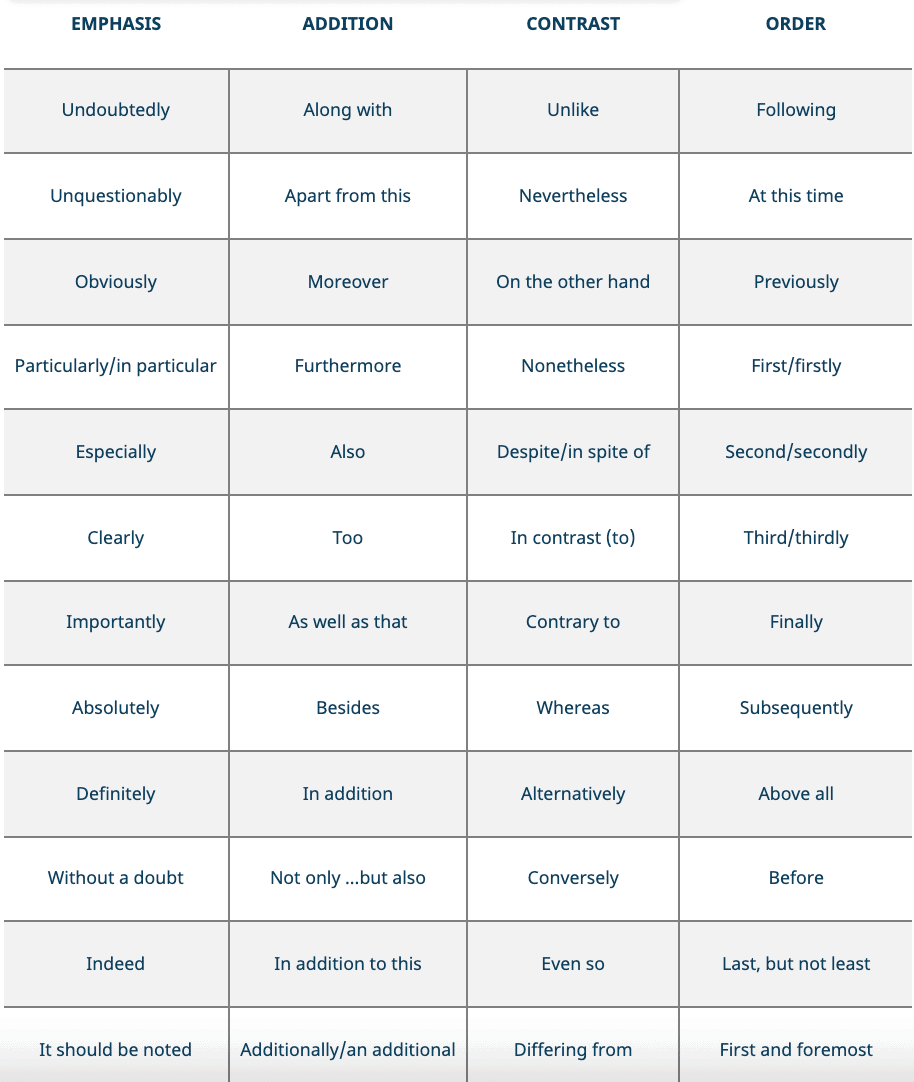
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Transition sentences | Tips & examples for clear writing

Transition Sentences | Tips & Examples for Clear Writing
Published on June 9, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on July 23, 2023.
Clear transitions are crucial to clear writing: They show the reader how different parts of your essay, paper, or thesis are connected. Transition sentences can be used to structure your text and link together paragraphs or sections.
… In this case, the researchers concluded that the method was unreliable.
However , evidence from a more recent study points to a different conclusion . …
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Transitioning between paragraphs, transitioning to a new section, transitions within a paragraph, other interesting articles.
When you start a new paragraph , the first sentence should clearly express:
- What this paragraph will discuss
- How it relates to the previous paragraph
The examples below show some examples of transition sentences between paragraphs and what they express.
Placement of transition sentences
The beginning of a new paragraph is generally the right place for a transition sentence. Each paragraph should focus on one topic, so avoid spending time at the end of a paragraph explaining the theme of the next one.
The first dissenter to consider is …
However, several scholars dissent from this consensus. The first one to consider is …
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
While transitions between paragraphs are generally a single sentence, when you start a new section in a longer text, you may need an entire transition paragraph. Transitioning to a new section involves summarizing the content of the previous section and expressing how the new one will build upon or depart from it.
For example, the following sentences might be an effective transition for a new section in a literary analysis essay.
Having established that the subjective experience of time is one of Mann’s key concerns in The Magic Mountain , it is now possible to explore how this theme facilitates the novel’s connection with World War I. The war itself is not narrated in the book, but rather hinted at as something awaiting Castorp beyond the final pages. In this way, Mann links his protagonist’s subjective experience of time to more than just his illness; it is also used to explore the period leading up to the outbreak of war.
As in academic writing generally, aim to be as concise as you can while maintaining clarity: If you can transition to a new section clearly with a single sentence, do so, but use more when necessary.
It’s also important to use effective transitions within each paragraph you write, leading the reader through your arguments efficiently and avoiding ambiguity.
The known-new contract
The order of information within each of your sentences is important to the cohesion of your text. The known-new contract , a useful writing concept, states that a new sentence should generally begin with some reference to information from the previous sentence, and then go on to connect it to new information.
In the following example, the second sentence doesn’t follow very clearly from the first. The connection only becomes clear when we reach the end.
By reordering the information in the second sentence so that it begins with a reference to the first, we can help the reader follow our argument more smoothly.
Note that the known-new contract is just a general guideline. Not every sentence needs to be structured this way, but it’s a useful technique if you’re struggling to make your sentences cohere.
Transition words and phrases
Using appropriate transition words helps show your reader connections within and between sentences. Transition words and phrases come in four main types:
- Additive transitions, which introduce new information or examples
- Adversative transitions, which signal a contrast or departure from the previous text
- Causal transitions, which are used to describe cause and effect
- Sequential transitions, which indicate a sequence
The table below gives a few examples for each type:
Grouping similar information
While transition words and phrases are essential, and every essay will contain at least some of them, it’s also important to avoid overusing them. One way to do this is by grouping similar information together so that fewer transitions are needed.
For example, the following text uses three transition words and jumps back and forth between ideas. This makes it repetitive and difficult to follow.
Rewriting it to group similar information allows us to use just one transition, making the text more concise and readable.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, July 23). Transition Sentences | Tips & Examples for Clear Writing. Scribbr. Retrieved April 2, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/transition-sentences/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, transition words & phrases | list & examples, how to write topic sentences | 4 steps, examples & purpose, academic paragraph structure | step-by-step guide & examples, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Writing Transitions

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
A discussion of transition strategies and specific transitional devices.
Good transitions can connect paragraphs and turn disconnected writing into a unified whole. Instead of treating paragraphs as separate ideas, transitions can help readers understand how paragraphs work together, reference one another, and build to a larger point. The key to producing good transitions is highlighting connections between corresponding paragraphs. By referencing in one paragraph the relevant material from previous paragraphs, writers can develop important points for their readers.
It is a good idea to continue one paragraph where another leaves off. (Instances where this is especially challenging may suggest that the paragraphs don't belong together at all.) Picking up key phrases from the previous paragraph and highlighting them in the next can create an obvious progression for readers. Many times, it only takes a few words to draw these connections. Instead of writing transitions that could connect any paragraph to any other paragraph, write a transition that could only connect one specific paragraph to another specific paragraph.
Transitional Words and Phrases
One of your primary goals as a writer is to present ideas in a clear and understandable way. To help readers move through your complex ideas, you want to be intentional about how you structure your paper as a whole as well as how you form the individual paragraphs that comprise it. In order to think through the challenges of presenting your ideas articulately, logically, and in ways that seem natural to your readers, check out some of these resources: Developing a Thesis Statement , Paragraphing , and Developing Strategic Transitions: Writing that Establishes Relationships and Connections Between Ideas.
While clear writing is mostly achieved through the deliberate sequencing of your ideas across your entire paper, you can guide readers through the connections you’re making by using transitional words in individual sentences. Transitional words and phrases can create powerful links between your ideas and can help your reader understand your paper’s logic.
In what follows, we’ve included a list of frequently used transitional words and phrases that can help you establish how your various ideas relate to each other. We’ve divided these words and phrases into categories based on the common kinds of relationships writers establish between ideas.
Two recommendations: Use these transitions strategically by making sure that the word or phrase you’re choosing matches the logic of the relationship you’re emphasizing or the connection you’re making. All of these words and phrases have different meanings, nuances, and connotations, so before using a particular transitional word in your paper, be sure you understand its meaning and usage completely, and be sure that it’s the right match for your paper’s logic. Use these transitional words and phrases sparingly because if you use too many of them, your readers might feel like you are overexplaining connections that are already clear.
Categories of Transition Words and Phrases
Causation Chronology Combinations Contrast Example
Importance Location Similarity Clarification Concession
Conclusion Intensification Purpose Summary
Transitions to help establish some of the most common kinds of relationships
Causation– Connecting instigator(s) to consequence(s).
accordingly as a result and so because
consequently for that reason hence on account of
since therefore thus
Chronology– Connecting what issues in regard to when they occur.
after afterwards always at length during earlier following immediately in the meantime
later never next now once simultaneously so far sometimes
soon subsequently then this time until now when whenever while
Combinations Lists– Connecting numerous events. Part/Whole– Connecting numerous elements that make up something bigger.
additionally again also and, or, not as a result besides even more
finally first, firstly further furthermore in addition in the first place in the second place
last, lastly moreover next second, secondly, etc. too
Contrast– Connecting two things by focusing on their differences.
after all although and yet at the same time but
despite however in contrast nevertheless nonetheless notwithstanding
on the contrary on the other hand otherwise though yet
Example– Connecting a general idea to a particular instance of this idea.
as an illustration e.g., (from a Latin abbreviation for “for example”)
for example for instance specifically that is
to demonstrate to illustrate
Importance– Connecting what is critical to what is more inconsequential.
chiefly critically
foundationally most importantly
of less importance primarily
Location– Connecting elements according to where they are placed in relationship to each other.
above adjacent to below beyond
centrally here nearby neighboring on
opposite to peripherally there wherever
Similarity– Connecting to things by suggesting that they are in some way alike.
by the same token in like manner
in similar fashion here in the same way
likewise wherever
Other kinds of transitional words and phrases Clarification
i.e., (from a Latin abbreviation for “that is”) in other words
that is that is to say to clarify to explain
to put it another way to rephrase it
granted it is true
naturally of course
finally lastly
in conclusion in the end
to conclude
Intensification
in fact indeed no
of course surely to repeat
undoubtedly without doubt yes
for this purpose in order that
so that to that end
to this end
in brief in sum
in summary in short
to sum up to summarize

Improving Your Writing Style
This is an accordion element with a series of buttons that open and close related content panels.
Clear, Concise Sentences
Use the active voice
Put the action in the verb
Tidy up wordy phrases
Reduce wordy verbs
Reduce prepositional phrases
Reduce expletive constructions
Avoid using vague nouns
Avoid unneccessarily inflated words
Avoid noun strings
Connecting Ideas Through Transitions
Using Transitional Words and Phrases
Writing Studio
Common transition words and phrases.
In an effort to make our handouts more accessible, we have begun converting our PDF handouts to web pages. Download this page as a PDF: Transitions Return to Writing Studio Handouts
Transitions clarify the logic of your argument by orienting your reader as you develop ideas between sentences and paragraphs. These tools should alert readers to shifts in your argument while and also maintain the smoothness and clarity of your prose. Below, you’ll find some of the most commonly used transition categories and examples of each. Depending on the example, these suggestions may be within sentences or at the beginning of sentences.
Transitions by Category
1. addition.
Use when presenting multiple ideas that flow in the same direction, under the same heading/ idea also, another, finally, first, first of all, for one thing, furthermore, in addition, last of all, likewise, moreover, next, and, second, the third reason
2. Sequence/ Order
Use to suggest a temporal relationship between ideas; places evidence in sequence first, second (etc.), next, last, finally, first of all, concurrently, immediately, prior to, then, at that time, at this point, previously, subsequently, and then, at this time, thereafter, previously, soon, before, after, followed by, after that, next, before, after, meanwhile, formerly, finally, during
3. Contrast
Use to demonstrate differences between ideas or change in argument direction but, however, in contrast, on the other hand, on the contrary, yet, differ, difference, balanced against, differing from, variation, still, on the contrary, unlike, conversely, otherwise, on the other hand, however
4. Exception
Use to introduce an opposing idea however, whereas, on the other hand, while, instead, in spite of, yet, despite, still, nevertheless, even though, in contrast, but, but one could also say…
5. Comparison
Use to demonstrate similarities between ideas that may not be under the same subject heading or within the same paragraph like, likewise, just, in a different way / sense, whereas, like, equally, in like manner, by comparison, similar to, in the same way, alike, similarity, similarly, just as, as in a similar fashion, conversely
6. Illustration
Use to develop or clarify an idea, to introduce examples, or to show that the second idea is subordinate to the first for example, to illustrate, on this occasion, this can be seen, in this case, specifically, once, to illustrate, when/where, for instance, such as, to demonstrate, take the case of, in this case
7. Location
Use to show spatial relations next to, above, below, beneath, left, right, behind, in front, on top, within
8. Cause and Effect
Use to show that one idea causes, or results from, the idea that follows or precedes it because, therefore, so that, cause, reason, effect, thus, consequently, since, as a result, if…then, result in
9. Emphasis
Use to suggest that an idea is particularly important to your argument important to note, most of all, a significant factor, a primary concern, a key feature, remember that, pay particular attention to, a central issue, the most substantial issue, the main value, a major event, the chief factor, a distinctive quality, especially valuable, the chief outcome, a vital force, especially relevant, most noteworthy, the principal item, above all, should be noted
10. Summary or Conclusion
Use to signal that what follows is summarizing or concluding the previous ideas; in humanities papers, use these phrases sparingly. to summarize, in short, in brief, in sum, in summary, to sum up, in conclusion, to conclude, finally
Some material adapted from Cal Poly Pomona College Reading Skills Program and “ Power Tools for Technical Communication .”
Writing Effective Sentence Transitions (Advanced)
Transitions are the rhetorical tools that clarify the logic of your argument by orienting your reader as you develop ideas between sentences and paragraphs. The ability to integrate sentence transitions into your prose, rather than simply throwing in overt transition signals like “in addition,” indicates your mastery of the material. (Note: The visibility of transitions may vary by discipline; consult with your professor to get a better sense of discipline or assignment specific expectations.)
Transition Signals
Transition signals are words or phrases that indicate the logic connecting sets of information or ideas. Signals like therefore, on the other hand, for example, because, then, and afterwards can be good transition tools at the sentence and paragraph level. When using these signals, be conscious of the real meaning of these terms; they should reflect the actual relationship between ideas.
Review Words
Review words are transition tools that link groups of sentences or whole paragraphs. They condense preceding discussion into a brief word or phrase. For example: You’ve just completed a detailed discussion about the greenhouse effect. To transition to the next topic, you could use review words like “this heat-trapping process” to refer back to the green house effect discussion. The relative ability to determine a cogent set of review words might signal your own understanding of your work; think of review words as super-short summaries of key ideas.
Preview words
Preview words condense an upcoming discussion into a brief word or phrase. For example: You’ve just explained how heat is trapped in the earth’s atmosphere. Transitioning to the theory that humans are adding to that effect, you could use preview words like “sources of additional CO2 in the atmosphere include” to point forward to that discussion.
Transition Sentences
The strongest and most sophisticated tools, transition sentences indicate the connection between the preceding and upcoming pieces of your argument. They often contain one or more of the above transition tools. For example: You’ve just discussed how much CO2 humans have added to the atmosphere. You need to transition to a discussion of the effects. A strong set of transition sentences between the two sections might sound like this:
“These large amounts of CO2 added to the atmosphere may lead to a number of disastrous consequences for residents of planet earth. The rise in global temperature that accompanies the extra CO2 can yield effects as varied as glacial melting and species extinction.”
In the first sentence, the review words are “These large amounts of CO2 added to the atmosphere”; the preview words are “number of disastrous consequences”; the transition signals are “may lead to.” The topic sentence of the next paragraph indicates the specific “disastrous consequences” you will discuss.
If you don’t see a way to write a logical, effective transition between sentences, ideas or paragraphs, this might indicate organizational problems in your essay; you might consider revising your work.
Some material adapted from Cal Poly Pomona College Reading Skills Program and “ Power Tools for Technical Communication .”
Last revised: 07/2008 | Adapted for web delivery: 05/2021
In order to access certain content on this page, you may need to download Adobe Acrobat Reader or an equivalent PDF viewer software.

Microsoft 365 Life Hacks > Writing > How to effectively write and use transitions in an essay
How to effectively write and use transitions in an essay
The key to an effective argumentative essay —and to any successful piece of writing—is the ability to transition between paragraphs and ideas smoothly. Bouncing between various ideas can confuse the reader. Learn how you can link your arguments together through effective paragraph transitions.

The importance of outlining your essay
Don’t go blind into your argument. Just like a building, a strong essay begins with a strong foundation and structure. A typical five-paragraph essay will have the following:
- Introduction: The introduction paragraph is where you should show the reader what you aim to write about. This is where you set the tone of your argument: are you writing formally or informally, taking a positive or negative stance, or refuting a specific issue or person? Your thesis statement will go at the end of your introduction paragraph.
- Argument 1: The next three paragraphs are where you expand on your argument. Begin with a topic sentence that serves as an overview of your intended position, before you introduce statistics, quotes, and other forms of research.
- Argument 2: A general rule is that you should introduce broader points to your argument before going into detail. Linking these paragraphs together will be vital to forming a cohesive argument.
- Argument 3: Bring your readers to your viewpoint with persuasion, based on your research: whether it’s through quotes from experts, or logical reasoning, this is where your passion in your argument can shine.
- Conclusion: Here, you summarize the points that you’ve just made. Remind the reader of your thesis statement from your introduction, and concisely sum up the arguments you’ve made in previous paragraphs. If you are asking the reader to act, here is where you bring up a call to action.

Write with Confidence using Editor
Elevate your writing with real-time, intelligent assistance
The five-paragraph essay is a time-tested form of rhetoric. However, the way you link these paragraphs can make or break the effectiveness of your argument.
How to use paragraph transitions
Creating a transition between the paragraphs of your essay will bring out the relation between the points you’re making. Transitions can also provide your readers with a direction on where your argument is headed, so that they might better understand the rhetorical path that you are leading them on.
After you identify the subject and angle of your paragraphs, consider the relationships between these points: do they tell a narrative, or are they linked by chronological or another order? Both can be used to format your argument, as long as the path toward your thesis statement is clear.
What is the link between the points of research that you have found? Are the statistics connected, or do they contrast? Both can be effective points and counterpoints to form a transition. What are the central ideas of your points of argument?
Effective transition words to use
No matter if you’re comparing or contrasting your argumentative paragraphs, you can always begin a sentence with words or phrases that flow into each other.
These words can link arguments together:
Consequently, these words draw contrasts between ideas:
Microsoft’s thesaurus and grammar tools can help you expand your vocabulary with synonyms and grammatical checks that will lend credence to your writing. For more tips on forming an ideal essay, check out these tips from Microsoft 365 on how to improve your writing skills.
Get started with Microsoft 365
It’s the Office you know, plus the tools to help you work better together, so you can get more done—anytime, anywhere.
Topics in this article
More articles like this one.

What is independent publishing?
Avoid the hassle of shopping your book around to publishing houses. Publish your book independently and understand the benefits it provides for your as an author.

What are literary tropes?
Engage your audience with literary tropes. Learn about different types of literary tropes, like metaphors and oxymorons, to elevate your writing.

What are genre tropes?
Your favorite genres are filled with unifying tropes that can define them or are meant to be subverted.

What is literary fiction?
Define literary fiction and learn what sets it apart from genre fiction.

Everything you need to achieve more in less time
Get powerful productivity and security apps with Microsoft 365

Explore Other Categories
- How it works
How to Use Transitions in an Essay
Published by Alaxendra Bets at August 18th, 2021 , Revised On August 22, 2023
Not sure how to use transition words for essays? Unable to figure out where you can place transition words within an essay? Here is all you need to know about transitions in an essay .
We overlook the importance of transitions in an essay. While the essayists themselves can see all the connections between the topic , paragraphs , topic sentences , introduction , main body, and conclusion , it’s usually not the case for the readers who generally struggle to figure out how it all fits together, particularly if no transition words or sentences are used.
So if you are worried about your readers being unable to see the relationships and connections that may seem obvious to you, then you might want to learn to use transitions in academic writing.
Remember that it is vitally important to see your writing from the readers’ perspective to achieve the grade you have worked so hard for .
A clear understanding of the connection in an essay is of utmost importance, but to do so, you will need to relate what you are saying to what you have already said previously.
Here are some techniques to enable you to get your readers to follow your design of writing.
The Known-new Contract Technique
One common way to help your readers establish connections is to make use of the known-new contract technique. This method takes into consideration both cohesion between sentences and agreement of topic matter.
With the known-new contract, you will need to think through the sequence of information in a sentence, which you can achieve by following the below three rules;
- Start each new sentence by mentioning the information that the preceding sentence ended with.
- Each sentence should end by reflecting on a new piece of information.
- Avoid starting sentences with new information.
If you can expertly incorporate this technique in your writing, your readers will undoubtedly understand any new piece of information with familiarity with the context.
With this writing style, you will link new information with old information without additional effort.
Can you see the use of a known-new contract in the below paragraph?
Each sentence in your essay should begin with information that the previous sentence ended by reflecting on a new piece of information.
If you can expertly and consistently integrate new information with old information, your readers will undoubtedly understand any new information with familiarity with the context.
As you can see in the above example, the second sentence starts concerning the first sentence’s information. So the readers can easily understand the relationship between the two sentences.
However, if the two sentences do not have the same topic matter, the cohesion between them will break, which will result in the two sentences appearing detached and unrelated.
Use of Transition Words and Phrases
The known-new contract ensures the most natural and effective transitions in an essay. However, if the known-new contract doesn’t seem to work for you, there are other ways to achieve an effective transition between sentences and paragraphs , such as the use of transition words and phrases.
There are four significant types of transitions words and phrases;
- Signposting phrases such as first of all, for instance, in this example, etc.
- Conjunctive adverbs such as moreover, instead, thus, however, furthermore, etc.
- Relative pronouns such as that, who, who, whomever, whoever, when, what, etc.
- Subordinating conjunctions such as since, unless, when, until, so that, and so, how, if, because, therefore, after, although, etc.
All transition words and phrases indicate the connection between what you are saying and what’s already been said previously.
As a writer, you will need to make appropriate use of these words and phrases to establish the relationship between sentences, particularly when the relationship between sentences doesn’t seem to be clear in the first place.
Combine Similar Information
Another way to ensure the readers find your writing easy to understand is to combine similar information within the essay. By now, you might have noticed that the use of transition words and the known-new contract technique adds to the document’s word count (because both these methods repeat known information at the beginning of sentences).
So a natural way to limit the use of new words is to eliminate the need for transition words, which you can typically achieve by combining similar information into one segment in the essay.
Want to know what essay structure and style will work best for your assignment?
Problem fixed! We can write any type of essay in any referencing style. We ensure every essay written is beyond your expectations.

Paragraph Transitions
Transitioning between paragraphs will require you to place the transitions at the beginnings of the new paragraph.
Avoid using transitions at the end of the preceding paragraphs because, in ideal circumstances, you want each paragraph of your essay to focus on one aspect of your essay topic . This will also allow you to combine similar information together (as we just learned above).
Transitions are forward-looking in nature, which means they give an insight into what is to follow or the topic matter that new paragraphs and sentences will incorporate. Using a transition at the start of new paragraph signals focus on the content matter of the new paragraph.
Unlike transitions between sentences that establish a connection between sentences, transitions in paragraphs focus on developing the relationship between the old and the new paragraph.
For this very reason, transitioning between paragraphs will require you to shed light on the central argument in the previous paragraph and relate it to the information provided in the present paragraph.
Here are a few things for you to consider when writing a paragraph transition;
- Is the new paragraph continuation of a related point discussed in the previous paragraph?
- Does the new paragraph extract or deduce some information from the preceding paragraph?
- Does it second the argument presented in the previous paragraph or offer a counter perspective?
Also Read: How Long is an Essay in Academic Writing?
Final Thoughts!
We have learned to use transition words and phrases in this article, but occasionally you may need to write full transition sentences. This is especially true for longer academic writing pieces, such as a dissertation where you might not express the transitions clearly with the help of transition words and phrases.
While you want to be as concise as possible, you cannot compromise the clarity of transitions.
So if you are unable to transition using words and phrases with clarity, it will make sense to write a full transition sentence. Similarly, if a transition sentence doesn’t do the job, you can consider writing a transition paragraph.
Need Help With Essay Writing?
At ResearchProspect, we have a team of hundreds of expert essay writers. No matter how urgent and complex your essay might seem, our Masters and Ph.D. qualified writers are capable of delivering a first-class essay even on a few hours’ notice.
Learn More About Our Essay Services Order Your Bespoke Essay Now
Frequently Asked Questions
What are transition words and examples.
Transition words are phrases that link ideas, enhancing the flow of writing. Examples:
- Addition : Furthermore, in addition, moreover.
- Contrast : However, on the other hand, yet.
- Cause-Effect : Therefore, as a result, consequently.
- Comparison : Similarly, likewise, in the same way.
- Conclusion : In conclusion, to sum up, ultimately.
- Time : Meanwhile, subsequently, eventually. These words guide readers through your text, making it coherent and organised.
You May Also Like
Having problems with writing a thesis statement for an essay? This article can help you in writing a tremendous essay thesis statement.
Not sure about how to organize an essay? This article is designed to provide a brief yet compact view to master the skill of organization of essay.
Before you totally lose your mind here let’s see whether the broken argument in an essay needs to be dumped or just neatly reworked and fixed.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works
How to Use Transition Sentences: Definition, Tips, and Examples

Transition sentences are crucial components of written and spoken language that serve as bridges between different ideas, paragraphs, or sections within a piece of writing. These sentences smoothly guide the reader from one point to another, ensuring coherence and logical progression in the narrative. Transition sentences play a vital role in maintaining the flow of a text, helping readers navigate through complex information or arguments with ease.
The primary function of transition sentences is to establish connections and relationships between different text parts, creating a sense of unity and coherence. By using transitional words or phrases, writers create a cohesive and well-organized structure, enhancing the overall readability and comprehension of their work. They can take various forms, including words like "however," "meanwhile," or phrases like "on the other hand." Students who use our essay writing service receive their papers where transitional words and sentences are used on point.
What Are Transition Sentences Explained
Transitional sentences are crucial links within a written or spoken discourse, aiding in the seamless connection between ideas, paragraphs, or sections. These sentences play a pivotal role in ensuring a cohesive narrative flow and logical progression, enhancing the overall clarity and comprehension of the text. Here are several examples:
- Addition Transition: “Building on this idea, the next section delves into…”
- Contrast Transition: “While the previous paragraph discussed the benefits, it is essential to examine the drawbacks…”
- Causation Transition: “The initial steps in the process set the foundation; consequently, the final stages produce tangible results…”
- Time Transition: “As the narrative unfolds, the protagonist's journey takes unexpected turns, ultimately leading to a surprising climax…”
- Comparison Transition: “In contrast to the traditional approach, the modern methodology offers a more efficient and streamlined solution…”
These transitional sentences exemplify how authors seamlessly guide readers through shifts in thought, emphasize relationships between ideas, and ensure a coherent and engaging narrative structure. Remember that before you learn how to use transitions, we recommend you read this guide on how to write an essay introduction .
What Are Good Transition Sentences
Good transition sentences are the linchpin of effective writing, ensuring a seamless flow of ideas and maintaining the reader's engagement. These sentences serve as roadways, connecting one thought to the next and guiding the audience through the narrative. Achieving a balance between cohesion and variety is essential for crafting effective transitions, which can be seen in the examples of transition sentences below.
Consider the transition from one paragraph to another. Instead of abruptly shifting topics, a good transition sentence introduces the upcoming idea while connecting it to the previous one. For example, "Having explored the historical context of the Industrial Revolution, we now delve into its profound socio-economic impacts."
Another critical function of transition sentences is to indicate contrasts or contradictions in ideas. By using words like "however," "on the contrary," or "in contrast," writers signal a shift. For instance, "The benefits of renewable energy are undeniable. However, it is crucial to acknowledge the challenges associated with its widespread implementation."
Time transitions are indispensable for chronological order. "In the following years" or "Meanwhile" are cues that seamlessly guide the reader through the timeline of events. For instance, "The initial phase of the project laid the groundwork. Meanwhile, unforeseen challenges arose during the implementation stage."
To highlight similarities or draw comparisons between ideas, phrases like "similarly," "in the same vein," or "likewise" prove valuable. For example, "Just as the scientific method revolutionized research in the natural sciences, applying a similar empirical approach can advance social sciences."
Good transition sentences are versatile tools that elevate writing by ensuring coherence, progression, and reader understanding. A thoughtful integration of transitions contributes to the overall rhythm and clarity of the narrative, enhancing the impact of the written work. If you are just about to write your paper and want to know the difference between Metaphors and Analogies, we suggest you take a look at our guide to help you find a good topic ideas example.
How to Write a Transition Sentence
When writing a transition sentence, there are three very important aspects to consider: The logical relationship between the ideas, Wording, and Placement. Use this as a rule of thumb; you will always write good transition sentences.
Start with identifying the relationship between the key point and the ideas. Ask yourself whether to contrast them, make a smooth connection, summarize the point, or bring in a new idea. Once you know why you need an effective transition, consider half of the job done.
The wording of transitions is equally important. You must choose words that express the relationship between the previous paragraph and a new one. Every language has common transitional words that smoothly make logical connections between the ideas. There are so many that you can easily avoid overusing the same transition words and phrases. The following examples of transition sentences will give you a clearer understanding of the concept: 'In conclusion…', 'On the other hand…' 'Previously mentioned…' and so on.
The right placement helps you outline the logical connections more effortlessly. You should put the transition words where they fit naturally. Usually, it's either at the beginning of a new paragraph or at the end to let the reader know you are about to draw conclusions.
All the above is an ABC of how to write a transition sentence. Follow our guide; you will master the art of transitional devices in no time.
You can be interested: Metaphors and Analogies: How to Use Them in Your Academic Life

Looking for Professional Help with Your Essay Writing?
Our team of expert writers will get you a cohesive essay with timely transitional sentences. Become the top student in your class!
Transition Sentences Between Paragraphs
Transition sentences between paragraphs play a pivotal role in weaving a cohesive tapestry of ideas, guiding readers through the narrative with fluidity and clarity. These sentences act as connective tissue, smoothly transitioning from one paragraph to the next, enhancing the overall readability of the text.
Consider the scenario where a narrative shifts from introducing a problem to presenting a solution. A well-crafted transition sentence can bridge this gap seamlessly. For instance, "Having identified the challenges, let's now explore viable solutions that can pave the way for meaningful change."
Similarly, when delving into a contrasting idea, a transition sentence becomes the compass that guides readers through the shift in perspective. "While the benefits of technology are evident, it is imperative to acknowledge the potential drawbacks that accompany such rapid advancements."
Time transitions are indispensable when narrating a sequence of events. "As the story unfolds" or "In the subsequent years" serve as cues, allowing readers to effortlessly follow the chronological progression of the narrative. For example, "The initial experiments yielded promising results. In the subsequent years, researchers encountered unforeseen challenges that reshaped the trajectory of their investigations."
Furthermore, comparison transitions help draw parallels between concepts. "In a similar vein" or "Likewise" act as highways, linking one idea to another for a smoother transition. "Just as the characters in the novel undergo personal growth, the storyline also evolves, creating a nuanced exploration of human experiences."
In general, transition words and sentences are the architects of narrative coherence, ensuring that readers navigate through the text seamlessly. By strategically placing these transitions, writers can guide their audience through shifts in ideas, perspectives, and timelines, creating a harmonious and engaging reading experience. If you are just about to write your paper and want to know how to write a hypothesis, we suggest you take a look at our guide to help you find a good example of topic ideas.
You can be interested: How to Write a Hypothesis
Where to Place Transition Sentences
Transition sentences are powerful tools, but their effectiveness depends on strategic placement within a text. Correct usage enhances coherence, while incorrect placement can disrupt the flow. Let's explore where to appropriately position these sentences with examples.
.webp)
Placing a transition sentence at the start of a new paragraph signals a shift in focus, preparing the reader for what lies ahead. This ensures a logical progression.
- Correct: "Having examined the historical context, we now shift our focus to the societal impacts of the Industrial Revolution."
- Incorrect: "The Industrial Revolution, a turning point in history. Its impacts on society were profound."
Within a paragraph, transitions can signal a shift in perspective, introducing contrast or contradiction smoothly without abrupt interruptions.
- Correct: "The advantages of renewable energy are evident; however, challenges in infrastructure remain significant."
- Incorrect: "Renewable energy has numerous benefits. The challenges in infrastructure are, however, significant."
Transition sentences guide readers through time, indicating progression. Placing them at natural breakpoints helps readers follow the chronological sequence effortlessly.
- Correct: "The project's initiation marked a period of excitement. Subsequently, unforeseen challenges altered the course."
- Incorrect: "The project's initiation marked a period of excitement. However, unforeseen challenges altered the course."
When comparing ideas, transitions can smoothly connect concepts, creating a link that aids in understanding relationships.
- Correct: "The scientific method revolutionized natural sciences. In a similar vein, applying empirical approaches can advance social sciences."
- Incorrect: "The scientific method revolutionized natural sciences. Likewise, empirical approaches can advance social sciences."
Concluding with a transition sentence summarizes key points, guiding readers out of the main discussion gracefully.
- Correct: "In conclusion, the evidence supports the hypothesis. However, further research is needed to explore long-term effects."
- Incorrect: "The evidence supports the hypothesis. In conclusion, further research is needed to explore long-term effects."
By placing transition sentences strategically, writers guide readers through the narrative, creating a coherent and engaging reading experience. Incorrect usage disrupts the flow, making it essential to consider the context and purpose when incorporating these transitions.
Transition Sentences Between Sections
Transition sentences serve as pathways, seamlessly connecting different segments of your text and ensuring a cohesive and logical flow. These sentences play a pivotal role in guiding readers through shifts in themes, perspectives, chronological progressions, or comparative analyses. For instance, when transitioning from an exploration of historical context to an in-depth analysis of the economic ramifications of the Industrial Revolution, the text might gracefully progress: "Having delved into the historical backdrop, the narrative now shifts focus to the economic repercussions of the Industrial Revolution, shedding light on its profound impact on commerce and societal structures."
Similarly, in contrasting perspectives, a transition sentence such as "While the benefits of renewable energy are evident, a closer examination reveals potential challenges in its widespread implementation. This nuanced perspective prompts a deeper exploration of the complexities inherent in adopting sustainable practices on a global scale."
In cases of chronological progression, a transition like "With the foundation laid, the narrative progresses to the crucial developments during the implementation phase. This chronological shift allows readers to follow the evolution of ideas, connecting past events to present implications and fostering a comprehensive understanding."
Likewise, during comparative analyses, a transition sentence such as "In contrast to traditional methodologies, the discussion now centers on the innovative approaches that have reshaped the field. This shift in focus invites readers to critically evaluate the transformative impact of progressive strategies and their implications for future practices."
In conclusion, transition sentences between sections are indispensable for maintaining coherence and guiding readers through different thematic or analytical shifts. The strategic use of these sentences provides clarity and ensures a seamless reading experience, allowing readers to navigate through diverse ideas with ease. Keep in mind that you can always order an essay online if anything seems too difficult or you don’t have time to deal with the assignment personally.
Transition Sentences Within Paragraphs
Let’s find out how to use transition sentences to connect ideas, ensuring a seamless flow of thoughts. They are like subtle guides that help readers navigate through the evolving narrative. For instance, when introducing additional information, consider a transition like: "Moreover, the data suggests a clear correlation between regular exercise and improved mental well-being." This transition smoothly leads the reader to a deeper understanding by introducing supporting evidence.
In cases of contrasting ideas, a transition sentence can gracefully shift the focus. Imagine exploring technological advancements and social inequality, with a transition like: "On the contrary, some argue that technological advancements may exacerbate social inequality rather than alleviate it." This transition introduces an opposing viewpoint without causing abrupt disruption, encouraging a more nuanced examination of the topic.
For sequential progression, a transition sentence paves the way for the next step in reasoning. Visualize transitioning from theoretical discussions to practical implications: "Following this line of reasoning, the next logical step is to examine the practical implications of these theoretical frameworks in real-world scenarios." This transition guides the reader through the logical progression of ideas within the paragraph, enhancing overall comprehension.
As you can see, transition sentences within paragraphs are subtle tools that enhance readability by smoothly connecting thoughts and ideas. These examples illustrate how these transitions create a cohesive and engaging reading experience.
Transition Words and Phrases
What transforms ordinary sentences into transition sentences? The answer lies in transition words that serve as the guiding signposts, steering your writing's flow from one thought to the next.
The choice of a transition word in a sentence is crucial to your reader's ability to comprehend your writing, as seemingly identical sentences can take on vastly different meanings with different transition words. Let's delve into quick examples illustrating how the selection of words can reshape an idea:
Consider the following sentences:
- We love to try different local restaurants and explore new cuisines. Recently, we tried two new restaurants downtown.
- We love to try different local restaurants and explore new cuisines. Hence, we tried two new restaurants downtown.
- We love to try different local restaurants and explore new cuisines. On the whole, we tried two new restaurants downtown.
Observe how the foodies' point undergoes a dramatic shift simply by substituting various transition words and phrases. This exemplifies the profound impact of word choice on the overall meaning of a sentence. While working on short assignments like essays, this information might seem easy. But when longer papers are due, one may easily get lost in the abundance of transition words and phrases scattered around the document. That’s why we have a professional coursework writing service that can help you with this matter.
Explore the following list of commonly used transition words and phrases tailored for specific transitions:
Transition Words and Phrases to Communicate Similarities
When highlighting similarities between ideas, events, or concepts in your writing, the careful use of transition words is essential. These linguistic tools serve as bridges, guiding your readers through parallel thoughts seamlessly.
- In the same vein
- Correspondingly
- Similarly to
- Analogously
Transition Words and Phrases to Express Emphasis
Adding emphasis to key points in your writing can significantly impact the reader's understanding and engagement. Transition words designed for emphasis play a crucial role in signaling the importance of specific ideas.
- Undoubtedly
- Unquestionably
Transition Words and Phrases to Demonstrate Cause and Effect
Unraveling the cause-and-effect relationship in your writing requires the strategic use of transition words. These words guide readers through the logical progression of events and help them understand the connections between actions.
- Consequently
- As a result
Transition Words and Phrases to Denote Position
When conveying the spatial or logical arrangement of ideas, transition words indicating position become invaluable. They provide clarity and structure, allowing readers to follow the sequential or spatial organization of your content.
- Adjacent to
- Furthermore
- In the background
- In the foreground
Transition Words and Phrases to Illustrate a Sequence
Sequencing ideas in your writing demands a smooth flow to keep readers engaged. Transition words that denote sequence act as navigational tools, guiding your audience through a logical progression of events.
- Subsequently
- In the meantime
Transition Words and Phrases to Show Examples
Providing examples enhances the clarity and credibility of your writing. Transition words tailored for illustrating examples help seamlessly integrate supporting details into your narrative.
- For example
- For instance
- In particular
- To illustrate
- Specifically
Logical Connectors Examples
When it comes to logical connectors English grammar offers a wide range of words and phrases you can use to enrich your text. Below you will find a logical connectors table full of logical connectors examples from our dissertation writing services .
Incorporating transition sentences and phrases is an indispensable skill for any proficient writer. These linguistic tools act as the adhesive that binds individual thoughts, creating a seamless and coherent narrative. The strategic use of transitional elements ensures readers can effortlessly follow the flow of ideas, enhancing comprehension and engagement. Through the judicious selection of transition words, writers wield the power to guide their audience through a logical journey, connecting concepts and building a narrative that is both compelling and easily digestible.
Moreover, the importance of employing transitional sentences extends beyond mere stylistic finesse. It is a fundamental aspect of effective communication, whether in academic writing, professional documents, or creative pieces. As seen in the examples of transition sentences, they not only facilitate the smooth progression of ideas but also serve as cues for readers, signaling shifts in tone, perspective, or logical structure. Our dissertation writing service can help you with smooth transitions between paragraphs and sections of text in complex documents such as theses and capstones.
Too Busy and Need Help from a Writing Assistant?
No worries! Our writing assistants know how to get you that A+
Related Articles
.webp)
How to write a transition sentence
- December 4, 2023
Transitions show the reader how different parts of your essay, paper, or thesis are connected.
Transition sentences will help you create a well-structured research paper or essay with sentences that flow naturally from one point to the next. So it is essential to learn how to effectively create transition sentences.
What is a transition?
A transition in writing is a word or phrase and a sentence that connects one concept to the next. This link can be made within a paragraph or between paragraphs.
Transitions are an important aspect of academic writing, as they help to create a cohesive and well-structured document that is easy for the reader to follow.
Transition word example
....Many people enjoy playing video games, but there are also those who view them as a waste of time. On the other hand Transition example within a paragraph , some experts argue that video games can actually be beneficial for cognitive development.
In this example, the transition part is “On the other hand”, which signals to the reader that a contrasting viewpoint is about to be presented.
Transition sentence example
Paragraphs from an essay about exercise
There are several benefits to regular exercise, such as improved cardiovascular health and increased strength and endurance ....(paragraph continues)... However, it is important to keep in mind that exercise can also pose certain risks, especially if proper precautions are not taken. Transition sentence: Signals the change of focus for the first sentence of next paragraph One of the most common risks associated with exercise is injury, which can range from minor sprains and strains to more serious issues like fractures and dislocations The first sentence of the following paragraph ....(paragraph continues) ....(paragraph continues)
In this example, this transition sentence signals to the reader that a shift in focus is occurring and prepares them for the discussion of exercise risks in the next paragraph.
Now that you’ve had a basic introduction to what a transition is, let’s dig deeper into the topic by seeing even more examples.
Transition between paragraphs
With this type of transition, you simply state a hint from the following paragraph to prepare the reader what’s coming. In other words, you create a link between two consecutive paragraphs.
Let’s have a look at the example below.
The paragraph tells the difficulties the company faced, but the last sentence hints the steps taken, and the following starts explaining these steps.
Transitions between paragraphs example
In recent months, the corporation has faced several difficulties. Sales have been declining, and competition has intensified, putting pressure on the company's bottom line. Despite these challenges, the company is taking steps to turn things around. Transition sentence Management has adopted cost-cutting initiatives to diversify its revenue streams and is seeking new markets. These efforts are projected to provide better financial results in the following quarters.... ...paragraph continues.
The transition above shows the reader how the two paragraphs are connected.
In below example, the transition sentence with “However” indicates how it relates to the previous paragraph.
Transitions between paragraphs example 2
...(Paragraph starts) ...(Paragraph continues) The usage of technology has transformed how we live and work. As a result, we have access to many products that make our lives more accessible and efficient, from cell phones to computers. However, this increased dependence on technology has also raised concerns about its impact on our well-being. Transition sentence According to research, excessive screen usage has been linked to eye strain, migraines, and poor sleep patterns. It is critical to exercise moderation and create good technology habits to reduce these detrimental consequences.
Now, this transition below connects the two paragraphs by demonstrating that the incident stated in the first paragraph was a result of the event described in the second paragraph.
Transition sentence example 3
A strong storm slammed the city Wednesday night, causing widespread damage and power disruptions. Other trees were uprooted, and several structures were damaged. The storm was the result of the convergence of several weather systems over the region. Transition sentence Meteorologists had been watching the passage of these weather systems for several days and had issued a severe weather warning. However, despite the notice, the severity of the storm took many inhabitants by surprise.
Choosing transition words
When moving the emphasis from one detail to another, there are literally dozens of transition phrases to select from. Here are some samples of some of the categories and word combinations accessible to you to give you a broad sense of options.
Things to consider when choosing transition words
Your answers to these four fundamental questions should make it easier for you to figure out which types of transition words might work best at the start of each paragraph .
- What exactly is the point of this paragraph? Is it to present, inform, convince, address a different point of view, review or emphasize previously mentioned concepts?
- Is the concept I’m presenting in this paragraph related to or supportive of any other concept or argument presented in the essay so far?
- Is the argument I’m making in this paragraph presenting a new perspective or idea?
- Is the concept I’m presenting different from or dependent on other concepts discussed in the essay?
Transitions within a paragraph
The known-new contract.
A valuable writing idea is the known-new contract, which infers that a new sentence should start with reference to information from the prior sentence and then relate it to new information.
The known-new contract transition example
Original paragraph The internet has revolutionized the way we communicate with one another. It allows us to connect with people all over the world, access a wealth of information, and even shop online. However, with all these benefits come certain risks, such as identity theft, online scams, and cyberbullying. Paragraph with known-new contract While Transition word the internet has brought about many benefits, including Transition word the ability to connect with people from all over the world, access to vast amounts of information, and online shopping, it also poses certain risks. These risks Highlighting the known information include identity theft, online scams, and cyberbullying, among others.
Start by composing a sentence
As seen from the above example, in the first half of the sentence, start with something that the reader already knows. Towards the end of the sentence, tell the reader something new.
Compose a new sentence
As this information is now known, start with the new information from the previous sentence. Near the end of the sentence, tell the reader something new.
The known-new contract is only a suggestion. It’s not necessary to build every sentence this way, but it’s a good strategy to follow if you’re having trouble keeping your sentences together.
In-depth transition examples
- The British were no match for Napoleon and his navy. In fact, Napoleon lost nearly every sea engagement he fought. The French army was a formidable force. It conquered most of continental Europe under Napoleon’s instructions.
- The British were no match for Napoleon and his navy. In fact, Napoleon lost nearly every sea engagement he fought. The French army, on the other hand, was extremely strong and powerful. It conquered most of continental Europe under Napoleon’s instructions.
- The historical society held a bake sale, car wash, and book fair in October. The department chair was ecstatic with the student's achievements. The historical society does not have sufficient funds to travel to Ottawa. The students are all highly dissatisfied.
- The historical society held a bake sale, car wash, and book fair in October. The department chair was ecstatic with the students’ achievements. Despite their best efforts, the historical organization was unable to raise enough funds to travel to Ottawa. The students are all highly dissatisfied.
- In Book A, the characters are faced with the moral dilemma of a disputed inheritance, which is a large sum of money. The inheritance in Book B is an ancient house. The characters in Book B are confronted with a similar issue.
- In Book A, the characters are faced with a moral dilemma: a disputed inheritance. Despite the fact that the inheritance in Book B is an ancient house rather than a large sum of money, the essence of the situation is very similar.
Transition best practices
Only use a transition sentence when discussing two different concepts.
You don’t need a transition in a paragraph that discusses the same two topics or examples.
Avoid excessive use of transition words
While transition words like “in addition,” “however,” and “also” can be highly useful, they should be used in moderation. Otherwise, the paper will come out as pretentious.
Don’t try connecting two ideas forcefully
If two concepts are placed next to each other in your paper but do not appear to be linked, one of them may not belong or should be relocated to a separate part.
Transition sentences are necessary for a well-structured paper as they offer new ideas and assist the reader’s comprehension. If you follow these steps and tips, writing excellent transition sentences won’t be too hard. Before writing, feel free to analyze our sample essays .
Recently on Tamara Blog
How to write a discussion essay (with steps & examples), writing a great poetry essay (steps & examples), how to write a process essay (steps & examples), writing a common app essay (steps & examples), how to write a synthesis essay (steps & examples), how to write a horror story.

How to Use Transitions in an Essay – Tutorial with Examples
One of your main tasks in writing an essay is to help the reader make connections and understand your writing well. Transitions allow you to do that. They help ensure that the reading process flows smoothly.
I’m Tutor Phil, and in this tutorial I’ll show you how to use transitions effectively in your essays and research papers.
Four Rules of Using Transitions in Academic Writing
Rule 1. structure your essay well.
If your essay has a clear structure, this will minimize the need for transitions. Remember – you shouldn’t really need a lot of transitional words and phrases in your essay.
Use transitions in places where they are most likely to help the reader make the necessary connection and move along. And if your flow of ideas in the essay is clear, that alone is the single most important quality of your writing.
So, if you’re new to essay writing, I highly recommend my tutorial on essay writing for beginners .
Rule 2. Trust the reader
If you trust yourself to write a well-structured essay, then you should trust the reader to understand what you have written.
Don’t use transitions to summarize what you just wrote.
When you pause to remind the reader what you just stated – whether in a section or a paragraph – this makes them feel that you’re wasting their time. Nobody likes stuff repeated to them over and over.
Besides, this signals a lack of trust both in the writer and the reader. Instead, use transitions only to move the reader forward in your essay. I’ll show you exactly how.
Rule 3. Proceed from general to specific
Going from general to specific is a mode in which you should be writing your essay. And transitions should help you accomplish this.
Let’s leave it at that for now because the examples in this tutorial will illustrate this perfectly. But for now just keep in mind that transitions are a great way to help you move from general to specific in your essay.
Rule 4. Use transitions on multiple levels
Transitions can be used to move into a section, a paragraph, or a sentence. When transitioning into a section or a paragraph, use the transition within the lead sentence.
If you’re not familiar with lead sentences or need to brush them up, here is my short and sweet tutorial on lead sentences .
Transitions also come in handy when introducing or leading into a smaller bit of writing, such as a sentence or part of a paragraph.
10 Categories of Transitions with Examples
1. transitions that indicate similarity.
These are transitions that allow you to introduce material that is similar to what came before. You can use these transitions to add material to your essay.
These are such words and phrases as:
- By the same token
“Mozart and Haydn wrote music primarily for the emerging upper middle class. Similarly, Beethoven adhered to the musical tastes of this sliver of the society early in his career.”
2. Contrary Transitions
These are important and powerful transitions that tell the reader that something opposite to what they just read is coming. These include such words and phrases as:
- Nevertheless
- Notwithstanding
- Despite (or “In spite of”)
- On the other hand
“Mozart and Haydn wrote music primarily for the upper middle class and nobility. Beethoven did the same because his sustenance depended on it. However, his creative spirit yearned to write highly evolved and complex music aimed at the connoisseur.”
Another Version (with a different transition)
“Mozart and Haydn wrote music primarily for the upper middle class and nobility. Conversely, Beethoven yearned to write highly evolved and complex music aimed at the connoisseur.”
The Counterargument
One of the ways transitions in this category can be used is to expand your essay while adding validity to your argument.
Let’s say you’re making an argument that Beethoven was an amazingly innovative composer. And you have provided some evidence to support this claim.
Here is how you can use a counterargument to add content and make your point even stronger. You can suggest that others may disagree with your point. But they miss the mark for one or more important reasons.
For example:
“ Some contemporary critics of Beethoven argued that his music was needlessly complex and failed to please much of the public. However , they were quite shortsighted. Beethoven’s music continues to please audiences hundreds of years later while the names of his critics are lost in the shuffle of history.”
You can use the counterargument technique to add a couple of juicy paragraphs to your essay. Here’s a video I created which will show you how:
3. Transitions of Order and Sequence
These are very useful when enumerating or listing items. These are such words as:
A great place to use these transitions is in the thesis statement.
“Going to college presents great advantages. First, college graduates earn more than those without a degree. Second, higher education enriches a person’s inner world. Finally, college is a great way to start friendships that will last a lifetime.”
4. Time Transitions
These words and phrases specify or change the time in which the reader finds herself. Here are some of them:
- In the meantime
- Subsequently
“Two of the men were on the lookout. Meanwhile, the third and fourth were busy cleaning out the store.”

5. Place Transitions
These transitions indicate location or change of location:
- In front of
“In front of the school stood a hot dog stand, students’ favorite food spot.”
6. Transitions into Examples/Specificity
These very important transitions indicate that a specific piece of information is about to support a more general statement that just came before. These are such words and phrases as:
- For example
- For instance
- To illustrate
- Specifically
- To be more specific
“Some kids love school. For example, my son is always excited to go to school because he loves to socialize and to learn.”
“Some subjects are crucial to students’ intellectual development. To be more specific, they cultivate such skills and abilities as critical thinking, decision making, and argumentation.”
7. Transitions of Emphasis or Focus
Use these transitions sparingly because they are often unnecessary. These are such words and phrases as:
- Importantly
“Indeed, Beethoven was an innovative composer.”
“Naturally, Beethoven’s patrons adored him.”
8. Transitions of Cause and Effect
These are very important transitions that I often call Power Words. ( Here is my article on Power Words where you can learn more about them .)
- Consequently
“Mozart wrote some of the most original music with catchy melodies. In effect, he quickly gained the favor of the Viennese.”
9. Transitions Indicating Additional Material
Use these transitions when you want to add a new category or kind of material to support an argument. These words and phrases include:
- Furthermore
- In addition
“The nobles of Vienna adored Mozart for his musical genius and wit. Besides, he knew how to please them by writing music for soirees and social events that were all the rage at the time.”
10. Concluding Transitions
These transitions allow you to signal the coming of the final section, paragraph, or sentence. Definitely use them in the beginning of a conclusion paragraph. These are such words and phrases as:
- To conclude
- In conclusion
- In the final analysis
“In the final analysis, both Mozart and Beethoven enjoyed great success and formidable challenges as composers in their lifetimes.”
Hope this was helpful ( source ). Now go ahead and make these transitions a working part of your writing skills.
Tutor Phil is an e-learning professional who helps adult learners finish their degrees by teaching them academic writing skills.
Recent Posts
How to Write an Essay about Why You Want to Become a Nurse
If you're eager to write an essay about why you want to become a nurse, then you've arrived at the right tutorial! An essay about why you want to enter the nursing profession can help to...
How to Write an Essay about Why You Deserve a Job
If you're preparing for a job application or interview, knowing how to express why you deserve a role is essential. This tutorial will guide you in crafting an effective essay to convey this...
Understanding Transition Sentences (For Essays and Writing with Examples)

What are transition sentences? And how do they work? Is there a correct way to use them? And an incorrect way? Understanding transition sentences is critical when writing essays, articles, or any type of logical flow.
Learn what transitional sentences are in this short guide…
What are transition sentences?
When you write an article, essay (or anything), you’ll want to write it in a logical sequence. You start with an introduction, highlight your points, and then end with a conclusion. Throughout your writing, you would be using sentences to express your thought. To make your writing effective, you need to link the sentences together in a logical way .
This is where transition sentences can be helpful.
As the name suggests, a transition sentence links the thoughts you are expressing in your writing. They make use of words and phrases that act as a bridge between different parts of your writing.
Transition sentences allow your reader to move smoothly from one section to another. Without transition sentences, your reader might not be able to understand the link between different parts of your writing.
What makes a good transition sentence?
Look at this example:
The CEO was very clear that productivity and efficiency were the two key things he would focus on. However , the legacy systems followed by the company acted as a detriment. Tech modernization was the solution that would enhance productivity and efficiency.
Sentences one and three make sense by themselves. But it is important to establish a relationship between the two. This is what the second sentence does . It acts as a bridge (or transition) between the first and third sentences. By doing so, it helps the writer communicate their ideas more effectively.
A good transition sentence would bring clarity by linking ideas expressed in the sentences before and after it. Words and phrases like ‘however,’ ‘in contrast,’ ‘for instance,’ ‘in fact,’ and ‘therefore’ can get used to help make the transition.

Many transition words are available to use. Choose the appropriate word for the situation.
For example, if you want to show the sequence between two sentences, you can use a word like ‘then’ or ‘after.’ If you want to emphasize a point through the transition, you can use ‘indeed,’ ‘especially,’ or ‘particularly.’
Transition words can be used at the start of the sentence ( e.g. , Surely , you are not going to go now!). It can also be used within the sentence (e.g., I rejected the job offer because the salary was lesser than my present pay ).
Here are a few tips that will help you use transition words correctly:
- When sentences within a paragraph sound abrupt or awkward, you need to use transition words to link them.
- Choose the correct transition word that is appropriate to the situation. A wrong selection can make your reader confused.
- When moving from one idea to another, use a transition word to let the reader know.
- Don’t make the mistake of overusing transition words. Too many transition words can end up making your writing look messy.
List of words for transition sentences
Some common words used in transition sentences are:
- Furthermore
- Nevertheless
- Specifically
List of phrases for transition sentences
Transition sentences would use both words and phrases as the bridge. A few phrases that are used include:
- In other words
- On the contrary
- As a result
- In the long run
- As you can see
- In the following
- In the previous
- Having established
- Most importantly
- For example/instance
- By the time
5 Examples of Transitions (Types of Transitions)
Conjunctive adverbs can be used to establish the logical link between ideas. They can be classified under five heads. It must be noted some words appear in multiple categories.
Of addition
- Additionally
- In addition
- In the same way
The following example will make this clear.
First , put a pan on the stove and heat it. Next , add oil to the pan.
In the above, first and next act as the transition and are adding on to what is being said previously.
Of contrast
These words establish a contrast or difference while making the transition.
- In contrast
- Even though
- At any rate
- In spite of that
- On the other hand
The island was not the paradise we were hoping for. On the contrary , it was dirty, noisy, and had unmanageable traffic.
The above example brings out a contrast between expectations and reality.
Of comparison
- By comparison
- In the same manner
Jonathan is crazy about chess. His daughter is similarly a big fan of the board game.
In this example, the word similarly shows a comparison between father and daughter. You may note the transition word need not be at the start of the sentence. It can be placed anywhere.
These transition words are indicative of a result. It shows the result of the previous sentence/idea.
- Consequently
Their star player was suffering from a hamstring injury and could not play. Hence , their team faced a humiliating defeat on match day.
The star player’s absence resulted in the team’s defeat. The transition word ‘Hence’ in the example is the bridge between the cause/event and the result.
Some transition words show relationships in time. They include:
- Simultaneously
- Subsequently
The speaker will be a bit late for the talk. Meanwhile , let’s ask the participants to share their views on the program .
As the speaker will be late, there is time left. So, the participants are asked to share their views and opinions. In this example, ‘Meanwhile’ is a transition word that shows relationship to time.
Subordinating conjunctions and transition sentences
You can use a subordinating conjunction in a sentence to join a dependent clause to an independent clause .
Example: When the postman came, my dog greeted him with a volley of barks.
In this example, the word ‘when’ is the subordinating conjunction that joins ‘the postman came’ and ‘my dog greeted him …’
The subordinating conjunction serves a special purpose here. It acts as a transition between two ideas. The use of the coordinating conjunction provides a logical flow.
Example: He is smarter than you are.
In this example, “than” is the subordinating conjunction that connects ‘He is smarter’ and ‘you are.’ It provides the bridge or transition between the two clauses .
Let’s look at another example to understand this. There are two clauses – ‘The spring arrives’ and ‘my hay fever gets aggravated. A subordinating conjunction can link the two. We can use ‘As’ here. So, the sentence would now read – ‘ As the spring arrives, my hay fever gets aggravated.’
Correlative conjunctions and transition sentences
The correlative conjunction shows a correlation between two words or phrases within a sentence. They play a key role in transition sentences. The use of a correlative conjunction ensures a smooth flow between two sentences or ideas.
Example: My boss totally ignored my work. Neither my hard work nor my punctuality impressed him. So, I decided to move on and look for a new job.
In the above example, sentences one and three are independent and convey the meaning clearly. However, the second sentence acts as a transition explaining why sentence one leads to sentence two.
In the second sentence, we see the use of neither … nor. This combination of words acts as correlative conjunctions in this example.
Some other words that work as correlative conjunctions are:
- Either … or
- Neither … nor
- Whether … or
- Not only … Also
Whether you want to have dinner or prefer to skip it is entirely left to you.
The above example uses Whether … or as correlative conjunctions in the sentence.
Examples of transition sentences
Examples of transition sentences:
Communicate similarities
To communicate similarities, you can use transitional words like:
Examples of sentences where the transition word communicates similarities:
- He decided to join the army just as his brother had done five years back.
- You can fly this plane the same way you flew the trainer jet; there is no real difference.
- All the employees in the Production department come from the neighboring town . Similarly , the store staff is also from that town.
Express emphasis
Words like ‘especially,’ ‘above all,’ ‘particularly’, ‘indeed,’ in fact,’ and ‘in particular’ can be used to express emphasis. When used in transition sentences, they emphasize the idea express previously.
- She was overweight. In fact , it won’t be wrong to say she was grossly obese.
- I liked the blue dress in particular .
- Indeed , it won’t be wrong to say that her arrogance led to the engagement’s breakup.
- There is a lot of focus on improving public services, especially education.
Cause and effect
Transition sentences can be very helpful in showing cause and effect or result. The following words can be used for this:
- Accordingly
- At that time
- They spent the entire semester binge-watching shows. Consequently , they failed to obtain pass marks on any of the papers.
- There are just ten items left in stock. Hence , it would be better if we suspend taking new orders at present.
- The tests revealed that his blood pressure and cholesterol levels were very high. As a result , the doctor decided that he had to increase the dosage of his medicines.
Position or place can be indicated through the use of transition words like:
- At the back
Here are some example sentences:
- Walk towards the bookshelf. Adjacent to the shelf is a table, that’s where you will find the money.
- The house was located a few yards from the river. Next to the house was the scary-looking tree.
- You will see the building with the red flag. The storeroom is at the back of this building.
Describe a sequence
Transition words are perfect to use while describing a sequence. The words that can be used are:
- Followed by
- First , write down all the numbers in the form of a list. Next , add all the numbers. Finally , write down the total.
- Initially , three employees were working on the project. Subsequently , the project grew the numbers rise to twenty.
- The private plane owned by the CEO was the first to land. This was followed by the helicopter containing the crew.
To show examples
Transition words can be used to show examples or illustrate a particular point. Some words to use are:
- For example
- For instance
- Illustrated by
- As an example
- In this case
- On this occasion
- To illustrate
- To demonstrate
- The speaker displayed the blueprint of the equipment on the screen. To illustrat e its working, he showed a video.
- There are seven tools you can use to solve this problem. As an example , I will talk about the fishbone diagram.
- Different essential oils can help you feel relaxed. For instance , using lavender oil makes you feel refreshed and rejuvenated.
How to use transition sentences between paragraphs
Transition sentences can get used within a paragraph. It also can get used between paragraphs.
This is important since the transition sentence provides a flow between paragraphs . It allows the readers to understand the relationship between the ideas expressed in those two different paragraphs.
When you start writing a paragraph , show a link to the previous paragraph in the first sentence. This establishes a bridge between both paragraphs.
Here’s an example:
There is no doubt that the effects of pollution by industries. This is why activists call for a ban on industries to stop pollution.
Despite the previous argument , we must also think about the economy. Banning industries will bring the economy to a standstill.
This example, ‘despite the previous argument’ is used to transition between the two paragraphs.
In contrast, the first part calls for a ban on industries, and the second discusses the economic effect. Using a transition allows for a smooth flow between the two.
Examples of transition sentences for essays
The use of transitions is very important in essays. An essay is written to convey an idea, opinion, or viewpoint. To ensure its effectiveness, transition sentences are needed at different parts of the essay. Transition sentences are needed between sentences, between sections, and at the conclusion of the essay.
A few examples of this:
- Having established that a large majority of students have internet access, we can conclude t hat e-learning is a distinct possibility.
- All the employees have a smartphone. In fact , most of them connect to the company’s Wi-Fi using their phone.
Examples of transition words for concluding sentences
Transition sentences are used throughout a write-up. It is imperative that the conclusion also has a transition. Your write-up needs to end with a summary of what you are trying to say. Or with a call-to-action. Using transition words in the conclusion can help you achieve this.
A few transition words you can consider using are:
- In conclusion
- As shown above
- On the whole
- Generally speaking
- To summarize
- To summarize , sustained use of this medicine offers significant benefits to patients.
- In summary, democracy has many limitations but no other acceptable alternative.
- Ultimately , it all boils down to the decision taken by the customer.
- In short , the best option available is to get funds from a new investor.
Sentence structure
More on sentence structure:
- Dangling modifier
- Transition sentences
- Active voice
- Passive voice
- Adverbial clause
- Parallelism
- Transition Sentences Tips and Examples for Clear Writing
- Transitional devices
- How to Use Transition Sentences for Smoother Writing
- Transition Words: Examples in Sentences, Paragraphs & Essays
Inside this article
Fact checked: Content is rigorously reviewed by a team of qualified and experienced fact checkers. Fact checkers review articles for factual accuracy, relevance, and timeliness. Learn more.

About the author
Dalia Y.: Dalia is an English Major and linguistics expert with an additional degree in Psychology. Dalia has featured articles on Forbes, Inc, Fast Company, Grammarly, and many more. She covers English, ESL, and all things grammar on GrammarBrain.
Core lessons
- Abstract Noun
- Accusative Case
- Active Sentence
- Alliteration
- Adjective Clause
- Adjective Phrase
- Adverbial Clause
- Appositive Phrase
- Body Paragraph
- Compound Adjective
- Complex Sentence
- Compound Words
- Compound Predicate
- Common Noun
- Comparative Adjective
- Comparative and Superlative
- Compound Noun
- Compound Subject
- Compound Sentence
- Copular Verb
- Collective Noun
- Colloquialism
- Conciseness
- Conditional
- Concrete Noun
- Conjunction
- Conjugation
- Conditional Sentence
- Comma Splice
- Correlative Conjunction
- Coordinating Conjunction
- Coordinate Adjective
- Cumulative Adjective
- Dative Case
- Declarative Statement
- Direct Object Pronoun
- Direct Object
- Dangling Modifier
- Demonstrative Pronoun
- Demonstrative Adjective
- Direct Characterization
- Definite Article
- Doublespeak
- Equivocation Fallacy
- Future Perfect Progressive
- Future Simple
- Future Perfect Continuous
- Future Perfect
- First Conditional
- Gerund Phrase
- Genitive Case
- Helping Verb
- Irregular Adjective
- Irregular Verb
- Imperative Sentence
- Indefinite Article
- Intransitive Verb
- Introductory Phrase
- Indefinite Pronoun
- Indirect Characterization
- Interrogative Sentence
- Intensive Pronoun
- Inanimate Object
- Indefinite Tense
- Infinitive Phrase
- Interjection
- Intensifier
- Indicative Mood
- Juxtaposition
- Linking Verb
- Misplaced Modifier
- Nominative Case
- Noun Adjective
- Object Pronoun
- Object Complement
- Order of Adjectives
- Prepositional Phrase
- Past Simple Tense
- Past Continuous Tense
- Past Perfect Tense
- Past Progressive Tense
- Present Simple Tense
- Present Perfect Tense
- Personal Pronoun
- Personification
- Persuasive Writing
- Parallel Structure
- Phrasal Verb
- Predicate Adjective
- Predicate Nominative
- Phonetic Language
- Plural Noun
- Punctuation
- Punctuation Marks
- Preposition
- Preposition of Place
- Parts of Speech
- Possessive Adjective
- Possessive Determiner
- Possessive Case
- Possessive Noun
- Proper Adjective
- Proper Noun
- Present Participle
- Quotation Marks
- Relative Pronoun
- Reflexive Pronoun
- Reciprocal Pronoun
- Subordinating Conjunction
- Simple Future Tense
- Stative Verb
- Subjunctive
- Subject Complement
- Subject of a Sentence
- Sentence Variety
- Second Conditional
- Superlative Adjective
- Slash Symbol
- Topic Sentence
- Types of Nouns
- Types of Sentences
- Uncountable Noun
- Vowels and Consonants
Popular lessons

Stay awhile. Your weekly dose of grammar and English fun.

The world's best online resource for learning English. Understand words, phrases, slang terms, and all other variations of the English language.
- Abbreviations
- Editorial Policy
How to Write the AP Lit Prose Essay with Examples
March 30, 2024

AP Lit Prose Essay Examples – The College Board’s Advanced Placement Literature and Composition Course is one of the most enriching experiences that high school students can have. It exposes you to literature that most people don’t encounter until college , and it helps you develop analytical and critical thinking skills that will enhance the quality of your life, both inside and outside of school. The AP Lit Exam reflects the rigor of the course. The exam uses consistent question types, weighting, and scoring parameters each year . This means that, as you prepare for the exam, you can look at previous questions, responses, score criteria, and scorer commentary to help you practice until your essays are perfect.
What is the AP Lit Free Response testing?
In AP Literature, you read books, short stories, and poetry, and you learn how to commit the complex act of literary analysis . But what does that mean? Well, “to analyze” literally means breaking a larger idea into smaller and smaller pieces until the pieces are small enough that they can help us to understand the larger idea. When we’re performing literary analysis, we’re breaking down a piece of literature into smaller and smaller pieces until we can use those pieces to better understand the piece of literature itself.
So, for example, let’s say you’re presented with a passage from a short story to analyze. The AP Lit Exam will ask you to write an essay with an essay with a clear, defensible thesis statement that makes an argument about the story, based on some literary elements in the short story. After reading the passage, you might talk about how foreshadowing, allusion, and dialogue work together to demonstrate something essential in the text. Then, you’ll use examples of each of those three literary elements (that you pull directly from the passage) to build your argument. You’ll finish the essay with a conclusion that uses clear reasoning to tell your reader why your argument makes sense.
AP Lit Prose Essay Examples (Continued)
But what’s the point of all of this? Why do they ask you to write these essays?
Well, the essay is, once again, testing your ability to conduct literary analysis. However, the thing that you’re also doing behind that literary analysis is a complex process of both inductive and deductive reasoning. Inductive reasoning takes a series of points of evidence and draws a larger conclusion. Deductive reasoning departs from the point of a broader premise and draws a singular conclusion. In an analytical essay like this one, you’re using small pieces of evidence to draw a larger conclusion (your thesis statement) and then you’re taking your thesis statement as a larger premise from which you derive your ultimate conclusion.
So, the exam scorers are looking at your ability to craft a strong thesis statement (a singular sentence that makes an argument), use evidence and reasoning to support that argument, and then to write the essay well. This is something they call “sophistication,” but they’re looking for well-organized thoughts carried through clear, complete sentences.
This entire process is something you can and will use throughout your life. Law, engineering, medicine—whatever pursuit, you name it—utilizes these forms of reasoning to run experiments, build cases, and persuade audiences. The process of this kind of clear, analytical thinking can be honed, developed, and made easier through repetition.
Practice Makes Perfect
Because the AP Literature Exam maintains continuity across the years, you can pull old exam copies, read the passages, and write responses. A good AP Lit teacher is going to have you do this time and time again in class until you have the formula down. But, it’s also something you can do on your own, if you’re interested in further developing your skills.
AP Lit Prose Essay Examples
Let’s take a look at some examples of questions, answers and scorer responses that will help you to get a better idea of how to craft your own AP Literature exam essays.
In the exam in 2023, students were asked to read a poem by Alice Cary titled “Autumn,” which was published in 1874. In it, the speaker contemplates the start of autumn. Then, students are asked to craft a well-written essay which uses literary techniques to convey the speaker’s complex response to the changing seasons.
The following is an essay that received a perfect 6 on the exam. There are grammar and usage errors throughout the essay, which is important to note: even though the writer makes some mistakes, the structure and form of their argument was strong enough to merit a 6. This is what your scorers will be looking for when they read your essay.
Example Essay
Romantic and hyperbolic imagery is used to illustrate the speaker’s unenthusiastic opinion of the coming of autumn, which conveys Cary’s idea that change is difficult to accept but necessary for growth.
Romantic imagery is utilized to demonstrate the speaker’s warm regard for the season of summer and emphasize her regretfulness for autumn’s coming, conveying the uncomfortable change away from idyllic familiarity. Summer, is portrayed in the image of a woman who “from her golden collar slips/and strays through stubble fields/and moans aloud.” Associated with sensuality and wealth, the speaker implies the interconnection between a season and bounty, comfort, and pleasure. Yet, this romantic view is dismantled by autumn, causing Summer to “slip” and “stray through stubble fields.” Thus, the coming of real change dethrones a constructed, romantic personification of summer, conveying the speaker’s reluctance for her ideal season to be dethroned by something much less decorated and adored.
Summer, “she lies on pillows of the yellow leaves,/ And tries the old tunes for over an hour”, is contrasted with bright imagery of fallen leaves/ The juxtaposition between Summer’s character and the setting provides insight into the positivity of change—the yellow leaves—by its contrast with the failures of attempting to sustain old habits or practices, “old tunes”. “She lies on pillows” creates a sympathetic, passive image of summer in reaction to the coming of Autumn, contrasting her failures to sustain “old tunes.” According to this, it is understood that the speaker recognizes the foolishness of attempting to prevent what is to come, but her wishfulness to counter the natural progression of time.
Hyperbolic imagery displays the discrepancies between unrealistic, exaggerated perceptions of change and the reality of progress, continuing the perpetuation of Cary’s idea that change must be embraced rather than rejected. “Shorter and shorter now the twilight clips/The days, as though the sunset gates they crowd”, syntax and diction are used to literally separate different aspects of the progression of time. In an ironic parallel to the literal language, the action of twilight’s “clip” and the subject, “the days,” are cut off from each other into two different lines, emphasizing a sense of jarring and discomfort. Sunset, and Twilight are named, made into distinct entities from the day, dramatizing the shortening of night-time into fall. The dramatic, sudden implications for the change bring to mind the switch between summer and winter, rather than a transitional season like fall—emphasizing the Speaker’s perspective rather than a factual narration of the experience.
She says “the proud meadow-pink hangs down her head/Against the earth’s chilly bosom, witched with frost”. Implying pride and defeat, and the word “witched,” the speaker brings a sense of conflict, morality, and even good versus evil into the transition between seasons. Rather than a smooth, welcome change, the speaker is practically against the coming of fall. The hyperbole present in the poem serves to illustrate the Speaker’s perspective and ideas on the coming of fall, which are characterized by reluctance and hostility to change from comfort.
The topic of this poem, Fall–a season characterized by change and the deconstruction of the spring and summer landscape—is juxtaposed with the final line which evokes the season of Spring. From this, it is clear that the speaker appreciates beautiful and blossoming change. However, they resent that which destroys familiar paradigms and norms. Fall, seen as the death of summer, is characterized as a regression, though the turning of seasons is a product of the literal passage of time. Utilizing romantic imagery and hyperbole to shape the Speaker’s perspective, Cary emphasizes the need to embrace change though it is difficult, because growth is not possible without hardship or discomfort.
Scoring Criteria: Why did this essay do so well?
When it comes to scoring well, there are some rather formulaic things that the judges are searching for. You might think that it’s important to “stand out” or “be creative” in your writing. However, aside from concerns about “sophistication,” which essentially means you know how to organize thoughts into sentences and you can use language that isn’t entirely elementary, you should really focus on sticking to a form. This will show the scorers that you know how to follow that inductive/deductive reasoning process that we mentioned earlier, and it will help to present your ideas in the most clear, coherent way possible to someone who is reading and scoring hundreds of essays.
So, how did this essay succeed? And how can you do the same thing?
First: The Thesis
On the exam, you can either get one point or zero points for your thesis statement. The scorers said, “The essay responds to the prompt with a defensible thesis located in the introductory paragraph,” which you can read as the first sentence in the essay. This is important to note: you don’t need a flowery hook to seduce your reader; you can just start this brief essay with some strong, simple, declarative sentences—or go right into your thesis.
What makes a good thesis? A good thesis statement does the following things:
- Makes a claim that will be supported by evidence
- Is specific and precise in its use of language
- Argues for an original thought that goes beyond a simple restating of the facts
If you’re sitting here scratching your head wondering how you come up with a thesis statement off the top of your head, let me give you one piece of advice: don’t.
The AP Lit scoring criteria gives you only one point for the thesis for a reason: they’re just looking for the presence of a defensible claim that can be proven by evidence in the rest of the essay.
Second: Write your essay from the inside out
While the thesis is given one point, the form and content of the essay can receive anywhere from zero to four points. This is where you should place the bulk of your focus.
My best advice goes like this:
- Choose your evidence first
- Develop your commentary about the evidence
- Then draft your thesis statement based on the evidence that you find and the commentary you can create.
It will seem a little counterintuitive: like you’re writing your essay from the inside out. But this is a fundamental skill that will help you in college and beyond. Don’t come up with an argument out of thin air and then try to find evidence to support your claim. Look for the evidence that exists and then ask yourself what it all means. This will also keep you from feeling stuck or blocked at the beginning of the essay. If you prepare for the exam by reviewing the literary devices that you learned in the course and practice locating them in a text, you can quickly and efficiently read a literary passage and choose two or three literary devices that you can analyze.
Third: Use scratch paper to quickly outline your evidence and commentary
Once you’ve located two or three literary devices at work in the given passage, use scratch paper to draw up a quick outline. Give each literary device a major bullet point. Then, briefly point to the quotes/evidence you’ll use in the essay. Finally, start to think about what the literary device and evidence are doing together. Try to answer the question: what meaning does this bring to the passage?
A sample outline for one paragraph of the above essay might look like this:
Romantic imagery
Portrayal of summer
- Woman who “from her golden collar… moans aloud”
- Summer as bounty
Contrast with Autumn
- Autumn dismantles Summer
- “Stray through stubble fields”
- Autumn is change; it has the power to dethrone the romance of Summer/make summer a bit meaningless
Recognition of change in a positive light
- Summer “lies on pillows / yellow leaves / tries old tunes”
- Bright imagery/fallen leaves
- Attempt to maintain old practices fails: “old tunes”
- But! There is sympathy: “lies on pillows”
Speaker recognizes: she can’t prevent what is to come; wishes to embrace natural passage of time
By the time the writer gets to the end of the outline for their paragraph, they can easily start to draw conclusions about the paragraph based on the evidence they have pulled out. You can see how that thinking might develop over the course of the outline.
Then, the speaker would take the conclusions they’ve drawn and write a “mini claim” that will start each paragraph. The final bullet point of this outline isn’t the same as the mini claim that comes at the top of the second paragraph of the essay, however, it is the conclusion of the paragraph. You would do well to use the concluding thoughts from your outline as the mini claim to start your body paragraph. This will make your paragraphs clear, concise, and help you to construct a coherent argument.
Repeat this process for the other one or two literary devices that you’ve chosen to analyze, and then: take a step back.
Fourth: Draft your thesis
Once you quickly sketch out your outline, take a moment to “stand back” and see what you’ve drafted. You’ll be able to see that, among your two or three literary devices, you can draw some commonality. You might be able to say, as the writer did here, that romantic and hyperbolic imagery “illustrate the speaker’s unenthusiastic opinion of the coming of autumn,” ultimately illuminating the poet’s idea “that change is difficult to accept but necessary for growth.”
This is an original argument built on the evidence accumulated by the student. It directly answers the prompt by discussing literary techniques that “convey the speaker’s complex response to the changing seasons.” Remember to go back to the prompt and see what direction they want you to head with your thesis, and craft an argument that directly speaks to that prompt.
Then, move ahead to finish your body paragraphs and conclusion.
Fifth: Give each literary device its own body paragraph
In this essay, the writer examines the use of two literary devices that are supported by multiple pieces of evidence. The first is “romantic imagery” and the second is “hyperbolic imagery.” The writer dedicates one paragraph to each idea. You should do this, too.
This is why it’s important to choose just two or three literary devices. You really don’t have time to dig into more. Plus, more ideas will simply cloud the essay and confuse your reader.
Using your outline, start each body paragraph with a “mini claim” that makes an argument about what it is you’ll be saying in your paragraph. Lay out your pieces of evidence, then provide commentary for why your evidence proves your point about that literary device.
Move onto the next literary device, rinse, and repeat.
Sixth: Commentary and Conclusion
Finally, you’ll want to end this brief essay with a concluding paragraph that restates your thesis, briefly touches on your most important points from each body paragraph, and includes a development of the argument that you laid out in the essay.
In this particular example essay, the writer concludes by saying, “Utilizing romantic imagery and hyperbole to shape the Speaker’s perspective, Cary emphasizes the need to embrace change though it is difficult, because growth is not possible without hardship or discomfort.” This is a direct restatement of the thesis. At this point, you’ll have reached the end of your essay. Great work!
Seventh: Sophistication
A final note on scoring criteria: there is one point awarded to what the scoring criteria calls “sophistication.” This is evidenced by the sophistication of thought and providing a nuanced literary analysis, which we’ve already covered in the steps above.
There are some things to avoid, however:
- Sweeping generalizations, such as, “From the beginning of human history, people have always searched for love,” or “Everyone goes through periods of darkness in their lives, much like the writer of this poem.”
- Only hinting at possible interpretations instead of developing your argument
- Oversimplifying your interpretation
- Or, by contrast, using overly flowery or complex language that does not meet your level of preparation or the context of the essay.
Remember to develop your argument with nuance and complexity and to write in a style that is academic but appropriate for the task at hand.
If you want more practice or to check out other exams from the past, go to the College Board’s website .

Brittany Borghi
After earning a BA in Journalism and an MFA in Nonfiction Writing from the University of Iowa, Brittany spent five years as a full-time lecturer in the Rhetoric Department at the University of Iowa. Additionally, she’s held previous roles as a researcher, full-time daily journalist, and book editor. Brittany’s work has been featured in The Iowa Review, The Hopkins Review, and the Pittsburgh City Paper, among others, and she was also a 2021 Pushcart Prize nominee.
- 2-Year Colleges
- Application Strategies
- Best Colleges by Major
- Best Colleges by State
- Big Picture
- Career & Personality Assessment
- College Essay
- College Search/Knowledge
- College Success
- Costs & Financial Aid
- Dental School Admissions
- Extracurricular Activities
- Graduate School Admissions
- High School Success
- High Schools
- Law School Admissions
- Medical School Admissions
- Navigating the Admissions Process
- Online Learning
- Private High School Spotlight
- Summer Program Spotlight
- Summer Programs
- Test Prep Provider Spotlight

“Innovative and invaluable…use this book as your college lifeline.”
— Lynn O'Shaughnessy
Nationally Recognized College Expert
College Planning in Your Inbox
Join our information-packed monthly newsletter.
I am a... Student Student Parent Counselor Educator Other First Name Last Name Email Address Zip Code Area(s) s of Interest Business Computer Science Engineering Fine/Performing Arts Humanities Mathematics STEM Pre-Med Psychology Social Studies/Sciences Submit
Ultimate Guide to Writing Your College Essay
Tips for writing an effective college essay.
College admissions essays are an important part of your college application and gives you the chance to show colleges and universities your character and experiences. This guide will give you tips to write an effective college essay.
Want free help with your college essay?
UPchieve connects you with knowledgeable and friendly college advisors—online, 24/7, and completely free. Get 1:1 help brainstorming topics, outlining your essay, revising a draft, or editing grammar.
Writing a strong college admissions essay
Learn about the elements of a solid admissions essay.
Avoiding common admissions essay mistakes
Learn some of the most common mistakes made on college essays
Brainstorming tips for your college essay
Stuck on what to write your college essay about? Here are some exercises to help you get started.
How formal should the tone of your college essay be?
Learn how formal your college essay should be and get tips on how to bring out your natural voice.
Taking your college essay to the next level
Hear an admissions expert discuss the appropriate level of depth necessary in your college essay.
Student Stories
Student Story: Admissions essay about a formative experience
Get the perspective of a current college student on how he approached the admissions essay.
Student Story: Admissions essay about personal identity
Get the perspective of a current college student on how she approached the admissions essay.
Student Story: Admissions essay about community impact
Student story: admissions essay about a past mistake, how to write a college application essay, tips for writing an effective application essay, sample college essay 1 with feedback, sample college essay 2 with feedback.
This content is licensed by Khan Academy and is available for free at www.khanacademy.org.
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Guest Essay
A.I.-Generated Garbage Is Polluting Our Culture

By Erik Hoel
Mr. Hoel is a neuroscientist and novelist and the author of The Intrinsic Perspective newsletter.
Increasingly, mounds of synthetic A.I.-generated outputs drift across our feeds and our searches. The stakes go far beyond what’s on our screens. The entire culture is becoming affected by A.I.’s runoff, an insidious creep into our most important institutions.
Consider science. Right after the blockbuster release of GPT-4, the latest artificial intelligence model from OpenAI and one of the most advanced in existence, the language of scientific research began to mutate. Especially within the field of A.I. itself.

Adjectives associated with A.I.-generated text have increased in peer reviews of scientific papers about A.I.
Frequency of adjectives per one million words
Commendable

A study published this month examined scientists’ peer reviews — researchers’ official pronouncements on others’ work that form the bedrock of scientific progress — across a number of high-profile and prestigious scientific conferences studying A.I. At one such conference, those peer reviews used the word “meticulous” more than 34 times as often as reviews did the previous year. Use of “commendable” was around 10 times as frequent, and “intricate,” 11 times. Other major conferences showed similar patterns.
Such phrasings are, of course, some of the favorite buzzwords of modern large language models like ChatGPT. In other words, significant numbers of researchers at A.I. conferences were caught handing their peer review of others’ work over to A.I. — or, at minimum, writing them with lots of A.I. assistance. And the closer to the deadline the submitted reviews were received, the more A.I. usage was found in them.
If this makes you uncomfortable — especially given A.I.’s current unreliability — or if you think that maybe it shouldn’t be A.I.s reviewing science but the scientists themselves, those feelings highlight the paradox at the core of this technology: It’s unclear what the ethical line is between scam and regular usage. Some A.I.-generated scams are easy to identify, like the medical journal paper featuring a cartoon rat sporting enormous genitalia. Many others are more insidious, like the mislabeled and hallucinated regulatory pathway described in that same paper — a paper that was peer reviewed as well (perhaps, one might speculate, by another A.I.?).
What about when A.I. is used in one of its intended ways — to assist with writing? Recently, there was an uproar when it became obvious that simple searches of scientific databases returned phrases like “As an A.I. language model” in places where authors relying on A.I. had forgotten to cover their tracks. If the same authors had simply deleted those accidental watermarks, would their use of A.I. to write their papers have been fine?
What’s going on in science is a microcosm of a much bigger problem. Post on social media? Any viral post on X now almost certainly includes A.I.-generated replies, from summaries of the original post to reactions written in ChatGPT’s bland Wikipedia-voice, all to farm for follows. Instagram is filling up with A.I.-generated models, Spotify with A.I.-generated songs. Publish a book? Soon after, on Amazon there will often appear A.I.-generated “workbooks” for sale that supposedly accompany your book (which are incorrect in their content; I know because this happened to me). Top Google search results are now often A.I.-generated images or articles. Major media outlets like Sports Illustrated have been creating A.I.-generated articles attributed to equally fake author profiles. Marketers who sell search engine optimization methods openly brag about using A.I. to create thousands of spammed articles to steal traffic from competitors.
Then there is the growing use of generative A.I. to scale the creation of cheap synthetic videos for children on YouTube. Some example outputs are Lovecraftian horrors, like music videos about parrots in which the birds have eyes within eyes, beaks within beaks, morphing unfathomably while singing in an artificial voice, “The parrot in the tree says hello, hello!” The narratives make no sense, characters appear and disappear randomly, and basic facts like the names of shapes are wrong. After I identified a number of such suspicious channels on my newsletter, The Intrinsic Perspective, Wired found evidence of generative A.I. use in the production pipelines of some accounts with hundreds of thousands or even millions of subscribers.
As a neuroscientist, this worries me. Isn’t it possible that human culture contains within it cognitive micronutrients — things like cohesive sentences, narrations and character continuity — that developing brains need? Einstein supposedly said : “If you want your children to be intelligent, read them fairy tales. If you want them to be very intelligent, read them more fairy tales.” But what happens when a toddler is consuming mostly A.I.-generated dream-slop? We find ourselves in the midst of a vast developmental experiment.
There’s so much synthetic garbage on the internet now that A.I. companies and researchers are themselves worried, not about the health of the culture, but about what’s going to happen with their models. As A.I. capabilities ramped up in 2022, I wrote on the risk of culture’s becoming so inundated with A.I. creations that when future A.I.s are trained, the previous A.I. output will leak into the training set, leading to a future of copies of copies of copies, as content became ever more stereotyped and predictable. In 2023 researchers introduced a technical term for how this risk affected A.I. training: model collapse . In a way, we and these companies are in the same boat, paddling through the same sludge streaming into our cultural ocean.
With that unpleasant analogy in mind, it’s worth looking to what is arguably the clearest historical analogy for our current situation: the environmental movement and climate change. For just as companies and individuals were driven to pollute by the inexorable economics of it, so, too, is A.I.’s cultural pollution driven by a rational decision to fill the internet’s voracious appetite for content as cheaply as possible. While environmental problems are nowhere near solved, there has been undeniable progress that has kept our cities mostly free of smog and our lakes mostly free of sewage. How?
Before any specific policy solution was the acknowledgment that environmental pollution was a problem in need of outside legislation. Influential to this view was a perspective developed in 1968 by Garrett Hardin, a biologist and ecologist. Dr. Hardin emphasized that the problem of pollution was driven by people acting in their own interest, and that therefore “we are locked into a system of ‘fouling our own nest,’ so long as we behave only as independent, rational, free-enterprisers.” He summed up the problem as a “tragedy of the commons.” This framing was instrumental for the environmental movement, which would come to rely on government regulation to do what companies alone could or would not.
Once again we find ourselves enacting a tragedy of the commons: short-term economic self-interest encourages using cheap A.I. content to maximize clicks and views, which in turn pollutes our culture and even weakens our grasp on reality. And so far, major A.I. companies are refusing to pursue advanced ways to identify A.I.’s handiwork — which they could do by adding subtle statistical patterns hidden in word use or in the pixels of images.
A common justification for inaction is that human editors can always fiddle around with whatever patterns are used if they know enough. Yet many of the issues we’re experiencing are not caused by motivated and technically skilled malicious actors; they’re caused mostly by regular users’ not adhering to a line of ethical use so fine as to be nigh nonexistent. Most would be uninterested in advanced countermeasures to statistical patterns enforced into outputs that should, ideally, mark them as A.I.-generated.
That’s why the independent researchers were able to detect A.I. outputs in the peer review system with surprisingly high accuracy: They actually tried. Similarly, right now teachers across the nation have created home-brewed output-side detection methods , like adding hidden requests for patterns of word use to essay prompts that appear only when copied and pasted.
In particular, A.I. companies appear opposed to any patterns baked into their output that can improve A.I.-detection efforts to reasonable levels, perhaps because they fear that enforcing such patterns might interfere with the model’s performance by constraining its outputs too much — although there is no current evidence this is a risk. Despite public pledges to develop more advanced watermarking, it’s increasingly clear that the companies are dragging their feet because it goes against the A.I. industry’s bottom line to have detectable products.
To deal with this corporate refusal to act we need the equivalent of a Clean Air Act: a Clean Internet Act. Perhaps the simplest solution would be to legislatively force advanced watermarking intrinsic to generated outputs, like patterns not easily removable. Just as the 20th century required extensive interventions to protect the shared environment, the 21st century is going to require extensive interventions to protect a different, but equally critical, common resource, one we haven’t noticed up until now since it was never under threat: our shared human culture.
Erik Hoel is a neuroscientist, a novelist and the author of The Intrinsic Perspective newsletter.
The Times is committed to publishing a diversity of letters to the editor. We’d like to hear what you think about this or any of our articles. Here are some tips . And here’s our email: [email protected] .
Follow the New York Times Opinion section on Facebook , Instagram , TikTok , WhatsApp , X and Threads .
To revisit this article, visit My Profile, then View saved stories .
- Backchannel
- Newsletters
- WIRED Insider
- WIRED Consulting
Estelle Erasmus
How to Resist the Temptation of AI When Writing

Whether you're a student, a journalist, or a business professional, knowing how to do high-quality research and writing using trustworthy data and sources, without giving in to the temptation of AI or ChatGPT , is a skill worth developing.
As I detail in my book Writing That Gets Noticed , locating credible databases and sources and accurately vetting information can be the difference between turning a story around quickly or getting stuck with outdated information.
For example, several years ago the editor of Parents.com asked for a hot-take reaction to country singer Carrie Underwood saying that, because she was 35, she had missed her chance at having another baby. Since I had written about getting pregnant in my forties, I knew that as long as I updated my facts and figures, and included supportive and relevant peer-reviewed research, I could pull off this story. And I did.
The story ran later that day , and it led to other assignments. Here are some tips I’ve learned that you should consider mastering before you turn to automated tools like generative AI to handle your writing work for you.
Identify experts, peer-reviewed research study authors, and sources who can speak with authority—and ideally, offer easily understood sound bites or statistics on the topic of your work. Great sources include professors at major universities and media spokespeople at associations and organizations.
For example, writer and author William Dameron pinned his recent essay in HuffPost Personal around a statistic from the American Heart Association on how LGBTQ people experience higher rates of heart disease based on discrimination. Although he first found the link in a secondary source (an article in The New York Times ), he made sure that he checked the primary source: the original study that the American Heart Association gleaned the statistic from. He verified the information, as should any writer, because anytime a statistic is cited in a secondary source, errors can be introduced.
Jen Malia, author of The Infinity Rainbow Club series of children’s books (whom I recently interviewed on my podcast ), recently wrote a piece about dinosaur-bone hunting for Business Insider , which she covers in her book Violet and the Jurassic Land Exhibit.
After a visit to the Carnegie Museum of Natural History in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, Malia, whose books are set in Philadelphia, found multiple resources online and on the museum site that gave her the history of the Bone Wars , information on the exhibits she saw, and the scientific names of the dinosaurs she was inspired by. She also used the Library of Congress’ website, which offers digital collections and links to the Library of Congress Newspaper Collection.
Malia is a fan of searching for additional resources and citable documents with Google Scholar . “If I find that a secondary source mentions a newspaper article, I’m going to go to the original newspaper article, instead of just stopping there and quoting,” she says.
Julian Chokkattu

Brenda Stolyar

Adrienne So
Your local public library is a great source of free information, journals, and databases (even ones that generally require a subscription and include embargoed research). For example, your search should include everything from health databases ( Sage Journals , Scopus , PubMed) to databases for academic sources and journalism ( American Periodical Series Online , Statista , Academic Search Premier ) and databases for news, trends, market research, and polls (t he Harris Poll , Pew Research Center , Newsbank , ProPublica ).
Even if you find a study or paper that you can’t access in one of those databases, consider reaching out to the study’s lead author or researcher. In many cases, they’re happy to discuss their work and may even share the study with you directly and offer to talk about their research.
For journalist Paulette Perhach’s article on ADHD in The New York Times, she used Epic Research to see “dual team studies.” That's when two independent teams address the same topic or question, and ideally come to the same conclusions. She recommends locating research and experts via key associations for your topic. She also likes searching via Google Scholar but advises filtering it for studies and research in recent years to avoid using old data. She suggests keeping your links and research organized. “Always be ready to be peer-reviewed yourself,” Perhach says.
When you are looking for information for a story or project, you might be inclined to start with a regular Google search. But keep in mind that the internet is full of false information, and websites that look trustworthy can sometimes turn out to be businesses or companies with a vested interest in you taking their word as objective fact without additional scrutiny. Regardless of your writing project, unreliable or biased sources are a great way to torpedo your work—and any hope of future work.
Author Bobbi Rebell researched her book Launching Financial Grownups using the IRS’ website . “I might say that you can contribute a certain amount to a 401K, but it might be outdated because those numbers are always changing, and it’s important to be accurate,” she says. “AI and ChatGPT can be great for idea generation,” says Rebell, “but you have to be careful. If you are using an article someone was quoted in, you don’t know if they were misquoted or quoted out of context.”
If you use AI and ChatGPT for sourcing, you not only risk introducing errors, you risk introducing plagiarism—there is a reason OpenAI, the company behind ChatGPT, is being sued for downloading information from all those books.
Audrey Clare Farley, who writes historical nonfiction, has used a plethora of sites for historical research, including Women Also Know History , which allows searches by expertise or area of study, and JSTOR , a digital library database that offers a number of free downloads a month. She also uses Chronicling America , a project from the Library of Congress which gathers old newspapers to show how a historical event was reported, and Newspapers.com (which you can access via free trial but requires a subscription after seven days).
When it comes to finding experts, Farley cautions against choosing the loudest voices on social media platforms. “They might not necessarily be the most authoritative. I vet them by checking if they have a history of publication on the topic, and/or educational credentials.”
When vetting an expert, look for these red flags:
- You can’t find their work published or cited anywhere.
- They were published in an obscure journal.
- Their research is funded by a company, not a university, or they are the spokesperson for the company they are doing research for. (This makes them a public relations vehicle and not an appropriate source for journalism.)
And finally, the best endings for virtually any writing, whether it’s an essay, a research paper, an academic report, or a piece of investigative journalism, circle back to the beginning of the piece, and show your reader the transformation or the journey the piece has presented in perspective.
As always, your goal should be strong writing supported by research that makes an impact without cutting corners. Only then can you explore tools that might make the job a little easier, for instance by generating subheads or discovering a concept you might be missing—because then you'll have the experience and skills to see whether it's harming or helping your work.
You Might Also Like …
In your inbox: Introducing Politics Lab , your guide to election season
Google used her to tout diversity. Now she’s suing for discrimination
Our in-house physics whiz explains how heat pumps work
The big questions the Pentagon’s new UFO report fails to answer
AirPods Pro or AirPods Max? These are the best Apple buds for your ears

Michael Calore

Reece Rogers

Boone Ashworth
WIRED COUPONS

Dyson promo code: 20% off all purchases + free shipping

GoPro Promo Code: 15% off Cameras and Accessories

Up to +30% Off with your Samsung promo code

Extra 5% Off with Dell Coupon Code

Free Logomaker at VistaPrint

Newegg Coupon: Take up to 60% Off monitors, PCs & more
More From Forbes
Writing Cover Letters For A Career Change: Tips And Examples
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
Embarking on a career change is a pivotal moment, fraught with uncertainty but brimming with potential. And especially in cases where your resume might not directly align with the job at hand, your cover letter becomes the narrative that connects the dots. A well-crafted cover can illuminate your strengths, align your past experiences with your future aspirations, and persuade potential employers to see the value you bring.
The Importance Of A Cover Letter In Career Changes
In career transitions, your cover letter is your storyteller. It explains the why and the how of your career change, showcasing your enthusiasm and demonstrating how your background equips you with unique perspectives and transferable skills. It addresses potential concerns about your career shift head-on, presenting your transition as an asset rather than a liability.
Tips For Writing A Career Change Cover Letter
1. Personalize Your Approach : Address the letter to a specific person whenever possible. Doing so demonstrates attention to detail and a genuine interest in the position. You want to show that you’re not conducting a generic job search, but that you’ve done your research. You’ve perused (not skimmed) the company website and you read that 20-page yearly report from the CEO. You’ve even read their blog and can quote freely from it. You’ve educated yourself.
2. Emphasize Transferable Skills : Highlight the skills and experiences from your previous roles that are relevant to the new position. Be specific and quantify achievements where possible.
3. Show Enthusiasm and Commitment : Employers want to know that you are genuinely interested in the new field. Express your passion for the career change and your eagerness to contribute.
Apple Just Released A Major Upgrade For Samsung Galaxy Watch 6, Pixel Watch
Trump posts 175 million bond thanks to billionaire don hankey, caitlin clark erupts for 41 points as iowa advances to final four with revenge win over lsu.
4. Tailor Your Narrative : Connect your past experiences to the job you're applying for, demonstrating how your unique background can bring a fresh perspective to the role.
5. Address Potential Concerns : Be upfront about your career change, framing it as a positive decision guided by clear motivation and a strong understanding of the new field.
6. End with a Strong Call to Action : Conclude by expressing your desire to discuss your application further in an interview, showing proactivity and determination.
7. Use Strategic Language : Avoid clichéd adjectives. Opt for vivid, specific language that paints a clear picture of your capabilities and achievements.
Example: General Career Change Cover Letter
Dear [Hiring Manager's Name],
I am excited to apply for the [Position] at [Company], transitioning from a career in [Current Industry] to [New Industry]. My experience in [Current Industry] has equipped me with valuable skills that I am eager to apply in [New Industry]. For instance, while working as [Previous Position], I developed a keen ability to [transferable skill], resulting in [specific achievement].
In [Current Industry], I honed my skills in [relevant skill] and demonstrated my ability to [relevant achievement], directly benefiting my team by [specific outcome]. I am particularly drawn to [New Industry] because [reason for interest], and I am enthusiastic about the opportunity to bring my [specific skill] and [another skill] to the [Position] at [Company].
[Your Name]
Tweaks For Various Career Stages
Whether you are making a change early in your career or transitioning later, your cover letter should reflect your rationale and excitement for this new path.
Example: Early Career Cover Letter
As someone at the early stages of my career, I am eager to leverage the foundational skills I gained in [Initial Field], such as [specific skill], in [New Field]. My recent role as [Previous Position] allowed me to develop [relevant skills or experiences], which align closely with the requirements of the [Position] at [Company].
Example: Late Career Cover Letter
Transitioning into [New Field] at this point in my career is a deliberate and enthusiastic choice, driven by my deep-seated interest in [aspect of New Field]. With extensive experience in [Previous Field], I bring a wealth of knowledge and a unique perspective that can contribute to innovative solutions and strategies at [Company].
Tweaks For White And Blue-Collar Roles
Transitioning between white and blue-collar roles offers a unique opportunity to highlight diverse skills and experiences.
Example: White To Blue Collar Cover Letter
I am eager to apply the strategic and managerial skills honed in my white-collar career to the hands-on, dynamic environment of [Blue Collar Field]. My experience in [White Collar Role], where I developed [specific skills], aligns well with the challenges and responsibilities of the [Blue Collar Position] at [Company].
Example: Blue To White Collar Cover Letter
Transitioning from [Blue Collar Field] to [White Collar Field], I bring practical, on-the-ground experience that can inform and enhance the strategic decisions in [White Collar Role]. My background in [Blue Collar Role], where I mastered [specific skills], equips me with a unique perspective beneficial for the [White Collar Position] at [Company].
Including A Career Change Statement On Your Resume/CV
While your cover letter is the ideal place to elaborate on your career change, your resume/CV should also reflect this transition. A brief career change statement, positioned at the beginning of your resume, can effectively set the context for your career narrative. This statement should succinctly convey your transition, emphasizing your commitment to the new field and highlighting any transferable skills or relevant experiences.
How To Craft A Career Change Statement For Your Resume
1. Objective Statement : Begin with a clear, concise objective that outlines your career goals and demonstrates your enthusiasm for your new field.
2. Summary of Qualifications : Follow your objective with a brief summary of your most relevant qualifications, focusing on skills and experiences that transition well into your new career.
3. Highlight Transferable Skills : Clearly identify and emphasize any skills from your previous career that are pertinent to your new path. This not only demonstrates your capability but also shows your proactive approach in aligning your skill set with the new role's requirements.
4. Tailor Your Experience : Adjust the descriptions of your past positions to highlight the responsibilities and achievements most relevant to your desired career path. Use quantifiable achievements to underscore your adaptability and impact.
5. Education and Training : If you have pursued any education or training relevant to your new field, highlight this prominently on your resume to illustrate your dedication and commitment to your career change.
Make Your Language Unique
To avoid sounding like everyone else, remember to use distinctive and precise adjectives in your cover letter and resume. For instance:
- Instead of "experienced," try "seasoned" or "accomplished," providing specific examples that demonstrate this experience, like spearheading a successful project or leading a team to exceed its targets.
- Replace "passionate" with "enthused" or "committed," detailing a project or initiative you pursued with zeal, which can resonate more authentically with hiring managers.
- Substitute "results-driven" with "outcome-focused," illustrating this with a particular scenario where your focus on results led to tangible success for your organization.
Your cover letter and resume are your advocates, narrating your professional journey and articulating why you are not just seeking a new job, but embarking on a new career with purpose and passion. By carefully crafting these documents to reflect your individual story, you position yourself as a memorable and compelling candidate, someone who stands out from the crowd.

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
Psych Times
- Relationships
- Mental Health
How to Write an Essay in One Day: An Ultimate Guide

Writing a one-day essay might sound like a hard task to do, but with the right strategy, one can achieve this. Be it a procrastinator or someone with insufficient time, this article will teach you how to beat it with maximum efficiency. It covers everything from brainstorming ideas, constituting a solid thesis statement, and organizing your thoughts for a well-written essay. Through a little bit of focus and determined effort, you will be amazed at your abilities.
Understanding the assignment requirements
Understanding the assignment’s requirements is crucial to writing a successful essay as fast as possible.
- Read the essay prompt carefully . It might seem a bit corny, but to get all the details right to the point, you need to comprehend what the essay is asking you to do. Seek keywords intended to provide you with the approach to use, such as “analyze,” “compare,” or “discuss.” If you have difficulty understanding the prompts for essays, you can turn to the quick essay writing service FastEssay. This company processes students’ “ write an essay for me ” requests and provides fast online help for all types of papers. Do not worry, the experts working there are always happy to help and can write an essay even today.
- Identify the main topic. Know the primary subject of your paper, which can be the theme of the essay. This will prevent you from being distracted and save you from runts.
- Note down any specific instructions. Make sure there are any particular directions given by your teacher or professor, such as format guidelines, word count limit, and/or recommended sources.
- Pay attention to deadlines . Note down promptly when the essay is submitted in order for you to arrange the time properly. Look into breaking up the writing process into separate pieces to avert panic at the end.
- Clarify any uncertainties. If you are unsure about one of the steps of the task, do not be shy of asking your teacher or professor for clarification. Prevention is better than cure. Seeking help early is better than trying to manage an issue later on.
Then, by doing so, you will be ready to overcome the assignment and build a paper that is logical and precise.
Conducting research and gathering information
It is highly recommended that, prior to the writing of your essay, you collect some information that will enable you to strengthen your opinions and ideas. Here’s some advice on how you can conduct research effectively.
First, find out the essential components or subject areas to be discussed in your essay from the prompt. It will save you time and greatly increase your ability to focus, allowing you to find all the essential information for your work. As an introductory stage, refer to your textbook, class notes, and any necessary readings provided by your instructors.
Second, the aim is to use credible materials that can be found in books, academic journals, and reliable websites. Make sure to test the trustworthiness of each resource on which you are working by confirming that its author is reputable, and its publication date is recent. Start searching for reliable sources that are neutral, recent, and applicable to your argument.
Third, write down the main ideas contained in what you learn while citing all the sources from which you get each piece of information. Doing so will ensure the efficiency of bibliography generation, which will help you understand the sources later on when writing a paper.
Finally, to present a balanced perspective, you will have to incorporate various viewpoints and debates related to your topic. It will assist you to go beyond a single perspective and reinforce your own side.
Creating a solid thesis statement
Creating a strong thesis statement lays the foundation for your essay and tells your readers what to expect.
- Understand the purpose. Your thesis statement will be the main point in your paper. The introductory part of the persuasive essay should precisely give the main argument or position you will address.
- Analyze the prompt. Go through the prompt again and determine what the crucial issues or queries are that are lying behind it. Those aspects determine the focus of your thesis, which should be put in line with them.
- Take a clear stance. Choose whether you take the position against or the position supporting the issue. Do you oppose or undermine a concept? The thesis sentence of your article should correspond to the position.
- Make it specific. Avoid general or nondescript statements. You should make your thesis statement specific and purposeful, stating what the essay will be about covering in your paper.
- Provide a roadmap. The thesis statement can also be used to introduce the topic of discussion and the areas you will be covering in the subsequent paragraphs.
Make sure you get a good, balanced statement that covers key points, and in that way, it is easy to follow the storyline in general.
Developing supporting arguments
Once you have your thesis statement, it’s time to build your essay around it with strong supporting arguments.
Identify key points. Split your thesis up into minor points or paragraphs that serve as evidence of your main idea.
Provide evidence. Utilize the numbers, instances, quotations, or some statistics to defeat each of your supporting positions. As a result, the argumentation makes the essay more convincing and solid as well.
Organize logically. Paragraphs should be arranged in a logical sequence to make your support arguments easily understandable. Sentence connections provide ease of reading for your reader and ensure that the plot of your composition flows smoothly.
Stay focused. Make certain that all the supporting pieces of your argument are directly and logically related to the thesis statement and serve to expound your beliefs.
Introduce incontrovertible points to defend your thesis. They can be foundations so that your readers are inclined to agree with you.
Refining and polishing your essay
Once you’ve written your essay, it’s important to refine and polish it to ensure it’s clear, coherent, and well-organized.
- Edit for clarity. During the final step, go through your essay and check to make sure the ideas that you want to express are clear and presentable. For any verbiage or sentences that add more than what is indicated.
- Check for coherence. Make sure that every paragraph logically comes in as a continuation of the rest, having a connection with one another and arguments that are coherent and compatible with each other. Make use of transitional clauses to advance coherence between various elements of the writing.
- Proofread for errors. Check proper spelling, grammar, and punctuation and target an improvement in sentence structure and vocabulary, especially the use of active voice.
- Seek feedback. Incorporate your friend’s, family member’s, or teacher’s commentary for feedback into your essay. Such tests could help you to find things that you haven’t thought about before and are definitely worth trying.
Through skillful editing of your essay , it is possible to raise the level of writing and, therefore, make it more exciting and convincing to the reader.
You may also like
April 4, 2024
Mouth Tape for Mild OSA – Let’s Learn About This Condition
6 signs of addiction and how to overcome it, top 10 tips for improving posture and spinal health, top 10 reasons you shouldn’t ignore your mental health, dream big: nine tips for starting a business with limited capital, offshore company establishment in 2024, eco-friendly living: 10 simple changes for a sustainable home, 8 home improvement projects that pay off in the long run.
April 3, 2024
What is the Importance of Physical Therapy?
Collaborative effort strengthens gambling regulation between british and swedish authorities, what percentage of gamblers have a problem, everything you need to know about dentures.
2024 Global Learning Challenge
Is Using an Essay Writing Service Considered Cheating?
Oliva Campbell
Our organization.
CollegeEssay.org
What is the name of your solution?
Provide a one-line summary of your solution..
Debunking Misconceptions and Embracing Academic Support
In what city, town, or region is your solution team headquartered?
In what country is your solution team headquartered.
- United States
What type of organization is your solution team?
Film your elevator pitch., what specific problem are you solving.
Is Using an Essay Writing Service Considered Cheating? Debunking Misconceptions and Embracing Academic Support
In the contemporary academic landscape, the utilization of essay writing service has sparked a debate regarding its ethical implications. Some perceive it as a form of cheating, while others argue it as a legitimate means of seeking academic support. As we delve into this discussion, it's imperative to explore both perspectives and shed light on the role of essay writing services in academia.
What is your solution?
Understanding the Controversy The Ethical Dilemma
The crux of the debate lies in the ethical dilemma surrounding the use of essay writing services. Traditional notions of academic integrity emphasize the importance of individual effort and originality in scholarly pursuits. From this standpoint, outsourcing the task of essay writing may seem like circumventing academic rigor and ethical standards.
Perceived Academic Dishonesty
Critics often equate using essay writing services to academic dishonesty, arguing that it undermines the learning process and devalues the significance of genuine scholarly achievements. They view it as a shortcut to academic success, devoid of the essential elements of critical thinking, research, and academic growth.
Legitimate Academic Support
On the contrary, proponents of essay writing services advocate for a nuanced understanding of academic support. They argue that seeking assistance from professional writers does not inherently constitute cheating but rather serves as a supplementary resource to enhance learning outcomes. Best Essay writing service can provide valuable guidance, especially for students grappling with complex topics or facing time constraints.
Who does your solution serve, and in what ways will the solution impact their lives?

Debunking Misconceptions Collaboration, Not Duplication
Contrary to popular belief, engaging with essay writing services does not entail passively submitting pre-written essays as one's own work. Instead, it involves collaboration between students and professional writers to develop custom essays tailored to their unique requirements. The final product reflects the student's input, understanding, and perspective, albeit with expert guidance.
Learning Opportunity
Essay writing services offer a valuable learning opportunity by providing model essays that serve as exemplars of academic writing standards. Students can analyze these essays to understand proper structuring, argumentation techniques, and citation practices, thereby honing their own writing skills. Additionally, interacting with professional writers fosters a deeper understanding of subject matter and research methodologies.
Academic Support System
Rather than undermining academic integrity, essay writing services complement existing support systems within educational institutions. They function as supplementary resources that assist students in navigating academic challenges effectively. By offering personalized assistance, these services empower students to overcome obstacles and achieve their academic goals.
Embracing Academic Support Fostering Academic Success
Ultimately, the goal of essay writing services is to facilitate academic success by providing students with the necessary tools and guidance to excel in their studies. By availing these services, students can alleviate academic pressure, meet deadlines, and improve their overall learning experience. Moreover, the support offered by essay writing services can enhance students' confidence and motivation, leading to greater academic achievements.
Ethical Considerations
While utilizing essay writing services is permissible within ethical boundaries, it's essential for students to uphold academic integrity and honesty. They should utilize these services responsibly, ensuring that the essays produced are used for reference purposes and serve as aids in their own academic endeavors. Transparency and integrity should guide students' interactions with essay writing services to maintain the ethical integrity of academic pursuits.
In conclusion, the debate surrounding the use of essay writing services underscores the complexities inherent in modern education. While some may view it as a contentious issue mired in ethical ambiguity, a nuanced perspective reveals its potential as a valuable academic support tool. By dispelling misconceptions and embracing the role of essay writing services as supplementary resources, students can leverage these services responsibly to enhance their academic journey. Ultimately, the ethical considerations lie in how students utilize these services to foster their academic growth while upholding principles of integrity and honesty in their scholarly pursuits.
How are you and your team well-positioned to deliver this solution?
Leveraging CollegeEssay.org and MyPerfectWords.com for Optimal Results
In the quest for academic excellence and ethical scholarship, students can enhance their learning journey by leveraging reputable essay writing services such as CollegeEssay.org and MyPerfectWords.com. These platforms offer a myriad of features and benefits designed to support students in achieving their academic goals while upholding principles of integrity and honesty.
Customized Essay Writing Services
Both CollegeEssay.org and MyPerfectWords.com prioritize delivering custom-written essays tailored to each student's unique requirements. By availing of their services, students can collaborate with professional writers to develop high-quality essays that meet academic standards and reflect their individual insights and perspectives.
Expert Guidance and Support
The teams of skilled writers at CollegeEssay.org and MyPerfectWords.com possess expertise in various subjects and disciplines, ensuring that students receive expert guidance and support across a wide range of academic topics. From research and outlining to drafting and editing, these platforms offer comprehensive assistance at every stage of the writing process.
Timely Delivery and Flexible Deadlines
Meeting deadlines is paramount in academic pursuits, and both CollegeEssay.org and MyPerfectWords.com prioritize timely delivery of essays. With flexible deadlines ranging from 6 to 24 hours, students can rely on these platforms to accommodate urgent essay requests without compromising on quality or accuracy.
24/7 Customer Support
Navigating the intricacies of essay writing can be daunting, but with 24/7 customer support and their reliable research paper writing service available at CollegeEssay.org, students can seek assistance and clarification at any time. Multilingual support teams ensure accessibility for students from diverse linguistic backgrounds, fostering a supportive and inclusive environment.
Originality and Plagiarism-Free Guarantee
Maintaining academic integrity is non-negotiable, and both CollegeEssay.org and MyPerfectWords.com uphold rigorous standards of originality and authenticity. Essays produced by these platforms undergo thorough plagiarism checks, ensuring that students receive 100% original and plagiarism-free content with every order.
Transparent Pricing and Payment Options
Affordability is a key consideration for students, and MyPerfectWords.com offer cheapest research paper writing service transparent pricing structures and flexible payment options. With prices starting at just $11/page and the option to pay 50% upfront and 50% upon completion, these platforms provide cost-effective solutions that fit students' budgets.

Which dimension of the Challenge does your solution most closely address?
Which of the un sustainable development goals does your solution address.
- 4. Quality Education
What is your solution’s stage of development?
Please share details about why you selected the stage above..
Revision and Refund Policies
Student satisfaction is paramount, and both CollegeEssay.org and MyPerfectWords.com offer revision and refund policies to ensure that students are fully satisfied with the essays they receive. Students can request revisions free of charge until they are completely satisfied with the final product, and a 100% money-back guarantee ensures peace of mind in case of any unforeseen issues.
Why are you applying to Solve?
In conclusion, students seeking academic support and assistance with essay writing can benefit greatly from utilizing reputable platforms such as CollegeEssay.org and MyPerfectWords.com. With features such as customized essay writing services, expert guidance and support, timely delivery, 24/7 customer support, originality guarantees, transparent pricing, and flexible payment options, these platforms provide comprehensive solutions to students' academic needs. By leveraging the services offered by CollegeEssay.org and MyPerfectWords.com, students can enhance their academic performance, alleviate academic pressure, and foster a deeper understanding of course materials, all while upholding principles of integrity and academic honesty.
In which of the following areas do you most need partners or support?
- Legal or Regulatory Matters
Who is the Team Lead for your solution?
Solution team.
The Solve team will review your report and remove any inappropriate content.
Why is this item inappropriate?
We use cookies.
We use cookies and other tracking technologies to improve your browsing experience on our website and to understand where our visitors are coming from. By browsing our website, you consent to our use of cookies and other tracking technologies.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Clear transitions are crucial to clear writing: They show the reader how different parts of your essay, paper, or thesis are connected. Transition sentences can be used to structure your text and link together paragraphs or sections. Example of a transition sentence for a new paragraph. In this case, the researchers concluded that the method ...
Transitions. Transitions help your readers move between ideas within a paragraph, between paragraphs, or between sections of your argument. When you are deciding how to transition from one idea to the next, your goal should be to help readers see how your ideas are connected—and how those ideas connect to the big picture.
A transition between paragraphs can be a word or two (however, for example, similarly), a phrase, or a sentence. Transitions can be at the end of the first paragraph, at the beginning of the second paragraph, or in both places. Transitions within paragraphs: As with transitions between sections and paragraphs, transitions within paragraphs act ...
Clear transitions are crucial to clear writing: they connect different parts of your essay and structure your text. This video will walk you through the use ...
Writing Transitions. Good transitions can connect paragraphs and turn disconnected writing into a unified whole. Instead of treating paragraphs as separate ideas, transitions can help readers understand how paragraphs work together, reference one another, and build to a larger point. The key to producing good transitions is highlighting ...
Transitional words and phrases can create powerful links between ideas in your paper and can help your reader understand the logic of your paper. However, these words all have different meanings, nuances, and connotations. Before using a particular transitional word in your paper, be sure you understand its meaning and usage completely and be sure…
The writer also uses the transition word however to indicate the contrast between the two sentences. Writing Transitions between Paragraphs: Use transitions to show relationships between paragraphs. No matter how well-constructed each paragraph may be on its own, your paragraphs must be logically connected to make your essay a coherent whole.
Common Transition Words and Phrases. ... 9. Emphasis. Use to suggest that an idea is particularly important to your argument important to note, most of all, a significant factor, a primary concern, a key feature, remember that, pay particular attention to, a central issue, the most substantial issue, the main value, a major event, the chief factor, a distinctive quality, especially valuable ...
3. The "Connecting Back to Your Topic" Transition. With this approach, you establish your central topic, then connect back to it in your transition sentences. Notice in the " Translating " essay, for example, how each transition sentence connects back to the central theme:
Use our guide for tips on how to outline your novel. 2. Identify the subject of each paragraph. Once you've consulted your outline, it's time to hone in on the main ideas of the paragraphs on either side of your transition. A good transition will have something to say about both the preceding paragraph and the new paragraph.
Argument 1: The next three paragraphs are where you expand on your argument. Begin with a topic sentence that serves as an overview of your intended position, before you introduce statistics, quotes, and other forms of research. Argument 2: A general rule is that you should introduce broader points to your argument before going into detail.
Harvard College Writing Center 5 Asking Analytical Questions When you write an essay for a course you are taking, you are being asked not only to create a product (the essay) but, more importantly, to go through a process of thinking more deeply about a question or problem related to the course. By writing about a
Paragraph Transitions. Transitioning between paragraphs will require you to place the transitions at the beginnings of the new paragraph. Avoid using transitions at the end of the preceding paragraphs because, in ideal circumstances, you want each paragraph of your essay to focus on one aspect of your essay topic.This will also allow you to combine similar information together (as we just ...
Writing a transition statement starts with identifying the relationship that the transition is trying to convey. It's also important to know the type of essay being written as well.
Transition sentences are crucial components of written and spoken language that serve as bridges between different ideas, paragraphs, or sections within a piece of writing. These sentences smoothly guide the reader from one point to another, ensuring coherence and logical progression in the narrative. Transition sentences play a vital role in ...
Transition sentences are necessary for a well-structured paper as they offer new ideas and assist the reader's comprehension. If you follow these steps and tips, writing excellent transition sentences won't be too hard. Before writing, feel free to analyze our sample essays.
Four Rules of Using Transitions in Academic Writing. Rule 1. Structure your essay well. If your essay has a clear structure, this will minimize the need for transitions. Remember - you shouldn't really need a lot of transitional words and phrases in your essay. Use transitions in places where they are most likely to help the reader make the ...
Many transition words are available to use. Choose the appropriate word for the situation.. For example, if you want to show the sequence between two sentences, you can use a word like 'then' or 'after.' If you want to emphasize a point through the transition, you can use 'indeed,' 'especially,' or 'particularly.'. Transition words can be used at the start of the sentence ...
writing, let us briefly discuss the types of transitions your writing will use. The types of transitions available to you are as diverse as the circumstances in which you need to use them. A transition can be a single word, a phrase, a sentence, or an entire paragraph. In
Additionally, she's held previous roles as a researcher, full-time daily journalist, and book editor. Brittany's work has been featured in The Iowa Review, The Hopkins Review, and the Pittsburgh City Paper, among others, and she was also a 2021 Pushcart Prize nominee. AP Lit Prose Essay Examples - we analyze the strengths and weaknesses of ...
Sample College Essay 2 with Feedback. This content is licensed by Khan Academy and is available for free at www.khanacademy.org. College essays are an important part of your college application and give you the chance to show colleges and universities your personality. This guide will give you tips on how to write an effective college essay.
A.I.-Generated Garbage Is Polluting Our Culture. Mr. Hoel is a neuroscientist and novelist and the author of The Intrinsic Perspective newsletter. Increasingly, mounds of synthetic A.I.-generated ...
Follow these tips to produce stronger writing that stands out on the web even in the age of AI and ChatGPT. Whether you're a student, a journalist, or a business professional, knowing how to do ...
Tips For Writing A Career Change Cover Letter. 1. Personalize Your Approach: Address the letter to a specific person whenever possible. Doing so demonstrates attention to detail and a genuine ...
Note down promptly when the essay is submitted in order for you to arrange the time properly. Look into breaking up the writing process into separate pieces to avert panic at the end. Clarify any uncertainties. If you are unsure about one of the steps of the task, do not be shy of asking your teacher or professor for clarification.
Essay writing services offer a valuable learning opportunity by providing model essays that serve as exemplars of academic writing standards. Students can analyze these essays to understand proper structuring, argumentation techniques, and citation practices, thereby honing their own writing skills. Additionally, interacting with professional ...