How to Write a Discursive Essay: Tips to Succeed & Examples
So, you need to accomplish your discursive essay writing. The typical questions most students ask are: How do you write it? What is discursive essay?
Our specialists will write a custom essay specially for you!
A discursive essay is an academic paper that involves a discussion on a particular topic. It is usually assigned to college students. You may be required to write a paper wherein you have to do one of the following:
- argue for the issue or against it;
- present your points of view on both sides;
- provide your unprejudiced opinion on that matter.
Don’t panic!
Check out the tips from Custom-writing.org experts below. They will assist you in discursive writing and encourage you to examine essay examples. Moreover, in this article, you’ll also learn about different types of discursive essay, and its introduction, main body, and conclusion structure.
- ❓ What Is It?
- 🏁 Main Types

Introduction
- Basic Don’Ts
- ✏️ Frequent Questions
❓ What Is a Discursive Essay?
First of all, let’s figure out what the discursive essay is.
You may think it’s similar to the argumentative essay. Yes, but there’s a difference between them in the structure and purpose of these two types of assignments:
Just in 1 hour! We will write you a plagiarism-free paper in hardly more than 1 hour
We will take a detailed look at how to structure a discursive essay later, and now let’s find out what are the types of this assignment.
Keep reading!
🏁 Discursive Essay: Main Types
You have to think more critically and more in-depth when reviewing all viewpoints and aspects of discursive writing. Check these three main types of essay writing:
- Opinion Essay requires the author’s opinion on an issue which is stated in the introductory paragraph. It should be clearly presented and followed by reasons and supporting examples. Also, this essay paper should contain an opposing argument that comes before the conclusion. The writer must explain to readers why the mentioned argument is considered to be unconvincing. The writer’s opinion should be restated/summarized in the conclusion.
- For and Against Essay provides readers with a thorough debate on the topic with the help of opposing points of view. Each point should be discussed objectively and described in details. The introductory paragraph puts the issue under consideration. The main body of this essay paper should present examples, reasons, and arguments supported by justifications. The author’s own opinion with balanced reflections on the topic should be stated only in conclusion.
- Essay Suggesting Solution to a Problem discusses problems and finds the main solutions. The introduction paragraph explicitly declares a problem and analyses its causes and consequences. The main body of the essay should offer some suggestions for a possible solution to the problem and potential state consequences or expected results. In conclusion, author’s opinion should be distinctly summarized.
📑 How to Write a Discursive Essay
Well, it’s time to talk about the structure of a discursive essay. Like most of the assignments, a discursive paper starts with an introduction and ends with a conclusion:
The first question you may ask is how to start a discursive essay introduction. Simple!
Receive a plagiarism-free paper tailored to your instructions. Cut 20% off your first order!
- Give your readers a hook – something that would sound interesting to them.
- Provide a short explanation of the problem. You may use quotations, as well as rhetorical questions.
- Show your readers both sides of the arguments and sum up.
You may be wondering…
Is there something I should avoid in my discursive essay introduction?
Yes. No stereotypes and generalizations, please!
The next step under formal essay writing you should take is to compose the body.

There are a few points you should remember:
Get an originally-written paper according to your instructions!
- First and foremost: stay unprejudiced . Assess all of the aspects of an issue. Leave your feelings behind or for another essay type.
- Second: build your argumentation . If you have several arguments for your viewpoint—provide them in separate paragraphs. This will help you to keep your essay comprehensible and distinct. Don’t forget to submit supporting evidence.
- Third: write the body of an essay in an alternate manner. What does it mean? If your first paragraph supports the paper’s argument, then in the second paragraph you should write something in the opposite of it. Such a combination of supporting and opposite paragraphs will make your essay look apparent, and well researched. Besides, it will help you to remain neutral.
- Fourth: include topic sentences and evidence . Write a summary of the argument at the beginning of the paragraph. It will allow the reader to easier understand what the paragraph is about. Provide evidence to show that you’re not making the facts up.
Well, you’ve almost finished your writing. Now you should focus on the last section. Keep reading, and you will learn how to write a conclusion for a discursive essay.
- In the last section, you should summarize your article including the main points, specified in the body paragraphs.
- You may also logically express your opinion. Remember: it should resonate with your evidence stated in the body paragraphs.
- Don’t repeat findings, just summarize them.
Keep it short. Your conclusion length should not exceed one paragraph.
👍 Do’s and Don’ts
Do you want more discursive essay writing tips? Fine! Just check them below:
Basic Do’s of a Discursive Essay
- Write in formal, impersonal style.
- Introduce each point in a separate paragraph
- Use topic sentences for each paragraph
- Write well-developed paragraphs
- Give reasons and examples for each point
- Use sequencing
- Use linking words and phrases
- Make references to other sources and make sure that you follow proper citation style
- Identify used sources
Basic Don’Ts of a Discursive Essay
- Don’t use short forms, like I’ll, don’t, they’ve
- Don’t use informal/colloquial language, for example: old as the hills, ain’t, gonna, etc.
- Don’t use very emotional language, since it might make your discursive article look prejudiced
- Don’t use over-generalizations. Extending the features of some elements from a group more than it is reasonable will lead to generous and inaccurate conclusions.
- Don’t express your personal opinion too insistently
- Don’t refer to statistics without proper referencing (check our citation guides )
- Don’t use personal examples, leave it for a personal experience essay
Well, now you know what discursive essay means, what are its main types, and how to structure it.

Discursive Essay Topics
- Discussion of risk factors that impact human health.
- Discuss the necessity of understanding cultural heritage to provide efficient health care.
- Analyze different opinions on withdrawing patients’ treatment.
- Examine different views on the Civil War .
- Discuss what hostile emotional states are and how they impact human life.
- Discuss the meaning of metaphors used by Virgil in Aeneid .
- Describe different opinions on telehealth in nursing homes.
- The ethicality of stem cell technology.
- Explore the effectiveness of motivational interviewing .
- Discuss how people present themselves online .
- Discuss the reasons for Coca-Cola’s marketing success.
- Analyze the food safety issues and the ways to improve the situation.
- Examine the essential meaning of sleep for people’s physical and mental health.
- Explore various complications of working with groups .
- Discussion of the modern issues with virtue ethics .
- Describe different views on the definition of love .
- Give the for and against arguments considering food security technologies .
- Discuss how the concept of the American dream is presented in the film The Great Gatsby .
- Analyze the influence of family problems on children and suggest ways to improve the situation.
- Present the various points of view on the ethical concepts of Buddhism .
- Examine the attitudes towards the problem of homelessness and the suggested ways of its solution.
- Explore different opinions on the American revolution and its consequences.
- Discuss various policies and views around the globe on abortion .
- Discussion of the history of food foraging in different communities.
- Multiple thoughts on civility on the Internet .
- Analyze arguments on the effectiveness of hand sanitizers .
- Discuss the importance of visual aids in learning.
- Present and evaluate the theories of international development .
- Discuss how to prevent the spread of the West Nile Virus (WNV).
- Is embracing renewable energy sources beneficial for both environment and the global economy?
- Examine the correctness of the statement that the ideology of pleasure is the foundation of social activism .
- Discussion of the ethical dilemma of population control.
- Discuss the ethics of experimental studies .
- Analyze the topic of gun violence and gun control laws.
- Explore the reasons for opioid crises in the US.
- Give arguments for and against random drug testing .
- Discuss the problem of endangered species .
- Express your opinion on the necessity of parents to be included in children’s education .
- Present your attitude towards working in a bureaucratic organization .
- Discuss the issue of the nursing shortage and suggest a solution.
- Give different viewpoints on the definition of beauty .
- Analyze the problem of police misconduct .
- Discuss the description of violence of African people in literature .
- Examine the views on Gardner’s multiple intelligence theory .
- Describe the various opinions on mysticism and express your attitude towards it.
- Discuss the diverse standpoints on spirituality .
- Is nature protection an urgent problem?
- Analyze different ideas on physical privacy at work .
- Discussion on the Jewish heritage in nursing.
- Examine the views on the meaning of life .
Good luck with your discussions and discursive essays! Be sure to check out the articles on our blog for more academic wisdom. By the way, on the Custom-Writing website, you may find the best essay topics for your academic writing.
And don’t forget to share your opinion in the comments below.
You might also be interested in:
- Friendship Essay: Writing Guide & Topic Ideas about Friendship
- Teamwork Essay: Quick Guide on How to Write a Good Paper
- Compare and Contrast Essay Writing Tips and Examples
- Transportation Essay: Writing Tips and Brilliant Topics
✏️ Discursive Essay FAQ
There is no one definitely correct answer to this question. Like any other essay, the text should have a clear structure with an introduction, body, and conclusion. The most important thing is that the overall book needs to be cohesive, persuasive, and exciting to read.
An example of a step by step guide is:
1. Take a closer look at the topic, think about the points to cover.
2. Choose the most relevant points and compose the Body of the essay.
3. Add an appropriate Introduction and Conclusion.
To write a good conclusion, you need to have the rest of the essay finished. Does the body of your essay present well-structured points? Great, then see what you can conclude based on that. If possible, make a connection between the introduction and the conclusion.
To ensure that your essay has a perfect structure, start with creating an outline. Based on such a plan, you can present your points step by step. Your text should have a relevant introduction, several points in the main body (with examples), and a logical conclusion.
🔗 References
- Writing an Opinion Essay: Grace Fleming, ThoughtCo
- How to Write a Good Argumentative Essay: Easy Step-by-Step Guide: Master Class
- Ending the Essay: Conclusions: Harvard College Writing Center
- Academic Writing Style: University of Southern California
- Cite Your Sources: Library Guides at University of California, Santa Cruz
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to LinkedIn
- Share to email

How to write a narrative essay? To do that, you need to know what a narrative essay is. It is an academic text usually written as a story and containing all the usual elements of a story. Narrative essays are often personal, experiential, and creative. Still, they should be made...
![history discursive essay examples College Essay Writing 101—the Comprehensive Guide [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/student-girl-making-notes-in-a-copybook-with-a-pencil-e1565634333206-284x153.png)
So, you can’t wait to get into college and join a fraternity, sorority, or student union. Well, we have some incredibly useful tips and helpful information for college admission essay writing! Remember: getting into college takes more than money. And outstanding essays get you great college scholarships!
![history discursive essay examples Americanism Essay: Examples, Tips & Topics [2024 Update]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/american-flag-284x153.jpg)
It’s not hard to see why Americanism is one of the most popular essay topics. The concept of Americanism is in the center of the US identity. Writing an essay about it is an excellent way to find out more about this great country.

An art critique paper involves a comprehensive analysis and assessment of an artwork. Though this looks a bit complicated, the task doesn’t require a lot of time if you have sufficient critique writing skills. It’s an interesting assignment for students of art colleges as well as high schoolers. All you...

An article review is an academic assignment that invites you to study a piece of academic research closely. Then, you should present its summary and critically evaluate it using the knowledge you’ve gained in class and during your independent study. If you get such a task at college or university,...

Short essays answer a specific question on the subject. They usually are anywhere between 250 words and 750 words long. A paper with less than 250 words isn’t considered a finished text, so it doesn’t fall under the category of a short essay. Essays of such format are required for...

When you hear the phrase “spiritual leadership,” you probably think it’s only associated with religion. But did you know that this form of leadership can also be found in business? The book Spiritual Leadership: Moving People on to God’s Agenda by Henry and Richard Blackaby is a good starting point...

High school and college students often face challenges when crafting a compare-and-contrast essay. A well-written paper of this kind needs to be structured appropriately to earn you good grades. Knowing how to organize your ideas allows you to present your ideas in a coherent and logical manner This article by...

“If a tree falls in the forest, does it make a sound?” is one of the most debatable philosophical questions regarding observation and perception. Many tried to answer it, including the English philosopher John Locke. Do you need to explore Locke’s perspective on this question in your essay? You are on the right...

The long-standing debate surrounding abortion has many opponents and advocates. Groups known as Pro-Choice and Pro-Life argue which approach is better, with no easy solution in sight. This ethical complexity is what makes abortion a popular topic for argumentative writing. As a student, you need to tackle it appropriately. If...

What is the most important part of any essay or research paper? Of course, it’s the thesis statement—a sentence that expresses the paper’s main idea and guides the readers through your arguments. But where do you place the thesis? You’ve probably answered, “in the introduction.” However, that’s not all of...

If you’re a student, you’ve heard about a formal essay: a factual, research-based paper written in 3rd person. Most students have to produce dozens of them during their educational career. Writing a formal essay may not be the easiest task. But fear not: our custom-writing team is here to guide...
It’s very helpful!

Glad to hear that! Thank you for your feedback!
it’s a good site to learn from. However, it will be perfect if there is a small essay to clear the mess understanding from the advice
This was so helpful , thank you God bless you
Thanks for the feedback! Your opinion is very important for us!
Very good site,thank so much for your effort in writing the posts.
Thank you, Tameka!
thank you my n word 👨🏿🦳
thank you so much!!!! is there any way to access an annotated example to help?
Thank you so much. That really helped me with writing my essay.
thanku so much for increasing my knowledge
Thanks for the feedback, Malik! Much appreciated.
Thank you. It was really helpful. It has answered all my questions.
Thank you for your feedback, Martha. It means a lot for us!

26 Planning a Discursive Essay
Discursive essay – description.
A discursive essay is a form of critical essay that attempts to provide the reader with a balanced argument on a topic, supported by evidence. It requires critical thinking, as well as sound and valid arguments (see Chapter 25) that acknowledge and analyse arguments both for and against any given topic, plus discursive essay writing appeals to reason, not emotions or opinions. While it may draw some tentative conclusions, based on evidence, the main aim of a discursive essay is to inform the reader of the key arguments and allow them to arrive at their own conclusion.
The writer needs to research the topic thoroughly to present more than one perspective and should check their own biases and assumptions through critical reflection (see Chapter 30).
Unlike persuasive writing, the writer does not need to have knowledge of the audience, though should write using academic tone and language (see Chapter 20).
Choose Your Topic Carefully
A basic guide to choosing an assignment topic is available in Chapter 23, however choosing a topic for a discursive essay means considering more than one perspective. Not only do you need to find information about the topic via academic sources, you need to be able to construct a worthwhile discussion, moving from idea to idea. Therefore, more forward planning is required. The following are decisions that need to be considered when choosing a discursive essay topic:
- These will become the controlling ideas for your three body paragraphs (some essays may require more). Each controlling idea will need arguments both for and against.
- For example, if my topic is “renewable energy” and my three main (controlling) ideas are “cost”, “storage”, “environmental impact”, then I will need to consider arguments both for and against each of these three concepts. I will also need to have good academic sources with examples or evidence to support my claim and counter claim for each controlling idea (More about this in Chapter 27).
- Am I able to write a thesis statement about this topic based on the available research? In other words, do my own ideas align with the available research, or am I going to be struggling to support my own ideas due to a lack of academic sources or research? You need to be smart about your topic choice. Do not make it harder than it has to be. Writing a discursive essay is challenging enough without struggling to find appropriate sources.
- For example, perhaps I find a great academic journal article about the uptake of solar panel installation in suburban Australia and how this household decision is cost-effective long-term, locally stored, and has minimal, even beneficial environmental impact due to the lowering of carbon emissions. Seems too good to be true, yet it is perfect for my assignment. I would have to then find arguments AGAINST everything in the article that supports transitioning suburbs to solar power. I would have to challenge the cost-effectiveness, the storage, and the environmental impact study. Now, all of a sudden my task just became much more challenging.
- There may be vast numbers of journal articles written about your topic, but consider how relevant they may be to your tentative thesis statement. It takes a great deal of time to search for appropriate academic sources. Do you have a good internet connection at home or will you need to spend some quality time at the library? Setting time aside to complete your essay research is crucial for success.
It is only through complete forward planning about the shape and content of your essay that you may be able to choose the topic that best suits your interests, academic ability and time management. Consider how you will approach the overall project, not only the next step.
Research Your Topic
When completing a library search for online peer reviewed journal articles, do not forget to use Boolean Operators to refine or narrow your search field. Standard Boolean Operators are (capitalized) AND, OR and NOT. While using OR will expand your search, AND and NOT will reduce the scope of your search. For example, if I want information on ageism and care giving, but I only want it to relate to the elderly, I might use the following to search a database: ageism AND care NOT children. Remember to keep track of your search strings (like the one just used) and then you’ll know what worked and what didn’t as you come and go from your academic research.
The UQ Library provides an excellent step-by-step guide to searching databases:
Searching in databases – Library – University of Queensland (uq.edu.au)
Did you know that you can also link the UQ Library to Google Scholar? This link tells you how:
Google Scholar – Library – University of Queensland (uq.edu.au)
Write the Thesis Statement
The concept of a thesis statement was introduced in Chapter 21. The information below relates specifically to a discursive essay thesis statement.
As noted in the introduction to this chapter, the discursive essay should not take a stance and therefore the thesis statement must also impartially indicate more than one perspective. The goal is to present both sides of an argument equally and allow the reader to make an informed and well-reasoned choice after providing supporting evidence for each side of the argument.
Sample thesis statements: Solar energy is a cost -effective solution to burning fossil fuels for electricity , however lower income families cannot afford the installation costs .
Some studies indicate that teacher comments written in red may have no effect on students’ emotions , however other studies suggest that seeing red ink on papers could cause some students unnecessary stress. [1]
According to social justice principles, education should be available to all , yet historically, the intellectually and physically impaired may have been exempt from participation due to their supposed inability to learn. [2]
This is where your pros and cons list comes into play. For each pro, or positive statement you make, about your topic, create an equivalent con, or negative statement and this will enable you to arrive at two opposing assertions – the claim and counter claim.
While there may be multiple arguments or perspectives related to your essay topic, it is important that you match each claim with a counter-claim. This applies to the thesis statement and each supporting argument within the body paragraphs of the essay.
It is not just a matter of agreeing or disagreeing. A neutral tone is crucial. Do not include positive or negative leading statements, such as “It is undeniable that…” or “One should not accept the view that…”. You are NOT attempting to persuade the reader to choose one viewpoint over another.
Leading statements / language will be discussed further, in class, within term three of the Academic English course.
Thesis Structure:
- Note the two sides (indicated in green and orange)
- Note the use of tentative language: “Some studies”, “may have”, “could cause”, “some students”
- As the thesis is yet to be discussed in-depth, and you are not an expert in the field, do not use definitive language
- The statement is also one sentence, with a “pivot point” in the middle, with a comma and signposting to indicate a contradictory perspective (in black). Other examples include, nevertheless, though, although, regardless, yet, albeit. DO NOT use the word “but” as it lacks academic tone. Some signposts (e.g., although, though, while) may be placed at the start of the two clauses rather than in the middle – just remember the comma, for example, “While some studies suggest solar energy is cost-effective, other critical research questions its affordability.”
- Also note that it is based on preliminary research and not opinion: “some studies”, “other studies”, “according to social justice principles”, “critical research”.
Claims and Counter Claims
NOTE: Please do not confuse the words ‘claim’ and ‘counter-claim’ with moral or value judgements about right/wrong, good/bad, successful/unsuccessful, or the like. The term ‘claim’ simply refers to the first position or argument you put forward (whether for or against), and ‘counter-claim’ is the alternate position or argument.
In a discursive essay the goal is to present both sides equally and then draw some tentative conclusions based on the evidence presented.
- To formulate your claims and counter claims, write a list of pros and cons.
- For each pro there should be a corresponding con.
- Three sets of pros and cons will be required for your discursive essay. One set for each body paragraph. These become your claims and counter claims.
- For a longer essay, you would need further claims and counter claims.
- Some instructors prefer students to keep the pros and cons in the same order across the body paragraphs. Each paragraph would then have a pro followed by a con or else a con followed by a pro. The order should align with your thesis; if the thesis gives a pro view of the topic followed by a negative view (con) then the paragraphs should also start with the pro and follow with the con, or else vice versa. If not aligned and consistent, the reader may easily become confused as the argument proceeds. Ask your teacher if this is a requirement for your assessment.

Use previous chapters to explore your chosen topic through concept mapping (Chapter 18) and essay outlining (Chapter 19), with one variance; you must include your proposed claims and counter claims in your proposed paragraph structures. What follows is a generic model for a discursive essay. The following Chapter 27 will examine this in further details.
Sample Discursive Essay Outline
The paragraphs are continuous; the dot-points are only meant to indicate content.
Introduction
- Thesis statement
- Essay outline (including 3 controlling ideas)
Body Paragraphs X 3 (Elaboration and evidence will be more than one sentence, though the topic, claim and counter claim should be succinct)
- T opic sentence, including 1/3 controlling ideas (the topic remains the same throughout the entire essay; it is the controlling idea that changes)
- A claim/assertion about the controlling idea
- E laboration – more information about the claim
- E vidence -academic research (Don’t forget to tell the reader how / why the evidence supports the claim. Be explicit in your E valuation rather than assuming the connection is obvious to the reader)
- A counter claim (remember it must be COUNTER to the claim you made, not about something different)
- E laboration – more information about the counter claim
- E vidence – academic research (Don’t forget to tell the reader how / why the evidence supports the claim. Be explicit in your E valuation rather than assuming the connection is obvious to the reader)
- Concluding sentence – L inks back to the topic and/or the next controlling idea in the following paragraph
Mirror the introduction. The essay outline should have stated the plan for the essay – “This essay will discuss…”, therefore the conclusion should identify that this has been fulfilled, “This essay has discussed…”, plus summarise the controlling ideas and key arguments. ONLY draw tentative conclusions BOTH for and against, allowing the reader to make up their own mind about the topic. Also remember to re-state the thesis in the conclusion. If it is part of the marking criteria, you should also include a recommendation or prediction about the future use or cost/benefit of the chosen topic/concept.
A word of warning, many students fall into the generic realm of stating that there should be further research on their topic or in the field of study. This is a gross statement of the obvious as all academia is ongoing. Try to be more practical with your recommendations and also think about who would instigate them and where the funding might come from.
This chapter gives an overview of what a discursive essay is and a few things to consider when choosing your topic. It also provides a generic outline for a discursive essay structure. The following chapter examines the structure in further detail.
- Inez, S. M. (2018, September 10). What is a discursive essay, and how do you write a good one? Kibin. ↵
- Hale, A., & Basides, H. (2013). The keys to academic English. Palgrave ↵
researched, reliable, written by academics and published by reputable publishers; often, but not always peer reviewed
assertion, maintain as fact
The term ‘claim’ simply refers to the first position or argument you put forward (whether for or against), and ‘counter-claim’ is the alternate position or argument.
Academic Writing Skills Copyright © 2021 by Patricia Williamson is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
How to Write a Discursive Essay: Awesome Guide and Template

Interesting fact: Did you know that the term "discursive" is derived from the Latin word "discursus," which means to run about or to traverse? This reflects the nature of a discursive essay, as it involves exploring various perspectives, moving through different points of view, and presenting a comprehensive discussion on a given topic.
In this article, you will find out about a discursive essay definition, learn the difference between a discourse and an argumentative essay, gain practical how-to tips, and check out a discursive essay example.
What Is a Discursive Essay
A discursive essay definition is a type of formal writing that presents a balanced analysis of a particular topic. Unlike an argumentative essay, which takes a firm stance on a single perspective and seeks to persuade the reader to adopt that viewpoint, a discursive essay explores multiple sides of an issue.
The goal of a discursive essay is to provide a comprehensive overview of the subject, presenting different arguments, counterarguments, and perspectives in a structured and organized manner.
This type of essay encourages critical thinking and reasoned discourse. It typically includes an introduction that outlines the topic and sets the stage for the discussion, followed by a series of body paragraphs that delve into various aspects of the issue. The essay may also address counterarguments and opposing viewpoints.
Finally, a discursive essay concludes by summarizing the key points and often leaves room for the reader to form their own informed opinion on the matter. This form of writing is commonly assigned in academic settings, allowing students to demonstrate their ability to analyze complex topics and present a well-reasoned exploration of diverse viewpoints. In case you find this type of composition too difficult, just say, ‘ write my paper ,’ and professional writers will take care of it.
Ready to Transform Your Essays?
From discursive writing to academic triumphs, let your words soar with our essay writing service!
Difference Between a Discursive Essay and an Argumentative
The main difference between discursive essays and argumentative lies in their overall purpose and approach to presenting information.
- Discursive: The primary purpose of a discursive essay is to explore and discuss various perspectives on a given topic. How to write a discursive essay is about providing a comprehensive overview of the subject matter by presenting different arguments, opinions, and viewpoints without necessarily advocating for a specific stance.
- Argumentative: In contrast, an argumentative essay is designed to persuade the reader to adopt a particular viewpoint or take a specific action. It presents a clear and focused argument in favor of the writer's position, often addressing and refuting opposing views.
Tone and Language:
- Discursive: The tone of a discursive essay is generally more balanced and objective. It allows for a more open exploration of ideas, and the language used is often neutral and formal.
- Argumentative: An argumentative essay tends to have a more assertive tone. The language is focused on presenting a compelling case from the writer's perspective, and there may be a sense of conviction in the presentation of evidence and reasoning.
- Discursive Essay: A discursive essay typically follows a more flexible structure. It may present multiple points of view in separate sections, allowing for a free-flowing exploration of the topic.
- Argumentative Essay: When learning how to write an argumentative essay, students usually follow a more rigid structure, with a clear introduction, thesis statement, body paragraphs that present evidence and arguments, and a conclusion that reinforces the writer's stance.
Conclusion:
- Discursive Essay: The conclusion of a discursive essay often summarizes the main points discussed and may leave room for the reader to form their own opinion on the matter.
- Argumentative Essay: The conclusion of an argumentative essay reinforces the writer's position and may include a call to action or a clear statement of the desired outcome.
While both types of essays involve critical thinking and analysis, the key distinction lies in their ultimate goals and how they approach the presentation of information.
Types of Discursive Essay
Before writing a discursive essay, keep in mind that they can be categorized into different types based on their specific purposes and structures. Here are some common types of discursive essays:
.webp)
Opinion Essays:
- Purpose: Expressing and supporting personal opinions on a given topic.
- Structure: The essay presents the writer's viewpoint and provides supporting evidence, examples, and arguments. It may also address counterarguments to strengthen the overall discussion.
Problem-Solution Essays:
- Purpose: Identifying a specific problem and proposing effective solutions.
- Structure: The essay introduces the problem, discusses its causes and effects, and presents possible solutions. It often concludes with a recommendation or call to action.
Compare and Contrast Essays:
- Purpose: Analyzing similarities and differences between two or more perspectives, ideas, or approaches.
- Structure: The essay outlines the key points of each perspective, highlighting similarities and differences. A balanced analysis is provided to give the reader a comprehensive understanding.
Cause and Effect Essays:
- Purpose: Exploring the causes and effects of a particular phenomenon or issue.
- Structure: The essay identifies the primary causes and examines their effects or vice versa. It may delve into the chain of events and their implications.
Argumentative Essays:
- Purpose: Presenting a strong argument in favor of a specific viewpoint.
- Structure: The essay establishes a clear thesis statement, provides evidence and reasoning to support the argument, and addresses opposing views. It aims to persuade the reader to adopt the writer's perspective.
Pro-Con Essays:
- Purpose: Evaluating the pros and cons of a given issue.
- Structure: The essay presents the positive aspects (pros) and negative aspects (cons) of the topic. It aims to provide a balanced assessment and may conclude with a recommendation or a summary of the most compelling points.
Exploratory Essays:
- Purpose: Investigating and discussing a topic without necessarily advocating for a specific position.
- Structure: The essay explores various aspects of the topic, presenting different perspectives and allowing the reader to form their own conclusions. It often reflects a process of inquiry and discovery.
These types of discursive essays offer different approaches to presenting information, and the choice of type depends on the specific goals of the essay and the preferences of the writer.
How to Write a Discursive Essay
Unlike other forms of essay writing, a discursive essay demands a unique set of skills, inviting writers to navigate through diverse perspectives, present contrasting viewpoints, and weave a tapestry of balanced arguments.
You can order custom essay right now to save time to get ready to delve into the art of crafting a compelling discursive essay, unraveling the intricacies of structure, language, and critical analysis. Whether you're a seasoned essayist or a novice in the realm of formal writing, this exploration promises to equip you with the tools needed to articulate your thoughts effectively and engage your audience in thoughtful discourse.
.webp)
Discursive Essay Format
The format of a discursive essay plays a crucial role in ensuring a clear, well-organized, and persuasive presentation of multiple perspectives on a given topic. Here is a typical discursive essay structure:
1. Introduction:
- Hook: Begin with a captivating hook or attention-grabbing statement to engage the reader's interest.
- Contextualization: Provide a brief overview of the topic and its relevance, setting the stage for the discussion.
- Thesis Statement: Clearly state the main argument or the purpose of the essay. In a discursive essay, the thesis often reflects the idea that the essay will explore multiple viewpoints without necessarily taking a firm stance.
2. Body Paragraphs:
- Topic Sentences: Start each body paragraph with a clear topic sentence that introduces the main point or argument.
- Presentation of Arguments: Devote individual paragraphs to different aspects of the topic, presenting various arguments, perspectives, or evidence. Ensure a logical flow between paragraphs.
- Address Counterarguments: Acknowledge and address opposing viewpoints to strengthen the overall credibility of your essay.
- Supporting Evidence: Provide examples, statistics, quotations, or other forms of evidence to bolster each argument.
3. Transitions:
- Logical Transitions: Use transitional phrases and words to ensure a smooth and logical flow between paragraphs and ideas. This helps readers follow your line of reasoning.
4. Conclusion:
- Restate Thesis: Summarize the main argument or purpose of the essay without introducing new information.
- Brief Recap: Provide a concise recap of the key points discussed in the body paragraphs.
- Closing Thoughts: Offer some closing thoughts or reflections on the significance of the topic. You may also leave room for the reader to consider their own stance.
5. Language and Style:
- Formal Tone: Maintain a formal and objective tone throughout the essay.
- Clarity and Coherence: Ensure that your ideas are presented clearly and that there is coherence in your argumentation.
- Varied Sentence Structure: Use a variety of sentence structures to enhance readability and engagement.
6. References (if applicable):
- Citations: If you use external sources, cite them appropriately according to the citation style required (e.g., APA, MLA).
Remember, flexibility exists within this format, and the specifics may vary based on the assignment requirements or personal writing preferences. Tailor the structure to suit the demands of your discourse and the expectations of your audience.
Introduction
A discursive essay introduction serves as the gateway to a thought-provoking exploration of diverse perspectives on a given topic. Here's how to structure an effective discursive essay introduction:
- Begin with a compelling hook that captures the reader's attention. This could be a striking statistic, a thought-provoking quote, a relevant anecdote, or a rhetorical question.
- Offer a brief context or background information about the topic. This helps orient the reader and sets the stage for the discussion to follow.
- Clearly state the purpose of the essay. This often involves indicating that the essay will explore various perspectives on the topic without necessarily advocating for a specific stance.
- Provide a brief overview of the different aspects or arguments that will be explored in the essay.
- Conclude the introduction with a clear and concise thesis statement.
Remember that besides writing compositions, you still have to do math homework , which is something we can help you with right now!
Writing a discursive essay involves crafting the body of your discursive essay. The number of paragraphs in the body should correspond to the arguments presented, with an additional paragraph dedicated to the opposing viewpoint if you choose to disclose both sides of the argument. If you opt for this approach, alternate the order of the body paragraphs—supporting arguments followed by counterarguments.
Each body paragraph in your discursive essay should focus on a distinct idea. Begin the paragraph with the main idea, provide a concise summary of the argument, and incorporate supporting evidence from reputable sources.
In the concluding paragraph of the body, present potential opposing arguments and counter them. Approach this section as if engaging in a debate, strategically dismantling opposing viewpoints.
While composing the body of a discursive essay, maintain a cohesive narrative. Although individual paragraphs address different arguments, refrain from titling each paragraph—aim for a seamless flow throughout the essay. Express your personal opinions exclusively in the conclusion.
Key guidelines for writing the body of a discursive essay:
- Remain Unbiased: Prioritize objectivity. Evaluate all facets of the issue, leaving personal sentiments aside.
- Build Your Argumentation: If you have multiple arguments supporting your viewpoint, present them in separate, well-structured paragraphs. Provide supporting evidence to enhance clarity and credibility.
- Use an Alternate Writing Style: Present opposing viewpoints in an alternating manner. This means that if the first paragraph supports the main argument, the second should present an opposing perspective. This method enhances clarity and research depth and ensures neutrality.
- Include Topic Sentences and Evidence: Commence each paragraph with a topic sentence summarizing the argument. This aids reader comprehension. Substantiate your claims with evidence, reinforcing the credibility of your discourse.
By adhering to these principles, you can construct a coherent and well-supported body for your discursive essay.
Conclusion
Writing an effective conclusion is crucial to leaving a lasting impression on your reader. Here are some tips to guide you in crafting a compelling and impactful conclusion:
- Begin your conclusion by summarizing the key points discussed in the body of the essay.
- Remind the reader of your thesis statement, emphasizing the primary purpose of your discursive essay.
- Address the broader significance or implications of the topic.
- Explain why the issue is relevant and underscore the importance of considering multiple perspectives in understanding its complexity.
- Reiterate the balanced nature of your essay. Emphasize that you have explored various viewpoints and arguments without necessarily taking a firm stance.
- Reinforce the idea that your goal was to present a comprehensive analysis.
- If applicable, suggest possible recommendations or solutions based on the insights gained from the essay.
- Encourage the reader to reflect on the topic independently.
- Pose open-ended questions or invite them to consider the implications of the arguments presented.
- Resist the temptation to introduce new information or arguments in the conclusion.
- Keep the tone of your conclusion professional and thoughtful.
- Conclude your essay with a strong, memorable closing statement.
- Carefully review your conclusion to ensure clarity and coherence. Edit for grammar, punctuation, and overall writing quality to present a polished final product.
By incorporating these tips into your discursive essay conclusion, you can effectively summarize your arguments, leave a lasting impression, and prompt thoughtful reflection from your readers. Consider using our term paper writing service if you have to deal with a larger assignment that requires more time and effort.
Yays and Nays of Writing Discourse Essays
In learning how to write a discursive essay, certain do's and don'ts serve as guiding principles throughout the writing process. By adhering to these guidelines, writers can navigate the complexities of presenting arguments, counterarguments, and nuanced analyses, ensuring the essay resonates with clarity and persuasiveness.
- Conduct thorough research on the topic to ensure a well-informed discussion.
- Present multiple perspectives on the issue, exploring various arguments and viewpoints.
- Maintain a balanced and neutral tone. Present arguments objectively without expressing personal bias.
- Structure your essay logically with a clear introduction, body, and conclusion. Use paragraphs to organize your ideas effectively.
- Topic Sentences:
- Include clear topic sentences at the beginning of each paragraph to guide the reader through your arguments.
- Support your arguments with credible evidence from reputable sources to enhance the credibility of your essay.
- Use transitional words and phrases to ensure a smooth flow between paragraphs and ideas.
- Engage in critical analysis. Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of different arguments and viewpoints.
- Recap key points in the conclusion, summarizing the main arguments and perspectives discussed in the essay.
- Carefully proofread your essay to correct any grammar, spelling, or punctuation errors.
- Don't express personal opinions in the body of the essay. Save personal commentary for the conclusion.
- Don't introduce new information or arguments in the conclusion. This section should summarize and reflect on existing content.
- Don't use overly emotional or subjective language. Maintain a professional and objective tone throughout.
- Don't rely on personal opinions without sufficient research. Ensure that your arguments are supported by credible evidence.
- Don't have an ambiguous or unclear thesis statement. Clearly state the purpose of your essay in the introduction.
- Don't ignore counterarguments. Acknowledge and address opposing viewpoints to strengthen your overall argument.
- Don't use overly complex language if it doesn't add to the clarity of your arguments. Strive for clarity and simplicity in your writing.
- Don't present ideas in a disorganized manner. Ensure that there is a logical flow between paragraphs and ideas.
- Don't excessively repeat the same points. Present a variety of arguments and perspectives to keep the essay engaging.
- Don't ignore the guidelines provided for the essay assignment. Follow any specific instructions or requirements given by your instructor or institution.
Feeling exhausted and overwhelmed with all this new information? Don't worry! Buy an essay paper of any type that will be prepared for you individually based on all your instructions.
Discursive Essay Examples
Discursive essay topics.
Writing a discursive essay on a compelling topic holds immense importance as it allows individuals to engage in a nuanced exploration of diverse perspectives. A well-chosen subject encourages critical thinking and deepens one's understanding of complex issues, fostering intellectual growth.
The process of exploring a good topic enhances research skills as writers delve into varied viewpoints and gather evidence to support their arguments. Moreover, such essays contribute to the broader academic discourse, encouraging readers to contemplate different facets of a subject and form informed opinions.
- The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Employment.
- Should Social Media Platforms Regulate Content for Misinformation?
- Exploring the Ethics of Cloning in Contemporary Science.
- Universal Basic Income: A Solution for Economic Inequality?
- The Role of Technology in Shaping Modern Education.
- Nuclear Energy: Sustainable Solution or Environmental Risk?
- The Effects of Video Games on Adolescent Behavior.
- Cybersecurity Threats in the Digital Age: Balancing Privacy and Security.
- Debunking Common Myths Surrounding Climate Change.
- The Pros and Cons of Genetically Modified Organisms (GMOs).
- Online Education vs. Traditional Classroom Learning.
- The Impact of Social Media Influencers on Consumer Behavior.
- The Ethics of Animal Testing in Medical Research.
- Universal Healthcare: Addressing Gaps in Healthcare Systems.
- The Role of Government in Regulating Cryptocurrencies.
- The Influence of Advertising on Body Image and Self-Esteem.
- Renewable Energy Sources: A Viable Alternative to Fossil Fuels?
- The Implications of Space Exploration on Earth's Resources.
- Is Censorship Justified in the Arts and Entertainment Industry?
- Examining the Impact of Globalization on Cultural Identity.
- The Morality of Capital Punishment in the 21st Century.
- Should Genetic Engineering be Used for Human Enhancement?
- Social Media and Its Influence on Political Discourse.
- Balancing Environmental Conservation with Economic Development.
- The Role of Gender in the Workplace: Achieving Equality.
- Exploring the Impact of Fast Fashion on the Environment.
- The Benefits and Risks of Autonomous Vehicles.
- The Influence of Media on Perceptions of Beauty.
- Legalization of Marijuana: Addressing Medical and Social Implications.
- The Impact of Antibiotic Resistance on Global Health.
- The Pros and Cons of a Cashless Society.
- Exploring the Relationship Between Technology and Mental Health.
- The Role of Government Surveillance in Ensuring National Security.
- Addressing the Digital Divide: Ensuring Access to Technology for All.
- The Impact of Social Media on Political Activism.
- The Ethics of Animal Rights and Welfare.
- Nuclear Disarmament: Necessity or Utopian Ideal?
- The Effects of Income Inequality on Societal Well-being.
- The Role of Education in Combating Systemic Racism.
- The Influence of Pop Culture on Society's Values and Norms.
- Artificial Intelligence and Its Impact on Creative Industries.
- The Pros and Cons of Mandatory Vaccination Policies.
- The Role of Women in Leadership Positions: Breaking the Glass Ceiling.
- Internet Privacy: Balancing Personal Security and Data Collection.
- The Impact of Social Media on Youth Mental Health.
- The Morality of Animal Agriculture and Factory Farming.
- The Rise of Online Learning Platforms: Transforming Education.
- Addressing the Digital Gender Gap in STEM Fields.
- The Impact of Global Tourism on Local Cultures and Environments.
- Exploring the Implications of 3D Printing Technology in Various Industries.
By the way, we have another great collection of narrative essay topics to get your creative juices flowing.
Wrapping Up
Throughout this guide, you have acquired valuable insights into the art of crafting compelling arguments and presenting diverse perspectives. By delving into the nuances of topic selection, structuring, and incorporating evidence, you could hone your critical thinking skills and sharpen your ability to engage in informed discourse.
This guide serves as a roadmap, offering not just a set of rules but a toolkit to empower students in their academic journey. As you embark on future writing endeavors, armed with the knowledge gained here, you can confidently navigate the challenges of constructing well-reasoned, balanced discursive essays that contribute meaningfully to academic discourse and foster a deeper understanding of complex issues. If you want to continue your academic learning journey right now, we suggest that you read about the IEEE format next.
Overwhelmed by Essays?
Let professional writers be your writing wingman. No stress - just success!
Related Articles
.webp)
- Buy Custom Assignment
- Custom College Papers
- Buy Dissertation
- Buy Research Papers
- Buy Custom Term Papers
- Cheap Custom Term Papers
- Custom Courseworks
- Custom Thesis Papers
- Custom Expository Essays
- Custom Plagiarism Check
- Cheap Custom Essay
- Custom Argumentative Essays
- Custom Case Study
- Custom Annotated Bibliography
- Custom Book Report
- How It Works
- +1 (888) 398 0091
- Essay Samples
- Essay Topics
- Research Topics
- Uncategorized
- Writing Tips
How to Write a Discursive Essay
November 17, 2023
A discursive essay is a type of academic writing that presents both sides of an argument or issue. Unlike an argumentative essay where you take a clear stance and defend it, a discursive essay allows you to explore different perspectives and provide an objective analysis. It requires careful research, critical thinking, and the ability to present logical arguments in a structured manner.
In a discursive essay, you are expected to examine the topic thoroughly, present evidence and examples to support your points, and address counterarguments to demonstrate a balanced understanding of the issue. The purpose is not to persuade the reader to take a particular side, but rather to present a comprehensive view of the topic. By mastering the art of writing a discursive essay, you can effectively convey complex ideas and contribute to meaningful discussions on various subjects.
What’s different about writing a discursive essay
Writing a discursive essay differs from other types of essays in several ways. Here are some key differences to consider when approaching this particular form of academic writing:
- Explores multiple perspectives: Unlike an argumentative essay, a discursive essay examines different viewpoints on a given topic. It requires you to gather information, analyze various arguments, and present a balanced view.
- Structured presentation: A discursive essay follows a clear structure that helps organize your thoughts and arguments. It typically consists of an introduction, several body paragraphs discussing different arguments, and a conclusion.
- Impartiality and objectivity: While other essays may require you to take a stance or defend a particular position, a discursive essay aims for objectivity. You should present arguments and evidence without bias and demonstrate a fair understanding of each viewpoint.
- Importance of research: Good research is essential for a discursive essay. You should gather information from reliable sources, consider various perspectives, and present evidence to support your ideas.
- Addressing counterarguments: In a discursive essay, it is crucial to acknowledge and address counterarguments. By doing so, you show a comprehensive understanding of the topic and strengthen your own argument.
- Use of transitions: To maintain coherence and provide a smooth flow of ideas, appropriate transitions should be used to link paragraphs and signal shifts between arguments.
By recognizing these key differences and adapting your writing style accordingly, you can effectively write a discursive essay that engages the reader and presents a well-rounded discussion of the topic.
Step-by-Step Discursive Essay Writing Guide
Selecting a topic.
Selecting a topic for a discursive essay is a crucial first step in the writing process. Here are some considerations to help you choose an appropriate and engaging topic:
- Relevance: Select a topic that is relevant and holds significance in the current context. It should be something that sparks interest and discussion among readers.
- Controversy: Look for topics that have multiple perspectives and controversial viewpoints. This will allow you to explore different arguments and present a balanced analysis.
- Research opportunities: Choose a topic that offers ample research opportunities. This ensures that you have access to reliable sources and enough material to support your arguments.
- Personal interest: It is easier to write about a topic that you are genuinely interested in. Consider your own passion and areas of expertise when selecting a subject for your essay.
- Scope and depth: Ensure that the chosen topic is neither too broad nor too narrow. It should provide enough scope for thorough analysis and discussion within the word limit of your essay.
Remember, the topic sets the foundation for your discursive essay. Take time to consider these factors and select a topic that aligns with your interests, research capabilities, and the potential to present a well-rounded discussion.
Possible Discursive Essay Topics:
- The impact of social media on society.
- Should euthanasia be legalized?
- Pros and cons of genetically modified organisms (GMOs).
- The influence of technology on human interactions.
- Is homeschooling more beneficial than traditional schooling?
- The effects of climate change on the environment.
- Should animal testing be banned?
- The advantages and disadvantages of globalization.
- The ethics of capital punishment.
- The legalization of marijuana: pros and cons.
Write the Thesis Statement
The thesis statement in a discursive essay serves as the central argument or main claim that sets the tone for the entire essay. It typically appears in the introductory paragraph and guides the reader’s understanding of the essay’s purpose and direction. Here are some key points to consider when crafting an effective thesis statement for a discursive essay:
- Clear stance: The thesis statement should clearly express your position or viewpoint on the topic. It should present a concise statement that reflects your overall argument or analysis.
- Controversy: The thesis statement should highlight the controversy or debate surrounding the topic. It should indicate that there are multiple perspectives to be explored and that you will discuss them in a balanced manner.
- Specificity: The thesis statement should not be too vague or general. It should address a specific aspect of the topic that you will focus on in your essay.
- Clarity: The thesis statement should be clear and easy to understand. It should provide a clear sense of direction for the reader, indicating the main points that will be discussed in the essay.
- Strong and compelling: The thesis statement should be strong and compelling, capturing the attention of the reader. It should be a statement that provokes thoughtful analysis and discussion.
By considering these factors, you can develop a thesis statement that effectively sets the tone for your discursive essay and captures the essence of your argument or analysis.
Conducting Research
Conducting thorough research is a critical step in writing a discursive essay. Here are some essential tips to help you effectively gather information and sources:
- Define your research question: Clearly define the question or issue you want to explore in your essay. This will guide your research and help you stay focused.
- Use a variety of sources: Gather information from a diverse range of sources, such as books, scholarly articles, reputable websites, and academic journals. This will ensure a well-rounded and comprehensive understanding of the topic.
- Evaluate the credibility of sources: Assess the reliability and credibility of each source before including it in your essay. Consider factors such as author credentials, publication date, peer-reviewed status, and the reputation of the source.
- Take organized notes: As you read and review your sources, take organized notes to keep track of key points, quotes, and references. This will make it easier to cite sources accurately later.
- Analyze and synthesize information: Analyze the information you have gathered and synthesize it into coherent arguments. Identify common themes, patterns, and conflicting viewpoints that will form the basis of your essay.
- Address counterarguments: Remember to consider and address counterarguments in your research. Engaging with opposing viewpoints will strengthen your arguments and demonstrate a well-rounded understanding of the topic.
By following these research strategies, you can gather reliable and varied sources to support your discursive essay, ensuring a balanced and well-informed discussion of the topic.
Writing the Introduction
The introduction sets the tone and direction for a discursive essay, providing context and background information on the topic. Here are some key elements to include when writing the introduction to a discursive essay:
- Grab the reader’s attention: Use a hook or attention-grabbing statement to draw the reader in and generate interest in the topic.
- Introduce the topic: Clearly state the topic and provide some background information to contextualize the issue.
- Define key terms: Define any key terms related to the topic that may be unfamiliar to the reader.
- Present the thesis statement: Clearly state your main argument or claim, which sets the tone for the rest of the essay.
- Outline the structure: Briefly outline the main points or arguments that will be addressed in the essay.
- Write in a discursive style: Use a discursive style of writing in the introduction that presents multiple viewpoints on the topic.
By including these elements, you can craft an effective introduction to your discursive essay that engages the reader, establishes the context for the topic, and clearly presents your thesis statement. Remember to present a balanced analysis of multiple viewpoints, maintaining the discursive style of the essay.
Presenting Arguments and Counterarguments
Presenting arguments and counterarguments is a crucial aspect of writing a discursive essay. Here are some strategies to effectively structure and present your arguments and counterarguments:
- Identify key arguments: Begin by identifying the main arguments or perspectives related to the topic. These arguments will form the basis of your essay and provide a framework for your analysis.
- Develop supporting evidence: Gather relevant evidence, examples, statistics, or expert opinions to support each argument. This evidence should be well-researched and credible to strengthen your claims.
- Present arguments in a logical order: Organize your arguments in a logical and coherent manner. You can choose to present each argument separately, dedicating individual paragraphs to each one or use a point-counterpoint approach where you counter each argument with a counterargument.
- Address counterarguments: Acknowledge and include counterarguments in your essay to demonstrate a comprehensive understanding of the topic. Refute counterarguments by presenting contrasting evidence or providing a persuasive rebuttal.
- Provide balanced analysis: While presenting arguments and counterarguments, ensure a balanced analysis that gives due weight to each viewpoint. Avoid bias and strive for objectivity by presenting evidence from various perspectives.
- Use transition words and phrases: Utilize appropriate transition words and phrases to guide the reader through the presentation of arguments and counterarguments. Examples include “on the one hand,” “however,” “in contrast,” “nevertheless,” etc.
By following these strategies, you can effectively present arguments and counterarguments in your discursive essay, demonstrating a comprehensive understanding of the topic and engaging the reader in a thoughtful analysis.
Writing the Body Paragraphs
When writing the body paragraphs of a discursive essay, it’s important to present a balanced and well-structured analysis of the topic. Here are some key strategies to consider:
- Organize your paragraphs: Each body paragraph should focus on a single argument or idea. Start with a clear topic sentence that introduces the main point of the paragraph.
- Provide evidence and examples: Support your arguments with evidence, facts, statistics, or examples from credible sources. This will enhance the validity and persuasiveness of your arguments.
- Use logical reasoning: Present clear and coherent reasoning to connect your evidence with your main argument. Use logic and critical thinking to explain the relevance and significance of your evidence.
- Consider opposing viewpoints: Acknowledge potential counterarguments and address them within your body paragraphs. Refute counterarguments using logical and evidence-based reasoning.
- Use paragraphs for different viewpoints: If you’re discussing multiple perspectives or arguments within the same essay, dedicate separate paragraphs to each viewpoint. Clearly indicate transitions between paragraphs to maintain a coherent flow.
- Include topic sentences and transitions: Begin each paragraph with a topic sentence that clearly states the main idea. Use transitional words and phrases to guide the reader smoothly from one paragraph to the next.
Remember, in a discursive essay, the body paragraphs should explore various arguments and perspectives related to the topic, providing a balanced analysis and supporting evidence. By following these strategies, you can construct well-organized and compelling body paragraphs for your discursive essay.
Incorporating Evidence and Examples
Effectively incorporating evidence and examples is crucial in a discursive essay to support your arguments and strengthen your analysis. Here are some strategies to consider when integrating evidence:
- Choose credible sources: Gather evidence from reputable and reliable sources such as scholarly articles, books, authoritative websites, or academic journals. This ensures the validity and credibility of the evidence.
- Use a variety of evidence: Draw from a range of sources to provide a well-rounded perspective on the topic. This can include facts, statistics, expert opinions, case studies, or historical examples.
- Provide context: When presenting evidence, provide context to help the reader understand its significance. Explain the relevance of the evidence to your argument and how it supports your main points.
- Analyze and interpret evidence: Avoid simply regurgitating evidence. Instead, analyze and interpret it, explaining how it supports your argument and contributes to your overall analysis.
- Quote and paraphrase effectively: When using direct quotes, ensure they are relevant and support your argument. Use accurate paraphrasing to summarize and restate ideas from your sources.
- Cite your sources correctly: Properly cite your sources using a citation style appropriate for your academic field, such as APA, MLA, or Chicago. This gives credit to the original authors and avoids plagiarism.
By incorporating evidence and examples effectively, you can provide a solid foundation for your arguments in a discursive essay, enhancing your credibility and persuasiveness.
Addressing Counterarguments
Addressing counterarguments is an essential component of a discursive essay as it demonstrates critical thinking and strengthens your overall argument. Here are some strategies to effectively address counterarguments:
- Identify counterarguments: Identify the main counterarguments or opposing viewpoints related to your topic. This shows that you have considered different perspectives on the issue.
- Understand the counterarguments: Thoroughly analyze and understand the counterarguments before addressing them. This will help you develop a strong response based on evidence and reasoning.
- Refute the counterarguments: Present a persuasive rebuttal to counterarguments by providing evidence or logical reasoning that challenges or disproves them.
- Anticipate objections: Address potential objections or criticisms that readers might have. Proactively refute these objections by providing additional evidence or presenting alternative perspectives.
- Acknowledge validity: Recognize the validity of certain counterarguments or aspects of opposing viewpoints. This demonstrates fairness and strengthens your overall argument by showing that you have carefully considered all sides.
- Use transitional phrases: Use transitional phrases such as “however,” “although,” or “on the other hand,” to seamlessly introduce counterarguments and your responses.
By effectively addressing counterarguments, you can strengthen your own argument and demonstrate a comprehensive understanding of the topic. Engaging with opposing viewpoints in a fair and persuasive manner enhances the overall credibility and impact of your discursive essay.
Concluding the Discursive Essay
Concluding your discursive essay is an opportunity to summarize your main points and leave a lasting impression on the reader. Here are some strategies to effectively conclude your essay:
- Restate your thesis statement: Begin your conclusion by restating your thesis statement in a concise and clear manner. This reminds the reader of your main argument and reinforces its significance.
- Summarize your main points: Provide a brief summary of the main points you discussed in the body paragraphs. This helps to reinforce the key arguments and evidence presented throughout the essay.
- Emphasize the significance of your argument: Highlight the importance and relevance of your argument in relation to the broader context or real-world implications. This helps to leave a lasting impact on the reader.
- Address counterarguments: Briefly acknowledge the counterarguments you addressed in the essay and reiterate why your main argument is stronger or more compelling.
- Offer a final thought or call to action: Conclude your essay by offering a final thought, reflection, or call to action that encourages the reader to further consider the topic or take action.
- Provide closure: End your conclusion by providing a sense of closure to the essay. This can be achieved by offering a conclusive statement or returning to an anecdote or example mentioned earlier in the essay.
By following these strategies, you can effectively conclude your discursive essay, leaving a strong and memorable impression on the reader while summarizing the key points and reinforcing the significance of your argument.
Sociology Research Topics Ideas
Importance of Computer in Nursing Practice Essay
History Research Paper Topics For Students
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy. We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related emails.
Latest Articles
Navigating the complexities of a Document-Based Question (DBQ) essay can be daunting, especially given its unique blend of historical analysis...
An introduction speech stands as your first opportunity to connect with an audience, setting the tone for the message you...
Embarking on the journey to write a rough draft for an essay is not just a task but a pivotal...
I want to feel as happy, as your customers do, so I'd better order now
We use cookies on our website to give you the most relevant experience by remembering your preferences and repeat visits. By clicking “Accept All”, you consent to the use of ALL the cookies. However, you may visit "Cookie Settings" to provide a controlled consent.
History MasterClass IEB
This MasterClass covers some important topics and skills that students need to master for the Grade 12 IEB History examinations. These topics and skills can be examined within either the Paper I or Paper II formats.

- 04:01:26 hours on-demand videos
- Access until 31 December 2024
- Access on mobile and PC devices
- All 14 IEB Subjects
- Understand the use and importance of evidence in History.
- Tips on how to answer essay-type questions.
- The skill of extended writing.
- How to study for an extended writing examination question.
- How to study for a discursive essay examination question.
- A deeper, detailed understanding of the Cold War topic.
- How to study for the Cold War topic and how to approach the different questions that can be asked in the examination.
- How to write paragraph and essay answers, with emphasis on writing technique.
- Understand source analysis.
- Tips on how to analyse sources.
- History Sample video Preview 00:02:03
- What is evidence? 00:32:02
- Paragraph and essay writing 00:23:31
- Source-based essay writing 00:37:55
- Extended writing 00:12:27
- Discursive Essay - The Cold War 00:31:23
- History Paper 2 00:44:28
- Exam Techniques 00:41:02
- Coming of Democracy 00:16:35
- Coloured pens
The History MasterClass Series of videos was produced to highlight, clarify and refine the most important concepts, as described in the History Subject Assessment Guidelines (SAGs). The concepts learnt prior to Grade 12 are not explicitly covered as individual topics but are reinforced to the extent that they apply to the Grade 12 syllabus.
These videos summarise the important concepts related to each topic. They provide students with skills in order to expand the context related to the question, enabling them to answer examination questions with deeper and greater understanding.
The videos further address common mistakes that students make and point out how to avoid them. An effort is made to expose students to various ways in which the content can be examined. This is done by working through common examination-style questions and discussing the logic behind each answer; in this way, students are later able to apply this acquired knowledge to a multitude of diverse questions, rather than simply rote learning solutions.
A student who watches this MasterClass Series attentively - and then reinforces the explanations given by actively working through multiple past paper questions - will be thoroughly prepared for the final examinations.
Mumsy Malinga is a senior History teacher and Faculty Head of Humanities at Redhill School in Morningside, Sandton. Her areas of interest are gender studies and social history. Prior to her appointment at Redhill School, Mumsy worked as a History educator and Head of Department at St Stithians Girls College and at St Mary’s School in Waverley.
Mumsy is the current internal moderator (History) at the Independent Examinations Board (IEB). Mumsy has been involved in Teacher Training Workshops for the GDE, co-authored a History textbook and has done work for both uMalusi and the Department of Education, which includes History Curriculum Review. Currently, she is part of the SU-UIC Curriculum and Assessment Sub-Committee.
Subject preview: History MasterClass IEB
Lesson preview:
of
How would you rate this subject overall, write a public review.
- Redhill School
Are you sure to delete this information ?
How to Write a Good Discursive Essay?
05 June, 2020
7 minutes read
Author: Elizabeth Brown
What does a discursive essay mean? We have an answer to this and many other questions in our article. Welcome to the world of ideal essay writing. Ever wanted to build buzz for your text? We know you do. And we also know how you can do that with minimum effort and little diligence. So forget about your trivial academic essays - they are not as exciting as a discursive one. Ready to dive in?

What is Discursive Writing?

For all those who wanted to know the discursive essay meaning, here it is: a discursive essay is a writing piece, in which the focal element is devoted to an argument. That is, discursive writing presupposes developing a statement that ignites active discussions. After this essay, readers should be motivated to express their own opinions regarding the topic. Discursive essays have much in common with argumentative and persuasive papers, but these are not to be confused. Despite some similarities, discursive writing is a separate type of work that has its specific features and nuances. What we do want you to remember about discursive essays is that you need to concentrate on the power of thought rather than factology and pieces of evidence. In short, your mind is the only tool required to persuade and interest others on the topic you choose.
Discursive Essay Format
Now that we’ve figured out what is discursive writing, it’s time to focus more on the “skeleton” of discursive essay. Like any other piece of writing, discursive essays have clear requirements that help to glue their elements into a coherent paper. By the way, there are many writing services available which can help you present an excellent academic essay. So if you need professional assistance with your task, check them out. But if you want to do it yourself, you can simply take any discursive essay example from the web and use it as a starting point for your paper.
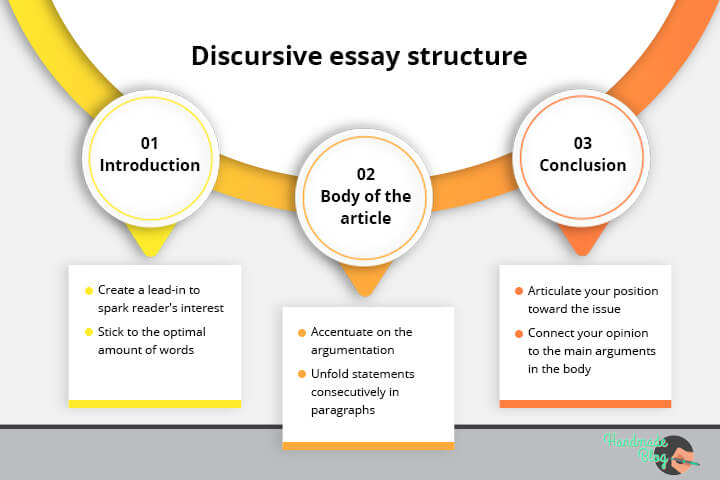
As for the discursive structure itself, you need to start your essay with an introduction in the first place. Create a lead-in that’ll spark the reader’s interest and make them genuinely responsive to the topic. Also, make sure that your introduction is neither small nor extensive. Stick to the optimal amount of words that’ll be sufficient for readers to get the general idea of your essay.
Another essential aspect of an effective intro is your opinion. It’s worthy of note that some discursive essays might require no particular stance on the topic. In situations like this, wait until the end of an essay comes, and only then share your personal view on the matter. This way, readers will understand the neutral tone throughout the piece, shape their own thoughts about it, and later decide whether to agree with yours or not.
In the paragraphs that follow, you’ll need to accentuate on the argumentation. There’s no room for vague and unarticulate expressions at this point. Quite the contrary – you need to unfold your statements consecutively, in a couple of paragraphs, to depict the entire image of your stance for or against the topic. And don’t forget to link your discursive text to supporting evidence.
The last section is the conclusion. Your finishing remarks should clearly articulate your position toward this or that issue, with a close connection to the main ideas in the essay body.
Discursive Essay Thesis
To construct a good thesis for your discursive essay, you’ll need to describe the general stance your work will argue. Here, it’s important to back up the thesis statement with points. These are the opinions that support your thesis and allow to create an affirmative structure for the entire paper.
Discursive Essay Linking Words

The points you use while writing a discursive essay need to flow smoothly so that readers could see a logical organization of the work. For this, you can use transition words that’ll make your paper easily readable and crisp. For example, if you want to list some points, opt for such words as firstly, to begin with, secondly, lastly, finally, etc. If you wish to point at advantages or disadvantages, consider using these transitions: the main/greatest/ first advantage of… is …, another positive side is…, an additional drawback is, another negative aspect of…is…
How to Write an Introduction for a Discursive Essay?
The introductory part is the critical aspect of creating a good discursive essay. In this section, specific attention should centralize on what your topic is all about. Therefore, it needs to be presented with clarity, be informative, and attention-grabbing. How to make your intro sentence for discursive essay memorable? You can start with a spicy anecdote to add humor to discussion. Another powerful way for hooking readers is stating a quote or opinion of experts and famous influencers. This will add to the credibility of your statements, making readers more motivated to read your work.
How to Write a Discursive Essay Conclusion?
Your discursive essay ending is the climax of your argument, a final link that organically locks up a chain of previously described points. This part is devoted to the restatement of the main arguments that sum up your attitude to the topic. And just like with introduction, the conclusion should leave a trace in readers’ minds. To achieve this result, your closing paragraph should include a call to action, warning or any other food for thought that will encourage people to ponder on the issue and make relevant conclusions.
Discursive Essay Topics
The ideas for discursive papers are so versatile that it’s hard to compile all of them in one list. For such list will extend to kilometers. However, we’ve collected some of them for you to facilitate your work on this task. So here are some discursive essay examples you can use any time:

As you understand now, discursive writing definition and discursive essay definition are not as scary as they seem from the first glance. Even though the art of this type of paper is hard to master, over time, you’ll notice significant progress. All you need for this is practice and a little bit of patience to understand the subtle nuances of this task and develop the skill of writing confidently. And if you ever wondered what is an essay, a team of professional academic essay writers can give a helping hand and provide you with a top-notch paper.

A life lesson in Romeo and Juliet taught by death
Due to human nature, we draw conclusions only when life gives us a lesson since the experience of others is not so effective and powerful. Therefore, when analyzing and sorting out common problems we face, we may trace a parallel with well-known book characters or real historical figures. Moreover, we often compare our situations with […]

Ethical Research Paper Topics
Writing a research paper on ethics is not an easy task, especially if you do not possess excellent writing skills and do not like to contemplate controversial questions. But an ethics course is obligatory in all higher education institutions, and students have to look for a way out and be creative. When you find an […]

Art Research Paper Topics
Students obtaining degrees in fine art and art & design programs most commonly need to write a paper on art topics. However, this subject is becoming more popular in educational institutions for expanding students’ horizons. Thus, both groups of receivers of education: those who are into arts and those who only get acquainted with art […]

- Business Intelligence Assignment Help
- Lab Report Writing Service
- Nursing Assignment Help
- Buy Response Essay
- CPM Homework Answers
- Do My Chemistry Homework
- Buy Argumentative Essay
- Do Your Homework
- Biology Essay Writers
- Business Development Assignment Help
- Best Macroeconomics Assignment Help
- Best Financial Accounting Assignment Help
- PHP Assignment Help
- Science Assignment Help
- Audit Assignment Help
- Perdisco Accounting Assignment Help
- Humanities Assignment Help
- Computer Network Assignment Help
- Arts and Architecture Assignment Help
- How it works
How to Write a Discursive Essay: Tips, Examples, and Structure
Calculate the price of your order:.

Mastering the Art of Writing a Discursive Essay
Table of contents.
Introduction
Understanding Discursive Essays
Discursive essay writing tips, discursive essay structure, examples of discursive essays, picking the right discursive essay topics, discursive essay format, crafting a strong discursive essay outline, writing an effective discursive essay introduction, nailing the discursive essay conclusion.
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on how to write a discursive essay effectively. If you’re unfamiliar with this type of essay or want to improve your skills, you’ve come to the right place! This guide will cover How to Write a Discursive Essay , examples, and strategies to help you craft a compelling discursive essay.
Are you ready to master this art of writing ? This article will explain a discursive essay and explore various aspects such as writing tips, structure, examples, and format. So, let’s dive right in and unveil the key elements of an impressive discursive essay.

Before we delve into the nitty-gritty of writing a discursive essay , let’s take a moment to understand its nature and purpose. A discursive essay presents a balanced argument on a particular topic by exploring different perspectives. It requires the writer to consider different viewpoints, present evidence, and critically analyze the subject matter.
Writing a discursive essay can be challenging, but you can excel in this art form with the right approach. Here are some valuable tips that will help you write a discursive essay effectively:
- Choose an Engaging Topic: Select a topic that is interesting and relevant to your audience. This will make the essay more engaging and enjoyable to read.
- Thorough Research: Gather extensive information from reliable sources to support your arguments and counterarguments.
- Plan and Outline: Take the time to plan and create an outline before diving into the writing process. This will help you organize your thoughts and arguments effectively.
- Clear Introduction: Start with a concise introduction that provides context and grabs the reader’s attention. Clearly state your thesis or main argument.
- Well-structured Paragraphs: Divide your essay into paragraphs that focus on specific points. Each paragraph should present a new idea or support a previous one.
- Logical Flow: Maintain a logical flow using transitional words and phrases that connect your ideas and paragraphs smoothly.
- Balance Your Arguments: Ensure a balance in presenting the pros and cons of each perspective. This will demonstrate your fairness and critical thinking skills.
- Support with Evidence: Provide evidence, facts, and examples to support your claims and make your arguments more persuasive.
- Use Clear Language: Avoid jargon and overly complex language. Opt for clear, concise, and precise language that is easy for readers to comprehend.
- Proofread and Edit: Always revise, proofread, and edit your essay to ensure clarity, coherence, and proper grammar usage.
Following these tips, you’ll be well-equipped to write an impressive discursive essay that effectively presents your arguments and engages your readers.
A well-structured discursive essay enhances readability and ensures that your arguments are coherent. Here’s a suggested structure that you can follow:
- Hook the reader with an attention-grabbing statement or anecdote.
- Introduce the topic and provide background information.
- Present your thesis statement or main argument.
- Start each paragraph with a topic sentence introducing a new argument or perspective.
- Provide evidence, examples, and supporting details to justify your claims.
- Address counterarguments and present rebuttals, showing your ability to consider different viewpoints.
- Use transitional words to maintain a smooth flow between paragraphs.
- Summarize the main points discussed in the essay.
- Restate your thesis statement while considering the arguments presented.
- End with a thought-provoking statement or call to action.
By adhering to this structure, your discursive essay will be well-organized and easy for readers to follow.
To gain a better understanding of how discursive essays are written, let’s explore a couple of examples:
Example 1: The Impact of Social Media
Introduction: The growing influence of social media in society.
Main Body: Discussing the positive and negative aspects of social media on communication, mental health, privacy, and relationships.
Conclusion: Weighing the overall impact of social media and proposing ways to harness its strengths and mitigate its drawbacks.
Example 2: The Pros and Cons of School Uniforms
Introduction: Introducing the debate on school uniforms.
Main Body: Exploring the arguments supporting school uniforms (such as fostering discipline and equality) and arguments against them (such as limiting self-expression).
Conclusion: Evaluating the advantages and disadvantages of school uniforms and suggesting potential compromises.
These examples illustrate how discursive essays analyze various perspectives on a topic while maintaining a balanced approach.
Choosing an engaging and relevant topic is crucial to capturing your readers’ attention. Here are some popular discursive essay topics to consider:
- Is social media beneficial or detrimental to society?
- Should the death penalty be abolished worldwide?
- Are genetically modified organisms (GMOs) safe for consumption?
- Should recreational marijuana use be legalized?
- Are video games responsible for the rise in violence among youth?
When selecting a topic, ensure it is captivating, allows for multiple viewpoints, and is backed by sufficient research material.
While there is flexibility in formatting a discursive essay, adhering to a standard format enhances clarity and readability. Consider following this general format:
- Font type and size: Times New Roman, Arial, or Calibri with a 12-point font size.
- Line spacing: Double-spaced throughout the essay.
- Page margins: 1-inch margins on all sides.
- Title page: Include the essay title, your name, course name, instructor’s name, and submission date (if applicable).
- Header: Insert a header with your last name and page number (top-right corner).
A consistent format will make your essay more professional and easier to navigate.

Before writing your discursive essay, creating an outline that organizes your thoughts and arguments effectively is essential. Here’s a sample outline to help you get started:
I. Introduction
B. Background information
C. Thesis statement
II. Main Body
A. Argument 1
1. Supporting evidence
2. Examples
B. Argument 2
C. Argument 3
1 . Supporting evidence
2 . Examples
III. Counterarguments and Rebuttals
A. Counterargument 1
1 . Rebuttal evidence
B. Counterargument 2
C . Counterargument 3
IV. Conclusion
A. Summary of main points
B . Restating the thesis statement
C. Call to action or thought-provoking statement
By structuring your ideas in an outline, you’ll have a clear roadmap for your essay, ensuring that your arguments flow logically.
The introduction of your discursive essay plays a vital role in capturing your reader’s attention and setting the tone for the essay. Here’s how you can make your introduction compelling:
Start With an Engaging Hook: Begin with a captivating opening sentence, such as a surprising statistic, an intriguing question, or a compelling anecdote related to your topic.
Provide Necessary Background Information: Briefly explain the topic and its relevance to the reader.
Present Your Thesis Statement: Clearly state your main argument or thesis, which will guide your essay’s direction and focus.
You’ll establish a strong foundation for your discursive essay by crafting an engaging and informative introduction.
The conclusion of your discursive essay should effectively summarize your main points and leave a lasting impression on your readers. Here’s how you can achieve this:
Summarize the Main Points: Briefly recap the key arguments and perspectives discussed in the essay.
Restate Your Thesis Statement: Reiterate your main argument while considering the various perspectives.
Call to Action or Thought-Provoking Statement: End your essay with a compelling statement or encourage readers to explore the topic further, sparking discussion and reflection.
By crafting a powerful conclusion, you’ll leave a lasting impact on your readers, ensuring they walk away with a clear understanding of your essay’s message.
Congratulations! You’ve now comprehensively understood how to write a discursive essay effectively. Remember to choose an engaging topic, conduct thorough research, create a clear structure, and present balanced arguments while considering different perspectives. Following these guidelines and incorporating our tips, you’ll be well-equipped to craft a compelling discursive essay.
So, start writing your discursive essay following our comprehensive guide. Unlock your writing potential and captivate your readers with an impressive discursive essay that showcases your analytical skills and ability to present compelling arguments. Happy writing!

Frequently Asked Questions About “How to Write a Discursive Essay Effectively”
What is a discursive essay, and how does it differ from other types of essays.
A discursive essay explores a particular topic by presenting different perspectives and arguments. It differs from other essays, emphasizing balanced, unbiased discussion rather than a single, strong stance.
How should I choose a topic for my discursive essay?
Select a topic that allows for multiple viewpoints and has room for discussion. Controversial issues or topics with various opinions work well, providing ample material for exploration.
What is the typical structure of a discursive essay?
A discursive essay typically has an introduction, several body paragraphs, and a conclusion. The introduction sets the stage, the body paragraphs present different viewpoints, and the conclusion summarizes the key points and your stance.
Is it necessary to choose a side in a discursive essay?
While you don’t have to take a definite side, you should present a balanced view. However, some essay prompts may ask you to argue for or against a particular position.
How do I start the introduction of a discursive essay?
Begin with a hook to capture the reader’s attention, provide background information, and clearly state the issue you will discuss. End the introduction with a thesis statement that outlines your approach.
Should I use formal language in a discursive essay?
Yes, maintain a formal and objective tone. Avoid using first-person pronouns and aim for clarity and precision in your language.
How many viewpoints should I include in the body paragraphs?
Include at least two or three well-developed viewpoints. Ensure that each paragraph focuses on a specific aspect or argument related to the topic.
How do I transition between paragraphs in a discursive essay?
Use transitional phrases to move smoothly from one idea to the next. This helps maintain a logical flow and coherence in your essay.
Can I include personal opinions in a discursive essay?
While you can present your opinions, remaining objective and supporting your views with evidence is crucial. The emphasis should be on presenting a well-rounded discussion rather than expressing personal bias.

How do I conclude a discursive essay effectively?
Summarize the main points discussed in the body paragraphs, restate your thesis nuancedly, and offer a closing thought or call to action. Avoid introducing new information in the conclusion.
Basic features
- Free title page and bibliography
- Unlimited revisions
- Plagiarism-free guarantee
- Money-back guarantee
- 24/7 support
On-demand options
- Writer's samples
- Part-by-part delivery
- Overnight delivery
- Copies of used sources
- Expert Proofreading
Paper format
- 275 words per page
- 12 pt Arial/Times New Roman
- Double line spacing
- Any citation style (APA, MLA, CHicago/Turabian, Havard)
Guaranteed originality
We guarantee 0% plagiarism! Our orders are custom made from scratch. Our team is dedicated to providing you academic papers with zero traces of plagiarism.
Affordable prices
We know how hard it is to pay the bills while being in college, which is why our rates are extremely affordable and within your budget. You will not find any other company that provides the same quality of work for such affordable prices.
Best experts
Our writer are the crème de la crème of the essay writing industry. They are highly qualified in their field of expertise and have extensive experience when it comes to research papers, term essays or any other academic assignment that you may be given!
Calculate the price of your order
Expert paper writers are just a few clicks away
Place an order in 3 easy steps. Takes less than 5 mins.

How to write an introduction for a history essay

Every essay needs to begin with an introductory paragraph. It needs to be the first paragraph the marker reads.
While your introduction paragraph might be the first of the paragraphs you write, this is not the only way to do it.
You can choose to write your introduction after you have written the rest of your essay.
This way, you will know what you have argued, and this might make writing the introduction easier.
Either approach is fine. If you do write your introduction first, ensure that you go back and refine it once you have completed your essay.
What is an ‘introduction paragraph’?
An introductory paragraph is a single paragraph at the start of your essay that prepares your reader for the argument you are going to make in your body paragraphs .
It should provide all of the necessary historical information about your topic and clearly state your argument so that by the end of the paragraph, the marker knows how you are going to structure the rest of your essay.
In general, you should never use quotes from sources in your introduction.
Introduction paragraph structure
While your introduction paragraph does not have to be as long as your body paragraphs , it does have a specific purpose, which you must fulfil.
A well-written introduction paragraph has the following four-part structure (summarised by the acronym BHES).
B – Background sentences
H – Hypothesis
E – Elaboration sentences
S - Signpost sentence
Each of these elements are explained in further detail, with examples, below:
1. Background sentences
The first two or three sentences of your introduction should provide a general introduction to the historical topic which your essay is about. This is done so that when you state your hypothesis , your reader understands the specific point you are arguing about.
Background sentences explain the important historical period, dates, people, places, events and concepts that will be mentioned later in your essay. This information should be drawn from your background research .
Example background sentences:
Middle Ages (Year 8 Level)
Castles were an important component of Medieval Britain from the time of the Norman conquest in 1066 until they were phased out in the 15 th and 16 th centuries. Initially introduced as wooden motte and bailey structures on geographical strongpoints, they were rapidly replaced by stone fortresses which incorporated sophisticated defensive designs to improve the defenders’ chances of surviving prolonged sieges.
WWI (Year 9 Level)
The First World War began in 1914 following the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand. The subsequent declarations of war from most of Europe drew other countries into the conflict, including Australia. The Australian Imperial Force joined the war as part of Britain’s armed forces and were dispatched to locations in the Middle East and Western Europe.
Civil Rights (Year 10 Level)
The 1967 Referendum sought to amend the Australian Constitution in order to change the legal standing of the indigenous people in Australia. The fact that 90% of Australians voted in favour of the proposed amendments has been attributed to a series of significant events and people who were dedicated to the referendum’s success.
Ancient Rome (Year 11/12 Level)
In the late second century BC, the Roman novus homo Gaius Marius became one of the most influential men in the Roman Republic. Marius gained this authority through his victory in the Jugurthine War, with his defeat of Jugurtha in 106 BC, and his triumph over the invading Germanic tribes in 101 BC, when he crushed the Teutones at the Battle of Aquae Sextiae (102 BC) and the Cimbri at the Battle of Vercellae (101 BC). Marius also gained great fame through his election to the consulship seven times.
2. Hypothesis
Once you have provided historical context for your essay in your background sentences, you need to state your hypothesis .
A hypothesis is a single sentence that clearly states the argument that your essay will be proving in your body paragraphs .
A good hypothesis contains both the argument and the reasons in support of your argument.
Example hypotheses:
Medieval castles were designed with features that nullified the superior numbers of besieging armies but were ultimately made obsolete by the development of gunpowder artillery.
Australian soldiers’ opinion of the First World War changed from naïve enthusiasm to pessimistic realism as a result of the harsh realities of modern industrial warfare.
The success of the 1967 Referendum was a direct result of the efforts of First Nations leaders such as Charles Perkins, Faith Bandler and the Federal Council for the Advancement of Aborigines and Torres Strait Islanders.
Gaius Marius was the most one of the most significant personalities in the 1 st century BC due to his effect on the political, military and social structures of the Roman state.
3. Elaboration sentences
Once you have stated your argument in your hypothesis , you need to provide particular information about how you’re going to prove your argument.
Your elaboration sentences should be one or two sentences that provide specific details about how you’re going to cover the argument in your three body paragraphs.
You might also briefly summarise two or three of your main points.
Finally, explain any important key words, phrases or concepts that you’ve used in your hypothesis, you’ll need to do this in your elaboration sentences.
Example elaboration sentences:
By the height of the Middle Ages, feudal lords were investing significant sums of money by incorporating concentric walls and guard towers to maximise their defensive potential. These developments were so successful that many medieval armies avoided sieges in the late period.
Following Britain's official declaration of war on Germany, young Australian men voluntarily enlisted into the army, which was further encouraged by government propaganda about the moral justifications for the conflict. However, following the initial engagements on the Gallipoli peninsula, enthusiasm declined.
The political activity of key indigenous figures and the formation of activism organisations focused on indigenous resulted in a wider spread of messages to the general Australian public. The generation of powerful images and speeches has been frequently cited by modern historians as crucial to the referendum results.
While Marius is best known for his military reforms, it is the subsequent impacts of this reform on the way other Romans approached the attainment of magistracies and how public expectations of military leaders changed that had the longest impacts on the late republican period.
4. Signpost sentence
The final sentence of your introduction should prepare the reader for the topic of your first body paragraph. The main purpose of this sentence is to provide cohesion between your introductory paragraph and you first body paragraph .
Therefore, a signpost sentence indicates where you will begin proving the argument that you set out in your hypothesis and usually states the importance of the first point that you’re about to make.
Example signpost sentences:
The early development of castles is best understood when examining their military purpose.
The naïve attitudes of those who volunteered in 1914 can be clearly seen in the personal letters and diaries that they themselves wrote.
The significance of these people is evident when examining the lack of political representation the indigenous people experience in the early half of the 20 th century.
The origin of Marius’ later achievements was his military reform in 107 BC, which occurred when he was first elected as consul.
Putting it all together
Once you have written all four parts of the BHES structure, you should have a completed introduction paragraph. In the examples above, we have shown each part separately. Below you will see the completed paragraphs so that you can appreciate what an introduction should look like.
Example introduction paragraphs:
Castles were an important component of Medieval Britain from the time of the Norman conquest in 1066 until they were phased out in the 15th and 16th centuries. Initially introduced as wooden motte and bailey structures on geographical strongpoints, they were rapidly replaced by stone fortresses which incorporated sophisticated defensive designs to improve the defenders’ chances of surviving prolonged sieges. Medieval castles were designed with features that nullified the superior numbers of besieging armies, but were ultimately made obsolete by the development of gunpowder artillery. By the height of the Middle Ages, feudal lords were investing significant sums of money by incorporating concentric walls and guard towers to maximise their defensive potential. These developments were so successful that many medieval armies avoided sieges in the late period. The early development of castles is best understood when examining their military purpose.
The First World War began in 1914 following the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand. The subsequent declarations of war from most of Europe drew other countries into the conflict, including Australia. The Australian Imperial Force joined the war as part of Britain’s armed forces and were dispatched to locations in the Middle East and Western Europe. Australian soldiers’ opinion of the First World War changed from naïve enthusiasm to pessimistic realism as a result of the harsh realities of modern industrial warfare. Following Britain's official declaration of war on Germany, young Australian men voluntarily enlisted into the army, which was further encouraged by government propaganda about the moral justifications for the conflict. However, following the initial engagements on the Gallipoli peninsula, enthusiasm declined. The naïve attitudes of those who volunteered in 1914 can be clearly seen in the personal letters and diaries that they themselves wrote.
The 1967 Referendum sought to amend the Australian Constitution in order to change the legal standing of the indigenous people in Australia. The fact that 90% of Australians voted in favour of the proposed amendments has been attributed to a series of significant events and people who were dedicated to the referendum’s success. The success of the 1967 Referendum was a direct result of the efforts of First Nations leaders such as Charles Perkins, Faith Bandler and the Federal Council for the Advancement of Aborigines and Torres Strait Islanders. The political activity of key indigenous figures and the formation of activism organisations focused on indigenous resulted in a wider spread of messages to the general Australian public. The generation of powerful images and speeches has been frequently cited by modern historians as crucial to the referendum results. The significance of these people is evident when examining the lack of political representation the indigenous people experience in the early half of the 20th century.
In the late second century BC, the Roman novus homo Gaius Marius became one of the most influential men in the Roman Republic. Marius gained this authority through his victory in the Jugurthine War, with his defeat of Jugurtha in 106 BC, and his triumph over the invading Germanic tribes in 101 BC, when he crushed the Teutones at the Battle of Aquae Sextiae (102 BC) and the Cimbri at the Battle of Vercellae (101 BC). Marius also gained great fame through his election to the consulship seven times. Gaius Marius was the most one of the most significant personalities in the 1st century BC due to his effect on the political, military and social structures of the Roman state. While Marius is best known for his military reforms, it is the subsequent impacts of this reform on the way other Romans approached the attainment of magistracies and how public expectations of military leaders changed that had the longest impacts on the late republican period. The origin of Marius’ later achievements was his military reform in 107 BC, which occurred when he was first elected as consul.
Additional resources

What do you need help with?
Download ready-to-use digital learning resources.

Copyright © History Skills 2014-2024.
Contact via email
Mots. Les langages du politique
Accueil Tous les numéros 94 Outils et enjeux du discours poli... The Discursive Construction of Hi...
The Discursive Construction of History. Brief Considerations
Texte intégral, discourse studies and the re/writing of history.
1 In recent years, much research in Discourse Studies and Critical Discourse Studies has started to analyse the many dimensions of national and transnational “identity politics” and to investigate how the discursive construction of such identities draws on collective and individual memories, on hegemonic and common sense narratives, and on myths which are proposed as constitutive for national identification (see below:“Discourses of/about the past(s). Overview of research”). Indeed, one might claim that the entire field of “language and politics” in post-war Europe (particularly since the 1960’s and 1980’s) was triggered by the desire to understand the influence of persuasive rhetoric in and on totalitarian regimes and related major catastrophes in the 20 th century, thus trying to come to terms with the traumatic pasts in Europe and beyond (Wodak, De Cillia, 2006, 2007). In this way, it is very timely to consider the range of research, theories, and methodologies employed to investigate this domain in a special issue dedicated to “thirty years of Mots. Les langages du politique ”.
2 It is obvious however, that many answers to overarching questions are still missing, such as how should one deal with “traumatic” pasts that are prevalent in every society ? How should one deal with perpetrators and victims ? Should one focus on a common future and “forget the past” ? Can a “clean break” be achieved ? What are the functions and risks of such a “clean break” ? And if silence occurs, what are the consequences, for perpetrators, victims, and society as a whole ? In particular, one question remains are there any global traits with respect to dealing with individual and collective memories ? In the following, I summarise some of the most important research related to these questions from the perspective of (Critical) Discourse Studies.
Discourses of/about the past(s). Overview of research
- 1 De Cillia, Wodak, 2009a ; Forchtner, 2010 ; Stockholm-Banke, 2009 ; Ensink, 2009 ; Reisigl, 2008 ; (...)
2 Achugar, 2008 ; Anthonissen, Blommaert, 2006 ; Verdoolaege, 2008.
3 Blommaert, 2005 ; Carrard, 2010 ; Ensink, Sauer, 2003 ; Heer et al. , 2008 ; Wodak, 2006a, 2006b.
4 Blommaert, 2003 ; Czy ż ewski, 2009 ; Kovàcs, Wodak, 2003 ; Pollak, Wodak, 2008.
5 Wodak et al. , 2009 ; Suleiman, 2010 ; Blackledge, 2004.
6 Pollak, 2002 ; Ribeiro, 2010 ; Zimmerman, 2009.
3 Recent research focuses on a range of salient oral, written, and visual genres, such as commemorative speeches at various salient national or transnational days in the Netherlands, Denmark, the US and the UK, Austria and Germany 1 , the discourses of truth and reconciliation tribunals in South Africa, Chile, and Argentina 2 , accounts and experiences of victims (and perpetrators) in the Congo, Austria, France, Poland, and Germany 3 , the argumentation inherent in election posters insinuating and functionalising past events as well as related xenophobic and anti-Semitic stereotypes (in Austria and the UK) (Distelberger, 2009; Richardson, Wodak, 2009a, 2009b), television debates and documentaries discussing competing narratives of national pasts, in Poland, Hungary, Germany, Austria, the Soviet Union, the UK, and France 4 , the effect of commemorative exhibitions (Uhl, 2008), the discursive construction of national identities in Austria, Palestine or the UK 5 , debates in the (Austrian, Israeli or Portuguese) press about the juxtaposition of victims and perpetrators 6 or about issues of restitution (De Cillia, Wodak, 2009b), and representations of victims and perpetrators in school books in Austria and Japan (Barnard, 2003; Loitfellner, 2008).
7 Benke, Wodak, 2003 ; Wodak et al. , 1990 ; Engel, Wodak, 2009.
4 Of course, some studies also investigate counter-discourses by politicians and political parties who continuously endorse revisionist views of the past and attempt to justify or indeed deny past war crimes 7 . Specific linguistic-rhetorical patterns are also under investigation in this context, such as conceptual metaphors and their blending or the implicatures and presuppositions as employed, for example, in Hitler’s Mein Kampf (Chilton, 2007; Musolff, 2009), and the coded languages of racism, xenophobia, and anti-Semitism as well as the related indirect pragmatic devices used to discriminate against certain marginalised social groups or to promote a “politics of denial” (Van Dijk, 1993; Wodak, 2007).
An integrative interdisciplinary framework
Comparing and/or equating .
5 This brief overview is, of course, not a finite list; however, the range of countries and investigated topics becomes apparent, linked to the emergence of historical and political science literature best summarised in Judt (2007). Judt’s seminal book Post-War presents a comprehensive and detailed account of different aspects of the world’s responses to (the aftermath of) World War II. He succeeds, in illustrating how specific and indeed diverse the responses in various parts of the world and countries were and are to salient traumatic experiences of the past.
6 In this vein, Pelinka (2009, p. 49) argues that
[I]n dealing with war crimes and crimes against humanity, three different, sometimes conflicting patterns have been developed since 1945. The three patterns can be distinguished according to their different guarding principles Justice Perpetrators must be brought to court and convicted. Truth All major aspects of the crimes must become known to the public. Peace At the end of any process, social reconciliation must become possible.
7 He continues that “in the short run, neglecting justice and truth in favour of peace and reconciliation may have a positive impact on stabilizing democracy in a peaceful way; but in the long run, such a neglect has its price especially regarding social peace” ( ibid .).
8 More specifically, Pelinka claims that, on the one hand, “without comparing the quality and the quantity of evidence, any debate about conflicting narratives loses any kind of academic liability and responsibility” (p. 50), thus comparison should take place, always in a context-dependent way. On the other hand, however, comparisons should not lead to any equation of traumatic events. Thus, Pelinka emphasises that
Fascism is not fascism is not fascism. Too easily the term fascism is used to blur significant differences between different regimes. Spain under Franco is not Italy under Mussolini is not Austria under Dollfuß is not Portugal under Salazar is not Hungary under Horthy – and they all are not Germany under Hitler. All these different types of fascism or semi-fascism have a lot in common – non-democratic rule, oppression of political opponents, ending the rule of law. But the intensity of suppression as well as the existence of a monopolistic mass party make a lot of difference – not to speak of the Holocaust which is the decisive quality of nazism and not of fascism in general. ( Ibid ., p. 53)
9 Careful deconstruction of many current debates about the past in different parts of the world illustrates indeed that certain terms become ubiquitous – such as “Holocaust” or “fascism”. Following Pelinka’s argument (which I endorse), it is obvious that terms lose their distinctiveness when used to label similar but very different events and experiences in different national contexts. Such terms then tend to be employed like “empty signifiers” and their context-dependent meanings become blurred. Hence, research about past events necessarily has to consider the socio-political and historical contexts of each experience and avoid undifferentiated generalisations.
Four models of coping with traumatic pasts
10 Assmann (2009, p. 31 ff.) distinguishes between four ways in which societies deal with traumatic pasts. She refers to them as dialogic forgetting ; remembering in order to prevent forgetting ; remembering in order to forget ; and dialogic remembering . The first – dialogic forgetting – is defined as a model for peace agreed upon by two parties that had engaged in violence in order to keep an explosive past at bay. This kind of forgetting is not to be set equal with the suppression of memories by one side of the conflict; rather, this serves, as Assmann argues, to achieve closure and allow societies to “move on”. One of the examples mentioned in this thought-provoking essay are the many traumatic incidents in Spain under Franco until Spanish Prime-minister Zapatero’s “memory law” 2007, which for the first time encouraged Spanish people to remember.
11 “Remembering in order to prevent forgetting” is typical for asymmetric instances of violence. The paradigmatic case in hand is the genocide against Jews and Roma during the Nazi regime (the “Holocaust”). As Assmann claims
[R]emembering was the only adequate response to such collectively destructive and devastating experiences. It was rediscovered not only as a therapeutic remedy for the survivors but also as a spiritual and ethical obligation for the millions of dead victims. Thus slowly but inevitably, the pact of forgetting was transformed into a “pact of remembering”. The aim of such a pact is to transform the asymmetric experience of violence into symmetric forms of remembering. ( Ibid ., p. 35)
12 The aim of the third model is also forgetting, but the way to achieve this aim leads through remembering. Remembering in this case (for example, in South Africa or in Chile) is introduced as a therapeutic tool to cleanse and to reconcile. Many linguistic studies have investigated the effect of the Truth and Reconciliation Commission in South Africa (Anthonissen, Blommaert, 2006; Verdoolaege, 2008). Although, of course, only some perpetrators were brought to justice and not all voices of victims were heard, this procedure enabled South African society to avoid a civil war. Finally, Assmann mentions a utopian model, the model of “dialogic remembering” “Two countries engage in a dialogic memory if they face a shared history of mutual violence by mutually acknowledging their own guilt and empathy with the suffering they have inflicted on others” ( ibid ., 40). Assmann mentions some first attempts at dialogic remembering. For example, she lists the Warsaw uprising, a seminal event commemorated in Poland, which was unknown to Germans because it is fully eclipsed – for the German public – by the Warsaw ghetto uprising. Simultaneously, Germans have reclaimed the firebombing of Dresden for their national memory, but they have neglected the Leningrade Blockade (1941-1944) by the German Wehrmacht , through which 700 000 Russians were starved to death; and so forth. Recently, such neglected events are increasingly finding their way into history school books and public debates.
Discourse and social change
13 In accordance with the two above mentioned theoretical frameworks by Pelinka and Assmann, it is necessary, I believe, to integrate these with concepts from discourse analysis. In this context, the notions of intertextuality , recontextualisation and entextualisation present themselves for further theorizing (Wodak, Fairclough, 2010; Blommaert, 2003).
14 An important assumption common to various approaches to CDS is that processes of social change are in part processes of change in discourse , and that change in discourse may, subject to certain conditions, have constructive effects on processes of social change more generally. The challenge is to develop theories of social change which coherently integrate discourse and relations between discourses and other elements or moments of the social process, and methodologies for focusing specifically on these relations, and the particular place and impact of discourse, in inter-disciplinary research on social change (Fairclough, 1992; Krzy ż anowski, Wodak, 2009). Since events and texts are linked to, affected by and have effects on other events and texts in different places and at different times, the major challenge implies developing ways to address broadly spatial and temporal relationships between events and texts (i.e. intertextuality ; Kristeva, 1986).
15 Struggles for hegemony of various competing narratives of the past which can be reconstructed in a longitudinal way require very subtle context-dependent analyses. In this way, the theorization of contexts becomes crucial to any dialectic analysis (see below “Levels of context”). Thus, we assume that social and historical change occurs on several levels at different times and with different speed (or sometimes not at all); thus non-simultaneity needs, to be accounted for in differentiated, context-dependent ways. These intricate and complex processes also suggest the necessity of the concept of glocalization of understanding how more global processes are being implemented, recontextualized and thus changed on local/regional/national levels (Krzy ż anowski, Wodak, 2009; “ model of circular non-simultaneous transformation ”).
- 8 In a similar vein, Blommaert (2003, p. 177) employs the term entextualisation which guides the “pr (...)
16 Recontextualization as one of the salient linguistic processes governing historical change is concretely manifested in the intertextuality and interdiscursivity of texts (Wodak, Fairclough, 2010). The intertextuality of a text is a matter of how elements of other texts (words, phrases, arguments, topics, or larger elements) are incorporated within it; the interdiscursivity of a text is the particular combination of different discourses and different genres that characterizes the text, and how the deployment of particular discourses and genres links the text to other intertextually related texts. Recontextualization is often textually realized in the mixing of “new” recontextualized elements and “old” elements, such as particular words, expressions, arguments, topoi , rhetorical devices and so forth, and discourses and genres. The tensions, contradictions and antinomies which recontextualization gives rise to can be textually identified and analysed by focusing upon such textual mixing or hybridity 8 .
Levels of context
17 The concept of context is an inherent part of discourse analysis. In the course of investigating complex social problems, it is necessary to draw on multiple theoretical approaches to analyse given contexts and relate these to texts. To make this possible in a meaningful way, decisions must be made about the theoretical foundations and interdisciplinarity of discourse analysis. This is why I have proposed the Four-Level Model of context elsewhere which I summarise briefly below.
18 This triangulatory approach is based on a concept of context which takes into account four levels
19 – the co-text of each utterance or clause;
20 – the con-text in the macro-text; the genre analysis;
21 – the socio-political context of the speech event.
22 The intertextual and interdiscursive relationships of the respective speech event to other relevant events.
23 When analysing narratives about past events, a systematic investigation of context-dependent layers of debate proves valuable as illustrated, for example, in deconstructing instances of the politics of denial (Heer et al. , 2008).
Perspectives
24 Although this paper – due to restrictions on space – can only cover part of the most important research on “coping with traumatic pasts” from a discourse-analytic perspective, it is obvious that all dimensions and levels of language and communication can be functionalized to achieve “re/writing of history”. This paper aims primarily at raising awareness of the “power of the written and spoken word”, in all public and private contexts in our lives. Careful and critical reading/listening and viewing is required in order to understand the implied meanings, which are frequently controversial and conflicting.
Bibliographie
Achugar M., 2008, What we Remember The Construction of Memory in Military Discourse , Amsterdam, Philadelphia, Benjamins.
Anthonissen C., Blommaert J. eds, 2006, Critical Linguistic Perspectives on Coping with Traumatic Pasts Case Studies , Special Issue, Journal of Language and Politics , Amsterdam, Philadelphia, Benjamins.
Assmann A., 2009, “From collective violence to a common future: four models for dealing with a traumatic past”, Memory and Justice , R. Wodak, G. Auer-Boreo eds, Vienna, Passagen Verlag, p. 31-48.
Barnard C., 2003, “Pearl Harbour in Japanese high school history schoolbooks”, Re/Reading the Past. Critical and Functional Perspectives on Time and Value , J. R. Martin, R. Wodak eds, Amsterdam, Philadelphia, Benjamins, p. 247-271.
Benke G., Wodak R., 2003, “The discursive construction of individual memories. How Austrian ‘Wehrmacht’ soldiers remember WWII”, Re/Reading the Past. Critical and Functional Perspectives on Time and Value , J. R. Martin, R. Wodak eds, Amsterdam, Philadelphia, Benjamins, p. 115-138.
Billig M., Condor S., Edwards D., Gane M., Middleton D., Radley A., 1988, Ideological Dilemmas. A Social Psychology of Everyday Thinking , London, Sage.
Blackledge A., 2004, Discourse and Power in a Multilingual World , Amsterdam, Philadelphia, Benjamins.
Blommaert J., 2003, “Orthopraxy, writing and identity”, Re/Reading the Past. Critical and Functional Perspectives on Time and Value , J. R. Martin, R. Wodak eds, Amsterdam, Philadelphia, Benjamins, p. 177-194.
— 2005, Discourse , Cambridge, Cambridge University Press
Carrard Ph., 2010, The French Who Fought for Hitler: Memories from the Outcasts , Cambridge, Cambridge University Press.
Charteris-Black J., 2006, Politicians and Rhetoric , Basingstoke, Palgrave.
Chilton P., 2007, “Missing links in mainstram CDA: modules, blends, and the critical instinct”, A New Agenda in (Critical) Discourse Analysis , R. Wodak, P. Chilton eds, Amsterdam, Philadelphia, Benjamins, p. 19-52.
Czyżewski M., 2009, “The Polish debate around fear by Jan Tomasz Gross from the perspective of the intermediary discourse analysis”, Memory and Justice , R. Wodak, G. Auer-Boreo eds, Vienna, Passagen Verlag, p. 147-168.
De Cillia R., Wodak R., 2009a, “Restitution: Yes, but…”, Memory and Justice , R. Wodak, G. Auer-Boreo eds, Vienna, Passagen Verlag, p. 195-212.
— 2009b, Gedenken im « Gedankenjahr ». Zur diskursiven Konstruktion österreichischer Identitäten im Jubiläumsjahr 2005 , Innsbruck, Studien Verlag.
Engel J., Wodak R., 2009, “Kalkulierte Ambivalenz: Storungen und das Gedankenjahr: Die Causen Siegfried Kampl und John Gudenus”, Gedenken im « Gedankenjahr ». Zur diskursiven Konstruktion österreichischer Identitäten im Jubiläumsjahr 2005 , Innsbruck, Studien Verlag, p. 79-100.
Ensink T., 2009, “Resolving antagonistic tensions. Some discourse analytic reflections on verbal commemorative practices”, Memory and Justice , R. Wodak, G. Auer-Boreo eds, Vienna, Passagen Verlag, p. 169-194.
Ensink T., Sauer C. eds, 2003, The Art Of Commemoration , Amsterdam, Philadelphia, Benjamins.
Fairclough N., 1992, Discourse and Social Change , London, Polity.
Forchtner B., 2010, “Judge-Penitence Discourses in Germany, Denmark, and Austria”, Unpublished PhD Thesis, Lancaster University.
Heer H., Manoschek W., Pollak A., Wodak R. eds, 2008, The Discursive Construction of History: Remembering the Wehrmacht’s War of Annihilation , Basingstoke, Palgrave (translated from the German: Wie Geschichte gemacht wird. Zur Konstruktion von Erinnerungen an Wehrmacht und Zweiten Weltkrieg , Vienna, Czernin, 2003).
Judt T., 2007, Post-War , London, Penguin.
Kovács A., Wodak R. eds, 2003, NATO, Neutrality, and National Identity , Vienna, Böhlau.
Kristeva J., 1986, The Kristeva Reader , T. Moi éd., Oxford, Basil Blackwell.
Krzyżanowski M., Wodak R., 2009, “Theorising and analysing social change in Central and Eastern Europe: the contribution of critical discourse analysis”, Discourse and Transformation in Central and Eastern Europe, A. Galasińska, M. Krzy ż anowski eds, Basingstoke, Palgrave, p. 17-40.
Loitfellner S., 2008, “The appalling toll in Austrian lives…”, The Discursive Construction of History: Remembering the Wehrmacht’s War of Annihilation, H. Heer et al. eds, Basingstoke, Palgrave, p. 155-174.
Martin J. R., Wodak R. eds, 2003, Re/reading the past. Critical and Functional Perspectives on Time and Value , Amsterdam, Philadelphia, Benjamins.
Musolff A., 2009, “Metaphor in the history of ideas and discourses: how can we interpret a medieval version of the body-state analogy ?”, Metaphor and Discourse , Musolff A., Zinken J. eds, Basingstoke, Palgrave, p. 233-247.
Pelinka A., 2009, “Justice, truth, and peace. Three dimension of consequences”, Memory and Justice , R. Wodak, G. Auer-Boreo eds, Vienna, Passagen Verlag, p. 48-66.
Pollak A., 2002, Die Wehrmachtslegende in Österreich , Vienna, Böhlau Verlag.
Pollak A., Wodak R., 2008, “Crime scene: Wehrmacht exhibition”, The Discursive Construction of History: Remembering the Wehrmacht’s War of Annihilation , H. Heer et al. eds, Basingstoke, Palgrave, p. 207-226.
Reisigl M., 2008, “Rhetoric of political speeches”, Analyzing the Public Sphere: Handbook of Applied Linguistics , vol. IV, R. Wodak, V. Koller eds, Berlin, De Gruyter.
Ribeiro F., 2010, “The Discursive Construction of Portuguese Identity”, Unpublished PhD Thesis, Lancaster University.
Richardson J. E., Wodak R., 2009a, “The impact of visual racism: Visual arguments in political leaflets of Austrian and British far-right parties”, Controversia , 6, p. 45-77.
— 2009b, “ Recontextualising fascist ideologies of the past: right-wing discourses on employment and nativism in Austria and the United Kingdom ”, Critical Discourse Studies , 6 (4), p. 251-267.
Richardson J. E., Wodak R. eds, 2009c, Critical Discourse Studies , 6 (10), Discourse, History, and Memory , Special Issue.
Slavickova T., 2010, “The Memorial Day Speeches of US Presidents”, Unpublished PhD Thesis, Lancaster University.
Stockholm-Banke C., 2009, “The Legacies of the Holocaust in Scandinavian small state foreign policy”, Justice and Memory. Confronting traumatic pasts. An international comparison , R. Wodak, G. Auer-Boreo eds, Vienna, Passagen Verlag, p. 265-277.
Suleiman U., 2010, Too Many Truths… Too Many Broken Dreams. At-Taqiyya in Arab-Palestinian Political Discourse , Amsterdam, Philadelphia, Benjamins.
Thiesmeyer L. ed., 2003, Discourse and Silencing , Amsterdam, Philadelphia, Benjamins.
Uhl H., 2008, “Interpreting the ‘War of Annihilation’”, The Discursive Construction of History:Remembering the Wehrmacht’s War of Annihilation, H. Heer et al. eds, Basingstoke, Palgrave, p. 251-266.
Van Dijk T. A., 1993, “Denying racism:elite discourse and racism”, Racism and Migration in Western Europe , J. Solomos, J. Wrench eds, Oxford, Berg, p. 179-193.
Verdoolaege A., 2008, Reconciliation Discourse , Amsterdam, Philadelphia, Benjamins.
Wodak R., 2001, “The discourse-historical approach”, Methods of Critical Discourse Analysis , R. Wodak, M. Meyer eds, London, Sage, p. 63-94.
— 2006a, “History in the making: the making of history”, Journal of Language and Politics , 5 (1).
— 2006b, “Blaming and denying”, Elsevier Encyclopedia for Language and Linguistics (2 nd edition), K. Brown ed., Oxford, Elsevier.
— 2007, “Pragmatics and critical discourse analysis. A cross-disciplinary analysis, Pragmatics and Cognition , 15 (1), p. 203-225 (translated into French: “ Pragmatique et analyse de discours critique: un exemple d’une analyse à la croisée des disciplines” , Semen , 27, 2009, p. 97-126).
— 2009, The Discourse of Politics in Action: Politics as Usual , Basingstoke, Palgrave.
Wodak R., De Cillia R., 2006, “Politics and Language: Overview”, Encyclopedia of Language and Linguistics (2 nd revised edition), K. Brown ed., vol. 9, Oxford, Elsevier, p. 707-719. [ne faudrait-il pas que De Cillia apparaisse avant Wodak ? Même question pour tous les titres de Wodak et autres cités ci-après]
— 2007, “Commemorating the past: the discursive construction of official narratives about the rebirth of the Second Austrian Republic”, Discourse and Communication , 1 (3), p. 337-363.
Wodak R., Fairclough N., 2010, “ Recontextualizing European higher education policies: the cases of Austria and Romania ”, Critical Discourse Studies , 7 (1), p. 19-40.
Wodak R., De Cillia R., Reisigl M., Liebhart K., 2009 [1999], The Discursive Construction of National Identity , Edinburgh, Endingburgh University Press (2 nd revised edition).
Wodak R., Menz F., Mitten R., Stern F., 1994, Die Sprachen der Vergangenheiten. Öffentliches Gedenken in österreichischen und deutschen Medien , Frankfurt-am-Main, Suhrkamp.
Wodak R., Pelikan J., Nowak P., Gruber H., De Cillia R., Mitten R., 1990, « Wir sind alle unschuldige Täter ». Diskurshistorische Studien zum Nachkriegsantisemitismus , Frankfurt-am-Main, Suhrkamp.
Wodak R., Auer-Boreo G. eds, 2009, Memory and Justice , Vienna, Passagenverlag.
ZIMMERMAN M., 2009, “Israel’s prenatal memory: born 1948 - traumatized 1938”, Memory and Justice , R. Wodak, G. Auer-Boreo eds, Vienna, Passagen Verlag, p. 309-316.
1 De Cillia, Wodak, 2009a ; Forchtner, 2010 ; Stockholm-Banke, 2009 ; Ensink, 2009 ; Reisigl, 2008 ; Charteris-Black, 2007 ; Slavickova, 2010 ; Wodak et al. , 1994.
8 In a similar vein, Blommaert (2003, p. 177) employs the term entextualisation which guides the “production of historical text”. Thus Blommaert argues, entextualisation means “setting / desetting / resetting events in particular (morally and politically loaded) time frames, and this in turn involves the usual power differences of entextualisation: access to contextual spaces, the importance of ‘the record’, orientation towards authoritative voices, shifts in referential and indexical frames and so on”.
Pour citer cet article
Référence papier.
Ruth Wodak , « The Discursive Construction of History. Brief Considerations » , Mots. Les langages du politique , 94 | 2010, 57-65.
Référence électronique
Ruth Wodak , « The Discursive Construction of History. Brief Considerations » , Mots. Les langages du politique [En ligne], 94 | 2010, mis en ligne le 06 novembre 2012 , consulté le 07 avril 2024 . URL : http://journals.openedition.org/mots/19862 ; DOI : https://doi.org/10.4000/mots.19862
Lancaster University [email protected]
Articles du même auteur
- La construction discursive de l’identité nationale [Texte intégral] The discursive construction of national identities La construcción discursiva de la identidad nacional Paru dans Mots. Les langages du politique , 127 | 2021
- « Right-wing populist parties endorse what can be recognised as the “arrogance of ignorance” » [Texte intégral] Entretien de Ruth Wodak avec Silvia Nugara « Les partis populistes de droite cautionnent ce qu’on peut qualifier comme l’“arrogance de l’ignorance” » « Los partidos políticos de derecha respaldan lo que se puede calificar como la “arrogancia de la ignorancia” » Paru dans Mots. Les langages du politique , 115 | 2017
Droits d’auteur
Le texte et les autres éléments (illustrations, fichiers annexes importés), sont « Tous droits réservés », sauf mention contraire.
Derniers numéros
- 133 | 2023 La République au-delà du slogan
- 132 | 2023 Les mots du vote de la Rome antique à la Révolution française
- 131 | 2023 La diversité en discours : contextes, formes et dispositifs
- 130 | 2022 Circulation des discours dans les récits complotistes
- 129 | 2022 Migration et crise : une co-occurrence encombrante
- 128 | 2022 Le multilinguisme dans les organisations internationales
Numéros en texte intégral
- 127 | 2021 Discours climatosceptiques
- 126 | 2021 Le travail et ses maux
- 125 | 2021 Discours de haine dans les réseaux socionumériques
- 124 | 2020 Chanter le collectif
- 123 | 2020 De la racine à l’extrémisme : discours des radicalités politiques et sociales
- 122 | 2020 Reprendre la parole de l’autre en politique
- 121 | 2019 Restons groupés ! La construction discursive des relations sociales
- 120 | 2019 Nom d’un parti ! Pour une onomastique partisane
- 119 | 2019 Les mots de l’écologie
- 118 | 2018 Discours post-attentats
- 117 | 2018 Les « petites phrases »
- 116 | 2018 Dire ou ne pas dire la « race » en France aujourd'hui
- 115 | 2017 Les discours de la crise économique
- 114 | 2017 Le rapport, entre description et recommandation
- 113 | 2017 Écrire le genre
- 112 | 2016 Discours présidentiels et de présidentielles
- 111 | 2016 Normes et usages de la langue en politique
- 110 | 2016 Le geste, emblème politique
- 109 | 2015 Discours d’Amérique latine. Identités et conflits
- 108 | 2015 Thèmes et thématiques dans le discours politique
- 107 | 2015 Discours d'autorité : des discours sans éclat(s) ?
- 106 | 2014 Regards sur le post-colonialisme linguistique
- 105 | 2014 Couleurs politiques
- 104 | 2014 Les livres de journalistes politiques
- 103 | 2013 Le silence en politique
- 102 | 2013 Les discours sur l'enseignement supérieur et la recherche
- 101 | 2013 Le discours politique portugais
- 100 | 2012 Chiffres et nombres dans l'argumentation politique
- 99 | 2012 Fictions politiques
- 98 | 2012 Publicité et politique
- 97 | 2011 Les collectivités territoriales en quête d'identité
- 96 | 2011 Les discours politiques. Approches interactionnistes et multimodales
- 95 | 2011 Sigles et acronymes en politique
- 94 | 2010 Trente ans d’étude des langages du politique (1980-2010)
- 93 | 2010 Figures et filiations dans le discours politique latino-américain
- 92 | 2010 Rumeurs en politique
- 91 | 2009 Que devient le pamphlet ?
- 90 | 2009 Présidentielle 2007. Scènes de genre
- 89 | 2009 2007. Débats pour l’Élysée
- 88 | 2008 Discours politique, discours expert
- 87 | 2008 Chrononymes. La politisation du temps
- 86 | 2008 Toponymes. Instruments et enjeux
- 85 | 2007 Violence et démocratie en Amérique latine
- 84 | 2007 Politiquement sportif
- 83 | 2007 Dire la démocratie aujourd’hui
- 82 | 2006 L’emprunt et sa glose
- 81 | 2006 Suisse, laboratoire politique européen ?
- 80 | 2006 La politique mise au net
- 79 | 2005 Discours de violence au nom de la foi
- 78 | 2005 Usages politiques du genre
- 77 | 2005 Proximité
- 76 | 2004 Guerres et paix. Débats, combats, polémiques
- 75 | 2004 Émotion dans les médias
- 74 | 2004 Langue(s) et nationalisme(s)
- 73 | 2003 Les discours de la guerre
- 72 | 2003 La ville, entre dire et faire
- 71 | 2003 Mondialisation(S)
- 70 | 2002 La politique en chansons
- 69 | 2002 Révolutions
- 68 | 2002 Les métaphores spatiales en politique
Numéros sur Persée
Tous les numéros, appels à contributions.
- Appels en cours
- Appels clos
- Présentation
- Notes aux auteurs
- Lire et relire
Informations
- Crédits et informations légales
- Politiques de publication
Suivez-nous
Lettres d’information
- La Lettre d’OpenEdition
Affiliations/partenaires

ISSN électronique 1960-6001
Voir la notice dans le catalogue OpenEdition
Plan du site – Flux de syndication
Politique de confidentialité – Gestion des cookies – Signaler un problème
Nous adhérons à OpenEdition – Édité avec Lodel – Accès réservé
Vous allez être redirigé vers OpenEdition Search
Discursive Essay Writing Guide [+Examples]
Students obtain various types of assignments during their studies. Each task is different and has strict requirements and guidelines to follow. A discursive essay example is considered to be one of the most challenging types of essay writing for college students. Many of them don’t see the difference between a discursive and argumentative essay. Yet, each essay type has distinct features that we are going to talk about here. If you were assigned to craft this paper and you have doubts, here are professional tips and advice on topics to select and create a stellar discursive essay plan.
How to Write a Discursive Essay
First of all, every college student who is assigned to craft this paper needs to understand that discursive essay topics can be different from those of an argumentative essay . On one hand, these pieces of writing can be similar as they both are essay types and have three main parts. On the other hand, discursive essay ideas differ in the purpose and structure.
Good discursive essay topics provide an unprejudiced and reliable assessment of a certain problem. Yes, the topic should also be controversial leaving each student an opportunity to select their point of view and arguments to support one side. But discursive essay examples demonstrate a more balanced and formal discussion. It shouldn’t be absolutely neutral but the author needs to reflect both sides of the problem and present enough arguments and facts to support each side.
What Is a Discursive Essay?
So, once you realize that this is a separate type of assignment that shouldn’t be crafted the same way you write other academic tasks, let’s talk about the discursive essay definition. So, its definition is rather simple: this is a type of academic assignment that is aimed to discuss a particular issue or problem. The author should demonstrate both sides of the problem without stating his or her personal opinion.
When choosing higher discursive essay topics, it is necessary to admit that the style of this task should be kept formal and impersonal compared to other written assignments. The structure is strict and similar to essay on science : you should submit an introduction, the main body, and the conclusion. Each separate question should be discussed in a separate paragraph so that the readers can distinguish what you are writing about and how many arguments you provide.

Main Types of Discursive Essay Writing
Did you know that there are three main types of this assignment? Depending on the type you were assigned or you select, there may be different features to include in your text. Here they are:
- Opinion Essay – if you have this type of paper in your discursive essay topics list, you should keep in mind that it demands your opinion of a problem you are going to discuss. This opinion needs to be mentioned in the discursive essay introduction and followed by examples and reasons. Another fact is that the opposing argument should be stated before the conclusion and you should explain why you found this argument unconvincing. The summary needs to be present in the conclusion.
- Essay Offering Solution to a Problem – as you can notice from the name of this discursive essay meaning, the author should discuss the issue and try to find solutions. The issue should be stated in the introduction, and possible solutions should be mentioned in the body paragraphs. Each solution goes for a separate paragraph of the main body. The writer’s opinion is usually summarized in the conclusion of a discursive essay template.
- For and Against Essay – this is a task written in the form of a debate with opposing opinions. You should be ready to describe every point of view, present facts, and be objective. The introduction of discursive essay topics higher English states the problem you are going to discuss. The main body demonstrates reasons, examples, and facts. The conclusion is finally for the writer’s opinion on the problem.
Discursive Essay Structure
Now let’s talk more about the structure of this academic assignment. As a scholarship essay , almost all essays have a strict structure that should be followed by students who want to obtain the highest grades. Here is how to structure a discursive essay:

Introduction
Many students wonder how to start a discursive essay. What should they mention in the first part? It is simple as that – all you need to do is state the issue and show some “hook” for the readers to follow. Think about ways to attract the attention of the lecturer. You may want to start with a rhetorical question or add a famous quote. Either way, you need to demonstrate both sides of the issue even if it’s Scottish independence discursive essay.
Here is what you need to remember when building your main part of the assignment: assess every aspect of the problem and stay unbiased when describing the points of view. Your own opinion can be mentioned only in the conclusion of the discursive essay examples in higher English. More than that, it is essential to insert at least three arguments to support your opinion. Start each argument with the new paragraph so that the readers can distinguish each reason. Be precise and distinct when you provide evidence and facts. This is how to write a discursive essay in higher English.
There are many discursive essay topics UK – make certain you select the one you understand and know how to use this structure. So, the conclusion is the last section of your task. This is a part where you can summarize the viewpoints mentioned above and express your own point of view. Don’t write too many sentences here and don’t copy what you’ve written in the introduction.
Top Ten Discursive Essay Topics
Here are several examples of good discursive essay topics for higher English as well as just interesting discursive essay topics for students to select from. If you have doubts and don’t know what topic to choose, you can opt for one from our list.
- Zoos present good sources of knowledge and entertainment but they foster the misery of cage animals. Should they be abolished?
- Modern digital technology: is it good or bad?
- Present education system: is it good or bad?
- Healthy food is often more expensive than junk food. Should it be like that?
- The influence of social media on teenagers today.
- Is it true that Google is bringing the end to our privacy these days?
- Uniforms limit expression and freedom. Should we ban them in schools?
- A child with two parents is less hard-working compared to a child with a single parent.
- What are the effects of cyberbullying and how harmful can it be?
- Should schoolchildren learn religion as a part of their curriculum?
To sum up, it can be challenging to select the right discursive essay topic and structure your paper in a proper way. If you follow the above-mentioned advice and remember to proofread your document at the end, you will increase your chances of receiving the highest grades at college. Good luck!
Christopher Ferguson
Chris is energetic and creative Academic Tutor. He provides educational assistance and help students to improve their academic performance. He supplies students with the necessary tools for better understanding their level and needs to achieve academic goals. Got an excellent communication and problem solving skills and gives support to create a personalized learning experience for all students.

How to Write an Academic Essay [Writing Tips for Students]
Nobody says that college or university life is easy. While some people believe that students have...

Immigration Essay: How To Write The Perfect One?
Immigration is a hot-button issue in many countries. With debates over immigration policies...
I really like how they give profound meaning into what they write, and how it makes the reader feel. I know that it makes me feel alive and interested in reading more. Personally, I love to write and t type, I would love to be able to write more and know what I should talk about. I’m very glad for those authors who take their time to write the stories they do for us to be able to read and be inspired by the message we read. Adding on to that also, being able to use what we read and apply it to what we want to write.
Leave a comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
History Essay Examples

Top History Essay Examples To Get Inspired By
Published on: May 4, 2023
Last updated on: Jan 31, 2024

Share this article
History essays are a crucial component of many academic programs, helping students to develop their critical thinking, research, and writing skills.
However, writing a great history essay is not always easy, especially when you are struggling to find the right approach. This is where history essay examples come in handy.
By reading and examining samples of successful history essays, you can gain inspiration, learn new ways to approach your topic. Moreover, you can develop a better understanding of what makes a great history essay.
In this blog, you will find a range of history essay examples that showcase the best practices in history essay writing.
Read on to find useful examples.
On This Page On This Page -->
Sample History Essays
Explore our collection of excellent history paper examples about various topics. Download the pdf examples for free and read to get inspiration for your own essay.
History Essay Samples for Middle School
The Impact of Ancient Civilizations on Modern Society
The Rise and Fall of the Roman Empire
The Causes and Consequences of the American Revolution
History Writing Samples for High School Students
The Impact of the Industrial Revolution on Society
Grade 10 History Essay Example: World War 1 Causes and Effects
Grade 12 History Essay Example: The Impact of Technology on World War II
Ancient History Essay Examples
The Societal and Political Structures of the Maya Civilization
The Role of Phoenicians in the Development of Ancient Mediterranean World
The Contributions of the Indus Civilization
Medieval History Essay Examples
The Crusades Motivations and Consequences
The Beginning of Islamic Golden Age
The Black Death
Modern History Essay Examples
The Suez Crisis and the End of British Dominance
The Rise of China as an Economic Powerhouse
World History Essay Examples
The Role of the Silk Road in Shaping Global Trade and Culture
The Rise and Fall of the Ottoman Empire
The Legacy of Ancient Greek Philosophy and Thought

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
American History Essay Examples
The Civil Rights Movement and its Impact on American Society
The American Civil War and its Aftermath
The Role of Women in American Society Throughout History
African History Essay Examples
The Impact of Colonialism on African Societies
The Rise and Fall of the Mali Empire
European History Essay Examples
The Protestant Reformation and the Rise of Protestantism in Europe
The French Revolution and its Impact on European Politics and Society
The Cold War and the Division of Europe
Argumentative History Essay Examples
Was the US Civil War Primarily About Slavery or States
The Effects of British Colonization on Colonies
Art History Essay Examples
The Influence of Greek and Roman Art on Neoclassicism
The Depiction of Women in Art Throughout History
The Role of Art in the Propaganda of Fascist Regimes
How to Use History Essay Examples
History essay examples are a valuable tool for students looking for inspiration and guidance on how to approach their own essays.
By analyzing successful essays, you can learn effective writing techniques that can be expected in a high-quality history essay.
Here are some tips that will help you take full advantage of the samples above.
Tips for Effectively Using History Essay Examples
- Analyze the Structure:
Pay close attention to how the essay is organized, including the introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion. Look for how the author transitions between paragraphs and the use of evidence to support their argument.
- Study the Thesis Statement:
The thesis statement is the backbone of any successful history essay. Analyze how the author crafted their thesis statement, and consider how you can apply this to your own writing.
- Take Note of the Evidence:
Effective history essays rely on using strong evidence to support their arguments. Take note of the sources and types of evidence used in the essay. Consider how you can apply similar evidence to support your own arguments.
- Pay Attention to the Formatting and Other Academic Formalities:
The sample essays also demonstrate how you can incorporate academic formalities and standards while keeping the essay engaging. See how these essays fulfill academic standards and try to follow them in your own writing.
- Practice Writing:
While analyzing history essay examples can be helpful, it is important to also practice writing your own essays. Use the examples as inspiration, but try to craft your own unique approach to your topic.
History essays are an essential aspect of learning and understanding the past. By using history essay examples, students can gain inspiration on how to develop their history essays effectively.
Furthermore, following the tips outlined in this blog, students can effectively analyze these essay samples and learn from them.
However, writing a history essay can still be challenging.
Looking for an online essay writing service that specializes in history essays? Look no further!
Our history essay writing service is your go-to source for well-researched and expertly crafted papers.
And for an extra edge in your academic journey, explore our AI essay writing tool . Make history with your grades by choosing our online essay writing service and harnessing the potential of our AI essay writing tool.
Get started today!
Cathy A. (Law, Marketing)
For more than five years now, Cathy has been one of our most hardworking authors on the platform. With a Masters degree in mass communication, she knows the ins and outs of professional writing. Clients often leave her glowing reviews for being an amazing writer who takes her work very seriously.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!

Legal & Policies
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Terms of Use
- Refunds & Cancellations
- Our Writers
- Success Stories
- Our Guarantees
- Affiliate Program
- Referral Program
- AI Essay Writer
Disclaimer: All client orders are completed by our team of highly qualified human writers. The essays and papers provided by us are not to be used for submission but rather as learning models only.
Essay – examples & model answers | B2 First (FCE)
FCE Essay Examples: Topic (Environment)
Example exam task:, example answer (grade: 3), example answer:.
I think that my country has problems with pollution to the environment like all other countries. This problem is normal for Russia. We have big problems with transport because there are too much cars in our country. And because of that we have problems with atmospeer, air in my city and in all Russia is really dirty and sometimes I can’t make a sigh because it smells around me and of course around that cars on the road. I’ve heard about tradition of one country. They don’t go anywhere by car one day a month or a year, they just use bycicle or their feet. I think it could be very good if we had a tradition like that.
So, what about the rivers and the seas? Yeah, there are some really good and clean rivers and seas where you can go, but there are not many of them. Once I saw the river OB in my city, it was about two years ago but I stil remember that in some places it was not blue, it was green or purple I didn’t really understand because it had different colours.
I don’t know what should we do. Maybe we should just open our eyes and look what we did. But Russian people don’t care about the world around them many people care only about themselves an that’s all.
So, the best idea is look around and try to do something good for our planet and for us and our children.
FCE, CAE, CPE
Practice, write & improve, examiners comments & grade:, example answer (grade: 3-4).
To begin with pollution and damage to the environment is the most serious and difficult problem for countries of all over the world. Scientists of different countries predict a global ecocatastrophe if people won’t change their attitude to our planet.
First of all a huge damage to the environment brings a transport. People can’t imagine their living without cars, buses, trains, ships and planes. But it’s an open secret that one of disadvantage of these accustomed things is harmful exhaust. Needless to say that use of environment friendly engines helps us to save atmosphere from pollution.
In addition to this our rivers and seas are in not less danger situation. It’s a fact of common knowledge that numerous factories and plants pour off their waste to ponds. Obviously that cleaning manufacturing water helps to avoid extinction of ocean residents.
Apart from this I’m inclined to believe that every person can and must contribute to solving this important problem. Doing a little steps for protection our environment every day we will be able to save our Earth. And it’s a task of each of us.
Model Answer (Grade: 5)
DEVELOPMENT VS ENVIRONMENT
If we surf the web looking for pollution and environmental catastrophes, we will find out that every country in the world suffers them. This is a natural consequence of the struggle between development and environment.
If a country decided to live isolated from the rest of the world, living on what it can naturally grow and produce, it surely wouldn’t be highly polluted. But we all want exotic food and technological items from all over the world, so we have to pay the price.
Investing on electrical transport would benefit the environment a lot. Even more if this electricity came from a natural source of energy like wind, rivers and solar boards. It’s difficult to achieve this because petrol companies will fight against these actions.
We also have to take care of our rivers and seas. We all have heard about factories throwing highly toxic substances to rivers, without minimizing their poisoning effects. A really strict law should be applied to fine these factories and make them change their policy.
But what about ourselves? We also can do a lot! If, when possible, we bought larger packs of food, we would be producing less rubbish. And this is only an example!
FCE Essay Examples: Topic (Fashion)
In today’s world, the fashion industry has a strong importance in people’s lives. The fashion industry say to the society what to wear and creates new types of clothes all the time.
Some people claim that the fashion industry has a bad effect on people’s lives, they say that the fashion industry creates clothes that the society has to wear. Furthermore, the clothes’ price is extremely high and people, who can’t afford it, should not be in the society.
In the other hand, the fashion industry guide the people to be in a good appearance, because, nowadays, the appearance of the person is more important than the person itself.
In my opinion, the fashion industry doesn’t has a bad influence on people’s lives. It’s something which was created to help people what to wear.
Example Answer (Grade: 4)
Fashion industry is very a discussed subject nowadays: they create and design new clothes everyday in order to satisfy some people needs.
There are many people who claim that the fashion industry is important and good for society. According to them, this industry design beautiful clothes and thanks to that every person can wear shirts, trousers or any acessory which is on today’s fashion.
On the other hand, the fashion industry in some people opinion, controls the market of clothes and because of that they can’t wear what they want to. In addition, the industry can increase the price of clothes, forcing people who don’t want to be “oldfashioned” to buy and pay a large amount of money to keep “beautiful”.
In my opinion, we can’t let the fashion industry decide what we must or musn’t wear. We shouldn’t judge people for its appearance,because that is not important. We must wear whatever we like, want and feel confortable with.
The society we live today is characterised by technology in constant development, fast speed processes, information travelling and getting to people at a blink of an eye and a complex web of social networking. In this context, the fashion industry is becoming increasingly important and having a more and more paramount role in our lives.
On one hand, the fashion industry is undeniably a source of profit and income. It hires millions of people all over the world and generates millions of dollars every year. Furthermore, such profitable business is also believed to be able to spread and make known the culture of a people, encouraging and enhancing a better understanding of each other.
Nevertheless, for those who are neither impressed nor motivated by numbers and figures, the fashion industry is seen as one which segregates people, isolating those who not fit their laws and commands. It is stated that people place too much importance on appearance and the material, world, sadly true, and the fashion industry just spurs on such situation. Moreover, not only are the costs of fashion item unrealistically high, it is thought to be a money better spent on more pressing issues, such as poverty and hunger.
I do believe that the fashion industry, as it is today, has a harmful effect, because it values a minority of people in detriment to the majority. However, it has such a wide reach that, it put into a good use, it can save lives.
FCE Essay Examples: Topic (Languages)
“There are more reasons to learn a foreign language than to pass a test”
Everything around us revolves around language(s), it is the most important thing in our lives. Society would just not function without it. They are It is our future and I would personaly love to learn as many as I possibly can.
Not everything in life is done because it is necessary. Learning a new language can be a lot of fun. Many people only do it as a hoby, or their knowledge is something that brings them pride and pleasure.
Secondly, we have people who do it simply to challenge themselves. Truly I believe that having a great outcome that stems from your hard work and dedication to learn something new is a wonderful way to challenge prove your ability to yourself and others. Then there is travelling. It is very important to be able to understand and have a conversation with someone abroad, unless you would like to get lost or worse.
To conclude, I think that learning a new language is an amazing thing no matter why you do it. It is always better to do things out of enjoyment, but even if you do it for a test, that knowledge will always be useful.
Learning a a foreign languages is very important nowadays. English, in particular, is essential because it allows is spoken all over the world. That’s the reason why we start studying it from the age of six years old. Going abroad and being able to speak to native people is very satisfying and that’s why I want to improve my knowledge about foreign languages.
I decided to take this exam to know how high my level of English is, but also because I need this certification to go abroad next summer. I really want to come back to Cornwall, an amazing region in the South-West of England. I’ve been there twice with my family, but now I want to go alone. Only being there to England I can really improve my English comprehension and speaking skills.
Fortunately I can will have some English lessons which taught in English at university and I can’t wait for it because it will be an interesting challenge for me. Studying foreign languages is essential to live and to travel. It isn’t simple and I surely have to challenge myself everyday, but the result is so satisfying that we I can’t do without it.
FCE Essay Example: Topic (History)
A very common topic that is being discussed nowadays is wether schools should teach subjects that some may consider useless later in life. A clear example is history, since it is quite difficult to learn and does not help us in day-to-day activities.
However, many people do not realize the importance of it or that it affects our lives today. For example, our political system would not be this way if it weren’t for the Ancient Greeks, numerous politicians and wars who helped shape democracy and our constitution. Yet it is still thought that it’s useless.
In addition, it is very important that we never forget about our past since we must know where we were standing years ago. Moreover, there are some things, such as World War II, that we have to remember to prevent them from happening again. We should also know where we we were standing a century ago: our origins, our identity. The more you learn about your ethnicity, the better.
All in all, I think that it is extremely important to learn about one’s own country’s history. Anyone who gets the chance to do this should not waste it, since they are very fortunate to have this opportunity
Would you pass B2 First (FCE)?

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Start with an introduction to the topic. Discuss each essay question in a single paragraph. Begin each paragraph with a powerful issue sentence. Paragraphs with one point usually followed by a counterpoint paragraph. Its style is general for essays as the reader should understand what you stand for.
Narrative Essays. A narrative essay tells a story. It is usually written in informal language, and it usually incorporates aspects of descriptive writing. It uses details to tell a story and draw the reader in. Think of all the classic fairy-tales, like Cinderella, or Goldilocks and the Three Bears. These are all examples of narrative writing.
A discursive essay is a form of critical essay that attempts to provide the reader with a balanced argument on a topic, supported by evidence. It requires critical thinking, as well as sound and valid arguments (see Chapter 25) that acknowledge and analyse arguments both for and against any given topic, plus discursive essay writing appeals to ...
Each element of this structure is explained further, with examples, below: 1. Topic Sentence. Your very first sentence should clearly state what point from your hypothesis you are going to be arguing in this paragraph. The more specific you are about your point, the better your topic sentence will be.
1. Introduction: Hook: Begin with a captivating hook or attention-grabbing statement to engage the reader's interest. Contextualization: Provide a brief overview of the topic and its relevance, setting the stage for the discussion. Thesis Statement: Clearly state the main argument or the purpose of the essay.
Identify key arguments: Begin by identifying the main arguments or perspectives related to the topic. These arguments will form the basis of your essay and provide a framework for your analysis. Develop supporting evidence: Gather relevant evidence, examples, statistics, or expert opinions to support each argument.
A common and effective kind of essay is the kind that attempts to prove the validity of a hypothesis. For example, suppose the reading on popular religion in the Middle Ages led you to the conclusion that peasants were more pagan than Christian. This conclusion is your hypothesis, and your essay must present evidence in support of it.
How to study for a discursive essay examination question. A deeper, detailed understanding of the Cold War topic. ... History Sample video. Preview. 00:02:03. What is evidence? 00:32:02. Paragraph and essay writing. 00:23:31. Source-based essay writing. 00:37:55. Extended writing. 00:12:27.
If you understand how each part works and fits into the overall essay, you are well on the way to creating a great assessment piece. Most essays will require you to write: 1 Introduction Paragraph. 3 Body Paragraphs. 1 Concluding Paragraph.
The points you use while writing a discursive essay need to flow smoothly so that readers could see a logical organization of the work. For this, you can use transition words that'll make your paper easily readable and crisp. For example, if you want to list some points, opt for such words as firstly, to begin with, secondly, lastly, finally ...
These examples illustrate how discursive essays analyze various perspectives on a topic while maintaining a balanced approach. Picking the Right Discursive Essay Topics Choosing an engaging and relevant topic is crucial to capturing your readers' attention.
1. Background sentences. The first two or three sentences of your introduction should provide a general introduction to the historical topic which your essay is about. This is done so that when you state your hypothesis, your reader understands the specific point you are arguing about. Background sentences explain the important historical ...
A discursive essay is one of four guest of dissertations you'll encounter in your reviews. These are. the Telling Editorial; the Argumentative Essay; the Descriptive Essay; and, of course, the Discursive Essay; We'll get back to these four is a secondary (they're quite useful into understanding our prolix essay). First, let's focus on ...
Discourse studies and the re/writing of History. 1 In recent years, much research in Discourse Studies and Critical Discourse Studies has started to analyse the many dimensions of national and transnational "identity politics" and to investigate how the discursive construction of such identities draws on collective and individual memories, on hegemonic and common sense narratives, and on ...
Use catchy phrases and anecdote. Provide an overview. Make it short. Should have background information. How to Write the Body of a Discursive Essay. Remain unbiased. Arrange your points logically, starting from the strongest argument. Flesh your paragraph. How to Write the Conclusion of a Discursive Essay.
State your opinion in the introduction, supported by examples and reasons. Present the opposing argument before the conclusion, explaining why you find it unconvincing. Summarize your important points in the conclusion. 2. Essay providing a solution to a problem. Focus on discussing an issue and proposing solutions.
For and Against Essay - this is a task written in the form of a debate with opposing opinions. You should be ready to describe every point of view, present facts, and be objective. The introduction of discursive essay topics higher English states the problem you are going to discuss. The main body demonstrates reasons, examples, and facts.
For grant requests, funding pitches, program proposals, or any other kind of education or nonprofit presentation, this Prezi template is the way to generate interest and momentum. Like all Prezi education templates and Prezi nonprofit templates, it's easily customizable. W W For grant requests, funding pitches, progra….
Tips for Effectively Using History Essay Examples. Analyze the Structure: Pay close attention to how the essay is organized, including the introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion. Look for how the author transitions between paragraphs and the use of evidence to support their argument. Study the Thesis Statement:
Cold War Discursive Essay (Grade 12 IEB) Course. History. Institution. Elkanah House. Detailed essay, easy to read and understand, created by pupil who got an 'A' in history for final Matric exam 2019. Preview 1 out of 2 pages.
Compare and Contrast Essay: The Palaeolithic Vs. the Neolithic Periods. The Neolithic Revolution ; For roughly 2.5 million years, people lived on Earth barring leaving a written file of their lives, but they left different sorts of remains and artifacts.
Do you know what a Band 6 discursive essay looks like? You need to see what you need to produce before you can produce one yourself, right? In this article, A Matrix student shares her Band 6 Discursive essay. Read this sample and see how a discursive response differs to a traditional persuasive response.
FCE Essays - Sample/model answers and examiner comments. An essay is always written for the teacher. It should answer the question given by addressing both content points and providinga new content point of the writer's own. The essay should be well organised, with an introduction and an appropriate conclusion,and should be written in an appropriate register and tone