

LibAnswers: Referencing
How do i reference gibbs' reflective cycle in apa (7th ed.).
Wherever possible you should use the original work.
Gibbs, G. (1988). Learning by doing: A guide to teaching and learning methods. Further Education Unit.
Secondary referencing If you have not read the original you must make this clear by referring to the work in which you found the reference. In the reference list only include details of the work that you read.
In-text citation Gibbs’ reflective cycle (1988) as cited in Jasper (2013) shows that… or Gibbs’ reflective cycle is a seminal theory in reflective practice (Gibbs, 1988, as cited in Jasper, 2013).
In the reference list Jasper, M. (2013). Beginning reflective practice (2nd ed.). Cengage Learning.
- APA (7th ed.)
- Paramedics APA (7th ed.)
- Nursing APA (7th ed.)
- Social Work APA (7th ed.)
- Last Updated May 18, 2021
- Views 55889
- Answered By Elen Davies
FAQ Actions
- Share on Facebook
Comments (0)

- Schools & departments

Gibbs' Reflective Cycle
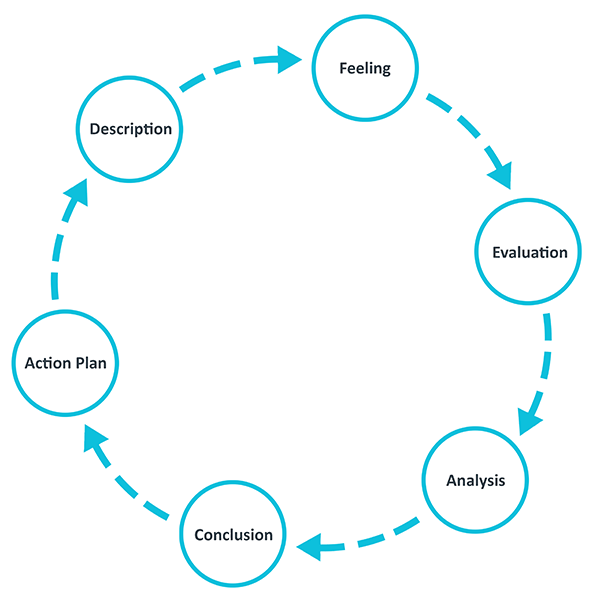
One of the most famous cyclical models of reflection leading you through six stages exploring an experience: description, feelings, evaluation, analysis, conclusion and action plan.
Gibbs' Reflective Cycle was developed by Graham Gibbs in 1988 to give structure to learning from experiences. It offers a framework for examining experiences, and given its cyclic nature lends itself particularly well to repeated experiences, allowing you to learn and plan from things that either went well or didn’t go well. It covers 6 stages:
- Description of the experience
- Feelings and thoughts about the experience
- Evaluation of the experience, both good and bad
- Analysis to make sense of the situation
- Conclusion about what you learned and what you could have done differently
- Action plan for how you would deal with similar situations in the future, or general changes you might find appropriate.
Below is further information on:
- The model – each stage is given a fuller description, guiding questions to ask yourself and an example of how this might look in a reflection
- Different depths of reflection – an example of reflecting more briefly using this model
This is just one model of reflection. Test it out and see how it works for you. If you find that only a few of the questions are helpful for you, focus on those. However, by thinking about each stage you are more likely to engage critically with your learning experience.
This model is a good way to work through an experience. This can be either a stand-alone experience or a situation you go through frequently, for example meetings with a team you have to collaborate with. Gibbs originally advocated its use in repeated situations, but the stages and principles apply equally well for single experiences too. If done with a stand-alone experience, the action plan may become more general and look at how you can apply your conclusions in the future.
For each of the stages of the model a number of helpful questions are outlined below. You don’t have to answer all of them but they can guide you about what sort of things make sense to include in that stage. You might have other prompts that work better for you.
Description
Here you have a chance to describe the situation in detail. The main points to include here concern what happened. Your feelings and conclusions will come later.
Helpful questions:
- What happened?
- When and where did it happen?
- Who was present?
- What did you and the other people do?
- What was the outcome of the situation?
- Why were you there?
- What did you want to happen?
Example of 'Description'
Here you can explore any feelings or thoughts that you had during the experience and how they may have impacted the experience.
- What were you feeling during the situation?
- What were you feeling before and after the situation?
- What do you think other people were feeling about the situation?
- What do you think other people feel about the situation now?
- What were you thinking during the situation?
- What do you think about the situation now?
Example of 'Feelings'
Here you have a chance to evaluate what worked and what didn’t work in the situation. Try to be as objective and honest as possible. To get the most out of your reflection focus on both the positive and the negative aspects of the situation, even if it was primarily one or the other.
- What was good and bad about the experience?
- What went well?
- What didn’t go so well?
- What did you and other people contribute to the situation (positively or negatively)?
Example of 'Evaluation'
The analysis step is where you have a chance to make sense of what happened. Up until now you have focused on details around what happened in the situation. Now you have a chance to extract meaning from it. You want to target the different aspects that went well or poorly and ask yourself why. If you are looking to include academic literature, this is the natural place to include it.
- Why did things go well?
- Why didn’t it go well?
- What sense can I make of the situation?
- What knowledge – my own or others (for example academic literature) can help me understand the situation?
Example of 'Analysis'
Conclusions.
In this section you can make conclusions about what happened. This is where you summarise your learning and highlight what changes to your actions could improve the outcome in the future. It should be a natural response to the previous sections.
- What did I learn from this situation?
- How could this have been a more positive situation for everyone involved?
- What skills do I need to develop for me to handle a situation like this better?
- What else could I have done?
Example of a 'Conclusion'
Action plan.
At this step you plan for what you would do differently in a similar or related situation in the future. It can also be extremely helpful to think about how you will help yourself to act differently – such that you don’t only plan what you will do differently, but also how you will make sure it happens. Sometimes just the realisation is enough, but other times reminders might be helpful.
- If I had to do the same thing again, what would I do differently?
- How will I develop the required skills I need?
- How can I make sure that I can act differently next time?
Example of 'Action Plan'
Different depths of reflection.
Depending on the context you are doing the reflection in, you might want use different levels of details. Here is the same scenario, which was used in the example above, however it is presented much more briefly.
Adapted from
Gibbs G (1988). Learning by Doing: A guide to teaching and learning methods. Further Education Unit. Oxford Polytechnic: Oxford.

- Calculators
- Swot Analysis
- Pestle Analysis
- Five Forces Analysis
- Organizational Structure
- Copywriting
- Research Topics
- Student Resources
Services We Provide

Resources We Provide

Login / Register

- Learn From Your Past Experience with Gibb’s Reflective Cycle
- Exploring Different Types of Reflection Models with Examples
You must have heard about Gibbs' reflective cycle. It is a widely prominent reflective cycle that helps individuals to work through past experiences and improve future practices. Gibbs' The reflective cycle was developed by Graham Gibbs in 1988 with the main aim of structuring individual learnings from past experiences (Markkanen et al., 2020). Effective utilization of this cycle offers a wide opportunity to examine past experiences and improve future actions.
Table of Contents
Six stages of gibbs' reflective cycle.
- Example of Gibbs' reflective cycle
Hence, the efficacious use of Gibbs' reflective cycle helps individuals to learn from past experiences that went well as well as past experiences that did not. The 6 stages of Gibbs' cycle include description, feelings, evaluation, analysis, conclusion, and action plan (Smith & Roberts, 2015).
For each step of this framework, you can work on a set of helpful questions given below to properly reflect on your past experiences and situations.
Stage 1: Description
The first step in Gibbs' reflective cycle is a description where you get an opportunity to properly describe a situation based on your experience. The following questions can assist you in describing your experience are
- What happened? In this, you will explain the factual information about the experience you want to reflect upon.
- Why did it happen? In this, you will underline the main reason behind the occurrence of the event.
- What did you do? While answering this question, you will highlight all the actions taken by you.
- Who was present? In this, you will highlight all the people that were present during the event.
- What were the major outcomes? In this, you will underline the results of the actions that were taken by you.
Using these questions, you will provide complete background information about an incident as well as a factual description of the event you want to reflect upon.
Stage 2: Feelings
The second step in Gibbs’ reflective cycle is an analysis of your feelings where you can describe your thoughts as well as feelings in detail to reflect on the corresponding experience of your feelings. You can reflect on this phase on the basis of a few assisting questions given below:
- What did you feel? In this section, you will highlight your feelings during the experience.
- Why did you feel this way? You will highlight the major reasons behind feeling the way you were feeling.
- How did other external factors influence your feelings? In this section, you will underline the positive or negative influence of other external factors such as the environment, and other involved people on your feelings.
- How did other internal factors influence your feelings? In this section, you will highlight the influence of various internal factors such as mindset, attitude, and physical or mental health.
These questions will help you to describe your feelings and the way in detail and will also assist in making the reader understand your emotional aspect from the incident you are reflecting upon.
Stage 3: Evaluation
In the evaluation phase, you get a chance to properly evaluate what worked well and what didn't work well. This phase includes the evaluation of experiences from both good as well as bad points, allowing you to mentally create a report of the experience. Below given are the questions that can be answered in this phase
- What worked well? In this, you will highlight the positive outcomes of your actions throughout the experience.
- What didn't work well? This will highlight all the negative outcomes of your actions taken by you throughout the experience.
- What did you contribute? Through this question, you will highlight your contribution to the whole experience.
- What did others contribute? While answering this question, you will highlight the actions of others that were involved in the situation.
- What was missing? In this, you will highlight the actions that were missing in the experience as per your opinion.
Based on these questions, you can honestly and objectively evaluate the past situation which will also help you in setting a base for future actions.

Stage 4: Analysis
In an analysis phase, you can make sense of a whole situation and determine the exact meaning of a situation along with the reasons for its success or failure. Some helpful questions for the analysis phase of Gibbs’ reflective cycle include
- Why did things not work well? In this, you will point out the reason as per your knowledge that contributed to the failures of your actions in your experience.
- Why did things go well? Through this section, you will highlight the reasons behind the success of your actions.
- What is the exact meaning that we can drive from a situation? While answering this question, you will highlight the overall analysis of the situation.
Based on the analysis, you can get a clear picture of the situation and ensure that every aspect of the situation is covered and understood meticulously.
Stage 5: Conclusion
After a proper situation analysis, you can also conclude the whole situation by reflecting on your learnings. In this phase, you can highlight changes that you need to make to your actions while dealing with future situations. In this phase, a list of questions includes
- What did you learn? In this, you will highlight all of your main learnings of the situation.
- What skills do you need to gain to handle situations more effectively? Through this, you will highlight the requirements of the skills for handling the situation better in the future.
- What else could you have done to deal with situations differently? In this, you will highlight the alternative actions that you could have taken to respond to the same situation in a different manner.
After the analysis, in the conclusion phase, using the above questions, you will clearly outline your learnings and the skills gained through the experience.
Stage 6: Action plan
In the action plan stage in Gibbs’ reflective cycle, you can plan to deal with future situations. It is an important phase of this reflective cycle as this phase helps to determine ways to deal with similar situations in the future and actions that you need to take to improve your ability to deal with various situations. Some questions that can be considered in this stage include
- How will you deal with this situation more effectively in the future? In this, you will highlight the actions that you have thought of that will help you in dealing with a similar situation differently in the future.
- How will you develop your skills and abilities to deal with similar situations? In this situation, you will highlight the methods in which you will develop the skills for dealing with situations more effectively.
After understanding the cycle, let us now take an example of reflective practice in health education to reflect on the learning situation using Gibbs’ reflective cycle.
Gibbs’ reflective cycle example in health education
Case assessment - This reflective example will highlight the experience of students in a group task of completing a health project. In this, a student will reflect upon a group task assigned to students during their MSc in health practice.
While doing my MSc in health practice, I was required to engage in various group work assignments and during a certain group work task, my team members decided to divide tasks among group members. All team members encouraged me to divide the tasks among the team. I divided tasks among team members according to their knowledge regarding various healthcare practices to ensure that all tasks are completed within a set deadline. All team members encouraged me to divide the tasks among the team. I divided tasks among team members according to their knowledge regarding various healthcare practices to ensure that all tasks are completed within a set deadline. However, I failed to consider the risk of various contingencies in completing projects and the same occurred when one of our team members was hospitalized due to some health emergency which resulted in a lack of task completion assigned to that team member. My whole team was present when I got a call from the injured team member about the accident that occurred to him. This then resulted in an increased burden to complete tasks among team members and failure to complete a task on time.
Before beginning the health project, I was very confident regarding my team management capabilities. I felt that our team will be able to complete assigned tasks on time due to my strong knowledge and abilities. I was already feeling very guilty that our project got delayed because of my lack of planning but the external factors made me feel even worse. Other than that, I felt like it was my overconfidence that made me feel more guilty because things did not work as planned.
During the group health project, a thing that worked well was the effort of team members to complete work within the extended deadline was cooperation as well as motivation among all team members. However, I believe that the hospitalization of one team member resulted in a lack of task completion on time. I felt that contingency planning is one most important requirement in a team project which was missing in this project. Thus, I believe that I am also responsible for the bad repercussions of this situation as I failed to properly plan and did not consider the risks of contingencies in a group. But still, till the end, everyone contributed effectively and did not lose hope till the end and gave their best.
I think the major reasons behind the successful completion were group efforts, cooperation abilities, self-identification of strengths, effective division of tasks, and ability to help others. However, the only thing that created a problem in completing a project is a lack of time management and planning capabilities. Through this whole experience, I believe that I need to focus on improving my time management skills as well as leading the ability to effectively manage group tasks.
After getting into this group health project, I got to know that time management and contingency planning are important skills that every project manager needs to possess to effectively manage group tasks. I also found that team management is possible only through the cooperation of team members as well as their effort to give the best results to a team project. I learned that as a project manager, it is always better to have a contingency plan ready for implementation than to develop one as risk is taking its toll (Heimann, J. F. 2000). However, I found that various problems can arise in a group task which could be managed effectively by making contingency plans for such situations in advance. I would have prepared contingency plans in the beginning and I believe that it would have helped me in dealing with situations differently.
In order to deal with this situation in the future, I have decided that I will use various time management tools such as PERT and CPM while planning various group tasks to keep separate times for various contingencies. For enhancing my time management and planning skills, I have decided to use time management skills such as making time tables and assigning time blocks for each task. If a similar situation occurs again in the future, I will ensure that in the planning phase only, I take time for contingency planning and plan things accordingly.
How to reference Gibbs reflective cycle?
To reference Gibbs' reflective cycle, include the author's name "Gibbs" and the publication year (if available) in parentheses. For instance, in APA style, it would be: (Gibbs, 1988). If you use a direct quote, add the page number as well.
Can Gibbs' Reflective Model be used in any profession?
Yes, the model is versatile and applicable in various professions and fields, including education, healthcare, social work, and more.
What are the disadvantages of Gibb's reflective cycle?
Gibbs' reflective cycle lacks a strong theoretical foundation and may not suit complex or long-term learning experiences. Some of you may even find its structured approach restrictive that could potentially overlook unique aspects of individual experiences. Additionally, it may not be universally applicable to various learning contexts.
Previous Model
Markkanen, P., Välimäki, M., Anttila, M., & Kuuskorpi, M. (2020). A reflective cycle: Understanding challenging situations in a school setting. Educational Research, 62(1), 46-62. https://doi.org/10.1080/00131881.2020.1711790
Smith, J., & Roberts, R. (2015). Reflective Practice. Vital Signs For Nurses, 222-230. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119139119.ch14
Heimann, J. F. (2000). Contingency planning as a necessity. Paper presented at Project Management Institute Annual Seminars & Symposium, Houston, TX. Newtown Square, PA: Project Management Institute.
Copyright © 2023 CrowJack. All Rights Reserved

How it works
For Business
Join Mind Tools
Article • 5 min read
Gibbs' Reflective Cycle
Helping people learn from experience.
By the Mind Tools Content Team

Many people find that they learn best from experience.
However, if they don't reflect on their experience, and if they don't consciously think about how they could do better next time, it's hard for them to learn anything at all.
This is where Gibbs' Reflective Cycle is useful. You can use it to help your people make sense of situations at work, so that they can understand what they did well and what they could do better in the future.
What Is Gibbs' Reflective Cycle?
Professor Graham Gibbs published his Reflective Cycle in his 1988 book " Learning by Doing ." It's particularly useful for helping people learn from situations that they experience regularly, especially when these don't go well.
Gibbs' cycle is shown below.
Figure 1 – Gibbs' Reflective Cycle
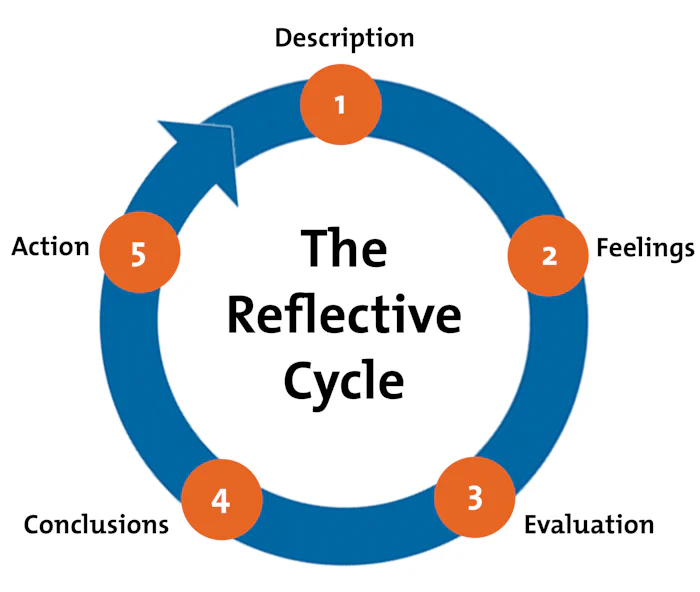
From "Learning by Doing" by Graham Gibbs. Published by Oxford Polytechnic, 1988.
Gibbs' original model had six stages. The stage we haven't covered here is "Analysis" – we've included this as part of the Evaluation stage.
Using the Model
You can use the model to explore a situation yourself, or you can use it with someone you're coaching – we look at coaching use in this article, but you can apply the same approach when you're on your own.
To structure a coaching session using Gibbs' Cycle, choose a situation to analyze and then work through the steps below.
Step 1: Description
First, ask the person you're coaching to describe the situation in detail. At this stage, you simply want to know what happened – you'll draw conclusions later.
Consider asking questions like these to help them describe the situation:
- When and where did this happen?
- Why were you there?
- Who else was there?
- What happened?
- What did you do?
- What did other people do?
- What was the result of this situation?
Step 2: Feelings
Next, encourage them to talk about what they thought and felt during the experience. At this stage, avoid commenting on their emotions.
Use questions like these to guide the discussion:
- What did you feel before this situation took place?
- What did you feel while this situation took place?
- What do you think other people felt during this situation?
- What did you feel after the situation?
- What do you think about the situation now?
- What do you think other people feel about the situation now?
It might be difficult for some people to talk honestly about their feelings. Use Empathic Listening at this stage to connect with them emotionally, and to try to see things from their point of view.
You can use the Perceptual Positions technique to help this person see the situation from other people's perspectives.
Step 3: Evaluation
Now you need to encourage the person you're coaching to look objectively at what approaches worked, and which ones didn't.
- What was positive about this situation?
- What was negative?
- What went well?
- What didn't go so well?
- What did you and other people do to contribute to the situation (either positively or negatively)?
If appropriate, use a technique such as the 5 Whys to help your team member uncover the root cause of the issue.
Step 4: Conclusions
Once you've evaluated the situation, you can help your team member draw conclusions about what happened.
Encourage them to think about the situation again, using the information that you've collected so far. Then ask questions like these:
- How could this have been a more positive experience for everyone involved?
- If you were faced with the same situation again, what would you do differently?
- What skills do you need to develop, so that you can handle this type of situation better?

Step 5: Action
You should now have some possible actions that your team member can take to deal with similar situations more effectively in the future.
In this last stage, you need to come up with a plan so that they can make these changes.
Once you've identified the areas they'll work on, get them to commit to taking action, and agree a date on which you will both review progress.
Frequently Asked Questions About Gibbs' Reflective Cycle
What is purpose of Gibbs' Reflective Cycle?
The reflective cycle is a way to better learn from experience. It can be used to help people learn from mistakes, to make sense of situations, and analyse and refelct on their reactions to different situations.
What are the six stages of reflection?
The stages of Gibbs' Reflective Cycle are the following: descrition, feelings, evaluation, conclusion, and action. In the original model Gibbs included a sixth stage, analysis, which we've included in the evaluation stage.
What is the difference between Gibbs and Kolb's reflective cycles?
David Kolb's cycle has only four stages: concrete experience, reflective observation, abstract conceptualization, and active experimentation. Kolb's model is more about explaining the concept of what he calls "experiential learning" – whereas Gibbs' cycle is an attempt to provide a practical method for learning from experience.
This tool is structured as a cycle, reflecting an ongoing coaching relationship. Whether you use it this way depends on the situation and your relationship with the person being coached.
Graham Gibbs published his Reflective Cycle in 1988. There are five stages in the cycle:
- Description.
- Evaluation.
- Conclusions.
You can use it to help team members think about how they deal with situations, so that they can understand what they did wel and where they need to improve.
You've accessed 1 of your 2 free resources.
Get unlimited access
Discover more content
The addie model.
Developing Learning Sessions from the Ground Up
Five Moments of Learning Need
Increase the Value of Learning Tools By Providing Them When Needed
Add comment
Comments (0)
Be the first to comment!

Get 20% off your first year of Mind Tools
Our on-demand e-learning resources let you learn at your own pace, fitting seamlessly into your busy workday. Join today and save with our limited time offer!
Sign-up to our newsletter
Subscribing to the Mind Tools newsletter will keep you up-to-date with our latest updates and newest resources.
Subscribe now
Business Skills
Personal Development
Leadership and Management
Member Extras
Most Popular
Newest Releases

Pain Points Podcast - Balancing Work And Kids

Pain Points Podcast - Improving Culture
Mind Tools Store
About Mind Tools Content
Discover something new today
Pain points podcast - what is ai.
Exploring Artificial Intelligence
Pain Points Podcast - How Do I Get Organized?
It's Time to Get Yourself Sorted!
How Emotionally Intelligent Are You?
Boosting Your People Skills
Self-Assessment
What's Your Leadership Style?
Learn About the Strengths and Weaknesses of the Way You Like to Lead
Recommended for you
The value curve model.
Chart a New Direction for Your Company
Business Operations and Process Management
Strategy Tools
Customer Service
Business Ethics and Values
Handling Information and Data
Project Management
Knowledge Management
Self-Development and Goal Setting
Time Management
Presentation Skills
Learning Skills
Career Skills
Communication Skills
Negotiation, Persuasion and Influence
Working With Others
Difficult Conversations
Creativity Tools
Self-Management
Work-Life Balance
Stress Management and Wellbeing
Coaching and Mentoring
Change Management
Team Management
Managing Conflict
Delegation and Empowerment
Performance Management
Leadership Skills
Developing Your Team
Talent Management
Problem Solving
Decision Making
Member Podcast

- Gibbs' Reflective Cycle
May 9, 2023
Delve into Gibbs' Reflective Cycle, a powerful tool fostering critical thinking, deep learning, and professional growth through reflection.
Main, P (2023, May 09). Gibbs' Reflective Cycle. Retrieved from https://www.structural-learning.com/post/gibbs-reflective-cycle
What is Gibbs' Reflective Cycle?
Gibbs' Reflective Cycle is a popular model for reflection, acting as a structured method to enable individuals to think systematically about the experiences they had during a specific situation.
Gibbs’ Reflective Cycle is a widely used and accepted model of reflection . Developed by Graham Gibbs in 1988 at Oxford Polytechnic, now Oxford Brookes University, this reflective cycle framework is widely used within various fields such as healthcare, education, and management to enhance professional and personal development . It has since become an integral part of reflective practice, allowing individuals to reflect on their experiences in a structured way.
The cycle consists of six stages which must be completed in order for the reflection to have a defined purpose. The first stage is to describe the experience. This is followed by reflecting on the feelings felt during the experience, identifying what knowledge was gained from it, analyzing any decisions made in relation to it and considering how this could have been done differently.
The final stage of the cycle is to come up with a plan for how to approach similar experiences in future.
Gibbs' Reflective Cycle encourages individuals to consider their own experiences in a more in-depth and analytical way, helping them to identify how they can improve their practice in the future.
A survey from the British Journal of Midwifery found that 63% of healthcare professionals regularly used Gibbs' Reflective Cycle as a tool for reflection.
"Reflection is a critical component of professional nursing practice and a strategy for learning through practice. This integrative review synthesizes the literature on nursing students’ reflection on their clinical experiences." – Beverly J. Bowers, RN, PhD
The Six Stages of Gibbs' Reflective Cycle
The Gibbs reflective cycle consists of six distinct stages: Description, Feelings, Evaluation, Analysis, Conclusion, and Action Plan. Each stage prompts the individual to examine their experiences through questions designed to incite deep and critical reflection. For instance, in the 'Description' stage, one might ask: "What happened?". This questioning method encourages a thorough understanding of both the event and the individual's responses to it.
To illustrate, let's consider a student nurse reflecting on an interaction with a patient. In the 'Description' stage, the student might describe the patient's condition, their communication with the patient, and the outcome of their interaction. Following this, they would move on to the 'Feelings' stage, where they might express how they felt during the interaction, perhaps feeling confident, anxious, or uncertain.
The 'Evaluation' stage would involve the student reflecting on their interaction with the patient, considering how they could have done things differently and what went well. In the 'Analysis' stage, the student might consider the wider implications of their actions and how this impacted on the patient's experience.
Finally, in the 'Conclusion' stage, the student would summarise their reflections by noting what they have learned from the experience. They would then set an 'Action Plan' for how they will apply this newfound knowledge in their future practice.
Gibbs' Reflective Cycle is a useful tool for nurses to utilize in order to reflect on their past experiences and improve their practice. By using reflective questions , nurses can actively engage in reflection and identify areas for improvement.
- Description : Start by objectively recounting the experience. Helpful questions to ask include: What happened? Who was involved? When and where did this occur?
- Feelings : Capture your emotional response to the experience. It's essential to acknowledge both positive and negative emotions, as they significantly affect our interpretation of the event.
- Evaluation : Assess the good and bad aspects of the experience. What worked well, and what didn't? What were the positive impacts and negative consequences?
- Analysis : Dig deeper into understanding why things unfolded as they did. This analysis stage is where you draw on relevant literature and professional knowledge to interpret the experience.
- Conclusion : Determine what you could have done differently and what you've learned from the experience.
- Action Plan : Develop a plan detailing what you'll do if a similar situation arises in the future.

Examples of the Reflective Model in Practice
The Gibbs Reflective Cycle, a model of reflection, can be a powerful tool for learning and personal development across various vocations. Here are five fictional examples:
- Nursing : A nurse named Jane had a challenging interaction with a patient. Using the Gibbs Reflective Cycle, she first described the situation and her initial reactions. She then reflected on her feelings, identifying negative emotions that arose. During the analysis stage, she realized that her communication skills needed improvement. She concluded that better communication could have led to a more positive outcome. Finally, she developed a personal development plan to improve her communication skills, demonstrating the positive impacts of deep level reflection.
- Teaching : A teacher, Mr. Smith, had difficulty managing his classroom . He used the Gibbs Reflective Cycle to reflect on a particularly chaotic day. He identified negative aspects of his classroom management strategy and, through critical thinking, realized that he needed to set clearer expectations for his students. He then developed a plan to implement these changes, showing how the approach to reflection can lead to actionable improvements .
- Customer Service : Sarah, a customer service representative, received constructive feedback from a customer who was dissatisfied with the service. She used the Gibbs Reflective Cycle to reflect on the interaction, identifying her feelings of disappointment and analyzing what went wrong. She concluded that she needed to improve her problem-solving skills and developed a plan to do so.
- Management : A manager, Tom, struggled with delegating tasks to his team. He used the Gibbs Reflective Cycle to reflect on a project that was delayed due to his reluctance to delegate. He identified his fear of losing control as a negative emotion and realized during the analysis stage that trust in his team was crucial. He then developed a plan to practice delegation in future projects.
- Counseling : A counselor, Dr. Lee, felt that her recent sessions with a client were not productive. She used the Gibbs Reflective Cycle to reflect on these sessions . She identified feelings of frustration and, upon analysis, realized that she needed to adjust her counseling techniques to better suit her client's needs. She then developed a plan to implement these changes.
These examples illustrate how the Gibbs Reflective Cycle can facilitate learning and reflection across different vocations, leading to personal and professional growth.
An Exploration of Gibbs' Model
Gibbs' Reflective Cycle offers a structured approach to reflection, making it a helpful tool for educators and learners alike. The model encourages critical reflection , stimulating the ability to analyze experiences through questions and transform them into valuable learning opportunities.
Experiential Learning , a concept closely tied with reflection, suggests that we learn from our experiences, particularly when we engage in reflection and active experimentation . Gibbs' model bridges the gap between theory and practice, offering a framework to capture and analyze experiences in a meaningful way.
By using Gibbs' model, educators can guide students through their reflective process , helping them extract valuable lessons from their positive and negative experiences.

Application of Gibbs' Reflective Cycle in Real-World Scenarios
The flexibility and simplicity of Gibbs' Reflective Cycle make it widely applicable in various real-world scenarios, from personal situations to professional practice.
For instance, Diana Eastcott, a nursing educator, utilized Gibbs' model to facilitate her students' reflection on their clinical practice experience. The students were encouraged to reflect on their clinical experiences, analyze their reactions and feelings, and construct an action plan for future patient interactions. This process not only enhanced their professional knowledge but also fostered personal growth and emotional resilience.
In another example, Bob Farmer, a team leader in a tech company, used Gibbs' Cycle to reflect on a project that didn't meet expectations. He guided his team through the reflective process, helping them identify areas for improvement and develop strategies for better future outcomes.
These scenarios underline the versatility of Gibbs' model, demonstrating its value in both educational and professional settings.
- ( Gibbs Reflective Cycle , University of Northampton, https://www.northampton.ac.uk )
- ( Gibbs' Reflective Cycle , Oxford Brookes University, https://www.brookes.ac.uk )
- ( Reflective Practice , San Francisco State University, https://www.sfsu.edu )

Gibbs' Reflective Cycle for Personal and Professional Development
The use of Gibbs' Reflective Cycle can have profound effects on personal and professional development. It aids in recognizing strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement, providing an avenue for constructive feedback and self-improvement.
In the context of professional development , Gibbs' model promotes continuous learning and adaptability. By transforming bad experiences into learning opportunities, individuals can enhance their competencies and skills , preparing them for similar future situations.
Moreover, the reflective cycle promotes emotional intelligence by encouraging individuals to explore their feelings and reactions to different experiences. Acknowledging and understanding negative emotions can lead to increased resilience, better stress management, and improved interpersonal relationships.

Transforming Experiences into Learning: The Role of Gibbs' Reflective Cycle
Gibbs' Reflective Cycle is a practical tool that transforms experiences into learning. It incorporates principles of Experiential Learning and emphasizes the importance of abstract conceptualization and active experimentation in the learning process.
In the field of education, Gibbs' model can significantly influence teaching methods. It encourages educators to incorporate reflective practices in their teaching methods, promoting a deeper understanding of course material and facilitating the application of theoretical knowledge in practical scenarios.
Moreover, the model can be used to encourage students to reflect on their experiences, both within and outside the classroom, and learn from them. This process fosters critical thinking, problem-solving skills, and personal growth, equipping students with the skills they need for lifelong learning.
Embracing Gibbs cycle in your organisation
Here's a list of guidance tips for organizations interested in embracing Gibbs' Reflective Cycle as their professional development model.
- Understanding the Gibbs Reflective Cycle : Before implementing, ensure that everyone in the organization understands the Gibbs Reflective Cycle model. This model consists of six stages: Description, Feelings, Evaluation, Analysis, Conclusion, and Action Plan. The goal is to encourage deep level reflection on experiences to foster learning and improve future actions.
- Promote a Culture of Reflection : Encourage everyone in the organization to incorporate reflection into their daily routine. Reflection should not be seen as an added task, but rather as an integral part of the professional development process.
- Use Real-Life Situations : For the methods in education to be effective, use real-life situations when applying the Gibbs Reflective Cycle. This way, employees can relate to the experiences, making the reflection process more relevant and meaningful.
- Encourage Sharing of Reflections : Create a safe space for individuals to share their reflections. This could be through team meetings, one-on-one sessions with managers, or through online platforms. Sharing allows for collective learning and may provide different perspectives on the same situation.
- Integrate Reflective Practice in Training Programs : Use the Gibbs Reflective Cycle in training programs. After each training session, encourage participants to go through the reflective cycle. This can help them understand the training content better and apply it in their work.
- Link Reflection to Personal Development : Connect the outcome of the reflection to personal development plans. The Action Plan stage of the cycle should feed into the individual's personal development plan, helping them identify areas of strength and areas needing improvement.
- Provide Guidance and Support : Provide guidance and support in the early stages of implementing the Gibbs Reflective Cycle. This could include providing templates or guides, or offering training on how to use the model effectively.
- Continuous Review and Feedback : Regularly review the use of the Gibbs Reflective Cycle in your organization and provide feedback. This will help ensure that the model is being used effectively and is helping individuals in their professional development.
- Model Reflective Practice : Leaders and managers should model reflective practice themselves. This shows that the organization values reflective practice and can motivate employees to engage in it themselves.
- Celebrate Success : Recognize and celebrate when reflective practice leads to positive changes or improvements. This can motivate employees to continue using the Gibbs Reflective Cycle in their professional development.

What is the Difference Between Kolb's and Gibbs' Reflective Cycle?
Both Kolb's Experiential Learning Theory and Gibbs' Reflective Cycle are influential learning methods used extensively in education and professional development. While they share similarities, such as promoting a cyclical learning process and fostering a deeper understanding of experiences, there are key differences.
Kolb's cycle consists of four stages: Concrete Experience, Reflective Observation, Abstract Conceptualization, and Active Experimentation. It focuses more on the transformation of direct experience into knowledge, emphasizing the role of experience in learning.
On the other hand, Gibbs' cycle, with its six stages, places a greater emphasis on emotions and their impact on learning. For example, a team leader might use Kolb's cycle to improve operational skills after a failed project, focusing on what happened and how to improve. However, using Gibbs' cycle, the same leader would also reflect on how the failure made them feel, and how those feelings might have influenced their decision-making.
Other notable Learning Methods and Cycles
Please note that each of these theories or models has been developed and refined over time, and they each have their own strengths and weaknesses depending on the specific learning context or goals.
Adopting the Cycle in Education
Gibbs' Reflective Cycle is an invaluable tool for nurturing professional skills and fostering personal growth. By systematically integrating this reflective model into educational practices, institutions can significantly enhance their students' professional development.
Here are seven innovative ways educational institutions can harness the power of Gibbs' Reflective Cycle to boost skill acquisition , operational proficiency, leadership capabilities, and personal skills mastery.
- Incorporate Reflective Practice in Curriculum: Educational institutions can incorporate Gibbs' Reflective Cycle into their curriculum, making it a regular part of learning. This can encourage students to develop professional skills by continually reflecting on their experiences and learning from them.
- Real-World Scenarios: By using real-world situations or case studies, educational institutions can provide practical instances for students to apply the reflective cycle. This will help them understand the type of situation they might encounter in their professional life and how to handle it.
- Promote Skill Acquisition: Gibbs' cycle can be used as a tool for skill acquisition. By reflecting on their performance in various tasks and projects, students can identify their strengths and areas that need improvement. This can aid in the development of operational skills, leadership skills, and personal skills.
- Professional Development Workshops: Educational institutions can organize workshops that focus on the application of Gibbs' Reflective Cycle for professional development. These workshops could provide hands-on training on how to use the cycle effectively.
- Reflective Journals: Encourage students to keep a reflective journal. This practice can help students regularly apply Gibbs' cycle, promoting introspection, and the development of key leadership skills.
- Mentorship Programs: Implement mentorship programs where experienced professionals guide students in applying Gibbs' Reflective Cycle. This can provide students with valuable insights into how reflective practice can enhance their professional skills.
- Assessments Based on Reflection: Design assessments that value reflective practice. Instead of solely focusing on theoretical knowledge, consider students' ability to reflect on their experiences and learn from them. This approach can make learning more engaging and relevant to real-world situations.
In the journey of life and work, we continuously encounter new situations, face challenges, and make decisions that shape our personal and professional trajectory. It's in these moments that Gibbs' Reflective Cycle emerges as a guiding compass, providing a structured framework to analyze experiences, draw insights, and plan our future course of action.
Underlying the model is the philosophy of lifelong learning. By encouraging critical reflection, it empowers us to not just passively experience life, but to actively engage with it, to question, and to learn. It's through this reflection that we move from the realm of 'doing' to 'understanding', transforming experiences into knowledge.
Moreover, the model emphasizes the importance of an action-oriented approach. It propels us to use our reflections to plan future actions, promoting adaptability and growth. Whether you're an educator using the model to enhance your teaching methods , a student exploring the depths of your learning process, or a professional striving for excellence in your field, Gibbs' Reflective Cycle can be a powerful tool.
In an ever-changing world, where the pace of change is accelerating, the ability to learn, adapt, and evolve is paramount. Reflective practices, guided by models such as Gibbs', provide us with the skills and mindset to navigate this change effectively. They empower us to learn from our past, be it positive experiences or negative experiences, and use these lessons to shape our future.
From fostering personal growth and emotional resilience to enhancing professional practice and shaping future outcomes , the benefits of Gibbs' Reflective Cycle are manifold. As we continue our journey of growth and learning, this model serves as a beacon, illuminating our path and guiding us towards a future of continuous learning and development.
- Reflection in Learning and Professional Development
- The Reflective Practitioner
- Reflective Practice: The Teacher in the Mirror
- The Impact of Reflective Practice on Teaching Effectiveness
- Reflective Practice: A Guide for Nurses and Midwives
- Reflective practice in nursing
- Learning by Doing: A Guide to Teaching and Learning Methods
- Gibbs’ Reflective Cycle
Enhance Learner Outcomes Across Your School
Download an Overview of our Support and Resources
We'll send it over now.
Please fill in the details so we can send over the resources.
What type of school are you?
We'll get you the right resource
Is your school involved in any staff development projects?
Are your colleagues running any research projects or courses?
Do you have any immediate school priorities?
Please check the ones that apply.
Download your resource
Thanks for taking the time to complete this form, submit the form to get the tool.
Reflective writing: Gibbs
- What is reflection? Why do it?
- What does reflection involve?
- Reflective questioning
- Reflective writing for academic assessment
- Types of reflective assignments
- Differences between discursive and reflective writing
- Sources of evidence for reflective writing assignments
- Linking theory to experience
- Reflective essays
- Portfolios and learning journals, logs and diaries
- Examples of reflective writing
- Video summary
- Bibliography
On this page:
Gibbs' framework “emphasises the importance of being able to generalise, to transfer knowledge and insights gained from one situation to another ” Williams et al., Reflective Writing
Gibbs' Reflective Cycle
Similar to Kolb's Learning Cycle , Gibbs (1988) Reflective Cycle also provides a structure for a reflective essay.
The structure of a piece of reflective writing, whether it be an essay or learning log entry, might consist of six components or paragraphs that follow Gibb’s cycle:
Model of Gibbs' Reflective Cycle

Criticism of this framework
Don't let it put you off using Gibbs' Reflective Cycle, but do take into account that there has been some criticism about it's lack of depth. For example, the Open University suggest the following:
Despite the further breakdown, it can be argued that this model could still result in fairly superficial reflection as it doesn’t refer to critical thinking/analysis or reflection. It doesn’t take into consideration assumptions that you may hold about the experience, the need to look objectively at different perspectives, and there doesn’t seem to be an explicit suggestion that the learning will result in a change of assumptions, perspectives or practice. You could legitimately respond to the question ‘What would you do next time?’ by answering that you would do the same, but does that constitute deep level reflection?
Open University (2014) in OpenLearn
The Reflective Cycle has six distinctive stages, leading from a description of the event/experience through to conclusions and consideration for future events.
- << Previous: Kolb
- Next: Schön >>
- Last Updated: Jan 19, 2024 10:56 AM
- URL: https://libguides.hull.ac.uk/reflectivewriting
- Login to LibApps
- Library websites Privacy Policy
- University of Hull privacy policy & cookies
- Website terms and conditions
- Accessibility
- Report a problem
404 Not found

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
If you have not read the original you must make this clear by referring to the work in which you found the reference. In the reference list only include details of the work that you read. Gibbs’ reflective cycle (1988) as cited in Jasper (2013) shows that…. Gibbs’ reflective cycle is a seminal theory in reflective practice (Gibbs, 1988 ...
Overview. Gibbs' Reflective Cycle was developed by Graham Gibbs in 1988 to give structure to learning from experiences. It offers a framework for examining experiences, and given its cyclic nature lends itself particularly well to repeated experiences, allowing you to learn and plan from things that either went well or didn’t go well.
Gibbs' The reflective cycle was developed by Graham Gibbs in 1988 with the main aim of structuring individual learnings from past experiences (Markkanen et al., 2020). Effective utilization of this cycle offers a wide opportunity to examine past experiences and improve future actions. Hence, the efficacious use of Gibbs' reflective cycle helps ...
Professor Graham Gibbs published his Reflective Cycle in his 1988 book " Learning by Doing ." It's particularly useful for helping people learn from situations that they experience regularly, especially when these don't go well. Gibbs' cycle is shown below. Figure 1 – Gibbs' Reflective Cycle. Figure 1 - Gibbs' Reflective Cycle.
Studies on teaching reflection have identified its value for training students in critical thinking and improving self-regulated learning. Considering Gibbs’ Reflective Cycle framework, in this article, we detail the design, implementation, and evaluation of a reflective writing assignment integrated into a lower-year undergraduate public ...
Gibbs’ reflective cycle Gibbs (1988, p.49) created his “structured debriefing” to support experiential learning. It was designed as a continuous cycle of improvement for a repeated experience but can also be used to reflect on a standalone experience. One of the key things about Gibbs is the acknowledgement of the importance of Feelings ...
Gibbs' Reflective Cycle is a practical tool that transforms experiences into learning. It incorporates principles of Experiential Learning and emphasizes the importance of abstract conceptualization and active experimentation in the learning process. In the field of education, Gibbs' model can significantly influence teaching methods.
Gibbs' Reflective Cycle. Similar to Kolb's Learning Cycle, Gibbs (1988) Reflective Cycle also provides a structure for a reflective essay. The structure of a piece of reflective writing, whether it be an essay or learning log entry, might consist of six components or paragraphs that follow Gibb’s cycle:
Gibbs' Mirroring Cycle was developed by Graham Gibbs includes 1988 to give structure to learning from experiences. Is provides a framework for examining experiences, and given its cyclic nature lends itself particularly well to replay experiential, allowing you to get and plan from things that be went well or didn’t go well.
Here are the key things to remember about using the Gibbs reflective cycle: It has six steps - describe, feelings, evaluate, analyse, conclusion, action plan. It structures reflections by moving from facts to analysis and meaning-making. Reflect soon after complex or emotional experiences.