Log in using your username and password
- Search More Search for this keyword Advanced search
- Latest content
- Current issue
- BMJ Journals More You are viewing from: Google Indexer

You are here
- Volume 25, Issue 1
- Critical appraisal of qualitative research: necessity, partialities and the issue of bias
- Article Text
- Article info
- Citation Tools
- Rapid Responses
- Article metrics
- http://orcid.org/0000-0001-5660-8224 Veronika Williams ,
- Anne-Marie Boylan ,
- http://orcid.org/0000-0003-4597-1276 David Nunan
- Nuffield Department of Primary Care Health Sciences , University of Oxford, Radcliffe Observatory Quarter , Oxford , UK
- Correspondence to Dr Veronika Williams, Nuffield Department of Primary Care Health Sciences, University of Oxford, Oxford OX2 6GG, UK; veronika.williams{at}phc.ox.ac.uk
https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjebm-2018-111132
Statistics from Altmetric.com
Request permissions.
If you wish to reuse any or all of this article please use the link below which will take you to the Copyright Clearance Center’s RightsLink service. You will be able to get a quick price and instant permission to reuse the content in many different ways.
- qualitative research
Introduction
Qualitative evidence allows researchers to analyse human experience and provides useful exploratory insights into experiential matters and meaning, often explaining the ‘how’ and ‘why’. As we have argued previously 1 , qualitative research has an important place within evidence-based healthcare, contributing to among other things policy on patient safety, 2 prescribing, 3 4 and understanding chronic illness. 5 Equally, it offers additional insight into quantitative studies, explaining contextual factors surrounding a successful intervention or why an intervention might have ‘failed’ or ‘succeeded’ where effect sizes cannot. It is for these reasons that the MRC strongly recommends including qualitative evaluations when developing and evaluating complex interventions. 6
Critical appraisal of qualitative research
Is it necessary.
Although the importance of qualitative research to improve health services and care is now increasingly widely supported (discussed in paper 1), the role of appraising the quality of qualitative health research is still debated. 8 10 Despite a large body of literature focusing on appraisal and rigour, 9 11–15 often referred to as ‘trustworthiness’ 16 in qualitative research, there remains debate about how to —and even whether to—critically appraise qualitative research. 8–10 17–19 However, if we are to make a case for qualitative research as integral to evidence-based healthcare, then any argument to omit a crucial element of evidence-based practice is difficult to justify. That being said, simply applying the standards of rigour used to appraise studies based on the positivist paradigm (Positivism depends on quantifiable observations to test hypotheses and assumes that the researcher is independent of the study. Research situated within a positivist paradigm isbased purely on facts and consider the world to be external and objective and is concerned with validity, reliability and generalisability as measures of rigour.) would be misplaced given the different epistemological underpinnings of the two types of data.
Given its scope and its place within health research, the robust and systematic appraisal of qualitative research to assess its trustworthiness is as paramount to its implementation in clinical practice as any other type of research. It is important to appraise different qualitative studies in relation to the specific methodology used because the methodological approach is linked to the ‘outcome’ of the research (eg, theory development, phenomenological understandings and credibility of findings). Moreover, appraisal needs to go beyond merely describing the specific details of the methods used (eg, how data were collected and analysed), with additional focus needed on the overarching research design and its appropriateness in accordance with the study remit and objectives.
Poorly conducted qualitative research has been described as ‘worthless, becomes fiction and loses its utility’. 20 However, without a deep understanding of concepts of quality in qualitative research or at least an appropriate means to assess its quality, good qualitative research also risks being dismissed, particularly in the context of evidence-based healthcare where end users may not be well versed in this paradigm.
How is appraisal currently performed?
Appraising the quality of qualitative research is not a new concept—there are a number of published appraisal tools, frameworks and checklists in existence. 21–23 An important and often overlooked point is the confusion between tools designed for appraising methodological quality and reporting guidelines designed to assess the quality of methods reporting. An example is the Consolidate Criteria for Reporting Qualitative Research (COREQ) 24 checklist, which was designed to provide standards for authors when reporting qualitative research but is often mistaken for a methods appraisal tool. 10
Broadly speaking there are two types of critical appraisal approaches for qualitative research: checklists and frameworks. Checklists have often been criticised for confusing quality in qualitative research with ‘technical fixes’ 21 25 , resulting in the erroneous prioritisation of particular aspects of methodological processes over others (eg, multiple coding and triangulation). It could be argued that a checklist approach adopts the positivist paradigm, where the focus is on objectively assessing ‘quality’ where the assumptions is that the researcher is independent of the research conducted. This may result in the application of quantitative understandings of bias in order to judge aspects of recruitment, sampling, data collection and analysis in qualitative research papers. One of the most widely used appraisal tools is the Critical Appraisal Skills Programme (CASP) 26 and along with the JBI QARI (Joanna Briggs Institute Qualitative Assessment and Assessment Instrument) 27 presents examples which tend to mimic the quantitative approach to appraisal. The CASP qualitative tool follows that of other CASP appraisal tools for quantitative research designs developed in the 1990s. The similarities are therefore unsurprising given the status of qualitative research at that time.
Frameworks focus on the overarching concepts of quality in qualitative research, including transparency, reflexivity, dependability and transferability (see box 1 ). 11–13 15 16 20 28 However, unless the reader is familiar with these concepts—their meaning and impact, and how to interpret them—they will have difficulty applying them when critically appraising a paper.
The main issue concerning currently available checklist and framework appraisal methods is that they take a broad brush approach to ‘qualitative’ research as whole, with few, if any, sufficiently differentiating between the different methodological approaches (eg, Grounded Theory, Interpretative Phenomenology, Discourse Analysis) nor different methods of data collection (interviewing, focus groups and observations). In this sense, it is akin to taking the entire field of ‘quantitative’ study designs and applying a single method or tool for their quality appraisal. In the case of qualitative research, checklists, therefore, offer only a blunt and arguably ineffective tool and potentially promote an incomplete understanding of good ‘quality’ in qualitative research. Likewise, current framework methods do not take into account how concepts differ in their application across the variety of qualitative approaches and, like checklists, they also do not differentiate between different qualitative methodologies.
On the need for specific appraisal tools
Current approaches to the appraisal of the methodological rigour of the differing types of qualitative research converge towards checklists or frameworks. More importantly, the current tools do not explicitly acknowledge the prejudices that may be present in the different types of qualitative research.
Concepts of rigour or trustworthiness within qualitative research 31
Transferability: the extent to which the presented study allows readers to make connections between the study’s data and wider community settings, ie, transfer conceptual findings to other contexts.
Credibility: extent to which a research account is believable and appropriate, particularly in relation to the stories told by participants and the interpretations made by the researcher.
Reflexivity: refers to the researchers’ engagement of continuous examination and explanation of how they have influenced a research project from choosing a research question to sampling, data collection, analysis and interpretation of data.
Transparency: making explicit the whole research process from sampling strategies, data collection to analysis. The rationale for decisions made is as important as the decisions themselves.
However, we often talk about these concepts in general terms, and it might be helpful to give some explicit examples of how the ‘technical processes’ affect these, for example, partialities related to:
Selection: recruiting participants via gatekeepers, such as healthcare professionals or clinicians, who may select them based on whether they believe them to be ‘good’ participants for interviews/focus groups.
Data collection: poor interview guide with closed questions which encourage yes/no answers and/leading questions.
Reflexivity and transparency: where researchers may focus their analysis on preconceived ideas rather than ground their analysis in the data and do not reflect on the impact of this in a transparent way.
The lack of tailored, method-specific appraisal tools has potentially contributed to the poor uptake and use of qualitative research for informing evidence-based decision making. To improve this situation, we propose the need for more robust quality appraisal tools that explicitly encompass both the core design aspects of all qualitative research (sampling/data collection/analysis) but also considered the specific partialities that can be presented with different methodological approaches. Such tools might draw on the strengths of current frameworks and checklists while providing users with sufficient understanding of concepts of rigour in relation to the different types of qualitative methods. We provide an outline of such tools in the third and final paper in this series.
As qualitative research becomes ever more embedded in health science research, and in order for that research to have better impact on healthcare decisions, we need to rethink critical appraisal and develop tools that allow differentiated evaluations of the myriad of qualitative methodological approaches rather than continuing to treat qualitative research as a single unified approach.
- Williams V ,
- Boylan AM ,
- Lingard L ,
- Orser B , et al
- Brawn R , et al
- Van Royen P ,
- Vermeire E , et al
- Barker M , et al
- McGannon KR
- Dixon-Woods M ,
- Agarwal S , et al
- Greenhalgh T ,
- Dennison L ,
- Morrison L ,
- Conway G , et al
- Barrett M ,
- Mayan M , et al
- Lockwood C ,
- Santiago-Delefosse M ,
- Bruchez C , et al
- Sainsbury P ,
- ↵ CASP (Critical Appraisal Skills Programme). date unknown . http://www.phru.nhs.uk/Pages/PHD/CASP.htm .
- ↵ The Joanna Briggs Institute . JBI QARI Critical appraisal checklist for interpretive & critical research . Adelaide : The Joanna Briggs Institute , 2014 .
- Stephens J ,
Contributors VW and DN: conceived the idea for this article. VW: wrote the first draft. AMB and DN: contributed to the final draft. All authors approve the submitted article.
Competing interests None declared.
Provenance and peer review Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Correction notice This article has been updated since its original publication to include a new reference (reference 1.)
Read the full text or download the PDF:

- Teesside University Student & Library Services
- Learning Hub Group
Critical Appraisal for Health Students
- Critical Appraisal of a qualitative paper
- Critical Appraisal: Help
- Critical Appraisal of a quantitative paper
- Useful resources
Appraisal of a Qualitative paper : Top tips

- Introduction
Critical appraisal of a qualitative paper
This guide aimed at health students, provides basic level support for appraising qualitative research papers. It's designed for students who have already attended lectures on critical appraisal. One framework for appraising qualitative research (based on 4 aspects of trustworthiness) is provided and there is an opportunity to practise the technique on a sample article.
Support Materials
- Framework for reading qualitative papers
- Critical appraisal of a qualitative paper PowerPoint
To practise following this framework for critically appraising a qualitative article, please look at the following article:

Schellekens, M.P.J. et al (2016) 'A qualitative study on mindfulness-based stress reduction for breast cancer patients: how women experience participating with fellow patients', Support Care Cancer , 24(4), pp. 1813-1820.
Critical appraisal of a qualitative paper: practical example.
- Credibility
- Transferability
- Dependability
- Confirmability
How to use this practical example
Using the framework, you can have a go at appraising a qualitative paper - we are going to look at the following article:
Step 1. take a quick look at the article, step 2. click on the credibility tab above - there are questions to help you appraise the trustworthiness of the article, read the questions and look for the answers in the article. , step 3. click on each question and our answers will appear., step 4. repeat with the other aspects of trustworthiness: transferability, dependability and confirmability ., questioning the credibility:, who is the researcher what has been their experience how well do they know this research area, was the best method chosen what method did they use was there any justification was the method scrutinised by peers is it a recognisable method was there triangulation ( more than one method used), how was the data collected was data collected from the participants at more than one time point how long were the interviews were questions asked to the participants in different ways, is the research reporting what the participants actually said were the participants shown transcripts / notes of the interviews / observations to ‘check’ for accuracy are direct quotes used from a variety of participants, how would you rate the overall credibility, questioning the transferability, was a meaningful sample obtained how many people were included is the sample diverse how were they selected, are the demographics given, does the research cover diverse viewpoints do the results include negative cases was data saturation reached, what is the overall transferability can the research be transferred to other settings , questioning the dependability :, how transparent is the audit trail can you follow the research steps are the decisions made transparent is the whole process explained in enough detail did the researcher keep a field diary is there a clear limitations section, was there peer scrutiny of the researchwas the research plan shown to peers / colleagues for approval and/or feedback did two or more researchers independently judge data, how would you rate the overall dependability would the results be similar if the study was repeated how consistent are the data and findings, questioning the confirmability :, is the process of analysis described in detail is a method of analysis named or described is there sufficient detail, have any checks taken place was there cross-checking of themes was there a team of researchers, has the researcher reflected on possible bias is there a reflexive diary, giving a detailed log of thoughts, ideas and assumptions, how do you rate the overall confirmability has the researcher attempted to limit bias, questioning the overall trustworthiness :, overall how trustworthy is the research, further information.
See Useful resources for links, books and LibGuides to help with Critical appraisal.
- << Previous: Critical Appraisal: Help
- Next: Critical Appraisal of a quantitative paper >>
- Last Updated: Aug 25, 2023 2:48 PM
- URL: https://libguides.tees.ac.uk/critical_appraisal
This website is intended for healthcare professionals

- { $refs.search.focus(); })" aria-controls="searchpanel" :aria-expanded="open" class="hidden lg:inline-flex justify-end text-gray-800 hover:text-primary py-2 px-4 lg:px-0 items-center text-base font-medium"> Search
Search menu
Barker J, Linsley P, Kane R, 3rd edn. London: Sage; 2016
Ethical guidelines for educational research. 2018; https://tinyurl.com/c84jm5rt
Bowling A Research methods in health, 4th edn. Maidenhead: Open University Press/McGraw-Hill Education; 2014
Gliner JA, Morgan GAMahwah (NJ): Lawrence Erlbaum Associates; 2000
Critical Skills Appraisal Programme checklists. 2021; https://casp-uk.net/casp-tools-checklists
Cresswell J, 4th edn. London: Sage; 2013
Grainger A Principles of temperature monitoring. Nurs Stand. 2013; 27:(50)48-55 https://doi.org/10.7748/ns2013.08.27.50.48.e7242
Jupp VLondon: Sage; 2006
Continuing professional development (CPD). 2021; http://www.hcpc-uk.org/cpd
London: NHS England; 2017 http://www.hee.nhs.uk/our-work/advanced-clinical-practice
Kennedy M, Burnett E Hand hygiene knowledge and attitudes: comparisons between student nurses. Journal of Infection Prevention. 2011; 12:(6)246-250 https://doi.org/10.1177/1757177411411124
Lindsay-Smith G, O'Sullivan G, Eime R, Harvey J, van Ufflen JGZ A mixed methods case study exploring the impact of membership of a multi-activity, multi-centre community group on the social wellbeing of older adults. BMC Geriatrics. 2018; 18 https://bmcgeriatr.biomedcentral.com/track/pdf/10.1186/s12877-018-0913-1.pdf
Morse JM, Pooler C, Vann-Ward T Awaiting diagnosis of breast cancer: strategies of enduring for preserving self. Oncology Nursing Forum. 2014; 41:(4)350-359 https://doi.org/10.1188/14.ONF.350-359
Revalidation. 2019; http://revalidation.nmc.org.uk
Parahoo K Nursing research, principles, processes and issues, 3rd edn. Basingstoke: Palgrave Macmillan; 2014
Polit DF, Beck CT Nursing research, 10th edn. Philadelphia (PA): Wolters Kluwer; 2017
Critiquing a published healthcare research paper
Angela Grainger
Nurse Lecturer/Scholarship Lead, BPP University, and editorial board member
View articles · Email Angela

Research is defined as a ‘systematic inquiry using orderly disciplined methods to answer questions or to solve problems' ( Polit and Beck, 2017 :743). Research requires academic discipline coupled with specific research competencies so that an appropriate study is designed and conducted, leading to the drawing of relevant conclusions relating to the explicit aim/s of the study.
Relevance of research to nursing and health care
For those embarking on a higher degree such as a master's, taught doctorate, or a doctor of philosophy, the relationship between research, knowledge production and knowledge utilisation becomes clear during their research tuition and guidance from their research supervisor. But why should other busy practitioners juggling a work/home life balance find time to be interested in healthcare research? The answer lies in the relationship between the outcomes of research and its relationship to the determination of evidence-based practice (EBP).
The Health and Care Professions Council (HCPC) and the Nursing and Midwifery Council (NMC) require registered practitioners to keep their knowledge and skills up to date. This requirement incorporates being aware of the current EBP relevant to the registrant's field of practice, and to consider its application in relation to the decisions made in the delivery of patient care.
Advanced clinical practitioners (ACPs) are required to be involved in aspects of research activities ( Health Education England, 2017 ). It is for this reason that practitioners need to know how EBP is influenced by research findings and, moreover, need to be able to read and interpret a research study that relates to a particular evidence base. Reading professional peer-reviewed journals that have an impact factor (the yearly average number of citations of papers published in a previous 2-year period in a given journal is calculated by a scientometric index giving an impact factor) is evidence of continuing professional development (CPD).
CPD fulfils part of the HCPC's and the NMC's required professional revalidation process ( HCPC, 2021 ; NMC, 2019 ). For CPD in relation to revalidation, practitioners can give the publication details of a research paper, along with a critique of that paper, highlighting the relevance of the paper's findings to the registrant's field of practice.
Defining evidence-based practice
According to Barker et al (2016:4.1) EBP is the integration of research evidence and knowledge to current clinical practice and is to be used at a local level to ensure that patients receive the best quality care available. Because patients are at the receiving end of EBP it is important that the research evidence is credible. This is why a research study has to be designed and undertaken rigorously in accordance with academic and scientific discipline.
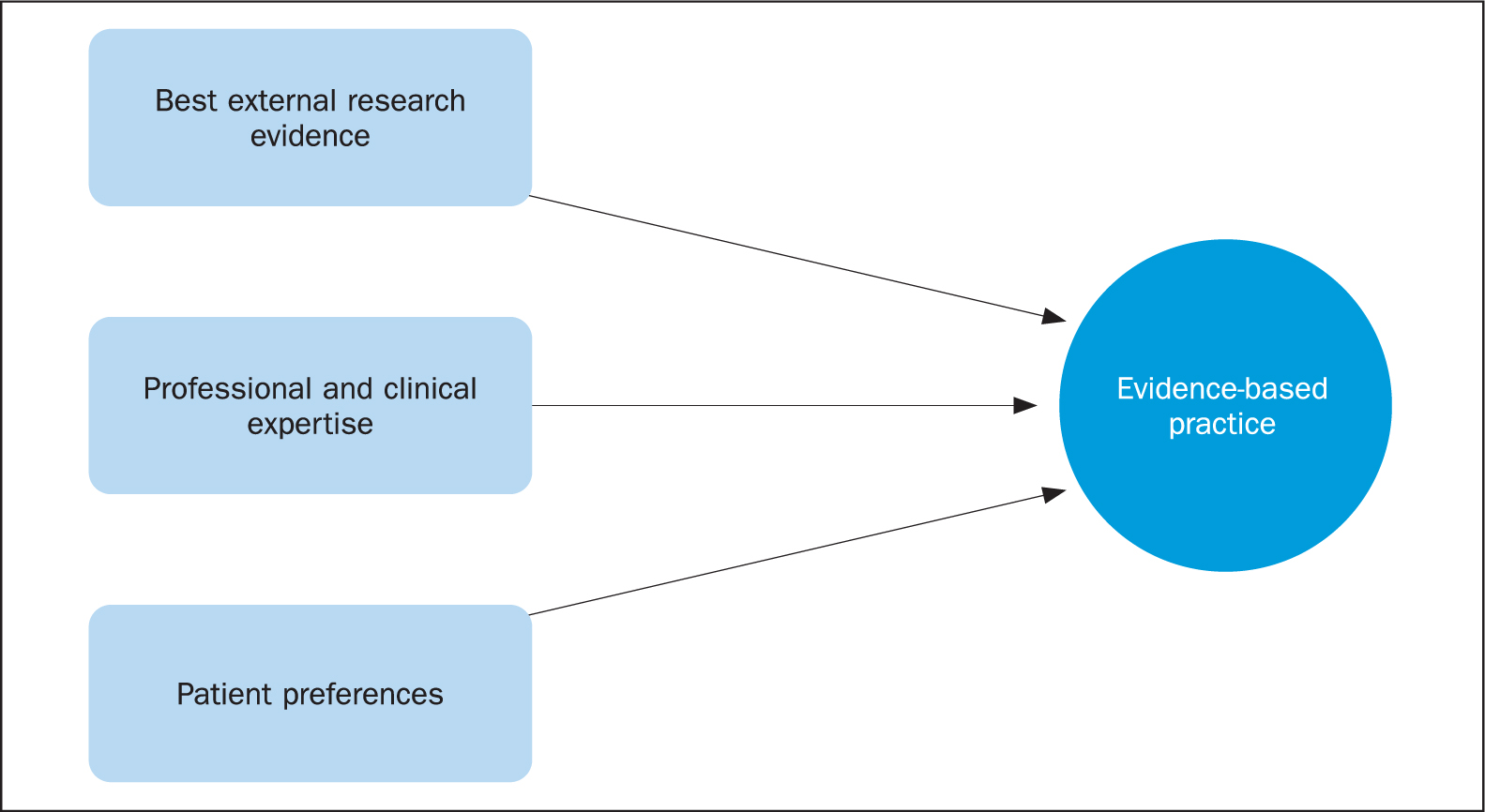
The elements of EBP
EBP comprises three elements ( Figure 1 ). The key element is research evidence, followed by the expert knowledge and professional opinion of the practitioner, which is important especially when there is no research evidence—for example, the most appropriate way to assist a patient out of bed, or perform a bed bath. Last, but in no way of least importance, is the patient's preference for a particular procedure. An example of this is the continued use of thermal screening dots for measuring a child's temperature on the forehead, or in the armpit because children find these options more acceptable than other temperature measuring devices, which, it is argued, might give a more accurate reading ( Grainger, 2013 ).
Understanding key research principles
To interpret a published research study requires an understanding of key research principles. Research authors use specific research terms in their publications to describe and to explain what they have done and why. So without an awareness of the research principles underpinning the study, how can readers know if what they are reading is credible?
Validity and reliability have long been the two pillars on which the quality of a research study has been judged ( Gliner and Morgan, 2000 ). Validity refers to how accurately a method measures what it is intended to measure. If a research study has a high validity, it means that it produces results that correspond to real properties, characteristics, and variations in the part of the physical or social world that is being studied ( Jupp, 2006 ).
Reliability is the extent to which a measuring instrument, for example, a survey using closed questions, gives the same consistent results when that survey is repeated. The measurement is considered reliable if the same result can be consistently achieved by using the same methods under the same circumstances ( Parahoo, 2014 ).
The research topic is known as the phenomenon in a singular sense, or phenomena if what is to be researched is plural. It is a key principle of research that it is the nature of the phenomenon, in association with the study's explicit research aim/s, that determines the research design. The research design refers to the overall structure or plan of the research ( Bowling, 2014 :166).
Methodology means the philosophy underpinning how the research will be conducted. It is essential for the study's research design that an appropriate methodology for the conduct and execution of the study is selected, otherwise the research will not meet the requirements of being valid and reliable. The research methods will include the design for data sampling, how recruitment into the study will be undertaken, the method/s used for the actual data collection, and the subsequent data analysis from which conclusions will be drawn (see Figure 2 ).

Quantitative, qualitative, and mixed-methods studies
A quantitative methodology is where the phenomenon lends itself to an investigation of data that can be numerically analysed using an appropriate statistical test/s. Quantitative research rests on the philosophical view that science has to be neutral and value-free, which is why precise measurement instruments are required ( Box 1 ). Quantitative research is influenced by the physical sciences such as mathematics, physics, and chemistry. The purpose of quantitative studies is to identify whether there are any causal relationships between variables present in the phenomenon. In short, a variable is an attribute that can vary and take on different values, such as the body temperature or the heart rate ( Polit and Beck, 2017 :748).
Quantitative studies can sometimes have a hypothesis. A hypothesis is a prediction of the study's outcome, and the aim of the study is to show either that the hypothesis is demonstrated as proven, or that it is not proven. Often a hypothesis is about a predicted relationship between variables. There are two types of variables, independent and dependent. An independent variable causes a change in the specific phenomenon being studied, while a dependent variable is the change in that phenomenon. The first example in Box 1 might help to clarify the difference.
An example of a hypothesis would be that older people who have a history of falls have a reduction in the incidence of falls due to exercise therapy. The causal relationship is between the independent variable— the exercise therapy—and the dependent variable—a falls reduction.
A qualitative methodology aims to explore a phenomenon with the aim of understanding the experience of the phenomenon from the perspective of those affected by it. Qualitative research is influenced by the social and not the physical sciences. Concepts and themes arise from the researcher/s interpretation of the data gained from observations and interviews. The collected data are non-numerical and this is the distinction from a quantitative study. The data collected are coded in accordance with the type of method being used in the research study, for example, discourse analysis; phenomenology; grounded theory. The researcher identifies themes from the data descriptions, and from the data analysis a theoretical understanding is seen to emerge.
A qualitative methodology rests on the philosophical view that science cannot be neutral and value-free because the researcher and the participants are part of the world that the research study aims to explore.
Unlike quantitative studies, the results of which can often be generalised due to the preciseness of the measuring instruments, qualitative studies are not usually generalisable. However, knowledge comparisons can be made between studies that have some similarity of focus. For example, the uncovering of causative or aggravating factors leading to the experiences of pain management for oncology patients, and for patients who have rheumatoid arthritis, or another long-term health problem for which pain is a characteristic feature. The validity of a qualitative study relates to the accurate representation of the data collected and analysed, and which shows that data has been saturated, meaning no new data or analysed findings are forthcoming. This is demonstrated in a clear data audit trail, and the study's findings are therefore seen as credible (see the second example in Box 1 ).
Box 1.Research study examples
- An example of a quantitative research study Kennedy and Burnett (2011) conducted a survey to determine whether there were any discernible differences in knowledge and attitudes between second- and third-year pre-registration nursing students toward hand-hygiene practices. The collected data and its subsequent analysis is presented in numerical tables and graphs, but these are supported by text explaining the research findings and how these were ascertained. For full details, see 10.1177/1757177411411124
- 2. An example of a qualitative research study Morse et al (2014) undertook an exploratory study to see what coping strategies were used by women awaiting a possible diagnosis of breast cancer. Direct quotes from the study participants appeared in the writing up of the research because it is a requirement of qualitative research that there be a transparent data audit trail. The research showed two things, both essential requirements of qualitative research. First, how the collected data were saturated to ensure that no data had been left inadequately explored, or that the data coding had been prematurely closed and, second, having captured the breadth and depth of the data findings, the researchers showed how the direct quotes were thematically coded to reveal the women's coping strategies. For full details, see 10.1188/14.ONF.350-359
- 3. An example of a mixed-methods study Lindsay-Smith et al (2018) investigated and explored the impact on elderly people's social wellbeing when they were members of a community that provided multi-activities. The study combined a quantitative survey that recorded participants' sociodemographic characteristics and measured participation in activities with a focus group study to gauge participants' perceptions of the benefits of taking part in the activities. For full details, see https://bmcgeriatr.biomedcentral.com/track/pdf/10.1186/s12877-018-0913-1.pdf
Sometimes a study cannot meet its stated research aims by using solely a quantitative or a qualitative methodology, so a mixed-methods approach combining both quantitative and qualitative methods for the collection and analysis of data are used. Cresswell (2013) explains that, depending on the aim and purpose of the study, it is possible to collect either the quantitative data first and analyse these, followed by the qualitative data and their analysis. This is an explanatory/exploratory sequence. Or the qualitative data may be collected first and analysed, followed by the quantitative; an exploratory/explanatory process. Whichever approach is used, the cumulative data analyses have to be synthesised to give a clear picture of the overall findings ( Box 1 ).
The issue of bias
Bias is a negative feature of research because it relates to either an error in the conceptualisation of the study due to the researcher/s adopting a skewed or idiosyncratic perspective, or to errors in the data analysis. Bias will affect the validity and reliability of a study, so it is important that any bias is eliminated in quantitative studies, or minimised and accounted for in qualitative studies.
Scientific and ethical approval
It should be noted that, before any research study proceeds, the research proposal for that study must have been reviewed and agreed to by a scientific and ethics committee. The purpose of a scientific and ethics committee is to see that those recruited into a study are not harmed or damaged, and that the study will contribute to the advancement of knowledge. The committee pays particular attention to whether any bias might have been introduced to a study. The researchers will have detailed the reason why the study is required, the explicit aim/s and purpose of the study, the methodology of the study, and its subsequent design, including the chosen research methods for the collection of the data (sampling and study recruitment), and what method/s will be used for data analysis.
A literature review is undertaken and the established (published) international literature on the research topic is summarised to highlight what is already known on the topic and/or to show any topic gaps that have not yet been researched. The British Educational Research Association (BERA) (2018) also gives guidance for research proposals that are deemed to be educational evaluation studies, including ‘close-practice’ research studies. Any ethical issues such as how people will be recruited into the study, the gaining of informed voluntary consent, any conflict of interest between the researcher/s and the proposed research topic, and whether the research is being funded or financially supported by a particular source will also have been considered.
Critiquing a published research paper
It is important to remember that a published paper is not the research report. It is a sample of the research report. The research author/s are presenting their research findings as a succinct summary. Only a passing mention might be made that ethical approval and voluntary informed consent were obtained. However, readers can be assured that all publications in leading journals with a good reputation are subject to an external peer review process. Any concerns about a paper's content will have been ironed out prior to publication.
It will be apparent that there are several particular research designs. The Critical Skills Appraisal Programme (CASP) provides online information to help the interpretation of each type of study, and does this by providing questions to help the reader consider and critique the paper ( CASP, 2021 ).
General points for critiquing a paper include the following:
- The paper should be readable and have explicit statements on the purpose of the research, its chosen methodology and design
- Read the paper thoroughly to get a feel for what the paper is saying
- Consider what the researcher/s says about any ethical issues and how these have been handled
- Look at how the data were collected and analysed. Are the explanations for these aspects clear? In a quantitative study, are any graphs or charts easy to understand and is there supporting text to aid the interpretation of the data? In a qualitative study, are direct quotes from the research participants included, and do the researcher/s show how data collected from interviews and observations were coded into data categories and themes?
- In a mixed-method study, how are the quantitative and qualitative analyses synthesised?
- Do the conclusions seem to fit the handling of the data's analysis?
- An important test of validity is whether the study's title relates well to the content of the paper and, conversely, whether the content reflect a corresponding match to the study's title.
Finally, remember that the research study could have been conducted using a different methodological design provided the research aims would still have been met, but a critique of the paper relates to what has been published and not what otherwise might have been done.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Useful terms. Some of the qualitative approaches used in nursing research include grounded theory, phenomenology, ethnography, case study (can lend itself to mixed methods) and narrative analysis. The data collection methods used in qualitative research include in depth interviews, focus groups, observations and stories in the form of diaries ...
This essay critically appraises a research article, Using CASP (critical appraisal skills programme, 2006) and individual sections of Bellini & Rumrill: guidelines for critiquing research articles (Bellini &Rumrill, 1999). The title of this article is; 'Clinical handover in the trauma setting: A qualitative study of paramedics and trauma team ...
In this essay, the author will undertake a critical evaluation of an identified qualitative research study. The article will be reviewed using the Cormack (2000) framework for evaluation of primary research articles, and will draw on other published research on qualitative methodologies to evaluate the article and its importance for nursing knowledge and practice.
Qualitative Critique: Missed Nursing Care 5 Enhancement of Rigor. To enhance the validity of the data, it was analyzed by two different researchers independently of each other. A qualitative analysis software was also used, which should assist to eliminate opinions and influence of the researcher. From what the researcher describes in this
methods. Because of this and its subjective nature, qualitative research it is often regarded as more difficult to critique. Nevertheless, an evidenced-based profession such as nursing cannot accept research at face value, and nurses need to be able to determine the strengths and limitations of qualitative as well as quantitative research ...
In crit-ically appraising qualitative research, steps need to be taken to ensure its rigour, credibility and trustworthiness. (table 1). Some of the qualitative approaches used in nursing research include grounded theory, phenomenology, ethnography, case study (can lend itself to mixed methods) and narrative analysis.
Qualitative research in nursing is a fairly common practice because it helps to explore a particular phenomenon. These are not generalized data but results relating to a specific situation, transmitted not with the help of statistical data but through a description of processes and phenomena. ... This essay, "Critique of a Qualitative Research ...
Introduction. Developing and maintaining proficiency in critiquing research have become a core skill in today's evidence-based nursing. In addition, understanding, synthesising and critiquing research are fundamental parts of all nursing curricula at both pre- and post-registration levels (NMC, 2011).This paper presents a guide, which has potential utility in both practice and when undertaking ...
There are three main types of qualitative research which are commonly used in nursing: Ethnography, Grounded Theory and Pheno- menology. The philosophical approach of each of these methodologies differs and directs the research process from the conceptual phase through data collection, analysis and interpretation.
Qualitative evidence allows researchers to analyse human experience and provides useful exploratory insights into experiential matters and meaning, often explaining the 'how' and 'why'. As we have argued previously1, qualitative research has an important place within evidence-based healthcare, contributing to among other things policy on patient safety,2 prescribing,3 4 and ...
Baker, J. A., Canvin, K., & Berzins, K. (2019). The relationship between workforce characteristics and perception of quality of care in mental health: A qualitative study. International Journal of Nursing Studies, 100, 1-21. Web. This essay, "Qualitative Research Critique" is published exclusively on IvyPanda's free essay examples database.
Critiquing A Research Article Qualitative Nursing Essay. Info: 2024 words (8 pages) Nursing Essay Published: 11th Feb 2020. Tagged: research. The problem being researched in the article is significant in nursing since it identifies the process, stressors and adjustment strategies of a novice nurse transforming into an expert nurse.
Critique research articles mean careful and critical appraisal of strength and limitations of a piece of research, rather than hunting for and exposing mistake (Polt and Beck 2008). A critical review is an evaluation of an academic article or essay. It makes judgment, positive or negative, about the text using various criteria.
Using the framework, you can have a go at appraising a qualitative paper - we are going to look at the following article: Schellekens, M.P.J. et al (2016) 'A qualitative study on mindfulness-based stress reduction for breast cancer patients: how women experience participating with fellow patients', Support Care Cancer, 24(4), pp. 1813-1820. Step 1.
The Interview Methods Of Qualitative Research. Qualitative Research ; Qualitative research has been used for a long time, it is an effective way of gaining an insight to individual's experiences, opinions, behaviours, thoughts, feelings and how they see themselves or others.
APPRAISING THE RESEARCH EVIDENCE. Some aspects of appraising a research article are the same whether the study is quantitative, qualitative, or mixed methods (Dale, 2005, Gray and Grove, 2017).Caldwell, Henshaw, and Taylor (2011) described the development of a framework for critiquing health research, addressing both quantitative and qualitative research with one list of questions.
The interview guide was semi-structured, with open-ended questions to probe on points of interest (Morrow 2005), build participant rapport (Ravenek and Rudman 2013) and discover in-depth, rich ...
Critiquing a published healthcare research paper. Research is defined as a 'systematic inquiry using orderly disciplined methods to answer questions or to solve problems' ( Polit and Beck, 2017 :743). Research requires academic discipline coupled with specific research competencies so that an appropriate study is designed and conducted ...
Critiquing A Research Article Qualitative Nursing Essay. The problem being researched in the article is significant in nursing since it identifies the process, stressors and adjustment strategies of a novice nurse transforming into an expert nurse. This research could assist in developing new policies on institutional level to allow new ...
the researcher has made three assumptions: Adequate sleep is necessary for patients. Sleeping medications are not the most healthful type. of sleep enhancer. One of the roles of nurses is to try ...
The results wer e discussed appropriat ely- No misinterpretation. 11. Streng ths motioned are the true strengths. 12. Limitations are r eported do not aff ec t the applicability of the study-. 13 ...
Frameworks for critiquing research articles. Download electronic versions of tables 7.2 and 7.3 in the text to print off and help you when critiquing quantitative and qualitative research articles. Find out more, read a sample chapter, or order an inspection copy if you are a lecturer, from the.