- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2023 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support

The Nature vs. Nurture Debate
Genetic and Environmental Influences and How They Interact
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Verywell / Joshua Seong
- Definitions
- Interaction
- Contemporary Views
Nature refers to how genetics influence an individual's personality, whereas nurture refers to how their environment (including relationships and experiences) impacts their development. Whether nature or nurture plays a bigger role in personality and development is one of the oldest philosophical debates within the field of psychology .
Learn how each is defined, along with why the issue of nature vs. nurture continues to arise. We also share a few examples of when arguments on this topic typically occur, how the two factors interact with each other, and contemporary views that exist in the debate of nature vs. nurture as it stands today.
Nature and Nurture Defined
To better understand the nature vs. nurture argument, it helps to know what each of these terms means.
- Nature refers largely to our genetics . It includes the genes we are born with and other hereditary factors that can impact how our personality is formed and influence the way that we develop from childhood through adulthood.
- Nurture encompasses the environmental factors that impact who we are. This includes our early childhood experiences, the way we were raised , our social relationships, and the surrounding culture.
A few biologically determined characteristics include genetic diseases, eye color, hair color, and skin color. Other characteristics are tied to environmental influences, such as how a person behaves, which can be influenced by parenting styles and learned experiences.
For example, one child might learn through observation and reinforcement to say please and thank you. Another child might learn to behave aggressively by observing older children engage in violent behavior on the playground.
The Debate of Nature vs. Nurture
The nature vs. nurture debate centers on the contributions of genetics and environmental factors to human development. Some philosophers, such as Plato and Descartes, suggested that certain factors are inborn or occur naturally regardless of environmental influences.
Advocates of this point of view believe that all of our characteristics and behaviors are the result of evolution. They contend that genetic traits are handed down from parents to their children and influence the individual differences that make each person unique.
Other well-known thinkers, such as John Locke, believed in what is known as tabula rasa which suggests that the mind begins as a blank slate . According to this notion, everything that we are is determined by our experiences.
Behaviorism is a good example of a theory rooted in this belief as behaviorists feel that all actions and behaviors are the results of conditioning. Theorists such as John B. Watson believed that people could be trained to do and become anything, regardless of their genetic background.
People with extreme views are called nativists and empiricists. Nativists take the position that all or most behaviors and characteristics are the result of inheritance. Empiricists take the position that all or most behaviors and characteristics result from learning.
Examples of Nature vs. Nurture
One example of when the argument of nature vs. nurture arises is when a person achieves a high level of academic success . Did they do so because they are genetically predisposed to elevated levels of intelligence, or is their success a result of an enriched environment?
The argument of nature vs. nurture can also be made when it comes to why a person behaves in a certain way. If a man abuses his wife and kids, for instance, is it because he was born with violent tendencies, or is violence something he learned by observing others in his life when growing up?
Nature vs. Nurture in Psychology
Throughout the history of psychology , the debate of nature vs. nurture has continued to stir up controversy. Eugenics, for example, was a movement heavily influenced by the nativist approach.
Psychologist Francis Galton coined the terms 'nature versus nurture' and 'eugenics' and believed that intelligence resulted from genetics. Galton also felt that intelligent individuals should be encouraged to marry and have many children, while less intelligent individuals should be discouraged from reproducing.
The value placed on nature vs. nurture can even vary between the different branches of psychology , with some branches taking a more one-sided approach. In biopsychology , for example, researchers conduct studies exploring how neurotransmitters influence behavior, emphasizing the role of nature.
In social psychology , on the other hand, researchers might conduct studies looking at how external factors such as peer pressure and social media influence behaviors, stressing the importance of nurture. Behaviorism is another branch that focuses on the impact of the environment on behavior.
Nature vs. Nurture in Child Development
Some psychological theories of child development place more emphasis on nature and others focus more on nurture. An example of a nativist theory involving child development is Chomsky's concept of a language acquisition device (LAD). According to this theory, all children are born with an instinctive mental capacity that allows them to both learn and produce language.
An example of an empiricist child development theory is Albert Bandura's social learning theory . This theory says that people learn by observing the behavior of others. In his famous Bobo doll experiment , Bandura demonstrated that children could learn aggressive behaviors simply by observing another person acting aggressively.
Nature vs. Nurture in Personality Development
There is also some argument as to whether nature or nurture plays a bigger role in the development of one's personality. The answer to this question varies depending on which personality development theory you use.
According to behavioral theories, our personality is a result of the interactions we have with our environment, while biological theories suggest that personality is largely inherited. Then there are psychodynamic theories of personality that emphasize the impact of both.
Nature vs. Nurture in Mental Illness Development
One could argue that either nature or nurture contributes to mental health development. Some causes of mental illness fall on the nature side of the debate, including changes to or imbalances with chemicals in the brain. Genetics can also contribute to mental illness development, increasing one's risk of a certain disorder or disease.
Mental disorders with some type of genetic component include autism , attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), bipolar disorder , major depression , and schizophrenia .
Other explanations for mental illness are environmental. This includes being exposed to environmental toxins, such as drugs or alcohol, while still in utero. Certain life experiences can also influence mental illness development, such as witnessing a traumatic event, leading to the development of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
Nature vs. Nurture in Mental Health Therapy
Different types of mental health treatment can also rely more heavily on either nature or nurture in their treatment approach. One of the goals of many types of therapy is to uncover any life experiences that may have contributed to mental illness development (nurture).
However, genetics (nature) can play a role in treatment as well. For instance, research indicates that a person's genetic makeup can impact how their body responds to antidepressants. Taking this into consideration is important for getting that person the help they need.
Interaction Between Nature and Nurture
Which is stronger: nature or nurture? Many researchers consider the interaction between heredity and environment—nature with nurture as opposed to nature versus nurture—to be the most important influencing factor of all.
For example, perfect pitch is the ability to detect the pitch of a musical tone without any reference. Researchers have found that this ability tends to run in families and might be tied to a single gene. However, they've also discovered that possessing the gene is not enough as musical training during early childhood is needed for this inherited ability to manifest itself.
Height is another example of a trait influenced by an interaction between nature and nurture. A child might inherit the genes for height. However, if they grow up in a deprived environment where proper nourishment isn't received, they might never attain the height they could have had if they'd grown up in a healthier environment.
A newer field of study that aims to learn more about the interaction between genes and environment is epigenetics . Epigenetics seeks to explain how environment can impact the way in which genes are expressed.
Some characteristics are biologically determined, such as eye color, hair color, and skin color. Other things, like life expectancy and height, have a strong biological component but are also influenced by environmental factors and lifestyle.
Contemporary Views of Nature vs. Nurture
Most experts recognize that neither nature nor nurture is stronger than the other. Instead, both factors play a critical role in who we are and who we become. Not only that but nature and nurture interact with each other in important ways all throughout our lifespan.
As a result, many in this field are interested in seeing how genes modulate environmental influences and vice versa. At the same time, this debate of nature vs. nurture still rages on in some areas, such as in the origins of homosexuality and influences on intelligence .
While a few people take the extreme nativist or radical empiricist approach, the reality is that there is not a simple way to disentangle the multitude of forces that exist in personality and human development. Instead, these influences include genetic factors, environmental factors, and how each intermingles with the other.
Schoneberger T. Three myths from the language acquisition literature . Anal Verbal Behav . 2010;26(1):107-31. doi:10.1007/bf03393086
National Institutes of Health. Common genetic factors found in 5 mental disorders .
Pain O, Hodgson K, Trubetskoy V, et al. Identifying the common genetic basis of antidepressant response . Biol Psychiatry Global Open Sci . 2022;2(2):115-126. doi:10.1016/j.bpsgos.2021.07.008
Moulton C. Perfect pitch reconsidered . Clin Med J . 2014;14(5):517-9 doi:10.7861/clinmedicine.14-5-517
Levitt M. Perceptions of nature, nurture and behaviour . Life Sci Soc Policy . 2013;9:13. doi:10.1186/2195-7819-9-13
Bandura A, Ross D, Ross, SA. Transmission of aggression through the imitation of aggressive models . J Abnorm Soc Psychol. 1961;63(3):575-582. doi:10.1037/h0045925
Chomsky N. Aspects of the Theory of Syntax .
Galton F. Inquiries into Human Faculty and Its Development .
Watson JB. Behaviorism .
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
- Type 2 Diabetes
- Heart Disease
- Digestive Health
- Multiple Sclerosis
- COVID-19 Vaccines
- Occupational Therapy
- Healthy Aging
- Health Insurance
- Public Health
- Patient Rights
- Caregivers & Loved Ones
- End of Life Concerns
- Health News
- Thyroid Test Analyzer
- Doctor Discussion Guides
- Hemoglobin A1c Test Analyzer
- Lipid Test Analyzer
- Complete Blood Count (CBC) Analyzer
- What to Buy
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Medical Expert Board
What Are Nature vs. Nurture Examples?
How is nature defined, how is nurture defined, the nature vs. nurture debate, nature vs. nurture examples, what is empiricism (extreme nurture position), contemporary views of nature vs. nurture.
Nature vs. nurture is an age-old debate about whether genetics (nature) plays a bigger role in determining a person's characteristics than lived experience and environmental factors (nurture). The term "nature vs. nature" was coined by English naturalist Charles Darwin's younger half-cousin, anthropologist Francis Galton, around 1875.
In psychology, the extreme nature position (nativism) proposes that intelligence and personality traits are inherited and determined only by genetics.
On the opposite end of the spectrum, the extreme nurture position (empiricism) asserts that the mind is a blank slate at birth; external factors like education and upbringing determine who someone becomes in adulthood and how their mind works. Both of these extreme positions have shortcomings and are antiquated.
This article explores the difference between nature and nurture. It gives nature vs. nurture examples and explains why outdated views of nativism and empiricism don't jibe with contemporary views.
Thanasis Zovoilis / Getty Images
In the context of nature vs. nurture, "nature" refers to genetics and heritable factors that are passed down to children from their biological parents.
Genes and hereditary factors determine many aspects of someone’s physical appearance and other individual characteristics, such as a genetically inherited predisposition for certain personality traits.
Scientists estimate that 20% to 60% percent of temperament is determined by genetics and that many (possibly thousands) of common gene variations combine to influence individual characteristics of temperament.
However, the impact of gene-environment (or nature-nurture) interactions on someone's traits is interwoven. Environmental factors also play a role in temperament by influencing gene activity. For example, in children raised in an adverse environment (such as child abuse or violence), genes that increase the risk of impulsive temperamental characteristics may be activated (turned on).
Trying to measure "nature vs. nurture" scientifically is challenging. It's impossible to know precisely where the influence of genes and environment begin or end.
How Are Inherited Traits Measured?
“Heritability” describes the influence that genes have on human characteristics and traits. It's measured on a scale of 0.0 to 1.0. Very strong heritable traits like someone's eye color are ranked a 1.0.
Traits that have nothing to do with genetics, like speaking with a regional accent ranks a zero. Most human characteristics score between a 0.30 and 0.60 on the heritability scale, which reflects a blend of genetics (nature) and environmental (nurture) factors.
Thousands of years ago, ancient Greek philosophers like Plato believed that "innate knowledge" is present in our minds at birth. Every parent knows that babies are born with innate characteristics. Anecdotally, it may seem like a kid's "Big 5" personality traits (agreeableness, conscientiousness, extraversion, neuroticism, and openness) were predetermined before birth.
What is the "Big 5" personality traits
The Big 5 personality traits is a theory that describes the five basic dimensions of personality. It was developed in 1949 by D. W. Fiske and later expanded upon by other researchers and is used as a framework to study people's behavior.
From a "nature" perspective, the fact that every child has innate traits at birth supports Plato's philosophical ideas about innatism. However, personality isn't set in stone. Environmental "nurture" factors can change someone's predominant personality traits over time. For example, exposure to the chemical lead during childhood may alter personality.
In 2014, a meta-analysis of genetic and environmental influences on personality development across the human lifespan found that people change with age. Personality traits are relatively stable during early childhood but often change dramatically during adolescence and young adulthood.
It's impossible to know exactly how much "nurture" changes personality as people get older. In 2019, a study of how stable personality traits are from age 16 to 66 found that people's Big 5 traits are both stable and malleable (able to be molded). During the 50-year span from high school to retirement, some traits like agreeableness and conscientiousness tend to increase, while others appear to be set in stone.
Nurture refers to all of the external or environmental factors that affect human development such as how someone is raised, socioeconomic status, early childhood experiences, education, and daily habits.
Although the word "nurture" may conjure up images of babies and young children being cared for by loving parents, environmental factors and life experiences have an impact on our psychological and physical well-being across the human life span. In adulthood, "nurturing" oneself by making healthy lifestyle choices can offset certain genetic predispositions.
For example, a May 2022 study found that people with a high genetic risk of developing the brain disorder Alzheimer's disease can lower their odds of developing dementia (a group of symptoms that affect memory, thinking, and social abilities enough to affect daily life) by adopting these seven healthy habits in midlife:
- Staying active
- Healthy eating
- Losing weight
- Not smoking
- Reducing blood sugar
- Controlling cholesterol
- Maintaining healthy blood pressure
The nature vs. nurture debate centers around whether individual differences in behavioral traits and personality are caused primarily by nature or nurture. Early philosophers believed the genetic traits passed from parents to their children influence individual differences and traits. Other well-known philosophers believed the mind begins as a blank slate and that everything we are is determined by our experiences.
While early theories favored one factor over the other, experts today recognize there is a complex interaction between genetics and the environment and that both nature and nurture play a critical role in shaping who we are.
Eye color and skin pigmentation are examples of "nature" because they are present at birth and determined by inherited genes. Developmental delays due to toxins (such as exposure to lead as a child or exposure to drugs in utero) are examples of "nurture" because the environment can negatively impact learning and intelligence.
In Child Development
The nature vs. nurture debate in child development is apparent when studying language development. Nature theorists believe genetics plays a significant role in language development and that children are born with an instinctive ability that allows them to both learn and produce language.
Nurture theorists would argue that language develops by listening and imitating adults and other children.
In addition, nurture theorists believe people learn by observing the behavior of others. For example, contemporary psychologist Albert Bandura's social learning theory suggests that aggression is learned through observation and imitation.
In Psychology
In psychology, the nature vs. nurture beliefs vary depending on the branch of psychology.
- Biopsychology: Researchers analyze how the brain, neurotransmitters, and other aspects of our biology influence our behaviors, thoughts, and feelings. emphasizing the role of nature.
- Social psychology: Researchers study how external factors such as peer pressure and social media influence behaviors, emphasizing the importance of nurture.
- Behaviorism: This theory of learning is based on the idea that our actions are shaped by our interactions with our environment.
In Personality Development
Whether nature or nurture plays a bigger role in personality development depends on different personality development theories.
- Behavioral theories: Our personality is a result of the interactions we have with our environment, such as parenting styles, cultural influences, and life experiences.
- Biological theories: Personality is mostly inherited which is demonstrated by a study in the 1990s that concluded identical twins reared apart tend to have more similar personalities than fraternal twins.
- Psychodynamic theories: Personality development involves both genetic predispositions and environmental factors and their interaction is complex.
In Mental Illness
Both nature and nurture can contribute to mental illness development.
For example, at least five mental health disorders are associated with some type of genetic component ( autism , attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) , bipolar disorder , major depression, and schizophrenia ).
Other explanations for mental illness are environmental, such as:
- Being exposed to drugs or alcohol in utero
- Witnessing a traumatic event, leading to post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
- Adverse life events and chronic stress during childhood
In Mental Health Therapy
Mental health treatment can involve both nature and nurture. For example, a therapist may explore life experiences that may have contributed to mental illness development (nurture) as well as family history of mental illness (nature).
At the same time, research indicates that a person's genetic makeup may impact how their body responds to antidepressants. Taking this into consideration is important for finding the right treatment for each individual.
What Is Nativism (Extreme Nature Position)?
Innatism emphasizes nature's role in shaping our minds and personality traits before birth. Nativism takes this one step further and proposes that all of people's mental and physical characteristics are inherited and predetermined at birth.
In its extreme form, concepts of nativism gave way to the early 20th century's racially-biased eugenics movement. Thankfully, "selective breeding," which is the idea that only certain people should reproduce in order to create chosen characteristics in offspring, and eugenics, arranged breeding, lost momentum during World War II. At that time, the Nazis' ethnic cleansing (killing people based on their ethnic or religious associations) atrocities were exposed.
Philosopher John Locke's tabula rasa theory from 1689 directly opposes the idea that we are born with innate knowledge. "Tabula rasa" means "blank slate" and implies that our minds do not have innate knowledge at birth.
Locke was an empiricist who believed that all the knowledge we gain in life comes from sensory experiences (using their senses to understand the world), education, and day-to-day encounters after being born.
Today, looking at nature vs. nature in black-and-white terms is considered a misguided dichotomy (two-part system). There are so many shades of gray where nature and nurture overlap. It's impossible to tease out how inherited traits and learned behaviors shape someone's unique characteristics or influence how their mind works.
The influences of nature and nurture in psychology are impossible to unravel. For example, imagine someone growing up in a household with an alcoholic parent who has frequent rage attacks. If that child goes on to develop a substance use disorder and has trouble with emotion regulation in adulthood, it's impossible to know precisely how much genetics (nature) or adverse childhood experiences (nurture) affected that individual's personality traits or issues with alcoholism.
Epigenetics Blurs the Line Between Nature and Nurture
"Epigenetics " means "on top of" genetics. It refers to external factors and experiences that turn genes "on" or "off." Epigenetic mechanisms alter DNA's physical structure in utero (in the womb) and across the human lifespan.
Epigenetics blurs the line between nature and nurture because it says that even after birth, our genetic material isn't set in stone; environmental factors can modify genes during one's lifetime. For example, cannabis exposure during critical windows of development can increase someone's risk of neuropsychiatric disease via epigenetic mechanisms.
Nature vs. nurture is a framework used to examine how genetics (nature) and environmental factors (nurture) influence human development and personality traits.
However, nature vs. nurture isn't a black-and-white issue; there are many shades of gray where the influence of nature and nurture overlap. It's impossible to disentangle how nature and nurture overlap; they are inextricably intertwined. In most cases, nature and nurture combine to make us who we are.
Waller JC. Commentary: the birth of the twin study--a commentary on francis galton’s “the history of twins.” International Journal of Epidemiology . 2012;41(4):913-917. doi:10.1093/ije/dys100
The New York Times. " Major Personality Study Finds That Traits Are Mostly Inherited ."
Medline Plus. Is temperament determined by genetics?
Feldman MW, Ramachandran S. Missing compared to what? Revisiting heritability, genes and culture . Phil Trans R Soc B . 2018;373(1743):20170064. doi:10.1098/rstb.2017.0064
Winch C. Innatism, concept formation, concept mastery and formal education: innatism, concept formation and formal education . Journal of Philosophy of Education . 2015;49(4):539-556. doi:10.1111/1467-9752.12121
Briley DA, Tucker-Drob EM. Genetic and environmental continuity in personality development: A meta-analysis . Psychological Bulletin . 2014;140(5):1303-1331. doi:10.1037/a0037091
Damian RI, Spengler M, Sutu A, Roberts BW. Sixteen going on sixty-six: A longitudinal study of personality stability and change across 50 years . Journal of Personality and Social Psychology . 2019;117(3):674-695. doi:10.1037/pspp0000210
Tin A, Bressler J, Simino J, et al. Genetic risk, midlife life’s simple 7, and incident dementia in the atherosclerosis risk in communities study . Neurology . Published online May 25, 2022. doi:10.1212/WNL.0000000000200520
Levitt M. Perceptions of nature, nurture and behaviour . Life Sci Soc Policy . 2013;9(1):13. doi:10.1186/2195-7819-9-13
Ross EJ, Graham DL, Money KM, Stanwood GD. Developmental consequences of fetal exposure to drugs: what we know and what we still must learn . Neuropsychopharmacology. 2015 Jan;40(1):61-87. doi: 10.1038/npp.2014.14
World Health Organization. Lead poisoning .
Bandura, A., Ross, D., & Ross, S. A. Transmission of aggression through imitation of aggressive models . The Journal of Abnormal and Social Psychology, 1961; 63 (3), 575–582 doi:10.1037/h0045925
Krapfl JE. Behaviorism and society . Behav Anal. 2016;39(1):123-9. doi:10.1007/s40614-016-0063-8
Bouchard TJ Jr, Lykken DT, McGue M, Segal NL, Tellegen A. Sources of human psychological differences: the Minnesota Study of Twins Reared Apart . Science. 1990 Oct 12;250(4978):223-8. doi: 10.1126/science.2218526
National Institutes of Health. Common genetic factors found in 5 mental disorders .
Franke HA. Toxic Stress: Effects, Prevention and Treatment . Children (Basel). 2014 Nov 3;1(3):390-402. doi: 10.3390/children1030390
Pain O, Hodgson K, Trubetskoy V, et al. Identifying the common genetic basis of antidepressant response . Biol Psychiatry Global Open Sci . 2022;2(2):115-126. doi:10.1016/j.bpsgos.2021.07.008
National Human Genome Research Institute. Eugenics and Scientific Racism .
OLL. The Works of John Locke in Nine Volumes .
Toraño EG, García MG, Fernández-Morera JL, Niño-García P, Fernández AF. The impact of external factors on the epigenome: in utero and over lifetime . BioMed Research International . 2016;2016:1-17. doi:10.1155/2016/2568635
Smith A, Kaufman F, Sandy MS, Cardenas A. Cannabis exposure during critical windows of development: epigenetic and molecular pathways implicated in neuropsychiatric disease . Curr Envir Health Rpt . 2020;7(3):325-342. doi:10.1007/s40572-020-00275-4
By Christopher Bergland Christopher Bergland is a retired ultra-endurance athlete turned medical writer and science reporter.
Nature vs. Nurture

The nature versus nurture debate is about the relative influence of an individual's innate attributes as opposed to the experiences from the environment one is brought up in, in determining individual differences in physical and behavioral traits. The philosophy that humans acquire all or most of their behavioral traits from "nurture" is known as tabula rasa ("blank slate").
In recent years, both types of factors have come to be recognized as playing interacting roles in development. So several modern psychologists consider the question naive and representing an outdated state of knowledge . The famous psychologist, Donald Hebb, is said to have once answered a journalist's question of "Which, nature or nurture, contributes more to personality?" by asking in response, "Which contributes more to the area of a rectangle, its length or its width?"
Comparison chart
Nature vs. nurture in the iq debate.
Evidence suggests that family environmental factors may have an effect upon childhood IQ, accounting for up to a quarter of the variance. On the other hand, by late adolescence this correlation disappears, such that adoptive siblings are no more similar in IQ than strangers. Moreover, adoption studies indicate that, by adulthood, adoptive siblings are no more similar in IQ than strangers (IQ correlation near zero), while full siblings show an IQ correlation of 0.6. Twin studies reinforce this pattern: monozygotic (identical) twins raised separately are highly similar in IQ (0.86), more so than dizygotic (fraternal) twins raised together (0.6) and much more than adoptive siblings (almost 0.0). Consequently, in the context of the "nature versus nurture" debate, the "nature" component appears to be much more important than the "nurture" component in explaining IQ variance in the general adult population of the United States .
The TEDx Talk below, featuring renowned entomologist Gene Robinson , discusses how the science of genomics strongly suggests both nature and nurture actively affect genomes, thus playing important roles in development and social behavior:
Nature vs. Nurture in Personality Traits
Personality is a frequently-cited example of a heritable trait that has been studied in twins and adoptions. Identical twins reared apart are far more similar in personality than randomly selected pairs of people. Likewise, identical twins are more similar than fraternal twins. Also, biological siblings are more similar in personality than adoptive siblings. Each observation suggests that personality is heritable to a certain extent.
However, these same study designs allow for the examination of environment as well as genes. Adoption studies also directly measure the strength of shared family effects. Adopted siblings share only family environment. Unexpectedly, some adoption studies indicate that by adulthood the personalities of adopted siblings are no more similar than random pairs of strangers. This would mean that shared family effects on personality wane off by adulthood. As is the case with personality, non-shared environmental effects are often found to out-weigh shared environmental effects. That is, environmental effects that are typically thought to be life-shaping (such as family life) may have less of an impact than non-shared effects, which are harder to identify.
Moral Considerations of the Nature vs. Nurture Debate

Some observers offer the criticism that modern science tends to give too much weight to the nature side of the argument, in part because of the potential harm that has come from rationalized racism. Historically, much of this debate has had undertones of racist and eugenicist policies — the notion of race as a scientific truth has often been assumed as a prerequisite in various incarnations of the nature versus nurture debate. In the past, heredity was often used as "scientific" justification for various forms of discrimination and oppression along racial and class lines. Works published in the United States since the 1960s that argue for the primacy of "nature" over "nurture" in determining certain characteristics, such as The Bell Curve, have been greeted with considerable controversy and scorn. A recent study conducted in 2012 has come up with the verdict that racism, after all, isn't innate.
A critique of moral arguments against the nature side of the argument could be that they cross the is-ought gap. That is, they apply values to facts. However, such appliance appears to construct reality. Belief in biologically determined stereotypes and abilities has been shown to increase the kind of behavior that is associated with such stereotypes and to impair intellectual performance through, among other things, the stereotype threat phenomenon.
The implications of this are brilliantly illustrated by the implicit association tests (IATs) out of Harvard . These, along with studies of the impact of self-identification with either positive or negative stereotypes and therefore "priming" good or bad effects, show that stereotypes, regardless of their broad statistical significance, bias the judgements and behaviours of members and non-members of the stereotyped groups.
Homosexuality
Being gay is now considered a genetic phenomenon rather than being influenced by the environment. This is based on observations such as:
- About 10% of the population is gay. This number is consistent across cultures throughout the world. If culture and society — i.e., nurture — were responsible for homosexuality, the percentage of population that is gay would vary across cultures.
- Studies of identical twins have shown that if one sibling is gay, the probability that the other sibling is also gay is greater than 50%.
More recent studies have indicated that both gender and sexuality are spectrums rather than strictly binary choices.
Epigenetics
Genetics is a complex and evolving field. A relatively newer idea in genetics is the epigenome . Changes happen to DNA molecules as other chemicals attach to genes or proteins in a cell. These changes constitute the epigenome. The epigenome regulates activity of cells by "turning genes off or on", i.e., by regulating which genes are expressed. This is why even though all cells have the same DNA (or genome), some cells grow into brain cells while others turn into liver and others into skin.
Epigenetics suggests a model for how the environment (nurture) may affect an individual by regulating the genome (nature). More information about epigenetics can be found here .
Philosophical Considerations of the Nature vs. Nurture Debate
Are the traits real.
It is sometimes a question whether the "trait" being measured is even a real thing. Much energy has been devoted to calculating the heritability of intelligence (usually the I.Q., or intelligence quotient), but there is still some disagreement as to what exactly "intelligence" is.
Determinism and Free Will
If genes do contribute substantially to the development of personal characteristics such as intelligence and personality, then many wonder if this implies that genes determine who we are. Biological determinism is the thesis that genes determine who we are. Few , if any, scientists would make such a claim; however, many are accused of doing so.
Others have pointed out that the premise of the "nature versus nurture" debate seems to negate the significance of free will. More specifically, if all our traits are determined by our genes, by our environment, by chance , or by some combination of these acting together, then there seems to be little room for free will. This line of reasoning suggests that the "nature versus nurture" debate tends to exaggerate the degree to which individual human behavior can be predicted based on knowledge of genetics and the environment. Furthermore, in this line of reasoning, it should also be pointed out that biology may determine our abilities, but free will still determines what we do with our abilities.
- Wikipedia: Nature versus nurture
- Nature vs Nurture: Racism isn't Innate - National Journal
- Nature vs. Nurture: The Debate on Psychological Development - YouTube
- Epigenetics - PBS
Related Comparisons

Share this comparison via:
If you read this far, you should follow us:
"Nature vs Nurture." Diffen.com. Diffen LLC, n.d. Web. 7 Apr 2024. < >
Comments: Nature vs Nurture
Anonymous comments (5).
October 10, 2012, 8:50am Somewhere, someone has to be scratching their head and saying...what about free will? What about man's ability to reason? Nature and nurture do not complete the picture. They are influences, but we should not reduce the human mind and spirit to such base concepts. — 69.✗.✗.87
September 13, 2012, 1:25pm we were assigned to be on the "nature" side, to defend it. and the information I got from here made me "encouraged" to win on our debate, and has provided me a chance of having a high grade tomorrow. thanks.. — 109.✗.✗.162
February 28, 2013, 7:28pm nature all the way — 170.✗.✗.19
June 18, 2009, 1:54pm we were assigned to be on the "nature" side, to defend it. and the information I got from here made me "encouraged" to win on our debate, and has provided me a chance of having a high grade tomorrow. thanks.. — 124.✗.✗.255
May 9, 2014, 2:03pm Nurture an nature can change becose it is unchangeble to the personality. — 141.✗.✗.231
- Fraternal Twins vs Identical Twins
- Psychiatry vs Psychology
- Genotype vs Phenotype
- Left Brain vs Right Brain
- Behaviourism vs Constructivism
- Anthropology vs Sociology
- Ethnicity vs Race
- Allele vs Gene
Edit or create new comparisons in your area of expertise.
Stay connected
© All rights reserved.
May 11, 2020
Will the Nature-Nurture Debate Ever End?
Biology writer Carl Zimmer answers questions on heredity, CRISPR, human enhancement, immortality and the coronavirus
By John Horgan

Karl Withakay Wikimedia (CC BY-SA 4.0)
This article was published in Scientific American’s former blog network and reflects the views of the author, not necessarily those of Scientific American
Back in the pre-pandemic era, I was really looking forward to April 8. On that date, Carl Zimmer was going to give a talk at my school, Stevens Institute of Technology, about his latest book, She Has Her Mother’s Laugh . For decades, Zimmer has reported on biology in The New York Times and other publications and in books, 13 so far . Mother’s Laugh tells the epic tale of our attempts to plumb the mysteries of heredity and to improve ourselves with that knowledge. The book is a marvelous work of history—Zimmer’s account of the early days of eugenics in the U.S. is especially gripping—as well as a detailed, up-to-date report on CRISPR and other advances that add urgency to old debates about human enhancement. Zimmer is an engaging story-teller and insatiable reporter, who visits scientists in their labs and even volunteers to be a subject. As a result, while discussing the remarkable diversity of creatures dwelling on and in our bodies, he can tell you that his own bellybutton harbors a bacterium, Marimonas , also found in the Mariana Trench. In lieu of Carl’s April 8 talk, here he answers questions about genetics and related topics. – John Horgan
Horgan: How did you end up in the science-writing racket, anyway? Any regrets?
Zimmer: I feel incredibly lucky to have this job. It wasn't anything I thought about with any foresight. I loved to write, and I loved science. A couple years out of college, I got a job as an assistant copy editor at the science magazine Discover . There, I got a great training in how to fact-check and report on science. I stayed there for ten years before heading out on my own.
On supporting science journalism
If you're enjoying this article, consider supporting our award-winning journalism by subscribing . By purchasing a subscription you are helping to ensure the future of impactful stories about the discoveries and ideas shaping our world today.
Horgan: Why the focus on biology? When you started out, wasn’t physics going to solve everything?
Zimmer: As a junior reporter at Discover , I had to write about all sorts of stuff--astronomy, geoscience, physics, technology, and so on. But I found that biology was always the field that managed to surprise me the most. Evolution has gone off in such crazy directions in the past four billion years, and the tools biologists have to study life have grown incredibly powerful over the past few decades.
Horgan: I sometimes worry I’m too mean to scientists. Do you ever worry you’re too nice?
Zimmer: As a fact-checker, you learn that no one should be given a pass. When I report on a story, I talk with outside experts to see if researchers I'm writing about are really delivering on what they claim. And it's also important to keep up with what social scientists and philosophers have to say--because science doesn't happen in a vacuum and can have dangerous consequences.
Horgan: What’s the biggest thing that’s happened in science since you started writing about it?
Zimmer: DNA sequencing. It changed everything, from the study of Neanderthals to tracking the covid-19 pandemic.
Horgan: In 2009 you quit the online chat show Bloggingheads.tv , on which we once spoke , because it gave a platform to creationists. Have your feelings about creationism evolved over the past decade?
Zimmer: No. Creationists have not done any good science since then, while evolutionary biology has leapt forward in dramatic fashion.
Horgan: Whenever I criticize scientific racism , or sexism , people call me an unscientific social justice warrior. I know this happens to you, too . How do you deal with these people?
Zimmer: People try to deflect from weak arguments by accusing their opponents of being contemptible.
Horgan: Is CRISPR living up to its hype? If so, will it help gene therapy, finally, take off?
Zimmer: CRISPR is already a mainstay of scientific research, for testing how genes work and how mutations affect health. It's already into clinical trials for diseases like sickle cell anemia just few years after its invention. We have yet to see how well it will work in those applications. But it's unquestionably one of the most important advances in the history of biology.
Horgan: By the time I reached the end of She Has Her Mother’s Laugh , I wasn’t sure whether you think genetic enhancement of humans is feasible, or desirable. Could you clarify?
Zimmer: I think anyone who pretends to have a simple answer is wrong. The answer depends not only on the complexity of biology, but also on what we really want from genetic enhancement. We are already carrying out genetic enhancement when parents with Huntington's disease pick embryos for IVF without the mutation. But I'm skeptical that any manipulation will affect, say, intelligence--certainly not more than what a decent education and a healthy childhood can offer.
Horgan: Will there be any more revolutions in our understanding of heredity?
Zimmer: It's not possible to predict revolutions that haven't happened. But I think that scientists will learn a lot about how epigenetic changes can be carried down through generations--if not in humans, then in other animals and plants.
Horgan: Will our knowledge ever be so complete that the nature/nurture debate finally ends?
Zimmer: I can't rule it out, but it won't be easy. It's relatively easy to study how genes influence variation, but the environment is so vast and complex it may not submit to simple experiments with clear results. Still, there are some very impressive experiments that are grappling with these challenges.
Horgan: Are radical life extension, and possibly immortality, feasible?
Zimmer: I'm not holding my breath. Aging is the result of so many factors that it's hard to see how any simple intervention can change it much. Immortality just seems biologically silly to me.
Horgan: I can’t resist asking: what do you think of the U.S. response to the coronavirus?
Zimmer: A disaster.
Further Reading :
Was Darwin Wrong ?
How Can We Curb the Spread of Scientific Racism?
Should Research on Race and IQ Be Banned ?
My Problem with “Taboo” Behavioral Genetics? The Science Stinks !
Quest for Intelligence Genes Turns Out More Dubious Results
Have Researchers Really Discovered Any Genes for Behavior ?
Defending Stephen Jay Gould’s Crusade Against Biological Determinism
Darwin Was Sexist, and So Are Many Modern Scientists
Do Women Want to be Oppressed ?
Google Engineer Fired for Sexist Memo Isn’t a Hero
See also my free, online book Mind-Body Problems: Science, Subjectivity & Who We Really Are , also available as a Kindle e-book and paperback.
Nature vs nurture debate is 'totally dead in science,' says neuroscientist

A doctor looks at PET brain scans in Phoenix on August 14, 2018. A big study to help Medicare officials decide whether to start covering brain scans to check for Alzheimer’s disease missed its goals for curbing emergency room visits and hospitalizations. The results announced on July 30, 2020 call into question whether the costly tests are worth it for a disease that currently has no cure.Our brains are incredibly nimble pieces of machinery, and are actively being rewired and rewritten in response to gathered experience. According to David Eagleman, a neuroscientist at Stanford University, the physical impact of this rewiring is so drastic that imaging is capable of distinguishing the motor cortex of a violinist from that of a pianist.
Eagleman is the author of the book Livewired: The Inside Story of the Ever-Changing Brain, and he walks us through how our daily habits — and forces including social feedback, shifting relevance and curiosity — can reshape our phenomenally-flexible and hardy brains.
Three Takeaways:
- Humans arrive in the world uniquely unfinished, unlike zebras or alligators, who are born knowing how to swim or walk (or figure it out within hours), according to Eagleman. Rather than coming “pre-programmed,” human babies absorb the culture, language, and movements of the world they observe, allowing them to springboard off the knowledge of those who have come before them.
- Eagleman has suggested the term “livewired” to describe the adaptability of the brain — a living system “rewriting its own circuitry every moment of your life.” He prefers this over brain plasticity, the term conventionally used to capture the brain’s flexibility, because he believes likening the brain’s adaptability to how plastic holds its shape mischaracterizes its dynamism.
- The internet’s impact on how children learn encourages Eagleman, who says the brain learns best and is the most flexible when it's curious. Children’s ability to now ask search engines questions, whenever inspiration strikes, has empowered them to receive instantaneous answers “right in the context of their curiosity.”
Nature vs. Nurture Debate In Psychology
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
The nature vs. nurture debate in psychology concerns the relative importance of an individual’s innate qualities (nature) versus personal experiences (nurture) in determining or causing individual differences in physical and behavioral traits. While early theories favored one factor over the other, contemporary views recognize a complex interplay between genes and environment in shaping behavior and development.
Key Takeaways
- Nature is what we think of as pre-wiring and is influenced by genetic inheritance and other biological factors.
- Nurture is generally taken as the influence of external factors after conception, e.g., the product of exposure, life experiences, and learning on an individual.
- Behavioral genetics has enabled psychology to quantify the relative contribution of nature and nurture concerning specific psychological traits.
- Instead of defending extreme nativist or nurturist views, most psychological researchers are now interested in investigating how nature and nurture interact in a host of qualitatively different ways.
- For example, epigenetics is an emerging area of research that shows how environmental influences affect the expression of genes.
The nature-nurture debate is concerned with the relative contribution that both influences make to human behavior, such as personality, cognitive traits, temperament and psychopathology.
Examples of Nature vs. Nurture
Nature vs. nurture in child development.
In child development, the nature vs. nurture debate is evident in the study of language acquisition . Researchers like Chomsky (1957) argue that humans are born with an innate capacity for language (nature), known as universal grammar, suggesting that genetics play a significant role in language development.
Conversely, the behaviorist perspective, exemplified by Skinner (1957), emphasizes the role of environmental reinforcement and learning (nurture) in language acquisition.
Twin studies have provided valuable insights into this debate, demonstrating that identical twins raised apart may share linguistic similarities despite different environments, suggesting a strong genetic influence (Bouchard, 1979)
However, environmental factors, such as exposure to language-rich environments, also play a crucial role in language development, highlighting the intricate interplay between nature and nurture in child development.
Nature vs. Nurture in Personality Development
The nature vs. nurture debate in personality psychology centers on the origins of personality traits. Twin studies have shown that identical twins reared apart tend to have more similar personalities than fraternal twins, indicating a genetic component to personality (Bouchard, 1994).
However, environmental factors, such as parenting styles, cultural influences, and life experiences, also shape personality.
For example, research by Caspi et al. (2003) demonstrated that a particular gene (MAOA) can interact with childhood maltreatment to increase the risk of aggressive behavior in adulthood.
This highlights that genetic predispositions and environmental factors contribute to personality development, and their interaction is complex and multifaceted.
Nature vs. Nurture in Mental Illness Development
The nature vs. nurture debate in mental health explores the etiology of depression. Genetic studies have identified specific genes associated with an increased vulnerability to depression, indicating a genetic component (Sullivan et al., 2000).
However, environmental factors, such as adverse life events and chronic stress during childhood, also play a significant role in the development of depressive disorders (Dube et al.., 2002; Keller et al., 2007)
The diathesis-stress model posits that individuals inherit a genetic predisposition (diathesis) to a disorder, which is then activated or exacerbated by environmental stressors (Monroe & Simons, 1991).
This model illustrates how nature and nurture interact to influence mental health outcomes.

Nature vs. Nurture of Intelligence
The nature vs. nurture debate in intelligence examines the relative contributions of genetic and environmental factors to cognitive abilities.
Intelligence is highly heritable, with about 50% of variance in IQ attributed to genetic factors, based on studies of twins, adoptees, and families (Plomin & Spinath, 2004).
Heritability of intelligence increases with age, from about 20% in infancy to as high as 80% in adulthood, suggesting amplifying effects of genes over time.
However, environmental influences, such as access to quality education and stimulating environments, also significantly impact intelligence.
Shared environmental influences like family background are more influential in childhood, whereas non-shared experiences are more important later in life.
Research by Flynn (1987) showed that average IQ scores have increased over generations, suggesting that environmental improvements, known as the Flynn effect , can lead to substantial gains in cognitive abilities.
Molecular genetics provides tools to identify specific genes and understand their pathways and interactions. However, progress has been slow for complex traits like intelligence. Identified genes have small effect sizes (Plomin & Spinath, 2004).
Overall, intelligence results from complex interplay between genes and environment over development. Molecular genetics offers promise to clarify these mechanisms. The nature vs nurture debate is outdated – both play key roles.
Nativism (Extreme Nature Position)
It has long been known that certain physical characteristics are biologically determined by genetic inheritance.
Color of eyes, straight or curly hair, pigmentation of the skin, and certain diseases (such as Huntingdon’s chorea) are all a function of the genes we inherit.
These facts have led many to speculate as to whether psychological characteristics such as behavioral tendencies, personality attributes, and mental abilities are also “wired in” before we are even born.
Those who adopt an extreme hereditary position are known as nativists. Their basic assumption is that the characteristics of the human species as a whole are a product of evolution and that individual differences are due to each person’s unique genetic code.
In general, the earlier a particular ability appears, the more likely it is to be under the influence of genetic factors. Estimates of genetic influence are called heritability.
Examples of extreme nature positions in psychology include Chomsky (1965), who proposed language is gained through the use of an innate language acquisition device. Another example of nature is Freud’s theory of aggression as being an innate drive (called Thanatos).
Characteristics and differences that are not observable at birth, but which emerge later in life, are regarded as the product of maturation. That is to say, we all have an inner “biological clock” which switches on (or off) types of behavior in a pre-programmed way.
The classic example of the way this affects our physical development are the bodily changes that occur in early adolescence at puberty.
However, nativists also argue that maturation governs the emergence of attachment in infancy , language acquisition , and even cognitive development .
Empiricism (Extreme Nurture Position)
At the other end of the spectrum are the environmentalists – also known as empiricists (not to be confused with the other empirical/scientific approach ).
Their basic assumption is that at birth, the human mind is a tabula rasa (a blank slate) and that this is gradually “filled” as a result of experience (e.g., behaviorism ).
From this point of view, psychological characteristics and behavioral differences that emerge through infancy and childhood are the results of learning. It is how you are brought up (nurture) that governs the psychologically significant aspects of child development and the concept of maturation applies only to the biological.
For example, Bandura’s (1977) social learning theory states that aggression is learned from the environment through observation and imitation. This is seen in his famous bobo doll experiment (Bandura, 1961).

Also, Skinner (1957) believed that language is learned from other people via behavior-shaping techniques.
Evidence for Nature
- Biological Approach
- Biology of Gender
- Medical Model
Freud (1905) stated that events in our childhood have a great influence on our adult lives, shaping our personality.
He thought that parenting is of primary importance to a child’s development , and the family as the most important feature of nurture was a common theme throughout twentieth-century psychology (which was dominated by environmentalists’ theories).
Behavioral Genetics
Researchers in the field of behavioral genetics study variation in behavior as it is affected by genes, which are the units of heredity passed down from parents to offspring.
“We now know that DNA differences are the major systematic source of psychological differences between us. Environmental effects are important but what we have learned in recent years is that they are mostly random – unsystematic and unstable – which means that we cannot do much about them.” Plomin (2018, xii)
Behavioral genetics has enabled psychology to quantify the relative contribution of nature and nurture with regard to specific psychological traits. One way to do this is to study relatives who share the same genes (nature) but a different environment (nurture). Adoption acts as a natural experiment which allows researchers to do this.
Empirical studies have consistently shown that adoptive children show greater resemblance to their biological parents, rather than their adoptive, or environmental parents (Plomin & DeFries, 1983; 1985).
Another way of studying heredity is by comparing the behavior of twins, who can either be identical (sharing the same genes) or non-identical (sharing 50% of genes). Like adoption studies, twin studies support the first rule of behavior genetics; that psychological traits are extremely heritable, about 50% on average.
The Twins in Early Development Study (TEDS) revealed correlations between twins on a range of behavioral traits, such as personality (empathy and hyperactivity) and components of reading such as phonetics (Haworth, Davis, Plomin, 2013; Oliver & Plomin, 2007; Trouton, Spinath, & Plomin, 2002).
Implications
Jenson (1969) found that the average I.Q. scores of black Americans were significantly lower than whites he went on to argue that genetic factors were mainly responsible – even going so far as to suggest that intelligence is 80% inherited.
The storm of controversy that developed around Jenson’s claims was not mainly due to logical and empirical weaknesses in his argument. It was more to do with the social and political implications that are often drawn from research that claims to demonstrate natural inequalities between social groups.
For many environmentalists, there is a barely disguised right-wing agenda behind the work of the behavioral geneticists. In their view, part of the difference in the I.Q. scores of different ethnic groups are due to inbuilt biases in the methods of testing.
More fundamentally, they believe that differences in intellectual ability are a product of social inequalities in access to material resources and opportunities. To put it simply children brought up in the ghetto tend to score lower on tests because they are denied the same life chances as more privileged members of society.
Now we can see why the nature-nurture debate has become such a hotly contested issue. What begins as an attempt to understand the causes of behavioral differences often develops into a politically motivated dispute about distributive justice and power in society.
What’s more, this doesn’t only apply to the debate over I.Q. It is equally relevant to the psychology of sex and gender , where the question of how much of the (alleged) differences in male and female behavior is due to biology and how much to culture is just as controversial.
Polygenic Inheritance
Rather than the presence or absence of single genes being the determining factor that accounts for psychological traits, behavioral genetics has demonstrated that multiple genes – often thousands, collectively contribute to specific behaviors.
Thus, psychological traits follow a polygenic mode of inheritance (as opposed to being determined by a single gene). Depression is a good example of a polygenic trait, which is thought to be influenced by around 1000 genes (Plomin, 2018).
This means a person with a lower number of these genes (under 500) would have a lower risk of experiencing depression than someone with a higher number.
The Nature of Nurture
Nurture assumes that correlations between environmental factors and psychological outcomes are caused environmentally. For example, how much parents read with their children and how well children learn to read appear to be related. Other examples include environmental stress and its effect on depression.
However, behavioral genetics argues that what look like environmental effects are to a large extent really a reflection of genetic differences (Plomin & Bergeman, 1991).
People select, modify and create environments correlated with their genetic disposition. This means that what sometimes appears to be an environmental influence (nurture) is a genetic influence (nature).
So, children that are genetically predisposed to be competent readers, will be happy to listen to their parents read them stories, and be more likely to encourage this interaction.
Interaction Effects
However, in recent years there has been a growing realization that the question of “how much” behavior is due to heredity and “how much” to the environment may itself be the wrong question.
Take intelligence as an example. Like almost all types of human behavior, it is a complex, many-sided phenomenon which reveals itself (or not!) in a great variety of ways.
The “how much” question assumes that psychological traits can all be expressed numerically and that the issue can be resolved in a quantitative manner.
Heritability statistics revealed by behavioral genetic studies have been criticized as meaningless, mainly because biologists have established that genes cannot influence development independently of environmental factors; genetic and nongenetic factors always cooperate to build traits. The reality is that nature and culture interact in a host of qualitatively different ways (Gottlieb, 2007; Johnston & Edwards, 2002).
Instead of defending extreme nativist or nurturist views, most psychological researchers are now interested in investigating how nature and nurture interact.
For example, in psychopathology , this means that both a genetic predisposition and an appropriate environmental trigger are required for a mental disorder to develop. For example, epigenetics state that environmental influences affect the expression of genes.
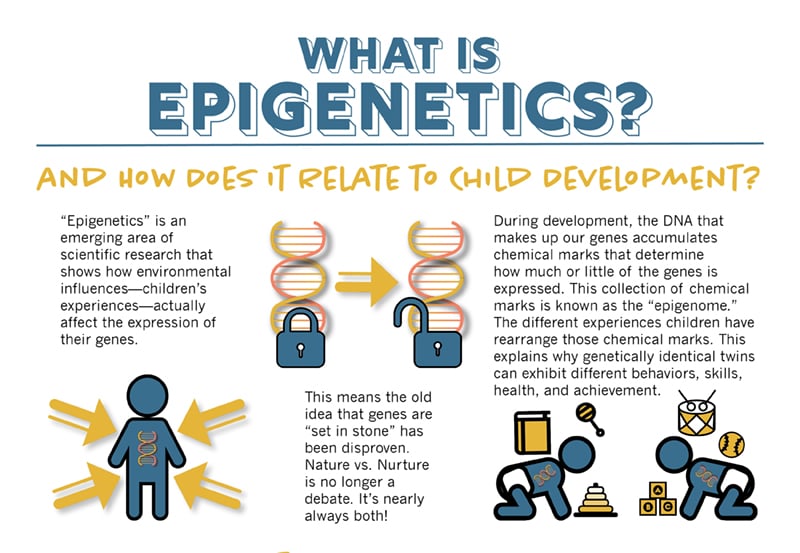
What is Epigenetics?
Epigenetics is the term used to describe inheritance by mechanisms other than through the DNA sequence of genes. For example, features of a person’s physical and social environment can effect which genes are switched-on, or “expressed”, rather than the DNA sequence of the genes themselves.
Stressors and memories can be passed through small RNA molecules to multiple generations of offspring in ways that meaningfully affect their behavior.
One such example is what is known as the Dutch Hunger Winter, during last year of the Second World War. What they found was that children who were in the womb during the famine experienced a life-long increase in their chances of developing various health problems compared to children conceived after the famine.
Epigenetic effects can sometimes be passed from one generation to the next, although the effects only seem to last for a few generations. There is some evidence that the effects of the Dutch Hunger Winter affected grandchildren of women who were pregnant during the famine.
Therefore, it makes more sense to say that the difference between two people’s behavior is mostly due to hereditary factors or mostly due to environmental factors.
This realization is especially important given the recent advances in genetics, such as polygenic testing. The Human Genome Project, for example, has stimulated enormous interest in tracing types of behavior to particular strands of DNA located on specific chromosomes.
If these advances are not to be abused, then there will need to be a more general understanding of the fact that biology interacts with both the cultural context and the personal choices that people make about how they want to live their lives.
There is no neat and simple way of unraveling these qualitatively different and reciprocal influences on human behavior.
Epigenetics: Licking Rat Pups
Michael Meaney and his colleagues at McGill University in Montreal, Canada conducted the landmark epigenetic study on mother rats licking and grooming their pups.
This research found that the amount of licking and grooming received by rat pups during their early life could alter their epigenetic marks and influence their stress responses in adulthood.
Pups that received high levels of maternal care (i.e., more licking and grooming) had a reduced stress response compared to those that received low levels of maternal care.
Meaney’s work with rat maternal behavior and its epigenetic effects has provided significant insights into the understanding of early-life experiences, gene expression, and adult behavior.
It underscores the importance of the early-life environment and its long-term impacts on an individual’s mental health and stress resilience.
Epigenetics: The Agouti Mouse Study
Waterland and Jirtle’s 2003 study on the Agouti mouse is another foundational work in the field of epigenetics that demonstrated how nutritional factors during early development can result in epigenetic changes that have long-lasting effects on phenotype.
In this study, they focused on a specific gene in mice called the Agouti viable yellow (A^vy) gene. Mice with this gene can express a range of coat colors, from yellow to mottled to brown.
This variation in coat color is related to the methylation status of the A^vy gene: higher methylation is associated with the brown coat, and lower methylation with the yellow coat.
Importantly, the coat color is also associated with health outcomes, with yellow mice being more prone to obesity, diabetes, and tumorigenesis compared to brown mice.
Waterland and Jirtle set out to investigate whether maternal diet, specifically supplementation with methyl donors like folic acid, choline, betaine, and vitamin B12, during pregnancy could influence the methylation status of the A^vy gene in offspring.
Key findings from the study include:
Dietary Influence : When pregnant mice were fed a diet supplemented with methyl donors, their offspring had an increased likelihood of having the brown coat color. This indicated that the supplemented diet led to an increased methylation of the A^vy gene.
Health Outcomes : Along with the coat color change, these mice also had reduced risks of obesity and other health issues associated with the yellow phenotype.
Transgenerational Effects : The study showed that nutritional interventions could have effects that extend beyond the individual, affecting the phenotype of the offspring.
The implications of this research are profound. It highlights how maternal nutrition during critical developmental periods can have lasting effects on offspring through epigenetic modifications, potentially affecting health outcomes much later in life.
The study also offers insights into how dietary and environmental factors might contribute to disease susceptibility in humans.
Bandura, A. Ross, D., & Ross, S. A. (1961). Transmission of aggression through the imitation of aggressive models. Journal of Abnormal and Social Psychology , 63, 575-582
Bandura, A. (1977). Social learning theory . Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Bouchard, T. J. (1994). Genes, Environment, and Personality. Science, 264 (5166), 1700-1701.
Bowlby, J. (1969). Attachment. Attachment and loss: Vol. 1. Loss . New York: Basic Books.
Caspi, A., Sugden, K., Moffitt, T. E., Taylor, A., Craig, I. W., Harrington, H., … & Poulton, R. (2003). Influence of life stress on depression: moderation by a polymorphism in the 5-HTT gene. Science , 301 (5631), 386-389.
Chomsky, N. (1957). Syntactic structures. Mouton de Gruyter.
Chomsky, N. (1965). Aspects of the theory of syntax . MIT Press.
Dube, S. R., Anda, R. F., Felitti, V. J., Edwards, V. J., & Croft, J. B. (2002). Adverse childhood experiences and personal alcohol abuse as an adult. Addictive Behaviors , 27 (5), 713-725.
Flynn, J. R. (1987). Massive IQ gains in 14 nations: What IQ tests really measure. Psychological Bulletin , 101 (2), 171.
Freud, S. (1905). Three essays on the theory of sexuality . Se, 7.
Galton, F. (1883). Inquiries into human faculty and its development . London: J.M. Dent & Co.
Gottlieb, G. (2007). Probabilistic epigenesis. Developmental Science, 10 , 1–11.
Haworth, C. M., Davis, O. S., & Plomin, R. (2013). Twins Early Development Study (TEDS): a genetically sensitive investigation of cognitive and behavioral development from childhood to young adulthood . Twin Research and Human Genetics, 16(1) , 117-125.
Jensen, A. R. (1969). How much can we boost I.Q. and scholastic achievement? Harvard Educational Review, 33 , 1-123.
Johnston, T. D., & Edwards, L. (2002). Genes, interactions, and the development of behavior . Psychological Review , 109, 26–34.
Keller, M. C., Neale, M. C., & Kendler, K. S. (2007). Association of different adverse life events with distinct patterns of depressive symptoms. American Journal of Psychiatry , 164 (10), 1521-1529.
Monroe, S. M., & Simons, A. D. (1991). Diathesis-stress theories in the context of life stress research: implications for the depressive disorders. Psychological Bulletin , 110 (3), 406.
Oliver, B. R., & Plomin, R. (2007). Twins” Early Development Study (TEDS): A multivariate, longitudinal genetic investigation of language, cognition and behavior problems from childhood through adolescence . Twin Research and Human Genetics, 10(1) , 96-105.
Petrill, S. A., Plomin, R., Berg, S., Johansson, B., Pedersen, N. L., Ahern, F., & McClearn, G. E. (1998). The genetic and environmental relationship between general and specific cognitive abilities in twins age 80 and older. Psychological Science , 9 (3), 183-189.
Plomin, R., & Petrill, S. A. (1997). Genetics and intelligence: What’s new?. Intelligence , 24 (1), 53-77.
Plomin, R. (2018). Blueprint: How DNA makes us who we are . MIT Press.
Plomin, R., & Bergeman, C. S. (1991). The nature of nurture: Genetic influence on “environmental” measures. behavioral and Brain Sciences, 14(3) , 373-386.
Plomin, R., & DeFries, J. C. (1983). The Colorado adoption project. Child Development , 276-289.
Plomin, R., & DeFries, J. C. (1985). The origins of individual differences in infancy; the Colorado adoption project. Science, 230 , 1369-1371.
Plomin, R., & Spinath, F. M. (2004). Intelligence: genetics, genes, and genomics. Journal of personality and social psychology , 86 (1), 112.
Plomin, R., & Von Stumm, S. (2018). The new genetics of intelligence. Nature Reviews Genetics , 19 (3), 148-159.
Skinner, B. F. (1957). Verbal behavior . Acton, MA: Copley Publishing Group.
Sullivan, P. F., Neale, M. C., & Kendler, K. S. (2000). Genetic epidemiology of major depression: review and meta-analysis. American Journal of Psychiatry , 157 (10), 1552-1562.
Szyf, M., Weaver, I. C., Champagne, F. A., Diorio, J., & Meaney, M. J. (2005). Maternal programming of steroid receptor expression and phenotype through DNA methylation in the rat . Frontiers in neuroendocrinology , 26 (3-4), 139-162.
Trouton, A., Spinath, F. M., & Plomin, R. (2002). Twins early development study (TEDS): a multivariate, longitudinal genetic investigation of language, cognition and behavior problems in childhood . Twin Research and Human Genetics, 5(5) , 444-448.
Waterland, R. A., & Jirtle, R. L. (2003). Transposable elements: targets for early nutritional effects on epigenetic gene regulation . Molecular and cellular biology, 23 (15), 5293-5300.
Further Information
- Genetic & Environmental Influences on Human Psychological Differences
Evidence for Nurture
- Classical Conditioning
- Little Albert Experiment
- Operant Conditioning
- Behaviorism
- Social Learning Theory
- Bronfenbrenner’s Ecological Systems Theory
- Social Roles
- Attachment Styles
- The Hidden Links Between Mental Disorders
- Visual Cliff Experiment
- Behavioral Genetics, Genetics, and Epigenetics
- Epigenetics
- Is Epigenetics Inherited?
- Physiological Psychology
- Bowlby’s Maternal Deprivation Hypothesis
- So is it nature not nurture after all?
Evidence for an Interaction
- Genes, Interactions, and the Development of Behavior
- Agouti Mouse Study
- Biological Psychology
What does nature refer to in the nature vs. nurture debate?
In the nature vs. nurture debate, “nature” refers to the influence of genetics, innate qualities, and biological factors on human development, behavior, and traits. It emphasizes the role of hereditary factors in shaping who we are.
What does nurture refer to in the nature vs. nurture debate?
In the nature vs. nurture debate, “nurture” refers to the influence of the environment, upbringing, experiences, and social factors on human development, behavior, and traits. It emphasizes the role of external factors in shaping who we are.
Why is it important to determine the contribution of heredity (nature) and environment (nurture) in human development?
Determining the contribution of heredity and environment in human development is crucial for understanding the complex interplay between genetic factors and environmental influences. It helps identify the relative significance of each factor, informing interventions, policies, and strategies to optimize human potential and address developmental challenges.

Nature vs. Nurture
Reviewed by Psychology Today Staff
The expression “nature vs. nurture” describes the question of how much a person's characteristics are formed by either “nature” or “nurture.” “Nature” means innate biological factors (namely genetics ), while “nurture” can refer to upbringing or life experience more generally.
Traditionally, “nature vs. nurture” has been framed as a debate between those who argue for the dominance of one source of influence or the other, but contemporary experts acknowledge that both “nature” and “nurture” play a role in psychological development and interact in complex ways.
- The Meaning of Nature vs. Nurture
- The Nature-vs.-Nurture Debate
- Identifying Genetic and Environmental Factors

The wording of the phrase “nature vs. nurture” makes it seem as though human individuality— personality traits, intelligence , preferences, and other characteristics—must be based on either the genes people are born with or the environment in which they grew up. The reality, as scientists have shown, is more complicated, and both these and other factors can help account for the many ways in which individuals differ from each other.
The words “nature” and “nurture” themselves can be misleading. Today, “ genetics ” and “environment” are frequently used in their place—with one’s environment including a broader range of experiences than just the nurturing received from parents or caregivers. Further, nature and nurture (or genetics and environment) do not simply compete to influence a person, but often interact with each other; “nature and nurture” work together. Finally, individual differences do not entirely come down to a person’s genetic code or developmental environment—to some extent, they emerge due to messiness in the process of development as well.
A person’s biological nature can affect a person’s experience of the environment. For example, a person with a genetic disposition toward a particular trait, such as aggressiveness, may be more likely to have particular life experiences (including, perhaps, receiving negative reactions from parents or others). Or, a person who grows up with an inclination toward warmth and sociability may seek out and elicit more positive social responses from peers. These life experiences could, in turn, reinforce an individual’s initial tendencies. Nurture or life experience more generally may also modify the effects of nature—for example, by expanding or limiting the extent to which a naturally bright child receives encouragement, access to quality education , and opportunities for achievement.
Epigenetics—the science of modifications in how genes are expressed— illustrates the complex interplay between “nature” and “nurture.” An individual’s environment, including factors such as early-life adversity, may result in changes in the way that parts of a person’s genetic code are “read.” While these epigenetic changes do not override the important influence of genes in general, they do constitute additional ways in which that influence is filtered through “nurture” or the environment.

Theorists and researchers have long battled over whether individual traits and abilities are inborn or are instead forged by experiences after birth. The debate has had broad implications: The real or perceived sources of a person’s strengths and vulnerabilities matter for fields such as education, philosophy , psychiatry , and clinical psychology. Today’s consensus—that individual differences result from a combination of inherited and non-genetic factors—strikes a more nuanced middle path between nature- or nurture-focused extremes.
The debate about nature and nurture has roots that stretch back at least thousands of years, to Ancient Greek theorizing about the causes of personality. During the modern era, theories emphasizing the role of either learning and experience or biological nature have risen and fallen in prominence—with genetics gaining increasing acknowledgment as an important (though not exclusive) influence on individual differences in the later 20th century and beyond.
“Nature versus nurture” was used by English scientist Francis Galton. In 1874, he published the book English Men of Science: Their Nature and Nurture , arguing that inherited factors were responsible for intelligence and other characteristics.
Genetic determinism emphasizes the importance of an individual’s nature in development. It is the view that genetics is largely or totally responsible for an individual’s psychological characteristics and behavior. The term “biological determinism” is often used synonymously.
The blank slate (or “tabula rasa”) view of the mind emphasizes the importance of nurture and the environment. Notably described by English philosopher John Locke in the 1600s, it proposed that individuals are born with a mind like an unmarked chalkboard and that its contents are based on experience and learning. In the 20th century, major branches of psychology proposed a primary role for nurture and experience , rather than nature, in development, including Freudian psychoanalysis and behaviorism.

Modern scientific methods have allowed researchers to advance further in understanding the complex relationships between genetics, life experience, and psychological characteristics, including mental health conditions and personality traits. Overall, the findings of contemporary studies underscore that with some exceptions—such as rare diseases caused by mutations in a single gene—no one factor, genetic or environmental, solely determines how a characteristic develops.
Scientists use multiple approaches to estimate how important genetics are for any given trait, but one of the most influential is the twin study. While identical (or monozygotic) twins share the same genetic code, fraternal (or dizygotic) twins share about 50 percent of the same genes, like typical siblings. Scientists are able to estimate the degree to which the variation in a particular trait, like extraversion , is explained by genetics in part by analyzing how similar identical twins are on that trait, compared to fraternal twins. ( These studies do have limitations, and estimates based on one population may not closely reflect all other populations.)
It’s hard to call either “nature” or “nurture,” genes or the environment, more important to human psychology. The impact of one set of factors or the other depends on the characteristic, with some being more strongly related to one’s genes —for instance, autism appears to be more heritable than depression . But in general, psychological traits are shaped by a balance of interacting genetic and non-genetic influences.
Both genes and environmental factors can contribute to a person developing mental illness. Research finds that a major part of the variation in the risk for psychiatric conditions such as autism spectrum disorder, anxiety disorders, depression, and schizophrenia can be attributed to genetic differences. But not all of that risk is genetic, and life experiences, such as early-life abuse or neglect, may also affect risk of mental illness (and some individuals, based on their genetics, are likely more susceptible to environmental effects than others).
Like other psychological characteristics, personality is partly heritable. Research suggests less than half of the difference between people on measures of personality traits can be attributed to genes (one recent overall estimate is 40 percent). Non-genetic factors appear to be responsible for an equal or greater portion of personality differences between individuals. Some theorize that the social roles people adopt and invest in as they mature are among the more important non-genetic factors in personality development.

How do we make sense of new experiences? Ultimately, it's about how we categorize them—which we often do by "lumping" or "splitting" them.

How are twin studies used to answer questions related to the nature-and-nurture debate?

All I ask of strangers in the store—don't judge me as being less competent because my hair is grey and my skin well-textured. I’m just out doing my best, as we all are.

The new Biophilia Reactivity Hypothesis argues our attraction to the natural world is not an instinct but a measurable temperament trait.

A Personal Perspective: How can Adam Grant's newest book help OCD sufferers? In more ways than you think.

Do selfish genes mean that humans are designed to be selfish?

Are classical musicians more "craft" and jazz musicians more "creative"? A question for debate.
Where all beliefs and behavior come from.
Many people will outlive their money because of not saving for the future. Sadly, many people are also going to run out of health before they run out of life. Here's how not to.

Our cultures shape us in profound ways. The latest research from cultural psychology offers fascinating insights into the nature-nurture interaction.
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Support Group
- International
- New Zealand
- South Africa
- Switzerland
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Therapy Center NEW
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

Understanding what emotional intelligence looks like and the steps needed to improve it could light a path to a more emotionally adept world.
- Coronavirus Disease 2019
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience
- Subject List
- Take a Tour
- For Authors
- Subscriber Services
- Publications
- African American Studies
- African Studies
- American Literature
- Anthropology
- Architecture Planning and Preservation
- Art History
- Atlantic History
- Biblical Studies
- British and Irish Literature
- Childhood Studies
- Chinese Studies
- Cinema and Media Studies
- Communication
- Criminology
- Environmental Science
- Evolutionary Biology
- International Law
- International Relations
- Islamic Studies
- Jewish Studies
- Latin American Studies
- Latino Studies
- Linguistics
- Literary and Critical Theory
- Medieval Studies
- Military History
- Political Science
- Public Health
- Renaissance and Reformation
- Social Work
- Urban Studies
- Victorian Literature
- Browse All Subjects
How to Subscribe
- Free Trials
In This Article Expand or collapse the "in this article" section Nature versus Nurture Debate in Psychology
Introduction, general overviews.
- Conceptual Problems
- Biological Constraints, Predispositions, and Preparedness in Learning
- Critical Periods
- Innate Knowledge
- Heritability
- Behavioral Epigenetics
Related Articles Expand or collapse the "related articles" section about
About related articles close popup.
Lorem Ipsum Sit Dolor Amet
Vestibulum ante ipsum primis in faucibus orci luctus et ultrices posuere cubilia Curae; Aliquam ligula odio, euismod ut aliquam et, vestibulum nec risus. Nulla viverra, arcu et iaculis consequat, justo diam ornare tellus, semper ultrices tellus nunc eu tellus.
- Developmental Psychology (Cognitive)
- Developmental Psychology (Social)
- Evolutionary Psychology
- Life-Span Development
Other Subject Areas
Forthcoming articles expand or collapse the "forthcoming articles" section.
- Data Visualization
- Remote Work
- Workforce Training Evaluation
- Find more forthcoming articles...
- Export Citations
- Share This Facebook LinkedIn Twitter
Nature versus Nurture Debate in Psychology by Hunter Honeycutt LAST MODIFIED: 12 January 2023 DOI: 10.1093/obo/9780199828340-0305
The nature-nurture dichotomy is a long-standing and pervasive framework for thinking about the causal influences believed to be operating during individual development. In this dichotomy, nature refers to factors (e.g., genes, genetic programs, and/or biological blueprints) or forces (e.g., heredity and/or maturation) inherent to the individual that predetermine the development of form and function. Nurture generally refers to all the remaining, typically “external,” causal factors (e.g., physical and social conditions) and processes (e.g., learning and experience) that influence development. The nature versus nurture debate in psychology deals with disagreements about the extent to which the development of traits in humans and animals reflects the relative influence of nature and nurture. It is commonly stated that psychologists have moved on from asking whether traits (or variation in traits) develop from nature or nurture, to recognize instead that both nature and nurture work together or “interact” to produce outcomes, although exactly how to view the interaction is a matter of much debate. While acknowledging the interaction of nature and nurture, one’s theoretical models and research focus might emphasize the prominence of one over the other. Thus, nativists focus more on the importance of innate factors or forces operating on development, whereas empiricists focus more on experiential or environmental factors. However, not everyone finds value in thinking about development in terms of nature and nurture. By the middle of the twentieth century, some psychologists, biologists, and philosophers began to view nature-nurture as a conceptually deficient and biologically implausible dichotomy that oversimplifies the dynamics of behavior and development. Such people espouse some variant of “developmental systems theory” and seek to eliminate or otherwise fuse the nature-nurture division.
The works in this section are mostly trade books that provide general introductions to the nature-nurture debate across a variety of topical areas in psychology, all of which would be suitable for use in classes with undergraduate students at all levels. Goldhaber 2012 contrasts four popular perspectives on the nature-nurture issue and would be a good place to start for anyone unfamiliar with the nature-nurture debate in psychology. Nativist perspectives are represented by Pinker 2002 , Plomin 2018 , and Vallortigara 2021 . An empiricist-leaning position on behavior development is put forth in Schneider 2012 . Developmental systems theory is promoted in Blumberg 2005 and Moore 2002 . Two edited books are included and both are better suited for advanced undergraduate- or graduate-level students. The first edited book, Coll, et al. 2013 , focuses on the nature-nurture issue across a range of topics and perspectives in psychology. The other, Mayes and Lewis 2012 , presents empiricist (or environmentalist) perspectives on child development.
Bateson, P. 2017. Behaviour, development and evolution . Cambridge, UK: OpenBook Publishers.
DOI: 10.11647/OBP.0097
Written by a distinguished ethologist who draws extensively from his work on animal behavior, this book argues that the nature-nurture division is neither valid nor helpful in capturing the complex system of factors that influence behavioral development. Topics include imprinting and attachment, parent-offspring relations, the influence of early-life experiences on later-life outcomes, problems with genetic determinism, and the role of behavior in evolutionary change.
Blumberg, M. S. 2005. Basic instinct: The genesis of novel behavior . New York: Thunder’s Mouth Press.
Consistent with developmental systems theory, Blumberg presents an overview of the conceptual and empirical limitations of nativism in explanations of behavioral and neural development in animals and cognitive development in humans.
Coll, C. G., E. L. Bearer, and R. M. Lerner, eds. 2013. Nature-nurture: The complex interplay of genetic and environmental influences on human behavior and development . New York: Psychology Press.
The contents of this edited volume are almost entirely original works with commentary that span multiple disciplines (psychology, biology, economics, philosophy) and multiple perspectives (behavioral genetics and developmental systems theory) on the nature-nurture issue.
Goldhaber, D. 2012. The nature-nurture debates: Bridging the gap . Cambridge, UK: Cambridge Univ. Press.
DOI: 10.1017/CBO9781139022583
Goldhaber reviews four major perspectives (behavior genetics, environmentalism, evolutionary psychology, and developmental systems theory) on the nature-nurture issue. He argues we should reject reductionist views based on either genetic determinism or environmental determinism in favor of more holistic, interactionist approaches.
Mayes, L. C., and M. Lewis, eds. 2012. The Cambridge handbook of environment in human development . Cambridge, UK: Cambridge Univ. Press.
This handbook explores a wide variety of ways in which the environment influences child development. Chapters cover conceptual frameworks and methodological issues in thinking about and studying environmental influences as well reviewing ways in which environmental contexts and systems influence specific aspects of child development.
Moore, D. S. 2002. The dependent gene: The fallacy of nature vs. nurture . New York: Henry Holt.
This book provides an introduction to the developmental systems theory take on the nature-nurture issue particularly as it relates to genetic determinism, heritability and heredity.
Pinker, S. 2002. The blank slate: The modern denial of human nature . New York: Viking.
In this best-selling book, Pinker draws on evidence from behavioral genetics, evolutionary psychology, and cognitive psychology to argue for a nativist position concerning human nature.
Plomin, R. 2018. Blueprint: How DNA makes us who we are . Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Plomin reviews traditional and more modern evidence from behavioral genetics to argue that genes are the primary factor in bringing about psychological differences between people. Moreover, he argues that many “environmental” factors operating on development are themselves strongly influenced by genetic differences.
Schneider, S. M. 2012. The science of consequences: How they affect genes, change the brain, and impact our world . Amherst, NY: Prometheus Books.
Schneider presents a view grounded in behavior analysis to argue for the critical role that the consequences of genetic activity, neural activity, and behavioral activity play in individual development. While emphasizing environmental (or experiential) factors influencing development, this book also highlights the systemic and interactive nature of developmental systems across multiple levels of analysis.
Vallortigara, G. 2021. Born knowing: Imprinting and the origins of knowledge . Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
DOI: 10.7551/mitpress/14091.001.0001
Drawing upon research in comparative cognition and comparative neuroscience, much of it his own, Vallortigara argues that animals, including humans, enter the world with a set of unlearned, innate or instinctive behaviors and neural circuits that bias or predispose subsequent learning and development.
back to top
Users without a subscription are not able to see the full content on this page. Please subscribe or login .
Oxford Bibliographies Online is available by subscription and perpetual access to institutions. For more information or to contact an Oxford Sales Representative click here .
- About Psychology »
- Meet the Editorial Board »
- Abnormal Psychology
- Academic Assessment
- Acculturation and Health
- Action Regulation Theory
- Action Research
- Addictive Behavior
- Adolescence
- Adoption, Social, Psychological, and Evolutionary Perspect...
- Advanced Theory of Mind
- Affective Forecasting
- Affirmative Action
- Ageism at Work
- Allport, Gordon
- Alzheimer’s Disease
- Ambulatory Assessment in Behavioral Science
- Analysis of Covariance (ANCOVA)
- Animal Behavior
- Animal Learning
- Anxiety Disorders
- Art and Aesthetics, Psychology of
- Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and Psychology
- Assessment and Clinical Applications of Individual Differe...
- Attachment in Social and Emotional Development across the ...
- Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) in Adults
- Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) in Childre...
- Attitudinal Ambivalence
- Attraction in Close Relationships
- Attribution Theory
- Authoritarian Personality
- Bayesian Statistical Methods in Psychology
- Behavior Therapy, Rational Emotive
- Behavioral Economics
- Behavioral Genetics
- Belief Perseverance
- Bereavement and Grief
- Biological Psychology
- Birth Order
- Body Image in Men and Women
- Bystander Effect
- Categorical Data Analysis in Psychology
- Childhood and Adolescence, Peer Victimization and Bullying...
- Clark, Mamie Phipps
- Clinical Neuropsychology
- Clinical Psychology
- Cognitive Consistency Theories
- Cognitive Dissonance Theory
- Cognitive Neuroscience
- Communication, Nonverbal Cues and
- Comparative Psychology
- Competence to Stand Trial: Restoration Services
- Competency to Stand Trial
- Computational Psychology
- Conflict Management in the Workplace
- Conformity, Compliance, and Obedience
- Consciousness
- Coping Processes
- Correspondence Analysis in Psychology
- Counseling Psychology
- Creativity at Work
- Critical Thinking
- Cross-Cultural Psychology
- Cultural Psychology
- Daily Life, Research Methods for Studying
- Data Science Methods for Psychology
- Data Sharing in Psychology
- Death and Dying
- Deceiving and Detecting Deceit
- Defensive Processes
- Depressive Disorders
- Development, Prenatal
- Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM...
- Discrimination
- Dissociative Disorders
- Drugs and Behavior
- Eating Disorders
- Ecological Psychology
- Educational Settings, Assessment of Thinking in
- Effect Size
- Embodiment and Embodied Cognition
- Emerging Adulthood
- Emotional Intelligence
- Empathy and Altruism
- Employee Stress and Well-Being
- Environmental Neuroscience and Environmental Psychology
- Ethics in Psychological Practice
- Event Perception
- Expansive Posture
- Experimental Existential Psychology
- Exploratory Data Analysis
- Eyewitness Testimony
- Eysenck, Hans
- Factor Analysis
- Festinger, Leon
- Five-Factor Model of Personality
- Flynn Effect, The
- Forensic Psychology
- Forgiveness
- Friendships, Children's
- Fundamental Attribution Error/Correspondence Bias
- Gambler's Fallacy
- Game Theory and Psychology
- Geropsychology, Clinical
- Global Mental Health
- Habit Formation and Behavior Change
- Health Psychology
- Health Psychology Research and Practice, Measurement in
- Heider, Fritz
- Heuristics and Biases
- History of Psychology
- Human Factors
- Humanistic Psychology
- Implicit Association Test (IAT)
- Industrial and Organizational Psychology
- Inferential Statistics in Psychology
- Insanity Defense, The
- Intelligence
- Intelligence, Crystallized and Fluid
- Intercultural Psychology
- Intergroup Conflict
- International Classification of Diseases and Related Healt...
- International Psychology
- Interviewing in Forensic Settings
- Intimate Partner Violence, Psychological Perspectives on
- Introversion–Extraversion
- Item Response Theory
- Law, Psychology and
- Lazarus, Richard
- Learned Helplessness
- Learning Theory
- Learning versus Performance
- LGBTQ+ Romantic Relationships
- Lie Detection in a Forensic Context
- Locus of Control
- Loneliness and Health
- Mathematical Psychology
- Meaning in Life
- Mechanisms and Processes of Peer Contagion
- Media Violence, Psychological Perspectives on
- Mediation Analysis
- Memories, Autobiographical
- Memories, Flashbulb
- Memories, Repressed and Recovered
- Memory, False
- Memory, Human
- Memory, Implicit versus Explicit
- Memory in Educational Settings
- Memory, Semantic
- Meta-Analysis
- Metacognition
- Metaphor, Psychological Perspectives on
- Microaggressions
- Military Psychology
- Mindfulness
- Mindfulness and Education
- Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory (MMPI)
- Money, Psychology of
- Moral Conviction
- Moral Development
- Moral Psychology
- Moral Reasoning
- Nature versus Nurture Debate in Psychology
- Neuroscience of Associative Learning
- Nonergodicity in Psychology and Neuroscience
- Nonparametric Statistical Analysis in Psychology
- Observational (Non-Randomized) Studies
- Obsessive-Complusive Disorder (OCD)
- Occupational Health Psychology
- Olfaction, Human
- Operant Conditioning
- Optimism and Pessimism
- Organizational Justice
- Parenting Stress
- Parenting Styles
- Parents' Beliefs about Children
- Path Models
- Peace Psychology
- Perception, Person
- Performance Appraisal
- Personality and Health
- Personality Disorders
- Personality Psychology
- Phenomenological Psychology
- Placebo Effects in Psychology
- Play Behavior
- Positive Psychological Capital (PsyCap)
- Positive Psychology
- Posttraumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
- Prejudice and Stereotyping
- Pretrial Publicity
- Prisoner's Dilemma
- Problem Solving and Decision Making
- Procrastination
- Prosocial Behavior
- Prosocial Spending and Well-Being
- Protocol Analysis
- Psycholinguistics
- Psychological Literacy
- Psychological Perspectives on Food and Eating
- Psychology, Political
- Psychoneuroimmunology
- Psychophysics, Visual
- Psychotherapy
- Psychotic Disorders
- Publication Bias in Psychology
- Reasoning, Counterfactual
- Rehabilitation Psychology
- Relationships
- Reliability–Contemporary Psychometric Conceptions
- Religion, Psychology and
- Replication Initiatives in Psychology
- Research Methods
- Risk Taking
- Role of the Expert Witness in Forensic Psychology, The
- Sample Size Planning for Statistical Power and Accurate Es...
- Schizophrenic Disorders
- School Psychology
- School Psychology, Counseling Services in
- Self, Gender and
- Self, Psychology of the
- Self-Construal
- Self-Control
- Self-Deception
- Self-Determination Theory
- Self-Efficacy
- Self-Esteem
- Self-Monitoring
- Self-Regulation in Educational Settings
- Self-Report Tests, Measures, and Inventories in Clinical P...
- Sensation Seeking
- Sex and Gender
- Sexual Minority Parenting
- Sexual Orientation
- Signal Detection Theory and its Applications
- Simpson's Paradox in Psychology
- Single People
- Single-Case Experimental Designs
- Skinner, B.F.
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Small Groups
- Social Class and Social Status
- Social Cognition
- Social Neuroscience
- Social Support
- Social Touch and Massage Therapy Research
- Somatoform Disorders
- Spatial Attention
- Sports Psychology
- Stanford Prison Experiment (SPE): Icon and Controversy
- Stereotype Threat
- Stereotypes
- Stress and Coping, Psychology of
- Student Success in College
- Subjective Wellbeing Homeostasis
- Taste, Psychological Perspectives on
- Teaching of Psychology
- Terror Management Theory
- Testing and Assessment
- The Concept of Validity in Psychological Assessment
- The Neuroscience of Emotion Regulation
- The Reasoned Action Approach and the Theories of Reasoned ...
- The Weapon Focus Effect in Eyewitness Memory
- Theory of Mind
- Therapies, Person-Centered
- Therapy, Cognitive-Behavioral
- Thinking Skills in Educational Settings
- Time Perception
- Trait Perspective
- Trauma Psychology
- Twin Studies
- Type A Behavior Pattern (Coronary Prone Personality)
- Unconscious Processes
- Video Games and Violent Content
- Virtues and Character Strengths
- Women and Science, Technology, Engineering, and Math (STEM...
- Women, Psychology of
- Work Well-Being
- Wundt, Wilhelm
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Legal Notice
- Accessibility
Powered by:
- [66.249.64.20|185.66.15.189]
- 185.66.15.189
October 1, 2006
Determining Nature vs. Nurture
Molecular evidence is finally emerging to inform the long-standing debate
By Douglas Steinberg
PSYCHOLOGISTS , psychiatrists and neuroscientists have jousted for years over how much of our behavior is driven by our genes versus the environments in which we grow up and live. Arguments have persisted because there has been little hard evidence to answer basic questions: How exactly do genes and environment interact to determine whether someone will become depressed, say, or schizophrenic? And can environmental interventions such as drugs or psychotherapy really alleviate disorders that are largely determined by genes?
A field called epigenetics has finally begun to address some of these issues. Its practitioners study how tiny molecules stick to, or become unstuck from, two main targets in a cell's nucleus: the DNA in and around a gene and the histones—the proteins around which chromosomes spool. These tiny molecules are known as methyl and acetyl groups, and their presence or absence at target sites controls whether particular genes can generate proteins, the workhorses of most physiological processes.
Until a couple of years ago, the conventional wisdom in biology held that such molecular changes occur in primitive cells, usually during embryonic and fetal development, not in mature cells such as a child's or adult's neurons. Then researchers proved that epigenetic changes are indeed at work in mature cells. Now studies are starting to show how environmental cues can stimulate epigenetic changes that could contribute to several psychiatric diseases. Systematic measurement of those changes could eventually indicate how the environment influences the genetic chemistry underlying many human behaviors.
On supporting science journalism
If you're enjoying this article, consider supporting our award-winning journalism by subscribing . By purchasing a subscription you are helping to ensure the future of impactful stories about the discoveries and ideas shaping our world today.
Schizophrenia and Depression
One condition that has begun to yield its epigenetic secrets is schizophrenia, which generally arises when people hit their late teens or twenties. “Something happens during puberty that causes changes in gene expression,” notes Dennis R. Grayson, an associate professor of psychiatry at the University of Illinois at Chicago.
That “something” is still unknown. Schizophrenia has not been definitively tied to mutant genes, even though it tends to run in families, and environmental factors show only weak statistical links to the disease's incidence. But it is becoming clearer that epigenetic alterations—triggered perhaps by a convergence of subtle influences—may play a role. Grayson and his colleagues Alessandro Guidotti and Erminio Costa autopsied the brains of schizophrenic patients and found that methyl groups were attached to a gene that helps to form connections between neurons. Earlier postmortem studies showed both a sharp reduction in this gene's activity and an increase in the activity of a gene that promotes attachments of methyl groups to DNA.
Experimental evidence links epigenetic changes to depression as well. Eric J. Nestler, psychiatry department chair at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center at Dallas, has proposed a potential animal model of the disease that includes epigenetic changes in the hippocampus, a memory-storing brain region that actually shrinks in some cases of human depression.
To develop this model, Nestler and his co-workers put a small adult male mouse into the cage of a far larger aggressive mouse, which soon attacked the newcomer. Ten minutes later they placed a plastic barrier between the mice, which stopped the attacks but did not stop the little rodent from seeing, hearing and smelling its nemesis. A small mouse placed in this situation for 10 days typically displayed depressionlike social avoidance.
The researchers discovered that such treatment also caused methyl groups to stick to histones (the DNA-spooling proteins) in the hippocampus. This action suppressed a gene that, as a result, failed to generate a protein suspected of helping the brain adapt to stress. What is more, the small mouse ceased exhibiting social avoidance when it received antidepressants, which restored the gene's activity.
Nestler says he does not know yet how a hostile environment prompts methyl groups to stick to histones, but his study suggested why the antidepressant works: it causes acetyl groups to attach to the histones, thereby counteracting the effects of the methyl groups. Nestler and other scientists are now trying to create compounds that will tinker with specific epigenetic mechanisms.
Maternal Influence
Fearfulness is another psychological condition that can arise from the epigenetic effects of environmental influences. Michael J. Meaney, a psychiatry professor at McGill University, has found that when a rat pup receives less licking and grooming from its mother it is more fearful and more reactive to stressors as it matures.
The team found that a hippocampal gene sheds methyl-group molecules during the first week of a pup's life if its mother is a “high licker.” Pups of low lickers do not prune the molecules. An adoption experiment proved that licking triggers these events: when the team entrusted pups born to mothers of one licking type to mothers of the other type, the genes' methyl status reflected the licking type of the adoptive parent. Licking is believed to exert its effect by raising the pups' thyroid-hormone production and activity of the neurotransmitter serotonin.
Meaney says he encountered “a fairly intense level of skepticism” when he first presented his results, because they imply that epigenetic changes can occur in mature cells, not just in the immature cells present in an embryo or fetus. The social implications of his work were also unsettling. The findings suggest that a mother's parenting style can have very different effects on the activity of a child's genes. Meaney and others are now also studying hundreds of human mother-infant pairs to learn how a stressful pregnancy might affect a baby's later development.
Applying epigenetics to the brain is just beginning, but the field is ramping up as technologies to monitor molecular changes improve. Do not expect the findings to bring speedy cures for psychiatric ills, however. For years, cancer researchers have investigated epigenetic influences on tumor formation, yet cancer remains unvanquished. Epigenetics may indeed unveil what is happening at the intersection of genes and environment—between nature and nurture—but we will be relying on psychiatrists and psychologists for a long time to come.
Advertisement
Goodbye, nature vs nurture
By Evelyn Fox Keller
15 September 2010

An entanglement of genes and environment
(Image: Julia Fullerton-Batten/Getty)
Talking about nature and nurture as separate, clear-cut forces is far adrift from the complexities of developmental science, says Evelyn Fox Keller
ONE of the most striking features of the nature/nurture debate, the argument over the relative roles of genes and environment in human nature, is the frequency with which we read it has been resolved (the answer is neither nature nor nurture, but both) while at the same time we see the debate refuses to die. So what is it that evokes such contradictory claims, that…
Sign up to our weekly newsletter
Receive a weekly dose of discovery in your inbox! We'll also keep you up to date with New Scientist events and special offers.
To continue reading, subscribe today with our introductory offers
No commitment, cancel anytime*
Offer ends 2nd of July 2024.
*Cancel anytime within 14 days of payment to receive a refund on unserved issues.
Inclusive of applicable taxes (VAT)
Existing subscribers
More from New Scientist
Explore the latest news, articles and features
Eclipse 2024 live: Watch the full NASA broadcast – latest
When is the next total solar eclipse visible from the uk, cannabis use in pregnancy may raise children’s risk of adhd and autism.
Subscriber-only
5 solar eclipse activities to do with children
Popular articles.
Trending New Scientist articles
- International edition
- Australia edition
- Europe edition

The big idea: is it time to stop talking about ‘nature versus nurture’?
The latest science shows that genes and environment are too deeply entwined to pit them against one another
W hen you hear people conversing in an unfamiliar language, why is it that you can’t even tell where one word ends and the next begins? If you are a native English speaker, why is it so challenging to get your mouth around a French or Hebrew “r”, which originates lower in the throat, or the “r” in Spanish or Italian, which is trilled on the tip of the tongue? Your ability to hear and make sounds, and to understand their meaning as language, is wired into your brain. How you acquire that wiring illuminates an age-old debate about human nature.
In the first few months of your life, your infant brain is bathed in all kinds of information from the world around you, through your senses. This sense data causes changes in your brain as your neurons fire in various patterns. Some collections of neurons fire together frequently, strengthening or tuning their connections and aiding learning. Others are used less and are pruned away, making room for more useful ones to form. This process of tuning and pruning is called plasticity, and it happens throughout your life, but enormously in the first few years.
One of the biggest sources of sense data for an infant brain is other people. As a consequence, your infant brain was tuned and pruned to detect fine differences in human speech, including a large inventory of consonant and vowel sounds, becoming expert in distinguishing one from another. But here’s the thing – babies tend to spend time with caregivers who speak the same language, so you probably missed out on many sounds found only in other languages. That’s one reason you may find it hard to produce or even discern these unfamiliar sounds today.
This brings us to the age-old debate I mentioned: are your deepest characteristics and abilities present at birth, or are they formed by your experiences in the world? In other words, is nature or nurture the prime mover? We know that part of who you are comes from genes, which contain instructions to build your body and wire your brain. We also know that the culture you grow up in can shape your brain and body in fundamental ways.
Few scientists today would say that 100% of your attributes are inborn or are learned; the debate tends to be about where to draw the dividing line. Newer evidence, however, suggests that the dividing line doesn’t really exist. Your environment, it turns out, causes certain genes to turn on and off, a process called epigenetics. You also have genes that regulate how much the environment affects you. Genes and environment are so deeply entwined, like lovers in a fiery tango, that it’s fundamentally unhelpful to call them separate names like “nature” and “nurture”.
Take the idea of sleeping on a piece of furniture called a bed, by yourself or with a partner, in a designated room called a “bedroom”, for a long chunk of time like eight hours. Such ideas are actually wired into your brain by experience and guide your expectations and actions. You can tell because it feels somehow “wrong” to change the habit. If you and your whole family all slept on straw mats in one room every night, and you had to wake up every two hours to tend the fire, it would feel unnatural to you, despite the fact that other cultures live this way.
Even emotions such as joy, sadness and fear, which feel inborn and automatic, are in fact a product of culture. Suppose you see someone make a wide-eyed, gasping face. If you grew up in a western society, you are likely to perceive fear in that face, but if you grew up in Melanesia, you’re more likely to perceive threat and aggression.
Culture allows one generation to pass information on to the next without it having to be carried by genes. Your childhood caregivers curated your physical and social world, and your brain wired itself to that world. You perpetuate that world and eventually pass your culture on to the following generation through your words and actions, wiring their brains in turn. This cultural inheritance is an efficient, flexible partner to genetic inheritance, and means that the process of evolution doesn’t require all our wiring instructions to be in genes. The way your brain becomes tuned to the languages you hear as a baby is just one example. Similarly, if you’re exposed to adversity in early life, it may activate certain genes and suppress others, wiring your brain to deal with adversity that may arise in the future. Unfortunately, this wiring also makes you more vulnerable to depression, anxiety, heart disease and diabetes in adulthood. If you have children, you might pass some of these characteristics on to them through epigenetic changes .
Cultural practices even shape the genetic evolution of our entire species, by influencing who is available to reproduce with whom, and which children are more likely to live to reproductive age. Wealth, social class, laws, war and other human inventions empower one group over another, changing the odds on whether certain people will have children together, or at all. Political and religious polarisation ensures that people with different beliefs will scarcely speak to one another, let alone date or mate. Parents who vaccinate their children against deadly diseases, or choose not to, likewise make waves in the gene pool. This is how humans, by virtue of the cultures we create, nudge the evolutionary trajectory of our species.
Culture is not a mere moderator of our biology, then, but a fully fledged cause. I’m not saying that your culture determines your destiny, but then neither do your genes. Together, your genes and the world you live in make you who you are (for better or for worse). We are therefore all partly responsible for wiring each other’s brains, and the brains of the next generation, through our words and actions. That’s the lesson of the latest science: there need be no “versus” in the equation. We simply have the kind of nature that requires nurture, and they are utterly intertwined.
Lisa Feldman Barrett is a professor of psychology at Northeastern University , Boston, and the author of Seven and a Half Lessons About the Brain .
Further reading
Not by Genes Alone: How Culture Transformed Human Evolution by Peter J Richerson and Robert Boyd (Chicago, £27)
Sense and Nonsense: Evolutionary Perspectives on Human Behaviour by Gillian R Brown and Kevin N Laland (Oxford, £34.49)
The Triple Helix by Richard Lewontin (Harvard, £24.95)
- Health, mind and body books
- The big idea
- Science and nature books
Most viewed
Nature vs. Nurture: The Biology of Sexuality
MED prof speaks tonight on whether sexual orientation has genetic basis
Kimberly cornuelle.

Homosexuality was considered a mental illness when Richard Pillard was in medical school. It was the 1950s and the School of Medicine professor of psychiatry was at the University of Rochester. At the time, the American Psychological Association still listed homosexuality as a disorder and psychologists and psychiatrists were trained on ways to treat it.
The first psychological test undertaken to determine whether there was a biological explanation for homosexuality was in 1957. With a grant from the National Institute of Mental Health , Karen Hooker studied the relationship between homosexuality and psychological development and illness. Hooker studied both homosexuals and heterosexuals—matched for age, intelligence, and education level. The subjects were then given three psychological tests: the Rorschach, the Thematic Apperception Test (TAT), and the Make-a-Picture-Story Test (MAPS). Hooker found no major differences in the answers given by the two groups. Because of the similar scores, she concluded that sexuality is not based on environmental factors.
In 1973, based on Hooker’s findings, the American Psychiatric Association removed homosexuality from its Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Psychological Disorders and in 1975, released a public statement that homosexuality was not a mental disorder.
There have been numerous studies designed to determine whether or not homosexuality has a genetic cause. Among the most notable were a series of studies Pillard and J. Michael Bailey, a professor of psychology at Northwestern University, conducted in the early 1990s that found that homosexuality is largely biologically determined, not environmentally influenced. In their findings, published in the Archives of General Psychiatry , they argued that decades of psychiatric research into social and cultural causes show “small effect size and are causally ambiguous.”
Pillard and Bailey examined identical and fraternal twin brothers—as well as nonrelated brothers who had been adopted—in an effort to see if there was a genetic explanation for homosexuality. They found that if one identical twin was gay, 52 percent of the time the other was also; the figure was 22 percent for fraternal twins, and only 5 percent for nonrelated adopted brothers. Pillard and Bailey’s findings have been debated in the intervening decades.
Pillard is quick to point out that much about how sexual orientation is determined remains a mystery. “It’s really hard to come up with any definite statement about the situation,” he says. “I think some sort of genetic influence seems very likely, but beyond that, what really can we say? And the answer is: not a lot.”
BU Today caught up with Pillard to talk about the lecture he will deliver tonight, titled Born This Way: The Biology of Sexual Orientation. The talk is part of the OUTlook Lecture series , sponsored by the LGBTQ ministry at Marsh Chapel.
BU Today : Has your research found that sexual orientation is biologically determined? Pillard: I think so. But nobody knows for sure what causes a person to be either gay or straight. It’s one of the great mysteries of science, at least of biological science.
Can you talk about the twin research you’ve conducted? What we did was to recruit groups of twins, identical and fraternal twins. And the theory is if a particular trait is genetic, the identical twins would be more alike than the fraternal twins. The results were that they were more alike. The identical twins were far more similar than the fraternal twins.
Is there evidence that life experiences play a role in sexual orientation? It’s a hard question to answer, because by “experience,” we’re talking about when kids are in the very first years of their life. If you’re going to do research about it, you’re doing research on people 20 or 30 years later, so it’s really hard to look back with certainty on what happened to them in those early years.
But a lot of people have tried, and have said things like, ‘Well, it depends on the fact that your mother was overprotective or that your father was distant or absent.’ You have to reconstruct those theories from events of long ago. And how do you know the mother really was overprotective—you have to depend on what the subject in your study is remembering about his early years. And that could be easily falsified.
Your research suggests that there is often a familial pattern in homosexuality. Yes. It seems to us that being gay runs in families much more frequently than you would expect by chance alone. And the pattern is hard to specify: that is, in some cases they’re brothers and sisters, in some cases it’s parents and children, or aunts and uncles. So it’s hard to put that into theory given what we know about genes and behavior, which is to say, not a lot.
What made you decide on this research? What was your motivation? Well, because there are so many gay people in my family, including me. It just seemed like a logical thing to do. At the time that I was searching for a problem, that popped out.
I think that the future of this kind of research belongs to people who are geneticists, people who are expert in gene mapping. These are the sort of bench scientists, where I am more interested in clinical things. I would be very interested if something came of this—that is, when the day comes where genes are mapped, I’d be very interested in that. But, it’s not something that I’m equipped to do.
Do you think that because attitudes are changing and acceptance of the LGBT community is becoming more prevalent, people are more willing to accept the possibility that sexual orientation is determined biologically? It’s hard to say. Insofar as people look at evidence, it’s clearly biological. The objection to homosexuality comes exclusively from the conservative religious streak, who say, ‘Well, the Bible forbids it, therefore we must be guided by what the Bible says.’ But there’s no other evidence. Lesbians and gay men don’t do worse at their jobs, they are just as good as friends and citizens. As more gay people are out and open about their orientation, the general population realizes, ‘Well, they’re pretty much the same as everybody else.’
When I was in my medical school training in the 1950s, the only places you heard about gay people being were in prison or a mental hospital. So the assumption was, well they’re all quite bizarre. Then in the late 1960s, when civil rights were being granted to people of color and to women and finally to gays, it was realized that they’re like everybody else. I think most people now have friends or acquaintances who are gay. The average college student doesn’t think much about it.
Are you amazed at how far attitudes have changed? Yes, but it’s taken a long time—50 years is a long time. But it absolutely is changing. Even so, there are people who think that gays shouldn’t be teachers or who are against gay marriage.
Since we don’t really know all the answers, people can have any opinion that crosses their mind. But I think most scientists, most people who are familiar with the science of the area, would say it’s very likely that something genetic is afoot here.
Will you be talking about sexual orientation in any kind of religious context? I have to say I’m a hard-core atheist. I’m the last person who is qualified in any way to comment on theological matters. But I wonder what college students at BU think. Because I’m on the Medical Campus, I just don’t get the chance to rub shoulders with those on the Charles River Campus. It’ll be interesting to exchange views with them.
Because you’ll be presenting your evidence, and there’s no guesswork. It’s just the facts, ma’am.
Richard Pillard will discuss Born This Way: The Biology of Sexual Orientation at 7 p.m. Tuesday, November 16, in Stone Science Building, 675 Commonwealth Ave., Room B50. Questions will follow the presentation. At 7 p.m. on November 18, Ellen Perrin, a Tufts University professor of pediatrics, will talk about Where Did We Go Right: Children Raised by Same Sex Couples, at the School of Education, 2 Silber Way, Room 130. Charles Morris, a Boston College professor of communications, will talk about Queer(ing) Public Memory: LGBTQ Pasts and Their Presence at 7 p.m. December 7, in SED 130. The events, sponsored by the LGBTQ Ministry of Marsh Chapel, are free and open to the public. For more information, contact Liz Douglass at [email protected] .
Kimberly Cornuelle can be reached at [email protected] .
Explore Related Topics:
- Share this story
- 33 Comments Add
Kimberly Cornuelle Profile
Comments & Discussion
Boston University moderates comments to facilitate an informed, substantive, civil conversation. Abusive, profane, self-promotional, misleading, incoherent or off-topic comments will be rejected. Moderators are staffed during regular business hours (EST) and can only accept comments written in English. Statistics or facts must include a citation or a link to the citation.
There are 33 comments on Nature vs. Nurture: The Biology of Sexuality
Maybe you should also present the viewpoint of some notable researchers who believe homosexuality is NOT necessarily biologcallh predetermined. Because there is overwhelming evidence that points the other way too.
Personally I think it falls out somewhere in the middle between 100% nature and 100% nurture.
Christianity takes a lot of hits for being anti-gay but I have to say that in my Catholic high school the students were by far more supportive of gays than my public high school friends and especially my non-religious friends.
Doesn’t research that shows that family members are more likely to be gay if another is equally lend itself to the conclusion that “nurture” is the root cause? (seems this research could lead to either conclusion if they are not involving genetics, etc…_
That is exactly what I was thinking, if you have 2 kids and they both grow up in the same household (assuming how they are raised causes being gay), if one is gay than the other would most likely be gay as well since they are both in the same conditions
To “Maybe you should also”:
The speaker is not saying that it is 100% nature or nurture. I think he is saying that nature plays a big role, and now we have stronger evidence to confirm this. This does not imply that it is all nature. It only implies that the evidence we have for saying nature is now stronger. This is natural, because our tools for gathering and examining evidence have improved many fold over the past few decades.
It shows it is largely genetic because the experimenters used a control group. The control group, adopted siblings who are gay, had only a 5% correlation – the nurture made little impact and the genomes were utterly different. Furthermore, fraternal twins, who have genes as different as siblings but the same basic nurture, are 22% correlated, while nonfraternal twins, ones with much closer genetics, are 52% correlated. So nature plays a big role.
That is not a control group. A control would be identical twins raised together versus identical twins raised apart, in sufficient numbers so as to form a usable sample.
Using identical twins and fraternal twins raised in practically the same environment isn’t a control. It’s very interesting, but it makes no case for biological determinance. Twins are treated very differently from non-twin siblings. This really can’t be controlled for in a non-longitudinal study.
A person is no more born a homosexual than they are born a heterosexual. If my sexuality is genetic, then there also has to be a gene that explains the behavior of those involved in beastiality and sex with children (even infants). It is substantially more reasonable that a person is born sexual, period; and for any number of reasons, chooses how to act on that sexuality. This also explains how people’s views on how to “act out” their sexuality change over time.
Christian or not — sin or not — legal or not — people will act out their desires. Making this a genetic issue suddenly makes this “not my fault”. If I’m a drug addict, chances are somewhere along the line, I made a decision. If I’m a practicing homosexual, same thing. I choose.
If it’s genetic, then it isn’t my choice. My eyes are blue. That’s genetic.
wrong. first, the a priori “reasonableness” of your position is debatable. the notion that anyone chooses whom to be attracted to seems eminently unreasonable. second, even if the nurture side were more reasonable than the nature side, science does not answer questions by adverting to reasonableness. if it did, the earth would still be flat and an electron would be either a particle or a wave. while homosexuals do make the decision to have gay sex, that hardly implies that they decided to be attracted to same-sex partners. finally, because one element of sexuality is genetically determined, that does not mean that all elements of sexuality are. your eyes may be blue but mostly they just appear to be closed.
Sorry, nothing is debatable about it. If something is sexually genetic, then what makes incest wrong? Besides, the only reason people are against incest is because of deformations, but science and technology has invented… Wait for it… Birth Control and Condoms. OMG don’t say it is so?!
Besides, you seem to forgotten how we get over our ex’s.
Nothing in the results of this study are definitive and the “reasonableness” on both sides of this issue are about equally valid at this point in time. What should be obvious to every one though is the gay community is desperately looking for science to back them up that: they were born that way. It is about equally true that conservative are equally determined to have supporting evidence that being gay is environmental. The real scientists have yet to weigh in with any factual data that proves things either way. The Pyschologist leader of this study rightly said he is unqualified to make a genetic statement on the subject. Meanwhile both sides of this issue should be a little more humble and kindly toward each other. They have only anecdotal information and minor correlations. And that is not science.
This is a free country. Everyone is free to identify themselves with any gender they want, express themselves the way they want and sexually orient themselves to any gender they want, as long as they are not imposing their views on other adults.
Homosexuality is not a choice. Just like you don’t choose the color of your skin, you cannot choose whom you are sexually attracted to. If you can, sorry, but you are not heterosexual, you are bi-sexual. Virtually all major psychological and medical experts agree that sexual orientation is NOT a choice. Most gay people will tell you its not a choice. Common sense will tell you its not a choice. While science is relatively new to studying homosexuality, studies tend to indicate that its biological.
(Change *** to www) ***-news.uchicago.edu/releases/03/differential-brain-activation.pdf ***.newscientist.com/channel/sex/dn14146-gay-brains-structured-like-those-of-the-opposite-sex.html Gay, Straight Men’s Brain Responses Differ ***.foxnews.com/story/0,2933,155990,00.html ***.livescience.com/health/060224_gay_genes.html ***.springerlink.com/content/w27453600k586276/
Sure I can choose who I am sexually attracted to. Example: My ex’s.
Ah, but why are you not attracted to a person you once were before? The answer: the personality of the other person. At first, you were attracted to your “ex.” Over time, that attraction dissipated as you learned more about them, and no longer wanted to be with that person. What difference does the person’s scientific sex make? Not very much. Every person has their own distinct personality, which is where (I believe) the nurture element of this debate comes into play. For instance, does one choose to be viewed as annoying for telling the same stories over and over again? No. Most likely, that is the type of person they were raised around; however, that does not change the fact that for some reason, they were initially attracted to you. Surely, you’ve met someone who was attracted to you but you were not at all attracted to them. Maybe they were a normal person with no real “deformities,” mental or physical, you just simply did not want to be with that person on a more intimate level. Why? That’s just how you were wired. You do not choose who you want to be friends with if the other person does not want to be your friend as well. Love is not a conquest to be chosen; it is a treasure to be found.
the nature/nurture distinction is one that is increasingly irrelevant in current biological work, with the advance of epigenetics and the advanced understanding of developmental biology. framing this debate and most other discussions in these terms is not very fruitful… let’s say you have a whole array of genetic dispositions – what your physical and cultural environment exposes you to will have an enormous effect on which genes get turned on and off. this starts in the womb and never stops. nature or nurture? exactly.
I’m sorry. I know this type of argument encourages critical thinking and the mind in general, but your comment is simply stupid.
Of course it isn’t. It is logical, but you disagree with the conclusion. Either there are genetic elements to sexual preference or there are not.
The choice isn’t necessarily the attraction, as gay people and pedophiles will tell you. The choice is to act upon the attraction. If one isn’t religious and doesn’t believe homosexuality is immoral, it shouldn’t matter if a person acts on that attraction, as long as it is legal. If it is not legal, then regardless of one’s predilictions, one should not act on it.
We should not conflate the individual moral and biological arguments with societal decisions about what makes a society “work.”
There is nothing wrong with making a genetical sexual case for all matters of attraction. What is the difference between sexual attraction and those who can’t stop gambling? Or hoarding cats? Or addiction? The same reinforcing pleasure mechanisms in the brain are at work. That isn’t a causal argument, but there is no reason to exclude that premise because if one accepts that, one must accept a marriage argument for siblings and multiple partners. There is simply no biological distinction.
Policy matters should be argued on a basis of societal worth, not individuals’ preferences.
I agree entirely with this post. Especially the part about the comparison with bestiality and pedophilia; it logically makes sense. Reason triumphs in your argument…however, you will most likely be met with hostility…that is the way of the “emotionally driven”.
I agree with Pillard completely in that I believe homosexuality is a function of the way you’re wired; you’re born with it. No one would willingly choose to be a minority that society has ridiculed and deemed less than equal. I’m not gay but I am a middle-aged woman and I’ve dealt with discrimination from men my entire life. It is very difficult to be a minority – so why would anyone choose that if they could avoid it? I believe that Pillard’s work will be supported soon and there will be additional evidence brought forward to corroborate it.
What I found disturbing about the interview though was his assertion that he is a hard-core atheist. I would like to appeal to Pillard’s scientific side and ask that he read the book: “The Case for Christ: A Journalist’s Personal Investigation of the Evidence for Jesus” by Lee Strobel. It is written by an ex-atheist who set about making a case to debunk Jesus as the Christ. Instead he found, after extensive scientific and legal analysis, that it was impossible to draw that conclusion. As a result of his research Strobel is no longer an atheist.
It was Evelyn Hooker.
Ah Richard — what a delight to read your comments. Brought back so many wonderful memories of our work together at HCHS! Guess at our mutual age of 80 we are both still in there working to end discrimination toward GLBT persons. I have used the twin study in lectures here in Florida and found the audience excited about the results. I have no doubt orientation is genetic – how it is expressed, lived is nurture. That is no different than heterosexual orientation. It is curious how in the 21st century homosexuality still scares the hell out of people. Fear then brings corrupt theology and philosophy, and pseudoscience. Keep up the good work dear friend.
My 16 yr. old daughter recently “came out” to me. She expressed having felt “different” for quite some time and was only now able to understand what she was feeling. I held off telling my husband because I didn’t think he would accept what she was telling me. I finally did tell him and sure enough his response was, “let’s see how she feels in a few years”. I was speechless. We are at complete opposing sides on whether she was “born this way” or whether she is “choosing” to be gay. I’m so saddened by his response and I’m not sure how I deal with him going forward. I love and support my daughter 100% and want her to know that (I have told her so) If she knew how my husband felt I believe it would push them even farther apart (she chose not to tell him herself and told me I could)Do you have any advice?
You should know, Evelyn Hooker, not Karen Hooker, did the 1957 study.
http://psychology.ucdavis.edu/faculty_sites/rainbow/html/facts_mental_health.html http://dsmistory.umwblogs.org/dsm-iii/case-studies/ http://www.apa.org/monitor/2011/02/myth-buster.aspx
Anne Heche chose a man after being with a woman…Seems happy to me
Would this just be an anomaly?
To say that being attracted to the same sex is a choice is simplifying the debate to a fault. Like, I choose to have mashed potatoes over fries…REALLY? Ask most gay men about the earliest memories. Mine is typical. When I was 5 years old, I “knew I was different”… could I define “that” then (?), of course not. I didn’t know didly about sexuality then, much less morality. It wasn’t until I was 8 that I started acting out my sexuality, being only attracted to boys, and still, not really attaching “morality to it”…. then, as I hit my teens, I started noticing it as being anti social behavior, and not until then did I realize that society would treat me differently, thus, the struggle began. Please don’t inject into the fray terms like beastiality as a genetic phenomenon, and link it too sexual preference. We are discussing attraction to men or woman here.
1. Epigenetics: environmental factors and genes interact. 2. Abuse in childhood seems to be a pattern looking at my gay friends. I assume that often it feels safer to not become perpetrator themselves by abstaining from heterosexual sexuality. Have seen strong dissociative symptoms there and quite some violent behavior once sexuality switched from homosexuality to heterosexuality (yes, it did, in the gayest gay one can imagine). 3. Twin studies: it’s likely that identical twins identify more with each other than fraternal twins. From a psychological perspective it doesn’t make sense to believe twin studies to be indicator for genetic aspects. Then again: Epigenetics. 4. Fear and vulnerability: Gay people I know have a lot more of that than the usual heterosexual I know (who have a lot too). I don’t lie what stupid test this was for proving its not about environmental factors. There ARE differences. But it’s unlikely to detect them with a Rorschach test.
There are too many taboo topics intermingled. As long as researchers are not willing to look at these the findings won’t be anywhere near useful.
Um, plenty of researchers investigate sexual orientation. There is no evidence that child abuse causes male homosexuality, but instead that the early gender nonconformity that homosexuals usually show makes them targets for abuse and maltreatment. You can’t explain the fact that 2% of men are Fa’afafine in Samoa by claiming its a result of social influence, the Samoans (who are deeply Christian!) would laugh at you! They recognise this gender nonconformity early and put them into a third gender category (a man in the manner of a woman) because they do not approve of homosexuality. If you want to learn something I recommend the Bailey et al. review from 2016 which was authored by a number of leading researchers in this area: https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/full/10.1177/1529100616637616
At the moment, however, I suspect that rather than biology being destiny, our sexual preference is shaped by a combination of early experiences, peer pressure, opportunity, circumstances and fate. Do the heterosexuals reading this ever wonder how they ended up straight, especially since so many of you will have had crushes on or even sexual contact with someone of the same sex at some stage?
A bit disturbing. How does one explain t-e human anatomy? Men having organs specifically designed for a particular purpose and so are women? What of the reproduction function? If born that way, would that mean the end of the human race?
In response to Mukasa ^ . . .most heterosexual sex is not practiced with regard to ‘procreation’ anyway but rather for ‘recreation’. Is THIS ‘against nature’?
Post a comment. Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Latest from BU Today
Bu’s earth day celebrations, tenth annual giving day raises more than $3.8 million, bu freshman macklin celebrini named a hobey baker award finalist, photos of the month: a look back at march at bu, what’s hot in music this month: new releases, local concerts, the weekender: april 4 to 7, could this be the next snl bu student’s wicked smaht comedy troupe performs this weekend, determined to make the world a better place, giving day 2024: bu celebrates 10 years of giving back, your everything guide to landing an internship, building a powerhouse: how ashley waters put bu softball on the map, sex in the dark: a q&a event with sex experts, tips to watch and photograph the april 8 total solar eclipse safely, for cfa’s head of acting, huntington role required discretion, listening, biden’s biggest challenges to reelection—immigration, gaza, and even the economy, boston university drops five-day isolation requirement for covid, the weekender: march 28 to 31, bridge collapse creates conversation in bu structural mechanics class, terriers in charge: favor wariboko (cas’24), the bold world of marcus wachira.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Nature dictates the limits, and nurture defines where you fall within the boundaries. It's both. To quote my old genetics prof, "A good environment can overcome bad genes, and the variations of that statement are equally true." He gave a great example of this: Take two strains of corn, A and B.
The Nature vs. Nurture Debate. Nature refers to how genetics influence an individual's personality, whereas nurture refers to how their environment (including relationships and experiences) impacts their development. Whether nature or nurture plays a bigger role in personality and development is one of the oldest philosophical debates within ...
Nature vs. nurture is an age-old debate about whether genetics (nature) plays a bigger role in determining a person's characteristics than lived experience and environmental factors (nurture). The term "nature vs. nature" was coined by English naturalist Charles Darwin's younger half-cousin, anthropologist Francis Galton, around 1875.
The nature vs. nurture debate is the scientific, cultural, and philosophical debate about whether human culture, behavior, and personality are caused primarily by nature or nurture. Nature is ...
The nature versus nurture debate is about the relative influence of an individual's innate attributes as opposed to the experiences from the environment one is brought up in, in determining individual differences in physical and behavioral traits. The philosophy that humans acquire all or most of their behavioral traits from "nurture" is known as tabula rasa ("blank slate").
Trouble is, this nature vs nurture debate is fundamentally wrong-headed. Even before conception, our make-up is influenced by " epigenetic " factors: choices our parents make, chemicals they ...
The book is a marvelous work of history—Zimmer's account of the early days of eugenics in the U.S. is especially gripping—as well as a detailed, up-to-date report on CRISPR and other ...
Nature vs nurture debate is 'totally dead in science,' says neuroscientist. Apr 21 2021 The World. Share Image. Hana Kiros. A doctor looks at PET brain scans in Phoenix on August 14, 2018. A big study to help Medicare officials decide whether to start covering brain scans to check for Alzheimer's disease missed its goals for curbing emergency ...
The nature vs. nurture debate in psychology concerns the relative importance of an individual's innate qualities (nature) versus personal experiences (nurture) in determining or causing individual differences in physical and behavioral traits. While early theories favored one factor over the other, contemporary views recognize a complex interplay between genes and environment in shaping ...
The phrase "nature versus nurture" refers to a long-standing debate in human biology: to what extent is our behaviour shaped by our genes (nature) or by the environment in which we grow up and ...
The expression "nature vs. nurture" describes the question of how much a person's characteristics are formed by either "nature" or "nurture." "Nature" means innate biological ...
The nature versus nurture debate in psychology deals with disagreements about the extent to which the development of traits in humans and animals reflects the relative influence of nature and nurture. It is commonly stated that psychologists have moved on from asking whether traits (or variation in traits) develop from nature or nurture, to ...
More by Douglas Steinberg. This article was originally published with the title "Determining Nature vs. Nurture" in SA Mind Vol. 17 No. 5 (October 2006), p. 12. doi:10.1038 ...
Goodbye, nature vs nurture. By Evelyn Fox Keller. 15 September 2010. An entanglement of genes and environment. (Image: Julia Fullerton-Batten/Getty) Talking about nature and nurture as separate ...
The big idea: is it time to stop talking about 'nature versus nurture'? This article is more than 2 years old. ... How you acquire that wiring illuminates an age-old debate about human nature.
Because you'll be presenting your evidence, and there's no guesswork. It's just the facts, ma'am. Richard Pillard will discuss Born This Way: The Biology of Sexual Orientation at 7 p.m. Tuesday, November 16, in Stone Science Building, 675 Commonwealth Ave., Room B50. Questions will follow the presentation.
The battle of nature versus nurture, or rationalism versus empiricism, has so long been debated and has been addressed in so much literature that one would be hard pressed to find an educator who hasn't thought about this topic and considered the merits of each school of thought. This debate affects how educators view their students as well ...