- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
UPSC Coaching, Study Materials, and Mock Exams
Enroll in ClearIAS UPSC Coaching Join Now Log In
Call us: +91-9605741000

Solid Waste Management
Last updated on March 18, 2024 by ClearIAS Team

Solid waste management is the systematic process of collecting, treating, disposing, and recycling solid waste generated by human activities. Proper solid waste management is essential for environmental sustainability, public health, and the overall well-being of communities. Read here to learn more.
The increasing volume and complexity of waste associated with the modern economy is posing a serious risk to ecosystems and human health.
Every year, an estimated 11.2 billion tonnes of solid waste is collected worldwide and decay of the organic proportion of solid waste is contributing about 5 percent of global greenhouse gas emissions. Every year, an estimated 11.2 billion tons of solid waste are collected worldwide.
Of all the waste streams, waste from electrical and electronic equipment containing new and complex hazardous substances presents the fastest-growing challenge in both developed and developing countries.
Table of Contents
Solid waste is generated from various sources, including households, commercial establishments, industries, construction and demolition activities, and agricultural activities.
- Collection Systems: Efficient waste collection systems involve the organized gathering of waste from various sources.
- Segregation: The separation of waste at the source into different categories (e.g., recyclables, organic waste, and non-recyclables) facilitates effective waste management.
- Mode of Transport: Collected waste is transported to treatment and disposal facilities using trucks, containers, or other appropriate means.
- Efficiency: Proper planning of transportation routes and efficient logistics help minimize environmental impacts.
Waste Treatment
- Landfills: Non-recyclable and non-biodegradable waste is disposed of in landfills . Modern landfills incorporate liners and other measures to minimize environmental contamination.
- Incineration: Some areas use incineration to burn waste, reducing its volume and generating energy. However, this method raises environmental and air quality concerns.
- Composting: Organic waste, such as kitchen scraps and yard waste, can be composted to produce nutrient-rich soil.
Solid waste management in India
Waste generation in urban areas of India will be 0.7 kg per person per day in 2025, approximately four to six times higher than in 1999.

According to the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change, India currently generates 62 million tons of waste (both recyclable and non–recyclable) every year, with an average annual growth rate of 4%. Solid waste, plastic waste, and E-waste are the principal waste materials.
Policy Framework
- To promote and support the goals of the Swachh Bharat Unnat Bharat Abhiyan , the Solid Waste Management (SWM) Rules 2016, Plastic Waste Management (PWM) Rules, 2016 , and the E-waste (Management) Rules, 2016 have been notified.
Technology Advancement
- The use of emerging technologies such as automatic waste segregation, gasifiers, and pyrolysis units demonstrates a method to manage waste in India.
- Using Onsite waste processing like Composting/Biomethanation/ Bio CNG , gasifiers/pyrolysis, etc can transform the current waste management scenario in India.
Other initiatives
- The government of India has undertaken multiple large-scale national initiatives such as ‘Swachh Bharat Mission, ‘National Water Mission’ and ‘The Waste to Wealth Mission ” as a part of its commitment to effective waste & pollution management in India.
- The setting up of Decentralised Waste processing sites within Cities to cater to problems of fresh MSW and legacy waste management.
- The Waste to Wealth Mission has deployed a decentralized waste Processing technology park.
- One tonne of plastic is used to make one kilometer of road in India. India has built one lakh kilometers of roads in at least 11 states using discarded plastic.
Issues in India
- Lack of water, sanitation, and hygiene results in the loss of 400,000 lives per year in India.
- 600 million people – nearly half of India’s population – face acute water shortage, with close to 200,000 dying each year from polluted water.
- Nearly 70 percent of India’s water is contaminated, impacting three in four Indians and contributing to 20 percent of the country’s disease burden.
- More than 1 in 4 deaths of children under 5 years old are attributable to an unhealthy environment.
- A printed circuit board (PCB) (used in cellular phones and personal computers) contains about 280 g/ton of gold.
The Challenges of Solid Waste Management
- The unprecedented growth of urban areas leads to increased waste generation, putting immense pressure on existing waste management systems.
- Unplanned urbanization often results in inadequate infrastructure and services for waste collection and disposal.
- Solid waste comprises various materials, including plastics, paper, glass, metals, and organic waste. Each type requires specific treatment methods, making waste management a complex task.
- Improper disposal of hazardous waste poses environmental and health risks.
- Despite the potential for recycling and reuse, many regions struggle to establish efficient systems. Lack of awareness, infrastructure, and incentives hinder recycling efforts.
- Valuable resources are lost when materials that could be recycled end up in landfills.
- While waste-to-energy (WTE) technologies offer energy recovery from waste, concerns about air emissions and the environmental impact of incineration persist.
- Balancing the energy benefits with environmental considerations is crucial for sustainable waste management.
Strategies for Better Implementation of Solid Waste Management
- Developing comprehensive, integrated waste management systems that consider the entire waste lifecycle.
- Combining source reduction, recycling, composting, and responsible disposal to minimize environmental impact.
- Launching public awareness campaigns to educate communities about the importance of waste separation, recycling, and responsible waste disposal.
- Empowering individuals to make informed choices about their waste practices.
- Implementing EPR policies to hold manufacturers accountable for the end-of-life management of their products.
- Encouraging eco-friendly product design and packaging to reduce waste generation.
- Utilizing technology for efficient waste collection, including smart bins that monitor fill levels and optimize collection routes.
- Implementing data-driven solutions to enhance the overall effectiveness of waste management systems.
- Investing in research and development to innovate recycling technologies that can handle diverse materials and improve recycling rates.
- Supporting industries that use recycled materials in their production processes.
- Developing waste-to-energy facilities with advanced emission control technologies to minimize air pollutants.
- Ensuring stringent environmental regulations and monitoring to safeguard public health and the ecosystem.
- Involving communities in decision-making processes related to waste management.
- Fostering a sense of responsibility and ownership among residents for the waste generated in their neighborhoods.
- Enacting and enforcing strong waste management policies and regulations at the national and local levels.
- Providing incentives for businesses and individuals to adopt sustainable waste management practices.
- Facilitating collaboration between governments, non-governmental organizations (NGOs), and the private sector.
- Sharing best practices and technologies globally to address common waste management challenges.
- Promoting the principles of a circular economy , which emphasizes minimizing waste, maximizing resource use, and closing material loops.
- Encouraging product design that considers the entire lifecycle, from production to disposal.
One tonne of recycled paper saves approximately 17 trees, 2.5 barrels of oil, 4100 kWh of electricity, 4 cubic meters of landfill, and 31,780 liters of water.
Recycling has the potential to create six times more jobs and generate around INR 14 lakh crore of additional cost savings by 2030.
Effective solid waste management is essential for creating a sustainable and healthy environment. By implementing integrated systems, raising public awareness, and embracing innovative technologies, communities can address the challenges posed by increasing waste generation. Governments, businesses, and individuals all play crucial roles in adopting responsible waste management practices to build a cleaner, greener future.
Related articles:
- Biomining: How can it solve the problem of waste?
- Battery Waste Management
- Biomedical waste management
- Solar Waste Management
- Construction and Demolition waste management
-Article by Swathi Satish

Module Classes: Join Now!
Csat course.
Join CSAT Course
Current Affairs Course
Join Current Affairs Course
- UPSC Prelims Test Series
Join Prelims Test Series

About ClearIAS Team
ClearIAS is one of the most trusted learning platforms in India for UPSC preparation. Around 1 million aspirants learn from the ClearIAS every month.
Our courses and training methods are different from traditional coaching. We give special emphasis on smart work and personal mentorship. Many UPSC toppers thank ClearIAS for our role in their success.
Download the ClearIAS mobile apps now to supplement your self-study efforts with ClearIAS smart-study training.
Reader Interactions
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Don’t lose out without playing the right game!
Follow the ClearIAS Prelims cum Mains (PCM) Integrated Approach.
Join ClearIAS PCM Course Now
UPSC Online Preparation
- Union Public Service Commission (UPSC)
- Indian Administrative Service (IAS)
- Indian Police Service (IPS)
- IAS Exam Eligibility
- UPSC Free Study Materials
- UPSC Exam Guidance
- UPSC Syllabus
- UPSC Online
- UPSC Prelims
- UPSC Interview
- UPSC Toppers
- UPSC Previous Year Qns
- UPSC Age Calculator
- UPSC Calendar 2024
- About ClearIAS
- ClearIAS Programs
- ClearIAS Fee Structure
- IAS Coaching
- UPSC Coaching
- UPSC Online Coaching
- ClearIAS Blog
- Important Updates
- Announcements
- Book Review
- ClearIAS App
- Work with us
- Advertise with us
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions
- Talk to Your Mentor
Featured on

and many more...
- Skip to main content
India’s Largest Career Transformation Portal
Essay on Waste Management for Students [500 Words Essay]
January 5, 2021 by Sandeep
Essay on Waste Management: Effectively managing the segregation of waste and following the activities until their final disposal is termed waste management. The biggest concern about waste management technologies is to clear off the waste generated from every household. The process consists of several stages like waste collection, transportation and finally, disposal. Waste management is based on the type of waste, the level of harm it causes, and the waste’s infection quotient.
Essay on Waste Management 500 Words in English
Below we have provided the Waste Management Essay in English, suitable for class 6, 7, 8, 9 & 10.
The whole method of managing, treating, storing, shipping, reprocessing and disposing of chemical, human and environmental waste is known as waste management. Waste management is a global subject, but its implications are more evident in developing nations. With the growth in population , sub-urbanization, social and economic growth, marketing, etc., solid waste management that is a relatively colossal activity is becoming more complex. Official insubstantiality, economic constraints and a public approach to waste management have made the issue worse.
Waste management is essential for maintaining living beings’ well being and also for building a healthy atmosphere for the generations to come. It helps to minimize pollution and can substantially reduce emissions of gases such as carbon dioxide and methane from waste by adapting to effective waste management techniques. It also helps in avoiding infectious diseases.
Methods for Waste Management
- Incineration – Under this waste management system, public solid waste is buried for turning it into oil, dust, steam, ash and gases. It eliminates solid waste by about 31 per cent of the total amount.
- Landfills – Disposal of garbage and waste within landfills is one of the most common waste management methods. Under this process, problems such as garbage hazards and odour are eradicated. The waste is deposited at landfill sites.
- Composting – Composting is a method of biodegradation of waste management in which the agricultural waste, i.e., flora leftovers and pantry waste, is converted into flora feed. This method is used for organic-farming that often improves soil fertility.
- Recycling – In this waste management system, the waste products are reprocessed for reuse. The waste stuff is reprocessed for extracting resources or converting it into energy such as heat, electricity, coal.
- Anaerobic Digestion – Anaerobic digestion is the waste management method which with the aid of organic procedures degrades biological materials. It uses the surroundings free of germs and oxygen for decay. Composting requires air to aid in bacteria growth.
- Waste Minimization – This is the easiest way to handle waste and helps to generate less waste. Anyone can achieve declining waste by reducing waste creation and reprocessing and recycling of old resources. It is important to use sustainable products and to decrease the use of paper, plastics etc. The public input has a direct impact on the waste management system.
- Waste to Energy Conversion – Under this waste management process, non-biodegradable wastage is converted into energy sources such as coal, heat, or electricity. Both of these are sources of renewable energy as the non-biodegradable waste could be used repeatedly to produce electricity.
- Pyrolysis and Gasification – These two waste management methods are used to decompose the remaining organic materials by exposing them to a limited amount of oxygen and elevating the temperature. Oxygen is not used in the pyrolysis procedure and, only a minimal amount of oxygen is used in the gasification process.
Waste Management System in India
Waste management in India relies on sustainable growth, polluter speed and precautionary standards. These principles allow the regions and business foundations to behave responsibly and conscientiously on Earth by restoring the ecological balance, their actions in some way upset it. The expansion of waste generation as a side-effect of financial development has prompted numerous subordinate enactments to direct the mode of transfer and was rendered under the Environment Protection Act (EPA) enacted in the year 1986.
When we see waste generation in the context of India, according to Environment Ministry of the country, “62 million tonnes of waste is generated annually in the country at present, out of which 5.6 million tonnes is plastic waste, 0.17 million tonnes is biomedical waste, hazardous waste generation is 7.90 million tonnes per annum, and 15 lakh tonnes is e-waste. Only about 75-80 per cent of the municipal waste gets collected, and only 22-28 per cent of this waste is processed and treated.” (source: moef.gov.in, Minister of Environment, India)

Waste Management in India: Status, Challenges and Solutions – Explained, pointwise
- 1 Introduction
- 2 What is the status of Solid Waste Generation in India?
- 3 What are the challenges in Solid Waste Management in India?
- 4 What are the harmful impacts of poor Waste Management?
- 5 What steps have been taken by the Government regarding Waste Management?
- 6 What more steps can be taken to improve Waste Management?
- 7 Conclusion
Introduction
India is set to undergo rapid urbanization in the coming decade. One major challenge accompanying the urbanization is rapid rise in waste generation. Waste Management Processes and Systems in India will need to be upgraded to meet this challenge.
What is the status of Solid Waste Generation in India?
Overall Solid Waste Management Status
According to the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) the total quantity of Solid waste generated in the country is ~160,000 metric tonnes per day (TPD). ~153,000 TPD of waste is collected at a collection efficiency of ~96% . 80,000 TPD (50 %) of waste is treated and ~30,000 (18.4%) TPD is landfilled . ~50,000 TPD (31.2 %) of the total waste generated remains un-accounted .
Per-capita Solid Waste Generation has increased marginally from 118.7 gm/day in 2015-16 to 119.1 gm/day in 2020-21.
Maximum quantity of per capita solid waste is generated in Delhi.
Processing of solid waste has improved significantly from 19% in 2015-16 to ~50% in 2020-21 . In the corresponding period, proportion of solid waste landfilled has fallen from 54% to 18.4% .
100% of solid waste is treated in Chhattisgarh, followed by 89% in Daman & Diu and Dadra & Nagar Haveli (DDDNH) and 87% in Goa.
According to a World Bank Report, globally 2.01 billion tonnes of municipal solid waste is generated annually, of which at least ~33% is not managed in an environmentally safe manner . Global per capita waste generation is 740 gm/day (average) but varies from 110 gm/day to 4.54 kg/day across countries. High Income countries contribute 34% to global waste generation despite having only 16% of the population.
What are the challenges in Solid Waste Management in India?
Rising Waste Generation : Economic growth leads to increase in waste generation consequent to rise in consumption. Expansion of digital economy will lead to multifold increase in e-waste generation. In addition, rapidly expanding population will add to waste. A Planning Commission Report (2014) had estimated that India will generate 165 million tonnes by 2030 (~60 million tonnes annual in 2020).
Improper Waste Management : (a) Poor Processing : Only 50% of the waste is processed. ~30% is not accounted and ~20% ends up in landfills which is very poor method of disposal (b) Incorrect and Inadequate Segregation Techniques : There is poor segregation at source, Hazardous waste is not sealed and labeled which leads to their improper disposal. In addition e-waste is not disposed properly; (c) Reuse/recycling of waste occurs through scavengers in the informal sector and there is no Government collection of recyclables; (d) Often garbage is not placed in designated containers, leading to dirty streets.
Littering and Illegal Dumping : In terms of disposal, almost half of waste is placed in uncontrolled dumps; sanitary landfills with leachate collection and gas recovery are not available. This has detrimental environmental impacts
Lack of Financial Resources : Lack of financial resources with local bodies lead to understaffed and underpaid cleaning and sanitation departments. Collection infrastructure (like vehicles) is poorly maintained. Lack of funds prevents purchase of new equipment and vehicles.
Inconsistent Collection : Understaffing and under-compensation leads to inconsistent collection of waste. Sanitation workers do not serve all areas.
Inappropriate Infrastructure : Vehicles used to waste collection are not designed for this purpose. This often leads to overloading which results in spillage during transportation. Vehicles do not have lifting mechanisms, so loading is done manually which is unhygienic and hazardous.
Lack of Civic Responsibility : Limited environmental awareness combined with low motivation has inhibited innovation and the adoption of new technologies that could transform waste management in India. Public attitudes to waste are also a major barrier to improving SWM in India.
What are the harmful impacts of poor Waste Management?
Health Issues : (a) Improper and unscientific collection and handling leads to several diseases in sanitation workers; (b) Municipal waste is often mixed with hazardous and medical wastes, which exacerbates health threats; (c) Open burning of waste leads to formation of harmful particles which can cause lung diseases; (d) Poor collection leads to garbage dumps which act as breeding ground for rats and mosquitoes etc. Mosquitoes act as carriers of diseases like malaria and dengue.
Environmental Issues : (a) Unscientific dumping in landfill leads to formation of harmful chemicals which permeate into soil and groundwater. This renders groundwater unfit for drinking and cause multiple diseases; (b) Waste in landfills leads to formation of harmful gases leading to air pollution. Composition of gases depends upon type of waste but typically methane and carbon dioxide make up 90 to 98% of landfill gases. The remaining 2 to 10% includes nitrogen, oxygen, ammonia, sulfides, hydrogen and various other gases. They contribute to global warming as well; (c) A lot of land-based waste eventually ends up in sea leading to marine pollution.
Economic Impacts : (a) Expanding landfills occupy useful land and lead to wasteful utlization of an economic resource; (b) Recycling of waste can lead to cost economies and generate revenue as well. Poor waste management misses this useful opportunity; (c) Poor waste collection leads to clogging of drains, which has become a factor in urban flooding leading to economic losses; (d) Poor waste management leads to general filth in cities which impacts tourism potential.
What steps have been taken by the Government regarding Waste Management?
Institutional Arrangement : In India, waste management is governed by the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC), Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB), Ministry of Urban Development (MoUD), State Pollution Control Boards (SPCBs) and the ULBs (12th Schedule of the Constitution).
Policy and Legal Framework for Waste Management in India : The Government of India (GOI) has formulated various Rules and Regulations regarding solid waste management (SWM). These include Solid Waste Management Rules, e-Waste Management Rules, Plastic Waste Management Rules etc. These rules are updated periodically and have been formulated under the Environment Protection Act, 1986.
Solid Waste Management Rules, 2016 are applicable beyond municipal areas and include urban agglomerations, census towns, notified industrial townships, areas under the control of Indian Railways, airports, special economic zones, places of pilgrimage, religious and historical importance, and State and Central Government Organizations in their ambit.
Government Initiatives : (a) Swachha Bharat Mission – Urban (SBM-U) : With the enactment of new rules, door-to-door collection, segregation at source, etc. has been initiated; (b) Swaccha Survekshan : An annual survey of cleanliness, hygiene and sanitation in cities and towns across India is undertaken. It has been launched as a part of the SBM-U under the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA). It gives star ratings to garbage-free cities and towns on several factors and acts as incentives for cities to do better; (c) Swachhata Hi Sewa Campaign : It has been launched for ensuring cleanliness through the various stakeholders’ engagement in the ‘ Jan Andolan ‘ (National Movement); (d) Compost Banao , Compost Apnao Campaign : It is a multi-media campaign launched by MoHUA on waste-to-compost under SBM-(U). The aim is to encourage people to convert their kitchen waste into compost to be used as fertilizer and to reduce the amount of waste getting to landfill sites; (e) Promotion of Waste to Energy : The Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) launched Program on Energy from Urban, Industrial, Agricultural waste/residues and Municipal Solid Waste to promote setting up of Waste-to-Energy projects and to provide central financial assistance.
What more steps can be taken to improve Waste Management?
Scientific Waste Management : The waste management planning should be based on sound scientific and engineering studies. They should consider waste composition, capital and long-term operating costs, transport distances, and the geographical location of waste processing and disposal facilities. Comprehensive waste characterization studies are needed to obtain accurate data for solid waste management planning.
Waste Collection : To improve collection practices, a number of improvements should be considered, including more regular service by sweepers, daily waste collection (rather than alternate days), use of mechanized vehicles, better coordination between timing of waste generation and collection, and increased accessibility for waste collection vehicles.
Merging the informal and formal waste collection sectors has the potential to streamline the segregation and collection process.
Improved Practices : (a) Decentralized Solid Waste Management : It is an approach in which the informal sector provides source-segregated waste collection and treatment at the local level , avoiding transport to a centralized waste facility in order to reduce costs. Decentralized approaches may also promote more citizen and local stakeholder involvement in planning and decision-making; (b) Recycling : It has great potential to expand in India. Policies and regulations to support recycling are needed; (c) Processing : For treating organic waste processes like composting, vermi-composting and bio-methanation should be considered to reduce the amount of organic waste that goes to open dumps or landfills. Initiatives like Compost Apnao need to be scaled-up; (d) Sanitary Landfills : The conversion of existing dumps to sanitary landfills is a critical need. To accomplish this, the enforcement of rules, regulations, and bylaws, along with proper funding, are required. Technical expertise and financial feasibility are key barriers which must be addressed; (e) Smart Waste Management System : In the long term, technology like (Internet of Things) can be integrated into waste management e.g., RFID-Enabled Door-to-door waste collection monitoring can enhance collection efficiency and GPS based vehicle tracking can help in real time monitoring.
Waste-to-energy : Bio-methanation (anaerobic digestion) uses micro-organisms to convert the organic waste into methane, which can be used as fuel. Bio-methanation plants should be scaled up.
Strict Implementation of Rules : Waste Management Rules have incorporated have incorporated ‘ Polluter Pays Principle ‘. The rules need to be stringently implemented to penalize non-compliance.
Public Awareness : Self- help groups, residents’ welfare associations, and community-based organizations should be encouraged to educate and acquaint people with beneficial waste management strategies, including separation, recycling modes, and drop off centers for recyclables, as well as composting.
As India undergoes rapid urbanization, multifold increase in waste generation will provide a new governance challenge. The Government must scale up its existing efforts to improve waste management. At the same time, public participation is vital and without their contribution, Government efforts might remain ineffective.The refore, it is desired to place more emphasis on information, planning, funding, unified waste management along with community education. The 4 R’s philosophy of Reducing, Reusing, Recycling, and Recovering Resources should be actively encouraged.
Syllabus : GS III, Conservation, Environment Pollution and Degradation.
Source : The Hindu , CPCB , WB

Type your email…
Search Articles
Latest articles.
- UPSC Prelims Marathon 2nd April – Environment & Ecology – II – 2024
- [Answered] UPSC Mains Answer writing 1 April, 2024 I Mains Marathon
- 10 PM UPSC Current Affairs Quiz 1 April, 2024
- 9 PM UPSC Current Affairs Articles 1 April, 2024
- UPSC Prelims Marathon 1st April – Environment & Ecology – 2024
- 10 PM Daily UPSC Current Affairs 31st March – 2024 | Revision Test
- UPSC Prelims Marathon 31st March – Revision – 2024
- 10 PM UPSC Current Affairs Quiz 30 March, 2024
- 9 PM UPSC Current Affairs Articles 30 March, 2024
- [Answered] UPSC Mains Answer writing 29 Mar, 2024 I Mains Marathon
Prelims 2024 Current Affairs
- Art and Culture
- Indian Economy
- Science and Technology
- Environment & Ecology
- International Relations
- Polity & Nation
- Important Bills and Acts
- International Organizations
- Index, Reports and Summits
- Government Schemes and Programs
- Miscellaneous
- Species in news
- UPSC IAS Exam Pattern
- UPSC IAS Prelims
- UPSC IAS Mains
- UPSC IAS Interview
- UPSC IAS Optionals
- UPSC Notification
- UPSC Eligibility Criteria
- UPSC Online
- UPSC Admit Card
- UPSC Results
- UPSC Cut-Off
- UPSC Calendar
- Documents Required for UPSC IAS Exam
- UPSC IAS Prelims Syllabus
- General Studies 1
- General Studies 2
- General Studies 3
- General Studies 4
- UPSC IAS Interview Syllabus
- UPSC IAS Optional Syllabus

Solid Waste Management – UPSC Indian Society Notes

Table of Contents
Solid Waste Management Rules
The Solid Waste Management Rules in India were revised in 2016 to strengthen the legal framework for solid waste management in the country. Here are the key points of the Solid Waste Management Rules:
- Segregation of waste at the source: The rules mandate segregation of waste at the source into three categories – wet, dry and hazardous waste.
- Collection and transportation of waste: Local bodies are responsible for collecting and transporting the waste in a scientific manner.
- Treatment and disposal of waste: The rules emphasize on processing of waste to minimize the quantity of waste going to the landfill. Waste processing can be done through composting, biomethanation, waste to energy or recycling.
- Landfill management: The rules provide for scientific management of landfills with measures to prevent soil and groundwater contamination.
- Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR): The rules require manufacturers or brand owners to take responsibility for the waste generated by their products and ensure their proper disposal or recycling.
- Plastic waste management: The rules ban the use of plastic bags below 50 microns in thickness, and mandate that plastic waste must be collected and sent for recycling.
- Penalties for non-compliance: The rules provide for penalties for non-compliance, including fines and imprisonment.
Overall, the Solid Waste Management Rules provide a comprehensive framework for managing solid waste in India and promote the principles of reduce, reuse and recycle.
Solid Waste Management
Solid waste management is a major challenge in India due to the rapid growth of urban population, increase in consumption, and lack of proper disposal mechanisms. In many Indian cities, waste management systems are inadequate, leading to uncollected waste being dumped on streets and in open areas, causing environmental and health hazards.
To address this issue, the Indian government has launched various initiatives and programs aimed at improving solid waste management. Some of the key initiatives and programs include:
- Swachh Bharat Abhiyan: Launched in 2014, this program aims to clean up India’s streets, roads, and infrastructure. Under this program, the government has set a target of making India 100% open defecation-free and achieving scientific solid waste management.
- Waste-to-Energy Projects: Waste-to-energy projects convert waste into energy and help in reducing the volume of waste sent to landfills. Many cities in India have implemented such projects, including Delhi, Mumbai, and Hyderabad.
- Bioremediation: Bioremediation is a process of using microorganisms to degrade or remove contaminants from waste. This method is gaining popularity in India due to its low cost and environmental friendliness. The city of Pune has implemented a successful bioremediation project, which has reduced the volume of waste sent to landfills.
- Decentralized Composting: Decentralized composting involves the use of composting facilities at a local level to process organic waste. This method is cost-effective and reduces the burden on landfills. Bengaluru has implemented a decentralized composting program, which has reduced the volume of waste sent to landfills by 40%.
- Public Awareness and Education: Educating the public on the importance of waste segregation and proper disposal is crucial in improving solid waste management. The city of Surat has implemented a successful public awareness campaign, which has resulted in a significant reduction in waste sent to landfills.
Despite these initiatives and programs, solid waste management remains a major challenge in India. The lack of adequate infrastructure, technological solutions, and public awareness continue to hinder progress. However, with continued efforts and effective implementation of these initiatives, India can achieve sustainable solid waste management in the future.
1. What are the Solid Waste Management Rules 2016?
- The Solid Waste Management Rules 2016 are a set of regulations issued by the Government of India to address the management and disposal of solid waste in a responsible and environmentally sustainable manner.
2. What is the purpose of the Solid Waste Management Rules 2016?
- The rules aim to promote proper waste segregation, recycling, and the safe disposal of solid waste. They also emphasize waste reduction, the establishment of waste processing facilities, and the involvement of local authorities and communities.
3. How do solid waste management projects contribute to environmental protection?
- Solid waste management projects help reduce pollution, prevent the spread of diseases, minimize the burden on landfills, conserve resources through recycling, and promote sustainable waste disposal practices.
4. Why is proper solid waste management essential?
- Proper solid waste management is essential to protect public health, prevent environmental pollution, conserve resources, and promote sustainable development. It helps manage the growing volume of waste generated in urban areas and minimizes its adverse effects.
5. How does solid waste management differ from wastewater or sewage management?
- Solid waste management deals with the handling of solid materials, while wastewater or sewage management focuses on the treatment and disposal of liquid and semi-liquid waste from homes, industries, and commercial establishments. Both are crucial aspects of environmental management.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here
Visit our YouTube Channel – here
- Evolution of Indian Society – Indian Society Notes
- Internal Migration v/s External Migration – UPSC Indian Society Notes
- Minorities in India – Indian Society Notes
Gender Equity – UPSC Indian Society Notes
Edukemy Team
Constitutional provisions, laws, and policies for women in india –..., characteristics of migrants in india – upsc indian society notes, global multidimensional poverty index – indian society notes, government schemes for migration – upsc indian society notes, approach for women development since independence – upsc indian society..., urbanization – upsc indian society notes, constitutional provisions to promote national unity and integrity and initiatives..., women’s movement in india – upsc indian society notes, regionalism vs. nationalism, federalism and ways to combat regionalism –..., leave a comment cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Our website uses cookies to improve your experience. By using our services, you agree to our use of cookies Got it
Keep me signed in until I sign out
Forgot your password?
A new password will be emailed to you.
Have received a new password? Login here

Waste Management
Introduction:
Zero waste is a philosophy and environmental initiative aimed at eliminating waste by rethinking resource life cycles to conserve and recover resources, rather than disposing of them. It involves reducing, reusing, and recycling materials to prevent waste generation, ultimately aiming for a circular economy where no trash is sent to landfills, incinerators, or the ocean.
- Promote sustainable consumption and production patterns.
- Support the shift towards circularity.
- Raise awareness of the contribution of zero-waste initiatives to the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development.
Conclusion : International Day of Zero Waste propels the transition to a sustainable future, inspiring action, promoting responsible waste management, and fostering the adoption of circular economy principles. By raising awareness and supporting zero-waste practices, we contribute to a paradigm shift towards a more sustainable and environmentally conscious society.
Circular Economy
Introduction: A circular economy maximizes resource utilization by designing products for longevity, reuse, and recycling, creating a closed-loop system that minimizes waste and promotes sustainable development.
Key principles and strategies
- Reducing Waste and Pollution: Circular economy emphasizes waste prevention, efficient design, and eco-friendly production.
- Extending Prduct Life Cycles: Products designed to be durable, repairable, and upgradable for resource efficiency.
- Promoting Reuse and Recycling: Circular economy encourages repair, refurbishment, remanufacturing, and recycling.

Answer our survey to get FREE CONTENT

Feel free to get in touch! We will get back to you shortly
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Service
- Quality Enrichment Program (QEP)
- Total Enrichment Program (TEP)
- Ethics Marks Maximization Prog. 2024
- Interview Mentorship Program (IMP)
- Prelims Crash Course for UPSC 2024
- Science of Answer Writing (SAW)
- Intensive News Analysis (INA)
- Topper's UPSC PYQ Answer
- Essay Marks Maximization Program
- PSIR Optional
- News-CRUX-10
- Daily Headlines
- Geo. Optional Monthly Editorials
- Past Papers
- © Copyright 2024 - theIAShub
Talk To Our Counsellor

25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

Essay on Waste Management
- Updated on
- May 11, 2023

Every year, the amount of waste is doubling because of the increasing population around the world. The 3Rs, Reduce, Reuse, and Recycle should be followed to help in waste management. Waste management is the need of the hour and should be followed by individuals globally. This is also a common essay topic in the school curriculum and various academic and competitive exams like IELTS , TOEFL , SAT , UPSC , etc. In this blog, let us explore how to write an essay on Waste Management.
This Blog Includes:
Tips for writing an essay on waste management , what is the meaning of waste management, essay on waste management in 200 words, essay on waste management in 300 words .
To write an impactful and scoring essay, here are some tips on how to manage waste and write a good essay:
- The initial step is to write an introduction or background information about the topic
- You must use a formal style of writing and avoid using slang language.
- To make an essay more impactful, write dates, quotations, and names to provide a better understanding
- You can use jargon wherever it is necessary, as it sometimes makes an essay complicated
- To make an essay more creative, you can also add information in bulleted points wherever possible
- Always remember to add a conclusion where you need to summarise crucial points
- Once you are done, read through the lines and check spelling and grammar mistakes before submission
Waste management is the management of waste by disposal and recycling of it. It requires proper techniques while keeping in mind the environmental situations. For example, there are various methods and techniques through which the waste is disposed of. Some of these are Landfills, Recycling, Composting, etc. These methods are useful in disposing of waste without causing any harm to the environment.
Sample Essays on Waste Management
To help you write a perfect essay that would help you score well, here are some sample essays to give you an idea about the same.
One of the crucial aspects of today’s society is waste management. Due to a surge in population, the waste is generated in millions of tons day by day and affects the lives of a plethora of people across the globe. Mostly the affected people live in slums that are extremely close to the waste disposal areas; thus, they are highly prone to communicable and non-communicable diseases. These people are deprived of necessities to maintain a healthy life, including sanitation and proper hygiene.
There are various methods and techniques for disposing of waste including Composting, Landfills, Recycling, and much more. These methods are helpful in disposing of waste without being harmful to the environment. Waste management is helpful in protecting the environment and creating safety of the surrounding environment for humans and animals. The major health issue faced by people across the world is environmental pollution and this issue can only be solved or prevented by proper waste management so that a small amount of waste is there in the environment. One of the prominent and successful waste management processes, recycling enables us not only in saving resources but also in preventing the accumulation of waste. Therefore it is very important to teach and execute waste management.
The basic mantra of waste management is” Refuse, Reuse, Reduce, Repurpose, and Recycle”. Waste management is basically the collection or accumulation of waste and its disposal. This process involves the proper management of waste including recycling waste generated and even generating useful renewable energy from it. One of the most recent initiatives taken by various countries at the local, national and international levels, waste management is a way of taking care of planet earth. This responsible act helps in providing a good and stable environment for the present and future generations. In India, most animals get choked and struggle till death because they consume waste on the streets.
So far many lives are lost, not only animals but also humans due to a lack of proper waste management. There are various methods and techniques for disposing of waste including Composting, Landfills, Recycling, and much more. These methods are helpful in disposing of waste without being harmful to the environment. Waste management is helpful in protecting the environment and creating safety of the surrounding environment for humans and animals. This process of waste management evolved due to industrialization as prior to these inventions simple burying was sufficient for disposing of waste.
One of the crucial things to control waste is creating awareness among people and this can only be achieved only when the governments and stakeholders in various countries take this health issue seriously. To communicate with various communities and reach each end of the country, the message can be communicated through media and related platforms. People also need to participate in waste management procedures by getting self-motivated and taking care of activities of daily living. These steps to create consciousness about waste management are crucial to guarantee the success and welfare of the people and most importantly our planet earth.
Check Out Popular Essay Topics
- Essay on Population Explosion
- Essay on My Hobby
- Essay on Human Rights
- Essay On Sikkim
- Essay on Disaster Management
- Essay on Democracy
- Essay on Child Labour
- Essay on Global Warming
- Essay on Women’s Empowerment
- Essay on My Aim in Life
- Essay on India
- Essay on Education System
We hope this blog has helped you structure a terrific essay on waste management. Planning to ace your IELTS, get expert tips from coaches at Leverage Live by Leverage Edu .
Sonal is a creative, enthusiastic writer and editor who has worked extensively for the Study Abroad domain. She splits her time between shooting fun insta reels and learning new tools for content marketing. If she is missing from her desk, you can find her with a group of people cracking silly jokes or petting neighbourhood dogs.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *

Leaving already?
8 Universities with higher ROI than IITs and IIMs
Grab this one-time opportunity to download this ebook
Connect With Us
25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. take the first step today..

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test

Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
September 2024
January 2025
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.

Waste Management, Types, Process, Objective, Different Methods
Waste management or waste disposal includes the processes and actions required to manage waste from its inception to its final disposal. Check details on waste management here in this article.

Table of Contents
Waste Management
Waste management encompasses a multidisciplinary approach that integrates engineering principles, economics, urban and regional planning, management techniques, and social sciences. Its objective is to minimize the overall wastage within the system under consideration. A systematic waste management approach should address all types of resources at every stage. Notably, material constitutes a significant portion of the total production cost, making the management of wasted materials critically important (Arora, 2004).
According to the Environmental Protection Act of 1990, waste is defined as any undesirable material. This includes scrap material, effluents, or any surplus substance or item requiring disposal due to being damaged, worn out, contaminated, or otherwise polluted. Wastes are essentially those substances or objects that no longer serve a purpose within the business cycle or chain of utility. For instance, glass bottles that are returned or reused in their original form are not considered waste, whereas glass bottles collected by the public and sent for remoulding are classified as waste until they have been recovered. The Department of the Environment identifies four broad categories of potential waste:
- Items that are worn but still functional and can be used for their intended purpose (potentially after repair).
- Substances or items that can be immediately utilized for purposes other than by specialized waste recovery entities. For example, ash from a power station used in building materials.
- Degraded substances or items that can only be utilized by specialized waste recovery establishments. These remain classified as waste, even if sent for recovery for value, such as contaminated solvents or scrap. They are only considered recovered when the process is complete.
- Substances that the possessor no longer wants and for which they must pay for proper disposal.
Types of Waste
The rapid pace of economic development has led to an improved standard of living worldwide. This, in turn, has resulted in increased material consumption and subsequently, higher waste generation. Solid waste materials generated, particularly in urban areas, include:
- Organic waste
- Plastic waste
- Metal waste materials
- Glass waste materials
- Paper waste materials
- Electronic waste
- Other materials like ash, sand, grit, etc.
Waste Management Process
Ensuring Environmental Health and Resource Recovery. Waste management encompasses the collection, transportation, processing, recycling, or disposal of materials generated through human activity. This process is primarily aimed at mitigating their impact on both human health and the environment. Additionally, waste management strives to extract valuable resources from these materials. It covers a wide range of substances, including solid, liquid, gaseous, and radioactive, each requiring specialized methods and expertise for proper handling.
Studies have shown that waste management practices vary depending on factors like a nation’s level of development, urban or rural settings, and whether the waste is generated by residential or industrial sources. Typically, local government authorities oversee the management of non-hazardous waste from homes and institutions in metropolitan areas, while generators of non-hazardous commercial and industrial waste usually handle its management.
An efficient waste management system plays a crucial role in ensuring the smooth operation of various interconnected systems. These systems are vital for tasks such as waste containment and leachate management. Without regular examination, maintenance, improvement, and assessment of the components of a waste management system, even the most well-designed unit may not function optimally.
Effective implementation of a waste management system can lead to reduced costs in both the short and long term, provide protection for workers and local communities, and foster positive community relations. Furthermore, a successful waste management system necessitates the establishment of procedures for monitoring performance and tracking progress towards clearly defined environmental objectives.
Objective of Waste Management
The primary aim of waste management is to reduce waste generation, ultimately striving for an ideal system. Conversely, resource management seeks to maximize the efficient use of available resources. Both waste and resource management share a common objective: the optimal utilization of resources to enhance system efficiency and growth. However, their approaches differ (Arora, 2004).
To accomplish this objective, it is crucial to:
- Prevent the generation of waste.
- Encourage the reuse of waste.
- Support the biological recovery and material recycling of waste.
- Promote the energy utilization of waste that isn’t suitable for recycling.
- Ensure that the treatment and disposal of waste do not result in any harmful impacts.
Management literature has established that resource and waste management are interdependent and complement each other in achieving these goals.
Different Methods of waste disposal
The different methods of waste disposal have been mentioned below:
- In the age-old ritual of waste management, the Landfill emerges as a solemn guardian. It cradles our refuse in vacant urban spaces, a sacred resting place for our discarded tales. Covered in a quilt of soil, it guards against the specter of contamination. And trees, nature’s sentinels, are called upon, their roots tenderly embracing the soil, fortifying this sanctuary.
- The Landfill, if choreographed with care, waltzes as an economical and hygienic custodian of our waste. Yet, in the chaos of urban life, unplanned landfills sprout like wildflowers in forgotten corners, birthing environmental and health specters. Poisonous gases escape, toxic secrets seep, and the once vibrant vegetation bows in sorrow. The Landfill, a testament to our stewardship, a tale of caution, a dance of contradictions.
Incineration
- It is a carefully controlled process of burning or thermally treating mostly organic substances at high temperatures to release water, CO2, and thermal energy.
- Advantages: Produces power and is useful for handling big amounts of dangerous organic waste.
- Disadvantages: The installation is expensive (high equipment and labor costs) and produces harmful gases (HCL, CO, and SO2).
This process changes the condition of the solid into a liquid, and the liquid into a gas. The creation of energy can then be done using these treatment byproducts.
Gasification
The substance to be treated is immediately transformed into SynGas (synthetic gas), which is made up of carbon dioxide and hydrogen.
Bioremediation
Utilizing living creatures, primarily microbes, to transform environmental pollutants into less hazardous forms is known as bioremediation. For instance, a pseudonymous microbe may break down artificial pesticide.
The use of bioremediation techniques reduces exposure hazards for workers because they are more affordable than conventional approaches and allow for the on-site treatment of contaminants.
Waste Management UPSC
Waste management can be accomplished in one of two ways: trash reduction or recycling. Less waste will need to be transferred to landfills and incinerators if waste reduction and recycling efforts are consistent. As a result, there will be a significant decrease in the emission of greenhouse gases and other types of pollution. There will be less new product manufacturing as a result of reuse and recycling of existing items.
Sharing is caring!
Waste Management FAQs
What are the 4 types of waste management.
The 4 types of waste management are - Landfills, Recycling, Incineration and Composting
What is meant by waste management?
Waste management refers to the various schemes to manage and dispose of wastes. It can be by discarding, destroying, processing, recycling, reusing, or controlling wastes.
What are the 5 waste management techniques?
They include refuse, reduce, reuse, repurpose, and recycle.
Why is waste management important?
Reducing waste will not only protect the environment but will also save on costs or reduce expenses for disposal.
What is modern waste management?
Modern waste management strategies are geared towards sustainability.

Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

- UPSC Online Coaching
- UPSC Exam 2024
- UPSC Syllabus 2024
- UPSC Prelims Syllabus 2024
- UPSC Mains Syllabus 2024
- UPSC Exam Pattern 2024
- UPSC Age Limit 2024
- UPSC Calendar 2024
- UPSC Syllabus in Hindi
- UPSC Full Form

Recent Posts
- UPPSC Exam 2024
- UPPSC Calendar
- UPPSC Syllabus 2024
- UPPSC Exam Pattern 2024
- UPPSC Application Form 2024
- UPPSC Eligibility Criteria 2024
- UPPSC Admit card 2024
- UPPSC Salary And Posts
- UPPSC Cut Off
- UPPSC Previous Year Paper
BPSC Exam 2024
- BPSC 70th Notification
- BPSC 69th Exam Analysis
- BPSC Admit Card
- BPSC Syllabus
- BPSC Exam Pattern
- BPSC Cut Off
- BPSC Question Papers
IB ACIO Exam
- IB ACIO Salary
- IB ACIO Syllabus
CSIR SO ASO Exam
- CSIR SO ASO Exam 2024
- CSIR SO ASO Result 2024
- CSIR SO ASO Exam Date
- CSIR SO ASO Question Paper
- CSIR SO ASO Answer key 2024
- CSIR SO ASO Exam Date 2024
- CSIR SO ASO Syllabus 2024
Study Material Categories
- Daily The Hindu Analysis
- Daily Practice Quiz for Prelims
- Daily Answer Writing
- Daily Current Affairs
- Indian Polity
- Environment and Ecology
- Art and Culture
- General Knowledge
- Biographies

IMPORTANT EXAMS

- Terms & Conditions
- Return & Refund Policy
- Privacy Policy
To get Personalised DAF Based Questions for your Robust Interview Preparation.
- UPSC Online
- UPSC offline and Hybrid
- UPSC Optional Coaching
- UPPCS Online
- BPSC Online
- MPSC Online
- MPPSC Online
- WBPSC Online
- OPSC Online
- UPPCS Offline Coaching
- BPSC Offline Coaching
- UPSC Test Series
- State PSC Test Series
- DAILY CURRENT AFFAIRS
- SUBJECT WISE CURRENT AFFAIRS
- DAILY EDITORIAL ANALYSIS
- DAILY CURRENT AFFAIRS QUIZ
- Daily Prelims(MCQs) Practice
- Daily Mains Answer Writing
- Free Resources

- Offline Centers
- NCERT Notes
- UDAAN Notes
- UPSC Syllabus
- UPSC Prelims PYQs
- UPSC Mains PYQs
- Prelims Preparation

Plastic Pollution
Recently, Earth Observed its first Plastic Overshoot Day on 28 July, 2023.
More About News
- According to Swiss-based research consultancy Earth Action (EA) , on July 28, 2023, the Earth saw its first Plastic Overshoot Day.

- The global average consumption of plastic per person per year is 20.9 kg.
- In the first 208 days of 2023 , plastic waste is well-managed, meaning it is collected and then either recycled, incinerated or deposited in a sanitary landfill.
- Short-life plastics, encompassing plastic packaging and single-use plastic s, accounts for approximately 37% of the total plastic commercialized annually.
- By 2040 plastic production is set to double, with plastic pollution is expected to triple.
- 175 countries account for 41% of the total mismanaged waste , or 64,63 days, while 12 countries are responsible for 52% of the world’s mismanaged plastic waste , or 145 days of overshoot for 2023.
- 12 Countries: India, China, Brazil, Indonesia, Thailand, Russia, Mexico, the United States, Saudia Arabia, Democratic Republic of Congo, Iran and Kazakhstan.
- India ranks fourth in the MWI, with 98.55 per cent of generated waste being mismanaged and fares poorly in the management of plastics waste.
- Expected mismanaged waste in India in 2023 will be 7,300,752 tonnes of plastic .
- India will also be responsible for releasing an average of 3,30,764 tonnes of microplastics into waterways.
Global Plastic Pollution Crisis
- If this is to continue unchecked, there will be more plastic than fish in the ocean by 2050.
- Marine Plastic Pollution: More than 14 million metric tonnes of plastic enters and damages aquatic ecosystems annually.
- Climate Change: Greenhouse gas emissions associated with plastics are expected to account for 15 per cent of the total emissions allowable by 2050 if humanity is to limit global warming to 1.5°C.
- Out of this, close to half is disposed off as residues , which results in only 9% of plastic waste getting recycled.
- Another 19% gets incinerated , 50% ends up in landfill and 22% evades waste management systems.
Menace of Plastic Pollution in India
- India is the second-largest consumer of plastic globally, with packaging materials contributing significantly to the plastic waste generated.
- Plastic waste often ends up in landfills, rivers, and oceans , causing irreversible damage to the environment and marine life.
- Threat To Ecosystem: It threatens the biodiversity and health of marine and terrestrial ecosystems. Plastic can harm or kill wildlife, damage habitats, and d isrupt food webs.
- Threat to Humans: It poses risks to human health and well-being. Plastic can contaminate the food chain and expose humans to harmful chemicals, reduce the quality and enjoyment of natural environments, and increase the spread of diseases.
- Threat to Climate: It contributes to the climate crisis and resource depletion. Plastic emits greenhouse gases during its production, transportation, and degradation, and consumes large amounts of energy, water, and land.
- Creates social and economic costs and inequalities : Plastic can affect the livelihoods and incomes of people who depend on natural resources, such as fishers or farmers.
- Climate Injustice: Plastic can create environmental injustice and discrimination, as some communities or countries bear a disproportionate burden of plastic waste generation or disposal.
- Waste management is primarily f ocused on the collection and transportation of waste , while its d isposal remains largely neglected .
- This has r esulted in the pollution of water bodies and the emission of harmful gases like methane, which is a potent greenhouse gas.
Steps Taken to Reduce Menace of Plastic Pollution in India
- Single Use Plastic Ban: On July 1, 2022, a ban was imposed on the manufacture, import, stocking, distribution, sale and use of identified single-use plastic items, which have low utility and high littering potential
- Tamil Nadu launched a massive campaign on using cloth bags with vending machines set up under the Meendum Manjappai campaign;
- Uttar Pradesh is implementing the refillable model to promote reuse of packaging material.
- Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR): EPR is a framework that holds producers responsible for the entire lifecycle of their products, including their disposal.
- EPR is implemented in India through various policies and regulations, such as the Plastic Waste Management Rules (2016), and through collaborations between the government, NGOs, and other stakeholders.
- Circular economy: It is a resource efficient economy where waste and pollution are eliminated, products and materials are kept in use at their highest value for the longest time possible, and natural systems are regenerated.
Way Forward
- Global plastic production must be capped and reduced to prevent plastic pollution from tripling by 2040.
- Circular economy solutions can reduce pollution by 80% by 2040.
- Financial mechanisms and capacity-building are essential for participation and national legislation implementation.
- Global North countries that export their waste to Global South countries must be held accountable for supporting infrastructure development in importing countries by at least the volume they export annually.
- Implement effective segregation system s, establish recycling centers, and promote the adoption of advanced technologies for plastic waste processing.
- This can involve collaboration between the government, private sector, and civil society to develop innovative solutions.
- India has the capacity to process 14.2 million tonnes of plastic waste annually, accounting for 71% of primary plastic production.
News Source: Down to Earth
To get PDF version, Please click on "Print PDF" button.

- Recent Post
- Related Post
- Most Viewed Post

Nuclear Energy Summit 2024
The ART of India’s HIV/AIDS response
India’s Trade Reliance on China and EU Rising: UNCTAD
Vaikom Satyagraha
Katchatheevu Island
Genetic Profiling of Captive Elephants
Social Stock Exchange
Prime- minister’s egypt state visit, shanan power project, msp hike and its impact, natural rubber production in india: status, government initi..., latest comments, recent editorial.
Workers, not Tech, should be State’s Priority
Free Antiretroviral Therapy (ART) Initiative For H...
Bhagat Singh: Biography, Scholarly Works, and His ...
Protecting Children on Social Media Platforms: Rea...
On the DGCA and Flight Duty Time Limitation Norms
Popular current affairs
India’s Trade Reliance on China and EU Rising: U...
Our Courses

THE MOST LEARNING PLATFORM
Learn From India's Best Faculty
Our Initiatives
Beginner’s roadmap, quick links.

PW-Only IAS came together specifically to carry their individual visions in a mission mode. Infusing affordability with quality and building a team where maximum members represent their experiences of Mains and Interview Stage and hence, their reliability to better understand and solve student issues.
Subscribe our Newsletter
Sign up now for our exclusive newsletter and be the first to know about our latest Initiatives, Quality Content, and much more.
Contact Details
G-Floor,4-B Pusha Road, New Delhi, 110060
- +91 9920613613
- [email protected]
Download Our App

Biginner's Roadmap
Suscribe now form, to get early access of such quality content..
Join Us Now
(Promise! We Will Not Spam You.)
CURRENT AF.
<div class="new-fform">
Select centre Online Mode Hybrid Mode PWonlyIAS Delhi (ORN) PWonlyIAS Delhi (MN) PWonlyIAS Lucknow PWonlyIAS Patna Other
Select course UPSC Online PSC ONline UPSC + PSC ONLINE UPSC Offline PSC Offline UPSC+PSC Offline UPSC Hybrid PSC Hybrid UPSC+PSC Hybrid Other
</div>

Essay on Waste Management for Students and Teacher
500+ essay on waste management.
Essay on Waste Management -Waste management is essential in today’s society. Due to an increase in population, the generation of waste is getting doubled day by day. Moreover, the increase in waste is affecting the lives of many people.
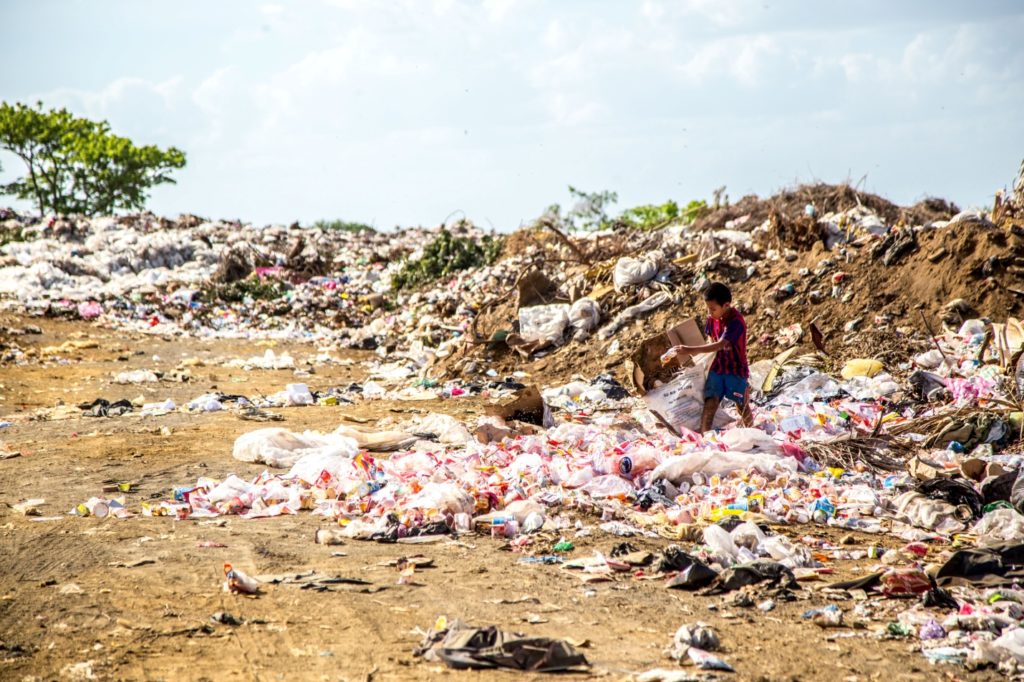

For instance, people living in slums are very close to the waste disposal area. Therefore there are prone to various diseases. Hence, putting their lives in danger. In order to maintain a healthy life, proper hygiene and sanitation are necessary. Consequently, it is only possible with proper waste management .
The Meaning of Waste Management
Waste management is the managing of waste by disposal and recycling of it. Moreover, waste management needs proper techniques keeping in mind the environmental situations. For instance, there are various methods and techniques by which the waste is disposed of. Some of them are Landfills, Recycling , Composting, etc. Furthermore, these methods are much useful in disposing of the waste without causing any harm to the environment.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Methods for Waste Management
Recycling – Above all the most important method is the recycling of waste. This method does not need any resources. Therefore this is much useful in the management of waste . Recycling is the reusing of things that are scrapped of. Moreover, recycling is further converting waste into useful resources.

Landfills – Landfills is the most common method for waste management. The garbage gets buried in large pits in the ground and then covered by the layer of mud. As a result, the garbage gets decomposed inside the pits over the years. In conclusion, in this method elimination of the odor and area taken by the waste takes place.
Composting – Composting is the converting of organic waste into fertilizers. This method increases the fertility of the soil. As a result, it is helpful in more growth in plants. Furthermore it the useful conversion of waste management that is benefiting the environment.
Advantages of Waste Management
There are various advantages of waste management. Some of them are below:
Decrease bad odor – Waste produces a lot of bad odor which is harmful to the environment. Moreover, Bad odor is responsible for various diseases in children. As a result, it hampers their growth. So waste management eliminates all these problems in an efficient way.
Reduces pollution – Waste is the major cause of environmental degradation. For instance, the waste from industries and households pollute our rivers. Therefore waste management is essential. So that the environment may not get polluted. Furthermore, it increases the hygiene of the city so that people may get a better environment to live in.
Reduces the production of waste -Recycling of the products helps in reducing waste. Furthermore, it generates new products which are again useful. Moreover, recycling reduces the use of new products. So the companies will decrease their production rate.
It generates employment – The waste management system needs workers. These workers can do various jobs from collecting to the disposing of waste. Therefore it creates opportunities for the people that do not have any job. Furthermore, this will help them in contributing to society.
Produces Energy – Many waste products can be further used to produce energy. For instance, some products can generate heat by burning. Furthermore, some organic products are useful in fertilizers. Therefore it can increase the fertility of the soil.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

Plastic Waste Management Essay

Introduction
Take a look around, and do you find anything that is not made from plastic? The pen with which you write, water bottle, mobile phone covers, everything and anything that is near you is made up of plastic. In this age, plastic has become an unavoidable part of our lives, but we need to switch to eco-friendly materials. Have you thought about how plastic waste is treated? What will you do with your used refill of the pen, or where do all the plastic covers end up? The essay on plastic waste management will give you answers to these questions. You can check out other trivia questions on BYJU’S website and make kids’ learning interesting.
Although the answers are disturbing, as they mostly turn up in landfills without decomposing or get burned down by emitting poisonous chemicals in the air, we can tackle this issue if we follow certain measures. Plastic pollution is becoming a grave concern, and that is why we need proper ways for plastic waste management.
Causes and Effects of Plastic Waste
Let us understand the impact of plastic waste on the environment through this plastic waste management essay in English. But first, let us see how plastic waste gets accumulates in our surroundings. It is considered that human negligence is the main culprit behind the cause of plastic waste. We carelessly throw plastic litter around, and they remain abandoned, thus polluting water and land resources. Even after years, they will not decompose and find their way into aquatic life, thereby threatening their lives. We must treat plastic waste differently from other garbage, and this highlights the importance of proper plastic waste management.
Plastic waste has serious effects on both the environment and living beings. If we just throw plastics around, it will act as a perfect breeding ground for mosquitoes and other insects and cause us acute diseases. As plastic waste does not degrade completely, they remain on the land for many years, which affects soil fertility. There is also a high chance of clogging drains and pipes when the plastic enters the drainage system. Besides, when small plastic covers and sachets are disposed of, they get eaten by animals and fishes, thus threatening their lives. Therefore, plastic waste is a grave threat to everything in the environment at all levels.
Ways for Plastic Waste Management
The best way for plastic waste management is through the 3 Rs – reduce, reuse and recycle. We can understand this further in BYJU’S essay on plastic waste management. We must reduce the use of plastic by carrying a cloth bag or paper bag while shopping and refusing to accept plastic bags from shops. We can also replace plastic containers with metal/wooden boxes to store goods and clothes. If you buy a bottled drink from a supermarket, remember not to throw away the plastic bottle after use, but instead, reuse it to store water or create something unique. In addition, we can recycle plastic and try to use recycled products. Apart from these, let us make a vow not to burn or dump plastics, as plastic waste management will only be complete with these measures.
If you found the plastic waste management essay informative, you can find similar essays on BYJU’S website to enhance kids’ learning experience.
Frequently Asked Questions on Plastic Waste Management Essay
What is meant by plastic waste management.
Plastic waste is a rising problem in the environment that pollutes air, water and land. There must be proper and effective methods to treat plastic waste, and this is known as plastic waste management.
How to reduce plastic waste?
Reducing, reusing and recycling plastic is the most sustainable way to reduce plastic waste. In doing so, the amount of plastic waste will decrease gradually, and thus we can save our environment.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

Call us @ 08069405205

Search Here

- An Introduction to the CSE Exam
- Personality Test
- Annual Calendar by UPSC-2024
- Common Myths about the Exam
- About Insights IAS
- Our Mission, Vision & Values
- Director's Desk
- Meet Our Team
- Our Branches
- Careers at Insights IAS
- Daily Current Affairs+PIB Summary
- Insights into Editorials
- Insta Revision Modules for Prelims
- Current Affairs Quiz
- Static Quiz
- Current Affairs RTM
- Insta-DART(CSAT)
- Insta 75 Days Revision Tests for Prelims 2024
- Secure (Mains Answer writing)
- Secure Synopsis
- Ethics Case Studies
- Insta Ethics
- Weekly Essay Challenge
- Insta Revision Modules-Mains
- Insta 75 Days Revision Tests for Mains
- Secure (Archive)
- Anthropology
- Law Optional
- Kannada Literature
- Public Administration
- English Literature
- Medical Science
- Mathematics
- Commerce & Accountancy
- Monthly Magazine: CURRENT AFFAIRS 30
- Content for Mains Enrichment (CME)
- InstaMaps: Important Places in News
- Weekly CA Magazine
- The PRIME Magazine
- Insta Revision Modules-Prelims
- Insta-DART(CSAT) Quiz
- Insta 75 days Revision Tests for Prelims 2022
- Insights SECURE(Mains Answer Writing)
- Interview Transcripts
- Previous Years' Question Papers-Prelims
- Answer Keys for Prelims PYQs
- Solve Prelims PYQs
- Previous Years' Question Papers-Mains
- UPSC CSE Syllabus
- Toppers from Insights IAS
- Testimonials
- Felicitation
- UPSC Results
- Indian Heritage & Culture
- Ancient Indian History
- Medieval Indian History
- Modern Indian History
- World History
- World Geography
- Indian Geography
- Indian Society
- Social Justice
- International Relations
- Agriculture
- Environment & Ecology
- Disaster Management
- Science & Technology
- Security Issues
- Ethics, Integrity and Aptitude

- Indian Heritage & Culture
- Enivornment & Ecology

Sansad TV: Food Waste Index Report 2024

Introduction:
It is a strange irony that on one hand the world is a victim of starvation and on the other hand crores of tonnes of food grains are wasted. You will be surprised to see the figures of food wastage and starvation released by the United Nations. It has been said in this report that more food grains are wasted every day than the number of people in the world who go to sleep hungry every day. Hotel and restaurant owners play the biggest role in this. In fact, the United Nations report states that in the year 2022, 19 percent of the total grain production globally, i.e. about 1.05 billion tonnes of grains, was wasted. The UN Environment Programme’s Food Waste Index report monitors countries’ progress in halving food waste by 2030.
Behaviour and attitude change needed to prevent food wastage
- The astonishing statistics of food waste attributed to households and their irresponsible consumption patterns means that change needs to begin in our own homes.
- Calculated purchasing when buying groceries, minimising single-use packaging wherever possible, ordering consciously from restaurants, and reconsidering extravagant buffet spreads at weddings can go a long way.
- At the community level, one can identify and get involved with organisations such as Coimbatore-based No Food Waste which aim to redistribute excess food to feed the needy and hungry.
- A strong sense of judiciousness in how we consume our food is the next logical step. We must attempt to change our “food abundance” mindset to a “food scarcity” one, working our way towards a zero-waste end goal.
Impact of food loss and waste:
- Reducing food losses and waste is essential in a world where the number of people affected by hunger has been slowly on the rise since 2014, and tons and tons of edible food are lost and/or wasted every day.
- When food is loss or wasted, all the resources that were used to produce this food -, including water, land, energy, labour and capital – go to waste. In addition, the disposal of food loss and waste in landfills, leads to greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to climate change.
- Further, several toxins and/or a black liquid known as leachate, oozes from the waste, which is absorbed by the soil/ground, leading to the contamination of ground water. These overflowing landfills have today become the root cause of blocked drains, soil and water pollution.
- As well as reducing pollution emitted by wasted food, lots of energy and resources are also conserved in the process. From growing crops, manufacturing, transportation, and selling of food — all of these processes consume energy and resources.
Importance of reducing food loss and waste:
- When reductions in food loss occur close to the farm, they are most effective in addressing food insecurity and in alleviating stress on land and water.
- When reductions in food waste occur downstream in the supply chain and at the consumer level they are key to cutting greenhouse gas emissions.
- The largest improvements in food security are likely to occur by reducing food losses in the early stages of the supply chain, especially on-farm and at harvest in countries with high levels of food insecurity.
- Nutrient loss due to quantitative and qualitative food loss and waste may represent a missed opportunity to reduce malnutrition and micronutrient deficiencies.
- Reduces methane emissions from landfills and lowers carbon footprint.
- Conserves energy and resources, preventing pollution involved in the growing, manufacturing, transporting, and selling food (not to mention hauling the food waste and then putting it in the landfill).
Way forward:
- Make the children aware of the importance of food and the impact of food waste on environment
- Make it a habit to give the uneaten food left from your household parties to donate to charities through NGOs in your area.
- Follow essential food safety techniques to avoid food waste
- Set up of food waste audit will help realize how and why food has been wasted.
- Maintain a correct temperature and good storage facility for perishables items
- Regular checking of temperatures, seals on fridges and freezers and rotation of stock to keep them fresh will bring down spoilage.
- In France, it is mandatory for supermarkets to donate unsold food items to charity or farmers to convert them into fertilizers
- Canada recovers unused food items from manufacturers, retailers, restaurants, etc. and delivers these food ingredients to be used to cook over 22,000 meals every day
- Sweden implemented a recycling revolution, wherein less than 1% of household waste ends up in landfills and of the 4.4 million tons of household waste produced every year, 2.2 million is converted into energy.

- Our Mission, Vision & Values
- Director’s Desk
- Commerce & Accountancy
- Previous Years’ Question Papers-Prelims
- Previous Years’ Question Papers-Mains
- Environment & Ecology
- Science & Technology

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Solid Waste Management. Last updated on March 18, 2024 by ClearIAS Team. Solid waste management is the systematic process of collecting, treating, disposing, and recycling solid waste generated by human activities. Proper solid waste management is essential for environmental sustainability, public health, and the overall well-being of communities.
Waste to Energy: A waste-to-energy or energy-from-waste plant converts municipal and industrial solid waste into electricity and/or heat for industrial processing. Plastic Waste Management (PWM) Rules, 2016: It mandates the generators of plastic waste to take steps to minimize generation of plastic waste, prevent littering of plastic waste, and ...
Methods for Waste Management. Incineration - Under this waste management system, public solid waste is buried for turning it into oil, dust, steam, ash and gases. It eliminates solid waste by about 31 per cent of the total amount. Landfills - Disposal of garbage and waste within landfills is one of the most common waste management methods.
Plastic Waste in India: According to the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB), India generates close to 26,000 tonnes of plastic a day and over 10,000 tonnes a day of plastic waste remains uncollected.; According to a Federation of Indian Chambers of Commerce and Industry (FICCI) study the plastic processing industry is estimated to grow to 22 million tonnes (MT) a year by 2020 from 13.4 MT ...
Overall Solid Waste Management Status. According to the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) the total quantity of Solid waste generated in the country is ~160,000 metric tonnes per day (TPD). ~153,000 TPD of waste is collected at a collection efficiency of ~96%. 80,000 TPD (50 %) of waste is treated and ~30,000 (18.4%) TPD is landfilled ...
Solid-Waste Management. Solid waste refers to all non-liquid wastes that include Solid as well as semi-solid wastes, but excluding Human and Animal excreta. Solid waste can create very serious health problems and an unpleasant living environment if not disposed of in a proper and a safe manner, such waste may then also provide breeding sites ...
Plastic has become one of the most pressing environmental issues that we are facing today. India is generating about 3.5 million tonnes of plastic waste annually. The huge volumes of leakages in plastic wastes demands a clarion call for a various efforts for plastic waste management in the country.
Insights into Issues: Waste Management The Government of India had notified the Municipal Solid Waste (Management and Handling) Rules in 2000, thereby making it mandatory for all urban local bodies in the country to engage in collection, segregation, secondary storage in covered bins, transportation in covered vehicles, processing through composting or waste-to-energy technologies and disposal ...
Here are the key points of the Solid Waste Management Rules: Segregation of waste at the source: The rules mandate segregation of waste at the source into three categories - wet, dry and hazardous waste. Collection and transportation of waste: Local bodies are responsible for collecting and transporting the waste in a scientific manner.
Conclusion: International Day of Zero Waste propels the transition to a sustainable future, inspiring action, promoting responsible waste management, and fostering the adoption of circular economy principles. By raising awareness and supporting zero-waste practices, we contribute to a paradigm shift towards a more sustainable and environmentally conscious society.
The first rule of waste management all over the world is that households must segregate their waste before it is collected from the doorstep. Also, the Solid Waste Management Rules 2016 in India prescribe the same. Waste segregation can help Indian cities 'get' cleaned up, as current modes of solid waste disposal just make the city to ...
Waste to Energy (WtE) The process of creating energy in the form of electricity and/or heat from the primary treatment of trash, or the processing of waste into a fuel source. Waste to Energy is an energy recovery method. Most WtE processes either create a combustible fuel commodity, such as methane, methanol, ethanol, or synthetic fuels, or ...
Essay on Waste Management in 300 Words. The basic mantra of waste management is" Refuse, Reuse, Reduce, Repurpose, and Recycle". Waste management is basically the collection or accumulation of waste and its disposal. This process involves the proper management of waste including recycling waste generated and even generating useful renewable ...
Waste Management UPSC. Waste management can be accomplished in one of two ways: trash reduction or recycling. Less waste will need to be transferred to landfills and incinerators if waste reduction and recycling efforts are consistent. As a result, there will be a significant decrease in the emission of greenhouse gases and other types of ...
Flawed Waste Management System in India: Municipal authorities are responsible for the collection and transportation of waste, while the waste's final disposal is usually left to informal waste pickers or landfill sites. ... Explore all centers Download UPSC Mains 2023 Question Papers PDF ...
Plastic Waste as a Global Phenomenon: Over 8.3 billion tonnes of plastic has been produced since 1950, and about 60% of that has ended up in landfills or in the natural environment. Only 9% of all plastic waste ever produced has been recycled and about 12% has been incinerated, while the remaining 79% has accumulated in landfills, dumps or the ...
Plastic Waste Management Rules, 2016 state that every local body has to be responsible for setting up infrastructure for segregation, collection, processing, and disposal of plastic waste.; Plastic Waste Management (Amendment) Rules 2018 introduced the concept of Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR).; A new national framework on plastic waste management is in the works, which will introduce ...
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas. Methods for Waste Management. Recycling - Above all the most important method is the recycling of waste. This method does not need any resources. Therefore this is much useful in the management of waste. Recycling is the reusing of things that are scrapped of.
E- Waste Management. E-Waste is short for Electronic-Waste and the term is used to describe old, end-of-life or discarded electronic appliances. It includes their components, consumables, parts and spares. It is categorised into 21 types under two broad categories: Information technology and communication equipment.
The best way for plastic waste management is through the 3 Rs - reduce, reuse and recycle. We can understand this further in BYJU'S essay on plastic waste management. We must reduce the use of plastic by carrying a cloth bag or paper bag while shopping and refusing to accept plastic bags from shops. We can also replace plastic containers ...
NGT's Directions: Further steps should be taken for scientific enforcement of E-Waste Management Rules, 2016 (EWMR) in the light of the reports of the CPCB. It noted gaps in collection targets, as the amount of e-waste collected in 2018-19 was 78,000 tonnes against a target of 1.54 lakh tonnes. There are clear governance deficits on the subject.
The UN Environment Programme's Food Waste Index report monitors countries' progress in halving food waste by 2030. Behaviour and attitude change needed to prevent food wastage. The astonishing statistics of food waste attributed to households and their irresponsible consumption patterns means that change needs to begin in our own homes.