Topic sentences and signposts make an essay's claims clear to a reader. Good essays contain both. Topic sentences reveal the main point of a paragraph. They show the relationship of each paragraph to the essay's thesis, telegraph the point of a paragraph, and tell your reader what to expect in the paragraph that follows. Topic sentences also establish their relevance right away, making clear why the points they're making are important to the essay's main ideas. They argue rather than report. Signposts , as their name suggests, prepare the reader for a change in the argument's direction. They show how far the essay's argument has progressed vis-ˆ-vis the claims of the thesis.
Topic sentences and signposts occupy a middle ground in the writing process. They are neither the first thing a writer needs to address (thesis and the broad strokes of an essay's structure are); nor are they the last (that's when you attend to sentence-level editing and polishing). Topic sentences and signposts deliver an essay's structure and meaning to a reader, so they are useful diagnostic tools to the writer—they let you know if your thesis is arguable—and essential guides to the reader
Forms of Topic Sentences
Sometimes topic sentences are actually two or even three sentences long. If the first makes a claim, the second might reflect on that claim, explaining it further. Think of these sentences as asking and answering two critical questions: How does the phenomenon you're discussing operate? Why does it operate as it does?
There's no set formula for writing a topic sentence. Rather, you should work to vary the form your topic sentences take. Repeated too often, any method grows wearisome. Here are a few approaches.
Complex sentences. Topic sentences at the beginning of a paragraph frequently combine with a transition from the previous paragraph. This might be done by writing a sentence that contains both subordinate and independent clauses, as in the example below.
Although Young Woman with a Water Pitcher depicts an unknown, middle-class woman at an ordinary task, the image is more than "realistic"; the painter [Vermeer] has imposed his own order upon it to strengthen it.
This sentence employs a useful principle of transitions: always move from old to new information. The subordinate clause (from "although" to "task") recaps information from previous paragraphs; the independent clauses (starting with "the image" and "the painter") introduce the new information—a claim about how the image works ("more than Ôrealistic'") and why it works as it does (Vermeer "strengthens" the image by "imposing order").
Questions. Questions, sometimes in pairs, also make good topic sentences (and signposts). Consider the following: "Does the promise of stability justify this unchanging hierarchy?" We may fairly assume that the paragraph or section that follows will answer the question. Questions are by definition a form of inquiry, and thus demand an answer. Good essays strive for this forward momentum.
Bridge sentences. Like questions, "bridge sentences" (the term is John Trimble's) make an excellent substitute for more formal topic sentences. Bridge sentences indicate both what came before and what comes next (they "bridge" paragraphs) without the formal trappings of multiple clauses: "But there is a clue to this puzzle."
Pivots. Topic sentences don't always appear at the beginning of a paragraph. When they come in the middle, they indicate that the paragraph will change direction, or "pivot." This strategy is particularly useful for dealing with counter-evidence: a paragraph starts out conceding a point or stating a fact ("Psychologist Sharon Hymer uses the term Ônarcissistic friendship' to describe the early stage of a friendship like the one between Celie and Shug"); after following up on this initial statement with evidence, it then reverses direction and establishes a claim ("Yet ... this narcissistic stage of Celie and Shug's relationship is merely a transitory one. Hymer herself concedes . . . "). The pivot always needs a signal, a word like "but," "yet," or "however," or a longer phrase or sentence that indicates an about-face. It often needs more than one sentence to make its point.
Signposts operate as topic sentences for whole sections in an essay. (In longer essays, sections often contain more than a single paragraph.) They inform a reader that the essay is taking a turn in its argument: delving into a related topic such as a counter-argument, stepping up its claims with a complication, or pausing to give essential historical or scholarly background. Because they reveal the architecture of the essay itself, signposts remind readers of what the essay's stakes are: what it's about, and why it's being written.
Signposting can be accomplished in a sentence or two at the beginning of a paragraph or in whole paragraphs that serve as transitions between one part of the argument and the next. The following example comes from an essay examining how a painting by Monet, The Gare Saint-Lazare: Arrival of a Train, challenges Zola's declarations about Impressionist art. The student writer wonders whether Monet's Impressionism is really as devoted to avoiding "ideas" in favor of direct sense impressions as Zola's claims would seem to suggest. This is the start of the essay's third section:
It is evident in this painting that Monet found his Gare Saint-Lazare motif fascinating at the most fundamental level of the play of light as well as the loftiest level of social relevance. Arrival of a Train explores both extremes of expression. At the fundamental extreme, Monet satisfies the Impressionist objective of capturing the full-spectrum effects of light on a scene.
The writer signposts this section in the first sentence, reminding readers of the stakes of the essay itself with the simultaneous references to sense impression ("play of light") and intellectual content ("social relevance"). The second sentence follows up on this idea, while the third serves as a topic sentence for the paragraph. The paragraph after that starts off with a topic sentence about the "cultural message" of the painting, something that the signposting sentence predicts by not only reminding readers of the essay's stakes but also, and quite clearly, indicating what the section itself will contain.
Copyright 2000, Elizabeth Abrams, for the Writing Center at Harvard University


Better Essays: Signposting

Improving your essays
Explore how to structure your assignments, introduce new topics and take your reader on a journey
Essays can be considered a journey from the introduction to the conclusion. You're the driver, your readers are the passengers, and signposts are the roads you choose to take. The principles discussed here apply to most types of assignment.
Not signposting your essay is a bit like sleeping on a journey and only waking up occasionally – it can be disorientating. You'll wonder where you are and how you got there. Your tutors can feel this way if your content isn't clearly signposted.
The examples below are suggestions and you don't need to reproduce them exactly; each word and phrase has a precise meaning so you should check their meaning before you use them. Most of these terms can be used in any section of an essay, but some will suits particular fields more than others.
What signposting means
Signposting means using words to tell your reader about the content of your essay to help them understand as clearly as possible. Here are three examples of signposts and what they mean:
Types of signposting
You can signposting using single words, short phrases, long phrases, or whole sentences. Examples of each are provided below:
- single words: however, furthermore, initially
- short phrases: in contrast, in conclusion, an additional point is
- sentence: Having discussed the reliability of the research, this report will next address its validity.
Signposting in the introduction, body and conclusion
These lists include some terms you could use for signposting in your introduction, main body and conclusion.
Signposting in the introduction
You could use an opening statement like this to signpost your introduction:
This essay will:
It will then:
To quantify what your essay will do, you could say: 'This essay will address three aspects'. You could also signpost how this will be done, for example: 'This essay will attempt to determine whether cats are better pets than dogs by analysing studies of their behaviour.'
Signposting in the body
These examples show a word or phrase and what it tells the reader:
- 'This essay will now' — introduces what is next
- 'Furthermore' — takes the point, issue, or data further
- 'In contrast' — includes a strong alternative or challenge
- 'However' — adds an alternative or challenge, but less strongly than the phrase 'In contrast'
Signposting don't always have a statement of intent (like 'It will then', or 'In addition'). You could say: 'Cats are often seen as less affectionate than dogs'.
Signposting in conclusions
You can use many terms and phrases from the introduction and main body of your essay in the conclusion too, but not all of them are appropriate. You shouldn't introduce new material in a conclusion and can use the past perfect tense ('This essay has focused on') or present tense ('This essay shows that').
Download our signposting for better essays revision sheet
Download this page as a PDF for your essay signposting revision notes.
Writing: flow and coherence

Commas and its
Reflective writing introduction

Find an undergraduate or postgraduate degree course that suits you at Portsmouth.

Guidance and support
Find out about the guidance and support you'll get if you need a helping hand with academic life – or life in general – when you study with us at Portsmouth.


- Place order
Signposting words and Phrases to use in Essays

Every professor or instructor will tell you that they undoubtedly enjoy reading and grading an essay or academic task where signposting words and phrases have been used. This is a secret that only the top grade and talented students have discovered. It is the reason they score As.

Essays that have a logical flow, where signposting words and phrases have been used, are appealing to read. When you signpost, no one struggles to read through your essay, identify your thoughts, claims, counterclaims, and arguments. In the end, such essays achieve their intended purpose, which then earns you the best grade.
Any student who aspires to score the best grades for their essays must master the art of signposting. Not only in essays but also in other academic tasks, assignments, or homework. It is a skill that sets you miles ahead of the rest.
In this guide, we take you through the best practices of signposting using examples for illustration and deep understanding before giving you a list of signposting words and phrases.
What is signposting?
You are probably wondering, "what are signposts in writing?" Let us begin by defining signposting before we head on to focus on signpost examples.
Signposting is a commonly used strategy when writing academic and professional papers. It refers to the use of phrases and words to guide readers through the content of a piece of written work such as an essay, research paper, term paper, proposal, or dissertation. It entails flagging the most significant parts of your arguments, signaling transitions, and clarifying any stakes of an argument.
Signposts are these words and phrases that help you articulate the structure of any given piece of writing to ensure that your writers flow with the ideas.
There are two classes of signposting: Major signposts and linking words and short phrases.
Major signposting entails the introduction , conclusion, and outlining of main arguments or the direction of arguments. It equally entails the use of opening phrases. On the other hand, linking words and short phrases encompass any connecting words that guide the readers through the main arguments by linking sentences, ideas, and paragraphs.
Example of signposting
To understand Biden's foreign policy for China, it is imperative to evaluate the policy direction of Trump's regime.
This example helps the reader to understand in advance that you will be taking them through the characteristics of Trump's foreign policy for China before exploring Biden's current foreign policy to China in a cross-comparative approach.
Another way to view the issue of global warming is'
In this example, you are trying to remind the reader that although you have covered some aspects of global warming, they should note another vital point.
How to Signpost in an Essay for more effortless Flow of Ideas
When you signpost, a reader whose mind is preoccupied can read your essay or piece of academic writing and understand your point without struggling. It is a bulletproof strategy that helps your readers comprehend each point. The readers can connect points, sentences, ideas, and paragraphs, which gives an ideal flow as they read.
Signposting also makes your writing enjoyable; you sound professional in your arguments. In addition, when you signpost, the structure of your essay, especially in the introduction, helps you present your arguments well.
Here are eight effective strategies , tips, and tricks you can use when signposting to write an essay that scores an A .
1. Use Verbs to Signpost
When introducing quotes or referring to the sources or references, use various verbs to signpost your readers that you are about to introduce a quote, then connect it to the main argument.
You can use verbs such as asserts, opines, contends, reasons, reports, concludes, demonstrates, claims, shows, concurs with, refutes, opposes, etc.
Be vigilant enough not to use the wrong verbs in a given context when using these verbs. Besides, ensure that you are precise. Use these verbs to endorse what the scholar said, refute or oppose what the scholar said, or compare the opinion of scholars on a given issue.
2. Use Retrospective Signposts to Reiterate
When writing an essay or dissertation, capturing your readers' attention becomes your ultimate goal. And while you capture their attention, you must also keep them motivated and engaged so they stick to your work.
One way to achieve this is by reminding the readers about the key points you have covered and where you are headed. You prepare your readers for what is coming.
You can use phrases such as "as is now evident," "as mentioned earlier," "in other words," "as a complement to the last point on," or "the main point is"
Using retrospective signposts can help you show how the previous points matter to the existing idea or argument. In addition, it helps the readers to take keen note of a point before introducing a new idea.
In most cases, you can do this at the end of paragraphs where you want to highlight the earlier point and expose its relevance to the essay question.
You can as well apply this strategy to your conclusion. Also, you can repeat complicated ideas, points, or arguments to avoid sparking controversy or creating abrupt surprises.
When you remind the readers about these key points, your intended direction, and your expected destination, you orient them through your reading to allow some good flow of ideas.
Repetition makes your readers get bored by reading something so many times. However, when you signpost these ideas, you help them see that you address a different point connected to the past ideas.
3. Effectively use Transitions
Transitions knit together ideas in an essay or academic writing task. Using transition words and phrases, you can link ideas in two sentences or paragraphs. You can use different transition words when writing, depending on your goal. Only ensure that your intention and the choice of a transition align.
You can illustrate your previous point using transitions such as 'for example,' 'for instance,' 'as an illustration,' or 'to further expound on.'
You can compare, show cause and consequence, or give additional points to what you have already covered. And when you use transitions, be wise enough not to overuse or place them for the sake of it.
Related Reading: How to write explosive compare and contrast essays.
4. Precisely use Signposts
Although signposting is intended for all the good reasons we have explained, your work will sound sloppy when abused. For instance, using words such as 'conversely' or 'however' in the wrong context makes you look foolish.
Resist any urge to sprinkle signposting words all over your written piece. Instead, you must be meticulous and link sentences, paragraphs, or ideas only when necessary.
Choose a transition or linking word that fits the context. For example, only use 'as a result' to signpost when the following idea is a consequence of an idea you previously wrote.
As usual, precise language will enable smooth and accurate communication with your audience; you must stick to it when writing your essay.
Related Read: How to make good paragraphs in an essay.
5. Signpost in your introduction
When signposting in the introduction, clearly elaborate:
- The overall aim of your essay, e.g., 'This essay argues'.'
- The main ideas you will discuss and in what order, e.g., 'First, second, third'.'
- The rationale of choosing your main argument for the topic, e.g., 'Given that'.' Or ''will form the key focus of this essay.'
- Quantify the content or aims of your essay, e.g., 'This essay discusses the three strategies'.'
In short, your introduction should present the essay's overall aim and share the points you discuss in the body paragraphs.
6. Signpost throughout the body paragraphs
You need to use paragraph breaks and subheadings to signpost through your essay. It is a way to keep the readers focused on the main points of your essay. However, you can only do this for long essays such as term papers, research papers, or dissertations.
Writing three to four sentences to effectively use paragraph breaks before starting another paragraph. Paragraph breaks are the single line space, indentation, or both that mark the end of one paragraph and the beginning of the next.
In your body paragraphs, you can tell your readers about specific points to come or what has been discussed already.
Example: Having discussed the overall direction of Trump's foreign policy, it is necessary to consider Biden's current policy.
You can equally use words and short phrases within the paragraphs. For example, you can use words such as 'Consequently,' 'as a result,' 'therefore,' 'alternatively,' or 'however' to signal direction.
7. Signpost in your conclusion
Like the introduction, the conclusion of an essay also plays a critical role - a signpost in your conclusion to bring some element of closure and close the loop for your readers.
To signpost well, look for the verbs you used in the introduction and use the same verbs in their past tense. For example, "t his essay has discussed and concluded."
Ensure that your conclusion reminds the readers about the main points, arguments, and reasoning you have achieved in your essay and how your essay has answered the question.
A good essay outline should help you signpost ideas in your conclusion. That way, you can craft a conclusion that satisfies your readers' appetite.
8. Ensure that your topic is clear earlier on
Provide a rationale for choosing your topic early enough. Then, you have a few seconds to capture the attention of your readers, after which you either keep or lose their interest.
To have your readers engaged in reading your essay past the title, let the reader know the direction. Begin by writing a great hook , providing a detailed background, and explaining how the topic is relevant to your essay. Also, ensure that your main arguments are clear off the bat.
List of Signposting Words and Phrases for Essays
Now that you understand what it is, its significance, and various approaches to achieve it, let's have a quick look at the phrases and words or signposts that you can use in your essay.
Introducing new idea
- Firstly, secondly, thirdly'
- First, second, third'.
- The first/next/final section'
- The current debate'.
- The current issue'.
Adding similar points
- In addition
- On the same note
Specifying a particular idea
- Considering
- Specifically
- In particular
- More specifically
- In relation to
- In terms of
- With respect to
Giving examples or illustrating
- For instance
- For example
- As an illustration
- This can be explained by
- To further illustrate
Summarizing ideas
- To conclude
- As evident from the discussion
- As is clear from the discussion above
- To summarize
- In conclusion
- The main issue that is apparent
- The main points here
- It is clear that
- The strength of this approach
Making comparison
- On the one hand
- On the other hand
- Compared to
- In comparison
- In contrast
- This contrasts'
- This conflicts'
- This is contrary
- Another angle
Linking or developing a new idea
- Having said that'.
- Picking from the last point
- Having established
- To further understand'
- To elaborate further
- In addition to
- As well as'
- Another issue'
- Of equal importance
- Extending the argument further
Related Reading: How to write a compare and contrast essay.
Final Remarks
Signposting is a single ingredient that makes your essay stronger, more understandable, and more flowing. In addition, it improves the taste of your essay even when your instructor is in no good mood.
Using the signposting tips and tricks we have discussed can help you achieve so much, even when writing a short essay, as you would with a longer essay.
When creating a good flow, the instructor or professor can identify with your argument. You invite them to your world and keep them to the end of the essay. Even as you signpost, be meticulous just as you would with transition words. Ensure that you use it sparingly and as necessary.
We have expert essay writers who can write a researched, structured, and organized essay if you are struggling with your essay. Leave planning, researching, outlining, drafting, and revising an essay to our writers and receive a top-grade grade essay.
Need a Discount to Order?
15% off first order, what you get from us.

Plagiarism-free papers
Our papers are 100% original and unique to pass online plagiarism checkers.

Well-researched academic papers
Even when we say essays for sale, they meet academic writing conventions.

24/7 online support
Hit us up on live chat or Messenger for continuous help with your essays.

Easy communication with writers
Order essays and begin communicating with your writer directly and anonymously.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to write an essay introduction | 4 steps & examples
How to Write an Essay Introduction | 4 Steps & Examples
Published on February 4, 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on July 23, 2023.
A good introduction paragraph is an essential part of any academic essay . It sets up your argument and tells the reader what to expect.
The main goals of an introduction are to:
- Catch your reader’s attention.
- Give background on your topic.
- Present your thesis statement —the central point of your essay.
This introduction example is taken from our interactive essay example on the history of Braille.
The invention of Braille was a major turning point in the history of disability. The writing system of raised dots used by visually impaired people was developed by Louis Braille in nineteenth-century France. In a society that did not value disabled people in general, blindness was particularly stigmatized, and lack of access to reading and writing was a significant barrier to social participation. The idea of tactile reading was not entirely new, but existing methods based on sighted systems were difficult to learn and use. As the first writing system designed for blind people’s needs, Braille was a groundbreaking new accessibility tool. It not only provided practical benefits, but also helped change the cultural status of blindness. This essay begins by discussing the situation of blind people in nineteenth-century Europe. It then describes the invention of Braille and the gradual process of its acceptance within blind education. Subsequently, it explores the wide-ranging effects of this invention on blind people’s social and cultural lives.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Step 1: hook your reader, step 2: give background information, step 3: present your thesis statement, step 4: map your essay’s structure, step 5: check and revise, more examples of essay introductions, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about the essay introduction.
Your first sentence sets the tone for the whole essay, so spend some time on writing an effective hook.
Avoid long, dense sentences—start with something clear, concise and catchy that will spark your reader’s curiosity.
The hook should lead the reader into your essay, giving a sense of the topic you’re writing about and why it’s interesting. Avoid overly broad claims or plain statements of fact.
Examples: Writing a good hook
Take a look at these examples of weak hooks and learn how to improve them.
- Braille was an extremely important invention.
- The invention of Braille was a major turning point in the history of disability.
The first sentence is a dry fact; the second sentence is more interesting, making a bold claim about exactly why the topic is important.
- The internet is defined as “a global computer network providing a variety of information and communication facilities.”
- The spread of the internet has had a world-changing effect, not least on the world of education.
Avoid using a dictionary definition as your hook, especially if it’s an obvious term that everyone knows. The improved example here is still broad, but it gives us a much clearer sense of what the essay will be about.
- Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein is a famous book from the nineteenth century.
- Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein is often read as a crude cautionary tale about the dangers of scientific advancement.
Instead of just stating a fact that the reader already knows, the improved hook here tells us about the mainstream interpretation of the book, implying that this essay will offer a different interpretation.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Next, give your reader the context they need to understand your topic and argument. Depending on the subject of your essay, this might include:
- Historical, geographical, or social context
- An outline of the debate you’re addressing
- A summary of relevant theories or research about the topic
- Definitions of key terms
The information here should be broad but clearly focused and relevant to your argument. Don’t give too much detail—you can mention points that you will return to later, but save your evidence and interpretation for the main body of the essay.
How much space you need for background depends on your topic and the scope of your essay. In our Braille example, we take a few sentences to introduce the topic and sketch the social context that the essay will address:
Now it’s time to narrow your focus and show exactly what you want to say about the topic. This is your thesis statement —a sentence or two that sums up your overall argument.
This is the most important part of your introduction. A good thesis isn’t just a statement of fact, but a claim that requires evidence and explanation.
The goal is to clearly convey your own position in a debate or your central point about a topic.
Particularly in longer essays, it’s helpful to end the introduction by signposting what will be covered in each part. Keep it concise and give your reader a clear sense of the direction your argument will take.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
As you research and write, your argument might change focus or direction as you learn more.
For this reason, it’s often a good idea to wait until later in the writing process before you write the introduction paragraph—it can even be the very last thing you write.
When you’ve finished writing the essay body and conclusion , you should return to the introduction and check that it matches the content of the essay.
It’s especially important to make sure your thesis statement accurately represents what you do in the essay. If your argument has gone in a different direction than planned, tweak your thesis statement to match what you actually say.
To polish your writing, you can use something like a paraphrasing tool .
You can use the checklist below to make sure your introduction does everything it’s supposed to.
Checklist: Essay introduction
My first sentence is engaging and relevant.
I have introduced the topic with necessary background information.
I have defined any important terms.
My thesis statement clearly presents my main point or argument.
Everything in the introduction is relevant to the main body of the essay.
You have a strong introduction - now make sure the rest of your essay is just as good.
- Argumentative
- Literary analysis
This introduction to an argumentative essay sets up the debate about the internet and education, and then clearly states the position the essay will argue for.
The spread of the internet has had a world-changing effect, not least on the world of education. The use of the internet in academic contexts is on the rise, and its role in learning is hotly debated. For many teachers who did not grow up with this technology, its effects seem alarming and potentially harmful. This concern, while understandable, is misguided. The negatives of internet use are outweighed by its critical benefits for students and educators—as a uniquely comprehensive and accessible information source; a means of exposure to and engagement with different perspectives; and a highly flexible learning environment.
This introduction to a short expository essay leads into the topic (the invention of the printing press) and states the main point the essay will explain (the effect of this invention on European society).
In many ways, the invention of the printing press marked the end of the Middle Ages. The medieval period in Europe is often remembered as a time of intellectual and political stagnation. Prior to the Renaissance, the average person had very limited access to books and was unlikely to be literate. The invention of the printing press in the 15th century allowed for much less restricted circulation of information in Europe, paving the way for the Reformation.
This introduction to a literary analysis essay , about Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein , starts by describing a simplistic popular view of the story, and then states how the author will give a more complex analysis of the text’s literary devices.
Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein is often read as a crude cautionary tale. Arguably the first science fiction novel, its plot can be read as a warning about the dangers of scientific advancement unrestrained by ethical considerations. In this reading, and in popular culture representations of the character as a “mad scientist”, Victor Frankenstein represents the callous, arrogant ambition of modern science. However, far from providing a stable image of the character, Shelley uses shifting narrative perspectives to gradually transform our impression of Frankenstein, portraying him in an increasingly negative light as the novel goes on. While he initially appears to be a naive but sympathetic idealist, after the creature’s narrative Frankenstein begins to resemble—even in his own telling—the thoughtlessly cruel figure the creature represents him as.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
Your essay introduction should include three main things, in this order:
- An opening hook to catch the reader’s attention.
- Relevant background information that the reader needs to know.
- A thesis statement that presents your main point or argument.
The length of each part depends on the length and complexity of your essay .
The “hook” is the first sentence of your essay introduction . It should lead the reader into your essay, giving a sense of why it’s interesting.
To write a good hook, avoid overly broad statements or long, dense sentences. Try to start with something clear, concise and catchy that will spark your reader’s curiosity.
A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your paper or essay . Everything else you write should relate to this key idea.
The thesis statement is essential in any academic essay or research paper for two main reasons:
- It gives your writing direction and focus.
- It gives the reader a concise summary of your main point.
Without a clear thesis statement, an essay can end up rambling and unfocused, leaving your reader unsure of exactly what you want to say.
The structure of an essay is divided into an introduction that presents your topic and thesis statement , a body containing your in-depth analysis and arguments, and a conclusion wrapping up your ideas.
The structure of the body is flexible, but you should always spend some time thinking about how you can organize your essay to best serve your ideas.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, July 23). How to Write an Essay Introduction | 4 Steps & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 1, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/introduction/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a thesis statement | 4 steps & examples, academic paragraph structure | step-by-step guide & examples, how to conclude an essay | interactive example, unlimited academic ai-proofreading.
✔ Document error-free in 5minutes ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
- How It Works
- Prices & Discounts
What is Signposting in an Essay (+ 43 Signposting Words)
Table of contents
Have you ever read any piece of academic work and come across phrases like “In this essay,” “this essay is about,” or “as we conclude?” These are signposting words or phrases, and we commonly use them in supporting points throughout an essay.
Essays need to have a logical flow and using signposting words can help you achieve that. They play an important role in keeping your readers focused on the point of discussion and the overall aim of the essay.
As a result, signposting in an essay is a technique you must have in your writing skillset . It is a surefire way to help readers understand your point or the connection between points, guide readers through your essay or remind them when you change direction and of key points.
In this article, we’ll dive deeper into what is signposting in an essay and also share 40 signposting words you can use.
Signposting in an Essay How It Works
Signposting gives your essays a certain flow and style that readers love. It shows how each point is connected, the link between paragraphs, what you are discussing, and where you are, so your readers can follow your essay with ease.
It involves using words and phrases that will require the reader much less concentration to understand your point.
Apart from helping the reader to easily follow your work, signposting in an essay makes your work enjoyable to read, as you will sound professional. Signposting the structure of your essay strengthens the presentation of your argument, especially when used in the introduction.
Here are six tips to keep in mind when using signposting words, to help you write an essay that stands out .
1. Address the main topic early on
You have only eight seconds to capture the reader’s attention. Besides, as little as 20% of readers read past the headline of an article or essay.
Your chances of having more people read past your essay headline lie in revealing to the reader where the text is heading early on.
Failure to do so, other things will distract them or they’ll begin to prejudice. As a result, don’t be afraid to tell readers what your essay is all about before you set off writing the meaty part of it.
For example, in your introduction, you can say, “this essay will discuss three factors affecting the gender pay gap...”.
2. Reiterate key points
As a writer, you can’t stop capturing your readers’ attention. You also need to keep them engaged and motivated to continue reading your essay.
You can achieve this by reminding your readers of where you are headed, key points, what you have covered, and what is coming. For example, you can use phrases like “the key point here is...” or “in other words...” or “I had already mentioned earlier that X == Y...”.
When you do so, it shows that the point matters and they need to take it into serious account. Another reason for reminding readers of the destination or key points is it brings them back to your essay just in case their minds wander away.
Consider also repeating complicated points—ones that are hard to comprehend because they may cause controversy or create unnecessary surprises.
Reminding readers of key points, destinations, and what you intend to write is a good orientation technique. So if you are talking about the same point, the reader will know from the repetition likewise, if you are talking about a different point.
3. Use paragraphs breaks and subheadings
Paragraph breaks and subheadings are also a form of signposting signals that keep readers focused on your essay by informing them when you are starting a new subsection or a new argument.
They are mostly ideal in longer essays such as research essays or after major headings like Methodology and Result which tend to get longer.
The trick around paragraph breaks is to use three to four paragraphs before starting another one. But we also know that some sentences will be shorter and others longer, so it is upon you to make the right judgment when using paragraph breaks or when splitting sentences.
Consider also using boldface to signal transition, while italics, underlining, and solid caps, keep the reader focused on your piece.
4. Use transitions well
Sometimes, a reader will easily understand how two sentences or paragraphs relate. Sometimes they won’t. If it is not obvious, make it obvious by adding transitions .
There are different transitions you can use to show different things. To illustrate a previous point, use “for example” or “for instance”.
To develop a point further, use “even more,” “in addition,” “furthermore,” or “similarly.” To contrast, a point, use “despite,” “however,” or “nevertheless.” This is just a snapshot. You can find more transitions in the next section of this text. Even so, cap the number of transitions you use to avoid boring the reader.
5. Write clear introductions and conclusions
Write clear introductions and conclusions . For instance, in the introduction, give the overall aim of the essay and share what will be discussed. In the body, signal what you intend to discuss and what is to come. Similarly, in conclusion, remind readers what you have discussed and whether you have answered the original question.
Essays tend to become complicated to read, and without a proper introduction and conclusion, your readers will lose interest.
It’s also a good idea to create an outline before you start drafting the essay. Outlines are like roadmaps. It gives your paper structure and guides you through the writing process.
6. Use signposting sparingly
The best way to communicate something to a reader more effectively and accurately is to use precise language and words. That is why it is prudent to carefully consider what words you are using and where in the text to place them. To avoid making your work look sloppy, avoid excessive signposting in an essay.
When you decide to link two paragraphs or two texts, think carefully about what words you would want to effectively convey your message. For example, if you choose a word like “in contrast,” ensure you want to add a strong alternative or challenge something. Do not use it if you want to add more weight to a previous point.
43 Signposting Words You Can Consider for your Essays
Having hinted at the importance of using signposting sparingly, we want to look at the common signposting words and phrases and where to use them to link your paragraphs or words so that your ideas have a logical connection and are easily understandable.
Here are the different ways you can use signposting, along with examples for inspiration.
A. To highlight a point
- Importantly
- More importantly
- Furthermore
- It is also important to highlight
B. Making a comparison
- In contrast
- On one hand
- On the other hand
- In comparison
- Another point to consider is
- Compared to
C. Summarizing
- In conclusion
- To summarize
- The (number) main points are
D. Giving an example
- For example
- This can be illustrated by
- For instance
E. Introducing a new perspective
- Illustrates
F. Adding a similar point
G. being more specific.
- In particular
- More specifically
- In relation to
- In terms of
- With respect to
In summary, we have discussed ways to make your writing or essay stronger, more easily understandable, and improve your writing as a whole through the use of signposting.
Order Now: High-Quality Essay, Written from Scratch
When your professors find your line of reasoning and links between ideas easy to follow and understandable, they will be more engaged. You can achieve this by using signposting sparingly, adding paragraph breaks and subheadings, repeating key points and phrases, and revealing the main point or argument at the start of your essay.
Wondering how to submit a well-structured essay that doesn’t bore your readers? Write to us at Writers Per Hour and we’ll get our professional writers on the job. From researching and outlining to drafting the easy and revising it, you’re sure to receive A-grade essays.
Share this article
Achieve Academic Success with Expert Assistance!
Crafted from Scratch for You.
Ensuring Your Work’s Originality.
Transform Your Draft into Excellence.
Perfecting Your Paper’s Grammar, Style, and Format (APA, MLA, etc.).
Calculate the cost of your paper
Get ideas for your essay
- Current Students
- News & Press
- Exam Technique for In-Person Exams
- Revising for 24 Hour Take Home Exams
- Introduction to 24 Hour Take Home Exams
- Before the 24 Hour Take Home Exam
- Exam Technique for 24 Hour Take Home Exams
- Structuring a Literature Review
- Writing Coursework under Time Constraints
- Reflective Writing
- Writing a Synopsis
- Structuring a Science Report
- Presentations
- How the University works out your degree award
- Personal Extenuating Circumstances (PEC)
- Accessing your assignment feedback via Canvas
- Inspera Digital Exams
- Writing Introductions and Conclusions
Paragraphing
- Reporting Verbs
Signposting
- Proofreading
- Working with a Proofreader
- Writing Concisely
- The 1-Hour Writing Challenge
- Apostrophes
- Semi-colons
- Run-on sentences
- How to Improve your Grammar (native English)
- How to Improve your Grammar (non-native English)
- Independent Learning for Online Study
- Reflective Practice
- Academic Reading
- Strategic Reading Framework
- Note-taking Strategies
- Note-taking in Lectures
- Making Notes from Reading
- Using Evidence to Support your Argument
- Integrating Scholarship
- Managing Time and Motivation
- Dealing with Procrastination
- How to Paraphrase
- Quote or Paraphrase?
- How to Quote
- Referencing
- Artificial Intelligence and Academic Integrity
- Use and limitations of generative AI
- Acknowledging use of AI
- Numeracy, Maths & Statistics
- Library Search
- Search Techniques
- Keeping up to date
- Evaluating Information
- Managing Information
- Thinking Critically about AI
- Using Information generated by AI
- Digital Capabilities
- SensusAccess
- Develop Your Digital Skills
- Digital Tools to Help You Study

Explore different ways of guiding the reader through your assignment.
- Newcastle University
- Academic Skills Kit
- Academic Writing
Signposting language can help you guide the reader through your writing and make sure the order is clear and flows well. These are small words or phrases that help the reader follow your argument, understand the relationship between your ideas and anticipate what’s going to come next.
These words may not seem important, but they’re really the glue that holds a piece of writing together. Without signposting language, writing can lose direction, become confused and read like a series of unrelated points. Try reading the paragraph without them and see how it changes the meaning.
Signposting words are useful in the introduction to signal your structure, and echoed in the first lines of paragraphs to indicate how the paragraphs relate to each other. They are also useful at sentence level to make the links between them clear. There are different kinds of links and relationships, so you need to choose a signposting word that does the right job.
Signposting of order
You can use these kinds of signposting words to direct the reader through your writing, provide a ‘roadmap’ for the order in which you’re going to talk about things, help them keep on track throughout and remind them of key information or anticipate questions. This kind of signposting can be especially useful for introductions, conclusions and when transitioning from one big idea to another or talking about methods and procedures.
Informs readers of the writing’s overall structure.
- First/Firstly,…
- To begin with…
- Second/Secondly,…
- Afterwards,…
- Following this…
- To conclude,…
Helps readers anticipate content that’ll appear later in the writing.
- In the following section…
- As we shall see,…
- As explored below,…
- As will be explained later,…
Reminds readers of important information mentioned earlier.
- In the previous section,…
- As we have seen,…
- As demonstrated above,…
- As indicated earlier,…
- As discussed previously,…
- Prior to this,…
- Initially,…
Helps readers identify where they are in the writing’s overall structure.
- Turning now to…
- Moving on to…
- Having considered…we will now consider…
- It is now necessary to…
- This section identifies…
Signposting of relations
You can use these kinds of signposting words to show that you are constructing logical steps in your argument, show the relationship between ideas and make it clear to the reader where you’re identifying similarities and differences, cause and effect, summaries, examples or particularly important pieces of information.
Tells the reader that this point builds on the previous.
- As well as,…
- In addition…
- Additionally,…
- What is more…
- To elaborate,…
Tells the reader that this point is a further example of the previous.
- Similarly,…
- Just as…, so too…
- In the same way,…
- Correspondingly,…
- Complementary to this…
Prepares the reader for an example.
- For example,…
- For instance,…
- To illustrate,…
- In particular,
- …including…
- …as can be seen in…
- …as demonstrated by…
- …exemplifies…
Tells the reader that this point is in opposition to the previous.
- In contrast,…
- In comparison,…
- Conversely,…
- On the other hand,…
- Otherwise,…
- Alternatively,…
- Despite this,…
- Nonetheless,…
- Nevertheless,…
- That aside,…
- While this may be true…
- Notwithstanding…
- Then again,…
- On the contrary,…
Tells the reader that this point is a result of the previous.
- Therefore,…
- Consequently,…
- Accordingly,…
- As a result,…
- This means that…
- This causes…
- For this reason…
- Because of this…
- In view of this,…
- With this in mind…
- It can be seen that…
- Resulting from this…
- This suggests that…
- Subsequently,…
Prepares the reader for a summary of previous points.
- In summary,…
- Altogether,…
- On the whole,…
- To review,…
Provides the reader with another way of saying the same thing.
- In other words,…
- Better still,…
- Stated otherwise,…
- That is to say,…
- Put simply...
- To look at this another way....
Helps the reader identify key information.
- In particular,…
- Especially…
- Importantly,…
- Furthermore,…
Tips for using signposting language
Choose wisely.
Signposting words aren’t interchangeable and can be really confusing for the reader if used inappropriately. So make sure you choose the right word to reflect the relationship you’re trying to communicate.
Use deliberately
You don’t need to use a signposting word in every sentence, so before you do ask yourself if it helps make the meaning clearer, or just bogs down the writing.
Edit carefully
When you want to get the wordcount down, you might be tempted to get rid of signposting words first so you can keep more of the information. This might not be as useful as it seems, though, because lots of information without any signposting can make it really difficult for the reader to understand what you’re trying to say.
Download this guide as a PDF
Explore different ways of guiding the reader through your assignment. **PDF Download**

More in this section
Find out how to structure an academic paragraph.
Reporting verbs
Explore different ways of referring to literature and foregrounding your voice.
Effective Signposting
Signposts are words or phrases that help articulate the structure of a piece of writing and ensure that readers don’t get lost. Signposting will flag the most important parts of an argument, signal transitions, and clarify the stakes of an argument.
Here are some examples of helpful signposts:
“This essay examines biblical symbolism in Moby-Dick . . . ” This signpost states the focus of the essay .
“After a review of recent scholarship on biblical symbolism, I consider how Melville relates funerary symbolism to both death and rebirth . . . ” This signpost clarifies how the author’s focus is distinguished from previous scholarship .
“My purpose in focusing on Queequeg’s coffin . . . ” This signpost clarifies the stakes of the author’s argument .
Single words and short phrases can be useful signposts, such as additionally , consequently , however , also , in contrast . But make sure to use these words correctly. However should be used to pivot to an opposing idea or to acknowledge another side of an argument, and consequently indicates that an idea is a result or consequence of a previously discussed idea or point. Signposts that identify the sequence or direction of your argument can also be effective: for example, first , next , then , finally ; or first , second , third , and so on.
Using signposts can improve your writing by giving it structure and direction, but excessive signposting creates unnecessary wordiness and can give the impression that you don’t trust the reader’s ability to follow your argument or that you’re grafting signposts on to compensate for a poorly articulated argument. Here are some signposts that may do more harm than good:
“ It’s important to note that Melville’s treatment . . . ” Show, don’t tell, what is important.
“ What I want to call attention to in this passage . . . ” Skip the wordy opening; lead with “In this passage . . . ”
“ I will now turn to the pulpit of Father Mapple . . . ” If you’ve signposted your essay’s structure at its beginning, you don’t have to give directions throughout .
“ As I argued in the previous section, the symbolism of the white whale . . . ” If the point has been well made, your reader will remember it. Summarize it briefly, but you don’t need to mention the earlier section .
Early drafts of an essay are likely to include some extra signposting, because you may be developing and revising the essay’s structure as you write. For this reason, it’s a good idea to read the final draft of a piece of writing with an eye toward its transitions and signposts, to make sure that they support and clarify your argument. At this stage of revision, you can eliminate any wordy or excessive signposts.
Frank Nzewi 07 October 2021 AT 10:10 AM
This topic is useful to me, because it clarifies the use of signposting.
Your e-mail address will not be published
Join the Conversation
We invite you to comment on this post and exchange ideas with other site visitors. Comments are moderated and subject to terms of service.
If you have a question for the MLA's editors, submit it to Ask the MLA!
Writing academically: Signposting
- Academic style
- Personal pronouns
- Contractions
- Abbreviations
- Signposting
- Paragraph structure
- Using sources in your writing
Jump to content on this page:
“Do not expect your reader to make the connections in your ideas ... make those connections explicit” Andy Gillet, Angela Hammond and Mary Martala, Successful Academic Writing
Signposting words and phrases are essential elements of academic writing - they make your writing flow. By making explicit how points are connected to each other you make it easier for your reader to follow your arguments . The reader is, after all, your marker and you don't want to make their job too hard. This page gives you a selection of common phrases that you can use to link together your paragraphs and so make logical connections between your ideas.

Signposts to introduce something new
One aspect which illustrates … can be identified as …
The current debate about … illustrates/identifies/highlights …
With regard to…/ with respect to…
Initially/secondly/finally, …

Continuing an argument with a related point
Furthermore, …
To further understand the role of …
In addition, …
Similarly, …
Likewise, …
What is more, …
Moreover, …
Another issue regarding … is …
Another line of thought on … is …

Going into more detail on a point/rephrasing
In particular, …
Specifically, …
Concentrating on …
By focusing on … in more detail, it is possible to …
To be more precise, …
In other words, …
To put simply … /To simplify, ...

Linking to a different point
Having established …, it is possible to consider …
… is one key issue; another of equal/ similar importance/significance is …
Also of importance is the issue of …

Reintroducing a topic
As discussed/explained earlier, …
The earlier discussion on … can be developed further here, …
As stated previously, …
As noted above, …

Introducing an opposing/alternative view
However, …
Conversely, …
In contrast, …
Alternatively, …
Nevertheless/Nonetheless, …
An alternative perspective is given by … who suggests/argues that …
Despite this, …
This conflicts with the view held by …

Reasoning/summarising the point
Consequently/As a consequence, …
Accordingly, …
Therefore, …
What this means/suggests is...
It could be concluded that …
The strength of such an approach is that …
For this reason …
Evidently*, …
Clearly/It is clear that, …*
Naturally*, …
It is clear that* …
In short, …
From this, it can be concluded/inferred/suggested that …
The evidence highlights that …
------ *Only use such phrases if you really are sure that your arguments cannot be challenged.
These are just a selection of the phrases you can you to make your writing flow and to keep the reader with you and following your line of argument. Academics often complain about a lack of this in assignments they mark so make sure you use them in your writing.
Don't overdo it . Only use signposts when they add clarity to your work. Some students try to put a signposting word into every sentence which can actually obscure meaning.
Be precise . The signposting words have very specific meanings. Only use a word like 'consequently' if you really mean that the following sentence is a true consequence of the previous one!
- << Previous: Abbreviations
- Next: Paragraph structure >>
- Last Updated: Nov 10, 2023 4:11 PM
- URL: https://libguides.hull.ac.uk/writing
- Login to LibApps
- Library websites Privacy Policy
- University of Hull privacy policy & cookies
- Website terms and conditions
- Accessibility
- Report a problem
NCI LIBRARY
Academic writing skills guide: signposting, transitions & linking words/phrases.
- Key Features of Academic Writing
- The Writing Process
- Understanding Assignments
- Brainstorming Techniques
- Planning Your Assignments
- Thesis Statements
- Writing Drafts
- Structuring Your Assignment
- How to Deal With Writer's Block
- Using Paragraphs
- Conclusions
- Introductions
- Revising & Editing
- Proofreading
- Grammar & Punctuation
- Reporting Verbs
- Signposting, Transitions & Linking Words/Phrases
- Using Lecturers' Feedback

Communications from the Library: Please note all communications from the library, concerning renewal of books, overdue books and reservations will be sent to your NCI student email account.
- << Previous: Reporting Verbs
- Next: Using Lecturers' Feedback >>
- Last Updated: Dec 15, 2023 10:00 AM
- URL: https://libguides.ncirl.ie/academic_writing_skills
How to Write an Essay Introduction (with Examples)

The introduction of an essay plays a critical role in engaging the reader and providing contextual information about the topic. It sets the stage for the rest of the essay, establishes the tone and style, and motivates the reader to continue reading.
Table of Contents
What is an essay introduction , what to include in an essay introduction, how to create an essay structure , step-by-step process for writing an essay introduction , how to write an introduction paragraph , how to write a hook for your essay , how to include background information , how to write a thesis statement .
- Argumentative Essay Introduction Example:
- Expository Essay Introduction Example
Literary Analysis Essay Introduction Example
Check and revise – checklist for essay introduction , key takeaways , frequently asked questions .
An introduction is the opening section of an essay, paper, or other written work. It introduces the topic and provides background information, context, and an overview of what the reader can expect from the rest of the work. 1 The key is to be concise and to the point, providing enough information to engage the reader without delving into excessive detail.
The essay introduction is crucial as it sets the tone for the entire piece and provides the reader with a roadmap of what to expect. Here are key elements to include in your essay introduction:
- Hook : Start with an attention-grabbing statement or question to engage the reader. This could be a surprising fact, a relevant quote, or a compelling anecdote.
- Background information : Provide context and background information to help the reader understand the topic. This can include historical information, definitions of key terms, or an overview of the current state of affairs related to your topic.
- Thesis statement : Clearly state your main argument or position on the topic. Your thesis should be concise and specific, providing a clear direction for your essay.
Before we get into how to write an essay introduction, we need to know how it is structured. The structure of an essay is crucial for organizing your thoughts and presenting them clearly and logically. It is divided as follows: 2
- Introduction: The introduction should grab the reader’s attention with a hook, provide context, and include a thesis statement that presents the main argument or purpose of the essay.
- Body: The body should consist of focused paragraphs that support your thesis statement using evidence and analysis. Each paragraph should concentrate on a single central idea or argument and provide evidence, examples, or analysis to back it up.
- Conclusion: The conclusion should summarize the main points and restate the thesis differently. End with a final statement that leaves a lasting impression on the reader. Avoid new information or arguments.

Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to write an essay introduction:
- Start with a Hook : Begin your introduction paragraph with an attention-grabbing statement, question, quote, or anecdote related to your topic. The hook should pique the reader’s interest and encourage them to continue reading.
- Provide Background Information : This helps the reader understand the relevance and importance of the topic.
- State Your Thesis Statement : The last sentence is the main argument or point of your essay. It should be clear, concise, and directly address the topic of your essay.
- Preview the Main Points : This gives the reader an idea of what to expect and how you will support your thesis.
- Keep it Concise and Clear : Avoid going into too much detail or including information not directly relevant to your topic.
- Revise : Revise your introduction after you’ve written the rest of your essay to ensure it aligns with your final argument.
Here’s an example of an essay introduction paragraph about the importance of education:
Education is often viewed as a fundamental human right and a key social and economic development driver. As Nelson Mandela once famously said, “Education is the most powerful weapon which you can use to change the world.” It is the key to unlocking a wide range of opportunities and benefits for individuals, societies, and nations. In today’s constantly evolving world, education has become even more critical. It has expanded beyond traditional classroom learning to include digital and remote learning, making education more accessible and convenient. This essay will delve into the importance of education in empowering individuals to achieve their dreams, improving societies by promoting social justice and equality, and driving economic growth by developing a skilled workforce and promoting innovation.
This introduction paragraph example includes a hook (the quote by Nelson Mandela), provides some background information on education, and states the thesis statement (the importance of education).
This is one of the key steps in how to write an essay introduction. Crafting a compelling hook is vital because it sets the tone for your entire essay and determines whether your readers will stay interested. A good hook draws the reader in and sets the stage for the rest of your essay.
- Avoid Dry Fact : Instead of simply stating a bland fact, try to make it engaging and relevant to your topic. For example, if you’re writing about the benefits of exercise, you could start with a startling statistic like, “Did you know that regular exercise can increase your lifespan by up to seven years?”
- Avoid Using a Dictionary Definition : While definitions can be informative, they’re not always the most captivating way to start an essay. Instead, try to use a quote, anecdote, or provocative question to pique the reader’s interest. For instance, if you’re writing about freedom, you could begin with a quote from a famous freedom fighter or philosopher.
- Do Not Just State a Fact That the Reader Already Knows : This ties back to the first point—your hook should surprise or intrigue the reader. For Here’s an introduction paragraph example, if you’re writing about climate change, you could start with a thought-provoking statement like, “Despite overwhelming evidence, many people still refuse to believe in the reality of climate change.”
Including background information in the introduction section of your essay is important to provide context and establish the relevance of your topic. When writing the background information, you can follow these steps:
- Start with a General Statement: Begin with a general statement about the topic and gradually narrow it down to your specific focus. For example, when discussing the impact of social media, you can begin by making a broad statement about social media and its widespread use in today’s society, as follows: “Social media has become an integral part of modern life, with billions of users worldwide.”
- Define Key Terms : Define any key terms or concepts that may be unfamiliar to your readers but are essential for understanding your argument.
- Provide Relevant Statistics: Use statistics or facts to highlight the significance of the issue you’re discussing. For instance, “According to a report by Statista, the number of social media users is expected to reach 4.41 billion by 2025.”
- Discuss the Evolution: Mention previous research or studies that have been conducted on the topic, especially those that are relevant to your argument. Mention key milestones or developments that have shaped its current impact. You can also outline some of the major effects of social media. For example, you can briefly describe how social media has evolved, including positives such as increased connectivity and issues like cyberbullying and privacy concerns.
- Transition to Your Thesis: Use the background information to lead into your thesis statement, which should clearly state the main argument or purpose of your essay. For example, “Given its pervasive influence, it is crucial to examine the impact of social media on mental health.”

A thesis statement is a concise summary of the main point or claim of an essay, research paper, or other type of academic writing. It appears near the end of the introduction. Here’s how to write a thesis statement:
- Identify the topic: Start by identifying the topic of your essay. For example, if your essay is about the importance of exercise for overall health, your topic is “exercise.”
- State your position: Next, state your position or claim about the topic. This is the main argument or point you want to make. For example, if you believe that regular exercise is crucial for maintaining good health, your position could be: “Regular exercise is essential for maintaining good health.”
- Support your position: Provide a brief overview of the reasons or evidence that support your position. These will be the main points of your essay. For example, if you’re writing an essay about the importance of exercise, you could mention the physical health benefits, mental health benefits, and the role of exercise in disease prevention.
- Make it specific: Ensure your thesis statement clearly states what you will discuss in your essay. For example, instead of saying, “Exercise is good for you,” you could say, “Regular exercise, including cardiovascular and strength training, can improve overall health and reduce the risk of chronic diseases.”
Examples of essay introduction
Here are examples of essay introductions for different types of essays:
Argumentative Essay Introduction Example:
Topic: Should the voting age be lowered to 16?
“The question of whether the voting age should be lowered to 16 has sparked nationwide debate. While some argue that 16-year-olds lack the requisite maturity and knowledge to make informed decisions, others argue that doing so would imbue young people with agency and give them a voice in shaping their future.”
Expository Essay Introduction Example
Topic: The benefits of regular exercise
“In today’s fast-paced world, the importance of regular exercise cannot be overstated. From improving physical health to boosting mental well-being, the benefits of exercise are numerous and far-reaching. This essay will examine the various advantages of regular exercise and provide tips on incorporating it into your daily routine.”
Text: “To Kill a Mockingbird” by Harper Lee
“Harper Lee’s novel, ‘To Kill a Mockingbird,’ is a timeless classic that explores themes of racism, injustice, and morality in the American South. Through the eyes of young Scout Finch, the reader is taken on a journey that challenges societal norms and forces characters to confront their prejudices. This essay will analyze the novel’s use of symbolism, character development, and narrative structure to uncover its deeper meaning and relevance to contemporary society.”
- Engaging and Relevant First Sentence : The opening sentence captures the reader’s attention and relates directly to the topic.
- Background Information : Enough background information is introduced to provide context for the thesis statement.
- Definition of Important Terms : Key terms or concepts that might be unfamiliar to the audience or are central to the argument are defined.
- Clear Thesis Statement : The thesis statement presents the main point or argument of the essay.
- Relevance to Main Body : Everything in the introduction directly relates to and sets up the discussion in the main body of the essay.

Writing a strong introduction is crucial for setting the tone and context of your essay. Here are the key takeaways for how to write essay introduction: 3
- Hook the Reader : Start with an engaging hook to grab the reader’s attention. This could be a compelling question, a surprising fact, a relevant quote, or an anecdote.
- Provide Background : Give a brief overview of the topic, setting the context and stage for the discussion.
- Thesis Statement : State your thesis, which is the main argument or point of your essay. It should be concise, clear, and specific.
- Preview the Structure : Outline the main points or arguments to help the reader understand the organization of your essay.
- Keep it Concise : Avoid including unnecessary details or information not directly related to your thesis.
- Revise and Edit : Revise your introduction to ensure clarity, coherence, and relevance. Check for grammar and spelling errors.
- Seek Feedback : Get feedback from peers or instructors to improve your introduction further.
The purpose of an essay introduction is to give an overview of the topic, context, and main ideas of the essay. It is meant to engage the reader, establish the tone for the rest of the essay, and introduce the thesis statement or central argument.
An essay introduction typically ranges from 5-10% of the total word count. For example, in a 1,000-word essay, the introduction would be roughly 50-100 words. However, the length can vary depending on the complexity of the topic and the overall length of the essay.
An essay introduction is critical in engaging the reader and providing contextual information about the topic. To ensure its effectiveness, consider incorporating these key elements: a compelling hook, background information, a clear thesis statement, an outline of the essay’s scope, a smooth transition to the body, and optional signposting sentences.
The process of writing an essay introduction is not necessarily straightforward, but there are several strategies that can be employed to achieve this end. When experiencing difficulty initiating the process, consider the following techniques: begin with an anecdote, a quotation, an image, a question, or a startling fact to pique the reader’s interest. It may also be helpful to consider the five W’s of journalism: who, what, when, where, why, and how. For instance, an anecdotal opening could be structured as follows: “As I ascended the stage, momentarily blinded by the intense lights, I could sense the weight of a hundred eyes upon me, anticipating my next move. The topic of discussion was climate change, a subject I was passionate about, and it was my first public speaking event. Little did I know , that pivotal moment would not only alter my perspective but also chart my life’s course.”
Crafting a compelling thesis statement for your introduction paragraph is crucial to grab your reader’s attention. To achieve this, avoid using overused phrases such as “In this paper, I will write about” or “I will focus on” as they lack originality. Instead, strive to engage your reader by substantiating your stance or proposition with a “so what” clause. While writing your thesis statement, aim to be precise, succinct, and clear in conveying your main argument.
To create an effective essay introduction, ensure it is clear, engaging, relevant, and contains a concise thesis statement. It should transition smoothly into the essay and be long enough to cover necessary points but not become overwhelming. Seek feedback from peers or instructors to assess its effectiveness.
References
- Cui, L. (2022). Unit 6 Essay Introduction. Building Academic Writing Skills .
- West, H., Malcolm, G., Keywood, S., & Hill, J. (2019). Writing a successful essay. Journal of Geography in Higher Education , 43 (4), 609-617.
- Beavers, M. E., Thoune, D. L., & McBeth, M. (2023). Bibliographic Essay: Reading, Researching, Teaching, and Writing with Hooks: A Queer Literacy Sponsorship. College English, 85(3), 230-242.
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- What is an Argumentative Essay? How to Write It (With Examples)
- How to Paraphrase Research Papers Effectively
- How to Cite Social Media Sources in Academic Writing?
- How Long Should a Chapter Be?
Similarity Checks: The Author’s Guide to Plagiarism and Responsible Writing
Types of plagiarism and 6 tips to avoid it in your writing , you may also like, word choice problems: how to use the right..., how to avoid plagiarism when using generative ai..., what are journal guidelines on using generative ai..., types of plagiarism and 6 tips to avoid..., similarity checks: the author’s guide to plagiarism and..., what is a master’s thesis: a guide for..., should you use ai tools like chatgpt for..., what are the benefits of generative ai for..., how to avoid plagiarism tips and advice for..., plagiarism checkers vs. ai content detection: navigating the....

Signposting in essays: A short guide
- When should you signpost?
Using signposts precisely
Retrospective signposts, examples of signposting phrases.
- Conclusion and further reading
It can make your work seem sloppy if you use signposting words in the wrong contexts. Avoid the temptation to dot signposting words throughout your text at random. Think carefully about the link between two paragraphs or phrases, and choose a word that effectively conveys that link. For example, 'however' should indicate that you are adding something to the previous point. Another example is 'consequently' - do not use it if the idea that follows is not truly a consequence of the previous one.
Remember: precise and concise language helps you to communicate accurately and effectively with you reader.
You can signpost your reader back to things you have already covered, as a reminder and summary to the reader. This should happen at the end of paragraphs, to highlight the point that you have made and its relevance to your essay question. You should also use retrospective signposting in your conclusion.
Example:
In order to understand the causes of the London Riots, it would be useful to apply sociological theories...
How it aids the reader:
The reader realises in advance that the writer is going to be using some theories to explore the causes of the London Riots.
Another aspect of Hardy's portrayal of Tess is...
This reminds the reader that at least one aspect has already been discussed, and another is about to be revealed.
- << Previous: When should you signpost?
- Next: Conclusion and further reading >>
- Last Updated: Nov 24, 2023 9:50 AM
- URL: https://libguides.bham.ac.uk/asc/essaysignposting
What Is Signposting in English and Why Does It Matter?
Published on, july 1, 2022, november 15, 2022, this article may contain affiliate links.
Signposting is a simple and easy-to-learn technique that can improve your listening, writing and even presentation skills. In fact, once you know this technique, you will see it everywhere! Let us explain it to you with this step-by-step guide.

Table of contents
A presentation is very similar to a school essay, if you think about it. Both have an introduction. Both have a conclusion. Both have a certain number of main points. An essay is a structured way of writing. A presentation is a structured way of speaking.
But when you read an essay, you know exactly where you are - you can look at the page and see if you are near the beginning of the essay or near the end. You can see which main point you’re reading, by glancing at the paragraphs.
What about when listening to a presentation? Do you know “where” you are? With a good presenter, the answer is yes! Because a good presenter uses a technique called signposting.
So what exactly is signposting?
Just like a signpost by the road that tells you where you are going, signposting in a presentation tells the listener what is coming next.
Here is an example:
Now that we have looked at the causes of work-related stress, let’s examine the solutions.
The first solution that I would like to highlight is…
The language used here clearly signals that the speaker is moving on from talking about the causes of stress to talking about the solutions.
When we use language like this, the structure of our presentation is clear and transparent to everyone listening. Remember, listeners like to know “where” they are in a presentation.
At the sentence level, we can use signposting language to show what we are about to say. Here’s an example:
The best thing about Steve is that he is a trustworthy friend.
The simple signposting phrase in bold tells the listener what to expect next in the sentence. It may seem like a trivial thing, but this style of communication greatly improves understanding.
Signposting can help you with your listening
So far, we have looked at signposting from the speaker’s point of view. However, signposting is also something that can help you with your listening.
Imagine that you hear this sentence:
George is a conscientious guy.
Let’s assume that conscientious is a word that you don’t know. Is the speaker saying something good about George or something bad? Did they say ‘conscientious' or ‘contentious’?
As a listener, you’ll still be puzzling over the word ‘conscientious’ as the speaker continues, and you will lose the flow of the conversation.
But, in fact, we usually speak like this:
What I like about George is that he is a conscientious guy.
Now that we can recognise the signpost (in bold), we can at least understand that being conscientious is a positive trait (it describes a person who likes to do the correct thing) and we know that the speaker didn’t say ‘contentious’ (argumentative). We can move on with the rest of the conversation.
If you are attending a lecture or a talk, listening for signposting language will help you structure your notes. As soon as you hear, “I’m going to mention three methods to lose weight…”, you can prepare a space to write method one, method two and method three.
You should especially listen out for cues that the speaker is moving on to a new topic, giving an example or ending the talk.
You need to listen for phrases like these:
- My next point is…
- The next main point is…
- The next thing I wish to highlight is…
- Now that we have discussed…, let’s move on to…
- For example…
- For instance…
- Here’s an example…
- To conclude…
- In conclusion…
- To conclude this talk, I would like to…
Signposting can help you with your writing
The main difference between writing and speaking is structure. When speaking, you simply say the first thing that comes to mind. But when writing, you take time to plan out what to say. You plan the order of your paragraphs and you plan the structure of your paragraphs (or at least, you should!).
However, simply planning out your structure is not enough. You need to make an effort to show the structure to the reader. We do this through signposting.
Imagine that you need to write a short essay or an article comparing large and small companies. The first paragraph might look like this:
Have you ever wondered whether it is best to work at a small or large company? This essay examines the advantages and disadvantages of both in order to help you make that decision.
Here are excerpts from the following paragraphs:
The benefits of working in a large company are … For example … On the other hand, large companies can be … An example is … A small company is good for … For instance … However, many small companies … A good example is … In conclusion …
Can you see how the signposting phrases make the structure clear to the reader? We can already see that the article will be easy to understand, no matter what the points are.
In the modern world, a large number of people skim and scan articles to get information quickly. The use of signposting makes it especially easy to do this.
Hence, if you use signposting, the speed readers of the world will thank you for it!
Signposting can help you with presentations
Remember how I said that a presentation is similar to an essay?
Look again at the signposting phrases that I suggested for an essay:
These same signposting phrases can be used in a presentation, too!
But let’s look at the introduction to a presentation. This is the part of a presentation where you lay out the structure of what is to come . Again, signposting phrases can help you do this.
Take a look at this introduction to a presentation on mental health issues at the workplace:
Have you ever felt stressed, neglected, alone or overwhelmed at the workplace? For some of us, these negative emotions can develop into serious mental health issues. As a workplace psychologist, I see this every day.
In my talk today, I’m going to discuss five different mental health issues. After that, I will walk you through ways to deal with each one. I will end my talk with a Q&A session where I’ll be glad to field any questions you may have.
After this simple introduction, the audience knows exactly what to expect. They will hear about five issues, followed by five solutions. They also know to expect a Q&A session. They’re now ready to begin the talk.
Signposting can help you in day-to-day communication
Casual, day-to-day conversation is not structured, like an essay or a presentation. Nevertheless, simple signposting at the sentence level can help us in daily communication.
Paula: Do you think this hat looks nice on me? Pablo: I don’t want to sound rude, but it looks quite silly.
Can you see what Pablo is doing here? He is afraid that he might upset Paula, so he leads in with a signposting phrase. This alerts Paula that he is going to say something sensitive and he wants her not to be upset. It also softens the harsh comment; we generally soften comments by saying them indirectly.
Here is a second example:
Pierre: There’s something I’ve been meaning to talk to you about. Pietro: Oh no! Am I in trouble? Pierre: Not exactly, but I have been receiving complaints from your coworkers…
Notice how Pierre doesn’t mention complaints at the beginning of the conversation. Instead, he uses the signposting phrase in bold.This phrase indicates that the topic of discussion will be serious, and that is why Pietro wonders if he is in trouble.
Pierre uses this technique to set the tone and expectations for the conversation.
Note how the two examples shown here are quite subtle . Understanding subtle and indirect meanings is an advanced language skill. This means that it is something you should look out for as you move up from intermediate to advanced level English.
My advice is to listen out for more examples of this kind of signposting, and write them down in your notebook when you hear them. Your ultimate goal is to use them yourself.
Signposting can help you with the IELTS test
The concept of signposting is used throughout IELTS exams .
IELTS listening passages are carefully scripted to include signposts to help you. In IELTS reading, the signposting phrases help give context when you need to guess the meaning of a word or phrase.
You will also be expected to use signposting language when you write and speak, and the examiner will look for examples. If you use signposting language correctly, you will score marks for ‘coherence and cohesion’ (the logical flow and connection of your writing/speaking).
In the writing section of the IELTS, coherence and cohesion provide 25% of the total marks.
If you are able to use signposting phrases, but do not always use them correctly, that indicates a band 6 score. At band 7, signposting phrases are used correctly and appropriately. At band 8+, use of signposting approaches the skill level of a native speaker.
Some examples of signposting
Here is a list of example signposting language to get you started. Remember, there are many more than we can list here.
Introducing a topic
- The topic of today’s talk is…
- Today, I would like to discuss…
- What I wish to talk about today is…
Developing a point
- Additionally…
- Furthermore…
Contrasting…
- Nevertheless…
- Even though…
Emphasising a point
- The important thing is…
- It is important to note that…
- The vital thing to understand about this is…
- To summarise what we have discussed…
- In conclusion, what I would like to say is…
Embrace signposting as a major feature of English
Perhaps you had never heard of signposting before reading this article.
If so, then I hope this article has opened the door to a major feature of the English language. The more you know about signposting, the more you will see and hear it everywhere.
You might also like
🌍 announcing…translations in 12 languages.
![signposting in essay introduction 10 Activities to Improve Your English Vocabulary [Self-Study Guide #6]](https://assets-global.website-files.com/5d70d85d6d5a384776dc97e4/636d1bfeca23fd0e93ef3ec0_Best%20English%20Vocabulary%20Activities.png)
10 Activities to Improve Your English Vocabulary [Self-Study Guide #6]

Synonym Practice | How Smart English Learners Improve Their Vocabulary
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
How to Write an Excellent Essay Introduction

3-minute read
- 27th September 2022
Love it or hate it, essay writing is a big part of student life. Writing a great essay might seem like a daunting task, especially when you’re staring at a blank document, but there are formulas you can follow to make sure your paper hits the mark.
When you plan your essays , don’t neglect your introduction! It might seem like a trivial part of the paper, but it can make it or break it. A badly written introduction can leave your reader feeling confused about the topic and what to expect from your essay.
To help your writing reach its full potential, we’ve put together a guide to writing an excellent essay introduction.
How to Write an Essay Introduction
An essay introduction has four main steps:
● Hook your reader
● Provide context
● Present your thesis statement
● Map your essay
Hook Your Reader
The first part of your introduction should be the hook. This is where you introduce the reader to the topic of the essay. A great hook should be clear, concise, and catchy. It doesn’t need to be long; a hook can be just one sentence.
Provide Context
In this section, introduce your reader to key definitions, ideas, and background information to help them understand your argument.
Present Your Thesis Statement
A thesis statement tells the reader the main point or argument of the essay. This can be just one sentence, or it can be a few sentences.
Map Your Essay
Before you wrap up your essay introduction, map it! This means signposting sections of your essay. The key here is to be concise. The purpose of this part of the introduction is to give your reader a sense of direction.
Here’s an example of an essay introduction:
Hook: Suspense is key for dramatic stories, and Shakespeare is well-known and celebrated for writing suspenseful plays.
Context: While there are many ways in which Shakespeare created suspension for his viewers, two techniques he used effectively were foreshadowing and dramatic irony. Foreshadowing is a literary device that hints at an event or situation that is yet to happen. Dramatic irony is a literary technique, originally used in Greek tragedy, by which the full significance of a character’s words or actions is clear to the audience or reader, although it is unknown to the character.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
Thesis statement: Foreshadowing and dramatic irony are two powerful techniques that Shakespeare used to create suspense in literature. These methods have been used to keep the reader intrigued, excited, or nervous about what is to come in many of his celebrated works.
Essay mapping: In this essay, I will be detailing how Shakespeare uses foreshadowing and dramatic irony to create suspense, with examples from Romeo and Juliet and Othello.
Pro tip: Essays take twists and turns. We recommend changing your introduction as necessary while you write the main text to make sure it fully aligns with your final draft.
Proofread and Editing
Proofreading is an essential part of delivering a great essay. We offer a proofreading and editing service for students and academics that will provide you with expert editors to check your work for any issues with:
● Grammar
● Spelling
● Formatting
● Tone
● Audience
● Consistency
● Accuracy
● Clarity
Want 500 words of your work proofread completely free of charge?
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
4-minute read
The Benefits of Using an Online Proofreading Service
Proofreading is important to ensure your writing is clear and concise for your readers. Whether...
2-minute read
6 Online AI Presentation Maker Tools
Creating presentations can be time-consuming and frustrating. Trying to construct a visually appealing and informative...
What Is Market Research?
No matter your industry, conducting market research helps you keep up to date with shifting...
8 Press Release Distribution Services for Your Business
In a world where you need to stand out, press releases are key to being...
How to Get a Patent
In the United States, the US Patent and Trademarks Office issues patents. In the United...
The 5 Best Ecommerce Website Design Tools
A visually appealing and user-friendly website is essential for success in today’s competitive ecommerce landscape....

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
Welcome Guest!
- IELTS Listening
- IELTS Reading
- IELTS Writing
- IELTS Writing Task 1
- IELTS Writing Task 2
- IELTS Speaking
- IELTS Speaking Part 1
- IELTS Speaking Part 2
- IELTS Speaking Part 3
- IELTS Practice Tests
- IELTS Listening Practice Tests
- IELTS Reading Practice Tests
- IELTS Writing Practice Tests
- IELTS Speaking Practice Tests
- All Courses
- IELTS Online Classes
- OET Online Classes
- PTE Online Classes
- CELPIP Online Classes
- Free Live Classes
- Australia PR
- Germany Job Seeker Visa
- Austria Job Seeker Visa
- Sweden Job Seeker Visa
- Study Abroad
- Student Testimonials
- Our Trainers
- IELTS Webinar
- Immigration Webinar
What is Signposting?
Updated On Dec 06, 2021

Share on Whatsapp
Share on Email
Share on Linkedin

Limited-Time Offer : Access a FREE 10-Day IELTS Study Plan!
Signposting means the usage of certain phrases and words that guide the reader through the content and help them articulate the structure in a way ensuring that the readers don’t get lost.
Why is it Important?
Your essay showcases a journey through your argument or discussion. The paragraphs act as a ladder to this journey. Signposts help to guide the reader through this and helps them read from the writer’s perspective. They suggest what will happen, constantly remind them of where they are at key points along the way, and indicate the direction your essay is going to head next.
Signposting can happen in your introduction and throughout your whole essay. One should include some element of signposting in each paragraph. Signposting can be useful for linking your paragraphs together. It also makes the reader feel as if you are in control of the structure and that your ideas are well organized.
Types Of Signposting
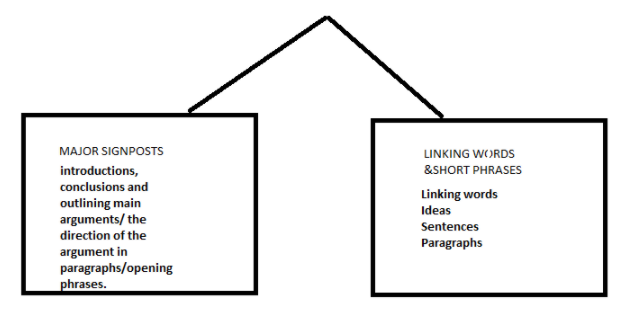
Major Signposts
Introduction:.
- This essay critically examines …
- This essay is organised in the following way: …
- The essay is divided into…main parts: part one will … part two …
- This essay seeks to investigate/evaluate/illustrate/discuss the impact of … in relation to …
- The aim of this study is to … / The purpose of this essay is to …
- This essay argues that …
- The major issue that needs to be addressed is …
- The main questions addressed in this paper are …
- This essay will [first] outline/examine/address/argue/demonstrate/focus on … and will [then] ascertain/establish/clarify/show/judge/prove … Next, it closely examines … in relation to … Finally, it focuses on … and how this affects …
- To understand the role of …, this essay provides a discussion of …
Body Paragraphs:
1.Introducing New Ideas:
- One aspect which illustrates …
- can be identified as …
- The current debate about …
- identifies an interesting viewpoint on …
- First(ly), … / second(ly), … / finally, …
- The first/next/final section provides a general discussion of …
2.Developing Ideas
- Having established …, this essay will now/next focus on …
- Building on from the idea that …,
- this section illustrates that …
- To further understand the role of …
- this section explores the idea that …
- Another line of thought on …
- Another/A second/ of equal importance is …
- This idea/theory had been extended/developed by….
3.Contrast View/ Disagreement/ Personal Opinions:
- However, another angle on this debate suggests that …
- In contrast to evidence which presents the view that…
- an alternative method illustrates that …
- However, not all research shows that…
- Some evidence confirms that …
- This conflicts/contrasts with/is contrary to the view held by …
Concluding Paragraphs:
- The evidence highlights that …
- It is clear that …
- The strength of such an approach is that …
- It is evident that..
- The source information confirms that..
Final Conclusion:
- In conclusion, … / To summarise, … / As has been shown …
- Clearly, this essay has shown that the main factors which impact upon … are …
- From the above, it is clear that …
- Several conclusions emerge from this analysis …
- The evidence presented has shown that …
- This essay has focussed on three factors affecting …
- It has been established that …
- To conclude I would say..
- IELTS Listening Answer Sheet
- IELTS listening recent actual test
- IELTS Listening preparation tips
- IELTS Listening Practice Test
- IELTS Listening Vocabulary
- How to Improve IELTS Listening Section 3 and 4?
Practice IELTS Listening based on question types

Start Preparing for IELTS: Get Your 10-Day Study Plan Today!
Whitney Houston
Houston has been in the field of IELTS for about eight years and has been associated with IELTSMaterial for the last two years. As an IELTS Expert, her contributions to the articles have been informative and original. Whitney has written about 200 informative articles for IELTSMaterial.com, which enables students to learn from her expertise. Whitney is also a good researcher, and thus any new information about the IELTS test can be found on our website, thanks to her. Whitney completed her graduation in Creative Writing at Glasgow University, Belfast. Having seen her foreign peers struggling to prepare for IELTS to find jobs abroad kindled her, and she began learning the techniques and strategies to crack the IELTS test to help her peers.
Explore other Listening Articles

Kasturika Samanta

Nehasri Ravishenbagam

Post your Comments
Recent articles.

Courtney Miller

Raajdeep Saha

Our Offices
Gurgaon city scape, gurgaon bptp.
Step 1 of 3
Great going .
Get a free session from trainer
Have you taken test before?
Please select any option
Get free eBook to excel in test
Please enter Email ID
Get support from an Band 9 trainer
Please enter phone number
Already Registered?
Select a date
Please select a date
Select a time (IST Time Zone)
Please select a time
Mark Your Calendar: Free Session with Expert on
Which exam are you preparing?
Great Going!

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Topic sentences also establish their relevance right away, making clear why the points they're making are important to the essay's main ideas. They argue rather than report. Signposts, as their name suggests, prepare the reader for a change in the argument's direction. They show how far the essay's argument has progressed vis-ˆ-vis the claims ...
Signposting in the introduction. You could use an opening statement like this to signpost your introduction: This essay will: It will then: To quantify what your essay will do, you could say: 'This essay will address three aspects'. You could also signpost how this will be done, for example: 'This essay will attempt to determine whether cats ...
Signposting also makes your writing enjoyable; you sound professional in your arguments. In addition, when you signpost, the structure of your essay, especially in the introduction, helps you present your arguments well. Here are eight effective strategies, tips, and tricks you can use when signposting to write an essay that scores an A. 1.
Table of contents. Step 1: Hook your reader. Step 2: Give background information. Step 3: Present your thesis statement. Step 4: Map your essay's structure. Step 5: Check and revise. More examples of essay introductions. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about the essay introduction.
Signposting the structure of your essay strengthens the presentation of your argument, especially when used in the introduction. Here are six tips to keep in mind when using signposting words, to help you write an essay that stands out. 1. Address the main topic early on. You have only eight seconds to capture the reader's attention.
Without signposting language, writing can lose direction, become confused and read like a series of unrelated points. Try reading the paragraph without them and see how it changes the meaning. Signposting words are useful in the introduction to signal your structure, and echoed in the first lines of paragraphs to indicate how the paragraphs ...
Effective Signposting. Signposts are words or phrases that help articulate the structure of a piece of writing and ensure that readers don't get lost. Signposting will flag the most important parts of an argument, signal transitions, and clarify the stakes of an argument. Here are some examples of helpful signposts:
Signposting words and phrases are essential elements of academic writing - they make your writing flow. By making explicit how points are connected to each other you make it easier for your reader to follow your arguments. The reader is, after all, your marker and you don't want to make their job too hard. This page gives you a selection of ...
Signposting throughout an essay. Throughout an essay you will probably use two types of signposting: small and large scale. ... Look at the verbs you have used in your introduction (eg, suggest, discuss, argue). In your introduction, these will probably have been used in the future tense. In your conclusion, you could use the same verbs but in ...
Signposts help to guide the reader through: they indicate what will happen; remind them of where they are at key points along the way; and indicate the direction your essay is going in. Signposting should happen throughout your whole essay as it helps to link your paragraphs together. There should be some element of signposting in each ...
There are two main types of signposting: Major Signposts: introductions, conclusions and outlining main arguments; the signalling of key points in paragraphs through topic sentences. Transitions & Linking Words/Phrases: connecting sentences/words that help guide the reader through the argument by linking ideas within your writing and indicating ...
Return to all guides. "Signposts" are short phrases that writers use to highlight the connections between ideas and sentences. Functions of Signposting Language. 1) They highlight a point. "The fish-tetrapod transition has been called the greatest step in vertebrate history (Long and Gordon, 2004) and even one of the most significant ...
Here are the key takeaways for how to write essay introduction: 3. Hook the Reader: Start with an engaging hook to grab the reader's attention. This could be a compelling question, a surprising fact, a relevant quote, or an anecdote. Provide Background: Give a brief overview of the topic, setting the context and stage for the discussion.
Using signposts precisely. It can make your work seem sloppy if you use signposting words in the wrong contexts. Avoid the temptation to dot signposting words throughout your text at random. Think carefully about the link between two paragraphs or phrases, and choose a word that effectively conveys that link. For example, 'however' should ...
Signposting. An essay can be thought of as a journey from the introduction to the conclusion. In this analogy you are the driver, and your readers are your passengers. Signposts are the roads on the map which you choose to take. Please note that, although this information sheet focuses on essays, the basic principles apply to most types of ...
Signposting is your not-so-secret weapon for doing this. I like to think of signposting as being of three different 'flavours'. There's overview signposting, summary signposting, and navigation signposting. Overview signpostingis the kind that you use in the introduction to your dissertation and also in the introduction of each of your ...
At band 7, signposting phrases are used correctly and appropriately. At band 8+, use of signposting approaches the skill level of a native speaker. Some examples of signposting. Here is a list of example signposting language to get you started. Remember, there are many more than we can list here. Introducing a topic. The topic of today's talk ...
Use signposting to show the reader the connections and relationships between the ideas you present. Use signposting throughout your writing so that you and the reader stay on track and can easily follow your work. Use a range of different signposting strategies: simple words and phrases, sub-headings, transition sentences, link words and reminders.
A thesis statement tells the reader the main point or argument of the essay. This can be just one sentence, or it can be a few sentences. Map Your Essay. Before you wrap up your essay introduction, map it! This means signposting sections of your essay. The key here is to be concise. The purpose of this part of the introduction is to give your ...
Do not use signposting for short essays, under 10-15 pages. Introduction-y Signposts Use these types of signposts near the beginning of your whole manuscript, and also in the beginning of each main sub-section. Introduction-y Signpost Examples is divided into two parts: part one will… Part two will… This Then/ Next, this… paper essay chapter
Signposting can happen in your introduction and throughout your whole essay. One should include some element of signposting in each paragraph. Signposting can be useful for linking your paragraphs together. It also makes the reader feel as if you are in control of the structure and that your ideas are well organized.