- CBSE Class 10th
- CBSE Class 12th
- UP Board 10th
- UP Board 12th
- Bihar Board 10th
- Bihar Board 12th
- Top Schools in India
- Top Schools in Delhi
- Top Schools in Mumbai
- Top Schools in Chennai
- Top Schools in Hyderabad
- Top Schools in Kolkata
- Top Schools in Pune
- Top Schools in Bangalore

Products & Resources
- JEE Main Knockout April
- Free Sample Papers
- Free Ebooks
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Syllabus
- NCERT Books
- RD Sharma Solutions
- Navodaya Vidyalaya Admission 2024-25
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11
- NCERT solutions for Class 10
- NCERT solutions for Class 9
- NCERT solutions for Class 8
- NCERT Solutions for Class 7
- JEE Main 2024
- JEE Advanced 2024
- BITSAT 2024
- View All Engineering Exams
- Colleges Accepting B.Tech Applications
- Top Engineering Colleges in India
- Engineering Colleges in India
- Engineering Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- Engineering Colleges Accepting JEE Main
- Top IITs in India
- Top NITs in India
- Top IIITs in India
- JEE Main College Predictor
- JEE Main Rank Predictor
- MHT CET College Predictor
- AP EAMCET College Predictor
- GATE College Predictor
- KCET College Predictor
- JEE Advanced College Predictor
- View All College Predictors
- JEE Main Question Paper
- JEE Main Mock Test
- JEE Main Registration
- JEE Main Syllabus
- Download E-Books and Sample Papers
- Compare Colleges
- B.Tech College Applications
- GATE 2024 Result
- MAH MBA CET Exam
- View All Management Exams
Colleges & Courses
- MBA College Admissions
- MBA Colleges in India
- Top IIMs Colleges in India
- Top Online MBA Colleges in India
- MBA Colleges Accepting XAT Score
- BBA Colleges in India
- XAT College Predictor 2024
- SNAP College Predictor
- NMAT College Predictor
- MAT College Predictor 2024
- CMAT College Predictor 2024
- CAT Percentile Predictor 2023
- CAT 2023 College Predictor
- CMAT 2024 Registration
- TS ICET 2024 Registration
- CMAT Exam Date 2024
- MAH MBA CET Cutoff 2024
- Download Helpful Ebooks
- List of Popular Branches
- QnA - Get answers to your doubts
- IIM Fees Structure
- AIIMS Nursing
- Top Medical Colleges in India
- Top Medical Colleges in India accepting NEET Score
- Medical Colleges accepting NEET
- List of Medical Colleges in India
- List of AIIMS Colleges In India
- Medical Colleges in Maharashtra
- Medical Colleges in India Accepting NEET PG
- NEET College Predictor
- NEET PG College Predictor
- NEET MDS College Predictor
- DNB CET College Predictor
- DNB PDCET College Predictor
- NEET Application Form 2024
- NEET PG Application Form 2024
- NEET Cut off
- NEET Online Preparation
- Download Helpful E-books
- LSAT India 2024
- Colleges Accepting Admissions
- Top Law Colleges in India
- Law College Accepting CLAT Score
- List of Law Colleges in India
- Top Law Colleges in Delhi
- Top Law Collages in Indore
- Top Law Colleges in Chandigarh
- Top Law Collages in Lucknow
Predictors & E-Books
- CLAT College Predictor
- MHCET Law ( 5 Year L.L.B) College Predictor
- AILET College Predictor
- Sample Papers
- Compare Law Collages
- Careers360 Youtube Channel
- CLAT Syllabus 2025
- CLAT Previous Year Question Paper
- AIBE 18 Result 2023
- NID DAT Exam
- Pearl Academy Exam
Animation Courses
- Animation Courses in India
- Animation Courses in Bangalore
- Animation Courses in Mumbai
- Animation Courses in Pune
- Animation Courses in Chennai
- Animation Courses in Hyderabad
- Design Colleges in India
- Fashion Design Colleges in Bangalore
- Fashion Design Colleges in Mumbai
- Fashion Design Colleges in Pune
- Fashion Design Colleges in Delhi
- Fashion Design Colleges in Hyderabad
- Fashion Design Colleges in India
- Top Design Colleges in India
- Free Design E-books
- List of Branches
- Careers360 Youtube channel
- NIFT College Predictor
- UCEED College Predictor
- NID DAT College Predictor
- IPU CET BJMC
- JMI Mass Communication Entrance Exam
- IIMC Entrance Exam
- Media & Journalism colleges in Delhi
- Media & Journalism colleges in Bangalore
- Media & Journalism colleges in Mumbai
- List of Media & Journalism Colleges in India
- CA Intermediate
- CA Foundation
- CS Executive
- CS Professional
- Difference between CA and CS
- Difference between CA and CMA
- CA Full form
- CMA Full form
- CS Full form
- CA Salary In India
Top Courses & Careers
- Bachelor of Commerce (B.Com)
- Master of Commerce (M.Com)
- Company Secretary
- Cost Accountant
- Charted Accountant
- Credit Manager
- Financial Advisor
- Top Commerce Colleges in India
- Top Government Commerce Colleges in India
- Top Private Commerce Colleges in India
- Top M.Com Colleges in Mumbai
- Top B.Com Colleges in India
- IT Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- IT Colleges in Uttar Pradesh
- MCA Colleges in India
- BCA Colleges in India
Quick Links
- Information Technology Courses
- Programming Courses
- Web Development Courses
- Data Analytics Courses
- Big Data Analytics Courses
- RUHS Pharmacy Admission Test
- Top Pharmacy Colleges in India
- Pharmacy Colleges in Pune
- Pharmacy Colleges in Mumbai
- Colleges Accepting GPAT Score
- Pharmacy Colleges in Lucknow
- List of Pharmacy Colleges in Nagpur
- GPAT Result
- GPAT 2024 Admit Card
- GPAT Question Papers
- NCHMCT JEE 2024
- Mah BHMCT CET
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Delhi
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Hyderabad
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Mumbai
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Maharashtra
- B.Sc Hotel Management
- Hotel Management
- Diploma in Hotel Management and Catering Technology
Diploma Colleges
- Top Diploma Colleges in Maharashtra
- UPSC IAS 2024
- SSC CGL 2024
- IBPS RRB 2024
- Previous Year Sample Papers
- Free Competition E-books
- Sarkari Result
- QnA- Get your doubts answered
- UPSC Previous Year Sample Papers
- CTET Previous Year Sample Papers
- SBI Clerk Previous Year Sample Papers
- NDA Previous Year Sample Papers
Upcoming Events
- NDA Application Form 2024
- UPSC IAS Application Form 2024
- CDS Application Form 2024
- CTET Admit card 2024
- HP TET Result 2023
- SSC GD Constable Admit Card 2024
- UPTET Notification 2024
- SBI Clerk Result 2024
Other Exams
- SSC CHSL 2024
- UP PCS 2024
- UGC NET 2024
- RRB NTPC 2024
- IBPS PO 2024
- IBPS Clerk 2024
- IBPS SO 2024
- Top University in USA
- Top University in Canada
- Top University in Ireland
- Top Universities in UK
- Top Universities in Australia
- Best MBA Colleges in Abroad
- Business Management Studies Colleges
Top Countries
- Study in USA
- Study in UK
- Study in Canada
- Study in Australia
- Study in Ireland
- Study in Germany
- Study in China
- Study in Europe
Student Visas
- Student Visa Canada
- Student Visa UK
- Student Visa USA
- Student Visa Australia
- Student Visa Germany
- Student Visa New Zealand
- Student Visa Ireland
- CUET PG 2024
- IGNOU B.Ed Admission 2024
- DU Admission
- UP B.Ed JEE 2024
- DDU Entrance Exam
- IIT JAM 2024
- IGNOU Online Admission 2024
- Universities in India
- Top Universities in India 2024
- Top Colleges in India
- Top Universities in Uttar Pradesh 2024
- Top Universities in Bihar
- Top Universities in Madhya Pradesh 2024
- Top Universities in Tamil Nadu 2024
- Central Universities in India
- CUET PG Admit Card 2024
- IGNOU Date Sheet
- CUET Mock Test 2024
- CUET Application Form 2024
- CUET PG Syllabus 2024
- CUET Participating Universities 2024
- CUET Previous Year Question Paper
- CUET Syllabus 2024 for Science Students
- E-Books and Sample Papers
- CUET Exam Pattern 2024
- CUET Exam Date 2024
- CUET Syllabus 2024
- IGNOU Exam Form 2024
- IGNOU Result
- CUET PG Courses 2024
Engineering Preparation
- Knockout JEE Main 2024
- Test Series JEE Main 2024
- JEE Main 2024 Rank Booster
Medical Preparation
- Knockout NEET 2024
- Test Series NEET 2024
- Rank Booster NEET 2024
Online Courses
- JEE Main One Month Course
- NEET One Month Course
- IBSAT Free Mock Tests
- IIT JEE Foundation Course
- Knockout BITSAT 2024
- Career Guidance Tool
Top Streams
- IT & Software Certification Courses
- Engineering and Architecture Certification Courses
- Programming And Development Certification Courses
- Business and Management Certification Courses
- Marketing Certification Courses
- Health and Fitness Certification Courses
- Design Certification Courses
Specializations
- Digital Marketing Certification Courses
- Cyber Security Certification Courses
- Artificial Intelligence Certification Courses
- Business Analytics Certification Courses
- Data Science Certification Courses
- Cloud Computing Certification Courses
- Machine Learning Certification Courses
- View All Certification Courses
- UG Degree Courses
- PG Degree Courses
- Short Term Courses
- Free Courses
- Online Degrees and Diplomas
- Compare Courses
Top Providers
- Coursera Courses
- Udemy Courses
- Edx Courses
- Swayam Courses
- upGrad Courses
- Simplilearn Courses
- Great Learning Courses
Access premium articles, webinars, resources to make the best decisions for career, course, exams, scholarships, study abroad and much more with
Plan, Prepare & Make the Best Career Choices
The Person I Admire The Most Essay
Essay On The Person I Admire The Most - They are the people who make us believe that good things do exist. We are blessed to have those people in our life. They are the people who motivate us to grow. Here are 100, 200 and 500-word essays on “The Person I Admire The Most”.
We all have someone or another whom we admire the most. We love the other person so much that we can do anything for the other person. They are the people who make us believe that good things do exist. We are blessed to have those people in our life. They are the people who motivate us to grow. These are the people who support us to the fullest. Here are some sample essays on “The Person I Admire The Most”.

100 Words On The Person I Admire The Most Essay
The person I admire the most is my sister. She is an inspiration to me. She motivates me to do things that I am not sure about. She takes care of me and supports me whenever I need her. She has achieved so much at such a young age. Her attitude, patience, and confidence really inspire me a lot. She does everything in such a perfect way and never complains about her responsibilities. She is such an inspiration to me that I try to infuse her values within me. She is a person who motivates me every time I need her.
200 Words On The Person I Admire The Most Essay
When asked about a particular person, I admire the most, a lot of names come across my mind. These include my mother, sister, father, and even a few celebrities' names come to my mind. I can proudly tell that the person I admire is my grandmother. She is a woman to be looked upon. She is a great lady who has not only given enough to her home as well as to the world. She is a superwoman who handles her work beautifully simultaneously with her family. For people, Wonder Woman is Gal Gadot, but for me, Wonder Woman is my grandmother.
Why My Grandmother Is My Hero
My grandmother secured a gold medal at her graduation. She was the first female officer in the Audit General Office all over the Northeast. She is also a poet, writer, and novelist. Her work is being published, and it is getting all the love from its readers. She has also done much social work. Due to her social work, she still gets immense love from people. She inspires me a lot. She teaches me it does not matter if you are a girl or a boy, if you have the will to do a particular task you can do it. I still have a lot to learn from her, and I will continue admiring her.
500 Words On The Person I Admire The Most Essay
We all have someone or another whom we admire the most. The person I admire the most is Virat Kohli.
Virat Kohli - the Person I Admire The Most
Virat Kohli is considered one of the most successful international cricketers, and I try to imbibe some of his virtues that will help them succeed in life. Virat has always inspired me with supremacy, success, and class in his game. Regardless of the team's situation during the match, Virat always tries to finish the game with self-determination, bravery, talent, and the ability to win.
I also try to succeed in my studies by drawing inspiration from his personality traits. What made Virat Kohli a youth icon is his passion for playing cricket and winning matches for his country. His commitment to his game is no longer a hidden fact. Virat has amassed runs in his successful career due to his involvement in match runs as he does not hand wickets easily to bowlers.
Why I Admire Virat Kohli
I still remember the Ipl season of 2016 when he scored 973 in a single tournament. He shocked everyone that it is possible for a man to be so good at a craft. He had stitches in his hands despite that he made a brilliant century. This day opened my eyes that we can do it whatever may be the circumstances. That day he became an idol for me. He showed that our interest comes secondary to that of the team's interest. It is one such instance of why I love him so much.
Virat Kohli: An Inspiration
His professionalism inspires me to pursue my goals regardless of the circumstances. Virat Kohli is a fitness icon in the sports world, and athletes and their fans look up to him for his fitness. His commitment towards fitness teaches me the value of healthy living and fitness. Self-discipline and practice are the most important aspects of his personality. To master his game, Virat practised more and more to succeed.
Having firmly established himself in every format among many fierce rivals, Kohli is undoubtedly one of the crowning jewels of Indian cricket. Virat Kohli is a symbol of passion and dedication.
A source of inspiration to the youngster, he is a disciplined batsman and was a prolific captain who had led the Indian side to success under his captaincy. His never giving attitude really makes me his fan. He has always motivated me and showed me the ray of hope that with passion everything can be achieved. He is an inspiration to millions including me. His infused values will remain forever in me and he will continue to be my idol.
Therefore we all have someone or the other who makes our love worth living. One who teaches us that the sky's the limit and one who always pushes us to go out of our comfort zone. They are the people who teach us to be the best version of ourselves and we should always hold onto these people and learn from them.
Explore Career Options (By Industry)
- Construction
- Entertainment
- Manufacturing
- Information Technology
Bio Medical Engineer
The field of biomedical engineering opens up a universe of expert chances. An Individual in the biomedical engineering career path work in the field of engineering as well as medicine, in order to find out solutions to common problems of the two fields. The biomedical engineering job opportunities are to collaborate with doctors and researchers to develop medical systems, equipment, or devices that can solve clinical problems. Here we will be discussing jobs after biomedical engineering, how to get a job in biomedical engineering, biomedical engineering scope, and salary.
Data Administrator
Database professionals use software to store and organise data such as financial information, and customer shipping records. Individuals who opt for a career as data administrators ensure that data is available for users and secured from unauthorised sales. DB administrators may work in various types of industries. It may involve computer systems design, service firms, insurance companies, banks and hospitals.
Ethical Hacker
A career as ethical hacker involves various challenges and provides lucrative opportunities in the digital era where every giant business and startup owns its cyberspace on the world wide web. Individuals in the ethical hacker career path try to find the vulnerabilities in the cyber system to get its authority. If he or she succeeds in it then he or she gets its illegal authority. Individuals in the ethical hacker career path then steal information or delete the file that could affect the business, functioning, or services of the organization.
Data Analyst
The invention of the database has given fresh breath to the people involved in the data analytics career path. Analysis refers to splitting up a whole into its individual components for individual analysis. Data analysis is a method through which raw data are processed and transformed into information that would be beneficial for user strategic thinking.
Data are collected and examined to respond to questions, evaluate hypotheses or contradict theories. It is a tool for analyzing, transforming, modeling, and arranging data with useful knowledge, to assist in decision-making and methods, encompassing various strategies, and is used in different fields of business, research, and social science.
Geothermal Engineer
Individuals who opt for a career as geothermal engineers are the professionals involved in the processing of geothermal energy. The responsibilities of geothermal engineers may vary depending on the workplace location. Those who work in fields design facilities to process and distribute geothermal energy. They oversee the functioning of machinery used in the field.
Remote Sensing Technician
Individuals who opt for a career as a remote sensing technician possess unique personalities. Remote sensing analysts seem to be rational human beings, they are strong, independent, persistent, sincere, realistic and resourceful. Some of them are analytical as well, which means they are intelligent, introspective and inquisitive.
Remote sensing scientists use remote sensing technology to support scientists in fields such as community planning, flight planning or the management of natural resources. Analysing data collected from aircraft, satellites or ground-based platforms using statistical analysis software, image analysis software or Geographic Information Systems (GIS) is a significant part of their work. Do you want to learn how to become remote sensing technician? There's no need to be concerned; we've devised a simple remote sensing technician career path for you. Scroll through the pages and read.
Geotechnical engineer
The role of geotechnical engineer starts with reviewing the projects needed to define the required material properties. The work responsibilities are followed by a site investigation of rock, soil, fault distribution and bedrock properties on and below an area of interest. The investigation is aimed to improve the ground engineering design and determine their engineering properties that include how they will interact with, on or in a proposed construction.
The role of geotechnical engineer in mining includes designing and determining the type of foundations, earthworks, and or pavement subgrades required for the intended man-made structures to be made. Geotechnical engineering jobs are involved in earthen and concrete dam construction projects, working under a range of normal and extreme loading conditions.
Cartographer
How fascinating it is to represent the whole world on just a piece of paper or a sphere. With the help of maps, we are able to represent the real world on a much smaller scale. Individuals who opt for a career as a cartographer are those who make maps. But, cartography is not just limited to maps, it is about a mixture of art , science , and technology. As a cartographer, not only you will create maps but use various geodetic surveys and remote sensing systems to measure, analyse, and create different maps for political, cultural or educational purposes.
Budget Analyst
Budget analysis, in a nutshell, entails thoroughly analyzing the details of a financial budget. The budget analysis aims to better understand and manage revenue. Budget analysts assist in the achievement of financial targets, the preservation of profitability, and the pursuit of long-term growth for a business. Budget analysts generally have a bachelor's degree in accounting, finance, economics, or a closely related field. Knowledge of Financial Management is of prime importance in this career.
Product Manager
A Product Manager is a professional responsible for product planning and marketing. He or she manages the product throughout the Product Life Cycle, gathering and prioritising the product. A product manager job description includes defining the product vision and working closely with team members of other departments to deliver winning products.
Underwriter
An underwriter is a person who assesses and evaluates the risk of insurance in his or her field like mortgage, loan, health policy, investment, and so on and so forth. The underwriter career path does involve risks as analysing the risks means finding out if there is a way for the insurance underwriter jobs to recover the money from its clients. If the risk turns out to be too much for the company then in the future it is an underwriter who will be held accountable for it. Therefore, one must carry out his or her job with a lot of attention and diligence.
Finance Executive
Operations manager.
Individuals in the operations manager jobs are responsible for ensuring the efficiency of each department to acquire its optimal goal. They plan the use of resources and distribution of materials. The operations manager's job description includes managing budgets, negotiating contracts, and performing administrative tasks.
Bank Probationary Officer (PO)
Investment director.
An investment director is a person who helps corporations and individuals manage their finances. They can help them develop a strategy to achieve their goals, including paying off debts and investing in the future. In addition, he or she can help individuals make informed decisions.
Welding Engineer
Welding Engineer Job Description: A Welding Engineer work involves managing welding projects and supervising welding teams. He or she is responsible for reviewing welding procedures, processes and documentation. A career as Welding Engineer involves conducting failure analyses and causes on welding issues.
Transportation Planner
A career as Transportation Planner requires technical application of science and technology in engineering, particularly the concepts, equipment and technologies involved in the production of products and services. In fields like land use, infrastructure review, ecological standards and street design, he or she considers issues of health, environment and performance. A Transportation Planner assigns resources for implementing and designing programmes. He or she is responsible for assessing needs, preparing plans and forecasts and compliance with regulations.
An expert in plumbing is aware of building regulations and safety standards and works to make sure these standards are upheld. Testing pipes for leakage using air pressure and other gauges, and also the ability to construct new pipe systems by cutting, fitting, measuring and threading pipes are some of the other more involved aspects of plumbing. Individuals in the plumber career path are self-employed or work for a small business employing less than ten people, though some might find working for larger entities or the government more desirable.
Construction Manager
Individuals who opt for a career as construction managers have a senior-level management role offered in construction firms. Responsibilities in the construction management career path are assigning tasks to workers, inspecting their work, and coordinating with other professionals including architects, subcontractors, and building services engineers.
Urban Planner
Urban Planning careers revolve around the idea of developing a plan to use the land optimally, without affecting the environment. Urban planning jobs are offered to those candidates who are skilled in making the right use of land to distribute the growing population, to create various communities.
Urban planning careers come with the opportunity to make changes to the existing cities and towns. They identify various community needs and make short and long-term plans accordingly.
Highway Engineer
Highway Engineer Job Description: A Highway Engineer is a civil engineer who specialises in planning and building thousands of miles of roads that support connectivity and allow transportation across the country. He or she ensures that traffic management schemes are effectively planned concerning economic sustainability and successful implementation.
Environmental Engineer
Individuals who opt for a career as an environmental engineer are construction professionals who utilise the skills and knowledge of biology, soil science, chemistry and the concept of engineering to design and develop projects that serve as solutions to various environmental problems.
Naval Architect
A Naval Architect is a professional who designs, produces and repairs safe and sea-worthy surfaces or underwater structures. A Naval Architect stays involved in creating and designing ships, ferries, submarines and yachts with implementation of various principles such as gravity, ideal hull form, buoyancy and stability.
Orthotist and Prosthetist
Orthotists and Prosthetists are professionals who provide aid to patients with disabilities. They fix them to artificial limbs (prosthetics) and help them to regain stability. There are times when people lose their limbs in an accident. In some other occasions, they are born without a limb or orthopaedic impairment. Orthotists and prosthetists play a crucial role in their lives with fixing them to assistive devices and provide mobility.
Veterinary Doctor
Pathologist.
A career in pathology in India is filled with several responsibilities as it is a medical branch and affects human lives. The demand for pathologists has been increasing over the past few years as people are getting more aware of different diseases. Not only that, but an increase in population and lifestyle changes have also contributed to the increase in a pathologist’s demand. The pathology careers provide an extremely huge number of opportunities and if you want to be a part of the medical field you can consider being a pathologist. If you want to know more about a career in pathology in India then continue reading this article.
Speech Therapist
Gynaecologist.
Gynaecology can be defined as the study of the female body. The job outlook for gynaecology is excellent since there is evergreen demand for one because of their responsibility of dealing with not only women’s health but also fertility and pregnancy issues. Although most women prefer to have a women obstetrician gynaecologist as their doctor, men also explore a career as a gynaecologist and there are ample amounts of male doctors in the field who are gynaecologists and aid women during delivery and childbirth.
An oncologist is a specialised doctor responsible for providing medical care to patients diagnosed with cancer. He or she uses several therapies to control the cancer and its effect on the human body such as chemotherapy, immunotherapy, radiation therapy and biopsy. An oncologist designs a treatment plan based on a pathology report after diagnosing the type of cancer and where it is spreading inside the body.
Audiologist
The audiologist career involves audiology professionals who are responsible to treat hearing loss and proactively preventing the relevant damage. Individuals who opt for a career as an audiologist use various testing strategies with the aim to determine if someone has a normal sensitivity to sounds or not. After the identification of hearing loss, a hearing doctor is required to determine which sections of the hearing are affected, to what extent they are affected, and where the wound causing the hearing loss is found. As soon as the hearing loss is identified, the patients are provided with recommendations for interventions and rehabilitation such as hearing aids, cochlear implants, and appropriate medical referrals. While audiology is a branch of science that studies and researches hearing, balance, and related disorders.
Hospital Administrator
The hospital Administrator is in charge of organising and supervising the daily operations of medical services and facilities. This organising includes managing of organisation’s staff and its members in service, budgets, service reports, departmental reporting and taking reminders of patient care and services.
For an individual who opts for a career as an actor, the primary responsibility is to completely speak to the character he or she is playing and to persuade the crowd that the character is genuine by connecting with them and bringing them into the story. This applies to significant roles and littler parts, as all roles join to make an effective creation. Here in this article, we will discuss how to become an actor in India, actor exams, actor salary in India, and actor jobs.
Individuals who opt for a career as acrobats create and direct original routines for themselves, in addition to developing interpretations of existing routines. The work of circus acrobats can be seen in a variety of performance settings, including circus, reality shows, sports events like the Olympics, movies and commercials. Individuals who opt for a career as acrobats must be prepared to face rejections and intermittent periods of work. The creativity of acrobats may extend to other aspects of the performance. For example, acrobats in the circus may work with gym trainers, celebrities or collaborate with other professionals to enhance such performance elements as costume and or maybe at the teaching end of the career.
Video Game Designer
Career as a video game designer is filled with excitement as well as responsibilities. A video game designer is someone who is involved in the process of creating a game from day one. He or she is responsible for fulfilling duties like designing the character of the game, the several levels involved, plot, art and similar other elements. Individuals who opt for a career as a video game designer may also write the codes for the game using different programming languages.
Depending on the video game designer job description and experience they may also have to lead a team and do the early testing of the game in order to suggest changes and find loopholes.
Radio Jockey
Radio Jockey is an exciting, promising career and a great challenge for music lovers. If you are really interested in a career as radio jockey, then it is very important for an RJ to have an automatic, fun, and friendly personality. If you want to get a job done in this field, a strong command of the language and a good voice are always good things. Apart from this, in order to be a good radio jockey, you will also listen to good radio jockeys so that you can understand their style and later make your own by practicing.
A career as radio jockey has a lot to offer to deserving candidates. If you want to know more about a career as radio jockey, and how to become a radio jockey then continue reading the article.
Choreographer
The word “choreography" actually comes from Greek words that mean “dance writing." Individuals who opt for a career as a choreographer create and direct original dances, in addition to developing interpretations of existing dances. A Choreographer dances and utilises his or her creativity in other aspects of dance performance. For example, he or she may work with the music director to select music or collaborate with other famous choreographers to enhance such performance elements as lighting, costume and set design.
Videographer
Multimedia specialist.
A multimedia specialist is a media professional who creates, audio, videos, graphic image files, computer animations for multimedia applications. He or she is responsible for planning, producing, and maintaining websites and applications.
Social Media Manager
A career as social media manager involves implementing the company’s or brand’s marketing plan across all social media channels. Social media managers help in building or improving a brand’s or a company’s website traffic, build brand awareness, create and implement marketing and brand strategy. Social media managers are key to important social communication as well.
Copy Writer
In a career as a copywriter, one has to consult with the client and understand the brief well. A career as a copywriter has a lot to offer to deserving candidates. Several new mediums of advertising are opening therefore making it a lucrative career choice. Students can pursue various copywriter courses such as Journalism , Advertising , Marketing Management . Here, we have discussed how to become a freelance copywriter, copywriter career path, how to become a copywriter in India, and copywriting career outlook.
Careers in journalism are filled with excitement as well as responsibilities. One cannot afford to miss out on the details. As it is the small details that provide insights into a story. Depending on those insights a journalist goes about writing a news article. A journalism career can be stressful at times but if you are someone who is passionate about it then it is the right choice for you. If you want to know more about the media field and journalist career then continue reading this article.
For publishing books, newspapers, magazines and digital material, editorial and commercial strategies are set by publishers. Individuals in publishing career paths make choices about the markets their businesses will reach and the type of content that their audience will be served. Individuals in book publisher careers collaborate with editorial staff, designers, authors, and freelance contributors who develop and manage the creation of content.
In a career as a vlogger, one generally works for himself or herself. However, once an individual has gained viewership there are several brands and companies that approach them for paid collaboration. It is one of those fields where an individual can earn well while following his or her passion.
Ever since internet costs got reduced the viewership for these types of content has increased on a large scale. Therefore, a career as a vlogger has a lot to offer. If you want to know more about the Vlogger eligibility, roles and responsibilities then continue reading the article.
Individuals in the editor career path is an unsung hero of the news industry who polishes the language of the news stories provided by stringers, reporters, copywriters and content writers and also news agencies. Individuals who opt for a career as an editor make it more persuasive, concise and clear for readers. In this article, we will discuss the details of the editor's career path such as how to become an editor in India, editor salary in India and editor skills and qualities.
Linguistic meaning is related to language or Linguistics which is the study of languages. A career as a linguistic meaning, a profession that is based on the scientific study of language, and it's a very broad field with many specialities. Famous linguists work in academia, researching and teaching different areas of language, such as phonetics (sounds), syntax (word order) and semantics (meaning).
Other researchers focus on specialities like computational linguistics, which seeks to better match human and computer language capacities, or applied linguistics, which is concerned with improving language education. Still, others work as language experts for the government, advertising companies, dictionary publishers and various other private enterprises. Some might work from home as freelance linguists. Philologist, phonologist, and dialectician are some of Linguist synonym. Linguists can study French , German , Italian .
Public Relation Executive
Travel journalist.
The career of a travel journalist is full of passion, excitement and responsibility. Journalism as a career could be challenging at times, but if you're someone who has been genuinely enthusiastic about all this, then it is the best decision for you. Travel journalism jobs are all about insightful, artfully written, informative narratives designed to cover the travel industry. Travel Journalist is someone who explores, gathers and presents information as a news article.
Quality Controller
A quality controller plays a crucial role in an organisation. He or she is responsible for performing quality checks on manufactured products. He or she identifies the defects in a product and rejects the product.
A quality controller records detailed information about products with defects and sends it to the supervisor or plant manager to take necessary actions to improve the production process.
Production Manager
Merchandiser.
A QA Lead is in charge of the QA Team. The role of QA Lead comes with the responsibility of assessing services and products in order to determine that he or she meets the quality standards. He or she develops, implements and manages test plans.
Metallurgical Engineer
A metallurgical engineer is a professional who studies and produces materials that bring power to our world. He or she extracts metals from ores and rocks and transforms them into alloys, high-purity metals and other materials used in developing infrastructure, transportation and healthcare equipment.
Azure Administrator
An Azure Administrator is a professional responsible for implementing, monitoring, and maintaining Azure Solutions. He or she manages cloud infrastructure service instances and various cloud servers as well as sets up public and private cloud systems.
AWS Solution Architect
An AWS Solution Architect is someone who specializes in developing and implementing cloud computing systems. He or she has a good understanding of the various aspects of cloud computing and can confidently deploy and manage their systems. He or she troubleshoots the issues and evaluates the risk from the third party.
Computer Programmer
Careers in computer programming primarily refer to the systematic act of writing code and moreover include wider computer science areas. The word 'programmer' or 'coder' has entered into practice with the growing number of newly self-taught tech enthusiasts. Computer programming careers involve the use of designs created by software developers and engineers and transforming them into commands that can be implemented by computers. These commands result in regular usage of social media sites, word-processing applications and browsers.
ITSM Manager
Information security manager.
Individuals in the information security manager career path involves in overseeing and controlling all aspects of computer security. The IT security manager job description includes planning and carrying out security measures to protect the business data and information from corruption, theft, unauthorised access, and deliberate attack
Business Intelligence Developer
Applications for admissions are open..

Aakash iACST Scholarship Test 2024
Get up to 90% scholarship on NEET, JEE & Foundation courses

JEE Main Important Chemistry formulas
As per latest 2024 syllabus. Chemistry formulas, equations, & laws of class 11 & 12th chapters

Resonance Coaching
Enroll in Resonance Coaching for success in JEE/NEET exams

TOEFL ® Registrations 2024
Thinking of Studying Abroad? Think the TOEFL® test. Register now & Save 10% on English Proficiency Tests with Gift Cards

ALLEN JEE Exam Prep
Start your JEE preparation with ALLEN

NEET 2024 Most scoring concepts
Just Study 32% of the NEET syllabus and Score upto 100% marks
Everything about Education
Latest updates, Exclusive Content, Webinars and more.
Download Careers360 App's
Regular exam updates, QnA, Predictors, College Applications & E-books now on your Mobile
Cetifications
We Appeared in
Home — Essay Samples — Life — Admired Person — My Father – A Person I Admire The Most
My Father – a Person I Admire The Most
- Categories: Admired Person Someone Who Inspires Me
About this sample

Words: 1488 |
Published: Dec 16, 2021
Words: 1488 | Pages: 3 | 8 min read
Table of contents
Introduction, the person i like most – my father, works cited.
- Dolan, A. (2020). The Importance of Role Models: Why You Need Them and How to Find Them. Psychology Today. Retrieved from https://www.psychologytoday.com/us/blog/happiness-purpose/202006/the-importance-role-models-why-you-need-them-and-how-find-them
- Johnson, R. A. (2015). The Power of Positive Role Models. The Huffington Post. Retrieved from https://www.huffpost.com/entry/the-power-of-positive-role-models_b_6349268
- Shukla, P. (2018). Importance of Father's Involvement in a Child's Life. LinkedIn. Retrieved from https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/importance-fathers-involvement-childs-life-pooja-shukla/
- The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica. (2021). Role Model. In Encyclopaedia Britannica. Retrieved from https://www.britannica.com/topic/role-model
- Shehan, C. (2018). The Impact of Parental Involvement on Children's Well-being. Psychology Today. Retrieved from https://www.psychologytoday.com/us/blog/singletons/201805/the-impact-parental-involvement-childrens-well-being
- Warneken, F., & Tomasello, M. (2006). Altruistic Helping in Human Infants and Young Chimpanzees. Science, 311(5765), 1301-1303. doi: 10.1126/science.1121448
- Hoff, E. (2006). How Social Contexts Support and Shape Language Development. Developmental Review, 26(1), 55-88. doi: 10.1016/j.dr.2005.11.002
- Bandura, A. (1991). Social Cognitive Theory of Moral Thought and Action. In W. M. Kurtines & J. L. Gewirtz (Eds.), Handbook of Moral Behavior and Development: Theory, Research, and Applications (Vol. 1, pp. 45-103). Psychology Press.
- Fletcher, G. J. O., Simpson, J. A., Thomas, G., & Giles, L. (1999). Ideals in Intimate Relationships. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 76(1), 72-89. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.76.1.72
- Sulloway, F. J. (1997). Born to Rebel: Birth Order, Family Dynamics , and Creative Lives. Vintage Books.

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Verified writer
- Expert in: Life

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
2 pages / 994 words
3 pages / 1329 words
1 pages / 535 words
7 pages / 3009 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online

Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Admired Person
I have always interacted with a lot of people who possess various characters and personalities. These interactions had various impacts on me on different degrees and with different impacts. The person who has made a huge impact [...]
During our lifetimes, we often encounter people who we get along with very well. Most of the time, those people who we meet can make a huge impact on our lives and make us see the world in a different perspective. It took me a [...]
The person I look up to is Michael Jordan. He is the star basketball player for the Chicago Bulls. He just recently led the Bulls to their sixth NBA championship. He is regarded by many as the greatest player in the history of [...]
“Hey you, why don’t you just give up?” “Are you sure this is right for you?” Some things you definitely do not hear from anyone who supports you. Of course, many people will tell you to keep pushing through life or any adversity [...]
Life's unpredictability and the impact of momentary changes on mood and circumstances Childhood admiration and love for grandmother The joy of spending time with her despite infrequent visits A sudden [...]
The most important person in my life is David..yes..he can be mean at times and I be rude to him as well and we always argue and I- ANYWAYS! Even though we don’t get along as much we still are friends. Im not going to bring up [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
Personal Essay Example: The Most Influential and Impactful People in My Life
Typically, high school students have a best friend that is relatively the same age as them. Well, my best friend is a middle-aged man. My best friend is my dad. When I think of someone who has impacted my life, my mind immediately goes to him. I think about all the things I have told him that can only come from a certain amount of trust. When you share a decent amount of trust with someone, a bond seems to form, one unlike any other. A bond that makes a person your best friend. My dad is and always will be my best friend.
For as long as I can remember, basketball has been one of my dad’s favorite things. He would always talk about his teams, who they were going to play, and how well the competition would be. My dad has coached girls basketball for eleven years, ranging from coaching seventh grade to ninth grade. I have always admired how connected my dad was with his teams. When I would go to his games, I could see how much trust he had in his players and how much trust they had in him. While playing a school sport, it is guaranteed that there will be some amount of drama. Players would try to tear the team apart by fomenting drama or parents will be insatiable with their child’s playing time. I heard about all of this at home. I would hear about how frustrated my dad was getting because he heard a parent complaining to another parent about his coaching skills. It has always been hard seeing him get frustrated with these sorts of things because he doesn’t normally let the words of parents get under his skin. He rarely brings up what they say and he barely ever shows that he is paying attention to what they are saying.
My dad has always been the kind of guy to push me to be my absolute best. He’s not the kind of guy to let me get away with putting half of my effort into anything. At work, my dad is a manager. Well, the manager of his department. He comes home all the time talking about how his coworkers will make him so mad because they seem like they don’t even want to be there. My dad has always told me, “If you’re going to do anything, always leave it all out there.” My dad and I both get very frustrated with ourselves when something is not going the way we want it to. My dad has managed to find something he calls the Reset Button. When he presses the Reset Button, he moves on from whatever is bothering and upsetting him. This magical button has never helped me. Brief exchanges of looks between me and my dad have always seemed to be my Reset Button. When I am frustrated and I make eye contact with my dad, it is almost like an entire conversation happens in thirty seconds. I don’t know if my dad means for that to happen, but it does. The words he says by saying nothing always seemed conducive to me. Like I know that no matter what happens, he is always going to be proud of me.
I have always been a gullible person. You say something to me and I will believe it. I have a hard time with confrontation; therefore, I always believe the best in people and put all my trust in them. My dad; however, people have to earn his trust. When we have conversations about my gullibility, the conversation almost always ends with me in tears. My dad always tells me that if I continue to believe the best in people, they will always run me over. I have never really comprehended what he meant. I would hear what he said, and I’ve heard it multiple times, but I continue to put all my trust and believe the best in everyone. My dad has never told me why he continuously asks me to stop being so gullible. Maybe it was because he got hurt in the past believing people too much and he doesn’t want me to go through that same pain; however, I have never been able to ask him why.
Collecting sports cards has become an obsession of my dads. Taking up an entire room in our house to be exact. To spend time with my dad, I went to a card show with him. As we rode in the car, I realized I had no idea what to expect going into the building; however, the excitement on my dad’s face made the uneasiness disappear. As we walked up to the exposition center and through the halls, I could see the excitement flowing from him. If you were to compare my dad and a kid in a candy shop at that exact moment, I truly believe you wouldn’t be able to tell a difference. When we finally got to the part of the building that was holding the card show, the countless tables full of objects ranging from cards to signed shoes astounded me. My father; however, was tremendously comfortable with the crowded environment. He made his way through the tables speaking the card addict lingo and by the time we were walking out the door, he was leaving with exactly what he had gone in looking for.
Car rides are always my favorite when I am with my dad. The things we talk about are all over the place. When you get in the car, you never really know what is going to happen. We could talk about sports, college, drama, or even the things that go on at home. My dad has always been the parent I feel more comfortable going up and talking to. When in the car with my dad, I feel safe. I feel like I can say anything and know that he is going to listen. Most of the time, when I am stressed about school, I always find myself talking to him about it in the car. At times, it feels like I am just talking to myself, but when that happens, I know my dad is listening to every word I say. I would say my dad is a very observant person. He always wants you to say everything and have your full stance before he chimes in with another component.
While my dad can be straightforward, he is also one of the most humorous people I know. My dad will always try to make us laugh and it always brings a smile to the whole family. When my dad busts out his dance moves from back in the day, the amount of laughter that fills the room is astronomical. Or when he unleashes his vocals, that’s a household favorite. If one of us kids has a bad day at school, my dad will tell us a funny story from work. I wouldn’t say my dad is a people pleaser, but I think that when he truly wants to make someone’s day, he will find a way to make them smile. The amount of joy that my dad has in him seems to surprise some people. Some people will say that my dad is scary. When really, once you get to know him, he is a pretty exceptional guy.
My dad has always told me and my siblings that no matter what we decide to do in life, he will support us no matter what. The belief in knowing that my dad has my back has always been so reassuring to me. When I decided to no longer take part in a sport that I had been participating in for what seems like forever, I truly thought my dad was going to be frustrated with me. I didn’t want him to believe I was just giving up. When he wasn’t upset, it took me by surprise. It had made me feel like the love my dad had for me had overridden his love for the sport and that he just wanted me to be happy. My whole life, having my dad’s approval on everything has been so important to me. One of my biggest goals ever since I was little has been to make my dad proud. My dad has been understanding of every decision I have made. When I decided on my career path, I could see how proud I was making him. The approval of my parents when choosing where I want to go to college and what I want to do after has always been important to me. I know no matter what I choose to do, my dad will be there and be my biggest supporter and scream my name the loudest at either my accomplishments or at my failure. I know he will be proud I tried and he will always be there to pick me up if I fall.
Dad, you have been one of the most influential and impactful people in my life. You have made me see things from a different perspective. You have helped me get through things that I wouldn’t have been able to get through on my own. You have had conversations with me about things that are incredibly important to consider regarding my future. You are someone I feel like I can always go to, no matter the reason. You have made me laugh harder and more uncontrollably than anyone else. You have made me feel safe, and you have made me feel loved. Dad, I am so grateful for everything you have done for me. You are my forever best friend.
Related Samples
- The Importance of Humor Essay Example
- Why Students Should Have A After School Job Persuasive Essay Example
- ENGL 101 Course Review
- Essay on Emotional Contagion
- Letter To My Future Grandchildren
- Tokenism, Discrimination and Intersectionality in the Workplace Essay Example
- The Importance Of Senior Citizens Essay Example
- Career as a Psychologist Essay Sample
- Personal Narrative Essay: Tradition to Watch The Sunset
- Personal Essay Example: Lessons I Have Learned In My Life
Didn't find the perfect sample?

You can order a custom paper by our expert writers
Descriptive Essay
Descriptive Essay About A Person You Admire
How to Craft the Perfect Descriptive Essay About A Person You Admire
People also read
Descriptive Essay - A Complete Guide
Descriptive Essay Examples & Writing Tips
Top 250+ Descriptive Essay Topics & Ideas
Creating a Descriptive Essay Outline - Format & Example
Crafting an Authentic Portrait: A Guide to Writing a Descriptive Essay About a Person
Writing a Descriptive Essay About Myself - Tips and Tricks
Writing a Descriptive Essay About A Place - Guide With Examples
Descriptive Essay About My Mother - A Guide to Writing
Delicious Descriptions: A Guide to Writing a Descriptive Essay About Food
Write A Descriptive Essay About Nature With This Guide
Learn Tips to Write a Descriptive Essay About Autumn - Step into the Golden Season
Are you looking for tips on how to write a descriptive essay about someone you admire? Do you have someone special in your life that you would like to immortalize through words?
A lot of people find writing a descriptive essay about a person quite challenging. But with the right structure and steps, you can easily create an engaging piece of writing.
Look no further! You’ll get these steps right here!
This article will provide you with examples and helpful advice that you need to craft an effective and engaging essay. Plus, we’ll show you what makes a great descriptive essay with examples.

Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers!
- 1. The Basics of Descriptive Essay
- 2. How to Write a Descriptive Essay About Someone You Admire
- 3. Descriptive Essay About a Person You Admire Examples
- 4. Key Points for Writing A Descriptive Essay On The Person I Admire The Most
The Basics of Descriptive Essay
A descriptive essay is an essay that requires the student to provide a detailed and precise description of their chosen subject.
When writing about a person, the goal is to introduce your reader to the person you are writing about.
You will want to include important facts about them and discuss their personality, including their beliefs, hobbies, and interests. You should also provide vivid examples that illustrate the person's characteristics.
Watch the video below to learn more about expository writing:
How to Write a Descriptive Essay About Someone You Admire
Now that you know what makes a great descriptive essay about a person , it’s time to start writing. Here are some steps that will help you create an effective and engaging essay:
1. Choose a Person You Admire:
Select someone who has impacted your life in a special way, or someone whose qualities you admire greatly. Look for role models in your life. In addition, it is important to choose someone you have enough information.
For example writing a descriptive essay about mother is easier than writing an essay about anyone else.
You can also polish your descriptive writing skills by writing on other descriptive essay topics .
2. Research the Person Thoroughly:
Before you begin writing, make sure you have enough information about the person. You can research by talking to people who know the person well, or reading books and articles written about them.
3. Create an Outline:
This helps keep your essay organized and focused. You can use the basic structure of an essay with an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion as a guide. So make sure you include all of the important points in your outline.
4. Use Vivid Language and Imagery:
Describe anything that stands out about the person, such as their physical appearance and mannerisms. Use powerful adjectives to give life to your essay and make it more interesting for your readers.
5. Include Relevant Examples:
Using real-life examples adds depth and texture to your essay. These can be anything from stories of when you met the person or a unique trait that they possess. Examples will also help make your essay more illustrative and descriptive.
6. Write an Effective Conclusion:
Your conclusion should serve as a summary of all the points you have discussed in your essay. Make sure to end on a positive note and provide your readers with a lasting impression of your subject’s character.
Reading some example essays will clarify it even more. So let's check out some examples below.
Descriptive Essay About a Person You Admire Examples
If you are given a task to write a paragraph about a person you admire, these examples will help you!
The Person I Admire The Most Essay 200 Words
The Person I Admire The Most Essay 250 Words
The Person I Admire Most 300 Words
Here are some more examples to get a better idea of how a descriptive essay looks like:
A Famous Person You Admire Essay
The Person I Admire The Most My Mother Essay
Descriptive Essay About A Person in My Life
You can read more descriptive essay examples on various other topics as well.
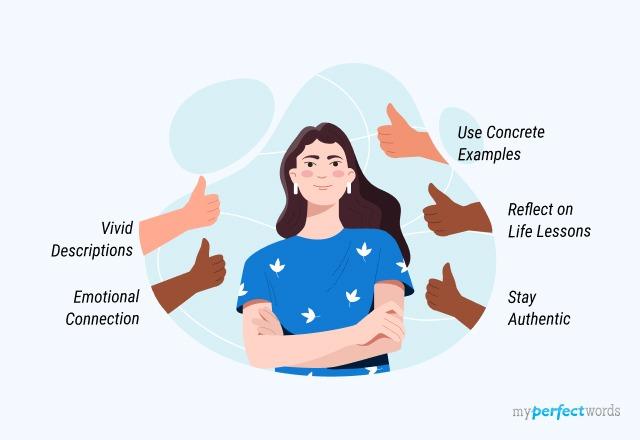
Key Points for Writing A Descriptive Essay On The Person I Admire The Most
Writing a descriptive essay about the person you admire the most can be a rewarding experience.
Here are some key points and tips to help you create an engaging and meaningful essay:
- Vivid Descriptions: Use descriptive language to paint a clear picture of the person, including their qualities, achievements, and impact.
- Emotional Connection: Explain the emotional connection you have with the person and why their presence is meaningful.
- Use Concrete Examples: Provide specific anecdotes and examples that illustrate the person's admirable qualities and actions.
- Reflect on Life Lessons: Discuss the lessons you've learned from this person and how they've influenced your personal growth and values.
- Stay Authentic: Be genuine and sincere in your writing. Your admiration for the person should come through as a heartfelt expression
To conclude,
Writing an engaging descriptive essay about someone you admire can be quite challenging, but it is definitely worth the effort. With these tips in mind, you will be well on your way to writing a great essay.
Do you need further professional help? Do you want to " hire someone to write my essay "? Don't worry! We've got you covered.
MyPerfectWords.com offers the top essay writing service for all types of essays. Our professional and experienced writers have years of experience in crafting high-quality custom essays.
So contact our descriptive essay writing service today. We guarantee you will be satisfied with the quality and accuracy of our work.

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Cathy has been been working as an author on our platform for over five years now. She has a Masters degree in mass communication and is well-versed in the art of writing. Cathy is a professional who takes her work seriously and is widely appreciated by clients for her excellent writing skills.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading
-10240.jpg&w=828&q=75)
- Play & Activities
- Life Skills
- Learning & Education
- Play & Learning

- Growth & Development
- Rhymes & Songs
- Preschool Locator
Essay On The Person I Admire The Most – 10 Lines, Short and Long Essay For Kids
Key Points To Remember When Writing An Essay On The Person I Admire The Most For Lower Primary Classes
10 lines on the person i admire the most for kids, paragraph on the person i admire the most for children, short essay on the person i admire the most for kids, long essay on the person i admire the most for children, what will your child learn from the essay on ‘the person i admire the most’.
Having a person whom you admire and consider an inspiration in life is of great importance. We all need someone who we can look up to, as well as count on for always being there to support you, and help you if needed. When you need guidance, this is the person whom you trust the most. You seek their advice as you regard them highly and look up to them with respect. This is the person whom you admire the most.
Children may feel admiration for their parents, grandparents, teachers or even their best friend. They hold this person close to their heart and value their presence in their lives. Children may be asked to write an essay on ‘The person i admire the most’ in English as an assignment in school. This topic is an emotional one, and kids will be required to write from their hearts. Expressing abstract feelings in words may be challenging for kids at first, but with practice, they can master their writing skills in no time.
Let us guide your child to write a beautiful essay on this topic with some important points and examples.
Before you begin writing an essay on the given topic, keep in mind the following points:
- Every essay should have a good introductory line and a concluding idea.
- Think about the topic and jot down the points that come to your mind.
- Arrange the points in a good sequence and elaborate on them to form meaningful sentences or paragraphs.
- Try to use a few new words to showcase your vocabulary on the topic, however be sure of the meaning of the word and its correct use in context.
- When writing about the person you admire, start by introducing the person, how they are related to you, and their unique qualities, and explain why you admire those qualities in them.
Let us begin with the simplest form of essay writing. When kids are newly introduced to essay writing, they can start by forming simple sentences and expressing their ideas in a few lines. Take a look at this example of an essay for classes 1 and 2 in 10 lines.
- The person I admire the most is my brother Arjun.
- He is my elder brother and also my best friend.
- The quality I admire the most about him is that he is very helpful.
- He always helps me with my studies whenever I have some difficulties understanding a lesson.
- He also helps my parents with all the work in the house like cleaning, laying out the dining table and going out on his bicycle to buy groceries.
- When he helps others selflessly, they feel very happy and wish well for him.
- He is also a very brave and strong boy.
- He is never scared of anything, and also takes care of me when I am scared of something like barking dogs on the streets or dark rooms.
- He always says that instead of getting scared, we must face our fears and defeat it.
- I admire his spirit and wish to be more like him.
As children progress academically, they will learn to write more coherent essays with several ideas connected together to form a small paragraph. For this, children will have to learn to weave individual points together to compose their essay. Check out this example of an essay on ‘The person I admire the most’.
The person I admire the most is my grandfather. He was in the army and has fought bravely to protect our country. Being an army person, the value he respects the most in life is discipline. He always teaches me about good behaviour and courteous manners. He always says, “Manners make a man” and also lives by this moral. Because of his courteousness, he is very well respected by everyone around him. All the family members have the highest regard for him. He is many generations older than me but he has always made me feel like he understands me well. So I go to him every time I need some guidance. One day when I had a fight with my sister, he explained to me that making up after a fight and extending the first hand of friendship can make me a better person. I followed his advice and the fight was immediately resolved. I admire my grandfather’s personality and conviction, and wish that I too become like him with my contribution to society and to the country.
Once your child learns how to weave their ideas into a paragraph, you can take it up a notch by teaching how to write a short essay on the given topic. In this essay for classes 1, 2 and 3, children will be required to make elaborate points and organise them in separate paragraphs with an introduction and conclusion. Take a look at this example to learn how to write a short essay:
I have many friends who are very dear to me. But the one I admire the most is my best friend Jia.
Jia is one of the best players in our school’s basketball team. Her biggest ambition is to play in the Olympics one day. She is an ace shooter and when she has the ball in her hand, there is no chance for it to miss the basket. While being excellent at sports, Jia is also very good in studies. She stands first in all the subjects in the class. Jia always remains an enthusiastic learner in class and her projects and assignments are always the most creative. She is also great at theatre. Last year, Jia took part in an English play had everyone spell-bound with her performance on the stage. She had observed her housekeeper very closely and had noted all her actions before performing the role on stage.
Jia is skilled at every activity. She has learnt this art from her mother. Her mother always taught her to put her heart and soul in everything she does. She often tells me that we should be focused and dedicated in all our pursuits. We cannot achieve much if our minds are diverted. This is the secret of her success.
I admire her for her attitude and all her achievements and wish to be like her.
When children are given an assignment to write an essay for class 3, they must put together all their knowledge, think of unique ideas, use their best vocabulary in the right context and elaborate on their points eloquently. A long essay needs a good introductory paragraph followed by a body with several well-thought out ideas and a good conclusion. Refer to these examples given below:
The Person I Admire Most – My Mother
The person I admire the most in the whole wide world is my mother. She is the most caring person in my life. She is my first, foremost and closest friend and I love her over and above everyone else.
My mother cares for me a lot and dedicated a lot of her time in helping me out throughout the day. She prepares delicious breakfast and some food for me to carry to school. When I come back from school, she talks to me all about my day and checks my homework. When it’s time for exams, she encourages me to study hard and avoid distractions. Sometimes I feel upset when she doesn’t let me watch TV for long hours and insists on studying more, but when I get a successful result, I realise that the entire credit goes to her motivation.
My mother used to work in a bank a few years back, but she left her job due to some dire situations during the pandemic. But she is a very dynamic lady. She soon started her own company that invests in small businesses and helps start-ups rise to success. Entrepreneurs consider her to be their biggest ray of hope and guiding light. Seeing how many people she has helped rise from dreamers to achievers is inspiring.
Even in the family, my mother is everyone’s favourite. She is always available to help everyone because she is an expert at everything. She cooks delicious meals, is great with home accounts and banking work, and has many other talents. She is great at crocheting, so on every special occasion, she gives handmade gifts to her friends and family.
What I love about my mother the most is that I can always depend on her. Whenever I tell her about some difficulty I face, she always guides me to come up with a solution. She encourages me to be independent and handle my own circumstances with her help and guidance whenever required. I can also trust her with anything, knowing that she will always have my back.
My mother is very strict with the discipline she expects us to maintain at home. If we break the rules, she gets upset and we must be ready to correct our mistakes, but all throughout, I know that she loves me and does it for me to learn the best habits.
She inspires me to be a strong, independent and successful woman. I admire all her qualities, especially how to be the best mother ever!
The Person I Admire Most – My Father
The person who I admire the most is my father. He is a dynamic man who has created a successful path for himself and others too. He is the best at everything he does, and yet is a humble and down-to-earth man.
My father is a doctor. Everyday, he works hard to care for all his patients and their health. I have noticed that even on holidays, he is occupied with following up about his patients’ care and ensuring they are getting better. He treats everyone with the best facilities that he can provide to them.
Becoming a doctor is not easy. It takes years of studies and a lot of money to go to medical college. My father’s family did not have enough means for higher education, but he earned a scholarship and created an opportunity for himself. My grandparents too are very proud of his hard work and success, and they always narrate his stories as an example for me to follow.
My father explained to me that despite good hospitals and clinics in the city, many people do not get good healthcare, because they do not have the means. To ensure that everyone gets the right medical attention, my father also runs a small clinic where he does check-ups for poor people at a nominal charge and provides medication at subsidised rates, so that everyone can afford medical care. He donates some of his own money to this cause to make sure that the clinic never has to say no to any patient. This selfless and generous act makes him a highly respected person in the city. I feel very proud that he is my father.
Despite being in a busy profession, my father spends a lot of quality time with me. We have a Sunday ritual of playing a ‘fathers vs children’ football match in our colony. Not only is he a great player himself, he also coaches me and all the other children to prepare for this weekend match. He is the coolest dad ever!
Because of my love and admiration for him, I don’t like to disappoint him in any way. The one thing he gets upset about is if I don’t work hard towards my studies. He always teaches me that studying hard is the biggest duty that children have towards the future of the society. Whether I score high marks or not, he insists that I must always give my 100% while studying and learning.
My father has taught me a lot, through such moral lessons as well as through the way he has led his own life. I admire his personality and wish to become just like him when I grow up.
The Person I Admire Most – My Teacher
A child’s first interaction beyond home is at school. Once children step out of their home and enter into the big world out there, the one person who holds their hands as a guiding force is their teacher.
I too had one such teacher whom I met on my first day at school. It is since that day that I admire my teacher, Geeta Ma’am, the most in the world. When I went to school for the first time, I was very nervous. I felt like crying and wanted to go back home. That is when Geeta Ma’am came up to me and told me, “It is only the brave ones that have the strength to take a step forward.” This thought inspired me and made take the brave step into the classroom which is where my independent journey started.
Geeta Ma’am is a really fun teacher. Whenever she teaches us something new, she makes us observe some examples of it in the real world to make our lessons more relatable. This way, we understand everything perfectly and never forget what we have once learnt. She comes up with many new and creative activities for us to do in school to make us learn better.
She is every students’ favourite teacher because she is never partial. She pays equal attention to every child, and makes sure no one in the class is too shy to ask their doubts. She is very fair and never favours one child over another.
Every teacher wants their students to focus on studies and score well in exams, but Geeta Ma’am believes in a balanced life. She encourages us to participate in many extracurricular activities to bring out our unique talents. Last month, our school announced a poetry writing competition. Geeta Ma’am encouraged me to participate in it, giving me the confidence that I had good writing skills. I never knew that I had this skill, but she recognised my talent and helped me perfect it. It was all due to her encouragement that I participated and won the competition!
Everyday I learn a lot from Geeta Ma’am, not just bookish knowledge but important life lessons too. She is one of my biggest force of motivation, and I admire her and highly respect her. I wish to accomplish something in life and make her proud.
When your child writes an essay about the person they admire the most, they get an opportunity to reflect upon some of the most desirable qualities in a person. They observe the traits of inspiring people and think about how to achieve these traits themselves.
Expressing these ideas on pen and paper is altogether a different ball game. Children will improve their thinking, analytical, writing and communication skills while writing an essay on this topic. They will expand their vocabulary and be able to express themselves more confidently.
Use the above given examples to guide your child how to write an essay on the person they admire the most. The points given here can serve as a foundation for ideas, based on which they can write the essay on their own.
Essay On I Love My Family for Kids Essay On ‘My Dream House’ for Children Good Manners Essay for Classes 1, 2 & 3
- Essays for Class 1
- Essays for Class 2
- Essays for Class 3
5 Recommended Books To Add To Your Child’s Reading List and Why
5 absolute must-watch movies and shows for kids, 15 indoor toys that have multiple uses and benefits, leave a reply cancel reply.
Log in to leave a comment

Most Popular
The best toys for newborns according to developmental paediatricians, the best toys for three-month-old baby brain development, recent comments.

FirstCry Intelli Education is an Early Learning brand, with products and services designed by educators with decades of experience, to equip children with skills that will help them succeed in the world of tomorrow.

Story Related Activities Designed to Bring the Story to Life and Create Fun Memories.


Online Preschool is the Only Way Your Child's Learning Can Continue This Year, Don't Wait Any Longer - Get Started!
©2021 All rights reserved
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Use

Welcome to the world of Intelli!
We have some FREE Activity E-books waiting for you. Fill in your details below so we can send you tailor- made activities for you and your little one.

Welcome to the world of intelli!
FREE guides and worksheets coming your way on whatsapp. Subscribe Below !!
THANK YOU!!!
Here are your free guides and worksheets.
- EssayBasics.com
- Pay For Essay
- Write My Essay
- Homework Writing Help
- Essay Editing Service
- Thesis Writing Help
- Write My College Essay
- Do My Essay
- Term Paper Writing Service
- Coursework Writing Service
- Write My Research Paper
- Assignment Writing Help
- Essay Writing Help
- Call Now! (USA) Login Order now
- EssayBasics.com Call Now! (USA) Order now
- Writing Guides
The Person I Admire The Most Is My Friend (Essay Sample)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Is there a friendship in your life that pushes you to become better? Is there anyone in mind that makes you think, “I admire my friend”?
This essay focuses on the author’s most meaningful friendship. She shares reasons why she admires this friend and recalls the impressive character traits she possesses. She also shares the lessons she learned from her friend who lives by example.
Inspired to write your own essay about the person you look up to? Check out our website for essay writing services that can help you piece together those avid praises for your best friends.
The Person I Admire The Most is My Friend
I know that everybody can think of a specific person who they admire in life. Whether it’s their character traits, physical features, or social skills, each human has a specific set of attractive things about them that are admirable to others.
The one person that I admire most in my life is my friend Prisca. I look up to and appreciate her simply because of her beauty, brains, and sophisticated nature.
It goes without saying that Prisca is known for her beauty. In fact, that’s what most people say first when they think of her. She has long, curly brown hair, brown eyes that are big and round like saucers, and a perfect body. She is four inches tall with slender legs and a bright and contagious smile. I admire her physical appearance that is enviable and eye-catching.
Prisca, My Best Friend
Prisca has personality traits that make her unique and admirable.
First, she is agreeable. Prisca is very kind; she is friendly, generous, and considerate. You can always expect her to be busy helping others. She is also mindful of how she supports her community. Moreover, she is very cooperative; she willingly and nicely works with other people to achieve a shared goal. Whenever she is free, she always pitches in to help me with my class assignments, and sometimes even hard chores in the house.
Her sophistication and sense of wisdom are commendable. She is hardworking and creative, and this is reflected in her amazing grades. She’s at the top of her class in all subjects and has won numerous competitions at school. She is a go-getter who believes in hard work and consistency.
For as long as I can remember, she has always been referred to as a good example in school, church, and the neighborhood. She is up-to-date and knowledgeable about current world events as she makes it a point to read a lot of books and newspapers. Her taste for fashion and accessories is great and admirable.
Life Lessons from Prisca
On many occasions, Prisca stays genuinely true to herself. She is definitely not a people-pleaser and is very clear on her values and convictions. She is true to who she is. She will not try to be a clone of other people just to be accepted. She speaks up when feeling annoyed to express and release her anger.
Prisca leads by example. She encourages all her friends and younger siblings to be disciplined by being disciplined herself. She is respectful towards everyone and obedient to authorities, and she always abides by rules and codes of behavior.
Moreover, Prisca is selfless. She always makes time to be there for people who need her help. She will give of herself, even when she doesn’t have much to share, whether it’s material or intangible needs. She is always more concerned about the needs and wishes of others and not her own. She takes an active part in community initiatives intended to help and improve the lives of the less fortunate in the locality.
She is straightforward and humble. She always stands by the truth even when faced with the dangers of being left by friends or being victimized. She barely tells lies. Most importantly, even with her wonderful accomplishments, she remains grounded. She doesn’t brag or show off to her peers and friends. She is down to earth and has never paraded around pridefully.
Every person has someone in his or her life that he or she admires for reasons best known to him or her. With Prisca, it’s the fact that she is comfortable with herself. Her beauty compounded with her character makes her a friend for keeps. She is someone I intend to keep in my life.
Whether you went to the same school or have known each other your whole life, you and the person you look up to should be in the kind of friendship that brings out the best in each other. I know that Prisca has always encouraged me to become the best I can be. I hope you have someone who can give you that kind of confidence boost, too.
Things I Admire About My Best Friend (Short Essay Sample)
Anyone who knows me knows how much I admire respect my good friend Prisca. We started hanging out in elementary school and the rest is history.
It was my mom who encouraged me to start a conversation with Prisca when we sat together in English class on the first day of school. I was feeling timid and shy and was drawn to how Prisca would easily befriend the other children. Even the teachers were fond of her because she knew how to have fun and make people laugh while learning at the same time.
I’m proud to call her one of my closest friends today. Prisca is the reason why I have the confidence and ability to connect with other people warmly. She helped me get over my nervousness in talking to others and accompanied me during breaks to converse with classmates.
I’ll never forget how wonderful a friend Prisca is. In fact, I wish everyone I know had someone like her. Not only is she the first reason I am able to do well in life today, but she also encourages me to relentlessly dream big for my future.
How To Write An Essay About Someone You Admire?
To craft a meaningful piece about the person you admire, think of the reasons why you admire him or her. Look at the different aspects of his or her life story – from the physical and social, to the mental and emotional. How does this person make you feel? How does this person encourage you? Are you a better person with him or her in your life? You can also talk about how the two of you met and what the circumstances were. Share what drew you to him or her in the first place, and how your friendship formed. Talk about the good times, but don’t leave out the challenges you both faced in your friendship.
The Qualities That Make A Person Admirable
There are many ways for someone to be admirable. He or she could be someone who leads by modeling first, so his or her authenticity and transparency are characteristics that are attractive to others. They could have a vast knowledge of a topic that other people wish they knew more about. They could be generous with their time. They could have the ability to hope during even the toughest and darkest of times. They could teach very well. They could make things happen just by their sheer influence. They could give the most sensible and practical advice and don’t offer an opinion that’s unsolicited. They generally make it hard for you to imagine life without them.


What does Emerson say about self-reliance?
In Emerson's essay “ Self-Reliance ,” he boldly states society (especially today’s politically correct environment) hurts a person’s growth.
Emerson wrote that self-sufficiency gives a person in society the freedom they need to discover their true self and attain their true independence.
Believing that individualism, personal responsibility , and nonconformity were essential to a thriving society. But to get there, Emerson knew that each individual had to work on themselves to achieve this level of individualism.
Today, we see society's breakdowns daily and wonder how we arrived at this state of society. One can see how the basic concepts of self-trust, self-awareness, and self-acceptance have significantly been ignored.
Who published self-reliance?
Ralph Waldo Emerson wrote the essay, published in 1841 as part of his first volume of collected essays titled "Essays: First Series."
It would go on to be known as Ralph Waldo Emerson's Self Reliance and one of the most well-known pieces of American literature.
The collection was published by James Munroe and Company.
What are the examples of self-reliance?
Examples of self-reliance can be as simple as tying your shoes and as complicated as following your inner voice and not conforming to paths set by society or religion.
Self-reliance can also be seen as getting things done without relying on others, being able to “pull your weight” by paying your bills, and caring for yourself and your family correctly.
Self-reliance involves relying on one's abilities, judgment, and resources to navigate life. Here are more examples of self-reliance seen today:
Entrepreneurship: Starting and running your own business, relying on your skills and determination to succeed.
Financial Independence: Managing your finances responsibly, saving money, and making sound investment decisions to secure your financial future.
Learning and Education: Taking the initiative to educate oneself, whether through formal education, self-directed learning, or acquiring new skills.
Problem-Solving: Tackling challenges independently, finding solutions to problems, and adapting to changing circumstances.
Personal Development: Taking responsibility for personal growth, setting goals, and working towards self-improvement.
Homesteading: Growing your food, raising livestock, or becoming self-sufficient in various aspects of daily life.
DIY Projects: Undertaking do-it-yourself projects, from home repairs to crafting, without relying on external help.
Living Off the Grid: Living independently from public utilities, generating your energy, and sourcing your water.
Decision-Making: Trusting your instincts and making decisions based on your values and beliefs rather than relying solely on external advice.
Crisis Management: Handling emergencies and crises with resilience and resourcefulness without depending on external assistance.
These examples illustrate different facets of self-reliance, emphasizing independence, resourcefulness, and the ability to navigate life autonomously.
What is the purpose of self reliance by Emerson?
In his essay, " Self Reliance, " Emerson's sole purpose is the want for people to avoid conformity. Emerson believed that in order for a man to truly be a man, he was to follow his own conscience and "do his own thing."
Essentially, do what you believe is right instead of blindly following society.
Why is it important to be self reliant?
While getting help from others, including friends and family, can be an essential part of your life and fulfilling. However, help may not always be available, or the assistance you receive may not be what you had hoped for.
It is for this reason that Emerson pushed for self-reliance. If a person were independent, could solve their problems, and fulfill their needs and desires, they would be a more vital member of society.
This can lead to growth in the following areas:
Empowerment: Self-reliance empowers individuals to take control of their lives. It fosters a sense of autonomy and the ability to make decisions independently.
Resilience: Developing self-reliance builds resilience, enabling individuals to bounce back from setbacks and face challenges with greater adaptability.
Personal Growth: Relying on oneself encourages continuous learning and personal growth. It motivates individuals to acquire new skills and knowledge.
Freedom: Self-reliance provides a sense of freedom from external dependencies. It reduces reliance on others for basic needs, decisions, or validation.
Confidence: Achieving goals through one's own efforts boosts confidence and self-esteem. It instills a belief in one's capabilities and strengthens a positive self-image.
Resourcefulness: Being self-reliant encourages resourcefulness. Individuals learn to solve problems creatively, adapt to changing circumstances, and make the most of available resources.
Adaptability: Self-reliant individuals are often more adaptable to change. They can navigate uncertainties with a proactive and positive mindset.
Reduced Stress: Dependence on others can lead to stress and anxiety, especially when waiting for external support. Self-reliance reduces reliance on external factors for emotional well-being.
Personal Responsibility: It promotes a sense of responsibility for one's own life and decisions. Self-reliant individuals are more likely to take ownership of their actions and outcomes.
Goal Achievement: Being self-reliant facilitates the pursuit and achievement of personal and professional goals. It allows individuals to overcome obstacles and stay focused on their objectives.
Overall, self-reliance contributes to personal empowerment, mental resilience, and the ability to lead a fulfilling and purposeful life. While collaboration and support from others are valuable, cultivating a strong sense of self-reliance enhances one's capacity to navigate life's challenges independently.
What did Emerson mean, "Envy is ignorance, imitation is suicide"?
According to Emerson, no kernel of nourishing corn can come to you independently, but every person is given a plot of ground to till.
In other words, Emerson believed that a person's main focus in life is to work on oneself, increasing their maturity and intellect, and overcoming insecurities, which will allow a person to be self-reliant to the point where they no longer envy others but measure themselves against how they were the day before.
When we do become self-reliant, we focus on creating rather than imitating. Being someone we are not is just as damaging to the soul as suicide.
Envy is ignorance: Emerson suggests that feeling envious of others is a form of ignorance. Envy often arises from a lack of understanding or appreciation of one's unique qualities and potential. Instead of being envious, individuals should focus on discovering and developing their talents and strengths.
Imitation is suicide: Emerson extends the idea by stating that imitation, or blindly copying others, is a form of self-destruction. He argues that true individuality and personal growth come from expressing one's unique voice and ideas. In this context, imitation is seen as surrendering one's identity and creativity, leading to a kind of "spiritual death."
What are the transcendental elements in Emerson’s self-reliance?
The five predominant elements of Transcendentalism are nonconformity, self-reliance, free thought, confidence, and the importance of nature.
The Transcendentalism movement emerged in New England between 1820 and 1836. It is essential to differentiate this movement from Transcendental Meditation, a distinct practice.
According to the Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy, Transcendentalism is characterized as "an American literary, political, and philosophical movement of the early nineteenth century, centered around Ralph Waldo Emerson." A central tenet of this movement is the belief that individual purity can be 'corrupted' by society.
Are Emerson's writings referenced in pop culture?
Emerson has made it into popular culture. One such example is in the film Next Stop Wonderland released in 1998. The reference is a quote from Emerson's essay on Self Reliance, "A foolish consistency is the hobgoblin of little minds."
This becomes a running theme in the film as a single woman (Hope Davis ), who is quite familiar with Emerson's writings and showcases several men taking her on dates, attempting to impress her by quoting the famous line, only to botch the line and also giving attribution to the wrong person. One gentleman says confidently it was W.C. Fields, while another matches the quote with Cicero. One goes as far as stating it was Karl Marx!
Why does Emerson say about self confidence?
Content is coming very soon.
Self-Reliance: The Complete Essay
Ne te quaesiveris extra."
Man is his own star; and the soul that can Render an honest and a perfect man, Commands all light, all influence, all fate ; Nothing to him falls early or too late. Our acts our angels are, or good or ill, Our fatal shadows that walk by us still." Epilogue to Beaumont and Fletcher's Honest Man's Fortune Cast the bantling on the rocks, Suckle him with the she-wolf's teat; Wintered with the hawk and fox, Power and speed be hands and feet.

Ralph Waldo Emerson left the ministry to pursue a career in writing and public speaking. Emerson became one of America's best known and best-loved 19th-century figures. More About Emerson
Ralph Waldo Emerson Self Reliance Summary
The essay “Self-Reliance,” written by Ralph Waldo Emerson, is, by far, his most famous piece of work. Emerson, a Transcendentalist, believed focusing on the purity and goodness of individualism and community with nature was vital for a strong society. Transcendentalists despise the corruption and conformity of human society and institutions. Published in 1841, the Self Reliance essay is a deep-dive into self-sufficiency as a virtue.
In the essay "Self-Reliance," Ralph Waldo Emerson advocates for individuals to trust in their own instincts and ideas rather than blindly following the opinions of society and its institutions. He argues that society encourages conformity, stifles individuality, and encourages readers to live authentically and self-sufficient lives.
Emerson also stresses the importance of being self-reliant, relying on one's own abilities and judgment rather than external validation or approval from others. He argues that people must be honest with themselves and seek to understand their own thoughts and feelings rather than blindly following the expectations of others. Through this essay, Emerson emphasizes the value of independence, self-discovery, and personal growth.
What is the Meaning of Self-Reliance?
I read the other day some verses written by an eminent painter which were original and not conventional. The soul always hears an admonition in such lines, let the subject be what it may. The sentiment they instill is of more value than any thought they may contain. To believe your own thought, to think that what is true for you in your private heart is true for all men, — that is genius.
Speak your latent conviction, and it shall be the universal sense; for the inmost in due time becomes the outmost,—— and our first thought is rendered back to us by the trumpets of the Last Judgment. Familiar as the voice of the mind is to each, the highest merit we ascribe to Moses, Plato, and Milton is, that they set at naught books and traditions, and spoke not what men but what they thought. A man should learn to detect and watch that gleam of light that flashes across his mind from within, more than the luster of the firmament of bards and sages. Yet he dismisses without notice his thought because it is his. In every work of genius, we recognize our own rejected thoughts: they come back to us with a certain alienated majesty.
Great works of art have no more affecting lessons for us than this. They teach us to abide by our spontaneous impression with good-humored inflexibility than most when the whole cry of voices is on the other side. Else, tomorrow a stranger will say with masterly good sense precisely what we have thought and felt all the time, and we shall be forced to take with shame our own opinion from another.
There is a time in every man's education when he arrives at the conviction that envy is ignorance; that imitation is suicide; that he must take himself for better, for worse, as his portion; that though the wide universe is full of good, no kernel of nourishing corn can come to him but through his toil bestowed on that plot of ground which is given to him to till. The power which resides in him is new in nature, and none but he knows what that is which he can do, nor does he know until he has tried. Not for nothing one face, one character, one fact, makes much impression on him, and another none. This sculpture in the memory is not without preestablished harmony. The eye was placed where one ray should fall, that it might testify of that particular ray. We but half express ourselves and are ashamed of that divine idea which each of us represents. It may be safely trusted as proportionate and of good issues, so it be faithfully imparted, but God will not have his work made manifest by cowards. A man is relieved and gay when he has put his heart into his work and done his best; but what he has said or done otherwise, shall give him no peace. It is a deliverance that does not deliver. In the attempt his genius deserts him; no muse befriends; no invention, no hope.
Trust Thyself: Every Heart Vibrates To That Iron String.
Accept the place the divine providence has found for you, the society of your contemporaries, and the connection of events. Great men have always done so, and confided themselves childlike to the genius of their age, betraying their perception that the absolutely trustworthy was seated at their heart, working through their hands, predominating in all their being. And we are now men, and must accept in the highest mind the same transcendent destiny; and not minors and invalids in a protected corner, not cowards fleeing before a revolution, but guides, redeemers, and benefactors, obeying the Almighty effort, and advancing on Chaos and the Dark.
What pretty oracles nature yields to us in this text, in the face and behaviour of children, babes, and even brutes! That divided and rebel mind, that distrust of a sentiment because our arithmetic has computed the strength and means opposed to our purpose, these have not. Their mind being whole, their eye is as yet unconquered, and when we look in their faces, we are disconcerted. Infancy conforms to nobody: all conform to it, so that one babe commonly makes four or five out of the adults who prattle and play to it. So God has armed youth and puberty and manhood no less with its own piquancy and charm, and made it enviable and gracious and its claims not to be put by, if it will stand by itself. Do not think the youth has no force, because he cannot speak to you and me. Hark! in the next room his voice is sufficiently clear and emphatic. It seems he knows how to speak to his contemporaries. Bashful or bold, then, he will know how to make us seniors very unnecessary.
The nonchalance of boys who are sure of a dinner, and would disdain as much as a lord to do or say aught to conciliate one, is the healthy attitude of human nature. A boy is in the parlour what the pit is in the playhouse; independent, irresponsible, looking out from his corner on such people and facts as pass by, he tries and sentences them on their merits, in the swift, summary way of boys, as good, bad, interesting, silly, eloquent, troublesome. He cumbers himself never about consequences, about interests: he gives an independent, genuine verdict. You must court him: he does not court you. But the man is, as it were, clapped into jail by his consciousness. As soon as he has once acted or spoken with eclat, he is a committed person, watched by the sympathy or the hatred of hundreds, whose affections must now enter into his account. There is no Lethe for this. Ah, that he could pass again into his neutrality! Who can thus avoid all pledges, and having observed, observe again from the same unaffected, unbiased, unbribable, unaffrighted innocence, must always be formidable. He would utter opinions on all passing affairs, which being seen to be not private, but necessary, would sink like darts into the ear of men, and put them in fear.

These are the voices which we hear in solitude, but they grow faint and inaudible as we enter into the world. Society everywhere is in conspiracy against the manhood of every one of its members. Society is a joint-stock company, in which the members agree, for the better securing of his bread to each shareholder, to surrender the liberty and culture of the eater. The virtue in most request is conformity. Self-reliance is its aversion. It loves not realities and creators, but names and customs.
Whoso would be a man must be a nonconformist. He who would gather immortal palms must not be hindered by the name of goodness, but must explore if it be goodness. Nothing is at last sacred but the integrity of your own mind. Absolve you to yourself, and you shall have the suffrage of the world. I remember an answer which when quite young I was prompted to make to a valued adviser, who was wont to importune me with the dear old doctrines of the church. On my saying, What have I to do with the sacredness of traditions, if I live wholly from within? my friend suggested, — "But these impulses may be from below, not from above." I replied, "They do not seem to me to be such; but if I am the Devil's child, I will live then from the Devil." No law can be sacred to me but that of my nature. Good and bad are but names very readily transferable to that or this; the only right is what is after my constitution, the only wrong what is against it. A man is to carry himself in the presence of all opposition, as if every thing were titular and ephemeral but he. I am ashamed to think how easily we capitulate to badges and names, to large societies and dead institutions. Every decent and well-spoken individual affects and sways me more than is right. I ought to go upright and vital, and speak the rude truth in all ways. If malice and vanity wear the coat of philanthropy, shall that pass? If an angry bigot assumes this bountiful cause of Abolition, and comes to me with his last news from Barbadoes, why should I not say to him, 'Go love thy infant; love thy wood-chopper: be good-natured and modest: have that grace; and never varnish your hard, uncharitable ambition with this incredible tenderness for black folk a thousand miles off. Thy love afar is spite at home.' Rough and graceless would be such greeting, but truth is handsomer than the affectation of love. Your goodness must have some edge to it, — else it is none. The doctrine of hatred must be preached as the counteraction of the doctrine of love when that pules and whines. I shun father and mother and wife and brother, when my genius calls me. The lintels of the door-post I would write on, Whim . It is somewhat better than whim at last I hope, but we cannot spend the day in explanation. Expect me not to show cause why I seek or why I exclude company. Then, again, do not tell me, as a good man did to-day, of my obligation to put all poor men in good situations. Are they my poor? I tell thee, thou foolish philanthropist, that I grudge the dollar, the dime, the cent, I give to such men as do not belong to me and to whom I do not belong. There is a class of persons to whom by all spiritual affinity I am bought and sold; for them I will go to prison, if need be; but your miscellaneous popular charities; the education at college of fools; the building of meeting-houses to the vain end to which many now stand; alms to sots; and the thousandfold Relief Societies; — though I confess with shame I sometimes succumb and give the dollar, it is a wicked dollar which by and by I shall have the manhood to withhold.
Virtues are, in the popular estimate, rather the exception than the rule. There is the man and his virtues. Men do what is called a good action, as some piece of courage or charity, much as they would pay a fine in expiation of daily non-appearance on parade. Their works are done as an apology or extenuation of their living in the world, — as invalids and the insane pay a high board. Their virtues are penances. I do not wish to expiate, but to live. My life is for itself and not for a spectacle. I much prefer that it should be of a lower strain, so it be genuine and equal, than that it should be glittering and unsteady. Wish it to be sound and sweet, and not to need diet and bleeding. The primary evidence I ask that you are a man, and refuse this appeal from the man to his actions. For myself it makes no difference that I know, whether I do or forbear those actions which are reckoned excellent. I cannot consent to pay for a privilege where I have intrinsic right. Few and mean as my gifts may be, I actually am, and do not need for my own assurance or the assurance of my fellows any secondary testimony.
What I must do is all that concerns me, not what the people think.
This rule, equally arduous in actual and in intellectual life, may serve for the whole distinction between greatness and meanness. It is the harder, because you will always find those who think they know what is your duty better than you know it. The easy thing in the world is to live after the world's opinion; it is easy in solitude to live after our own; but the great man is he who in the midst of the crowd keeps with perfect sweetness the independence of solitude.
The objection to conforming to usages that have become dead to you is, that it scatters your force. It loses your time and blurs the impression of your character. If you maintain a dead church, contribute to a dead Bible-society, vote with a great party either for the government or against it, spread your table like base housekeepers, — under all these screens I have difficulty to detect the precise man you are. And, of course, so much force is withdrawn from your proper life. But do your work, and I shall know you. Do your work, and you shall reinforce yourself. A man must consider what a blindman's-buff is this game of conformity. If I know your sect, I anticipate your argument. I hear a preacher announce for his text and topic the expediency of one of the institutions of his church. Do I not know beforehand that not possibly can he say a new and spontaneous word? With all this ostentation of examining the grounds of the institution, do I not know that he will do no such thing? Do not I know that he is pledged to himself not to look but at one side, — the permitted side, not as a man, but as a parish minister? He is a retained attorney, and these airs of the bench are the emptiest affectation. Well, most men have bound their eyes with one or another handkerchief, and attached themselves to some one of these communities of opinion. This conformity makes them not false in a few particulars, authors of a few lies, but false in all particulars. Their every truth is not quite true. Their two is not the real two, their four not the real four; so that every word they say chagrins us, and we know not where to begin to set them right. Meantime nature is not slow to equip us in the prison-uniform of the party to which we adhere. We come to wear one cut of face and figure, and acquire by degrees the gentlest asinine expression. There is a mortifying experience in particular, which does not fail to wreak itself also in the general history; I mean "the foolish face of praise," the forced smile which we put on in company where we do not feel at ease in answer to conversation which does not interest us. The muscles, not spontaneously moved, but moved by a low usurping wilfulness, grow tight about the outline of the face with the most disagreeable sensation.
For nonconformity the world whips you with its displeasure. And therefore a man must know how to estimate a sour face. The by-standers look askance on him in the public street or in the friend's parlour. If this aversation had its origin in contempt and resistance like his own, he might well go home with a sad countenance; but the sour faces of the multitude, like their sweet faces, have no deep cause, but are put on and off as the wind blows and a newspaper directs. Yet is the discontent of the multitude more formidable than that of the senate and the college. It is easy enough for a firm man who knows the world to brook the rage of the cultivated classes. Their rage is decorous and prudent, for they are timid as being very vulnerable themselves. But when to their feminine rage the indignation of the people is added, when the ignorant and the poor are aroused, when the unintelligent brute force that lies at the bottom of society is made to growl and mow, it needs the habit of magnanimity and religion to treat it godlike as a trifle of no concernment.
The other terror that scares us from self-trust is our consistency; a reverence for our past act or word, because the eyes of others have no other data for computing our orbit than our past acts, and we are loath to disappoint them.
But why should you keep your head over your shoulder? Why drag about this corpse of your memory, lest you contradict somewhat you have stated in this or that public place? Suppose you should contradict yourself; what then? It seems to be a rule of wisdom never to rely on your memory alone, scarcely even in acts of pure memory, but to bring the past for judgment into the thousand-eyed present, and live ever in a new day. In your metaphysics you have denied personality to the Deity: yet when the devout motions of the soul come, yield to them heart and life, though they should clothe God with shape and color. Leave your theory, as Joseph his coat in the hand of the harlot, and flee.
A foolish consistency is the hobgoblin of little minds, adored by little statesmen and philosophers and divines. With consistency a great soul has simply nothing to do. He may as well concern himself with his shadow on the wall. Speak what you think now in hard words, and to-morrow speak what to-morrow thinks in hard words again, though it contradict every thing you said to-day. — 'Ah, so you shall be sure to be misunderstood.' — Is it so bad, then, to be misunderstood? Pythagoras was misunderstood, and Socrates, and Jesus, and Luther, and Copernicus, and Galileo, and Newton, and every pure and wise spirit that ever took flesh. To be great is to be misunderstood.

I suppose no man can violate his nature.
All the sallies of his will are rounded in by the law of his being, as the inequalities of Andes and Himmaleh are insignificant in the curve of the sphere. Nor does it matter how you gauge and try him. A character is like an acrostic or Alexandrian stanza; — read it forward, backward, or across, it still spells the same thing. In this pleasing, contrite wood-life which God allows me, let me record day by day my honest thought without prospect or retrospect, and, I cannot doubt, it will be found symmetrical, though I mean it not, and see it not. My book should smell of pines and resound with the hum of insects. The swallow over my window should interweave that thread or straw he carries in his bill into my web also. We pass for what we are. Character teaches above our wills. Men imagine that they communicate their virtue or vice only by overt actions, and do not see that virtue or vice emit a breath every moment.
There will be an agreement in whatever variety of actions, so they be each honest and natural in their hour. For of one will, the actions will be harmonious, however unlike they seem. These varieties are lost sight of at a little distance, at a little height of thought. One tendency unites them all. The voyage of the best ship is a zigzag line of a hundred tacks. See the line from a sufficient distance, and it straightens itself to the average tendency. Your genuine action will explain itself, and will explain your other genuine actions. Your conformity explains nothing. Act singly, and what you have already done singly will justify you now. Greatness appeals to the future. If I can be firm enough to-day to do right, and scorn eyes, I must have done so much right before as to defend me now. Be it how it will, do right now. Always scorn appearances, and you always may. The force of character is cumulative. All the foregone days of virtue work their health into this. What makes the majesty of the heroes of the senate and the field, which so fills the imagination? The consciousness of a train of great days and victories behind. They shed an united light on the advancing actor. He is attended as by a visible escort of angels. That is it which throws thunder into Chatham's voice, and dignity into Washington's port, and America into Adams's eye. Honor is venerable to us because it is no ephemeris. It is always ancient virtue. We worship it today because it is not of today. We love it and pay it homage, because it is not a trap for our love and homage, but is self-dependent, self-derived, and therefore of an old immaculate pedigree, even if shown in a young person.
I hope in these days we have heard the last of conformity and consistency. Let the words be gazetted and ridiculous henceforward. Instead of the gong for dinner, let us hear a whistle from the Spartan fife. Let us never bow and apologize more. A great man is coming to eat at my house. I do not wish to please him; He should wish to please me, that I wish. I will stand here for humanity, and though I would make it kind, I would make it true. Let us affront and reprimand the smooth mediocrity and squalid contentment of the times, and hurl in the face of custom, and trade, and office, the fact which is the upshot of all history, that there is a great responsible Thinker and Actor working wherever a man works; that a true man belongs to no other time or place, but is the centre of things. Where he is, there is nature. He measures you, and all men, and all events. Ordinarily, every body in society reminds us of somewhat else, or of some other person. Character, reality, reminds you of nothing else; it takes place of the whole creation. The man must be so much, that he must make all circumstances indifferent. Every true man is a cause, a country, and an age; requires infinite spaces and numbers and time fully to accomplish his design; — and posterity seem to follow his steps as a train of clients. A man Caesar is born, and for ages after we have a Roman Empire. Christ is born, and millions of minds so grow and cleave to his genius, that he is confounded with virtue and the possible of man. An institution is the lengthened shadow of one man; as, Monachism, of the Hermit Antony; the Reformation, of Luther; Quakerism, of Fox; Methodism, of Wesley; Abolition, of Clarkson. Scipio, Milton called "the height of Rome"; and all history resolves itself very easily into the biography of a few stout and earnest persons.
Let a man then know his worth, and keep things under his feet. Let him not peep or steal, or skulk up and down with the air of a charity-boy, a bastard, or an interloper, in the world which exists for him. But the man in the street, finding no worth in himself which corresponds to the force which built a tower or sculptured a marble god, feels poor when he looks on these. To him a palace, a statue, or a costly book have an alien and forbidding air, much like a gay equipage, and seem to say like that, 'Who are you, Sir?' Yet they all are his, suitors for his notice, petitioners to his faculties that they will come out and take possession. The picture waits for my verdict: it is not to command me, but I am to settle its claims to praise. That popular fable of the sot who was picked up dead drunk in the street, carried to the duke's house, washed and dressed and laid in the duke's bed, and, on his waking, treated with all obsequious ceremony like the duke, and assured that he had been insane, owes its popularity to the fact, that it symbolizes so well the state of man, who is in the world a sort of sot, but now and then wakes up, exercises his reason, and finds himself a true prince.
Our reading is mendicant and sycophantic. In history, our imagination plays us false. Kingdom and lordship, power and estate, are a gaudier vocabulary than private John and Edward in a small house and common day's work; but the things of life are the same to both; the sum total of both is the same. Why all this deference to Alfred, and Scanderbeg, and Gustavus? Suppose they were virtuous; did they wear out virtue? As great a stake depends on your private act to-day, as followed their public and renowned steps. When private men shall act with original views, the lustre will be transferred from the actions of kings to those of gentlemen.
The world has been instructed by its kings, who have so magnetized the eyes of nations. It has been taught by this colossal symbol the mutual reverence that is due from man to man. The joyful loyalty with which men have everywhere suffered the king, the noble, or the great proprietor to walk among them by a law of his own, make his own scale of men and things, and reverse theirs, pay for benefits not with money but with honor, and represent the law in his person, was the hieroglyphic by which they obscurely signified their consciousness of their own right and comeliness, the right of every man.
The magnetism which all original action exerts is explained when we inquire the reason of self-trust.
Who is the Trustee? What is the aboriginal Self, on which a universal reliance may be grounded? What is the nature and power of that science-baffling star, without parallax, without calculable elements, which shoots a ray of beauty even into trivial and impure actions, if the least mark of independence appear? The inquiry leads us to that source, at once the essence of genius, of virtue, and of life, which we call Spontaneity or Instinct. We denote this primary wisdom as Intuition, whilst all later teachings are tuitions. In that deep force, the last fact behind which analysis cannot go, all things find their common origin. For, the sense of being which in calm hours rises, we know not how, in the soul, is not diverse from things, from space, from light, from time, from man, but one with them, and proceeds obviously from the same source whence their life and being also proceed. We first share the life by which things exist, and afterwards see them as appearances in nature, and forget that we have shared their cause. Here is the fountain of action and of thought. Here are the lungs of that inspiration which giveth man wisdom, and which cannot be denied without impiety and atheism. We lie in the lap of immense intelligence, which makes us receivers of its truth and organs of its activity. When we discern justice, when we discern truth, we do nothing of ourselves, but allow a passage to its beams. If we ask whence this comes, if we seek to pry into the soul that causes, all philosophy is at fault. Its presence or its absence is all we can affirm. Every man discriminates between the voluntary acts of his mind, and his involuntary perceptions, and knows that to his involuntary perceptions a perfect faith is due. He may err in the expression of them, but he knows that these things are so, like day and night, not to be disputed. My wilful actions and acquisitions are but roving; — the idlest reverie, the faintest native emotion, command my curiosity and respect. Thoughtless people contradict as readily the statement of perceptions as of opinions, or rather much more readily; for, they do not distinguish between perception and notion. They fancy that I choose to see this or that thing. But perception is not whimsical, but fatal. If I see a trait, my children will see it after me, and in course of time, all mankind, — although it may chance that no one has seen it before me. For my perception of it is as much a fact as the sun.
The relations of the soul to the divine spirit are so pure, that it is profane to seek to interpose helps. It must be that when God speaketh he should communicate, not one thing, but all things; should fill the world with his voice; should scatter forth light, nature, time, souls, from the centre of the present thought; and new date and new create the whole. Whenever a mind is simple, and receives a divine wisdom, old things pass away, — means, teachers, texts, temples fall; it lives now, and absorbs past and future into the present hour. All things are made sacred by relation to it, — one as much as another. All things are dissolved to their centre by their cause, and, in the universal miracle, petty and particular miracles disappear. If, therefore, a man claims to know and speak of God, and carries you backward to the phraseology of some old mouldered nation in another country, in another world, believe him not. Is the acorn better than the oak which is its fulness and completion? Is the parent better than the child into whom he has cast his ripened being? Whence, then, this worship of the past? The centuries are conspirators against the sanity and authority of the soul. Time and space are but physiological colors which the eye makes, but the soul is light; where it is, is day; where it was, is night; and history is an impertinence and an injury, if it be anything more than a cheerful apologue or parable of my being and becoming.
Man is timid and apologetic; he is no longer upright; 'I think,' 'I am,' that he dares not say, but quotes some saint or sage. He is ashamed before the blade of grass or the blowing rose. These roses under my window make no reference to former roses or to better ones; they are for what they are; they exist with God today. There is no time to them. There is simply the rose; it is perfect in every moment of its existence. Before a leaf bud has burst, its whole life acts; in the full-blown flower there is no more; in the leafless root there is no less. Its nature is satisfied, and it satisfies nature, in all moments alike. But man postpones or remembers; he does not live in the present, but with reverted eye laments the past, or, heedless of the riches that surround him, stands on tiptoe to foresee the future. He cannot be happy and strong until he too lives with nature in the present, above time.
This should be plain enough. Yet see what strong intellects dare not yet hear God himself, unless he speak the phraseology of I know not what David, or Jeremiah, or Paul. We shall not always set so great a price on a few texts, on a few lives. We are like children who repeat by rote the sentences of grandames and tutors, and, as they grow older, of the men of talents and character they chance to see, — painfully recollecting the exact words they spoke; afterwards, when they come into the point of view which those had who uttered these sayings, they understand them, and are willing to let the words go; for, at any time, they can use words as good when occasion comes. If we live truly, we shall see truly. It is as easy for the strong man to be strong, as it is for the weak to be weak. When we have new perception, we shall gladly disburden the memory of its hoarded treasures as old rubbish. When a man lives with God, his voice shall be as sweet as the murmur of the brook and the rustle of the corn.
And now at last the highest truth on this subject remains unsaid; probably cannot be said; for all that we say is the far-off remembering of the intuition. That thought, by what I can now nearest approach to say it, is this. When good is near you, when you have life in yourself, it is not by any known or accustomed way; you shall not discern the foot-prints of any other; not see the face of man; and you shall not hear any name;—— the way, the thought, the good, shall be wholly strange and new. It shall exclude example and experience. You take the way from man, not to man. All persons that ever existed are its forgotten ministers. Fear and hope are alike beneath it. There is somewhat low even in hope. In the hour of vision, there is nothing that can be called gratitude, nor properly joy. The soul raised over passion beholds identity and eternal causation, perceives the self-existence of Truth and Right, and calms itself with knowing that all things go well. Vast spaces of nature, the Atlantic Ocean, the South Sea, — long intervals of time, years, centuries, — are of no account. This which I think and feel underlay every former state of life and circumstances, as it does underlie my present, and what is called life, and what is called death.

Life only avails, not the having lived.
Power ceases in the instant of repose; it resides in the moment of transition from a past to a new state, in the shooting of the gulf, in the darting to an aim. This one fact the world hates is that the soul becomes ; for that forever degrades the past, turns all riches to poverty, all reputation to a shame, confounds the saint with the rogue, shoves Jesus and Judas equally aside. Why, then, do we prate of self-reliance? Inasmuch as the soul is present, there will be power, not confidence but an agent. To talk of reliance is a poor external way of speaking. Speak rather of that which relies, because it works and is. Who has more obedience than I masters me, though he should not raise his finger. Round him I must revolve by the gravitation of spirits. We fancy it rhetoric, when we speak of eminent virtue. We do not yet see that virtue is Height, and that a man or a company of men, plastic and permeable to principles, by the law of nature must overpower and ride all cities, nations, kings, rich men, poets, who are not.
This is the ultimate fact which we so quickly reach on this, as on every topic, the resolution of all into the ever-blessed ONE. Self-existence is the attribute of the Supreme Cause, and it constitutes the measure of good by the degree in which it enters into all lower forms. All things real are so by so much virtue as they contain. Commerce, husbandry, hunting, whaling, war, eloquence , personal weight, are somewhat, and engage my respect as examples of its presence and impure action. I see the same law working in nature for conservation and growth. Power is in nature the essential measure of right. Nature suffers nothing to remain in her kingdoms which cannot help itself. The genesis and maturation of a planet, its poise and orbit, the bended tree recovering itself from the strong wind, the vital resources of every animal and vegetable, are demonstrations of the self-sufficing, and therefore self-relying soul.
Thus all concentrates: let us not rove; let us sit at home with the cause. Let us stun and astonish the intruding rabble of men and books and institutions, by a simple declaration of the divine fact. Bid the invaders take the shoes from off their feet, for God is here within. Let our simplicity judge them, and our docility to our own law demonstrate the poverty of nature and fortune beside our native riches.
But now we are a mob. Man does not stand in awe of man, nor is his genius admonished to stay at home, to put itself in communication with the internal ocean, but it goes abroad to beg a cup of water of the urns of other men. We must go alone. I like the silent church before the service begins, better than any preaching. How far off, how cool, how chaste the persons look, begirt each one with a precinct or sanctuary! So let us always sit. Why should we assume the faults of our friend, or wife, or father, or child, because they sit around our hearth, or are said to have the same blood? All men have my blood, and I have all men's. Not for that will I adopt their petulance or folly, even to the extent of being ashamed of it. But your isolation must not be mechanical, but spiritual, that is, must be elevation. At times the whole world seems to be in conspiracy to importune you with emphatic trifles. Friend, client, child, sickness, fear, want, charity, all knock at once at thy closet door, and say, — 'Come out unto us.' But keep thy state; come not into their confusion. The power men possess to annoy me, I give them by a weak curiosity. No man can come near me but through my act. "What we love that we have, but by desire we bereave ourselves of the love."
If we cannot at once rise to the sanctities of obedience and faith, let us at least resist our temptations; let us enter into the state of war, and wake Thor and Woden, courage and constancy, in our Saxon breasts. This is to be done in our smooth times by speaking the truth. Check this lying hospitality and lying affection. Live no longer to the expectation of these deceived and deceiving people with whom we converse. Say to them, O father, O mother, O wife, O brother, O friend, I have lived with you after appearances hitherto. Henceforward I am the truth's. Be it known unto you that henceforward I obey no law less than the eternal law. I will have no covenants but proximities. To nourish my parents, to support my family I shall endeavour, to be the chaste husband of one wife, — but these relations I must fill after a new and unprecedented way. I appeal from your customs that I must be myself. I cannot break myself any longer for you, or you. If you can love me for what I am, we shall be the happier. If you cannot, I will still seek to deserve that you should. I will not hide my tastes or aversions. I will so trust that what is deep is holy, that I will do strongly before the sun and moon whatever inly rejoices me, and the heart appoints. If you are noble, I will love you; I will not hurt you and myself by hypocritical attentions if you are not. If you are true, but not in the same truth with me, cleave to your companions; I will seek my own. I do this not selfishly, but humbly and truly. It is alike your interest, and mine, and all men's, however long we have dwelt in lies, to live in truth. Does this sound harsh today? You will soon love what is dictated by your nature as well as mine, and, if we follow the truth, it will bring us out safe at last. — But so you may give these friends pain. Yes, but I cannot sell my liberty and my power, to save their sensibility. Besides, all persons have their moments of reason, when they look out into the region of absolute truth; then will they justify me, and do the same thing.
The populace think that your rejection of popular standards is a rejection of all standard, and mere antinomianism; and the bold sensualist will use the name of philosophy to gild his crimes. But the law of consciousness abides. There are two confessionals, in one or the other of which we must be shriven. You may fulfil your round of duties by clearing yourself in the direct , or in the reflex way. Consider whether you have satisfied your relations to father, mother, cousin, neighbour, town, cat, and dog; whether any of these can upbraid you. But I may also neglect this reflex standard, and absolve me to myself. I have my own stern claims and perfect circle. It denies the name of duty to many offices that are called duties. But if I can discharge its debts, it enables me to dispense with the popular code. If anyone imagines that this law is lax, let him keep its commandment one day.
And truly it demands something godlike in him who has cast off the common motives of humanity, and has ventured to trust himself for a taskmaster. High be his heart, faithful his will, clear his sight, that he may in good earnest be doctrine, society, law, to himself, that a simple purpose may be to him as strong as iron necessity is to others!
If any man consider the present aspects of what is called by distinction society , he will see the need of these ethics. The sinew and heart of man seem to be drawn out, and we are become timorous, desponding whimperers. We are afraid of truth, afraid of fortune, afraid of death, and afraid of each other. Our age yields no great and perfect persons. We want men and women who shall renovate life and our social state, but we see that most natures are insolvent, cannot satisfy their own wants, have an ambition out of all proportion to their practical force, and do lean and beg day and night continually. Our housekeeping is mendicant, our arts, our occupations, our marriages, our religion, we have not chosen, but society has chosen for us. We are parlour soldiers. We shun the rugged battle of fate , where strength is born.
If our young men miscarry in their first enterprises, they lose all heart.
Men say he is ruined if the young merchant fails . If the finest genius studies at one of our colleges, and is not installed in an office within one year afterwards in the cities or suburbs of Boston or New York, it seems to his friends and to himself that he is right in being disheartened, and in complaining the rest of his life. A sturdy lad from New Hampshire or Vermont, who in turn tries all the professions, who teams it , farms it , peddles , keeps a school, preaches, edits a newspaper, goes to Congress, buys a township, and so forth, in successive years, and always, like a cat, falls on his feet, is worth a hundred of these city dolls. He walks abreast with his days, and feels no shame in not 'studying a profession,' for he does not postpone his life, but lives already. He has not one chance, but a hundred chances. Let a Stoic open the resources of man, and tell men they are not leaning willows, but can and must detach themselves; that with the exercise of self-trust, new powers shall appear; that a man is the word made flesh, born to shed healing to the nations, that he should be ashamed of our compassion, and that the moment he acts from himself, tossing the laws, the books, idolatries, and customs out of the window, we pity him no more, but thank and revere him, — and that teacher shall restore the life of man to splendor, and make his name dear to all history.
It is easy to see that a greater self-reliance must work a revolution in all the offices and relations of men; in their religion; education; and in their pursuits; their modes of living; their association; in their property; in their speculative views.
1. In what prayers do men allow themselves! That which they call a holy office is not so much as brave and manly. Prayer looks abroad and asks for some foreign addition to come through some foreign virtue, and loses itself in endless mazes of natural and supernatural, and mediatorial and miraculous. It is prayer that craves a particular commodity, — anything less than all good, — is vicious. Prayer is the contemplation of the facts of life from the highest point of view. It is the soliloquy of a beholding and jubilant soul. It is the spirit of God pronouncing his works good. But prayer as a means to effect a private end is meanness and theft. It supposes dualism and not unity in nature and consciousness. As soon as the man is at one with God, he will not beg. He will then see prayer in all action. The prayer of the farmer kneeling in his field to weed it, the prayer of the rower kneeling with the stroke of his oar, are true prayers heard throughout nature, though for cheap ends. Caratach, in Fletcher's Bonduca, when admonished to inquire the mind of the god Audate, replies, —
"His hidden meaning lies in our endeavours; Our valors are our best gods."
Another sort of false prayers are our regrets. Discontent is the want of self-reliance: it is infirmity of will. Regret calamities, if you can thereby help the sufferer; if not, attend your own work, and already the evil begins to be repaired. Our sympathy is just as base. We come to them who weep foolishly, and sit down and cry for company, instead of imparting to them truth and health in rough electric shocks, putting them once more in communication with their own reason. The secret of fortune is joy in our hands. Welcome evermore to gods and men is the self-helping man. For him all doors are flung wide: him all tongues greet, all honors crown, all eyes follow with desire. Our love goes out to him and embraces him, because he did not need it. We solicitously and apologetically caress and celebrate him, because he held on his way and scorned our disapprobation. The gods love him because men hated him. "To the persevering mortal," said Zoroaster, "the blessed Immortals are swift."
As men's prayers are a disease of the will, so are their creeds a disease of the intellect . They say with those foolish Israelites, 'Let not God speak to us, lest we die. Speak thou, speak any man with us, and we will obey.' Everywhere I am hindered of meeting God in my brother, because he has shut his own temple doors, and recites fables merely of his brother's, or his brother's brother's God. Every new mind is a new classification. If it prove a mind of uncommon activity and power, a Locke, a Lavoisier, a Hutton, a Bentham, a Fourier, it imposes its classification on other men, and lo! a new system. In proportion to the depth of the thought, and so to the number of the objects it touches and brings within reach of the pupil, is his complacency. But chiefly is this apparent in creeds and churches, which are also classifications of some powerful mind acting on the elemental thought of duty, and man's relation to the Highest. Such as Calvinism, Quakerism, Swedenborgism. The pupil takes the same delight in subordinating everything to the new terminology, as a girl who has just learned botany in seeing a new earth and new seasons thereby. It will happen for a time, that the pupil will find his intellectual power has grown by the study of his master's mind. But in all unbalanced minds, the classification is idolized, passes for the end, and not for a speedily exhaustible means, so that the walls of the system blend to their eye in the remote horizon with the walls of the universe; the luminaries of heaven seem to them hung on the arch their master built. They cannot imagine how you aliens have any right to see, — how you can see; 'It must be somehow that you stole the light from us.' They do not yet perceive, that light, unsystematic, indomitable, will break into any cabin, even into theirs. Let them chirp awhile and call it their own. If they are honest and do well, presently their neat new pinfold will be too strait and low, will crack, will lean, will rot and vanish, and the immortal light, all young and joyful, million-orbed, million-colored, will beam over the universe as on the first morning.
2. It is for want of self-culture that the superstition of Travelling, whose idols are Italy, England, Egypt, retains its fascination for all educated Americans. They who made England, Italy, or Greece venerable in the imagination did so by sticking fast where they were, like an axis of the earth. In manly hours, we feel that duty is our place. The soul is no traveller; the wise man stays at home, and when his necessities, his duties, on any occasion call him from his house, or into foreign lands, he is at home still, and shall make men sensible by the expression of his countenance, that he goes the missionary of wisdom and virtue, and visits cities and men like a sovereign, and not like an interloper or a valet.
I have no churlish objection to the circumnavigation of the globe, for the purposes of art, of study, and benevolence, so that the man is first domesticated, or does not go abroad with the hope of finding somewhat greater than he knows. He who travels to be amused, or to get somewhat which he does not carry, travels away from himself, and grows old even in youth among old things. In Thebes, in Palmyra, his will and mind have become old and dilapidated as they. He carries ruins to ruins.
Travelling is a fool's paradise. Our first journeys discover to us the indifference of places. At home I dream that at Naples, at Rome, I can be intoxicated with beauty, and lose my sadness. I pack my trunk, embrace my friends, embark on the sea, and at last wake up in Naples, and there beside me is the stern fact, the sad self, unrelenting, identical, that I fled from. The Vatican, and the palaces I seek. But I am not intoxicated though I affect to be intoxicated with sights and suggestions. My giant goes with me wherever I go.
3. But the rage of travelling is a symptom of a deeper unsoundness affecting the whole intellectual action. The intellect is vagabond, and our system of education fosters restlessness. Our minds travel when our bodies are forced to stay at home. We imitate, and what is imitation but the travelling of the mind? Our houses are built with foreign taste; Shelves are garnished with foreign ornaments, but our opinions, our tastes, our faculties, lean, and follow the Past and the Distant. The soul created the arts wherever they have flourished. It was in his own mind that the artist sought his model. It was an application of his own thought to the thing to be done and the conditions to be observed. And why need we copy the Doric or the Gothic model? Beauty, convenience, grandeur of thought, and quaint expression are as near to us as to any, and if the American artist will study with hope and love the precise thing to be done by him, considering the climate, the soil, the length of the day, the wants of the people, the habit and form of the government, he will create a house in which all these will find themselves fitted, and taste and sentiment will be satisfied also.
Insist on yourself; never imitate. Your own gift you can present every moment with the cumulative force of a whole life's cultivation, but of the adopted talent of another, you have only an extemporaneous, half possession. That which each can do best, none but his Maker can teach him. No man yet knows what it is, nor can, till that person has exhibited it. Where is the master who could have taught Shakespeare? Where is the master who could have instructed Franklin, or Washington, or Bacon, or Newton? Every great man is a unique. The Scipionism of Scipio is precisely that part he could not borrow. Shakespeare will never be made by the study of Shakespeare. Do that which is assigned you, and you cannot hope too much or dare too much. There is at this moment for you an utterance brave and grand as that of the colossal chisel of Phidias, or trowel of the Egyptians, or the pen of Moses, or Dante, but different from all these. Not possibly will the soul all rich, all eloquent, with thousand-cloven tongue, deign to repeat itself; but if you can hear what these patriarchs say, surely you can reply to them in the same pitch of voice; for the ear and the tongue are two organs of one nature. Abide in the simple and noble regions of thy life, obey thy heart, and thou shalt reproduce the Foreworld again.

4. As our Religion, our Education, our Art look abroad, so does our spirit of society. All men plume themselves on the improvement of society, and no man improves.
Society never advances. It recedes as fast on one side as it gains on the other and undergoes continual changes; it is barbarous, civilized, christianized, rich and it is scientific, but this change is not amelioration. For everything that is given, something is taken. Society acquires new arts, and loses old instincts. What a contrast between the well-clad, reading, writing, thinking American, with a watch, a pencil, and a bill of exchange in his pocket, and the naked New Zealander, whose property is a club, a spear, a mat, and an undivided twentieth of a shed to sleep under! But compare the health of the two men, and you shall see that the white man has lost his aboriginal strength. If the traveller tell us truly, strike the savage with a broad axe, and in a day or two, the flesh shall unite and heal as if you struck the blow into soft pitch, and the same blow shall send the white to his grave.
The civilized man has built a coach, but has lost the use of his feet. He is supported on crutches, but lacks so much support of muscle. He has a fine Geneva watch, but he fails of the skill to tell the hour by the sun. A Greenwich nautical almanac he has, and so being sure of the information when he wants it, the man in the street does not know a star in the sky. The solstice he does not observe, the equinox he knows as little, and the whole bright calendar of the year are without a dial in his mind. His note-books impair his memory; his libraries overload his wit; the insurance office increases the number of accidents; and it may be a question whether machinery does not encumber; whether we have not lost by refinement some energy, by a Christianity entrenched in establishments and forms, some vigor of wild virtue. For every Stoic was a Stoic, but in Christendom, where is the Christian?
There is no more deviation in the moral standard than in the standard of height or bulk. No greater men are now than ever were. A singular equality may be observed between the great men of the first and of the last ages; nor can all the science, art, religion, and philosophy of the nineteenth century avail to educate greater men than Plutarch's heroes, three or four and twenty centuries ago. Not in time is the race progressive. Phocion, Socrates, Anaxagoras, Diogenes, are great men, but they leave no class. He who is really of their class will not be called by their name, but will be his own man, and, in his turn, the founder of a sect. The arts and inventions of each period are only its costume, and do not invigorate men. The harm of the improved machinery may compensate its good. Hudson and Behring accomplished so much in their fishing boats, as to astonish Parry and Franklin, whose equipment exhausted the resources of science and art. Galileo, with an opera-glass, discovered a more splendid series of celestial phenomena than anyone since. Columbus found the New World in an undecked boat. It is curious to see the periodical disuse and perishing of means and machinery, which were introduced with loud laudation a few years or centuries before. The great genius returns to essential man. We reckoned the improvements of the art of war among the triumphs of science, and yet Napoleon conquered Europe by the bivouac, which consisted of falling back on naked valor and disencumbering it of all aids. The Emperor held it impossible to make a perfect army, says Las Casas, "without abolishing our arms, magazines, commissaries, and carriages, until, in imitation of the Roman custom, the soldier should receive his supply of corn, grind it in his hand-mill, and bake his bread himself."
Society is a wave. The wave moves onward, but the water of which it is composed does not. The same particle does not rise from the valley to the ridge. Its unity is only phenomenal. The persons who make up a nation today, next year die, and their experience with them.
And so the reliance on Property, including the reliance on governments which protect it, is the want of self-reliance. Men have looked away from themselves and at things so long, that they have come to esteem the religious, learned, and civil institutions as guards of property, and they deprecate assaults on these, because they feel them to be assaults on property. They measure their esteem of each other by what each has, and not by what each is. But a cultivated man becomes ashamed of his property, out of new respect for his nature. Especially he hates what he has, if he see that it is accidental, — came to him by inheritance, or gift, or crime; then he feels that it is not having; it does not belong to him, has no root in him, and merely lies there, because no revolution or no robber takes it away. But that which a man is does always by necessity acquire, and what the man acquires is living property, which does not wait the beck of rulers, or mobs, or revolutions, or fire, or storm, or bankruptcies, but perpetually renews itself wherever the man breathes. "Thy lot or portion of life," said the Caliph Ali, "is seeking after thee; therefore, be at rest from seeking after it." Our dependence on these foreign goods leads us to our slavish respect for numbers. The political parties meet in numerous conventions; the greater the concourse, and with each new uproar of announcement, The delegation from Essex! The Democrats from New Hampshire! The Whigs of Maine! the young patriot feels himself stronger than before by a new thousand of eyes and arms. In like manner the reformers summon conventions, and vote and resolve in multitude. Not so, O friends! will the God deign to enter and inhabit you, but by a method precisely the reverse. It is only as a man puts off all foreign support, and stands alone, that I see him to be strong and to prevail. He is weaker by every recruit to his banner. Is not a man better than a town? Ask nothing of men, and in the endless mutation, thou only firm column must presently appear the upholder of all that surrounds thee. He who knows that power is inborn, that he is weak because he has looked for good out of him and elsewhere, and so perceiving, throws himself unhesitatingly on his thought, instantly rights himself, stands in the erect position, commands his limbs, works miracles; just as a man who stands on his feet is stronger than a man who stands on his head.
So use all that is called Fortune. Most men gamble with her, and gain all, and lose all, as her wheel rolls. But do thou leave as unlawful these winnings, and deal with Cause and Effect, the chancellors of God. In the Will work and acquire, and thou hast chained the wheel of Chance, and shalt sit hereafter out of fear from her rotations. A political victory, a rise of rents, the recovery of your sick, or the return of your absent friend, or some other favorable event, raises your spirits, and you think good days are preparing for you. Do not believe it. Nothing can bring you peace but yourself. Nothing can bring you peace but the triumph of principles.
Which quotation from "Self-reliance" best summarizes Emerson’s view on belief in oneself?
One of the most famous quotes from Ralph Waldo Emerson's "Self-Reliance" that summarizes his view on belief in oneself is:
"Trust thyself: every heart vibrates to that iron string."
What does Emerson argue should be the basis of human actions in the second paragraph of “self-reliance”?
In the second paragraph of "Self-Reliance," Emerson argues that individual conscience, or a person's inner voice, should be the basis of human actions. He writes, "Whoso would be a man must be a nonconformist." He believes that society tends to impose conformity and discourage people from following their own inner truth and intuition. Emerson encourages individuals to trust themselves and to act according to their own beliefs, instead of being influenced by the opinions of others. He argues that this is the way to live a truly authentic and fulfilling life.
Which statement best describes Emerson’s opinion of communities, according to the first paragraph of society and solitude?
According to the first paragraph of Ralph Waldo Emerson's " Society and Solitude, " Emerson has a mixed opinion of communities. He recognizes the importance of social interaction and the benefits of being part of a community but also recognizes the limitations that come with it.
He writes, "Society everywhere is in a conspiracy against the manhood of every one of its members." He argues that society can be limiting and restrictive, and can cause individuals to conform to norms and values that may not align with their own beliefs and desires. He believes that it is important for individuals to strike a balance between the benefits of social interaction and the need for solitude and self-discovery.
Which best describes Emerson’s central message to his contemporaries in "self-reliance"?
Ralph Waldo Emerson's central message to his contemporaries in "Self-Reliance" is to encourage individuals to trust in their own beliefs and instincts, and to break free from societal norms and expectations. He argues that individuals should have the courage to think for themselves and to live according to their own individual truth, rather than being influenced by the opinions of others. Through this message, he aims to empower people to live authentic and fulfilling lives, rather than living in conformity and compromise.
Yet, it is critical that we first possess the ability to conceive our own thoughts. Prior to venturing into the world, we must be intimately acquainted with our own selves and our individual minds. This sentiment echoes the concise maxim inscribed at the ancient Greek site of the Delphic Oracle: 'Know Thyself.'
In essence, Emerson's central message in "Self-Reliance" is to promote self-reliance and individualism as the key to a meaningful and purposeful life.

Understanding Emerson: "The American scholar" and his struggle for self-reliance.
Princeton University Press. ISBN 0-691-09982-0

Standford Encyclopedia of Philosophy
Other works from ralph waldo emerson for book clubs, the over-soul.
There is a difference between one and another hour of life, in their authority and subsequent effect. Our faith comes in moments; our vice is habitual.
The American Scholar
An Oration delivered before the Phi Beta Kappa Society, at Cambridge, August 31, 1837
Essays First Series
Essays: First Series First published in 1841 as Essays. After Essays: Second Series was published in 1844, Emerson corrected this volume and republished it in 1847 as Essays: First Series.
Emerson's Essays
Research the collective works of Ralph Waldo Emerson. Read More Essay
Self-Reliance
Emerson's most famous work that can truly change your life. Check it out
Early Emerson Poems
America's best known and best-loved poems. More Poems
- Skip to main content
- Skip to secondary menu
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
Study Today
Largest Compilation of Structured Essays and Exams
The Person I Like Most Essay – Essay on The person I like Most & I love Most
March 5, 2021 by Study Mentor Leave a Comment
Table of Contents
The person I like Most Paragraph Essay 1
Introduction.
In this long life, we meet a lot of people. Some people stay forever, and some come for a minimal period. It is estimated that we almost meet 80000 people in our life; out of them, only 14 are those who stay with us forever out of those 14. Only 5 are the people who love us unconditionally. Whenever somebody asks me about who is the person in my life that I like the most, I start thinking about the person who stayed with me whenever I needed someone awake the whole night for me who loved me unconditionally and will continue to do so forever he is my dad.
The person I like most – My dad
My dad is the person in my life that I like the most. There are a lot of reasons to say why he is the one whom I love the most. He has dedicated his whole life just for the sake of his family. Sometimes he did not buy new clothes so that we can buy new clothes. He sacrifices his dreams so that we may live our dreams. When I am asleep, he is working. He is the gold that I got in my life. Every day when I wake up, the first thing is I thank god for being born as his son, and the second thing I do is pray to him to give me power and blessing so that soon I can make my father free from all these responsibilities. I have a dream that a time will come when we will rest the whole buy himself whatever he wants, and I will work for him.
There were times in life when I was very low for myself regarding my status regarding my studies my future and I used to cry sitting alone at that time there was always a hand on my shoulder, and he was my dad. He’s my only role model and my only inspiration, and I wish to be like him. He was always behind me whenever I need him. He’s my god and my almighty. It doesn’t matter how busy he might be. He never forgets to call me. He makes a phone call to me every day. When I fail at doing things, he is the one who tries his best to help me stand up again and motivates me to work even harder. Without any hesitation, I can share my every problem with him because I know only he can give solution to all my questions. Infect he is the solution to my every problem.
He taught me the importance of hard work and dedication. He taught me to be self-sufficient in life. He has taught me what life is all about. Whenever I go to him with some problem, he just gives me a direction and left me to decide by myself about the solutions.
Dad is the person who sacrifices his dreams for the sake of our desires. My dad is the strength and faith of my family. He is my best friend and my companion for life. I wish that I can come across the life I want, and I may become capable enough to fulfill every dream of my dad. I remember that time when he only used to eat breakfast the whole day. The way he supports everyone is incredible. Not only for me, but he has the tendency and heart to help everybody that seeks help from him.
My dad is a great singer. His hobby is to sing, and yes, he sings very well. Whenever there is an occasion in the family, he always steps up on the stage and starts singing. He is a hilarious man. The way he handles everything, the bad or good, is incredible. He has taught me to help everybody, to respect everybody regardless of their age or anything. One thing that he always says is that every person should have an artistic hobby in life it could be painting, singing, dancing, etc. because whenever a person is going through some bad times, these hobbies will help him or her to cope with stress and will make them feel better. He never treated me like a son; instead, he treated me like his friend. The way he talks with me is like he is talking to a friend. One thing he taught me is that I should never in my life break someone’s heart. He is the most humble man I have seen in my life. My dad plays volleyball very well. He was the captain of his team while representing his team for a state tournament. Whatever he does, he put his full potential and effort to make it best. He is devoted to his family and society. He helps everybody in the organization.
One thing that I love about him the most is his discipline. It doesn’t matter how busy he might be. He never skips his morning exercise. Every morning he performs yoga and goes for a brisk walk. He taught me the importance of mental fitness, along with physical fitness. He always says that trust yourself and become whatever you want to be.
He believes in living a simple and sober life. He never gets attracted to luxury or any of those useless things. Whatever he earns, he takes out some amount of money for some social cause. The taught me why it is essential to help others. Besides being a good father or a husband, he is a beautiful and noble human being. He supports me in my every step and tells me about the wrong I am doing and the ways by which I can be better. He has always supported my mother in everything. Whether it be household work or social problems. Even after getting success in life, he hasn’t changed his nature.
My father is the best person in my life. He taught me what life is and the perfect way to live it. His values keep inspiring me to do good and become a better person in life. I will try to follow the path taught by him forever.
The person I like Most &The person I love Most Paragraph Essay 2
When this question is asked to someone, the general answer most will give is their parents. When I first came across this question, I was a bit startled when I realized that my answer is not similar to most of the people. So, I paused for a bit and thought about my answer and then realized that yes, it is true.
The person I like the most is my best friend . In fact, along with like, I admire my best friend. My best friend has been the constant pillar in my life that stayed with me till today through thick and thin. So, when I first realized that my answer is nowhere near like the others, I actually was surprised but there is no point in denying the truth after all if I can’t accept the truth about myself then I can never accept anyone else’s point of view.
So, here is the truth. My best friend after knowing this little fact will scream so loud that I am pretty sure everyone in our city will be able to hear it.
The question that why exactly I like my best fried the most arises almost instantly. The fact is there are so many reasons that I can’t possibly choose only one or two among them. However, I would list as many reasons as I can and will try to explain them too.
One of the reasons is that he is a good person. Everyone will think that as he is my best friend, I am saying this but the truth is that is not the fact at all. I admire him because he won’t hesitate to help anyone during their time of need. I can testify this as he had helped me so many times that I have lost count.
Whenever in whatever situation I needed help, he always helped. With him in my life I never felt alone. If I am sad then he will cheer me up or if I need someone to listen to me, he will be there and it doesn’t matter that it is 3 a.m. in the morning or midnight.
I remember one incident. I was upset about something my classmate said about me and when he found out, he came to my house with a bunch of chocolates to listen to me. He has been my constant rock in my life.
Another thing I like about him is his personality. He has an odd combination of childlike, goofy and serious personality. I till this date can’t figure out how he had all these personalities.
He sometime has a childlike ball of energy that likes to bug me with anything and everything and sometime he is the serious guy who needs me to mature a bit in life. When time comes, he even whacks my head if I am doing something wrong. He won’t hesitate to tell me to get my acts straight.
Most of the time he also acts like a retard kid who is high on sugar and sometimes I do worry that he is actually a retard. If he finds out I said this about him then he will simply say that it took me too long to figure this simple fact out.
He is also stubborn like a kid and also acts childishly sometimes. I personally think that he is a 10-year-old kid trapped in an adult’s body. He is sometimes too cute for his own good and rest of the time too stubborn to make me want to slap him (which I do by the way).
Another thing I admire about him is the way he handles a difficult situation with ease. When the situation arises, he steps up as a leader and handle the situation with absolute ease. He is a great leader and has no problem with leading.
He does not discriminate between his subordinates and treats everyone equally and divide the whole work among them with extreme precision. He respects people and knows to give compliment where it’s due and also won’t stop scolding someone if that person does not do the job given to him.
He is the kind of person that likes to take everyone along with him and reaches the goal together with everybody. He has all the qualities of a leader which I really admire about him. If he is determined to achieve a goal then he will do that along with everybody and won’t let anyone give up along the journey either. When a work is given to him, everyone knows that he will complete it with absolute precision.
He loves to protect everyone. He loves the people that are close to him and won’t tolerate anyone hurting those persons. He is protective even about his friends.
He is also supportive. He will encourage me to try out new things as without trying out different things I cannot say that I don’t like them. When I will try out new stuff (doesn’t matter how small or big the thing is), he will be there beside me on every step of the way and I don’t have the fear that he will leave me in the middle of the road.
He has so many qualities that I haven’t listed here. He is an amazing person and I like him as a person. Even if he weren’t my best friend, I still would have admired him because people, who spend a few minutes with him, cannot help but admire him. As his best friend I am proud to have him in my life.
He is a great person and his parents are immensely proud of him. If there were people more like him in this world, then it would have been really great as there would have been more people who are willing to help a stranger in their time of need. He has many admirable qualities and here I have listed very few of them.
Reader Interactions
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Top Trending Essays in March 2021
- Essay on Pollution
- Essay on my School
- Summer Season
- My favourite teacher
- World heritage day quotes
- my family speech
- importance of trees essay
- autobiography of a pen
- honesty is the best policy essay
- essay on building a great india
- my favourite book essay
- essay on caa
- my favourite player
- autobiography of a river
- farewell speech for class 10 by class 9
- essay my favourite teacher 200 words
- internet influence on kids essay
- my favourite cartoon character
Brilliantly
Content & links.
Verified by Sur.ly
Essay for Students
- Essay for Class 1 to 5 Students
Scholarships for Students
- Class 1 Students Scholarship
- Class 2 Students Scholarship
- Class 3 Students Scholarship
- Class 4 Students Scholarship
- Class 5 students Scholarship
- Class 6 Students Scholarship
- Class 7 students Scholarship
- Class 8 Students Scholarship
- Class 9 Students Scholarship
- Class 10 Students Scholarship
- Class 11 Students Scholarship
- Class 12 Students Scholarship
STAY CONNECTED
- About Study Today
- Privacy Policy
- Terms & Conditions
Scholarships
- Apj Abdul Kalam Scholarship
- Ashirwad Scholarship
- Bihar Scholarship
- Canara Bank Scholarship
- Colgate Scholarship
- Dr Ambedkar Scholarship
- E District Scholarship
- Epass Karnataka Scholarship
- Fair And Lovely Scholarship
- Floridas John Mckay Scholarship
- Inspire Scholarship
- Jio Scholarship
- Karnataka Minority Scholarship
- Lic Scholarship
- Maulana Azad Scholarship
- Medhavi Scholarship
- Minority Scholarship
- Moma Scholarship
- Mp Scholarship
- Muslim Minority Scholarship
- Nsp Scholarship
- Oasis Scholarship
- Obc Scholarship
- Odisha Scholarship
- Pfms Scholarship
- Post Matric Scholarship
- Pre Matric Scholarship
- Prerana Scholarship
- Prime Minister Scholarship
- Rajasthan Scholarship
- Santoor Scholarship
- Sitaram Jindal Scholarship
- Ssp Scholarship
- Swami Vivekananda Scholarship
- Ts Epass Scholarship
- Up Scholarship
- Vidhyasaarathi Scholarship
- Wbmdfc Scholarship
- West Bengal Minority Scholarship
- Click Here Now!!
Mobile Number
Have you Burn Crackers this Diwali ? Yes No

Essay on The Person I Like Most My Father
Students are often asked to write an essay on The Person I Like Most My Father in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on The Person I Like Most My Father
Introduction.
My father is the person I admire the most. He is my hero, always there for me and my biggest supporter.
His Character
He is honest, hardworking, and kind. He always puts our family first, teaching us the importance of love and unity.
His Influence
He inspires me to be a better person, guiding me with his wisdom. His strength and perseverance motivate me to face any challenge.
My father’s love and guidance make him the most likable person to me. I aspire to be as great as him one day.
250 Words Essay on The Person I Like Most My Father
The person I admire the most in my life is none other than my father. He is the one who instilled the values of discipline, hard work, and respect in me. His wisdom, humility, and resilience have greatly influenced the person I have become today.
My father is a person of exceptional character. He is humble, honest, and patient. He treats everyone with respect and kindness, regardless of their status in society. His integrity is unmatched, as he always stands by his principles even in the face of adversity.
His influence on my life is profound. He has always encouraged me to strive for excellence in every endeavor. He taught me the importance of being accountable for my actions and to always learn from my mistakes. His unwavering belief in my abilities has been instrumental in shaping my self-confidence and determination.
His Resilience
My father’s resilience is inspiring. Despite the numerous challenges he has faced, he has always maintained a positive outlook on life. He has taught me that setbacks are a part of life and that it is our response to these setbacks that truly defines us.
In conclusion, my father is the person I admire the most. His character, influence, and resilience have shaped me into the person I am today. I am grateful for his guidance and support, and I strive to emulate his virtues in my own life. His life serves as a testament to the fact that with hard work, determination, and integrity, one can overcome any obstacle and achieve their dreams.
500 Words Essay on The Person I Like Most My Father
The person I admire most is no other than my father. He is the pillar of strength, the embodiment of love, and the epitome of endurance in my life. His life is a testament to hard work, perseverance, and relentless pursuit of goals.
My Father – The Unyielding Pillar of Strength
My father’s strength is not merely physical, but it is a potent combination of mental resilience and emotional stability. He has faced numerous challenges in his life, each one more daunting than the last. Yet, he has always emerged victorious, teaching me that the strength of character is far more important than the strength of arms. His determination and willpower have inspired me to face my own fears and challenges, instilling in me the belief that I can overcome any obstacle that comes my way.
The Embodiment of Love
Love, as my father has shown me, is not merely a feeling but an action that requires sacrifice and understanding. His love for our family is not expressed through grand gestures or eloquent words, but through his everyday actions. He works tirelessly to provide for us, ensures that we are comfortable, and is always there to offer guidance and support. His love is a steady, reassuring presence, a constant reminder that no matter what happens, he will always be there for us.
An Epitome of Endurance
My father is a living example of endurance. He has faced numerous setbacks in his personal and professional life, yet he has never allowed these setbacks to deter him from his path. Instead, he uses them as stepping stones, learning from each experience and using it to better himself. His unwavering commitment to his goals and his ability to endure hardships have taught me the importance of resilience and determination.
Lessons from My Father
Perhaps the most important lesson I have learned from my father is the value of integrity. He has always maintained that one’s character is the most valuable asset one can possess. He has instilled in me the importance of honesty, respect, and humility. He has taught me to stand up for what is right, even if it is unpopular, and to never compromise on my principles.
In conclusion, my father is the person I admire the most. His strength, love, endurance, and integrity have shaped me into the person I am today. He is not just my father, but my mentor, my guide, and my role model. His life is a testament to the fact that with hard work, perseverance, and a strong moral compass, one can overcome any challenge and achieve their goals. I am grateful for his presence in my life and strive to live up to the example he has set.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
- Essay on Social Impact of COVID-19
- Essay on Importance of COVID-19 Vaccine
- Essay on How to Protect Yourself From COVID-19
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Questions? Call us:
Email:
- How it works
- Testimonials
Essay Writing
- Essay service
- Essay writers
- College essay service
- Write my essay
- Pay for essay
- Essay topics
Term Paper Writing
- Term paper service
- Buy term papers
- Term paper help
- Term paper writers
- College term papers
- Write my term paper
- Pay for term paper
- Term paper topic
Research Paper Writing
- Research paper service
- Buy research paper
- Research paper help
- Research paper writers
- College research papers
- Write my research paper
- Pay for research paper
- Research paper topics
Dissertation Writing
- Dissertation service
- Buy dissertation
- Dissertation help
- Dissertation writers
- College thesis
- Write my dissertation
- Pay for dissertation
- Dissertation topics
Other Services
- Custom writing services
- Speech writing service
- Movie review writing
- Editing service
- Assignment writing
- Article writing service
- Book report writing
- Book review writing
Popular request:
How to write effective essays on trust learn with us.
September 4, 2020
The entire human civilization is based on trust. We trust our loved ones, we trust our teachers, we trust our community and so on.

A trust essay highlights the importance of this powerful value. It tells you what is trust and how the absence of trust affects people individually and even the community at large. Here are some steps that you can follow to write a great essay on trust:
Trust Essay – Define The Concept
The first step when you start writing essays on trust is to define the word trust. Essentially, it is the faith that you have in another person. But trust is also a two way street. It is not just about you trusting someone but also about being that person that someone else can put their trust in.
Start by writing a short paragraph on trust with statements like “In the most basic form, trust is the confidence that you have in someone else.” You can then work in the subject of what makes a person trust another person.
Trust Essay Sample
Leadership and Trust Leadership refers to the power and ability of an individual to lead others. Leadership is often spoken about in terms of nobility, charisma, and the ability to inspire and mobilize others, each of which are positive qualities that exemplify leaders and vice versa. What goes ignored is that leaders can have those characteristics and look to use them for bad or evil. Leaders are not only at the heads of corporate organizations, community groups and churches; they are also the heads of manipulative and mind-altering cults and command their power and ability to influence the behavior of others. Leadership styles vary from person to person, as well as the motives for harnessing that leadership. From business executives to cult leaders, leadership manifests in ways that serve the greater good, however, that “greater good” depends on the motives, desires and personality of the leader. One iconic leader was Nelson Mandela, the face of the nonviolent uprising against the South African government and its racist policies and function. He was more than a leader, but a visionary capable of transformational leadership in a movement against the government that contributed to the lost lives and livelihoods of many, including himself. Mandela’s call to action for the South African people was reinforced and believed by his inimitable leadership. Mandela saw that the way that the government was running the nation through apartheid was, at the least, unsustainable and at the most, detrimental to society. Imprisoned for more than a quarter century On Robben Island along with several other activists, Mandela stood by his convictions and worked strategically to oppose and transform South Africa from the inside, finding that “the political prison of apartheid” (Schoemaker & Krupp, 2014) would have been far worse than serving out his prison sentence. He stood up to prisoners and guards, positioning himself as a man of nobility and dignity even though it came at the expense of his freedom and the realities of harsh prison life. As a leader, he researched other leaders and where they went wrong and where they went right. Observing the teachings of other nations and leaders, he hoped to inspire change by getting the South African government to deviate from a dangerous path that caused the decline of the country of Zimbabwe following a tumultuous and brutal period of dictatorship by Robert Mugabe. Mandela’s nobility shone through in wanting to nonviolently resist oppressors, instead surprising “with restraints and generosity.” Mandela called for peace when people wanted retribution and revenge, even if it was rightfully so. After being elected the first black president of South Africa, Mandela continued to inspire with his charisma and language, using inclusive pronouns like “we” and “our” to bridge gaps instead of widen them, calling on the people to act as a united front to bring about a new world. Nelson Mandela was a strategic leader who was able to harness his emotion and motivate people strongly enough to have continual support. On the contrary, leaders out to do what most perceive as harm have this drive as well—the key difference is in their motives and what they set out to achieve. For those who do not fall under the most understood category of leader, like cult leaders, how the world looks upon them is quite different. Cult leaders are those who often portray themselves as the next messiah, but to others not under their spell of charisma and manipulation, look like manipulators, deceivers and sociopaths. However, the charisma that allowed people like Charles Manson to manipulate and convince his “family” to commit heinous murders unlike the Hollywood scene had seen is not only within him. Back in the 1960s, Charles Manson recruited a group of devote followers he called “The Family,” who shared his love for hallucinogenic drugs and an unconventional lifestyle led off the grid. The key to Manson’s power and control was his ability to position himself and the members of his family as a superior elite that had to do whatever it took to protect themselves and the world. There was danger in his charisma, which allowed his notoriously warped and outrageous ideals to result in the brutal murders of actress Sharon Tate, who was eight months pregnant at the time, Leno and Rosemary LaBianca, Steven Parent and Abigail Folger, heiress to the Folger Coffee fortune. Manson and his followers had a strong sense of moral values that, in their minds, made them better than the untouchable Hollywood elite. He used his own painful, shattered past to draw in people who had been stripped of their identity—if they ever had one—and fulfilled their needs, creating a dangerous connection between their self-esteem and worth and his provisions. Manson sought out people like him who had no sense of stability or identity; he was born without a name to a young, fleeting mother raised in a strictly religious household whose baby’s father abandoned her and their son. While he never directly carried out any of the murders. In prison, Manson studied religion as a tool of control and as he fluctuated between imprisonment and freedom, he harnessed the art of manipulation through advice for other criminals and books like How to Win Friends and Influence People (Romano, 2017). Manson, now deceased, has gone down in history as a symbol of the rebellious hippie counterculture that culminated in gleeful carnage, spurred by a strong distaste for the wealthy, racism and prejudice, and shared lifelong social rejection. As a leader, he is in no way comparable to Nelson Mandela or those like him, but his reign is a painful reminder of cult leadership and pseudo-transformational leadership that captivates and motivates people just as much as nobility does. Leadership has to be understood in a context that allows both good and evil to prosper. History demonstrates that there are those who are looking for positive change like Nelson Mandela, as well as those who want the ultimate revenge and unending, unquestionable power like Charles Manson. To understand both is to understand where and how leadership can go right and wrong, although the concept itself is broad and complex in definition and application.
The Role Of Trust In Relationships
Essays about trust are almost impossible to write without some reference to relationships. The bottom line is that every relationship that you have from neighbours, friends, relatives to your spouse is based on trust.
In fact, you can write an entire essay on trust in a relationship. Why it is important and how breaking someone’s trust is the hardest thing to recover from.
When we trust someone, we also expect that they reciprocate the same, while maintaining our trust and not hide anything from us. This love, faith, and trust can be a subject of discussion in your essay with respect to couples and relationships. You can also break down your trust essays into several layers such as the absence of trust leading to suspicion. And suspicion leading to the breach of trust by snooping or prying into the private mails and texts of the other person.
Betrayal and trust are vital turning points in any relationship. You can use other examples of breach of trust like cheating on a partner to show the effect that it has on love and faith between partners. It is also a great topic to use to define trust itself.
How Trust Affects The Community At Large
We vote for someone because we trust that they are good enough to run the country. A group of people in a corporate follow their team leader’s instruction because they trust that the latter is leading them to success. When parents leave their kids with a baby sitter, it is all about trust.
The point is that without trust, there would be no community. This is a great subject for your trust definition essay. It also gives you a new perspective and approach that is different from the relationship angle. There are enough instances of breach of trust within a community to include in your essays on trust. This will help you explore the definition of trust better.
The community angle gives you a lot more content for trust essay writing. You can talk about recent world events or even take references from history to show how trust plays a massive role in the community. There and endless examples of betrayal in history that have uprooted thriving kingdoms.
It is easier to write a definition essay on trust using these concepts because you can highlight both the angles. First, why trust is important in a society and why being a trustworthy individual is equally important.
Essays On Trust – Dealing With Them The Right Way
While writing an essay about trust, try to give relatable examples from real-life that establish trust between two people. This is the easiest way to bring out the definition of trust in its true essence.
If you need any writing assistance for your college essay, get in touch with us today. You can also go through a trust essay example to help you understand how to approach this subject with more depth and variety.

Take a break from writing.
Top academic experts are here for you.
- How To Write An Autobiography Guideline And Useful Advice
- 182 Best Classification Essay Topics To Learn And Write About
- How To Manage Stress In College: Top Practical Tips
- How To Write A Narrative Essay: Definition, Tips, And A Step-by-Step Guide
- How To Write Article Review Like Professional
- Great Problem Solution Essay Topics
- Creating Best Stanford Roommate Essay
- Costco Essay – Best Writing Guide
- How To Quote A Dialogue
- Wonderful Expository Essay Topics
- Research Paper Topics For 2020
- Interesting Persuasive Essay Topics
- Entertainment
- Environment
- Information Science and Technology
- Social Issues
Home Essay Samples Life
Essay Samples on Trust
Understanding the impact of broken trust in human relationships.
We all have emotional needs, please consider basic survival needs such as water, air, food, and shelter. Meeting these physical needs means you can live, but you need more to make life meaningful. You can see or touch things like friendship, feelings, security, or appreciation,...
- Communication in Relationships
- Relationship
The Importance of Trust in Building Strong Workplace Relationships
Trust is built on consistency as we interact with different kinds of individuals and build relationships with them based on desire behaviors and attitudes. A lack of trust leads to the desire to control a situation oneself as you believe the only person you can...
- Organizational Culture
Reasons to Be Hardworking, Forgiving, Honest and Trustworthy
Being forgiving is a difficult trait to have especially if someone damaged one badly. The time when the person I trusted the most in the world, my best friend stole from my family and stabbed me in the back, it taught me that in order...
- Forgiveness
Maintaining Trust: Importance of Telling the Truth
Have you ever wondered if lying is right or wrong? Have you ever lied and been tricked into telling the truth? Most people have been tricked by pretty much everyone. Lying according to research is always wrong. Most people feel guilty about lying and almost...
- Communication
The Link Between Apologies and the Willingness of Low Status Groups to Seek Help
This work extends research on intergroup apology by examining the influence of an apology on the willingness of low status group members to seek assistance from the high status outgroup. In line with our hypothesis, we found that under unstable status relations, Israeli Arab participants...
Stressed out with your paper?
Consider using writing assistance:
- 100% unique papers
- 3 hrs deadline option
Organizational Trust And National Culture And Trust
Organizational trust is impacted by the reality that there has been eroding confidence levels in multiple stratas of society. In addition, this erosion in confidence has been evidenced by waning trust hinted at by Furedi (1997), who suggests that “human beings appear to have lost...
- Organization
Trust As The Missing Root Relating To Education, Institutions And Economic Development
The institution being studied was established on with the goals of training persons for competent service and the world of work. The core values of the institution were based on philosophies centred on trust. Years after its establishment, that selected tertiary institution is struggling with...
Trust In Relation To Gender & To Years Of Service, Trust And Category Of Worker
Xie and Peng, in their work emphazised how corporations can repair customer trust following negative publicity. They contend that, especially in handling crisis situations, when there are distinct trusting targets needing varying levels of handling of trust repair, competence-based, benevolence-based and integrity-based trust are compulsory....
Overview Of The Main Thrusts In Negotiation
Negotiation is a deliberate procedure including diverse performing actors with various interests or objectives, distinctive dispositions and procedures prompting a circumstance were individuals are attempting to change these distinctions with a specific end goal to achieve an understanding. The willing ness to discover an answer...
- Negotiation
The Road By Cormac McCarthey: The Theme Of Trust In The Book
When I started reading I was doing as I had no choice. Though after reading the first few pages I wanted to keep going out of curiosity. The boy and his papa had me wondering how the story ends in there horrible cannibalism world. Their...
The Theme of Trust in "The Legend" by Marie Lu
“Trust but verify,” this was a famous quote said by the 40th U.S President, Ronald Reagan. June, one of the main characters in the book, Legend, learns how to apply this lesson to herself. In the novel, June is a 15-year-old, patriotic girl who has...
- Literature Review
Best topics on Trust
1. Understanding the Impact of Broken Trust in Human Relationships
2. The Importance of Trust in Building Strong Workplace Relationships
3. Reasons to Be Hardworking, Forgiving, Honest and Trustworthy
4. Maintaining Trust: Importance of Telling the Truth
5. The Link Between Apologies and the Willingness of Low Status Groups to Seek Help
6. Organizational Trust And National Culture And Trust
7. Trust As The Missing Root Relating To Education, Institutions And Economic Development
8. Trust In Relation To Gender & To Years Of Service, Trust And Category Of Worker
9. Overview Of The Main Thrusts In Negotiation
10. The Road By Cormac McCarthey: The Theme Of Trust In The Book
11. The Theme of Trust in “The Legend” by Marie Lu
- Perseverance
- Personal Experience
- Personality
- Reconstruction
Need writing help?
You can always rely on us no matter what type of paper you need
*No hidden charges
100% Unique Essays
Absolutely Confidential
Money Back Guarantee
By clicking “Send Essay”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement. We will occasionally send you account related emails
You can also get a UNIQUE essay on this or any other topic
Thank you! We’ll contact you as soon as possible.

- Table of Contents
- Random Entry
- Chronological
- Editorial Information
- About the SEP
- Editorial Board
- How to Cite the SEP
- Special Characters
- Advanced Tools
- Support the SEP
- PDFs for SEP Friends
- Make a Donation
- SEPIA for Libraries
- Entry Contents
Bibliography
Academic tools.
- Friends PDF Preview
- Author and Citation Info
- Back to Top
Trust is important, but it is also dangerous. It is important because it allows us to depend on others—for love, for advice, for help with our plumbing, or what have you—especially when we know that no outside force compels them to give us these things. But trust also involves the risk that people we trust will not pull through for us, for if there were some guarantee they would pull through, then we would have no need to trust them. [ 1 ] Trust is therefore dangerous. What we risk while trusting is the loss of valuable things that we entrust to others, including our self-respect perhaps, which can be shattered by the betrayal of our trust.
Because trust is risky, the question of when it is warranted is of particular importance. In this context, “warranted” means justified or well-grounded meaning, respectively, that the trust is rational (e.g., it is based on good evidence) or that it successfully targets a trustworthy person. If trust is warranted in these senses, then the danger of it is either minimized as with justified trust or eliminated altogether as with well-grounded trust. Leaving the danger of trust aside, one could also ask whether trust is warranted in the sense of being plausible. Trust may not be warranted in a particular situation because it is simply not plausible; the conditions necessary for it do not exist, as is the case when people feel only antagonism toward one another. This entry on trust is framed as a response to the general question of when trust is warranted, where “warranted” is broadly construed to include “justified”, “well-grounded” and “plausible”.
A complete philosophical answer to this question must explore the various philosophical dimensions of trust, including the conceptual nature of trust and trustworthiness, the epistemology of trust, the value of trust, and the kind of mental attitude trust is. To illustrate how each of these matters is relevant, note that trust is warranted, that is,
- plausible, again, only if the conditions required for trust exist (e.g., some optimism about one another’s ability). Knowing what these conditions are requires understanding the nature of trust.
- well-grounded, only if the trustee (the one trusted) is trustworthy, which makes the nature of trustworthiness important in determining when trust is warranted.
- justified, sometimes when the trustee is not in fact trustworthy, which suggests that the epistemology of trust is relevant.
- justified, often because some value will emerge from the trust or because it is valuable in and of itself. Hence, the value of trust is important.
- plausible, only when it is possible for one to develop trust, given one’s circumstances and the sort of mental attitude trust is. For instance, trust may not be the sort of attitude that one can will oneself to have without any evidence of a person’s trustworthiness.
This piece explores these different philosophical issues about trust. It deals predominantly with interpersonal trust, which arguably is the dominant paradigm of trust. Although some philosophers write about trust that is not interpersonal, including trust in groups (Hawley 2017), institutional trust (i.e., trust in institutions; see, e.g., Potter 2002; Govier 1997; Townley and Garfield 2013), trust in government (e.g., Hardin 2002; Budnik 2018) or science (e.g., Oreskes 2019), self-trust (Govier 1993; Lehrer 1997; Foley 2001; McLeod 2002; Goering 2009; Jones 2012b; Potter 2013), and trust in robots (e.g., Coeckelbergh 2012, Sullins 2020), most would agree that these forms of “trust” are coherent only if they share important features of (i.e., can be modeled on) interpersonal trust. The assumption going forward therefore is that the dominant paradigm is interpersonal.
In addition, while this entry focuses mainly on trust and trustworthiness, it also covers distrust (more so in this version than in previous versions). Distrust has received surprisingly little attention from philosophers, although it has recently become a topic of serious concern for some of them, particularly those who are interested in the politics of trust and distrust in societies marked by oppression and privilege. Relevant issues include when distrust is warranted by people who experience oppression and how misplaced distrust (i.e., in the oppressed) can be overcome by people who are privileged. This entry delves into these matters and also summarizes the few theories that exist about the nature of distrust.
1.1 Motives-based theories
1.2 non-motives-based theories, 1.3 distrust, 2.1 truth- vs. end-directed rationality, 2.2 internalism vs. externalism, 2.3 social and political climate, 3. the value of trust, 4. trust and the will, 5. conclusion, other internet resources, related entries, 1. the nature of trust and trustworthiness.
Trust is an attitude we have towards people whom we hope will be trustworthy, where trustworthiness is a property not an attitude. Trust and trustworthiness are therefore distinct although, ideally, those whom we trust will be trustworthy, and those who are trustworthy will be trusted. For trust to be plausible in a relationship, the parties to the relationship must have attitudes toward one another that permit trust. Moreover, for trust to be well-grounded, both parties must be trustworthy. (Note that here and throughout, unless specified otherwise, “trustworthiness” is understood in a thin sense according to which X is trustworthy for me just in case I can trust X .)
Trusting requires that we can, (1) be vulnerable to others—vulnerable to betrayal in particular; (2) rely on others to be competent to do what we wish to trust them to do; and (3) rely on them to be willing to do it. [ 2 ] Notice that the second two conditions refer to a connection between trust and reliance. For most philosophers, trust is a kind of reliance although it is not mere reliance (Goldberg 2020). Rather, trust involves reliance “plus some extra factor” (Hawley 2014: 5). Controversy surrounds this extra factor, which generally concerns why the trustor (i.e., the one trusting) would rely on the trustee to be willing to do what they are trusted to do.
Trustworthiness is likewise a kind of reliability, although it’s not obvious what kind. Clear conditions for trustworthiness are that the trustworthy person is competent and willing to do what they are trusted to do. Yet this person may also have to be willing for certain reasons or as a result of having a certain kind of motive for acting (e.g., they care about the trustor).
This section explains these various conditions for trust and trustworthiness and highlights the controversy that surrounds the condition about motive and relatedly how trust differs from mere reliance. Included at the end is some discussion about the nature of distrust.
Let me begin with the idea that the trustor must accept some level of vulnerability or risk (Becker 1996; Baier 1986). Minimally, what this person risks, or is vulnerable to, is the failure by the trustee to do what the trustor is depending on them to do. The trustor might try to reduce this risk by monitoring or imposing certain constraints on the behavior of the trustee; but after a certain threshold perhaps, the more monitoring and constraining they do, the less they trust this person. Trust is relevant “before one can monitor the actions of … others” (Dasgupta 1988: 51) or when out of respect for others one refuses to monitor them. One must be content with them having some discretionary power or freedom, and as a result, with being somewhat vulnerable to them (Baier 1986; Dasgupta 1988).
One might think that if one is relying while trusting—that is, if trust is a species of reliance—then accepted vulnerability would not be essential for trust. Do we not rely on things only when we believe they will actually happen? And if we believe that, then we don’t perceive ourselves as being vulnerable. Many philosophers writing on trust and reliance say otherwise. They endorse the view of Richard Holton, who writes, “When I rely on something happening … I [only] need to plan on it happening; I need to work around the supposition that it will [happen]” (Holton 1994: 3). I need not be certain of it happening and I could even have doubts that it will happen (Goldberg 2020). I could therefore accept that I am vulnerable. I could do that while trusting if trust is a form of reliance.
What does trusting make us vulnerable to, in particular? Annette Baier writes that “trusting can be betrayed, or at least let down, and not just disappointed” (1986: 235). In her view, disappointment is the appropriate response when one merely relied on someone to do something but did not trust them to do it. To elaborate, although people who monitor and constrain others’ behavior may rely on them, they do not trust them if their reliance can only be disappointed rather than betrayed. One can rely on inanimate objects, such as alarm clocks, but when they break, one is not betrayed though one might be disappointed. This point reveals that reliance without the possibility of betrayal (or at least “let down”) is not trust; people who rely on one another in a way that makes this reaction impossible do not trust one another.
But does trust always involve the potential for betrayal? “Therapeutic trust” may be an exception (Nickel 2007: 318; and for further exceptions, see, e.g., Hinchman 2017). To illustrate this type of trust, consider parents who
trust their teenagers with the house or the family car, believing that their [children] may well abuse their trust, but hoping by such trust to elicit, in the fullness of time, more responsible and responsive trustworthy behaviour. (McGeer 2008: 241, her emphasis; see also Horsburgh 1960 and Pettit 1995)
Therapeutic trust is not likely to be betrayed rather than merely be disappointed. It is unusual in this respect (arguably) and in other respects that will become evident later on in this entry. The rest of this section deals with usual rather than unusual forms of trust and trustworthiness.
Without relying on people to display some competence, we also can’t trust them. We usually trust people to do certain things, such as look after our children, give us advice, or be honest with us, which we wouldn’t do that if we thought they lacked the relevant skills, including potentially moral skills of knowing what it means to be honest or caring (Jones 1996: 7). Rarely do we trust people completely (i.e., A simply trusts B ). Instead, “trust is generally a three-part relation: A trusts B to do X ” (Hardin 2002: 9)—or “ A trusts B with valued item C ” (Baier 1986) or A trusts B in domain D (D’Cruz 2019; Jones 2019). [ 3 ] To have trust in a relationship, we do not need to assume that the other person will be competent in every way. Optimism about the person’s competence in at least one area is essential, however.
When we trust people, we rely on them not only to be competent to do what we trust them to do, but also to be willing or motivated to do it. We could talk about this matter either in terms of what the trustor expects of the trustee or in terms of what the trustee possesses: that is, as a condition for trust or for trustworthiness (and the same is true, of course, of the competence condition). For simplicity’s sake and to focus some of this section on trustworthiness rather than trust, the following refers to the motivation of the trustee mostly as a condition for trustworthiness.
Although both the competence and motivational elements of trustworthiness are crucial, the exact nature of the latter is unclear. For some philosophers, it matters only that the trustee is motivated, where the central problem of trustworthiness in their view concerns the probability that this motivation will exist or endure (see, e.g., Hardin 2002: 28; Gambetta 1988b). Jones calls these “risk-assessment views” about trust (1999: 68). According to them, we trust people whenever we perceive that the risk of relying on them to act a certain way is low and so we rely on (i.e., “trust”) them. They are trustworthy if they are willing, for whatever reason, to do what they are trusted to do. Risk-assessment theories make no attempt to distinguish between trust and mere reliance and have been criticized for this reason (see, e.g., Jones 1999).
By contrast, other philosophers say that just being motivated to act in the relevant way is not sufficient for trustworthiness; according to them, the nature of the motivation matters, not just its existence or duration. It matters in particular, they say, for explaining the trust-reliance distinction, which is something they aim to do. The central problem of trustworthiness for them is not simply whether but also how the trustee is motivated to act. Will that person have the kind of motivation that makes trust appropriate? Katherine Hawley identifies theories that respond to this question as “motives-based” theories (2014).
To complicate matters, there are “non-motives-based theories”, which are also not risk-assessment theories (Hawley 2014). They strive to distinguish between trust and mere reliance, though not by associating a particular kind of motive with trustworthiness. Since most philosophical debate about the nature of trust and trustworthiness centers on theories that are either motives-based or non-motives-based, let me expand on each of these categories.
Philosophers who endorse this type of theory differ in terms of what kind of motive they associate with trustworthiness. For some, it is self-interest, while for others, it is goodwill or an explicitly moral motive, such as moral integrity or virtue. [ 4 ]
For example, Russell Hardin defines trustworthiness in terms of self-interest in his “encapsulated interests” account (2002). He says that trustworthy people are motivated by their own interest to maintain the relationship they have with the trustor, which in turn encourages them to encapsulate the interests of that person in their own interests. In addition, trusting people is appropriate when we can reasonably expect them to encapsulate our interests in their own, an expectation which is missing with mere reliance.
Hardin’s theory may be valuable in explaining many different types of trust relationships, including those between people who can predict little about one another’s motives beyond where their self-interest lies. Still, his theory is problematic. To see why, consider how it applies to a sexist employer who has an interest in maintaining relationships with women employees, who treats them reasonably well as a result, but whose interest stems from a desire to keep them around so that he can daydream about having sex with them. This interest conflicts with an interest the women have in not being objectified by their employer. At the same time, if they were not aware of his daydreaming—say they are not—then he can ignore this particular interest of theirs. He can keep his relationships with them going while ignoring this interest and encapsulating enough of their other interests in his own. And this would make him trustworthy on Hardin’s account. But is he trustworthy? The answer is “no” or at least the women themselves would say “no” if they knew the main reason for their employment. The point is that being motivated by a desire to maintain a relationship (the central motivation of a trustworthy person on the encapsulated interests view) may not require one to adopt all of the interests of the trustor that would actually make one trustworthy to that person. In the end, the encapsulated interests view seems to describe only reliability, not trustworthiness. The sexist employer may reliably treat the women well, because of his interest in daydreaming about them, but he is not trustworthy because of why he treats them well.
A different type of theory is what Jones calls a “will-based” account, which finds trustworthiness only where the trustee is motivated by goodwill (Jones 1999: 68). This view originates in the work of Annette Baier and is influential, even outside of moral philosophy (e.g., in bioethics and law, especially fiduciary law; see, e.g., Pellegrino and Thomasma 1993, O’Neill 2002, and Fox-Decent 2005). According to it, a trustee who is trustworthy will act out of goodwill toward the trustor, to what or to whom the trustee is entrusted with, or both. While many readers might find the goodwill view problematic—surely we can trust people without presuming their goodwill!—it is immune to a criticism that applies to Hardin’s theory and also to risk-assessment theories. The criticism is that they fail to require that the trustworthy person care about (i.e., feel goodwill towards) the trustor, or care about what the trustor cares about. As we have seen, such caring appears to be central to a complete account of trustworthiness.
The particular reason why care may be central is that it allows us to grasp how trust and reliance differ. The above suggested that they differ because only trust can be betrayed (or at least let down). But why is that true? Why can trust be betrayed, while mere reliance can only be disappointed? The answer Baier gives is that betrayal is the appropriate response to someone on whom one relied to act out of goodwill, as opposed to ill will, selfishness, or habit bred out of indifference (1986: 234–5; see also Baier 1991). Those who say that trusting could involve relying on people to act instead on motives like ill will or selfishness will have trouble distinguishing between trust and mere reliance.
While useful in some respects, Baier’s will-based account is not perfect. Criticisms have been made that suggest goodwill is neither necessary nor sufficient for trustworthiness. It is not necessary because we can trust other people without presuming that they have goodwill (e.g., O’Neill 2002; Jones 2004), as we arguably do when we put our trust in strangers.
As well as being unnecessary, goodwill may not be sufficient for trustworthiness, and that is true for at least three reasons. First, someone trying to manipulate you—a “confidence trickster” (Baier 1986)—could “rely on your goodwill without trusting you”, say, to give them money (Holton 1994: 65). You are not trustworthy for them, despite your goodwill, because they are not trusting you but rather are just trying to trick you. Second, basing trustworthiness on goodwill alone cannot explain unwelcome trust. We do not always welcome people’s trust, because trust can be burdensome or inappropriate. When that happens, we object not to these people’s optimism about our goodwill (who would object to that?), but only to the fact that they are counting on us. Third, we can expect people to be reliably benevolent toward us without trusting them (Jones 1996: 10). We can think that their benevolence is not shaped by the sorts of values that for us are essential to trustworthiness. [ 5 ]
Criticisms about goodwill not being sufficient for trustworthiness have prompted revisions to Baier’s theory and in some cases to the development of new will-based theories. For example, in response to the first criticism—about the confidence trickster—Zac Cogley argues that trust involves the belief not simply that the trustee will display goodwill toward us but that this person owes us goodwill (2012). Since the confidence trickster doesn’t believe that their mark owes them goodwill, they don’t trust this person, and neither is this person trustworthy for them. In response to the second criticism—the one about unwelcome trust—Jones claims that optimism about the trustee’s goodwill must be coupled with the expectation that the trustee will be “favorably moved by the thought that [we are] counting on her” (1996: 9). Jones does that in her early work on trust where she endorses a will-based theory. Finally, in response to the third concern about goodwill not being informed by the sorts of values that would make people trustworthy for us, some maintain that trust involves an expectation about some shared values, norms, or interests (Lahno 2001, 2020; McLeod 2002, 2020; Mullin 2005; Smith 2008). (To be clear, this last expectation tends not to be combined with goodwill to yield a new will-based theory.)
One final criticism of will-based accounts concerns how “goodwill” should be interpreted. In much of the discussion above, it is narrowly conceived so that it involves friendly feeling or personal liking. Jones urges us in her early work on trust to understand goodwill more broadly, so that it could amount to benevolence, conscientiousness, or the like, or friendly feeling (1996: 7). But then in her later work, she worries that by defining goodwill so broadly we
turn it into a meaningless catchall that merely reports the presence of some positive motive, and one that may or may not even be directed toward the truster. (2012a: 67)
Jones abandons her own will-based theory upon rejecting both a narrow and a broad construal of goodwill. (The kind of theory she endorses now is a trust responsive one; see below.) If her concerns about defining goodwill are valid, then will-based theories are in serious trouble.
To recapitulate about encapsulated-interest and will-based theories, they say that a trustworthy person is motivated by self-interest or goodwill, respectively. Encapsulated-interest theories struggle to explain how trustworthiness differs from mere reliability, while will-based theories are faced with the criticism that goodwill is neither necessary nor sufficient for trustworthiness. Some philosophers who say that goodwill is insufficient develop alternative will-based theories. An example is Cogley’s theory according to which trust involves a normative expectation of goodwill (2012).
The field of motives-based theories is not exhausted by encapsulated-interest and will-based theories, however. Other motives-based theories include those that describe the motive of trustworthy people in terms of a moral commitment, moral obligation, or virtue. To expand, consider that one could make sense of the trustworthiness of a stranger by presuming that the stranger is motivated not by self-interest or goodwill, but by a commitment to stand by their moral values. In that case, I could trust a stranger to be decent by presuming just that she is committed to common decency. Ultimately, what I am presuming about the stranger is moral integrity, which some say is the relevant motive for trust relations (those that are prototypical; see McLeod 2002). Others identify this motive similarly as moral obligation, and say it is ascribed to the trustee by the very act of trusting them (Nickel 2007; for a similar account, see Cohen and Dienhart 2013). Although compelling in some respects, the worry about these theories is that they moralize trust inappropriately by demanding that the trustworthy person have a moral motive (see below and also Mullin 2005; Jones 2017).
Yet one might insist that it is appropriate to moralize trust or at least moralize trustworthiness, which we often think of as a virtuous character trait. Nancy Nyquist Potter refers to the trait as “full trustworthiness”, and distinguishes it from “specific trustworthiness”, which is trustworthiness that is specific to certain relationships (and equivalent to the thin sense of trustworthiness I have used throughout; 2002: 25). To be fully trustworthy, one must have a disposition to be trustworthy toward everyone, according to Potter. Let us call this the “virtue” account.
It may sound odd to insist that trustworthiness is a virtue or, in other words, a moral disposition to be trustworthy (Potter 2002: 25; Hardin 2002: 32). What disposition exactly is it meant to be? A disposition normally to honor people’s trust? That would be strange, since trust can be unwanted if the trust is immoral (e.g., being trusted to hide a murder) or if it misinterprets the nature of one’s relationship with the trustee (e.g., being trusted to be friends with a mere acquaintance). Perhaps trustworthiness is instead a disposition to respond to trust in appropriate ways, given “who one is in relation” to the trustor and given other virtues that one possesses or ought to possess (e.g., justice, compassion) (Potter 2002: 25). This is essentially Potter’s view. Modeling trustworthiness on an Aristotelian conception of virtue, she defines a trustworthy person as “one who can be counted on, as a matter of the sort of person he or she is, to take care of those things that others entrust to one and (following the Doctrine of the Mean) whose ways of caring are neither excessive nor deficient” (her emphasis; 16). [ 6 ] A similar account of trustworthiness as a virtue—an epistemic one, specifically—can be found in the literature on testimony (see Frost-Arnold 2014; Daukas 2006, 2011).
Criticism of the virtue account comes from Karen Jones (2012a). As she explains, if being trustworthy were a virtue, then being untrustworthy would be a vice, but that can’t be right because we can never be required to exhibit a vice, yet we can be required to be untrustworthy (84). An example occurs when we are counted on by two different people to do two incompatible things and being trustworthy to the one demands that we are untrustworthy to the other (83). To defend her virtue theory, Potter would have to insist that in such situations, we are required either to disappoint someone’s trust rather than be untrustworthy, or to be untrustworthy in a specific not a full sense. [ 7 ]
Rather than cling to a virtue theory, however, why not just accept the thin conception of trustworthiness (i.e., “specific trustworthiness”), according to which X is trustworthy for me just in case I can trust X ? Two things can be said. First, the thick conception—of trustworthiness as a virtue—is not meant to displace the thin one. We can and do refer to some people as being trustworthy in the specific or thin sense and to others as being trustworthy in the full or thick sense. Second, one could argue that the thick conception explains better than the thin one why fully trustworthy people are as dependable as they are. It is ingrained in their character. They therefore must have an ongoing commitment to being accountable to others, and better still, a commitment that comes from a source that is compatible with trustworthiness (i.e., virtue as opposed to mere self-interest).
An account of trustworthiness that includes the idea that trustworthiness is a virtue will seem ideal only if we think that the genesis of the trustworthy person’s commitment matters. If we believe, like risk-assessment theorists, that it matters only whether, not how, the trustor will be motivated to act, then we could assume that ill will can do the job as well as a moral disposition. Such controversy explains how and why motives-based and risk-assessment theories diverge from one another.
A final category are theories that base trustworthiness neither on the kind of motivation a trustworthy person has nor on the mere willingness of this person to do what they are relied on to do. These are non-motives-based and also non-risk-assessment theories. The conditions that give rise to trustworthiness according to them reside ultimately in the stance the trustor takes toward the trustee or in what the trustor believes they ought to be able to expect from this person (i.e., in normative expectations of them). These theories share with motives-based theories the goal of describing how trust differs from mere reliance.
An example is Richard Holton’s theory of trust (1994). Holton argues that trust is unique because of the stance the trustor takes toward the trustee: the “participant stance”, which involves treating the trustee as a person—someone who is responsible for their actions—rather than simply as an object (see also Strawson 1962 [1974]). In the case of trust specifically, the stance entails a readiness to feel betrayal (Holton 1994: 4). Holton’s claim is that this stance and this readiness are absent when we merely rely on someone or something.
Although Holton’s theory has garnered positive attention (e.g., by Hieronymi 2008; McGeer 2008), some do find it dissatisfying. For example, some argue that it does not obviously explain what would justify a reaction of betrayal, rather than mere disappointment, when someone fails to do what they are trusted to do (Jones 2004; Nickel 2007). They could fail to do it just by accident, in which case feelings of betrayal would be inappropriate (Jones 2004). Others assert, by contrast, that taking the participant stance toward someone
does not always mean trusting that person: some interactions [of this sort] lie outside the realm of trust and distrust. (Hawley 2014: 7)
To use an example from Hawley, my partner could come to rely on me to make him dinner every night in a way that involves him taking the participant stance toward me. But he needn’t trust me to make him dinner and so needn’t feel betrayed if I do not. He might know that I am loath for him to trust me in this regard: “to make this [matter of making dinner] a matter of trust” between us (Hawley 2014: 7).
Some philosophers have expanded on Holton’s theory in a way that might deflect some criticism of it. Margaret Urban Walker emphasizes that in taking a participant stance, we hold people responsible (2006: 79). We expect them to act not simply as we assume they will , but as they should . We have, in other words, normative rather than merely predictive expectations of them. Call this a “normative-expectation” theory, which again is an elaboration on the participant-stance theory. Endorsed by Walker and others (e.g., Jones 2004 and 2012a; Frost-Arnold 2014), this view explains the trust-reliance distinction in terms of the distinction between normative and predictive expectations. It also describes the potential for betrayal in terms of the failure to live up a normative expectation.
Walker’s theory is non-motives-based because it doesn’t specify that trustworthy people must have a certain kind of motive for acting. She says that trustworthiness is compatible with having many different kinds of motives, including, among others, goodwill, “pride in one’s role”, “fear of penalties for poor performance”, and “an impersonal sense of obligation” (2006: 77). What accounts for whether someone is trustworthy in her view is whether they act as they should, not whether they are motivated in a certain way. (By contrast, Cogley’s normative-expectation theory says that the trustworthy person both will and ought to act with goodwill. His theory is motives-based.)
Prominent in the literature is a kind of normative-expectation theory called a “trust- (or dependence-) responsive” theory (see, e.g., Faulkner and Simpson 2017: 8; Faulkner 2011, 2017; Jones 2012a, 2017, 2019; McGeer and Petit 2017). According to this view, being trustworthy involves being appropriately responsive to the reason you have to do X —what you are being relied on (or “counted on”; Jones 2012a) to do—when it’s clear that someone is in fact relying on you. The reason you have to do X exists simply because someone is counting on you; other things being equal, you should do it for this reason. Being appropriately responsive to it, moreover, just means that you find it compelling (Jones 2012a: 70–71). The person trusting you expects you to have this reaction; in other words, they have a normative expectation that the “manifest fact of [their] reliance will weigh on you as a reason for choosing voluntarily to X ” (McGeer and Pettit 2017: 16). This expectation is missing in cases of mere reliance. When I merely rely on you, I do not expect my reliance to weigh on you as I do when I trust you.
Although trust-responsive theories might seem motives-based, they are not. One might think that to be trustworthy, they require that you to be motivated by the fact that you are being counted on. Instead, they demand only that you be appropriately responsive to the reason you have to do what you are being depended on to do. As Jones explains, you could be responsive in this way and act ultimately out of goodwill, conscientiousness, love, duty, or the like (2012a: 66). The reaction I expect of you, as the trustor, is compatible with you acting on different kinds of motives, although to be clear, not just any motive will do (not like in Walker’s theory); some motives are ruled out, including indifference and ill will (Jones 2012a: 68). Being indifferent or hateful towards me means that you are unlikely to view me counting on you as a reason to act. Hence, if I knew you were indifferent or hateful, I would not expect you to be trust responsive.
Trust-responsive theories are less restrictive than motives-based theories when it comes to defining what motives people need to be trustworthy. At the same time, they are more restrictive when it comes to stating whether, in order to be trustworthy or trusted, one must be aware that one is being counted on. One couldn’t be trust responsive otherwise. In trusting you, I therefore must “make clear to you my assumption that you will prove reliable in doing X ” (McGeer and Pettit 2017: 16). I do not have to do that by contrast if, in trusting you, I am relying on you instead to act with a motive like goodwill. Baier herself allows that trust can exist where the trustee is unaware of it (1986: 235; see also Hawley 2014; Lahno 2020). For her, trust is ubiquitous (Jones 2017: 102) in part for this reason; we trust people in a myriad of different ways every single day, often without them knowing it. If she’s right about this fact, then trust-responsive theories are incomplete.
These theories are also vulnerable to objections raised against normative-expectation theories, because they are again a type of normative-expectation theory. One such concern comes from Hawley. In writing about both trust and distrust, she states that
we need a story about when trust, distrust or neither is objectively appropriate—what is the worldly situation to which (dis)trust] is an appropriate response? When is it appropriate to have (dis)trust-related normative expectations of someone? (2014: 11)
Normative-expectation theories tend not to provide an answer. And trust-responsive theories suggest only that trust-related normative expectations are appropriate when certain motives are absent (e.g., ill will), which may not to be enough.
Hawley responds to the above concern within her “commitment account” of trust (2014, 2019). This theory states that in trusting others, we believe that they have a commitment to doing what we are trusting them to do (2014: 10), a fact which explains why we expect them to act this way, and also why we fail to do so in cases like that of my partner relying on me to make dinner; he knows I have no commitment to making his dinner (or anyone else’s) repeatedly. For Hawley, the relevant commitments
can be implicit or explicit, weighty or trivial, conferred by roles and external circumstances, default or acquired, welcome or unwelcome. (2014: 11)
They also needn’t actually motivate the trustworthy person. Her theory is non-motives-based because it states that to
be trustworthy, in some specific respect, it is enough to behave in accordance with one’s commitment, regardless of motive. (2014: 16)
Similarly, to trust me to do something, it is enough to believe that I
have a commitment to do it, and that I will do it, without believing that I will do it because of my commitment. (2014: 16; her emphasis)
Notice that unlike trust-responsive theories, the commitment account does not require that the trustee be aware of the trust in order to be trustworthy. This person simply needs to have a commitment and to act accordingly. They don’t even need to be committed to the trustor, but rather could be committed to anyone and one could trust them to follow through on that commitment (Hawley 2014: 11). So, relying on a promise your daughter’s friend makes to her to take her home from the party would count as an instance of trust (Hawley 2014: 11). In this way, the commitment account is less restrictive than trust-responsive theories are. In being non-motives-based, Hawley’s theory is also less restrictive than any motives-based theory. Trust could truly be ubiquitous if she’s correct about the nature of it.
Like the other theories considered here, however, the commitment account is open to criticisms. One might ask whether Hawley gives a satisfactory answer to the question that motivates her theory: when can we reasonably have the normative expectations of someone that go along with trusting them? Hawley’s answer is, when this person has the appropriate commitment, where “commitment” is understood very broadly. Yet where the relevant commitment is implicit or unwelcome, it’s unclear that we can predict much about the trustee’s behavior. In cases like these, the commitment theory may have little to say about whether it is reasonable to trust.
A further criticism comes from Andrew Kirton (2020) who claims that we sometimes trust people to act contrary to what they are committed to doing. His central example involves a navy veteran, an enlisted man, whose ship sunk at sea and who trusted those who rescued them (navy men) to ignore a commitment they had to save the officers first, because the officers were relatively safe on lifeboats compared to the enlisted men who were struggling in the water. Instead the rescuers adhered to their military duty, and the enlisted man felt betrayed by them for nearly letting him drown. Assuming it is compelling, this example shows that trust and commitment can come apart and that Hawley’s theory is incomplete. [ 8 ]
The struggle to find a complete theory of trust has led some philosophers to be pluralists about trust—that is, to say, “we must recognise plural forms of trust” (Simpson 2012: 551) or accept that trust is not just one form of reliance, but many forms of it (see also Jacoby 2011; Scheman 2020; McLeod 2020). Readers may be led to this conclusion from the rundown I’ve given of the many different theories of trust in philosophy and the objections that have been raised to them. Rather than go in the direction of pluralism, however, most philosophers continue to debate what unifies all trust such that it is different from mere reliance. They tend to believe that a unified and suitably developed motives-based theory or non-motives-based theory can explain this difference, although there is little consensus about what this theory should be like.
In spite of there being little settled agreement in philosophy about trust, there are thankfully things we can say for certain about it that are relevant to deciding when it is warranted. The trustor must be able to accept that by trusting, they are vulnerable usually to betrayal. Also, the trustee must be competent and willing to do what the trustor expects of them and may have to be willing because of certain attitudes they have. Last, in paradigmatic cases of trust, the trustor must be able to rely on the trustee to exhibit this competence and willingness.
As suggested above, distrust has been somewhat of an afterthought for philosophers (Hawley 2014), [ 9 ] although their attention to it has grown recently. As with trust and trustworthiness, philosophers would agree that distrust has certain features, although the few who have developed theories of distrust disagree ultimately about the nature of it.
The following are features of distrust that are relatively uncontroversial (see D’Cruz 2020):
- Distrust is not just the absence of trust since it is possible to neither distrust nor trust someone (Hawley 2014: 3; Jones 1996: 16; Krishnamurthy 2015). There is gap between the two—“the possibility of being suspended between” them (Ullmann-Margalit 2004 [2017: 184]). (For disagreement, see Faulkner 2017.)
- Although trust and distrust are not exhaustive, they are exclusive; one cannot at the same time trust and distrust someone about the same matter (Ullmann-Margalit 2004 [2017: 201]).
- Distrust is “not mere nonreliance” (Hawley 2014: 3). I could choose not to rely on a colleague’s assistance because I know she is terribly busy, not because I distrust her.
- Relatedly, distrust has a normative dimension. If I distrusted a colleague for no good reason and they found out about it, then they would probably be hurt or angry. But the same reaction would not accompany them knowing that I decided not to rely on them (Hawley 2014). Being distrusted is a bad thing (Domenicucci and Holton 2017: 150; D’Cruz 2019: 935), while not being relied on needn’t be bad at all.
- Distrust is normally a kind of nonreliance, just as trust is a kind (or many kinds) of reliance. Distrust involves “action-tendencies” of avoidance or withdrawal (D’Cruz 2019: 935–937), which make it incompatible with reliance—or at least complete reliance. We can be forced to rely on people we distrust, yet even then, we try to keep them at as safe a distance as possible.
Given the relationship between trust and distrust and the similarities between them (e.g., one is “richer than [mere] reliance” and the other is “richer than mere nonreliance”; Hawley 2014: 3), one would think that any theory of trust should be able to explain distrust and vice versa. Hawley makes this point and criticizes theories of trust for not being able to make sense of distrust (2014: 6–9). For example, will-based accounts imply that distrust must be nonreliance plus an expectation of ill will, yet the latter is not required for distrust. I could distrust someone because he is careless, not because he harbors ill will toward me (Hawley 2014: 6).
Hawley defends her commitment account of trust, in part, because she believes it is immune to the above criticism. It says that distrust is nonreliance plus the belief that the person distrusted is committed to doing what we will not rely on them to do. In spite of them being committed in this way (or so we believe), we do not rely on them (2014: 10). This account does not require that we impute any particular motive or feeling to the one distrusted, like ill will. At the same time, it tells us why distrust is not mere nonreliance and also why it is normative; the suspicion of the one distrusted is that they will fail to meet a commitment they have, which is bad.
Some have argued that Hawley’s theory of distrust is subject to counterexamples, however (D’Cruz 2020; Tallant 2017). For example, Jason D’Cruz describes a financier who “buys insurance on credit defaults, positioning himself to profit when borrowers default” (2020: 45). The financier believes that the borrowers have a commitment not to default, and he does not rely on them to meet this commitment. The conclusion that Hawley’s theory would have us reach is that he distrusts the borrowers, which doesn’t seem right.
A different kind of theory of distrust can be found in the work of Meena Krishnamurthy (2015), who is interested specifically in the value that distrust has for political democracies, and for political minorities in particular (2015). She offers what she calls a “narrow normative” account of distrust that she derives from the political writings of Martin Luther King Jr. The account is narrow because it serves a specific purpose: of explaining how distrust can motivate people to resist tyranny. It is normative because it concerns what they ought to do (again, resist; 392). The theory states that distrust is the confident belief that others will not act justly. It needn’t involve an expectation of ill will; King’s own distrust of white moderates was not grounded in such an expectation (Krishnamurthy 2015: 394). To be distrusting, one simply has to believe that others will not act justly, whether out of fear, ignorance, or what have you.
D’Cruz complains that Krishnamurthy’s theory is too narrow because it requires a belief that the one distrusted will fail to do something (i.e., act justly) (2020); but one can be distrustful of someone—say a salesperson who comes to your door (Jones 1996)—without predicting that they will do anything wrong or threatening. D’Cruz does not explain, however, why Krishnamurthy needs to account for cases like these in her theory, which again is meant to serve a specific purpose. Is it important that distrust can take a form other than “ X distrusts Y to [do] Φ” for it to motivate political resistance (D’Cruz 2020: 45)? D’Cruz’s objection is sound only if the answer is “yes”.
Nevertheless, D’Cruz’s work is helpful in showing what a descriptive account of distrust should look like—that is, an account that unlike Krishnamurthy’s, tracks how we use the concept in many different circumstances. He himself endorses a normative-expectation theory, according to which distrust involves
a tendency to withdraw from reliance or vulnerability in contexts of normative expectation, based on a construal of a person or persons as malevolent, incompetent, or lacking integrity. (2019: 936)
D’Cruz has yet to develop this theory fully, but once he does so, it will almost certainly be a welcome addition to the scant literature in philosophy on distrust.
In summary, among the relatively few philosophers who have written on distrust, there is settled agreement about some of its features but not about the nature of distrust in general. The agreed-upon features tell us something about when distrust is warranted (i.e., plausible). For distrust in someone to be plausible, one cannot also trust that person, and normally one will not be reliant on them either. Something else must be true as well, however. For example, one must believe that this person is committed to acting in a certain way but will not follow through on this commitment. The “something else” is crucial because distrust is not the negation of trust and neither is it mere nonreliance.
Philosophers have said comparatively little about what distrust is, but a lot about how distrust tends to be influenced by negative social stereotypes that portray whole groups of people as untrustworthy (e.g., Potter 2020; Scheman 2020; D’Cruz 2019; M. Fricker 2007). Trusting attitudes are similar—who we trust can depend significantly on social stereotypes, positive ones—yet there is less discussion about this fact in the literature on trust. This issue concerns the rationality (more precisely, the ir rationality) of trust and distrust, which makes it relevant to the next section, which is on the epistemology of trust.
2. The Epistemology of Trust
Writings on this topic obviously bear on the issue of when trust is warranted (i.e., justified). The central epistemological question about trust is, “Ought I to trust or not?” That is, given the way things seem to me, is it reasonable for me to trust? People tend to ask this sort of question only in situations where they can’t take trustworthiness for granted—that is, where they are conscious of the fact that trusting could get them into trouble. Examples are situations similar to those in which they have been betrayed in the past or unlike any they have ever been in before. The question, “Ought I to trust?” is therefore particularly pertinent to a somewhat odd mix of people that includes victims of abuse or the like, as well as immigrants and travelers.
The question “Ought I to distrust?” has received comparatively little attention in philosophy despite it arguably being as important as the question of when to trust. People can get into serious trouble by distrusting when they ought not to, rather than just by trusting when they ought not to. The harms of misplaced distrust are both moral and epistemic and include dishonoring people, being out of harmony with them, and being deprived of knowledge via testimony (D’Cruz 2019; M. Fricker 2007). Presumably because they believe that the harms of misplaced trust are greater (D’Cruz 2019), philosophers—and consequently I, in this entry—focus more on the rationality of trusting, as opposed to distrusting.
Philosophical work that is relevant to the issue of how to trust well appears either under the general heading of the epistemology or rationality of trust (e.g., Baker 1987; Webb 1992; Wanderer and Townsend 2013) or under the specific heading of testimony—that is, of putting one’s trust in the testimony of others. This section focuses on the epistemology of trust generally rather than on trust in testimony specifically. There is a large literature on testimony (see the entry in this encyclopedia) and on the related topic of epistemic injustice, both of which I discuss only insofar as they overlap with the epistemology of trust.
Philosophers sometimes ask whether it could ever be rational to trust other people. This question arises for two reasons. First, it appears that trust and rational reflection (e.g., on whether one should be trusting) are in tension with one another. Since trust inherently involves risk, any attempt to eliminate that risk through rational reflection could eliminate one’s trust by turning one’s stance into mere reliance. Second, trust tends to give us blinkered vision: it makes us resistant to evidence that may contradict our optimism about the trustee (Baker 1987; Jones 1996 and 2019). For example, if I trust my brother not to harm anyone, I will resist the truth of any evidence to the contrary. Here, trust and rationality seem to come apart.
Even if some of our trust could be rational, one might insist that not all of it could be rational for various reasons. First, if Baier is right that trust is ubiquitous (1986: 234), then we could not possibly subject all of it to rational reflection. We certainly could not reflect on every bit of knowledge we’ve acquired through the testimony of others, such as that the earth is round or Antarctica exists (Webb 1993; E. Fricker 1995; Coady 1992). Second, bioethicists point out that some trust is unavoidable and occurs in the absence of rational reflection (e.g., trust in emergency room nurses and physicians; see Zaner 1991). Lastly, some trust—namely the therapeutic variety—purposefully leaps beyond any evidence of trustworthiness in an effort to engender trustworthiness in the trustee. Is this sort of trust rational? Perhaps not, given that there isn’t sufficient evidence for it.
Many philosophers respond to the skepticism about the rationality of trust by saying that rationality, when applied to trust, needs to be understood differently than it is in each of the skeptical points above. There, “rationality” means something like this: it is rational to believe in something only if one has verified that it will happen or done as much as possible to verify it. For example, it is rational for me to believe that my brother has not harmed anyone only if the evidence points in that direction and I have discovered that to be the case. As we’ve seen, problems exist with applying this view of rationality to trust, yet it is not the only option; this view is both “truth-directed” and “internalist”, while the rationality of trust could instead be “end-directed” or “externalist”. Or it could be internalist without requiring that we have done the evidence gathering just discussed. Let me expand on these possibilities, starting with those that concern truth- or end-directed rationality.
In discussing the rationality of trust, some authors distinguish between these two types of rationality (also referred to as epistemic vs. strategic rationality; see, e.g., Baker 1987). One could say that we are rational in trusting emergency room physicians, for example, not necessarily because we have good reason to believe that they are trustworthy (our rationality is not truth-directed), but because by trusting them, we can remain calm in a situation over which we have little control (our rationality is therefore end-directed). Similarly, it may be rational for me to trust my brother not because I have good evidence of his trustworthiness but rather because trusting him is essential to our having a loving relationship. [ 10 ]
Trust can be rational, then, depending on whether one conceives of rationality as truth-directed or end-directed. Notice that it matters also how one conceives of trust, and more specifically, whether one conceives of it as a belief in someone’s trustworthiness (see section 4 ). If trust is a belief, then whether the rationality of trust can be end-directed will depend on whether the rationality of a belief can be end-directed. To put the point more generally, how trust is rationally justified will depend on how beliefs are rationally justified (Jones 1996).
Some of the literature on trust and rationality concerns whether the rationality of trust can indeed be end-directed and also what could make therapeutic trust and the like rational. Pamela Hieronymi argues that the ends for which we trust cannot provide reasons for us to trust in the first place (2008). Considerations about how useful or valuable trust is do not bear on the truth of a trusting belief (i.e., a belief in someone’s trustworthiness). But Hieronymi claims that trust, in a pure sense at least, always involves a trusting belief. How then does she account for trust that is motivated by how therapeutic (i.e., useful) the trust will be? She believes that trust of this sort is not pure or full-fledged trust. As she explains, people can legitimately complain about not being trusted fully when they are trusted in this way, which occurs when other people lack confidence in them but trust them nonetheless (2008: 230; see also Lahno 2001: 184–185).
By contrast, Victoria McGeer believes that trust is more substantial or pure when the available evidence does not support it (2008). She describes how trust of this sort—what she calls “substantial trust”—could be rational and does so without appealing to how important it might be or to the ends it might serve, but instead to whether the trustee will be trustworthy. [ 11 ] According to McGeer, what makes “substantial trust” rational is that it involves hope that the trustees will do what they are trusted to do, which “can have a galvanizing effect on how [they] see themselves, as trustors avowedly do, in the fullness of their potential” (2008: 252; see also McGeer and Pettit 2017). Rather than complain (as Hieronymi would assume that trustees might) about trustors being merely hopeful about their trustworthiness, they could respond well to the trustors’ attitude toward them. Moreover, if it is likely that they will respond well—in other words, that they will be trust-responsive—then the trust in them must be epistemically rational. That is particularly true if being trustworthy involves being trust-responsive, as it does for McGeer (McGeer and Pettit 2017).
McGeer’s work suggests that all trust—even therapeutic trust—can be rational in a truth-directed way. As we’ve seen, there is some dispute about whether trust can be rational in just an end-directed way. What matters here is whether trust is the sort of attitude whose rationality could be end-directed.
Philosophers who agree that trust can be rational (in a truth- or end-directed way or both) tend to disagree about the extent to which reasons that make it rational must be accessible to the trustor. Some say that these reasons must be available to this person in order for their trust to be rational; in that case, the person is or could be internally justified in trusting as they do. Others say that the reasons need not be internal but can instead be external to the trustor and lie in what caused the trust, or, more specifically, in the epistemic reliability of what caused it. The trustor also needn’t have access to or be aware of the reliability of these reasons. The latter’s epistemology of trust is externalist, while the former’s is internalist.
Some epistemologists write as though trust is only rational if the trustor themselves has rationally estimated the likelihood that the trustee is trustworthy. For example, Russell Hardin implies that if my trust in you is rational, then
I make a rough estimate of the truth of [the] claim … that you will be trustworthy under certain conditions … and then I correct my estimate, or “update,” as I obtain new evidence on you. (2002: 112)
On this view, I must have reasons for my estimate or for my updates (Hardin 2002: 130), which could come from inductive generalizations I make about my past experience, from my knowledge that social constraints exist that will encourage your trustworthiness or what have you. Such an internalist epistemology of trust is valuable because it coheres with the commonsense idea that one ought to have good reasons for trusting people (i.e., reasons grounded in evidence that they will be trustworthy) particularly when something important is at stake (E. Fricker 1995). One ought, in other words, to be epistemically responsible in one’s trusting (see Frost-Arnold 2020).
Such an epistemology is also open to criticisms, however. For example, it suggests that rational trust will always be partial rather than complete, given that the rational trustor is open to evidence that contradicts their trust on this theory, while someone who trusts completely in someone else lacks such openness. The theory also implies that the reasons for trusting well (i.e., in a justified way) are accessible to the trustor, at some point or another, which may simply be false. Some reasons for trust may be too “cunning” for this to be the case. Relevant here is the reason for trusting discussed by Philip Pettit (1995): that trust signals to people that they are being held in esteem, which is something they will want to maintain; they will honor the trust because they are naturally “esteem-seeking”. (Note that consciously having this as a reason for trusting—of using people’s need for esteem to get what you want from them—is incompatible with actually trusting (Wanderer and Townsend 2013: 9), if trust is motives-based and the required motive is something other than self-interest.)
Others say that reasons for trust are usually too numerous and varied to be open to the conscious consideration of the trustor (e.g., Baier 1986). There can be very subtle reasons to trust or distrust someone—for example, reasons that have to do with body language, with systematic yet veiled forms of oppression, or with a complicated history of trusting others about which one can’t easily generalize. Factors like these can influence trustors without them knowing it, sometimes making their trust irrational (e.g., because it is informed by oppressive biases), and other times making it rational.
The concern about there being complex reasons for trusting explain why some philosophers defend externalist epistemologies of trust. Some do so explicitly (e.g., McLeod 2002). They argue for reliabilist theories that make trust rationally justified if and only if it is formed and sustained by reliable processes (i.e., “processes that tend to produce accurate representations of the world”, such as drawing on expertise one has rather than simply guessing; Goldman 1992: 113; Goldman and Beddor 2015 [2016]). Others gesture towards externalism (Webb 1993; Baier 1986), as Baier does with what she calls “a moral test for trust”. The test is that
knowledge of what the other party is relying on for the continuance of the trust relationship would … itself destabilize the relation. (1986: 255)
The other party might be relying on a threat advantage or the concealment of their untrustworthiness, in which case the trust would probably fail the test. Because Baier’s test focuses on the causal basis for trust, or for what maintains the trust relation, it is externalist. Also, because the trustor often cannot gather the information needed for the test without ceasing to trust the other person (Baier 1986: 260), the test cannot be internalist.
Although an externalist theory of trust deals well with some of the worries one might have with an internalist theory, it has problems of its own. One of the most serious issues is the absence of any requirement that trustors themselves have good (motivating) reasons for trusting, especially when their trust makes them seriously vulnerable. Again, it appears that common sense dictates the opposite: that sometimes as trustors, we ought to be able to back up our decisions about when to trust. The same is true about our distrust presumably: that sometimes we ought to be able to defend it. Assuming externalists mean for their epistemology to apply to distrust and not just to trust, their theory violates this bit of common sense as well. Externalism about distrust also seems incompatible with a strategy that some philosophers recommend for dealing with biased distrust. The strategy is to develop what they call “corrective trust” (e.g., Scheman 2020) or “humble trust” (D’Cruz 2019), which demands a humble skepticism toward distrust that aligns with oppressive stereotypes and efforts at correcting the influence of these stereotypes (see also M. Fricker 2007). The concern about an externalist epistemology is that it does not encourage this sort of mental work, since it does not require that we reflect on our reasons for distrusting or trusting.
There are alternatives to the kinds of internalist and externalist theories just discussed, especially within the literature on testimony. [ 12 ] For example, Paul Faulkner develops an “assurance theory” of testimony that interprets speaker trustworthiness in terms of trust-responsiveness. Recall that on a trust-responsiveness theory of trust, being trusted gives people the reason to be trustworthy that someone is counting on them. They are trustworthy if they are appropriately responsive to this reason, which, in the case of offering testimony, involves giving one’s assurance that one is telling the truth (Adler 2006 [2017]). Faulkner uses the trust-responsiveness account of trust, along with a view of trust as an affective attitude (see section 4 ), to show “how trust can ground reasonable testimonial uptake” (Faulkner and Simpson 2017: 6; Faulkner 2011 and 2020).
He proposes that A affectively trust S if and only if A depends on S Φ-ing, and expects his dependence on S to motivate S to Φ—for A ’s dependence on S to be the reason for which S Φs …. As a result, affective trust is a bootstrapping attitude: I can choose to trust someone affectively and my doing so creates the reasons which justify the attitude. (Faulkner and Simpson 2017: 6)
Most likely, A (the trustor) is aware of the reasons that justify his trust or could be aware of them, making this theory an internalist one. The reasons are also normative and non-evidentiary (Faulkner 2020); they concern what S ought to do because of A ’s dependence, not what S will do based on evidence that A might gather about S . This view doesn’t require that A have evidentiary reasons, and so it is importantly different than the internalist epistemology discussed above. But it is then also subject to the criticisms made of externalist theories that they don’t require the kind of scrutiny of our trusting attitudes that we tend to expect and probably ought to expect in societies where some people are stereotyped as more trusting than others.
Presumably to avoid having to defend any particular epistemology of trust, some philosophers provide just a list of common justifiers for it (i.e., “facts or states of affairs that determine the justification status of [trust]”; Goldman 1999: 274), which someone could take into account in deciding when to trust (Govier 1998; Jones 1996). Included on these lists are such factors as the social role of the trustee, the domain in which the trust occurs, an “agent-specific” factor that concerns how good a trustor the agent tends to be (Jones 1996: 21), and the social or political climate in which the trust occurs. Philosophers have tended to emphasize this last factor as a justification condition for trust, and so let me elaborate on it briefly.
Although trust is paradigmatically a relation that holds between two individuals, forces larger than those individuals inevitably shape their trust and distrust in one another. Social or political climate contributes to how (un)trustworthy people tend to be and therefore to whether trust and distrust are justified. For example, a climate of virtue is one in which trustworthiness tends to be pervasive, assuming that virtues other than trustworthiness tend to enhance it (Baier 2004). [ 13 ] A climate of oppression is one in which untrustworthiness is prevalent, especially between people who are privileged and those who are less privileged (Baier 1986: 259; Potter 2002: 24; D’Cruz 2019). “Social trust”, as some call it, is low in these circumstances (Govier 1997; Welch 2013).
Social or political climate has a significant influence on the default stance that we ought to take toward people’s trustworthiness (see, e.g., Walker 2006). We need such a stance because we can’t always stop to reflect carefully on when to trust (i.e., assuming that some rational reflection is required for trusting well). Some philosophers say that the correct stance is trust and do so without referring to the social or political climate; Tony Coady takes this sort of position, for example, on our stance toward others’ testimony (Coady 1992). Others disagree that the correct stance could be so universal and claim instead that it is relative to climate, as well as to other factors such as domain (Jones 1999).
Our trust or distrust may be prima facie justified if we have the correct default stance, although most philosophers assume that it could only be fully justified (in a truth- or end-directed way) by reasons that are internal to us (evidentiary or non-evidentiary reasons) or by the causal processes that created the attitude in the first place. Whichever epistemology of trust we choose, it ought to be sensitive to the tension that exists between trusting somebody and rationally reflecting on the grounds for that trust. It would be odd, to say the least, if what made an attitude justified destroyed that very attitude. At the same time, our epistemology of trust ought to cohere as much as possible with common sense, which dictates that we should inspect rather than have pure faith in whatever makes us seriously vulnerable to other people, which trust can most definitely do.
Someone who asks, “When is trust warranted?” might be interested in knowing what the point of trust is. In other words, what value does it have? Although the value it has for particular people will depend on their circumstances, the value it could have for anyone will depend on why trust is valuable, generally speaking. Trust can have enormous instrumental value and may also have some intrinsic value. In discussing its instrumental value, this section refers to the “goods of trust”, which can benefit the trustor, the trustee, or society in general. They are therefore social and/or individual goods. What is more and as emphasized throughout, these goods tend to accompany justified trust, rather than any old trust. [ 14 ] Like the other sections of this entry, this one focuses predominantly though not exclusively on trust; it also mentions recent work on the value of distrust.
Consider first the possibility that trust has intrinsic value. If trust produced no goods independent of it, would there be any point in trusting? One might say “yes”, on the grounds that trust is (or can be; O’Neil 2012: 311) a sign of respect for others. (Similarly, distrust is a sign of disrespect; D’Cruz 2019.) If true, this fact about trust would make it intrinsically worthwhile, at least so long as the trust is justified. Presumably, if it was unjustified, then the respect would be misplaced and the intrinsic value would be lost. But these points are speculative, since philosophers have said comparatively little about trust being worthwhile in itself as opposed to worthwhile because of what it produces, or because of what accompanies it. The discussion going forward centers on the latter, more specifically on the goods of trust.
Turning first to the instrumental value of trust to the trustor , some argue that trusting vastly increases our opportunities for cooperating with others and for benefiting from that cooperation, although of course we would only benefit if people we trusted cooperated as well (Gambetta 1988b; Hardin 2002; Dimock 2020). Trust enhances cooperation, while perhaps not being necessary for it (Cook et al. 2005; Skyrms 2008). Because trust removes the incentive to check up on other people, it makes cooperation with trust less complicated than cooperation without it (Luhmann 1973/1975 [1979]).
Trust can make cooperation possible, rather than simply easier, if trust is essential to promising. Daniel Friedrich and Nicholas Southwood defend what they call the “Trust View” of promissory obligation (2011), according to which “making a promise involves inviting another individual to trust one to do something” (2011: 277). If this view is correct, then cooperation through promising is impossible without trust. Cooperation of this sort will also not be fruitful unless the trust is justified.
Trusting provides us with goods beyond those that come with cooperation, although again, for these goods to materialize, the trust must be justified. Sometimes, trust involves little or no cooperation, so that the trustor is completely dependent on the trustee while the reverse is not true. Examples are the trust of young children in their parents and the trust of severely ill or disabled people in their care providers. Trust is particularly important for these people because they tend to be powerless to exercise their rights or to enforce any kind of contract. The trust they place in their care providers also contributes to them being vulnerable, and so it is essential that they can trust these people (i.e., that their trust is justified). The goods at stake for them are all the goods involved in having a good or decent life.
Among the specific goods that philosophers associate with trusting are meaningful relationships or attachments (rather than simply cooperative relationships that further individual self-interests; Harding 2011, Kirton forthcoming) as well as knowledge and autonomy. [ 15 ] To expand, trust allows for the kinds of secure attachments that some developmental psychologists (“attachment” theorists) believe are crucial to our well-being and to our ability to be trusting of others (Bowlby 1969–1980; Ainsworth 1969; see Kirton 2020; Wonderly 2016). Particularly important here are parent-child relationships (McLeod et al. 2019).
Trust is also crucial for knowledge, given that scientific knowledge (Hardwig 1991), moral knowledge (Jones 1999), and almost all knowledge in fact (Webb 1993) depends for its acquisition on trust in the testimony of others. The basic argument for the need to trust what others say is that no one person has the time, intellect, and experience necessary to independently learn facts about the world that many of us do know. Examples include the scientific fact that the earth is round, the moral fact that the oppression of people from social groups different from our own can be severe (Jones 1999), and the mundane fact that we were born on such-in-such a day (Webb 1993: 261). Of course, trusting the people who testify to these facts could only generate knowledge if the trust was justified. If we were told our date of birth by people who were determined oddly to deceive us about when we were born, then we would not know when we were born.
Autonomy is another good that flows from trust insofar as people acquire or exercise autonomy only in social environments where they can trust people (or institutions, etc.) to support their autonomy. Feminists in particular tend to conceive of autonomy this way—that is, as a relational property (Mackenzie and Stoljar 2000). Many feminists emphasize that oppressive social environments can inhibit autonomy, and some say explicitly that conditions necessary for autonomy (e.g., adequate options, knowledge relevant to one’s decisions) exist only with the help of people or institutions that are trustworthy (e.g., Oshana 2014; McLeod and Ryman 2020). Justified trust in others to ensure that these conditions exist is essential for our autonomy, if autonomy is indeed relational. [ 16 ]
Goods of trust that are instrumental to the well-being of the trustee also do not materialize unless the trust is justified. Trust can improve the self-respect and moral maturity of this person. Particularly if it involves reliance on a person’s moral character, trust can engender self-respect in the trustee (i.e., through them internalizing the respect signaled by that trust). Being trusted can allow us to be more respectful not only toward ourselves but also toward others, thus enhancing our moral maturity. The explicit goal of therapeutic trust is precisely to bring about this end. The above ( section 2 ) suggests that therapeutic trust can be justified in a truth-directed way over time, provided that the trust has its intended effect of making the trustee more trustworthy (McGeer 2008; Baker 1987: 12). Clearly, for therapeutic trust to benefit the trustee, it would have to be justified in this way, meaning that the therapy would normally have to work.
Finally, there are social goods of trust that are linked with the individual goods of cooperation and moral maturity. The former goods include the practice of morality, the very existence of society perhaps, as well as strong social networks. Morality itself is a cooperative activity, which can only get off the ground if people can trust one another to try, at least, to be moral. For this reason, among others, Baier claims that trust is “the very basis of morality” (2004: 180). It could also be the very basis of society, insofar as trust in our fellow citizens to honor social contracts makes those contracts possible.
A weaker claim is that trust makes society better or more livable. Some argue that trust is a form of “social capital”, meaning roughly that it enables “people to work together for common purposes in groups and organizations” (Fukuyama 1995: 10; quoted in Hardin 2002: 83). As a result, “high-trust” societies have stronger economies and stronger social networks in general than “low-trust” societies (Fukuyama 1995; Inglehart 1999). Of course, this fact about high-trust societies could only be true if, on the whole, the trust within them was justified—that is, if trustees tended not to “defect” and destroy chances for cooperating in the future.
The literature on distrust suggests that there are goods associated with it too. For example, there is the social good discussed by Krishnamurthy of “securing democracy by protecting political minorities from tyranny” (2015: 392). Distrust as she understands it (a confident belief that others will not act justly) plays this positive role when it is justified, which is roughly when the threat of tyranny or unjust action is real. Distrust in general is valuable when it is justified—for the distrustors at least, who protect themselves from harm. By contrast, the people distrusted tend to experience negative effects on their reputation or self-respect (D’Cruz 2019).
Both trust and distrust are therefore valuable particularly when they are justified. The value of justified trust must be very high if without it, we can’t have morality or society and can’t be morally mature, autonomous, knowledgeable, or invested with opportunities for collaborating with others. Justified distrust is also essential, for members of minority groups especially. Conversely, trust or distrust that is unjustified can be seriously problematic. Unjustified trust, for example, can leave us open to abuse, terror, and deception.
Trust may not be warranted (i.e., plausible) because the agent has lost the ability to trust or simply cannot bring themselves to trust. People can lose trust in almost everyone or everything as a result of trauma (Herman 1991). The trauma of rape, for example, can profoundly reduce one’s sense that the world is a safe place with caring people in it (Brison 2002). By contrast, people can lose trust just in particular people or institutions. They can also have no experience trusting in certain people or institutions, making them reluctant to do so. They or others might want them to become more trusting. But the question is, how can that happen? How can trust be restored or generated?
The process of building trust is often slow and difficult (Uslaner 1999; Baier 1986; Lahno 2020), and that is true, in part, because of the kind of mental attitude trust is. Many argue that it is not the sort of attitude we can simply will ourselves to have. At the same, it is possible to cultivate trust. [ 17 ] This section focuses on these issues, including what kind of mental attitude trust is (e.g., a belief or an emotion). Also discussed briefly is what kind of mental attitude distrust is. Like trust, distrust is an attitude that people may wish to cultivate, particularly when they are too trusting.
Consider first why one would think that trust can’t be willed. Baier questions whether people are able “to trust simply because of encouragement to trust” (1986: 244; my emphasis). She writes,
“Trust me!” is for most of us an invitation which we cannot accept at will—either we do already trust the one who says it, in which case it serves at best as reassurance, or it is properly responded to with, “Why should and how can I, until I have cause to?”. (my emphasis; 1986: 244)
Baier is not a voluntarist about trust, just as most people are not voluntarists about belief. In other words, she thinks that we can’t simply decide to trust for purely motivational rather than epistemic reasons (i.e., merely because we want to, rather than because we have reason to think that the other person is or could be trustworthy; Mills 1998). That many people feel compelled to say, “I wish I could trust you”, suggests that Baier’s view is correct; wishing or wanting is not enough. But Holton interprets Baier’s view differently. According to him, Baier’s point is that we can never decide to trust, not that we can never decide to trust for motivational purposes (1994). This interpretation ignores, however, the attention that Baier gives to situations in which all we have is encouragement (trusting “simply because of encouragement”). The “cause” she refers to (“Why should and how can I, until I have cause to [trust]?”; 1986: 244) is an epistemic cause. Once we have one of those, we can presumably decide whether to trust on the basis of it. [ 18 ] But we cannot decide to trust simply because we want to, according to Baier.
If trust resembles belief in being non-voluntary, then perhaps trust itself is a belief. Is that right? Many philosophers claim that it is (e.g., Hieronymi 2008; McMyler 2011; Keren 2014), while others disagree (e.g., Jones 1996; Faulkner 2007; D’Cruz 2019). The former contend that trust is a belief that the trustee is trustworthy, at least in the thin sense that the trustee will do what he is trusted to do (Keren 2020). Various reasons exist in favour of such theories, doxastic reasons (see Keren 2020) including that these theories suggest it is impossible to trust a person while holding the belief that this person is not trustworthy, even in the thin sense. Most of us accept this impossibility and would want any theory of trust to explain it. A doxastic account does so by saying that we can’t believe a contradiction (not knowingly anyway; Keren 2020: 113).
Those who say that trust is not a belief claim that it is possible to trust without believing the trustee is trustworthy. [ 19 ] Holton gives the nice example of trusting a friend to be sincere without believing that the friend will be sincere (1994: 75). Arguably, if one already believed that to be the case, then one would have no need to trust the friend. It is also possible to believe that someone is trustworthy without trusting that person, which suggests that trust couldn’t just be a belief in someone’s trustworthiness (McLeod 2002: 85). I might think that a particular person is trustworthy without trusting them because I have no cause to do so. I might even distrust them despite believing that they are trustworthy (Jones 1996, 2013). As Jones explains, distrust can be recalcitrant in parting “company with belief” (D’Cruz 2019: 940; citing Jones 2013), a fact which makes trouble for doxastic accounts not just of trust but of distrust too (e.g., Krishnamurthy 2015). The latter must explain how distrust could be a belief that someone is untrustworthy that could exist alongside the belief that the person is trustworthy.
Among the alternatives to doxasticism are theories stating that trust is an emotion, a kind of stance (i.e., the participant stance; Holton 1994), or a disposition (Kappel 2014; cited in Keren 2020). The most commonly held alternative is the first: that trust is an emotion. Reasons in favour of this view include the fact that trust resembles an emotion in having characteristics that are unique to emotions, at least according to an influential account of them (de Sousa 1987; Calhoun 1984; Rorty 1980; Lahno 2001, 2020). For example, emotions narrow our perception to “fields of evidence” that lend support to the emotions themselves (Jones 1996: 11). When we are in the grip of an emotion, we therefore tend to see facts that affirm its existence and ignore those that negate it. To illustrate, if I am really angry at my mother, then I tend to focus on things that justify my anger while ignoring or refusing to see things that make it unjustified. I can only see those other things once my anger subsides. Similarly with trust: if I genuinely trust my mother, my attention falls on those aspects of her that justify my trust and is averted from evidence that suggests she is untrustworthy (Baker 1987). The same sort of thing happens with distrust, according to Jones (Jones 2019). She refers to this phenomenon as “affective looping”, which, in her words, occurs when “a prior emotional state provides grounds for its own continuance” (2019: 956). She also insists that only affective-attitude accounts of trust and distrust can adequately explain it (2019).
There may be a kind of doxastic theory, however, that can account for the affective looping of trust, if not of distrust. Arnon Keren, whose work focuses specifically on trust, defends what he calls an “impurely doxastic” theory. He describes trust as believing in someone’s trustworthiness and responding to reasons (“preemptive” ones) against taking precautions that this person will not be trustworthy (Keren 2020, 2014). Reasons for trust are themselves reasons of this sort, according to Keren; they oppose actions like those of carefully monitoring the behavior of the trustee or weighing the available evidence that this person is trustworthy. The trustor’s response to these preemptive reasons would explain why this person is resistant (or at least not attune) to counter evidence to their trust (Keren 2014, 2020).
Deciding in favour of an affective-attitude theory or a purely or impurely doxastic one is important for understanding features of trust like affective looping. Yet it may have little bearing on whether or how trust can be cultivated. For, regardless of whether trust is a belief or an emotion, presumably we can cultivate it by purposefully placing ourselves in a position that allows us to focus on evidence of people’s trustworthiness. The goal here could be self-improvement: that is, becoming more trusting, in a good way so that we can reap the benefits of justified trust. Alternatively, we might be striving for the improvement of others: making them more trustworthy by trusting them therapeutically. Alternatively still, we could be engaging in “corrective trust”. (See the above discussions of therapeutic and corrective trust.)
This section has centered on how to develop trust and how to account for facts about it such as the blinkered vision of the trustor. Similar facts about distrust were also mentioned: those that concern what kind of mental attitude it is. Theorizing about whether trust and distrust are beliefs, emotions or something else allows us to appreciate why they have certain features and also how to build these attitudes. The process for building them, which may be similar regardless of whether they are beliefs or emotions, will be relevant to people who don’t trust enough or who trust too much.
This entry as a whole has examined an important practical question about trust: “When is trust warranted?” Also woven into the discussion has been some consideration of when distrust is warranted. Centerstage has been given to trust, however, because philosophers have debated it much more than distrust.
Different answers to the question of when trust is warranted give rise to different philosophical puzzles. For example, in response, one could appeal to the nature of trust and trustworthiness and consider whether the conditions are ripe for them (e.g., for the proposed trustor to rely on the trustee’s competence). But one would first have to settle the difficult issue of what trust and trustworthiness are, and more specifically, how they differ from mere reliance and reliability, assuming there are these differences.
Alternatively, in deciding whether trust is warranted, one could consider whether trust would be rationally justified or valuable. One would consider these things simultaneously when rational justification is understood in an end-directed way, making it dependent on trust’s instrumental value. With respect to rational justification alone, puzzles arise when trying to sort out whether reasons for trust must be internal to trustors or could be external to them. In other words, is trust’s epistemology internalist or externalist? Because good arguments exist on both sides, it’s not clear how trust is rationally justified. Neither is it entirely clear what sort of value trust can have, given the nature of it. For example, trust may or may not have intrinsic moral value depending on whether it signals respect for others.
Lastly, one might focus on the fact that trust cannot be warranted when it is impossible, which is the case when the agent does not already exhibit trust and cannot simply will themselves to have it. While trust is arguably not the sort of attitude that one can just will oneself to have, trust can be cultivated. The exact manner or extent to which it can be cultivated, however, may depend again on what sort of mental attitude it is.
Since one can respond to the question, “When is trust warranted?” by referring to each of the above dimensions of trust, a complete philosophical answer to this question is complex. The same is true about the question of when to distrust, because the same dimensions (the epistemology of distrust, its value, etc.) are relevant to it. Complete answers to these broad questions about trust and distrust would be philosophically exciting and also socially important. They would be exciting both because of their complexity and because they would draw on a number of different philosophical areas, including epistemology, philosophy of mind, and value theory. The answers would be important because trust and distrust that are warranted contribute to the foundation of a good society, where people thrive through healthy cooperation with others, become morally mature human beings, and are not subject to social ills like tyranny or oppression.
- Adler, Jonathan, 2006 [2017], “Epistemological Problems of Testimony”, The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy (Winter 2017 Edition), Edward N. Zalta (ed.), URL = < https://plato.stanford.edu/archives/win2017/entries/testimony-episprob/ >.
- Ainsworth, Mary D. Salter, 1969, “Object Relations, Dependency, and Attachment: A Theoretical Review of the Infant-Mother Relationship”, Child Development , 40(4): 969–1025.
- Baier, Annette, 1986, “Trust and Antitrust”, Ethics , 96(2): 231–260. doi:10.1086/292745
- –––, 1991, Two lectures on “Trust”: Lecture 1, “Trust and Its Vulnerabilities” and Lecture 2, “Sustaining Trust”, in Tanner Lectures on Human Values (Volume 13), Salt Lake City, UT: University of Utah Press, pp. 109–174. [ Baier 1991 available online (pdf) ]
- –––, 2004, “Demoralization, Trust, and the Virtues”, in Setting the Moral Compass: Essays by Women Philosophers , Cheshire Calhoun (ed.), New York, NY: Oxford University Press, pp. 176–189.
- Baker, Judith, 1987, “Trust and Rationality”, Pacific Philosophical Quarterly , 68(1): 1–13. doi:10.1111/j.1468-0114.1987.tb00280.x
- Becker, Lawrence C., 1996, “Trust as Noncognitive Security about Motives”, Ethics , 107(1): 43–61. doi:10.1086/233696
- Blackburn, Simon, 1998, Ruling Passion: A Theory of Practical Reasoning , Oxford: Clarendon Press.
- 1969, Volume I: Attachment
- 1973, Volume II: Separation, Anxiety and Anger
- 1980, Volume III: Loss, Sadness and Depression
- Brison, Susan J., 2002, Aftermath: Violence and the Remaking of the Self , Princeton NJ: Princeton University Press.
- Budnik, Christian, 2018, “Trust, Reliance, and Democracy”, International Journal of Philosophical Studies , 26(2): 221–239. doi:10.1080/09672559.2018.1450082
- Calhoun, Cheshire (ed.), 1984, “Cognitive Emotions?” in What is an Emotion? Classic Readings in Philosophical Psychology , Cheshire Calhoun and Robert C. Solomon (eds), New York: Oxford University Press, pp. 327–342.
- Coady, C.A.J., 1992, Testimony: A Philosophical Study , Oxford: Clarendon Press. doi:10.1093/0198235518.001.0001
- Coeckelbergh, Mark, 2012, “Can We Trust Robots?”, Ethics and Information Technology , 14(1): 53–60. doi:10.1007/s10676-011-9279-1
- Cogley, Zac, 2012, “Trust and the Trickster Problem”, Analytic Philosophy , 53(1): 30–47. doi:10.1111/j.2153-960X.2012.00546.x
- Cohen, Marc A. and John Dienhart, 2013, “Moral and Amoral Conceptions of Trust, with an Application in Organizational Ethics”, Journal of Business Ethics , 112(1): 1–13. doi:10.1007/s10551-012-1218-5
- Cook, Karen S., Russell Hardin, and Margaret Levi, 2005, Cooperation Without Trust? , New York: Russell Sage Foundation.
- Dasgupta, Partha, 1988, “Trust as a Commodity”, in Gambetta 1988a: 49–72.
- Daukas, Nancy, 2006, “Epistemic Trust and Social Location”, Episteme , 3(1–2): 109–124. doi:10.3366/epi.2006.3.1-2.109
- –––, 2011, “Altogether Now: A Virtue-Theoretic Approach to Pluralism in Feminist Epistemology”, in Feminist Epistemology and Philosophy of Science , Heidi E. Grasswick (ed.), Dordrecht: Springer Netherlands, 45–67. doi:10.1007/978-1-4020-6835-5_3
- D’Cruz, Jason, 2019, “Humble Trust”, Philosophical Studies , 176(4): 933–953. doi:10.1007/s11098-018-1220-6
- –––, 2020, “Trust and Distrust”, in Simon 2020: 41–51.
- de Sousa, Ronald, 1987, The Rationality of Emotion , Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
- Dimock, Susan, 2020, “Trust and Cooperation”, in Simon 2020: 160–174.
- Domenicucci, Jacopo and Richard Holton, 2017, “Trust as a Two-Place Relation”, in Faulkner and Simpson 2017: 150–161. doi:10.1093/acprof:oso/9780198732549.003.0009
- Faulkner, Paul, 2007, “A Genealogy of Trust”, Episteme , 4(3): 305–321. doi:10.3366/E174236000700010X
- –––, 2011, Knowledge on Trust , Oxford: Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/acprof:oso/9780199589784.001.0001
- –––, 2015, “The Attitude of Trust Is Basic”, Analysis , 75(3): 424–429. doi:10.1093/analys/anv037
- –––, 2017, “The Problem of Trust”, in Faulkner and Simpson 2017: 110–129. doi:10.1093/acprof:oso/9780198732549.003.0007
- –––, 2020, “Trust and Testimony”, in Simon 2020: 329–340.
- Faulkner, Paul and Thomas Simpson (eds), 2017, The Philosophy of Trust , Oxford: Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/acprof:oso/9780198732549.001.0001
- Foley, Richard, 2001, Intellectual Trust in Oneself and Others , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. doi:10.1017/CBO9780511498923
- –––, 2005, “Universal Intellectual Trust”, Episteme , 2(1): 5–12. doi:10.3366/epi.2005.2.1.5
- Fox-Decent, Evan, 2005, “The Fiduciary Nature of State Legal Authority”, Queen’s Law Journal , 31: 259–310.
- Fricker, Elizabeth, 1995, “Critical Notice: Telling and Trusting: Reductionism and Anti-Reductionism in the Epistemology of Testimony”, Mind , 104(414): 393–411. doi:10.1093/mind/104.414.393
- Fricker, Miranda, 2007, Epistemic Injustice: Power and the Ethics of Knowing , Oxford: Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/acprof:oso/9780198237907.001.0001
- Friedrich, Daniel and Nicholas Southwood, 2011, “Promises and Trust”, in Promises and Agreements: Philosophical Essays , Hanoch Sheinman (ed.), Oxford: Oxford University Press, pp. 275–292.
- Frost-Arnold, Karen, 2014, “Imposters, Tricksters, and Trustworthiness as an Epistemic Virtue”, Hypatia , 29(4): 790–807. doi:10.1111/hypa.12107
- –––, 2020, “Trust and Epistemic Responsibility”, in Simon 2020: 64–75.
- Fukuyama, Francis, 1995, Trust: The Social Virtues and the Creation of Prosperity , New York, NY: The Free Press.
- Gambetta, Diego (ed.), 1988a, Trust: Making and Breaking Cooperative Relations , New York: Basil Blackwell.
- –––, 1988b, “Can We Trust Trust?” in Gambetta 1988a: 213–237.
- Goering, Sara, 2009, “ Postnatal Reproductive Autonomy: Promoting Relational Autonomy and Self-Trust in New Parents”, Bioethics , 23(1): 9–19. doi:10.1111/j.1467-8519.2008.00678.x
- Goldberg, Sanford C., 2020, “Trust and Reliance”, in Simon 2020: 97–108.
- Goldman, Alvin I., 1992, Liaisons: Philosophy Meets the Cognitive and Social Sciences , Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
- –––, 1999, “Internalism Exposed”:, Journal of Philosophy , 96(6): 271–293. doi:10.2307/2564679
- Goldman, Alvin and Bob Beddor, 2015 [2016], “Reliabilist Epistemology”, Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy (Winter 2016 Edition), Edward N. Zalta (ed.), URL = https://plato.stanford.edu/archives/win2016/entries/reliabilism/ >.
- Govier, Trudy, 1992a, “Trust, Distrust, and Feminist Theory”, Hypatia , 7(1): 16–33. doi:10.1111/j.1527-2001.1992.tb00695.x
- –––, 1992b, “Distrust as a Practical Problem”, Journal of Social Philosophy , 23(1): 52–63. doi:10.1111/j.1467-9833.1992.tb00484.x
- –––, 1993, “Self-Trust, Autonomy, and Self-Esteem”, Hypatia , 8(1): 99–120. doi:10.1111/j.1527-2001.1993.tb00630.x
- –––, 1997, Social Trust and Human Communities , Montreal and Kingston: McGill-Queen’s University Press.
- –––, 1998, Dilemmas of Trust , Montreal and Kingston: McGill-Queen’s University Press.
- Hardin, Russell, 2002, Trust and Trustworthiness , New York, NY: Russell Sage Foundation.
- ––– (ed.), 2004, Distrust , New York: Russell Sage Foundation.
- Harding, Matthew, 2011, “Responding to Trust: Responding to Trust”, Ratio Juris , 24(1): 75–87. doi:10.1111/j.1467-9337.2010.00475.x
- Hardwig, John, 1991, “The Role of Trust in Knowledge”, The Journal of Philosophy , 88(12): 693–708. doi:10.2307/2027007
- Hawley, Katherine, 2014, “Trust, Distrust and Commitment”, Noûs , 48(1): 1–20. doi:10.1111/nous.12000
- –––, 2017, “Trustworthy Groups and Organizations”, in Faulkner and Simpson 2017: 52–70. doi:10.1093/acprof:oso/9780198732549.003.0014
- –––, 2019, How to Be Trustworthy , Oxford: Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/oso/9780198843900.001.0001
- Herman, Judith Lewis, 1991, Trauma and Recovery , New York: Basic Books.
- Hertzberg, Lars, 1988, “On the Attitude of Trust”, Inquiry , 31(3): 307–322. doi:10.1080/00201748808602157
- Hieronymi, Pamela, 2008, “The Reasons of Trust”, Australasian Journal of Philosophy , 86(2): 213–236. doi:10.1080/00048400801886496
- Hinchman, Edward S., 2003, “Trust and Diachronic Agency”, Noûs , 37(1): 25–51. doi:10.1111/1468-0068.00427
- –––, 2017, “On the Risks of Resting Assured: An Assurance Theory of Trust”, in Faulkner and Simpson 2017: 52–70. doi:10.1093/acprof:oso/9780198732549.003.0004
- Hollis, Martin, 1998, Trust Within Reason , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. doi:10.1017/CBO9780511612244
- Holton, Richard, 1994, “Deciding to Trust, Coming to Believe”, Australasian Journal of Philosophy , 72(1): 63–76. doi:10.1080/00048409412345881
- Horsburgh, H. J. N., 1960, “The Ethics of Trust”, The Philosophical Quarterly , 10(41): 343–354. doi:10.2307/2216409
- Inglehart, Ronald, 1999, “Trust, Well-Being and Democracy”, in Warren 1999: 88–120. doi:10.1017/CBO9780511659959.004
- Jacoby, Brennan, 2011, Trust and Betrayal: A Conceptual Analysis , Ph.D. Dissertation, Philosophy Department, Macquarie University. [ Jacoby 2011 available online ]
- Jones, Karen, 1996, “Trust as an Affective Attitude”, Ethics , 107(1): 4–25. doi:10.1086/233694
- –––, 1999, “Second-Hand Moral Knowledge”, The Journal of Philosophy , 96(2): 55–78. doi:10.2307/2564672
- –––, 2004, “Trust and Terror”, in Moral Psychology: Feminist Ethics and Social Theory , Peggy DesAutels and Margaret Urban Walker (eds), Lanham, MD: Rowman & Littlefield, pp. 3–18.
- –––, 2012a, “Trustworthiness”, Ethics , 123(1): 61–85. doi:10.1086/667838
- –––, 2012b, “The Politics of Intellectual Self-Trust”, Social Epistemology , 26(2): 237–251. doi:10.1080/02691728.2011.652215
- –––, 2013, “Distrusting the Trustworthy”, in Reading Onora O’Neill , David Archard, Monique Deveaux, Neil Manson, and Daniel. Weinstock (eds), New York: Routledge, ch. 13.
- –––, 2017, “‘But I Was Counting On You!’”, in Faulkner and Simpson 2017: 91–109. doi:10.1093/acprof:oso/9780198732549.003.0006
- –––, 2019, “Trust, Distrust, and Affective Looping”, Philosophical Studies , 176(4): 955–968. doi:10.1007/s11098-018-1221-5
- Kappel, Klemens, 2014, “Believing on Trust”, Synthese , 191(9): 2009–2028. doi:10.1007/s11229-013-0376-z
- Keren, Arnon, 2014, “Trust and Belief: A Preemptive Reasons Account”, Synthese , 191(12): 2593–2615. doi:10.1007/s11229-014-0416-3
- –––, 2020, “Trust and Belief”, in Simon 2020: 109–120.
- Kirton, Andrew, 2020, “Matters of Trust as Matters of Attachment Security”, International Journal of Philosophical Studies , 28(5): 583–602. doi:10.1080/09672559.2020.1802971
- Krishnamurthy, Meena, 2015, “(White) Tyranny and the Democratic Value of Distrust”, The Monist , 98(4): 391–406. doi:10.1093/monist/onv020
- Lagerspetz, Olli, 1998, Trust: The Tacit Demand , (Library of Ethics and Applied Philosophy 1), Dordrecht: Springer Netherlands. doi:10.1007/978-94-015-8986-4
- Lahno, Bernd, 2001, “On the Emotional Character of Trust”, Ethical Theory and Moral Practice , 4(2): 171–189. doi:10.1023/A:1011425102875
- –––, 2020, “Trust and Emotion”, in Simon 2020: 147–159.
- Lehrer, Keith, 1997, Self-Trust: A Study of Reason, Knowledge, and Autonomy , New York: Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/acprof:oso/9780198236658.001.0001
- Luhmann, Niklas, 1973/1975 [1979], Vertrauen , Stuttgart: Ferdinand Enke Verlag, 1973, and Macht , Stuttgart, Ferdinand Enke Verlag, 1975. Both translated in Trust and Power: Two Works , Howard Davies, John Raffan and Kathryn Rooney (trans.), Toronto: Wiley, 1979.
- Mackenzie, Catriona and Natalie Stoljar (eds), 2000, Relational Autonomy: Feminist Perspectives on Autonomy, Agency, and the Social Self , New York: Oxford University Press.
- McGeer, Victoria, 2008, “Trust, Hope and Empowerment”, Australasian Journal of Philosophy , 86(2): 237–254. doi:10.1080/00048400801886413
- McGeer, Victoria and Philip Pettit, 2017, “The Empowering Theory of Trust”, in Faulkner and Simpson 2017: 15–35. doi:10.1093/acprof:oso/9780198732549.003.0002
- McLeod, Carolyn, 2002, Self-Trust and Reproductive Autonomy , Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
- –––, 2020, “Damage to Trust”, in her Conscience in Reproductive Health Care: Prioritizing Patient Interests , Oxford: Oxford University Press, pp. 65–87. doi:10.1093/oso/9780198732723.003.0004
- McLeod, Carolyn and Emma Ryman, 2020, “Trust, Autonomy, and the Fiduciary Relationship”, in Fiduciaries and Trust: Ethics, Politics, Economics, and Law , Paul B. Miller and Matthew Harding (eds), Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, pp. 74–86. doi:10.1017/9781108616225.006
- McLeod, Carolyn, Lorraine Davies, Nicole Fice, Leona Bruijns, Emily Cichocki, Hale Doguoglu, Heather Stewart, Austin Horn, Jaclyn Rekis, and Tara Filipovich, 2019, “Time to Attach: An Argument in Favour of EI Attachment Benefits”, report created for Ontario’s Adoptive Parents Association and the Adoption Council of Canada, McLeod et al. 2019 available online .
- McMyler, Benjamin, 2011, Testimony, Trust, and Authority , Oxford: Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/acprof:oso/9780199794331.001.0001
- Mills, Eugene, 1998, “The Unity of Justification”, Philosophy and Phenomenological Research , 58(1): 27–50. doi:10.2307/2653629
- Mullin, Amy, 2005, “Trust, Social Norms, and Motherhood”, Journal of Social Philosophy , 36(3): 316–330. doi:10.1111/j.1467-9833.2005.00278.x
- Nickel, Philip J., 2007, “Trust and Obligation-Ascription”, Ethical Theory and Moral Practice , 10(3): 309–319. doi:10.1007/s10677-007-9069-3
- O’Neil, Collin, 2012, “Lying, Trust, and Gratitude: Lying, Trust, and Gratitude”, Philosophy & Public Affairs , 40(4): 301–333. doi:10.1111/papa.12003
- O’Neill, Onora, 2002, Autonomy and Trust in Bioethics , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. doi:10.1017/CBO9780511606250
- Oreskes, Naomi, 2019, Why Trust Science? Princeton NJ: Princeton University Press.
- Oshana, Marina, 2014, “Trust and Autonomous Agency”, Res Philosophica , 91(3): 431–447. doi:10.11612/resphil.2014.91.3.10
- Pellegrino, Edmund D. and David C. Thomasma, 1993, The Virtues in Medical Practice , New York: Oxford University Press.
- Pettit, Philip, 1995, “The Cunning of Trust”, Philosophy & Public Affairs , 24(3): 202–225. doi:10.1111/j.1088-4963.1995.tb00029.x
- Potter, Nancy Nyquist, 2002, How Can I be Trusted? A Virtue Theory of Trustworthiness , Lanham, MD: Rowman & Littlefield.
- –––, 2013, “Narrative Selves, Relations of Trust, and Bipolar Disorder”, Philosophy, Psychiatry, & Psychology , 20(1): 57–65.
- –––, 2020, “Interpersonal Trust”, in Simon 2020: 243–255.
- Rorty, Amélia Oksenberg, 1980, “Explaining Emotions”, in Explaining Emotions , Amélia Oksenberg Rorty (ed.), Berkeley, CA: University of California Press, 103–126.
- Scheman, Nancy, 2020, “Trust and Trustworthiness”, in Simon 2020: 28–40.
- Simon, Judith (ed.), 2020, The Routledge Handbook of Trust and Philosophy , New York: Routledge. doi:10.4324/9781315542294
- Simpson, Thomas W., 2012, “What Is Trust?”, Pacific Philosophical Quarterly , 93(4): 550–569. doi:10.1111/j.1468-0114.2012.01438.x
- Skyrms, Brian, 2008, “Trust, Risk, and the Social Contract”, Synthese , 160(1): 21–25. doi:10.1007/s11229-006-9075-3
- Smith, Matthew Noah, 2008, “Terrorism, Shared Rules and Trust”, Journal of Political Philosophy , 16(2): 201–219. doi:10.1111/j.1467-9760.2006.00273.x
- Strawson, P. F., 1962 [1974], “Freedom and Resentment”, Proceedings of the British Academy , 48: 1–25. Reprinted in his Freedom and Resentment , London: Methuen, 1974, pp. 1–25.
- Sullins, John P., 2020, “Trust in Robots”, in Simon 2020: 313–325.
- Tallant, Jonathan, 2017, “Commitment in Cases of Trust and Distrust”, Thought: A Journal of Philosophy , 6(4): 261–267. doi:10.1002/tht3.259
- Townley, Cynthia and Jay L. Garfield, 2013, “Public Trust”, in Trust: Analytic and Applied Perspectives , Pekka Makela and Cynthia Townley (eds), Amsterdam: Rodopi Press, pp. 95–107.
- Ullmann-Margalit, Edna, 2004 [2017], “Trust, Distrust, and In Between”, in Distrust (Russell Sage Foundation series on trust), Russell Hardin (ed.), New York: Russell Sage Foundation, 60–82. Reprinted in her Normal Rationality: Decisions and Social Order , Avishai Margalit and Cass R. Sunstein (eds.), Oxford: Oxford University Press, pp. 184–202.
- Uslaner, Eric M., 1999, “Democracy and Social Capital”, in Warren 1999: 121–150. doi:10.1017/CBO9780511659959.005
- Walker, Margaret Urban, 2006, Moral Repair: Reconstructing Moral Relations After Wrongdoing , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Wanderer, Jeremy and Leo Townsend, 2013, “Is it Rational to Trust?” Philosophy Compass , 8(1): 1–14. doi:10.1111/j.1747-9991.2012.00533.x
- Warren, Mark E. (ed.), 1999, Democracy and Trust , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. doi:10.1017/CBO9780511659959
- Webb, Mark Owen, 1992, “The Epistemology of Trust and the Politics of Suspicion”, Pacific Philosophical Quarterly , 73(4): 390–400. doi:10.1111/j.1468-0114.1992.tb00346.x
- –––, 1993, “Why I Know About As Much As You: A Reply to Hardwig”:, The Journal of Philosophy , 90(5): 260–270. doi:10.2307/2940913
- Welch, Shay, 2013, “Transparent Trust and Oppression”, Critical Review of International Social and Political Philosophy , 16(1): 45–64. doi:10.1080/13698230.2011.597582
- Wonderly, Monique Lisa, 2016, “On Being Attached”, Philosophical Studies , 173(1): 223–242. doi:10.1007/s11098-015-0487-0
- Zaner, Richard M., 1991, “The Phenomenon of Trust in the Patient-Physician Relationship”, in Ethics, Trust, and the Professions: Philosophical and Cultural Aspects , Edmund D. Pellegrino, Robert M. Veatch, and John P. Langan (eds.), Washington, DC: Georgetown University Press, pp. 45–67.
How to cite this entry . Preview the PDF version of this entry at the Friends of the SEP Society . Look up topics and thinkers related to this entry at the Internet Philosophy Ontology Project (InPhO). Enhanced bibliography for this entry at PhilPapers , with links to its database.
- “ A Question of Trust ”, 2002 BBC Reith Lecture by Onora O’Neill.
- Russell Sage Foundation Program on Trust .
- “ Building Trust ”, by Donald J. Johnston, OECD Observer , December 2003, 240/241.
- “ Trust and Mistrust ”, with Jorah Dannenberg, Philosophy Talk , 29 December 2013.
- “ On Trust and Philosophy ”, OpenLearn, The Open University.
- “ The Philosophy of Trust: Key Findings ”, The Trust Project at Northwestern University.
Aristotle, General Topics: ethics | autonomy: in moral and political philosophy | autonomy: personal | emotion | epistemology: social | faith | feminist philosophy, interventions: social epistemology | feminist philosophy, topics: perspectives on autonomy | feminist philosophy, topics: perspectives on the self | friendship | justification, epistemic: internalist vs. externalist conceptions of | reliabilist epistemology | rights: of children | scientific knowledge: social dimensions of | testimony: epistemological problems of
Acknowledgments
Thanks to Julie Ponesse, Ken Chung, and Hale Doguoglu for their research assistance, to Andrew Botterell for his helpful comments, and to the Lupina Foundation and Western University for funding.
Copyright © 2020 by Carolyn McLeod
- Accessibility
Support SEP
Mirror sites.
View this site from another server:
- Info about mirror sites
The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy is copyright © 2023 by The Metaphysics Research Lab , Department of Philosophy, Stanford University
Library of Congress Catalog Data: ISSN 1095-5054

Boston College Libraries

The Answer Wall
Answering questions at Boston College O’Neill Library
I trust people easily. A friend says it’s not a good thing. What do u suggest answer wall?
It’s not not a good thing. Trusting people are wonderful when they are surrounded by others deserving of that trust. Unfortunately, many people are not and will use your trusting nature to take advantage of you. That’s just something that you will have to get used to if you’re going to easily trust people, and it will often end in disappointment (or worse) for you. However, you will also get to experience the joy of having trusted someone that no one else did and that person coming through for you, or repaying that trust in kind. That’s such a wonderful feeling and perhaps one of the most human experiences there is. Knowing how much to trust is something that you will be constantly calibrating for the rest of your life.
Nigerian takes to the water to raise mental health awareness

The Reuters Daily Briefing newsletter provides all the news you need to start your day. Sign up here.
Reporting by Seun Sanni, writing by Ope Adetayo, editing by Nick Macfie
Our Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. , opens new tab

Gunmen have killed at least 21 villagers in Nigerian state of Kogi, residents said on Friday, the latest clash between herders and farmers in Africa's most populous nation fueled by growing pressure on land resources.
Cameroon's football federation (FECAFOOT) held an emergency meeting on Saturday and asked its president to propose an alternative coach for the national team, deepening a standoff with the sports ministry.

Mexico breaks relations with Ecuador after embassy stormed
Glas, convicted twice for corruption, was holed up in the embassy since seeking political asylum in December, a request Mexico granted earlier on Friday.
Airline passengers in parts of the United Kingdom and Ireland faced travel disruption at airports on Saturday due to flight cancellations as a storm swept across both countries and left thousands of Irish homes with power outages.


The Juwan Howard interview: Regrets, lost trust and the end of his Michigan coaching career
ANN ARBOR, Mich. — Juwan Howard entered a South State Street restaurant through the backdoor last week, slipping in to meet at a secluded second-floor table. The 51-year-old has had a lot of attention on him this year, over the last five seasons as Michigan head men’s basketball coach, and for most of his life as a 19-year NBA veteran , Michigan alum and McDonald’s All-American.
Advertisement
On March 15, Howard was fired after an 8-24 season that included a 3-17 mark in the Big Ten Conference. The ending, a meeting with athletic director Warde Manuel, was as abrupt as his beginning, a tear-filled May 2019 news conference welcoming a Fab Five icon back to campus, was ceremonious.
Howard, in his first one-on-one interview in at least two years, wanted to put his version of events on various issues and incidents of his tenure on the record as he moves on from Michigan. That’s what will be presented here.
The surgery
Early in the conversation, Howard lifted his shirt to reveal the incision running down the middle of his chest from beneath his collarbone to the bottom of his sternum.
In June 2023, Howard traveled to Los Angeles to accompany his son Jett and former Wolverine Kobe Bufkin for pre-NBA Draft workouts. He got winded on a hotel treadmill but attributed it to asthma. After returning to Michigan, it happened again. This time he was dizzy.
At Schembechler Hall, he met with U-M athletic doctors, who suggested he see a cardiologist. A CT scan revealed blood clots. He was put on blood thinners and scheduled for an MRI.
Howard told his wife, Jenine, that it was no big deal. He tried to believe that, too, but the day after his MRI, Howard learned that blood clots were found in his lungs and an unruptured aneurysm was discovered in his aorta. The blood clots, he says, were saving his life.
Howard was placed on medications and waited 14 weeks for the surgery, thinking every day that the aneurysm might burst.
“I was scared,” Howard says. “But I never admitted that. I didn’t show it in front of my wife or my family, and I never showed it in front of my staff.”
A Sept. 15 surgery resected an aortic aneurysm and repaired Howard’s aortic valve. That day, the school announced the successful surgery. Howard had told his players only one day earlier, a decision he now regrets.
“I didn’t want to scare the players in a way where they might not want to finish out their years here and enter the transfer portal, or where the players I was recruiting might not want to come,” he says. “To go through and explain if I’m going to be here or not, if I’m going to be coaching. I ultimately decided to keep it close to the vest.”

From the Borscht Belt to voice of the Final Four, Ian Eagle's next act
The decision to coach in 2023-24
The procedure lasted nine hours. Doctors set his recovery time at 6-12 weeks. He spent 15 days in the hospital post-op.
Howard told assistant coach Howard Eisley, a lifelong friend, that he would return in two weeks. He saw doctors’ recommendations as races to win, not timelines to live by. And he suffered for it.
“I thought I was a Marvel hero, but this was real life stuff I was dealing with, and I was extremely naive,” he says. “I was impatient with the process.”
Howard wasn’t fully recovered when he returned to the Michigan bench for a November trip to the Battle 4 Atlantis in the Bahamas, he says. Multiple complications emerged throughout the season. He rarely slept through the night. Doctors advised him to step away and undergo another surgery to address an atrial flutter that sapped his energy and caused severe discomfort. He was scheduled to undergo a 7 a.m. procedure following a Jan. 23 road game at Purdue, but heavy snow grounded Michigan’s return flight. Howard’s surgery was canceled and he declined to reschedule it in-season, against doctors’ recommendations and to Jenine’s displeasure.
The surgery is scheduled for April 19.
Doctors never advised Howard to take off the entire 2023-24 season, but implored him not to come back early. He did precisely that.
“You can allow your competitiveness and take control over, you know, what you know in your heart,” Howard says. “If I could go back and do it all over again, I would’ve taken time off to really get help. I should’ve listened more to the doctors and my wife. There were days that I wouldn’t get any sleep and could barely get out of bed, but I’d go in there and try to act like I was fine.”
The decision to coach in 2023-24, Howard says, was “an obligation to his players and staff.” Three players had committed to Michigan out of the transfer portal the prior spring.
The decision not to step aside midseason when his condition clearly wasn’t improving, he says, was “alpha male stuff.”
“That’s where that badge of honor comes in from,” Howard says, adding that he doesn’t regret finishing out the season once he decided to return. “Was that probably the right approach you take looking back on it? No, but if I had to do it again, I would do it again.”
The Jon Sanderson incident
On Dec. 7, three days before a game at Iowa, Howard had a confrontation with strength and conditioning coach Jon Sanderson. The incident changed the contours of the 2023-24 season. While Sanderson’s version of events was reported via leaked internal documents, Howard has not previously spoken publicly about the incident.
While standing on the opposite side of the floor before a Thursday afternoon practice, Howard heard his son Jace Howard yelling at an athletic trainer. Howard says he shouted: “Yo, look, Jace, stop.”
“I’m his father, right?” he says. “He knew that look and knew that voice, right? So he stopped immediately.”
According to Howard, Sanderson got involved, adding: “Jace, you don’t talk to a superior like that!”
“Which is true,” Howard says. “I agree. But then he kept going. Jon said, ‘Jace, that’s bullsh–!’ You don’t talk to a superior that way, this is the sh— I’m talking about.’”
Howard says he called off Sanderson, telling him he was handling it.
Here, according to Howard, Sanderson yelled that he’d recently endured “the same bullsh–” from another player.
Howard says he responded: “Yo, Jon, chill the f— out. I told you I got it.”
Howard says he had no intentions of escalating the tension.
“I’m like three weeks into returning to the facility and have an incision on my chest,” Howard says. “Also, I’m not stupid. After the Wisconsin situation, I said I would never, ever, ever put myself in a situation like that again, where I put my hands on anyone, where it results in any type of physical friction, and second, that I would never put our players in an unsafe environment, and the last part, to never embarrass the entire university and my family. So am I gonna try to fight (Sanderson)? (He’s) 6-8 and strong as sh–.”
Howard says he cursed at Sanderson, using “a bad choice of words,” and told him to “get the f— out of my gym.”
Howard says Sanderson “tried to come at me and fight,” but assistant coaches Saddi Washington and Eisley held him back. “I was like, whoa, this is serious.
“So then, I say, ‘Forget it, guys, let him go, we’re about to start practice.’ So we go to the other court in the practice facility, circle up like we always do, and went over the practice plan.”
Howard says he called Manuel that night. Sanderson sent his version of events to university human resources, and Manuel advised Howard to do the same.
“Then I come to find out Jon’s email to HR got leaked,” Howard says. “Juwan’s email to HR did not get leaked.”
Howard says that, after Sanderson missed practices that Friday and Saturday, he sent a text message to Sanderson.
Pulling out his phone, Howard shared the text.
Unfortunately we haven’t seen you in two days. Hopefully we can meet when you return!
Sanderson did not reply.
On Dec. 15, following a human resources review, the university cleared Howard of any wrongdoing. He returned to full-time head coaching capacities the following day for a home game against Eastern Michigan .
Sanderson left the men’s basketball program, shifting to work with some of the school’s Olympic sports teams. He resigned on March 1, reaching a settlement agreement with the university that included a non-disclosure clause.
The Wisconsin situation
Following a 77-63 loss in February 2022 at Kohl Center, Howard exchanged words with Wisconsin coach Greg Gard in the postgame handshake line. In an ensuing skirmish, Howard struck Badgers assistant coach Joe Krabbenhoft in the head.
“I will always regret how that situation happened, and I will always take full blame for it, because (I) can automatically say, ‘Oh, that wasn’t me,'” he says. “But, yes, it was. I could’ve controlled that and handled that situation better. That’s what I’ll always bang my head about. I had the opportunity to apologize publicly, but I also did so privately to the coaches at Wisconsin. We talked. And we moved on and got past the situation. But I can’t sit here and ask people to forget that that ever happened. I take full ownership of it.”
People did not forget. What happened at Wisconsin followed some heated 2020-21 exchanges between Howard and Maryland coach Mark Turgeon, including a restrained Howard yelling to Turgeon, “I’ll f—ing kill you,” during a Big Ten tournament game.
Howard feels he’ll likely never shake the stigma of what happened that day and thinks about it often.
“I should’ve shook (Gard’s) hand and kept going,” he says.
Asked why he struck Krabbenhoft, Howard says: “I just felt threatened. Someone’s approaching you, they’re saying some words at you, I felt a threat. But look, that’s all it was — just words. He didn’t put his hands on me, I shouldn’t have put my hands on him.”
Howard says he regrets that day’s postgame news conference, when he spoke of what happened casually. He says it wasn’t until a silent bus ride to the airport that afternoon when the gravity set in.
“I remember thinking, like, what did you do, man?” Howard says.
Howard says he told Manuel that day: “If you want to fire me or suspend me, you have every right. I apologize.”
Howard was told by Manuel to enter an anger management program during a five-game suspension. Howard agreed and met with a counselor. “After two sessions, she told me, ‘You don’t need anger management,'” he says. “Seriously. I wouldn’t bullsh— you.”
Howard says he is not a violent person, but understands why perceptions around him changed severely after Wisconsin.
“It hurt me in a lot of ways,” he says. “I know that’s part of the ‘angry Black man’ perception that’s out there. It left people with a perception that anything I do — whether it’s get a technical, which, a lot of coaches get technicals, or the situation with Jon, where you hear his side of it and his lawyer’s side of it — anything I’m involved in, it’s Juwan who started it.”
The perception problem
Howard says that since he was a college and NBA player he’s strongly and purposefully avoided attention.
“There was a lot of pressure, a lot of scrutiny, so I kind of created a bubble, where I didn’t let a lot of folks in,” Howard says. “I was super protective. With that, came a lot of criticism. So I lost trust.”
At Michigan, Howard’s public persona was about as limited as any coach in his position.
“Folks really don’t know me at all, whatsoever, and part of that is my fault,” Howard says. “Could I have been more politically correct like some of these other guys at other programs, done a better job of playing that game? Letting the world into my private life? If that would’ve saved my job, then yeah, I should’ve.”
Yet Howard also feels “people put a shield up on me that I didn’t ask for,” one that existed even internally at Michigan, creating communication problems within the program, problems that ultimately emerged in the fallout of the Sanderson incident.
“Whether it was their own insecurities or what,” Howard says. “Because no one ever came to me and said like, ‘Hey, I’m having a hard time communicating with you.’ No one ever said to me that they were under the impression that I didn’t want to work with them. I think there might have been a degree of intimidation, whether it’s my stature, whether it was me coming from the NBA world, whether it was what I did in my NBA career as a player and a coach, that folks felt a little intimidated by it. I never wanted to give that impression. Granted, I’m not the most talkative or outgoing, but I think I’m engaging.”
In the end, Howard says he wishes he’d opened up more. He wishes people knew junior forward Will Tschetter keeps a garden in his backyard, where he and Jenine grow jalapeño, kale, bell peppers, lettuce. He wishes he’d been more open about his feelings on going from one-game shy of the Elite Eight in March 2021 to outcast in March 2022. He wishes he hadn’t been so reticent about his heart surgery. He wishes people knew that, during the interview, former captain Eli Brooks called to check in on him.
He says he wishes he let people get to know him.
The NIL hurdle
Howard first spoke out publicly about Michigan athletics’ approach to Name, Image and Likeness funding in August 2022, saying the school needed to better embrace college athletics’ tide change. He says now the issue remained throughout his tenure.
“I’ll say this — we needed help,” Howard says. “I asked for help when it came to the NIL two years ago. We didn’t get the help. It ruffled some feathers with some folks.”
After losing in the 2023 NIT, Howard says he met with Michigan president Santa Ono, Manuel, six regents and a variety of coaches from the athletic department, including representatives from football. Howard said men’s basketball needed to upgrade its locker room, but also needed NIL help . But help never came.
“We lost one of our best players because he felt he wasn’t being valued when it comes to NIL,” Howard says, alluding to All-American center Hunter Dickinson , now at Kansas.
“I didn’t have the resources to go and build a roster for this past season,” he says. “The guys that committed were guys I had past relationships with.
“We had two more scholarships, but as we were going through the recruiting process with other players, we got all the way to third base, but couldn’t bring them home because they were looking for an NIL commitment and I couldn’t offer it.”
Howard says he landed high-profile transfer commitments from Texas Tech ’s Terrence Shannon Jr. (now at Illinois) and North Carolina’s Caleb Love (Arizona) without NIL guarantees.
While there was NIL money available for players in his program, Howard says the program did not have the support of an aggressive, basketball-focused collective like some other marquee men’s basketball programs. He says he proposed adding a program general manager three years ago but was told “we did not have the funding for a new hire.” In February, before Manuel hired new coach Dusty May, Michigan announced it would team with Altius Sports Partners to hire an on-campus executive general manager for NIL.
As for some perceptions that Howard, himself, wasn’t assertive in raising NIL funds, he rejected the theory and says he embraced fundraising. He added the program is falling far behind in facilities, notably locker rooms, weight rooms, practice spaces, and he attempted to raise funds for renovations.
Howard said he hopes May has more funds available to build a roster.
“He’ll need it.”

On March 15, Howard met with Manuel to present his plan to fix Michigan basketball. He laid out his ideas, mainly stressing the need for more NIL support. Howard says he told Manuel that a few people had approached him looking to help men’s basketball, especially after the football national championship.
After about 45 minutes, Manuel stepped away briefly. When he returned, he told Howard the school was going to move in a different direction.
“I asked him why,” Howard says. “He said, ‘Well, I don’t trust this will work.’”
Howard says his tenure is full of great memories, but lots of what-ifs. Michigan was on the doorstep of the 2021 Final Four. The next year, it was supposed to “build up around a young core” of Caleb Houstan , Moussa Diabate , Bufkin and Frankie Collins as Dickinson anchored things.
Except Houstan and Diabate turned pro after one year, Bufkin turned pro after two years, and Collins transferred. The next year, his son Jett went to the NBA after one season in Ann Arbor.
“We were fortunate to be in a situation to empower and teach and develop, because those were our guys and we were able to put them in position to pursue their goals and dreams,” Howard says. “But, really, it was never the plan to recruit one-and-dones.”
All that outgoing talent, and university admission issues with possible transfers like Love and Shannon Jr. along with what Howard calls “some other bad breaks along the way,” make him wonder, what if?
Howard shrugs and smiles.
“I’m not here today to fight for my legacy,” he says. “What I’ve done, and what this university has done for me, there are no regrets. I’m happy. I’m also grateful, and will be forever grateful.”
Howard attended a Michigan women’s NCAA Tournament game after being fired. He went because one of the first messages he received after surgery was a video from coach Kim Barnes Arico and the women’s team, all wishing him well. It was the first time he cried after the surgery, and he hasn’t forgotten it.
“Listen, I’ll forever be a fan of Kim and her program, so I’m going to go and support them,” Howard says. “I’m not going to hide under a freakin’ rock. No way.”
Howard says he’ll likely be at a men’s game next season to support his former players. His son Jace could still be on the team. He’ll be at graduation in the spring.
As far as work goes, Howard has no immediate plans.
“I’m going to focus on my health,” he says. “I’m still in (rehabilitative) therapy. That’s my main priority. I’m not where I want to be health-wise, but I’m getting there.”
He will, in time, return to coaching, most likely in the NBA.
“This is not the end, and it will not be the end-all, be-all of my coaching career,” he says.
Howard says he has “a ton of respect” for May, the coach now occupying his old office, and wishes him well.
“I’m never going to be bitter about the situation and how it ended,” Howard says. “I respect that people have jobs to do. Sometimes in this profession, you have to make tough decisions. I’m not saying this was a tough decision, it was probably an easy decision. Who knows? But I’m a Michigan man through and through. … I’m just sad I’m leaving a lot sooner than I expected to.”
(Illustration: Eamonn Dalton / The Athletic ; photo: Luke Hales / Getty Images)
Get all-access to exclusive stories.
Subscribe to The Athletic for in-depth coverage of your favorite players, teams, leagues and clubs. Try a week on us.

Brendan Quinn covers college basketball and golf for The Athletic. He came to The Athletic from MLive Media Group, where he covered Michigan and Michigan State basketball. Prior to that, he covered Tennessee basketball for the Knoxville News Sentinel. Follow Brendan on Twitter @ BFQuinn
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Guest Essay
There’s No Such Thing as an American Bible

By Esau McCaulley
Contributing Opinion Writer
The presumptive Republican nominee for president of the United States, who weeks ago started selling shoes , is now peddling Bibles. During Holy Week.
What’s special about this Bible? So many things. For example, according to a promotional website, it’s the only Bible endorsed by Donald Trump. It’s also the only one endorsed by the country singer Lee Greenwood. Admittedly, the translation isn’t distinctive — it’s your standard King James Version — but the features are unique. This Bible includes the Constitution, the Bill of Rights, the Declaration of Independence, the Pledge of Allegiance and part of the lyrics of Mr. Greenwood’s song “God Bless the USA.” Perhaps most striking, the cover of the Bible does not include a cross or any symbol of the Christian tradition; instead, it is emblazoned with the American flag.
While part of me wants to laugh at the absurdity of it — and marvel at the sheer audacity — I find the messaging unsettling and deeply wrong. This God Bless the USA Bible, as it’s officially named, focuses on God’s blessing of one particular people. That is both its danger and, no doubt for some, its appeal.
Whether this Bible is an example of Christian nationalism I will leave to others. It is at least an example of Christian syncretism, a linking of certain myths about American exceptionalism and the Christian faith. This is the American church’s consistent folly: thinking that we are the protagonists in a story that began long before us and whose main character is in fact the Almighty.
Holy Week is the most sacred portion of the Christian calendar, a time when the church recounts the central events of our faith’s narrative, climaxing in the death and resurrection of Jesus. That story, unlike the parochial God Bless the USA Bible, does not belong to any culture.
Holy Week is celebrated on every continent and in too many languages to number. Some of the immigrants Mr. Trump declared were “ poisoning the blood” of America will probably shout “Christ is risen!” this Easter. Many of them come from the largely Christian regions of Latin America and the Caribbean. They may have entered the country with Bibles in their native tongues nestled securely among their other belongings.
One of the beauties of the Christian faith is that it leaps over the lines dividing countries, leading the faithful to call fellow believers from very different cultures brothers and sisters. Most of the members of this international community consist of the poor living in Africa, Asia and Latin America. There are more Spanish-speaking Christians than English- speaking ones .
If there are central messages that emerge from the variety of services that take place during Holy Week, for many Christians they are the setting aside of power to serve, the supremacy of love, the offer of divine forgiveness and the vulnerability of a crucified God.
This is not the stuff of moneymaking schemes or American presidential campaigns.
It was Pontius Pilate , standing in as the representative of the Roman Empire, who sentenced Jesus to death. The Easter story reminds believers that empires are more than willing to sacrifice the innocent if it allows rulers to stay in power. The church sees Christ’s resurrection as liberating the believer from the power of sin. The story challenges imperial modes of thinking, supplanting the endless pursuit of power with the primacy of love and service.
Easter, using the language of St. Augustine, represents the victory of the City of God over the City of Man. It declares the limits of the moral reasoning of nation-states and has fortified Christians who’ve resisted evil regimes such as fascists in South America, Nazis in Germany, apartheid in South Africa and segregation in the United States.
For any politician to suppose that a nation’s founding documents and a country music song can stand side by side with biblical texts fails at a theological and a moral level. I can’t imagine people in other countries going for anything like it. It is hard to picture a modern “God Bless England” Bible with elements of British common law appended to Christianity’s most sacred texts.
I am glad for the freedoms that we share as Americans. But the idea of a Bible explicitly made for one nation displays a misunderstanding of the story the Bible attempts to tell. The Christian narrative culminates in the creation of the Kingdom (and family) of God, a transnational community united by faith and mutual love.
Roman Catholics , Anglicans and Orthodox Christians, who together claim around 1.5 billion members, describe the Bible as a final authority in matters of faith. Evangelicals, who have overwhelmingly supported Mr. Trump over the course of three election cycles, are known for their focus on Scripture, too. None of these traditions cite or refer to any American political documents in their doctrinal statements — and for good reason.
This Bible may be unique in its form, but the agenda it pursues has recurred throughout history. Christianity is often either co-opted or suppressed; it is rarely given the space to be itself. African American Christians have long struggled to disentangle biblical texts from their misuse in the United States. There is a reason that the abolitionist Frederick Douglass said that between the Christianity of this land (America) and the Christianity of Christ, he recognized the “widest possible difference.”
And while Christianity was used to give theological cover to North American race-based chattel slavery, it was violently attacked in places like El Salvador and Uganda, when leaders including the archbishops Oscar Romero and Janani Luwum spoke out against political corruption.
The work of the church is to remain constantly vigilant to maintain its independence and the credibility of its witness. In the case of this particular Bible, discerning what is happening is not difficult. Christians are being played. Rather than being an appropriate time to debut a patriotic Bible, Easter season is an opportune moment for the church to recover the testimony of the supremacy of the cross over any flag, especially one on the cover of a Bible.
Esau McCaulley ( @esaumccaulley ) is a contributing Opinion writer, the author of “ How Far to the Promised Land: One Black Family’s Story of Hope and Survival in the American South ” and an associate professor of New Testament at Wheaton College.
The Times is committed to publishing a diversity of letters to the editor. We’d like to hear what you think about this or any of our articles. Here are some tips . And here’s our email: [email protected] .
Follow The New York Times Opinion section on Facebook , Instagram , TikTok , WhatsApp , X and Threads .
- International edition
- Australia edition
- Europe edition

Exclusive: Trump Media saved in 2022 by Russian-American under criminal investigation
Trump’s social media company went public relying partly on loans from trust managed by person of interest to prosecutors
Donald Trump’s social media company Trump Media managed to go public last week only after it had been kept afloat in 2022 by emergency loans provided in part by a Russian-American businessman under scrutiny in a federal insider-trading and money-laundering investigation.
The former US president stands to gain billions of dollars – his stake is currently valued at about $4bn – from the merger between Trump Media and Technology Group and the blank-check company Digital World Acquisition Corporation, which took the parent company of Truth Social public.
But Trump Media almost did not make it to the merger after regulators opened a securities investigation into the merger in 2021 and caused the company to burn through cash at an extraordinary rate as it waited to get the green light for its stock market debut.
The situation led Trump Media to take emergency loans, including from an entity called ES Family Trust, which opened an account with Paxum Bank, a small bank registered on the Caribbean island of Dominica that is best known for providing financial services to the porn industry.
Through leaked documents, the Guardian has learned that ES Family Trust operated like a shell company for a Russian-American businessman named Anton Postolnikov, who co-owns Paxum Bank and has been a subject of a years-long joint federal criminal investigation by the FBI and the Department of Homeland Security (DHS) into the Trump Media merger.
The existence of the trust has previously been reported by the Guardian and the Washington Post. However, who controlled the account, how the trust was connected to Paxum Bank, and how the money had been funneled through the trust to Trump Media was unknown.
The new details about the trust are drawn from documents including: Paxum Bank records showing Postolnikov having access to the trust’s account, the papers that created the trust showing as its settlor a lawyer in St Petersburg, Russia, and three years of the trust’s financial transactions.
The concern surrounding the loans to Trump Media is that ES Family Trust may have been used to complete a transaction that Paxum itself could not.
Paxum Bank does not offer loans in the US as it lacks a US banking license and is not regulated by the FDIC. Postolnikov appears to have used the trust to loan money to help save Trump Media – and the Truth Social platform – because his bank itself could not furnish the loan.
Postolnikov, the nephew of Aleksandr Smirnov, an ally of the Russian president, Vladimir Putin , has not been charged with a crime. In response to an email to Postolnikov seeking comment, a lawyer in Dominica representing Paxum Bank warned of legal action for reporting the contents of the leaked documents.
There is also no indication that Trump or Trump Media had any idea about the nature of the loans beyond that they were opaque, nor has the company or its executives been accused of wrongdoing. A spokesperson for Trump Media did not respond to a request for comment.
After this story was published, a lawyer representing Trump Media said in a statement: “The Guardian continues to propagate its false narrative that TMTG has these fake connections to Russia. It is a hoax. Litigation will continue on this point and we are confident that The Guardian will ultimately be held responsible for its defamation and this story should be retracted.”
But Postolnikov has been under increasing scrutiny in the criminal investigation into the Trump Media merger. Most recently, he has been listed on search warrant affidavits alongside several associates – one of whom was indicted last month for money laundering on top of earlier insider-trading charges.
Postolnikov and the trust
In late 2021, Trump Media was facing financial trouble after the original planned merger with Digital World was delayed indefinitely when the Securities and Exchange Commission opened an investigation into the merger, Trump Media’s since-ousted co-founder-turned-whistleblower Will Wilkerson recounted in an interview.
Part of the problem was that Trump Media struggled to get financing because traditional banks were reluctant to lend millions to Trump’s social media company in the wake of the January 6 Capitol attack, Wilkerson said.
Trump Media eventually found some lenders, including ES Family Trust, but the sequence of events was curious.
ES Family Trust was established on 18 May 2021, its creation papers show. Postolnikov’s “user” access to the account was “verified” on 30 November 2021 by a Paxum Bank manager in Dominica . The trust was funded for the first time on 2 December 2021.
Trump Media then received the loans from ES Family Trust: $2m on 23 December 2021, and $6m on 17 February 2022.
The loans came in the form of convertible promissory notes, meaning ES Family Trust would gain a major stake in Trump Media because it was offering the money in exchange for Trump Media agreeing to convert the loan principal into “shares of Company Stock”.
Oddly, the notes were never signed. But the investment in Trump Media proved to be huge: while precise figures can only be known by Trump Media, ES Family Trust’s stake in Trump Media is worth between $20m and $40m even after the sharp decline of the company’s share price in the wake of a poor earnings report.
The ES Family Trust account also appears to have benefited Postolnikov personally. As the criminal investigation into the Trump Media deal intensified towards the end of last year, the trust recorded several transfers to Postolnikov with the subject line “Partial Loan Return”.
In total, the documents showed that the trust transferred $4.8m to Postolnikov’s account, although $3m was inexplicably “reversed”.
(On 17 July 2023, Postolnikov received $300,000. On 17 October 2023, Postolnikov received $1.5m, before it was reversed the next day; later the same day, Postolnikov again received $1.5m, which was also reversed. On 19 October 2023, Postolnikov received the $1.5m for a third and final time.)
The reason for the trust’s creation remains unknown. Aside from the money that went to Trump Media, the trust’s statements show the trust has directly invested money with only two other companies: $10.8m to Eleven Ventures LLC, a venture capital firm, and $1m to Wedbush Securities, a wealth management firm.
The current status of ES Family Trust is also unknown. The trust’s address is listed as a residential home in Hollywood, Florida. But, according to the property website Redfin, the six-bedroom home appears to have been sold in December 2023.
The creation papers also contained something notable: a declaration that, if the original trustee – a Paxum employee named Angel Pacheco – stepped down from the role, his successor would be a certain individual named Michael Shvartsman.
Sprawling money-laundering investigation
Last month, federal prosecutors charged Michael Shvartsman, a close associate of Postolnikov, with money laundering in a superseding indictment after previously charging him and two others in July with insider-trading Digital World shares. Shvartsman and his co-defendants pleaded not guilty.
At least part of the evidence against Shvartsman came from a confidential informant for the DHS, court filings show: in one March 2023 meeting with the informant and an associate, Shvartsman mentioned a friend who owned a bank in Dominica and made bridge loans to Trump Media.
“[Shvartsman] stated that a friend of his owns a bank in the island of Dominica and would be able to provide banking services to Russian and Ukraine Nationals if the [confidential informant] had other clients in need of that service,” the DHS report said .
“[Shvartsman’s associate] told the [confidential informant] that he does not think the SEC would be able to go after [Shvartsman] for his part in the investment but mentioned that [Shvartsman] essentially provided ‘bridge financing’ for the firm behind the Truth Social media platform,” it said.
The unredacted parts of the DHS report do not specify whether the “friend” was Postolnikov and what the “bridge financing” referred to – but the report left open the possibility that Shvartsman also had a role with the trust.
A lawyer for Shvartsman declined to comment on his client’s relationship with Postolnikov. A spokesperson for the US attorney’s office for the southern district of New York also declined to comment.
It is unclear whether federal prosecutors are aware that Trump Media was propped up by Postolnikov via ES Family Trust. At the same time, the money-laundering investigation surrounding the Trump Media merger and the scrutiny on Postolnikov appears to have ballooned in recent months.
The investigation into potential money laundering appears to have started after Wilkerson’s lawyers Phil Brewster, Stephen Bell and Patrick Mincey alerted the US attorney’s office in the southern district of New York to the ES Family Trust loans in October 2022.
Months later, in June 2023, the FBI expanded its investigation to work jointly with the Department of Homeland Security’s El Dorado taskforce, which specializes in money laundering, and its Illicit Proceeds and Foreign Corruption group, which targets corrupt foreign officials who use US entities to launder illicit funds.
- Donald Trump
- Social media
- Digital media
- Vladimir Putin
Most viewed
We've detected unusual activity from your computer network
To continue, please click the box below to let us know you're not a robot.
Why did this happen?
Please make sure your browser supports JavaScript and cookies and that you are not blocking them from loading. For more information you can review our Terms of Service and Cookie Policy .
For inquiries related to this message please contact our support team and provide the reference ID below.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Here are 100, 200 and 500-word essays on "The Person I Admire The Most". We all have someone or another whom we admire the most. We love the other person so much that we can do anything for the other person. They are the people who make us believe that good things do exist. We are blessed to have those people in our life.
He is a very reserved man, but has a great sense of humor, and always know how to put a smile on my face. My father stands tall among men. He lives by great principles and I am proud of him. He is very honest and courageous. He will not grudge any trouble he may have to undergo to be on the side of truth.
Short Essay on Trust 150 Words in English. Trust is the essential quality of the way we live our everyday life. Trust is a quality of being trustworthy; loyal; reliable. The base of any relationship, friendship, business, or organization is the trust between them. Trusting someone means to rely on someone completely.
I have always been a gullible person. You say something to me and I will believe it. I have a hard time with confrontation; therefore, I always believe the best in people and put all my trust in them. My dad; however, people have to earn his trust. When we have conversations about my gullibility, the conversation almost always ends with me in ...
The Person I Admire The Most Essay (100 Words) The person I admire the most is my mother. She is a remarkable woman who has always shown unwavering love and support for our family. Her selflessness, resilience, and dedication to her role as a mother have left a lasting impression on me. She is a source of inspiration with her kind heart, strong ...
500 Words Essay on Person I Admire The Most Introduction. In life, we come across many people who inspire us with their actions, words, or just by being themselves. The person I admire the most is my grandmother. She is like a bright star in my life, guiding me with her wisdom, love, and strength.
The person who I admire the most is my father. He is a dynamic man who has created a successful path for himself and others too. He is the best at everything he does, and yet is a humble and down-to-earth man. My father is a doctor. Everyday, he works hard to care for all his patients and their health.
Whether it's their character traits, physical features, or social skills, each human has a specific set of attractive things about them that are admirable to others. The one person that I admire most in my life is my friend Prisca. I look up to and appreciate her simply because of her beauty, brains, and sophisticated nature.
In conclusion, my mother is the person I admire the most. Her selflessness, strength, love, and guidance have been instrumental in shaping the person I am today. Her influence extends far beyond her role as a mother, making her an inspiration to all who have the privilege of knowing her. I am proud to call her my mother and am forever grateful ...
Published in 1841, the Self Reliance essay is a deep-dive into self-sufficiency as a virtue. In the essay "Self-Reliance," Ralph Waldo Emerson advocates for individuals to trust in their own instincts and ideas rather than blindly following the opinions of society and its institutions. He argues that society encourages conformity, stifles ...
The person I like Most &The person I love Most Paragraph Essay 2. When this question is asked to someone, the general answer most will give is their parents. When I first came across this question, I was a bit startled when I realized that my answer is not similar to most of the people. So, I paused for a bit and thought about my answer and ...
1. This essay sample was donated by a student to help the academic community. Papers provided by EduBirdie writers usually outdo students' samples. Cite This Essay. Download. A leader that I admire is Mr. Jamison Chandler, the Director of the Jazz Band at KIPP AMP Middle School. I admire his vision to educate and inspire students in our ...
My mom is the one that is always there, the person I can count on, the one that will never turn her back on me. The one that supports, helps, sympathizes, hugs, kisses, gives me confidence, comforts, listens, makes me laugh, cheers me up and wipes my tears. She will definitely be the one that I always admire and love the most.
Trust is one of the foundations for any relationship because it allows people to open up and connect with each other. Without trust, one will feel distant and sometimes even hostile when around others. Trusting someone can be the difference between that person becoming a friend or just remaining an acquaintance.
250 Words Essay on The Person I Like Most My Father Introduction. The person I admire the most in my life is none other than my father. He is the one who instilled the values of discipline, hard work, and respect in me. His wisdom, humility, and resilience have greatly influenced the person I have become today. His Character. My father is a ...
Here are some steps that you can follow to write a great essay on trust: Trust Essay - Define The Concept. The first step when you start writing essays on trust is to define the word trust. Essentially, it is the faith that you have in another person. But trust is also a two way street. It is not just about you trusting someone but also about ...
Organizational Trust And National Culture And Trust. 7. Trust As The Missing Root Relating To Education, Institutions And Economic Development. 8. Trust In Relation To Gender & To Years Of Service, Trust And Category Of Worker. 9. Overview Of The Main Thrusts In Negotiation. 10. The Road By Cormac McCarthey: The Theme Of Trust In The Book. 11.
Believe yourself. Trust yourself. You will tackle those shortcomings... Free Essay: Trust is a small word that holds a lot of meaning and significance. It's confidence placed in a person by making that person the nominal owner... Trust plays a big role in most people's life and when you break that trust there is not much a person can do to gain ...
People can lose trust in almost everyone or everything as a result of trauma (Herman 1991). The trauma of rape, for example, can profoundly reduce one's sense that the world is a safe place with caring people in it (Brison 2002). By contrast, people can lose trust just in particular people or institutions.
By Lavinia Spalding. March 29, 2024. Too early in life, the male species began to fail me. As an adolescent, I was lied to, cheated on, harassed and assaulted. As a young adult, more of the same ...
Question:. Write an essay on the person you trust the most . Answer:. MY BEST FRIEND. The person whom I trust the most is my best friend.His name is Rishi and he lives in my locality. We go to the same school . He has been my best friend since we were little kids , we went to kindergarten together too.
.essay on the person I trust the most - 49876161. Answer: Trust is the very thing that everybody in this world desires, or at least should desire from one another.
Trusting people are wonderful when they are surrounded by others deserving of that trust. Unfortunately, many people are not and will use your trusting nature to take advantage of you. That's just something that you will have to get used to if you're going to easily trust people, and it will often end in disappointment (or worse) for you ...
Nigerian swimmer Akinrodoye Samuel has tried to raise awareness on mental health in Africa's most populous nation, swimming nearly 12 km (7.45 miles), the length of the longest bridge in Lagos ...
The decision to coach in 2023-24. The procedure lasted nine hours. Doctors set his recovery time at 6-12 weeks. He spent 15 days in the hospital post-op.
Cite This Essay. Download. Of all the famous figures, Michelle Obama is the person I admire the most, and I'm going to tell you why. Firstly, Mitchelle Obama is relatable to others. I really admire her communication skills. She is able to convince her opponents or the public audience to believe in her leadership.
Here are some tips. And here's our email: [email protected]. Follow The New York Times Opinion section on Facebook, Instagram, TikTok, WhatsApp, X and Threads. 602. 602. Trump's God Bless ...
ES Family Trust was established on 18 May 2021, its creation papers show. Postolnikov's "user" access to the account was "verified" on 30 November 2021 by a Paxum Bank manager in Dominica .
Connecting decision makers to a dynamic network of information, people and ideas, Bloomberg quickly and accurately delivers business and financial information, news and insight around the world