The essentials of nursing leadership: A systematic review of factors and educational interventions influencing nursing leadership
Affiliations.
- 1 Faculty of Nursing, Edmonton Clinic Health Academy, University of Alberta, 11405 87 Ave NW, Edmonton, AB T6G 1C9, Canada. Electronic address: [email protected].
- 2 Department of Nutrition, Dietetics and Food, School of Clinical Sciences at Monash Health, Monash University, Level 1, 264 Ferntree Gully Rd, Notting Hill, VIC 3168, Australia.
- 3 Faculty of Nursing, Edmonton Clinic Health Academy, University of Alberta, 11405 87 Ave NW, Edmonton, AB T6G 1C9, Canada.
- 4 Faculty of Nursing, Edmonton Clinic Health Academy, University of Alberta, 11405 87 Ave NW, Edmonton, AB T6G 1C9, Canada; Technical High School of Campinas, State University of Campinas (UNICAMP), Barão Geraldo, Campinas - São Paulo 13083-970, Brazil.
- PMID: 33383271
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2020.103842
Background: Nursing leadership plays a vital role in shaping outcomes for healthcare organizations, personnel and patients. With much of the leadership workforce set to retire in the near future, identifying factors that positively contribute to the development of leadership in nurses is of utmost importance.
Objectives: To identify determining factors of nursing leadership, and the effectiveness of interventions to enhance leadership in nurses.
Design: We conducted a systematic review, including a total of nine electronic databases.
Data sources: Databases included: Medline, Academic Search Premier, Embase, PsychInfo, Sociological Abstracts, ABI, CINAHL, ERIC, and Cochrane.
Review methods: Studies were included if they quantitatively examined factors contributing to nursing leadership or educational interventions implemented with the intention of developing leadership practices in nurses. Two research team members independently reviewed each article to determine inclusion. All included studies underwent quality assessment, data extraction and content analysis.
Results: 49,502 titles/abstracts were screened resulting in 100 included manuscripts reporting on 93 studies (n=44 correlational studies and n=49 intervention studies). One hundred and five factors examined in correlational studies were categorized into 5 groups experience and education, individuals' traits and characteristics, relationship with work, role in the practice setting, and organizational context. Correlational studies revealed mixed results with some studies finding positive correlations and other non-significant relationships with leadership. Participation in leadership interventions had a positive impact on the development of a variety of leadership styles in 44 of 49 intervention studies, with relational leadership styles being the most common target of interventions.
Conclusions: The findings of this review make it clear that targeted educational interventions are an effective method of leadership development in nurses. However, due to equivocal results reported in many included studies and heterogeneity of leadership measurement tools, few conclusions can be drawn regarding which specific nurse characteristics and organizational factors most effectively contribute to the development of nursing leadership. Contextual and confounding factors that may mediate the relationships between nursing characteristics, development of leadership and enhancement of leadership development programs also require further examination. Targeted development of nursing leadership will help ensure that nurses of the future are well equipped to tackle the challenges of a burdened health-care system.
Keywords: Interventions; Leadership; Nursing workforce; Systematic Review.
Copyright © 2020. Published by Elsevier Ltd.

Publication types
- Systematic Review
- Delivery of Health Care*
- Leadership*
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
16 Emerging Nursing Leadership Issues
Brendalynn Ens; Susan Bazylewski; and Judy Boychuk Duchscher
A leader these days needs to be a host — one who convenes diversity; who convenes all viewpoints in creative processes where our mutual intelligence can come forth.
— Margaret Wheatley
Introduction
Health care in all sectors is changing at a rapid pace. As nursing leadership and nursing management evolve with this change, the need for new leadership approaches, strategies, and ideas to be actioned becomes more evident. This evolution includes two broad critical aspects:
- responsiveness, responsibility, accountability, and engagement of all nurses (regardless of position) within the health care system; and
- proactive and strategic, collaborative actions to be taken by nurse managers and others in formal leadership roles to ensure changing health care priorities are managed.
Learning Objectives
- Recognize rapidly changing approaches to nursing management and leadership within unit-level environments in Saskatchewan, in Canada, and around the world.
- Assess changing care priorities and turbulent issues within our current health system, and approaches to managing them.
- Identify the importance of business acumen skills and concepts as expectations for administrative roles.
- Recognize the importance of, and approaches for, client- and family-centred care and shared decision making as critical concepts for collaborative and effective care management.
- Determine the importance of the manager or leader’s personal journey planning for fruitful and fulfilling career development and professional growth.
- Recognize transition shock.
- Describe the five foundational elements of professional role transition for new nurses.
16.1 Transformational Leadership and Change: The Nursing Management Landscape
The rate of change is not going to slow down anytime soon. If anything, competition in most industries will probably speed up even more in the next few decades. — John P. Kotter ( 1995 )
An Evolving National and Provincial Landscape
Health care environments have evolved over the years to become highly complex with less predictability; they are constantly undergoing change and restructuring. This has been a result of many factors. The most crucial are changes in the health of populations served and their subsequent health needs paired with available resources and capacity of the health system to meet these needs. Additional factors impacting health care over the past two decades include: increases in the use of technology, a rapidly changing multigenerational workforce, changing requirements of management accountabilities, a greater emphasis on performance measurement, the challenge of managing with scarce resources, rapid growth in inter- and intra-professional teams with changes in scope of practice, and higher consumer expectations. These many factors have influenced and impacted the roles of nurse managers and leaders in ways that have not traditionally been experienced in organizations.
In July of 2011, the Canadian Nurses Association and the Canadian Medical Association published “Principles to Guide Health Care Transformation in Canada . ” In response to health care system transformation and restructuring across Canada, this document was developed to provide a common framework to guide regional and jurisdictional change. It identifies the importance of following the five principles of the Canada Health Act and incorporates the Triple Aim Framework from the Institute for Healthcare Improvement (IHI). The principles in this document are focused around three main themes: (1) enhance the health care experience, (2) improve population health, and (3) improve value for money. These three themes are now a critical focus in nurse managers’ work environments today ( CNA & CMA, 2011 ).
A second document published by the Canadian Nurses Association titled “Registered Nurses: Stepping Up to Transform Health Care” ( CNA, 2012 ) outlines many examples of how registered nurses are putting key principles into action based on the three main themes. Illustrations are provided of the innovative ways in which nurses are improving our health system across Canada today. On a national level, both publications serve as guiding framework documents for nurse managers and leaders in today’s health care environment pointing to new ways of working together across care boundaries to better meet the health needs of the populations we serve.
On a provincial level, Saskatchewan is now beginning a large-scale transformation of its health care system. In December of 2016, a report on system restructuring titled “Optimizing and Integrating Patient-Centered Care” was released by an appointed Advisory Panel of the Saskatchewan government. This panel released 14 recommendations, with a key recommendation focused on consolidating existing health authorities into one provincial authority to “achieve administrative efficiencies and improvements to patient care” ( Saskatchewan Advisory Panel, 2016 , p. 3 ).
Two earlier Saskatchewan reports that continue to influence the nursing management landscape in the province today include the “Primary Health Care Framework Report” ( Saskatchewan Health, 2012 ) and the “Patient First Review” ( Saskatchewan Health, 2009 ), both of which identify transformational opportunities for our health care system and nursing management.
Significance for Management and Leadership
These previously mentioned reports emphasize the need for nurse managers and leaders to employ the necessary skills to manage increased complexity in this changing landscape. Managers are required to think beyond the traditional silos and extend their view to focus on the patient journey along a care continuum. As our evolving Canadian health care system places more emphasis on health promotion, primary care, and community-based care, nurse leaders are also being challenged to move from organizations that have had a more controlling and directive style of management to one where engagement, empowerment, and recognition of the unique strengths of all individuals are essential. Because of system transformations, two key areas of change for nurse leaders in our health care system relate to workforce impacts and management system changes .
Workforce Impacts
Despite challenges associated with a changing workforce and increased accountability for scare resources, nurse leaders and managers provide a crucial function in creating healthy work environments. There is growing evidence in the nursing literature about the positive impact of a healthy work environment on staff satisfaction, retention, patient outcomes, and organizational performance ( Sherman & Pross, 2010 ).
A key factor in the changing workforce is the multigeneration al makeup of health care organizations today. Our current workforces consist of mixed generations at all levels. Sherman (2006 ) identifies four generations with distinct attitudes, beliefs, work habits, and expectations, noting that this age diversity will continue for years to come. Spinks and Moore (2007 ) reported on Canadian generational diversity along with cultural diversity seen at all levels of organizations.
Another major challenge facing nurse leaders today is creating healthy work environments, keeping staff engaged and effectively retained. Mate and Rakover (2016 ) examined the concept of sustaining improvement in health care, taking into account changes in the Saskatoon Health Region (now part of the Provincial Health Authority) during this time of transformation, emphasizing the critical role of leadership both at the unit level and on the front line. They emphasize that nurse leaders are local champions who must work directly with staff engagement through coaching, team building, daily communicating, and demonstrating the ability to consistently function and manage the new standard processes in order to sustain achievements.
Another workforce impact is the rapidly changing nature of intra- and interprofessional teams. As health systems transform and more attention is paid to the care continuum and the patient and family journey, there is a heightened focus on effective functioning of all teams in touch with the patient and family. Scope of practice changes required to keep up to the changing population needs have led to changes in health care providers’ role on the many teams with whom the patient intersects across the care continuum. The changing nature of teams now requires managers to be attuned to role and scope changes to ensure care is effectively coordinated and integrated during the patient journey.
As early as 1973, in his review of health care in Canada, Robertson recommended the education and deployment of nurse practitioners (NPs) across the health care system, as a way to improve continuity of care and promote efficiency in the system ( Stahlke, Rawson, & Pituskin, 2017, p. 488 ). NPs are “registered nurses who have additional education and nursing experience, which enables them to:
autonomously diagnose and treat illnesses; order and interpret tests; prescribe medications; and perform procedures.” ( Canadian Nurses Association, 2016 )
Dorothy Pringle (2007 ) stated that NPs meet the “needs of patients that are not being adequately met by the healthcare system with its current configuration of roles” ( p. 5 ). Their additional education and advanced skill set support them in providing leadership in health care. The role and performance of NPs has been found to be comparable to physicians across many aspects of care ( Stahlke et al. , 2017 ). Their study, referenced in the Research Note below, examines patient perspectives on NP care and further identifies the value of the NP within the health care system.
Research Note
Stahlke, S., Rawson, K., & Pituskin, E. (2017). Patient perspectives on nurse practitioner care in oncology in Canada. Journal of Nursing Scholarship, 49 (5), 487–495. doi:10.1111/jnu.12313
“The purpose of this study was to add to what is known about patient satisfaction with nurse practitioner (NP) care, from the perspective of breast cancer patients who were followed by an NP” ( Stahlke et al., 2017, p. 487 ).
Nine patients in an outpatient breast cancer clinic were interviewed about their experiences with NP-led care. These experiences were highly consistent among the patients. Patients were initially surprised that they would receive their ongoing care from a NP. However, as care progressed, several of them were relieved to be assigned to the NP, because those assigned to the doctor were the “sicker” people. They were seen by the NP for almost their entire course of treatment. Patients were comfortable and confident in the NP care; however, they continued to believe that the physician was in charge. The NPs were “described as being more ‘hands-on’ and it was said that ‘they look at the bigger picture . . . dealing more with the individual’ and tapping into the patient’s own strength and resources for healing” ( Stahlke et al., 2017, p. 491 ).
“Despite any initial misgivings or misunderstandings, these patients unanimously felt strongly positive about their NP-led care experiences, explaining that the NP was ‘a bonus’ (P6). That ‘the experience was wonderful’ (P5) and ‘she was just terrific with me’ (P5). One summed up the general sentiment, saying, ‘I’ve just been so fortunate. It was a gift. She’s a gift’ (P9)” ( Stahlke et al., p. 491 ).
Application to practice
Despite the role ambiguity between the physician and NP, the patients valued the leadership of the NP in their care. Patient satisfaction is documented as being closely linked with better patient outcomes ( Thrasher & Purc-Stephenson, 2008 ) and consequently the value of the NP role has become more evident. “NPs hold the potential to transform the patient experience and offer access to excellent, patient-centred care” ( Stahlke et al., p. 492 ).
Figure 16.1.1 Celebration of the Birth of the Saskatchewan Association of Nurse Practitioners

Focusing on Quality Improvement: Management systems changes
Saskatchewan has been engaged in a transformational approach to management systems through a method of provincial strategy-setting “to set priorities, determine goals for the system, establish plans to achieve the agreed-upon goals locally and provincially, and measure progress toward these goals” ( Health Quality Council, 2010). These changes have lead to an increased inclusion of nurses in decision making at various levels. As of 2013, all management staff in Saskatchewan received training on the Lean management system, a quality assurance approach. The training contained a consistent management approach for all leaders and managers in the province with standard processes that cascade up and down the management hierarchy. This approach and increased transparency of organizational direction required managers and leaders to develop and sharpen their communication skills, along with their skills for engaging staff and leading change initiatives. A greater emphasis on performance measurement also required managers and leaders to develop new skills for data collection to monitor various aspects of their unit’s performance, to learn how to display data on charts and graphs, and to use this information to tell a story about how the care aligns with and contributes to the overall provincial strategic directions. Inherent in this approach are concrete activities such as visibility walls, daily huddles at all levels of the organizations, and quarterly and annual reviews. As leaders of these activities, nurse managers and local unit leaders are required to engage staff on a daily basis as they communicate overall direction to their staff and work to build engagement in outcomes. These new processes are highly inclusive of all members of the health care team including patients and families.
Overall Impact on Leadership Styles
Chapter 1 of this textbook described various leadership styles. Strengths-based nursing leadership “redirects the focus from deficits, problems and weaknesses to use strengths that include assets and resources to manage problems and overcome and contain weaknesses” ( Gottlieb, Gottlieb , & Shamian, 2012 , p. 1 ). This style is also seen to support an environment of intra-professional teams and is a perspective that places the person and family at the centre of care.
Essential Learning Activity 16.1.1
For additional local information on the role and scope of nursing practice, consult the Saskatchewan Registered Nurses’ Association webpage on Nursing Practice Resources .
From the Field
Be able to clearly articulate what the transformed organization will look like to staff by providing concrete information on what you know as a manager, and what you don’t know, and regularly getting up-to-date, reliable information during the change.
Increase communication frequency and methods with staff during transformative change, using a variety of methods and communicating the same message a minimum of seven times.
16.2 Managing Turbulent Times and Responding to Competing Priorities
Chapter 1 of this textbook outlined the necessity for nurse leaders and scholars to study and understand the principles of a complex adaptive system ( Pangman & Pangman, 2010 ). Adding to these principles, nurse leaders need to be knowledgeable and responsive to environmental factors and changes affecting or creating turbulence within their local health care realms.
Turbulence Explained
T urbulence can be viewed as any upheaval or change (sudden or gradual) from normal. In health care, it relates to sudden or continuous times of uncertainty, or irregularities in resources, changing budgets, or adjusted strategic priorities. It involves issues impacted by changing political or administrative leadership, policy, or funding models, and by the evolution of care delivery methods, a refocusing on safety or risk issues, the introduction of new technologies or treatments, or staff attrition and adjustments in a facility. For nurse managers and leaders, it can result in competing priorities and complex decision-making processes.
In health care settings, it may be easiest for the nurse leader to consider turbulence as occurring on two separate levels: (1) broader changes at the high levels (i.e., national policy change or impact; national or provincial demographics or statistics); and (2) focused change at the more grassroots levels (i.e., regional, hospital, or unit). A change at the higher levels inevitably (and eventually) affects the grassroots levels over time.
Turbulence often intersects at the broad (federal) and local (regional) levels of health care. Both levels can have significant direct and indirect impact on local care and decision making for nurse leaders, even if at first glance they appear not to be relevant. Based on need and the span of control, nurse managers may find themselves having to respond promptly by making staffing adjustments, training staff on new skills, purchasing new equipment, decommissioning old or outdated treatments or equipment, re-directing program priorities, changing budget priorities, or even introducing new programs to ensure safety and quality. Decisions during turbulent times need to be thoughtfully and carefully made in a timely way, using the best available research, local data, and consultative sources.
Vigilance about relevant turbulence and knowing who to consult for accurate information and data will assist the nurse leader in being well informed and to anticipate turbulence before it occurs unexpectedly and leads to unanticipated results. Proactive responsiveness will support the development of trust and collaboration with colleagues and staff and ensure seamless transitions of care for clients.
Proactive Responsiveness: Being Well Informed
Being caught off-guard by unexpected turbulence requiring immediate change or a quick decision is never ideal for nurse managers or leaders. Whenever possible, they prefer to avoid having to react quickly and fix a local issue without thoughtful consideration. In order to move from reactive to proactive, nurse leaders and managers should understand both high-level and grassroots issues affecting their local health care environments.
This requires the nurse leader or manager to be well informed and know where to find the best resources. Table 16.2.1 provides credible information on emerging priorities and resources.
Domino Effects of Change
The mere introduction of a single new medical treatment, innovation, or health technology (e.g., device) into one department in a health care system can resonate and spread to other departments within that system rapidly. Hospital services that may be affected (directly or indirectly) include housekeeping, information technology/information management, health records, diagnostic imaging, laundry services, and other clinical departments. Unexpected costs, costly software updates, additional staffing, or process or protocol changes may be required to keep up with what is required from a new treatment introduction. For these reasons, it is critical for ongoing, open communication with other departments to occur in advance of any new changes.
A final turbulent adjustment for many health care systems and managers is the shift away from the focus on disease or illness and toward wellness and preventive strategies ( PHAC, 2016 ). Health care leaders encourage funding models that support preventive programs and services, including screening programs. With limited budgets, managing this shift toward preventive approaches can be costly and must be balanced with urgent acute and long-term care service needs for all clients in the health system ( CNA, 2012 ).
- Know and use appropriate and credible online sources to verify facts, statistics, and data.
- Keep abreast of changing demographics both locally and nationally to anticipate change and need for modifications to service.
- Pay attention to local government priorities for funding to support local program development and respond to shifting priorities (e.g., preventive services).
- Communicate planned changes and new ideas effectively to others to ensure you have collaboration and support to move your new ideas forward. Consult with experts and others who may be affected (directly or indirectly) with planned innovations or changes.
- Refer to the SRNA’s “ Standards and Foundation Competencies for the Practice of Registered Nurses .”
Essential Learning Activity 16.2.1
1. Imagine you are a nurse manager tasked with purchasing a new large piece of equipment for your department. Physicians and nurses from your unit just heard about it at a trade show in England. They would like you to purchase it as soon as possible to try out with patients here in Saskatchewan.
Review “ 13 Considerations for Making an Evidence-Informed Decision ” on the Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health website and consider which factors may be most important for you to assess prior to making a decision.
2. What thoughts do you have about the health of seniors in your community and growing old (in general)?
Make a brief list of what you believe about their seniors’ health, then read the Myths associated with an aging population section of “The Chief Public Health Officer’s Report on the State of Public Health in Canada 2014—Public Health in the Future” on the Public Health Agency of Canada website. How did you compare?
16.3 Business Acumen and Tangible Skills
Traditionally, the head nurse position within a hospital unit was primarily concerned with managing clinical issues and coordination of care with appropriate staff. These roles are changing rapidly as health care and leadership roles are evolving in nursing. Now more than ever, nurse managers may or may not require clinical expertise to fulfill their duties. Instead, they require practical business skills, tools, and tactics for comprehensively managing departments and ensuring personal career success.
To be successful change agents, managers, and leaders must strive to acquire and use business skills and develop acumen , the ability to make good judgements in an efficient and well-informed way.
Business Skills and Tactics
Table 16.3.1 highlights specific practical business skills and tactics now required for formal nurse leaders and managers to fulfill their roles effectively. Where appropriate, additional online resources and links have been included for further study.
Communication at work must reflect an appropriate business writing style befitting professional practice environments. Table 16.3.2 outlines some of the considerations relevant to various methods of communication.
- Educate yourself on necessary business acumen.
- Educate yourself and plan ahead, even if the future is unpredictable.
- What you do with your budget impacts others. Coordinate and share your budget plans with other similar departments that could be affected by plans you have for change, quality improvement, and enhancement in services and care.
- Focus on patient outcomes. For example, “If I make X change in care in my unit, it will result in a better care experience for the patient and shorter hospitalization times.”
16.4 Patient and Family Collaboration for Care Delivery
As health systems have moved from a disease-oriented approach toward a model focused more on health prevention, promotion, and wellness, so too has the philosophical foundation of how patients and families are engaged in care. Traditionally, patient and family involvement in care was more visible and more accepted by health care providers in specific clinical areas such as pediatrics, obstetrics, oncology, and palliative care. Now this expectation from consumers is being extended to all sectors of the care continuum. A key transformational shift in the health care landscape over the past two decades has been a focus on the concept of patient – and family – centred care (PFCC) also known as person – centred care (according to the Canadian Partnership Against Cancer), or client – and family – centred care (CFCC) (by Accreditation Canada). These definitions are now widely used to define the inclusiveness and collaboration with patients and families in determining their care and outcomes at all touch points of the care continuum. For purposes of this section of this chapter, the terms patient , client , and resident will be used interchangeably.
Definitions
The Institute of Patient- and Family-Centered Care ( IPFCC, 2017 ) defines PFCC as “an approach to the planning, delivery, and evaluation of health care that is grounded in mutually beneficial partnerships among health care providers, patients, and families.” The four key concepts espoused by the IPFCC and followed within Canada and Saskatchewan are:
Dignity and respect. Health care practitioners listen to and honor patient and family perspectives and choices. Patient and family knowledge, values, beliefs, and cultural backgrounds are incorporated into the planning and delivery of care.
Information sharing. Health care practitioners communicate and share complete and unbiased information with patients and families in ways that are affirming and useful. Patients and families receive timely, complete, and accurate information to effectively participate in decision making.
Participation. Patients and families are encouraged and supported in participating in care and decision making at the level they choose.
Collaboration. Patients, families, health care practitioners, and health care leaders collaborate in policy and program development, implementation, and evaluation, in research, in facility design, and in professional education, as well as in the delivery of care.
Essential Learning Activity 16.4.1
For a historical perspective on the evolution of PFCC, see “ Partnering with Patients and Families To Design a Patient- and Family-Centered Health Care System: A Roadmap for the Future ,” published by the IPFCC.
The IPFCC’s definition is aligned with that of Accreditation Canada , which defines client and family centred care (CFCC) as “an approach that fosters respectful, compassionate, culturally appropriate, and competent care that responds to the needs, values, beliefs, and preferences of clients and their family members” ( 2015 ). In CFCC, the word client also means patients and residents. At the heart of PFCC is the concept of working “with” the patient instead of doing “to” or “for.” This key concept puts the client and family at the centre of the care as opposed to a model where the provider’s perspective is dominant, so the health care provider and the client have a true partnership.
Putting Patients First
In 2009, Saskatchewan released its “ Patient First Report,” which started Saskatchewan on a focused transformational journey to embed PFCC/CFCC into the culture of health care in the province. The key recommendation from this report stated:
That the health system make patient- and family-centred care the foundation principal aim of the Saskatchewan health system, through a broad policy framework to be adopted system wide. Developed in collaboration with patients, families, providers and health system leaders, this policy framework should serve as an overarching guide for health care organizations, professional groups and others to make the Patient First philosophy a reality in all workplaces. ( Saskatchewan Health, 2009 , p. 8 )
Saskatchewan is now actively engaged in strategic efforts to advance patient- and family-centred care in this province and has set targets and measures to achieve this culture change.
Essential Learning Activity 16.4.2
For more information on specific targets and goals of quality health work in Saskatchewan health care, please review the following websites and documents:
The Saskatchewan Patient- and Family-Centred Care Guiding Coalition’s newsletter (Fall 2016), Putting Patients First .
Saskatchewan Health Quality Council’s report , “ Shared decision making: Helping the system and patients make quality health care decisions .”
Changing Effects of Patient- and Family-Centred Care
This new collaborative approach to care delivery has a major impact on how health care providers engage with patients and families in our system, and the subsequent involvement and influence of the nurse manager or leader. One specific area that managers and leaders must pay attention to is related to the changing expectations of clients and their family members who have increased access to information through technology. This includes expectations for information flow between care providers and increased expectations around shared decision making and meaningful engagement. One of the key tenets of PFCC is “every patient, every time.” This culture change involves all levels of health care providers from care providers to support service staff.
Essential Learning Activity 16.4.3
For more information on the changing effects of patient- and family-centered care, see the patient engagement resource hub on the website of the Canadian Foundation for Healthcare Improvement.
Review the following websites and consider how their information impacts local management environments:
Institute for Patient- and Family-Centred Care, Free Downloads—Reports/Roadmaps
For more information on innovations in advancing patient- and family-centered care in hospitals, see the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality’s web page Advancing the Practice of Patient- and Family-Centered Care in Hospitals .
- Gain increased knowledge in PFCC as a sound foundation for a leadership role.
- Increase knowledge on specific examples of successful ways that patients and families have collaborated for their care, and work with patients and families to implement change in your work area (e.g., including patients and families during hospital rounds, changing meal times in long-term care to accommodate resident preferences).
- Enhance communication skills for collaboration and engagement with patients and families as individuals and in groups, such as patient councils. Learn the difference in stakeholder roles, in terms of which are input and consultation and which are decision making, and be able to articulate this to patients and family members.
- Develop communication skills to engage patients and families in participating in and improving care. See examples outlined in the Registered Nurses’ Association of Ontario’s clinical best practice guidelines (2015) for person- and family-centred care.
- Develop skills in coaching and mentoring diverse groups of staff, patients, and family members. Develop skill in conflict resolution for helping staff handle challenging patient or family issues.
- Be alert to current issues that will impact an increased emphasis on patient and family engagement in care, such as medical assistance in dying and advanced care directives.
- Learn how to educate and direct patients and families to credible resources, particularly on the internet.
- Learn communication processes for appropriate disclosure of errors in an effective manner and include patients as part of quality improvement.
- Ensure that you and your staff understand how to maintain patient privacy and confidentiality with increased family involvement.
- Sharpen skills in measuring patient experience. For example, develop mechanisms to hear routine feedback from patients and families and use this to improve care.
16.5 Managing Stress and Self-Care Practices
Today’s nurse manager roles are diverse and constantly changing. Multiple priorities and complex pressures affect nearly every aspect of a manager’s day-to-day activities. Urgent and non-urgent considerations often intersect and can negatively impact the time and resources available for efficient, optimal decision making. In some instances, ambiguity and missing data can complicate decision-making processes. Priorities are sometimes set and then re-adjusted based on time-sensitive data, higher-level turbulent issues, or patient care management needs. Leading and managing in this environment is the new health care norm.
Within this chaos and non-stop change, it is critical for the nurse manager or leader to keep top of mind their primary leadership responsibility to organizations and their staff and to ensure proactive and positive oversight and safe, appropriate quality care for patients. Managers need to expect and anticipate change and be able to communicate effectively and collaborate easily with others to move health care forward. The use of complexity theory to explain and provide a framework for the ever-changing environmental priorities was discussed in Chapters 1 and 3.
There is no one best way to manage change in an organization. Pragmatic and logical thinking must be at the forefront of every consideration. Proactively supporting and promoting change is both a demanding and fatiguing task. Without careful consideration of internal strengths, self-awareness, and resilience coping mechanisms, it is easy for nurse leaders to experience negative impacts on their lives and behaviours. Sometimes the deleterious effects such as fatigue may not be realized, but may eventually lead to burnout , which may be displayed as emotional exhaustion, cynicism, and personal inefficacy ( Laschinger & Fida, 2014 ).
Now more than ever, self-care is essential for managers and leaders as a proactive and continuing activity. Self-care always begins with strategic awareness of strengths, skills, and abilities that you as a manager or leader possess. It has been said that the best leaders do not rely on their positional power, but rather focus on their best attributes and assets to enhance and succeed at their roles ( Rath & Conchie, 2009 ). Similarly, Gottlieb et al . ( 2012) discussed strengths-based leadership as a multifaceted concept involving the development of not just tangible knowledge and skills but also of an un-anxious mindset that allows individuals to utilize their best developed strengths for problem management, while focusing on development of weaker skills over time. Their theory of strengths-based leadership extends beyond self-assessment to further recognize strengths in others on a team and among those we collaborate with. Additionally, evidence related to how you as a leader think and view the world also impacts your actions and behaviours. Mindfulness and mindset of the manager are critical in navigating this complexity, as discussed in previous chapters.
Connecting to a leadership framework assists in focusing the personal growth of managers. Closely tied to the work of Rath and Conchie (2009 ) is the management framework of LEADS in a Caring Environment, now supported and endorsed by the Canadian College of Health Leaders. LEADS correlates to: L eading self, E ngaging others, A chieving results, D eveloping coalitions, and transforming S ystems.
Leading self as the first step in the LEADS framework highlights how essential it is for a manager or leader to consciously embark on a personal journey of self-awareness, introspection, and recognition of their skills, intuitive character strengths, and expertise. It is not an expectation for managers or leaders to be good at everything, but a strategic plan for self-care and personal journey development can begin if they are first aware of their strengths as well as weaker areas to work on.
- Consult and complete the leadership and management competency assessment tools from the following two documents to recognize areas of management or leadership strengths, as well as those that may need attention: SRNA’s Standards and Foundation Competencies for the Practice of Registered Nurses and CNA’s Canadian Nurse Practitioner Core Competency Framework .
- Consider approaches to using emotional intelligence for decision making and for engaging others effectively ( Bradberry & Greaves, 2009 ), and consider your strengths as part of your strengths-based leadership approach ( Gottleib et al., 2012 ).
- Use the results of competency assessment tools to help you set goals for career and professional development learning. Stick to these goals and evaluate them regularly ( Echevarria, Patterson, & Krouse, 201 7 ).
- Be aware of physical and mental cues from your body that you may be becoming overwhelmed or need a “time-out” from complex and fast-paced environments. Negotiating for time to ponder and strategically consider options almost always leads to more successful decision making.
- Take care of your personal health by practising healthy lifestyle habits; specifically, pay attention to adequate sleep, healthy eating, exercise, and stress management activities.
- Identify a mentor—someone in a similar or higher management or leadership position who you look up to and aspire to emulate. Consult with your mentor and coordinate a relationship for feedback, advice, and support to guide your personal growth as a manager or leader over time.
- Practise good time management and resource management skills to support efficiencies and streamlined processes. Self-motivation skills and cues are important to ensure you keep on task and that you meet deadlines for reports or commitments.
- Schedule protected time in your work schedule to periodically review your strengths and approaches. Think outside the box in terms of creativity and ways to enhance your personal growth.
16.6 International Nursing Leadership
This chapter has explored critical emerging leadership issues in nursing with a focus on the Canadian, and specifically the Saskatchewan, context. Now it is time to look at nursing around the world. In the following activity, spend time with Dr. Judith Shamian, President of the International Council of Nurses (2013–2017), as she discusses global health and nursing as part of the Global Leadership Series hosted by the Sick Kids Centre for Global Child Health.
Essential Learning Activity 16.6.1
Watch this video “ Sustainable Development Goals: Global Health and Nursing ” (56:10), which is part of the Global Leadership Series hosted by the Centre for Global Child Health. In this video, Dr. Judith Shamian discusses global nursing and sustainable development goals. Then answer the following questions:
- How is the Canadian Nurses Association (CNA) linked to the International Council of Nurses (ICN)?
- Why does Dr. Shamian state that money spent on health care workers is an investment?
- What are the three “buzzwords” that Dr. Shamian mentions?
- Identify the sustainable development goals (SDGs) for the world.
- How can you, as a nurse leader, work to assist citizens of the world to achieve these goals?
16.7 Foundational Elements of Professional Role Transition for New Nurses
There are foundational intersecting elements that feed into the new graduate nurse’s (NGN) initial experience in the workplace: (1) stability, (2) predictability, (3) familiarity, (4) consistency, and (5) success (Duchscher, 2012). When all is in order, these elements put us in the driver’s seat of our own experience.
Figure 16.7.1 Quality Workplace Factors for New Nursing Graduates
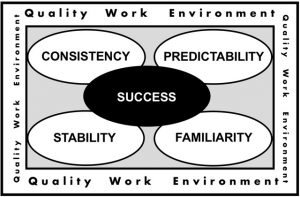
Stability refers to how steady the circumstances and situation are for you during your transition experience; essentially, stability refers to that which is unlikely to change or deteriorate. Stability is a fundamental feature of homeostasis , which even from a purely bio-physiologic perspective is something all humans seek. When you think about optimizing stability remember to think personally as well as professionally. Try to consider work that provides you with clinical situations that are stable, in a context that doesn’t constantly change. For this reason, floating (or being on a team that goes from unit to unit on a daily basis) does not provide for stability of patient population. Further to this, contexts where a patient’s clinical presentation is highly dynamic, or whose level of illness is such that there is a near certain likelihood of instability or decompensation (i.e., emergency or critical care), are precarious for the NGNs growing knowledge base. The immature pattern recognition capacity of the new practitioner renders the NGNs response to this kind of clinical volatility challenging. Finally, if you feel like your home life is unstable (i.e., things feel chaotic or stressful at home), the stability of your workplace is even more important. The reverse is also true: a stable home life is critical if you lack stability in the workplace.
Predictability for NGNs relates to their ability to know: (1) WHAT they will do (e.g., What level of performance is expected of me now that I am a graduate nurse? What do I need to do in this role? Am I comfortable enough with those in charge to tell them when I am in over my head?); (2) WHERE they will do it (Where am I working? Am I going to the same workplace every shift or floating to multiple units? If I have to start as a casual employee, how can I get enough hours without exposing myself to too many unfamiliar workplaces?); (3) WHEN they will do it (Am I working 8-hour or 12-hour shifts? What is the rotation? When X happens [a code, a death, a distraught patient, a diagnosis of a sexually transmitted infection, a suicide in the community], how do I respond?); (4) WHO will they do it with (Who will I be working with? Who do I go to if I have questions? Who can fire me? Who can I trust?); and (5) HOW they will do it (What are the differences between what I did as a student and what is expected of me now as a graduate nurse? What will I do if I come up against something I have never done before? Are things done differently here relative to where I practised as a student?).
Familiarity speaks to the saying, “I’ve seen this before,” and perhaps even “…and I know what to do about it.” If you were privileged to be employed as a senior student or spend your final practicum (or capstone or consolidated learning experience) on the unit or in the practice context where you intend to work as a graduate nurse, the lack of familiarity may not contribute as much to your transition stress. Even knowing where to get what you need to do your work is a relief of transition stress (e.g., where the STD kits are in the clinic or where the special bags of N/S with 20meqK+/L are located on the unit).
Knowing who’s who in the practice area is very helpful. While many NGNs experience phenomenal collegiality with their senior counterparts, there are equal numbers who are quickly introduced to, or warned about, those individuals to avoid because they “eat their young.” A new workplace is a bit like a minefield—you obviously need to keep moving but no one tells you where the mines are planted (sometimes even they don’t know) and not all mines have obvious triggers that you can see before they explode. It is in the area of familiarity that nursing residency/internship programs (also sometimes called a graduate nurse program or a transition facilitation program) or less formal sup e rnumerary staffing arrangements have significant impact on a transition experience. Supernumerary staffing means that you work with patients and your colleagues without being given an actual assignment. The advantage of this is that you can move around your new environment, taking advantage of various learning experiences, getting to know your colleagues and the patient demographic without the stress of predetermined workload expectations. Mentorship or preceptorship programs constitute another approach to familiarizing you with your roles and responsibilities as a new nurse. The concept of mentor usually encompasses a longer-term, more personally professional relationship between a novice and experienced nurse. Conversely, the role of preceptor is often associated with the transferring of skill knowledge and therefore is often used in the context of a pairing between a nursing student and a senior nursing guide. Having said that, preceptors can also be expert clinical nurses who are buddied with a new nurse for the purposes of teaching them about the roles, routines, and responsibilities related to their new workplace. Along those lines, it is thought that we can be assigned a preceptor, but that a mentor is someone we choose, as this relationship requires a more personal connection between mentor and mentee.
Consistency is the experience of being exposed to a similarly presenting event, situation, concept, or idea, which affords you a level of familiarity and predictability. From a purely logical perspective, consistency is defined as that which does not contain contradictions. Here are some of the inconsistencies to watch for as you enter professional practice:
- The practice environment is more often than not constructed to ensure efficiency and productivity over effectiveness and quality.
- Health care institutions must function within budgets that are influenced by many competing sociopolitical and economic factors. This means that there will often be tension between the ethics-based, value-driven motivations of health care providers and the fiscal and human resource limitations of the health care system.
- When you graduate from an educational program that encourages independent critical thinking, it is a bit disconcerting to find yourself relatively dependent on the experienced nurses around you. You may feel a sense that you should be independent—you think others are expecting you to perform independently and this is what you often expect of yourself. Confusion reigns when you quickly come to realize that so much of what you are doing and seeing is new. The inconsistency is between what you think people expect of you, what you expected of yourself as a student, and the recognition of your own limitations as a new practitioner.
When experiencing inconsistencies, remember to stay grounded in the fundamental objectives of a NGN:
- Gain a sense of the roles and responsibilities of a graduate nurse.
- Create a workload organizational system that works for you.
- Learn how to manage your time within a gradually increased workload complexity.
- Learn the routines of your workplace.
- See and experience a variety of “normal” and “abnormal” situations under controlled conditions.
- Debrief with a trusted experienced colleague, nursing educator, or mentor about clinical situations to gain a depth of understanding of clinical patterns and the relationships between those patterns and the judgements that arise out of them.
- Gain confidence in performing the fundamental skills required of a nurse in the setting where you work. (The skills of an expert nurse are not simply tasks, but a complex and layered portfolio of roles and responsibilities enacted in an infinitely varied set of sequences and combinations and under dynamic, fluid and often intense and risk-laden conditions.)
- Assess patients of increasing complexity at varying levels of stability.
- Learn how to work on a team—and learn about your team.
- Get to know the dynamics of your workplace. What is “nursing” to your colleagues and how is nursing valued within your institution and community?
- Pursue a balance between your personal life and professional life.
- Learn who you are (again) now that you are not consumed by studying and academic deadlines.
- Have fun again!
Essential Learning Activity 16.7.1
Watch the video “ Duchscher’s New Graduate Nurse Transition Stages ” (19:53) by Dr. Judy Boychuk Duchscher who discusses new graduate nurse transition stages. Refer also to the following Figures 16.7.2 and 16.7.3. More information on new graduate nurse transition can be found on the Nursing the Future website. Answer the following questions:
- Describe the stages of transition. What recommendations does Dr. Duchscher give for each stage?
- Where do the majority of new nurses usually find employment? Why?
- What is flow? Give an example of flow.
- What is the difference between accommodating and adjusting?
Figure 16.7.2 Transition Stages Model
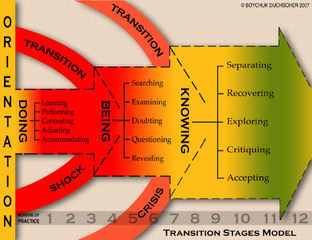
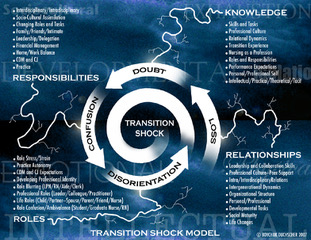
Figure 16.7. 3 Transition Shock Model Enlarge image: Dec10 Transition Shock Model
Given the multiple challenges and uncertainty now and into the future, it is imperative for nurse managers and leaders to continue to enhance their leadership effectiveness. Carroll (2006) describes several effective ways to become a nurse leader, regardless of your current training or position. Among these, the following relate directly to nursing management and the journey toward career success:
- Make a commitment to lifelong learning through a self-development plan.
- Find your passion and begin to build and develop your strengths in this area.
- Get involved in the nursing community and keep abreast of changing issues affecting nursing.
- Understand your personal leadership style and how it impacts your work.
After completing this chapter, you should now be able to:
- Propose the importance of the manager or leader’s personal journey planning for fruitful and fulfilling career development and professional growth.
Figure 16.7.4 Letter from Katherine McKenzie Ross to All New Nursing Graduates

- Select a manager you know from one of your clinical sites. Interview this manager to gain insights into the nursing management. Consider asking the following questions: Why did you become a manager? How would you describe your management style? What turbulent changes have you seen in the health system in the past two to five years? How have you adapted to this changing management landscape?
- What are the key findings of the “ Optimizing and Integrating Patient-Centred Care ” 2016 report? How do you think these findings will impact managers and leaders in Saskatchewan?
- What are three key considerations for nurse managers when assisting with the implementation of an electronic health records system in a nursing unit?
- Review the current age of the patient population in a clinical setting you are or have been in. What are the key health challenges that each age group faces and how are they reflected in your chosen setting? What are you going to do to maximize this engagement in care for this patient group?
- Assess the current activities underway in each of your clinical settings to promote PFCC.
- Consider the rapidly changing and emerging uses of wireless devices and the internet in everyday patient care. Do you think that wireless applications in health care settings improve the efficiency of care delivery systems? Why or why not? How could we measure return-on-investment for these wireless delivery systems over the long term?
- Reflect on your own career path in nursing. What content in this chapter will be useful to you regardless of the type of leader you become in nursing (e.g., bedside, unit leader, manager, director)?
- Looking back to the Global Leadership Series video by Dr. Shamian, how will you find a “spot at the table”? What is your ten-year plan?
Accreditation Canada. (2015). Client Family Centred Care. Retrieved from https://accreditation.ca/patients-families/
Bradberry, T. & Greaves, J. (2009). Emotional Intelligence 2.0 . San Diego, CA: TalentSmart.
Canadian Nurses Association [CNA]. (2016). Nurse practitioners . Retrieved from https://www.cna-aiic.ca/professional-development/advanced-nursing-practice/nurse-practitioners
Canadian Nurses Association [CNA]. (2012). Primary health care [Position statement] . Retrieved from https://www.cna-aiic.ca/~/media/cna/page-content/pdf-en/primary-health-care-position-statement.pdf?la=en
Canadian Nurses Association and Canadian Medical Association. (2011). Principles to guide health care transformation in Canada . Retrieved from https://www.cna-aiic.ca/~/media/cna/files/en/guiding_principles_hc_e.pdf
Carroll, P. (2006). Nursing leadership and management: A practical guide . Clifton Park, NJ: Thomson Delmar Learning.
Duchscher, J. E. B. (2012). From Surviving to Thriving: Navigating the First Year of Professional Nursing Practice (2nd ed.). Calgary, AB: Nursing the Future.
Duchscher, J. E. B. (2009). Transition shock: The initial stage of role adaptation for newly-graduated Registered Nurses. Journal of Advanced Nursing, 65 (5), 1103–13.
Duchscher, J. E. B. (2008). A process of becoming: The stages of new nursing graduate professional role transition. Journal of Continuing Nursing Education , 39(10), 441–450.
Echevarria, I. M., Patterson, B. J., & Krouse, A. (2016). Predictors of transformational leadership of nurse managers. Journal of Nursing Management, 25 (3), 167–175. doi:10.1111/jonm.12452
Gottleib, L., Gottleib, B., & Shamian, J. (2012). Principles of strengths-based nursing leadership for strengths-based nursing care: A new paradigm for nursing and healthcare for the 21st century. Nursing Leadership , 25 (2), 38–50. doi:10.12927/cjnl.2012.22960
Health Quality Council, Saskatchewan. (2010). Shared decision making : Helping the system and patients make quality health care decision . Retrieved from http://hqc.sk.ca/Portals/0/documents/Shared_Decision_Making_Report_April_08_2010.pdf
Institute for Patient- and Family-Centered Care [IPFCC]. (2017). Advancing the practice of patient – and family – centered care in hospitals . Retrieved from http://www.ipfcc.org/resources/getting_started.pdf
Kotter, J. P. (1995). Leading change: Why transformational efforts fail. Harvard Business Review. Retrieved from http://www.gsbcolorado.org/uploads/general/PreSessionReadingLeadingChange-John_Kotter.pdf
Laschinger, H. K., & Fida, R. (2014). New nurses’ burnout and workplace wellbeing: The influence of authentic leadership and psychological capital. Burnout Res earch , 1 (1), 19–28. doi:10.1016/j.burn.2014.03.002
Mate, K., & Rakover, J. (2016). Four steps to sustaining improvement in health care. Harvard Business Review . Retrieved from https://hbr.org/2016/11/4-steps-to-sustaining-improvement-in-health-care
Pangman, V. C., & Pangman, C. H. (2010). Nursing leadership from a Canadian perspective. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
Pringle, D. (2007). From the editor-in-chief. Nurse practitioner role: Nursing needs it. Nursing Leadership (1910-622X) , 20 (2), 1–5. Retrieved from http://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=rzh&AN=109846474&site=ehost-live
Public Health Agency of Canada [PHAC]. (2016). Health status of Canadians , 2016 . Retrieved from https://www.canada.ca/content/dam/hc-sc/healthy-canadians/migration/publications/department-ministere/state-public-health-status-2016-etat-sante-publique-statut/alt/pdf-eng.pdf
Rath, T., & Conchie, B. (2008). Strengths- b ased leadership. New York: Gallup Press.
Saskatchewan Advisory Panel on Health System Restructure. (2016). Optimizing and integrating patient care . Retrieved from http://s3.documentcloud.org/documents/3251960/Saskatchewan-Advisory-Panel-on-Health-System.pdf
Saskatchewan Health. (2012). Patient centred, community designed, team delivered: A framework for achieving a high performing primary health care system in Saskatchewan . Retrieved from http://publications.gov.sk.ca/documents/13/81547-primary-care-framework.pdf
Saskatchewan Health. (2009). For patients’ s ake : Patient First Review Commissioner’s Report to the Saskatchewan Minister of Health . Retrieved from https://www.saskatchewan.ca/government/health-care-administration-and-provider-resources/saskatchewan-health-initiatives/patient-first-review
Sherman, R. (2006). Leading a multigenerational nursing workforce: Issues, challenges and strategies. Online Journal of Issues in Nursing , 11 (2), manuscript 2. doi:10.3912/OJIN.Vol11No02Man02
Sherman, R., & Pross, E. (2010). Growing future nurse leaders to build and sustain healthy work environments at the unit level. Online Journal of Issues in Nursing , 15 (1), manuscript 1. doi: 10.3912/OJIN.Vol15No01Man01
Spinks, N., & Moore, C. (2007). The changing workforce, workplace and nature of work: Implications for health human resource management. Nursing Leadership , 20 (3), 26–41. doi:10.12927/cjnl.2007.19286
Thrasher, C., & Purc-Stephenson, R. (2008). Patient satisfaction with nurse practitioner care in emergency departments in Canada. Journal of the American Academy of Nurse Practitioners, 20 (5), 231–237. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-7599.2008.00312.x
Wheatley, M. “35 Magnificent Margaret J. Wheatley Quotes,” BrandonGaille.com (blog) Retrieved from http://brandongaille.com/35-magnificent-margaret-j-wheatley-quotes/
Leadership and Influencing Change in Nursing Copyright © 2018 by Brendalynn Ens; Susan Bazylewski; and Judy Boychuk Duchscher is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

110+ Research Topics on Nursing Leadership and Management: A Comprehensive Guide for Nursing Students
- Carla Johnson
- September 6, 2023
- Nursing Topics and Ideas
Nursing Leadership and Management play pivotal roles in the healthcare sector, ensuring the efficient and effective delivery of patient care. For nursing students, understanding these concepts is not just essential; it’s a critical component of their education. This article will explore research topics on Nursing Leadership and Management, provide 10 PICOT (Population, Intervention, Comparison, Outcome, Time) question examples, and offer project ideas and research topics tailored specifically for nursing students. Let’s embark on this educational journey together.
Understanding Nursing Leadership and Management
Nursing Leadership and Management are two distinct yet interconnected domains that contribute to the overall success of healthcare organizations. Leadership encompasses qualities such as inspiration, vision, and empowerment. In contrast, management focuses on the organization, coordination, and efficient utilization of resources. To help nursing students grasp these concepts better, here are 10 PICOT question examples:
- P: Pediatric population in a general hospital; I: Implementation of a structured pediatric care training program; C: Hospitals without structured pediatric training; O: Improved pediatric patient outcomes; T: 1 year. How does the implementation of a structured pediatric care training program in general hospitals affect pediatric patient outcomes over a year compared to hospitals without such programs?
- P: Nurses working in a surgical unit; I: Implementation of electronic health records (EHRs); C: Nurses using paper-based records; O: Efficiency and accuracy in patient documentation; T: 6 months. What is the impact of implementing electronic health records on the efficiency and accuracy of patient documentation among nurses working in a surgical unit within a 6-month period, compared to those using paper-based records?
- P: Geriatric patients in long-term care facilities; I: Introduction of regular falls prevention exercises; C: Facilities without scheduled exercise programs; O: Reduction in fall rates among geriatric residents; T: 9 months. How does the introduction of regular falls prevention exercises in long-term care facilities affect the rate of falls among geriatric residents over a 9-month period, compared to facilities without scheduled exercise programs?
- P: ICU nurses; I: Implementation of a stress management program; C: ICU nurses without stress management interventions; O: Decreased stress levels and improved job satisfaction; T: 3 months. What is the impact of implementing a stress management program on ICU nurses’ stress levels and job satisfaction over a 3-month period, compared to ICU nurses without such interventions?
- P: Patients with chronic pain; I: Utilization of a multidisciplinary pain management approach; C: Patients receiving conventional pain management; O: Improved pain control and quality of life; T: 12 weeks. How does the utilization of a multidisciplinary pain management approach impact pain control and quality of life among patients with chronic pain over a 12-week period, compared to those receiving conventional pain management?
- P: Emergency department staff; I: Implementation of a communication skills training program; C: Emergency department staff without communication training; O: Enhanced communication and teamwork; T: 6 months. What is the effect of implementing a communication skills training program on communication and teamwork among emergency department staff over a 6-month period, compared to staff without such training?
- P: Diabetes patients in primary care settings; I: Adoption of a telehealth monitoring system; C: Patients receiving traditional in-person care; O: Improved glycemic control; T: 1 year. How does the adoption of a telehealth monitoring system impact glycemic control among diabetes patients in primary care settings over a year, compared to those receiving traditional in-person care?
- P: Post-surgical patients; I: Implementation of a standardized post-operative care protocol; C: Patients receiving individualized post-operative care ; O: Decreased post-operative complications; T: 3 months. What is the impact of implementing a standardized post-operative care protocol on post-operative complications among surgical patients over a 3-month period, compared to patients receiving individualized post-operative care?
- P: Oncology nurses; I: Participation in regular self-care workshops; C: Oncology nurses without self-care workshops; O: Reduced burnout and improved job satisfaction; T: 6 months. How does participation in regular self-care workshops affect burnout levels and job satisfaction among oncology nurses over a 6-month period, compared to those who do not attend such workshops?
- P: Patients with hypertension; I: Implementation of a home blood pressure monitoring program ; C: Patients not using home monitoring; O: Better blood pressure control; T: 8 weeks. What is the effect of implementing a home blood pressure monitoring program on blood pressure control among patients with hypertension over an 8-week period, compared to those not using home monitoring?
Evidence-Based Practice (EBP) Project Ideas
- Evaluating the impact of leadership styles on nurse job satisfaction.
- Assessing the effectiveness of nurse-to-patient ratios on patient outcomes.
- Investigating the role of nurse leaders in promoting a culture of safety.
- Analyzing the relationship between nurse leadership and patient satisfaction.
- Examining the influence of management practices on nurse turnover rates.
- Investigating the impact of nurse manager support on staff well-being.
- Assessing the use of technology in nurse scheduling and its effects on workload.
- Exploring strategies for improving nurse communication in healthcare teams.
- Analyzing the role of transformational leadership in nursing education.
- Investigating the implementation of evidence-based nursing practices in healthcare settings.
- Evaluating the effectiveness of nurse-led interventions in chronic disease management.
- Examining the impact of nurse staffing levels on healthcare-associated infections.
- Investigating the role of leadership in promoting diversity and inclusion in nursing.
- Analyzing the use of performance metrics in nurse management.
- Assessing the effects of nurse leadership development programs.
- Investigating the impact of nurse manager decision-making on patient safety .
- Exploring strategies for nurse manager succession planning.
- Analyzing the influence of nurse leadership on staff morale and motivation.
- Assessing the implementation of shared governance models in nursing units.
- Investigating the role of nurse leaders in promoting evidence-based practice.
Nursing Capstone Project Ideas
- Developing a leadership training program for novice nurses .
- Implementing a quality improvement project in a healthcare unit.
- Analyzing the financial impact of nurse staffing models on hospitals.
- Investigating the role of nurse managers in promoting patient-centered care.
- Assessing the effectiveness of nurse-led telehealth initiatives.
- Designing and implementing a change management plan in a healthcare organization.
- Evaluating the impact of nurse leadership on interdisciplinary collaboration.
- Investigating the use of data analytics in nurse management decisions.
- Developing a strategic plan for nursing workforce development.
- Creating a resource allocation strategy for nurse managers.
- Implementing a mentorship program for new nurse leaders.
- Analyzing the effects of nurse manager turnover on unit performance.
- Developing a nurse manager communication toolkit.
- Evaluating the role of nurse leaders in healthcare policy advocacy .
- Investigating the impact of nurse leader education on patient outcomes.
- Designing and implementing a patient safety improvement project.
- Assessing the effectiveness of nurse-led patient education programs.
- Developing a leadership development program for nursing students.
- Investigating the influence of nurse leadership on healthcare disparities .
- Designing a nurse manager competency assessment tool.
Nursing Research Paper Topics
- The role of emotional intelligence in nurse leadership.
- Strategies for reducing nurse burnout in healthcare organizations.
- Nurse leadership’s impact on healthcare quality and patient safety.
- The relationship between nurse job satisfaction and patient outcomes.
- The use of technology in nurse scheduling and workforce management.
- The effectiveness of leadership development programs for nurses.
- Nurse manager strategies for promoting a culture of safety .
- The impact of nurse staffing levels on patient mortality rates.
- The role of nurse leaders in promoting evidence-based practice.
- Strategies for improving nurse communication in healthcare teams.
- The influence of nurse leadership on healthcare policy advocacy.
- The use of performance metrics in nurse management decisions.
- The relationship between nurse manager support and staff well-being.
- The effectiveness of shared governance models in nursing units.
- Nurse leadership’s role in promoting diversity and inclusion.
- Strategies for nurse manager succession planning.
- The financial implications of nurse staffing models on hospitals.
- The impact of nurse leader education on healthcare disparities.
- Nurse-led telehealth initiatives and their effects on patient care.
- The use of data analytics in nurse management decisions.
Nursing Research Questions
- How does nurse leadership style affect staff morale and job satisfaction ?
- What are the key factors contributing to nurse turnover in healthcare organizations?
- How does nurse-to-patient ratio impact patient outcomes in critical care units?
- What strategies can nurse managers implement to reduce medication errors?
- How do nurse leaders influence the adoption of evidence-based practices?
- What is the relationship between nurse manager support and nurse engagement?
- How do nurse leaders promote a culture of safety in healthcare settings?
- What are the barriers to effective nurse-physician communication?
- How can nurse managers effectively allocate resources in healthcare units?
- What role do nurse leaders play in addressing healthcare disparities?
- How can nurse leaders advocate for policy changes to improve patient care?
- What are the best practices for nurse manager succession planning?
- How does nurse leadership impact the adoption of healthcare technology?
- What strategies can nurse leaders employ to improve interdisciplinary collaboration ?
- How do nurse leaders address diversity and inclusion in nursing teams?
- What impact does nurse leadership development have on patient outcomes?
- How can nurse managers effectively manage workload and prevent burnout?
- What are the financial implications of different nurse staffing models?
- How do nurse-led telehealth initiatives influence patient care and outcomes?
- What role does data analytics play in nurse management decisions?
Essay Topic Ideas and Examples
- The Impact of Transformational Leadership in Nursing: A Comprehensive Analysis.
- Nursing Leadership Styles and Their Effects on Team Dynamics .
- Managing Change in Healthcare: The Role of Nurse Leaders.
- The Importance of Emotional Intelligence in Nurse Leadership.
- Nurse Burnout and Its Consequences on Patient Care.
- The Influence of Nurse Leadership on Evidence-Based Practice.
- Nurse Staffing Ratios and Their Impact on Patient Safety.
- Strategies for Effective Nurse-Physician Communication.
- Diversity and Inclusion in Nursing Leadership: Challenges and Opportunities.
- The Role of Nurse Leaders in Promoting a Culture of Safety.
- Nurse Manager Competencies: What Makes an Effective Leader?
- The Financial Implications of Nurse Staffing Models in Healthcare.
- Telehealth in Nursing: Opportunities and Challenges.
- Data-Driven Decision-Making in Nurse Management.
- Strategies for Preventing Nurse Burnout and Enhancing Well-Being.
- The Evolution of Nursing Leadership: Past, Present, and Future.
- Nurse Leadership in Healthcare Policy Advocacy.
- Shared Governance Models in Nursing: An In-Depth Analysis.
- Leadership Development Programs for Aspiring Nurse Leaders.
- The Influence of Nurse Leadership on Patient Satisfaction.
- Nurse Managers and the Implementation of Quality Improvement Initiatives.
- Nurse Leadership and Its Impact on Nursing Education.
- Nurse Scheduling and Workforce Management: Best Practices.
- Nurse-Led Initiatives in Chronic Disease Management.
- Patient-Centered Care: The Role of Nurse Leaders in Implementation.
- Nurse Leadership in Addressing Healthcare Disparities .
- Managing Nurse Turnover: Strategies for Retention.
- The Use of Technology in Nurse Scheduling and Workforce Optimization.
- Strategies for Enhancing Nurse Communication in Multidisciplinary Teams.
- The Future of Nurse Leadership: Trends and Challenges.
The opportunities for exploration, research, and personal growth are boundless in Nursing Leadership and Management. This comprehensive guide has equipped nursing students with a foundation to understand these crucial concepts, provided 10 PICOT question examples, and offered an extensive list of project ideas, research topics, essay prompts, and research questions. As you embark on your academic journey, remember that knowledge is power, and seeking assistance when needed can be valuable. Should you require further support or guidance, consider seeking our professional writing services to help you navigate the intricate path of nursing education with ease and excellence. Your future as a skilled and compassionate nurse leader awaits; embrace it with confidence and determination.
Q1: What is leadership and management in nursing?
A1: Leadership in nursing refers to the ability to inspire, guide, and empower the nursing team to achieve common goals. On the other hand, management involves the organization, coordination, and allocation of resources to ensure efficient healthcare delivery.
Q2: Why is nursing leadership and management important?
A2: Nursing leadership and management are crucial for maintaining patient safety, improving healthcare quality, enhancing staff satisfaction, and effectively utilizing resources in healthcare organizations.
Q3: What are the objectives of nurse leadership and management?
A3: The objectives of nurse leadership and management include ensuring patient safety, promoting evidence-based practice , fostering a positive work environment, optimizing resource utilization, and achieving high-quality patient outcomes.
Q4: What are the activities of nursing leadership and management?
A4: Activities in nursing leadership and management encompass tasks such as setting goals and objectives, planning patient care, organizing staff and resources, directing nursing teams, coordinating care, and evaluating outcomes to continuously improve healthcare delivery.
Working On an Assignment With Similar Concepts Or Instructions?
A Page will cost you $12, however, this varies with your deadline.
We have a team of expert nursing writers ready to help with your nursing assignments. They will save you time, and improve your grades.
Whatever your goals are, expect plagiarism-free works, on-time delivery, and 24/7 support from us.
Here is your 15% off to get started. Simply:
- Place your order ( Place Order )
- Click on Enter Promo Code after adding your instructions
- Insert your code – Get20
All the Best,
Get A 100% Plagiarism-Free Nursing Paper
Related samples.
- Medical Safety Competency Comprehensive Nursing Essay Example
- Descriptive Analytics in Organizations Comprehensive Solved Nursing Essay Example
- Interventions in the Management of Elderly Persons Comprehensive Solved Nursing Essay Example
- Final Care Coordination Plan Comprehensive Solved Nursing Essay Example
- Developmental Assessment and the School-Aged Child Comprehensive Solved Nursing Essay Example
Nursing Topics
- Academic Writing Guides
- Advanced Cardiac Care Nursing
- Advanced Community Health Nursing
- Advanced Critical Care Nursing
- Advanced Health Assessment
- Advanced Mental Health Nursing
- Advanced Nursing Ethics
- Advanced Nursing Informatics
- Advanced Occupational Health Nursing
- Advanced Pathophysiology
- Advanced Pediatric Nursing
- Advanced Pharmacology
- Gerontological Nursing
- Healthcare Policy and Advocacy
- Healthcare Quality Improvement
- Nurse Practitioner
- Nursing Education and Curriculum Development
- Nursing Leadership and Management
- Nursing Research and Evidence-Based Practice
- Nursing Theories
- Population Health and Epidemiology
- Assignment Help
- Chamberlain University
- Grand Canyon University (GCU)
- MSN Nursing Papers Examples
- APA NURSING PAPER EXAMPLE
- capstone project
- community health nursing assignments
- comprehensive assessment
- graphic organizer
- Nursing Care Plan
- Nursing Case study
- nursing informatics assignments
- Nursing Leadership Essay
- Shadow Health
- tina jones shadow health
- Windshield Survey Examples
- Nursing Essays
- PICOT Paper Examples
- Walden University
- Women's Health Nursing
Important Links
Knowledge base, utilize our guides & services for flawless nursing papers: custom samples available.
MSNSTUDY.com helps students cope with college assignments and write papers on various topics. We deal with academic writing, creative writing, and non-word assignments.
All the materials from our website should be used with proper references. All the work should be used per the appropriate policies and applicable laws.
Our samples and other types of content are meant for research and reference purposes only. We are strongly against plagiarism and academic dishonesty.
We Accept:

- Scroll to top
- Dark Light Dark Light
85+ Leadership and Management in Nursing Essay Topic Ideas & Examples
- Author Jermaine Huey
- Published April 14, 2023
Leadership and management are essential components of nursing practice that are critical to ensuring quality patient care and improving healthcare outcomes. In this post, we’ll discuss the importance of leadership and management in nursing and provide examples of how these concepts can be exemplified in practice.

Effective leadership and management in nursing are crucial for promoting patient safety, enhancing the quality of care, and improving patient outcomes. According to a study by the American Nurses Association, effective nursing leadership is positively associated with patient outcomes, including reduced mortality rates, shorter hospital stays, and higher patient satisfaction scores. Effective management in nursing is also essential for ensuring efficient healthcare delivery, managing resources effectively, and addressing healthcare challenges.
By exemplifying leadership and management in nursing practice, healthcare providers can promote a culture of excellence, collaboration, and innovation, ultimately leading to better patient outcomes and improved healthcare delivery.
Examples of Leadership and Management in Nursing
- Transformational Leadership in Nursing Practice
- The Role of Emotional Intelligence in Nursing Leadership
- Change Management in Healthcare Organizations
- Effective Communication in Leadership and Management in Nursing
- The Importance of Interprofessional Collaboration in Healthcare Leadership
- The Use of Data Analytics in Nursing Management and Leadership
- The Impact of Nursing Leadership on Staff Retention and Turnover
- The Role of Leadership in Promoting Patient Safety in Healthcare Settings
- The Use of Evidence-Based Practice in Nursing Leadership and Management
- The Importance of Continuous Professional Development in Nursing Leadership and Management
- The Role of Nursing Leadership in Addressing Healthcare Disparities
- The Importance of Nursing Leadership in Policy Development and Advocacy
- The Use of Lean Management Principles in Nursing Practice
- The Impact of Nursing Leadership on Organizational Culture and Climate
- The Use of Coaching and Mentoring in Nursing Leadership and Management
Leadership and management are essential components of nursing practice that are critical to ensuring quality patient care, improving healthcare outcomes, and addressing healthcare challenges. By exemplifying leadership and management in nursing practice, healthcare providers can promote a culture of excellence, collaboration, and innovation, ultimately leading to better patient outcomes and improved healthcare delivery.
Leadership and Management in Nursing Essay Topics/Ideas
- The Role of Nursing Leadership in Promoting Patient-Centered Care
- Effective Communication in Nursing Leadership and Management
- The Impact of Nursing Leadership on Staff Morale and Job Satisfaction
- The Use of Quality Improvement Processes in Nursing Management
- The Importance of Interprofessional Collaboration in Nursing Leadership and Management
- The Role of Emotional Intelligence in Nursing Leadership and Management
- The Use of Technology in Nursing Leadership and Management
- The Importance of Ethical Principles in Nursing Leadership and Management
- The Impact of Nursing Leadership on Healthcare Policy and Advocacy
- The Role of Nursing Leadership in Healthcare Innovation and Change Management
- The Importance of Nursing Leadership in Addressing Staff Burnout and Compassion Fatigue
- The Use of Shared Governance in Nursing Leadership and Management
- The Impact of Nursing Leadership on Patient Safety in Healthcare Settings
- The Importance of Nursing Leadership in Addressing Healthcare Access and Equity
- The Role of Nursing Leadership in Promoting Diversity and Inclusion in Healthcare
- The Use of Servant Leadership in Nursing Practice
- The Impact of Nursing Leadership on Healthcare Costs and Resource Management
- The Importance of Nursing Leadership in Disaster Preparedness and Response
- The Use of Transformational Leadership in Nursing Practice
- The Role of Nursing Leadership in Addressing Healthcare Workforce Shortages
- The Impact of Nursing Leadership on Healthcare Outcomes and Quality Improvement
- The Importance of Nursing Leadership in Promoting Health Equity and Social Justice
- The Use of Collaborative Leadership in Nursing Practice
Controversial Leadership and Management in Nursing Essay Topics to Write About
- The Ethics of Nursing Leadership and Management
- The Impact of Gender and Diversity on Nursing Leadership and Management
- The Use of Marijuana in Nursing Leadership and Management
- The Role of Social Justice in Nursing Leadership and Management
- The Ethics of Nursing Leadership and Management in End-of-Life Care
- The Use of Medical Marijuana in Nursing Leadership and Management
- The Impact of Sexual Orientation and Gender Identity on Nursing Leadership and Management
- The Ethics of Nursing Leadership and Management in Care for Incarcerated Patients
- The Use of Psychotropic Medications in Nursing Leadership and Management
- The Impact of Religion and Spirituality on Nursing Leadership and Management
- The Ethics of Nursing Leadership and Management in Care for Patients with Substance Use Disorders
- The Use of Complementary and Alternative Medicine in Nursing Leadership and Management
- The Impact of Cultural Competence on Nursing Leadership and Management
- The Ethics of Nursing Leadership and Management in Care for Patients with Mental Illness
- The Use of Medical Marijuana in Nursing Leadership and Management for Pain Management
- The Impact of Socioeconomic Status on Nursing Leadership and Management
- The Ethics of Nursing Leadership and Management in Care for Patients with Disabilities
- The Use of Electroconvulsive Therapy in Nursing Leadership and Management
- The Impact of Age and Aging on Nursing Leadership and Management
- The Ethics of Nursing Leadership and Management in Care for Patients with Chronic Illnesses.
Latest Leadership and Management in Nursing Essay Topics to Write About
- The Impact of Nursing Leadership on Patient Satisfaction in Healthcare Settings
- The Role of Nursing Leadership in Promoting Health Equity and Social Justice
- The Use of Artificial Intelligence in Nursing Leadership and Management
- Effective Change Management in Nursing Leadership
- The Importance of Emotional Intelligence in Nursing Leadership
- The Use of Quality Improvement Processes in Nursing Leadership and Management
- The Role of Nursing Leadership in Addressing Staff Burnout and Compassion Fatigue
Leadership and Management in Nursing Research Questions
- What are the key components of effective nursing leadership and management?
- How can nursing leadership promote patient-centered care in healthcare settings?
- What is the impact of nursing leadership on healthcare outcomes and quality improvement?
- How can nursing leadership effectively address healthcare disparities and promote health equity?
- What is the role of emotional intelligence in nursing leadership and management?
- How can nursing leadership effectively manage change in healthcare organizations?
- What are the ethical considerations related to nursing leadership and management?
- What is the impact of cultural competence on nursing leadership and management?
- How can nursing leadership effectively address staff burnout and compassion fatigue?
- What is the role of nursing leadership in promoting healthcare innovation and change management?
- What is the impact of nursing leadership on healthcare costs and resource management?
- How can nursing leadership effectively address healthcare workforce shortages?
- How can nursing leadership effectively promote interprofessional collaboration in healthcare settings?
- What is the impact of shared governance on nursing leadership and management?
- How can nursing leadership effectively utilize quality improvement processes in healthcare organizations?
- What is the role of nursing leadership in addressing healthcare policy and advocacy?
- How can nursing leadership effectively address healthcare access and equity?
- What is the impact of nursing leadership on patient safety in healthcare settings?
- How can nursing leadership effectively address the challenges of disaster preparedness and response?
- What is the impact of nursing leadership on organizational culture and climate?
FAQs Related to Leadership and Management in Nursing -nursing leadership and management
Q: what is the difference between leadership and management in nursing.
A: Leadership in nursing refers to the ability to inspire, motivate, and guide others toward a common goal, while management in nursing refers to the ability to plan, organize, and coordinate resources to achieve that goal. While both are important, leadership is more focused on interpersonal skills and vision, while management is more focused on technical skills and operations. (difference between leadership and management)
Q: Why is leadership important in nursing?
A: Effective leadership in nursing is important for promoting patient safety, enhancing the quality of care, and improving healthcare outcomes. Nursing leaders are responsible for establishing a culture of excellence, collaboration, and innovation in healthcare settings, which is critical for achieving these goals.
Q: What are some examples of leadership in nursing?
A: Examples of leadership in nursing include empowering and motivating staff, leading by example, promoting a culture of safety and quality improvement, fostering interprofessional collaboration, advocating for patients’ needs and rights, and promoting professional development for staff.
Q: How can nurses develop their leadership skills?
A: Nurses can develop their leadership skills by seeking out educational and professional development opportunities, seeking mentorship and coaching from experienced nursing leaders, participating in leadership training programs, and actively seeking out leadership roles and responsibilities.
People Also Ask:
- What are the qualities of effective nursing leaders?
- How can nursing leadership promote interprofessional collaboration in healthcare settings?
- What is the impact of nursing leadership on staff morale and job satisfaction?
Conclusion:
In conclusion, effective leadership and management are essential components of nursing practice that are critical for promoting patient safety, enhancing the quality of care, and improving healthcare outcomes. By exemplifying leadership in nursing, healthcare providers can promote a culture of excellence, collaboration, and innovation, ultimately leading to better patient outcomes and improved healthcare delivery.
Call-to-Action:
If you need assistance with writing leadership and management in nursing essay, hire a top writer to get your paper done effectively and efficiently. Click on the order now button to place your order.
Jermaine Huey
We use cookies to give you the best experience. Cookie Policy
Nursing Leadership and Personal Skills Personal Essay
Introduction.
Strong leadership is required to establish a healthy working environment at all levels of an organization. Evidence shows that the presence of a nurse leader in an emergency department of a health facility makes the working environment healthy while at the same time increasing staff retention. In line with this, the American Association of Critical Care Nurses has revealed that for optimal performance of staff and improved patient care, nurse leadership needs to be developed. I have realized the importance of nurse leadership. For this reason, I intend to share my experience at my workplace and relate it with various theories, leadership styles, and technology.
Experience with the Supervisor
As quoted by Lachlan Mclean, “You can only lead others when you are willing to go.” My Emergency Room Director at Providence Park in the Emergency Department (ED) is an example of this. She allows us to help and motivate each other to become better through teamwork. She creates a positive working environment where all nurses can improve themselves through creativity and sharing of information. At one time, she asked for my opinion on the ED and on how she could make it better. It was an excellent opportunity to be creative and contribute to the improvement of this department.
Emergency Nurses Association (ENA)
The Emergency Nurses Association was formed to serve emergency nurses in different ways. The main purpose of ENA is to enhance service delivery through continuous training, research, and funding of other projects. The services offered by ENA ensure continuous improvement of service delivery. It also assists in finding solutions to new problems in the field of nursing (Hammond & Zimmermann, 2012). In addition, ENA provides an opportunity for one to contest for a position in management. One crucial role of ENA in the emergency room (ER) is leadership training. Leadership training is essential in the emergency room as it contributes to coordination and teamwork. ENA has gone further to partner with ENA Foundation in order to improve service delivery.
Time Management
According to Magnet’s Model of transformational leadership, time management, and leadership cannot be separated. My area of operation deals with emergencies and patients in critical conditions. As such, time wastage jeopardizes the lives of patients. In sharpening my time management skills, I have resorted to prioritizing and delegating duties. Prioritizing has allowed me to deal with urgent issues while delegation has enabled me to seek the help of my subordinates. Otherwise, as a team leader, possession of such qualities has enabled me to inspire and create a sense of commitment among my team members.
Leadership Skills
The issues of leadership and management have been taken to mean the same thing. However, a manager exerts authority over others. This means that, others are not involved in decision-making unlike in leadership where the views of all stakeholders are taken into consideration. Since leadership calls for the participation of all, it is important that managers possess some leadership skills to enhance teamwork.
Nurse leaders can execute their functions efficiently depending on how powerful they are. There are various sources of power. They include the legislative, professional qualification and personal qualities. The legislative provides rules and regulations meant to guide the activities of nurses. They govern the responsibilities of a nurse and determine the steps to take in various situations (Lauby, 2010). Secondly, possession of professional skills gives nurses the power to act according to their level of qualification. Finally, personal qualities determine the nurses’ ability to lead.
My personal skills have a significant impact on my leadership skills. I am very persistent, determined and communicative. My persistent nature has enabled me to stay focused on achieving my goals. My determination has kept me going even when faced with challenges. Moreover, I am very communicative. This quality has enabled me to develop a good working relationship with my workmates. However, I don’t like being criticized. This quality has affected my performance as a team leader and had severe adverse impacts on the results of the team. For this reason, I am trying very hard to change my behavior for the benefit of my group and patients (Manojlovich, 2007).
Change and Conflict Handling
Nurses, apart from executing their duties, also act as change agents. They initiate changes that impact the nursing field. One way through which they bring change is by contesting various political positions. When they win in such contests, they can push for favorable legislation (Barker & DeNisco, 2013). Another way is by applying various organizational and change theories. Organizational theories are applied in specific contexts to bring orderliness while change theories are mainly applied to bring about behavioral changes which help nurses to co-exist and relate well with patients. This helps to avoid the emergence of conflicts.
Conflicts are bound to arise in any setting and the nursing field is no exception. As such, methods of handling conflicts are necessary. One of the effective ways is through compromise. Another alternative is the avoiding strategy, where the focus is on creating delays in conflicts so that measures to combat them are put in place.
Leadership and Differences in Character
The issues of culture and gender have resulted in a number of differences among people. These differences have had an impact on performance at work. According to Lieberman (2015), men originated from Mars while women came from Venus. This difference according to him has had an impact on the style of communication. A good nurse leader should appreciate such differences and devise a plan to overcome them.
Emotional Intelligence
Nurse leaders should possess Emotional Intelligence (EI) skills. EI enables them to read emotions and make the necessary adjustments according to the perceived emotional state of their subordinates (Cassady & Eissa, 2008). Cassady and Eissa (2008) illustrated this by carrying out an experiment using a nurse who worked in a very busy ED of a hospital. The nurse was subjected to different types and levels of stressful situations. In this case, emotions were frayed and as a result the nurse was unable to function well. EI enables leaders to strike a balance between work performance and emotion, and as such enables the application of measures that ensure emotions do not affect the performance of nurses.
Nursing Informatics
Nursing Informatics is the use of information systems and electronic health records in the provision of health services. It helps nurse leaders to carry out their functions efficiently by making information readily available to them. The same systems assist in administration by helping in relaying information quickly. However, nursing Informatics may detach leaders from their subordinates and for this reason kill the spirit of teamwork (McCartney, 2004).
Nurse leaders perform numerous duties in emergency departments which require them to possess excellent leadership skills that will enable them to work efficiently with other nurses towards the realization of optimal results. They should be able to gauge the performance of their subordinates by reading their emotions. Finally, leadership is not only about applying what you have learned. Rather, it is about developing personal skills. Good personal skills combined with what I have discussed above will result in the best performance.
Barker, M., & DeNisco, S. M. (2013). Advanced practice nursing: Evolving roles for the transformation of the profession . Boston: Jones & Bartlett.
Cassady, J., & Eissa, A. (2008). Emotional intelligence: Perspective from educational and positive psychology . New York: Peter Lang.
Lauby, S. (2004). 7 Types of Power in the Workplace. Web.
Lieberman, S. (2015). Differences in Male and Female Communication Styles. Web.
Manojlovich, M. (2007). Power and Empowerment in Nursing: Looking Backward to Inform the Future. Web.
McCartney, P. (2004). Leadership in nursing informatics. Journal of Obstet Gynecol Neonatal Nurses , 33 (3), 371-380.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2022, May 19). Nursing Leadership and Personal Skills. https://ivypanda.com/essays/nursing-leadership-and-personal-skills/
"Nursing Leadership and Personal Skills." IvyPanda , 19 May 2022, ivypanda.com/essays/nursing-leadership-and-personal-skills/.
IvyPanda . (2022) 'Nursing Leadership and Personal Skills'. 19 May.
IvyPanda . 2022. "Nursing Leadership and Personal Skills." May 19, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/nursing-leadership-and-personal-skills/.
1. IvyPanda . "Nursing Leadership and Personal Skills." May 19, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/nursing-leadership-and-personal-skills/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Nursing Leadership and Personal Skills." May 19, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/nursing-leadership-and-personal-skills/.
- The Emergency Nurses Association Development
- Intensive Care Unit Nurses' Education Needs
- Serial Killers: Tommy Lynn Sells
- Informatics Nurses, Their Roles and Skills
- Organizational Informatics
- Health Informatics in the United States
- Informatics as an Approach and a Theory
- Public Health Informatics
- Overview of Nursing Informatics
- Research and Evaluation in Nursing Informatics
- PICOT Assignment Analysis
- Effective Ethical, Moral, and Legal Leadership
- Prioritizing Safety and Enhancing Nurses’ Proficiency
- Comparing Philosophies and Missions in Nursing
- The Comfort Theory of Nursing Used in Education
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- v.60; Jan-Dec 2023
- PMC10265372
Impact of Nurse Leaders Behaviors on Nursing Staff Performance: A Systematic Review of Literature
Nourah alsadaan.
1 Jouf University, Sakaka, Saudi Arabia
Basma Salameh
2 Arab American University, Jenin, Palestine
Fadia Ahmed Abdelkader Elsaid Reshia
3 Mansoura University, Mansoura, Egypt
Reem F. Alruwaili
Majed alruwaili, shaimaa ahmed awad ali, abeer nuwayfi alruwaili, gehan refat hefnawy, maha suwailem s. alshammari, afrah ghazi rumayh alrumayh, alya olayan alruwaili, linda katherine jones.
4 Charles Sturt University, Wagga Wagga, NSW, Australia
Nursing leadership is critical in facilitating and improving nurse performance, which is essential for providing quality care and ensuring patient safety. The aim of this study is to explore the relationship between nursing leadership and nurse performance by understanding the leadership behaviors and factors that motivate nurses to perform well. To study the factors that nurses believe motivate them to perform better, a systematic review was undertaken, correlating these factors to leadership behaviors/styles. The PRISMA guidelines were followed to identify relevant articles. After applying the selection criteria, 11 articles were included in the final analysis. Overall, 51 elements that influence nurses’ motivation to perform better were found and categorized into 6 categories, including autonomy, competencies, relatedness, individual nursing characteristics, relationships and support, and leadership styles/practices. It has been discovered that both direct and indirect nursing leadership behaviors affect nurses’ performance. A better understanding of the factors that motivate nurses to perform well and facilitating them in the work environment through leadership behaviors/styles can improve nurses’ performance. There is a need to increase research on nurse leadership and nurses’ performance in the current innovative and technologically integrated work environment to identify new factors of influence.
- What do we already know about this topic?
- Effective leadership in nursing can have a positive impact on nurse performance, job satisfaction, and patient outcomes.
- How does your research contribute to the field?
- It can provide new insights and understanding of how different leadership styles and practices impact nurse performance and patient outcomes
- What are your research’s implications toward theory, practice, or policy?
- To identify effective leadership practices that promote positive work environments, better nurse performance, and ultimately better patient outcomes, thus leading to improved patient contentment, safety, and care quality.
Introduction
Nurses are essential resources in hospitals as they spend more time with patients than any other healthcare personnel. Therefore, they play a significant role in ensuring quality care and patients’ safety by improving their performance. Despite accounting for 50% of the global healthcare workforce, 1 there is a severe shortage of nursing personnel in almost all countries. Developed countries such as the USA need an additional 275 000 nurses from 2020 to 2030. 2 According to the International Council of Nurses, there is a need for 13 million nurses globally to fill the shortage gap in the future. 3
The shortage of nurses has resulted in an increasing workload for existing nurses, significantly affecting their work life and performance, which can have a direct impact on the quality of care delivered. 4 Nursing performance is influenced by cognitive, physical, and organizational factors. 5 Various factors such as high workloads, lack of technological support, 6 skills and competencies (eg, problem-solving ability, nursing informatics competencies), 7 communication skills and confidence, 8 commitment, 9 quality of work life, 10 job stress, 11 and motivation 12 can significantly influence nursing performance. It is interesting to observe that most of these factors are a part of leadership management, focusing on providing training and support and addressing the issues affecting nurses.
Quality leadership was identified to be one of the major factors for promoting behaviors among the nurses for exhibiting greater responsibility and physical activity. 13 Similarly, workplace incivility from supervisors was identified to be negatively related to nursing performance. 14 Nursing leadership behaviors play a crucial role in shaping nursing performance, thereby achieving the organizational goals of ensuring the delivery of quality care and achieving better patient outcomes. 15 - 17 Considering the nursing leadership theories, transformational and transactional leadership styles 18 , 19 and their impact on nurses’ satisfaction, burnout, and resilience have received lot of attention. 17 , 18 , 20 However, most of the studies investigated the leadership styles influence on the factors affecting the nursing performance, but very few studies have focused on the leadership factors influencing the nurses’ motivation to perform well. An attempt in this aspect was made in a study 21 through the systematic review, but it only included studies till 2006. However, major changes have been observed in the factors influencing nursing performance in the past decade. The use of the internet and telecommunication technologies have significantly changed the quality of work of nurses, and led to the new forms of remote practices such as telenursing. 22 Furthermore, advanced innovative technologies such as artificial intelligence, intelligent systems such as IoTs 23 , 24 have significantly contributed to the nursing practice. 25 , 26 Additionally, due to the sudden surge of patients caused by the recent Covid-19 pandemic, nurses have experienced heightened levels of burnout, 27 which has significantly affected nurses work-life balance and their performance. 28 , 29 Furthermore, the COVID-19 pandemic has rendered the nursing shortage a critical issue on a global scale, according to the ICN study report 2023. 30 There are issues including understaffing and low job satisfaction, as well as an aging nursing workforce and a lack of young individuals entering the profession. The report highlighted that nurses’ shortage has grown significantly from 30.6 million in 2019 after the pandemic began. Furthermore, it identified that key research from surveys and reviews in the past 3 years, after the emergence of Covid-19 pandemic, there is a significant increase in nurses burn-out. This has resulted in burn-out nurses either leaving their employment or reducing their work hours, which has led to additional burden of work, increasing levels of stress among the resilient working nurses. 30 Therefore, significant changes in the factors that influence nurses’ motivation to perform well might have occurred. Considering these developments, it is necessary to extend the review conducted in Brady Germain and Cummings, 21 to identify the new developments in the research arena. For that, the purpose of this study is to conduct a systematic review for examining the factors related to nurses’ leadership and nurses’ performance. To achieve this objective, the following research questions are formulated.
- RQ1: What factors do nurses think affect their drive to excel in their work? The ambition and aptitude of the nurses to achieve their companies’ objectives of high-quality care and patient safety serve as the benchmarks for performance in this context.
- RQ2: Which leadership traits are associated with strong nurse performance? In this context, behaviors are described as the traits or tactics used by leaders to control nurses’ performance in order to accomplish organizational objectives, such as patient safety and high-quality care.
Materials and Methods
The protocol for this study is registered with PROSPERO (registration number: CRD42023387324), the registration date 15/01/2023.
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines 33 was used for conducting the systematic review of recent literature and reporting the findings relating to nursing leadership attributes and nursing performance.
Search Methods
Various databases, including CINAHL, Cochrane, EMBASE, HealthSTAR, Medline, and PsychINFO, were utilized to search for relevant studies. The search terms “nursing performance,” “nurse motivation,” “nursing leadership,” and “nursing leadership behaviors” were combined using Boolean operators “AND” and “OR.” To improve search sensitivity, keywords from the identified studies were also used in the search process. Only studies published in English were considered. Additionally, studies published within the last 20 years were included to ensure the search was current and covered new literature since the previous study by 23. Therefore, those studies before 2003 are excluded. Inclusion and exclusion criteria, as presented in Table 1 , were applied for selecting studies. Figure 1 provides a detailed overview of the search strategy used to select studies.
Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria.

PRISMA flow diagram.
Quality Appraisal
Two methods were used to rate the methodological quality of the chosen studies. The PRISMA 31 methodological quality criterion, which contains 27 elements, was used to systematic reviews. TREND 32 was used to evaluate quasi-experimental studies. TREND 32 comprises 22 criteria. The last criterion received a “yes,” a “no,” or a “unclear” rating. The “yes” items were added up to create a total score for each study, which ranged from zero to the total number of items that were examined. Studies with low methodological quality were deemed to be omitted from the review if they received a score of less than or equal to 50% on the evaluated items. Studies were deemed to be of medium or high quality and included in the review if they scored more than 50% on the analyzed items.
Data Extraction
Quantitative studies were the source of data, which encompassed details such as the author, publication year, research aim, sample size, methodology employed, independent and dependent variables, measurement criteria, reliability and validity of the measures, analytical techniques, and findings. The number of studies examined and the key conclusions were retrieved for systematic reviews.

Search Outcomes
Initially, 1632 articles were identified from different electronic databases, and 16 articles were identified through manual searching of journals, resulting in a total of 1648 articles. After removing 587 duplicates, 1061 articles were screened for titles and abstracts. Out of these, 984 articles were excluded based on title and abstract assessment, and 77 articles were selected for full-text reviews. After reviewing the full-text articles, 64 articles did not meet the inclusion criteria and were excluded. Finally, 13 articles were deemed eligible for quality assessment. Two articles did not meet quality criteria and were excluded resulting in 11 articles that are included in this review (See Figure 1 ).
Study Characteristics
Table 2 exhibits the attributes of the studies that were incorporated in this review. It can be observed that 6 studies were published recently (1 study in 2020, 3 studies in 2021, and 2 studies in 2022). Majority of the participants in most of the studies were females and were aged above 30 years with high work experience.
Summary of Study Characteristics Included in This Review.
Focusing on the leadership styles, 3 studies considered the effect of different leadership styles on nursing performance, 2 studies exclusively focused on transformational leadership, one each on sustainable leadership, entrepreneurial leadership, and servant leadership. There were 10 studies that have adopted quantitative approach of survey in data collection, and different analysis techniques were utilized in these studies. Only one systematic review was included that focused on the leadership attributes and nursing performance.
Theoretical Framework
Theories in research provides a rationale for developing hypothesis and testing the relationship between the variables, 44 and therefore it is important that the research studies should be guided by theoretical framework or a model that either confirmation of existing theory or generating new theories. Ten out of the 11 studies in this review were guided by a theoretical framework or a model. Six studies 33 - 37 ,45 in this review adopted leadership theories or developed a model for testing the leadership attributes on nursing performance. Social exchange theory and self-determination theories were used in Kül and Sönmez, 38 supporting the role of servant leadership in developing the innovative behavior of nurses (guided by social exchange) and motivating them in improving their performance by developing autonomy, competence and relatedness (self-determination theory: extrinsic motivation from leaders leading to intrinsic motivation among nurses). 39 Another study conducted by Salanova et al 40 emphasized the significance of social interactions in the work environment in improving self-efficacy by adopting social cognitive theory, where self-efficacy is considered as the primary personal resource, and transformational leadership as contextual resource for motivating nurses. In extending the leadership theories, another study 41 linked it with Innovative work behavior theory.
This theory contends that while functional competences give entrepreneurial nursing leaders the ability to inspire nurses to take innovative action while providing care, personal competencies enable them to establish an innovative vision. This builds confidence and commitment to adopting new ideas. 42 , 43 Wang et al 37 argued that leadership is a position that can be achieved by gaining skills, which contradicts leadership theories that suggest some people are born leaders. This also contradicts psychological theory that women have low aggressiveness and avoid leadership positions 46 , 47 However, recent studies focus on theories relevant to changes in the nursing industry, including the introduction of innovative technologies and new business models such as gig economy and eHealth. Many frameworks continue to focus on leadership styles such as transformational and transactional styles and relevant attributes that have been extensively researched over the past few decades. 21 However, new leadership attributes such as nursing informatics leadership, in light of growing influence of technology and industry policies in the quality care sector, have been neglected.
Measures of Nurse Performance
Twenty-two distinct measurement instruments were employed to evaluate the various factors that influence nursing performance in relationship with nursing leadership attributes. Five studies used questionnaires developed by authors for measuring nurses’ performance in relation to different aspects such as motivation, engagement, self-efficacy, performance, problem solving skills, and job satisfaction. Multifactor leadership questionnaires or its components were used in 3 studies focusing on different leadership styles and their impact on nursing performance as a part of the study model designed by respective authors. 34 , 35 , 40 Other major instruments used for measuring nurses’ performance related attributes include Caring Efficacy Scale, nurses’ activity scale, 45 Nurses performance evaluation checklist, 34 , 38 Innovative work behavior scale, 38 generic job satisfaction scale, 35 and innovative work behavior questionnaire. 41
Factors Influencing Nurses’ Performances
A total of 51 different factors that affected the nurses’ performance were identified from the studies included in the review ( Table 3 ). These factors were grouped into 6 categories including autonomy, competencies, relatedness, individual nurse characteristics, relationships and support, and leadership practices.
Factors Affecting Nurses’ Performance.
Three studies 33 , 38 , 45 examined the influence of autonomy related factors on nurses’ performance. Manojlovich 45 identified that strong nursing leadership behavior can contribute to the empowerment and self-efficacy on practice behaviors of the nurses, indicating that nursing leaders should provide more access to structural empowerment factors for nurses and exhibit unit-level nursing leadership. Kim and Sim 33 suggest that utilizing action-oriented and self-reward strategies, along with constructive thinking, can improve self-efficacy and empower individuals, leading to a significant improvement in their performance.
However, it is also observed that nursing performance can be affected by their communication abilities, indicating that in developing autonomy, communication skills play a significant role. Kül and Sönmez 38 identified that servant leadership attributes, such as being humanistic, empathetic, mutually beneficial, and service-oriented, can empower nurses to develop innovative behavior, which can improve their job performance. Innovative behaviors reflect an autonomy in nurses’ attitudes, where they autonomously take decisions in developing new ideas and new ways of delivering care, thereby improving the performance.
Competencies
Four studies 37 , 36 , 41 , 48 examined the influence of competencies related factors on the nurses’ performance. Few of these studies reflected new approaches in leadership and their impact on new areas of performance. For instance, Bagheri and Akbari 41 found that entrepreneurial leadership has positively influenced nurses’ innovation work behavior such as ideas exploration, generation, implementation, and championing, which can improve the overall performances and can support the achievement of organizational goals such as sustainability. Similarly, by creating a positive work environment and effectively managing resources and transformational leadership practices, nurse managers can significantly improve sustainability of nursing leadership. Moreover, Fing et al 36 found that competencies such as treating employees like family members, guiding them, and letting them make independent decisions have led to improvements in several areas that can impact nurses’ performance. These improvements include decision-making, the ability to accept criticism and suggestions. 36 Wang et al 48 found that leaders’ skills, such as idealized influence and intellectual stimulation, have a significant positive impact on nurses’ self-efficacy and work engagement.
Relatedness
Relatedness reflects how the nurse managers relate them to nurses and vice versa, which is reflected in their behavior toward each other. The study conducted by El-Azim et al 34 was the only study that did not find a significant statistical relationship between nursing leadership styles and nurses’ performance.
Individual Nurse Characteristics
Two studies have identified individual nursing characteristics related to nurses’ performance. The interest of nurses’ in taking up extra roles in addition to the existing roles supported by the nurse managers supported by transformational leadership practices through increased work engagement. 40 The findings of this study indicated that through supportive leadership practices, extra-role performance can be enhanced which in turn increases hospital efficacy. Wang et al 48 identified that psychological safety (a belief that nurses won’t be punished or humiliated for sharing ideas, concerns, and issues) could effectively improve nurses’ performance.
Relationships and Support
Wang et al 37 assessed the impact of nursing performance on nursing leadership along with other variables. They found that a caring and supportive work environment can positively affect nurses’ behavior and performance, and in turn, nursing leadership. This emphasizes the need for support from nursing leaders. 37
Leadership Styes/Practices
Although leadership practices were considered in most of the studies, significant approaches can be analyzed from 3 studies. Firstly, as discussed in the autonomy section, servant leadership approaches, such as humanistic, empathic, mutual benefit, and service-oriented approaches, can improve nurses’ competencies and skills, especially their ability to express themselves, communicate, and apply innovative ideas. Secondly, both transformational and transactional approaches, such as motivation, support, contingent rewards, and intellectual stimulation, can improve nurses’ satisfaction levels and job performance. 35 Thirdly, paternalistic leadership practices, such as treating nurses as family members, and laissez-faire practices, such as enabling nurses to make independent decisions, were identified as improving nurses’ performance. However, paternalistic approaches were found to be more influential than laissez-faire approaches. Fourthly, entrepreneurial leadership practices, such as driving innovation, risk-taking, and passion for work, were identified as promoting innovative behavior among nurses, which can improve their performance.
This study mainly focused on examining the link between nursing leadership and nurses’ performance by assessing the factors that nurses believed had an impact on their motivation to perform well; and the leadership behaviors that correlate with nurses’ performance. There has been a significant rise in the identification of number of factors that nurses perceive to be influencing their performance in the recent literature. This study has identified 51 such factors from research studies published since 2005, compared to a study conducted by Ronquillo et al 23 which included studies from 1995 to 2006, identifying 25 factors. This development indicates that significant progress can be observed in the research related to nurses’ leadership and nurses’ performance. One of the interesting findings in the review is that most of the studies (10 out of 11) were quantitative and adopted survey strategy for data collection; and only one study adopted systematic review approach, indicating the gaps in adoption of different methodological approaches in the research, which can contribute to diverse findings.
Most of the previous studies adopted social theories and the self-determination theory in assessing the relationship between nursing leadership and nurses’ performance. As a result, few studies mainly focused on the nurses’ approaches in providing quality care through social interaction, rather than on their personal attributes such as satisfaction, quality of life, and motivation. However, some studies attempted to develop theoretical models, 34 , 35 , 40 indicating the emergence of various constructs and relations between nursing leadership and nurses’ performance. One of the effective qualities of leaders is promoting autonomy among the team and making them self-reliant by developing skills and competencies to improve overall processes. Accordingly, from the findings ( Table 3 ), it was observed that the majority of the factors identified were in relation to leadership practices that focused on promoting autonomy and competencies among nurses
In the past few years, significant developments can be observed in the adoption of Industry technologies such as the Internet of Things, Artificial Intelligence, Cloud computing, block chain technology etc., 49 - 52 giving rise to new form of leadership such as nursing informatics leadership. 53 , 54 These developments can influence various factors within hospital settings, including organizational culture, workload, motivation, values in hospital settings that can directly or indirectly influence nursing performance. However, no studies were identified in this review which considered these developments in identifying the factors that influence nurses’ performance. Studies reviewed indicated that nursing leadership can influence autonomy, 33 , 38 , 45 relatedness, 34 competencies, 36 , 37 , 41 , 48 individual characteristics, 40 , 48 and relationships and support, 37 as perceived by nurses influencing their motivation to perform well. In addition, leadership practices were identified to be nurses’ abilities to perform well. Furthermore, leadership behaviors that support autonomy, inclusivity, transformation (improving skills, innovation abilities, and competencies), and staff prioritization (caring, paternalistic behavior, empathy) can result in high nursing performance. 33 , 38 , 45 It is important that nurse leaders share organizational goals to encourage staff, offer suggestions, and receive feedback on innovative practices for achieving goals in a cooperative and supportive work culture. The studies reviewed suggest leadership plays a crucial role in influencing nurses’ performance in various areas, such as innovation, decision-making, and work engagement. 36 , 37 , 41 , 48 Furthermore, new approaches to leadership, such as entrepreneurial leadership and transformational leadership practices, can positively impact nurses’ performance and support the achievement of organizational goals such as sustainability. 41 Therefore, it is important for nurse managers to continuously develop their leadership skills and create a positive work environment that supports nurses’ ability to perform well. 36 By doing so, nurse managers can help to create practice environments that promote nurses’ ability to perform their roles effectively, thus enhancing overall nursing performance.
While one study included in the review did not find any significant statistical association between nursing leadership styles and nurses’ performance, it suggested that further research is needed to better analyze the relationship between nursing leadership and nurses’ performance by adopting relatedness factors in the areas of advanced leadership approaches and providing performance appraisal. 34 This highlights the importance of considering relatedness factors in nursing leadership to support nurses’ performance and promote positive relationships between nurse managers and nurses.
The results of Salanova et al 40 study highlight the significance of nurse managers adopting transformational leadership practices to increase nurses’ interest in taking up extra roles, which can lead to improved hospital efficacy. Additionally, promoting psychological safety in the workplace can create a supportive work environment that encourages open communication and enhances nurses’ performance. 48 This indicates the nurses should have enough freedom with nurse managers for sharing their opinions without any hesitation or fear, which may benefit both of them.
Therefore, nursing leadership has a significant impact on nurses’ perceptions of the factors that influence their motivation to perform. This impact can be both direct and indirect. Therefore, it is essential to have competent nursing leaders to create practice settings that can foster nurses’ capacity to succeed. In other words, the link between nursing leadership and nurses’ success is critical, and it is necessary to prioritize leadership development in the nursing profession to achieve optimal patient outcomes.
As observed from the recent report by ICN, 30 the lack of strategic and systematic approach by the employers and policymakers is one of the key challenges associated with rising nursing problems. In this context, it may be implied that effective leadership approaches coupled with systematic management of nursing resources could be one of the effective ways to improve nursing performance, retention, and reduced burn-out rates. Accordingly, apart from the patient-related aspects, personal, co-worker, organizational, and societal related factors were identified to be the significantly contributing factors of nurses’ burn-out during the pandemic, 55 highlighting the issues with nurses’ leadership and organizational/employer approaches. In this context, a systematic review on interventions to reduce occupational stress and burn-out, 56 observed that the interventions were effective when they focus at individual level and organization directed, implying the strategic and systematic approach adopted by the employers and led by nursing leaders, with an individualized focus, signifying the relevance of transformational, motivational, and supportive leadership styles. For instance, spiritual intelligence among nursing leaders was identified to be influencing nursing managers’ competencies in managing stress and burn-out, 57 and similar strategies could be directed by employers to effectively manage nursing resources. Such streamlined approaches may be effective in not only improving nurses’ performance, but also in addressing the challenges such as nurses’ burn-out, retention, and increasing stress in the post-pandemic era.
Implications for Nurse Researchers
The findings from this review supports a theoretical model ( Figure 2 ) on factors that influences nurses’ motivation to perform well, which may be tested and evaluated in future research. Analyzing published research till date in this review has suggested that leadership practices that support autonomy, competencies, and relatedness through inclusive approaches reflect that nurses’ contributions are valued and this process resulted in increased motivation of nurses to perform well. In addition, leadership practices that support innovation (entrepreneurial), and cooperative culture (transformational) were identified to be more influencing in improving nurses’ motivation to perform better. Although, different leadership practices and their relationship with nurses’ performance were investigated, significant changes have been observed in the nursing work environment in the past few years. The introduction of innovative technologies and business models, such as the gig economy and online health services, is among the many changes. These changes can lead to new leadership practices and new factors that influences nurses’ performance, such as informatics competencies and skills, remote work culture. These are some areas that future researchers can investigate to identify new leadership practices and the factors that influence nurses’ performance. Furthermore, sustainability has become a core component of all organizations, including healthcare. Therefore, it is important to examine leadership behaviors that can have an impact on nurses’ abilities to help achieve sustainable organizational goals. Furthermore, unexpected disasters such as the recent Covid-19 pandemic has significantly increased the burden on nursing care. Leadership practices in such a highly demanding workload environment and their impact on nurses’ abilities to provide quality care and achieve better patient outcomes could be examined. Finally, it is evident from the review that most of the studies have adopted quantitative methods. Diverse methodological framework adoption can contribute to the quality of research. Therefore, future researchers should focus on adopting other frameworks such as qualitative, and mixed methods in conducting the research.

Proposed theoretical model.
Implications for Nurse Leaders
Nursing performance is a key factor influencing the sustainability of nursing leadership. 37 Therefore, nurse leaders must adopt various leadership practices and behaviors that improve nursing performance, especially those that increase nurses’ motivation to perform better. Leadership practices that encourage employees’ motivation can influence organizational practices and goals. 58 As nurse leaders carry huge workloads, their work effectiveness can be affected, 59 which create barriers and challenges in achieving optimal nursing performance and ultimately providing high-quality care. Addressing nurse leaders’ workload is therefore necessary to enhance their ability to influence nurses and improve overall nursing performance.
Limitations
This review has a few potential limitations. It can be observed that 10 out of the 11 studies reviewed adopted quantitative methods, reflecting the limitation of including diverse methodological studies. Furthermore, reporting bias may exist as published studies tend to over-report positive findings. Many studies used self-designed scales to measure nurses’ performance, and others used different tools, limiting the validity and generalizability of findings. Most of the studies in this review are cross-sectional correlation studies and may be prone to bias 44, but they are helpful in examining the relationship between nursing leadership practices, behaviors, and nurses’ performance, which is the main purpose of this study.
Conclusions
Providing quality care and ensuring patients’ safety are fundamental goals for all healthcare organizations. Since nurses are the primary healthcare providers who spend a significant amount of time with patients delivering care and services, they have a crucial role in achieving these objectives. Nurse leaders who manage the nursing resources are the key personnel who are responsible for overseeing the quality of care and patients’ safety, and therefore they need to encourage nurses’ in better understanding the patients’ needs and values. Strong nurse leaders are effective in implementing evidence-based practices to ensure that these objectives are achieved, as research showed that nursing leadership can both directly and indirectly influence nurses’ performance. The present review has identified 51 factors that nurses categorize under 6 domains, which they believe motivate them to perform effectively. These included autonomy, relatedness, competencies, individual nurse characteristics, relationships and support, and leadership practices/styles. Comprehending these actors is essential and necessary for nurse leaders to promote quality of care and to achieve organizational goals such as sustainability, growth and innovativeness. Therefore, nurse leaders should strive to understand and identify the factors that motivate nurses to perform well and accordingly should address/facilitate these factors through their behavior or leadership styles.
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Funding: The author(s) received no financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Ethical Approval: Our study did not require an ethical board approval because systematic reviews generally do not need ethics committee or institutional review board approval,

Leadership essays
Nursing role in global health, practice experience, psychodynamic approach with transformative approach for organizational change, leadership in health sciences and nursing, advocacy in nursing leadership, power to influence, accountable care organizations for nurse leaders, impact of ehr on the management of patients’ health: implementation plan, what do you need to know about leadership essays.
Good nurses who are successful in their leadership roles can motivate and support their teams, coordinate resources to promote teamwork, and collaborate with others to achieve quality patient care. That’s why creating leadership essays aimed at developing qualities like decisiveness, problem-solving ability, having a vision of the future, and inspiring others to reach that vision are standard and significant writing assignments you may face during your studies.
Key Features of a Good Leadership Essay
Nursing leaders must make difficult decisions and have the communication and organizational skills to manage multiple tasks. They must also be able to quickly predict and respond to current changes in the healthcare system, advocate for their patient’s needs, and provide a safe and productive workplace. These principles are fully displayed in the leadership essay via the following things especially.
Appropriate Topic That is Relevant & Exciting
When choosing leadership essay topics, the best ones are related to the issues that significantly impact society as a whole and healthcare providers particularly – worldwide, nationally, and locally. Such essays differ in their practicality and solutions aimed to improve some aspects of nursing care. So try to avoid generic or utopian ideas that have nothing to do with actual clinical cases and real life.
Careful Research
Of course, you need to do your best to prepare and process materials for leadership essays. This can be difficult both due to the amount of information and finding relevant sources if your topic is narrow or poorly understood. So, naturally, you should be ready to dig deep to find unique hidden facts to write about in your essay.
Top Quality Leadership Essay Examples Just for You
Writing an essay on leadership could be an exciting experience but challenging if you’re facing the task at first or don’t know what to write about. Having some good examples as references may help a lot. So we’ve collected the broadest range of samples to help you to understand how to handle essay writing on leadership and provide valuable insights on how to prepare a quality paper effortlessly, what it should involve, and how to manage the content properly.
Why You Should Check Out Our Leadership Essays Examples
First, there’s a wide range of papers’ examples on various topics. Thus, you’ll easily find what you need via intuitive search. Next, it’s worth mentioning all our leadership essay examples are crafted by professional writers with backgrounds in their respective fields. These writing specialists deeply understand the subjects and top-tier content-producing skills. Besides, the writers know well what college professors expect from students, so you can undoubtedly use any of the paper examples, ensuring it meets the highest academic standards.
How Can Nursing Leadership Essay Samples Help You?
Try to search through your subject or topic to get an example of something particular or surf via category. In any case, every nursing leadership essay sample gives you good ideas on how to format and structure the paper to meet requirements properly. You’ll also learn from the attention to how the writer used elements such as language, tone, and word choice to create a powerful article.
While our samples are completely free, they could be helpful or damaging to a student, depending on how they use them. The best way to use our sample essay about leadership is to learn from it and apply that knowledge to your own work. But don’t try to copy parts of the text from them, as good work is original and completely unique.
Cannot Find the Right Free Essay Leadership Example?
Here are many of well-written samples, so you’ll have no difficulties finding one that can help. However, feel free to turn to our experts for assistance if you still have not picked up the right leadership essay example. Moreover, proficient nursing writers can always assist you in producing your own paper per your instructions and unique demands.
- AACN Synergy Model
- Advanced Practice Nurse (ADN)
- American Nurses’ Association (ANA)
- Communication

40 Nursing concept analysis paper Topics to Use for BSN, MSN, & dNP
- Dr. Rachel Andel
- February 14, 2024
- Nursing Topics and Ideas

Are you working on a Nursing Concept Analysis Paper? We have compiled a list of Nursing concept analysis paper topics for your nursing paper.
Before checking the topics, here’s a simple step-by-step guide on writing a nursing concept analysis paper. If this is your first time writing a concept analysis paper, the outline below should help you start your paper.
Working On Nursing Concept Analysis Paper?
Get a 100% plagiarism-free paper sent directly to your email in 3-6 hours.
Check our more comprehensive guide on How to Write a Nursing concept analysis paper
20+ BSN Nursing Concept Analysis Paper Topics
Here’s a list of 20 current nursing concept analysis paper topics to use for your nursing paper:
- Patient-centered care in the ICU
- Ethical considerations in nursing informatics
- Cultural competence in pediatric nursing
- Person-centered communication in geriatric care
- Pain management strategies in palliative care
- Leadership styles in nursing management
- Compassion fatigue among oncology nurses
- The impact of technology on nursing practice
- Health disparities among marginalized communities
- Interprofessional collaboration in mental health nursing
- Evidence-based practice in pediatric nursing
- Nursing interventions for sleep disturbances in postpartum women
- Resilience and burnout prevention in critical care nursing
- Self-care practices for nursing students
- Ethical dilemmas in end-of-life care
- The role of mindfulness in nursing practice
- Nurse advocacy for patient safety
- Health promotion strategies for adolescent populations
- Cultural diversity in maternity nursing
- Challenges and strategies for nursing education in the digital era
MSN Nursing Concept Analysis Paper Ideas
- Nursing leadership styles and their impact on patient outcomes
- The concept of empathy in nursing and its role in patient care
- Exploring cultural competence in nursing practice
- Analyzing the concept of pain management in nursing
- The role of technology in improving patient safety in nursing
- Examining the concept of patient advocacy in nursing
- Exploring the impact of evidence-based practice on nursing outcomes
- Analyzing the concept of teamwork and collaboration in nursing
- The role of effective communication in nursing care
- Understanding the concept of patient empowerment in nursing practice
- Exploring the ethical implications of nursing research
- Analyzing the concept of holistic nursing care
- Understanding the importance of self-care for nurses
- Exploring the concept of cultural diversity in nursing
- Analyzing the impact of stress and burnout on nursing professionals
- Understanding the role of nursing informatics in healthcare delivery
- Exploring the concept of patient education in nursing practice
- Analyzing the importance of ethics in nursing decision-making
- Understanding the concept of patient-centered care in nursing
- Exploring the role of nursing in disaster preparedness and response.
DNP Nursing Concept Analysis Topic Ideas
Here is a list of 20 Doctor of Nursing Practice (DNP) Nursing Concept Analysis Topic Ideas for your nursing research paper:
- Pain management in pediatric patients
- Nurse-patient communication in critical care settings
- Family-centered care in neonatal intensive care units (NICUs)
- Cross-cultural nursing care and its impact on patient outcomes
- Ethical considerations in end-of-life care
- The role of technology in nursing education
- Interprofessional collaboration in healthcare teams
- Nursing leadership styles and their influence on organizational culture
- Patient safety in medication administration
- Nursing interventions for managing postoperative pain
- Healthcare disparities among marginalized populations
- The impact of evidence-based practice on patient outcomes
- Nursing care for patients with chronic illnesses
- The role of nurse educators in preparing future nurses
- Transitioning to practice: Challenges faced by new graduate nurses
- Nursing informatics: Enhancing healthcare data management
- Ethical dilemmas in psychiatric nursing
- Holistic nursing care and its impact on patient well-being
- Nursing interventions for promoting self-care in older adults
- The role of cultural competence in providing culturally sensitive care
Outline of a Nursing Concept Analysis Paper
- Start with a clear and concise introduction that introduces the concept you are analyzing, provides a clear summary, and guides you on what areas you’ll cover.
- The Ideal length of the introduction for your nursing concept analysis paper is around 250 words or two well-structured introductory paragraphs.
- Offer a precise and comprehensive definition of the concept under consideration. Consult reputable nursing literature and sources for an authoritative definition. (250 words)
- Conduct a thorough literature review to explore how the concept is used and understood in the nursing field (750 words)
- Identify and discuss the essential attributes and characteristics of the concept. This involves breaking down the concept into its key elements. (300 words)
- Explore the factors that precede or lead to the occurrence of the concept (antecedents). Examine the outcomes or results associated with the concept (consequences).(300 words)
- Develop a model case that exemplifies the concept in its fullest form. This serves as an illustrative and comprehensive example (250 words)
- Identify Borderline and Related Cases(1000 words)
- Antecedents – What must occur/be in place for the Nursing concept to exist/function properly
- Consequences – Results from impaired antecedents
- Discuss empirical referents and how they can be used to assess or measure the concept. (300 words)
- Summarize the key findings and insights gained from the concept analysis (250 words)
- Ensure proper citation of all sources used in your concept analysis. Follow the appropriate citation style (e.g., APA, MLA) per your instructor’s guidelines.
Working On an Assignment With Similar Concepts Or Instructions?
A Page will cost you $12, however, this varies with your deadline.
We have a team of expert nursing writers ready to help with your nursing assignments. They will save you time, and improve your grades.
Whatever your goals are, expect plagiarism-free works, on-time delivery, and 24/7 support from us.
Here is your 15% off to get started. Simply:
- Place your order ( Place Order )
- Click on Enter Promo Code after adding your instructions
- Insert your code – Get20
All the Best,
Have a subject expert Write for You Now
Have a subject expert finish your paper for you, edit my paper for me, have an expert write your dissertation's chapter, what you'll learn.
Working On A Paper On This Topic?
Use our nursing writing service and save your time. We guarantee high quality, on-time delivery, and 100% confidentiality.
- Nursing Careers
- Nursing Paper Solutions
- Nursing Theories
- Nursing Writing Guides
Related Posts
- How to become a Hospice Nurse
- How to Become a Labor and Delivery Nurse
- Role of an Intensive Care Unit Nurse: How to Become, Role and Requirements
Important Links
Knowledge base, paper examples, nursing writing services.
Nursingstudy.org helps students cope with college assignments and write papers on various topics. We deal with academic writing, creative writing, and non-word assignments.
All the materials from our website should be used with proper references. All the work should be used per the appropriate policies and applicable laws.
Our samples and other types of content are meant for research and reference purposes only. We are strongly against plagiarism and academic dishonesty.
Phone: +1 628 261 0844
Mail: [email protected]

We Accept:

@2015-2024, Nursingstudy.org
Top Nursing Argumentative Essay Topics: Engage in Thought-Provoking Debates

This article was written in collaboration with Christine T. and ChatGPT, our little helper developed by OpenAI.

Nursing is a diverse and evolving field, constantly presenting new challenges and debates. As a nursing student or professional, engaging in these discussions allows you to develop critical thinking and writing skills while expanding your field knowledge. This blog post will explore various nursing argumentative essay topics to help you find inspiration for your next paper.
Patient Care and Ethics
- The ethics of administering experimental treatments to terminally ill patients
- Balancing patient autonomy and nurse responsibility in care decisions
- Addressing cultural and religious beliefs in end-of-life care
- The role of informed consent in patient care and treatment decisions
- Ethical considerations in the allocation of scarce medical resources
- The ethics of withholding information from patients for their benefit
- Patient privacy and confidentiality in the age of electronic health records
- Comparing faith practices in healthcare: Sikhism, Judaism, Bahaism, and Christianity
- The ethics of using restraints in patient care
- The ethical implications of non-compliance with prescribed treatments
- The role of nursing in advocating for patients’ rights
- Ethical considerations in caring for patients with mental health disorders
- The ethics of mandatory vaccinations for healthcare workers
- Addressing moral distress among nurses in patient care situations
- The ethics of caring for patients who refuse life-saving treatments
- The role of advance directives in ethical decision-making for patient care
- Ethical considerations in the care of patients with substance use disorders
- The ethics of healthcare rationing in times of crisis
- The ethical implications of assisted reproductive technologies
- Addressing ethical dilemmas in neonatal and pediatric nursing
- The ethics of pain management in nursing practice
- Pediatric oncology: working towards better treatment through evidence-based research
- Ethical considerations in the care of patients with dementia and cognitive decline
- The ethics of genetic testing and personalized medicine in patient care
- The ethical implications of clinical trials and research involving human subjects
- The role of nursing in addressing ethical issues related to organ transplantation
- Ethical considerations in the care of prisoners and detainees
- The ethics of involuntary treatment and psychiatric care
- Euthanasia: an analysis of utilitarian approach
- Addressing ethical challenges in the care of patients with disabilities
- The ethical implications of medical tourism and cross-border healthcare
- The role of nursing in addressing ethical issues related to global health
- Ethical considerations in the care of military veterans and their families
- The ethics of surrogate decision-making in patient care
- Addressing ethical challenges in the care of patients with chronic and terminal illnesses
- The role of nursing in promoting patient advocacy and self-determination
- Ethical considerations in the care of patients with rare diseases and conditions
- The ethics of care rationing in the context of an aging population
- The role of nursing in addressing ethical issues related to access to healthcare
- Ethical considerations in the care of patients during public health emergencies
- The ethics of triage and prioritization of care in emergencies
- The role of nursing in promoting environmental sustainability and addressing ethical issues related to climate change
- Ethical challenges in the care of patients at the end of life
Medical Studies Overwhelming?
Delegate Your Nursing Papers to the Pros!
Get 15% Discount
+ Plagiarism Report for FREE
Technological Advancements in Nursing
- The impact of electronic health records on nursing practice and patient care
- The role of telemedicine in expanding access to healthcare services
- How wearables and remote monitoring devices are changing nursing care
- The integration of artificial intelligence in nursing practice and decision-making
- The use of virtual reality in nursing education and training
- Ethical considerations in the use of advanced technologies in nursing practice
- The role of robotics in patient care and nursing support
- The impact of mobile health apps on nursing practice and patient engagement
- The use of big data and analytics in improving patient outcomes and nursing practice
- The role of 3D printing in medical device innovation and patient care
- The integration of telehealth in the management of chronic conditions
- The use of social media and online platforms for professional development and networking in nursing
- Usability, integration, and interoperability of healthcare technology
- The impact of advanced diagnostics and imaging technologies on nursing practice
- The role of blockchain technology in improving healthcare data security and management
- The use of gamification in nursing education and patient engagement
- The impact of technology on nursing workflow and time management
- The role of virtual assistants and chatbots in patient care and nursing support
- Clinical laboratory IT security: challenges, implications, and solutions
- The use of augmented reality in nursing education and practice
- The integration of telepsychiatry and mental health services in nursing care
- The impact of technology on nurse-patient communication and relationship-building
- The role of electronic prescribing and medication management systems in reducing medication errors
- The use of telemonitoring and remote care in the management of high-risk pregnancies
- The impact of technology on infection control and prevention in healthcare settings
- The role of smart home technologies in supporting aging-in-place and home-based care
- The use of technology in promoting self-care and patient empowerment
- Safeguarding patient information: nursing informatics best practices for privacy and security in healthcare
- The integration of genomics and personalized medicine in nursing practice
- The role of technology in addressing healthcare disparities and promoting health equity
- The impact of technology on nursing workforce planning and resource allocation
- The use of predictive analytics in identifying high-risk patients and improving care coordination
- The role of technology in promoting interprofessional collaboration and communication in healthcare
- The impact of technology on nursing education and the development of future nursing competencies
- The role of technology in supporting disaster response and emergency preparedness in nursing
- The use of technology in promoting patient safety and reducing medical errors
- The impact of technology on nursing leadership and management
- The role of technology in addressing the social determinants of health and promoting community health
- The integration of technology in palliative and end-of-life care
- The use of technology in enhancing patient engagement and satisfaction in nursing care
- The role of technology in promoting evidence-based practice and research in nursing
- The impact of technology on nursing ethics and professional boundaries
- The role of technology in addressing the global nursing shortage and promoting workforce sustainability
Nursing Education and Professional Development
- The role of simulation-based learning in nursing education
- The impact of online learning on nursing education outcomes
- Integrating cultural competence in nursing curricula
- Strategies for promoting lifelong learning in nursing practice
- The role of mentorship in nursing professional development
- Addressing the transition from student nurse to professional nurse
- The impact of interprofessional education on nursing practice and patient outcomes
- The role of nursing preceptorship in clinical education
- Strategies for reducing nursing student attrition and promoting retention
- The integration of evidence-based practice in nursing education
- The role of reflective practice in nursing professional development
- Addressing the nursing faculty shortage: Challenges and solutions
- The impact of standardized testing on nursing education and practice
- The role of nursing leadership development in healthcare transformation
- Strategies for enhancing critical thinking skills in nursing education
- Global health learning in nursing and health care disparities
- The impact of clinical experience on nursing students’ confidence and competence
- The role of continuing education in maintaining nursing competency and licensure
- Addressing the needs of diverse learners in nursing education
- The impact of technology on nursing education and the development of digital literacy skills
- Digital healthcare and organizational learning: enhancing patient care through technology and knowledge management
- The role of nursing education in promoting health literacy and patient education
- Strategies for promoting resilience and self-care in nursing education
- The impact of global health experiences on nursing students’ cultural competence and professional development
- The role of nurse educators in shaping the future of nursing practice
- Addressing the challenges of teaching nursing ethics and professional values
- The impact of accreditation standards on nursing education and program quality
- The role of professional nursing organizations in supporting continuing education and development
- Strategies for fostering a culture of learning and professional growth in nursing practice
- The impact of nursing education on patient outcomes and quality of care
- The role of nursing education in addressing healthcare disparities and promoting health equity
- The integral role of nurses in healthcare systems: the importance of education and experience
- Addressing the challenges of teaching and assessing clinical judgment in nursing education
- The impact of nursing education on workforce development and nursing shortages
- The role of nursing education in promoting environmental sustainability and planetary health
- Strategies for promoting effective communication and teamwork in nursing education
- The impact of nursing education on patient safety and error prevention
- The role of nursing education in promoting innovation and entrepreneurship in healthcare
- Addressing the needs of adult learners and nontraditional students in nursing education
- The impact of nursing education on interprofessional collaboration and healthcare team dynamics
- The role of nursing education in promoting ethical decision-making and moral courage in practice
- Strategies for enhancing nursing students’ clinical reasoning and decision-making skills
- The impact of nursing education on the development of professional identity and role socialization
Healthcare Policies and Nursing Practice
- The role of nurses in shaping healthcare policy and advocating for reform
- The impact of the Affordable Care Act on nursing practice and patient care
- Addressing the nursing shortage: policy initiatives and workforce strategies
- Understanding the impact of the American Healthcare System Regulatory Acts
- The role of nursing scope of practice regulations on healthcare delivery and outcomes
- The impact of healthcare reimbursement policies on nursing practice and patient care
- The role of nursing in addressing the opioid crisis: policy and practice implications
- The impact of public health policies on nursing practice and community health
- The role of nursing in promoting healthcare access and reducing disparities
- The impact of healthcare quality and safety regulations on nursing practice
- The role of nursing in implementing evidence-based practice guidelines and policies
- The impact of health information technology policies on nursing practice and patient care
- The role of nursing in addressing social determinants of health through policy and practice interventions
- The impact of nurse staffing regulations on patient outcomes and workforce planning
- The role of nursing in promoting health literacy and patient-centered care through policy and practice initiatives
- Healthcare management: career paths and requirements
- The impact of healthcare privacy and confidentiality policies on nursing practice and patient trust
- The role of nursing in promoting environmental sustainability and climate change policies in healthcare
- The impact of healthcare workforce diversity policies on nursing practice and cultural competence
- The role of nursing in promoting global health and addressing international healthcare challenges
- The impact of mental health policies on nursing practice and the care of patients with mental health disorders
- The role of nursing in promoting value-based care and payment models in healthcare
- The impact of healthcare cost containment policies on nursing practice and resource allocation
- The role of nursing in promoting patient safety and quality improvement through policy and practice initiatives
- The impact of healthcare reform on nursing education and workforce development
- Understanding the US health care reform: necessity, challenges, and implementation
- The role of nursing in promoting health equity and addressing healthcare disparities through policy and practice interventions
- The impact of healthcare policies on nursing leadership and management roles
- The role of nursing in promoting interprofessional collaboration and teamwork through policy and practice initiatives
- The impact of healthcare policies on the integration of technology in nursing practice and patient care
- The role of nursing in promoting ethical decision-making and moral courage through policy and practice initiatives
- The impact of healthcare policies on nursing practice in rural and underserved communities
- The role of nursing in promoting innovation and entrepreneurship in healthcare through policy and practice initiatives
- Combating health care-associated infections: a community-based approach
- The impact of healthcare policies on advanced practice nursing roles and scope of practice
- The role of nursing in promoting palliative and end-of-life care through policy and practice initiatives
- The impact of healthcare policies on infection control and prevention in nursing practice and patient care
- The role of nursing in addressing the challenges of an aging population through policy and practice initiatives
- The impact of healthcare policies on nursing practice in the care of patients with chronic and complex conditions
- The role of nursing in promoting patient advocacy and self-determination through policy and practice initiatives
- The impact of healthcare policies on nursing practice in disaster response and emergency preparedness
- The role of nursing in promoting evidence-based practice and research through policy and practice initiatives
- The impact of healthcare policies on nursing practice in the care of vulnerable and high-risk populations
- The role of nursing in addressing the global nursing shortage and promoting workforce sustainability through policy and practice initiatives
Cultural Competence and Health Equity
- The role of cultural competence in reducing healthcare disparities
- Integrating cultural competence into nursing education and practice
- Addressing implicit bias in nursing practice and patient care
- The impact of cultural competence on patient satisfaction and outcomes
- The role of nursing in promoting health literacy among diverse populations
- Strategies for effective communication with patients from diverse backgrounds
- Mental health and gender inequality
- The impact of cultural competence on nurse-patient relationship-building and trust
- The role of nursing in addressing social determinants of health and promoting health equity
- Addressing the challenges of providing culturally competent care in rural and remote settings
- The impact of cultural competence on interprofessional collaboration and teamwork
- Bridging the gap: tackling maternal and child health disparities between developed and underdeveloped countries
- The role of nursing in promoting cultural competence in healthcare organizations
- Addressing health disparities among LGBTQ+ populations through culturally competent nursing care
- The impact of cultural competence on the prevention and management of chronic diseases
- The role of nursing in promoting culturally competent mental health care
- Addressing health disparities among immigrant and refugee populations through culturally competent nursing care
- The impact of cultural competence on patient safety and error prevention
- The role of nursing in promoting cultural competence in palliative and end-of-life care
- Addressing health disparities among indigenous populations through culturally competent nursing care
- The impact of cultural competence on the care of patients with disabilities
- The role of nursing in promoting culturally competent care for patients with substance use disorders
- Addressing health disparities among racial and ethnic minority populations through culturally competent nursing care
- The impact of cultural competence on the care of patients with rare diseases and conditions
- The role of nursing in promoting culturally competent care in global health settings
- Addressing the challenges of providing culturally competent care in disaster response and emergency preparedness
- The impact of cultural competence on nursing leadership and management
- The role of nursing in promoting culturally competent care in the context of an aging population
- Addressing health disparities among low-income populations through culturally competent nursing care
- The impact of cultural competence on nursing practice in the care of patients with complex and chronic conditions
- The role of nursing in promoting culturally competent care for military veterans and their families
- Addressing health disparities among women and girls through culturally competent nursing care
- The impact of cultural competence on nursing practice in the care of patients with infectious diseases
- The role of nursing in promoting culturally competent care for incarcerated individuals and detainees
- Addressing health disparities among individuals with limited English proficiency through culturally competent nursing care
- The impact of cultural competence on nursing practice in the care of patients at the end of life
- The role of nursing in promoting culturally competent care in the context of climate change and environmental health
- Addressing health disparities among individuals experiencing homelessness through culturally competent nursing care
- The impact of cultural competence on nursing practice in the care of patients with traumatic experiences
- The role of nursing in promoting culturally competent care in the context of medical tourism and cross-border healthcare
- Addressing health disparities among individuals with low health literacy through culturally competent nursing care
- The impact of cultural competence on nursing practice in the care of vulnerable and high-risk populations
Mental Health and Burnout in Nursing
- The prevalence of burnout among nursing professionals
- Strategies for preventing and addressing nurse burnout
- The impact of nurse burnout on patient care and outcomes
- The role of nursing leadership in addressing mental health and burnout
- Promoting self-care and resilience among nursing professionals
- The impact of nurse burnout on job satisfaction and retention
- The role of nursing education in addressing mental health and burnout
- Strategies for fostering a healthy work-life balance in nursing
- The impact of nurse burnout on interprofessional collaboration and teamwork
- The role of peer support and mentorship in addressing mental health and burnout
- The impact of nurse burnout on nursing errors and patient safety
- The role of workplace wellness programs in addressing mental health and burnout
- Strategies for managing stress and anxiety in nursing practice
- The impact of nurse burnout on professional development and career progression
- The role of professional nursing organizations in addressing mental health and burnout
- The impact of nurse burnout on healthcare costs and resource allocation
- The role of nursing research in understanding and addressing mental health and burnout
- Strategies for promoting emotional intelligence and self-awareness in nursing practice
- The impact of nurse burnout on the nursing workforce and workforce planning
- The role of nursing in promoting mental health and well-being among patients and families
- The impact of nurse burnout on ethical decision-making and moral distress
- The role of nursing in addressing mental health disparities and stigma
- Strategies for promoting a culture of empathy and compassion in nursing practice
- The impact of nurse burnout on nurse-patient communication and relationship-building
- The role of nursing in addressing mental health needs in rural and underserved communities
- The impact of nurse burnout on nursing advocacy and policy engagement
- The role of nursing in promoting mental health and well-being in global health settings
- Strategies for addressing mental health and burnout among nursing students and new graduates
- The impact of nurse burnout on nursing education and faculty well-being
- The role of nursing in addressing mental health needs in disaster response and emergency preparedness
- The impact of nurse burnout on nursing practice in the care of patients with mental health disorders
- The role of nursing in promoting mental health and well-being in the context of an aging population
- Strategies for addressing mental health and burnout among advanced practice nurses
- The impact of nurse burnout on nursing practice in the care of patients with chronic and complex conditions
- The role of nursing in promoting mental health and well-being among military veterans and their families
- The impact of nurse burnout on nursing practice in the care of patients with substance use disorders
- The role of nursing in addressing mental health needs in the context of climate change and environmental health
- Strategies for addressing mental health and burnout among nurses working with vulnerable and high-risk populations
- The impact of nurse burnout on nursing practice in the care of patients at the end of life
- The role of nursing in promoting mental health and well-being in the context of healthcare innovation and change
Now that you have a list of thought-provoking nursing argumentative essay topics, you can engage in meaningful debates and expand your knowledge in the field. Consider various perspectives, use credible sources to support your arguments, and practice clear, concise writing. Happy writing!
📎 Related Articles
1. Mental Health Nursing Research Topics: Inspiring Ideas for Students 2. Top Nursing Topics for Discussion: Engaging Conversations for Healthcare Professionals 3. Key EBP Nursing Topics: Enhancing Patient Results through Evidence-Based Practice 4. Top Nursing Research Topics for Students and Professionals 5. Nursing Debate Topics: The Importance of Discussing and Debating Nursing Issues 6. Exploring Controversial Issues in Nursing: Key Topics and Examples 7. Pediatric Nursing Research Topics for Students: A Comprehensive Guide
Table of content
Crafted with Care:
Nursing Essays!
Precision, Passion, & Professionalism in Every Page.
625 Good Nursing Research Topics, Ideas, and EBP
18 January 2024
last updated
Nursing research topics encompass various aspects of patient care, such as pain management strategies, promoting mental health, prevention of chronic diseases, impacts of caregiving, healthcare policy, telehealth effectiveness, and neonatal nursing. They also involve studying the effectiveness of nursing models, patient satisfaction, nursing ethics, holistic nursing techniques, and evidence-based practice (EBP). Research in various nursing areas can contribute significantly to improving patient outcomes, streamlining healthcare processes, and enhancing the professional development of nurses. By exploring different nursing research topics, people can continue to push the boundaries of nursing science and clinical application.
Hot Nursing Research Topics
- Exploring the Impact of Telemedicine in Patient-Centered Care
- Effectiveness of Pain Management Techniques in Palliative Care
- Roles of Nursing in Improving Healthcare Accessibility in Rural Areas
- Strategies for Preventing Nurse Burnout and Ensuring Occupational Well-Being
- Advances in Neonatal Care: A Focus on the Role of Nursing
- Patient Safety Measures in High-Risk Surgical Procedures
- Implementing Technological Innovation in Geriatric Nursing
- Effects of Nursing Leadership Styles on Team Morale and Patient Outcomes
- Mental Health Considerations for Nurses During Global Pandemics
- Promoting Self-Management of Chronic Diseases: Nurse-Led Initiatives
- Evaluating the Efficiency of Evidence-Based Practice in Oncology Nursing
- Assessing the Role of Nursing in Multidisciplinary Healthcare Teams
- Addressing Cultural Competence in Nursing: Benefits and Challenges
- Analyzing the Impact of Home Healthcare Nursing on Patient Rehabilitation
- Strategies for Handling Ethical Dilemmas in Nursing Practice
- Pediatric Nursing: Dealing With Emotional and Psychological Aspects of Child Care
- Quality of Life Enhancement in Patients With Terminal Illness: A Nursing Perspective
- The Role of Nurses in Implementing Antibiotic Stewardship Programs
- Nursing Education: Trends, Challenges and Opportunities in the 21st Century
- The Intersection of Nursing and Artificial Intelligence: The Future of Patient Care

Easy Nursing Research Topics
- Improving Patient Care Through Evidence-Based Practice
- Technological Advancements in Pain Management
- Mental Health Awareness in Pediatric Nursing
- The Role of Student and Registered Nurses in Chronic Disease Management
- Telemedicine’s Impact on Nursing Practice
- Holistic Approaches to Palliative Care
- The Effect of Nurse-Patient Ratios on the Quality of Care
- Nursing Intervention Strategies for Substance Abuse
- Stress Management Techniques for Nursing Professionals
- Elder Care: Prevention of Falls in Nursing Homes
- Developing Cultural Competence in Nursing Practice
- The Influence of Artificial Intelligence on Nursing
- Ethics in End-of-Life Care Decisions
- Impact of Nurse Leadership Styles on Patient Outcomes
- Strategies for Improving Communication in Nursing
- Nursing Practices for Neonatal Intensive Care Units
- Role of Nutrition in Wound Healing: Nursing Perspectives
- Use of Simulation Training in Nursing Education
- Integration of Yoga and Meditation in Nursing Practice
- The Future of Home Health Care: A Nursing Perspective
Interesting Nursing Research Topics
- Impacts of Sleep Quality on Nurses’ Performance
- Exploring the Role of Nurses in Community Health
- Patient Safety Measures in High-Risk Hospital Wards
- Strategies for Managing Burnout Among Nursing Staff
- Innovations in Geriatric Nursing: Trends and Techniques
- Ethical Dilemmas in Pediatric Nursing: Case Studies
- Roles of Nurses in Managing Chronic Pain
- Understanding Patient Perception of Nurses’ Empathy
- Neonatal Nursing: Challenges and Coping Mechanisms
- Implications of Nursing Shortage on Healthcare Quality
- Addressing Language Barriers in Multicultural Nursing
- Improving Handover Communication in Nursing Shift Changes
- The Impact of Nursing Leadership on Patient Satisfaction
- Strategies for Enhancing Mental Health Nursing Practice
- Roles of Nurses in Health Promotion and Education
- The Influence of Family Involvement in Palliative Care
- Barriers to Advancement in the Nursing Profession
- Roles of Registered Nurse Practitioners in Primary Care
- Application of Telehealth in Modern Nursing Practice
High School Nursing Research Topics
- The Role of School Nurses in Child Health Education
- Understanding the Basics of Pediatric Nursing
- Exploring Career Paths in the Nursing Profession
- Importance of Mental Health Awareness in Nursing Practice
- First Aid: Essential Skills for Nurses
- The Role of Nurses in Preventing School Bullying
- Ethical Considerations in Nursing: A Discussion
- Introduction to Palliative Care: A Nursing Perspective
- The Impact of Nutrition on Patient Recovery: Nurses’ Role
- Learning About Patient Confidentiality in Nursing
- Role of Nurses in Managing Chronic Illnesses
- Nursing Intervention Techniques for Childhood Obesity
- Emotional Intelligence in Nursing: Why It Matters
- Nursing and Care for the Elderly: An Introduction
- How Do Nurses Contribute to Holistic Patient Care?
- Significance of Good Communication Skills in Nursing
- The Role of Nurses in Vaccination Campaigns
- Dealing With Stress: Strategies for Nurses
- Importance of Hygiene in Nursing Practice
- Understanding the Basics of Neonatal Nursing
Nursing Research Topics for College Students
- The Impact of Nurse-Patient Ratio on the Quality of Care
- Mental Health Stigma in Healthcare: A Nursing Perspective
- Challenges in Pediatric Nursing: A Comprehensive Review
- The Role of Nurses in Pain Management: Ethical Considerations
- Advanced Practice Nursing: Exploring the Scope and Limitations
- Improving Patient Safety: Strategies for Error Reduction in Nursing
- Telemedicine and Its Implications for the Nursing Profession
- Nurses’ Role in Implementing Preventive Health Measures
- Exploring the Mental Health of Nurses: Coping Mechanisms and Support
- The Ethics of End-of-Life Care: A Nursing Perspective
- Understanding the Complexities of Neonatal Intensive Care Nursing
- Innovations in Nursing Education: Trends and Challenges
- Influence of Cultural Competency on Nursing Practice
- Evaluating the Effectiveness of Nursing Leadership Styles
- Roles of Nursing in the Management of Chronic Illnesses
- The Impact of Technology on Nursing Practice: A Critical Analysis
- Nurse Burnout: Causes, Effects and Prevention Strategies
- The Influence of Nursing Care on Patient Satisfaction
- Importance of Communication Skills in Palliative Care Nursing
- The Role of Nurses in Advancing Healthcare Policy and Advocacy
University Nursing Research Topics
- Examining the Role of Nurses in Health Promotion and Disease Prevention
- The Impact of Hospital-Acquired Infections on Nursing Practice
- Role of Nurses in Managing Patient Experience During Healthcare Delivery
- Exploring the Ethical Challenges in Geriatric Nursing
- The Importance of Cultural Competence in Global Nursing Practice
- The Role of Nurses in Palliative Care: Bridging the Gap
- Telehealth and Its Impact on Nursing Practice and Patient Care
- Understanding the Mental Health Implications of Nursing Stress and Burnout
- The Effect of Nurse-led Patient Education on Disease Management
- Impacts of Interprofessional Communication and Collaboration on the Quality of Care in Nursing
- Pediatric Nursing: Techniques for Reducing Pain and Anxiety in Children
- Advanced Practice Nurses: Advocates for Health Policy and Reform
- Role of Nursing in Managing Chronic Conditions like Diabetes and Hypertension
- Holistic Nursing Practice: The Integration of Mind, Body, and Spirit
- The Effect of Evidence-Based Practice on Nursing Outcomes
- Nurses’ Role in Addressing Health Disparities in Underserved Communities
- Analyzing the Effect of Nurse Staffing on Patient Safety and Quality of Care
- Strategies for Promoting Self-Care Among Nurses: An Essential Component of Healthcare
- The Future of Nursing: Preparing for the Impact of Climate Change on Health
Clinical List of 468 Research Topics for Nursing
Pediatric nursing research topics.
- Managing Pain in Pediatric Patients: Strategies and Challenges
- The Impact of Family-Centered Care in Pediatric Nursing
- Use of Play Therapy in Pediatric Patient Recovery
- Pediatric Mental Health: Role and Responsibility of Nurses
- Effective Communication Techniques With Pediatric Patients
- The Influence of Technology on Pediatric Nursing Care
- Pediatric Palliative Care: Principles and Practices
- Autism Spectrum Disorder: Nursing Approaches and Management
- Nutrition Assessment in Pediatric Nursing: Best Practices
- Nursing Care for Pediatric Patients With Rare Genetic Disorders
- Strategies for Improving Vaccination Rates in Pediatric Populations
- Roles of Nurses in Managing Pediatric Chronic Illnesses
- Pediatric Oncology: Providing Care and Support to Child Cancer Patients
- Pediatric Nursing in Intensive Care Units: Stress Factors and Coping Mechanisms
- Childhood Obesity: Prevention and Management in Pediatric Nursing
- Supporting Families of Children Living With Disabilities: Role of Pediatric Nurses
- The Impact of Hospital Design on Pediatric Patient Well-Being
- Approaches to Pediatric Trauma Care: Best Nursing Practices
- Pediatric Medication Administration: Safety Measures and Error Prevention
Geriatric Nursing Research Topics
- The Impact of Geriatric Nursing on Patient Quality of Life
- Exploring Best Practices in Pain Management for Elderly Patients
- The Role of Geriatric Nurses in End-of-Life Care
- Challenges in Nursing Care for Elderly Patients With Dementia
- The Use of Technology in Enhancing Geriatric Nursing Practice
- Cultural Sensitivity in Geriatric Nursing: Necessity and Implementation
- Assessment and Management of Depression in Elderly Patients
- Geriatric Nursing and the Promotion of Healthy Aging
- The Influence of Family Involvement in Geriatric Nursing Care
- Fall Prevention Strategies in Geriatric Care: Role of Nurses
- Nutritional Assessment and Care in Geriatric Nursing
- Ethical Issues in Geriatric Nursing: A Case Study Approach
- Roles of Geriatric Nursing in Managing Chronic Diseases
- Impacts of Social Isolation on Health Outcomes in Elderly Patients
- Implementing Person-Centered Care in Geriatric Nursing
- Sleep Disorders in Elderly Patients: Assessment and Management
- Geriatric Rehabilitation: The Role of Nurses in Recovery and Therapy
- The Effectiveness of Cognitive Stimulation Therapy in Dementia Care
- The Importance of Communication Skills in Geriatric Nursing
Midwifery Nursing Research Topics
- The Impact of Midwifery-Led Care on Maternal and Neonatal Outcomes
- Roles of Midwives in Promoting Natural Childbirth: A Systematic Review
- Midwifery and Home Births: An Analysis of Safety and Satisfaction
- Understanding the Role of Midwives in Antenatal and Postnatal Mental Health
- Challenges and Solutions for Improving Midwifery Education
- The Influence of Midwifery Care on Reducing Cesarean Section Rates
- Midwifery in Rural Settings: Challenges and Opportunities
- Exploring the Role of Midwives in Promoting Breastfeeding
- The Impact of Cultural Competence in Midwifery Care
- Midwives’ Roles in Advocating for Women’s Reproductive Rights
- Understanding the Transition Process From Student Midwife to Practicing Midwife
- Comparative Analysis of Midwife-led Care vs. Obstetrician-led Care
- Examining Burnout and Stress Among Midwives: Implications for Practice
- Role of Midwives in Advancing LGBTQ+ Inclusive Care
- The Use of Technology, Internet, and Digital Tools in Midwifery Practice
- Exploring the Impact of Midwifery Care on Maternal Mortality Rates
- Addressing Domestic Violence: The Critical Role of Midwives
- Midwifery and Holistic Care: Incorporating Complementary Therapies into Practice
- The Role of Midwives in Health Promotion and Education
- Barriers to Accessing Midwifery Services: A Socioeconomic Analysis
Mental Health Nursing Research Topics
- Unveiling the Efficacy of Mindfulness-Based Interventions in Alleviating Anxiety Symptoms Among Adolescents
- Delving into the Role of Social Support in Nurturing Resilience Among Individuals With Schizophrenia
- Examining the Influence of Art Therapy on Enhancing Emotional Expression Among Patients With Major Depressive Disorder
- Probing the Link Between Childhood Trauma and the Emergence of Borderline Personality Disorder
- Assessing the Effectiveness of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy in Mitigating Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder in Children
- Investigating the Impact of Exercise on Mitigating Symptoms of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Among Veterans
- Scrutinizing the Effects of Stigma on Help-Seeking Behavior Among Individuals With Bipolar Disorder
- Exploring the Relationship Between Sleep Disturbances and Suicidal Ideation in Adolescents
- Illuminating the Role of Family Therapy in Enhancing Communication Patterns among Families of Individuals With Substance Use Disorders
- Examining the Impact of Peer Support Programs on Safeguarding Against Relapse in Individuals With Substance Use Disorders
- Investigating the Effectiveness of Animal-Assisted Therapy in Mitigating Aggression Among Psychiatric Inpatients
- Unraveling the Factors Influencing Medication Adherence Among Individuals With Schizophrenia
- Unearthing the Relationship Between Childhood Abuse and the Development of Eating Disorders in Adolescents
- Evaluating the Efficacy and Effectiveness of Dialectical Behavior Therapy in Addressing Self-Harming Behaviors Among Borderline Personality Disorder Patients
- Investigating the Effectiveness of Virtual Reality Exposure Therapy in Treating Phobias
- Exploring Valid Links Between Social Media Use and Body Image Dissatisfaction among Young Adults
- Assessing the Impact of Traumatic Brain Injury on Mental Health Outcomes Among Military Personnel
- Investigating the Effectiveness of Music Therapy in Alleviating Anxiety, Stress, and Depression in Older Adults With Dementia
- Understanding the Role of Cultural Factors in Shaping Help-Seeking Behavior Among Minority Populations With Mental Illness
Health Promotion Nursing Research Topics
- Promoting Healthy Aging: Strategies for Enhancing the Quality of Life Among Older Adults
- The Role of Nursing Professionals in Promoting Sexual Health and Safe Practices Among Adolescents
- Implementing Smoking Cessation Methods and Interventions in Primary Care Settings: Identifying Best Practices and Assessing Outcomes
- Enhancing Mental Health and Well-Being Among College Students: Interventions and Support Systems
- Assessing the Effectiveness of HIV/AIDS Prevention Programs Among At-Risk Populations
- Workplace Wellness Programs: Evaluating Their Impact on Employee Health Outcomes and Productivity
- The Role of Nurses in Leading Health Promotion Interventions for Managing Chronic Diseases
- Promoting Vaccination Uptake and Building Vaccine Confidence in the Community: The Role of Nurses
- Exploring the Effectiveness of Community-Based Programs for Weight Management to Prevent Obesity
- Addressing Health Disparities in Underserved Populations: Cultural Competence in Health Promotion
- Supporting Breastfeeding Initiation and Duration: Strategies to Assist and Empower New Mothers
- Assessing the Impact of Nutrition Education on Eating Habits and Nutritional Status of School Children
- Promoting Injury Prevention and Raising Safety Awareness: Contributions of Nurses to Public Health Education
- Strategies for Encouraging Physical Activity among Sedentary Populations: Promoting Behavior Change
- Improving Medication Adherence among Patients With Chronic Diseases: Strategies and Nurse-led Interventions
- Nurse-Led Interventions for Promoting Healthy Sleep Habits and Hygiene Practices
- Evaluating the Effectiveness of Health Education Programs in Encouraging Adolescents to Make Healthy Lifestyle Choices
- Implementing Vaccination Programs in Schools: Overcoming Challenges and Identifying Best Practices
- Enhancing Health Literacy: Empowering Patients to Take Active Control of Their Health
- Promoting Healthy Work-Life Balance among Healthcare Professionals: Strategies for Self-Care and Resilience
Discussion Nursing Research Topics
- The Impact of Education and Nurse Staffing Levels on Patient Outcomes and Healthcare Costs
- Exploring Technology Integration in Nursing Education and Clinical Practice
- Addressing the Global Nursing Shortage: Strategies for Recruitment, Retention, and Workforce Planning
- Advancing Evidence-Based Practice in Nursing: Bridging the Gap Between Research and Practice
- Discussing the Contributions of Advanced Practice Nurses in Primary Care Settings
- Culturally Competent Nursing Practice: Challenges and Strategies for Healthcare Professionals
- Integrating Complementary and Alternative Medicine in Contemporary Nursing Practice
- Nurse Burnout: Implications for Patient Care and Strategies for Retention
- Trauma-Informed Care in Nursing: Understanding the Impact and Implementing Best Practices
- Addressing the Opioid Crisis: Nursing Strategies and Interventions
- Nursing Leadership: Enhancing Patient Safety and Quality of Care
- Ethical Considerations in End-of-Life Care: Perspectives From Nursing Practice
- Simulation-Based Training in Nursing Education: Enhancing Clinical Competence
- Fostering Patient-Centered Care in Nursing: Empowerment and Engagement Strategies
- Reducing Health Disparities in Vulnerable Populations: Innovative Nursing Interventions
- Effective Communication Strategies in Nurse-Patient Interactions: Enhancing Patient Outcomes
- Team-Based Care Models in Nursing: Examining Effectiveness and Implementation
- Promoting Mental Health and Well-Being in Nursing Practice: Holistic Approaches and Interventions
- Advancing Health Equity: Nursing Advocacy and Social Justice Initiatives
Adult Nursing Research Topics
- Enhancing the Quality of Care for Older Adults: Strategies for Person-Centered Nursing Practice
- Managing Chronic Illness in Adult Populations: Innovative Approaches to Improve Health Outcomes
- Promoting Healthy Aging: Interventions for Disease Prevention and Health Promotion in Older Adults
- Addressing the Healthcare Services and Mental Health Needs of Older Adults: Exploring Effective Nursing Interventions
- Exploring the Nursing Challenges in Managing Multiple Chronic Conditions in Older Adults
- Enhancing Medication Safety in Adult Care Settings: Strategies to Prevent Adverse Drug Events
- Nursing Leadership in Adult Care: Fostering Collaborative and Evidence-Based Practice
- The Impact of Nursing Staffing Levels on Patient Outcomes in Adult Healthcare Settings
- Promoting Healthy Lifestyles in Adults: Strategies for Health Behavior Change and Risk Reduction
- Exploring the Role of Advanced Practice Nurses in Adult Primary Care
- Advancing Cultural Competence in Adult Nursing: Meeting the Diverse Needs of Patients
- Addressing Health Disparities in Underserved Adult Populations: A Nursing Perspective
- The Use of Technology in Adult Nursing: Enhancing Communication and Care Delivery
- Promoting Safety and Preventing Falls in Older Adults: Evidence-Based Nursing Interventions
- Managing Pain in Adult Patients: Integrating Non-Pharmacological Approaches in Nursing Practice
- The Role of Family in Adult Patient Care: Engaging and Supporting Caregivers
- Advancing Evidence-Based Practice in Adult Nursing: Bridging the Gap Between Research and Clinical Settings
- Exploring the Nursing Challenges in Managing Complex Wound Care in Adult Patients
- Promoting Continuity of Care in Adult Nursing: Strategies for Effective Transitions and Care Coordination
Quantitative and Qualitative Nursing Research Topics
- Association Between Nurse-Patient Ratios and Quality of Care Outcomes in Acute Care Settings Explored
- Lived Experience of Nurses in High-Stress Work Environments Understood: A Qualitative Inquiry
- The Importance of a Communication Skills Training Program for Nursing Students Examined: A Mixed Methods Approach
- Impact of Patient Education Interventions on Medication Adherence in Chronic Disease Management Assessed
- Perceived Barriers and Facilitators to Evidence-Based Practice Implementation in Nursing Explored
- Relationship Between Nurse Leadership Styles and Staff Satisfaction in Healthcare Organizations Investigated
- Factors Influencing Nurse Retention in Rural Healthcare Settings Understood: A Grounded Theory Study
- Impact of Nurse-Initiated Interventions on Patient Outcomes in Acute Care Settings Explored
- Experiences of Nurses Providing Palliative Care Examined: A Phenomenological Investigation
- Effectiveness of Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction Programs in Reducing Burnout Among Nurses Assessed
- Factors Affecting Job Satisfaction Among Nurse Educators Explored: A Quantitative Analysis
- Perceptions of Patients and Families Regarding Cultural Competence in Nursing Care Investigated
- Experiences of Nurses Working With Diverse Populations Understood: A Qualitative Inquiry
- Effectiveness of Simulation-Based Training in Enhancing Nursing Competencies Examined
- Impact of Nurse-Managed Interventions on Patient Safety Outcomes in Long-Term Care Facilities Assessed
- Challenges and Benefits of Interprofessional Collaboration in Healthcare Teams Explored: A Mixed Methods Study
- Experiences of Nurses Providing End-of-Life Care in Intensive Care Units Investigated: A Phenomenological Approach
- Effectiveness of Telehealth in Improving Access to Care and Health Outcomes in Underserved Populations Assessed
- Factors Influencing the Implementation, Adoption, and Use of Electronic Health Records in Nursing Practice Understood
- Relationship Between Nurse Staffing and Patient Falls in Acute Care Hospitals Examined: A Quantitative Analysis
Critical Care Nursing Research Topics
- Innovative Approaches in Critical Care Nursing: Advancing Patient Outcomes
- Navigating Ethical Dilemmas in Critical Care: Complex Decision-Making in Nursing Practice
- Technology Integration in Critical Care Nursing: Enhancing Patient Monitoring and Care
- Effective Teamwork and Communication: Promoting Interprofessional Collaboration in Critical Care
- Safe and Effective Medication Administration: Managing Complex Regimens in Critical Care
- Family Involvement in Critical Care: Impact and Engagement in the Care Process
- Alleviating Suffering: Optimizing Pain Management in Critical Care
- Cultural Sensitivity in Critical Care Nursing: Providing Culturally Competent Care
- Comfort and Dignity: Enhancing End-of-Life Care in Critical Care Settings
- Preventing Healthcare-Associated Infections: Evidence-Based Practices in Critical Care
- Patient Safety in Critical Care Environments: Error Prevention and Risk Management
- Psychological Impact of Critical Illness: Support for Patients and Families in Critical Care
- Simulation in Critical Care Education: Enhancing Knowledge and Skills for Nursing Professionals
- Seamless Transitions in Critical Care: Promoting Continuity of Care
- Culturally Competent Critical Care: Addressing Ethnocultural Considerations
- Advancing Critical Care Nursing Research: Identifying Knowledge Gaps and Opportunities
- Critical Care Nurses in Disaster Response: Preparedness, Resilience, and Adaptive Capacity
- Job Satisfaction and Retention: Impact of Critical Care Environment on Nurses
- Empowering Families: Family-Centered Care in Critical Care Settings
Healthcare Management Nursing Research Topics
- The Relationship Between Healthcare Organizations and Nursing Leadership Styles: A Mixed Methods Study Exploring Staff Satisfaction
- Factors Influencing Job Satisfaction Among Nurse Managers: A Quantitative Analysis Examined
- Experiences of Nurses in Managing Ethical Dilemmas in Healthcare Settings: A Qualitative Inquiry
- Staffing Ratios and Patient Safety Outcomes in Acute Care Hospitals: A Comparative Study
- Perceptions of Healthcare Providers Regarding Interprofessional Collaboration in Patient Care Analyzed
- Technology’s Role in Enhancing Medication Management Practices in Long-Term Care Facilities Investigated
- Factors Affecting Nurse Retention in Magnet-Designated Hospitals Explored: A Mixed Methods Approach
- Relationship Between Nursing Workload and Patient Outcomes in Intensive Care Units Examined: A Comparative Analysis
- Emotional Intelligence’s Impact on Nurse-Physician Collaboration Investigated: A Cross-Sectional Study
- Barriers to Effective Communication Among Interdisciplinary Healthcare Teams Analyzed
- Implementation and Outcomes of Evidence-Based Practice in Nursing Investigated: A Longitudinal Study
- Nursing Informatics in Enhancing Patient-Centered Care: Perceptions of Healthcare Providers Explored
- Experiences of Nurses in Managing Conflict in Multicultural Healthcare Environments Examined: A Qualitative Inquiry
- Effectiveness of Leadership Development Programs in Enhancing Nursing Leadership Competencies Assessed: A Quantitative Analysis
- Factors Influencing Nurse Satisfaction in Rural Healthcare Settings Analyzed: A Comparative Study
- Perceived Benefits and Challenges of Telehealth Implementation in Primary Care Settings Explored
- Impacts of Nurse-Managed Interventions on Quality-of-Care Outcomes in Home Healthcare Investigated: A Mixed Methods Study
- Factors Affecting Adoption of Electronic Health Records in Nursing Practice Explored: A Qualitative Inquiry
- Effectiveness of Patient Education Interventions in Improving Self-Management of Chronic Diseases Assessed: A Quantitative Study
Emergency Nursing Research Topics
- Emergency Nursing Care for Pediatric Trauma Patients: Special Considerations
- Mental Health Management in the Emergency Department: Enhancing Care Delivery
- Triage Protocols in the Emergency Department: An In-depth Analysis
- Effectiveness of Disaster Preparedness Training among Emergency Nurses
- Emergency Department Crowding: Understanding Causes and Developing Solutions
- Critical Care for Acute Stroke Patients: Best Practices in Emergency Nursing
- Simulation Training in Emergency Nursing: Assessing its Effectiveness
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder among Emergency Nurses: Identifying Risk Factors
- Pain Management in the Emergency Department: Current Practices and Challenges
- Workplace Violence in Emergency Departments: Prevention and Coping Strategies
- Patient Safety Culture in Emergency Departments: Evaluating Measures and Outcomes
- Point of Care Ultrasound: Training and Utilization among Emergency Nurses
- Disaster Response: Role of Emergency Nurses in Mass Casualty Incidents
- Nurses’ Perceptions of Palliative Care in Emergency Departments
- Information Technology in Emergency Nursing: Adoption and Utility
- Critical Incident Stress Management for Emergency Nurses: An Evaluation
- Emergency Nursing Care for Patients With Sepsis: Guidelines and Outcomes
- Advanced Practice Emergency Nursing: Roles, Challenges, and Future Directions
- Resuscitation Decision-Making in Emergency Care: Ethical Considerations
- Compassion Fatigue among Emergency Nurses: Causes and Mitigation Strategies
Obstetrics Nursing Research Topics
- Prenatal Education: Effective Strategies for Expectant Mothers
- Nurse-Led Interventions to Reduce Cesarean Section Rates: A Review
- High-Risk Pregnancies: Advanced Nursing Care and Management
- Postpartum Depression: Detection and Management in Obstetric Care
- Pregnancy and Childbirth Experiences of Women With Disabilities: A Qualitative Study
- Home Births: Assessing Safety and Obstetric Nursing Roles
- Promoting Breastfeeding: Evidence-Based Strategies in Obstetric Nursing
- Preeclampsia Management: Best Practices in Obstetric Nursing Care
- Cultural Competence in Obstetric Nursing: Meeting the Needs of Diverse Populations
- Obstetric Nursing Care for Teenage Mothers: Unique Considerations and Challenges
- Pain Management in Labor and Delivery: An Evaluation of Non-Pharmacological Methods
- Maternal Mortality: Exploring Preventive Measures in Obstetric Care
- Prenatal Care Utilization: Identifying Barriers and Promoting Access
- Birthing Practices Across Cultures: A Comparative Analysis
- Neonatal Resuscitation: Advanced Training and Preparedness in Obstetric Nursing
- Perinatal Palliative Care: Preparing Families for Infant Loss
- Midwifery Care vs. Medical Model of Birth: Outcomes and Patient Satisfaction
- Stress and Burnout among Obstetric Nurses: Causes and Coping Strategies
- Fathers in the Birth Room: Obstetric Nurses’ Perceptions and Experiences
Neonatal Nursing Research Topics
- Pain Management in Neonates: Best Practices in Non-Pharmacological Interventions
- Neonatal Sepsis: Early Detection and Nursing Management
- Nutritional Needs of Preterm Infants: Evidence-Based Nursing Care
- Skin-to-Skin Contact: Investigating Outcomes in Neonatal Intensive Care Units
- Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome: Improving Nursing Care for Drug-Exposed Infants
- Palliative Care in Neonatology: Challenges and Best Practices
- Stress in Parents of Neonates Admitted to the NICU: Nursing Support Strategies
- Prevention of Hypothermia in Very Low Birth Weight Infants: Nursing Interventions
- Simulation Training in Neonatal Resuscitation: Impact on Nursing Competence
- Breast Milk vs. Formula: Evaluating Outcomes in Neonates With Congenital Heart Disease
- Nursing Care for Neonates With Respiratory Distress Syndrome: Current Guidelines
- Neonatal Jaundice: Improving Parental Education and Nursing Care
- Neurodevelopmental Outcomes in Preterm Infants: The Role of Neonatal Nurses
- Noise Levels in the NICU: Implications for Neonatal Health and Development
- Kangaroo Mother Care: Evaluating Implementation in Different Cultural Contexts
- Ethical Considerations in Neonatal End-of-Life Care: A Nursing Perspective
- Nursing Management of Infants With Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome: A Systematic Review
- Prevention of Retinopathy of Prematurity: Nursing Strategies and Outcomes
- Neonatal Nurse Practitioners: Evaluating Their Contribution to NICU Outcomes
- Quality of Life of NICU Graduates: Long-Term Outcomes and Nursing Interventions
Women’s Health Nursing Research Topics
- Cardiovascular Disease in Women: Nursing Strategies for Prevention and Management
- Postpartum Depression: Identifying Risk Factors and Promoting Early Intervention
- Breast Cancer Screening: Improving Adherence Through Nursing Interventions
- Osteoporosis in Postmenopausal Women: Preventive Strategies in Nursing Practice
- Women’s Sexual Health: Addressing Taboos and Promoting Open Dialogue
- Menopause and Mental Health: Unraveling the Complex Relationship
- Domestic Violence: Nursing Interventions and Support Strategies
- Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Vaccination: Strategies to Increase Uptake
- Female Genital Mutilation: A Global Health Issue and Nursing Response
- Health Literacy Among Women: A Tool for Promoting Self-Care
- Cervical Cancer: Early Detection and Management in Nursing Practice
- Preconception Care: Enhancing Women’s Health Before Pregnancy
- Nursing Care for Women With Endometriosis: Management of Chronic Pain
- Female Veterans’ Health: Unique Challenges and Specialized Care Needs
- Women’s Health in Refugee Populations: Access and Equity Issues
- Maternal Obesity: Implications for Pregnancy Outcomes and Interventions
- Fibromyalgia in Women: Improving Diagnosis and Management
- Body Image Disturbances in Women: Prevention and Treatment Approaches
- Health Consequences of Early Marriage in Girls: A Global Perspective
Ethics Nursing Research Topics
- Ethical Dilemmas in End-of-Life Care: A Nursing Perspective
- Patient Autonomy in Nursing Care: Challenges and Solutions
- Nurses’ Perceptions of Ethical Climate in Healthcare Institutions
- Bioethical Issues in Genomic Nursing: Navigating Uncharted Territory
- Nurse Whistleblowing: Balancing Professional Responsibility and Personal Risk
- Ethical Considerations in Pediatric Palliative Care: A Critical Review
- Euthanasia and Assisted Dying: A Nursing Ethics Exploration
- Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare: Ethical Implications for Nursing Practice
- Ethical Challenges in Global Health Nursing: A Cross-Cultural Examination
- Nurses’ Ethical Competence: Evaluating Education and Training Programs
- Organ Transplantation: Ethical Dilemmas in Nursing Practice
- Nurse Leaders’ Roles in Promoting Ethical Climate in Nursing Units
- Rationing Care in Times of Scarcity: Ethical Considerations for Nurses
- Health Information Privacy: Navigating Ethical Concerns in Nursing Practice
- Research Ethics in Nursing: Safeguarding Rights of Human Subjects
- Ethics of Care in Nursing: Revitalizing the Concept for Modern Practice
- Nursing Ethics in Mental Health: Autonomy vs. Beneficence Dilemmas
- Ethical Aspects of Informed Consent in Nursing Research and Practice
- Decision-Making in Neonatal Intensive Care: Ethical Dimensions
- Ethical Considerations in Disaster Nursing: Providing Care in Crisis Situations
Intervention Nursing Research Topics
- Fall Prevention Interventions in Geriatric Nursing: A Systematic Review
- Early Mobilization in ICU Patients: Nursing Strategies and Outcomes
- Promoting Medication Adherence: Evaluation of Nurse-Driven Interventions
- Non-Pharmacological Interventions for Anxiety in Pediatric Patients: A Systematic Review
- Nurse-Led Cognitive Stimulation Therapy for Patients With Dementia
- Improving Sleep Quality in Hospitalized Patients: Nursing Interventions and Results
- Pressure Ulcer Prevention in High-Risk Patients: Nurse-Led Interventions
- Mindfulness-Based Interventions for Stress Reduction in Nursing Staff
- Nursing Interventions to Improve Nutritional Status in Cancer Patients
- Therapeutic Communication in Mental Health Nursing: Evidence-Based Strategies
- Implementing Delirium Prevention Strategies: Nursing Interventions in the ICU
- Nursing Interventions for Smoking Cessation: Evaluating Effectiveness
- Self-Management Support for Patients With Diabetes: Nurse-Led Interventions
- Improving Physical Activity in Patients With Cardiovascular Disease: Nursing Approaches
- Holistic Interventions for Palliative Care: An Integrative Nursing Approach
- Optimizing Hydration in Elderly Patients: Nurse-Led Initiatives
- Breathlessness Management in Patients With COPD: Nursing Interventions and Outcomes
- Nursing Strategies for Enhancing Family Engagement in the ICU
- Reducing Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infections: Evidence-Based Nursing Interventions
Leadership Nursing Research Topics
- Transformational Leadership in Nursing: Enhancing Patient Outcomes
- Effectiveness of Shared Governance Models in Nursing Practice
- Exploring the Relationship Between Leadership Styles and Nurse Retention
- Servant Leadership in Nursing: A Review of Empirical Studies
- Mentoring in Nursing: Strategies for Developing Future Leaders
- Emotional Intelligence in Nursing Leadership: A Comparative Analysis
- Analyzing the Leadership Competencies Needed for Telehealth Nursing
- Distributed Leadership in Multidisciplinary Healthcare Teams: An Empirical Review
- Authentic Leadership and its Influence on Nurse Job Satisfaction
- Leadership Development Programs in Nursing: A Critical Appraisal
- Transformation Through Leadership: Nurse Managers Navigating Change
- Nursing Leadership in Disaster Response: A Case-Based Review
- Clinical Leadership: Key Skills for Advanced Practice Nurses
- Leadership and Ethical Decision-Making in Nursing Practice
- Fostering Innovation in Nursing Through Transformational Leadership
- Cross-Cultural Leadership in Nursing: A Global Perspective
- Leadership Styles and Organizational Culture in Nursing Practice
- Leadership Challenges in Rural Nursing: Strategies for Improvement
- Nursing Leadership in Palliative Care: An Underexplored Dimension
- Leadership Transition in Nursing: Identifying Succession Planning Best Practices
Practitioner Nursing Research Topics
- Managing Chronic Pain: Best Practices for Nurse Practitioners
- Optimizing Patient Education Strategies in Chronic Disease Management
- Holistic Approaches to Mental Health Care in Nursing Practice
- Child Abuse Identification and Reporting: Training Needs for Nurses
- Addressing Health Literacy in Diverse Patient Populations
- Strategies for Improving Medication Adherence in Elderly Patients
- Ethical Dilemmas in Palliative Care: A Nurse Practitioner’s Perspective
- Obesity Prevention and Intervention: A Nursing Practice Approach
- Integrating Telemedicine in Primary Care: Challenges and Opportunities for Nurses
- Promoting Healthy Lifestyle Choices: The Efficacy of Nurse-led Interventions
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder in Veterans: Implications for Nursing Practice
- Diabetes Management in Primary Care: Nurse Practitioner Strategies
- Substance Abuse Prevention and Treatment: Nursing Approaches
- Examining Burnout and Resilience Among Nurse Practitioners
- Cultural Competence in Nursing Practice: Enhancing Patient Care
- Nurse Practitioners in the Emergency Room: Opportunities and Challenges
- Pediatric Vaccination: Addressing Parental Concerns and Misconceptions
- Implementing Shared Decision-Making in Nursing Practice
- Home Health Care: Optimizing Nurse Involvement and Patient Outcomes
Psychiatric Nursing Research Topics
- Psychoeducation in Schizophrenia Management: A Nursing Perspective
- Caring for Patients With Eating Disorders: Nursing Approaches
- Nursing Interventions for Patients With Major Depressive Disorder
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder: Therapeutic Approaches in Psychiatric Nursing
- Effectiveness of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy in Psychiatric Nursing
- Nursing Strategies for Managing Co-Morbid Mental Health and Substance Abuse Disorders
- Care for Patients With Dementia: Psychiatric Nursing Approaches
- Psychiatric Nursing Interventions for Patients With Anxiety Disorders
- The Relationship Between Sleep Quality, Dreams, and Mental Health: Implications for Psychiatric Nursing
- Bipolar Disorder Management: Best Practices in Psychiatric Nursing
- Holistic Care for Patients With Personality Disorders: A Psychiatric Nursing Perspective
- Therapeutic Communication Techniques in Psychiatric Nursing
- Efficacy of Mindfulness-Based Interventions in Psychiatric Nursing
- Promoting Self-Care in Patients With Chronic Mental Illness
- Management of Suicidal Patients: A Guide for Psychiatric Nurses
- Mental Health Promotion Strategies for Adolescents: A Nursing Perspective
- Ethical Dilemmas in Psychiatric Nursing: An In-Depth Analysis
- Improving Medication Adherence in Patients with Severe Mental Illness
- Psychosocial Rehabilitation: Role of Psychiatric Nurses
- Psychiatric Nursing Care for Patients With Autism Spectrum Disorder
Child Nursing Research Topics
- Managing Pediatric Pain: Evidence-Based Practices for Nurses
- Childhood Obesity: Prevention Strategies in Nursing
- Autism Spectrum Disorder: Nursing Interventions and Care
- Pediatric Palliative Care: An In-depth Analysis for Nurses
- Addressing Mental Health Issues in Pediatric Nursing
- Vaccine Hesitancy: Strategies for Nurse-Led Parent Education
- Nursing Care for Neonates: Practices and Challenges
- Childhood Asthma Management: A Nursing Approach
- Pediatric Oncology: Nursing Strategies for Comprehensive Care
- Type 1 Diabetes in Children: Nursing Management and Education
- Childhood Trauma: Implications for Pediatric Nursing
- Evaluating the Effectiveness of Child Life Specialists in Pediatric Care
- Child Abuse Identification: Training Needs for Pediatric Nurses
- Cystic Fibrosis: A Comprehensive Approach to Nursing Care
- Transitioning Care for Adolescents With Chronic Conditions
- Management of Congenital Heart Diseases: Implications for Pediatric Nurses
- Ethical Issues in Pediatric Nursing: Consent, Confidentiality, and Beyond
- Nursing Care for Children With Rare Genetic Disorders
- Pediatric Advanced Life Support: Training and Implementation in Nursing Practice
- Effectiveness of Play Therapy in Pediatric Nursing
Elderly Nursing Research Topics
- Dementia Care in Nursing: Current Practices and Challenges
- Promoting Healthy Aging: The Contribution of Nurses
- Palliative and End-of-Life Care in Geriatric Nursing
- Treatment, Intervention, and Management of Chronic Pain in the Elderly
- Mental Health Issues in Geriatric Population: A Nursing Perspective
- Medication Management for Older Adults: Nursing Strategies
- Osteoporosis Management: Nursing Care and Patient Education
- Alzheimer’s Disease: Improving the Quality of Life Through Nursing Care
- Strategies for Dealing With Elder Abuse in Nursing Practice
- Promoting Independent Activities of Daily Living for Older Adults
- Cardiovascular Disease Management in Geriatric Nursing
- Coping With Grief and Loss in Older Adults: A Nursing Approach
- Enhancing Communication With Elderly Patients Suffering From Hearing Loss
- Addressing Nutritional Needs of the Elderly: A Role for Nurses
- Nursing Care for Elderly Patients With Diabetes
- Transitioning to Residential Aged Care: A Guide for Nurses
- Ethical Dilemmas in Elderly Care: Informed Consent, Autonomy, and Beyond
- Nurse-led Health Promotion Interventions for Older Adults
- Implementing Family-Centered Care in Geriatric Nursing
Primary Healthcare Nursing Research Topics
- Chronic Disease Management in Primary Care: Nursing Strategies
- Implementing Preventive Health Measures: A Nursing Approach
- Health Promotion and Education in Primary Care: The Nurse’s Perspective
- Pediatric Care in Primary Health Settings: Nursing Practices
- Addressing Mental Health Issues in Primary Care Nursing
- Patient-Centered Care in Primary Health Settings: A Nursing Approach
- Implementing Telehealth in Primary Care: The Role of Nurses
- Management of Acute Illnesses in Primary Care: Nursing Strategies
- Nursing Interventions for Lifestyle-Related Conditions in Primary Care
- Elderly Care in Primary Health Settings: Opportunities and Challenges for Nurses
- Health Literacy: The Role of Nurses in Primary Care Settings
- Nursing Strategies for Addressing Substance Abuse in Primary Care
- Family-Centered Care in Primary Health Settings: Nursing Practices
- Optimizing Medication Management in Primary Care Nursing
- Reducing Health Disparities Through Community-Based Nursing Care
- Navigating Ethical Dilemmas in Primary Care Nursing
- Cancer Screening and Early Detection: Implications for Primary Care Nurses
- Incorporating Genomic Medicine in Primary Care: A Nursing Perspective
- Nurse-Led Clinics in Primary Care: Outcomes and Efficacy
Careers Nursing Research Topics
- Career Satisfaction Among Nurses: Influencing Factors and Outcomes
- Exploring the Transition From Student to Registered Nurse
- Nurse Retention Strategies in the Healthcare Industry
- The Trajectory of Advanced Practice Nursing Careers: An Empirical Study
- Navigating Leadership Roles in Nursing: Opportunities and Challenges
- Investigating Burnout and Resilience Among Nurses Across Different Specialties
- Exploring Barriers to Men Entering the Nursing Profession
- Work-Life Balance Among Nurses: Strategies and Outcomes
- Mentorship Programs in Nursing: Efficacy and Outcomes
- Job Stress and Coping Strategies Among Nurses in High-Stress Environments
- The Influence of Organizational Culture on Nurse Job Satisfaction
- Nursing Education Pathways: Outcomes and Career Progression
- Exploring the Effectiveness of Continuing Professional Development for Nurses
- Nursing in Rural Areas: Career Opportunities and Challenges
- Ethical Issues Encountered by Nurses: Impact on Career Progression
- Balancing Clinical and Administrative Roles in Nurse Management
- Influence of Leadership Styles on Nursing Team Performance
- Addressing Diversity and Inclusion in Nursing Workforce
- The Experience of Foreign-Educated Nurses in the U.S. Healthcare System
- Impacts of Technological Advancements on Nursing Practice and Career Progression
Controversial Nursing Research Topics
- End-of-Life Decisions: Ethical Dilemmas Encountered by Nurses
- Balancing Patient Autonomy and Public Health in Vaccine Hesitancy
- Controversies Surrounding Mandatory Overtime for Nurses
- Nursing and Assisted Suicide: Ethical Considerations
- Exploring the Legality and Ethics of Patient Restraints in Nursing
- Confidentiality in Nursing: Rights of Minors vs. Parental Consent
- The Controversy Over Prescriptive Authority for Advanced Practice Nurses
- Cultural Competence in Nursing: Controversies and Challenges
- Ethics of Involuntary Psychiatric Treatment: A Nursing Perspective
- Controversies Surrounding the Use of Complementary and Alternative Medicine in Nursing Practice
- Nurse Participation in Abortion Services: Ethical and Legal Considerations
- Addressing Moral Distress in Nursing: Causes and Coping Strategies
- The Debate Over Full Practice Authority for Nurse Practitioners
- Forced Medication Administration: Ethical Implications for Nursing
- Genetic Testing and Privacy: Implications for Nursing Practice
- Rationing of Care in Nursing: Ethical Considerations
- Controversies Surrounding the Role of Nurses in Euthanasia
- Informed Consent in Pediatric Nursing: Controversial Aspects
- Substance Abuse Among Nurses: Causes, Implications, and Controversial Solutions
- Dilemmas in Advanced Directives: A Nursing Perspective
Evidence-Based Nursing Practice Research Topics
- Incorporating Evidence-Based Practice in Nursing Education: Strategies and Outcomes
- Roles of Evidence-Based Practice in Enhancing Patient Outcomes in Oncology Nursing
- Evidence-Based Nursing Practices in Chronic Pain Management
- Evidence-Based Approaches to Reducing Hospital Readmission Rates
- Mental Health Care: Implementing Evidence-Based Practices in Nursing
- Evidence-Based Nursing Interventions for Patients With Diabetes
- Promoting Evidence-Based Practice in Pediatric Nursing
- Strategies for Enhancing Evidence-Based Practice in Geriatric Nursing
- Evidence-Based Nursing Care for Patients With Cardiovascular Diseases
- The Role of Clinical Decision Frameworks and Support Systems in Promoting Evidence-Based Practice
- Evidence-Based Nursing Strategies for Preventing Hospital-Acquired Infections
- Application of Evidence-Based Practice in Wound Care Nursing
- Evidence-Based Practice in Home Health Care Nursing: Challenges and Opportunities
- Quality Improvement Initiatives and Evidence-Based Practice in Nursing
- Roles of Evidence-Based Practice in Managing Obstetric Complications
- Application of Evidence-Based Practice in Critical Care Nursing
- Evidence-Based Practice in Psychiatric Nursing: Implementation and Outcomes
- Roles of Clinical Practice Guidelines in Evidence-Based Nursing
- Evidence-Based Nursing Strategies for Managing End-of-Life Care
20 Top Nursing Research Topic Questions
- How Can Evidence-Based Practice Improve Pediatric Nursing Outcomes?
- What Are Effective Strategies for Managing Work-Related Stress in Nursing?
- Which Interventions Are Most Effective in Promoting Mental Health Among Nurses?
- How Do Ethical Considerations Influence Decision-Making in Palliative Nursing Care?
- What Is the Relationship Between Leadership Styles and Nurse Job Satisfaction?
- How Can Nursing Interventions Improve Outcomes for Patients With Chronic Heart Failure?
- Can Telehealth Implementation Improve the Quality of Care in Rural Nursing Practice?
- What Are the Implications of Genomic Medicine for the Future of Nursing Practice?
- How Can Nurses Effectively Address the Challenge of Antibiotic Resistance?
- What Strategies Can Enhance Cultural Competence in Nursing Practice?
- How Effective Are Nurse-Led Health Promotion Programs in Primary Care Settings?
- What Is the Role of Nursing in Managing Chronic Illnesses Like Diabetes and Hypertension?
- How Can Simulation Training Enhance Clinical Skills Among Student Nurses?
- How Does Organizational Culture Influence Nurse Retention and Job Satisfaction?
- What are the Primary Challenges of Implementing Family-Centered Care in Pediatric Nursing?
- How Can Nursing Interventions Improve the Quality of Life for Elderly Patients?
- What Are the Most Effective Strategies for Pain Management in Nursing?
- How Do Ethical Dilemmas in Elderly Care Affect Nursing Practice and Decision-Making?
- How Can Nurses Contribute to Reducing Health Disparities in Underserved Populations?
- What Role Does Nursing Play in the Management of Public Health Crises and Challenges Like the COVID-19 Pandemic?
To Learn More, Read Relevant Articles
405 social media essay topics & list ideas, 431 music essay topics & ideas.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
7. The Impact of Transformational Leadership on Nursing Teams: Fostering a Culture of Excellence and Patient-Centeredness. 8. The Qualities and Competencies of.... Read More. View our collection of nurse leadership essays. Find inspiration for topics, titles, outlines, & craft impactful nurse leadership papers.
Nurse leaders must foster a culture of collaboration, encouraging open communication, mutual support, and shared decision-making among their teams. Topic Examples. The role of nurse leaders in promoting effective teamwork. Strategies for building trust and collaboration among nursing teams.
Background: Nursing leadership plays a vital role in shaping outcomes for healthcare organizations, personnel and patients. With much of the leadership workforce set to retire in the near future, identifying factors that positively contribute to the development of leadership in nurses is of utmost importance.
The link to nursing leadership is obvious—ethics, positive change, purpose, growth, and social connection are all part of who we are as nurses and nurse leaders. The most common relational leadership styles are transformational, authentic, and servant. All three leadership styles have connections to healthy work environments and staff ...
It involves issues impacted by changing political or administrative leadership, policy, or funding models, and by the evolution of care delivery methods, a refocusing on safety or risk issues, the introduction of new technologies or treatments, or staff attrition and adjustments in a facility.
Essay Topic Ideas and Examples. The Impact of Transformational Leadership in Nursing: A Comprehensive Analysis. Nursing Leadership Styles and Their Effects on Team Dynamics. Managing Change in Healthcare: The Role of Nurse Leaders. The Importance of Emotional Intelligence in Nurse Leadership. Nurse Burnout and Its Consequences on Patient Care.
Explore PICOT Question Examples on Nurse Leadership, nurse leadership challenges and opportunities, along with examples of PICOT questions, EBP, capstone project ideas, research paper topics, and nursing essay ideas. Get insights from professional nursing writers.
What is already known about the topic? • Relational leadership styles in healthcare organizations are critical for improving staff and client health outcomes. ... What this paper adds • Factors such as age, nursing experience and emotional intelligence may be positively correlated with leadership behavior and practice, however weak study ...
Leadership and Management in Nursing Essay Topics/Ideas. The Role of Nursing Leadership in Promoting Patient-Centered Care; ... If you need assistance with writing leadership and management in nursing essay, hire a top writer to get your paper done effectively and efficiently. Click on the order now button to place your order. Related.
In a nursing organization, improving the quality of healthcare delivered by the department to be equal with the organizational performance is a key role of leadership (Marquis and Huston, 2015). Nursing leadership is essential in the clinical setting and plays an important role in the development of the nurse as an individual or as a professional.
We will write a custom essay on your topic a custom Essay on Nursing Leadership and Personal Skills. 808 writers online . Learn More . Experience with the Supervisor. As quoted by Lachlan Mclean, "You can only lead others when you are willing to go." My Emergency Room Director at Providence Park in the Emergency Department (ED) is an ...
Professionalism and Leadership: Leaders in nursing build vital relationships and collaborate with various health care teams on sensitive topics. Using critical thinking skills allows those in nursing leadership roles to analyze decisions impacting the organization. They then clearly explain the rationale in a manner that encourages staff support.
What do we already know about this topic? Effective leadership in nursing can have a positive impact on nurse performance, job satisfaction, and patient outcomes. ... Studies reviewed indicated that nursing leadership can influence autonomy, 33,38,45 relatedness, 34 competencies, 36,37,41,48 individual characteristics, 40,48 and relationships ...
The Importance of Effective nursing leadership Today Today, the nursing profession is under unprecedented pressures to deliver high quality patient-centered care in the wake of the ongoing global coronavirus pandemic. In far too … peak of the pandemic is fully experienced. Against this backdrop, identifying ways that professional nurses can help achieve this goal by assuming appropriate ...
Paper Type: 1200 Word Essay Examples. Leadership in Nursing. Definitions, Theories, and Styles of Leadership Developing future nurse leaders is one of the greatest challenges faced by the nursing profession (Mahoney, 2001). Powerful leadership skills are needed by all nurses—those providing direct care to those in top management positions.
Nursing Leadership and Management a. PAGES 4 WORDS 1572. Nursing management is a vital part of an effective healthcare system. It is a partner in professional satisfaction for nurses and a partner in achieving good health for individuals and societies alike (Oulton, 2006). Being a nurse manager is a very tough job that requires a strong ...
Rating · 4.8/5. Introduction Globalization refers to increased connectedness and interdependence of humans and health disparities such as high mortality rate, life expectancy, nutritional status, burden of diseases among others. Global health is... Topics: Nursing Practice Communication Healthcare Leadership. View full sample.
568 Nursing Essay Topics & Ideas. Exploring nursing essay topics can span a vast range of areas, such as critical care techniques, ethical decision-making, or the role of nurses in public health. Students or registered nurses (RN) may delve into the complexities of pediatric nursing, comparing it with geriatric nursing and its unique challenges.
Here's a list of 20 current nursing concept analysis paper topics to use for your nursing paper: Patient-centered care in the ICU. Ethical considerations in nursing informatics. Cultural competence in pediatric nursing. Person-centered communication in geriatric care. Pain management strategies in palliative care.
Developing Effective Nurse Leaders in a Challenging Climate. According to our 2022 Nurse Salary Report, the vacancy rate for registered nurses was almost 10% in 2020, with a third of hospitals reporting a vacancy rate higher than 10%. Nurse turnover rates stood at about 22% in 2021. These numbers represent a continuation of trends that began ...
Exploring Controversial Issues in Nursing: Key Topics and Examples. 7. Pediatric Nursing Research Topics for Students: A Comprehensive Guide. Explore various nursing argumentative essay topics to inspire thought-provoking discussions and help you develop strong critical thinking and writing skills.
team. 18 January 2024. last updated. Nursing research topics encompass various aspects of patient care, such as pain management strategies, promoting mental health, prevention of chronic diseases, impacts of caregiving, healthcare policy, telehealth effectiveness, and neonatal nursing. They also involve studying the effectiveness of nursing ...
List of latest Nursing Leadership Ideas and topics . Qualities of an outstanding nurse leader; Managing stress as a nurse leader; Strategies to develop nurse leaders; The critical areas of nursing leadership; Significance of nursing leadership with healthcare management; A review on ethical nursing practice; The fundamentals of nursing leadership