Renewable Energy
Renewable energy comes from sources that will not be used up in our lifetimes, such as the sun and wind.
Earth Science, Experiential Learning, Engineering, Geology

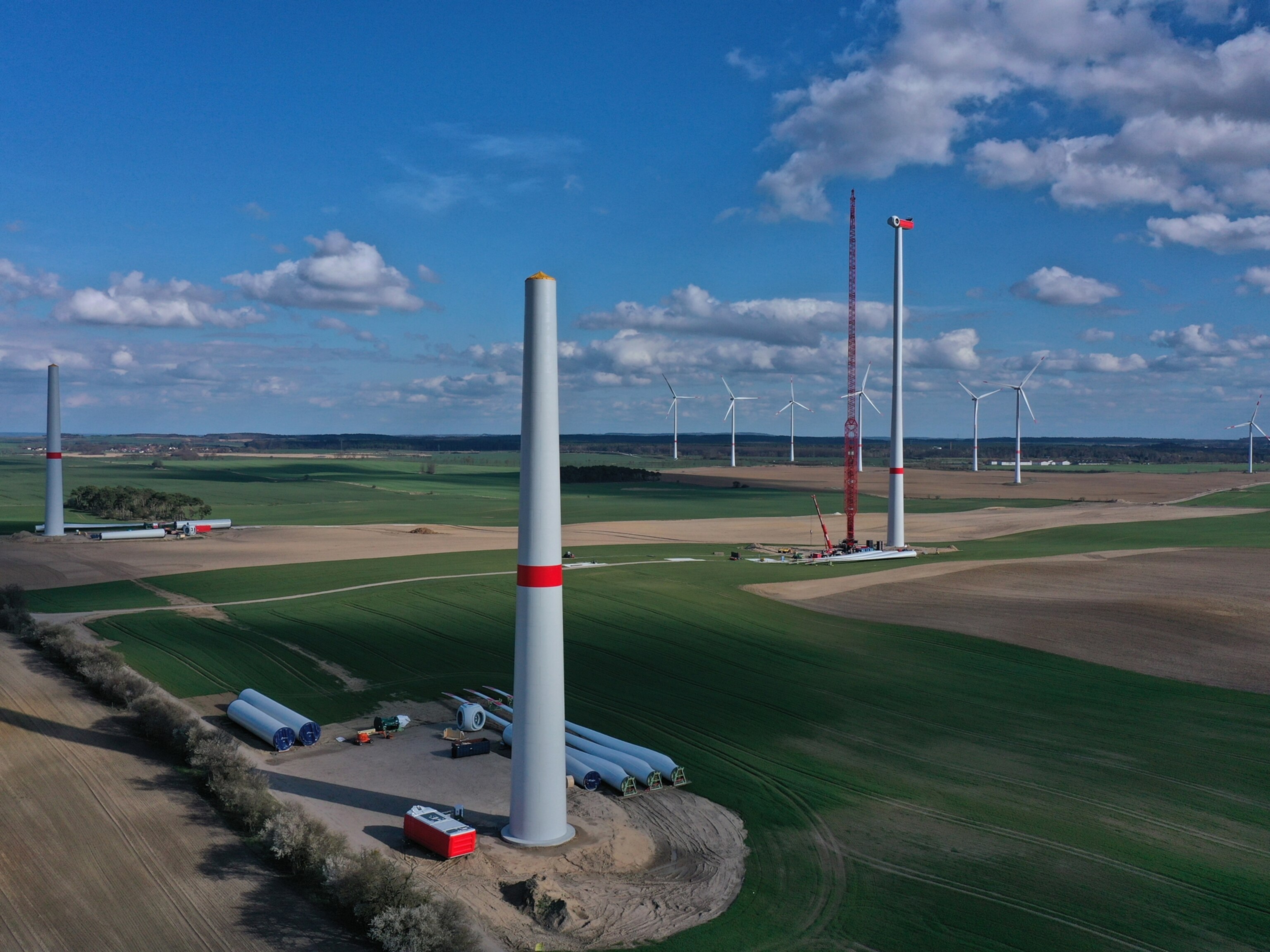
Wind Turbines in a Sheep Pasture
Wind turbines use the power of wind to generate energy. This is just one source of renewable energy.
Photograph by Jesus Keller/ Shutterstock

The wind, the sun, and Earth are sources of renewable energy . These energy sources naturally renew, or replenish themselves.
Wind, sunlight, and the planet have energy that transforms in ways we can see and feel. We can see and feel evidence of the transfer of energy from the sun to Earth in the sunlight shining on the ground and the warmth we feel when sunlight shines on our skin. We can see and feel evidence of the transfer of energy in wind’s ability to pull kites higher into the sky and shake the leaves on trees. We can see and feel evidence of the transfer of energy in the geothermal energy of steam vents and geysers .
People have created different ways to capture the energy from these renewable sources.
Solar Energy
Solar energy can be captured “actively” or “passively.”
Active solar energy uses special technology to capture the sun’s rays. The two main types of equipment are photovoltaic cells (also called PV cells or solar cells) and mirrors that focus sunlight in a specific spot. These active solar technologies use sunlight to generate electricity , which we use to power lights, heating systems, computers, and televisions.
Passive solar energy does not use any equipment. Instead, it gets energy from the way sunlight naturally changes throughout the day. For example, people can build houses so their windows face the path of the sun. This means the house will get more heat from the sun. It will take less energy from other sources to heat the house.
Other examples of passive solar technology are green roofs , cool roofs, and radiant barriers . Green roofs are completely covered with plants. Plants can get rid of pollutants in rainwater and air. They help make the local environment cleaner.
Cool roofs are painted white to better reflect sunlight. Radiant barriers are made of a reflective covering, such as aluminum. They both reflect the sun’s heat instead of absorbing it. All these types of roofs help lower the amount of energy needed to cool the building.
Advantages and Disadvantages There are many advantages to using solar energy. PV cells last for a long time, about 20 years.
However, there are reasons why solar power cannot be used as the only power source in a community. It can be expensive to install PV cells or build a building using passive solar technology.
Sunshine can also be hard to predict. It can be blocked by clouds, and the sun doesn’t shine at night. Different parts of Earth receive different amounts of sunlight based on location, the time of year, and the time of day.
Wind Energy
People have been harnessing the wind’s energy for a long, long time. Five-thousand years ago, ancient Egyptians made boats powered by the wind. In 200 B.C.E., people used windmills to grind grain in the Middle East and pump water in China.
Today, we capture the wind’s energy with wind turbines . A turbine is similar to a windmill; it has a very tall tower with two or three propeller-like blades at the top. These blades are turned by the wind. The blades turn a generator (located inside the tower), which creates electricity.
Groups of wind turbines are known as wind farms . Wind farms can be found near farmland, in narrow mountain passes, and even in the ocean, where there are steadier and stronger winds. Wind turbines anchored in the ocean are called “ offshore wind farms.”
Wind farms create electricity for nearby homes, schools, and other buildings.
Advantages and Disadvantages Wind energy can be very efficient . In places like the Midwest in the United States and along coasts, steady winds can provide cheap, reliable electricity.
Another great advantage of wind power is that it is a “clean” form of energy. Wind turbines do not burn fuel or emit any pollutants into the air.
Wind is not always a steady source of energy, however. Wind speed changes constantly, depending on the time of day, weather , and geographic location. Currently, it cannot be used to provide electricity for all our power needs.
Wind turbines can also be dangerous for bats and birds. These animals cannot always judge how fast the blades are moving and crash into them.
Geothermal Energy
Deep beneath the surface is Earth’s core . The center of Earth is extremely hot—thought to be over 6,000 °C (about 10,800 °F). The heat is constantly moving toward the surface.
We can see some of Earth’s heat when it bubbles to the surface. Geothermal energy can melt underground rocks into magma and cause the magma to bubble to the surface as lava . Geothermal energy can also heat underground sources of water and force it to spew out from the surface. This stream of water is called a geyser.
However, most of Earth’s heat stays underground and makes its way out very, very slowly.
We can access underground geothermal heat in different ways. One way of using geothermal energy is with “geothermal heat pumps.” A pipe of water loops between a building and holes dug deep underground. The water is warmed by the geothermal energy underground and brings the warmth aboveground to the building. Geothermal heat pumps can be used to heat houses, sidewalks, and even parking lots.
Another way to use geothermal energy is with steam. In some areas of the world, there is underground steam that naturally rises to the surface. The steam can be piped straight to a power plant. However, in other parts of the world, the ground is dry. Water must be injected underground to create steam. When the steam comes to the surface, it is used to turn a generator and create electricity.
In Iceland, there are large reservoirs of underground water. Almost 90 percent of people in Iceland use geothermal as an energy source to heat their homes and businesses.
Advantages and Disadvantages An advantage of geothermal energy is that it is clean. It does not require any fuel or emit any harmful pollutants into the air.
Geothermal energy is only avaiable in certain parts of the world. Another disadvantage of using geothermal energy is that in areas of the world where there is only dry heat underground, large quantities of freshwater are used to make steam. There may not be a lot of freshwater. People need water for drinking, cooking, and bathing.
Biomass Energy
Biomass is any material that comes from plants or microorganisms that were recently living. Plants create energy from the sun through photosynthesis . This energy is stored in the plants even after they die.
Trees, branches, scraps of bark, and recycled paper are common sources of biomass energy. Manure, garbage, and crops , such as corn, soy, and sugar cane, can also be used as biomass feedstocks .
We get energy from biomass by burning it. Wood chips, manure, and garbage are dried out and compressed into squares called “briquettes.” These briquettes are so dry that they do not absorb water. They can be stored and burned to create heat or generate electricity.
Biomass can also be converted into biofuel . Biofuels are mixed with regular gasoline and can be used to power cars and trucks. Biofuels release less harmful pollutants than pure gasoline.
Advantages and Disadvantages A major advantage of biomass is that it can be stored and then used when it is needed.
Growing crops for biofuels, however, requires large amounts of land and pesticides . Land could be used for food instead of biofuels. Some pesticides could pollute the air and water.
Biomass energy can also be a nonrenewable energy source. Biomass energy relies on biomass feedstocks—plants that are processed and burned to create electricity. Biomass feedstocks can include crops, such as corn or soy, as well as wood. If people do not replant biomass feedstocks as fast as they use them, biomass energy becomes a non-renewable energy source.
Hydroelectric Energy
Hydroelectric energy is made by flowing water. Most hydroelectric power plants are located on large dams , which control the flow of a river.
Dams block the river and create an artificial lake, or reservoir. A controlled amount of water is forced through tunnels in the dam. As water flows through the tunnels, it turns huge turbines and generates electricity.
Advantages and Disadvantages Hydroelectric energy is fairly inexpensive to harness. Dams do not need to be complex, and the resources to build them are not difficult to obtain. Rivers flow all over the world, so the energy source is available to millions of people.
Hydroelectric energy is also fairly reliable. Engineers control the flow of water through the dam, so the flow does not depend on the weather (the way solar and wind energies do).
However, hydroelectric power plants are damaging to the environment. When a river is dammed, it creates a large lake behind the dam. This lake (sometimes called a reservoir) drowns the original river habitat deep underwater. Sometimes, people build dams that can drown entire towns underwater. The people who live in the town or village must move to a new area.
Hydroelectric power plants don’t work for a very long time: Some can only supply power for 20 or 30 years. Silt , or dirt from a riverbed, builds up behind the dam and slows the flow of water.
Other Renewable Energy Sources
Scientists and engineers are constantly working to harness other renewable energy sources. Three of the most promising are tidal energy , wave energy , and algal (or algae) fuel.
Tidal energy harnesses the power of ocean tides to generate electricity. Some tidal energy projects use the moving tides to turn the blades of a turbine. Other projects use small dams to continually fill reservoirs at high tide and slowly release the water (and turn turbines) at low tide.
Wave energy harnesses waves from the ocean, lakes, or rivers. Some wave energy projects use the same equipment that tidal energy projects do—dams and standing turbines. Other wave energy projects float directly on waves. The water’s constant movement over and through these floating pieces of equipment turns turbines and creates electricity.
Algal fuel is a type of biomass energy that uses the unique chemicals in seaweed to create a clean and renewable biofuel. Algal fuel does not need the acres of cropland that other biofuel feedstocks do.
Renewable Nations
These nations (or groups of nations) produce the most energy using renewable resources. Many of them are also the leading producers of nonrenewable energy: China, European Union, United States, Brazil, and Canada
Articles & Profiles
Media credits.
The audio, illustrations, photos, and videos are credited beneath the media asset, except for promotional images, which generally link to another page that contains the media credit. The Rights Holder for media is the person or group credited.
Last Updated
March 18, 2024
User Permissions
For information on user permissions, please read our Terms of Service. If you have questions about how to cite anything on our website in your project or classroom presentation, please contact your teacher. They will best know the preferred format. When you reach out to them, you will need the page title, URL, and the date you accessed the resource.
If a media asset is downloadable, a download button appears in the corner of the media viewer. If no button appears, you cannot download or save the media.
Text on this page is printable and can be used according to our Terms of Service .
Interactives
Any interactives on this page can only be played while you are visiting our website. You cannot download interactives.
Related Resources
- ENVIRONMENT
Renewable energy, explained
Solar, wind, hydroelectric, biomass, and geothermal power can provide energy without the planet-warming effects of fossil fuels.
In any discussion about climate change , renewable energy usually tops the list of changes the world can implement to stave off the worst effects of rising temperatures. That's because renewable energy sources such as solar and wind don't emit carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases that contribute to global warming .
Clean energy has far more to recommend it than just being "green." The growing sector creates jobs , makes electric grids more resilient, expands energy access in developing countries, and helps lower energy bills. All of those factors have contributed to a renewable energy renaissance in recent years, with wind and solar setting new records for electricity generation .
For the past 150 years or so, humans have relied heavily on coal, oil, and other fossil fuels to power everything from light bulbs to cars to factories. Fossil fuels are embedded in nearly everything we do, and as a result, the greenhouse gases released from the burning of those fuels have reached historically high levels .
As greenhouse gases trap heat in the atmosphere that would otherwise escape into space, average temperatures on the surface are rising . Global warming is one symptom of climate change, the term scientists now prefer to describe the complex shifts affecting our planet’s weather and climate systems. Climate change encompasses not only rising average temperatures but also extreme weather events, shifting wildlife populations and habitats, rising seas , and a range of other impacts .
Of course, renewables—like any source of energy—have their own trade-offs and associated debates. One of them centers on the definition of renewable energy. Strictly speaking, renewable energy is just what you might think: perpetually available, or as the U.S. Energy Information Administration puts it, " virtually inexhaustible ." But "renewable" doesn't necessarily mean sustainable, as opponents of corn-based ethanol or large hydropower dams often argue. It also doesn't encompass other low- or zero-emissions resources that have their own advocates, including energy efficiency and nuclear power.
Types of renewable energy sources
Hydropower: For centuries, people have harnessed the energy of river currents, using dams to control water flow. Hydropower is the world's biggest source of renewable energy by far, with China, Brazil, Canada, the U.S., and Russia the leading hydropower producers . While hydropower is theoretically a clean energy source replenished by rain and snow, it also has several drawbacks.
FREE BONUS ISSUE
Large dams can disrupt river ecosystems and surrounding communities , harming wildlife and displacing residents. Hydropower generation is vulnerable to silt buildup, which can compromise capacity and harm equipment. Drought can also cause problems. In the western U.S., carbon dioxide emissions over a 15-year period were 100 megatons higher than they normally would have been, according to a 2018 study , as utilities turned to coal and gas to replace hydropower lost to drought. Even hydropower at full capacity bears its own emissions problems, as decaying organic material in reservoirs releases methane.
Dams aren't the only way to use water for power: Tidal and wave energy projects around the world aim to capture the ocean's natural rhythms. Marine energy projects currently generate an estimated 500 megawatts of power —less than one percent of all renewables—but the potential is far greater. Programs like Scotland’s Saltire Prize have encouraged innovation in this area.
Wind: Harnessing the wind as a source of energy started more than 7,000 years ago . Now, electricity-generating wind turbines are proliferating around the globe, and China, the U.S., and Germany are the leading wind energy producers. From 2001 to 2017 , cumulative wind capacity around the world increased to more than 539,000 megawatts from 23,900 mw—more than 22 fold.
You May Also Like

Can energy harnessed from Earth’s interior help power the world?

How the historic climate bill will dramatically reduce U.S. emissions

5 environmental victories from 2021 that offer hope
Some people may object to how wind turbines look on the horizon and to how they sound, but wind energy, whose prices are declining , is proving too valuable a resource to deny. While most wind power comes from onshore turbines, offshore projects are appearing too, with the most in the U.K. and Germany. The first U.S. offshore wind farm opened in 2016 in Rhode Island, and other offshore projects are gaining momentum . Another problem with wind turbines is that they’re a danger for birds and bats, killing hundreds of thousands annually , not as many as from glass collisions and other threats like habitat loss and invasive species, but enough that engineers are working on solutions to make them safer for flying wildlife.
Solar: From home rooftops to utility-scale farms, solar power is reshaping energy markets around the world. In the decade from 2007 and 2017 the world's total installed energy capacity from photovoltaic panels increased a whopping 4,300 percent .
In addition to solar panels, which convert the sun's light to electricity, concentrating solar power (CSP) plants use mirrors to concentrate the sun's heat, deriving thermal energy instead. China, Japan, and the U.S. are leading the solar transformation, but solar still has a long way to go, accounting for around two percent of the total electricity generated in the U.S. in 2017. Solar thermal energy is also being used worldwide for hot water, heating, and cooling.
Biomass: Biomass energy includes biofuels such as ethanol and biodiesel , wood and wood waste, biogas from landfills, and municipal solid waste. Like solar power, biomass is a flexible energy source, able to fuel vehicles, heat buildings, and produce electricity. But biomass can raise thorny issues.
Critics of corn-based ethanol , for example, say it competes with the food market for corn and supports the same harmful agricultural practices that have led to toxic algae blooms and other environmental hazards. Similarly, debates have erupted over whether it's a good idea to ship wood pellets from U.S. forests over to Europe so that it can be burned for electricity. Meanwhile, scientists and companies are working on ways to more efficiently convert corn stover , wastewater sludge , and other biomass sources into energy, aiming to extract value from material that would otherwise go to waste.
Geothermal: Used for thousands of years in some countries for cooking and heating, geothermal energy is derived from the Earth’s internal heat . On a large scale, underground reservoirs of steam and hot water can be tapped through wells that can go a mile deep or more to generate electricity. On a smaller scale, some buildings have geothermal heat pumps that use temperature differences several feet below ground for heating and cooling. Unlike solar and wind energy, geothermal energy is always available, but it has side effects that need to be managed, such as the rotten egg smell that can accompany released hydrogen sulfide.
Ways to boost renewable energy
Cities, states, and federal governments around the world are instituting policies aimed at increasing renewable energy. At least 29 U.S. states have set renewable portfolio standards —policies that mandate a certain percentage of energy from renewable sources, More than 100 cities worldwide now boast at least 70 percent renewable energy, and still others are making commitments to reach 100 percent . Other policies that could encourage renewable energy growth include carbon pricing, fuel economy standards, and building efficiency standards. Corporations are making a difference too, purchasing record amounts of renewable power in 2018.
Wonder whether your state could ever be powered by 100 percent renewables? No matter where you live, scientist Mark Jacobson believes it's possible. That vision is laid out here , and while his analysis is not without critics , it punctuates a reality with which the world must now reckon. Even without climate change, fossil fuels are a finite resource, and if we want our lease on the planet to be renewed, our energy will have to be renewable.
Related Topics
- SUSTAINABILITY
- RENEWABLE ENERGY
- GEOTHERMAL ENERGY
- SOLAR POWER
- HYDROELECTRIC POWER
- CLIMATE CHANGE

Activists fear a new threat to biodiversity—renewable energy

How the Ukraine war is accelerating Germany's renewable energy transition

What’s at stake at COP26—the crucial global climate summit

We took the Great American Road Trip—in electric cars

Climate change goals and oil production are clashing in the U.S.
- History & Culture
- Environment
- Paid Content
History & Culture
- History Magazine
- Mind, Body, Wonder
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Your US State Privacy Rights
- Children's Online Privacy Policy
- Interest-Based Ads
- About Nielsen Measurement
- Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information
- Nat Geo Home
- Attend a Live Event
- Book a Trip
- Inspire Your Kids
- Shop Nat Geo
- Visit the D.C. Museum
- Learn About Our Impact
- Support Our Mission
- Advertise With Us
- Customer Service
- Renew Subscription
- Manage Your Subscription
- Work at Nat Geo
- Sign Up for Our Newsletters
- Contribute to Protect the Planet
Copyright © 1996-2015 National Geographic Society Copyright © 2015-2024 National Geographic Partners, LLC. All rights reserved

Renewable Energy
Renewable energy sources are growing quickly and will play a vital role in tackling climate change..
Since the Industrial Revolution, the energy mix of most countries across the world has become dominated by fossil fuels. This has major implications for the global climate, as well as for human health. Three-quarters of global greenhouse gas emissions result from the burning of fossil fuels for energy. Fossil fuels are responsible for large amounts of local air pollution – a health problem that leads to at least 5 million premature deaths each year.
To reduce CO 2 emissions and local air pollution, the world needs to rapidly shift towards low-carbon sources of energy – nuclear and renewable technologies.
Renewable energy will play a key role in decarbonizing our energy systems in the coming decades. But how rapidly is our production of renewable energy changing? What technologies look most promising in transforming our energy mix?
In this article we look at the data on renewable energy technologies across the world; what share of energy they account for today, and how quickly this is changing.
Renewable energy generation
How much of our primary energy comes from renewables.
We often hear about the rapid growth of renewable technologies in media reports. But how much of an impact has this growth had on our energy systems?
In this interactive chart, we see the share of primary energy consumption that came from renewable technologies – the combination of hydropower, solar, wind, geothermal, wave, tidal, and modern biofuels. Traditional biomass – which can be an important energy source in lower-income settings is not included.
Note that this data is based on primary energy calculated by the 'substitution method' which attempts to correct for the inefficiencies in fossil fuel production. It does this by converting non-fossil fuel sources to their 'input equivalents': the amount of primary energy that would be required to produce the same amount of energy if it came from fossil fuels.
Approximately one-seventh of the world's primary energy is now sourced from renewable technologies.
Note that this is based on renewable energy's share in the energy mix. Energy consumption represents the sum of electricity, transport, and heating. We look at the electricity mix later in this article.
Breakdown of renewables in the energy mix
In the section above we looked at what share renewable technologies collectively accounted for in the energy mix.
In the charts shown here, we look at the breakdown of renewable technologies by their components – hydropower, solar, wind, and others.
The first chart shows this as a stacked area chart, which allows us to more readily see the breakdown of the renewable mix and the relative contribution of each. The second chart is shown as a line chart, allowing us to see more clearly how each source is changing over time.
Globally we see that hydropower is by far the largest modern renewable source. However, we also see wind and solar power both growing rapidly.
Renewables in the electricity mix
How much of our electricity comes from renewables.
In the sections above we looked at the role of renewables in the total energy mix . This includes not only electricity but also transport and heating. Electricity forms only one component of energy consumption.
Since transport and heating tend to be harder to decarbonize – they are more reliant on oil and gas – renewables tend to have a higher share in the electricity mix versus the total energy mix.
This interactive chart shows the share of electricity that comes from renewable technologies.
Globally, almost one-third of our electricity comes from renewables.
Hydropower generation
Hydroelectric power has been one of our oldest and largest sources of low-carbon energy. Hydroelectric generation at scale dates back more than a century, and is still our largest renewable source – excluding traditional biomass, it still accounts for approximately half of renewable generation.
However, the scale of hydroelectric power generation varies significantly across the world. This interactive chart shows its contribution by country.
Share of primary energy that comes from hydropower
This interactive chart shows the share of primary energy that comes from hydropower.
Share of electricity that comes from hydropower
This interactive chart shows the share of electricity that comes from hydropower.
Wind energy
Wind energy generation.
This interactive chart shows the amount of energy generated from wind each year. This includes both onshore and offshore wind farms.
Wind generation at scale – compared to hydropower, for example – is a relatively modern renewable energy source but is growing quickly in many countries across the world.
Installed wind capacity
The previous section looked at the energy output from wind farms across the world. Energy output is a function of power (installed capacity) multiplied by the time of generation.
Energy generation is therefore a function of how much wind capacity is installed. This interactive chart shows installed wind capacity – including both onshore and offshore – across the world.
Share of primary energy that comes from wind
This interactive chart shows the share of primary energy that comes from wind.
Share of electricity that comes from wind
This interactive chart shows the share of electricity that comes from wind.
Solar energy
Solar energy generation.
This interactive chart shows the amount of energy generated from solar power each year.
Solar generation at scale – compared to hydropower, for example – is a relatively modern renewable energy source but is growing quickly in many countries across the world.
Installed solar capacity
The previous section looked at the energy output from solar across the world. Energy output is a function of power (installed capacity) multiplied by the time of generation.
Energy generation is therefore a function of how much solar capacity is installed. This interactive chart shows installed solar capacity across the world.
Share of primary energy that comes from solar
This interactive chart shows the share of primary energy that comes from solar power.
Share of electricity that comes from solar
This interactive chart shows the share of electricity that comes from solar power.
Biofuel production
Traditional biomass – the burning of charcoal, organic wastes, and crop residues – was an important energy source for a long period of human history. It remains an important source in lower-income settings today. However, high-quality estimates of energy consumption from these sources are difficult to find. The Energy Institute Statistical Review of World Energy – our main data source on energy – only publishes data on commercially traded energy, so traditional biomass is not included.
However, modern biofuels are included in this energy data. Bioethanol and biodiesel – fuel made from crops such as corn, sugarcane, hemp, and cassava – are now a key transport fuel in many countries.
This interactive chart shows modern biofuel production across the world.
Installed geothermal capacity
This interactive chart shows the installed capacity of geothermal energy across the world.
Cite this work
Our articles and data visualizations rely on work from many different people and organizations. When citing this article, please also cite the underlying data sources. This article can be cited as:
BibTeX citation
Reuse this work freely
All visualizations, data, and code produced by Our World in Data are completely open access under the Creative Commons BY license . You have the permission to use, distribute, and reproduce these in any medium, provided the source and authors are credited.
The data produced by third parties and made available by Our World in Data is subject to the license terms from the original third-party authors. We will always indicate the original source of the data in our documentation, so you should always check the license of any such third-party data before use and redistribution.
All of our charts can be embedded in any site.
Our World in Data is free and accessible for everyone.
Help us do this work by making a donation.

Search the United Nations
- What Is Climate Change
- Myth Busters
- Renewable Energy
- Finance & Justice
- Initiatives
- Sustainable Development Goals
- Paris Agreement
- Climate Ambition Summit 2023
- Climate Conferences
- Press Material
- Communications Tips
What is renewable energy?
Renewable energy is energy derived from natural sources that are replenished at a higher rate than they are consumed. Sunlight and wind, for example, are such sources that are constantly being replenished. Renewable energy sources are plentiful and all around us.
Fossil fuels - coal, oil and gas - on the other hand, are non-renewable resources that take hundreds of millions of years to form. Fossil fuels, when burned to produce energy, cause harmful greenhouse gas emissions, such as carbon dioxide.
Generating renewable energy creates far lower emissions than burning fossil fuels. Transitioning from fossil fuels, which currently account for the lion’s share of emissions, to renewable energy is key to addressing the climate crisis.
Renewables are now cheaper in most countries, and generate three times more jobs than fossil fuels.
Here are a few common sources of renewable energy:
SOLAR ENERGY
Solar energy is the most abundant of all energy resources and can even be harnessed in cloudy weather. The rate at which solar energy is intercepted by the Earth is about 10,000 times greater than the rate at which humankind consumes energy.
Solar technologies can deliver heat, cooling, natural lighting, electricity, and fuels for a host of applications. Solar technologies convert sunlight into electrical energy either through photovoltaic panels or through mirrors that concentrate solar radiation.
Although not all countries are equally endowed with solar energy, a significant contribution to the energy mix from direct solar energy is possible for every country.
The cost of manufacturing solar panels has plummeted dramatically in the last decade, making them not only affordable but often the cheapest form of electricity. Solar panels have a lifespan of roughly 30 years , and come in variety of shades depending on the type of material used in manufacturing.
WIND ENERGY
Wind energy harnesses the kinetic energy of moving air by using large wind turbines located on land (onshore) or in sea- or freshwater (offshore). Wind energy has been used for millennia, but onshore and offshore wind energy technologies have evolved over the last few years to maximize the electricity produced - with taller turbines and larger rotor diameters.
Though average wind speeds vary considerably by location, the world’s technical potential for wind energy exceeds global electricity production, and ample potential exists in most regions of the world to enable significant wind energy deployment.
Many parts of the world have strong wind speeds, but the best locations for generating wind power are sometimes remote ones. Offshore wind power offers t remendous potential .
GEOTHERMAL ENERGY
Geothermal energy utilizes the accessible thermal energy from the Earth’s interior. Heat is extracted from geothermal reservoirs using wells or other means.
Reservoirs that are naturally sufficiently hot and permeable are called hydrothermal reservoirs, whereas reservoirs that are sufficiently hot but that are improved with hydraulic stimulation are called enhanced geothermal systems.
Once at the surface, fluids of various temperatures can be used to generate electricity. The technology for electricity generation from hydrothermal reservoirs is mature and reliable, and has been operating for more than 100 years .
Hydropower harnesses the energy of water moving from higher to lower elevations. It can be generated from reservoirs and rivers. Reservoir hydropower plants rely on stored water in a reservoir, while run-of-river hydropower plants harness energy from the available flow of the river.
Hydropower reservoirs often have multiple uses - providing drinking water, water for irrigation, flood and drought control, navigation services, as well as energy supply.
Hydropower currently is the largest source of renewable energy in the electricity sector. It relies on generally stable rainfall patterns, and can be negatively impacted by climate-induced droughts or changes to ecosystems which impact rainfall patterns.
The infrastructure needed to create hydropower can also impact on ecosystems in adverse ways. For this reason, many consider small-scale hydro a more environmentally-friendly option , and especially suitable for communities in remote locations.
OCEAN ENERGY
Ocean energy derives from technologies that use the kinetic and thermal energy of seawater - waves or currents for instance - to produce electricity or heat.
Ocean energy systems are still at an early stage of development, with a number of prototype wave and tidal current devices being explored. The theoretical potential for ocean energy easily exceeds present human energy requirements.
Bioenergy is produced from a variety of organic materials, called biomass, such as wood, charcoal, dung and other manures for heat and power production, and agricultural crops for liquid biofuels. Most biomass is used in rural areas for cooking, lighting and space heating, generally by poorer populations in developing countries.
Modern biomass systems include dedicated crops or trees, residues from agriculture and forestry, and various organic waste streams.
Energy created by burning biomass creates greenhouse gas emissions, but at lower levels than burning fossil fuels like coal, oil or gas. However, bioenergy should only be used in limited applications, given potential negative environmental impacts related to large-scale increases in forest and bioenergy plantations, and resulting deforestation and land-use change.
For more information on renewable sources of energy, please check out the following websites:
International Renewable Energy Agency | Renewables
International Energy Agency | Renewables
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change | Renewable Sources of Energy
UN Environment Programme | Roadmap to a Carbon-Free Future
Sustainable Energy for All | Renewable Energy

Renewable energy – powering a safer future
What is renewable energy and why does it matter? Learn more about why the shift to renewables is our only hope for a brighter and safer world.

Five ways to jump-start the renewable energy transition now
UN Secretary-General outlines five critical actions the world needs to prioritize now to speed up the global shift to renewable energy.

Climate issues
Learn more about how climate change impacts are felt across different sectors and ecosystems, and why we must nurture rather than exploit nature’s resources to advance climate action.
Facts and figures
- What is climate change?
- Causes and effects
- Myth busters
Cutting emissions
- Explaining net zero
- High-level expert group on net zero
- Checklists for credibility of net-zero pledges
- Greenwashing
- What you can do
Clean energy
- Renewable energy – key to a safer future
- What is renewable energy
- Five ways to speed up the energy transition
- Why invest in renewable energy
- Clean energy stories
- A just transition
Adapting to climate change
- Climate adaptation
- Early warnings for all
- Youth voices
Financing climate action
- Finance and justice
- Loss and damage
- $100 billion commitment
- Why finance climate action
- Biodiversity
- Human Security
International cooperation
- What are Nationally Determined Contributions
- Acceleration Agenda
- Climate Ambition Summit
- Climate conferences (COPs)
- Youth Advisory Group
- Action initiatives
- Secretary-General’s speeches
- Press material
- Fact sheets
- Communications tips
The Understand Energy Learning Hub is a cross-campus effort of the Precourt Institute for Energy .

Introduction to Renewable Energy
Exploring our content.
Fast Facts View our summary of key facts and information. ( Printable PDF, 270 KB )
Before You Watch Our Lecture Maximize your learning experience by reviewing these carefully curated readings we assign to our students.
Our Lecture Watch the Stanford course lecture.
Additional Resources Find out where to explore beyond our site.

Fast Facts About Renewable Energy
Principle Energy Uses: Electricity, Heat Forms of Energy: Kinetic, Thermal, Radiant, Chemical
The term “renewable” encompasses a wide diversity of energy resources with varying economics, technologies, end uses, scales, environmental impacts, availability, and depletability. For example, fully “renewable” resources are not depleted by human use, whereas “semi-renewable” resources must be properly managed to ensure long-term availability. The most renewable type of energy is energy efficiency, which reduces overall consumption while providing the same energy service. Most renewable energy resources have significantly lower environmental and climate impacts than their fossil fuel counterparts.
The data in these Fast Facts do not reflect two important renewable energy resources: traditional biomass, which is widespread but difficult to measure; and energy efficiency, a critical strategy for reducing energy consumption while maintaining the same energy services and quality of life. See the Biomass and Energy Efficiency pages to learn more.
Significance
14% of world 🌎 9% of US 🇺🇸
Electricity Generation
30% of world 🌎 21% of US 🇺🇸
Global Renewable Energy Uses
Electricity 65% Heat 26% Transportation 9%
Global Consumption of Renewable Electricity Change
Increase: ⬆ 33% (2017 to 2022)
Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency measures such as LED light bulbs reduce the need for energy in the first place
Renewable Resources
Wind Solar Ocean
Semi-Renewable Resources
Hydro Geothermal Biomass
Renewable Energy Has Vast Potential to Meet Global Energy Demand
Solar >1,000x global demand Wind ~3x global demand
Share of Global Energy Demand Met by Renewable Resources
Hydropower 7% Wind 3% Solar 2% Biomass <2%
Share of Global Electricity Generation Met by Renewable Resources
Hydropower 15% Wind 7% Solar 5% Biomass & Geothermal <3%
Global Growth
Hydropower generation increase ⬆6% Wind generation increase ⬆84% Solar generation increase ⬆197% Biofuels consumption increase ⬆23% (2017-2022)
Largest Renewable Energy Producers
China 34% 🇨🇳 US 10% 🇺🇸 of global renewable energy
Highest Penetration of Renewable Energy
Norway 72% 🇳🇴 of the country’s primary energy is renewable
(China is at 16%, the US is at 11%)
Largest Renewable Electricity Producers
China 31% 🇨🇳 US 11% 🇺🇸 of global renewable electricity
Highest Penetration of Renewable Electricity
Albania, Bhutan, CAR, Lesotho, Nepal, & Iceland 100%
Iceland, Ethiopia, Paraguay, DRC, Norway, Costa Rica, Uganda, Namibia, Eswatini, Zambia, Tajikistan, & Sierra Leone > 90% of the country’s primary electricity is renewable
(China is at 31%, the US is at 22%)
Share of US Energy Demand Met by Renewable Resources
Biomass 5% Wind 2% Hydro 1% Solar 1%
Share of US Electricity Generation Met by Renewable Resources
Wind 10% Hydropower 6% Solar 3% Biomass 1%
US States That Produce the Most Renewable Electricity
Texas 21% California 11% of US renewable energy production
US States With Highest Penetration of Renewable Electricity
Vermont >99% South Dakota 84% Washington 76% Idaho 75% of state’s total generation comes from renewable fuels
Renewable Energy Expansion Policies
The Inflation Reduction Act continued tax credits for new renewable energy projects in the US.

Production Tax Credit (PTC)
Tax credit of $0.0275/kWh of electricity produced at qualifying renewable power generation sites
Investment Tax Credit (ITC)
Tax credit of 30% of the cost of a new qualifying renewable power generation site
To read more about the credit qualifications, visit this EPA site .
*LCOE (levelized cost of electricity) - price for which a unit of electricity must be sold for system to break even
Important Factors for Renewable Site Selection
- Resource availability
- Environmental constraints and sensitivities, including cultural and archeological sites
- Transmission infrastructure
- Power plant retirements
- Transmission congestion and prices
- Electricity markets
- Load growth driven by population and industry
- Policy support
- Land rights and permitting
- Competitive and declining costs of wind, solar, and energy storage
- Lower environmental and climate impacts (social costs) than fossil fuels
- Expansion of competitive wholesale electricity markets
- Governmental clean energy and climate targets and policies
- Corporate clean energy targets and procurement of renewable energy
- No fuel cost or fuel price volatility
- Retirements of old and/or expensive coal and nuclear power plants
- Most renewable resources are abundant, undepletable
- Permitting hurdles and NIMBY/BANANA* concerns
- Competition from subsidized fossil fuels and a lack of price for their social cost (e.g., price on carbon)
- Site-specific resources means greater need to transport energy/electricity to demand
- High initial capital expenditure requirements required to access fuel cost/operating savings
- Intermittent resources
- Inconsistent governmental incentives and subsidies
- Managing environmental impacts to the extent that they exist
*NIMBY - not in my backyard; BANANA - build absolutely nothing anywhere near anything
Climate Impact: Low to High

- Solar, wind, geothermal, and ocean have low climate impacts with near-zero emissions; hydro and biomass can have medium to high climate impact
- Hydro: Some locations have greenhouse gas emissions due to decomposing flooded vegetation
- Biomass: Some crops require significant energy inputs, land use change can release carbon dioxide and methane
Environmental Impact: Low to High
- Most renewable energy resources have low environmental impacts, particularly relative to fossil fuels; some, like biomass, can have more significant impacts
- No air pollution with the exception of biomass from certain feedstocks
- Can have land and habitat disruption for biomass production, solar, and hydro
- Potential wildlife impacts from wind turbines (birds and bats)
- Modest environmental impacts during manufacturing, transportation, and end of life
Updated January 2024
Before You Watch Our Lecture on Introduction to Renewable Energy
We assign videos and readings to our Stanford students as pre-work for each lecture to help contextualize the lecture content. We strongly encourage you to review the Essential reading below before watching our lecture on Introduction to Renewable Energy . Include the Optional and Useful readings based on your interests and available time.
- The Sustainable Energy in America 2023 Factbook (Executive Summary pp. 5-11) . Bloomberg New Energy Finance. 2023. (7 pages) Provides valuable year-over-year data and insights on the American energy transformation.
Optional and Useful
- Renewables 2023 Global Status Report (Global Overview pp. 11-40) . REN21. 2023. (30 pages). Documents the progress made in the renewable energy sector and highlights the opportunities afforded by a renewable-based economy and society.
Our Lecture on Introduction to Renewable Energy
This is our Stanford University Understand Energy course lecture that introduces renewable energy. We strongly encourage you to watch the full lecture to gain foundational knowledge about renewable energy and important context for learning more about specific renewable energy resources. For a complete learning experience, we also encourage you to review the Essential reading we assign to our students before watching the lecture.

Presented by: Kirsten Stasio , Adjunct Lecturer, Civil and Environmental Engineering, Stanford University; CEO, Nevada Clean Energy Fund (NCEF) Recorded on: November 16, 2022 Duration: 52 minutes
Table of Contents
(Clicking on a timestamp will take you to YouTube.) 00:00 What Does "Renewable" Mean? 12:56 What Role Do Renewables Play In Our Energy Use? 20:29 What Factors Affect Renewable Energy Project Development? 52:13 Conclusion
Lecture slides available upon request .
Additional Resources About Renewable Energy
Stanford university.
- Precourt Institute for Energy Renewable Energy , Energy Efficiency
- Stanford Energy Club
- Energy Modeling Forum
- Sustainable Stanford
- Sustainable Finance Initiative
- Mark Jacobson - Renewable energy
- Michael Lepech - Life-cycle analysis
- Leonard Ortolano - Environmental and water resource planning
- Chris Field - Climate change, land use, bioenergy, solar energy
- David Lobell - Climate change, agriculture, biofuels, land use
- Sally Benson - Climate change, energy, carbon capture and storage
Government and International Organizations
- International Energy Agency (IEA) Renewables Renewables 2022 Repor .
- National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL)
- US Department of Energy (DOE) Office of Energy Efficiency & Renewable Energy (EERE)
- US Energy Information Administration (EIA) Renewable Energy Explained
- US Energy Information Administration (EIA) Energy Kids Renewable Energy
- US Energy Information Administration (EIA) Today in Energy Renewables
Non-Governmental Organizations (NGOs)
- Carnegie Institution for Science Biosphere Sciences and Engineering
- The Solutions Project
Other Resources
- REN21: Renewable Energy Policy Network for the 21st Century
- REN21 Renewables 2023 Global Status Report Renewables in Energy Supply
- BloombergNEF (BNEF)
- Renewable Energy World
- World of Renewables
- Energy Upgrade California
- Windustry Community Wind Toolbox
Next Topic: Energy Efficiency Other Energy Topics to Explore
Fast Facts Sources
- Energy Mix (World 2022): Energy Institute. Statistical Review of World Energy . 2023.
- Energy Mix (US 2022): US Energy Information Agency (EIA). Total Energy: Energy Overview, Table 1.3 .
- Electricity Mix (World 2022): Energy Institute. Statistical Review of World Energy . 2023.
- Electricity Mix (US 2022): US Energy Information Agency (EIA). Total Energy: Electricity, Table 7.2a.
- Global Solar Use (2022): REN21. Renewables 2023 Global Status Report: Renewables in Energy Supply , page 42. 2023
- Global Consumption of Renewable Electricity Change (2017-2022): Energy Institute. Statistical Review of World Energy . 2023.
- Renewable Energy Potential: Perez & Perez. A Fundamental Look at Energy Reserves for the Planet . 2009
- Share of Global Energy Demand (2022): Energy Institute. Statistical Review of World Energy . 2023.
- Share of Global Electricity Demand (2022): Energy Institute. Statistical Review of World Energy . 2023.
- Global Growth (2017-2022): Energy Institute. Statistical Review of World Energy . 2023.
- Largest Renewable Energy Producers (World 2022): International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA). Renewable Capacity Statistics 2023 . 2023.
- Highest Penetration Renewable Energy (World 2022): Our World in Data. Renewable Energy . 2023.
- Largest Renewable Electricity Producers (World 2022): Energy Institute. Statistical Review of World Energy . 2023.
- Highest Penetration Renewable Electricity (World 2022): Our World in Data. Renewable Energy . 2023.
- Share of US Energy Demand (2022): Energy Information Administration (EIA). Electric Power Monthly. 2023.
- Share of Electricity Generation (2022): Energy Information Administration (EIA). Electric Power Monthly. 2023.
- States with Highest Generation (2022): Energy Information Administration (EIA). Electric Power Monthly. 2023.
- States with Highest Penetration (2021): Energy Information Administration (EIA). State Profile and Energy Estimates. 2023.
- LCOE of US Renewable Resources: Lazard. LCOE. April 2023.
- LCOE of US Non Renewable Resources: Lazard. LCOE. April 2023.
More details available on request . Back to Fast Facts
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
AP®︎/College Environmental science
Course: ap®︎/college environmental science > unit 5.
- Renewable and nonrenewable energy resources
Renewable and nonrenewable energy sources
- Global energy use
- Intro to energy resources and consumption
- Nonrenewable energy sources are those that are consumed faster than they can be replaced. Nonrenewable energy sources include nuclear energy as well as fossil fuels such as coal, crude oil, and natural gas. These energy sources have a finite supply, and often emit harmful pollutants into the environment.
- Renewable energy sources are those that are naturally replenished on a relatively short timescale. Renewable energy sources include solar, wind, hydroelectric, and geothermal energy. They also include biomass and hydrogen fuels. These energy sources are sustainable and generate fewer greenhouse gas emissions than fossil fuels.
Want to join the conversation?
- Upvote Button navigates to signup page
- Downvote Button navigates to signup page
- Flag Button navigates to signup page
Read our research on: Gun Policy | International Conflict | Election 2024
Regions & Countries
2. public opinion on renewables and other energy sources.
Americans’ concerns about climate change have put energy production of fossil fuels and the carbon gases these fuels emit at the center of public discussions about climate and the environment. Those debates coupled with long-standing economic pressures to decrease reliance on other countries for energy needs have raised attention to renewable forms of energy including solar and wind power.
Public opinion about energy issues is widely supportive of expanding both solar and wind power but more closely divided when it comes to expanding fossil fuel energies such as coal mining, offshore oil and gas drilling, and hydraulic fracturing for oil and natural gas. While there are substantial party and ideological divides over increasing fossil fuel and nuclear energy sources, strong majorities of all party and ideology groups support more solar and wind production.
Most Americans know the U.S. is producing more energy today
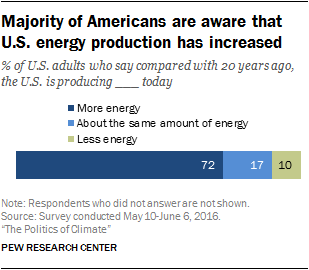
Majorities across demographic, educational and political groups say the U.S. is producing more energy today. Awareness of this trend is especially high among those with postgraduate degrees (86% compared with 64% among those with high school degrees or less). Men are more inclined to say the U.S. is producing more energy than women (79% vs. 66%), while Democrats are modestly more likely than Republicans to say this (79% vs. 65%).
Strong public support for more wind and solar, closer divides over nuclear and fossil fuels
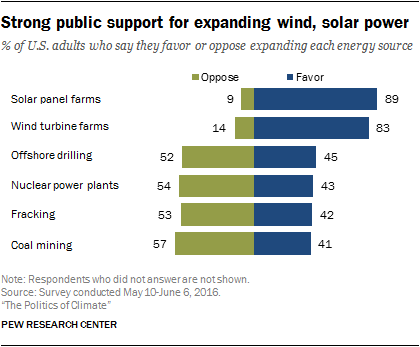
Fully 89% of Americans favor more solar panel farms, just 9% oppose. A similarly large share supports more wind turbine farms (83% favor, 14% oppose).
By comparison, the public is more divided over expanding the production of nuclear and fossil fuel energy sources. Specifically, 45% favor more offshore oil and gas drilling, while 52% oppose. Similar shares support and oppose expanding hydraulic fracturing or “fracking” for oil and gas (42% favor and 53% oppose). Some 41% favor more coal mining, while a 57% majority opposes this.
And, 43% of Americans support building more nuclear power plants, while 54% oppose. Past Pew Research Center surveys on energy issues, using somewhat different question wording and survey methodology, found opinion broadly in keeping with this new survey. For example, the balance of opinion in a 2014 Pew Research Center survey about building more nuclear power plants was similar (45% favor, 51% oppose), and some 52% of Americans favored and 44% opposed allowing more offshore oil and gas drilling in that survey.
Most Republicans and Democrats favor expanding renewables; there are strong divides over expanding fossil fuels
Across the political spectrum, large majorities support expansion of solar panel and wind turbine farms. Some 83% of conservative Republicans favor more solar panel farms; so, too, do virtually all liberal Democrats (97%). Similarly, there is widespread agreement across party and ideological groups in favor of expanding wind energy.
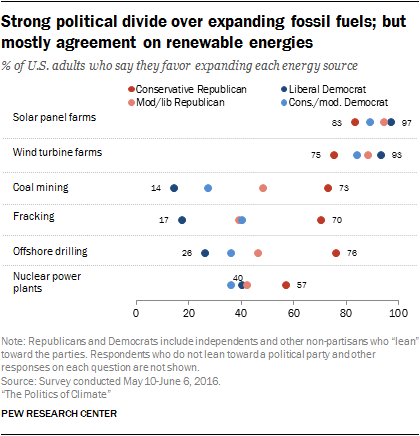
The political divide over expanding nuclear energy is smaller. Some 57% of conservative Republicans, and 51% of all Republicans, favor more nuclear power plants. Democrats lean in the opposite direction with 59% opposed and 38% in favor of more nuclear power plants.
As also found in past Pew Research Center surveys , women are less supportive of expanding nuclear power than men, even after controlling for politics and education. Some 34% of women favor and 62% oppose more nuclear plants. Men are more closely divided on this issue: 52% favor and 46% oppose. Men and women hold more similar views on other energy issues.
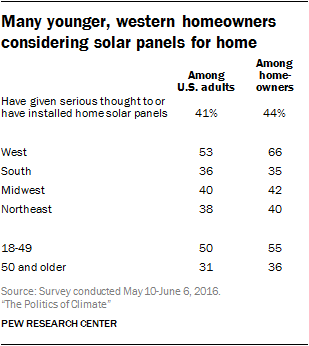
Many Americans are giving serious thought to having solar panels at home
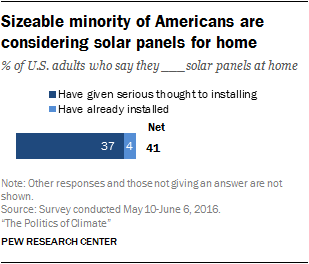
These figures are similar among homeowners. Some 44% of homeowners have already installed (4%) or have given serious thought to installing (40%) solar panels at home.
- Pew Research Center in 2014 asked a related question – whether the amount of energy produced in the United States had been increasing, decreasing or staying the same in recent years. In that survey, 54% of Americans said the amount of energy produced had been increasing, while 27% said it had been staying the same and 10% said it had been decreasing. ↩
Add Pew Research Center to your Alexa
Say “Alexa, enable the Pew Research Center flash briefing”
Report Materials

Table of Contents
How americans view electric vehicles, fast facts about international views of climate change as biden attends un cop26 conference, 67% of americans perceive a rise in extreme weather, but partisans differ over government efforts to address it, most u.s. latinos say global climate change and other environmental issues impact their local communities, on climate change, republicans are open to some policy approaches, even as they assign the issue low priority, most popular.
About Pew Research Center Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
- News & Updates
The Future of Sustainable Energy
26 June, 2021
Share this on social media:

Building a sustainable energy future calls for leaps forward in both technology and policy leadership. State governments, major corporations and nations around the world have pledged to address the worsening climate crisis by transitioning to 100% renewable energy over the next few decades. Turning those statements of intention into a reality means undertaking unprecedented efforts and collaboration between disciplines ranging from environmental science to economics.
There are highly promising opportunities for green initiatives that could deliver a better future. However, making a lasting difference will require both new technology and experts who can help governments and organizations transition to more sustainable practices. These leaders will be needed to source renewables efficiently and create environmentally friendly policies, as well as educate consumers and policymakers. To maximize their impact, they must make decisions informed by the most advanced research in clean energy technology, economics, and finance.
Current Trends in Sustainability
The imperative to adopt renewable power solutions on a worldwide scale continues to grow even more urgent as the global average surface temperature hits historic highs and amplifies the danger from extreme weather events . In many regions, the average temperature has already increased by 1.5 degrees , and experts predict that additional warming could drive further heatwaves, droughts, severe hurricanes, wildfires, sea level rises, and even mass extinctions.
In addition, physicians warn that failure to respond to this dire situation could unleash novel diseases : Dr. Rexford Ahima and Dr. Arturo Casadevall of the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine contributed to an article in the Journal of Clinical Investigation that explained how climate change could affect the human body’s ability to regulate its own temperature while bringing about infectious microbes that adapt to the warmer conditions.
World leaders have accepted that greenhouse gas emissions are a serious problem that must be addressed. Since the Paris Agreement was first adopted in December 2015, 197 nations have signed on to its framework for combating climate change and preventing the global temperature increase from reaching 2 degrees Celsius over preindustrial levels.
Corporate giants made their own commitments to become carbon neutral by funding offsets to reduce greenhouse gases and gradually transitioning into using 100% renewable energy. Google declared its operations carbon neutral in 2017 and has promised that all data centers and campuses will be carbon-free by 2030. Facebook stated that it would eliminate its carbon footprint in 2020 and expand that commitment to all the organization’s suppliers within 10 years. Amazon ordered 100,000 electric delivery vehicles and has promised that its sprawling logistics operations will arrive at net-zero emissions by 2040.
Despite these promising developments, many experts say that nations and businesses are still not changing fast enough. While carbon neutrality pledges are a step in the right direction, they don’t mean that organizations have actually stopped using fossil fuels . And despite the intentions expressed by Paris Agreement signatories, total annual carbon dioxide emissions reached a record high of 33.5 gigatons in 2018, led by China, the U.S., and India.
“The problem is that what we need to achieve is so daunting and taxes our resources so much that we end up with a situation that’s much, much worse than if we had focused our efforts,” Ferraro said.
Recent Breakthroughs in Renewable Power
An environmentally sustainable infrastructure requires innovations in transportation, industry, and utilities. Fortunately, researchers in the private and public sectors are laying the groundwork for an energy transformation that could make the renewable energy of the future more widely accessible and efficient.
Some of the most promising areas that have seen major developments in recent years include:
Driving Electric Vehicles Forward
The technical capabilities of electric cars are taking great strides, and the popularity of these vehicles is also growing among consumers. At Tesla’s September 22, 2020 Battery Day event, Elon Musk announced the company’s plans for new batteries that can be manufactured at a lower cost while offering greater range and increased power output .
The electric car market has seen continuing expansion in Europe even during the COVID-19 pandemic, thanks in large part to generous government subsidies. Market experts once predicted that it would take until 2025 for electric car prices to reach parity with gasoline-powered vehicles. However, growing sales and new battery technology could greatly speed up that timetable .
Cost-Effective Storage For Renewable Power
One of the biggest hurdles in the way of embracing 100% renewable energy has been the need to adjust supply based on demand. Utilities providers need efficient, cost-effective ways of storing solar and wind power so that electricity is available regardless of weather conditions. Most electricity storage currently takes place in pumped-storage hydropower plants, but these facilities require multiple reservoirs at different elevations.
Pumped thermal electricity storage is an inexpensive solution to get around both the geographic limitations of hydropower and high costs of batteries. This approach, which is currently being tested , uses a pump to convert electricity into heat so it can be stored in a material like gravel, water, or molten salts and kept in an insulated tank. A heat engine converts the heat back into electricity as necessary to meet demand.
Unlocking the Potential of Microgrids
Microgrids are another area of research that could prove invaluable to the future of power. These systems can operate autonomously from a traditional electrical grid, delivering electricity to homes and business even when there’s an outage. By using this approach with power sources like solar, wind, or biomass, microgrids can make renewable energy transmission more efficient.
Researchers in public policy and engineering are exploring how microgrids could serve to bring clean electricity to remote, rural areas . One early effort in the Netherlands found that communities could become 90% energy self-sufficient , and solar-powered microgrids have now also been employed in Indian villages. This technology has enormous potential to change the way we access electricity, but lowering costs is an essential step to bring about wider adoption and encourage residents to use the power for purposes beyond basic lighting and cooling.
Advancing the Future of Sustainable Energy
There’s still monumental work to be done in developing the next generation of renewable energy solutions as well as the policy framework to eliminate greenhouse gases from our atmosphere. An analysis from the International Energy Agency found that the technologies currently on the market can only get the world halfway to the reductions needed for net-zero emissions by 2050.
To make it the rest of the way, researchers and policymakers must still explore possibilities such as:
- Devise and implement large-scale carbon capture systems that store and use carbon dioxide without polluting the atmosphere
- Establish low-carbon electricity as the primary power source for everyday applications like powering vehicles and heat in buildings
- Grow the use of bioenergy harnessed from plants and algae for electricity, heat, transportation, and manufacturing
- Implement zero-emission hydrogen fuel cells as a way to power transportation and utilities
However, even revolutionary technology will not do the job alone. Ambitious goals for renewable energy solutions and long-term cuts in emissions also demand enhanced international cooperation, especially among the biggest polluters. That’s why Jonas Nahm of the Johns Hopkins School of Advanced International Studies has focused much of his research on China’s sustainable energy efforts. He has also argued that the international community should recognize China’s pivotal role in any long-term plans for fighting climate change.
As both the leading emitter of carbon dioxide and the No. 1 producer of wind and solar energy, China is uniquely positioned to determine the future of sustainability initiatives. According to Nahm, the key to making collaboration with China work is understanding the complexities of the Chinese political and economic dynamics. Because of conflicting interests on the national and local levels, the world’s most populous nation continues to power its industries with coal even while President Xi Jinping advocates for fully embracing green alternatives.
China’s fraught position demonstrates that economics and diplomacy could prove to be just as important as technical ingenuity in creating a better future. International cooperation must guide a wide-ranging economic transformation that involves countries and organizations increasing their capacity for producing and storing renewable energy.
It will take strategic thinking and massive investment to realize a vision of a world where utilities produce 100% renewable power while rows of fully electric cars travel on smart highways. To meet the challenge of our generation, it’s more crucial than ever to develop leaders who understand how to apply the latest research to inform policy and who can take charge of globe-spanning sustainable energy initiatives .
About the MA in Sustainable Energy (online) Program at Johns Hopkins SAIS
Created by Johns Hopkins University School of Advanced International Studies faculty with input from industry experts and employers, the Master of Arts in Sustainable Energy (online) program is tailored for the demands of a rapidly evolving sector. As a top-11 global university, Johns Hopkins is uniquely positioned to equip graduates with the skills they need to confront global challenges in the transition to renewable energy.
The MA in Sustainable Energy curriculum is designed to build expertise in finance, economics, and policy. Courses from our faculty of highly experienced researchers and practitioners prepare graduates to excel in professional environments including government agencies, utility companies, energy trade organizations, global energy governance organizations, and more. Students in the Johns Hopkins SAIS benefit from industry connections, an engaged network of more than 230,000 alumni, and high-touch career services.
Request Information
To learn more about the MA in Sustainable Energy (online) and download a brochure , fill out the fields below, or call +1 410-648-2495 or toll-free at +1 888-513-5303 to talk with one of our admissions counselors.
Johns Hopkins University has engaged AllCampus to help support your educational journey. AllCampus will contact you shortly in response to your request for information. About AllCampus . Privacy Policy . You may opt out of receiving communications at any time.
* All Fields are Required. Your Privacy is Protected.
Connect with us
- Email: [email protected]
- Local Phone: +1 410-648-2495 (Local)
- Toll-Free Phone: +1 888-513-5303 (Toll-Free)
Towards Sustainable Energy: A Systematic Review of Renewable Energy Sources, Technologies, and Public Opinions
Ieee account.
- Change Username/Password
- Update Address
Purchase Details
- Payment Options
- Order History
- View Purchased Documents
Profile Information
- Communications Preferences
- Profession and Education
- Technical Interests
- US & Canada: +1 800 678 4333
- Worldwide: +1 732 981 0060
- Contact & Support
- About IEEE Xplore
- Accessibility
- Terms of Use
- Nondiscrimination Policy
- Privacy & Opting Out of Cookies
A not-for-profit organization, IEEE is the world's largest technical professional organization dedicated to advancing technology for the benefit of humanity. © Copyright 2024 IEEE - All rights reserved. Use of this web site signifies your agreement to the terms and conditions.
.png)
This Is the Future: Essay on Renewable Energy

Today the world population depends on nonrenewable energy resources. With the constantly growing demand for energy, natural gas, coal, and oil get used up and cannot replenish themselves.
Aside from limited supply, heavy reliance on fossil fuels causes planetary-scale damage. Sea levels are rising. Heat-trapping carbon dioxide increased the warming effect by 45% from 1990 to 2019. The only way to tackle the crisis is to start the transition to renewable energy now.
What is renewable energy? It is energy that comes from replenishable natural resources like sunlight, wind, thermal energy, moving water, and organic materials. Renewable resources do not run out. They are cost-efficient and renew faster than they are consumed. How does renewable energy save money? It creates new jobs, supports economic growth, and decreases inequitable fossil fuel subsidies.
At the current rates of production, some fossil fuels will not even last another century. This is why the future depends on reliable and eco-friendly resources. This renewable energy essay examines the types and benefits of renewable energy and its role in creating a sustainable future.
Top 5 Types of Renewable Energy: The Apollo Alliance Rankings
There are many natural resources that can provide people with clean energy. To make a list of the five most booming types of renewable energy on the market today, this energy essay uses data gathered by the Apollo Alliance. It is a project that aims to revolutionize the energy sector of the US with a focus on clean energy.
The Apollo Alliance unites businesses, community leaders, and environmental experts to support the transition to more sustainable and efficient living. Their expert opinion helped to compile information about the most common and cost-competitive sources of renewable energy. However, if you want to get some more in-depth research, you can entrust it to an essay writer . Here’s a quick overview of renewable energy resources that have a huge potential to substitute fossil fuels.
Solar Renewable Energy
The most abundant and practically endless resource is solar energy. It can be turned into electricity by photovoltaic systems that convert radiant energy captured from sunlight. Solar farms could generate enough energy for thousands of homes.
An endless supply is the main benefit of solar energy. The rate at which the Earth receives it is 10,000 times greater than people can consume it, as a paper writer points out based on their analysis of research findings. It can substitute fossil fuels and deliver people electricity, hot water, cooling, heat, etc.
The upfront investment in solar systems is rather expensive. This is one of the primary limitations that prevent businesses and households from switching to this energy source at once. However, the conclusion of solar energy is still favorable. In the long run, it can significantly decrease energy costs. Besides, solar panels are gradually becoming more affordable to manufacture and adopt, even at an individual level.
Wind Renewable Energy
Another clean energy source is wind. Wind farms use the kinetic energy of wind flow to convert it into electricity. The Appolo Alliance notes that, unlike solar farms, they can’t be placed in any location. To stay cost-competitive, wind farms should operate in windy areas. Although not all countries have the right conditions to use them on a large scale, wind farms might be introduced for some energy diversity. The technical potential for it is still tremendous.
Wind energy is clean and safe for the environment. It does not pollute the atmosphere with any harmful products compared to nonrenewable energy resources.
The investment in wind energy is also economically wise. If you examine the cost of this energy resource in an essay on renewable resources, you’ll see that wind farms can deliver electricity at a price lower than nonrenewable resources. Besides, since wind isn’t limited, its cost won’t be influenced by the imbalance of supply and demand.
Geothermal Renewable Energy
Natural renewable resources are all around us, even beneath the ground. Geothermal energy can be produced from the thermal energy from the Earth’s interior. Sometimes heat reaches the surface naturally, for example, in the form of geysers. But it can also be used by geothermal power plants. The Earth’s heat gets captured and converted to steam that turns a turbine. As a result, we get geothermal energy.
This source provides a significant energy supply while having low emissions and no significant footprint on land. A factsheet and essay on renewable resources state that geothermal plants will increase electricity production from 17 billion kWh in 2020 to 49.8 billion kWh in 2050.
However, this method is not without limitations. While writing a renewable resources essay, consider that geothermal energy can be accessed only in certain regions. Geological hotspots are off-limits as they are vulnerable to earthquakes. Yet, the quantity of geothermal resources is likely to grow as technology advances.
Ocean Renewable Energy
The kinetic and thermal energy of the ocean is a robust resource. Ocean power systems rely on:
- Changes in sea level;
- Wave energy;
- Water surface temperatures;
- The energy released from seawater and freshwater mixing.
Ocean energy is more predictable compared to other resources. As estimated by EPRI, it has the potential to produce 2640 TWh/yr. However, an important point to consider in a renewable energy essay is that the kinetic energy of the ocean varies. Yet, since it is ruled by the moon’s gravity, the resource is plentiful and continues to be attractive for the energy industry.
Wave energy systems are still developing. The Apollo energy corporation explores many prototypes. It is looking for the most reliable and robust solution that can function in the harsh ocean environment.
Another limitation of ocean renewable energy is that it may cause disruptions to marine life. Although its emissions are minimal, the system requires large equipment to be installed in the ocean.
Biomass Renewable Energy
Organic materials like wood and charcoal have been used for heating and lighting for centuries. There are a lot more types of biomass: from trees, cereal straws, and grass to processed waste. All of them can produce bioenergy.
Biomass can be converted into energy through burning or using methane produced during the natural process of decomposition. In an essay on renewable sources of energy, the opponents of the method point out that biomass energy is associated with carbon dioxide emissions. Yet, the amount of released greenhouse gases is much lower compared to nonrenewable energy use.
While biomass is a reliable source of energy, it is only suitable for limited applications. If used too extensively, it might lead to disruptions in biodiversity, a negative impact on land use, and deforestation. Still, Apollo energy includes biomass resources that become waste and decompose quickly anyway. These are organic materials like sawdust, chips from sawmills, stems, nut shells, etc.
What Is the Apollo Alliance?
The Apollo Alliance is a coalition of business leaders, environmental organizations, labor unions, and foundations. They all unite their efforts in a single project to harness clean energy in new, innovative ways.
Why Apollo? Similarly to President John F. Kennedy’s Apollo Project, Apollo energy is a strong visionary initiative. It is a dare, a challenge. The alliance calls for the integrity of science, research, technology, and the public to revolutionize the energy industry.
The project has a profound message. Apollo energy solutions are not only about the environment or energy. They are about building a new economy. The alliance gives hope to building a secure future for Americans.
What is the mission of the Apollo Alliance?
- Achieve energy independence with efficient and limitless resources of renewable energy.
- Pioneer innovation in the energy sector.
- Build education campaigns and communication to inspire new perceptions of energy.
- Create new jobs.
- Reduce dependence on imported fossil fuels.
- Build healthier and happier communities.
The transformation of the industry will lead to planet-scale changes. The Apollo energy corporation can respond to the global environmental crisis and prevent climate change.
Apollo renewable energy also has the potential to become a catalyst for social change. With more affordable energy and new jobs in the industry, people can bridge the inequality divide and build stronger communities.
Why Renewable Energy Is Important for the Future
Renewable energy resources have an enormous potential to cover people’s energy needs on a global scale. Unlike fossil fuels, they are available in abundance and generate minimal to no emissions.
The burning of fossil fuels caused a lot of environmental problems—from carbon dioxide emissions to ocean acidification. Research this issue in more detail with academic assistance from essay writer online . You can use it to write an essay on renewable sources of energy to explain the importance of change and its global impact.
Despite all the damage people caused to the planet, there’s still hope to mitigate further repercussions. Every renewable energy essay adds to the existing body of knowledge we have today and advances research in the field. Here are the key advantages and disadvantages of alternative energy resources people should keep in mind.
Advantage of Green Energy
The use of renewable energy resources has a number of benefits for the climate, human well-being, and economy:
- Renewable energy resources have little to no greenhouse gas emissions. Even if we take into account the manufacturing and recycling of the technologies involved, their impact on the environment is significantly lower compared to fossil fuels.
- Renewable energy promotes self-sufficiency and reduces a country’s dependence on foreign fuel. According to a study, a 1% increase in the use of renewable energy increases economic growth by 0.21%. This gives socio-economic stability.
- Due to a lack of supply of fossil fuels and quick depletion of natural resources, prices for nonrenewable energy keep increasing. In contrast, green energy is limitless and can be produced locally. In the long run, this allows decreasing the cost of energy.
- Unlike fossil fuels, renewable energy doesn’t emit air pollutants. This positively influences health and quality of life.
- The emergence of green energy plants creates new jobs. Thus, Apollo energy solutions support the growth of local communities. By 2030, the transition to renewable energy is expected to generate 10.3 million new jobs.
- Renewable energy allows decentralization of the industry. Communities get their independent sources of energy that are more flexible in terms of distribution.
- Renewable energy supports equality. It has the potential to make energy more affordable to low-income countries and expand access to energy even in remote and less fortunate neighborhoods.
Disadvantages of Non-Conventional Energy Sources
No technology is perfect. Renewable energy resources have certain drawbacks too:
- The production of renewable energy depends on weather conditions. For example, wind farms could be effective only in certain locations where the weather conditions allow it. The weather also makes it so that renewable energy cannot be generated around the clock.
- The initial cost of renewable energy technology is expensive. Both manufacturing and installation require significant investment. This is another disadvantage of renewable resources. It makes them unaffordable to a lot of businesses and unavailable for widespread individual use. In addition, the return on investment might not be immediate.
- Renewable energy technology takes up a lot of space. It may affect life in the communities where these clean energy farms are installed. They may also cause disruptions to wildlife in the areas.
- One more limitation a renewable resources essay should consider is the current state of technology. While the potential of renewable energy resources is tremendous, the technology is still in its development phase. Therefore, renewable energy might not substitute fossil fuels overnight. There’s a need for more research, investment, and time to transition to renewable energy completely. Yet, some diversity of energy resources should be introduced as soon as possible.
- Renewable energy resources have limited emissions, but they are not entirely pollution-free. The manufacturing process of equipment is associated with greenhouse gas emissions while, for example, the lifespan of a wind turbine is only 20 years.
For high school seniors eyeing a future rich with innovative endeavors in renewable energy or other fields, it's crucial to seek financial support early on. Explore the top 10 scholarships for high school seniors to find the right fit that can propel you into a future where you can contribute to the renewable energy movement and beyond. Through such financial support, the road to making meaningful contributions to a sustainable future becomes a tangible reality.
Renewable energy unlocks the potential for humanity to have clean energy that is available in abundance. It leads us to economic growth, independence, and stability. With green energy, we can also reduce the impact of human activity on the environment and stop climate change before it’s too late.
So what’s the conclusion of renewable energy? Transitioning to renewable energy resources might be challenging and expensive. However, most experts agree that the advantages of green energy outweigh any drawbacks. Besides, since technology is continuously evolving, we’ll be able to overcome most limitations in no time.

Frequently asked questions
She was flawless! first time using a website like this, I've ordered article review and i totally adored it! grammar punctuation, content - everything was on point
This writer is my go to, because whenever I need someone who I can trust my task to - I hire Joy. She wrote almost every paper for me for the last 2 years
Term paper done up to a highest standard, no revisions, perfect communication. 10s across the board!!!!!!!
I send him instructions and that's it. my paper was done 10 hours later, no stupid questions, he nailed it.
Sometimes I wonder if Michael is secretly a professor because he literally knows everything. HE DID SO WELL THAT MY PROF SHOWED MY PAPER AS AN EXAMPLE. unbelievable, many thanks
You Might Also Like
.png)
New Posts to Your Inbox!
Stay in touch

- Youth Program
- Wharton Online
- Business Journal Articles
- Environment
- The World Economy
Can Renewable Energy Solve the Global Climate Change Challenge?

Share Article:
Google Classroom:
Maanasa Mendu is relying on innovation and electric charges to tackle the global energy crisis. The freshman at Mason High School in Mason, Ohio, will travel this month to St. Paul, Minnesota, as a top 10 national finalist in the 2016 Discovery Education 3M Young Scientist Challenge. While there, she’ll present her invention that helps make wind power a globally applicable energy source. “Wind power is a powerful and popular form of renewable energy with enormous potential,” says Mendu in her competition video. “We need to make wind power an efficient and globally applicable energy source.” Mendu has created a device that uses piezoelectricity materials that are eco-friendly and cost-efficient to provide wind power to the world.
Mendu’s invention and passion for the future of energy generation are well in tune with the critical needs of the global economy. The adoption of renewable energy, generated from natural resources like sunlight, wind, tides, plant growth and geothermal heat, is a key strategy in combatting greenhouse gas emission-fueled climate change, which the World Economic Forum identifies each year as a serious global risk. Traditional fossil fuels like coal, natural gas and petroleum – which renewables seek to replace — contribute to the air pollution that causes global warming.
An article published this month by our parent publication, Knowledge@Wharton, explores today’s market for wind and solar power and the realities of climate change. Says Wharton business economics professor Arthur van Benthem: “The renewable energy industry has experienced dramatic growth over the last couple of years.”
Here are some fast facts shared by van Benthem and other climate change experts about the global challenge to deal with greenhouse gas emissions:
- Wind and solar power prices have plunged. As the cost of renewable generation nears the cost of fossil-fueled electricity, more people are likely to spend money to install this energy and use it.
- Projections about future wind and solar deployment have become more optimistic, especially in the U.S. Bloomberg New Energy Finance, a company that analyzes the energy system, expects total installed solar will more than quadruple between now and 2022, on the strength of continued cost declines. And the projection made in the year 2000 by the International Energy Agency of how much wind power capacity there would be in 2040 has been revised upward, fivefold.
- Solar power use in the U.S. is on the rise in part because companies have found efficient ways to acquire customers, process the applications and install the panels on people’s roofs. SolarCity, based in Silicon Valley, Calif., is one of the country’s leading residential solar companies. Tesla, the electric-power car company founded by Elon Musk, is expected to acquire SolarCity in November.
- The power generation industry is only responsible for a part of the nation’s greenhouse gas emissions. The other sectors combined — which include transportation, heating and cooling, cement making and industry — make up a larger share of emissions than power.
- As part of the Paris Climate Change Agreement, reached in December 2015, every nation pledged to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- Electric vehicles can help nations meet their emissions-reductions targets, but not everyone is convinced just yet that they need to buy an electric car. Sales of electric vehicles have been far lower than what some of the more optimistic observers in the industry had projected a few years back.
- Chevy’s Bolt and the upcoming Tesla 3 are expected to have ranges of 200 miles, for the same price at which cars were selling six years ago, which should help.
- In order for a true renewable energy revolution, governments need to cap fossil fuel emissions – designate a level above which emissions can’t exceed. The oil industry opposes this move, but experts believe such drastic measures will lead to more green innovations and emissions-abatement technologies. In other words, more and more scientists and entrepreneurs will think like Maanasa Mendu.
Related Links
- K@W: Solar and Wind Power Are Growing — but Won’t Solve Climate Change
- 2016 Discovery Education 3M Young Scientist Challenge
- Elon Musk, Lyndon Rive, and the Plan to Put Solar Panels on Every Roof in America
- Green Car Reports
- K@W: What Are the Gains from the Paris Climate Accord?
- The World Economic Forum
Conversation Starters
Can the growth in renewables like wind and solar alone solve the climate change challenge? Why or why not?
Do you have any personal experience with renewable energy? For example, solar panels on the roof of your house? Is renewable energy a topic of interest in your school or your community? What about the use of electric cars? Research some local strategies for fighting the effects of greenhouse gas emissions.
Why do you think the oil industry opposes capping fossil fuel emissions? Similarly, The Obama administration attempted to cap emissions through the Clean Air Act, but the legislation is under review by the Supreme Court . Why would there be opposition to laws and changes that clean our air and help to save the planet? Discuss different dimensions of the relationship between business and the environment.
Using the “Related Links,” research SolarCity. Who is Lyndon Rive? What did you learn about him and the business of renewable energy deployment, in particular solar power?
3 comments on “ Can Renewable Energy Solve the Global Climate Change Challenge? ”
1750 is generally accepted as the beginning of the Industrial Revolution, CO2 levels were 278 PPM. CO2 levels are now 400 PPM. 67% of all electrical power in this country is produced from fossil fuels. BUT fossil fuels only accounts for 30% of all sources of carbon gas associated with Climate Change. 100% renewables is only 30% of the problem. The first power plant was built in 1882.
World population reached 1 billion in 1804, just under 3 billion in the 50s when CO2 begin to rise, just over 5 billion in 1992 when the UN Conference on the Environment and Development is held in Rio de Janeiro that resulted in the Framework Convention on Climate Change, 6 billion in 99 and 7 billion in 2011. Climate Change is the result of carbon gas emissions which are caused by Industrialization which is driven by Population growth. By 2023, world population will have increased 33% over 1999. Many scientists consider game over at 9-10 billion.
CO2 levels are now over 400 PPM. To reduce CO2 levels in our atmosphere ONLY 1 PPM requires the removal of 7.81 billion tons of CO2 PLUS THE AMOUNT WE ARE NOW ADDING. To put this in perspective, Ivanpah 400 Mwe Solar Power Plant will offset 400,000 tons/yr of GHG. It would require 19,525 Ivanpahs to offset CO2 levels 1 PPM.
Weather is the state of the atmosphere at a place and time as regards to heat, dryness, sunshine, wind, rain, etc. Climate is the weather conditions prevailing in an area in general or over a long period. Climate Change is a Long Term change in global or regional climate patterns. Climate Change does not 10-20 years make, to short of a period. The weather service uses super computers to predict the weather one day in advance and sometimes wrong. All of this complexity we experience as “weather” is simply the result of uneven heating of the Earth, and the atmosphere ‘trying’ to reduce the differences in temperature. Note hurricanes generally start near the equator. A hurricane’s source of energy or fuel is water vapor which is evaporated from the ocean surface and rises to the upper atmosphere where it condenses into clouds and heat radiated into space keeping the planet cool. Surface ocean temperatures are cooler after a hurricane. So even minor global temperature increases may not be the proof needed and one reason there isn’t any consensus among scientists. To determine Climate Change we need to observe Changes in migratory patterns of animals and changes in plant habitats.
This is a very informative comment. After reading it, I have a few responses. First you address the fact that 100% renewables are only 30% of the problem. I would argue that they solve for even less, especially given the difficulty of implementing clean energy sources. In order to solve the problem, we need the right policies and legislation to actually implement the technologies in an effective manner. This part has always been harder. People like familiarity, and the status quo is as familiar as it gets, even if the status quo is extremely problematic. Therefore, even with fully developed renewables that are becoming more and more affordable, people are still more likely to stick with something that has always worked for them: fossil fuels.
Next, you name statistics about world population. I agree that we are approaching our carrying capacity and we really need to start thinking about ways to combat this. There have been many efforts to decrease fertility rates including China’s one-child policy, raising the minimum legal age for marriage, providing low-cost, safe access to contraception and other reproductive healthcare, and improving education and workforce opportunities for women. The UN says that 42% of governments have adopted one or more policies to lower their fertility levels. While the government should not actively try to limit families to a certain size through legislation, such as the one-child policy, workforce and education equality for women is a must, as well as safe and reliable access to healthcare. If these two beneficial actions happen to decrease fertility rates, then I definitely support them as a means to slow the growth of the world population and feel that they should be implemented universally.
Moving on, I found your next point to be very insightful. It really highlighted all the work that we have to do and how decreasing a single ppm would actually require that we remove several billion tons of CO2 from the atmosphere. Your visualization about the Ivanpah 400 Mw Solar Power Plant depicted just how much CO2 is still in the atmosphere, how much we have left to solve, and how pressing this issue is. However, you should consider how the climate crisis is a complex issue that requires solutions in renewable energy, population management, and policy. Industrialization and population may be inherently linked, but enacting green policies is undoubtedly a step in the right direction. Doing something as simple as creating a law that prevents companies from selling internal-combustion-engines immediately puts a large dent in the 3 billion metric tons of CO2 that come from just passenger cars each year. However, this is even greater, since most of the cars in the US are not even passenger cars, they are SUVs and trucks, so by preventing companies from selling gas-guzzlers, we take a huge chunk out of the emissions from passenger cars and we take out of the additional emissions from SUVs and trucks. Another simple legislation is making net-metering widely used. Net metering is when renewable sources are used to power each home, individually, and the excess power goes to the grid, which offsets the price of using the utility for customers, incentivizing them to do it.
On your last point, while I see the reasoning, I have to disagree. The evidence of climate change is blinding. The difference between weather and climate is that weather is a short-term gauge, which you can see in the Weather app on your phone, whereas climate is a long-term measurement. The complexities in weather are not from the atmosphere trying to reduce the heat of the Earth. Weather, even with our advanced technology, is practically impossible to predict because of how chaotic it is. There are so many different aspects to consider, wind patterns, temperature, geography, topography, humidity, precipitation, atmospheric pressure, and the list goes on. Weather complexity cannot be simplified to the idea of “uneven heating” in the Earth and the atmosphere trying to cool itself.
Furthermore, I was intrigued by your theory about how climate change can only be proven by the migratory patterns of animals and birds. While I do not necessarily agree with this point, I am curious to see your logic behind it.
We are a carbon cycle life, we exhale carbon dioxide and are flatulence is methane or CH4. Our plastics, pharmaceuticals, and just about everything we consume contains carbon. The amount of carbon in our atmosphere began its meteoric rise about the time of the beginning of the industrial revolution. Therefore carbon gases are the result of industrialization. Industrialization is production of cars and everything else that makes are life easier and is driven by Population growth. 68% of our elect power is from fossil fuels, but Power is only 30% of the carbon gas problem. But note from above, our problem is not carbon gases but with our explosive population growth we have reach the limit of the planet to support us without drastic changes in lifestyle.
RE was a Project Manager with engineering and construction of the world first utility scale solar power stations at Luz Kramer, pending solar direct steam patent and developer of several solar power plants. But I don’t sell cars
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Related Articles
The conversation: 3 things to know about the direction of data analytics, workplace etiquette: would you ‘ghost’ your employer.
Going Right
April 29, 2016
Renewable Energy Persuasive Essay
Robert Caba
Dr. Freymiller
12 April 2016
Out with the Old, In with the Re(new)able
The United States has been operating as a country using limited fossil fuels, but what happens when it all runs out? Would it not be more beneficial to never find out? Renewable energy, energy that is not depleted after its use, is limitless and more sustainable than any other source in energy history. To initiate the clean energy movement is expensive, but there are countless benefits ranging from individual to global impacts in going completely renewable. The first recorded use of renewable energy was harnessing wind power to drive ships over water about 7000 years ago (Darling). However, renewable energy has been around as long as Earth has existed: wind, sun, geothermal, biomass and many more. Clean energy sources can be harnessed to produce electricity, process heat, fuel and other chemicals with significantly less impact on the environment. In 2014, renewable energy sources accounted for fourteen percent of America’s total electricity use (“Renewable Energy Sources”), a four percent incline from the prior year. Completely diverting from fossil fuels to renewable energy clearly is not a new concept for a select few of innovative countries. A few countries, for example, are Costa Rica, Norway and Iceland, all of whom have ran on renewable energy for the entire 2015 calendar year, diving deep into their own land’s resources and utilizing volcanic presence to produce energy (Rosecrance & Thompson 7). Following in the footsteps of Costa Rica and a few other third world countries, major economic powerhouses and biggest users of fossil fuels like the United States should convert to clean energy as a way to benefit the economy, environment and overall health of the country.
As a consumer, one is worried about how abandoning a safe form of energy and transitioning to something new can help or hurt their wallet. Not only can renewable energy help save money, it can also help make money. A 150 billion dollar investment into this new industry would result in 1.7 million job opportunities, reducing the unemployment rate in America by an entire percentage (Pollin & Heintz). The reason for the potential high employment rate is because the industry is labor intensive in the means of installation and maintenance, requiring a lot of manpower for ultimate success. However, the more we wait the more future benefits we are currently losing. In an American Solar Energy Association (ASES) report in 2009, they stated “the 2008 predictions for renewable energy industry in 2030 are significantly lower than the 2007 predictions (National Research Council 169).” Unlike fossil fuels, which are subject to volatile pricing fluctuating over time depending on the market, renewable energy is relatively “free” after installation, using natural resources. The process of transportation and maintenance is minimized allowing prices to stay constant throughout the years. The only way price can head is down; for instance, clean energy is more affordable than 25 years ago. In particular, wind energy, the fastest growing source of power, prices have declined from forty cents per kilowatt per hour to less than five cents per kilowatt per hour (“The Energy Story”), a remarkable change and a huge upside in favor of the conversion. As time continues, technology should continue its progression resulting in cheaper mediums to acquire the energy. Despite of this, the conversion should take place now so results are maximized for the future. All in all, clean energy can both save Americans money while help them make money, the perfect win-win for producers and consumers alike.
Abstaining from burning countless, yet limited fossil fuels every day and polluting the environment is the single biggest benefactor for moving towards a cleaner approach. Not only would greenhouse gas emissions, as well as other pollutants that cause smog and acid rain, reach minimal levels, but also the country is consequently assisting in the reduction of the global warming speed and effects. Unlike fossil fuels, which are unable to be replenished easily, renewable energy is limitless, feeding from natural resources. With the global and national population expected to continue rising, the demand for energy will follow. There is a multitude of different approaches to acquire renewable energy including the most used types: solar and wind power. Specifically, solar energy is the epitome of sustainability and efficiency, calculated through production and prices. Despite the massive amounts of energy used yearly nationwide, “the sunlight falling on the United States in one day contains more than twice the energy we consume in an entire year ( The Energy Story ).” As for wind power, “California [alone] has enough wind gusts to produce 11 percent of the world’s wind electricity ( The Energy Story).” Wind turbines take up a lot of space but still allow the area around it, usually farms, to be used regularly. In the United Kingdom, for comparison, the government set a target for renewable energy to make up 15 percent of their total energy expense by 2020. This motive results in a 34 percent cut in the country’s carbon emission in the same time span (National Research Council 180). Needless to say, renewable energy will make landmark strides in the progression towards a cleaner, better environment. The most important thing on this Earth is this Earth, and it’s society’s job to maintain it.
As well as helping the environment and wallets, renewable energy can help with everyone’s health. By cutting the emission of greenhouse gasses and fossil fuels, air pollution decreases. Air pollution, primarily those contributed through coal burning power plants emitting fine-particulate pollutants, is most associated with causing health problems, chiefly lung cancer. The Environment Protection Agency (EPA) predicts that conversion, or even standards, will prevent at least 100,000 heart attacks and asthma attacks per year. Additionally, EPA also estimates a projected 1,100 billion dollar income in health benefits due to avoiding illnesses and deaths (U.S. EPA). As a form of partnership, the health industry could invest a portion of this money into the clean air movement due to its beneficial health impacts and help make installation cheaper. A majority of these pollutants are associated with dangerous levels of climate change, this century’s biggest threat to human health. Climate change, a change in global climate patterns, “will increasingly jeopardize the fundamental requirements for health, including clean urban air, safe and sufficient drinking-water, a secure and nutritious food supply, and adequate shelter (World Health Organization).” Climate change is the main contributor and accelerator towards global warming. Global warming increases the risk of two deadly diseases: Plague and Ebola, to name a few. For Plague, changes in temperature and rainfall will affect rodent populations as well as the infected fleas they carry. Additionally, Ebola outbreaks tend to follow serious downpours or droughts, a likely result of climate change (Biello). The movement would not only lower the pollution rate and risk of infection, but also save countless lives across the globe during the process.
America, along with most other countries, needs to initiate their plans towards a more sustainable, cleaner form of energy. Renewable energy helps increase the production of the economy through the addition of million of jobs. Simultaneously, energy prices would be lower, also helping the consumer save money. However, it is vital to start now. The longer the wait, the less benefits are reaped. Likewise, the clean air movement will mark the beginning of recovery for the environment. Greenhouse gases and other emission will reach all time lows, possibly zero. This deduction is important to slow the rate of climate change and global warming. Stopping climate change and gas emissions in its tracks would also lead to more health benefits. There are dozens of deadly diseases and carriers that spawn from the irregular climate patterns. Also, climate change could affect physiological needs by lessening safe drinking water, food supply and shelter. The United States has a reputation of being an innovator, a leader for many countries. Why has it been so lackadaisical with something so important to everything in today’s society? It has a history of being scared of change; people are too comfortable with life as it is, but it could be better. With the United States recently moving in the right direction, it will be better.
Works Cited
Biello, David. “Diseases Due to Climate Change.” Scientific American . N.p., 8 Oct. 2008. Web. 9 Apr. 2016.
Darling, David. “Wind Energy.” Encyclopedia of Alternative Energy . N.p., n.d. Web. 11 Apr. 2016.
National Research Council, and Chinese Academy of Sciences. The Power of Renewables: Opportunities and Challenges for China and the United States . Washington, D.C.: National Academies, 2010. Print.
Pollin, Robert, and James Heintz. “The Economic Benefits of Investing in Clean Energy.” Center for American Progress . N.p., 18 June 2009. Web. 06 Apr. 2016.
“Renewable Energy Sources – Energy Explained, Your Guide To Understanding Energy – Energy Information Administration.” EIA . US Energy Information Administration, 17 Mar. 2015. Web. 11 Apr. 2016.
Rosecrance, Richard, and Peter Thompson. “Global Trends in Sustainable Energy Investment.” Annual Review of Political Science 6.1 (2003): 7. UNEP . United Nations Environment Programme, 13 Oct. 2014. Web. 10 Apr. 2016.
“The Energy Story – Chapter 17: Renewable Energy vs. Fossil Fuels.” The Energy Story . California Energy Commission, n.d. Web. 11 Apr. 2016.
U.S. EPA. “Cleaning Up Toxic Air Pollution.” Benefits and Costs of Cleaning up Toxic Air Pollution (n.d.): n. pag. EPA . Environment Protection Agency. Web. 10 Apr. 2016.
World Health Organization. Renewable Energy (n.d.): 7. WHO . World Health Organization, 2012. Web. 10 Apr. 2016.
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
Renewable energy articles from across Nature Portfolio
Renewable energy is energy that comes from sources that are readily replenishable on short-timescales. Examples of these are solar radiation, wind, and biomass.
Breaking the reaction chain
Wide band gap perovskite solar cells suffer from halide segregation, which hampers their use in tandem solar cells. Now, researchers develop an additive with redox and defect passivating capabilities to suppress halide migration, enabling perovskite–organic tandems with over 25% efficiency.
- Aleksandra B. Djurišić
Related Subjects
- Geothermal energy
- Hydroelectricity
- Hydrogen energy
- Solar energy
- Wind energy
Latest Research and Reviews
From home energy management systems to energy communities: methods and data
- Antonio Ruano
- Maria da Graça Ruano
Performance optimization of interleaved boost converter with ANN supported adaptable stepped-scaled P&O based MPPT for solar powered applications
- K. Krishnaram
- T. Suresh Padmanabhan
- S. Senthilkumar
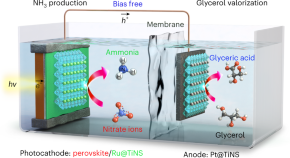
Bias-free solar NH 3 production by perovskite-based photocathode coupled to valorization of glycerol
Photoelectrocatalytic nitrate reduction offers an opportunity for a lower carbon route to ammonia production but has not been realized due to poor efficiency. Here an efficient modified lead halide perovskite photocathode is coupled to glycerol oxidation anode resulting in a bias-free photocurrent density greater than 20 mA cm −2 .
- Ahmad Tayyebi
- Rashmi Mehrotra
- Ji-Wook Jang
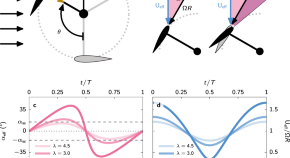
Optimal blade pitch control for enhanced vertical-axis wind turbine performance
Vertical-axis wind turbines offer untapped opportunities for energy generation but suffer from dynamic stall in strong winds. Here, authors implement individual blade pitch control to benefit from stall vortices instead of suppressing them, tripling the power coefficient and reducing load transients by 70%.
- Sébastien Le Fouest
- Karen Mulleners
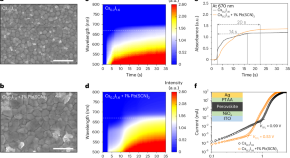
Suppression of phase segregation in wide-bandgap perovskites with thiocyanate ions for perovskite/organic tandems with 25.06% efficiency
Wide-bandgap perovskite solar cells suffer from phase segregation. Zhang et al. show that thiocyanate ions overcome the issue by occupying iodide vacancies while regulating crystallization, enabling perovskite/organic tandem cells with 25.06% efficiency.
- Zhichao Zhang
- Weijie Chen
- Yongfang Li
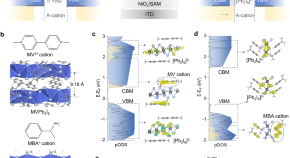
Harnessing strong aromatic conjugation in low-dimensional perovskite heterojunctions for high-performance photovoltaic devices
The large organic cations in low-dimensional perovskite often introduces carrier mobility anisotropy and impedes charge transport. Here, authors report perovskite heterojunction with strong aromatic conjugated perovskites, realizing certified efficiency of over 25% in stable perovskite solar cells.
- Zonglong Zhu
News and Comment

How climate change is affecting global timekeeping
Melting polar ice could delay major time adjustment, and the strange connection between brain inflammation and memory.
- Elizabeth Gibney
- Nick Petrić Howe
Delivery of CO
- James Gallagher
Tolerance testing
- Giulia Tregnago

A view of wind turbines drives down home values — but only briefly
House prices drop by 1% if wind turbines are close and visible, but they rebound quickly.
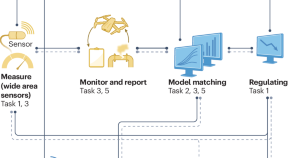
Sensing fugitive hydrogen emissions
For the transition to a sustainable energy sector, massive hydrogen production and use is crucial. There is growing awareness of a connection between an indirect global warming potential and the production of hydrogen, so its fugitive emissions must be addressed. This Comment emphasizes the need for affordable hydrogen-sensing methods to benefit safety, energy efficiency and the climate.
- Sudipta Chatterjee
- Kuo-Wei Huang
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
April 5, 2024
Renewable Energy Shatters Records in the U.S.
The U.S. has never had as much wind, solar and hydropower. But experts say it’s not enough to meet future electricity demand
By Benjamin Storrow & E&E News

CLIMATEWIRE | Renewable energy is breaking records across the U.S.
Wind and solar accounted for 76 percent of electricity production in Texas’ primary power grid last Friday. The next day, New England set its own record, with 45 percent of its power coming from wind, solar and hydropower.
Within the last month, grid operators have reported record solar generation in the Midwest, record wind generation in New York and record renewable generation in the mid-Atlantic, according to data collected by GridStatus.io , a website that monitors electricity markets around the country.
On supporting science journalism
If you're enjoying this article, consider supporting our award-winning journalism by subscribing . By purchasing a subscription you are helping to ensure the future of impactful stories about the discoveries and ideas shaping our world today.
The milestones represent a snapshot in time, a mere hour of a day when renewable generation surges on one of the country’s regional electric grids, all of which remain firmly dependent on fossil fuels.
But together they paint a picture of an evolving power system. Wind generated almost twice the electricity as coal last year on the grid managed by the Electric Reliability Council of Texas, which serves about 90 percent of the state's power demand. Rooftop solar regularly tops generation in New England on sunny days.
Even gas- and coal-rich grids like PJM Interconnection, which runs through states from New Jersey to Illinois, have started to observe a shift. All of PJM’s top 10 days for solar generation have occurred within the last two months, though renewables remain a fraction of the grid's total power mix.
“It shows how quickly you can add these new resources,” said Ric O’Connell, executive director of GridLab, a clean energy consulting firm. “We can move fast. These grids do evolve quickly.”
The records owe in part to the changing season. Mild spring temperatures mean demand eases for heating or cooling, resulting in less electricity consumption. That, coupled with growing solar and wind generation, pushes up the percentage of green energy on grids across the country.
But the records also reflect several years of robust renewable growth. Developers installed 60 gigawatts of new solar capacity nationally between 2019 and 2023, double the amount installed in all years prior, according to Energy Information Administration data. Wind capacity is up 57 percent over that period, despite a lag in installations last year, the federal figures show.
Easing of supply chain constraints, coupled with federal tax credits for clean energy, have accelerated the trend. The U.S. installed 32.7 GW of new battery, solar and wind capacity last year, beating the record of 31.5 GW set in 2021, EIA data shows.
But whether renewables can continue to grow at the rate needed to drive down emissions and meet an expected spike in electricity demand is an open question. The Rhodium Group, an energy modeling firm, estimates the U.S. needs to install between 32 GW and 95 GW of new wind and solar capacity every year through 2035 in order to cut emissions 32 percent to 51 percent compared to 2005 levels.
“From a climate perspective these records are great, but they are still not enough to get emissions down to the level we want,” said Melissa Lott, a professor who studies the power sector at Columbia University’s Climate School.
The renewable records come at a critical moment. Grid operators are sounding alarms about their ability to keep pace with projected increases in electricity demand, which is expected to grow due to a proliferation of new data centers, electric vehicles and heat pumps.
PJM anticipates that electricity demand will grow by an average of 2.3 percent annually over the next 10 years, up from the 1.4 percent growth it predicted last year. ERCOT set 10 new demand records over a one-month period last summer. The New York Independent System Operator thinks the combination of rising demand and retiring fossil fuel generators could leave New York City facing a shortage of energy supplies by 2026.
"We need to grow the resources much quicker than we are,” said Kevin Lanahan, vice president of external affairs at the New York Independent System Operator, where renewable generation reached a record 44 percent of load March 17.
There is a growing imbalance between new facilities coming online and the amount of power needed to keep the system running, he said.
He added, “we’re concerned about that growing imbalance and we need to site more resources on the system to fill this growing gap.”
Renewables and other carbon-free electricity sources need to grow faster than electricity demand for emissions to fall. But new projects face challenges connecting to the grid. They range from clogged interconnection queues, with grid operators facing a stack of applications from developers seeking to plug in their projects, to siting and transmission constraints.
Still, the renewable records posted in recent weeks show that it is possible to move quickly to address those challenges, said GridLab’s O’Connell. He pointed to recent installations in Texas and California.
ERCOT has added more than 14 GW of new solar since 2020, or about 16 percent of the Texas grid’s peak demand. Almost 7.5 GW of new battery capacity was added to the California Independent System Operator’s system between 2021 and 2023, or about 14 percent of the Golden State’s peak demand.
“That’s a lot,” O’Connell said. “The future is here.”
This story also appears in Energywire.
Reprinted from E&E News with permission from POLITICO, LLC. Copyright 2024. E&E News provides essential news for energy and environment professionals.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The wind, the sun, and Earth are sources of renewable energy . These energy sources naturally renew, or replenish themselves. Wind, sunlight, and the planet have energy that transforms in ways we can see and feel. We can see and feel evidence of the transfer of energy from the sun to Earth in the sunlight shining on the ground and the warmth we ...
In contrast, renewable energy sources accounted for nearly 20 percent of global energy consumption at the beginning of the 21st century, largely from traditional uses of biomass such as wood for heating and cooking.By 2015 about 16 percent of the world's total electricity came from large hydroelectric power plants, whereas other types of renewable energy (such as solar, wind, and geothermal ...
Hydropower: For centuries, people have harnessed the energy of river currents, using dams to control water flow. Hydropower is the world's biggest source of renewable energy by far, with China ...
In contrast, most renewable energy sources produce little to no global warming emissions. Even when including "life cycle" emissions of clean energy (ie, the emissions from each stage of a technology's life—manufacturing, installation, operation, decommissioning), the global warming emissions associated with renewable energy are minimal [].
There are many ways to use renewable energy. Most of us already use renewable energy in our daily lives. Hydropower Hydropower is our most mature and largest source of renewable power, pro-ducing about 10 percent of the nation's electricity. Existing hydropower capacity is about 77,000 megawatts (MW). Hydro-power plants convert the energy in ...
Renewable energy sources are growing quickly and will play a vital role in tackling climate change. This page was first published in December 2020 and last revised in January 2024. Since the Industrial Revolution, the energy mix of most countries across the world has become dominated by fossil fuels. This has major implications for the global ...
Renewable energy is energy derived from natural sources that are replenished at a higher rate than they are consumed. Sunlight and wind, for example, are such sources that are constantly ...
The term "renewable" encompasses a wide diversity of energy resources with varying economics, technologies, end uses, scales, environmental impacts, availability, and depletability. For example, fully "renewable" resources are not depleted by human use, whereas "semi-renewable" resources must be properly managed to ensure long-term ...
Renewable Energy Availability. A recent study concluded that renewable energy sources, based on wind, water, and sunlight (abbreviated as WWS; not including biomass), could provide all new energy globally by 2030, and replace all current non-renewable energy sources by 2050 (Jacobson and Delucchi 2011, p. 1154).
Even if just one multi-billion dollar company transitioned to renewable energy as their main source of energy, that would make a massive difference in the carbon emissions released. Any argument made against this topic should be immediately dismissed because this is the only solution. ... Essay on Renewable Energy. (2022, December 27 ...
Renewable energy sources include solar, wind, hydroelectric, and geothermal energy. They also include biomass and hydrogen fuels. These energy sources are sustainable and generate fewer greenhouse gas emissions than fossil fuels. Renewable and nonrenewable energy sources. Clockwise from top left: a solar power station, a wind farm, a ...
All energy sources have some impact on our environment. Fossil fuels—coal, oil, and natural gas—do substantially more harm than renewable energy sources by most measures, including air and water pollution, damage to public health, wildlife and habitat loss, water use, land use, and global warming emissions.. However, renewable sources such as wind, solar, geothermal, biomass, and ...
The United States is producing more energy from fossil fuels and has ticked up production of renewable sources such as wind and solar. A large majority of Americans (72%) say the United States is producing more energy than it did 20 years ago. Far smaller shares say the U.S. is producing the same level (17%) or less energy (10%) than it did 20 ...
Request Information. To learn more about the MA in Sustainable Energy (online) and download a brochure, fill out the fields below, or call +1 410-648-2495 or toll-free at +1 888-513-5303 to talk with one of our admissions counselors. Johns Hopkins University has engaged AllCampus to help support your educational journey.
The use of renewable energy resources, such as solar, wind, and biomass will not diminish their availability. Sunlight being a constant source of energy is used to meet the ever-increasing energy need. This review discusses the world's energy needs, renewable energy technologies for domestic use, and highlights public opinions on renewable energy. A systematic review of the literature was ...
According to a study, a 1% increase in the use of renewable energy increases economic growth by 0.21%. This gives socio-economic stability. Due to a lack of supply of fossil fuels and quick depletion of natural resources, prices for nonrenewable energy keep increasing. In contrast, green energy is limitless and can be produced locally.
Renewable energy, green energy, or low-carbon energy is energy from renewable resources that are naturally replenished on a human timescale.Renewable resources include sunlight, wind, the movement of water, and geothermal heat. Although most renewable energy sources are sustainable, some are not.For example, some biomass sources are considered unsustainable at current rates of exploitation.
The adoption of renewable energy, generated from natural resources like sunlight, wind, tides, plant growth and geothermal heat, is a key strategy in combatting greenhouse gas emission-fueled climate change, which the World Economic Forum identifies each year as a serious global risk. Traditional fossil fuels like coal, natural gas and ...
Tidal power generators are the most predictable and affordable source of energy. For example, The Bay of Fundy in Canada has the world's highest tides, which reach speeds up to 17 kph generating 700 kilowatts of power compared to 600 kilowatts produced by wind turbines (Meyer 66). Therefore, the global implementation of renewable sources is a ...
The first recorded use of renewable energy was harnessing wind power to drive ships over water about 7000 years ago (Darling). However, renewable energy has been around as long as Earth has existed: wind, sun, geothermal, biomass and many more. Clean energy sources can be harnessed to produce electricity, process heat, fuel and other chemicals ...
Renewable energy is energy that comes from sources that are readily replenishable on short-timescales. Examples of these are solar radiation, wind, and biomass. Wide band gap perovskite solar ...
Renewable Energy Argumentative Essay. This essay sample was donated by a student to help the academic community. Papers provided by EduBirdie writers usually outdo students' samples. Recently, some people believe that nuclear, solar, wind and hydropower provide cheap and clean energy. The advantages of these sources of power far outweigh their ...
Renewable Energy. CLIMATEWIRE | Renewable energy is breaking records across the U.S. Wind and solar accounted for 76 percent of electricity production in Texas' primary power grid last Friday ...
Compared to other bioenergy sources, sorghum straw pellets could potentially surpass cane bagasse (26.3%) and wood (23.4%) in contributing to Australia's bioelectricity potential. This potential could enable Australia to provide and export clean, reliable, and affordable energy while creating new income opportunities for sorghum growers.
A smart grid is a power grid that integrates user-generated renewable electricity sources such as solar panels and wind turbines with the company's main grid. This small generator is called a microgrid. A smart meter is needed in the 4.0 revolution era to control and determine the use of voltage, current, power, and electrical energy used and integrate two energy sources at once from renewable ...