This is one place where the adage “show, don’t tell” really shines.
Consider these dialogue examples:
“How is she, Doctor?” “Well Mr. Stuffington, I don’t have to remind you that your daughter, the sole heiress to your estate and currently engaged to the Baron of Flippingshire, has suffered a grievous injury when she fell from her horse last Sunday. We don’t need to discuss right now whether or not you think her jealous maid was responsible; what matters is your daughter’s well being. As to your question, I’m afraid it’s very unlikely that she’ll ever walk again.” Can’t you just feel your arm aching to throw the poor book across the room? There’s a lot of important information here, but you can find subtler ways to work it into your story. Let’s try again: “How is she, Doctor?” “Well Mr. Stuffington, your daughter took quite a blow from that horse—worse than we initially thought. I’m afraid it’s very unlikely that she’ll ever walk again.” “And what am I supposed to say to Flippingshire?” “The Baron? I suppose you’ll have to tell him that his future wife has lost the use of her legs.”
And so forth. To create good dialogue exposition, look for little ways to work in the details of your story, instead of piling it up in one great clump.

2. Too much small talk
We looked at how each line of dialogue needs a specific purpose above. Very often small talk in a story happens because the writer doesn’t know what the scene is about. Small talk doesn’t move the scene along unless it’s there for a reason. If you’re not sure, ask yourself what each character wants in this moment.
For example, imagine you’re in an office, and two characters are talking by the water cooler. How was your weekend, what did you think of the game, how’s your wife doing, are those new shoes, etc etc. Can’t you just feel the reader’s will to live slipping away?
But what about this: your characters are talking by the water cooler—Character A and Character B. Character A knows that his friend is inside Character B’s office looking for evidence of corporate espionage, so A is doing everything he can to stop B from going in. How was your weekend, what did you think of the game, how’s your wife doing, are those new shoes, literally anything just to keep him talking. Suddenly these benign little phrases have a purpose.
If you find your characters slipping into small talk, double check that it’s there for a purpose, and not just a crutch to keep you from moving forward in your scene. When writing dialogue, Make each line of dialogue earn its place.
3. Too much repetition
Variation is the spice of a good story. To keep your readers engaged, avoid using the same sentence structure and the same dialogue tags over and over again. Using “he said” and “she said” is effective and clear cut, but only for about three beats. After that, try switching to an action tag instead or letting the line of dialogue stand on its own.

You can also experiment with varying the length of your sentences or groupings of sentences. By changing up the rhythm of your story regularly, you’ll keep it feeling fresh and present for the reader.
Effective dialogue examples from literature
With all of these tips and tricks in mind, let’s look at how other writers have used good dialogue to elevate their stories.
Eleanor Oliphant is Completely Fine , by Gail Honeyman
“I’m going to pick up a carryout and head round to my mate Andy’s. A few of us usually hang out there on Saturday nights, fire up the playstation, have a smoke and a few beers.” “Sounds utterly delightful,” I said. “What about you?” he asked. I was going home, of course, to watch a television program or read a book. What else would I be doing? “I shall return to my flat,” I said. “I think there might be a documentary about komodo dragons on BBC4 later this evening.”
In this dialogue example, the author gives her characters two very distinctive voices. From just a few words we can begin to see these people very clearly in our minds—and with this distinction comes the tension that drives the story. Dialogue is an excellent place to show your character dynamics using speech patterns and word choices.
Pride and Prejudice , by Jane Austen
“My dear Mr. Bennet,” said his lady to him one day, “have you heard that Netherfield Park is let at last?” Mr. Bennet replied that he had not. “But it is,” returned she; “for Mrs. Long has just been here, and she told me all about it.” Mr. Bennet made no answer. “Do you not want to know who has taken it?” cried his wife impatiently. “You want to tell me, and I have no objection to hearing it.” This was invitation enough. “Why, my dear, you must know, Mrs. Long says that Netherfield is taken by a young man of large fortune from the north of England; that he came down on Monday in a chaise and four to see the place, and was so much delighted with it, that he agreed with Mr. Morris immediately; that he is to take possession before Michaelmas, and some of his servants are to be in the house by the end of next week.”
In this famous dialogue example, the author illustrates the relationship between these two characters clearly and succinctly. Their dialogue shows Mr. B’s stalwart, tolerant love for his wife and Mrs. B’s excitement and propensity for gossip. The author shows us everything we need to know about these people in just a few lines.
Dinner in Donnybrook , by Maeve Binchy
“Look, I thought you ought to know, we’ve had a very odd letter from Carmel.” “A what… from Carmel?” “A letter. Yes, I know it’s sort of out of character, I thought maybe something might be wrong and you’d need to know…” “Yes, well, what did she say, what’s the matter with her?” “Nothing, that’s the problem, she’s inviting us to dinner.” “To dinner?” “Yes, it’s sort of funny, isn’t it? As if she wasn’t well or something. I thought you should know in case she got in touch with you.” “Did you really drag me all the way down here, third years are at the top of the house you know, I thought the house had burned down! God, wait till I come home to you. I’ll murder you.” “The dinner’s in a month’s time, and she says she’s invited Ruth O’Donnell.” “Oh, Jesus Christ.”
This dialogue example is a telephone conversation between two people. The lack of dialogue tags or action tags allows the words to come to the forefront and immerses us in their back-and-forth conversation. Even though there are no tags to indicate the speakers, the language is simple and straightforward enough that the reader always knows who’s talking. Through this conversation the author slowly builds the tension from the benign to the catastrophic within a domestic setting.
Compelling dialogue is the key to a good story
A writer has a lot riding on their characters’ dialogue, and learning how to write dialogue is a critical skill for any writer. When done well, it can leaves a lasting impact on the reader. But when dialogue is clumsy and awkward, it can drag your story down and make your reader feel like they’re wasting their time.
But if you keep these tips in mind, listen to dialogue in your everyday life, and practice , you’ll be sure to create realistic dialogue that brings your story to life.
Get feedback on your writing today!
Scribophile is a community of hundreds of thousands of writers from all over the world. Meet beta readers, get feedback on your writing, and become a better writer!
Join now for free

Related articles

What is a Writer’s Voice & Tips for Finding Your Writing Voice

What is Dialect in Literature? Definition and Examples

How to Write a Sex Scene

Dialogue Tag Format: What are Speech Tags? With Examples

What is Alliteration? Definition, examples and tips

Nonfiction Writing Checklist for Your Book

How to Write Dialogue: Tips & Examples

Written by Eira Edwards
18 may 2023, art of storytelling.
This post may include affiliate links. That means we may earn a commission if you buy through recommended links. See our full disclaimer policy .
Great dialogue can drive the story forward, heighten tension and emotionally charge the scene.
But writing dialogue can be challenging—especially great dialogue. Though it’s essential for your book because stiff and unnatural dialogue can make the characters and the story feel less believable. And nobody wants that.
So, where do you start writing natural conversations that engage readers? In this article, we’ll look at some tips and tricks on how to write good dialogue, as well as some dialogue examples from well-known literature.
Why dialogue is important
Dialogue is a crucial element of storytelling that helps bring characters to life and move the plot forward. Readers can gain insight into a character’s thoughts, emotions and motivations through dialogue.
Well-crafted dialogue can add tension, conflict or humour to a story, making it more engaging and memorable.
Dialogue can convey information and build relationships between characters—which is essential for creating a rich and immersive narrative.
Take a look at this dialogue example from Great Expectations by Charles Dickens:
“Hold your noise!” cried a terrible voice, as a man started up from among the graves at the side of the church porch. “Keep still, you little devil, or I’ll cut your throat!”
That right there pulls me in. Magwitch’s first words to Pip—a deadly threat. The scene takes place in a graveyard, which adds to the sinister feeling. You’ve also got a great sense of Magwitch immediately. It reads beautifully and naturally, and it’s memorable.
Formatting dialogue in your novel
Here are five steps to remember when it comes to formatting your dialogue:
1. Characters’ dialogue goes within quotation marks. Everything else, such as description and dialogue tags, go outside quotation marks.
Example: “Hiya, Kate,” Ben said, grinning. “Fancy a swim?”
2. A new line shows a change of speaker.
Example: “Hiya, Kate,” Ben said, grinning. “Fancy a swim?” “Not today,” Kate said. “I’m helping out Matt at the farm.”
3. Punctuation stays inside quotation marks.
4. You can use double or single quotation marks, but stay consistent.
5. Dialogue begins with a capital letter unless it’s interrupted by a tag or action, in which case the same sentence continues, and lowercase is used to continue the dialogue.
9 tips for writing natural-sounding dialogue
So, back to that big question—how do you write dialogue that sounds natural? Let’s dive into my nine top tips.
1. Use contractions
Casual speech comes with contractions—shortened phrases like “it’s”, “isn’t” and “wouldn’t”.
Without contractions, dialogue can sound stiff and formal, making it difficult for readers to connect with the characters.
Contractions help us communicate faster and speed up the flow of conversations. They can also make dialogue more realistic because you can mimic how people really speak.
2. Vary sentence length and structure
We often use short, straightforward sentences that are easy to understand. But we can also speak in long, complex sentences when the situation calls for it.
With that in mind, mix up sentence lengths and structures to create a natural flow. Remember, consistently short sentences or long sentences can become quite rigid and monotonous.
3. Include pauses and interruptions
Real-life conversations are rarely scripted. Introduce pauses and interruptions to make dialogue feel spontaneous.
Interruptions and pauses can emphasise crucial points or build tension.
However, too many pauses can cause the writing to appear disjointed or confusing. Strike a balance between using pauses and interruptions effectively to maintain the structure and coherence of the writing.
4. Use regional accents sparingly
Accents are hard to write. They’re even harder to read. That’s why you should use them with caution.
Dialogue is a report of what words are spoken, and not necessarily how they’re spoken. And while accents might add authenticity, they can also pull the reader out of the action.
So, if you’re tempted to write dialogue using phonetic spelling, make sure it has a purpose. But more than that—does the character’s accent drive the plot forward? Is the dialect enriching the story? If it’s essential, consider other techniques that convey a character’s accent. For example, sprinkle colloquial language or words from their native language into the character’s dialogue.
5. Keep your dialogue tags simple
Elaborate dialogue tags help express additional information or create a specific tone or mood in some situations. However, more complex dialogue tags might distract readers from the scene.
Using simple dialogue tags such as “said,” “asked,” or “replied” can help to keep the focus on the dialogue itself and allow the reader to follow the conversation more easily.
6. Show, don’t tell
Dialogue can convey much more than just information. It can reveal character traits and emotions.
You could achieve this by displaying a character’s feelings through action, sensory elements and language. When a character is upset, they may clench their fists, raise their voice and speak in short, sharp words. You could show a character with anxiety through fidgeting, avoiding eye contact and stumbling over their words.
Subtext—the underlying meaning beneath the words spoken—can also be conveyed through dialogue. You can create a sense of ambiguity or irony, allowing readers to interpret the conversation in multiple ways and pulling them further into the story.
Find out more information in our guide to Show, Don’t Tell .
7. Avoid exposition dumps
Exposition dumps (otherwise known as info dumps) give readers a lot of information in dialogue. It can feel forced, leaving readers confused and overwhelmed.
Integrating exposition naturally can better engage readers without disrupting the flow of the narrative.
Instead, find ways to reveal information through actions and reactions.
You can also provide details gradually rather than all at once. And, as we looked at earlier, showing, rather than telling, the reader crucial information about characters, places and events, allows them to discover things for themselves and remain engaged in the story.
8. Small talk isn’t always engaging
Small talk adds authenticity, but too much can slow down the story and bore readers.
It’s important to strike a balance between using small talk to add depth to the characters and keeping the dialogue focused while moving the story on.
Establishing the personality of a specific character is one way to use short talk effectively. For example, an assertive character may use small talk to assert authority, while a shy character may use it to avoid feeling too awkward.
9. Cut clichés
Encountering a cliché in a story can throw readers off the narrative’s flow and create a sense of unoriginality or lack of creativity in the writing.
To prevent your characters from feeling predictable and one-dimensional, it’s crucial to steer clear of using stereotypes or clichés in your dialogue. This helps to ensure that the dialogue is fresh, original and authentic to each character’s unique voice and perspective.
How dialogue reveals character
Dialogue reveals a character’s thoughts, emotions and motivations. A character’s speech can even indicate their background, education and personality.
Imagine a character who speaks in a formal and polite tone. Do you consider them respectful, courteous and well-educated? Let’s say a character talks in a bold and vulgar manner. Would you consider them to be rude and insensitive? Possibly.
It would be difficult to tell who was who if everyone talked in the same formal and courteous tone. That’s why dialogue also helps to distinguish your characters from one another.
Physical acts and gestures can strengthen or contradict the way a character communicates. A person who speaks boldly and assertively may appear powerful and in control, but nervous twitches may indicate underlying fears.
Dialogue helps to build a sense of the character and helps to drive the plot. Consider a character who avoids direct questions or changes the subject. They may be hiding something.
Other words for said
While plenty of substitutes for “said” can be used to spice up your dialogue, use them with moderation to avoid drawing attention away from the conversation.
With this in mind, here are some of my favourite alternatives for the dialogue tag:
Frequently asked questions about great dialogue in fiction
How do you start dialogue.
When starting a line of dialogue, the first word within the quotation marks should be capitalised.
For example: He asked, “What day is it?”
You may consider beginning a conversation with a statement or question that grabs the reader’s attention and draws them into the scene.
What is an example of a dialogue?
Pick up a book and start flipping through the pages. You’ll quickly come across several passages containing characters’ dialogue.
Here’s one example of brilliant dialogue from F. Scott Fitzgerald’s The Great Gatsby :
“You’re a rotten driver,” I protested. “Either you ought to be more careful, or you oughtn’t to drive at all.” “I am careful.” “No, you’re not.” “Well, other people are,” she said lightly. “What’s that got to do with it?” “They’ll keep out of my way,” she insisted. “It takes two to make an accident.” “Suppose you met somebody just as careless as yourself.” “I hope I never will,” she answered. “I hate careless people. That’s why I like you.” Her gray, sun-strained eyes stared straight ahead, but she had deliberately shifted our relations, and for a moment I thought I loved her.
What is another word for said?
There are plenty of other words for said that you can use to add variation to your writing.
Some examples include “whispered”, “murmured” and “yelled”. Using a variety of dialogue tags can help to create more dynamic and engaging conversations, and can also help to convey different emotions or tones.
Remember, it’s important to use dialogue tags in moderation and to avoid overusing them in a way that feels forced or unnatural.
Get fresh eyes on your writing
Writing great dialogue is crucial to creating engaging and memorable stories.
Crafting natural dialogue involves consideration of the characters’ personalities, goals and motivations, and the setting of the scene.
However, even the most skilled writers may miss mistakes and typos in their dialogue. That’s where my proofreading services can help. Don’t let errors distract from the power of your dialogue.
For more information, take a look at my Proofreading Services .

Written By Eira Edwards
Eira is a writer and editor from the South of England with over five years of experience as a Content Manager, helping clients perfect their copy.
She has a degree in English Literature and Language, which she loves putting to work by working closely with fiction authors.
When she’s not working on manuscripts, you can find her in the woods with her partner and dog, or curling up with a good book.
Also on the Blog

Descriptive Adjectives
by Eira Edwards | Feb 9, 2024
Sometimes your writing needs a little extra sparkle, and descriptive adjectives can help with that. When used...

Best Enemies to Lovers Books
by Eira Edwards | Feb 7, 2024
Are you a sucker for a good enemies-to-lovers book? If you're looking for your next read, look no further! This...

Best Books on Creative Writing
by Eira Edwards | Jan 21, 2024
Whether you're an experienced writer or a beginner, there's always something new to discover about creativity and...
Cookies on Beyond the Chapter. We use cookies to provide visitors with the best possible experience on our website. These include functionality cookies and targeting cookies, which may be used in our marketing efforts. This allows us to personalise content, enhance site navigation and analyse site usage. By clicking “Accept All” you consent to our use of cookies. For more details, read our Cookie Policy and Privacy Statement.
How to Write Dialogue: Formatting & Examples 💬

Want to give more life and depth to your storytelling? We can explain how by showing you how to write dialogue.
Dialogue refers to the spoken exchanges between characters in a story or composition. It serves a vital role in any story, breathing life into characters and propelling the narrative forward. It transforms characters from figments of imagination into relatable beings, voicing their deepest thoughts, emotions, and motivations. Through dialogue, readers gain insight into a character’s personality, background, and relationships. It also fuels tension, conflict, and camaraderie among characters, heightening the story’s dynamics. Read on to learn how to write dialogue that captivates your audience.

Inner and outer dialogue 💭
There are two types of dialogue: inner and outer.
Inner dialogue, aka internal monologue, reveals a character’s thoughts, feelings, and reflections happening within their mind. It offers a window into their inner world, exposing their true intentions and struggles.
Outer dialogue, on the other hand, encompasses the words spoken between characters — conversations, debates, arguments, and interactions with others.
Both inner and outer dialogues are indispensable for writers. They serve as vehicles for conveying information, developing characters, and captivating readers. By skillfully blending these elements, writers can craft engaging, authentic dialogue that enriches the narrative experience.
How to write dialogue with examples 🗣️
When learning how to write dialogue, punctuation and formatting are essential. They clarify the speaker, convey the tone, and ensure the conversation flows smoothly.
These are the general rules for dialogue:
- Each speaker's dialogue should be written in a new paragraph or on a new line, allowing readers to easily follow the conversation.
- A comma should separate dialogue tags, such as “he said” or “she asked,” from the dialogue unless the quoted sentence calls for a question mark or exclamation point. The dialogue should always be enclosed in quotation marks. For instance: “Hello,” she said.
- If a character's speech extends beyond one paragraph, each new paragraph should begin with quotation marks, but only the end of the final paragraph gets the closing quotation marks.
- Punctuation marks like periods and commas are placed inside the quotation marks if they are part of the dialogue.
Careful attention to these rules will make your dialogue clear and enjoyable to read. Here are a few examples of how dialogue formatting and punctuation are used in different scenarios:
Single line ☝️
In this format, the dialogue appears as a standalone line without additional tags or descriptions. It is commonly used for brief exchanges or when the speaker is already clear from the context.
Under the soft moonlight, Jake dropped down on one knee, producing a small velvet box. His partner, Clara, gasped.
“I can’t believe you did that!”
Single line with a dialogue tag 🏷️
A dialogue tag identifies the speaker. It is separated from the dialogue by a comma. The tag can be placed before, in the middle, or after the dialogue.
Mary said, “I’ll be there in five minutes.”
“I’m so excited!” exclaimed John.
Questions 🤨
Wondering how to write a question in dialogue? Questions are punctuated with a question mark and follow similar formatting as regular dialogue lines.
“Did you finish your homework?” she inquired.
He asked, “What time is the meeting?”
Body language description 🕺
Body language descriptions provide context or show how a character is speaking. These descriptions can be integrated within the dialogue or presented as separate sentences.
“I’m not sure,” she said, scratching her head.
He sighed and looked away, saying, “I don’t know what to do.”
8 steps to write a dialogue 🪜
Before starting to write your dialogue, you should have already brainstormed and outlined your desired outcome. But creating dialogue that achieves these goals isn't always straightforward. We'll break down the essential steps for crafting effective dialogue in a clear, easy-to-understand manner.
1- Get to know your characters 🦸
Before writing dialogue, it's essential to fully understand your characters' personalities, backgrounds, motivations, and relationships. This will help you create dialogue that feels genuine to their traits.
2- Set the stage 🌄
Visualize the scene and imagine how the physical environment and character positions might influence their dialogue and actions.
3- Establish the purpose 🥅
Determine the objective of the dialogue in terms of plot development, character growth, or conveying essential information. This clarity will shape the content and direction of the conversation.
4- Embrace conflict 💥
Compelling dialogue often involves conflict or tension between characters. Explore differing opinions, goals, or misunderstandings to create excitement and maintain reader engagement.
5- Structure your dialogue 🧱
Outline the main points or beats of the dialogue, considering the flow of information, emotional shifts, and desired pacing. This structure will maintain coherence and keep the dialogue focused.
6- Add depth with subtext 🫥
People don’t always say what they mean. Infuse the dialogue with subtext, allowing characters to imply or subtly express their true thoughts and emotions. This adds complexity and engages the readers in deciphering underlying meanings.
7- Show, don’t tell 🎭
Instead of directly stating thoughts and emotions, let the characters’ words and actions reveal them. Show their reactions, incorporate body language, and use verbal cues to bring the dialogue to life.
8- Polish through revision ✨
After drafting the dialogue, carefully review and refine it for clarity, relevance, and impact. Remove any unnecessary or repetitive lines and ensure consistency with each character’s voice.
Tips for creating outstanding dialogue 🏅
Mastering the art of writing dialogue is essential to becoming a better writer . Here are several tips to help you create captivating and effective dialogues as a freelance writer:
- Prioritize natural language: Your dialogue should reflect how real people speak, incorporating realistic language, slang, and tone for each character. Avoid overly formal or forced dialogue that doesn't sound genuine. Read dialogue aloud to ensure it sounds natural and has a smooth rhythm and pacing.
- Actions over explanation: Instead of directly explaining information or emotions through dialogue, let your characters' words and interactions demonstrate their thoughts and feelings. This approach adds depth and subtlety to the conversation.
- Keep it concise and purposeful: Ensure your dialogue is concise and focused, avoiding unnecessary or lengthy exchanges . Trim any dialogue that doesn't contribute to character development, plot advancement, or the story.
- Use dialogue tags effectively: Dialogue tags like "said," "asked," or "replied" assign spoken words to the correct character. Additionally, consider using action beats or facial expressions to identify speakers, adding variety to your writing.
- Develop unique character voices: A clear writing style is good, but your characters should sound distinct. Give each character a unique way of speaking, reflecting their personality, background, and beliefs. Vary their vocabulary, sentence structure, and speech patterns to create dynamic and differentiated dialogue.
- Find a balance between dialogue and narration : Blend dialogue with narrative descriptions and actions to create a well-rounded story. This combination provides context, sets the scene, and gives readers a break from continuous dialogue.
- Create tension: Infuse your dialogue with conflict and suspense to keep readers invested and the narrative exciting. Use pauses and silence to convey emotions and indicate unspoken thoughts.
Red flags to avoid 🚩
When crafting dialogue, certain pitfalls can disrupt the flow and believability of your story. Here are key red flags to watch out for, ensuring your dialogue remains compelling and authentic.
- Avoid pointless conversations. Ensure that each dialogue serves a purpose in your story, whether moving the plot forward, revealing character traits, or conveying important information. Avoid including conversations that lack relevance or don't contribute to the overall narrative.
- Be cautious of using dialogue solely for delivering information. This might seem at odds with the previous point, but balancing the two is crucial. Find creative ways to incorporate exposition into the narrative through actions, descriptions, or other storytelling techniques, rather than relying on characters as mere vessels for backstory or plot explanations.
- Vary the use of dialogue tags to avoid monotony and distraction. There are many ways to write dialogue. Instead of repeatedly using the same tags like "said" or "asked," incorporate action beats, facial expressions, or body language to attribute dialogue and add diversity.
- Abstain from excessive or exaggerated tags that describe how the dialogue was spoken unless they are necessary for the scene. Although varying your tags is important, sometimes you should let the context and dialogue convey the desired tone.
Start a dialogue with clients on Contra 🗨️
Dialogue is an indispensable tool in storytelling. It breathes life into characters, driving them off the page and into the minds and hearts of readers. It adds depth to a narrative and creates a sense of realism. Without dialogue, a story is a mere narration of events with no emotional resonance. Ultimately, mastering dialogue is a critical skill for every writer aiming to create compelling and engaging stories.
Ready to take control of your freelance writing career ? Join Contra today and unlock a world of opportunity. Discover a commission-free platform designed specifically for freelancers like you, connecting you with clients who value your skills and expertise. Sign up now and start writing your own success story.
Essential Grammar Rules: How to Write With Excellence ✍️
Related articles.

How to Write Dialogue That Adds Depth to Your Storytelling 💬

How to Write a Novel: A Guide to Creating a Future Classic 🐣📖

15 Creative Writing Exercises to Improve Your Writing Skills 🌈

Allusion Figurative Language: Definition & 5 Examples 🤓

A Guide to Storytelling Marketing: Examples That Inspire 🧚

Point of View: How to Craft Compelling Narratives 👁️
Start your independent journey.

Hire top independents

How To Write Engaging Dialogue

(Full disclosure: If you do so, I earn a commission. Thank you.)
Related Posts

Taglines Make Characters Memorable
Taglines or catch phrases make it easy for readers to remember a character. When they are done right, even years later, we recall the character with clarity.

Book Review: In Leah’s Wake by Terri Giuliano Long
In her debut novel, In Leah’s Wake , Terri Giuliano Long explores the aftermath created when a teenage soccer star falls for a party-loving boy with a drug-dealing past.

Creative Ways To Capture Research Notes
When my research for my novel-in-progress required hiking in freezing weather, taking notes the traditional way didn’t work well. Here’s a couple of ideas of how to use technology for even better results.

Optimal Word Count for a Novel Manuscript
Whether you hope to get published the traditional way or plan to self-publish, the word count of your completed work is important. Here’s the scoop.
Join Our Newsletter
Join our newletter to receive the latest writing and storytelling tips and techniques.
Thank you for joining!
Join our list.
Get notified by email when new information is published.
You have Successfully Subscribed!
Pin it on pinterest.
Writers' Center
Eastern Washington University
Creative Writing
Dialogue and monologue, dialogue punctuation, dialogue tags.
- Creative Nonfiction
[ Back to resource home ]

[email protected] 509.359.2779
Cheney Campus JFK Library Learning Commons
Spokane Campus Catalyst Building C451 and C452
Stay Connected! Instagram Facebook
Dialogue is a verbal exchange between two or more characters. Monologue is a verbal expression from only one character.
One of the most important ways to bring creative writing to life is through conversations among characters. To make those conversations clear, proper dialogue formatting and punctuation is important. Fortunately, there are only a few simple rules or conventions to keep in mind when writing dialogue.
Quotation Marks
Dialogue/ monologue is usually denoted by quotation marks.
“How do I set apart the words a character is saying from the rest of the text?” Skylar asked.
Change of Speaker
Indent for a new paragraph every time a different character speaks.
“How can I show the reader that a different character is speaking in this scene?” Quinton asked. He took a bite out of his sandwich. “All you have to do is indent for a new paragraph. That will signal that the speaker has changed,” said Jaclyn. Quinton drank some water. He nodded. “It’s so easy!”
Dialogue tags are signals that tell the reader which character is speaking. There are three types of dialogue tags.
1. Said Tags
The first type of dialogue tag can be referred to as the “said tag.” “Said tags” utilize verbs for communicating words. Examples of “said tags” are shown below in bold .
“I love writing dialogue,” said Jackson. “Do you love writing?” asked Cooper. “I love the EWU Writers’ Center!” Devon shouted. “It is important to be quiet,” Lacey whispered.
Note that punctuation goes inside the quotation marks, and periods change to commas since with “said tags” the spoken words are part of the same sentence as the tag. For the same reason “said” and “asked” are not capitalized in the above examples.
2. Action Tags
The second kind of dialogue tag can be referred to as the “action tag.” “Action tags” are simply sentences in which the character who is about to speak or has recently spoken does or thinks something. The reader understands who has said the words based on their close proximity to the action. Dialogue that is tagged with action is shown in bold below. Note that with action tags, the action sentence and the spoken words are separate sentences, and are punctuated accordingly.
Tyler threw open the door and ran into the room. “You guys! You’ll never believe what I saw outside! It was incredible.” “What are you talking about, Tyler? You're weird.” Montague put aside his video game controller. “It is not weird. It is dignified.” Tyler couldn’t believe Montague had said something so mean. He ran from the room in tears. Taylor cried and cried all the way home. “Why do I have the hardest life?”
3. Combination Tags
The third type of dialogue tag can be referred to as the “combination tag.” This type of dialogue tag combines the “said tag” with the “action tag.” An example of dialogue tagged with a “combination tag” is shown below.
“Dialogue tags are very useful,” Reginald said, typing his masterpiece novel.
“I like ice cream,” Charlie said, enjoying a tasty treat.
As shown above, the “combination tag” begins with a said tag, followed by a comma, and a gerund phrase.
Mixing Tags
It is perfectly acceptable and expected that “said tags,” “action tags,” and “combination tags” will be mixed together in the same scene to create variety. Furthermore, sometimes the reader might have a clear understanding of which character is speaking when there is no dialogue tag at all. See the example below.
“We should totally consume several slices of delish pepperoni pizza for dinner tonight,” Ahbdi said. Fernando dropped his sandwich on the floor. “No, Ahbdi! I will not consume pizza!” “Why not? Why won’t you consume pizza?” “Because I will only eat sandwiches!” Ahbdi shouted, stomping his feet. “And stop saying the word ‘consume.’”
Sometimes dialogue tags are used in the middle of dialogue. This should be punctuated like the examples above. More dialogue simply continues after the tag.
“The mechanic told me my brakes are broken,” Rudolpho said. “I guess that is important.” “I drive a motorcycle.” Hitomi leaned on the counter. “Does that turn you on?”
Dialogue Tags on Steroids
The goal with dialogue tags is that they should be somewhat invisible, that is, that they do not call attention to themselves, leaving the reader fully immersed in the scene. Some writers may worry about using the word “said” in too many “said tags.” However, the idea is that the word “said” is hardly noticed, so that the reader sees the name of the character speaking and moves on, staying in the scene.
Try to avoid dialogue tags “on steroids,” or dialogue tags that call attention to themselves and become distracting. Examples of dialogue tags on steroids are below.
“I do not think you should have such strong dialogue tags,” Frederick expostulated. “My head will fricking explode if I do not use strong dialogue tags!” Logan exclaimed. “But why?” Frederick asked. “Because they make me sound sophisticated,” Logan answered. “Why do you think they sound sophisticated?” Frederick inquired. “Because I am the smartest man in the world,” Logan replied.
In addition to these steroid dialogue tags being tedious and exhausting, many of them are not necessary. The reader knows that Frederick is asking a question, and he knows that Logan is answering. Thus, these dialogue tags become even more tedious because they are redundant.
- Next: Fiction >>
- Last Updated: Mar 24, 2022 9:21 PM
- URL: https://research.ewu.edu/writers_c_fiction

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Enroll now. 4. Kazuo Ishiguro, Never Let Me Go. Here, friends Tommy and Kathy have a conversation after Tommy has had a meltdown. After being bullied by a group of boys, he has been stomping around in the mud, the precise reaction they were hoping to evoke from him. "Tommy," I said, quite sternly.
Tip #1: Create Character Voices. Dialogue is a great way to reveal your characters. What your characters say, and how they say it, can tell us so much about what kind of people they are. Some characters are witty and gregarious. Others are timid and unobtrusive. Speech patterns vary drastically from person to person.
Format & Punctuation. Examples. Tips for Dialogue. Say the dialogue out loud. Cut small talk when writing dialogue. Keep your dialogue brief and impactful. Give each character a unique voice. Add world-appropriate slang. Be consistent with the characters' voices.
2. Make your character's wants clear. In a post about how to approach how to write dialogue it may seem contradictory to say this, but a good rule for dialogue writing in a scene is to write the dialogue last. After building out the other elements of your story (your arcs, acts, scenes, and story beats) you will have a better sense of how each ...
An attribution, also known as an identifier or tag, is the part of the sentence that follows a piece of dialogue. For example: "John said." In his creative writing lectures, Brandon Sanderson shares a few useful tips. Try to place the attribution as early as possible to help make it clear in the reader's mind who is speaking.
Try these four prompts to hone your dialogue-writing skills. 1. Go to a public place where people tend to talk to one another. Try a cafe, bar, or public transportation. Spend 10 minutes eavesdropping on a conversation. Record everything they say and how they say it as specifically as you can.
If dialogue is attributed using a tag such as 'she said' (read more on dialogue tags below), use a comma and not a period/full stop. For example: "Writing dialogue is harder than I thought." She said. "Writing dialogue is harder than I thought," she said. ️. Remember: the tag continues the sentence. 5.
It just makes it harder to read. Here's an example of this in action: "I'm not sure how to write dialogue," Johnny said to Sally. Sally looked Johnny in the eyes and smiled. "It's really not that hard," she said as she touched his cheek. "That's easy for you to say.
PRACTICE. Create two characters with opposing desires. For example, a mother and daughter are fighting. The mother wants her daughter to stay at an in-state college or university. The daughter wants to go as far away as possible. Write their argument but here's the trick: don't take sides.
Keep only the ones that contribute something to the story. 6. Vary word choices and rhythms. The greatest dialogue examples in writing use distinctive character voices; each character sounds a little bit different, because they have their own personality.
3. Include pauses and interruptions. Real-life conversations are rarely scripted. Introduce pauses and interruptions to make dialogue feel spontaneous. Interruptions and pauses can emphasise crucial points or build tension. However, too many pauses can cause the writing to appear disjointed or confusing.
Writing good dialogue means balancing the natural flow of human conversation with the conventions of creative writing — a herculean task, especially for those who are first starting the craft. Whether you're a seasoned writing vet or a complete newbie, hopefully the suggestions and examples in this article will help you find that balance.
3. Every new speaker gets a new paragraph. Every dialogue begins with a new paragraph. Each time a character says something, even if it is only a word, the dialogue should begin on a new paragraph. Here's a dialogue writing example: "Don't worry, the information they have of our whereabouts is misleading.".
Find creative ways to incorporate exposition into the narrative through actions, descriptions, or other storytelling techniques, rather than relying on characters as mere vessels for backstory or plot explanations. Vary the use of dialogue tags to avoid monotony and distraction. There are many ways to write dialogue.
Here are tips for writing dialogue that captures readers' imaginations and keeps them turning pages. 1. Remove Names from Your Dialogue. A common mistake that inexperienced writers make is to include names repetitively in the dialogue. Here's an example: "Mary, let me buy you lunch.".
Here are his writing tips for how to add good dialogue and compelling conversations to your own writing: 1. Let a conversation tell the story. It's better to show your characters' personalities through what they say to one another, rather than describe how they are feeling. 2.
Dialogue examples from famous authors can help discover how to understand it and create your own. Get tips for writing dialogue and proper formatting, too.
Plus, examine examples, formats, and tips for writing dialogue. Build your creative skills through weekly lectures, reading and writing assignments, and group critiques. You can also expect to read Write Great Fiction: Dialogue by Gloria Kempton. By the end of this workshop, you will have all the tools and resources you need to create ...
Enclose dialogue in double quotation marks and use single quotation marks when a character quotes another character within their dialogue. Knowing how to punctuate dialogue properly can ensure that your reader stays immersed in the story. 8. Use dialogue tags that are evocative. Repeating the word "said" over and over can make for dull ...
Use single quotation marks for indirect dialogue or thoughts. If a character quotes someone else, use single quotation marks ('') within the main dialogue. Example: "The manager told me, 'The sale starts today,'" I said. Use dialogue tags to attribute speech.
Dialogue Tags. Dialogue tags are signals that tell the reader which character is speaking. There are three types of dialogue tags. 1. Said Tags. The first type of dialogue tag can be referred to as the "said tag." "Said tags" utilize verbs for communicating words. Examples of "said tags" are shown below in bold.