
25 Counterargument Examples

A counterargument is a response, rebuttal, or refutation of an argument with your own argument. Its purpose is to oppose and disprove a theory that someone else has put forward.
We use counterarguments extensively in debates as well as argumentative essay writing.
When teaching essay writing, I teach my students to always present counterarguments to their opponents’ points of view. This helps them to strengthen their own argument and demonstrate awareness of potential rebuttals.
Below are some methods, with examples, that could be used – be it in essay writing, debates, or any other communication genre.
Counterargument Examples
1. empirical challenges.
An empirical challenge is, simply, a rebuttal that challenges the facts presented by the opponent, showing that their facts are wrong and yours are right.
To undermine your opponent’s set of facts, it will be your job to present facts that show that the opponent’s supposed facts are wrong, perhaps due to misreading data or cherry-picking.
Then, you would need to present concrete information, data, or evidence that negates the claim or conclusion of an opponent’s argument.
The core strength of empirical challenges is in their reliance on hard facts and numbers, which are difficult to refute without equally credible opposing data.
Example of Empirical Challenge: If your opponent argues that global warming isn’t a serious issue, an empirical challenge would be to provide scientific data or research studies showing the increase in global temperatures and the harmful effects.
See Also: Empirical Evidence Examples
2. Challenging the Relevance
Challenging the relevance means questioning whether your opponent’s argument or perspective is applicable to the discussion at hand.
This sort of counter-argument seeks to destabilize your opponent’s view by showing that, while their facts or arguments might be sound in isolation, they do not bear any relation to, or are unfit for, the topic at hand, making them irrelevant.
The power of relevance challenge lays in its ability to destabilize your opponent’s argument without needing to directly dispute the truth of their claims.
Example of Challenging the Relevance: You will often find this argument when comparing the usefulness of various research methodologies for a research project. Multiple research methods may be valid, but there’s likely one that’s best for any given study.
See Also: Relevance Examples
3. Reductio ad absurdum
Reductio ad absurdum is a latin term that means reducing to the absurd . This method involves demonstrating the absurdity of an opponent’s argument by showing its illogical or extreme consequences.
The goal is to show that if the argument were valid, it would inevitably lead to senseless or ridiculous outcomes.
The application of reductio ad absurdum is especially effective in debates or discussions where flawed logic or hyperbolic statements are used to influence the audience’s opinion, as it discredits the credibility of the other person’s argument.
Example of Reductio ad absurdum : Consider a scenario where someone argues for the total removal of all regulations on vehicle speed to improve the efficiency of transportation. You can counter this argument through reductio ad absurdum by stating, “By that logic, let’s allow cars to travel at 200 miles per hour down residential streets. After all, it would make the mail delivery much faster!” It becomes evident that permitting extremely high speeds could lead to dangerous conditions and potential for disastrous accidents.
4. Pointing Out Logical Fallacies
The strategy of pointing out logical fallacies involves identifying and highlighting flaws in your opponent’s reasoning.
In a debate or discussion, logical fallacies are often subtle errors that lead to invalid conclusions or arguments.
By identifying these fallacies, you avoid being swayed by flawed reasoning and instead promote cognizant, logical thought.
Successful use of this strategy requires a good understanding of the different kinds of logical fallacies , such as straw man fallacies, ad hominem attacks, and appeals to ignorance.
Example of Pointing Out Logical Fallacies: Consider an argument where your opponent asserts, “All cats I’ve ever seen have been aloof, so all cats must be aloof.” This is a hasty generalization fallacy, where a conclusion about all members of a group is drawn from inadequate sample size.
5. Counterexamples
A counterexample is an example that opposes or contradicts an argument or theory proposed by another.
The use of a counterexample is a practical and powerful means of rebutting an argument or theory that has been presented as absolute or universally applicable.
When you provide a singular example that contradicts your opponent’s proposed theory, it demonstrates the theory isn’t universally true and therefore, weakens their argument.
However, this tactic requires sound knowledge and a good command of subject matter to be able to identify and present valid exceptions.
Example of Counterexamples: Consider an argument where someone states that “Mammals can’t lay eggs.” A solid counterexample would be the platypus, a mammal that does lay eggs. This single example is sufficient to contradict the universal claim.
6. Using Hypotheticals
Hypothetical situations, in essence, are imagined scenarios used to refute your opponent’s point of view. It’s, in essence, an example that is plausible, but not real.
Using hypotheticals assists in clarifying the ramifications of a particular argument, policy, or theory. When a hypothetical scenario effectively illustrates the flaws or shortcomings of your opponent’s viewpoint, it can completely unsettle their position.
However, care must be taken to frame the hypotheticals reasonably and realistically, lest they distort the argument or derail the conversation.
Example of Using Hypotheticals: If someone argues that raising the minimum wage will lead to job loss, you could counter with a hypothetical that if businesses paid their employees more, those employees would have more spending power, bolstering the economy and creating more jobs.
7. Comparison and Contrast
Comparison and contrast entails directly comparing your argument to your opponent’s, showing the strength of your perspective and the weakness of the opponent’s.
This tool allows you to support your arguments or disprove your opponent’s by using existing examples or situations that illustrate your point clearly.
The technique relies heavily on the logical thinking of comparing two or more entities in a manner that is informative, convincing, and significant to the argument.
Example of Comparison and Contrast: Let’s say, for instance, you are arguing against privatization of public utilities. You could compare the rates and services of private utilities to those of public ones showing that private companies often charge more for the same services, thereby supporting your argument against privatization.
See More: Compare and Contrast Examples
8. Challenging Biases
Challenging biases involves questioning the objectivity of your opponent’s argument by pointing out the predispositions that may influence their perspective.
Biases can greatly affect the validity and reliability of an argument because they can skew the interpretation of information and hinder fair judgement.
By challenging biases, you can expose the partiality in your opponent’s argument, thereby diminishing its credibility and persuasiveness.
However, it’s important to respectfully and tactfully challenge biases to prevent the discussion from turning into a personal attack.
Example of Challenging Biases: If your opponent is a staunch supporter of a political party and they provide an argument that solely favors this party, you could challenge their bias by questioning whether their support for the party is unduly influencing their viewpoint, hence the need for them to consider the opposing perspectives.
See More: List of Different Biases
9. Ethical Dispute
Ethical disputes involve challenging your opponent’s argument based on moral values or principles.
Ethics play a crucial role in shaping people’s beliefs, attitudes, and actions. Therefore, ethical disputes can serve as powerful counterarguments, especially in debates concerning sensitive or controversial topics.
If your opponent’s position contradicts generally accepted ethical norms or values, you can point this out to weaken their argument.
Just remember, ethics can occasionally be subjective and personal, so it’s important to approach ethical disputes with sensitivity and respect.
Example of Ethical Dispute: If your opponent supports factory farming based on economic benefits, you could challenge their argument by pointing out the ethical issues related to animal welfare and the environment.
10. Challenging the Source
Challenging the source is a tactic used to question the credibility or reliability of the information used by your opponent in their argument.
This technique focuses on examining the origin of the evidence presented, probing whether the source is credible, trusted, and free from bias.
To do this, I recommend using this media literacy framework .
If the source used by your opponent is flawed, biased or unreliable, their argument loses credibility, making your position stronger.
Example of Challenging the Source: If your opponent uses an obscure blog as their primary source of their argument on a scientific topic, you could challenge the source by questioning its credibility and offering information from reputable scientific journals instead.
See More: Good Sources for Essay Writing
A Full List of Methods for Counterargument
- Empirical challenges
- Challenging the relevance
- Reductio ad absurdum
- Pointing out logical fallacies
- Counterexamples
- Using hypotheticals
- Comparison and contrast
- Challenging biases
- Ethical dispute
- Challenging the source
- Questioning assumptions
- Slippery slope argument
- Challenging a false dichtomy
- Historical Precedent
- Anecdotal Evidence
- Challenging the Definition
- Socratic Questioning
- Highlighting Unintended Consequences
- Appeal to Emotion
- Challenging the Frame
- Highlighting Inconsistencies
- Challenging Completeness
- Temporal Challenge
- Offering alternative explanations
- Exposing oversimplifications
- Appeal to authority
Counterargument is an essential skill for debaters and essay writers. You need to be able to know and understand strategies for countering the arguments of your opponents to position your argument in the best light possible. To do this, we have to vectors of attack: First, you can undermine their arguments and demonstrate the flaws. Second, you can present your argument as stronger.
The key, however, is to ensure your arguments are as airtight and foolproof as possible to prevent effective rebuttals to your own counterarguments!

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 5 Top Tips for Succeeding at University
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 50 Durable Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 100 Consumer Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 30 Globalization Pros and Cons
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
When you write an academic essay, you make an argument: you propose a thesis and offer some reasoning, using evidence, that suggests why the thesis is true. When you counter-argue, you consider a possible argument against your thesis or some aspect of your reasoning. This is a good way to test your ideas when drafting, while you still have time to revise them. And in the finished essay, it can be a persuasive and (in both senses of the word) disarming tactic. It allows you to anticipate doubts and pre-empt objections that a skeptical reader might have; it presents you as the kind of person who weighs alternatives before arguing for one, who confronts difficulties instead of sweeping them under the rug, who is more interested in discovering the truth than winning a point.
Not every objection is worth entertaining, of course, and you shouldn't include one just to include one. But some imagining of other views, or of resistance to one's own, occurs in most good essays. And instructors are glad to encounter counterargument in student papers, even if they haven't specifically asked for it.
The Turn Against
Counterargument in an essay has two stages: you turn against your argument to challenge it and then you turn back to re-affirm it. You first imagine a skeptical reader, or cite an actual source, who might resist your argument by pointing out
- a problem with your demonstration, e.g., that a different conclusion could be drawn from the same facts, a key assumption is unwarranted, a key term is used unfairly, certain evidence is ignored or played down;
- one or more disadvantages or practical drawbacks to what you propose;
- an alternative explanation or proposal that makes more sense.
You introduce this turn against with a phrase like One might object here that... or It might seem that... or It's true that... or Admittedly,... or Of course,... or with an anticipated challenging question: But how...? or But why...? or But isn't this just...? or But if this is so, what about...? Then you state the case against yourself as briefly but as clearly and forcefully as you can, pointing to evidence where possible. (An obviously feeble or perfunctory counterargument does more harm than good.)
The Turn Back
Your return to your own argument—which you announce with a but, yet, however, nevertheless or still —must likewise involve careful reasoning, not a flippant (or nervous) dismissal. In reasoning about the proposed counterargument, you may
- refute it, showing why it is mistaken—an apparent but not real problem;
- acknowledge its validity or plausibility, but suggest why on balance it's relatively less important or less likely than what you propose, and thus doesn't overturn it;
- concede its force and complicate your idea accordingly—restate your thesis in a more exact, qualified, or nuanced way that takes account of the objection, or start a new section in which you consider your topic in light of it. This will work if the counterargument concerns only an aspect of your argument; if it undermines your whole case, you need a new thesis.
Where to Put a Counterargument
Counterargument can appear anywhere in the essay, but it most commonly appears
- as part of your introduction—before you propose your thesis—where the existence of a different view is the motive for your essay, the reason it needs writing;
- as a section or paragraph just after your introduction, in which you lay out the expected reaction or standard position before turning away to develop your own;
- as a quick move within a paragraph, where you imagine a counterargument not to your main idea but to the sub-idea that the paragraph is arguing or is about to argue;
- as a section or paragraph just before the conclusion of your essay, in which you imagine what someone might object to what you have argued.
But watch that you don't overdo it. A turn into counterargument here and there will sharpen and energize your essay, but too many such turns will have the reverse effect by obscuring your main idea or suggesting that you're ambivalent.
Counterargument in Pre-Writing and Revising
Good thinking constantly questions itself, as Socrates observed long ago. But at some point in the process of composing an essay, you need to switch off the questioning in your head and make a case. Having such an inner conversation during the drafting stage, however, can help you settle on a case worth making. As you consider possible theses and begin to work on your draft, ask yourself how an intelligent person might plausibly disagree with you or see matters differently. When you can imagine an intelligent disagreement, you have an arguable idea.
And, of course, the disagreeing reader doesn't need to be in your head: if, as you're starting work on an essay, you ask a few people around you what they think of topic X (or of your idea about X) and keep alert for uncongenial remarks in class discussion and in assigned readings, you'll encounter a useful disagreement somewhere. Awareness of this disagreement, however you use it in your essay, will force you to sharpen your own thinking as you compose. If you come to find the counterargument truer than your thesis, consider making it your thesis and turning your original thesis into a counterargument. If you manage to draft an essay without imagining a counterargument, make yourself imagine one before you revise and see if you can integrate it.
Gordon Harvey (adapted from The Academic Essay: A Brief Anatomy), for the Writing Center at Harvard University

Top 10 Tips for Writing a Strong Position Paper
As scientists and researchers, you might be familiar with objective research papers, which tend to consider both sides of an argument and present findings based on facts. But are you aware of another important piece of academic writing known as the position paper? In this article, we will discuss different aspects that make position paper share expert tips on writing a great position paper that clearly presents an argument or opinion.
Table of Contents
What Is a Position Paper?
A position paper discusses a controversial issue and focuses on one aspect of an argument, providing valuable insights on how to interpret issues where science is ambiguous. It can also act as a medium for scientists and researchers to put forth solutions to resolve problems. Similar to objective research papers, position papers are still rooted in facts, statistics, evidence, and data. Additionally, they further enable authors to take a position on what these facts and data are telling us.
The purpose of a position paper is to gather support for an opinion on an issue by explaining the author’s stance and providing factual evidence to back it up. It critically evaluates the position, acknowledging its strengths and weaknesses.
Types of Position Paper
There are several types of position papers, each serving a unique purpose.
Ready to gauge your understanding of position papers? Take our short quiz today!
Fill the Details to Check Your Score

How to Write a Position Paper?
1. choosing a good topic.
Selecting a good topic for your position paper is just as important as having a well-structured paper that presents a strong argument. A well-written paper about an uninteresting or uncontroversial topic is simply a waste of time and effort. So how can you best choose a topic for your argument ?
Like all types of research, you should begin with preliminary research. A good topic for a position paper will answer yes to the following questions :
- Does the topic represent a genuine controversy?
- Are there two clear positions?
- Do you care enough to argue for one of those positions?
- Is the scope of the topic manageable?
Once you have found a topic that meets these criteria, you will need to conduct research to build a solid case in favor of your argument. This means finding supporting evidence (for both sides!) just as you would for an ordinary research paper . By including supporting evidence for the opposing side, you will be able to more clearly refute the conflicting arguments. In other words, you can point out weaknesses in the evidence cited by the opposing side or highlight strengths of evidence that supports your stand in comparison.
2. Conducting a Preliminary Research
Conducting preliminary research is crucial before delving into any topic. Evaluate evidence quality from reputable sources institutional websites, white papers, policies, scholarly articles, research reports, etc. Stay objective, dedicating some time for research. Be adaptable; reconsider your topic if evidence is lacking or contradictory. Prioritize quality over quantity in source selection. This ensures a well-supported and credible argument.
3. Crafting and Testing Your Thesis Statement
Crafting a thesis statement is a pivotal step in developing a coherent paper. This statement depicts your stance on the topic. A clear and focused thesis statement serves as the backbone of your argument, guiding the reader and shaping the trajectory of your analysis. Once established, subject it to rigorous examination by challenging it.
While it may seem counterintuitive, actively challenging your own thesis statement is a vital exercise in academic integrity and intellectual rigor. By earnestly considering opposing viewpoints and potential counterarguments, you not only demonstrate a comprehensive understanding of the subject matter but also fortify your position through logical reasoning and evidence-based support.
4. Collecting Supporting Evidence
When gathering evidence for your position paper, prioritize relevance and credibility. Use expert quotes sparingly, ensuring they directly support your argument. Prefer research-based evidence over anecdotes, focusing on quality rather than quantity. Verify the credibility of sources and regularly update evidence to reflect the latest research. Following these guidelines enhances the credibility and persuasiveness of your paper.
5. Drafting and Structuring the Position paper
The structure of a position paper is flexible, but it should generally follow a simple flow that clearly conveys the problem and the position of the author(s). A position paper should begin by clearly stating the problem and its relevance to the scientific community or even to the society as a whole. It should then address the main position of the author. For example:
a. Background: For decades, the WHO has urged the adoption of a tax on unhealthy foods to discourage the consumption of products that are harmful to our health.
b. Relevance: Sugar has been shown to have a negative impact on health, and play a major role in the rising obesity rates in America.
c. Position: The United States should adopt a tax on drinks with added sugar, to reduce the consumption of sugar, and promote healthier eating habits.
The author should then clearly list the common arguments and possible objections against this position. To continue with our example:
Argument 1: A sugary drink tax that focuses on soda may not impact other products that have an equally negative health impact such as fruit juice or candy.
Argument 2: A sugary drink tax is regressive and places a financial burden on the poorest consumers.
A strong position paper acknowledges the validity of the counter-arguments and then puts forth reasons why the author’s position is still the correct one. In our example paper, the author can address the counter-arguments in the next section like so:
Counter-argument 1: It is true that a sugary drink tax would not impact all sources of added sugar in the average American diet. However, it would still have a significant impact on a major source of added sugar to achieve its goal of reducing overall sugar consumption.
Counter-argument 2: All consumption taxes are regressive. A sugary drink tax would be most effective accompanied by subsidies for healthy foods such as fruit and vegetables.
Finally, summarize your main points and re-state your position in your conclusion. All arguments in the paper should be backed up by facts, data, and evidence , with proper citation attributed to your sources. In this way, a position paper is no different from an ordinary research paper . If you wish, you can include a brief literature review in your discussion of the background of the issue. While such a literature review is not essential, it can make your paper stronger.
Ten Tips for Writing a Strong Position Paper
Now that we know what a position paper is, let us review some tips to write a great position paper.
- Select a timely, relevant topic with two clear opposing sides.
- Conduct thorough preliminary research, collecting evidence supporting arguments for and against your position.
- Identify your intended audience. You should tailor your tone depending on who the paper is written for (the public, other scientists, policymakers, etc.).
- Clearly state your position on the topic.
- List and refute the counter-arguments to your position.
- Include supporting data and evidence to back up your argument.
- Properly attribute your sources using correct citation .
- Keep it simple! Position papers don’t need to go into excessive detail . Present your points clearly and briefly.
- Each paragraph in the paper should discuss a single idea.
- Have someone proofread your paper to ensure it reads well and looks professional.
A position paper can be a great way to expand your horizons and write a new type of research paper. Use these ten tips to write an effective position paper!
Are you seeking advice on writing a position paper? Seek professional assistance to craft a compelling argument in your position paper that effectively communicates your perspective to the scientific community.
Frequently Asked Questions
The length of a position paper can vary depending on the requirements set by the institution or conference. However, typically, position papers are concise and focused documents, usually ranging from 1,000 to 2,000 words.
The purpose of a position paper is to articulate an author's stance on a particular issue or topic, backed by factual evidence and logical reasoning.
Characteristics of a position paper include: 1.Focus on a controversial issue or topic. 2.Clear statement of author's stance or position. 3.Incorporation of factual evidence, statistics, and data. 4.Acknowledgment of counterarguments and addressing them effectively. 5.Concise and well-structured presentation of arguments.
Very informative
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Reporting Research
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for data interpretation
In research, choosing the right approach to understand data is crucial for deriving meaningful insights.…

Comparing Cross Sectional and Longitudinal Studies: 5 steps for choosing the right approach
The process of choosing the right research design can put ourselves at the crossroads of…

- Career Corner
Unlocking the Power of Networking in Academic Conferences
Embarking on your first academic conference experience? Fear not, we got you covered! Academic conferences…

Research Recommendations – Guiding policy-makers for evidence-based decision making
Research recommendations play a crucial role in guiding scholars and researchers toward fruitful avenues of…

- AI in Academia
Disclosing the Use of Generative AI: Best practices for authors in manuscript preparation
The rapid proliferation of generative and other AI-based tools in research writing has ignited an…
Intersectionality in Academia: Dealing with diverse perspectives
Meritocracy and Diversity in Science: Increasing inclusivity in STEM education
Avoiding the AI Trap: Pitfalls of relying on ChatGPT for PhD applications

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

What should universities' stance be on AI tools in research and academic writing?
Counterarguments
A counterargument involves acknowledging standpoints that go against your argument and then re-affirming your argument. This is typically done by stating the opposing side’s argument, and then ultimately presenting your argument as the most logical solution. The counterargument is a standard academic move that is used in argumentative essays because it shows the reader that you are capable of understanding and respecting multiple sides of an argument.
Counterargument in two steps
Respectfully acknowledge evidence or standpoints that differ from your argument.
Refute the stance of opposing arguments, typically utilizing words like “although” or “however.”
In the refutation, you want to show the reader why your position is more correct than the opposing idea.
Where to put a counterargument
Can be placed within the introductory paragraph to create a contrast for the thesis statement.
May consist of a whole paragraph that acknowledges the opposing view and then refutes it.
- Can be one sentence acknowledgements of other opinions followed by a refutation.
Why use a counterargument?
Some students worry that using a counterargument will take away from their overall argument, but a counterargument may make an essay more persuasive because it shows that the writer has considered multiple sides of the issue. Barnet and Bedau (2005) propose that critical thinking is enhanced through imagining both sides of an argument. Ultimately, an argument is strengthened through a counterargument.
Examples of the counterargument structure
- Argument against smoking on campus: Admittedly, many students would like to smoke on campus. Some people may rightly argue that if smoking on campus is not illegal, then it should be permitted; however, second-hand smoke may cause harm to those who have health issues like asthma, possibly putting them at risk.
- Argument against animal testing: Some people argue that using animals as test subjects for health products is justifiable. To be fair, animal testing has been used in the past to aid the development of several vaccines, such as small pox and rabies. However, animal testing for beauty products causes unneeded pain to animals. There are alternatives to animal testing. Instead of using animals, it is possible to use human volunteers. Additionally, Carl Westmoreland (2006) suggests that alternative methods to animal research are being developed; for example, researchers are able to use skin constructed from cells to test cosmetics. If alternatives to animal testing exist, then the practice causes unnecessary animal suffering and should not be used.
Harvey, G. (1999). Counterargument. Retrieved from writingcenter.fas.harvard.edu/pages/counter- argument
Westmoreland, C. (2006; 2007). “Alternative Tests and the 7th Amendment to the Cosmetics Directive.” Hester, R. E., & Harrison, R. M. (Ed.) Alternatives to animal testing (1st Ed.). Cambridge: Royal Society of Chemistry.
Barnet, S., Bedau, H. (Eds.). (2006). Critical thinking, reading, and writing . Boston, MA: Bedford/St. Martin’s.
Contributor: Nathan Lachner

- Walden University
- Faculty Portal
Writing a Paper: Responding to Counterarguments
Basics of counterarguments.
When constructing an argument, it is important to consider any counterarguments a reader might make. Acknowledging the opposition shows that you are knowledgeable about the issue and are not simply ignoring other viewpoints. Addressing counterarguments also gives you an opportunity to clarify and strengthen your argument, helping to show how your argument is stronger than other arguments.
Incorporating counterarguments into your writing can seem counterintuitive at first, and some writers may be unsure how to do so. To help you incorporate counterarguments into your argument, we recommend following the steps: (a) identify, (b) investigate, (c) address, and (d) refine.
Identify the Counterarguments
First you need to identify counterarguments to your own argument. Ask yourself, based on your argument, what might someone who disagrees counter in response? You might also discover counterarguments while doing your research, as you find authors who may disagree with your argument.
For example, if you are researching the current opioid crisis in the United States, your argument might be: State governments should allocate part of the budget for addiction recovery centers in communities heavily impacted by the opioid crisis . A few counterarguments might be:
- Recovery centers are not proven to significantly help people with addiction.
- The state’s money should go to more pressing concerns such as...
- Establishing and maintaining a recovery center is too costly.
- Addicts are unworthy of assistance from the state.
Investigate the Counterarguments
Analyze the counterarguments so that you can determine whether they are valid. This may require assessing the counterarguments with the research you already have or by identifying logical fallacies . You may also need to do additional research.
In the above list, the first three counterarguments can be researched. The fourth is a moral argument and therefore can only be addressed in a discussion of moral values, which is usually outside the realm of social science research. To investigate the first, you could do a search for research that studies the effectiveness of recovery centers. For the second, you could look at the top social issues in states around the country. Is the opioid crisis the main concern or are there others? For the third, you could look for public financial data from a recovery center or interview someone who works at one to get a sense of the costs involved.
Address the Counterarguments
Address one or two counterarguments in a rebuttal. Now that you have researched the counterarguments, consider your response. In your essay, you will need to state and refute these opposing views to give more credence to your argument. No matter how you decide to incorporate the counterargument into your essay, be sure you do so with objectivity, maintaining a formal and scholarly tone .
Considerations when writing:
- Will you discredit the counteragument by bringing in contradictory research?
- Will you concede that the point is valid but that your argument still stands as the better view? (For example, perhaps it is very costly to run a recovery center, but the societal benefits offset that financial cost.)
- Placement . You can choose to place the counterargument toward the beginning of the essay, as a way to anticipate opposition, or you can place it toward the end of the essay, after you have solidly made the main points of your argument. You can also weave a counterargument into a body paragraph, as a way to quickly acknowledge opposition to a main point. Which placement is best depends on your argument, how you’ve organized your argument, and what placement you think is most effective.
- Weight . After you have addressed the counterarguments, scan your essay as a whole. Are you spending too much time on them in comparison to your main points? Keep in mind that if you linger too long on the counterarguments, your reader might learn less about your argument and more about opposing viewpoints instead.
Refine Your Argument
Considering counterarguments should help you refine your own argument, clarifying the relevant issues and your perspective. Furthermore, if you find yourself agreeing with the counterargument, you will need to revise your thesis statement and main points to reflect your new thinking.
Templates for Responding to Counterarguments
There are many ways you can incorporate counterarguments, but remember that you shouldn’t just mention the counterargument—you need to respond to it as well. You can use these templates (adapted from Graff & Birkenstein, 2009) as a starting point for responding to counterarguments in your own writing.
- The claim that _____ rests upon the questionable assumption that _____.
- X may have been true in the past, but recent research has shown that ________.
- By focusing on _____, X has overlooked the more significant problem of _____.
- Although I agree with X up to a point, I cannot accept the overall conclusion that _____.
- Though I concede that _____, I still insist that _____.
- Whereas X has provided ample evidence that ____, Y and Z’s research on ____ and ____ convinces me that _____ instead.
- Although I grant that _____, I still maintain that _____.
- While it is true that ____, it does not necessarily follow that _____.
Graff, G., & Birkenstein, C. (2009). They say/I say: The moves that matter in academic writing (2 nd ed.). Norton.
Didn't find what you need? Search our website or email us .
Read our website accessibility and accommodation statement .
- Previous Page: Addressing Assumptions
- Next Page: Revising
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.
- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » Position Paper – Example, Format and Writing Guide
Position Paper – Example, Format and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Position Paper
Definition:
Position paper is a written document that presents an argument or stance on a particular issue or topic. It outlines the author’s position on the issue and provides support for that position with evidence and reasoning. Position papers are commonly used in academic settings, such as in Model United Nations conferences or debates, but they can also be used in professional or political contexts.
Position papers typically begin with an introduction that presents the issue and the author’s position on it. The body of the paper then provides evidence and reasoning to support that position, often citing relevant sources and research. The conclusion of the paper summarizes the author’s argument and emphasizes its importance.
Types of Position Paper
There are several types of position papers, including:
- Advocacy Position Paper : This type of position paper presents an argument in support of a particular issue, policy, or proposal. It seeks to persuade the reader to take a particular action or adopt a particular perspective.
- Counter-Argument Position Paper: This type of position paper presents an argument against a particular issue, policy, or proposal. It seeks to convince the reader to reject a particular perspective or course of action.
- Problem-Solution Position Paper : This type of position paper identifies a problem and presents a solution to it. It seeks to convince the reader that the proposed solution is the best course of action to address the identified problem.
- Comparative Position Paper : This type of position paper compares and contrasts two or more options, policies, or proposals. It seeks to convince the reader that one option is better than the others.
- Historical Position Paper : This type of position paper examines a historical event, policy, or perspective and presents an argument based on the analysis of the historical context.
- Interpretive Position Paper : This type of position paper provides an interpretation or analysis of a particular issue, policy, or proposal. It seeks to persuade the reader to adopt a particular perspective or understanding of the topic.
- Policy Position Paper: This type of position paper outlines a specific policy proposal and presents an argument in support of it. It may also address potential objections to the proposal and offer solutions to address those objections.
- Value Position Paper: This type of position paper argues for or against a particular value or set of values. It seeks to convince the reader that a particular value or set of values is more important or better than others.
- Predictive Position Paper : This type of position paper makes predictions about future events or trends and presents an argument for why those predictions are likely to come true. It may also offer suggestions for how to prepare for or respond to those events or trends.
- Personal Position Paper : This type of position paper presents an individual’s personal perspective or opinion on a particular issue. It may draw on personal experiences or beliefs to support the argument.
Position Paper Format
Here is a format you can follow when writing a position paper:
- Introduction: The introduction should provide a brief overview of the topic or issue being discussed. It should also provide some background information on the issue and state the purpose of the position paper.
- Definition of the problem : This section should describe the problem or issue that the position paper addresses. It should explain the causes and effects of the problem and provide evidence to support the claims made.
- Historical perspective : This section should provide a historical perspective on the issue or problem, outlining how it has evolved over time and what previous attempts have been made to address it.
- The organization’s stance : This section should present the organization’s stance on the issue or problem. It should provide evidence to support the organization’s position and explain the rationale behind it. This section should also address any counterarguments or alternative perspectives.
- Proposed solutions: This section should provide proposed solutions or recommendations to address the problem or issue. It should explain how the proposed solutions align with the organization’s stance and provide evidence to support their effectiveness.
- Conclusion: The conclusion should summarize the organization’s position on the issue or problem and restate the proposed solutions or recommendations. It should also encourage further discussion and action on the issue.
- References: Include a list of references used to support the claims made in the position paper.
How to Write Position Paper
Here are the steps to write a position paper:
- Choose your topic: Select a topic that you are passionate about or have knowledge of. It could be related to social, economic, environmental, political, or any other issues.
- Research: Conduct thorough research on the topic to gather relevant information and supporting evidence. This could include reading scholarly articles, reports, books, and news articles.
- Define your position: Once you have gathered sufficient information, identify the main arguments and formulate your position. Consider both the pros and cons of the issue.
- Write an introduction : Start your position paper with a brief introduction that provides some background information on the topic and highlights the key points that you will discuss in the paper.
- Present your arguments: In the body of your paper, present your arguments in a logical and coherent manner. Each argument should be supported by evidence from your research.
- Address opposing views : Acknowledge and address the opposing views on the issue. Provide counterarguments that refute these views and explain why your position is more valid.
- Conclusion : In the conclusion, summarize your main points and reiterate your position on the topic. You can also suggest some solutions or actions that can be taken to address the issue.
- Edit and proofread : Finally, edit and proofread your position paper to ensure that it is well-written, clear, and free of errors.
Position Paper Example
Position Paper Example structure is as follows:
- Introduction:
- A brief overview of the issue
- A clear statement of the position the paper is taking
- Background:
- A detailed explanation of the issue
- A discussion of the history of the issue
- An analysis of any previous actions taken on the issue
- A detailed explanation of the position taken by the paper
- A discussion of the reasons for the position taken
- Evidence supporting the position, such as statistics, research, and expert opinions
- Counterarguments:
- A discussion of opposing views and arguments
- A rebuttal of those opposing views and arguments
- A discussion of why the position taken is more valid than the opposing views
- Conclusion:
- A summary of the main points of the paper
- A call to action or recommendation for action
- A final statement reinforcing the position taken by the paper
- References:
- A list of sources used in the paper, cited in an appropriate citation style
Purpose of Position Paper
Here are some of the most common purposes of position papers:
- Advocacy: Position papers are often used to promote a particular point of view or to advocate for a specific policy or action.
- Debate : In a debate, participants are often required to write position papers outlining their argument. These papers help the debaters clarify their position and provide evidence to support their claims.
- Negotiation : Position papers can be used as part of negotiations to establish each party’s position on a particular issue.
- Education : Position papers can be used to educate the public, policymakers, and other stakeholders about complex issues by presenting a clear and concise argument supported by evidence.
- Decision-making : Position papers can be used by decision-makers to make informed decisions about policies, programs, or initiatives based on a well-reasoned argument.
- Research : Position papers can be used as a starting point for further research on a particular topic or issue.
When to Write Position Paper
Here are some common situations when you might need to write a position paper:
- Advocacy or lobbying : If you are part of an organization that is advocating for a specific policy change or trying to influence decision-makers, a position paper can help you articulate your organization’s position and provide evidence to support your arguments.
- Conferences or debates: In academic or professional settings, you may be asked to write a position paper to present your perspective on a particular topic or issue. This can be a useful exercise to help you clarify your thoughts and prepare for a debate or discussion.
- Public relations: A position paper can also be used as a tool for public relations, to showcase your organization’s expertise and thought leadership on a particular issue.
- Internal communications: Within an organization, a position paper can be used to communicate a particular stance or policy to employees or stakeholders.
Advantages of Position Paper
There are several advantages to writing a position paper, including:
- Organizing thoughts : Writing a position paper requires careful consideration of the issue at hand, and the process of organizing thoughts and arguments can help you clarify your own position.
- Demonstrating expertise: Position papers are often used in academic and professional settings to demonstrate expertise on a particular topic. Writing a well-researched and well-written position paper can help establish your credibility and expertise in a given field.
- Advocacy: Position papers are often used as a tool for advocacy, whether it’s advocating for a particular policy or for a specific point of view. Position papers can help persuade others to adopt your position on an issue.
- Facilitating discussion : Position papers can be used to facilitate discussion and debate on a particular issue. By presenting different perspectives on an issue, position papers can help foster dialogue and lead to a better understanding of the topic at hand.
- Providing a framework for action: Position papers can also be used to provide a framework for action. By outlining specific steps that should be taken to address an issue, a position paper can help guide decision-making and policy development.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

What is Art – Definition, Types, Examples

What is Anthropology – Definition and Overview

What is Literature – Definition, Types, Examples

Economist – Definition, Types, Work Area

Anthropologist – Definition, Types, Work Area

What is History – Definitions, Periods, Methods
The Study Blog : Tips
8 counter argument examples to help you write a strong essay.
By Evans Oct 26, 2020
A one-sided essay is like a beautiful dish with no flavor. Everyone looks at it, but nobody wants to partake of it. An essay presenting one side of a debate shows that you are not reasonable. Instead of persuading your readers, it ends up feeling like you’re just forcing an opinion on them. How do you change this? How do you make your essay interesting and persuasive? Counter argument! You heard me right. Using the counter argument is one of the best ways that you can strengthen your essay.

Before we proceed further, what exactly is a counter-argument? An academic essay means that you need to come up with a thesis, a strong one at that, and even stronger points that support that particular thesis . You also need to come up with an argument that opposes your thesis. This is what we call a counter-argument. It is basically, an argument that is against your thesis.
Are tight deadlines, clashing assignments, and unclear tasks giving you sleepless nights?
Do not panic, hire a professional essay writer today.
What is the purpose of a counter-argument?
When writing an essay, especially to persuade, you need to put yourself in the shoes of your readers. What are they likely to think about your thesis? How can they possibly argue against it? What questions might they have against the idea you are trying to sell to them? A counter-argument allows you to creatively and wisely respond to these questions. A counter-argument clears any doubts that your reader may have on your argument. It also shows them that you are the bigger person by actually addressing arguments against your thesis.
Counter argument examples
Let’s say your argument is about getting the patient to consent to it, rather than have the doctors decide on it.
A reader might argue: a patient may be too sickly to even consent for euthanasia.
Refutal: you can refute the counter-argument by proving that it is possible to get a patient in the right frame long enough to sign the consent form.
Overprotective parents
Argument: overprotective parents often treat their grown-up children like babies. As a result, these children grow to be very dependent on the parents and unable to make decisions on their own.
Counter-argument: parents have seen more than their children. Protecting them from the problems they encountered saves the children from getting hurt.
Refutal: Though parents think that shielding their grown children protects them from the dangerous world, they only end up protecting children from living. As a result, if such a child makes a mistake, it might be very hard for them to recover from it.
Getting a dog as a pet for young children
Argument: getting a dog as a pet for younger children is not a very good idea as children may not understand how to take care of the dog.
Counter-argument: having a pet teaches the children responsibility.
Rebuttal: While it is true that having a pet can teach kids how to become more responsible, the fact remains that taking care of a pet is a full-time job. A pet is not like a toy that you can discard when tired of it. Young kids may not have the stamina or the time to take care of a pet.
Exposure to technology
Argument: Technology provides children with an amazing learning experience. Children who have been exposed to technology learn pretty first how to deal and respond to different situations better than students who have no exposure to technology.
You may also like: How to write a technology essay: tips, topics, and examples
Counter argument: early exposure to entertainment and violence affects the cognitive skills of a child.
Rebuttal: Although some form of technology may affect the cognitive skills of a child, it doesn’t mean that children should be kept away from technology. There are learning programs that provide a better learning experience as compared to formal education. Doing away with technology is not the answer. The answer is controlling what children are exposed to.
Argument: taking part in elections is not only a right but a responsibility that every citizen should participate in.
Counter-argument: It is better not to vote than vote in a corrupt person.
Rebuttal: While you might feel like not taking part in the voting process keeps you from the guilt of choosing the wrong person, the truth is that you only give other people the right to choose for you. This means that if a corrupt person gets in, you’re still responsible for not voting for a better candidate.
Argument: Smoking should not be allowed on campuses.
Counter-argument: smoking is not illegal, especially to someone above 18 years old. Since it is not illegal, students should be allowed to smoke within the campus vicinity.
Rebuttal: indeed, smoking is not illegal. However, smoking on campus can prove to be fatal especially to students with health issues such as asthma. It is widely known that smoking affects not just the person holding the cigar but everyone else around them. Therefore, to keep students safe, smoking should not be allowed on campus.
Animal testing
Argument: animals should not be used as test subjects.
Counter-argument: animals happen to be the best test method for health products
Rebuttal: While it is true that over the years animals have been used as test subjects, it doesn’t change the fact that these tests often subject animals to excruciating pain. Research shows that there are better alternatives that can be used, thereby saving animals from unnecessary pain.
Cyberbullying
Argument: Cyberbullying is a serious issue and therefore it is very important to understand how to protect yourself from cyberbullies.
Counter-argument: the victims do not need to learn how to protect themselves and use the internet fearfully. The internet should be made secure for every user and all cyberbullying should be put to jail.
Rebuttal: nobody deserves to be afraid while using the internet. However, while it is a very good idea to have all cyberbullies jailed, that remains to be just a dream. This is because almost everyone can be a cyber-bully at one point or another. It, therefore, remains your responsibility to protect yourself and also learn how to handle cyberbullying.
Earn Good Grades Without Breaking a Sweat
✔ We've helped over 1000 students earn better grades since 2017. ✔ 98% of our customers are happy with our service

Final thoughts
As the examples show, a good persuasive essay should contain your thesis statement , a counter-argument, and a rebuttal of the counter-argument. This makes your essay strong, very persuasive, and with a very good flavor.
You may also like: The little secret why your friends are earning better grades
Popular services
The little secret why your friends are earning better grades.
Hire an Expert from our write my essay service and start earning good grades.
Can Someone Write My Paper for Me Online? Yes, We Can!
Research topics
Essay Topics
Popular articles
Six Proven ways to cheat Turnitin with Infographic
Understanding Philosophy of Nursing: Complete Guide With Examples
50+ Collection of the Most Controversial Argumentative Essay Topics
50+ Economics research Topics and Topic Ideas for dissertation
20+ Interesting Sociology research topics and Ideas for Your Next Project
RAISE YOUR HAND IF YOU ARE TIRED OF WRITING COLLEGE PAPERS!
Hire a professional academic writer today.
Each paper you order from us is of IMPECCABLE QUALITY and PLAGIARISM FREE
Use code PPH10 to get 10% discount. Terms and condition apply.

Ready to hire a professional essay writer?
Each paper you receive from us is plagiarism-free and will fetch you a good grade. We are proud to have helped 10,000+ students achieve their academic dreams. Enjoy our services by placing your order today.

Write my paper
Do my assignment
Essay writing help
Research paper help
College homework help
Essay writing guide
College admission essay
Writing a research paper
Paper format for writing
Terms & conditions
Privacy Policy
Cookie Policy
Money-Back Guarantee
Our services

Copyright © 2017 Paper Per Hour. All rights reserved.
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
How to Write a Position Paper
Last Updated: March 22, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Emily Listmann, MA and by wikiHow staff writer, Danielle Blinka, MA, MPA . Emily Listmann is a private tutor in San Carlos, California. She has worked as a Social Studies Teacher, Curriculum Coordinator, and an SAT Prep Teacher. She received her MA in Education from the Stanford Graduate School of Education in 2014. There are 8 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 235,658 times.
Just like an argument paper, a position paper supports one side of an issue, similar to in a debate. Your goal will be to provide convincing evidence to the reader that your position is the correct stance to take on an issue. You can write a great position paper by choosing your position carefully, developing your argument, drafting your paper, and revising and editing your work.
Position Paper Outline and Example

Choosing Your Position

- For example, you wouldn’t want to write a paper arguing that children need proper care, as no one would disagree with that stance.
- A better topic may be taking a stance on what should be done if children are not receiving proper care.

- Visit your local library to find books, journals, and newspapers.
- Access online databases, credible websites, and news sources.
- To decide if a source is credible , look for peer-reviewed journals, check the credentials of the author, locate the information in two separate sources, and check the date to make sure the information is the most recent available. You should also avoid self-published sources.

- Looking at both sides not only helps you pick the best position, it will also help you choose a good counterargument. [3] X Research source
- For example, if you are writing a paper about whether or not your community should invest in new park equipment, your two sides would be either in favor of the new park equipment or against it. A pro of buying new equipment might be purchasing safer equipment, while a con would be the expense of the purchase.

- In some cases, it’s easier to argue a position if you don’t have strong opinions either way. This is because you can focus on the evidence, not on your personal views.

- While you don’t have to change your position to fit your audience, you may want to adjust your reasons behind the position or the counter-argument you choose.
Building Your Argument

- If possible, look for supporting reasons that are shown through 2 or more different pieces of evidence, as this will make your argument stronger.
- Use your assignment sheet or the parameters of your paper to determine how many supporting reasons you should include. For many academic papers, you will use 2 to 3 reasons.

- Use an organizing strategy that works for you.
- Compiling your evidence now will help you more easily write your paper.
- Keep in mind that it is important to cite your sources. If you use a direct quote from a source, then put it into quotation marks and identify the author when you use it. If you paraphrase or summarize something from a source, give credit to the author for the ideas.
- Don’t go overboard on including evidence! Remember that most of the ideas in the paper should be your own. It’s good to quote sources, but avoid quoting entire paragraphs from other sources. Keep your quotes to a sentence or two and try to avoid including more than one quote per paragraph.

- For example, if you are writing a position paper arguing that your community should purchase new playground equipment, your counter-argument could be that the purchase will be too expensive. To strengthen your argument, you would cite this possible point against you but show why it's not a valid reason to dismiss your position. A good way to do that would be to show that the equipment is worth the expense or that there is outside funding to pay for it.
- You will also want a piece of evidence that supports your counter-argument. This evidence, which should be easy to dismiss, will be included in your paper.
Drafting Your Paper

- One easy way to set up your argument in your thesis is to include both your counter-argument and claim, preceded by the word “although.” For example, “Although installing new playground equipment in the park will be expensive, new playground equipment would provide a safe play area for children and offer options for special needs children.”
- If you’re an expert writer, you may not need to include supporting reasons in your thesis. For example, “As parents learn the benefits and dangers of outside play, communities across the nation are turning their eyes toward their parks, making safe, accessible equipment a public necessity.” [11] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source

- Start with a hook that introduces your topic. For example, you could provide a statistic of how many children are injured on old playground equipment every year.
- Include a few sentences that provide more information on your topic, narrowing down toward your stance.
- End your introduction with your thesis.

- Follow the requirements for your paper, which may state how many paragraphs you should include.

- For example, you could write: “Installing new playground equipment would make the park more inclusive for special needs children because updated designs are accessible to those who are disabled.”

- Documented stories

- Without commentary, there is no link between your evidence and your position, leaving your argument weak.

- Restate your thesis. For example, "While new playground equipment is expensive, it's worth the investment because it serves the best interests of the community by providing children with a safe area to play and making the park more accessible for special needs children."
- Sum up your argument.
- End on a high note with a call to action. For example, "Children need a safe, accessible place to play, so the only choice is to install new park equipment in Quimby Park."

- If you don’t cite your sources, then you will be guilty of plagiarism. You could lose credit or face harsher penalties if you are caught stealing someone else’s words or ideas.
Revising and Editing Your Paper

- Before you change a word, re-read the sentence to make sure that the new suggestion fits. The spell checker may think that you mean one thing, while you really mean something else.

- Waiting at least a day is best. If you are short on time, wait at least 30 minutes before reviewing what you’ve written.

- If possible, have a friend or mentor read your paper and suggest edits or revisions.

- Combine short, choppy sentences, and break up long sentences.
- Fix sentence fragments and run-ons.

- If possible, ask a friend or mentor to proofread your final draft. They may be able to spot errors that you don’t see.

- If you are presenting or turning in a printed paper, check to see if you should place it in a presentation folder.
Community Q&A
- Avoid using the words “I” and “you” in your thesis. Thanks Helpful 7 Not Helpful 0
- Make sure that you stay focused on your claim throughout your paper and that all of the evidence you present in the paper is supporting your claim. Thanks Helpful 2 Not Helpful 0

- Give credit when you use someone else's opinion, statistics, facts or quotations. Avoid plagiarism by referencing and citing your sources. Thanks Helpful 10 Not Helpful 3
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://www.indeed.com/career-advice/career-development/how-to-write-a-position-paper
- ↑ https://www.cs.rutgers.edu/~rmartin/teaching/fall15/Writing_a_Position_Paper.pdf
- ↑ https://www.nmun.org/assets/documents/nmun-pp-guide.pdf
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/academic_writing/essay_writing/argumentative_essays.html
- ↑ https://bowiestate.libguides.com/c.php?g=442189&p=3014828
- ↑ https://opentextbc.ca/writingforsuccess/chapter/chapter-12-peer-review-and-final-revisions/
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/the_writing_process/proofreading/steps_for_revising.html
- ↑ https://academicguides.waldenu.edu/writingcenter/writingprocess/proofreading
About This Article

If you need to write a position paper, choose a topic that has at least 2 clear sides, then pick one of those sides as your position. Gather research from books, newspapers, academic journals, online databases, and other credible sources, making sure to cover your own position and at least one opposing side. Open your paper by stating your claim, or the position you have taken, then offer at least 2 pieces of evidence to support that stance. Identify and dismiss a counter-argument to your position as well. For tips on how to use topic sentences to link your paragraphs to your thesis, read on! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors

Reader Success Stories
Hannah Curry
May 22, 2018
Did this article help you?
Aug 17, 2016
Mitra Mohamadzadeh
Jan 30, 2018
Jul 26, 2016

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter
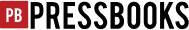
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
21 Argument, Counterargument, & Refutation
In academic writing, we often use an Argument essay structure. Argument essays have these familiar components, just like other types of essays:
- Introduction
- Body Paragraphs
But Argument essays also contain these particular elements:
- Debatable thesis statement in the Introduction
- Argument – paragraphs which show support for the author’s thesis (for example: reasons, evidence, data, statistics)
- Counterargument – at least one paragraph which explains the opposite point of view
- Concession – a sentence or two acknowledging that there could be some truth to the Counterargument
- Refutation (also called Rebuttal) – sentences which explain why the Counterargument is not as strong as the original Argument
Consult Introductions & Titles for more on writing debatable thesis statements and Paragraphs ~ Developing Support for more about developing your Argument.
Imagine that you are writing about vaping. After reading several articles and talking with friends about vaping, you decide that you are strongly opposed to it.
Which working thesis statement would be better?
- Vaping should be illegal because it can lead to serious health problems.
Many students do not like vaping.
Because the first option provides a debatable position, it is a better starting point for an Argument essay.
Next, you would need to draft several paragraphs to explain your position. These paragraphs could include facts that you learned in your research, such as statistics about vapers’ health problems, the cost of vaping, its effects on youth, its harmful effects on people nearby, and so on, as an appeal to logos . If you have a personal story about the effects of vaping, you might include that as well, either in a Body Paragraph or in your Introduction, as an appeal to pathos .
A strong Argument essay would not be complete with only your reasons in support of your position. You should also include a Counterargument, which will show your readers that you have carefully researched and considered both sides of your topic. This shows that you are taking a measured, scholarly approach to the topic – not an overly-emotional approach, or an approach which considers only one side. This helps to establish your ethos as the author. It shows your readers that you are thinking clearly and deeply about the topic, and your Concession (“this may be true”) acknowledges that you understand other opinions are possible.
Here are some ways to introduce a Counterargument:
- Some people believe that vaping is not as harmful as smoking cigarettes.
- Critics argue that vaping is safer than conventional cigarettes.
- On the other hand, one study has shown that vaping can help people quit smoking cigarettes.
Your paragraph would then go on to explain more about this position; you would give evidence here from your research about the point of view that opposes your own opinion.
Here are some ways to begin a Concession and Refutation:
- While this may be true for some adults, the risks of vaping for adolescents outweigh its benefits.
- Although these critics may have been correct before, new evidence shows that vaping is, in some cases, even more harmful than smoking.
- This may have been accurate for adults wishing to quit smoking; however, there are other methods available to help people stop using cigarettes.
Your paragraph would then continue your Refutation by explaining more reasons why the Counterargument is weak. This also serves to explain why your original Argument is strong. This is a good opportunity to prove to your readers that your original Argument is the most worthy, and to persuade them to agree with you.
Activity ~ Practice with Counterarguments, Concessions, and Refutations
A. Examine the following thesis statements with a partner. Is each one debatable?
B. Write your own Counterargument, Concession, and Refutation for each thesis statement.
Thesis Statements:
- Online classes are a better option than face-to-face classes for college students who have full-time jobs.
- Students who engage in cyberbullying should be expelled from school.
- Unvaccinated children pose risks to those around them.
- Governments should be allowed to regulate internet access within their countries.
Is this chapter:
…too easy, or you would like more detail? Read “ Further Your Understanding: Refutation and Rebuttal ” from Lumen’s Writing Skills Lab.
Note: links open in new tabs.
reasoning, logic
emotion, feeling, beliefs
moral character, credibility, trust, authority
goes against; believes the opposite of something
ENGLISH 087: Academic Advanced Writing Copyright © 2020 by Nancy Hutchison is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

English Current
ESL Lesson Plans, Tests, & Ideas
- North American Idioms
- Business Idioms
- Idioms Quiz
- Idiom Requests
- Proverbs Quiz & List
- Phrasal Verbs Quiz
- Basic Phrasal Verbs
- North American Idioms App
- A(n)/The: Help Understanding Articles
- The First & Second Conditional
- The Difference between 'So' & 'Too'
- The Difference between 'a few/few/a little/little'
- The Difference between "Other" & "Another"
- Check Your Level
- English Vocabulary
- Verb Tenses (Intermediate)
- Articles (A, An, The) Exercises
- Prepositions Exercises
- Irregular Verb Exercises
- Gerunds & Infinitives Exercises
- Discussion Questions
- Speech Topics
- Argumentative Essay Topics
- Top-rated Lessons
- Intermediate
- Upper-Intermediate
- Reading Lessons
- View Topic List
- Expressions for Everyday Situations
- Travel Agency Activity
- Present Progressive with Mr. Bean
- Work-related Idioms
- Adjectives to Describe Employees
- Writing for Tone, Tact, and Diplomacy
- Speaking Tactfully
- Advice on Monetizing an ESL Website
- Teaching your First Conversation Class
- How to Teach English Conversation
- Teaching Different Levels
- Teaching Grammar in Conversation Class
- Members' Home
- Update Billing Info.
- Cancel Subscription
- North American Proverbs Quiz & List
- North American Idioms Quiz
- Idioms App (Android)
- 'Be used to'" / 'Use to' / 'Get used to'
- Ergative Verbs and the Passive Voice
- Keywords & Verb Tense Exercises
- Irregular Verb List & Exercises
- Non-Progressive (State) Verbs
- Present Perfect vs. Past Simple
- Present Simple vs. Present Progressive
- Past Perfect vs. Past Simple
- Subject Verb Agreement
- The Passive Voice
- Subject & Object Relative Pronouns
- Relative Pronouns Where/When/Whose
- Commas in Adjective Clauses
- A/An and Word Sounds
- 'The' with Names of Places
- Understanding English Articles
- Article Exercises (All Levels)
- Yes/No Questions
- Wh-Questions
- How far vs. How long
- Affect vs. Effect
- A few vs. few / a little vs. little
- Boring vs. Bored
- Compliment vs. Complement
- Die vs. Dead vs. Death
- Expect vs. Suspect
- Experiences vs. Experience
- Go home vs. Go to home
- Had better vs. have to/must
- Have to vs. Have got to
- I.e. vs. E.g.
- In accordance with vs. According to
- Lay vs. Lie
- Make vs. Do
- In the meantime vs. Meanwhile
- Need vs. Require
- Notice vs. Note
- 'Other' vs 'Another'
- Pain vs. Painful vs. In Pain
- Raise vs. Rise
- So vs. Such
- So vs. So that
- Some vs. Some of / Most vs. Most of
- Sometimes vs. Sometime
- Too vs. Either vs. Neither
- Weary vs. Wary
- Who vs. Whom
- While vs. During
- While vs. When
- Wish vs. Hope
- 10 Common Writing Mistakes
- 34 Common English Mistakes
- First & Second Conditionals
- Comparative & Superlative Adjectives
- Determiners: This/That/These/Those
- Check Your English Level
- Grammar Quiz (Advanced)
- Vocabulary Test - Multiple Questions
- Vocabulary Quiz - Choose the Word
- Verb Tense Review (Intermediate)
- Verb Tense Exercises (All Levels)
- Conjunction Exercises
- List of Topics
- Business English
- Games for the ESL Classroom
- Pronunciation
- Teaching Your First Conversation Class
- How to Teach English Conversation Class
Argumentative Essays: The Counter-Argument & Refutation
An argumentative essay presents an argument for or against a topic. For example, if your topic is working from home , then your essay would either argue in favor of working from home (this is the for side) or against working from home.
Like most essays, an argumentative essay begins with an introduction that ends with the writer's position (or stance) in the thesis statement .
Introduction Paragraph
(Background information....)
- Thesis statement : Employers should give their workers the option to work from home in order to improve employee well-being and reduce office costs.
This thesis statement shows that the two points I plan to explain in my body paragraphs are 1) working from home improves well-being, and 2) it allows companies to reduce costs. Each topic will have its own paragraph. Here's an example of a very basic essay outline with these ideas:
- Background information
Body Paragraph 1
- Topic Sentence : Workers who work from home have improved well-being .
- Evidence from academic sources
Body Paragraph 2
- Topic Sentence : Furthermore, companies can reduce their expenses by allowing employees to work at home .
- Summary of key points
- Restatement of thesis statement
Does this look like a strong essay? Not really . There are no academic sources (research) used, and also...
You Need to Also Respond to the Counter-Arguments!
The above essay outline is very basic. The argument it presents can be made much stronger if you consider the counter-argument , and then try to respond (refute) its points.
The counter-argument presents the main points on the other side of the debate. Because we are arguing FOR working from home, this means the counter-argument is AGAINST working from home. The best way to find the counter-argument is by reading research on the topic to learn about the other side of the debate. The counter-argument for this topic might include these points:
- Distractions at home > could make it hard to concentrate
- Dishonest/lazy people > might work less because no one is watching
Next, we have to try to respond to the counter-argument in the refutation (or rebuttal/response) paragraph .
The Refutation/Response Paragraph
The purpose of this paragraph is to address the points of the counter-argument and to explain why they are false, somewhat false, or unimportant. So how can we respond to the above counter-argument? With research !
A study by Bloom (2013) followed workers at a call center in China who tried working from home for nine months. Its key results were as follows:
- The performance of people who worked from home increased by 13%
- These workers took fewer breaks and sick-days
- They also worked more minutes per shift
In other words, this study shows that the counter-argument might be false. (Note: To have an even stronger essay, present data from more than one study.) Now we have a refutation.
Where Do We Put the Counter-Argument and Refutation?
Commonly, these sections can go at the beginning of the essay (after the introduction), or at the end of the essay (before the conclusion). Let's put it at the beginning. Now our essay looks like this:
Counter-argument Paragraph
- Dishonest/lazy people might work less because no one is watching
Refutation/Response Paragraph
- Study: Productivity increased by 14%
- (+ other details)
Body Paragraph 3
- Topic Sentence : In addition, people who work from home have improved well-being .
Body Paragraph 4
The outline is stronger now because it includes the counter-argument and refutation. Note that the essay still needs more details and research to become more convincing.

Working from home may increase productivity.
Extra Advice on Argumentative Essays
It's not a compare and contrast essay.
An argumentative essay focuses on one topic (e.g. cats) and argues for or against it. An argumentative essay should not have two topics (e.g. cats vs dogs). When you compare two ideas, you are writing a compare and contrast essay. An argumentative essay has one topic (cats). If you are FOR cats as pets, a simplistic outline for an argumentative essay could look something like this:
- Thesis: Cats are the best pet.
- are unloving
- cause allergy issues
- This is a benefit > Many working people do not have time for a needy pet
- If you have an allergy, do not buy a cat.
- But for most people (without allergies), cats are great
- Supporting Details
Use Language in Counter-Argument That Shows Its Not Your Position
The counter-argument is not your position. To make this clear, use language such as this in your counter-argument:
- Opponents might argue that cats are unloving.
- People who dislike cats would argue that cats are unloving.
- Critics of cats could argue that cats are unloving.
- It could be argued that cats are unloving.
These underlined phrases make it clear that you are presenting someone else's argument , not your own.
Choose the Side with the Strongest Support
Do not choose your side based on your own personal opinion. Instead, do some research and learn the truth about the topic. After you have read the arguments for and against, choose the side with the strongest support as your position.
Do Not Include Too Many Counter-arguments
Include the main (two or three) points in the counter-argument. If you include too many points, refuting these points becomes quite difficult.
If you have any questions, leave a comment below.
- Matthew Barton / Creator of Englishcurrent.com
Additional Resources :
- Writing a Counter-Argument & Refutation (Richland College)
- Language for Counter-Argument and Refutation Paragraphs (Brown's Student Learning Tools)
EnglishCurrent is happily hosted on Dreamhost . If you found this page helpful, consider a donation to our hosting bill to show your support!
23 comments on “ Argumentative Essays: The Counter-Argument & Refutation ”
Thank you professor. It is really helpful.
Can you also put the counter argument in the third paragraph
It depends on what your instructor wants. Generally, a good argumentative essay needs to have a counter-argument and refutation somewhere. Most teachers will probably let you put them anywhere (e.g. in the start, middle, or end) and be happy as long as they are present. But ask your teacher to be sure.
Thank you for the information Professor
how could I address a counter argument for “plastic bags and its consumption should be banned”?
For what reasons do they say they should be banned? You need to address the reasons themselves and show that these reasons are invalid/weak.
Thank you for this useful article. I understand very well.
Thank you for the useful article, this helps me a lot!
Thank you for this useful article which helps me in my study.
Thank you, professor Mylene 102-04
it was very useful for writing essay
Very useful reference body support to began writing a good essay. Thank you!
Really very helpful. Thanks Regards Mayank
Thank you, professor, it is very helpful to write an essay.
It is really helpful thank you
It was a very helpful set of learning materials. I will follow it and use it in my essay writing. Thank you, professor. Regards Isha
Thanks Professor
This was really helpful as it lays the difference between argumentative essay and compare and contrast essay.. Thanks for the clarification.
This is such a helpful guide in composing an argumentative essay. Thank you, professor.
This was really helpful proof, thankyou!
Thanks this was really helpful to me
This was very helpful for us to generate a good form of essay
thank you so much for this useful information.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- Other Guides
- How to Write a Position Paper: Definition, Outline & Examples
- Speech Topics
- Basics of Essay Writing
- Essay Topics
- Other Essays
- Main Academic Essays
- Research Paper Topics
- Basics of Research Paper Writing
- Miscellaneous
- Chicago/ Turabian
- Data & Statistics
- Methodology
- Admission Writing Tips
- Admission Advice
- Student Life
- Studying Tips
- Understanding Plagiarism
- Academic Writing Tips
- Basics of Dissertation & Thesis Writing
- Essay Guides
- Research Paper Guides
- Formatting Guides
- Basics of Research Process
- Admission Guides
- Dissertation & Thesis Guides
How to Write a Position Paper: Definition, Outline & Examples

Table of contents
Use our free Readability checker
A position paper is a written statement that presents a particular perspective on any issue or topic. It typically argues a specific point of view and presents evidence to support that position. To write a position paper, you need to research and understand the topic, develop a supported argument, and address opposing viewpoints.
In this comprehensive guide, you will find all important information that will help you prepare this type of assignment. More specifically we will talk about:
- What is a position paper?
- How to write a position paper?
- Position paper example you could use for inspiration.
As an experienced paper writer team, we always come to support fellow students by providing them with helpful information and tips. Our readers can find detailed definitions and high-quality supporting materials on this website – all of that available for free!
What Is a Position Paper: Definition
First of all, let’s define it. Your position paper should clearly display and support your own view of a specific problem. Typically, position papers explore more or less controversial questions, which is why they must include argumentation supported by valid data. Providing evidence to the readers is the main distinctive feature of such an essay. Your work should demonstrate your ability to put up a strong case, not just describe your beliefs. Before you write a position paper, think it through and start with understanding your purpose. What do you try to tell your audience, and what is the best way to convey it? This helps with building good argumentation and structuring your essay.

Keep in mind that unlike a persuasive essay , convincing your readers to accept your point isn’t your primary task. Your piece should mainly focus on information that makes an argument strong. That’s why you should use supportive evidence that backs up your viewpoints.
Purpose of a Position Paper
Why do you need a position paper? First of all, it serves as great supporting material when talking about your viewpoint in front of an audience. Writing a position paper beforehand helps to organize your thoughts on the topic and set your defenses properly. Besides, you can use it when speaking to ensure you haven’t forgotten to mention something important. You might also be required to submit your paper before or after your speech. If it is your college or university assignment, this document will be your main output, which is why its structure and format are so important.
Position Paper Outline
One of the main first steps is preparing an outline for a position paper. After you’ve done some research and gathered enough data on your topic, spend additional time and create a concise draft. It should display your paper’s entire structure, including the key arguments, without going into much details. Your writing should follow a basic 5 paragraph essay outline . Once done with your plan, you can review it and easily spot major gaps or inconsistencies. Checking your work at this stage is typically much more productive than after writing the full text. Here is an example of position paper outline:
- Hook the reader with stats, numbers or facts
- Introduce the issue
- Include a thesis statement presenting your central idea and stand on the problem
- Present counterclaims
- Offer evidence that backs up counterarguments
- Refute the counter arguments using examples
- Strong opinion
- Supporting examples
- Restate your main claim
- Offer a course of action
Hopefully, this position paper template will speed up your progress with your own work. Check the attachments below – complete sample papers along with outlines are available there.

Position Paper Structure
What exactly does the structure of a position paper include? This is quite easy: similarly to any other scholarly essay, your position paper should contain three main parts:
Introduction
- Main body part
- Conclusion.
You’ll write a good position paper if you make it readable and concise in addition to preparing string argumentation backed by valid evidence. Otherwise, your poorly structured text won’t impress your readers. We’ve prepared more helpful information on how you should compose each of these sections. You can find it below, so please read it attentively. Also, check out the sample position papers available on this page. You can find more tips and ideas below.
Good introduction for a position paper should make your reader well familiar with the problem you are arguing about. This typically involves explaining why it is important for everyone or why you’ve decided to discuss it. Besides, the introduction must engage your audience so that they would be interested in hearing more about your position and evaluating its validity. This is how to start writing a position paper:
- Clearly state your position, giving the thesis statement.
- Give enough context about the problem and its background, explaining why you stand this ground.
- ‘Hook’ your readers by making it sound interesting.
The latter can be achieved by making some hints about upcoming evidence, using some kind of wordplay, or just making a suitable joke.
Body of a position paper is where its argumentation should be placed. When you make a position paper, be sure to divide it into logically interconnected paragraphs – each one for one of your major arguments expressed in the topic sentence . Make proper transitions between them. Leave at least one paragraph for the counter argumentation you may have faced and for its rebuttal. The evidence you’ve collected to support your claim should also be presented in the main body, together with quotes and references (if any). Remember to use solid and relevant data and avoid unnecessary facts, as they don’t bring value and may just make the text less readable. Pay attention to the consistency and readability of this section. Its structure and contents show how well you’ve built your argumentation. And that is what makes position papers persuasive.
This is how to write a conclusion for a position paper that adds real value to it:
- Properly summarize your argumentation, showing how it supports your take.
- Make it sound strong; ensure that it is logical and well-readable.
- Keep it brief, don’t repeat anything from the main part.
Remember that your proposition paper conclusion will be the last thing your audience reads, so making a strong and persuasive ending would help with leaving a good impression on it. You’ll find a conclusion template in one of the sections below.
How to Write a Position Paper in 9 Steps
Let’s get to the point – you must write a good position paper, and now you’re looking for some helpful tips on that. We’ve got your back! First and foremost, the best beginning is to set up a strong position. Otherwise, your essay will simply be uninteresting. Now make sure you can actually prove what it states. But that’s just the beginning: think about captivating headings, add some clever techniques and diligent work to that, keeping focus on your goal – and you’ll get an excellent paper. What should be added? Just keep reading. We’ve prepared an elaborate guide on how to write a position paper step by step. Let’s go and check it!
1. Choose a Topic
Creating position papers requires some hard work, but choosing a proper subject may save a lot of time and effort. If it is uninteresting or too narrow, that might result in an issue. Better to choose a topic that:
- Is relevant and controversial: this will draw your readers’ interest.
- Is understandable for you, so it would be easier for you to discuss some points about it.
- Has received some coverage in news, books, or other sources, making it simpler to find enough evidence about it.
Before commencing the writing process, search among good topics for position papers and select one most suitable for taking a point around it.
2. Do Research Before Writing a Position Paper
Conducting preliminary research for position papers is a key step before starting with actual writing. This is where you can collect evidence about your subject:
- Google it This is easier but remember to filter out results with low credibility.
- Media If this is a recent and big event, it should be mentioned in the news; make sure to pick the most credible resources.
- Check the sources used by books or articles written on the subject This way, you might find some ‘hidden gems’ that are difficult to google.
Don’t know if you’ll write a winning position paper? Follow the next steps closely. And don’t forget to explore the free samples available on this page, check their structure and style.
3. Draft a Position Paper Thesis
Thesis of a position paper is basically its foundation. Make it strong, and you’ll ensure your success. Don’t be too wordy. One sentence is enough to deliver your thesis and summarize your position on the topic. You can put it closer to the start or put it at the end of your introduction so that it summarizes the explanations you would give about the problem. Examples of a position paper thesis:
• Online education is cost-effective, being more affordable for both students and educational institutions. • Schools should offer low-income pupils summertime educational resources.
4. Create an Outline
Once you have decided about the direction you’re taking with your essay, proceed with the position essay outline. This step is often overlooked, but it will be much easier to find and correct mistakes and gaps at this early stage. So, writing a position paper outline actually saves you time. This is how to write a position paper outline:
- Keep it brief, just one sentence per idea. No need to always use full sentences, just make them readable.
- Include your thesis, mention the context, then write one sentence per each argument.
- Briefly summarize it, one sentence will suffice as well.
Don’t forget to review your outline carefully.
5. Begin Writing Your Position Paper
Once you’ve ensured the outline of an essay doesn’t have any gaps or logical flaws, go ahead and complete the full-text version. If you wonder how to start a position paper at this stage, begin with the introduction. You already have its shortened draft, so just add necessary details and list explanations if needed. But don’t give particular arguments or refute opposing opinions yet, those should come in the main body part. See how to write an introductory paragraph for a position paper in the next section.
Position Paper Introduction Example
Looking for introduction position paper examples? We’ve got one for you. Here’s how you can start your essay:
Traditional education is commonly regarded as a better alternative since live interaction with teachers often facilitates the learning process. However, given the ever-growing problem with student loans, the affordability of online education has become an important factor. Additionally, when studying online, people don’t have to commute, thus saving extra time and money. So, we can see that online education is more effective for common students.
Check our sample position paper for introduction examples. They are available for free download.
6. Include Evidence in Your Position Paper
As we’ve already explained, position papers must be backed by solid evidence. You have to prove your point, and that requires addressing it with data, not just stating it with confidence. When you write your position paper, there are two main requirements for backing your claim:
- collect valid and relevant data;
- present it in your text properly.
Here’s an example of evidence in a position paper:
As shown by many researchers (particularly by Kim and Norton in their work, 2018), more than 60% of students in the US attend online courses on a regular basis.
7. Provide Counterarguments and Refute Them
Still learning how to write position paper? If it is your first one, consider an important fact: ignoring evident contradictions to your claim doesn’t add credibility. Instead, you must work with counter arguments which is similar to writing an argumentative essay . You may be aware of the opposite opinions or think and assume which objections your opponents would make. Better mention them in your essay and show how you counter these claims. Here are some examples of counterarguments for position papers:
Evidently, e-learning doesn’t allow face-to-face interaction with your tutor, which may make it harder to exchange experience. However, the affordability factor still makes it a better choice, especially for motivated students. The price difference between traditional and online education might not be that big. But if we add the price of commuting and time spent on that, this difference becomes much bigger.
8. Summarize Your Position
When writing your position paper, it is important that you make it sound impressive in the end. Your position paper conclusion should properly summarize all arguments and rebuttal of counterarguments . Keep it brief, without repeating much, just highlight how all your findings support the claim. You can also add some extra notes, e.g., making additional assumptions, different predictions about this problem’s impact in the future, or hints about extra evidence you haven’t mentioned before to keep your text brief. This may help to make a lasting impression on your audience. Finally, review your conclusion once again, ensuring that it is logical and doesn’t contradict any claims, arguments, or assumptions provided above. Check the next section for an example of how to write a position paper conclusion.
Example of a Position Paper Conclusion
Need an actual conclusion for a position essay example? It can be something like this:
According to the statistical data presented above, e-learning is already gaining increasing popularity among students below 25 ages all over the globe. Since it is better compatible with the part-time work schedule most students have to follow, this format has actually proven its efficiency in recent years. And it is quite safe to assume it will become a new dominant way of education within the next decade or two.
You can also find the conclusion of a position paper essay example if you check the free samples that are available on this page.
9. Proofread Your Position Paper
After your position essay is complete, you absolutely should spend some extra time and review it again. Try adopting a critical view, putting yourself in your potential opponent’s shoes. Are there any logical gaps or grammar mistakes left? Paper position is not clear enough? Wrong source mentioned? Nearly every text has some issues to correct. Sometimes even evident typos are left overlooked when writing. It is best to have someone else review a position paper since its writer may be biased toward their own text. Another way is reading it aloud to yourself prior to submission. Some flaws may be uncovered this way too.
Position Paper Format
Your position papers format is another element that shouldn’t be overlooked. Proper headline and paragraph styles make your text more readable. Also, there might be specific requirements for making citations. All your evidence must be presented correctly so that it doesn’t get mixed with your own opinions. Format depends on the discipline. You might need to use one of the popular styles: MLA, APA, or Chicago. If you don’t see which one of them is required, better ask your tutor. You can find some position paper format sample in our free attachments, available below.
Position Paper Examples
Need an example of a position paper so that you could learn how all these recommendations can be implemented? We’ve got some for you! Scroll down to the bottom of the page, and you’ll find sample of position papers available for free download. Each position paper example essay has been written by professional research writers and can be used for inspiration or as a reference. Just don’t copy any of those materials in your own text, as you should only submit 100% original works. Position paper example 1
Position paper example 2
Position paper example 3
Position Paper Sample 4
Tips for Writing a Position Paper
Finally, some extra tips on writing a position paper that is really persuasive:
- Choose topics that are interesting for you. This will motivate you to discuss them.
- Plan ahead and consider your deadlines. Don’t spend too much time conducting the preliminary research or perfecting your argumentation if it is already valid.
- Pay attention to your sources. Some books or research might be considered dubious by your opponents or might have some obvious gaps.
- Review your position papers as many times as possible. Ideally, ask a person with an opposite side on this issue to read and refute it.
- Keep it professional. Maintain a confident tone but stay logical and correct, avoid emotional or derogatory remarks.
More examples of position papers are available here – you can check them below.
Final Thoughts on How to Write a Position Paper
So, in order to write a position paper, you need to choose an appropriate topic and elaborate on your position regarding the specific problem. Then you should defend it using logic, facts, and confidence. Still not clear what are position papers and how one should write them? Check out this sample position paper for students available below, and you’ll find all our tips illustrated there. Follow its structure and style, just don’t copy anything to avoid plagiarizing.
If you are stuck in any stage of the writing process, don’t hesitate to use professional academic writing services. StudyCrumb is always here for you to solve any academic challenge you may have. Let us know your task, and we will match you with the most fitting expert who can write an excellent position paper for you.
FAQ About a Position Paper
1. how long should a position paper be.
The length of a position paper is usually limited to one page and a half (up to 350 words). Don’t make it too long, stick to the facts and brief statements. When given with confidence, concise claims are more persuasive. At the same time better include all necessary evidence, not rely just on confidence. So don’t make it less than one page.
2. What are the kinds of support in a position paper?
You can use these support types in your position paper:
- Factual knowledge: either well-known facts (e.g., historical or biological) or data retrieved from credible sources;
- Statistical trends: always helpful for making assumptions but also need to be backed by sources;
- Informed opinion: citations from renowned specialists in fields related to your topic.
3. What is forbidden in a position paper?
When writing a position paper, avoid the following:
- Taking opinions for facts.
- Using threats or derogatory language as a means of persuasion.
- Comparing unrelated situations and making some conclusions from that.
- Copying other works without citing them.

Rachel R. Hill is a real educational devotee. She prides in writing exceptional general guides while listening to every need of students.
You may also like


Counter Argument

In the realm of persuasive writing, crafting a strong argument is essential to sway the audience’s perspective. However, to truly excel in the art of rhetoric, one must also be adept at presenting counterarguments. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of counter-arguments, exploring their definition, step-by-step guide, and addressing frequently asked questions. Whether you’re an aspiring writer or seeking to enhance your argumentative skills, this comprehensive resource will equip you with the necessary tools to construct compelling counter-arguments.
1. Argumentative Essay Example

2. Simple Argumentative Essay Example

Size: 200 KB
3. Counter Argument Essay Example

Size: 167 KB
4. Persuasive Essay Example

Size: 205 KB
5. Counter Argument Outline Example

Size: 392 KB
6. Counter Argument Rebuttal Example

Size: 204 KB
7. Counter Argument Paragraph Example

Size: 189 KB
8. Counter Argument Starters Example

Size: 72 KB
9. Counter Argument Concession Example

Size: 120 KB
10. Counter Argument Debate Example

Size: 139 KB
11. Position Paper Example

Size: 73 KB
12. Counter Argument Transition Example
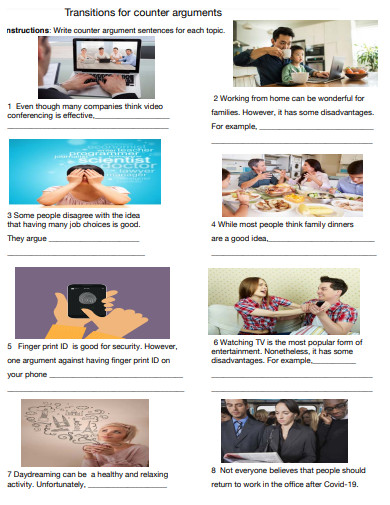
Size: 188 KB
13. Counter Argument Research Paper Example

Size: 282 KB
14. Counter Argument Thesis Statement Example

15. Counter Argument Essay Structure Example

Size: 152 KB
16. Counter Argument Opinion Essay Example

Size: 175 KB
17. Counter Argument Synthesis Essay Example

Size: 96 KB
18. Counter Argument Writing Example

Size: 14 KB
19. Counter Argument Social Media Example

Size: 207 KB
20. Counter Argument Counterclaim Example
Size: 160 KB
21. Counter Argument Format

Size: 130 KB
22. Teaching Counter Argument Example

Size: 119 KB
23. Counter Argument Example

Size: 404 KB
24. Counter Argument Refutation Example

Size: 142 KB
25. Counter Argument Activity Example

Size: 12 KB
26. Simple Counter Argument Example

Size: 41 KB
27. Counter Argument Worksheet Example
Size: 24 KB
28. Printable Counter Argument Example

Size: 106 KB
29. Counter Argument Conclusion Example

Size: 920 KB
30. Counter Argument in PDF

Size: 112 KB
What is a Counter Argument?
A counter-argument, often employed in an argument essay , is a powerful literary device used to challenge and refute opposing viewpoints. It serves as a potent means to anticipate and address potential objections that may arise in the minds of the audience. By acknowledging alternative perspectives and presenting well-reasoned counterpoints, writers can strengthen their own argument, adding depth and credibility to their discourse. Effective counterarguments showcase the writer’s ability to analyze multiple angles, fostering a more comprehensive understanding of the topic at hand.
How to Write a Counter Argument
Mastering the skill of crafting compelling counter-arguments requires a systematic approach. By following these steps, you can effectively incorporate counter-arguments into your writing, elevating the overall impact of your work.
Step 1: Thoroughly Understand Your Audience and Opposing Viewpoints
Before constructing a counter argument, it is imperative to familiarize yourself with your audience’s beliefs, values, and concerns. Analyze opposing viewpoints to identify the most compelling arguments against your own stance. By gaining a deep understanding of the opposing side, you can tailor your counter argument to resonate with the target audience.
Step 2: Choose the Most Potent Counterpoints
Select the strongest counterpoints that challenge your own argument. Look for weaknesses, inconsistencies, or evidence that contradicts your position. By choosing compelling counterpoints, you demonstrate your ability to engage with diverse perspectives and effectively address potential objections.
Step 3: Present Evidence and Support
Once you have identified the key counterpoints, substantiate your own argument with evidence and support that refutes the opposition. Utilize various persuasive techniques, such as analogies, understatement, or anecdotes, to bolster your counterargument and enhance its persuasiveness.
Step 4: Structure Your Counter Argument
Organize your counter-argument in a clear and logical manner, following an outline format . Present each counterpoint concisely and follow it with a well-reasoned rebuttal. By employing a coherent text structure , you ensure that your counterargument flows seamlessly within the overall framework of your writing.
How can counter arguments strengthen my overall argument?
Counter arguments introduce an element of intellectual rigor into your writing. By acknowledging and addressing opposing viewpoints, you demonstrate a thorough understanding of the topic, engendering trust and credibility in your audience. Furthermore, counter arguments provide an opportunity to preemptively address potential objections, making your argument more robust and persuasive.
Is it necessary to present counter arguments in every piece of writing?
While counter arguments can greatly enhance the quality of your writing, their inclusion is not mandatory for every piece. Consider the context, purpose, and audience of your work. If you anticipate significant opposition or if exploring alternative perspectives is crucial for the topic, incorporating counter-arguments becomes paramount.
Are there any effective techniques to make counter-arguments more persuasive?
To make your counter-arguments more persuasive, employ various rhetorical techniques such as appealing to emotions, presenting compelling evidence, or utilizing powerful language. Additionally, employing rhetorical devices like analogies , understatement , or anecdotes can add depth and impact to your counterargument, capturing the attention and interest of your readers.
In the realm of persuasive writing, mastering the art of counter-arguments is an indispensable skill. By diligently crafting and skillfully presenting counterpoints, writers can engage with opposing viewpoints and strengthen their overall argument. Through a strategic approach, understanding the target audience, and employing persuasive techniques, your counter-arguments will not only refute opposing perspectives but also enrich the discourse, making your writing more compelling and thought-provoking. So click here for 10+ short argumentative essay examples and explore 5+ argumentative essay examples for students , expanding your repertoire of persuasive writing strategies.
AI Generator
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
When writing your counterargument paragraph, you should respond to that other position. In your paragraph: Identify the opposing argument. Respond to it by discussing the reasons the argument is incomplete, weak, unsound, or illogical. Provide examples or evidence to show why the opposing argument is unsound, or provide explanations of how the ...
Counterargument Examples. 1. Empirical Challenges. An empirical challenge is, simply, a rebuttal that challenges the facts presented by the opponent, showing that their facts are wrong and yours are right. To undermine your opponent's set of facts, it will be your job to present facts that show that the opponent's supposed facts are wrong ...
Some counterarguments will directly address your thesis, while other counterarguments will challenge an individual point or set of points elsewhere in your argument. For example, a counterargument might identify. a problem with a conclusion you've drawn from evidence. a problem with an assumption you've made.
Counterargument. When you write an academic essay, you make an argument: you propose a thesis and offer some reasoning, using evidence, that suggests why the thesis is true. When you counter-argue, you consider a possible argument against your thesis or some aspect of your reasoning. This is a good way to test your ideas when drafting, while ...
Counter Argument. One way to strengthen your argument and demonstrate a comprehensive understanding of the issue you are discussing is to anticipate and address counter arguments, or objections. By considering opposing views, you show that you have thought things through, and you dispose of some of the reasons your audience might have for not ...
Counter-Argument 2 Cabrini University Writing Center - Revised 9/16 2) Cite an actual source, critic or group of critics, who might resist your argument Here many feminists would probably object that _____. But social Darwinists would certainly take issue with the argument that Nevertheless, both followers and critics of Malcolm X will probably argue that
A position paper is an evidence-based opinion about an issue. A strong position statement supported by arguments and counter-arguments is critical to convincing your audience that your opinion is valid and credible. Here are the top ten tips to write a great position paper and provide valuable perspectives to science.
Sample Outline for a Position Paper. I. Introduction. A. Introduce the topic. B. Provide background on the topic. C. Assert the thesis (your view of the issue) II. Counter Argument. A. Summarize the counterclaims. B. Provide supporting information for counterclaims.
Counterargument in two steps. Respectfully acknowledge evidence or standpoints that differ from your argument. Refute the stance of opposing arguments, typically utilizing words like "although" or "however.". In the refutation, you want to show the reader why your position is more correct than the opposing idea.
What is an Argumentative or Position Paper? In this type of assignment, you take a stand on a particular topic that is debatable. You present a clear and strong statement usually at the start of your paper that asserts your position on the topic. (See the Writing Center's handout on thesis statements for more help with this stage!).
Writing a paper can be challenging, especially when you have to address counterarguments that may oppose your main claim. In this academic guide, you will learn how to respond to counterarguments effectively and persuasively, using strategies such as refutation, concession, and rebuttal. This guide will help you improve your writing skills and achieve your course goals.
It may be tempting to just write a sentence or two explaining your opponent's argument and then spend paragraphs refuting that argument, but a good counter-argument is fair in the assessment of the opponent's position. Here are some tips: Provide a few fair reasons why someone could possibly have the perspective of your opposition.
A counter argument is any argument that is opposed to your thesis. It explains why your thesis - in part of in full - is incorrect, and uses evidence and logical reasoning to undermine your thesis. Given this definition, it seems unusual that you would want to prepare an argument that rebuts your own thesis. However, in some cases ...
Present your evidence: In addition to refuting your opponent's arguments, you will also want to present evidence supporting your position. Presenting evidence helps to strengthen your argument and make it more persuasive. 5. Be logical: When constructing your counterargument, use logic and reason. Avoid emotional appeals or fallacies that could ...
Position Paper. Definition: Position paper is a written document that presents an argument or stance on a particular issue or topic. It outlines the author's position on the issue and provides support for that position with evidence and reasoning. Position papers are commonly used in academic settings, such as in Model United Nations conferences or debates, but they can also be used in ...
Counter Argument. One way to strengthen your argument and demonstrate a comprehensive understanding of the issue you are discussing is to anticipate and address counter arguments or objections. By considering opposing views, you show that you have thought things through, and you dispose of some of the reasons your audience might have for not ...
Argument: taking part in elections is not only a right but a responsibility that every citizen should participate in. Counter-argument: It is better not to vote than vote in a corrupt person. Rebuttal: While you might feel like not taking part in the voting process keeps you from the guilt of choosing the wrong person, the truth is that you ...
End your introduction with your thesis. 3. Include at least 2 body paragraphs. A short position paper may only contain 2 body paragraphs - one for the counter-argument and one for the supportive points. However, most position papers will have 3 or 4 body paragraphs, with 2 dedicated to supportive evidence.
Debatable thesis statement in the Introduction. Argument - paragraphs which show support for the author's thesis (for example: reasons, evidence, data, statistics) Counterargument - at least one paragraph which explains the opposite point of view. Concession - a sentence or two acknowledging that there could be some truth to the ...
An argumentative essay presents an argument for or against a topic. For example, if your topic is working from home, then your essay would either argue in favor of working from home (this is the for side) or against working from home.. Like most essays, an argumentative essay begins with an introduction that ends with the writer's position (or stance) in the thesis statement.
4. Create an Outline. Once you have decided about the direction you're taking with your essay, proceed with the position essay outline. This step is often overlooked, but it will be much easier to find and correct mistakes and gaps at this early stage. So, writing a position paper outline actually saves you time.
Step 4: Structure Your Counter Argument. Organize your counter-argument in a clear and logical manner, following an outline format. Present each counterpoint concisely and follow it with a well-reasoned rebuttal. By employing a coherent text structure, you ensure that your counterargument flows seamlessly within the overall framework of your ...