Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to revise an essay in 3 simple steps

How to Revise an Essay in 3 Simple Steps
Published on December 2, 2014 by Shane Bryson . Revised on December 8, 2023 by Shona McCombes.
Revising and editing an essay is a crucial step of the writing process . It often takes up at least as much time as producing the first draft, so make sure you leave enough time to revise thoroughly. Although you can save considerable time using our essay checker .
The most effective approach to revising an essay is to move from general to specific:
- Start by looking at the big picture: does your essay achieve its overall purpose, and does it proceed in a logical order?
- Next, dive into each paragraph: do all the sentences contribute to the point of the paragraph, and do all your points fit together smoothly?
- Finally, polish up the details: is your grammar on point, your punctuation perfect, and your meaning crystal clear?
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Step 1: look at the essay as a whole, step 2: dive into each paragraph, step 3: polish the language, other interesting articles.
There’s no sense in perfecting a sentence if the whole paragraph will later be cut, and there’s no sense in focusing on a paragraph if the whole section needs to be reworked.
For these reasons, work from general to specific: start by looking at the overall purpose and organization of your text, and don’t worry about the details for now.
Double-check your assignment sheet and any feedback you’ve been given to make sure you’ve addressed each point of instruction. In other words, confirm that the essay completes every task it needs to complete.
Then go back to your thesis statement . Does every paragraph in the essay have a clear purpose that advances your argument? If there are any sections that are irrelevant or whose connection to the thesis is uncertain, consider cutting them or revising to make your points clearer.
Organization
Next, check for logical organization . Consider the ordering of paragraphs and sections, and think about what type of information you give in them. Ask yourself :
- Do you define terms, theories and concepts before you use them?
- Do you give all the necessary background information before you go into details?
- Does the argument build up logically from one point to the next?
- Is each paragraph clearly related to what comes before it?
Ensure each paragraph has a clear topic sentence that sums up its point. Then, try copying and pasting these topic sentences into a new document in the order that they appear in the paper.
This allows you to see the ordering of the sections and paragraphs of your paper in a glance, giving you a sense of your entire paper all at once. You can also play with the ordering of these topic sentences to try alternative organizations.
If some topic sentences seem too similar, consider whether one of the paragraphs is redundant , or if its specific contribution needs to be clarified. If the connection between paragraphs is unclear, use transition sentences to strengthen your structure.
Finally, use your intuition. If a paragraph or section feels out of place to you, even if you can’t decide why, it probably is. Think about it for a while and try to get a second opinion. Work out the organizational issues as best you can before moving on to more specific writing issues.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Next, you want to make sure the content of each paragraph is as strong as it can be, ensuring that every sentence is relevant and necessary:
- Make sure each sentence helps support the topic sentence .
- Check for redundancies – if a sentence repeats something you’ve already said, cut it.
- Check for inconsistencies in content. Do any of your assertions seem to contradict one another? If so, resolve the disagreement and cut as necessary.
Once you’re happy with the overall shape and content of your essay, it’s time to focus on polishing it at a sentence level, making sure that you’ve expressed yourself clearly and fluently.
You’re now less concerned with what you say than with how you say it. Aim to simplify, condense, and clarify each sentence, making it as easy as possible for your reader to understand what you want to say.
- Try to avoid complex sentence construction – be as direct and straightforward as possible.
- If you have a lot of very long sentences, split some of them into shorter ones.
- If you have a lot of very short sentences that sound choppy, combine some of them using conjunctions or semicolons .
- Make sure you’ve used appropriate transition words to show the connections between different points.
- Cut every unnecessary word.
- Avoid any complex word where a simpler one will do.
- Look out for typos and grammatical mistakes.
If you lack confidence in your grammar, our essay editing service provides an extra pair of eyes.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Bryson, S. (2023, December 08). How to Revise an Essay in 3 Simple Steps. Scribbr. Retrieved April 2, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/revising/
Is this article helpful?
Shane Bryson
Shane finished his master's degree in English literature in 2013 and has been working as a writing tutor and editor since 2009. He began proofreading and editing essays with Scribbr in early summer, 2014.
"I thought AI Proofreading was useless but.."
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
8.4 Revising and Editing
Learning objectives.
- Identify major areas of concern in the draft essay during revising and editing.
- Use peer reviews and editing checklists to assist revising and editing.
- Revise and edit the first draft of your essay and produce a final draft.
Revising and editing are the two tasks you undertake to significantly improve your essay. Both are very important elements of the writing process. You may think that a completed first draft means little improvement is needed. However, even experienced writers need to improve their drafts and rely on peers during revising and editing. You may know that athletes miss catches, fumble balls, or overshoot goals. Dancers forget steps, turn too slowly, or miss beats. For both athletes and dancers, the more they practice, the stronger their performance will become. Web designers seek better images, a more clever design, or a more appealing background for their web pages. Writing has the same capacity to profit from improvement and revision.
Understanding the Purpose of Revising and Editing
Revising and editing allow you to examine two important aspects of your writing separately, so that you can give each task your undivided attention.
- When you revise , you take a second look at your ideas. You might add, cut, move, or change information in order to make your ideas clearer, more accurate, more interesting, or more convincing.
- When you edit , you take a second look at how you expressed your ideas. You add or change words. You fix any problems in grammar, punctuation, and sentence structure. You improve your writing style. You make your essay into a polished, mature piece of writing, the end product of your best efforts.
How do you get the best out of your revisions and editing? Here are some strategies that writers have developed to look at their first drafts from a fresh perspective. Try them over the course of this semester; then keep using the ones that bring results.
- Take a break. You are proud of what you wrote, but you might be too close to it to make changes. Set aside your writing for a few hours or even a day until you can look at it objectively.
- Ask someone you trust for feedback and constructive criticism.
- Pretend you are one of your readers. Are you satisfied or dissatisfied? Why?
- Use the resources that your college provides. Find out where your school’s writing lab is located and ask about the assistance they provide online and in person.
Many people hear the words critic , critical , and criticism and pick up only negative vibes that provoke feelings that make them blush, grumble, or shout. However, as a writer and a thinker, you need to learn to be critical of yourself in a positive way and have high expectations for your work. You also need to train your eye and trust your ability to fix what needs fixing. For this, you need to teach yourself where to look.
Creating Unity and Coherence
Following your outline closely offers you a reasonable guarantee that your writing will stay on purpose and not drift away from the controlling idea. However, when writers are rushed, are tired, or cannot find the right words, their writing may become less than they want it to be. Their writing may no longer be clear and concise, and they may be adding information that is not needed to develop the main idea.
When a piece of writing has unity , all the ideas in each paragraph and in the entire essay clearly belong and are arranged in an order that makes logical sense. When the writing has coherence , the ideas flow smoothly. The wording clearly indicates how one idea leads to another within a paragraph and from paragraph to paragraph.
Reading your writing aloud will often help you find problems with unity and coherence. Listen for the clarity and flow of your ideas. Identify places where you find yourself confused, and write a note to yourself about possible fixes.
Creating Unity
Sometimes writers get caught up in the moment and cannot resist a good digression. Even though you might enjoy such detours when you chat with friends, unplanned digressions usually harm a piece of writing.
Mariah stayed close to her outline when she drafted the three body paragraphs of her essay she tentatively titled “Digital Technology: The Newest and the Best at What Price?” But a recent shopping trip for an HDTV upset her enough that she digressed from the main topic of her third paragraph and included comments about the sales staff at the electronics store she visited. When she revised her essay, she deleted the off-topic sentences that affected the unity of the paragraph.
Read the following paragraph twice, the first time without Mariah’s changes, and the second time with them.
Nothing is more confusing to me than choosing among televisions. It confuses lots of people who want a new high-definition digital television (HDTV) with a large screen to watch sports and DVDs on. You could listen to the guys in the electronics store, but word has it they know little more than you do. They want to sell what they have in stock, not what best fits your needs. You face decisions you never had to make with the old, bulky picture-tube televisions. Screen resolution means the number of horizontal scan lines the screen can show. This resolution is often 1080p, or full HD, or 768p. The trouble is that if you have a smaller screen, 32 inches or 37 inches diagonal, you won’t be able to tell the difference with the naked eye. The 1080p televisions cost more, though, so those are what the salespeople want you to buy. They get bigger commissions. The other important decision you face as you walk around the sales floor is whether to get a plasma screen or an LCD screen. Now here the salespeople may finally give you decent info. Plasma flat-panel television screens can be much larger in diameter than their LCD rivals. Plasma screens show truer blacks and can be viewed at a wider angle than current LCD screens. But be careful and tell the salesperson you have budget constraints. Large flat-panel plasma screens are much more expensive than flat-screen LCD models. Don’t let someone make you by more television than you need!
Answer the following two questions about Mariah’s paragraph:
Collaboration
Please share with a classmate and compare your answers.
- Now start to revise the first draft of the essay you wrote in Section 8 “Writing Your Own First Draft” . Reread it to find any statements that affect the unity of your writing. Decide how best to revise.
When you reread your writing to find revisions to make, look for each type of problem in a separate sweep. Read it straight through once to locate any problems with unity. Read it straight through a second time to find problems with coherence. You may follow this same practice during many stages of the writing process.
Writing at Work
Many companies hire copyeditors and proofreaders to help them produce the cleanest possible final drafts of large writing projects. Copyeditors are responsible for suggesting revisions and style changes; proofreaders check documents for any errors in capitalization, spelling, and punctuation that have crept in. Many times, these tasks are done on a freelance basis, with one freelancer working for a variety of clients.
Creating Coherence
Careful writers use transitions to clarify how the ideas in their sentences and paragraphs are related. These words and phrases help the writing flow smoothly. Adding transitions is not the only way to improve coherence, but they are often useful and give a mature feel to your essays. Table 8.3 “Common Transitional Words and Phrases” groups many common transitions according to their purpose.
Table 8.3 Common Transitional Words and Phrases
After Maria revised for unity, she next examined her paragraph about televisions to check for coherence. She looked for places where she needed to add a transition or perhaps reword the text to make the flow of ideas clear. In the version that follows, she has already deleted the sentences that were off topic.
Many writers make their revisions on a printed copy and then transfer them to the version on-screen. They conventionally use a small arrow called a caret (^) to show where to insert an addition or correction.

1. Answer the following questions about Mariah’s revised paragraph.
2. Now return to the first draft of the essay you wrote in Section 8 “Writing Your Own First Draft” and revise it for coherence. Add transition words and phrases where they are needed, and make any other changes that are needed to improve the flow and connection between ideas.
Being Clear and Concise
Some writers are very methodical and painstaking when they write a first draft. Other writers unleash a lot of words in order to get out all that they feel they need to say. Do either of these composing styles match your style? Or is your composing style somewhere in between? No matter which description best fits you, the first draft of almost every piece of writing, no matter its author, can be made clearer and more concise.
If you have a tendency to write too much, you will need to look for unnecessary words. If you have a tendency to be vague or imprecise in your wording, you will need to find specific words to replace any overly general language.
Identifying Wordiness
Sometimes writers use too many words when fewer words will appeal more to their audience and better fit their purpose. Here are some common examples of wordiness to look for in your draft. Eliminating wordiness helps all readers, because it makes your ideas clear, direct, and straightforward.
Sentences that begin with There is or There are .
Wordy: There are two major experiments that the Biology Department sponsors.
Revised: The Biology Department sponsors two major experiments.
Sentences with unnecessary modifiers.
Wordy: Two extremely famous and well-known consumer advocates spoke eloquently in favor of the proposed important legislation.
Revised: Two well-known consumer advocates spoke in favor of the proposed legislation.
Sentences with deadwood phrases that add little to the meaning. Be judicious when you use phrases such as in terms of , with a mind to , on the subject of , as to whether or not , more or less , as far as…is concerned , and similar expressions. You can usually find a more straightforward way to state your point.
Wordy: As a world leader in the field of green technology, the company plans to focus its efforts in the area of geothermal energy.
A report as to whether or not to use geysers as an energy source is in the process of preparation.
Revised: As a world leader in green technology, the company plans to focus on geothermal energy.
A report about using geysers as an energy source is in preparation.
Sentences in the passive voice or with forms of the verb to be . Sentences with passive-voice verbs often create confusion, because the subject of the sentence does not perform an action. Sentences are clearer when the subject of the sentence performs the action and is followed by a strong verb. Use strong active-voice verbs in place of forms of to be , which can lead to wordiness. Avoid passive voice when you can.
Wordy: It might perhaps be said that using a GPS device is something that is a benefit to drivers who have a poor sense of direction.
Revised: Using a GPS device benefits drivers who have a poor sense of direction.
Sentences with constructions that can be shortened.
Wordy: The e-book reader, which is a recent invention, may become as commonplace as the cell phone.
My over-sixty uncle bought an e-book reader, and his wife bought an e-book reader, too.
Revised: The e-book reader, a recent invention, may become as commonplace as the cell phone.
My over-sixty uncle and his wife both bought e-book readers.
Now return once more to the first draft of the essay you have been revising. Check it for unnecessary words. Try making your sentences as concise as they can be.
Choosing Specific, Appropriate Words
Most college essays should be written in formal English suitable for an academic situation. Follow these principles to be sure that your word choice is appropriate. For more information about word choice, see Chapter 4 “Working with Words: Which Word Is Right?” .
- Avoid slang. Find alternatives to bummer , kewl , and rad .
- Avoid language that is overly casual. Write about “men and women” rather than “girls and guys” unless you are trying to create a specific effect. A formal tone calls for formal language.
- Avoid contractions. Use do not in place of don’t , I am in place of I’m , have not in place of haven’t , and so on. Contractions are considered casual speech.
- Avoid clichés. Overused expressions such as green with envy , face the music , better late than never , and similar expressions are empty of meaning and may not appeal to your audience.
- Be careful when you use words that sound alike but have different meanings. Some examples are allusion/illusion , complement/compliment , council/counsel , concurrent/consecutive , founder/flounder , and historic/historical . When in doubt, check a dictionary.
- Choose words with the connotations you want. Choosing a word for its connotations is as important in formal essay writing as it is in all kinds of writing. Compare the positive connotations of the word proud and the negative connotations of arrogant and conceited .
- Use specific words rather than overly general words. Find synonyms for thing , people , nice , good , bad , interesting , and other vague words. Or use specific details to make your exact meaning clear.
Now read the revisions Mariah made to make her third paragraph clearer and more concise. She has already incorporated the changes she made to improve unity and coherence.

1. Answer the following questions about Mariah’s revised paragraph:
2. Now return once more to your essay in progress. Read carefully for problems with word choice. Be sure that your draft is written in formal language and that your word choice is specific and appropriate.
Completing a Peer Review
After working so closely with a piece of writing, writers often need to step back and ask for a more objective reader. What writers most need is feedback from readers who can respond only to the words on the page. When they are ready, writers show their drafts to someone they respect and who can give an honest response about its strengths and weaknesses.
You, too, can ask a peer to read your draft when it is ready. After evaluating the feedback and assessing what is most helpful, the reader’s feedback will help you when you revise your draft. This process is called peer review .
You can work with a partner in your class and identify specific ways to strengthen each other’s essays. Although you may be uncomfortable sharing your writing at first, remember that each writer is working toward the same goal: a final draft that fits the audience and the purpose. Maintaining a positive attitude when providing feedback will put you and your partner at ease. The box that follows provides a useful framework for the peer review session.
Questions for Peer Review
Title of essay: ____________________________________________
Date: ____________________________________________
Writer’s name: ____________________________________________
Peer reviewer’s name: _________________________________________
- This essay is about____________________________________________.
- Your main points in this essay are____________________________________________.
- What I most liked about this essay is____________________________________________.
These three points struck me as your strongest:
These places in your essay are not clear to me:
a. Where: ____________________________________________
Needs improvement because__________________________________________
b. Where: ____________________________________________
Needs improvement because ____________________________________________
c. Where: ____________________________________________
The one additional change you could make that would improve this essay significantly is ____________________________________________.
One of the reasons why word-processing programs build in a reviewing feature is that workgroups have become a common feature in many businesses. Writing is often collaborative, and the members of a workgroup and their supervisors often critique group members’ work and offer feedback that will lead to a better final product.
Exchange essays with a classmate and complete a peer review of each other’s draft in progress. Remember to give positive feedback and to be courteous and polite in your responses. Focus on providing one positive comment and one question for more information to the author.
Using Feedback Objectively
The purpose of peer feedback is to receive constructive criticism of your essay. Your peer reviewer is your first real audience, and you have the opportunity to learn what confuses and delights a reader so that you can improve your work before sharing the final draft with a wider audience (or your intended audience).
It may not be necessary to incorporate every recommendation your peer reviewer makes. However, if you start to observe a pattern in the responses you receive from peer reviewers, you might want to take that feedback into consideration in future assignments. For example, if you read consistent comments about a need for more research, then you may want to consider including more research in future assignments.
Using Feedback from Multiple Sources
You might get feedback from more than one reader as you share different stages of your revised draft. In this situation, you may receive feedback from readers who do not understand the assignment or who lack your involvement with and enthusiasm for it.
You need to evaluate the responses you receive according to two important criteria:
- Determine if the feedback supports the purpose of the assignment.
- Determine if the suggested revisions are appropriate to the audience.
Then, using these standards, accept or reject revision feedback.
Work with two partners. Go back to Note 8.81 “Exercise 4” in this lesson and compare your responses to Activity A, about Mariah’s paragraph, with your partners’. Recall Mariah’s purpose for writing and her audience. Then, working individually, list where you agree and where you disagree about revision needs.
Editing Your Draft
If you have been incorporating each set of revisions as Mariah has, you have produced multiple drafts of your writing. So far, all your changes have been content changes. Perhaps with the help of peer feedback, you have made sure that you sufficiently supported your ideas. You have checked for problems with unity and coherence. You have examined your essay for word choice, revising to cut unnecessary words and to replace weak wording with specific and appropriate wording.
The next step after revising the content is editing. When you edit, you examine the surface features of your text. You examine your spelling, grammar, usage, and punctuation. You also make sure you use the proper format when creating your finished assignment.
Editing often takes time. Budgeting time into the writing process allows you to complete additional edits after revising. Editing and proofreading your writing helps you create a finished work that represents your best efforts. Here are a few more tips to remember about your readers:
- Readers do not notice correct spelling, but they do notice misspellings.
- Readers look past your sentences to get to your ideas—unless the sentences are awkward, poorly constructed, and frustrating to read.
- Readers notice when every sentence has the same rhythm as every other sentence, with no variety.
- Readers do not cheer when you use there , their , and they’re correctly, but they notice when you do not.
- Readers will notice the care with which you handled your assignment and your attention to detail in the delivery of an error-free document..
The first section of this book offers a useful review of grammar, mechanics, and usage. Use it to help you eliminate major errors in your writing and refine your understanding of the conventions of language. Do not hesitate to ask for help, too, from peer tutors in your academic department or in the college’s writing lab. In the meantime, use the checklist to help you edit your writing.
Editing Your Writing
- Are some sentences actually sentence fragments?
- Are some sentences run-on sentences? How can I correct them?
- Do some sentences need conjunctions between independent clauses?
- Does every verb agree with its subject?
- Is every verb in the correct tense?
- Are tense forms, especially for irregular verbs, written correctly?
- Have I used subject, object, and possessive personal pronouns correctly?
- Have I used who and whom correctly?
- Is the antecedent of every pronoun clear?
- Do all personal pronouns agree with their antecedents?
- Have I used the correct comparative and superlative forms of adjectives and adverbs?
- Is it clear which word a participial phrase modifies, or is it a dangling modifier?
Sentence Structure
- Are all my sentences simple sentences, or do I vary my sentence structure?
- Have I chosen the best coordinating or subordinating conjunctions to join clauses?
- Have I created long, overpacked sentences that should be shortened for clarity?
- Do I see any mistakes in parallel structure?
Punctuation
- Does every sentence end with the correct end punctuation?
- Can I justify the use of every exclamation point?
- Have I used apostrophes correctly to write all singular and plural possessive forms?
- Have I used quotation marks correctly?
Mechanics and Usage
- Can I find any spelling errors? How can I correct them?
- Have I used capital letters where they are needed?
- Have I written abbreviations, where allowed, correctly?
- Can I find any errors in the use of commonly confused words, such as to / too / two ?
Be careful about relying too much on spelling checkers and grammar checkers. A spelling checker cannot recognize that you meant to write principle but wrote principal instead. A grammar checker often queries constructions that are perfectly correct. The program does not understand your meaning; it makes its check against a general set of formulas that might not apply in each instance. If you use a grammar checker, accept the suggestions that make sense, but consider why the suggestions came up.
Proofreading requires patience; it is very easy to read past a mistake. Set your paper aside for at least a few hours, if not a day or more, so your mind will rest. Some professional proofreaders read a text backward so they can concentrate on spelling and punctuation. Another helpful technique is to slowly read a paper aloud, paying attention to every word, letter, and punctuation mark.
If you need additional proofreading help, ask a reliable friend, a classmate, or a peer tutor to make a final pass on your paper to look for anything you missed.
Remember to use proper format when creating your finished assignment. Sometimes an instructor, a department, or a college will require students to follow specific instructions on titles, margins, page numbers, or the location of the writer’s name. These requirements may be more detailed and rigid for research projects and term papers, which often observe the American Psychological Association (APA) or Modern Language Association (MLA) style guides, especially when citations of sources are included.
To ensure the format is correct and follows any specific instructions, make a final check before you submit an assignment.
With the help of the checklist, edit and proofread your essay.
Key Takeaways
- Revising and editing are the stages of the writing process in which you improve your work before producing a final draft.
- During revising, you add, cut, move, or change information in order to improve content.
- During editing, you take a second look at the words and sentences you used to express your ideas and fix any problems in grammar, punctuation, and sentence structure.
- Unity in writing means that all the ideas in each paragraph and in the entire essay clearly belong together and are arranged in an order that makes logical sense.
- Coherence in writing means that the writer’s wording clearly indicates how one idea leads to another within a paragraph and between paragraphs.
- Transitional words and phrases effectively make writing more coherent.
- Writing should be clear and concise, with no unnecessary words.
- Effective formal writing uses specific, appropriate words and avoids slang, contractions, clichés, and overly general words.
- Peer reviews, done properly, can give writers objective feedback about their writing. It is the writer’s responsibility to evaluate the results of peer reviews and incorporate only useful feedback.
- Remember to budget time for careful editing and proofreading. Use all available resources, including editing checklists, peer editing, and your institution’s writing lab, to improve your editing skills.
Writing for Success Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.

Editing and Proofreading
What this handout is about.
This handout provides some tips and strategies for revising your writing. To give you a chance to practice proofreading, we have left seven errors (three spelling errors, two punctuation errors, and two grammatical errors) in the text of this handout. See if you can spot them!
Is editing the same thing as proofreading?
Not exactly. Although many people use the terms interchangeably, editing and proofreading are two different stages of the revision process. Both demand close and careful reading, but they focus on different aspects of the writing and employ different techniques.
Some tips that apply to both editing and proofreading
- Get some distance from the text! It’s hard to edit or proofread a paper that you’ve just finished writing—it’s still to familiar, and you tend to skip over a lot of errors. Put the paper aside for a few hours, days, or weeks. Go for a run. Take a trip to the beach. Clear your head of what you’ve written so you can take a fresh look at the paper and see what is really on the page. Better yet, give the paper to a friend—you can’t get much more distance than that. Someone who is reading the paper for the first time, comes to it with completely fresh eyes.
- Decide which medium lets you proofread most carefully. Some people like to work right at the computer, while others like to sit back with a printed copy that they can mark up as they read.
- Try changing the look of your document. Altering the size, spacing, color, or style of the text may trick your brain into thinking it’s seeing an unfamiliar document, and that can help you get a different perspective on what you’ve written.
- Find a quiet place to work. Don’t try to do your proofreading in front of the TV or while you’re chugging away on the treadmill. Find a place where you can concentrate and avoid distractions.
- If possible, do your editing and proofreading in several short blocks of time. Your concentration may start to wane if you try to proofread the entire text at one time.
- If you’re short on time, you may wish to prioritize. Make sure that you complete the most important editing and proofreading tasks.
Editing is what you begin doing as soon as you finish your first draft. You reread your draft to see, for example, whether the paper is well-organized, the transitions between paragraphs are smooth, and your evidence really backs up your argument. You can edit on several levels:
Have you done everything the assignment requires? Are the claims you make accurate? If it is required to do so, does your paper make an argument? Is the argument complete? Are all of your claims consistent? Have you supported each point with adequate evidence? Is all of the information in your paper relevant to the assignment and/or your overall writing goal? (For additional tips, see our handouts on understanding assignments and developing an argument .)
Overall structure
Does your paper have an appropriate introduction and conclusion? Is your thesis clearly stated in your introduction? Is it clear how each paragraph in the body of your paper is related to your thesis? Are the paragraphs arranged in a logical sequence? Have you made clear transitions between paragraphs? One way to check the structure of your paper is to make a reverse outline of the paper after you have written the first draft. (See our handouts on introductions , conclusions , thesis statements , and transitions .)
Structure within paragraphs
Does each paragraph have a clear topic sentence? Does each paragraph stick to one main idea? Are there any extraneous or missing sentences in any of your paragraphs? (See our handout on paragraph development .)
Have you defined any important terms that might be unclear to your reader? Is the meaning of each sentence clear? (One way to answer this question is to read your paper one sentence at a time, starting at the end and working backwards so that you will not unconsciously fill in content from previous sentences.) Is it clear what each pronoun (he, she, it, they, which, who, this, etc.) refers to? Have you chosen the proper words to express your ideas? Avoid using words you find in the thesaurus that aren’t part of your normal vocabulary; you may misuse them.
Have you used an appropriate tone (formal, informal, persuasive, etc.)? Is your use of gendered language (masculine and feminine pronouns like “he” or “she,” words like “fireman” that contain “man,” and words that some people incorrectly assume apply to only one gender—for example, some people assume “nurse” must refer to a woman) appropriate? Have you varied the length and structure of your sentences? Do you tends to use the passive voice too often? Does your writing contain a lot of unnecessary phrases like “there is,” “there are,” “due to the fact that,” etc.? Do you repeat a strong word (for example, a vivid main verb) unnecessarily? (For tips, see our handouts on style and gender-inclusive language .)
Have you appropriately cited quotes, paraphrases, and ideas you got from sources? Are your citations in the correct format? (See the UNC Libraries citation tutorial for more information.)
As you edit at all of these levels, you will usually make significant revisions to the content and wording of your paper. Keep an eye out for patterns of error; knowing what kinds of problems you tend to have will be helpful, especially if you are editing a large document like a thesis or dissertation. Once you have identified a pattern, you can develop techniques for spotting and correcting future instances of that pattern. For example, if you notice that you often discuss several distinct topics in each paragraph, you can go through your paper and underline the key words in each paragraph, then break the paragraphs up so that each one focuses on just one main idea.
Proofreading
Proofreading is the final stage of the editing process, focusing on surface errors such as misspellings and mistakes in grammar and punctuation. You should proofread only after you have finished all of your other editing revisions.
Why proofread? It’s the content that really matters, right?
Content is important. But like it or not, the way a paper looks affects the way others judge it. When you’ve worked hard to develop and present your ideas, you don’t want careless errors distracting your reader from what you have to say. It’s worth paying attention to the details that help you to make a good impression.
Most people devote only a few minutes to proofreading, hoping to catch any glaring errors that jump out from the page. But a quick and cursory reading, especially after you’ve been working long and hard on a paper, usually misses a lot. It’s better to work with a definite plan that helps you to search systematically for specific kinds of errors.
Sure, this takes a little extra time, but it pays off in the end. If you know that you have an effective way to catch errors when the paper is almost finished, you can worry less about editing while you are writing your first drafts. This makes the entire writing proccess more efficient.
Try to keep the editing and proofreading processes separate. When you are editing an early draft, you don’t want to be bothered with thinking about punctuation, grammar, and spelling. If your worrying about the spelling of a word or the placement of a comma, you’re not focusing on the more important task of developing and connecting ideas.
The proofreading process
You probably already use some of the strategies discussed below. Experiment with different tactics until you find a system that works well for you. The important thing is to make the process systematic and focused so that you catch as many errors as possible in the least amount of time.
- Don’t rely entirely on spelling checkers. These can be useful tools but they are far from foolproof. Spell checkers have a limited dictionary, so some words that show up as misspelled may really just not be in their memory. In addition, spell checkers will not catch misspellings that form another valid word. For example, if you type “your” instead of “you’re,” “to” instead of “too,” or “there” instead of “their,” the spell checker won’t catch the error.
- Grammar checkers can be even more problematic. These programs work with a limited number of rules, so they can’t identify every error and often make mistakes. They also fail to give thorough explanations to help you understand why a sentence should be revised. You may want to use a grammar checker to help you identify potential run-on sentences or too-frequent use of the passive voice, but you need to be able to evaluate the feedback it provides.
- Proofread for only one kind of error at a time. If you try to identify and revise too many things at once, you risk losing focus, and your proofreading will be less effective. It’s easier to catch grammar errors if you aren’t checking punctuation and spelling at the same time. In addition, some of the techniques that work well for spotting one kind of mistake won’t catch others.
- Read slow, and read every word. Try reading out loud , which forces you to say each word and also lets you hear how the words sound together. When you read silently or too quickly, you may skip over errors or make unconscious corrections.
- Separate the text into individual sentences. This is another technique to help you to read every sentence carefully. Simply press the return key after every period so that every line begins a new sentence. Then read each sentence separately, looking for grammar, punctuation, or spelling errors. If you’re working with a printed copy, try using an opaque object like a ruler or a piece of paper to isolate the line you’re working on.
- Circle every punctuation mark. This forces you to look at each one. As you circle, ask yourself if the punctuation is correct.
- Read the paper backwards. This technique is helpful for checking spelling. Start with the last word on the last page and work your way back to the beginning, reading each word separately. Because content, punctuation, and grammar won’t make any sense, your focus will be entirely on the spelling of each word. You can also read backwards sentence by sentence to check grammar; this will help you avoid becoming distracted by content issues.
- Proofreading is a learning process. You’re not just looking for errors that you recognize; you’re also learning to recognize and correct new errors. This is where handbooks and dictionaries come in. Keep the ones you find helpful close at hand as you proofread.
- Ignorance may be bliss, but it won’t make you a better proofreader. You’ll often find things that don’t seem quite right to you, but you may not be quite sure what’s wrong either. A word looks like it might be misspelled, but the spell checker didn’t catch it. You think you need a comma between two words, but you’re not sure why. Should you use “that” instead of “which”? If you’re not sure about something, look it up.
- The proofreading process becomes more efficient as you develop and practice a systematic strategy. You’ll learn to identify the specific areas of your own writing that need careful attention, and knowing that you have a sound method for finding errors will help you to focus more on developing your ideas while you are drafting the paper.
Think you’ve got it?
Then give it a try, if you haven’t already! This handout contains seven errors our proofreader should have caught: three spelling errors, two punctuation errors, and two grammatical errors. Try to find them, and then check a version of this page with the errors marked in red to see if you’re a proofreading star.
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Especially for non-native speakers of English:
Ascher, Allen. 2006. Think About Editing: An ESL Guide for the Harbrace Handbooks . Boston: Wadsworth Cengage Learning.
Lane, Janet, and Ellen Lange. 2012. Writing Clearly: Grammar for Editing , 3rd ed. Boston: Heinle.
For everyone:
Einsohn, Amy. 2011. The Copyeditor’s Handbook: A Guide for Book Publishing and Corporate Communications , 3rd ed. Berkeley: University of California Press.
Lanham, Richard A. 2006. Revising Prose , 5th ed. New York: Pearson Longman.
Tarshis, Barry. 1998. How to Be Your Own Best Editor: The Toolkit for Everyone Who Writes . New York: Three Rivers Press.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Revising and Editing
What is revision.
Once you have reached the point that you have a full rough draft, take some time to step away from the essay to get a newer and better perspective. Then begin revising.
Revising means reexamining and rethinking what you’ve written in earlier drafts. The process of revision is more cyclical than it is linear, but any revision process should have clear steps that help you focus on different elements of your writing.
A successful revision process should involve:
- Adding and deleting ideas extensively
- Rearranging ideas, paragraphs, sentences, phrases, and words
- Rewriting paragraphs and sentences for more variety, better flow, and more precise word choices
Keep in mind that successful revision is rarely accomplished quickly and easily. It is typical that you will work through the process of revising three or four rough drafts before you are finally satisfied and ready to call your essay finished.
Developing a Process for Revising
Just as writing is a deeply personal and individualized act, so is revising. This chapter, along with advice from your professors and classmates, can help you identify and develop skills for revising your writing. But in order for the shape and style of your revision process to ultimately prove useful to you, then your methods for revising must become uniquely your own. This means you might take bits and pieces of the advice in this chapter, and then mix that together to formulate your specific process for revising. Also keep in mind that as you evolve as a writer, and as you write across different genres, your revision process will likewise change. What is most important is that you view revision as a continual practice that you are committed to developing and refining over time.
A Top-Down Approach to Revising
It can be tempting to focus most of your revision efforts on the small stuff happening in your sentences. But this approach will usually lead to more work, especially if you end up realizing that perfectly edited paragraphs later need to be cut because they no longer fit with your overall purpose or structure.
Instead, you should use a top-down approach for revising. Doing so helps you address larger issues before focusing on smaller issues.
- Revise for overall meaning and structure. Your essay should develop a central point clearly and logically. The purpose, tone, and point-of-view of your essay should be suited for your audience and line up with your professor’s instructions.
- Revise for paragraph development. Check that your paragraphs are logically ordered, unified, and specific.
- Revise sentence structure. Make sure your sentences remain consistent with your overall tone, are varied in type and length, and state your ideas effectively and efficiently.
- Revise for word choices. You should strive to use specific rather than general terms, should rely on strong verbs, and should only use necessary modifiers.
Other Useful Strategies for Revising
Self-questioning. Just as we use questions to help us brainstorm and define our ideas, we can use question to revise and review our writing. The below questions can help you consider multiple levels and aspects of your writing.
- Voice: Does it sound like a real human being wrote this draft? Does your introduction project a clear sense of your purpose? Honestly, would someone other than your paid instructor or classmates read beyond the first paragraph of this essay?
- Audience: Does your writing use specific strategies or ideas to draw in a specific set of readers? Do you address the same audience throughout the essay? If you don’t, are you being intentional about shifting from one audience to another, and is that intention clear in your writing?
- Message: Are your main points strong and clear? Do you have ample support for each of them? Do your supporting details clearly support your main points?
- Tone: Are you using the proper tone for the genre of writing, and for your purpose and intended audience? Is your language too casual or not professional enough? Or does it come off as overly formal and stiff? Does your tone stay consistent throughout the draft?
- Attitude: Does your stance toward the topic stay consistent throughout the draft? If it doesn’t, do you explain the cause of the transformation in your attitude?
- Reception: Is your goal or intent for writing clear? How is this essay likely to be received by another reader? What kind of motivation, ideas, or emotions will this draft draw out of your readers? What will your readers do, think, or feel immediately after finishing this essay?
Reverse Outlining. In reverse outlining, you read through your rough draft so that you can identify the topic of each paragraph. This way, you can determine if each paragraph has a clear focus and if each paragraph fits the overall organization of your essay.
Reading Aloud. The act of reading your essay aloud allows you to hear it in the way a reader will. This also forces you to slow down and pay attention to all the words in your rough draft, helping you notice where your writing is clear and effective, or where your writing is unclear or ineffective. As a general rule, poorly structured sections or sentences are hard to read out loud, indicating you might need to rework those parts of your draft.
Getting Peer Feedback. No one becomes a good writer in a vacuum. Sometimes writing is done for ourselves, but, more often, writing is done to connect to others, to share thoughts, and to communicate something others need to know. Once you have a full rough draft, it’s important for you to get an understanding of how well your writing works for readers. Showing the writing to someone else is essential. You might do this in a writers’ circle or just with a friend who is good with words and giving feedback. If possible, it’s best to show your writing to several people to get more than one opinion. Receiving feedback helps you discover the strengths in your writing as well as areas that may be improved.
Getting Feedback from a Tutor. Tutoring is an effective way for you to receive knowledgeable one-on-one feedback about your writing. It can also be an effective way to help manage time. Once you have a rough draft, you should seek the advice of the college’s writing tutors. They can quickly help you identify weaknesses in your writing and then discuss options for improvement.
What is Editing?
Editing is part of revising. If most of the revision process encourages you to consider how elements of your draft work together, editing is when you start to focus on isolated issues of grammar, mechanics, punctuation, spelling, and typos.
Remember that it is extremely important not to focus on editing too early in the writing process. If you write one sentence or paragraph and immediately begin to edit it, your overall progress will be slowed. This is why you should revise thoroughly first, and then edit and proofread your essays toward the end of your writing process.
What To Look for While Editing Your Writing
Grammar refers to the way people use language rules and how words are used in a certain order to form phrases and clauses that relay a meaning for readers. The term syntax (the art of sentence structure) goes hand in hand with grammar.
It’s important to note that, since you use language every day, you already have internalized essential grammar rules. Whether you believe it or not, you already know a great deal about how English grammar works, even if you can’t identify many grammar concepts by name. Most college writers struggle with only one or two main grammar issues, like how to correctly use a comma or semicolon. Once you master these issues, you can confidently edit your own work.
For help with understanding the rules and concepts of English grammar, check out the Purdue OWL: Grammar Guide .
Mechanics and Punctuation
Mechanics are established rules within a language system, and sometimes include the individual decisions that writers make regarding the use of capitalization, underlining, italicizing, numbers versus numerals, the placement of specific punctuation marks, and how all this differs throughout English-speaking countries. For example, many mechanics and punctuation rules differ between American English and British English.
Punctuation refers to the symbols you use to help readers understand and process the information you wish to convey through the sentences you write. Somewhat like the notes within a piece of music help musicians move quickly or slowly through a composition, punctuation marks are used to control the flow and rhythm of your writing.
For help with understanding the rules and concepts of English grammar, check out the Purdue OWL: Mechanics Guide and the Purdue OWL: Punctuation Guide .
Other Key Issues to Look Out for While Editing
Precision of Words. In early parts of the drafting process, it’s common to use generic words that do not accurately capture our intended message. Once you reach the editing phase, you should be on the lookout for any generic word choices that can be changed to become more precise. One of the overall goals in academic writing, and in most forms of writing, is to use specific language and terms as often as possible.
Unnecessary Words. In addition to striving to be as precise as possible in your use of language, you should also try to remove any unnecessary words. Many students believe that words like really , very , just , and so on add an something important to their writing. However, words like these are overused and should be given special consideration. Each word in your writing should feel necessary to both you and your readers, and anything less than necessary should be removed or rewritten.
Repetition of Words and Phrases. The unintentional repetition of words and phrases is one of the most common oversights we make in our writing. We all have our go-to words and phrases—ones that come naturally to us as we speak and when we write. Because of this, you need to diligently check your writing for overuse of words and phrases. One of the best ways to do this is to read aloud while you edit. Doing so will allow you to hear and more easily notice the repetitions. Along with reading aloud, you can also use the search function in programs like Microsoft Word and Google Docs to quickly locate words and phrases you know you tend to repeat.
Spelling. We all have words that give us trouble as we write, even if we have learned how to spell those words. While spell-checkers can help us most of the time, they are not always correct, and it’s our responsibility to recognize which words we commonly misspell and edit our drafts to find spelling mistakes. Many of the words we misspell look or sound like other words, and for help identifying those words you should check out the Purdue OWL’s Common Words that Sound Alike .
Sources Used to Create this Chapter
Parts of this chapter were remixed from:
- Let’s Get Writing by Elizabeth Browning et. al., which was published under a CC-BY-NC-SA 4.0 license.
- English Composition by Ann Inoshita et. al., which was published under a CC-BY 4.0 license.
- English Composition I by Kimberly Miller-Davis, which was published under a CC-BY 4.0 license.
Starting the Journey: An Intro to College Writing Copyright © by Leonard Owens III; Tim Bishop; and Scott Ortolano is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Steps for Revising Your Paper

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Proofreading is primarily about searching your writing for errors, both grammatical and typographical, before submitting your paper for an audience (a teacher, a publisher, etc.). Use this resource to help you find and fix common errors.
When you have plenty of time to revise, use the time to work on your paper and to take breaks from writing. If you can forget about your draft for a day or two, you may return to it with a fresh outlook. During the revising process, put your writing aside at least twice—once during the first part of the process, when you are reorganizing your work, and once during the second part, when you are polishing and paying attention to details.
Use the following questions to evaluate your drafts. You can use your responses to revise your papers by reorganizing them to make your best points stand out, by adding needed information, by eliminating irrelevant information, and by clarifying sections or sentences.
Find your main point.
What are you trying to say in the paper? In other words, try to summarize your thesis, or main point, and the evidence you are using to support that point. Try to imagine that this paper belongs to someone else. Does the paper have a clear thesis? Do you know what the paper is going to be about?
Identify your readers and your purpose.
What are you trying to do in the paper? In other words, are you trying to argue with the reading, to analyze the reading, to evaluate the reading, to apply the reading to another situation, or to accomplish another goal?
Evaluate your evidence.
Does the body of your paper support your thesis? Do you offer enough evidence to support your claim? If you are using quotations from the text as evidence, did you cite them properly?
Save only the good pieces.
Do all of the ideas relate back to the thesis? Is there anything that doesn't seem to fit? If so, you either need to change your thesis to reflect the idea or cut the idea.
Tighten and clean up your language.
Do all of the ideas in the paper make sense? Are there unclear or confusing ideas or sentences? Read your paper out loud and listen for awkward pauses and unclear ideas. Cut out extra words, vagueness, and misused words.
Visit the Purdue OWL's vidcast on cutting during the revision phase for more help with this task.
Eliminate mistakes in grammar and usage.
Do you see any problems with grammar, punctuation, or spelling? If you think something is wrong, you should make a note of it, even if you don't know how to fix it. You can always talk to a Writing Lab tutor about how to correct errors.
Switch from writer-centered to reader-centered.
Try to detach yourself from what you've written; pretend that you are reviewing someone else's work. What would you say is the most successful part of your paper? Why? How could this part be made even better? What would you say is the least successful part of your paper? Why? How could this part be improved?
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
9 Revising and Editing Your Writing
University of Minnesota Libraries Publishing
Revision and Editing
Revising and editing are the two tasks you undertake to significantly improve your writing Both are very important elements of the writing process. You may think that a completed first draft means little improvement is needed. However, even experienced writers need to improve their drafts and rely on peers during revising and editing. You may know that athletes miss catches, fumble balls, or overshoot goals. Dancers forget steps, turn too slowly, or miss beats. For both athletes and dancers, the more they practice, the stronger their performance will become. Web designers seek better images, a more clever design, or a more appealing background for their web pages. Writing has the same capacity to profit from improvement and revision.
Understanding the Purpose of Revising and Editing
Revising and editing allow you to examine two important aspects of your writing separately, so that you can give each task your undivided attention.
- When you revise , you take a second look at your ideas. You might add, cut, move, or change information in order to make your ideas clearer, more accurate, more interesting, or more convincing.
- When you edit , you take a second look at how you expressed your ideas. You add or change words. You fix any problems in grammar, punctuation, and sentence structure. You improve your writing style. You make your essay into a polished, mature piece of writing, the end product of your best efforts.
When you are revising and editing you should always keep the genre, audience, and purpose of your text in mind. Many tips for revising and editing, including those here, are thought of with academic essays in mind. The type of writing that you do in your profession may require you to think differently about paragraph structure, sentence structure, vocabulary, etc.
Revising Stage 1
When you first begin revising, you should focus on the big picture. The following questions can help guide you with this:
- Do you have a clear thesis ? Do you know what idea or perspective you want your reader to understand upon reading your essay?
- Is your essay well organized ?
- Is each paragraph a building block in your essay: does each explain or support your thesis?
- Does it need a different shape? Do parts need to be moved?
- Do you fully explain and support the main ideas of your paper?
- Does your introduction provide background information that grabs the reader’s interest ?
- Does your conclusion summarize the key arguments and perspectives used in the paper?
- Are you saying in your essay what you want to say – maintaining your own “voice”?
- What is the strength of your paper? What is the weakness?
Revising Stage 2
The second stage of revising requires that you look at your content closely at the paragraph level. It’s now time to examine each paragraph, on its own, to see where you might need to revise. The following questions will guide you through the mid-view revision stage:
- Does each paragraph contain solid, specific information, or examples that support the point you are making?
- Are there are other facts, quotations, examples, or descriptions to add that can more clearly illustrate or provide evidence for the points you are making?
- Are there sentences, words, descriptions or information that you can delete because they do not add to the points you are making or may confuse the reader?
- Are the paragraphs in the right order – do they align with your essay outline sentence in the introduction ?
- Are your paragraphs overly long ? Does each paragraph explore one main idea ?
- Do you use clear transitions / signposting so the reader can follow your thinking?
- Are any paragraphs or parts of paragraphs repetitive and need to be deleted?
- Have you elaborated, explained, evaluated, and given examples that demonstrate your sound and valid reasoning
If you are working on a writing assignment in a group and each member is contributing a portion of the text, it is especially important that you revise the text for repeated information, especially general information that each group member might be using to provide context for their contribution. Also make sure that all information is contextualized for the reader. Sometimes a group member may give information thinking that another group member has provided context earlier in the text when they have not. Your audience should not be able to tell that multiple people contributed sections to the document. In the revision stage, each group member should read the entire text and make suggestions. It might also help to make an appointment with a tutor at the SDSU Writing Center .
Read the following paragraph from an academic essay. Click on the plus signs to see suggestions for revision
Editing Up Close
Once you have completed your revision and feel confident in your content, it’s time to begin the editing stage of your revision and editing process. The following questions will guide you through your editing:
- Are there any grammar errors , that is, have you been consistent in your use of tense, do your pronouns agree? Have you eliminated first-person pronouns?
- Have you accurately and effectively used punctuation ?
- Do you rely on strong verbs and nouns and maintain a good balance with adjectives and adverbs , using them to enhance descriptions but ensuring clear sentences?
- Have you avoided emotive language and hyperbole?
- Are your words as accurate as possible, for the sake of clarity?
- Do you define any technical or unusual terms you use?
- Are there extra words, clichés or colloquial terms in your sentences that you can delete ?
- Do you vary your sentence structure ?
- Have you accurately presented facts ; have you copied quotations precisely?
- If you are writing an academic essay, have you tried to be objective in your evidence and maintained academic tone?
- If writing a personal essay, is the narrative voice lively and interesting ?
- Have you spellchecked your paper? Have you proofread your paper – spellcheck does not address every error or incorrect word use?
- If you used sources, have you consistently documented all of the sources’ ideas and information using a standard citation and referencing style?
If you are writing a text in a group, you will want to make sure that your text has a unified voice and writing style. Your audience should not be able to tell that multiple people contributed to the text.
LICENSES AND ATTRIBUTIONS
- Revision and Editing and Understanding the Purpose of Revising and Editing. By : Minnesota Libraries Publishing Project. Located at : https://mlpp.pressbooks.pub/writingsuccess/chapter/8-4-revising-and-editing/ . Project : Writing for Success. Minor edits by : Stephanie Frame. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Revising Stage 1. By : Excelsior Online Writing Lab. Located at : https://owl.excelsior.edu/writing-process/revising-and-editing/revising-and-editing-revising-stage-1/ . License : CC BY: Attribution
- Revising Stage 2. By : Excelsior Online Writing Lab. Located at : https://owl.excelsior.edu/writing-process/revising-and-editing/revising-and-editing-revising-stage-2/. Minor edits by : Stephanie Frame. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Revising Stage 3. By : Excelsior Online Writing Lab. Located at : https://owl.excelsior.edu/writing-process/revising-and-editing/revising-and-editing-revising-stage-3/. Minor edits by : Stephanie Frame. License : CC BY: Attribution
Revising and Editing Your Writing Copyright © 2023 by University of Minnesota Libraries Publishing is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
GKT103: General Knowledge for Teachers – Essays
Revising and Editing
You've probably heard someone say they were going to revise or edit an essay. Did you know these are different things? When we revise, we think about the big picture in an essay: the thesis, the main ideas, the supporting details, the organization, etc. When we edit, we focus on the sentence-level points: spelling, grammar, word choices, etc. Both are important and must be done when we complete your essay on the exam. This resource provides strategies for revising and editing that you can practice before your exam to help you strengthen the final essay you submit.
See It in Practice
In this video cast, you'll see how our student addresses her revision and editing process using specific feedback on her essay from her professor. You'll be able to see how she uses the feedback to make her essay stronger and what revision looks like in comparison to editing.

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

7.1: Revising and Editing
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 20691

- Athena Kashyap & Erika Dyquisto
- City College of San Francisco via ASCCC Open Educational Resources Initiative

Revising and editing are two tasks you must undertake to significantly improve your essay. Both are very important elements of the writing process. You may think that a completed first draft means only a little improvement is needed. However, even experienced writers improve on their drafts and rely on peers during revising and editing. You know that athletes miss catches, fumble balls, or overshoot goals. Dancers forget steps, turn too slowly, or miss beats. Web designers seek better images, a more clever design, or a more appealing background for their web pages. For athletes, dancers, designers...the more they practice, the stronger their performance. Writing similarly needs constant revision and editing to become as close to perfect as one can get it.
Understanding the Purpose of Revising and Editing
Revising and editing allow you to examine two important aspects of your writing, separately. So, you can give each task your undivided attention.
- When you revise, you take a second look at your ideas. You might add, cut, move, or change information in order to make your ideas clearer, more accurate, more interesting, or more convincing.
- When you edit, you take a second look at how you expressed your ideas. You add or change words; fix problems in grammar, punctuation, and sentence structure; and improve your writing style. And that will make your essay into a polished, mature piece of writing--the end product of your best efforts.
How do you get the best out of your revisions and editing? Here are some strategies that writers have developed to ensure they look at their first drafts from a fresh perspective. Try them over the course of this semester; then keep using the ones that bring results.
- Take a break. You are proud of what you wrote, but you might be too close to it to make changes. Set aside your writing for a few hours or even a day until you can look at it objectively.
- Ask someone you trust for feedback and constructive criticism.
- Pretend you are one of your readers. Are you satisfied or dissatisfied? Why?
- Use the resources that your college provides. Find out where your school’s writing lab is located and ask about the assistance they provide online and in person.
Many people hear the words critic , critical , and criticism and pick up only negative vibes which provoke feelings that make them blush, grumble, or shout. However, as a writer and a thinker, you need to learn to be critical of yourself in a positive way (constructively) and have high expectations for your work. Train your eye and trust your ability to fix what needs fixing. For this, you need to teach yourself where to look.
What is Revision?
Revising is looking for ways to make your ideas clearer, stronger, and more convincing. When revising, you might add, cut, move, or change whole sentences or paragraphs. Revising is far more than just editing because, editing is correcting grammar, style, usage, and punctuation. Revising is really a re- vision of your entire essay: ideas, organization, development, grammar, and mechanics. You can follow the steps outlined below while revising.
So, how do you revise? There’s one main thing to keep in mind when revising: revise from “big” to “small.” There are three main parts to revision which we will be covering in this section which follow the illustration below:
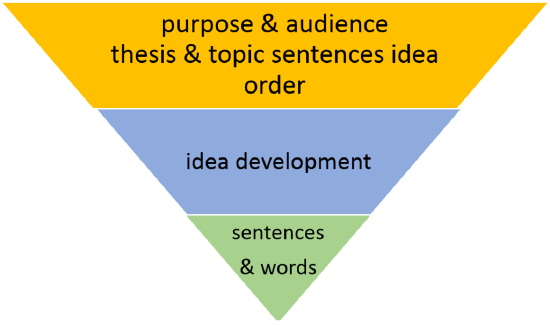
Revision Check-list
Directions: Print out a clean copy of the essay you plan to revise. Follow the steps below, marking your revision notes on this clean copy. Your instructor may want you to turn in this draft with revision notes.
Part I: Global Revisions
- Revise for unity: When you revise for unity, you are revising to make sure all of your points are related to your main point—they unite to support your main point. Sometimes it is easy to drift away from your main point, so you want to check each paragraph closely to make sure it is working to prove your thesis. Look for topic sentences that support your thesis. Then examine each paragraph, making sure every single sentence in the paragraph is working to support the topic sentence.
- Revise for support, detail, and analysis : Your support is your primary evidence, your quotes. Your detail is usually included in your explanation portion of your PIE paragraph that helps clarify the relationship of the support to the topic sentence, and your analysis is where you have explained the quote to make it clear to the reader how it supports your point. When revising, you want to make sure you have enough support, detail, and analysis to fully develop your point. Remember that you want to assume your reader is educated, but not necessarily abreast of the topics you are discussing. Mark on your page where you can include more support or better support. Identify how the two quotes relate to each other.
- Revise for coherence: When revising for coherence, you are checking to make sure that all of the support connects to make a clear, well-developed argument. Coherence is the glue that connects all of the parts together and allows the reader to easily follow the argument. The best way to improve coherence is to add transitions. Transitions are words, phrases, and sentences that connect ideas so that writing moves smoothly from one point to another. Transitions can be used to connect sentences within a paragraph, as well as to connect one paragraph to another.
Part II: Local Revisions—Sentences structure, grammar, syntax, and word choice
Directions: After you have complete all of the global revisions, follow these steps to revise for local issues in your writing.
1. Once you have marked all the grammar errors in your sentences, read through your essay again. This time look for places where you can combine sentences so that your sentence lengths are varied.
2. Read through your essay again, looking for places where you can make the sentence clearer or more concise by using more descriptive language. (Sometimes, if you find the right word, you can say something in one word that originally took you four words.)
3. Now you want to check all of your quotes. Check to make sure you have quoted the text exactly, that you have cited your sources properly, and that you have punctuated your citation correctly.
4. Start with the last sentence of your essay. Read through your entire essay from bottom to top out loud , looking at the sentence structure, grammar, and language.
5. If there is a particular grammar issue that you know you struggle with, read through your entire essay once just looking for that one error in your sentences. (Try not to get distracted. Staying focused on one error will really help you catch that particular error.) If you struggle with multiple errors, give each error one full read through from bottom to top.
6. Check your formatting one more time. Have you followed MLA style: 1” margins, double-spaced (even on the first page where you have your name block), page numbers with last name starting on the first page.
Creating Unity and Coherence
Follow your outline closely. That gives a reasonable guarantee that your writing will stay on purpose and not drift away from the controlling idea. Sometimes, when writers are rushed, are tired, or cannot find the right words, their writing may suffer. Their writing may no longer be clear and concise, and they may be adding information that is not needed to develop the main idea.
When a piece of writing has unity, all the ideas in each paragraph and in the entire essay clearly belong and are arranged in an order that makes logical sense; When the writing has coherence, the ideas flow smoothly. The wording clearly indicates how one idea leads to another within a paragraph and from paragraph to paragraph.
Reading your writing aloud will often help you find problems with unity and coherence. Listen for the clarity and flow of your ideas. Identify places where you find yourself confused, and write a note to yourself about possible fixes. (This is also a good time to give your draft to another person to see if they are confused anywhere.)
Many writers make their revisions on a printed copy and then transfer them to the version on-screen. They conventionally use a small arrow called a caret (^) to show where to insert an addition or correction.
Below is an example of a page of Andi's edited essay. They chose to make the changes on paper so they could get a good view of how the whole paper flows together. It is easier to do this on a printed paper than on the computer screen.

Answer the following questions about Andi’s revised paragraph.
A. 1. Do you agree with the transitions and other changes that Mariah made to the paragraph? Which would you keep and which were unnecessary? Explain. 2. What transition words or phrases did Andi add to her paragraph? Why did she choose each one? 3. What effect does adding additional sentences have on the coherence of the paragraph? Explain. When you read both versions aloud, which version has a more logical flow of ideas? Explain.
B. Now return to the first draft of the essay you wrote and revise it for coherence. Add transition words and phrases where they are needed, and make any other changes that are needed to improve the flow and connection between ideas.
Being Clear and Concise
Some writers are very methodical and painstaking when they write a first draft. Other writers unleash a lot of words in order to get out all that they feel they need to say. Do either of these composing styles match your style? Or is your composing style somewhere in between? No matter which description best fits you, the first draft of almost every piece of writing, no matter its author, can be made clearer and more concise.
If you have a tendency to write too much, you will need to look out for unnecessary words. If you have a tendency to be vague or imprecise in your wording, you will need to find specific words to replace any overly general language. More information about style and word choice can also be found in Chapter 11, " Clarity, Conciseness, and Style. "
Identifying Wordiness
Sometimes writers use too many words when fewer words will appeal more to their audience and better fit their purpose. Here are some common examples of wordiness to look for in your draft. Eliminating wordiness helps all readers, because it makes your ideas clear, direct, and straightforward.
Revised: The Biology Department sponsors two major experiments.
Revised: Two well-known consumer advocates spoke in favor of the proposed legislation.
Wordy: As a world leader in the field of green technology, the company plans to focus its efforts in the area of geothermal energy.
A report as to whether or not to use geysers as an energy source is in the process of preparation.
Revised: As a world leader in green technology, the company plans to focus on geothermal energy.
A report about using geysers as an energy source is in preparation.
Wordy: It might perhaps be said that using a GPS device is something that is a benefit to drivers who have a poor sense of direction.
Revised: Using a GPS device benefits drivers who have a poor sense of direction.
My over-sixty uncle bought an e-book reader, and his wife bought an e-book reader, too.
Revised: The e-book reader, a recent invention, may become as commonplace as the cell phone.
My over-sixty uncle and his wife both bought e-book readers.
Now return once more to the first draft of the essay you have been revising. Check it for unnecessary words. Try making your sentences as concise as they can be.
Choosing Specific, Appropriate Words
Most college essays should be written in formal English suitable for an academic situation. Follow these principles to be sure that your word choice is appropriate. For more information about word choice and academic style, see Chapter 11 .
- Avoid slang. Find alternatives to bummer , kewl , and rad .
- Avoid language that is overly casual. Write about “people” rather than “guys” unless you are trying to create a specific effect. A formal tone calls for formal language.
- Avoid contractions. Use do not in place of don’t , I am in place of I’m , have not in place of haven’t , and so on. Contractions are considered casual speech. Avoiding using contractions will also help you find proofreading mistakes.
- Avoid clichés. Overused expressions such as green with envy , face the music , better late than never , and similar expressions are empty of meaning and may not appeal to your audience.
- Be careful when you use words that sound alike but have different meanings. Some examples are allusion/illusion , complement/compliment , council/counsel , concurrent/consecutive , founder/flounder , and historic/historical . When in doubt, check a dictionary.
- Choose words with the connotations you want. Choosing a word for its connotations is as important in formal essay writing as it is in all kinds of writing. Compare the positive connotations of the word proud and the negative connotations of arrogant and conceited .
- Use specific words rather than overly general words. Find synonyms for thing , people , nice , good , bad , interesting , stuff, and other vague words. Or use specific details to make your exact meaning clear.
Now read the revisions Andi made to make her third paragraph clearer and more concise. They had already incorporated the changes for improving unity and coherence.

1. Answer the following questions about Andi's revised paragraph:
A. 1. Read the unrevised and the revised paragraphs aloud. Explain in your own words how changes in word choice have affected Andi’s writing. 2. Do you agree with the changes that Andi made to her paragraph? Which changes would you keep and which were unnecessary? Explain. What other changes would you have made? 3. What effect does removing contractions and the pronoun you have on the tone of the paragraph? How would you characterize the tone now? Why?
B. Now return once more to your essay in progress. Read carefully for problems with word choice. Be sure that your draft is written in formal language and that your word choice is specific and appropriate.
Completing a Peer Review
After working so closely with a piece of writing, writers often need to step back and ask for a more objective reader. What writers most need is feedback from readers who can respond only to the words on the page. When they are ready, writers show their draft to someone they respect and who can give an honest response about its strengths and weaknesses.
You, too, can ask a peer to read your draft when it is ready. After evaluating the feedback and assessing what is most helpful, the reader’s feedback will help you when you revise your draft. This process is called peer review.
Reading Your Own Drafts
Writers tend to read over their own papers pretty quickly, with the knowledge of what they are trying to argue already in their minds. Reading in this way can cause you to skip over gaps in your written argument because the gap-filler is in your head. A problem occurs when your reader falls into these gaps. Your reader wants you to make the necessary connections from one thought or sentence to the next. When you don’t, the reader can become confused or frustrated. Think about when you read something and you struggle to find the most important points or what the writer is trying to say. Isn’t that annoying? Doesn’t it make you want to quit reading and surf the web or call a friend?
Reading aloud
If you go to a tutoring session, you will probably hear the tutor say, “We always read papers out loud—would you like to read yours, or would you like to hear me read it?” Reading aloud has many benefits. Most people have far more experience listening to and speaking English than they do reading and editing it on the printed page. When reading your draft out loud or listening to someone else read it, your brain gets the information in a new way, and you may notice things that you didn’t see before.
As listeners, we need the order of ideas in a paper to make sense. We can’t flip back and forth from page to page to try to figure out what is going on or find information we need. When you hear your paper read out loud, you may recognize that you need to re-order the information in it or realize that there are gaps in your explanation. Listeners also need transitions to help us get from one main idea to the next. When you hear your paper, you may recognize places where you have moved from one topic to another too abruptly.
You may also hear errors in your sentences. Sometimes we leave out a word, mess things up as we copy and paste text, or make a grammatical mistake. These kinds of errors can be hard to see on the page, but sentences that contain them are very likely to sound wrong. For native speakers of English (and some non-native speakers, too), reading out loud is one of the most powerful proofreading techniques around.
Sometimes sentences aren’t grammatically incorrect, but they are still awkward in some way—too long, too convoluted, too repetitive. Problems like these are often easily heard. Hearing your paper can also help you get a sense of whether the tone is right. Does it sound too formal? Too chatty or casual? What kind of impression will your voice in this paper make on a reader? Sometimes hearing your words helps you get a more objective sense of the impression you are creating—listening puts in you in something more like the position your reader will be in as he/she moves through your text.
Work with a partner in your class and identify specific ways to strengthen each other’s essays. Although sharing your writing may feel uncomfortable at first, remember that each writer is working towards the same goal: a final draft that fits the audience and the purpose. Maintaining a positive attitude when providing feedback will put you and your partner at ease. The box that follows provides a useful framework for a peer review session.
This feels a little silly.
Reading aloud (or listening to your writing being read) takes some getting used to, but give it a try. You may be surprised at how much it can speed up your revision process!
Three-step revision process . Authored by: pattheprofessor. License: All Rights Reserved. License Terms: Standard YouTube license.
Peer Review Comments
Once you have a draft, get a person you trust to read your rough draft, and then ask them to talk to you about what they did and didn’t understand. (Now is not the time to talk about proofreading stuff, so make sure they ignore those issues for the time being). You will likely get one of the following responses or a combination of them:
If your listener/reader has tons of questions about what you are saying, then you probably need to explain more. Let’s say you are writing a paper on piranhas, and your reader says, “What’s a piranha? Why do I need to know about them? How would I identify one?” Those are vital questions that you clearly need to answer in your paper. You need more detail and elaboration.
If your reader seems confused, you probably need to explain more clearly. So if he says, “Are there piranhas in the lakes around here?” you may not need to give more examples, but rather focus on making sure your examples and points are clear.
If your reader looks bored and can repeat back to you more details than she needs to know to get your point, you probably explained too much. Excessive detail can also be confusing, because it can bog the reader down and keep her from focusing on your main points. You want your reader to say, “So it seems like your paper is saying that piranhas are misunderstood creatures that are essential to South American ecosystems,” not, “Uh… piranhas are important?” or, “Well, I know you said piranhas don’t usually attack people, and they’re usually around 10 inches long, and some people keep them in aquariums as pets, and dolphins are one of their predators, and…a bunch of other stuff, I guess?”
Sometimes it’s not the amount of explanation that matters, but the word choice and tone you adopt. Your word choice and tone need to match your audience’s expectations. For example, imagine you are researching piranhas; you find an article in National Geographic and another one in an academic journal for scientists. How would you expect the two articles to sound? National Geographic is written for a popular audience; you might expect it to have sentences like “The piranha generally lives in shallow rivers and streams in South America.” The scientific journal, on the other hand, might use much more technical language because it’s written for an audience of specialists. A sentence like “ Serrasalmus piraya lives in fresh and brackish intercoastal and proto-arboreal sub-tropical regions between the 45th and 38th parallels” might not be out of place in the journal. Generally, you want your reader to know enough material to understand the points you are making. It’s like the old forest/trees metaphor. If you give the reader nothing but trees, she won’t see the forest (your thesis, the reason for your paper). If you give her a big forest and no trees, she won’t know how you got to the forest (she might say, “Your point is fine, but you haven’t proven it to me”). You want the reader to say, “Nice forest, and those trees really help me to see it.”
Questions for Peer Review
Title of essay: ____________________________________________
Date: ____________________________________________
Writer’s name: ____________________________________________
Peer reviewer’s name: _________________________________________
- This essay is about____________________________________________.
- Your main points in this essay are____________________________________________.
- What I most liked about this essay is____________________________________________.
a. Point: ____________________________________________
Why: ____________________________________________
b. Point: ____________________________________________
c. Point: ____________________________________________
a. Where: ____________________________________________
Needs improvement because__________________________________________
b. Where: ____________________________________________
Needs improvement because ____________________________________________
c. Where: ____________________________________________
- The one additional change you could make that would improve this essay significantly is ____________________________________________.
Here is an additional, more specific peer review resource that you may use.
Writing at Work
One of the reasons why word-processing programs build in a 'reviewing' feature is that workgroups have become a common feature in many businesses. Writing is often collaborative, and the members of a workgroup and their supervisors often critique group members’ work and offer feedback that will lead to a better final product.
Exchange essays with a classmate and complete a peer review of each other’s draft in progress. Remember to give positive feedback as well as constructive criticism and to be courteous and polite in your responses. Focus on providing one positive comment and one question for more information to the author.
Using Feedback Objectively
The purpose of peer feedback is to receive constructive criticism of your essay.The peer reviewer is your first real audience, and you have the opportunity to learn what confuses and delights a reader so that you can improve your work before sharing the final draft with a wider audience (or your intended audience).
It may not be necessary to incorporate every recommendation your peer reviewer makes. However, if you start to observe a pattern in the responses you receive from peer reviewers, you might want to take that feedback into consideration in future assignments. For example, if you read consistent comments about a need for more research, then you may want to consider including more research in future assignments.
Using Feedback from Multiple Sources
You might receive feedback from more than one reader. In this situation, you may receive feedback from some readers who do not understand the assignment or who lack your involvement with and enthusiasm for it.
You need to evaluate the responses you receive according to two important criteria:
- Determine if the feedback supports the purpose of the assignment.
- Determine if the suggested revisions are appropriate to the audience.
Then, using these standards, accept or reject revision feedback.
Work with two partners. Go back to Exercises 3 in this lesson and compare your responses to Activity A, about Andi’s paragraph, with your partners’. Recall Andi’s purpose for writing, and their audience. Then, working individually, discuss where you agree and where you disagree about revision needs.
Proofreading, Editing, and Presentation
In Peer Review, the focus is on the larger content and structural issues, but when you have revised those parts of your paper, it is also important to edit and proofread for sentence structure, grammar, and formatting.
PROOFREADING QUESTIONS
Sentence Structure
Do all of your sentences make sense?
Are they connected with coordinators (FANBOYS) and subordinators to clarify meaning?
Transitions
Have you used additional transition words to help the reader understand how your sentences relate to each other?
Have you made sure you implemented what the class has practiced, and what you need to work on?
Have you used some of the words (especially verbs) you have learned?
Are they used correctly?
Have you formatted your paper according to MLA rules?
Is the essay in a folder?
Have you turned in everything your instructor has asked you to turn in? Typically, this may include (from top to bottom
- The final draft
- Feedback Sheet
- Peer Review sheet
- Rough draft
Remember to use the proper format when creating your finished assignment. Sometimes an instructor, a department, or a college, will require students to follow specific instructions on titles, margins, page numbers, or the location of the writer’s name. These requirements may be more detailed and rigid for research projects and term papers, which often observe the Modern Language Association (MLA) or American Psychological Association (APA) style guides.
To ensure the format is correct, follow any specific instructions, and make a final check before you submit an assignment.
Use this list to think about the question: What went well while writing your essay and what gave you trouble?
HOCs (Higher Order Concerns)
- Understanding the reading
- Summarizing the issue (for the introduction)
- Coming up with the thesis
- Sorting and organizing the information
- Deciding on the topics of the body paragraphs
- Writing the topic sentences
- Including information (details)
- Incorporating quotations
- Explaining or interpreting those details
- Summing up (concluding) the paragraphs
- Writing the conclusion
LOCs (Later Order Concerns)
- Writing clear sentences
- Using subordinators and coordinators (FANBOYS)
- Using transitions to connect ideas
- Checking grammar _____________________
- Proofreading for spelling and typos
- Formatting (MLA)
Write 1.5 pages (using separate paragraphs) and answer the question at the top of the page.
Also, if something gave you trouble, how did you work on it? Or, what will you do to work on it next time?
The following video offers a quick overview of the revision process, moving from “big” concepts to “small” sentence and language items.
Reading Aloud -- UNC Writing Center . Authored by: UNC Writing Center. License: All Rights Reserved. License Terms: Standard YouTube license.
Contributors
- Adapted from Writing for Success . Provided by: The Saylor Foundation. License: CC-NC-SA 3.0
- Adapted from Revision Overview in College Writing. Authored by: Susan Oaks. Provided by: Empire State College, SUNY OER Services. Project: College Writing. License: CC BY-NC:
- From Accelerated English . Authored by: Ashley Paul. Provided by: Libretext. License: CC-BY-SA
This page most recently updated on June 5, 2020.

The Admissions Strategist
Revising, editing & proofreading your college application essay: a guide.
Although it’s only 650 words , writing the Common App essay is a long and in-depth process.
That’s because these 650 words can have a major impact on whether or not you are accepted to the college of your choice.
The essay gives admissions officers insight into your personality, goals, and interests, plus an idea of how you will fit into and contribute to their college campus.
- For these reasons, revising and editing is an essential step in the college essay writing process. You want your essay to be clear, concise, engaging, and polished.
To accomplish this goal, use this checklist for revising and editing the college application essay.
11-Item Checklist
Revising means improving the overall piece of writing.
This includes enhancing clarity, word choice, and structure.
It may also mean adding new ideas, improving current ideas, or removing ideas that are unnecessary or off-topic.
When it comes to revising the college application essay, here are some items you should consider.
1. Does the essay clearly address the selected topic or prompt?
It’s very important that your college application essay fully addresses the topic you selected or were assigned.
This is the foundation of college essay revisions; nothing else matters if you don’t address the topic correctly.
For example, imagine you selected this prompt from the Common Application:
The lessons we take from obstacles we encounter can be fundamental to later success. Recount a time when you faced a challenge, setback, or failure. How did it affect you, and what did you learn from the experience?
First, make sure that your essay is directly related to the selected topic. It should be focused on a challenge or failure you have experienced and the lessons you learned as a result.
Additionally, ensure that you answered all parts of the question.
- An essay addressing this prompt, for example, would not be fully on topic if it only described a challenge you experienced.
- You must also explain how this challenge affected you and what you learned from the experience.
- Key words from the prompt (in this case “challenge,” or “setback,” and “lessons”) should be mentioned in the essay.
If your essay is off-topic or doesn’t address all parts of the question, you will need to do some revising.
You want to check the soundness of your essay and how it expands on the topic and conflict during the first draft revision .
The first draft is where you’ll make major changes, such as changing the structure, shifting the focus on the story, rewriting entire paragraphs, or even scrapping the entire essay.
2. Is the college essay well-organized?
The first paragraph of your essay should include some sort of thesis or main idea for the essay.
The rest of the essay should be organized around this thesis, with all additional paragraphs developing and supporting the main idea.
Each paragraph should also have its own subtopic, and all information within each paragraph should further develop and support the subtopic.
- For example, your introduction could mention a challenge (like being bullied growing up as a result of a speech impediment), how this challenge affected you (it was hurtful and made you self-conscious for a while), and the lessons you ultimately learned (to be confident in yourself regardless of what others say, to handle hardships with humor and positivity, etc.).
You could then have one paragraph focused on describing the challenge, one on discussing how the challenge affected you, and a third, longer paragraph explaining the lessons you learned as a result.
- You should also use transitions to smoothly connect ideas and help readers follow your thought process.
It’s important to note that an essay with a complex structure or storytelling arc still needs to have an effective and clear payoff. Complexity is no substitute for solid writing.
- If you think the story and its message are becoming too convoluted, chances are that it is. And if you already think it is, then your readers would definitely agree.
While there’s no need to write a five-paragraph essay (I really mean that), the following structure will help you write a clear essay with an easy-to-follow structure:
- Introduction (Keep this short and sweet; don’t get bogged down with the details.)
- Conflict (What happened? What’s the problem?)
- Solution (What did you do to proactively solve the problem?)
- Lessons learned (What did you learn from pursuing a solution or experiencing this conflict? How have your values changed? How have these changes shifted your perspective? How will you change moving forward?
3. Supporting details, examples & anecdotes
Each paragraph should be well-developed with specific details, examples, or anecdotes supporting your point.
The college essay is not the same as a typical academic essay, which may be dry and lacking in personality.
Instead, the college essay is intended to demonstrate your voice, personality, and uniqueness. It should be engaging and colorful.
- You should include vivid, specific details to bring your points to life.
- In this way, a college essay is similar to a more creative piece of writing.
- As you and your parents or high school counselor look over the first draft of it, find places to add colorful examples and concrete details to breathe some more life into your writing.
Make sure all details and examples help support and develop the main points you are trying to convey.
Having trouble coming up with details? Think of the following:
- Who was involved?
- What happened? What did you do?
- When did this occur? Is there an important chronological context?
- Where did this occur? Is the setting relevant to the story?
- Why did this happen? Why did you react or act the way you did?
- How did you go about solving this problem?
Important : There’s an important principle in writing called “Chekhov’s gun” – use this principle when evaluating whether details are relevant to your essay. So, what is Chekhov’s gun?
- If you’re going to mention something in your college essay, make sure it plays a role somewhere else in the story.
- Don’t describe the color of the sky and the sound of an instrument if they aren’t mentioned again in the essay or don’t influence the plot.
- If you describe a bully as “strong” or a problem as “habitual,” the conflict each is a part of should be influenced by the strength of the bully or repetition of the problem.
Chekhov’s gun is critical because it will help you trim word count and stay on message.
4. Voice & Personality
Another way to make the essay interesting and engaging is to ensure that it is written in your own unique voice .
- Of course, the essay shouldn’t include slang, and it shouldn’t read like a text message to your best friend. But it also shouldn’t sound stiff, forced, or unnatural.
It should read almost as if you are talking to a teacher you feel comfortable with, or to a favorite older relative.
- When revising the essay, make sure you didn’t include too many high-level vocabulary words in an effort to sound intellectual, as this can sound forced.
- You can even read the essay aloud to see if it flows naturally and “sounds” like you.
The essay should also give the admissions officer a glimpse of your personality.
- Does the essay accurately portray who you are beyond your GPA, SAT scores, and extracurricular activities?
- If not, spend some time making sure it captures your unique identity.
This is the climax of the entire process of the revisions process — your own voice, perspective, and lessons learned are the most important elements of the essay.
5. A Good Candidate for Admission
Remember that another key purpose of the college essay is to show your school of choice that you are a strong candidate for admission.
When reading your essay, the admissions officer should form an understanding of what you can contribute to a college campus.
Be sure that your essay paints you in a positive light.
The rest of your application has already provided information about your GPA, SAT scores, and other accomplishments, but what else should admissions officers know about you to see that you are a good candidate for admission?
- This could include your love of learning, curiosity, persistence, motivation, resilience, teamwork, kindness, work ethic, enthusiasm for the school, leadership abilities, etc.
Before you submit the essay, check that it highlights some of the qualities that will make you an excellent college student and an asset to any campus.
Also, consider sharing it with one or two friends or trusted adults to get a second opinion.
This is the Barebones Exercise, a helpful exercise to determine whether you told an effective story and demonstrated your personality, values, and themes:
- Grab a highlighter and print your college essay.
- Highlight the most important sentences of your essay. These sentences should include topic sentences, sentences that propel the story, and sentences that imply or state your values.
- Write or copy and paste those highlighted sentences into a new document.
- Organize the sentences by the order in which they appear in your college essay.
- Read the sentences in order. How does it sound?
- This is the barebones version of your essay. What message are you getting? Is your simplified story still a cohesive narrative?
- Does this barebones version of your essay still imply or state the newfound values found in the conclusion of your original essay? What will the college admissions officer learn about you?
All told, you want this barebones version to emit the same messages and important elements found in your real college essay.
The barebones version helps you momentarily remove complementary details and determine the central premise of your essay.
6. Do you stick to the topic?
We already talked about addressing the topic, but it’s important that you stick to it as well. Check the essay for any information that is off-topic or unnecessary.
- During the entire revision process, it’s important to keep this in mind: Do you stay on topic, and do you extrapolate values as the essay progresses?
An easy way to do this is to identify your thesis statement. Anything in the essay that does not support, develop, or relate to the thesis statement should be cut.
- It can be tempting to include unrelated information that you would like to share with admissions officers, but doing so will make the essay disorganized and difficult to follow.
Additionally, each paragraph should have its own subtopic.
- Anything that doesn’t support, develop, or relate to each paragraph’s topic sentence should also be cut or moved to another, more relevant paragraph.
Use the Barebones Exercise from the previous section. Here’s how it works when checking whether you stuck to your topic:
- Highlight your topic sentences.
- Underline the set-up sentences that immediately follow your topic sentences.
- Highlight your resolution.
- Now, read your highlighted topic sentences. Ask yourself whether they are properly telling the story.
- Read your set-up sentences that follow your topic sentences. Do they support the topic sentence or main idea of the story? Are you getting off track? Do you exaggerate or sound overconfident or doubtful? Are you providing unnecessary details? Your words are $100 bills. Spend your money wisely to abide by the word count.
- Read your resolution. Does it properly end the story in your own image? Is it a cliché? Are you using pop culture or literary phrases? Too many of these supplant your voice for an artificial one. Are you closing the loop? Open-ended endings are perfectly fine but difficult to execute. Make sure you’re ending the story on your own terms.
- Of course: Did you answer the essay prompt?
- Overall: Are you covering too much ground? If so, rewrite and decrease the scope of the essay. Your job is to write effectively, not compose the next Harry Potter entry.
7. A good mix of short and long sentences
Sentence variety gives writing rhythm and life. It can make essays easier to follow and more engaging.
For these reasons, it’s important that the essay doesn’t include too many short sentences or too many long sentences. Instead, it should include a mix of both.
- Read through your essay to be sure it’s not full of only short, choppy sentences or long sentences with many clauses. Try to add more variety to your sentence lengths before submitting the essay.
Still having trouble? Read your essay aloud by yourself or to a friend and ask how it sounds. Short and choppy? Or smooth and fluid?
Think of your essay as if it were a song. Songs with multiple notes sound far superior to songs with dull, awkward notes.
Editing means fixing basic errors like spelling, punctuation, capitalization, and word usage.
To edit effectively, try reading the essay backward. This helps you focus more on spelling and grammar without being distracted by the ideas in the essay.
Focus on one type of error at a time, and read slowly and carefully, sentence by sentence.
The last four items on our checklist will help you ensure that your college essay is error-free. This is the concluding chapter of the revisions process.
8. Are all words spelled correctly?
Spell check doesn’t catch everything. Homonyms, for example, go unnoticed by spell check.
Homonyms are words that sound the same but have different meanings, like “pair” and “pare,” or “they’re,” “their,” and “there.”
As long as you have spelled the word correctly, spell check won’t notice that the word itself is incorrect.
- The same goes for wrong words, like using “martial” instead of “marital.”
- “My favorite hobby it fishing.”
So relying on spell check could result in you turning in an essay that’s actually full of misspellings and wrong words.
Read carefully through the essay, ensuring that all words are spelled correctly and that you haven’t accidentally used an incorrect word.
9. Proper punctuation & capitalization
Check for proper use of commas, periods, parentheses, question marks, quotation marks and, if applicable, semicolons.
If you’re unsure about punctuation use, see if your English teacher is available to read over the essay and offer some suggestions.
Alternatively, research proper use of punctuation on the Internet or at the library.
- Additionally, the first word in each sentence should be capitalized, along with proper nouns (names of people and places) and the word “I.”
- For the most part, all other words should be lowercase.
Similar to the issue with spelling, programs don’t always notice grammar errors. If grammar and usage aren’t your strengths, you might not realize you’ve written something incorrectly. For example:
“My hard work has positively effected my grades.”
This might be the kind of error many people miss. Do you know the difference between affect and effect?
If not, it’s a good idea to ask someone.
Because grammatical rules can be complicated, it’s better to get help than to risk not using them correctly.

10. Do you abide by the word count?
You need to follow the word count the prompt provides.
- This is non-negotiable.
- Not following the word count implies to college admissions officers that you won’t follow the most basic rules on campus.
At first, your Common App essay should be 800 or 900 words long. Extra details and paragraphs in the preliminary stages are OK.
Now that you like the essence of your college essay, here’s a step-by-step process on trimming word count:
- You can find the most “fat” here because you likely started writing your essay thinking about big ideas.
- That means you tried to explain things and give full but ineffective context to your situation.
- Clichés are usually abundant in this part. Don’t use clichés. You’d be drowning out your writing.
- Be sure to lop off parts that needlessly explain your ending, but be careful not to eliminate useful aspects of your resolution.
- Do you repeat things in different words?
- Do you use clichés?
- Are your quotes of appropriate length?
- Do you overuse aphorisms?
- Are your similes of appropriate length? Do you use too many?
- Are your metaphors of appropriate length? Do you use too many?
- Do you use too many analogies? Are any of them excessively clumsy?
- Are any of them excessively clumsy?
- Are you trying too hard to sound smart?
- Do you use these words in everyday writing? If not, they might not be a good fit for your essay.
11. Sentence Structure
Check that word usage and sentence structure is grammatically correct as well. This includes:
- Subject-verb agreement
- Consistent verb tenses (not switching back and forth between past and present, for example)
- Are there any run-on sentences or sentence fragments?
- Are the antecedents (Ex: my mom, Mr. Hughes) for all pronouns (Ex: she, he) clear, and do pronouns and antecedents agree in number?
- Does the essay include any unnecessary adjectives or adverbs?
- Have you unintentionally left out any words, or included words that should be deleted?
Critical Tips to Help You With Proofreading
After you consult the checklist above, utilize the tips below help you write a stellar and mistake-free essay.
Read Your Essay Aloud
- This is probably the best tip for any piece of writing you plan to show someone, but it’s especially important for the college essay. Most professionals practice reading their work aloud to a small audience or to themselves.
- When you do this, you are far more likely to hear the errors your eyes tend to miss.
- Reading to an audience of one or more people can also be beneficial, because they can catch the errors you didn’t hear.
While reading aloud won’t always help you with typos, it will give you a sense of whether or not your phrasing is awkward, or your sentences are too wordy.
- Simply put, if it doesn’t sound right, it usually isn’t.
Treat reading your college essay aloud like a process. The more you do it, the more chances you have to evaluate particular phrases and sentences.
Proofreading Requires Taking a Step Back
For most writers, time can be incredibly valuable when drafting their work.
Tired eyes often miss simple mistakes, and the more we look at something we have written, the more immune we are to its flaws. That seems counterintuitive, but it’s true.
- There is simply no substitute for taking a break from your writing and coming back to it later.
When you approach your essay with a fresh look, it will seem like a totally new piece of writing. It’s not always the best writing, but that gives you the opportunity to make the necessary changes.
Print Your Essay
Like taking a break from your work, printing your writing allows you to see it in a completely different way . Most of us are used to only working on a computer, and we rarely print work out to edit.
- However, there is no substitute for marking up your writing with a pencil or pen.
Many people say that when they print out their writing, it seems like someone else wrote it. This is exactly the perspective you need to be a good judge of what’s on the page.
Proofreading With Different Eyes
Having another person proofread your work might not always be your favorite option.
Many of us aren’t very comfortable showing what we’ve written to other people, but having another person edit your work is incredibly helpful.
- This person could be a teacher, friend, or anyone else whose knowledge and writing expertise you trust.
- Y our current or former teachers have the advantage of knowing your writing well, so they are often the best people to consult.
Teachers have likely read many college essays in the past, so they are experts in correcting errors.
While your English teacher might be the obvious choice, consider showing your essay to a college counselor.
They, too, have read many personal essays, and they can help you with any stage of your editing process.
While your teachers know your writing, friends know you personally. They can be the best judges of whether you’re saying something in exactly the right way.
Of course, you are the writer, and it is entirely your choice which suggestions to take or leave, so consider the legitimacy of the advice you get before making any changes.
Save Multiple Drafts
Occasionally, you might proofread your college essay, making some changes to the original document without saving an original. Sometimes, those changes might not be what you want out of a final draft. In writing, it’s always helpful to see where you started.
- If you scrap something, keep the original version so you can remember how you expressed your thinking originally.
Make sure, when saving your drafts, that they are clearly marked to prevent confusion. You don’t want to make the mistake of sending the wrong draft in; there might not be any going back from that step.
Proofread Multiple Times
There is simply no substitute for putting the time and effort in to review your college essay. To maximize your editing skills, you need multiple opportunities to use them. By taking a break, printing your work, or reading aloud, you are automatically providing opportunities for multiple readings. You will probably find that when you do this, you will have opportunities to correct different types of errors. Keep going until your editing is complete.
Create the Ideal Setting
While this may sound obvious, minimizing distractions while proofreading allows for a sharper eye and better-focused attention on your work.
- If you are easily bothered by noise from other people or from music and television, find a quiet place where you can devote all of your attention to the task of editing. If music helps you focus, try that, too.
Editors thrive in the settings that make them feel comfortable and focused, so make sure to find yours.
Advice From a Writing Expert
Amy Ostroth, senior director of communications at Sweet Briar College, has this advice for students:
Proofreading and revising your college application essay — or even essays you might write for class — are important parts of the writing process. I use three strategies when I’m reviewing my own writing. First, read the piece backwards so you won’t be tempted to see what you meant to write instead of what you actually wrote. Second, read the piece out loud to yourself. Third, find a friend or family member and read the piece out loud to them. You’ll catch new things and they’ll be a second set of ears to hear things you might have missed!
Recap: College Essay Revisions, Edits & Proofreading
Plan, write, revise, and edit your college essay using this checklist, and you’ll be able to submit an engaging, precise, and polished final product. These items ensure the entire process of revisions is implemented in an even-keeled manner.
Learn how we can help you with college and career guidance! Check out our YouTube channel!
Click Here to Schedule a Free Consult!

Stay on track and ease your anxiety with our second-to-none college application assistance.

- Ethics & Honesty
- Privacy Policy
- Join Our Team
(732) 339-3835
Free online proofreading and essay editor
A reliable proofreading tool and essay editor for any writer or student, a complete environment.
Typely is more than just a proofreading tool. It's a complete writing environment.
Thousands of checks
More than a thousand checks are being performed and we've only scratched the surface.
Inspired by the greatest writers
Gain access to humanity’s collective understanding about the craft of writing.
A proofreading tool that does not bark at every tree
Typely is precise. Existing tools for proofreading raise so many false alarms that their advice cannot be trusted. Instead, the writer must carefully consider whether to accept or reject each change.
We aim for a tool so precise that it becomes possible to unquestioningly adopt its recommendations and still come out ahead — with stronger, tighter prose. Better to be quiet and authoritative than loud and unreliable.
Relax, focus, write your next masterpiece...
Writing presumes more than simply laying out words on a paper. Typely helps you get in the mood and keeps you focused, immersed and ready to write your story.
Whether you need a distraction-free environment, some chill relaxing sounds or a pomodoro timer to manage your time we got you covered.
Got questions? We have answers.
No. Typely is completely free and we plan on keeping it that way. We are considering some advanced features however that might be available under a premium plan.
The only limit we have applied thus far is on the number of characters you can submit and that is being set at a maximum of 50,000.
In theory yes but that will require a lot of work and professionals dedicated for this job. We are considering a way of letting the community participate somehow.
Typely does not do grammar checking because it's hard and almost impossible to get right. The aim for Typely is to be precise and reliable.
Ultimate Guide to Writing Your College Essay
Tips for writing an effective college essay.
College admissions essays are an important part of your college application and gives you the chance to show colleges and universities your character and experiences. This guide will give you tips to write an effective college essay.
Want free help with your college essay?
UPchieve connects you with knowledgeable and friendly college advisors—online, 24/7, and completely free. Get 1:1 help brainstorming topics, outlining your essay, revising a draft, or editing grammar.
Writing a strong college admissions essay
Learn about the elements of a solid admissions essay.
Avoiding common admissions essay mistakes
Learn some of the most common mistakes made on college essays
Brainstorming tips for your college essay
Stuck on what to write your college essay about? Here are some exercises to help you get started.
How formal should the tone of your college essay be?
Learn how formal your college essay should be and get tips on how to bring out your natural voice.
Taking your college essay to the next level
Hear an admissions expert discuss the appropriate level of depth necessary in your college essay.
Student Stories
Student Story: Admissions essay about a formative experience
Get the perspective of a current college student on how he approached the admissions essay.
Student Story: Admissions essay about personal identity
Get the perspective of a current college student on how she approached the admissions essay.
Student Story: Admissions essay about community impact
Student story: admissions essay about a past mistake, how to write a college application essay, tips for writing an effective application essay, sample college essay 1 with feedback, sample college essay 2 with feedback.
This content is licensed by Khan Academy and is available for free at www.khanacademy.org.
Revising and Editing
Learning objectives.
- Identify major areas of concern in the draft essay during revising and editing.
- Use peer reviews and editing checklists to assist revising and editing.
- Revise and edit the first draft of your essay and produce a final draft.
Revising and editing are the two tasks you undertake to significantly improve your essay. Both are very important elements of the writing process. You may think that a completed first draft means little improvement is needed. However, even experienced writers need to improve their drafts and rely on peers during revising and editing. You may know that athletes miss catches, fumble balls, or overshoot goals. Dancers forget steps, turn too slowly, or miss beats. For both athletes and dancers, the more they practice, the stronger their performance will become. Web designers seek better images, a more clever design, or a more appealing background for their web pages. Writing has the same capacity to profit from improvement and revision.
Understanding the Purpose of Revising and Editing
Revising and editing allow you to examine two important aspects of your writing separately, so that you can give each task your undivided attention.
- When you revise , you take a second look at your ideas. You might add, cut, move, or change information in order to make your ideas clearer, more accurate, more interesting, or more convincing.
- When you edit , you take a second look at how you expressed your ideas. You add or change words. You fix any problems in grammar, punctuation, and sentence structure. You improve your writing style. You make your essay into a polished, mature piece of writing, the end product of your best efforts.
How do you get the best out of your revisions and editing? Here are some strategies that writers have developed to look at their first drafts from a fresh perspective. Try them over the course of this semester; then keep using the ones that bring results.
- Take a break. You are proud of what you wrote, but you might be too close to it to make changes. Set aside your writing for a few hours or even a day until you can look at it objectively.
- Ask someone you trust for feedback and constructive criticism.
- Pretend you are one of your readers. Are you satisfied or dissatisfied? Why?
- Use the resources that your college provides. Find out where your school’s writing lab is located and ask about the assistance they provide online and in person.
Many people hear the words critic , critical , and criticism and pick up only negative vibes that provoke feelings that make them blush, grumble, or shout. However, as a writer and a thinker, you need to learn to be critical of yourself in a positive way and have high expectations for your work. You also need to train your eye and trust your ability to fix what needs fixing. For this, you need to teach yourself where to look.
Creating Unity and Coherence
Following your outline closely offers you a reasonable guarantee that your writing will stay on purpose and not drift away from the controlling idea. However, when writers are rushed, are tired, or cannot find the right words, their writing may become less than they want it to be. Their writing may no longer be clear and concise, and they may be adding information that is not needed to develop the main idea.
When a piece of writing has unity , all the ideas in each paragraph and in the entire essay clearly belong and are arranged in an order that makes logical sense. When the writing has coherence , the ideas flow smoothly. The wording clearly indicates how one idea leads to another within a paragraph and from paragraph to paragraph.
Reading your writing aloud will often help you find problems with unity and coherence. Listen for the clarity and flow of your ideas. Identify places where you find yourself confused, and write a note to yourself about possible fixes.
Creating Unity
Sometimes writers get caught up in the moment and cannot resist a good digression. Even though you might enjoy such detours when you chat with friends, unplanned digressions usually harm a piece of writing.
Mariah stayed close to her outline when she drafted the three body paragraphs of her essay she tentatively titled “Digital Technology: The Newest and the Best at What Price?” But a recent shopping trip for an HDTV upset her enough that she digressed from the main topic of her third paragraph and included comments about the sales staff at the electronics store she visited. When she revised her essay, she deleted the off-topic sentences that affected the unity of the paragraph.
Read the following paragraph twice, the first time without Mariah’s changes, and the second time with them.

Click on Image to Enlarge
1. Answer the following two questions about Mariah’s paragraph:
- Do you agree with Mariah’s decision to make the deletions she made? Did she cut too much, too little, or just enough? Explain.
- Is the explanation of what screen resolution means a digression? Or is it audience friendly and essential to understanding the paragraph? Explain.
Collaboration
Please share with a classmate and compare your answers.
Now start to revise the first draft of the essay you wrote in Section 8 “Writing Your Own First Draft.” Reread it to find any statements that affect the unity of your writing. Decide how best to revise.
When you reread your writing to find revisions to make, look for each type of problem in a separate sweep. Read it straight through once to locate any problems with unity. Read it straight through a second time to find problems with coherence. You may follow this same practice during many stages of the writing process.
Writing at Work
Creating coherence.
Careful writers use transitions to clarify how the ideas in their sentences and paragraphs are related. These words and phrases help the writing flow smoothly. Adding transitions is not the only way to improve coherence, but they are often useful and give a mature feel to your essays. Table 8.3 “Common Transitional Words and Phrases” groups many common transitions according to their purpose.
Table 8.3 Common Transitional Words and Phrases
After Maria revised for unity, she next examined her paragraph about televisions to check for coherence. She looked for places where she needed to add a transition or perhaps reword the text to make the flow of ideas clear. In the version that follows, she has already deleted the sentences that were off topic.

Click to Enlarge Image
Many writers make their revisions on a printed copy and then transfer them to the version on-screen. They conventionally use a small arrow called a caret (^) to show where to insert an addition or correction.
- Do you agree with the transitions and other changes that Mariah made to her paragraph? Which would you keep and which were unnecessary? Explain.
- What transition words or phrases did Mariah add to her paragraph? Why did she choose each one?
- What effect does adding additional sentences have on the coherence of the paragraph? Explain. When you read both versions aloud, which version has a more logical flow of ideas? Explain.
- Now return to the first draft of the essay you wrote in Section 8 “Writing Your Own First Draft” and revise it for coherence. Add transition words and phrases where they are needed, and make any other changes that are needed to improve the flow and connection between ideas.
Being Clear and Concise
Some writers are very methodical and painstaking when they write a first draft. Other writers unleash a lot of words in order to get out all that they feel they need to say. Do either of these composing styles match your style? Or is your composing style somewhere in between? No matter which description best fits you, the first draft of almost every piece of writing, no matter its author, can be made clearer and more concise.
If you have a tendency to write too much, you will need to look for unnecessary words. If you have a tendency to be vague or imprecise in your wording, you will need to find specific words to replace any overly general language.
Identifying Wordiness
Sometimes writers use too many words when fewer words will appeal more to their audience and better fit their purpose. Here are some common examples of wordiness to look for in your draft. Eliminating wordiness helps all readers, because it makes your ideas clear, direct, and straightforward.
- Sentences that begin with There is or There are . Wordy: There are two major experiments that the Biology Department sponsors. Revised: The Biology Department sponsors two major experiments.
- Sentences with unnecessary modifiers. Wordy: Two extremely famous and well-known consumer advocates spoke eloquently in favor of the proposed important legislation. Revised: Two well-known consumer advocates spoke in favor of the proposed legislation.
- Sentences in the passive voice or with forms of the verb to be . Sentences with passive-voice verbs often create confusion, because the subject of the sentence does not perform an action. Sentences are clearer when the subject of the sentence performs the action and is followed by a strong verb. Use strong active-voice verbs in place of forms of to be , which can lead to wordiness. Avoid passive voice when you can. Wordy: It might perhaps be said that using a GPS device is something that is a benefit to drivers who have a poor sense of direction. Revised: Using a GPS device benefits drivers who have a poor sense of direction.
Now return once more to the first draft of the essay you have been revising. Check it for unnecessary words. Try making your sentences as concise as they can be.
Choosing Specific, Appropriate Words
Most college essays should be written in formal English suitable for an academic situation. Follow these principles to be sure that your word choice is appropriate. For more information about word choice, see Chapter 4 “Working with Words: Which Word Is Right?”.
- Avoid slang. Find alternatives to bummer , kewl , and rad .
- Avoid language that is overly casual. Write about “men and women” rather than “girls and guys” unless you are trying to create a specific effect. A formal tone calls for formal language.
- Avoid contractions. Use do not in place of don’t , I am in place of I’m , have not in place of haven’t , and so on. Contractions are considered casual speech.
- Avoid clichés. Overused expressions such as green with envy , face the music , better late than never , and similar expressions are empty of meaning and may not appeal to your audience.
- Be careful when you use words that sound alike but have different meanings. Some examples are allusion/illusion , complement/compliment , council/counsel , concurrent/consecutive , founder/flounder , and historic/historical . When in doubt, check a dictionary.
- Choose words with the connotations you want. Choosing a word for its connotations is as important in formal essay writing as it is in all kinds of writing. Compare the positive connotations of the word proud and the negative connotations of arrogant and conceited .
- Use specific words rather than overly general words. Find synonyms for thing , people , nice , good , bad , interesting , and other vague words. Or use specific details to make your exact meaning clear.
Now read the revisions Mariah made to make her third paragraph clearer and more concise. She has already incorporated the changes she made to improve unity and coherence.

Click Image to Enlarge
- Read the unrevised and the revised paragraphs aloud. Explain in your own words how changes in word choice have affected Mariah’s writing.
- Do you agree with the changes that Mariah made to her paragraph? Which changes would you keep and which were unnecessary? Explain. What other changes would you have made?
- What effect does removing contractions and the pronoun you have on the tone of the paragraph? How would you characterize the tone now? Why?
- Now return once more to your essay in progress. Read carefully for problems with word choice. Be sure that your draft is written in formal language and that your word choice is specific and appropriate.
Completing a Peer Review
After working so closely with a piece of writing, writers often need to step back and ask for a more objective reader. What writers most need is feedback from readers who can respond only to the words on the page. When they are ready, writers show their drafts to someone they respect and who can give an honest response about its strengths and weaknesses.
You, too, can ask a peer to read your draft when it is ready. After evaluating the feedback and assessing what is most helpful, the reader’s feedback will help you when you revise your draft. This process is called peer review .
You can work with a partner in your class and identify specific ways to strengthen each other’s essays. Although you may be uncomfortable sharing your writing at first, remember that each writer is working toward the same goal: a final draft that fits the audience and the purpose. Maintaining a positive attitude when providing feedback will put you and your partner at ease. The box that follows provides a useful framework for the peer review session.
Questions for Peer Review
Title of essay: ____________________________________________
Date: ____________________________________________
Writer’s name: ____________________________________________
Peer reviewer’s name: _________________________________________
- This essay is about____________________________________________.
- Your main points in this essay are____________________________________________.
- What I most liked about this essay is____________________________________________.
- Point: ____________________________________________Why: ____________________________________________
- Where: ____________________________________________Needs improvement because__________________________________________
- Where: ____________________________________________Needs improvement because ____________________________________________
- The one additional change you could make that would improve this essay significantly is ____________________________________________.
Exchange essays with a classmate and complete a peer review of each other’s draft in progress. Remember to give positive feedback and to be courteous and polite in your responses. Focus on providing one positive comment and one question for more information to the author.
Using Feedback Objectively
The purpose of peer feedback is to receive constructive criticism of your essay. Your peer reviewer is your first real audience, and you have the opportunity to learn what confuses and delights a reader so that you can improve your work before sharing the final draft with a wider audience (or your intended audience).
It may not be necessary to incorporate every recommendation your peer reviewer makes. However, if you start to observe a pattern in the responses you receive from peer reviewers, you might want to take that feedback into consideration in future assignments. For example, if you read consistent comments about a need for more research, then you may want to consider including more research in future assignments.
Using Feedback from Multiple Sources
You might get feedback from more than one reader as you share different stages of your revised draft. In this situation, you may receive feedback from readers who do not understand the assignment or who lack your involvement with and enthusiasm for it.
You need to evaluate the responses you receive according to two important criteria:
- Determine if the feedback supports the purpose of the assignment.
- Determine if the suggested revisions are appropriate to the audience.
Then, using these standards, accept or reject revision feedback.
Work with two partners. Go back to Note 8.81 “Exercise 4” in this lesson and compare your responses to Activity A, about Mariah’s paragraph, with your partners’. Recall Mariah’s purpose for writing and her audience. Then, working individually, list where you agree and where you disagree about revision needs.
Editing Your Draft
If you have been incorporating each set of revisions as Mariah has, you have produced multiple drafts of your writing. So far, all your changes have been content changes. Perhaps with the help of peer feedback, you have made sure that you sufficiently supported your ideas. You have checked for problems with unity and coherence. You have examined your essay for word choice, revising to cut unnecessary words and to replace weak wording with specific and appropriate wording.
The next step after revising the content is editing. When you edit, you examine the surface features of your text. You examine your spelling, grammar, usage, and punctuation. You also make sure you use the proper format when creating your finished assignment.
Editing often takes time. Budgeting time into the writing process allows you to complete additional edits after revising. Editing and proofreading your writing helps you create a finished work that represents your best efforts. Here are a few more tips to remember about your readers:
- Readers do not notice correct spelling, but they do notice misspellings.
- Readers look past your sentences to get to your ideas—unless the sentences are awkward, poorly constructed, and frustrating to read.
- Readers notice when every sentence has the same rhythm as every other sentence, with no variety.
- Readers do not cheer when you use there , their , and they’re correctly, but they notice when you do not.
- Readers will notice the care with which you handled your assignment and your attention to detail in the delivery of an error-free document.
The first section of this book offers a useful review of grammar, mechanics, and usage. Use it to help you eliminate major errors in your writing and refine your understanding of the conventions of language. Do not hesitate to ask for help, too, from peer tutors in your academic department or in the college’s writing lab. In the meantime, use the checklist to help you edit your writing.
Editing Your Writing
- Are some sentences actually sentence fragments?
- Are some sentences run-on sentences? How can I correct them?
- Do some sentences need conjunctions between independent clauses?
- Does every verb agree with its subject?
- Is every verb in the correct tense?
- Are tense forms, especially for irregular verbs, written correctly?
- Have I used subject, object, and possessive personal pronouns correctly?
- Have I used who and whom correctly?
- Is the antecedent of every pronoun clear?
- Do all personal pronouns agree with their antecedents?
- Have I used the correct comparative and superlative forms of adjectives and adverbs?
- Is it clear which word a participial phrase modifies, or is it a dangling modifier?
Sentence Structure
- Are all my sentences simple sentences, or do I vary my sentence structure?
- Have I chosen the best coordinating or subordinating conjunctions to join clauses?
- Have I created long, overpacked sentences that should be shortened for clarity?
- Do I see any mistakes in parallel structure?
Punctuation
- Does every sentence end with the correct end punctuation?
- Can I justify the use of every exclamation point?
- Have I used apostrophes correctly to write all singular and plural possessive forms?
- Have I used quotation marks correctly?
Mechanics and Usage
- Can I find any spelling errors? How can I correct them?
- Have I used capital letters where they are needed?
- Have I written abbreviations, where allowed, correctly?
- Can I find any errors in the use of commonly confused words, such as to / too / two ?
Be careful about relying too much on spelling checkers and grammar checkers. A spelling checker cannot recognize that you meant to write principle but wrote principal instead. A grammar checker often queries constructions that are perfectly correct. The program does not understand your meaning; it makes its check against a general set of formulas that might not apply in each instance. If you use a grammar checker, accept the suggestions that make sense, but consider why the suggestions came up.
Proofreading requires patience; it is very easy to read past a mistake. Set your paper aside for at least a few hours, if not a day or more, so your mind will rest. Some professional proofreaders read a text backward so they can concentrate on spelling and punctuation. Another helpful technique is to slowly read a paper aloud, paying attention to every word, letter, and punctuation mark.
If you need additional proofreading help, ask a reliable friend, a classmate, or a peer tutor to make a final pass on your paper to look for anything you missed.
Remember to use proper format when creating your finished assignment. Sometimes an instructor, a department, or a college will require students to follow specific instructions on titles, margins, page numbers, or the location of the writer’s name. These requirements may be more detailed and rigid for research projects and term papers, which often observe the American Psychological Association (APA) or Modern Language Association (MLA) style guides, especially when citations of sources are included.
To ensure the format is correct and follows any specific instructions, make a final check before you submit an assignment.
With the help of the checklist, edit and proofread your essay.
Key Takeaways
- Revising and editing are the stages of the writing process in which you improve your work before producing a final draft.
- During revising, you add, cut, move, or change information in order to improve content.
- During editing, you take a second look at the words and sentences you used to express your ideas and fix any problems in grammar, punctuation, and sentence structure.
- Unity in writing means that all the ideas in each paragraph and in the entire essay clearly belong together and are arranged in an order that makes logical sense.
- Coherence in writing means that the writer’s wording clearly indicates how one idea leads to another within a paragraph and between paragraphs.
- Transitional words and phrases effectively make writing more coherent.
- Writing should be clear and concise, with no unnecessary words.
- Effective formal writing uses specific, appropriate words and avoids slang, contractions, clichés, and overly general words.
- Peer reviews, done properly, can give writers objective feedback about their writing. It is the writer’s responsibility to evaluate the results of peer reviews and incorporate only useful feedback.
- Remember to budget time for careful editing and proofreading. Use all available resources, including editing checklists, peer editing, and your institution’s writing lab, to improve your editing skills.
- Successful Writing. Authored by : Anonymous. Provided by : Anonymous. Located at : http://2012books.lardbucket.org/books/successful-writing/ . License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike

Privacy Policy

6 Best Paper Writing Services: Legitimate Essay Writing Services
A re you searching for essay assistance or a legitimate company that can compose your essay? There are hundreds or even thousands of essay writing services available online. Each claims to be the preeminent essay writer for pupils. Difficulty may arise when attempting to discern a legitimate writing service from a fraudulent one.
You did indeed read that accuratelyIf you are at a loss for words and the due date is quickly approaching, you can seek the assistance of reputable essay writing services.
A person might query, "How can I ascertain which service merits my confidence?" That is a valid concern. Because there are so many online options, becoming perplexed and uncertain about which ones to believe is simple.
At this point, we enter the picture. By navigating you through the bewildering world of these services, we will assist you in locating the finest paper writing services. We will discuss every aspect, from reputable companies with a track record of delivering high-quality work to websites that provide affordable prices without compromising standards.
This page addresses your inquiry regarding the optimal approach to obtaining an essay from a reputable academic service.
6 Best Paper Writing Services:
- ProWritingCrew
- EssayMasterz
- EssayScribez
- SkilledEssayWriter
- EssayLegend
- QualityEssayWriter
The sites were ranked by how good the papers were, how helpful the customer service was, and how much they cost. They don't use ChatGPT or any other AI tools to write material, so the papers they give you are original and can't be copied.
Difficulties In Writing
Writer's block: .
Writer's block, arguably the most infamous barrier, can manifest abruptly, devoid of any discernible path or strategy, leaving the author blank-spaced.
Lack of Inspiration:
Even when ideas flow, writers may need help finding inspiration or motivation to develop their thoughts into coherent writing pieces.
Time Constraints:
Balancing writing with other responsibilities such as work, school, or family commitments can be challenging, leading to limited time for writing or research.
Perfectionism:
The pursuit of perfection may induce writerly paralysis, wherein they laboriously revise and edit their work rather than progressing along the writing process.
Organization and Structure:
Determining a coherent framework and systematically arranging ideas can prove challenging, particularly when confronted with intricate subjects or protracted undertakings.
Research Challenges:
Conducting thorough research and finding credible sources can be time-consuming and overwhelming, particularly for topics that are unfamiliar or require in-depth analysis.
Self-Doubt:
Doubting one's writing abilities or fearing criticism from others can hinder creativity and confidence, making it difficult to express ideas effectively.
Procrastination:
Putting off writing tasks until the last minute can result in rushed and subpar work, which can lead to increased stress and lower-quality outcomes.
Editing and Proofreading:
Polishing and refining written work through editing and proofreading requires attention to detail and a critical eye, which can be challenging for some writers.
Writer's Fatigue:
Writing for extended periods can be mentally and physically exhausting, decreasing productivity and creativity over time.
1.ProWritingCrew
ProWritingCrew is a preeminent provider of academic papers recognized for its professionalism, dependability, and outstanding quality. They offer a vast array of services to accommodate the requirements of both students and professionals, utilizing a group of seasoned writers and editors. ProWritingCrew provides superior essays, research papers, dissertations, and individualized presentations to meet each client's needs.
Why I Think They Are the Best:
ProWritingCrew sets itself apart with its commitment to excellence and customer satisfaction. Its writers are highly qualified and proficient in various subjects, ensuring that every paper is well-researched and expertly written. Additionally, its transparent communication and prompt delivery make it a trusted choice for students and professionals worldwide.
Countries They Write For:
ProWritingCrew provides writing services to students and professionals worldwide, including the United States, Canada, the United Kingdom, Australia, and many more.
What Do They Offer Exactly:
ProWritingCrew offers a comprehensive range of writing services, including essay writing, research paper writing, dissertation writing, thesis writing, editing, proofreading, and more. They also provide custom writing services tailored to each client's needs and requirements.
Competitive rates.
In conclusion, ProWritingCrew is an exceptional option for individuals seeking dependable and superior paper writing services. They guarantee client satisfaction throughout the entire process through the utilization of their knowledgeable writers, clear and candid communication, and timely delivery.
2. EssayMasterz
EssayMasterz is a trustworthy paper writing service that helps students all over the world with their schoolwork. With a team of experienced writers and editors, EssayMasterz offers a wide range of services tailored to meet the diverse needs of students across various academic levels and disciplines.
EssayMasterz stands out as one of the best paper writing services due to its commitment to excellence, reliability, and customer satisfaction. Their team of expert writers possesses the necessary skills and expertise to deliver top-notch essays, research papers, dissertations, and more. Additionally, EssayMasterz prioritizes communication with clients to ensure that every paper meets their specific requirements and expectations.
EssayMasterz provides writing services to students from around the globe, including but not limited to the United States, Canada, the United Kingdom, Australia, and Europe.
EssayMasterz's pricing is reasonable and transparent. Rates vary depending on factors such as the type of paper, academic level, deadline, and word count.
In conclusion, EssayMasterz is a reliable and reputable paper writing service that excels in delivering high-quality academic assistance to students worldwide. With its experienced team of writers, commitment to customer satisfaction, and competitive pricing, it is a top choice for
students seeking expert writing support.
3. EssayScribez
EssayScribez is a trusted paper writing service that provides students high-quality academic assistance. With a team of skilled writers and editors, EssayScribez offers a range of services tailored to meet the diverse needs of students across various academic disciplines.
EssayScribez stands out as one of the best paper writing services due to its commitment to excellence, reliability, and customer satisfaction. Their team of expert writers possesses the necessary skills and expertise to deliver top-notch essays, research papers, dissertations, and more. Additionally, EssayScribez prioritizes communication with clients to ensure that every paper meets their specific requirements and expectations.
EssayScribez provides writing services to students from around the world, including the United States, Canada, the United Kingdom, Australia, and other countries.
The pricing at EssayScribez is competitive and transparent, with rates varying depending on factors such as the type of paper, academic level, deadline, and word count.
In conclusion, EssayScribez is a reputable paper writing service that delivers high-quality academic assistance to students worldwide. With its experienced team of writers, commitment to customer satisfaction, and competitive pricing, it is a top choice for students seeking expert
writing support.
4. SkilledEssayWriter
SkilledEssayWriter is a reputable paper writing service that provides high-quality academic assistance to students worldwide. With a team of experienced writers and editors, SkilledEssayWriter offers a wide range of services tailored to meet the diverse needs of students across various academic levels and disciplines.
SkilledEssayWriter stands out as one of the best paper writing services due to its commitment to excellence, reliability, and customer satisfaction. Their team of expert writers possesses the necessary skills and expertise to deliver top-notch essays, research papers, dissertations, and more. Additionally, SkilledEssayWriter prioritizes communication with clients to ensure that every paper meets their specific requirements and expectations.
SkilledEssayWriter provides writing services to students from around the globe, including but not limited to the United States, Canada, the United Kingdom, Australia, and Europe.
The pricing at SkilledEssayWriter is Student-friendly, with rates varying depending on factors such as the type of paper, academic level, deadline, and word count.
In conclusion, SkilledEssayWriter is a reliable and reputable paper writing service that delivers high-quality academic assistance to students worldwide. Their experienced team of writers, commitment to customer satisfaction, and competitive pricing make them a top choice for
5. EssayLegend
About essaylegend:.
EssayLegend is a trusted paper writing service committed to providing students with top-quality academic assistance. With a team of skilled writers and editors, EssayLegend offers various services tailored to meet the diverse needs of students across different academic disciplines.
EssayLegend stands out as one of the best paper writing services due to its dedication to excellence, reliability, and customer satisfaction. Their team of expert writers possesses the necessary skills and expertise to deliver high-quality essays, research papers, dissertations, and more. Moreover, EssayLegend strongly emphasizes communication with clients to ensure that every paper meets their specific requirements and expectations.
EssayLegend provides writing services to students from various countries worldwide, including the United States, Canada, the United Kingdom, Australia, and other international locations.
EssayLegend offers competitive and transparent pricing, with rates dependent on factors such as the type of paper, academic level, deadline, and word count.
In conclusion, EssayLegend is a reputable and reliable paper writing service known for delivering top-notch academic assistance to students worldwide. With its skilled team of writers, dedication to customer satisfaction, and competitive pricing, it is a preferred choice for students seeking expert writing support.
6. QualityEssayWriter
QualityEssayWriter is a distinguished paper writing service that provides students with exceptional academic assistance. With a team of proficient writers and editors, QualityEssayWriter offers a comprehensive range of services tailored to meet the diverse needs of students across various academic disciplines.
QualityEssayWriter earns its reputation as one of the best paper writing services due to its unwavering commitment to excellence, reliability, and customer satisfaction. Their team of seasoned writers possesses the requisite skills and expertise to deliver top-quality essays, research papers, dissertations, and more. Additionally, QualityEssayWriter prioritizes effective communication with clients to ensure that every paper meets their specific requirements and expectations.
QualityEssayWriter caters to students from across the globe, including but not limited to the United States, Canada, the United Kingdom, Australia, and other international locations.
The pricing at QualityEssayWriter is transparent and competitive. Rates vary based on factors such as the type of paper, academic level, deadline, and word count. They offer flexible pricing options to accommodate different budgets and needs, ensuring affordability without compromising quality.
How do I know if a paper writing service is legitimate?
Legitimate paper writing services typically have transparent policies, customer reviews, and clear communication channels. Look for services with verified testimonials and secure payment options to ensure legitimacy.
What factors should I consider when choosing a paper writing service?
Consider factors such as reputation, quality of writing, pricing, customer support, turnaround time, and guarantees offered by the service.
What if I need more than the quality of the paper I receive?
Reputable paper writing services typically offer revisions or refunds if you want more than the quality of the work. Check the service's policies regarding revisions and refunds before placing an order.
Do these paper-writing services provide any assurances?
Undoubtedly, authentic paper writing services frequently offer assurances, including confidentiality, money-back, and satisfaction. Consult the service's guarantee policies to understand your customer rights.
Do these paper writing services specialize in particular subject matters or academic levels?
Most paper writing services assist with various academic levels and topics. Whether one is a high school student or a doctoral candidate, there are services available that provide individualized educational support.
Conclusion:
Remember to use these services ethically and responsibly, adhere to academic integrity guidelines, and utilize the papers as valuable learning resources. With the support of these legitimate essay writing services, you can overcome educational challenges, excel in your studies, and embark on a path to success.
So, whether you're a student striving for academic excellence or a professional seeking expert writing assistance, the seven best paper writing services highlighted in this guide are your trusted partners in achieving your goals. Harness the power of these reputable services and confidently embark on your journey to academic and professional success.
Note: This article is for information purposes only and does not contain any recommendation from us for the readers.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
3.4 Revising and Editing
Learning objectives.
- Identify major areas of concern in the draft essay during revising and editing.
- Use peer reviews and editing checklists to assist revising and editing.
- Revise and edit the first draft of your essay and produce a final draft.
Revising and editing are the two tasks you undertake to significantly improve your essay. Both are very important elements of the writing process. You may think that a completed first draft means little improvement is needed. However, even experienced writers need to improve their drafts and rely on peers during revising and editing. You may know that athletes miss catches, fumble balls, or overshoot goals. Dancers forget steps, turn too slowly, or miss beats. For both athletes and dancers, the more they practice, the stronger their performance will become. Web designers seek better images, a more clever design, or a more appealing background for their web pages. Writing has the same capacity to profit from improvement and revision.
Understanding the Purpose of Revising and Editing
Revising and editing allow you to examine two important aspects of your writing separately, so that you can give each task your undivided attention.
- When you revise , you take a second look at your ideas. You might add, cut, move, or change information in order to make your ideas clearer, more accurate, more interesting, or more convincing.
- When you edit , you take a second look at how you expressed your ideas. You add or change words. You fix any problems in grammar, punctuation, and sentence structure. You improve your writing style. You make your essay into a polished, mature piece of writing, the end product of your best efforts.
How do you get the best out of your revisions and editing? Here are some strategies that writers have developed to look at their first drafts from a fresh perspective. Try them over the course of this semester; then keep using the ones that bring results.
- Take a break. You are proud of what you wrote, but you might be too close to it to make changes. Set aside your writing for a few hours or even a day until you can look at it objectively.
- Ask someone you trust for feedback and constructive criticism.
- Pretend you are one of your readers. Are you satisfied or dissatisfied? Why?
- Use the resources that your college provides. Find out where your school’s writing lab is located and ask about the assistance they provide online and in person.
Many people hear the words critic , critical , and criticism and pick up only negative vibes that provoke feelings that make them blush, grumble, or shout. However, as a writer and a thinker, you need to learn to be critical of yourself in a positive way and have high expectations for your work. You also need to train your eye and trust your ability to fix what needs fixing. For this, you need to teach yourself where to look.
Creating Unity and Coherence
Following your outline closely offers you a reasonable guarantee that your writing will stay on purpose and not drift away from the controlling idea. However, when writers are rushed, are tired, or cannot find the right words, their writing may become less than they want it to be. Their writing may no longer be clear and concise, and they may be adding information that is not needed to develop the main idea.
When a piece of writing has unity , all the ideas in each paragraph and in the entire essay clearly belong and are arranged in an order that makes logical sense. When the writing has coherence , the ideas flow smoothly. The wording clearly indicates how one idea leads to another within a paragraph and from paragraph to paragraph.
Reading your writing aloud will often help you find problems with unity and coherence. Listen for the clarity and flow of your ideas. Identify places where you find yourself confused, and write a note to yourself about possible fixes.
Creating Unity
Sometimes writers get caught up in the moment and cannot resist a good digression. Even though you might enjoy such detours when you chat with friends, unplanned digressions usually harm a piece of writing.
Mariah stayed close to her outline when she drafted the three body paragraphs of her essay she tentatively titled “Digital Technology: The Newest and the Best at What Price?” But a recent shopping trip for an HDTV upset her enough that she digressed from the main topic of her third paragraph and included comments about the sales staff at the electronics store she visited. When she revised her essay, she deleted the off-topic sentences that affected the unity of the paragraph.
Read the following paragraph twice, the first time without Mariah’s changes, and the second time with them.
Nothing is more confusing to me than choosing among televisions. It confuses lots of people who want a new high-definition digital television (HDTV) with a large screen to watch sports and DVDs on. You could listen to the guys in the electronics store, but word has it they know little more than you do. They want to sell what they have in stock, not what best fits your needs. You face decisions you never had to make with the old, bulky picture-tube televisions. Screen resolution means the number of horizontal scan lines the screen can show. This resolution is often 1080p, or full HD, or 768p. The trouble is that if you have a smaller screen, 32 inches or 37 inches diagonal, you won’t be able to tell the difference with the naked eye. The 1080p televisions cost more, though, so those are what the salespeople want you to buy. They get bigger commissions. The other important decision you face as you walk around the sales floor is whether to get a plasma screen or an LCD screen. Now here the salespeople may finally give you decent info . Plasma flat-panel television screens can be much larger in diameter than their LCD rivals. Plasma screens show truer blacks and can be viewed at a wider angle than current LCD screens. But be careful and tell the salesperson you have budget constraints. Large flat-panel plasma screens are much more expensive than flat-screen LCD models. Don’t let someone make you by more television than you need!
Answer the following two questions about Mariah’s paragraph:
- Do you agree with Mariah’s decision to make the deletions she made? Did she cut too much, too little, or just enough? Explain.
- Is the explanation of what screen resolution means a digression? Or is it audience friendly and essential to understanding the paragraph? Explain.
Collaboration: Please share with a classmate and compare your answers.
- Now start to revise the first draft of the essay you wrote in 3.1 Apply Prewriting Models . Reread it to find any statements that affect the unity of your writing. Decide how best to revise.
When you reread your writing to find revisions to make, look for each type of problem in a separate sweep. Read it straight through once to locate any problems with unity. Read it straight through a second time to find problems with coherence. You may follow this same practice during many stages of the writing process.
Connecting the Pieces: Writing at Work
Many companies hire copyeditors and proofreaders to help them produce the cleanest possible final drafts of large writing projects. Copyeditors are responsible for suggesting revisions and style changes; proofreaders check documents for any errors in capitalization, spelling, and punctuation that have crept in. Many times, these tasks are done on a freelance basis, with one freelancer working for a variety of clients.
Creating Coherence
Careful writers use transitions to clarify how the ideas in their sentences and paragraphs are related. These words and phrases help the writing flow smoothly. Adding transitions is not the only way to improve coherence, but they are often useful and give a mature feel to your essays. Table 3.4 “Common Transitional Words and Phrases” groups many common transitions according to their purpose.
Table 3.4 Common Transitional Words and Phrases
After Maria revised for unity, she next examined her paragraph about televisions to check for coherence. She looked for places where she needed to add a transition or perhaps reword the text to make the flow of ideas clear. In the version that follows, she has already deleted the sentences that were off topic.
Many writers make their revisions on a printed copy and then transfer them to the version on-screen. They conventionally use a small arrow called a caret (^) to show where to insert an addition or correction.

- Do you agree with the transitions and other changes that Mariah made to her paragraph? Which would you keep and which were unnecessary? Explain.
- What transition words or phrases did Mariah add to her paragraph? Why did she choose each one?
- What effect does adding additional sentences have on the coherence of the paragraph? Explain. When you read both versions aloud, which version has a more logical flow of ideas? Explain.
- Now return to the first draft of the essay you wrote in 3.1 Apply Prewriting Models and revise it for coherence. Add transition words and phrases where they are needed, and make any other changes that are needed to improve the flow and connection between ideas.
Being Clear and Concise
Some writers are very methodical and painstaking when they write a first draft. Other writers unleash a lot of words in order to get out all that they feel they need to say. Do either of these composing styles match your style? Or is your composing style somewhere in between? No matter which description best fits you, the first draft of almost every piece of writing, no matter its author, can be made clearer and more concise.
If you have a tendency to write too much, you will need to look for unnecessary words. If you have a tendency to be vague or imprecise in your wording, you will need to find specific words to replace any overly general language.
Identifying Wordiness
Sometimes writers use too many words when fewer words will appeal more to their audience and better fit their purpose. Here are some common examples of wordiness to look for in your draft. Eliminating wordiness helps all readers, because it makes your ideas clear, direct, and straightforward.
Sentences that begin with There is or There are .
Wordy: There are two major experiments that the Biology Department sponsors.
Revised: The Biology Department sponsors two major experiments.
Sentences with unnecessary modifiers.
Wordy: Two extremely famous and well-known consumer advocates spoke eloquently in favor of the proposed important legislation.
Revised: Two well-known consumer advocates spoke in favor of the proposed legislation.
Sentences with deadwood phrases that add little to the meaning. Be judicious when you use phrases such as in terms of , with a mind to , on the subject of , as to whether or not , more or less , as far as…is concerned , and similar expressions. You can usually find a more straightforward way to state your point.
Wordy: As a world leader in the field of green technology, the company plans to focus its efforts in the area of geothermal energy.
A report as to whether or not to use geysers as an energy source is in the process of preparation.
Revised: As a world leader in green technology, the company plans to focus on geothermal energy.
A report about using geysers as an energy source is in preparation.
Sentences with constructions that can be shortened.
Wordy: The e-book reader, which is a recent invention, may become as commonplace as the cell phone.
My over-sixty uncle bought an e-book reader, and his wife bought an e-book reader, too.
Revised: The e-book reader, a recent invention, may become as commonplace as the cell phone.
My over-sixty uncle and his wife both bought e-book readers.
Sentences in the passive voice or with forms of the verb to be . Sentences with passive-voice verbs often create confusion, because the subject of the sentence does not perform an action. Sentences are clearer when the subject of the sentence performs the action and is followed by a strong verb. Use strong active-voice verbs in place of forms of to be , which can lead to wordiness. Avoid passive voice when you can.
Wordy: It might perhaps be said that using a GPS device is something that is a benefit to drivers who have a poor sense of direction.
Revised: Using a GPS device benefits drivers who have a poor sense of direction.
Now return once more to the first draft of the essay you have been revising. Check it for unnecessary words. Try making your sentences as concise as they can be.
Choosing Specific, Appropriate Words
Most college essays should be written in formal English suitable for an academic situation. Follow these principles to be sure that your word choice is appropriate. For more information about word choice, see Chapter 8: Working with Words: Which Word Is Right? .
- Avoid slang. Find alternatives to bummer , kewl , and rad .
- Avoid language that is overly casual. Write about “men and women” rather than “girls and guys” unless you are trying to create a specific effect. A formal tone calls for formal language.
- Avoid contractions. Use do not in place of don’t , I am in place of I’m , have not in place of haven’t , and so on. Contractions are considered casual speech.
- Avoid clichés. Overused expressions such as green with envy , face the music , better late than never , and similar expressions are empty of meaning and may not appeal to your audience.
- Be careful when you use words that sound alike but have different meanings. Some examples are allusion/illusion , complement/compliment , council/counsel , concurrent/consecutive , founder/flounder , and historic/historical . When in doubt, check a dictionary.
- Choose words with the connotations you want. Choosing a word for its connotations is as important in formal essay writing as it is in all kinds of writing. Compare the positive connotations of the word proud and the negative connotations of arrogant and conceited .
- Use specific words rather than overly general words. Find synonyms for thing , people , nice , good , bad , interesting , and other vague words. Or use specific details to make your exact meaning clear.
Now read the revisions Mariah made to make her third paragraph clearer and more concise. She has already incorporated the changes she made to improve unity and coherence.

- Read the unrevised and the revised paragraphs aloud. Explain in your own words how changes in word choice have affected Mariah’s writing.
- Do you agree with the changes that Mariah made to her paragraph? Which changes would you keep and which were unnecessary? Explain. What other changes would you have made?
- What effect does removing contractions and the pronoun “ you” have on the tone of the paragraph? How would you characterize the tone now? Why?
- Now return once more to your essay in progress. Read carefully for problems with word choice. Be sure that your draft is written in formal language and that your word choice is specific and appropriate.
Completing a Peer Review
After working so closely with a piece of writing, writers often need to step back and ask for a more objective reader. What writers most need is feedback from readers who can respond only to the words on the page. When they are ready, writers show their drafts to someone they respect and who can give an honest response about its strengths and weaknesses.
You, too, can ask a peer to read your draft when it is ready. After evaluating the feedback and assessing what is most helpful, the reader’s feedback will help you when you revise your draft. This process is called peer review .
You can work with a partner in your class and identify specific ways to strengthen each other’s essays. Although you may be uncomfortable sharing your writing at first, remember that each writer is working toward the same goal: a final draft that fits the audience and the purpose. Maintaining a positive attitude when providing feedback will put you and your partner at ease. The box that follows provides a useful framework for the peer review session.
Questions for Peer Review
Title of essay: _________________________________________________
Date: _________________________________________________________
Writer’s name: ________________________________________________
Peer reviewer’s name: _________________________________________
- This essay is about_______________________________________.
- Your main points in this essay are_______________________________________________________.
- What I most liked about this essay is_________________________________________________________.
These three points struck me as your strongest:
a. Point: __________________________________________________
Why : _____________________________________________________
b. Point: __________________________________________________
c. Point: __________________________________________________
Why: _____________________________________________________
These places in your essay are not clear to me:
a. Where: _________________________________________________
Needs improvement because______________________________
b. Where: _________________________________________________
Needs improvement because _____________________________
c. Where: _________________________________________________
- The one additional change you could make that would improve this essay significantly is ___________________________________________________________.
One of the reasons why word-processing programs build in a reviewing feature is that workgroups have become a common feature in many businesses. Writing is often collaborative, and the members of a workgroup and their supervisors often critique group members’ work and offer feedback that will lead to a better final product.
Exchange essays with a classmate and complete a peer review of each other’s draft in progress. Remember to give positive feedback and to be courteous and polite in your responses. Focus on providing one positive comment and one question for more information to the author.
Using Feedback Objectively
The purpose of peer feedback is to receive constructive criticism of your essay. Your peer reviewer is your first real audience, and you have the opportunity to learn what confuses and delights a reader so that you can improve your work before sharing the final draft with a wider audience (or your intended audience).
It may not be necessary to incorporate every recommendation your peer reviewer makes. However, if you start to observe a pattern in the responses you receive from peer reviewers, you might want to take that feedback into consideration in future assignments. For example, if you read consistent comments about a need for more research, then you may want to consider including more research in future assignments.
Using Feedback from Multiple Sources
You might get feedback from more than one reader as you share different stages of your revised draft. In this situation, you may receive feedback from readers who do not understand the assignment or who lack your involvement with and enthusiasm for it.
You need to evaluate the responses you receive according to two important criteria:
- Determine if the feedback supports the purpose of the assignment.
- Determine if the suggested revisions are appropriate to the audience.
Then, using these standards, accept or reject revision feedback.
Work with two partners. Go back to Exercise 4 in this lesson and compare your responses to Activity A, about Mariah’s paragraph, with your partners’. Recall Mariah’s purpose for writing and her audience. Then, working individually, list where you agree and where you disagree about revision needs.
Editing Your Draft
If you have been incorporating each set of revisions as Mariah has, you have produced multiple drafts of your writing. So far, all your changes have been content changes. Perhaps with the help of peer feedback, you have made sure that you sufficiently supported your ideas. You have checked for problems with unity and coherence. You have examined your essay for word choice, revising to cut unnecessary words and to replace weak wording with specific and appropriate wording.
The next step after revising the content is editing. When you edit, you examine the surface features of your text. You examine your spelling, grammar, usage, and punctuation. You also make sure you use the proper format when creating your finished assignment.
Editing often takes time. Budgeting time into the writing process allows you to complete additional edits after revising. Editing and proofreading your writing helps you create a finished work that represents your best efforts. Here are a few more tips to remember about your readers:
- Readers do not notice correct spelling, but they do notice misspellings.
- Readers look past your sentences to get to your ideas—unless the sentences are awkward, poorly constructed, and frustrating to read.
- Readers notice when every sentence has the same rhythm as every other sentence, with no variety.
- Readers do not cheer when you use there , their , and they’re correctly, but they notice when you do not.
- Readers will notice the care with which you handled your assignment and your attention to detail in the delivery of an error-free document..
The first section of this book offers a useful review of grammar, mechanics, and usage. Use it to help you eliminate major errors in your writing and refine your understanding of the conventions of language. Do not hesitate to ask for help, too, from peer tutors in your academic department or in the college’s writing lab. In the meantime, use the checklist to help you edit your writing.
Editing Your Writing
- Are some sentences actually sentence fragments?
- Are some sentences run-on sentences? How can I correct them?
- Do some sentences need conjunctions between independent clauses?
- Does every verb agree with its subject?
- Is every verb in the correct tense?
- Are tense forms, especially for irregular verbs, written correctly?
- Have I used subject, object, and possessive personal pronouns correctly?
- Have I used who and whom correctly?
- Is the antecedent of every pronoun clear?
- Do all personal pronouns agree with their antecedents?
- Have I used the correct comparative and superlative forms of adjectives and adverbs?
- Is it clear which word a participial phrase modifies, or is it a dangling modifier?
Sentence Structure
- Are all my sentences simple sentences, or do I vary my sentence structure?
- Have I chosen the best coordinating or subordinating conjunctions to join clauses?
- Have I created long, over-packed sentences that should be shortened for clarity?
- Do I see any mistakes in parallel structure?
Punctuation
- Does every sentence end with the correct end punctuation?
- Can I justify the use of every exclamation point?
- Have I used apostrophes correctly to write all singular and plural possessive forms?
- Have I used quotation marks correctly?
Mechanics and Usage
- Can I find any spelling errors? How can I correct them?
- Have I used capital letters where they are needed?
- Have I written abbreviations, where allowed, correctly?
- Can I find any errors in the use of commonly confused words, such as to / too / two ?
Be careful about relying too much on spelling checkers and grammar checkers. A spelling checker cannot recognize that you meant to write principle but wrote principal instead. A grammar checker often queries constructions that are perfectly correct. The program does not understand your meaning; it makes its check against a general set of formulas that might not apply in each instance. If you use a grammar checker, accept the suggestions that make sense, but consider why the suggestions came up.
Proofreading requires patience; it is very easy to read past a mistake. Set your paper aside for at least a few hours, if not a day or more, so your mind will rest. Some professional proofreaders read a text backward so they can concentrate on spelling and punctuation. Another helpful technique is to slowly read a paper aloud, paying attention to every word, letter, and punctuation mark.
If you need additional proofreading help, ask a reliable friend, a classmate, or a peer tutor to make a final pass on your paper to look for anything you missed.
Remember to use proper format when creating your finished assignment. Sometimes an instructor, a department, or a college will require students to follow specific instructions on titles, margins, page numbers, or the location of the writer’s name. These requirements may be more detailed and rigid for research projects and term papers, which often observe the American Psychological Association (APA) or Modern Language Association (MLA) style guides, especially when citations of sources are included.
To ensure the format is correct and follows any specific instructions, make a final check before you submit an assignment.
With the help of the checklist, edit and proofread your essay.
Key Takeaways
- Revising and editing are the stages of the writing process in which you improve your work before producing a final draft.
- During revising, you add, cut, move, or change information in order to improve content.
- During editing, you take a second look at the words and sentences you used to express your ideas and fix any problems in grammar, punctuation, and sentence structure.
- Unity in writing means that all the ideas in each paragraph and in the entire essay clearly belong together and are arranged in an order that makes logical sense.
- Coherence in writing means that the writer’s wording clearly indicates how one idea leads to another within a paragraph and between paragraphs.
- Transitional words and phrases effectively make writing more coherent.
- Writing should be clear and concise, with no unnecessary words.
- Effective formal writing uses specific, appropriate words and avoids slang, contractions, clichés, and overly general words.
- Peer reviews, done properly, can give writers objective feedback about their writing. It is the writer’s responsibility to evaluate the results of peer reviews and incorporate only useful feedback.
- Remember to budget time for careful editing and proofreading. Use all available resources, including editing checklists, peer editing, and your institution’s writing lab, to improve your editing skills.
Putting the Pieces Together Copyright © 2020 by Andrew Stracuzzi and André Cormier is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
2024 Global Learning Challenge
Is Using an Essay Writing Service Considered Cheating?
Oliva Campbell
Our organization.
CollegeEssay.org
What is the name of your solution?
Provide a one-line summary of your solution..
Debunking Misconceptions and Embracing Academic Support
In what city, town, or region is your solution team headquartered?
In what country is your solution team headquartered.
- United States
What type of organization is your solution team?
Film your elevator pitch., what specific problem are you solving.
Is Using an Essay Writing Service Considered Cheating? Debunking Misconceptions and Embracing Academic Support
In the contemporary academic landscape, the utilization of essay writing service has sparked a debate regarding its ethical implications. Some perceive it as a form of cheating, while others argue it as a legitimate means of seeking academic support. As we delve into this discussion, it's imperative to explore both perspectives and shed light on the role of essay writing services in academia.
What is your solution?
Understanding the Controversy The Ethical Dilemma
The crux of the debate lies in the ethical dilemma surrounding the use of essay writing services. Traditional notions of academic integrity emphasize the importance of individual effort and originality in scholarly pursuits. From this standpoint, outsourcing the task of essay writing may seem like circumventing academic rigor and ethical standards.
Perceived Academic Dishonesty
Critics often equate using essay writing services to academic dishonesty, arguing that it undermines the learning process and devalues the significance of genuine scholarly achievements. They view it as a shortcut to academic success, devoid of the essential elements of critical thinking, research, and academic growth.
Legitimate Academic Support
On the contrary, proponents of essay writing services advocate for a nuanced understanding of academic support. They argue that seeking assistance from professional writers does not inherently constitute cheating but rather serves as a supplementary resource to enhance learning outcomes. Best Essay writing service can provide valuable guidance, especially for students grappling with complex topics or facing time constraints.
Who does your solution serve, and in what ways will the solution impact their lives?

Debunking Misconceptions Collaboration, Not Duplication
Contrary to popular belief, engaging with essay writing services does not entail passively submitting pre-written essays as one's own work. Instead, it involves collaboration between students and professional writers to develop custom essays tailored to their unique requirements. The final product reflects the student's input, understanding, and perspective, albeit with expert guidance.
Learning Opportunity
Essay writing services offer a valuable learning opportunity by providing model essays that serve as exemplars of academic writing standards. Students can analyze these essays to understand proper structuring, argumentation techniques, and citation practices, thereby honing their own writing skills. Additionally, interacting with professional writers fosters a deeper understanding of subject matter and research methodologies.
Academic Support System
Rather than undermining academic integrity, essay writing services complement existing support systems within educational institutions. They function as supplementary resources that assist students in navigating academic challenges effectively. By offering personalized assistance, these services empower students to overcome obstacles and achieve their academic goals.
Embracing Academic Support Fostering Academic Success
Ultimately, the goal of essay writing services is to facilitate academic success by providing students with the necessary tools and guidance to excel in their studies. By availing these services, students can alleviate academic pressure, meet deadlines, and improve their overall learning experience. Moreover, the support offered by essay writing services can enhance students' confidence and motivation, leading to greater academic achievements.
Ethical Considerations
While utilizing essay writing services is permissible within ethical boundaries, it's essential for students to uphold academic integrity and honesty. They should utilize these services responsibly, ensuring that the essays produced are used for reference purposes and serve as aids in their own academic endeavors. Transparency and integrity should guide students' interactions with essay writing services to maintain the ethical integrity of academic pursuits.
In conclusion, the debate surrounding the use of essay writing services underscores the complexities inherent in modern education. While some may view it as a contentious issue mired in ethical ambiguity, a nuanced perspective reveals its potential as a valuable academic support tool. By dispelling misconceptions and embracing the role of essay writing services as supplementary resources, students can leverage these services responsibly to enhance their academic journey. Ultimately, the ethical considerations lie in how students utilize these services to foster their academic growth while upholding principles of integrity and honesty in their scholarly pursuits.
How are you and your team well-positioned to deliver this solution?
Leveraging CollegeEssay.org and MyPerfectWords.com for Optimal Results
In the quest for academic excellence and ethical scholarship, students can enhance their learning journey by leveraging reputable essay writing services such as CollegeEssay.org and MyPerfectWords.com. These platforms offer a myriad of features and benefits designed to support students in achieving their academic goals while upholding principles of integrity and honesty.
Customized Essay Writing Services
Both CollegeEssay.org and MyPerfectWords.com prioritize delivering custom-written essays tailored to each student's unique requirements. By availing of their services, students can collaborate with professional writers to develop high-quality essays that meet academic standards and reflect their individual insights and perspectives.
Expert Guidance and Support
The teams of skilled writers at CollegeEssay.org and MyPerfectWords.com possess expertise in various subjects and disciplines, ensuring that students receive expert guidance and support across a wide range of academic topics. From research and outlining to drafting and editing, these platforms offer comprehensive assistance at every stage of the writing process.
Timely Delivery and Flexible Deadlines
Meeting deadlines is paramount in academic pursuits, and both CollegeEssay.org and MyPerfectWords.com prioritize timely delivery of essays. With flexible deadlines ranging from 6 to 24 hours, students can rely on these platforms to accommodate urgent essay requests without compromising on quality or accuracy.
24/7 Customer Support
Navigating the intricacies of essay writing can be daunting, but with 24/7 customer support and their reliable research paper writing service available at CollegeEssay.org, students can seek assistance and clarification at any time. Multilingual support teams ensure accessibility for students from diverse linguistic backgrounds, fostering a supportive and inclusive environment.
Originality and Plagiarism-Free Guarantee
Maintaining academic integrity is non-negotiable, and both CollegeEssay.org and MyPerfectWords.com uphold rigorous standards of originality and authenticity. Essays produced by these platforms undergo thorough plagiarism checks, ensuring that students receive 100% original and plagiarism-free content with every order.
Transparent Pricing and Payment Options
Affordability is a key consideration for students, and MyPerfectWords.com offer cheapest research paper writing service transparent pricing structures and flexible payment options. With prices starting at just $11/page and the option to pay 50% upfront and 50% upon completion, these platforms provide cost-effective solutions that fit students' budgets.

Which dimension of the Challenge does your solution most closely address?
Which of the un sustainable development goals does your solution address.
- 4. Quality Education
What is your solution’s stage of development?
Please share details about why you selected the stage above..
Revision and Refund Policies
Student satisfaction is paramount, and both CollegeEssay.org and MyPerfectWords.com offer revision and refund policies to ensure that students are fully satisfied with the essays they receive. Students can request revisions free of charge until they are completely satisfied with the final product, and a 100% money-back guarantee ensures peace of mind in case of any unforeseen issues.
Why are you applying to Solve?
In conclusion, students seeking academic support and assistance with essay writing can benefit greatly from utilizing reputable platforms such as CollegeEssay.org and MyPerfectWords.com. With features such as customized essay writing services, expert guidance and support, timely delivery, 24/7 customer support, originality guarantees, transparent pricing, and flexible payment options, these platforms provide comprehensive solutions to students' academic needs. By leveraging the services offered by CollegeEssay.org and MyPerfectWords.com, students can enhance their academic performance, alleviate academic pressure, and foster a deeper understanding of course materials, all while upholding principles of integrity and academic honesty.
In which of the following areas do you most need partners or support?
- Legal or Regulatory Matters
Who is the Team Lead for your solution?
Solution team.
The Solve team will review your report and remove any inappropriate content.
Why is this item inappropriate?
We use cookies.
We use cookies and other tracking technologies to improve your browsing experience on our website and to understand where our visitors are coming from. By browsing our website, you consent to our use of cookies and other tracking technologies.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Revising and editing an essay is a crucial step of the writing process. It often takes up at least as much time as producing the first draft, so make sure you leave enough time to revise thoroughly. Although you can save considerable time using our essay checker. The most effective approach to revising an essay is to move from general to specific:
Revising and editing are the two tasks you undertake to significantly improve your essay. Both are very important elements of the writing process. You may think that a completed first draft means little improvement is needed. However, even experienced writers need to improve their drafts and rely on peers during revising and editing.
Revision literally means to "see again," to look at something from a fresh, critical perspective. It is an ongoing process of rethinking the paper: reconsidering your arguments, reviewing your evidence, refining your purpose, reorganizing your presentation, reviving stale prose. But I thought revision was just fixing the commas and spelling ...
Why Revise. To make the draft more accessible to the reader. To sharpen and clarify the focus and argument. To improve and further develop ideas. Revision VS. Editing. Revising a piece of your own writing is more than just fixing errors—that's editing. Revision happens before editing. Revising involves re-seeing your essay from the eyes of a ...
Revising is about your content while editing is about sentence-level issues and typos. It's important to remember to allow yourself time to complete both parts of this process carefully. Revision is about seeing your writing again. Revising is an important step in the writing process, because it enables you to look at your writing more ...
Not exactly. Although many people use the terms interchangeably, editing and proofreading are two different stages of the revision process. Both demand close and careful reading, but they focus on different aspects of the writing and employ different techniques. Some tips that apply to both editing and proofreading. Get some distance from the text!
Revising and Editing What Is Revision? Once you have reached the point that you have a full rough draft, take some time to step away from the essay to get a newer and better perspective. Then begin revising. ... Your essay should develop a central point clearly and logically. The purpose, tone, and point-of-view of your essay should be suited ...
Steps for Revising Your Paper. When you have plenty of time to revise, use the time to work on your paper and to take breaks from writing. If you can forget about your draft for a day or two, you may return to it with a fresh outlook. During the revising process, put your writing aside at least twice—once during the first part of the process ...
9 Revising and Editing Your Writing University of Minnesota Libraries Publishing. ... You make your essay into a polished, mature piece of writing, the end product of your best efforts. When you are revising and editing you should always keep the genre, audience, and purpose of your text in mind. Many tips for revising and editing, including ...
See It in Practice. In this video cast, you'll see how our student addresses her revision and editing process using specific feedback on her essay from her professor. You'll be able to see how she uses the feedback to make her essay stronger and what revision looks like in comparison to editing. Video format not supported.
You should keep in mind that revising involves much more than just correcting errors in grammar, spelling, and punctuation. Revising involves editing your work for meaning and considering whether you have appropriate information for the essay question. You shouldn't waste time carefully correctinga paper that you haven't edited at all
Revising is looking for ways to make your ideas clearer, stronger, and more convincing. When revising, you might add, cut, move, or change whole sentences or paragraphs. Revising is far more than just editing because, editing is correcting grammar, style, usage, and punctuation. Revising is really a re- vision of your entire essay: ideas ...
A Tip for Both Revising and Editing. Finally, a good tip for both revision and editing is to use the resources available to you for feedback and help. If you're on a campus with a writing center, take advantage of it. If your online college offers an online writing tutorial service, submit your essay to that service for feedback.
The main difference between editing and revising is their focus. When one revises after the process of writing, they take a second look at your idea and information. The process of revising makes a piece of writing stronger by making the ideas of the writer clearer. You also make the information more engaging, interesting, accurate, or compelling.
For these reasons, revising and editing is an essential step in the college essay writing process. You want your essay to be clear, concise, engaging, and polished. To accomplish this goal, use this checklist for revising and editing the college application essay. 11-Item Checklist. Revising means improving the overall piece of writing.
Relax, focus, write your next masterpiece... Writing presumes more than simply laying out words on a paper. Typely helps you get in the mood and keeps you focused, immersed and ready to write your story. Whether you need a distraction-free environment, some chill relaxing sounds or a pomodoro timer to manage your time we got you covered.
Revising & Editing Process. Revision and editing are both important parts of the writing process, yet many students skip revision and don't spend enough time editing. It's important to remember that these steps are separate and that each step takes time. The following pages will help you develop strong revision and editing strategies for ...
Get 1:1 help brainstorming topics, outlining your essay, revising a draft, or editing grammar. Learn More about UPcheive. Writing a strong college admissions essay Learn about the elements of a solid admissions essay. Close Modal. Close Avoiding common admissions essay mistakes Learn some of the most common mistakes made on college essays ...
Revising and editing are the two tasks you undertake to significantly improve your essay. Both are very important elements of the writing process. You may think that a completed first draft means little improvement is needed. However, even experienced writers need to improve their drafts and rely on peers during revising and editing.
In conclusion, EssayScribez is a reputable paper writing service that delivers high-quality academic assistance to students worldwide. With its experienced team of writers, commitment to customer ...
3.4 Revising and Editing. Identify major areas of concern in the draft essay during revising and editing. Use peer reviews and editing checklists to assist revising and editing. Revise and edit the first draft of your essay and produce a final draft. Revising and editing are the two tasks you undertake to significantly improve your essay.
Students develop skills in public writing, community research, drafting and revision, editing and publication, audience analysis, digital rhetoric, and multimodal composition. WRLS students can choose from among a variety of electives to design their own course path in pursuit of a wide range of careers or graduate programs.
Kate Graeve Mr. Duitsman IWCC English Comp 1 29 February 2024 Writing Journey Throughout my first trimester of IWCC Composition, I have learned many tactics in order to advance my writing and keep up with the work that the class offered. During this class, we mainly focused on writing essays, revising, and reading other texts in order to learn ...
Student satisfaction is paramount, and both CollegeEssay.org and MyPerfectWords.com offer revision and refund policies to ensure that students are fully satisfied with the essays they receive. Students can request revisions free of charge until they are completely satisfied with the final product, and a 100% money-back guarantee ensures peace ...