Free Printable Narrative Writing Worksheets for 7th Grade
Narrative Writing: Discover a collection of free printable worksheets for Grade 7 Reading & Writing teachers, focusing on enhancing students' narrative writing skills and creativity.


Explore Narrative Writing Worksheets by Grades
- kindergarten
Explore Other Subject Worksheets for grade 7
- Social studies
- Social emotional
- Foreign language
- Reading & Writing
Explore printable Narrative Writing worksheets for 7th Grade
Narrative Writing worksheets for Grade 7 are an essential tool for teachers to help their students develop strong reading and writing skills. These worksheets focus on various aspects of narrative writing, such as creating engaging characters, building a compelling plot, and using descriptive language. By incorporating these worksheets into their lesson plans, teachers can provide their students with the necessary practice to improve their writing abilities. Additionally, these worksheets can be used to teach students about different types of narratives, such as fiction and nonfiction writing. As students progress through their Grade 7 curriculum, they will become more confident in their reading and writing abilities, thanks to the support provided by these valuable resources.
Quizizz is an excellent platform that offers a variety of educational resources, including Narrative Writing worksheets for Grade 7. Teachers can use Quizizz to create engaging and interactive quizzes, which can be used alongside the worksheets to assess students' understanding of the material. Furthermore, Quizizz offers a wide range of other resources, such as Reading & Writing activities and Nonfiction Writing exercises, which can be used to supplement the Narrative Writing worksheets. By incorporating Quizizz into their teaching strategies, teachers can provide a well-rounded and comprehensive approach to developing their students' reading and writing skills. This platform not only helps students improve their abilities but also makes learning fun and enjoyable, ensuring that students remain engaged and motivated throughout their Grade 7 journey.

45 Narrative Writing Prompts for 7th Grade
Preteens and teenagers have a lot to say, but they don’t always know just how to express their emotions or say what’s on their mind.
By implementing narrative writing into your curriculum, you give your students an outlet to experiment with in a safe and structured environment.
Below, you will find a list of narrative writing prompts to help your 7th graders let out some of their thoughts and get them writing about something that matters to them.
Using This Guide
You can use this guide to help students come out of their shell, or keep it handy for when they have some down time in between activities.
Consider challenging your students to write using one prompt a day for an entire school week, and express to them the importance of thinking deeply about the things they think, feel, and remember.
The Writing Prompts
- Write about a time when you felt proud of yourself.
- Tell the story of how you met your best friend.
- Write about a time when you felt left out of a group.
- Do you consider yourself to be a good ally? Explain.
- When was the last time you felt afraid? Write about what happened.
- If you could have any superpower, what would it be? Why?
- What is the thing you like most about yourself? What are some things you could do to improve this quality?
- Talk about a time when you felt misunderstood by an adult or authority figure.
- Explain what it means to be a good friend.
- What do you think is your worst habit? What steps could you take to break this habit?
- Write about a time when you realized you let someone down. How did you feel? How do you think they felt?
- If you could be a part of any fictional family, which would you choose? Why?
- What is your favorite way to spend time with your friends? Why?
- Write the step-by-step process of preparing your favorite food.
- Write about the last time you felt an adrenaline rush.
- Do you think social media is good or bad for teenagers? Explain your answer.
- What does school spirit mean to you? What are some ways you could show more school spirit?
- Write about a time when you felt publicly embarrassed. How was the situation resolved?
- What do you think it means to be successful in life? Use examples.
- Write about a time when you got in trouble for something that you didn’t do.
- Describe the funniest thing you’ve ever seen.
- Why is it important to keep trying even when something seems too hard?
- How do you normally spend New Year’s Eve?
- How is middle school different from elementary school? How are they the same?
- Write about the last time you apologized to someone. How did you both feel after?
- Have you ever been a victim of racial profiling? How did it make you feel?
- Talk about the last gift you received. Who was it from? Did you like it?
- Have you ever felt like someone invaded your privacy? Write about what happened.
- Is there a teacher who has made an impact on your education? What makes them special?
- Have you ever visited another country? What was it like? If you haven’t, where would you like to visit? Why?
- What would you do if you woke up tomorrow and discovered you were invisible?
- What is your favorite holiday? What makes it special?
- If you found $200 on the ground, what would you do with it? Explain your answer.
- Think of an important family photo. Write the story behind it.
- If your best friend were a season, which would they be? Why?
- How do you define failure? What are some steps you could take to ensure you succeed instead of failing?
- Describe your idea of the perfect snow day.
- Write about the last time you had a misunderstanding with someone. How was it resolved?
- If you could make one new rule for your school, what would it be? Why?
- Is there anything specific that makes you feel anxious? How do you face this thing?
- If you could get rid of one school rule, what would it be? Why?
- Do you think it’s more important to explore space or to explore the oceans? Explain your answer.
- Has anyone ever spoken over you or cut you off while you were saying something important? How did it make you feel?
- Have you ever performed on stage? Write about your experience.
- What is the scariest thing you’ve ever done?
Looking For More?
If you’re looking for something specific and can’t find it here, reach out and let us know. We’d love to help shape the minds of the future.

Narrative Essay
Narrative Essay Examples
10+ Interesting Narrative Essay Examples Plus Writing Tips!

People also read
Narrative Essay - A Complete Writing Guide with Examples
Writing a Personal Narrative Essay: Everything You Need to Know
Best Narrative Essay Topics 2023 for Students
Crafting a Winning Narrative Essay Outline: A Step-by-Step Guide
Many students struggle with crafting engaging and impactful narrative essays. They often find it challenging to weave their personal experiences into coherent and compelling stories.
If you’re having a hard time, don't worry!
We’ve compiled a range of narrative essay examples that will serve as helpful tools for you to get started. These examples will provide a clear path for crafting engaging and powerful narrative essays.
So, keep reading and find our expertly written examples!
- 1. Narrative Essay Definition
- 2. Narrative Essay Examples
- 3. Narrative Essay Examples for Students
- 4. Narrative Essay Topics
- 5. Narrative Essay Writing Tips
Narrative Essay Definition
Writing a narrative essay is a unique form of storytelling that revolves around personal experiences, aiming to immerse the reader in the author's world. It's a piece of writing that delves into the depths of thoughts and feelings.
In a narrative essay, life experiences take center stage, serving as the main substance of the story. It's a powerful tool for writers to convey a personal journey, turning experiences into a captivating tale. This form of storytelling is an artful display of emotions intended to engage readers, leaving the reader feeling like they are a part of the story.
By focusing on a specific theme, event, emotions, and reflections, a narrative essay weaves a storyline that leads the reader through the author's experiences.
The Essentials of Narrative Essays
Let's start with the basics. The four types of essays are argumentative essays , descriptive essays , expository essays , and narrative essays.
The goal of a narrative essay is to tell a compelling tale from one person's perspective. A narrative essay uses all components you’d find in a typical story, such as a beginning, middle, and conclusion, as well as plot, characters, setting, and climax.
The narrative essay's goal is the plot, which should be detailed enough to reach a climax. Here's how it works:
- It's usually presented in chronological order.
- It has a function. This is typically evident in the thesis statement's opening paragraph.
- It may include speech.
- It's told with sensory details and vivid language, drawing the reader in. All of these elements are connected to the writer's major argument in some way.
Before writing your essay, make sure you go through a sufficient number of narrative essay examples. These examples will help you in knowing the dos and don’ts of a good narrative essay.
It is always a better option to have some sense of direction before you start anything. Below, you can find important details and a bunch of narrative essay examples. These examples will also help you build your content according to the format.
Here is a how to start a narrative essay example:
Sample Narrative Essay
The examples inform the readers about the writing style and structure of the narration. The essay below will help you understand how to create a story and build this type of essay in no time.
Here is another narrative essay examples 500 words:
Narrative Essay Examples for Students
Narrative essays offer students a platform to express their experiences and creativity. These examples show how to effectively structure and present personal stories for education.
Here are some helpful narrative essay examples:
Narrative Essay Examples Middle School
Narrative Essay Examples for Grade 7
Narrative Essay Examples for Grade 8
Grade 11 Narrative Essay Examples
Narrative Essay Example For High School
Narrative Essay Example For College
Personal Narrative Essay Example
Descriptive Narrative Essay Example
3rd Person Narrative Essay Example
Narrative Essay Topics
Here are some narrative essay topics to help you get started with your narrative essay writing.
- When I got my first bunny
- When I moved to Canada
- I haven’t experienced this freezing temperature ever before
- The moment I won the basketball finale
- A memorable day at the museum
- How I talk to my parrot
- The day I saw the death
- When I finally rebelled against my professor
Need more topics? Check out these extensive narrative essay topics to get creative ideas!
Narrative Essay Writing Tips
Narrative essays give you the freedom to be creative, but it can be tough to make yours special. Use these tips to make your story interesting:
- Share your story from a personal viewpoint, engaging the reader with your experiences.
- Use vivid descriptions to paint a clear picture of the setting, characters, and emotions involved.
- Organize events in chronological order for a smooth and understandable narrative.
- Bring characters to life through their actions, dialogue, and personalities.
- Employ dialogue sparingly to add realism and progression to the narrative.
- Engage readers by evoking emotions through your storytelling.
- End with reflection or a lesson learned from the experience, providing insight.
Now you have essay examples and tips to help you get started, you have a solid starting point for crafting compelling narrative essays.
However, if storytelling isn't your forte, you can always turn to our essay writing service for help.
Our writers are specialists that can tackle any type of essay with great skill. With their experience, you get a top-quality, 100% plagiarism free essay everytime.
So, let our narrative essay writing service make sure your narrative essay stands out. Order now!

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Caleb S. has been providing writing services for over five years and has a Masters degree from Oxford University. He is an expert in his craft and takes great pride in helping students achieve their academic goals. Caleb is a dedicated professional who always puts his clients first.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading


21 Narrative Writing Examples
Written by Dan
Last updated February 14, 2024
Are you looking for the best narrative writing examples to use in your classroom? As an educator, finding engaging and compelling narrative stories that can capture your students’ imaginations can be challenging.
Narrative writing can open windows of opportunity to understand student perspectives while teaching critical literary skills and components.
This blog post’ll explore creative and interactive narrative writing examples to promote a positive learning experience for teachers and students alike!
Related : For more, check out our article on How To Make Writing Fun here.
Table of Contents
Section 1: The Awakening of Nature
As the morning sun shyly peeked over the horizon, a glistening dewdrop delicately clung to a leaf, reflecting the first light of day. It was as if Mother Nature herself had adorned the world with tiny diamonds.
“Good morning, world,” whispered the wind, playfully rustling the leaves, its voice echoing through the silent woods like a soft melody. A serene symphony of nature stirred every creature from their slumber.
Suddenly, a rabbit hopped out of its burrow, its fur as white as fresh snow, and its eyes sparkling with curiosity. “Another beautiful day,” it seemed to say, twitching its nose at the scent of fresh earth and blooming flowers.
Just then, a bird burst into song, its voice ringing out clear and true. A sweet serenade filled the air, as captivating as a nightingale’s enchanting tune. The forest, once quiet, now buzzed with the rhythm of life.
Section 2: The Magic of Childhood
In the heart of the city, there was a secret oasis known only to the children; a park where dreams took flight. It was like stepping into a storybook, complete with towering trees that stretched towards the sky, their branches reaching out like giant hands ready to catch any child brave enough to climb.
“Bet you can’t catch me!” shouted Sam, his laughter filling the air as he darted across the lush green grass. His words were a challenge, a spark that ignited the competitive spirit in his friends.
Sarah, with her pigtails bobbing, gave chase, her shoes thudding against the ground in a rhythmic pattern. She ran with the determination of a cheetah on the hunt, her eyes focused on Sam, who was now a small figure in the distance.
The park was their kingdom, a place where they could be pirates, explorers, or superheroes. It was where their imaginations roamed free, creating adventures as colorful as a painter’s palette.
Section 3: The Beauty of Love
In the quiet corner of a bustling café sat a couple, lost in their own world. They were like two stars drawn together by an invisible force, their love radiating warmth and light.
“Remember our first date here?” asked John, his eyes twinkling with nostalgia. His words hung in the air, painting a vivid picture of their past.
“Yes,” replied Emily, her voice soft and wistful. “It feels like ages ago, yet it seems like yesterday.” Her smile was as radiant as the sun breaking through the clouds after a summer rain, filling their small corner with a glow that only love can bring.
There was a comfortable silence as they reminisced, their hands intertwined on the table. Their love story was etched into every line of their faces, a testament to the enduring power of love.
Section 4: The Intricacies of Technology
The sun had barely risen when Alex, a software engineer, sat down at his desk. His fingers danced across the keyboard, coding with the elegance of a pianist playing a symphony. The screen, glowing like a solitary lighthouse in the dark room, reflected a world of ones and zeros, a language only understood by a select few.
“Another day, another code,” he murmured, his voice resonating with a quiet determination. His words were not just a statement, but a mantra that fueled his passion for technology.
Suddenly, an email notification popped up on his screen. It was from a tech startup, their proposal as captivating as the siren’s song. “We’re building a future beyond imagination,” it proclaimed, its promise echoing in the silence of the room.
In the world of technology, every day was a new challenge, a puzzle waiting to be solved. It was a thrilling ride that oscillated between triumph and despair, as unpredictable as a roller coaster yet as rewarding as discovering a hidden treasure.
Section 5: The Power of Art
In a quaint little studio tucked away in a bustling city, Sarah painted with a fervor that could only come from within. Her brush strokes were as fluid as a dancer’s movements, each one a testament to her talent.
“The canvas is my stage,” she would often say, her voice filled with a profound love for art. Her words were not merely a statement, but a proclamation of her dedication to her craft.
As the day turned into night, her painting began to come alive. The colors were as vibrant as a summer sunset, their brilliance illuminating the room. “Art is not just about creating something beautiful,” she mused, her eyes reflecting the glow of her creation. “It’s about pouring your soul onto the canvas.”
In the realm of art, every brush stroke was a new journey, an adventure that transported the artist to a world of endless possibilities. It was a dance between imagination and reality, as mesmerizing as a ballet performance under a moonlit sky.
Narrative Texts
Section 6: the thrill of sports.
The stadium was buzzing with excitement as the players took the field. The air was electric, charged with anticipation, as if the crowd was holding its collective breath.
“This is it, the moment we’ve been waiting for,” muttered Jake, his eyes fixed on the opponents. His words were not just a statement, but a battle cry that ignited the fire in his teammates’ hearts.
As the whistle blew, the game began. Each pass, each run, each tackle was executed with surgical precision, as coordinated as a well-choreographed dance. “This is not just a game,” echoed Jake’s voice, his determination palpable even amidst the deafening cheers.
In the world of sports, every game was a test of strength, skill, and spirit. It was a thrilling spectacle that brought together people from all walks of life, a celebration of human resilience, as inspiring as a phoenix rising from the ashes.
Section 7: The Magic of Music
In the quiet solitude of a dimly lit room, Ethan strummed his guitar with a grace that belied his years. His fingers moved with the agility of a seasoned musician, creating melodies that were as enchanting as a moonlit serenade.
“Each note is a story waiting to be told,” he whispered, his voice barely audible over the harmonious symphony he was weaving. His words were not just a sentiment but a testament to his profound connection with music.
As the night grew deeper, his composition evolved, each chord resonating with raw emotion. The music was as captivating as a symphony performed in an ancient cathedral, its echoes lingering long after the final note was played. “Music isn’t just about sounds,” he reflected, his eyes lost in the dance of shadows cast by his guitar. “It’s about capturing the essence of life in a melody.”
In the universe of music, each composition was a voyage across the sea of emotions. It was a mesmerizing dance between silence and sound, as captivating as the eternal dance of stars in the night sky.
Section 8: The Enigma of Science
In the sterile confines of a high-tech lab, Dr. Amelia peered through her microscope, her face illuminated by the artificial glow. Her hands moved with precision, handling the delicate samples with the care of a jeweler inspecting a priceless gem.
“Every atom is a mystery waiting to be unraveled,” she murmured, her voice echoing in the silent laboratory. Her words were not just a hypothesis, but a declaration of her unwavering curiosity for the unknown.
As hours turned into minutes, her research began to bear fruit. The results were as fascinating as the discovery of an alien civilization, their implications reverberating through the realms of science. “Science isn’t just about facts,” she mused, her gaze lost in the labyrinth of data on her screen. “It’s about challenging the boundaries of human knowledge.”
In the realm of science, every discovery was a step towards the unknown, a dance on the edges of human understanding. It was a journey as exciting as venturing into the unexplored corners of the universe.
Section 9: The Allure of Literature
In the serene comfort of her study, Emily penned down her thoughts with a passion that was almost palpable. Her pen moved across the page with a rhythm that mirrored the heartbeat of her story, each word a piece of her soul inked on paper.
Every sentence is a journey into the human psyche,” she mused, her voice blending with the soft rustle of pages. Her words were not just a thought, but a reflection of her deep-seated love for literature.
As the night draped its dark veil, her story began to take shape. The plot was as intriguing as a centuries-old mystery waiting to be uncovered, its twists and turns a testament to Emily’s literary prowess. “Writing isn’t just about narrating a tale,” she contemplated, her eyes gleaming with the satisfaction of a well-written chapter. “It’s about delving into the depths of human emotions.”
In the world of literature, every book was a key to a different world, an exploration into the vast expanse of human experience. It was a voyage as enthralling as sailing across the seas of time and space, discovering new lands of imagination and creativity.
Section 10: The Evolution of Robotics
In a high-tech laboratory bathed in the glow of neon lights, Dr. Lee worked tirelessly on his latest invention – a humanoid robot. Its metallic facade reflected the artificial light, creating an aura of intrigue around it. His fingers moved deftly over the control panel, programming commands with the precision of a master craftsman.
“Each code is a step towards artificial intelligence,” he mused, his voice barely audible over the hum of machinery. His words were not just an observation but a testament to his relentless pursuit of technological advancement.
As the night unfolded, the robot began to respond. Its movements were as fluid as a professional dancer’s, its mechanical eyes flickering with simulated life. “Robotics isn’t just about creating machines,” he pondered, watching his creation with a sense of accomplishment. “It’s about the fusion of creativity and engineering.”
In the realm of robotics, every innovation was a leap towards the future, a journey into the uncharted territories of technology. It was a thrilling exploration as captivating as the discovery of a new planet in the cosmos.
Section 11: The Revolution of Virtual Reality
In the heart of Silicon Valley, Sarah donned her VR headset, stepping into a world that existed beyond the confines of physical reality. The virtual landscape unfolded before her, its vivid imagery as mesmerizing as a Van Gogh painting.
“Every pixel is a window to another world,” she remarked, her voice brimming with excitement. Her words were not just a statement, but a proclamation of her fascination with virtual reality.
As the day transitioned into dusk, her virtual adventure escalated. The experiences were as enthralling as teleporting to an alien civilization, their realism challenging the boundaries of perception. “Virtual reality isn’t just about simulation,” she reflected, her eyes sparkling with awe. “It’s about transcending the limitations of our senses.”
In the universe of virtual reality, every session was a journey beyond the ordinary, an expedition into the realms of imagination. It was an experience as exhilarating as time-traveling into different eras of history.
Section 12: The Impact of Cybersecurity
In the nerve center of a leading tech company, Sean scanned through lines of computer code, his eyes alert for any signs of a potential breach. The glow from the multiple monitors illuminated his concentrated face, reflecting in his glasses.
“Every line of code can be a potential vulnerability,” he stated, his voice steady and serious. His words were not just a professional opinion but a reflection of his dedication to cybersecurity.
As minutes turned into hours, his vigilance paid off. The anomalies were as subtle as a chameleon blending into its surroundings, their detection a testament to Sean’s expertise. “Cybersecurity isn’t just about protecting data,” he contemplated, his fingers swiftly neutralizing the threat. “It’s about safeguarding our digital existence.”
In the world of cybersecurity, every threat detected was a victory over invisible adversaries, a silent battle fought in the digital realm. It was a responsibility as immense as guarding the secrets of a nation’s treasury.
Section 13: The Progress of Space Exploration
In a state-of-the-art control room at NASA, flight director Ava studied the telemetry data from their latest Mars rover. The screens around her were abuzz with information, each dataset a story of the rover’s journey on the red planet.
“Every byte of data is a clue to the mysteries of Mars,” she commented, her voice filled with wonder. Her words were not just an observation, but a declaration of her passion for space exploration.
As the Earth turned on its axis, the rover sent back stunning images. They were as breathtaking as the first photographs of Earth taken from the moon, their impact resonating throughout the scientific community.
“Space exploration isn’t just about reaching new frontiers,” she mused, her gaze fixed on the Martian landscape. “It’s about understanding our place in the universe.”
In the realm of space exploration, every mission was a leap into the unknown, a voyage into the cosmic ocean. It was a journey as awe-inspiring as the birth of a star in the distant galaxies.
Section 14: The Innovation of Quantum Computing
In a high-tech lab buzzing with activity, quantum physicist Dr. Raj worked on his cutting-edge quantum computer. The complex lattice of qubits and lasers before him was as mesmerizing as a symphony of light and energy.
“Every qubit is a step towards harnessing the power of quantum mechanics,” he noted, his voice echoing in the lab. His words were not just a statement, but a testament to his dedication to pushing the boundaries of computing.
As hours slipped into minutes, the quantum computer began to show promising results. The computations were as mind-boggling as deciphering an alien language, their speed outpacing traditional computers.
“Quantum computing isn’t just about faster calculations,” he reflected, watching the data stream on his monitor. “It’s about transforming how we solve complex problems.”
In the world of quantum computing, every breakthrough was a stride towards a paradigm shift in technology. It was an endeavor as exciting as unlocking the secrets of the universe itself.
Section 15: The Advancements in Artificial Intelligence
In the bustling hub of a leading tech company, AI researcher Lily fine-tuned the algorithms of her latest machine learning model. Her code, a labyrinth of functions and variables, was a testament to the intricacies of artificial intelligence.
“Every algorithm is a building block for intelligent machines,” she declared, her voice filled with determination. Her words were not just a professional opinion but a reflection of her commitment to AI research.
As the day turned into night, her machine learning model began to learn and adapt. The progress was as fascinating as watching a child learn to speak, its potential applications limitless.
“Artificial intelligence isn’t just about mimicking human intelligence,” she pondered, analyzing the results on her screen. “It’s about augmenting our capabilities and creating a symbiotic relationship with technology.”
In the domain of artificial intelligence, every innovation was a step towards a future where machines could think and learn. It was a journey as intriguing as deciphering the workings of the human brain.
Section 16: The Expansion of Virtual Reality Gaming
In the heart of a bustling game development studio, designer Marco was fine-tuning the graphics for their latest virtual reality game. The vibrant colors and lifelike textures on his screen were as enchanting as a digital masterpiece.
“Every pixel is a step towards total immersion,” he observed, his voice resonating with enthusiasm. His words were not just a remark, but a reflection of his passion for creating immersive gaming experiences.
As the day transitioned into evening, the game’s virtual world began to take shape. The landscapes were as captivating as a panoramic view of a fantastical land, their realism pushing the boundaries of virtual reality.
“VR gaming isn’t just about playing a game,” he pondered, testing the game on his VR headset. “It’s about living an adventure.”
In the universe of VR gaming, every new game was a journey into a different realm, an exploration into the limitless possibilities of virtual worlds. It was an experience as thrilling as teleporting into a different dimension.
Section 17: The Proliferation of Self-Driving Cars
In a state-of-the-art facility dedicated to autonomous vehicles, engineer Sofia was calibrating the sensors of a self-driving car. The complex network of radars, lidars, and cameras were as intricate as the human nervous system.
“Every sensor is an eye towards achieving full autonomy,” she stated, her voice echoing in the vast garage. Her words were not just a technical assessment, but a testament to her dedication to advancing autonomous technology.
As hours turned into minutes, the self-driving car began to navigate the test track flawlessly. The maneuvers were as precise as a professional driver’s, its decisions based on complex algorithms.
“Autonomous driving isn’t just about replacing the driver,” she reflected, monitoring the car’s performance. “It’s about enhancing safety and efficiency.”
In the world of self-driving cars, every successful test drive was a stride towards a future where cars could navigate without human intervention. It was a progression as fascinating as the evolution of transportation itself.
Section 18: The Advancements in Wearable Technology
In the design lab of a leading tech company, product developer Ryan was refining the features of their latest smartwatch. The sleek device on his workbench was as stylish as a high-end timepiece, its functionalities extending beyond just telling time.
“Every feature is a step towards seamless integration with our lives,” he remarked, his voice filled with excitement. His words were not just an evaluation, but a reflection of his commitment to enhancing wearable technology.
As the day turned into dusk, the smartwatch began to showcase its capabilities. The readings were as accurate as professional medical equipment, its user interface intuitive and user-friendly.
“Wearable tech isn’t just about gadgets,” he contemplated, testing the device’s fitness tracking feature. “It’s about personalizing technology to enrich our daily lives.”
In the realm of wearable technology, every new product was a leap towards a future where technology would be an integral part of our lives. It was a journey as intriguing as decoding the human genome.
Section 19: The Emergence of Quantum Internet
In a cutting-edge lab dedicated to quantum research, scientist Dr. Kim was working on the prototype for a quantum internet. The complex matrix of quantum entanglement and teleportation was as fascinating as a celestial constellation.
“Every entangled particle is a step towards unbreakable encryption,” she noted, her voice echoing with profound determination. Her words were not just an insight, but a testament to her unwavering dedication to quantum technologies.
As the day transitioned into night, the quantum internet prototype started showing promising results. The data transmission was as instantaneous as teleportation, its security unparalleled.
“Quantum internet isn’t just about faster communication,” she reflected, scrutinizing the test results. “It’s about revolutionizing the way we exchange information.”
In the world of quantum internet, every successful experiment was a stride towards a new era of communication. It was a journey as thrilling as venturing into a wormhole in space-time.
Section 20: The Evolution of Smart Cities
In the command center of a futuristic smart city, urban planner Alex was monitoring the city’s intelligent systems. The elaborate network of sensors and AI algorithms was as intricate as a digital ecosystem.
“Every sensor is an eye towards achieving sustainable urban living,” he stated, his voice filled with conviction. His words were not just an observation, but a declaration of his commitment to smart city initiatives.
As the sun set over the skyline, the city’s intelligent systems began to optimize various operations. The efficiency was as remarkable as a well-oiled machine, its impact significant on the city’s carbon footprint.
“Smart cities aren’t just about technology integration,” he contemplated, watching the live data feeds. “They’re about enhancing the quality of life for their inhabitants.”
In the realm of smart cities, every innovation was a leap towards a future where urban living would be sustainable and efficient. It was a progression as significant as the industrial revolution itself.
Section 21: The Advancements in Biotechnology
In the heart of a state-of-the-art biotech lab, scientist Maya was examining genetic sequences for her latest research. The strands of DNA on her computer screen were as mesmerizing as an intricate tapestry of life.
“Every gene is a piece of the puzzle towards understanding our biology,” she expressed, her voice echoing with fascination. Her words were not just a professional opinion, but a reflection of her passion for biotechnology.
As the day turned into evening, her genetic research began to yield insightful results. The findings were as enlightening as deciphering an ancient script, their implications far-reaching.
“Biotechnology isn’t just about manipulating genes,” she pondered, analyzing the data. “It’s about harnessing the power of life to improve health and wellbeing.”
In the world of biotechnology, every discovery was a step towards a future where diseases could be cured at the genetic level. It was a journey as intriguing as unraveling the mysteries of life itself.
Narrative writing is an essential part of the curriculum, fostering creativity, enhancing literary skills, and promoting critical thinking in students.
The examples shared in this blog post are a powerful tool to engage students and provoke their imagination.
Integrating these narrative writing examples into your teaching strategy allows you to create an interactive learning environment that encourages students to develop their narrative skills.
Remember, the ultimate goal is to teach students how to write and inspire them to tell their stories with confidence and creativity.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. what is narrative writing.
Narrative writing is a form of writing that tells a story. This could be a personal experience, an imagined event, or a sequence of events. The goal is to immerse the reader in the story through details, plot development, and character interaction.
2. Why is narrative writing important in schools?
Narrative writing is important in schools because it enhances students’ creativity, critical thinking, and communication skills. It allows students to express their thoughts and experiences, thereby improving their understanding of language and literature.
3. How can I use these narrative writing examples in my classroom?
These narrative writing examples can be used as models for students’ writing. Students can analyze these examples to understand the structure, style, and elements of a good narrative. You can also use them to spark discussion or as prompts for creative writing exercises.
4. How can I encourage my students to engage with narrative writing?
Encourage your students by creating an open and supportive environment where they feel comfortable sharing their stories. Provide constructive feedback, incorporate creative writing exercises, and use engaging narrative examples. Celebrate their progress and achievements to boost their confidence.
5. Can narrative writing be used across different subjects?
Absolutely! Narrative writing isn’t just for English or Literature classes. It can be used in History to narrate historical events, in Science to describe a process or phenomenon, or in Social Studies to explore different cultures and societies. The possibilities are endless!
Related Posts

- Grammar Explained: ‘Who, What, When, Where, Why, How’

About The Author
I'm Dan Higgins, one of the faces behind The Teaching Couple. With 15 years in the education sector and a decade as a teacher, I've witnessed the highs and lows of school life. Over the years, my passion for supporting fellow teachers and making school more bearable has grown. The Teaching Couple is my platform to share strategies, tips, and insights from my journey. Together, we can shape a better school experience for all.

Join our email list to receive the latest updates.
Add your form here

Narrative Writing | Student Writing Lessons | Student Writing Samples | Resource by Grade Level | Grades 2-5
Narrative Writing - Student Samples by Grade Level
Read Time 3 mins | Feb 24, 2021 11:03:06 AM | Written by: Toolbox

Are you looking to provide specific feedback to your students in order to improve their writing? These samples are annotated for the specific skills students applied effectively in their writing and suggestions are included for improvement. Download each sample and use them as a guide to analyze your own student samples and give you the language to provide feedback based on instruction. The suggested lessons can be found in the Empowering Writers Narrative guides.
A Step-by-Step Plan for Teaching Narrative Writing
July 29, 2018
Can't find what you are looking for? Contact Us

Listen to this post as a podcast:
Sponsored by Peergrade and Microsoft Class Notebook
This post contains Amazon Affiliate links. When you make a purchase through these links, Cult of Pedagogy gets a small percentage of the sale at no extra cost to you.
“Those who tell the stories rule the world.” This proverb, attributed to the Hopi Indians, is one I wish I’d known a long time ago, because I would have used it when teaching my students the craft of storytelling. With a well-told story we can help a person see things in an entirely new way. We can forge new relationships and strengthen the ones we already have. We can change a law, inspire a movement, make people care fiercely about things they’d never given a passing thought.
But when we study storytelling with our students, we forget all that. Or at least I did. When my students asked why we read novels and stories, and why we wrote personal narratives and fiction, my defense was pretty lame: I probably said something about the importance of having a shared body of knowledge, or about the enjoyment of losing yourself in a book, or about the benefits of having writing skills in general.
I forgot to talk about the power of story. I didn’t bother to tell them that the ability to tell a captivating story is one of the things that makes human beings extraordinary. It’s how we connect to each other. It’s something to celebrate, to study, to perfect. If we’re going to talk about how to teach students to write stories, we should start by thinking about why we tell stories at all . If we can pass that on to our students, then we will be going beyond a school assignment; we will be doing something transcendent.
Now. How do we get them to write those stories? I’m going to share the process I used for teaching narrative writing. I used this process with middle school students, but it would work with most age groups.
A Note About Form: Personal Narrative or Short Story?
When teaching narrative writing, many teachers separate personal narratives from short stories. In my own classroom, I tended to avoid having my students write short stories because personal narratives were more accessible. I could usually get students to write about something that really happened, while it was more challenging to get them to make something up from scratch.
In the “real” world of writers, though, the main thing that separates memoir from fiction is labeling: A writer might base a novel heavily on personal experiences, but write it all in third person and change the names of characters to protect the identities of people in real life. Another writer might create a short story in first person that reads like a personal narrative, but is entirely fictional. Just last weekend my husband and I watched the movie Lion and were glued to the screen the whole time, knowing it was based on a true story. James Frey’s book A Million Little Pieces sold millions of copies as a memoir but was later found to contain more than a little bit of fiction. Then there are unique books like Curtis Sittenfeld’s brilliant novel American Wife , based heavily on the early life of Laura Bush but written in first person, with fictional names and settings, and labeled as a work of fiction. The line between fact and fiction has always been really, really blurry, but the common thread running through all of it is good storytelling.
With that in mind, the process for teaching narrative writing can be exactly the same for writing personal narratives or short stories; it’s the same skill set. So if you think your students can handle the freedom, you might decide to let them choose personal narrative or fiction for a narrative writing assignment, or simply tell them that whether the story is true doesn’t matter, as long as they are telling a good story and they are not trying to pass off a fictional story as fact.
Here are some examples of what that kind of flexibility could allow:
- A student might tell a true story from their own experience, but write it as if it were a fiction piece, with fictional characters, in third person.
- A student might create a completely fictional story, but tell it in first person, which would give it the same feel as a personal narrative.
- A student might tell a true story that happened to someone else, but write it in first person, as if they were that person. For example, I could write about my grandmother’s experience of getting lost as a child, but I might write it in her voice.
If we aren’t too restrictive about what we call these pieces, and we talk about different possibilities with our students, we can end up with lots of interesting outcomes. Meanwhile, we’re still teaching students the craft of narrative writing.
A Note About Process: Write With Your Students
One of the most powerful techniques I used as a writing teacher was to do my students’ writing assignments with them. I would start my own draft at the same time as they did, composing “live” on the classroom projector, and doing a lot of thinking out loud so they could see all the decisions a writer has to make.
The most helpful parts for them to observe were the early drafting stage, where I just scratched out whatever came to me in messy, run-on sentences, and the revision stage, where I crossed things out, rearranged, and made tons of notes on my writing. I have seen over and over again how witnessing that process can really help to unlock a student’s understanding of how writing actually gets made.
A Narrative Writing Unit Plan
Before I get into these steps, I should note that there is no one right way to teach narrative writing, and plenty of accomplished teachers are doing it differently and getting great results. This just happens to be a process that has worked for me.
Step 1: Show Students That Stories Are Everywhere
Getting our students to tell stories should be easy. They hear and tell stories all the time. But when they actually have to put words on paper, they forget their storytelling abilities: They can’t think of a topic. They omit relevant details, but go on and on about irrelevant ones. Their dialogue is bland. They can’t figure out how to start. They can’t figure out how to end.
So the first step in getting good narrative writing from students is to help them see that they are already telling stories every day . They gather at lockers to talk about that thing that happened over the weekend. They sit at lunch and describe an argument they had with a sibling. Without even thinking about it, they begin sentences with “This one time…” and launch into stories about their earlier childhood experiences. Students are natural storytellers; learning how to do it well on paper is simply a matter of studying good models, then imitating what those writers do.
So start off the unit by getting students to tell their stories. In journal quick-writes, think-pair-shares, or by playing a game like Concentric Circles , prompt them to tell some of their own brief stories: A time they were embarrassed. A time they lost something. A time they didn’t get to do something they really wanted to do. By telling their own short anecdotes, they will grow more comfortable and confident in their storytelling abilities. They will also be generating a list of topic ideas. And by listening to the stories of their classmates, they will be adding onto that list and remembering more of their own stories.
And remember to tell some of your own. Besides being a good way to bond with students, sharing your stories will help them see more possibilities for the ones they can tell.
Step 2: Study the Structure of a Story
Now that students have a good library of their own personal stories pulled into short-term memory, shift your focus to a more formal study of what a story looks like.
Use a diagram to show students a typical story arc like the one below. Then, using a simple story—like this Coca Cola commercial —fill out the story arc with the components from that story. Once students have seen this story mapped out, have them try it with another one, like a story you’ve read in class, a whole novel, or another short video.
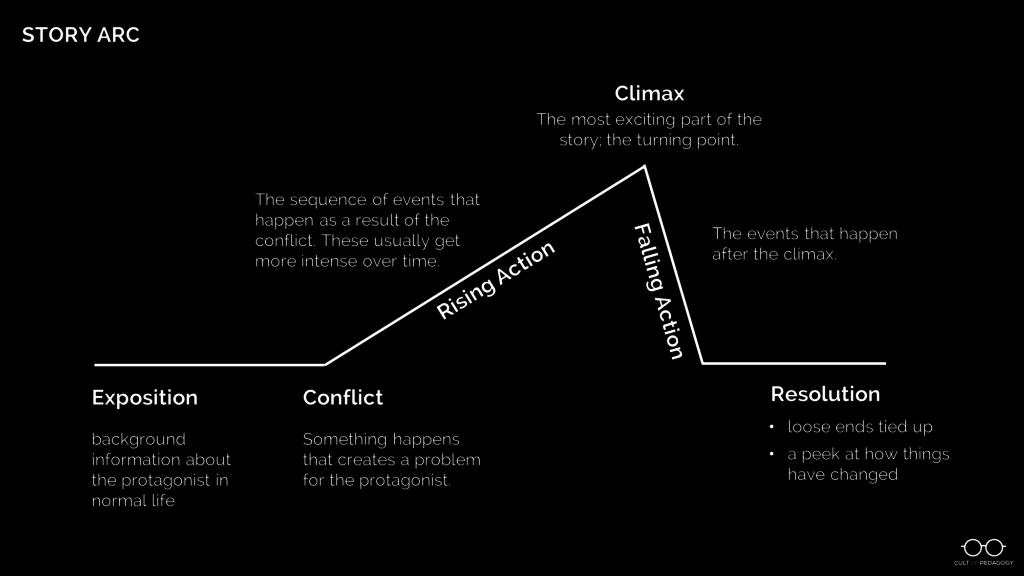
Step 3: Introduce the Assignment
Up to this point, students have been immersed in storytelling. Now give them specific instructions for what they are going to do. Share your assignment rubric so they understand the criteria that will be used to evaluate them; it should be ready and transparent right from the beginning of the unit. As always, I recommend using a single point rubric for this.
Step 4: Read Models
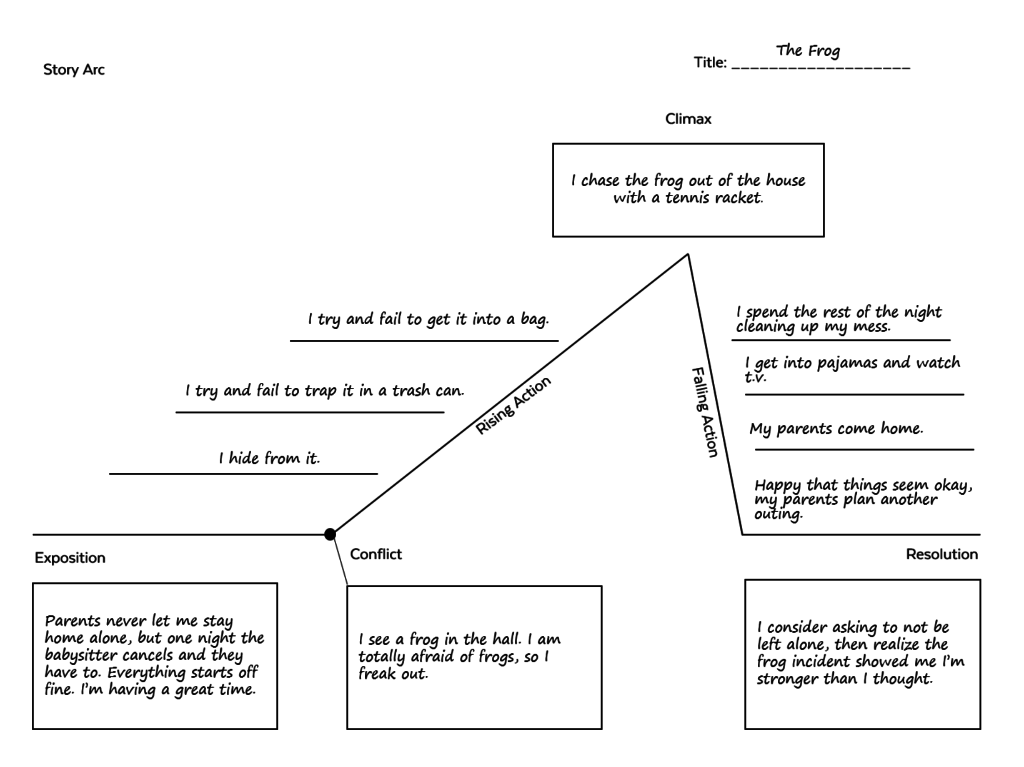
Once the parameters of the assignment have been explained, have students read at least one model story, a mentor text that exemplifies the qualities you’re looking for. This should be a story on a topic your students can kind of relate to, something they could see themselves writing. For my narrative writing unit (see the end of this post), I wrote a story called “Frog” about a 13-year-old girl who finally gets to stay home alone, then finds a frog in her house and gets completely freaked out, which basically ruins the fun she was planning for the night.
They will be reading this model as writers, looking at how the author shaped the text for a purpose, so that they can use those same strategies in their own writing. Have them look at your rubric and find places in the model that illustrate the qualities listed in the rubric. Then have them complete a story arc for the model so they can see the underlying structure.
Ideally, your students will have already read lots of different stories to look to as models. If that isn’t the case, this list of narrative texts recommended by Cult of Pedagogy followers on Twitter would be a good place to browse for titles that might be right for your students. Keep in mind that we have not read most of these stories, so be sure to read them first before adopting them for classroom use.
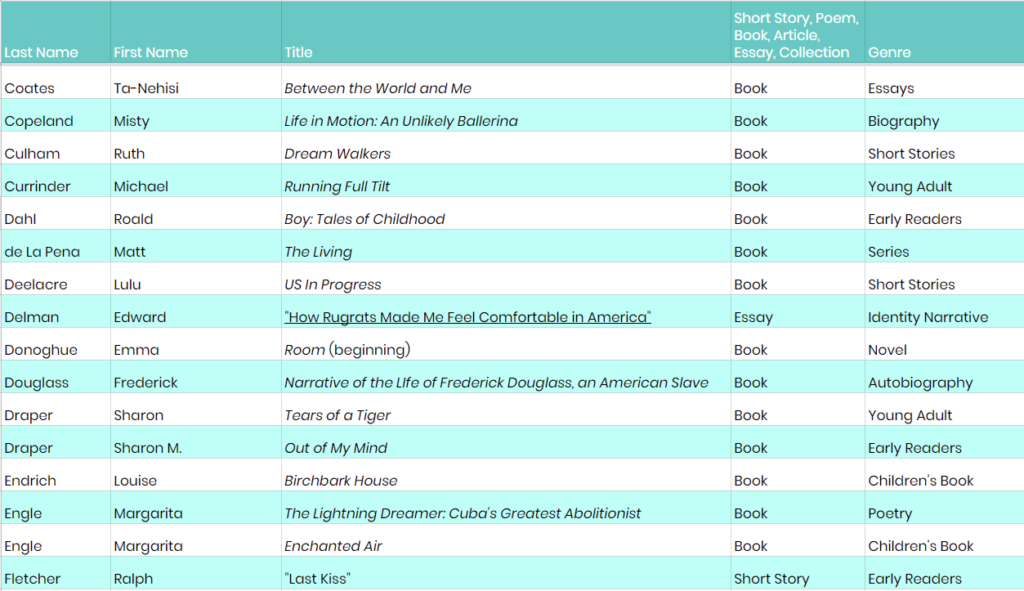
Click the image above to view the full list of narrative texts recommended by Cult of Pedagogy followers on Twitter. If you have a suggestion for the list, please email us through our contact page.
Step 5: Story Mapping
At this point, students will need to decide what they are going to write about. If they are stuck for a topic, have them just pick something they can write about, even if it’s not the most captivating story in the world. A skilled writer could tell a great story about deciding what to have for lunch. If they are using the skills of narrative writing, the topic isn’t as important as the execution.
Have students complete a basic story arc for their chosen topic using a diagram like the one below. This will help them make sure that they actually have a story to tell, with an identifiable problem, a sequence of events that build to a climax, and some kind of resolution, where something is different by the end. Again, if you are writing with your students, this would be an important step to model for them with your own story-in-progress.
Step 6: Quick Drafts
Now, have students get their chosen story down on paper as quickly as possible: This could be basically a long paragraph that would read almost like a summary, but it would contain all the major parts of the story. Model this step with your own story, so they can see that you are not shooting for perfection in any way. What you want is a working draft, a starting point, something to build on for later, rather than a blank page (or screen) to stare at.
Step 7: Plan the Pacing
Now that the story has been born in raw form, students can begin to shape it. This would be a good time for a lesson on pacing, where students look at how writers expand some moments to create drama and shrink other moments so that the story doesn’t drag. Creating a diagram like the one below forces a writer to decide how much space to devote to all of the events in the story.

Before students write a full draft, have them plan out the events in their story with a pacing diagram, a visual representation of how much “space” each part of the story is going to take up.
Step 8: Long Drafts
With a good plan in hand, students can now slow down and write a proper draft, expanding the sections of their story that they plan to really draw out and adding in more of the details that they left out in the quick draft.
Step 9: Workshop
Once students have a decent rough draft—something that has a basic beginning, middle, and end, with some discernible rising action, a climax of some kind, and a resolution, you’re ready to shift into full-on workshop mode. I would do this for at least a week: Start class with a short mini-lesson on some aspect of narrative writing craft, then give students the rest of the period to write, conference with you, and collaborate with their peers. During that time, they should focus some of their attention on applying the skill they learned in the mini-lesson to their drafts, so they will improve a little bit every day.
Topics for mini-lessons can include:
- How to weave exposition into your story so you don’t give readers an “information dump”
- How to carefully select dialogue to create good scenes, rather than quoting everything in a conversation
- How to punctuate and format dialogue so that it imitates the natural flow of a conversation
- How to describe things using sensory details and figurative language; also, what to describe…students too often give lots of irrelevant detail
- How to choose precise nouns and vivid verbs, use a variety of sentence lengths and structures, and add transitional words, phrases, and features to help the reader follow along
- How to start, end, and title a story
Step 10: Final Revisions and Edits
As the unit nears its end, students should be shifting away from revision , in which they alter the content of a piece, toward editing , where they make smaller changes to the mechanics of the writing. Make sure students understand the difference between the two: They should not be correcting each other’s spelling and punctuation in the early stages of this process, when the focus should be on shaping a better story.
One of the most effective strategies for revision and editing is to have students read their stories out loud. In the early stages, this will reveal places where information is missing or things get confusing. Later, more read-alouds will help them immediately find missing words, unintentional repetitions, and sentences that just “sound weird.” So get your students to read their work out loud frequently. It also helps to print stories on paper: For some reason, seeing the words in print helps us notice things we didn’t see on the screen.
To get the most from peer review, where students read and comment on each other’s work, more modeling from you is essential: Pull up a sample piece of writing and show students how to give specific feedback that helps, rather than simply writing “good detail” or “needs more detail,” the two comments I saw exchanged most often on students’ peer-reviewed papers.
Step 11: Final Copies and Publication
Once revision and peer review are done, students will hand in their final copies. If you don’t want to get stuck with 100-plus papers to grade, consider using Catlin Tucker’s station rotation model , which keeps all the grading in class. And when you do return stories with your own feedback, try using Kristy Louden’s delayed grade strategy , where students don’t see their final grade until they have read your written feedback.
Beyond the standard hand-in-for-a-grade, consider other ways to have students publish their stories. Here are some options:
- Stories could be published as individual pages on a collaborative website or blog.
- Students could create illustrated e-books out of their stories.
- Students could create a slideshow to accompany their stories and record them as digital storytelling videos. This could be done with a tool like Screencastify or Screencast-O-Matic .
So this is what worked for me. If you’ve struggled to get good stories from your students, try some or all of these techniques next time. I think you’ll find that all of your students have some pretty interesting stories to tell. Helping them tell their stories well is a gift that will serve them for many years after they leave your classroom. ♦
Want this unit ready-made?
If you’re a writing teacher in grades 7-12 and you’d like a classroom-ready unit like the one described above, including slideshow mini-lessons on 14 areas of narrative craft, a sample narrative piece, editable rubrics, and other supplemental materials to guide students through every stage of the process, take a look at my Narrative Writing unit . Just click on the image below and you’ll be taken to a page where you can read more and see a detailed preview of what’s included.

What to Read Next

Categories: Instruction , Podcast
Tags: English language arts , Grades 6-8 , Grades 9-12 , teaching strategies
50 Comments
Wow, this is a wonderful guide! If my English teachers had taught this way, I’m sure I would have enjoyed narrative writing instead of dreading it. I’ll be able to use many of these suggestions when writing my blog! BrP
Lst year I was so discouraged because the short stories looked like the quick drafts described in this article. I thought I had totally failed until I read this and realized I did not fai,l I just needed to complete the process. Thank you!
I feel like you jumped in my head and connected my thoughts. I appreciate the time you took to stop and look closely at form. I really believe that student-writers should see all dimensions of narrative writing and be able to live in whichever style and voice they want for their work.
Can’t thank you enough for this. So well curated that one can just follow it blindly and ace at teaching it. Thanks again!
Great post! I especially liked your comments about reminding kids about the power of storytelling. My favourite podcasts and posts from you are always about how to do things in the classroom and I appreciate the research you do.
On a side note, the ice breakers are really handy. My kids know each other really well (rural community), and can tune out pretty quickly if there is nothing new to learn about their peers, but they like the games (and can remember where we stopped last time weeks later). I’ve started changing them up with ‘life questions’, so the editable version is great!
I love writing with my students and loved this podcast! A fun extension to this narrative is to challenge students to write another story about the same event, but use the perspective of another “character” from the story. Books like Wonder (R.J. Palacio) and Wanderer (Sharon Creech) can model the concept for students.
Thank you for your great efforts to reveal the practical writing strategies in layered details. As English is not my first language, I need listen to your podcast and read the text repeatedly so to fully understand. It’s worthy of the time for some great post like yours. I love sharing so I send the link to my English practice group that it can benefit more. I hope I could be able to give you some feedback later on.
Thank you for helping me get to know better especially the techniques in writing narrative text. Im an English teacher for 5years but have little knowledge on writing. I hope you could feature techniques in writing news and fearute story. God bless and more power!
Thank you for this! I am very interested in teaching a unit on personal narrative and this was an extremely helpful breakdown. As a current student teacher I am still unsure how to approach breaking down the structures of different genres of writing in a way that is helpful for me students but not too restrictive. The story mapping tools you provided really allowed me to think about this in a new way. Writing is such a powerful way to experience the world and more than anything I want my students to realize its power. Stories are how we make sense of the world and as an English teacher I feel obligated to give my students access to this particular skill.
The power of story is unfathomable. There’s this NGO in India doing some great work in harnessing the power of storytelling and plots to brighten children’s lives and enlighten them with true knowledge. Check out Katha India here: http://bit.ly/KathaIndia
Thank you so much for this. I did not go to college to become a writing professor, but due to restructuring in my department, I indeed am! This is a wonderful guide that I will use when teaching the narrative essay. I wonder if you have a similar guide for other modes such as descriptive, process, argument, etc.?
Hey Melanie, Jenn does have another guide on writing! Check out A Step-by-Step Plan for Teaching Argumentative Writing .
Hi, I am also wondering if there is a similar guide for descriptive writing in particular?
Hey Melanie, unfortunately Jenn doesn’t currently have a guide for descriptive writing. She’s always working on projects though, so she may get around to writing a unit like this in the future. You can always check her Teachers Pay Teachers page for an up-to-date list of materials she has available. Thanks!
I want to write about the new character in my area
That’s great! Let us know if you need any supports during your writing process!
I absolutely adore this unit plan. I teach freshmen English at a low-income high school and wanted to find something to help my students find their voice. It is not often that I borrow material, but I borrowed and adapted all of it in the order that it is presented! It is cohesive, understandable, and fun. Thank you!!
So glad to hear this, Nicole!
Thanks sharing this post. My students often get confused between personal narratives and short stories. Whenever I ask them to write a short story, she share their own experiences and add a bit of fiction in it to make it interesting.
Thank you! My students have loved this so far. I do have a question as to where the “Frog” story mentioned in Step 4 is. I could really use it! Thanks again.
This is great to hear, Emily! In Step 4, Jenn mentions that she wrote the “Frog” story for her narrative writing unit . Just scroll down the bottom of the post and you’ll see a link to the unit.
I also cannot find the link to the short story “Frog”– any chance someone can send it or we can repost it?
This story was written for Jenn’s narrative writing unit. You can find a link to this unit in Step 4 or at the bottom of the article. Hope this helps.
I cannot find the frog story mentioned. Could you please send the link.? Thank you
Hi Michelle,
The Frog story was written for Jenn’s narrative writing unit. There’s a link to this unit in Step 4 and at the bottom of the article.
Debbie- thanks for you reply… but there is no link to the story in step 4 or at the bottom of the page….
Hey Shawn, the frog story is part of Jenn’s narrative writing unit, which is available on her Teachers Pay Teachers site. The link Debbie is referring to at the bottom of this post will take you to her narrative writing unit and you would have to purchase that to gain access to the frog story. I hope this clears things up.
Thank you so much for this resource! I’m a high school English teacher, and am currently teaching creative writing for the first time. I really do value your blog, podcast, and other resources, so I’m excited to use this unit. I’m a cyber school teacher, so clear, organized layout is important; and I spend a lot of time making sure my content is visually accessible for my students to process. Thanks for creating resources that are easy for us teachers to process and use.
Do you have a lesson for Informative writing?
Hey Cari, Jenn has another unit on argumentative writing , but doesn’t have one yet on informative writing. She may develop one in the future so check back in sometime.
I had the same question. Informational writing is so difficult to have a good strong unit in when you have so many different text structures to meet and need text-dependent writing tasks.
Creating an informational writing unit is still on Jenn’s long list of projects to get to, but in the meantime, if you haven’t already, check out When We All Teach Text Structures, Everyone Wins . It might help you out!
This is a great lesson! It would be helpful to see a finished draft of the frog narrative arc. Students’ greatest challenge is transferring their ideas from the planner to a full draft. To see a full sample of how this arc was transformed into a complete narrative draft would be a powerful learning tool.
Hi Stacey! Jenn goes into more depth with the “Frog” lesson in her narrative writing unit – this is where you can find a sample of what a completed story arc might look. Also included is a draft of the narrative. If interested in checking out the unit and seeing a preview, just scroll down to the bottom of the post and click on the image. Hope this helps!
Helped me learn for an entrance exam thanks very much
Is the narrative writing lesson you talk about in https://www.cultofpedagogy.com/narrative-writing/
Also doable for elementary students you think, and if to what levels?
Love your work, Sincerely, Zanyar
Hey Zanyar,
It’s possible the unit would work with 4th and 5th graders, but Jenn definitely wouldn’t recommend going any younger. The main reason for this is that some of the mini-lessons in the unit could be challenging for students who are still concrete thinkers. You’d likely need to do some adjusting and scaffolding which could extend the unit beyond the 3 weeks. Having said that, I taught 1st grade and found the steps of the writing process, as described in the post, to be very similar. Of course learning targets/standards were different, but the process itself can be applied to any grade level (modeling writing, using mentor texts to study how stories work, planning the structure of the story, drafting, elaborating, etc.) Hope this helps!
This has made my life so much easier. After teaching in different schools systems, from the American, to British to IB, one needs to identify the anchor standards and concepts, that are common between all these systems, to build well balanced thematic units. Just reading these steps gave me the guidance I needed to satisfy both the conceptual framework the schools ask for and the standards-based practice. Thank you Thank you.
Would this work for teaching a first grader about narrative writing? I am also looking for a great book to use as a model for narrative writing. Veggie Monster is being used by his teacher and he isn’t connecting with this book in the least bit, so it isn’t having a positive impact. My fear is he will associate this with writing and I don’t want a negative association connected to such a beautiful process and experience. Any suggestions would be helpful.
Thank you for any information you can provide!
Although I think the materials in the actual narrative writing unit are really too advanced for a first grader, the general process that’s described in the blog post can still work really well.
I’m sorry your child isn’t connecting with The Night of the Veggie Monster. Try to keep in mind that the main reason this is used as a mentor text is because it models how a small moment story can be told in a big way. It’s filled with all kinds of wonderful text features that impact the meaning of the story – dialogue, description, bold text, speech bubbles, changes in text size, ellipses, zoomed in images, text placement, text shape, etc. All of these things will become mini-lessons throughout the unit. But there are lots of other wonderful mentor texts that your child might enjoy. My suggestion for an early writer, is to look for a small moment text, similar in structure, that zooms in on a problem that a first grader can relate to. In addition to the mentor texts that I found in this article , you might also want to check out Knuffle Bunny, Kitten’s First Full Moon, When Sophie Gets Angry Really Really Angry, and Whistle for Willie. Hope this helps!
I saw this on Pinterest the other day while searching for examples of narritives units/lessons. I clicked on it because I always click on C.o.P stuff 🙂 And I wasn’t disapointed. I was intrigued by the connection of narratives to humanity–even if a student doesn’t identify as a writer, he/she certainly is human, right? I really liked this. THIS clicked with me.
A few days after I read the P.o.C post, I ventured on to YouTube for more ideas to help guide me with my 8th graders’ narrative writing this coming spring. And there was a TEDx video titled, “The Power of Personal Narrative” by J. Christan Jensen. I immediately remembered the line from the article above that associated storytelling with “power” and how it sets humans apart and if introduced and taught as such, it can be “extraordinary.”
I watched the video and to the suprise of my expectations, it was FANTASTIC. Between Jennifer’s post and the TEDx video ignited within me some major motivation and excitement to begin this unit.
Thanks for sharing this with us! So glad that Jenn’s post paired with another text gave you some motivation and excitement. I’ll be sure to pass this on to Jenn!
Thank you very much for this really helpful post! I really love the idea of helping our students understand that storytelling is powerful and then go on to teach them how to harness that power. That is the essence of teaching literature or writing at any level. However, I’m a little worried about telling students that whether a piece of writing is fact or fiction does not matter. It in fact matters a lot precisely because storytelling is powerful. Narratives can shape people’s views and get their emotions involved which would, in turn, motivate them to act on a certain matter, whether for good or for bad. A fictional narrative that is passed as factual could cause a lot of damage in the real world. I believe we should. I can see how helping students focus on writing the story rather than the truth of it all could help refine the needed skills without distractions. Nevertheless, would it not be prudent to teach our students to not just harness the power of storytelling but refrain from misusing it by pushing false narratives as factual? It is true that in reality, memoirs pass as factual while novels do as fictional while the opposite may be true for both cases. I am not too worried about novels passing as fictional. On the other hand, fictional narratives masquerading as factual are disconcerting and part of a phenomenon that needs to be fought against, not enhanced or condoned in education. This is especially true because memoirs are often used by powerful people to write/re-write history. I would really like to hear your opinion on this. Thanks a lot for a great post and a lot of helpful resources!
Thank you so much for this. Jenn and I had a chance to chat and we can see where you’re coming from. Jenn never meant to suggest that a person should pass off a piece of fictional writing as a true story. Good stories can be true, completely fictional, or based on a true story that’s mixed with some fiction – that part doesn’t really matter. However, what does matter is how a student labels their story. We think that could have been stated more clearly in the post , so Jenn decided to add a bit about this at the end of the 3rd paragraph in the section “A Note About Form: Personal Narrative or Short Story?” Thanks again for bringing this to our attention!
You have no idea how much your page has helped me in so many ways. I am currently in my teaching credential program and there are times that I feel lost due to a lack of experience in the classroom. I’m so glad I came across your page! Thank you for sharing!
Thanks so much for letting us know-this means a whole lot!
No, we’re sorry. Jenn actually gets this question fairly often. It’s something she considered doing at one point, but because she has so many other projects she’s working on, she’s just not gotten to it.
I couldn’t find the story
Hi, Duraiya. The “Frog” story is part of Jenn’s narrative writing unit, which is available on her Teachers Pay Teachers site. The link at the bottom of this post will take you to her narrative writing unit, which you can purchase to gain access to the story. I hope this helps!
Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Narrative Writing: A Complete Guide for Teachers and Students
MASTERING THE CRAFT OF NARRATIVE WRITING
Narratives build on and encourage the development of the fundamentals of writing. They also require developing an additional skill set: the ability to tell a good yarn, and storytelling is as old as humanity.
We see and hear stories everywhere and daily, from having good gossip on the doorstep with a neighbor in the morning to the dramas that fill our screens in the evening.
Good narrative writing skills are hard-won by students even though it is an area of writing that most enjoy due to the creativity and freedom it offers.
Here we will explore some of the main elements of a good story: plot, setting, characters, conflict, climax, and resolution . And we will look too at how best we can help our students understand these elements, both in isolation and how they mesh together as a whole.

WHAT IS A NARRATIVE?

A narrative is a story that shares a sequence of events , characters, and themes. It expresses experiences, ideas, and perspectives that should aspire to engage and inspire an audience.
A narrative can spark emotion, encourage reflection, and convey meaning when done well.
Narratives are a popular genre for students and teachers as they allow the writer to share their imagination, creativity, skill, and understanding of nearly all elements of writing. We occasionally refer to a narrative as ‘creative writing’ or story writing.
The purpose of a narrative is simple, to tell the audience a story. It can be written to motivate, educate, or entertain and can be fact or fiction.
A COMPLETE UNIT ON TEACHING NARRATIVE WRITING

Teach your students to become skilled story writers with this HUGE NARRATIVE & CREATIVE STORY WRITING UNIT . Offering a COMPLETE SOLUTION to teaching students how to craft CREATIVE CHARACTERS, SUPERB SETTINGS, and PERFECT PLOTS .
Over 192 PAGES of materials, including:

TYPES OF NARRATIVE WRITING
There are many narrative writing genres and sub-genres such as these.
We have a complete guide to writing a personal narrative that differs from the traditional story-based narrative covered in this guide. It includes personal narrative writing prompts, resources, and examples and can be found here.

As we can see, narratives are an open-ended form of writing that allows you to showcase creativity in many directions. However, all narratives share a common set of features and structure known as “Story Elements”, which are briefly covered in this guide.
Don’t overlook the importance of understanding story elements and the value this adds to you as a writer who can dissect and create grand narratives. We also have an in-depth guide to understanding story elements here .
CHARACTERISTICS OF NARRATIVE WRITING
Narrative structure.
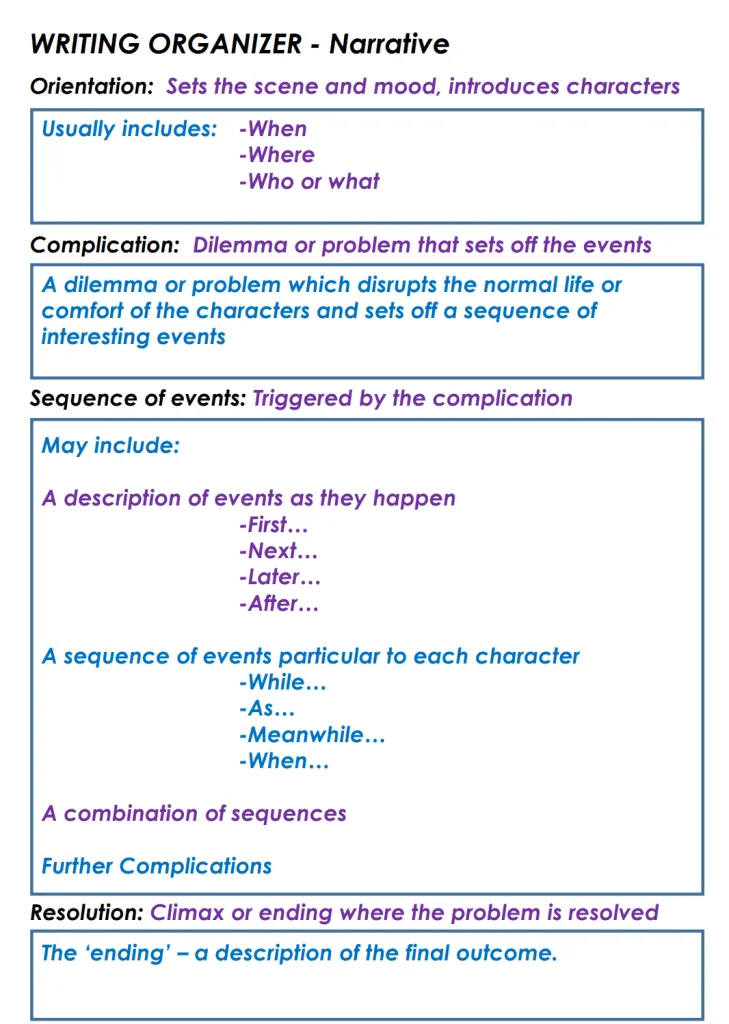
ORIENTATION (BEGINNING) Set the scene by introducing your characters, setting and time of the story. Establish your who, when and where in this part of your narrative
COMPLICATION AND EVENTS (MIDDLE) In this section activities and events involving your main characters are expanded upon. These events are written in a cohesive and fluent sequence.
RESOLUTION (ENDING) Your complication is resolved in this section. It does not have to be a happy outcome, however.
EXTRAS: Whilst orientation, complication and resolution are the agreed norms for a narrative, there are numerous examples of popular texts that did not explicitly follow this path exactly.
NARRATIVE FEATURES
LANGUAGE: Use descriptive and figurative language to paint images inside your audience’s minds as they read.
PERSPECTIVE Narratives can be written from any perspective but are most commonly written in first or third person.
DIALOGUE Narratives frequently switch from narrator to first-person dialogue. Always use speech marks when writing dialogue.
TENSE If you change tense, make it perfectly clear to your audience what is happening. Flashbacks might work well in your mind but make sure they translate to your audience.
THE PLOT MAP
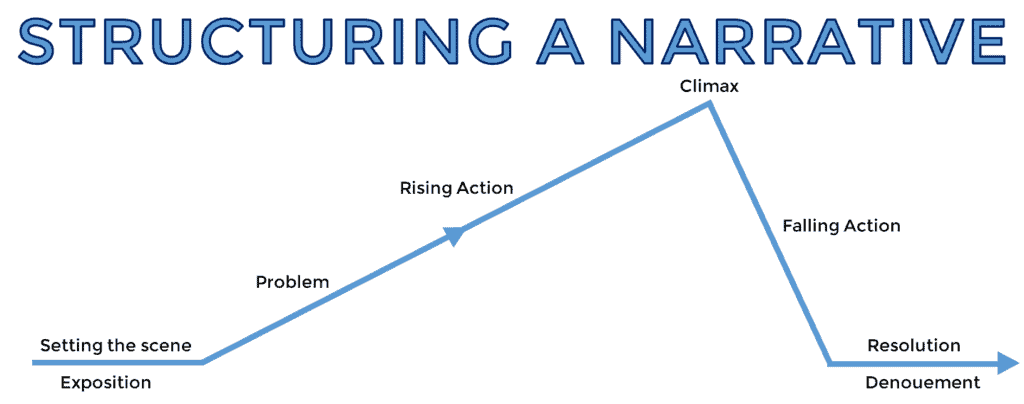
This graphic is known as a plot map, and nearly all narratives fit this structure in one way or another, whether romance novels, science fiction or otherwise.
It is a simple tool that helps you understand and organise a story’s events. Think of it as a roadmap that outlines the journey of your characters and the events that unfold. It outlines the different stops along the way, such as the introduction, rising action, climax, falling action, and resolution, that help you to see how the story builds and develops.
Using a plot map, you can see how each event fits into the larger picture and how the different parts of the story work together to create meaning. It’s a great way to visualize and analyze a story.
Be sure to refer to a plot map when planning a story, as it has all the essential elements of a great story.
THE 5 KEY STORY ELEMENTS OF A GREAT NARRATIVE (6-MINUTE TUTORIAL VIDEO)
This video we created provides an excellent overview of these elements and demonstrates them in action in stories we all know and love.

HOW TO WRITE A NARRATIVE
Now that we understand the story elements and how they come together to form stories, it’s time to start planning and writing your narrative.
In many cases, the template and guide below will provide enough details on how to craft a great story. However, if you still need assistance with the fundamentals of writing, such as sentence structure, paragraphs and using correct grammar, we have some excellent guides on those here.
USE YOUR WRITING TIME EFFECTIVELY: Maximize your narrative writing sessions by spending approximately 20 per cent of your time planning and preparing. This ensures greater productivity during your writing time and keeps you focused and on task.
Use tools such as graphic organizers to logically sequence your narrative if you are not a confident story writer. If you are working with reluctant writers, try using narrative writing prompts to get their creative juices flowing.
Spend most of your writing hour on the task at hand, don’t get too side-tracked editing during this time and leave some time for editing. When editing a narrative, examine it for these three elements.
- Spelling and grammar ( Is it readable?)
- Story structure and continuity ( Does it make sense, and does it flow? )
- Character and plot analysis. (Are your characters engaging? Does your problem/resolution work? )
1. SETTING THE SCENE: THE WHERE AND THE WHEN

The story’s setting often answers two of the central questions in the story, namely, the where and the when. The answers to these two crucial questions will often be informed by the type of story the student is writing.
The story’s setting can be chosen to quickly orient the reader to the type of story they are reading. For example, a fictional narrative writing piece such as a horror story will often begin with a description of a haunted house on a hill or an abandoned asylum in the middle of the woods. If we start our story on a rocket ship hurtling through the cosmos on its space voyage to the Alpha Centauri star system, we can be reasonably sure that the story we are embarking on is a work of science fiction.
Such conventions are well-worn clichés true, but they can be helpful starting points for our novice novelists to make a start.
Having students choose an appropriate setting for the type of story they wish to write is an excellent exercise for our younger students. It leads naturally onto the next stage of story writing, which is creating suitable characters to populate this fictional world they have created. However, older or more advanced students may wish to play with the expectations of appropriate settings for their story. They may wish to do this for comic effect or in the interest of creating a more original story. For example, opening a story with a children’s birthday party does not usually set up the expectation of a horror story. Indeed, it may even lure the reader into a happy reverie as they remember their own happy birthday parties. This leaves them more vulnerable to the surprise element of the shocking action that lies ahead.
Once the students have chosen a setting for their story, they need to start writing. Little can be more terrifying to English students than the blank page and its bare whiteness stretching before them on the table like a merciless desert they must cross. Give them the kick-start they need by offering support through word banks or writing prompts. If the class is all writing a story based on the same theme, you may wish to compile a common word bank on the whiteboard as a prewriting activity. Write the central theme or genre in the middle of the board. Have students suggest words or phrases related to the theme and list them on the board.
You may wish to provide students with a copy of various writing prompts to get them started. While this may mean that many students’ stories will have the same beginning, they will most likely arrive at dramatically different endings via dramatically different routes.

A bargain is at the centre of the relationship between the writer and the reader. That bargain is that the reader promises to suspend their disbelief as long as the writer creates a consistent and convincing fictional reality. Creating a believable world for the fictional characters to inhabit requires the student to draw on convincing details. The best way of doing this is through writing that appeals to the senses. Have your student reflect deeply on the world that they are creating. What does it look like? Sound like? What does the food taste like there? How does it feel like to walk those imaginary streets, and what aromas beguile the nose as the main character winds their way through that conjured market?
Also, Consider the when; or the time period. Is it a future world where things are cleaner and more antiseptic? Or is it an overcrowded 16th-century London with human waste stinking up the streets? If students can create a multi-sensory installation in the reader’s mind, then they have done this part of their job well.
Popular Settings from Children’s Literature and Storytelling
- Fairytale Kingdom
- Magical Forest
- Village/town
- Underwater world
- Space/Alien planet
2. CASTING THE CHARACTERS: THE WHO
Now that your student has created a believable world, it is time to populate it with believable characters.
In short stories, these worlds mustn’t be overpopulated beyond what the student’s skill level can manage. Short stories usually only require one main character and a few secondary ones. Think of the short story more as a small-scale dramatic production in an intimate local theater than a Hollywood blockbuster on a grand scale. Too many characters will only confuse and become unwieldy with a canvas this size. Keep it simple!
Creating believable characters is often one of the most challenging aspects of narrative writing for students. Fortunately, we can do a few things to help students here. Sometimes it is helpful for students to model their characters on actual people they know. This can make things a little less daunting and taxing on the imagination. However, whether or not this is the case, writing brief background bios or descriptions of characters’ physical personality characteristics can be a beneficial prewriting activity. Students should give some in-depth consideration to the details of who their character is: How do they walk? What do they look like? Do they have any distinguishing features? A crooked nose? A limp? Bad breath? Small details such as these bring life and, therefore, believability to characters. Students can even cut pictures from magazines to put a face to their character and allow their imaginations to fill in the rest of the details.
Younger students will often dictate to the reader the nature of their characters. To improve their writing craft, students must know when to switch from story-telling mode to story-showing mode. This is particularly true when it comes to character. Encourage students to reveal their character’s personality through what they do rather than merely by lecturing the reader on the faults and virtues of the character’s personality. It might be a small relayed detail in the way they walk that reveals a core characteristic. For example, a character who walks with their head hanging low and shoulders hunched while avoiding eye contact has been revealed to be timid without the word once being mentioned. This is a much more artistic and well-crafted way of doing things and is less irritating for the reader. A character who sits down at the family dinner table immediately snatches up his fork and starts stuffing roast potatoes into his mouth before anyone else has even managed to sit down has revealed a tendency towards greed or gluttony.
Understanding Character Traits
Again, there is room here for some fun and profitable prewriting activities. Give students a list of character traits and have them describe a character doing something that reveals that trait without ever employing the word itself.
It is also essential to avoid adjective stuffing here. When looking at students’ early drafts, adjective stuffing is often apparent. To train the student out of this habit, choose an adjective and have the student rewrite the sentence to express this adjective through action rather than telling.
When writing a story, it is vital to consider the character’s traits and how they will impact the story’s events. For example, a character with a strong trait of determination may be more likely to overcome obstacles and persevere. In contrast, a character with a tendency towards laziness may struggle to achieve their goals. In short, character traits add realism, depth, and meaning to a story, making it more engaging and memorable for the reader.
Popular Character Traits in Children’s Stories
- Determination
- Imagination
- Perseverance
- Responsibility
We have an in-depth guide to creating great characters here , but most students should be fine to move on to planning their conflict and resolution.
3. NO PROBLEM? NO STORY! HOW CONFLICT DRIVES A NARRATIVE

This is often the area apprentice writers have the most difficulty with. Students must understand that without a problem or conflict, there is no story. The problem is the driving force of the action. Usually, in a short story, the problem will center around what the primary character wants to happen or, indeed, wants not to happen. It is the hurdle that must be overcome. It is in the struggle to overcome this hurdle that events happen.
Often when a student understands the need for a problem in a story, their completed work will still not be successful. This is because, often in life, problems remain unsolved. Hurdles are not always successfully overcome. Students pick up on this.
We often discuss problems with friends that will never be satisfactorily resolved one way or the other, and we accept this as a part of life. This is not usually the case with writing a story. Whether a character successfully overcomes his or her problem or is decidedly crushed in the process of trying is not as important as the fact that it will finally be resolved one way or the other.
A good practical exercise for students to get to grips with this is to provide copies of stories and have them identify the central problem or conflict in each through discussion. Familiar fables or fairy tales such as Three Little Pigs, The Boy Who Cried Wolf, Cinderella, etc., are great for this.
While it is true that stories often have more than one problem or that the hero or heroine is unsuccessful in their first attempt to solve a central problem, for beginning students and intermediate students, it is best to focus on a single problem, especially given the scope of story writing at this level. Over time students will develop their abilities to handle more complex plots and write accordingly.
Popular Conflicts found in Children’s Storytelling.
- Good vs evil
- Individual vs society
- Nature vs nurture
- Self vs others
- Man vs self
- Man vs nature
- Man vs technology
- Individual vs fate
- Self vs destiny
Conflict is the heart and soul of any good story. It’s what makes a story compelling and drives the plot forward. Without conflict, there is no story. Every great story has a struggle or a problem that needs to be solved, and that’s where conflict comes in. Conflict is what makes a story exciting and keeps the reader engaged. It creates tension and suspense and makes the reader care about the outcome.
Like in real life, conflict in a story is an opportunity for a character’s growth and transformation. It’s a chance for them to learn and evolve, making a story great. So next time stories are written in the classroom, remember that conflict is an essential ingredient, and without it, your story will lack the energy, excitement, and meaning that makes it truly memorable.
4. THE NARRATIVE CLIMAX: HOW THINGS COME TO A HEAD!

The climax of the story is the dramatic high point of the action. It is also when the struggles kicked off by the problem come to a head. The climax will ultimately decide whether the story will have a happy or tragic ending. In the climax, two opposing forces duke things out until the bitter (or sweet!) end. One force ultimately emerges triumphant. As the action builds throughout the story, suspense increases as the reader wonders which of these forces will win out. The climax is the release of this suspense.
Much of the success of the climax depends on how well the other elements of the story have been achieved. If the student has created a well-drawn and believable character that the reader can identify with and feel for, then the climax will be more powerful.
The nature of the problem is also essential as it determines what’s at stake in the climax. The problem must matter dearly to the main character if it matters at all to the reader.
Have students engage in discussions about their favorite movies and books. Have them think about the storyline and decide the most exciting parts. What was at stake at these moments? What happened in your body as you read or watched? Did you breathe faster? Or grip the cushion hard? Did your heart rate increase, or did you start to sweat? This is what a good climax does and what our students should strive to do in their stories.
The climax puts it all on the line and rolls the dice. Let the chips fall where the writer may…
Popular Climax themes in Children’s Stories
- A battle between good and evil
- The character’s bravery saves the day
- Character faces their fears and overcomes them
- The character solves a mystery or puzzle.
- The character stands up for what is right.
- Character reaches their goal or dream.
- The character learns a valuable lesson.
- The character makes a selfless sacrifice.
- The character makes a difficult decision.
- The character reunites with loved ones or finds true friendship.
5. RESOLUTION: TYING UP LOOSE ENDS
After the climactic action, a few questions will often remain unresolved for the reader, even if all the conflict has been resolved. The resolution is where those lingering questions will be answered. The resolution in a short story may only be a brief paragraph or two. But, in most cases, it will still be necessary to include an ending immediately after the climax can feel too abrupt and leave the reader feeling unfulfilled.
An easy way to explain resolution to students struggling to grasp the concept is to point to the traditional resolution of fairy tales, the “And they all lived happily ever after” ending. This weather forecast for the future allows the reader to take their leave. Have the student consider the emotions they want to leave the reader with when crafting their resolution.
While the action is usually complete by the end of the climax, it is in the resolution that if there is a twist to be found, it will appear – think of movies such as The Usual Suspects. Pulling this off convincingly usually requires considerable skill from a student writer. Still, it may well form a challenging extension exercise for those more gifted storytellers among your students.
Popular Resolutions in Children’s Stories
- Our hero achieves their goal
- The character learns a valuable lesson
- A character finds happiness or inner peace.
- The character reunites with loved ones.
- Character restores balance to the world.
- The character discovers their true identity.
- Character changes for the better.
- The character gains wisdom or understanding.
- Character makes amends with others.
- The character learns to appreciate what they have.
Once students have completed their story, they can edit for grammar, vocabulary choice, spelling, etc., but not before!
As mentioned, there is a craft to storytelling, as well as an art. When accurate grammar, perfect spelling, and immaculate sentence structures are pushed at the outset, they can cause storytelling paralysis. For this reason, it is essential that when we encourage the students to write a story, we give them license to make mechanical mistakes in their use of language that they can work on and fix later.
Good narrative writing is a very complex skill to develop and will take the student years to become competent. It challenges not only the student’s technical abilities with language but also her creative faculties. Writing frames, word banks, mind maps, and visual prompts can all give valuable support as students develop the wide-ranging and challenging skills required to produce a successful narrative writing piece. But, at the end of it all, as with any craft, practice and more practice is at the heart of the matter.
TIPS FOR WRITING A GREAT NARRATIVE
- Start your story with a clear purpose: If you can determine the theme or message you want to convey in your narrative before starting it will make the writing process so much simpler.
- Choose a compelling storyline and sell it through great characters, setting and plot: Consider a unique or interesting story that captures the reader’s attention, then build the world and characters around it.
- Develop vivid characters that are not all the same: Make your characters relatable and memorable by giving them distinct personalities and traits you can draw upon in the plot.
- Use descriptive language to hook your audience into your story: Use sensory language to paint vivid images and sequences in the reader’s mind.
- Show, don’t tell your audience: Use actions, thoughts, and dialogue to reveal character motivations and emotions through storytelling.
- Create a vivid setting that is clear to your audience before getting too far into the plot: Describe the time and place of your story to immerse the reader fully.
- Build tension: Refer to the story map earlier in this article and use conflict, obstacles, and suspense to keep the audience engaged and invested in your narrative.
- Use figurative language such as metaphors, similes, and other literary devices to add depth and meaning to your narrative.
- Edit, revise, and refine: Take the time to refine and polish your writing for clarity and impact.
- Stay true to your voice: Maintain your unique perspective and style in your writing to make it your own.
NARRATIVE WRITING EXAMPLES (Student Writing Samples)
Below are a collection of student writing samples of narratives. Click on the image to enlarge and explore them in greater detail. Please take a moment to read these creative stories in detail and the teacher and student guides which highlight some of the critical elements of narratives to consider before writing.
Please understand these student writing samples are not intended to be perfect examples for each age or grade level but a piece of writing for students and teachers to explore together to critically analyze to improve student writing skills and deepen their understanding of story writing.
We recommend reading the example either a year above or below, as well as the grade you are currently working with, to gain a broader appreciation of this text type.
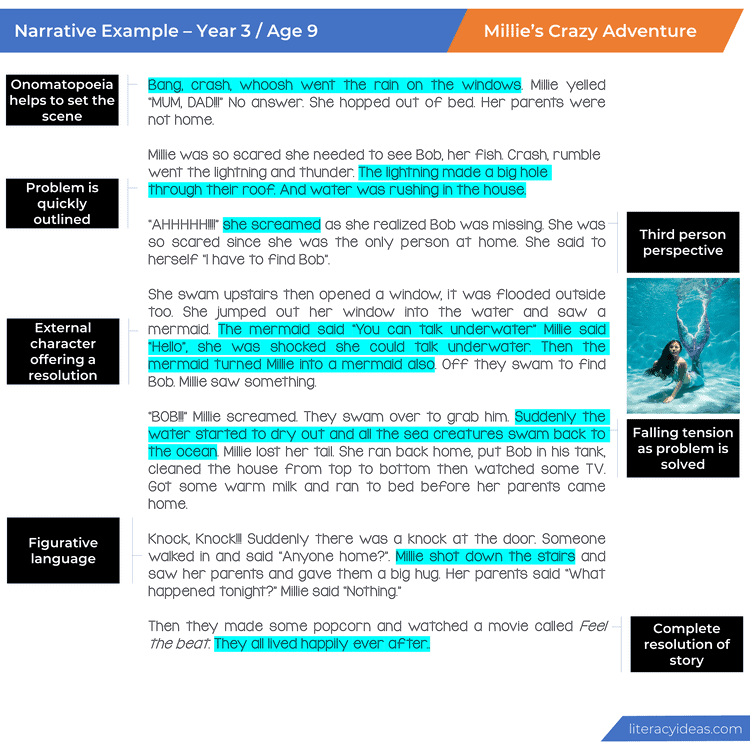
NARRATIVE WRITING PROMPTS (Journal Prompts)
When students have a great journal prompt, it can help them focus on the task at hand, so be sure to view our vast collection of visual writing prompts for various text types here or use some of these.
- On a recent European trip, you find your travel group booked into the stunning and mysterious Castle Frankenfurter for a single night… As night falls, the massive castle of over one hundred rooms seems to creak and groan as a series of unexplained events begin to make you wonder who or what else is spending the evening with you. Write a narrative that tells the story of your evening.
- You are a famous adventurer who has discovered new lands; keep a travel log over a period of time in which you encounter new and exciting adventures and challenges to overcome. Ensure your travel journal tells a story and has a definite introduction, conflict and resolution.
- You create an incredible piece of technology that has the capacity to change the world. As you sit back and marvel at your innovation and the endless possibilities ahead of you, it becomes apparent there are a few problems you didn’t really consider. You might not even be able to control them. Write a narrative in which you ride the highs and lows of your world-changing creation with a clear introduction, conflict and resolution.
- As the final door shuts on the Megamall, you realise you have done it… You and your best friend have managed to sneak into the largest shopping centre in town and have the entire place to yourselves until 7 am tomorrow. There is literally everything and anything a child would dream of entertaining themselves for the next 12 hours. What amazing adventures await you? What might go wrong? And how will you get out of there scot-free?
- A stranger walks into town… Whilst appearing similar to almost all those around you, you get a sense that this person is from another time, space or dimension… Are they friends or foes? What makes you sense something very strange is going on? Suddenly they stand up and walk toward you with purpose extending their hand… It’s almost as if they were reading your mind.
NARRATIVE WRITING VIDEO TUTORIAL

Teaching Resources
Use our resources and tools to improve your student’s writing skills through proven teaching strategies.
When teaching narrative writing, it is essential that you have a range of tools, strategies and resources at your disposal to ensure you get the most out of your writing time. You can find some examples below, which are free and paid premium resources you can use instantly without any preparation.
FREE Narrative Graphic Organizer
THE STORY TELLERS BUNDLE OF TEACHING RESOURCES

A MASSIVE COLLECTION of resources for narratives and story writing in the classroom covering all elements of crafting amazing stories. MONTHS WORTH OF WRITING LESSONS AND RESOURCES, including:
NARRATIVE WRITING CHECKLIST BUNDLE

OTHER GREAT ARTICLES ABOUT NARRATIVE WRITING

Narrative Writing for Kids: Essential Skills and Strategies

7 Great Narrative Lesson Plans Students and Teachers Love

Top 7 Narrative Writing Exercises for Students

How to Write a Scary Story
EL Education Curriculum
You are here.
- ELA 2019 G7:M1:U3:L5
Write a Narrative: Plan Character and Setting
In this lesson, daily learning targets, ongoing assessment.
- Technology and Multimedia
Supporting English Language Learners
Materials from previous lessons, new materials, closing & assessments, you are here:.
- ELA 2019 Grade 7
- ELA 2019 G7:M1
- ELA 2019 G7:M1:U3
Like what you see?
Order printed materials, teacher guides and more.
How to order
Help us improve!
Tell us how the curriculum is working in your classroom and send us corrections or suggestions for improving it.
Leave feedback
Focus Standards: These are the standards the instruction addresses.
- W.7.3a , W.7.5
Supporting Standards: These are the standards that are incidental—no direct instruction in this lesson, but practice of these standards occurs as a result of addressing the focus standards.
- RL.7.10 , W.7.4 , W.7.10 , L.7.6
- I can create a character profile for my narrative. ( W.7.3a , W.7.5 )
- I can create accurate settings based on the places I have read about. ( W.7.3a , W.7.5 )
- Opening A: Entrance Ticket: Unit 3, Lesson 5 ( W.7.3a )
- Work Time C: Narrative Writing Plan graphic organizer ( W.7.3a , W.7.4 , W.7.5 )
- Ensure there is a copy of Entrance Ticket: Unit 3, Lesson 5 at each student's workspace.
- Review the Narrative Writing checklist.
- Post the learning targets and applicable anchor charts (see Materials list).
Tech and Multimedia
- Work Time C: Ebook Nasreen's Secret School and projector to display it
Supports guided in part by CA ELD Standards 7.I.C.10, 7.II.C.6, and 7.II.C.7.
Important Points in the Lesson Itself
- To support ELLs, this lesson provides students with the opportunity to plan the character and setting for their narrative, using a graphic organizer. Using graphic organizers to preplan writing gives ELLs a chance to deliberately generate conceptual language related to a writing task prior to doing the task itself. This pre-rehearsed conceptual language then becomes an anchor of sorts for ELLs' writing, allowing them to focus more fully on the sometimes labor-intensive task of selecting concrete, specific language as they write.
- ELLs may find filling out the Narrative Writing Plan graphic organize r challenging because they may not know words that they can apply to each of the categories designated in the graphic organizer. Therefore, additional supports such as the ones below may be useful when introducing the Narrative Writing Plan graphic organizer.
- profile (A)
- character, setting (DS)
(A): Academic Vocabulary
(DS): Domain-Specific Vocabulary
- Close Readers Do These Things anchor chart (one for display; from Unit 1, Lesson 4, Opening A)
- Academic word wall (one for display; from Unit 1, Lesson 1, Opening A)
- Domain-specific word wall (one for display; from Unit 1, Lesson 1, Work Time B)
- Text Guide: A Long Walk to Water (for teacher reference) (from Unit 1, Lesson 2, Work Time A)
- Work to Become Ethical People anchor chart (one for display; from Unit 1, Lesson 2, Opening B)
- Questions about A Long Walk to Water anchor chart (one for display; from Unit 1, Lesson 2, Work Time A)
- Nasreen's Secret School (ebook to display and read aloud) (from Unit 3, Lesson 4, Work Time B)
- Device with which to display the ebook
- Narrative Writing Plan graphic organizer (example for teacher reference) (from Unit 3, Lesson 4, Work Time B)
- Vocabulary log (one per student; from Unit 1, Lesson 2, Opening A)
- A Long Walk to Water (text; one per student; from Unit 1, Lesson 1, Work Time C)
- Notes and articles from independent research reading and other nonfiction texts from this module (begun in Unit 1)
- Narrative Writing Plan graphic organizer (one per student and one for display; from Unit 3, Lesson 4, Work Time B)
- Narrative Writing checklist (one per student and one for display; from Unit 3, Lesson 4, Closing and Assessment A)
- Narrative Writing checklist ▲
- Homework: Create Illustrations (one per student; from Unit 3, Lesson 4, Homework A)
- Entrance Ticket: Unit 3, Lesson 5 (answers for teacher reference)
- Chart paper
- Work to Contribute to a Better World anchor chart (example for teacher reference)
- Work to Contribute to a Better World anchor chart (one for display; co-created in Work Time B)
- Entrance Ticket: Unit 3, Lesson 5 (one per student)
- Online or print dictionaries (including ELL and home language dictionaries; one per small groups of students)
- Synopsis: A Long Walk to Water , Ending Sections (one per student)
- Sticky notes (one of each gist color per student)
Each unit in the 6-8 Language Arts Curriculum has two standards-based assessments built in, one mid-unit assessment and one end of unit assessment. The module concludes with a performance task at the end of Unit 3 to synthesize students' understanding of what they accomplished through supported, standards-based writing.
Copyright © 2013-2024 by EL Education, New York, NY.
Get updates about our new K-5 curriculum as new materials and tools debut.
Help us improve our curriculum..
Tell us what’s going well, share your concerns and feedback.
Terms of use . To learn more about EL Education, visit eleducation.org
- For Schools
- For Teachers
- Teacher Hub
- Free resources
- For Seven Steppers
- NAPLAN Writing Success
- Free writing resources
- About Seven Steps
- Seven Steps and the Curriculum
- What are the Seven Steps?
- Success Stories
- In the Media
- Seven Steps Impact Report
- [FREE] Try Sizzling Starts
- Narrative Writing
- Persuasive Writing
- Informative Writing
No products in the cart.

- Your password must be 8 or more characters, including at least 1 upper case letter, 1 lower case letter and 1 number.
- Add new school
Narrative Writing Samples

See the difference the Seven Steps can make with these writing samples!
Below you’ll find a collection of resources to help unlock the fun, engaging and collaborative lessons of the Seven Steps. Learn the complete Seven Steps theory by attending a Workshop One: Seven Steps to Transform Writing or joining Teacher Hub .
Student Samples
A trip to the zoo … gone wrong step 2: sizzling starts.
TIP: The ‘before’ sample wastes time talking about what happens before they get to the zoo. Start with action, at the moment of change.
Improve your students’ introductions by learning the basics of Step 2: Sizzling Starts for free .
Mandy to the rescue Step 5: Show, Don’t Tell
TIP: When you tell , you tend to say something straight out, and it’s often boring. If you show, the writing is longer but can be far more powerful and convincing.
For more before and after examples, download the resource below.
Before and After Samples
STEP Step 2: Sizzling Starts, Step 3: Tightening Tension, Step 5: Show, Don’t Tell PURPOSE Teach RESOURCE TYPE Writing Samples & Exemplars YEAR F–10 RELATED The power to write
- Model how to improve a piece of narrative writing using the Seven Steps techniques.
- Annotations using Seven Steps terminology provide actionable feedback to students.

2020 Narrative Writing Competition Winners
STEP All Steps PURPOSE Teach RESOURCE TYPE Writing Samples & Exemplars YEAR F–10
Competition categories:
- The Astonishing Bicycle: A story, poem or diary entry
- Mistaken Identity: A short story or script for TV or radio
- A Visit to the Past: A short story and story graph
- A Curious Creature: A comic strip or manga.

NAPLAN narrative exemplars
Looking for annotated NAPLAN writing samples?

Professional Exemplars
Narrative texts demonstrating the seven steps.
STEP All Steps PURPOSE Teach RESOURCE TYPE List YEAR F–10
- Show students examples of the Seven Steps techniques in published texts.
- This handy list is sorted by Step and annotated with notes about how each text demonstrates a particular Seven Steps technique.
- Selection includes picture books and chapter books, from classics to more recent titles.

Narrative Videos Demonstrating the Seven Steps
- Show students examples of the Seven Steps techniques in filmmaking.
- This handy list is sorted by Step and annotated with notes about how each video clip demonstrates a particular Seven Steps technique.
- Selection includes animated short films, movie scenes and advertisements.

Harry Potter and the Philosopher’s Stone plotted on the Narrative Story Graph
AUTHOR JK Rowling STEP Step 1: Plan for Success PURPOSE Teach RESOURCE TYPE Story graphs YEAR 3–10
- Created for 2021 Book Week: Old Worlds, New Worlds, Other Worlds
- Demonstrate how this novel follows the basic narrative structure using the Seven Steps story graph.
- This resource is taken from our collection Fantasy Fiction on the Story Graph. You can access the full collection on Teacher Hub .

Dragonkeeper plotted on the Narrative Story Graph
AUTHOR Carole Wilkinson STEP Step 1: Plan for Success PURPOSE Teach RESOURCE TYPE Story graphs YEAR 3–10

Whitney and Britney, Chicken Divas plotted on the Narrative Story Graph.
AUTHOR Lucinda Gifford STEP Step 1: Plan for Success PURPOSE Teach RESOURCE TYPE Story graphs YEAR F–6
- Created for 2020 National Simultaneous Storytime
- Demonstrate how this picture book follows the basic narrative structure using the Seven Steps Narrative Story Graph.

Say Yes: A Story of Friendship, Fairness and a Vote for Hope plotted on the Narrative Story Graph.
AUTHOR Jennifer Castles STEP Step 1: Plan for Success PURPOSE Teach RESOURCE TYPE Story graphs YEAR F–6
- Created for 2020 Reconciliation Week Resource
Searching for Cicadas plotted on the Story/Writing Graph
AUTHOR Lesley Gibbes and Judy Watson STEP Step 1 PURPOSE Teach RESOURCE TYPE Story graphs YEAR F–6
- Searching for Cicadas by Lesley Gibbes and Judy Watson plotted on the Narrative Story Graph and Informative Writing Graph.
- Demonstrate how this hybrid picture book follows the basic structure for both narrative and informative texts.
- This picture book was shortlisted for the 2020 CBCA Book of the Year: Eve Pownall Award for Information Books.

One Runaway Rabbit plotted on the Narrative Story Graph
AUTHOR David Mezenthen and Mairead Murphy STEP Step 1 PURPOSE Teach RESOURCE TYPE Story graphs YEAR F–2
- One Runaway Rabbit by David Mezenthen and Mairead Murphy plotted on the Narrative Story Graph.
- This picture book was shortlisted for the 2020 CBCA Book of the Year: Early Childhood.
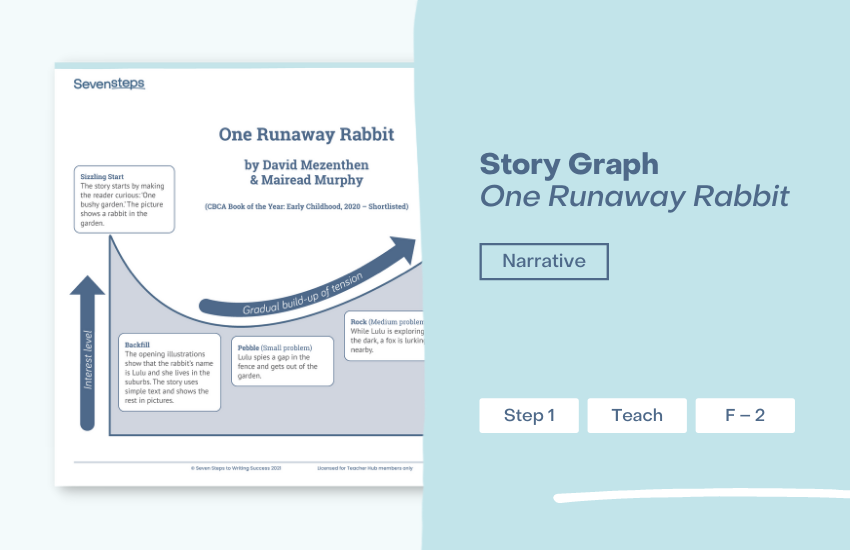
Alpacas with Maracas plotted on the Narrative Story Graph
AUTHOR Matt Cosgrove STEP Step 1: Plan for Success PURPOSE Teach RESOURCE TYPE Story graphs YEAR F–6
- Created for 2019 National Simultaneous Storytime

Dinner Table Fight – Dreamcatcher
STEP Step 4 PURPOSE Teach RESOURCE TYPE Writing sample YEAR 3–6
- This short play is based on a scene from Dreamcatcher by Jen McVeity.
- Ask students to rehearse the play in groups, then discuss what the dialogue reveals about each of the characters and the plot.
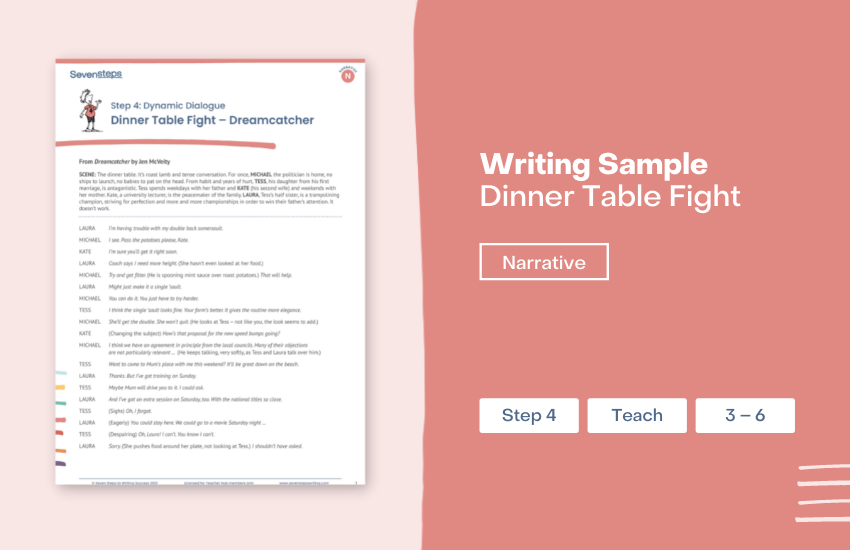
Books about Natural Disasters on the Story Graph
STEP Step 1 PURPOSE Teach RESOURCE TYPE Story graphs YEAR F–10 RELATED Resources for schools and teachers affected by bushfires
- Reading examples can help students to learn how to tell their own stories.
- Selection of stories about natural disasters (particularly bushfires) plotted on the Narrative Story Graph.

More narrative resources
Explore more classroom resources and make narrative writing fun with the Seven Steps!
Lesson plans and activities
Explore ready-made resources and discover how to teach the key concepts behind each Step.
Picture writing prompts
These visual prompts offer fun and quick writing practice to develop your students’ writing skills, one Step at a time.

Training and resources to transform student engagement and writing data.

- Abstract/Non-Verbal Reasoning Test
- Academic Assessment Services (AAS) Scholarship Test (Year 7)
- Brisbane State High School Selective Test (Sit in Grade 5)
- Brisbane State High School Selective Test (Sit in Grade 6)
- GATE Test (Gifted & Talented) Academic Selective Test - ASET in WA
- IELTS General Training Writing
- IGNITE Program South Australia Exam (a Selective Schools Test offered by ACER®)
- NAPLAN Grade 5
- Narrative Writing (Written Expression) Test
- NSW Selective Schools Test (HSPT)
- Numerical Reasoning Test
- Persuasive / Argumentative Writing Test (with Topics & Real-Life Examples)
- QLD Academies SMT Selective Grade 7 Entry
- Reading Comprehension Test Practice (Grade 5, Grade 6, Grade 7)
- Scholarship Tests (Year 7 – Level 1) offered by ACER®
- Scholarship Tests (Year 7) Offered by Edutest®
- SEAL/SEALP (Select Entry Accelerated Learning Program) Exams Offered by ACER®
- Select Entry Accelerated Learning Programs (SEAL/SEALP) Offered by Edutest®
- Test Practice Questions - Free Trial
- The ADF Aptitude Test (Defence Force YOU Session)
- Verbal Reasoning Tests
- Victorian Selective Schools Test
- ONLINE COURSES
- TEST PAPERS
- WRITING PROGRAMS
- SITE MEMBERSHIP
- WRITING CLUB
- BLOG & ARTICLES
- FREE VIDEOS
- WRITING PROMPTS
- SAMPLE ESSAYS
- MASTERCLASS VIDEOS
- Get Started
NAPLAN - Grade 7 - Narrative Writing
Writing prompts for NAPLAN Grade 7 for practice. This area contains prompts under the narrative writing genre.
QUESTION 001 - The Discovery Write a narrative (story) based on the idea of “A discovery”. Your story may be about a new scientific discovery. It may be the discovery of a hidden secret or a hidden place. It may be the discovery of traits in someone who you thought you knew well. Put thought into how you will: …
QUESTION 002 - A Mix-Up Write a narrative (story) based…
QUESTION 003 – A Journey Write a narrative (story) based…
QUESTION 004 – A reunion Write a narrative (story) based…
QUESTION 005 - Home Write at narrative (story) base…
QUESTION 006 - A Lesson Write a narrative (story) based…
QUESTION 007 - Having doubts Write a narrative (story) based…
QUESTION 008 - A new beginning Write a narrative (story) based…
QUESTION 009 - Something unusual Write a narrative (story) based…
Have A Question?
Jump to navigation
- Inside Writing
- Teacher's Guides
Student Models
- Writing Topics
- Minilessons
- Shopping Cart
- Inside Grammar
- Grammar Adventures
- CCSS Correlations
- Infographics
Student Writing Models
How do I use student models in my classroom?

When you need an example written by a student, check out our vast collection of free student models. Scroll through the list, or search for a mode of writing such as “explanatory” or “persuasive.”
Jump to . . .
Explanatory writing.
- How Much I Know About Space Explanatory Paragraph
- My Favorite Pet Explanatory Paragraph
- Sweet Spring Explanatory Paragraph
Narrative Writing
- A Happy Day Narrative Paragraph
- My Trip to Mexico Narrative Paragraph
Creative Writing
- Happy Easter Story Paragraph
- Leaf Person Story
Research Writing
- Parrots Report
- If I Were President Explanatory Paragraph
- My Dad Personal Narrative
- The Horrible Day Personal Narrative
Response to Literature
- One Great Book Book Review
- A Fable Story
- Ant Poem Poem
- The Missing Coin Story
- Winter Words Poem
- Horses Report
- Ladybugs Report
- How to Make Boiled Eggs How-To
Persuasive Writing
- Plastic, Paper, or Cloth? Persuasive Paragraph
- The Funny Dance Personal Narrative
- The Sled Run Personal Narrative
- Hello, Spring! Poem
- Cheetahs Report
Business Writing
- Dear Ms. Nathan Email
- My Favorite Place to Go Description
- My Mother Personal Essay
- Rules Personal Essay
- Shadow Fort Description
- Adopting a Pet from the Pound Editorial
- Letter to the Editor Letter to the Editor
- Ann Personal Narrative
- Grandpa, Chaz, and Me Personal Narrative
- Indy’s Life Story Personal Narrative
- Jet Bikes Personal Narrative
- The Day I Took the Spotlight Personal Narrative
- A Story of Survival Book Review
- Chloe’s Day Story
- Did You Ever Look At . . . Poem
- Dreams Poem
- I Am Attean Poem
- Sloppy Joes Poem
- The Civil War Poem
- The Haunted House Story
- The Terror of Kansas Story
- When I Was Upside Down Poem
- Deer Don’t Need to Flee to Stay Trouble-Free! Report
- Height-Challenged German Shepherd Report
- Friendship Definition
- What Really Matters News Feature
- Cheating in America Problem-Solution
- Hang Up and Drive Editorial
- Musical Arts Editorial
- Summer: 15 Days or 2 1/2 Months? Editorial
- A Cowboy's Journal Fictionalized Journal Entry
- Giving Life Personal Narrative
- The Great Paw Paw Personal Narrative
- The Racist Warehouse Personal Narrative
- Limadastrin Poem
- The Best Little Girl in the World Book Review
- How the Stars Came to Be Story
- Linden’s Library Story
- My Backyard Poem
- The Call Poem
- I Am Latvia Research Report
- Mir Pushed the Frontier of Space Research Report
- The Aloha State Research Report
- The Incredible Egg Observation Report
- Unique Wolves Research Report
- Dear Dr. Larson Email
Personal Writing
- A Lesson to Learn Journal
- Caught in the Net Definition
- From Bed Bound to Breaking Boards News Feature
- If Only They Knew Comparison-Contrast
- Save the Elephants Cause-Effect
- Student Entrepreneur Reaches for Dreams of the Sky News Feature
- Internet Plagiarism Problem-Solution
- Mosquito Madness Pet Peeve
- Anticipating the Dream Personal Narrative
- Huddling Together Personal Narrative
- H’s Hickory Chips Personal Narrative
- It’s a Boy! Personal Narrative
- My Greatest Instrument Personal Narrative
- Snapshots Personal Narrative
- Take Me to Casablanca Personal Narrative
- The Boy with Chris Pine Blue Eyes Personal Narrative
- The Climb Personal Narrative
- The House on Medford Avenue Personal Narrative
- Adam’s Train of Ghosts Music Review
- Diary of Gaspard Fictionalized Journal Entry
- My Interpretation of The Joy Luck Club Literary Analysis
- Mama’s Stitches Poem
- The KHS Press Play
- Rosa Parks Research Report
- The Killer Bean Research Report
- Mid-Project Report on History Paper Email
- Vegetarian Lunch Options at Bay High Email

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
168 South 3rd Avenue. Oakdale. CA. 95361. 209-847-0155. 7th Grade Writing Samples - Oakdale Joint Unified School District.
Narrative Writing worksheets for Grade 7 are an essential tool for teachers to help their students develop strong reading and writing skills. These worksheets focus on various aspects of narrative writing, such as creating engaging characters, building a compelling plot, and using descriptive language. By incorporating these worksheets into ...
45 Narrative Writing Prompts for 7th Grade. Preteens and teenagers have a lot to say, but they don't always know just how to express their emotions or say what's on their mind. By implementing narrative writing into your curriculum, you give your students an outlet to experiment with in a safe and structured environment.
Narrative Essay Definition. Writing a narrative essay is a unique form of storytelling that revolves around personal experiences, aiming to immerse the reader in the author's world. It's a piece of writing that delves into the depths of thoughts and feelings. In a narrative essay, life experiences take center stage, serving as the main substance of the story. It's a powerful tool for writers ...
Doing the Impossible. Worksheet. 1. Browse Printable 7th Grade Narrative Writing Worksheets. Award winning educational materials designed to help kids succeed. Start for free now!
Exploring perspective and voice, writing dialogue, developing creative characters. To demonstrate how to build suspense and resolve a mystery in a narrative. Constructing a plot, pacing, planting clues, and developing critical thinking. To provide an example of incorporating scientific ideas into a creative story.
These samples are annotated for the specific skills students applied effectively in their writing and suggestions are included for improvement. Download each sample and use them as a guide to analyze your own student samples and give you the language to provide feedback based on instruction. The suggested lessons can be found in the Empowering ...
If you're a writing teacher in grades 7-12 and you'd like a classroom-ready unit like the one described above, including slideshow mini-lessons on 14 areas of narrative craft, a sample narrative piece, editable rubrics, and other supplemental materials to guide students through every stage of the process, take a look at my Narrative Writing ...
A narrative can spark emotion, encourage reflection, and convey meaning when done well. Narratives are a popular genre for students and teachers as they allow the writer to share their imagination, creativity, skill, and understanding of nearly all elements of writing. We occasionally refer to a narrative as 'creative writing' or story writing.
New skills are introduced in the following: W.7.3b - Work Time A: Students learn about how description and dialogue can impact pacing. W.7.3b - Work Time B: Students apply their learning from the mini lesson to plan the pacing, dialogue, and description of their narrative. W.7.3c - Closing and Assessment A: Students review and use ...
2018 Released Items: Grade 7 Narrative Writing Task . The Narrative Writing Task focuses on one literary text. Students read the text, answer questions, and write a narrative response that is tied to and draws on the text. The 2018 blueprint for grade 7 Narrative Writing Task includes Evidence-Based Selected Response/Technology-Enhanced Constructed
Grade 7 Narrative. W.7.3 Write narratives to develop real or imagined experiences or events using effective technique, relevant descriptive details, and well-structured event sequences. Engage and orient the reader by establishing a context and point of view, introducing a narrator and/or characters; organize an event sequence that unfolds ...
W.7.3a - Work Time C: Students use the model narrative to plan the character and setting (s) of their own narratives about a Lost Child of Sudan. W.7.5 - Closing and Assessment A: Students share their plans with a partner to develop and strengthen their writing with peer support. The Think-Pair-Share protocol is used in this lesson.
Planning for narrative writing. Explore ready-made lesson plans, activities and planning exemplars to discover how to teach the key concepts behind each Step. Each lesson plan includes relevant links to the Australian Curriculum and NAPLAN marking criteria, plus a learning intention and success criteria to assist with planning and assessment.
CCSS.ELA-Literacy.W.7.9 Draw evidence from literary or informational texts to support analysis, reflection, and research. CCSS.ELA-Literacy.W.7.9a Apply grade 7 Reading standards to literature (e.g., "Compare and contrast a fictional portrayal of a time, place, or character and a historical account of the same period as a means of understanding
October (15 days) E - Engage and orient the reader by establishing a context and point of view and introducing a narrator and/or characters; organize an event sequence that unfolds naturally and logically to support the writer's purpose. Formative and Summative Assessment. PA CC EC: E07.C.1.3.1. Narrative Writing.
Before and After Samples. STEP Step 2: Sizzling Starts, Step 3: Tightening Tension, Step 5: Show, Don't Tell. PURPOSE Teach. RESOURCE TYPE Writing Samples & Exemplars. YEAR F-10. RELATED The power to write. Model how to improve a piece of narrative writing using the Seven Steps techniques.
I used narrative techniques, such as dialogue, pacing, and description to develop experiences, events and characters. (W.7.3d) I included precise words and phrases, relevant descriptive details and sensory language to capture action and convey experiences and events. Transitions (W.7.3c) shifts from one time frame or
Grade 7 Level 4 Writing Sample. Global warming has become a serious threat to our planet. Explain what we can do as citizens to reduce the effects of global warming. You may want to consider factors, such as: recycling. the impact of fossil fuels (oil, gas and coal) the impact of consumerism (buying things). View full size.
NAPLAN Grade 5; Narrative Writing (Written Expression) Test; NSW Selective Schools Test (HSPT) Numerical Reasoning Test; Persuasive / Argumentative Writing Test (with Topics & Real-Life Examples) QLD Academies SMT Selective Grade 7 Entry; Reading Comprehension Test Practice (Grade 5, Grade 6, Grade 7) Scholarship Tests (Year 7 - Level 1 ...
The post is now updated and includes a grand total of 60 writing prompts and essay ideas. Take a look and enjoy. Yeppers. As seventh graders get ready to transition into their turbulent teenage years, it's incredibly important for teachers to do everything they can to keep their students focused and grounded. Table of Contents.
Doing the Impossible. Worksheet. 1. Browse 7th Grade Narrative Writing Educational Resources. Award winning educational materials designed to help kids succeed. Start for free now!
Student Models. When you need an example written by a student, check out our vast collection of free student models. Scroll through the list, or search for a mode of writing such as "explanatory" or "persuasive.".