

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, should college athletes be paid an expert debate analysis.
Extracurriculars

The argumentative essay is one of the most frequently assigned types of essays in both high school and college writing-based courses. Instructors often ask students to write argumentative essays over topics that have “real-world relevance.” The question, “Should college athletes be paid?” is one of these real-world relevant topics that can make a great essay subject!
In this article, we’ll give you all the tools you need to write a solid essay arguing why college athletes should be paid and why college athletes should not be paid. We'll provide:
- An explanation of the NCAA and what role it plays in the lives of student athletes
- A summary of the pro side of the argument that's in favor of college athletes being paid
- A summary of the con side of the argument that believes college athletes shouldn't be paid
- Five tips that will help you write an argumentative essay that answers the question "Should college athletes be paid?"

The NCAA is the organization that oversees and regulates collegiate athletics.
What Is the NCAA?
In order to understand the context surrounding the question, “Should student athletes be paid?”, you have to understand what the NCAA is and how it relates to student-athletes.
NCAA stands for the National Collegiate Athletic Association (but people usually just call it the “N-C-double-A”). The NCAA is a nonprofit organization that serves as the national governing body for collegiate athletics.
The NCAA specifically regulates collegiate student athletes at the organization’s 1,098 “member schools.” Student-athletes at these member schools are required to follow the rules set by the NCAA for their academic performance and progress while in college and playing sports. Additionally, the NCAA sets the rules for each of their recognized sports to ensure everyone is playing by the same rules. ( They also change these rules occasionally, which can be pretty controversial! )
The NCAA website states that the organization is “dedicated to the well-being and lifelong success of college athletes” and prioritizes their well-being in academics, on the field, and in life beyond college sports. That means the NCAA sets some pretty strict guidelines about what their athletes can and can't do. And of course, right now, college athletes can't be paid for playing their sport.
As it stands, NCAA athletes are allowed to receive scholarships that cover their college tuition and related school expenses. But historically, they haven't been allowed to receive additional compensation. That meant athletes couldn't receive direct payment for their participation in sports in any form, including endorsement deals, product sponsorships, or gifts.
Athletes who violated the NCAA’s rules about compensation could be suspended from participating in college sports or kicked out of their athletic program altogether.

The Problem: Should College Athletes Be Paid?
You know now that one of the most well-known functions of the NCAA is regulating and limiting the compensation that student-athletes are able to receive. While many people might not question this policy, the question of why college athletes should be paid or shouldn't be paid has actually been a hot-button topic for several years.
The fact that people keep asking the question, “Should student athletes be paid?” indicates that there’s some heat out there surrounding this topic. The issue is frequently debated on sports talk shows , in the news media , and on social media . Most recently, the topic re-emerged in public discourse in the U.S. because of legislation that was passed by the state of California in 2019.
In September 2019, California governor Gavin Newsom signed a law that allowed college athletes in California to strike endorsement deals. An endorsement deal allows athletes to be paid for endorsing a product, like wearing a specific brand of shoes or appearing in an advertisement for a product.
In other words, endorsement deals allow athletes to receive compensation from companies and organizations because of their athletic talent. That means Governor Newsom’s bill explicitly contradicts the NCAA’s rules and regulations for financial compensation for student-athletes at member schools.
But why would Governor Newsom go against the NCAA? Here’s why: the California governor believes that it's unethical for the NCAA to make money based on the unpaid labor of its athletes . And the NCAA definitely makes money: each year, the NCAA upwards of a billion dollars in revenue as a result of its student-athlete talent, but the organization bans those same athletes from earning any money for their talent themselves. With the new California law, athletes would be able to book sponsorships and use agents to earn money, if they choose to do so.
The NCAA’s initial response to California’s new law was to push back hard. But after more states introduced similar legislation , the NCAA changed its tune. In October 2019, the NCAA pledged to pass new regulations when the board voted unanimously to allow student athletes to receive compensation for use of their name, image, and likeness.
Simply put: student athletes can now get paid through endorsement deals.
In the midst of new state legislation and the NCAA’s response, the ongoing debate about paying college athletes has returned to the spotlight. Everyone from politicians, to sports analysts, to college students are arguing about it. There are strong opinions on both sides of the issue, so we’ll look at how some of those opinions can serve as key points in an argumentative essay.

Let's take a look at the arguments in favor of paying student athletes!
The Pros: Why College Athletes Should B e Paid
Since the argument about whether college athletes should be paid has gotten a lot of public attention, there are some lines of reasoning that are frequently called upon to support the claim that college athletes should be paid.
In this section, we'll look at the three biggest arguments in favor of why college athletes should be paid. We'll also give you some ideas on how you can support these arguments in an argumentative essay.
Argument 1: The Talent Should Receive Some of the Profits
This argument on why college athletes should be paid is probably the one people cite the most. It’s also the easiest one to support with facts and evidence.
Essentially, this argument states that the NCAA makes millions of dollars because people pay to watch college athletes compete, and it isn’t fair that the athletes don't get a share of the profits
Without the student athletes, the NCAA wouldn’t earn over a billion dollars in annual revenue , and college and university athletic programs wouldn’t receive hundreds of thousands of dollars from the NCAA each year. In fact, without student athletes, the NCAA wouldn’t exist at all.
Because student athletes are the ones who generate all this revenue, people in favor of paying college athletes argue they deserve to receive some of it back. Otherwise, t he NCAA and other organizations (like media companies, colleges, and universities) are exploiting a bunch of talented young people for their own financial gain.
To support this argument in favor of paying college athletes, you should include specific data and revenue numbers that show how much money the NCAA makes (and what portion of that actually goes to student athletes). For example, they might point out the fact that the schools that make the most money in college sports only spend around 10% of their tens of millions in athletics revenue on scholarships for student-athletes. Analyzing the spending practices of the NCAA and its member institutions could serve as strong evidence to support this argument in a “why college athletes should be paid” essay.

I've you've ever been a college athlete, then you know how hard you have to train in order to compete. It can feel like a part-time job...which is why some people believe athletes should be paid for their work!
Argument 2: College Athletes Don’t Have Time to Work Other Jobs
People sometimes casually refer to being a student-athlete as a “full-time job.” For many student athletes, this is literally true. The demands on a student-athlete’s time are intense. Their days are often scheduled down to the minute, from early in the morning until late at night.
One thing there typically isn’t time for in a student-athlete’s schedule? Working an actual job.
Sports programs can imply that student-athletes should treat their sport like a full-time job as well. This can be problematic for many student-athletes, who may not have any financial resources to cover their education. (Not all NCAA athletes receive full, or even partial, scholarships!) While it may not be expressly forbidden for student-athletes to get a part-time job, the pressure to go all-in for your team while still maintaining your eligibility can be tremendous.
In addition to being a financial burden, the inability to work a real job as a student-athlete can have consequences for their professional future. Other college students get internships or other career-specific experience during college—opportunities that student-athletes rarely have time for. When they graduate, proponents of this stance argue, student-athletes are under-experienced and may face challenges with starting a career outside of the sports world.
Because of these factors, some argue that if people are going to refer to being a student-athlete as a “full-time job,” then student-athletes should be paid for doing that job.
To support an argument of this nature, you can offer real-life examples of a student-athlete’s daily or weekly schedule to show that student-athletes have to treat their sport as a full-time job. For instance, this Twitter thread includes a range of responses from real student-athletes to an NCAA video portraying a rose-colored interpretation of a day in the life of a student-athlete.
Presenting the Twitter thread as one form of evidence in an essay would provide effective support for the claim that college athletes should be paid as if their sport is a “full-time job.” You might also take this stance in order to claim that if student-athletes aren’t getting paid, we must adjust our demands on their time and behavior.
Argument 3: Only Some Student Athletes Should Be Paid
This take on the question, “Should student athletes be paid?” sits in the middle ground between the more extreme stances on the issue. There are those who argue that only the student athletes who are big money-makers for their university and the NCAA should be paid.
The reasoning behind this argument? That’s just how capitalism works. There are always going to be student-athletes who are more talented and who have more media-magnetizing personalities. They’re the ones who are going to be the face of athletic programs, who lead their teams to playoffs and conference victories, and who are approached for endorsement opportunities.
Additionally, some sports don't make money for their schools. Many of these sports fall under Title IX, which states that no one can be excluded from participation in a federally-funded program (including sports) because of their gender or sex. Unfortunately, many of these programs aren't popular with the public , which means they don't make the same revenue as high-dollar sports like football or basketball .
In this line of thinking, since there isn’t realistically enough revenue to pay every single college athlete in every single sport, the ones who generate the most revenue are the only ones who should get a piece of the pie.
To prove this point, you can look at revenue numbers as well. For instance, the womens' basketball team at the University of Louisville lost $3.8 million dollars in revenue during the 2017-2018 season. In fact, the team generated less money than they pay for their coaching staff. In instances like these, you might argue that it makes less sense to pay athletes than it might in other situations (like for University of Alabama football, which rakes in over $110 million dollars a year .)

There are many people who think it's a bad idea to pay college athletes, too. Let's take a look at the opposing arguments.
The Cons: Why College Athletes Shouldn't Be Paid
People also have some pretty strong opinions about why college athletes shouldn't be paid. These arguments can make for a pretty compelling essay, too!
In this section, we'll look at the three biggest arguments against paying college athletes. We'll also talk about how you can support each of these claims in an essay.
Argument 1: College Athletes Already Get Paid
On this side of the fence, the most common reason given for why college athletes should not be paid is that they already get paid: they receive free tuition and, in some cases, additional funding to cover their room, board, and miscellaneous educational expenses.
Proponents of this argument state that free tuition and covered educational expenses is compensation enough for student-athletes. While this money may not go straight into a college athlete's pocket, it's still a valuable resource . Considering most students graduate with nearly $30,000 in student loan debt , an athletic scholarship can have a huge impact when it comes to making college affordable .
Evidence for this argument might look at the financial support that student-athletes receive for their education, and compare those numbers to the financial support that non-athlete students receive for their schooling. You can also cite data that shows the real value of a college tuition at certain schools. For example, student athletes on scholarship at Duke may be "earning" over $200,000 over the course of their collegiate careers.
This argument works to highlight the ways in which student-athletes are compensated in financial and in non-financial ways during college , essentially arguing that the special treatment they often receive during college combined with their tuition-free ride is all the compensation they have earned.

Some people who are against paying athletes believe that compensating athletes will lead to amateur athletes being treated like professionals. Many believe this is unfair and will lead to more exploitation, not less.
Argument 2: Paying College Athletes Would Side-Step the Real Problem
Another argument against paying student athletes is that college sports are not professional sports , and treating student athletes like professionals exploits them and takes away the spirit of amateurism from college sports .
This stance may sound idealistic, but those who take this line of reasoning typically do so with the goal of protecting both student-athletes and the tradition of “amateurism” in college sports. This argument is built on the idea that the current system of college sports is problematic and needs to change, but that paying student-athletes is not the right solution.
Instead, this argument would claim that there is an even better way to fix the corrupt system of NCAA sports than just giving student-athletes a paycheck. To support such an argument, you might turn to the same evidence that’s cited in this NPR interview : the European model of supporting a true minor league system for most sports is effective, so the U.S. should implement a similar model.
In short: creating a minor league can ensure athletes who want a career in their sport get paid, while not putting the burden of paying all collegiate athletes on a university.
Creating and supporting a true professional minor league would allow the students who want to make money playing sports to do so. Universities could then confidently put earned revenue from sports back into the university, and student-athletes wouldn’t view their college sports as the best and only path to a career as a professional athlete. Those interested in playing professionally would be able to pursue this dream through the minor leagues instead, and student athletes could just be student athletes.
The goal of this argument is to sort of achieve a “best of both worlds” solution: with the development and support of a true minor league system, student-athletes would be able to focus on the foremost goal of getting an education, and those who want to get paid for their sport can do so through the minor league. Through this model, student-athletes’ pursuit of their education is protected, and college sports aren’t bogged down in ethical issues and logistical hang-ups.
Argument 3: It Would Be a Logistical Nightmare
This argument against paying student athletes takes a stance on the basis of logistics. Essentially, this argument states that while the current system is flawed, paying student athletes is just going to make the system worse. So until someone can prove that paying collegiate athletes will fix the system, it's better to maintain the status quo.
Formulating an argument around this perspective basically involves presenting the different proposals for how to go about paying college athletes, then poking holes in each proposed approach. Such an argument would probably culminate in stating that the challenges to implementing pay for college athletes are reason enough to abandon the idea altogether.
Here's what we mean. One popular proposed approach to paying college athletes is the notion of “pay-for-play.” In this scenario, all college athletes would receive the same weekly stipend to play their sport .
In this type of argument, you might explain the pay-for-play solution, then pose some questions toward the approach that expose its weaknesses, such as: Where would the money to pay athletes come from? How could you pay athletes who play certain sports, but not others? How would you avoid Title IX violations? Because there are no easy answers to these questions, you could argue that paying college athletes would just create more problems for the world of college sports to deal with.
Posing these difficult questions may persuade a reader that attempting to pay college athletes would cause too many issues and lead them to agree with the stance that college athletes should not be paid.

5 Tips for Writing About Paying College Athletes
If you’re assigned the prompt “Should college athletes be paid," don't panic. There are several steps you can take to write an amazing argumentative essay about the topic! We've broken our advice into five helpful tips that you can use to persuade your readers (and ace your assignment).
Tip 1: Plan Out a Logical Structure for Your Essay
In order to write a logical, well-organized argumentative essay, one of the first things you need to do is plan out a structure for your argument. Using a bare-bones argumentative outline for a “why college athletes should be paid” essay is a good place to start.
Check out our example of an argumentative essay outline for this topic below:
- The thesis statement must communicate the topic of the essay: Whether college athletes should be paid, and
- Convey a position on that topic: That college athletes should/ should not be paid, and
- State a couple of defendable, supportable reasons why college athletes should be paid (or vice versa).
- Support Point #1 with evidence
- Explain/interpret the evidence with your own, original commentary
- Support Point #2 with evidence
- Explain/interpret the evidence with your own, original commentary
- Support Point #3 with evidence
- New body paragraph addressing opposing viewpoints
- Concluding paragraph
This outline does a few things right. First, it makes sure you have a strong thesis statement. Second, it helps you break your argument down into main points (that support your thesis, of course). Lastly, it reminds you that you need to both include evidence and explain your evidence for each of your argumentative points.
While you can go off-book once you start drafting if you feel like you need to, having an outline to start with can help you visualize how many argumentative points you have, how much evidence you need, and where you should insert your own commentary throughout your essay.
Remember: the best argumentative essays are organized ones!
Tip 2: Create a Strong Thesis
T he most important part of the introduction to an argumentative essay claiming that college athletes should/should not be paid is the thesis statement. You can think of a thesis like a backbone: your thesis ties all of your essay parts together so your paper can stand on its own two feet!
So what does a good thesis look like? A solid thesis statement in this type of argumentative essay will convey your stance on the topic (“Should college athletes be paid?”) and present one or more supportable reasons why you’re making this argument.
With these goals in mind, here’s an example of a thesis statement that includes clear reasons that support the stance that college athletes should be paid:
Because the names, image, and talents of college athletes are used for massive financial gain, college athletes should be able to benefit from their athletic career in the same way that their universities do by getting endorsements.
Here's a thesis statement that takes the opposite stance--that college athletes shouldn’t be paid --and includes a reason supporting that stance:
In order to keep college athletics from becoming over-professionalized, compensation for college athletes should be restricted to covering college tuition and related educational expenses.
Both of these sample thesis statements make it clear that your essay is going to be dedicated to making an argument: either that college athletes should be paid, or that college athletes shouldn’t be paid. They both convey some reasons why you’re making this argument that can also be supported with evidence.
Your thesis statement gives your argumentative essay direction . Instead of ranting about why college athletes should/shouldn’t be paid in the remainder of your essay, you’ll find sources that help you explain the specific claim you made in your thesis statement. And a well-organized, adequately supported argument is the kind that readers will find persuasive!
Tip 3: Find Credible Sources That Support Your Thesis
In an argumentative essay, your commentary on the issue you’re arguing about is obviously going to be the most fun part to write. But great essays will cite outside sources and other facts to help substantiate their argumentative points. That's going to involve—you guessed it!—research.
For this particular topic, the issue of whether student athletes should be paid has been widely discussed in the news media (think The New York Times , NPR , or ESPN ).
For example, this data reported by the NCAA shows a breakdown of the gender and racial demographics of member-school administration, coaching staff, and student athletes. These are hard numbers that you could interpret and pair with the well-reasoned arguments of news media writers to support a particular point you’re making in your argument.
Though this may seem like a topic that wouldn’t generate much scholarly research, it’s worth a shot to check your library database for peer-reviewed studies of student athletes’ experiences in college to see if anything related to paying student athletes pops up. Scholarly research is the holy grail of evidence, so try to find relevant articles if you can.
Ultimately, if you can incorporate a mix of mainstream sources, quantitative or statistical evidence, and scholarly, peer-reviewed sources, you’ll be on-track to building an excellent argument in response to the question, “Should student athletes be paid?”

Having multiple argumentative points in your essay helps you support your thesis.
Tip 4: Develop and Support Multiple Points
We’ve reviewed how to write an intro and thesis statement addressing the issue of paying college athletes, so let’s talk next about the meat and potatoes of your argumentative essay: the body paragraphs.
The body paragraphs that are sandwiched between your intro paragraph and concluding paragraph are where you build and explain your argument. Generally speaking, each body paragraph should do the following:
- Start with a topic sentence that presents a point that supports your stance and that can be debated,
- Present summaries, paraphrases, or quotes from credible sources--evidence, in other words--that supports the point stated in the topic sentence, and
- Explain and interpret the evidence presented with your own, original commentary.
In an argumentative essay on why college athletes should be paid, for example, a body paragraph might look like this:
Thesis Statement : College athletes should not be paid because it would be a logistical nightmare for colleges and universities and ultimately cause negative consequences for college sports.
Body Paragraph #1: While the notion of paying college athletes is nice in theory, a major consequence of doing so would be the financial burden this decision would place on individual college sports programs. A recent study cited by the NCAA showed that only about 20 college athletic programs consistently operate in the black at the present time. If the NCAA allows student-athletes at all colleges and universities to be paid, the majority of athletic programs would not even have the funds to afford salaries for their players anyway. This would mean that the select few athletic programs that can afford to pay their athletes’ salaries would easily recruit the most talented players and, thus, have the tools to put together teams that destroy their competition. Though individual athletes would benefit from the NCAA allowing compensation for student-athletes, most athletic programs would suffer, and so would the spirit of healthy competition that college sports are known for.
If you read the example body paragraph above closely, you’ll notice that there’s a topic sentence that supports the claim made in the thesis statement. There’s also evidence given to support the claim made in the topic sentence--a recent study by the NCAA. Following the evidence, the writer interprets the evidence for the reader to show how it supports their opinion.
Following this topic sentence/evidence/explanation structure will help you construct a well-supported and developed argument that shows your readers that you’ve done your research and given your stance a lot of thought. And that's a key step in making sure you get an excellent grade on your essay!
Tip 5: Keep the Reader Thinking
The best argumentative essay conclusions reinterpret your thesis statement based on the evidence and explanations you provided throughout your essay. You would also make it clear why the argument about paying college athletes even matters in the first place.
There are several different approaches you can take to recap your argument and get your reader thinking in your conclusion paragraph. In addition to restating your topic and why it’s important, other effective ways to approach an argumentative essay conclusion could include one or more of the following:
While you don’t want to get too wordy in your conclusion or present new claims that you didn’t bring up in the body of your essay, you can write an effective conclusion and make all of the moves suggested in the bulleted list above.
Here’s an example conclusion for an argumentative essay on paying college athletes using approaches we just talked about:
Though it’s true that scholarships and financial aid are a form of compensation for college athletes, it’s also true that the current system of college sports places a lot of pressure on college athletes to behave like professional athletes in every way except getting paid. Future research should turn its attention to the various inequities within college sports and look at the long-term economic outcomes of these athletes. While college athletes aren't paid right now, that doesn’t necessarily mean that a paycheck is the best solution to the problem. To avoid the possibility of making the college athletics system even worse, people must consider the ramifications of paying college students and ensure that paying athletes doesn't create more harm than good.
This conclusion restates the argument of the essay (that college athletes shouldn't be paid and why), then uses the "Future Research" tactic to make the reader think more deeply about the topic.
If your conclusion sums up your thesis and keeps the reader thinking, you’ll make sure that your essay sticks in your readers' minds.

Should College Athletes Be Paid: Next Steps
Writing an argumentative essay can seem tough, but with a little expert guidance, you'll be well on your way to turning in a great paper . Our complete, expert guide to argumentative essays can give you the extra boost you need to ace your assignment!
Perhaps college athletics isn't your cup of tea. That's okay: there are tons of topics you can write about in an argumentative paper. We've compiled 113 amazing argumentative essay topics so that you're practically guaranteed to find an idea that resonates with you.
If you're not a super confident essay writer, it can be helpful to look at examples of what others have written. Our experts have broken down three real-life argumentative essays to show you what you should and shouldn't do in your own writing.

Ashley Sufflé Robinson has a Ph.D. in 19th Century English Literature. As a content writer for PrepScholar, Ashley is passionate about giving college-bound students the in-depth information they need to get into the school of their dreams.
Student and Parent Forum
Our new student and parent forum, at ExpertHub.PrepScholar.com , allow you to interact with your peers and the PrepScholar staff. See how other students and parents are navigating high school, college, and the college admissions process. Ask questions; get answers.

Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
The Case for Paying College Athletes
The case against paying college athletes, the era of name, image, and likeness (nil) profiting, why should college athletes be paid, is it illegal for college athletes to get paid, what percentage of americans support paying college athletes, the bottom line, should college athletes be paid.
The Case For and Against
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Headshot-4c571aa3d8044192bcbd7647dd137cf1.jpg)
Should college athletes be able to make money from their sport? When the National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) was founded in 1906, the organization’s answer was a firm “no,” as it sought to “ensure amateurism in college sports.”
Despite the NCAA’s official stance, the question has long been debated among college athletes, coaches, sports fans, and the American public. The case for financial compensation saw major developments in June 2021, when the U.S. Supreme Court ruled that the NCAA cannot limit colleges from offering student-athletes “education-related benefits.”
In response, the NCAA issued an interim policy stating that its student-athletes were permitted to profit off their name, image, and likeness (NIL) , but not to earn a salary. This policy will remain in place until a more “permanent solution” can be found in conjunction with Congress.
Meanwhile, the landscape continues to shift, with new cases, decisions, and state legislation being brought forward. College athletes are currently permitted to receive “cost of attendance” stipends (up to approximately $6,000), unlimited education-related benefits, and awards. A 2023 survey found that 67% of U.S. adults favor paying college athletes with direct compensation.
Key Takeaways
- Despite the NCAA reporting nearly $1.3 billion in revenue in 2023, student-athletes are restricted to limited means of compensation.
- Although college sports regularly generate valuable publicity and billions of dollars in revenue for schools, even the highest-grossing college athletes tend to see only a small fraction of this.
- One argument for paying college athletes is the significant time commitment that their sport requires, which can impact their ability to earn income and divert time and energy away from academic work.
- Student-athletes may face limited prospects after college for a variety of reasons, including a high risk of injury, fierce competition to enter professional leagues, and lower-than-average graduation rates.
- The developing conversation around paying college athletes must take into account the practical challenges of determining and administering compensation, as well as the potential impacts on players and schools.
There are numerous arguments in support of paying college athletes, many of which focus on ameliorating the athletes’ potential risks and negative impacts. Here are some of the typical arguments in favor of more compensation.
Financial Disparity
College sports generate billions of dollars in revenue for networks, sponsors, and institutions (namely schools and the NCAA). There is considerable money to be made from advertising and publicity, historically, most of which has not benefited those whose names, images, and likenesses are featured within it.
Of the 2019 NCAA Division I revenues ($15.8 billion in total), only 18.2% was returned to athletes through scholarships, medical treatment, and insurance. Additionally, any other money that goes back to college athletes is not distributed equally. An analysis of players by the National Bureau of Economic Research found major disparities between sports and players.
Nearly 50% of men’s football and basketball teams, the two highest revenue-generating college sports, are made up of Black players. However, these sports subsidize a range of other sports (such as men’s golf and baseball, and women’s basketball, soccer, and tennis) where only 11% of players are Black and which also tend to feature players from higher-income neighborhoods. In the end, financial redistribution between sports effectively funnels resources away from students who are more likely to be Black and come from lower-income neighborhoods toward those who are more likely to be White and come from higher-income neighborhoods.
Exposure and Marketing Value
Colleges’ finances can benefit both directly and indirectly from their athletic programs. The “Flutie Effect,” named after Boston College quarterback Doug Flutie, is an observed phenomenon whereby college applications and enrollments seem to increase after an unexpected upset victory or national football championship win by that college’s team. Researchers have also suggested that colleges that spend more on athletics may attract greater allocations of state funding and boost private donations to institutions.
Meanwhile, the marketing of college athletics is valued in the millions to billions of dollars. In 2023, the NCAA generated nearly $1.3 billion in revenue, $945.1 million of which came from media rights fees. In 2022, earnings from March Madness represented nearly 90% of the NCAA’s total revenue. Through this, athletes give schools major exposure and allow them to rack up huge revenues, which argues for making sure the players benefit, too.
Opportunity Cost, Financial Needs, and Risk of Injury
Because participation in college athletics represents a considerable commitment of time and energy, it necessarily takes away from academic and other pursuits, such as part-time employment. In addition to putting extra financial pressure on student-athletes, this can impact athletes’ studies and career outlook after graduation, particularly for those who can’t continue playing after college, whether due to injury or the immense competition to be accepted into a professional league.
Earning an income from sports and their significant time investment could be a way to diminish the opportunity cost of participating in them. This is particularly true in case of an injury that can have a long-term effect on an athlete’s future earning potential.
Arguments against paying college athletes tend to focus on the challenges and implications of a paid-athlete system. Here are some of the most common objections to paying college athletes.
Existing Scholarships
Opponents of a paid-athlete system tend to point to the fact that some college athletes already receive scholarships , some of which cover the cost of their tuition and other academic expenses in full. These are already intended to compensate athletes for their work and achievements.
Financial Implications for Schools
One of the main arguments against paying college athletes is the potential financial strain on colleges and universities. The majority of Division I college athletics departments’ expenditures actually surpass their revenues, with schools competing for players by hiring high-profile coaches, constructing state-of-the-art athletics facilities, and offering scholarships and awards.
With the degree of competition to attract talented athletes so high, some have pointed out that if college athletes were to be paid a salary on top of existing scholarships, it might unfairly burden those schools that recruit based on the offer of a scholarship.
‘Amateurism’ and the Challenges of a Paid-Athlete System
Historically, the NCAA has sought to promote and preserve a spirit of “amateurism” in college sports, on the basis that fans would be less interested in watching professional athletes compete in college sports, and that players would be less engaged in their academic studies and communities if they were compensated with anything other than scholarships.
The complexity of determining levels and administration of compensation across an already uneven playing field also poses a practical challenge. What would be the implications concerning Title IX legislation, for example, since there is already a disparity between male and female athletes and sports when it comes to funding, resources, opportunities, compensation, and viewership?
Another challenge is addressing the earnings potential of different sports (as many do not raise revenues comparable to high-profile sports like men’s football and basketball) or of individual athletes on a team. Salary disparities would almost certainly affect team morale and drive further competition between schools to bid for the best athletes.
In 2021, the U.S. Supreme Court ruled that the NCAA violated antitrust laws with its rules around compensation, holding that the NCAA’s current rules were “more restrictive than necessary” and that the NCAA could no longer “limit education-related compensation or benefits” for Division I football and basketball players.
In response, the NCAA released an interim policy allowing college athletes to benefit from their name, image, and likeness (NIL) , essentially providing the opportunity for players to profit off their personal brand through social media and endorsement deals. States then introduced their own rules around NIL, as did individual schools, whose coaches or compliance departments maintain oversight of NIL deals and the right to object to them in case of conflict with existing agreements.
Other court cases against the NCAA have resulted in legislative changes that now allow students to receive “cost of attendance” stipends up to a maximum of around $6,000 as well as unlimited education-related benefits and awards.
The future of NIL rules and student-athlete compensation remains to be seen. According to the NCAA, the intention is to “develop a national law that will help colleges and universities, student-athletes, and their families better navigate the name, image, and likeness landscape.” However, no timeline has been specified as of yet.
Common arguments in support of paying college athletes tend to focus on players’ financial needs, their high risk of injury, and the opportunity cost they face (especially in terms of academic achievement, part-time work, and long-term financial and career outlook). Proponents of paying college athletes also point to the extreme disparity between the billion-dollar revenues of schools and the NCAA and current player compensation.
Although the NCAA once barred student-athletes from earning money from their sport, legislation around compensating college athletes is changing. In 2021, the NCAA released an interim policy permitting college athletes to profit off their name, image, and likeness (NIL) through social media and endorsement and sponsorship deals. However, current regulations and laws vary by state.
In 2023, a nationally representative sample of U.S. adults found that 67% of respondents were in favor of paying college athletes with direct compensation. Sixty-four percent said they supported athletes’ rights to obtain employee status, and 59% supported their right to collectively bargain as a labor union .
Although the NCAA is under growing pressure to share its billion-dollar revenues with the athletes it profits from, debate remains around whether, how, and how much college athletes should be paid. Future policy and legislation will need to take into account the financial impact on schools and athletes , the value of exposure and marketing, pay equity and employment rights, pay administration, and the nature of the relationship between college athletes and the institutions they represent.
NCAA. “ History .”
Marquette Sports Law Review. “ Weakening Its Own Defense? The NCAA’s Version of Amateurism ,” Page 260 (Page 5 of PDF).
U.S. Supreme Court. “ National Collegiate Athletic Association v. Alston et al. ”
NCAA. “ NCAA Adopts Interim Name, Image and Likeness Policy .”
PBS NewsHour. “ Analysis: Who Is Winning in the High-Revenue World of College Sports? ”
Sportico. “ 67% of Americans Favor Paying College Athletes: Sportico/Harris Poll .”
Sportico. “ NCAA Took in Record Revenue in 2023 on Investment Jump .”
National Bureau of Economic Research. “ Revenue Redistribution in Big-Time College Sports .”
Appalachian State University, Walker College of Business. “ The Flutie Effect: The Influence of College Football Upsets and National Championships on the Quantity and Quality of Students at a University .”
Grand Canyon University. “ Should College Athletes Be Paid? ”
Flagler College Gargoyle. “ Facing Inequality On and Off the Court: The Disparities Between Male and Female Athletes .”
U.S. Department of Education. “ Title IX and Sex Discrimination .”
Congressional Research Service Reports. “ National Collegiate Athletic Association v. Alston and the Debate Over Student Athlete Compensation .”
NCSA College Recruiting. “ NCAA Name, Image, Likeness Rule .”
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-151311702-a935ed8794c64194a53b5741d4be05f3.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices

Point/Counterpoint: Paying College Athletes
The notion of paying college football players has been an ongoing debate since the early 1900’s. With current television revenue resulting from NCAA football bowl games and March Madness in basketball, there is now a clamoring for compensating both football and basketball players beyond that of an athletic scholarship. This article takes a point/counterpoint approach to the topic of paying athletes and may have potential implications/consequences for college administrators, athletes, and coaches. Dr. John Acquaviva defends the current system in which colleges provide an athletic scholarship that provides a “free college education” in return for playing on the university team. Dr. Dennis Johnson follows with a counterpoint making the case that athletes in these sports should receive compensation beyond that of a college scholarship and forwards five proposals to pay the athletes.
Key words: pay for play, athletic scholarships
Introduction: History of the National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA)
The idea of paying college athletes to compete dates back to what is considered to be the first intercollegiate competition. In a regatta between Harvard and Yale Universities, Harvard used a coxswain who was not even a student enrolled at the Ivy League school (5). Much like today’s universities whose appetites for appearances in corporate-sponsored “big money” football bowl events; Harvard may have used the non-student to please regatta sponsor Elkins Railroad (23).
In the late 1800’s, football played by college teams was a brutal sport but enjoyed by many fans. However, from 1900 to 1905, there were 45 players who died playing the sport (22). This prompted President Theodore Roosevelt to summon the presidents of Harvard, Yale, and Princeton, and threaten them with a ban unless the sport was modified. As a result of that meeting, a group of 62 university presidents convened to form the Intercollegiate Athletic Association in 1906. This group evolved into the NCAA in 1910, but as a group it only possessed supervisory power (22).
College football became even more popular in the period of 1920-1940. This was a time when commercialism in the educational system was being questioned on a variety of levels. One such fundamental question was posed in 1929 by Howard Savage, a staff member of the Carnegie Foundation. He raised a question in an article entitled Athletics in American College (originally published in 1930 but reprinted in 1999) “whether an institution in the social order whose primary purpose is the development of the intellectual life can at the same time serve an agency to promote business, industry, journalism, and organized athletics on an extensive commercial basis? More importantly, the report asked “can it (the university) concentrate its attention on securing teams that win, without impairing the sincerity and vigor of its intellectual purpose” (9, p.495)? Savage also states that “alumni devices for recruiting winning teams constitutes the most disgraceful phase of recent intercollegiate athletics” (9, p. 495). In sum, the original 1929 report claimed that “big time” college sports were not educational, but were entirely financial and commercial.
Athletes during the early and mid-1900’s were routinely recruited and paid to play; and there were several instances where individuals representing the schools were not enrolled as students. For example, there is one report of a Midwestern university using seven members of its team that included the town blacksmith, a lawyer, a livery man, and four railroad employees (5). Other athletes at colleges were given high paying jobs for which they did little or no work. In 1948, the NCAA adopted a “Sanity Code” that limited financial aid for athletes to tuition and fees, and required that aid otherwise be given based on need (5). In the early 1950’s, with the threat of several southern schools bolting from the NCAA, the code was revised to allow athletic scholarships to cover tuition, fees, and a living stipend.
However, by the mid-1950’s many schools were still struggling with the issue of offering athletic scholarships. Some university presidents ultimately decided to maintain the principles of amateurism and further serve the mission of higher education. Those were presidents of universities that today make up the Ivy League. They concluded that it was not in the best interest of their universities to award athletic scholarships, and have remained steadfast even today.
After passing Title IX in the mid 1970’s, the NCAA absorbed the Association for Intercollegiate Athletics for Women (AIAW) and began to govern women’s sport at the collegiate level. Over the past 50 years, the NCAA has also expanded into three divisions with a multitude of championship events on a yearly basis (20). There are more than 1,300 member institutions that represent an estimated 400,000 student athletes who participate in sport (21). The result of this growth and development are enormous increases in revenue. NCAA President Mark Emmert reports the NCAA revenues for the 2010-11 fiscal year is projected at $757 million, of which $452.2 million will go to Division I members (14).
While seemingly operating in a purely capitalistic/professional atmosphere, the NCAA continues to endorse an amateurism concept in college athletics. These competing, and often contradictory, values lead some college athletes in big time football and basketball programs to question the status quo of the present system through their words and actions. For example, many athletes are still attempting to get their “piece of the pie,” albeit under the table. And so it leads to our point-counterpoint.
Point: College Athletes Should Not Be Paid
The intensity of the argument to pay college athletes has escalated in the past few years. Perhaps it’s because of the current economic climate and everyone, including amateur athletes is looking for ways to make money? Or maybe it’s because many higher learning institutions have given the public access to their annual budget and readers focus on the profit of select athletic programs? Or maybe it is due to the absurd coaches’ salaries and the money that colleges make from football bowl games and basketball tournaments? Regardless, this has magnified the fact that the athletes see none of these profits and thus begs the simple question: “Where’s my share?” Perhaps a fair question, but to understand this argument better, a healthy debate is needed. So, here are some points to consider.
Point #1: Education is Money
Colleges and universities provide an invaluable and vital service to our communities: education. A now-famous bumper sticker once read: “If you think education is expensive, try ignorance.” To address that very slogan, the U.S. census bureau, as reported by Cheesman-Day and Newberger (7), expressed this best when they reported that the lifetime earnings for those with a college degree are over $1 million dollars more than non-graduates. Despite such a statistic, essays and op-ed columns continue to pour in from those who favor paying student-athletes while simultaneously refusing to acknowledge or accept the value of a college education. Is a college education priceless or not?
A sports-journalist in a recent national radio interview proposed that any argument against paying college athletes based on the sole reason that education is the prize is “antiquated”. But what seems antiquated and even shortsighted is the belief that paying a college athlete some (or even a lot of) money will solve all or even some of student’s long-term issues. The fear of the NCAA, as it should be, is that the mere notion of paying college athletes undermines the university’s primary purpose – education, something far more valuable than a modest annual stipend proposed by many. If it currently appears that the universities “don’t really care” about the athlete, paying them would intensify that belief, not dissolve it.
The irony in this dispute is that student-athletes do cost the university a substantial amount of money each year. For example, a full scholarship over four years can range between $30,000 and $200,000 depending if the institution is public or private (29). But let’s address this main point head on: There is an obvious lack of appreciation of a college degree from those in favor of paying athletes, and until a genuine gratitude for this concept develops, this argument will probably continue to linger.
Point #2: There Are Problems with Payment
Despite the well-documented scandals and corruption in college athletics (30), many would probably agree that paying athletes would exponentially increase the need for intense NCAA oversight – an enormous task by all accounts. Plus, there are the practical issues to consider. For example, how much should the athletes get paid and will payments be based on performance? What if the athlete gets hurt? What if the athlete is a bust and despite remaining on the team, doesn’t start or even play at all? – Issues that seem to raise far more questions than answers. But perhaps most important – What will happen to the non-revenue sports at the colleges who lose money from all of their sports programs – including football and basketball? It has been shown that only a fraction of Division I football and men’s basketball programs turn a profit (24, 20). The other Division I football and basketball programs as well as sports such as baseball, softball, golf, hockey, women’s basketball (minus a couple of notable programs), and just about all Division II sports not only fail to make money, but actually drain their athletic budgets. The outcome here would be inevitable: Forcing athletic departments to pay its football and basketball players would result in the eventual elimination of most, if not all, of the non-revenue sports. Is that what we want?
We cannot afford to be myopic on this issue. That is, there are only a limited number of programs that make big money, but yet there are hundreds of schools who absorb big losses at the cost of providing athletes a place to compete and earn a degree. The purpose of the NCAA, along with Amateur Athletic Union (AAU), Little League, and dozens of other organized forms of amateur sport is to provide a venue to play these sports – something we should not take for granted. The problem is that some have shifted in thinking that playing an organized sport is a right, whereas it still stands as a privilege.
Point #3: The University Offers More Than an Education
Concerts, lecture series by prominent people, on-stage productions, movies, intramural sports, fitness facilities, and a variety of clubs are all part of the typical university experience. Most students agree that colleges are self-contained acres of learning and socializing, all which takes place in a safe environment. It’s common for schools to subsidize the above-mentioned on-campus activities by adding fees to the tuition – which means that it’s free to a full-scholarship athlete. Other benefits to the athlete include the regular use of pristine gyms, well-manicured fields, athlete-only (and often team-only) workout facilities, sports medicine care, the opportunity to travel via away games, specialized meal plans and free foot gear and athletic attire. In addition, athletes are improving their trade from the best coaching minds in the sport; not to mention having access to some of the best nutrition and strength/conditioning personnel. And perhaps the most overlooked benefits are that the school provides the player with high-profile name recognition, a dedicated fan base, media exposure, and a competitive atmosphere with proven rivals, all of which took decades, effort and money for each institution to establish.
Point #4: The Athletic Department Has Its Role
Keep in mind that student-athletes are not employees of the university, rather they are students first and athletes second. The university can indeed make money from the sports programs; however, for those that do, the money simply goes back into the athletic program to fund the non-revenue sports (24). In fact, every year the NCAA sponsors over 80 national championships in three divisions, demonstrating the range and depth of their organization (20). While it is true that the champion in football and men’s basketball (and most other sports for that matter) seem to come from a relatively small pool of universities, it might be safe to assume that paying athletes would create an even bigger disparity since so few universities actually make money. Let’s face it, we are an underdog-loving country, and paying athletes would all but ensure that teams like Butler University, who made it to the Final Four in consecutive tournaments (2010 and 2011), will never do it again.
Point #5: Athletes Know the Deal
From the moment the full-scholarship papers are signed, each participant’s role is very clear: Schools accept the responsibility of the student’s tuition, meal plan, and boarding, while the athlete is provided with the opportunity to earn a degree, engage in college life and play their favorite sport in a well-organized, and often high profile fashion. The document signed by each student-athlete describes this agreement in an unmistakable manner. Although wordy and at times complex – a necessity due to the nature of the agreement – there’s no vagueness in the general arrangement or a hidden agenda from either party (10). A failure to honor the basic premise of any such contract would cause all forms of business – big or small – to crumble. If for some reason the university could be held liable for entrapment or some other form of dishonesty, then their athlete’s argument would stand on firmer ground. But frankly, the details of this agreement are well known by all involved, and rather strangely, no one seems to mind when signing them.
In conclusion, it should be noted that any NCAA improprieties or blatant corruption may have a carry-over effect into empathizing with the position given here. While corruption and other related-concerns are legitimate and need investigation, paying college athletes still remains a separate debate. It is vital to this process to view each NCAA issue independently and avoid making judgments on them as a whole. The position here is that, like many organizations, the NCAA should not be dismissed or discredited on one issue due to the mishandling of others. Further, if the contention is that many student athletes enter college unprepared or that athletics takes up too much time to excel (or even earn a degree), those are separate, but much needed arguments, and are not related to the issue of paying athletes.
Now more than ever, we live in an era of entitlement. At one time our country viewed the chance at higher education as a priceless commodity. However, it now seems that a college education is not held in the same esteem and worse yet, some see it as simply an opportunity to earn money. Although it is now evident that there has been a failure to convince much of the public of the true value of an education, keeping college athletes as pure amateurs remains the right thing to do.
Counter Point: Athletes in “Big-Time” Sports Should Be Paid
Introduction.
The argument that a college athletic scholarship is an equal quid pro quo for a college education has been utilized since athletic scholarships were approved by the NCAA in 1950’s. My colleague makes one point that is totally accurate – a college graduate can in fact make a great deal more money over a lifetime when compared to non-graduates. However, the remainder of the author’s points are half-truths and in reality just plain falsehoods. For instance, a “full athletic scholarships” do not provide a “free” education (as it does not cover all costs incurred from matriculation to graduation. In many cases, the university does not live up to its end of the bargain of providing an education; as evidenced by the dismal number in the graduation rates, especially among African Americans. Furthermore, the athletic scholarship is only a one-year (renewable) agreement that can be terminated by the coach or university in any given year for any reason.
In debating the pay-for-play issue in college athletics, the history of the governing body (i.e., currently the NCAA), their mission and view of amateurism, the past history of college athletes benefitting financially, and the degree to which athletes benefit from the university experience must all be examined. The counter point section of this paper addresses each point made by my colleague. Using the Eitzen (12) analogy comparing the NCAA and big-time athletic programs to the old southern plantation system will be the underpinning wellspring for the subject of athlete exploitation and the financial benefits enjoyed by the university derived from that plantation-like exploitation. An economic viewpoint will be presented to demonstrate the cartel-like atmosphere held by the NCAA while maintaining the illusion of amateurism.
Finally, five proposals that outline means to promote pay-for-play in NCAA Division I football and men’s basketball will be presented. The arguments that follow are specifically tailored for those two sports at schools who receive bonus money from the NCAA, as those universities and their coaches enjoy considerable revenue from TV contracts and sponsorships generated by bowl games and “March Madness” appearances.
Point #1: Athletic Scholarships Provide a “Free Education” is not correct
As mentioned, in the 1950’s the NCAA approved adding living stipends to athletic scholarships that previously included only tuition and fees. Today, the “full ride” scholarship can only include tuition, fees, room, board, and books. And as mentioned in the previous section, in some cases, depending on the school attended, that scholarship can be worth anywhere from $30,000 to $200,000, although the figures $20,000 to $100,000 over a four year period might be more accurate. In any case, that still does not cover the full cost of attending college.
The Collegiate Athletes Coalition (CAC) estimates that NCAA scholarships are worth about $2000 less than the cost of attending a university, as it does not account for expenses such as travel and sundries. Former Nebraska head football coach and United States Congressman, Tom Osborne (R-NE), calculates the gap between scholarship funding and the actual cost of attendance to be closer to $3,000. Even former NCAA President, Myles Brand, indicated that he favored increasing scholarship limits: “Ideally, the value of an athletically related scholarship would be increased to cover the full-cost of attendance, calculated at between $2,000 to $3000 more per year than is currently provided, I favor this approach of providing the full cost of attendance” (23, p.232).
So yes, the scholarship can be seen as pay for play, or at the very least, a quid pro quo for services rendered during a four year period. However, even with a full scholarship, an athlete will have to pay somewhere between $8,000 and $12,000 out of pocket to bridge the cost-of-living gap. Therefore, the full athletic scholarship does not provide a “free” education. Thus question remains: is the full scholarship a fair and equitable deal for the athlete?
Athlete Exploitation-The Plantation System
Eitzen (12) among others (27) makes the analogy that the NCAA operates like the “plantation system” of the old south. The coaches are the overseers who get work from the laborers (players) who provide riches for the masters (universities) while receiving little for their efforts. Perhaps slightly over-stated (obviously the athlete is not a slave, but maybe an indentured servant), the student–athlete is dominated, managed, and controlled, and they don’t receive a wage commensurate to their contribution as expressed in dollars earned by the university. Eitzen notes that athletes are sometimes mistreated physically and mentally and are often denied the rights and freedoms of other citizens. Ultimately, they have no real democratic recourse in an unjust system.
There are other similarities to the plantation analogy. Slaves were not free to leave the plantation much like an athlete cannot get out of a letter of intent (without penalty) and/or transfer without the penalty of sitting out a year. Much like the slaves who had no right to privacy, athletes are subject to mandatory drug testing (even though their coaches/masters are not tested), room checks, and limits on where they can and cannot go in the community. The athletes can be prohibited from political protests and the right to assemble. And finally, they can be subjected to mental cruelty and physical abuse (e.g., early morning torture sessions), all in order to create obedient slaves; student athletes.
Furthermore, collegiate athletics is often the only game in town for many of these athletes. For instance, football players must be in their third year of college or over the age of 21 to enter the National Football League (NFL). Basketball players, on the other hand, must attend college for one year or ultimately sit out a year before they can enter the National Basketball Association (NBA). Thus, the college game has become a “feeder system” similar to a minor professional league and it is in reality, “the only game in town.”
Point #2: Athletes Don’t Know the “Real” Deal
My colleague is partially correct in that most student athletes know that they are getting a scholarship that will allow them to go to school and play a sport. However, many don’t know the “real deal” as they generally have very little understanding they are about to enter a “plantation-like” system in which their scholarship in not guaranteed (i.e., renewable yearly) and can be terminated at any time. Student-athletes are also a led to believe that they will play and receive a college degree while possibly picking up a few fringe benefits along the way.
Take, for example, the recent stories regarding players like Reggie Bush, Cam Newton, or the players at Ohio State who received money and/or other benefits as a result of playing football. Even though student athletes know they will not get directly paid for playing, many desire and even expect some form of compensation. Slack (25) surveyed 3,500 current and retired football players in 1989 only to find that 31% had received under the table money during their college careers and 48% knew of others who had received payments. This seems to imply that while many recruits may indeed know “the deal”, they display their discontent by accepting payments or other benefits not currently allowed by the NCAA.
In reality, the statement “athletes know the deal” with regard to academic achievement and degree completion seems to lack substance. Dr. Nathan Tublitz, co-chair of the Coalition on Intercollegiate Athletes, an organization of 51 faculty senates whose purpose is to remind college presidents, athletic directors, and coaches that student athletes are students first. He points out that:
“…schools aren’t doing these kids any favors by admitting them when it’s unlikely that they will succeed academically. We bring 17 year-old kids, some of them from the inner city and we wine and dine them. They have female chaperones. We put them up in fancy hotels. They come here and see an incredibly fancy locker room with individual TV screens, air conditioning and videogames. They go in and see the new football stadium and the new $200 million basketball arena. They see a medical training facility that is stunningly beautiful with waterfalls, treadmill pools, and the sate-of-the-art medical and dental equipment. They come here and are treated like royalty. Until they break a leg or get put on the second string and they get set aside. Many don’t earn a degree. They don’t have the training or the skills to be independent after they leave the university. They’re lost (28, p.D10).”
When the scholarship is signed, the athlete and his family have reasonable expectations which include efforts by the coaching staff and university administration to meet all obligations of the contract. Additionally, my colleague notes, “that failure to honor the basic premise of any such contract would cause all forms of business – big or small – to crumble.” If the NCAA and athletic departments in higher education are a business, why are they allowed to act in a cartel-like fashion? And finally, do student athletes really know the “deal” when they penned their name on national signing day? It appears they don’t.
Point #3: The University Offers More than Education-It’s Possible-But Not Probable
Academic Detachment. My colleague also makes the claim that the university offers more than an education (e.g., concerts, lectures, intramurals, and clubs) in settings that enrich the college experience. Due to the plantation effect, however, many athletes are not able to take advantage of those events. For instance, few if any of the scholarship athletes would be allowed to play in an intramural contest for the coach’s fear of injury. Student athletes are also over-scheduled with study halls, practices, weight training sessions, film study, individual workouts, more practice, travel, and competition; all in an attempt to help athletes maintain focus on their sport.
Adler and Adler (1) spent five years recording systematic information regarding the athletes’ lives in a big-time college basketball program. After observing, interviewing, and traveling with them, they concluded that big-time basketball and being seriously engaged in academics were not compatible. They also found that freshmen had a period of optimism regarding academics when they first arrived on campus, but after about two semesters they found that the social isolation combined with the fatigue of training kept them from becoming involved in academic life.
Positive feedback these basketball players earned was always athletic-related and not academic. They soon learned what they had to do to stay eligible. Coaches made sure they scheduled classes that did not interfere with practices. Ultimately, the researchers realized that academic detachment was encouraged by the peer culture, and because of their social status (e.g., big man on campus), it became difficult for them to focus on academics.
Coakley (8) reported that not all of the athletes in the Adler & Adler (1) study experienced academic detachment. Those who entered college well-prepared with appropriate high school courses, strong parental support and an ability to develop relationships outside of sport were able to succeed in the classroom. It’s important to note that too many minority athletes from low socioeconomic environments struggle in academics – an issue that is often perpetuated by the coaches. For instance, Robert Smith, former running back for Minnesota Vikings and pre-med student while at Ohio State, needed two afternoon labs in the same semester. Since the labs conflicted with practice, coaches suggested that he drop them because of the commitment he made to play football. Against the wishes of the coaching staff, Smith took the classes but was forced to sit out the season as red shirt athlete; a further example of the plantation effect.
Benson (3) noted that one perspective was missing from the literature included a full expression from the black athletes point of view. Benson conducted a qualitative interview study of 12 African American students at a DI football program where the graduation rate was 31-40% for black football players compared to 60-70% of white football players. The results in this instance cannot be generalized due to the small sample size (N=12), but it does provide a snapshot of the thoughts regarding education and athletics of this group. Further, they reflect the results obtained by Adler & Adler (1).
Another major finding of the Benson (3) study was that the marginal academic performance was created by a series of interrelated practices engaged in by all significant members of the academic setting, including peers, coaches, advisors, teachers, and the student athletes themselves. It began in the recruitment, and continued through the first year. Black student athletes received the message that school was not important, and that as time passed, they had no real control over their destiny in the classroom. It was simply a matter of survival to keep the grade point average (GPA) to a point to be eligible. They all felt like the coaches did not “walk the talk” in terms of academics. They would just talk the academic game in public but then in reality they would have “fits” if classes ever interfered with the program. Simply put, student athletes learned it was a matter of survival and a basic expectation to maintain a GPA just high enough to remain eligible to compete (3).
“The Black Dumb Jock”. Harry Edwards (13) discussed the creation of the “black dumb jock” image prior to studies completed by Alder and Alder (1), Benson (3), and Coakley (8). He (i.e., Edwards) theorized that they were not born, but rather systematically created. The previous mentioned studies serve as evidence to support his statement (1, 3, 8). The exploitation of athletes is not solely an NCAA issue but a societal one. For example, Fred Butler was passed on through elementary, middle, and high school because he was a good football player. He graduated from high school reading at a second grade level and went to El Camino Junior College. There he took a number of physical activity classes while hoping to be drafted into the NFL. When no offer came, he played at California State University-Los Angeles for a year and a half. When again no offer came and his eligibility expired, he failed out of school within months with no degree, no offers to play pro ball, and no skills to use for employment. And he still could not read! (18). Similarly, Former NFL player Dexter Manley testified before a Senate Committee that he played four years at Oklahoma State University, only to leave the school illiterate. And the sad feature is that academic detachment from the university athletic department perspective doesn’t seem to be an issue because there are always more impoverished (and usually minority) kids waiting to come in and play.
Thus, student athletes in many cases cannot take advantage of the many extras offered by a college education. Why do athletes accept a diluted academic experience or the corruption of doctored transcripts, phantom courses, surrogate test takers, and tutors writing papers? Perhaps it is because they are disenfranchised under the current system, and will lose scholarships, starting roles, and eligibility if they complain. George Will argued that “College football and basketball are, for many players, vocations, not avocations, and academics are unsubstantiated rumors” (12, p.5). So do full scholarship athletes get a chance to take advantage of all the extras of the university experience? More than likely it is not the case especially when they can’t even hope for a meaningful degree.
NCAA as a Cartel. Kahn (16) examined the operation of the college football and basketball systems of the NCAA and offers lessons about the determinants and effects of supply and demand. Specifically he utilizes economic principles to calculate the value of college football player to a university. He notes that total ticket revenues for football and men’s basketball were $757 million in 1999, total value that exceeded the total ticket sales for all of professional baseball, football, and hockey that year. A figure indicating that the NCAA is a very successful business entity engaged in capitalism.
According to the cartel theory, the NCAA has “enforced collusive restrictions on payments for factors of production, including player compensation, recruiting expenses, and assistant coaches salaries; it has restricted output; and it has defeated potential rival groups (16, p. 211).” He notes, along with others (11, 15, 16, 30), that the NCAA can impose sanctions that range from scholarship reductions, elimination from post-season play to program death penalties (e.g., Southern Methodist football); and possibly even threaten a school’s academic accreditation. However, restriction of pay to players is the main way in which the organization acts to restrict competition.
Economists who have studied the NCAA “view it as a cartel that attempts to produce rents, both by limiting payments for inputs such as player compensation and by limiting output” (16, p.210). When looking at the rent values based on college football or men’s basketball players’ performances, they are paid below a competitive level of compensation based on estimates of marginal revenue product produced of these players (6). Their analysis considered the total revenue for a school and the number of players that were eventually drafted by a major professional league. Utilizing this framework they concluded that in 2005 dollars a draft-ready football player returned $495,000 to the university, while a draft-ready basketball player was worth $1.422 million for men’s basketball. And all of this compared to the approximately $40,000 paid in scholarship worth. This indicates that the NCAA does indeed use cartel power to pay top athletes less than the athlete’s market value.
Based on a workload of 1000 hours per year and an average scholarship value, economist Richard Sheehan (16) calculated the basic hourly wage of a college basketball player at $6.82 and a football player at $7.69. Coaches’ hourly wages, on the other hand, ranged from $250-$647 per hour (depending on salary). Again, using the Eitzen metaphor, the masters accumulate wealth at the slave’s expense, even though the athlete/slave’s health is jeopardized by participation (12).
Parent (23) notes the hypocrisy of the amateurism construct when looking at these capitalism issues. He notes that the former president of the University of Washington, William Gerberding, said, “As one contemplates the obvious fact that so many of the most gifted athletes are economically and educationally disadvantaged blacks, this becomes less and less defensible. I have become increasingly uncomfortable about having a largely white establishment maintaining an elaborate system of rules that deprives student-athletes, many of whom are non-white, of adequate financial support in the name of the ideals of amateurism” (p.236).
So, why do athletes tolerate this system? They do mainly because they are disenfranchised and fear losing their scholarships and eligibility if they complain. In essence, this pay-for-play discussion revolves around amateurism, as advertised by the NCAA, and its competing capitalistic drive for income. According to Tulsa Law School professor Ray Yasser, the best option for athletes to change the system for their benefit is to unite and “file an antitrust suit…against the NCAA and their universities, with the claim being that the NCAA and their universities are colluding to create a monopoly over the athlete’s ability to share in the profits generated from college athletics” (23, p.236).
While the points for maintaining the status quo were stated previously, there has been sufficient evidence presented in this section to stimulate discussion of paying players. The “play for a diploma” agreement is not happening in many cases, as the athlete failure rate indicates. Another example is national champion Connecticut men’s basketball program losing two scholarships for the upcoming season as a result of a poor Academic Performance Rating (APR) from the NCAA (11). Thus, the following pay for play proposals are being submitted for consideration.
Pay Proposals
It would appear that NCAA should get out of the commercial business of football and basketball and follow the Ivy League example of providing an environment that is truly amateur where student athletes actually are students first. That move would certainly place the student first in the student athlete term. However, it doesn’t seem pragmatic that either the NCAA or any of the major universities are in any hurry to turn away millions of dollars per year in profits. Therefore, it is time to consider some pay-for-pay proposals. California and Nebraska have already passed state legislation that would enable colleges to compensate athletes; however they are blocked by the NCAA from doing so (23). Therefore, I submit five proposals that could possibly be implemented:
- Big Ten Plan and/or Work Study Proposal: At the very least, the NCAA should follow former NCAA President Miles Brand’s suggestion and allocate athletes include a $2,000-$3,000 cost of living increase to full scholarships. Since athletes are supposedly only allowed to spend 20 hours per week involved with sport-related activities, this might actually be paid as 20 hours of work study or as a monthly living stipend. This would provide the athletes with the needed income for clothes, laundry, sundries, travel, and other small item expenses. Officials from the Big Ten are currently discussing a similar proposal that would help their athletes meet expenses not covered in an athletic scholarship. Big Ten commissioner Jim Delany reports league athletic directors and university officials have seriously discussed using some of their growing TV revenue to pay athletes more. This proposal which would give athletes a $2,000-$5,000 per year living stipend also has the support of current NCAA president Mark Emmert (2).
- SEC Game Pay Proposal: The Southeastern Conference, another of the big time football conferences recently entered into the pay for play discussion. University of South Carolina coach Steve Spurrier put forth a proposal at the recent conference meetings to pay players $300 per game. The proposal was supported by several other coaches. This type of a proposal could pay athletes anywhere from $300-$1000 per game based on time played per game. Since most players do not play more than 30 minutes a game, a player could be paid on a per-minute of competition basis. At a rate of $20 per minute a player could net $600 for a game and approximately $6000-$7,000 per season.
- Professional League Proposal: Ron Woods (27) puts forth a proposal submitted by Peter Plagensa, visiting professor at Middlebury College, regarding the pay-for-play issue. He appears to agree with the likes of Stanley Eitzen that the current practice of colleges and the NCAA do in fact “amount to a little more than a plantation system” (27, p. 67). He suggests that the big time college football and basketball maintain the million-dollar industry by making them an age 23 and under professional league. This proposal would allow universities to hire players as college staff (much like the cafeteria or groundskeepers) at moderate salaries plus room and board. Universities could also grant the athletes free academic classes until they earn a degree (even after playing days are over).
“College basketball players watch the coach roaming the sidelines in his $1,500 custom-make suit. They read about his $500.000 salary and $250,000 perk from a sneaker deal. They watch the schools sell jerseys (and T-shirts) with the player’s numbers on them. They see the athletic director and NCAA officials getting rich and you wonder why they might ask; hey where’s my share? What am I, a pack mule” (17, p.46)
My colleague has argued in point #2 that paying athletes raise a myriad of other issues, such as how much should they receive, what happens if an athlete gets hurt, and so on. That is a discussion for another time. First, we must agree that it is fair to compensate NCAA Division I football and basketball athletes beyond that of an athletic scholarship; then and only then may payout details be chronicled. Note: a reminder that we are only discussing compensation for the NCAA Division I-A football and basketball players; not the athletes in the AAU, Little League or other truly amateur venues of organized sport.
Throughout the history of the NCAA, college athletes have routinely received compensation beyond that of a full college scholarship (e.g., room and board, tuition, books). While such compensation is illegal, athletes like Reggie Bush and others receive under-the-table benefits as evidenced in the Slack survey (25).
Additionally, many athletes in “big time” programs do not receive a degree for their efforts in the athletic arena. Universities routinely admit students based on their athletic skills that are academically ill-prepared for success. As seen in the research (1, 3), many athletes that aspire to be academically successful soon lose hope with the over-scheduling and pressures of sport preparation. As a result, many college athletes, a majority of which are minorities, fail out of school once coaches have utilized their eligibility.
The NCAA functions like a cartel, keeping cost down while increasing profits. Rents for a draft-ready athlete earn the university somewhere between $500,000 for football and $1.422 million for men’s basketball (16), leading to a pseudo-plantation system where the coaches oversee the athletes demanding work and controlling their schedules on and off the field. This unbalanced system allows athletes to earn the equivalent of $6.80-$7.69 an hour (12) while coaches like Nick Saban of Alabama or Mack Brown of Texas earn over five million dollars a year (4).
If the NCAA continues as a corporate entity and acting in a cartel-like fashion making millions of dollars a year, implementing a plan to pay student athletes for playing must be considered. Otherwise, America’s institutions of higher learning should follow the Ivy League schools’ example and eliminate athletic scholarships, get out of the big time sport business, and get on with providing students with a complete educational experience.
Applications in Sport
Few discussions within sport are more common or controversial than the debate to pay college athletes. Some arguments are well thought and articulated, while others lack insight and are simply driven by passion. The purpose of this article is to provide the reader with a new perspective and some historical insight – all supported by the literature – regardless of their stance on this issue. Moreover, readers who may actually be heard by the NCAA may offer a position that has yet to be considered. The concession here is that despite any decision by the NCAA in the near future, we can be assured that college administrators, coaches, and athletes will continue this debate. However, their arguments may now be seen as relevant and more reasoned.
POSTSCRIPT: According to Michelle B. Hosick at the NCAA.org, the NCAA board of directors has moved on two issues discussed in this article since its submission. In April (2012), the board moved to implement a $2,000 allowance to an athlete’s full scholarship. They also voted to grant multi-year scholarships. However, both measures have been put on hold with the threat of an override vote by member institutions. On January 14, 2012 at the NCAA convention the board delayed implementation of the $2,000 supplement and sent it back to committee for revision at its April meeting. The multi-year scholarship issue will continue to be implemented on a conference-by-conference basis. And so the pay-for-play discussion continues.
- Adler, P. A., & Adler, P. (1999). College athletes in high-profile media sports: The consequences of glory. In Inside sports (pp. 162–70), edited by J. Coakley and P. Donnelly. London: Routledge.
- Bennett, B. (May 19, 2011). Big Ten considers pay research proposal . ESPN College Football. Retrieved from http://sports.espn.go.com/ncf/news/story?id=6564134.
- Benson, K. F. (2000) Constructing academic inadequacy: African American athletes’ stories of schooling. Journal of Higher Education, 71, 223- 46.
- Berkowitz, S., & Gardiner, A. (2011, May 17). Coach K made $4.7M in 2009. USA Today, 2C.
- Bronson, A. G. (1958). Clark W. Hetherington-Scientist and philosopher. Salt Lake City: University of Utah Press.
- Brown, R. W., & Jewell, T. R. (2006). The marginal revenue product of a women’s college basketball player. Industrial Relations, 45 (1), 96-101.
- Cheesman-Day, J., & Newberger, E. (2002). The big pay-off educational attainment and synthetic estimates of work-life earnings. Retrieved from www.census.gov/prod/2002pubs.
- Coakley, J. (2007). Sports in society: Issues and controversies. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill.
- Crowley, W. H. (1999). Athletics in American colleges. Journal of Higher Education, 70, 494-502.
- Cozzillio, M. J. (1989). The athletic scholarship and the college national letter of intent: A contract by any other name. Wayne Law Review, 35, 1275-1379.
- Eaton-Robb, P. (2011, May 20). UConn loses 2 men’s basketball scholarships. Norwich Bulletin. Retrieved from http://www.norwichbulletin.com/newsnow/x31866796/UConn-mens-hoops-loses-2-scholarships#axzz1NCVV1385.
- Eitzen, S. D. (2000, September). Slaves of big-time college sports: College athletes. USA Today (Society for the Advancement of Education), 125.
- Edwards, H. (1984). The black dumb jock: An American sports tragedy. College Board Review, 131, 8-13.
- Emmert, M. (2011). How it all adds up. NCAA Champion Magazine, 4 (2), 5.
- Fleisher, A. A., Goff, G. L., & Tollison, R. D. (1992). The National Collegiate Athletic Association: A study in cartel behavior. Chicago, IL: University Of Chicago Press.
- Kahn, L. M. (2007). Markets: Cartel behavior and amateurism in college sports. Journal of Economic Perspectives, 21, 209-226.
- Kornheiser, T. (1999, December 13). Six billion? Where’s mine? ESPN The Magazine, 46.
- Lapchick, R. (1989). Pass to play: student athletes and academics. National Education Association of the United States.
- Madesen, R. (2001). The role of the NCAA and the need for reform in big-time college sports. Academic Exchange – EXTRA. Retrieved from http:/www.unco.edu/AE-Extra/2001/3/NCAA.html.
- National Collegiate Athletic Association (2011). Why student-athletes are not paid to play. Retrieved from www.ncaa.org.
- National Collegiate Athletic Association (2010). 2009-10 guide for college bound student athlete: Where academics and athletic success is your goal. Indianapolis, IN: NCAA.
- Olterddorf, C. (1999). But what is the NCAA? What is the real purpose? And is it achieving it? Texas Alcalde, 28, 3-5.
- Parent, C. M. (2004, spring). Forward progress? An analysis of whether student-athletes should be paid? Virginia Sports & Entertainment Law Journal, 226-244.
- Rosner, S., & Shropshire, K. (2004). The business of sports. (pp.527-531). Ontario, Canada: Jones and Bartlett.
- Slack, A. (1991).The underground economy of college football. Sociology of Sport Journal, 8 (1), 1-15.
- Stewart, J., & Albanese, R. (2011, June 2). The Daily Show with Jon Stewart. [Television broadcast] New York: The Comedy Channel (MTV Networks Entertainment Group).
- Woods, R. B. (2007). Social issues in sport. Champaign, IL: Human Kinetics.
- Yost, M. (2008, March 19). A cultural conversation with Nathan Tublitz: Has serious academic reform of college athletics arrived? The Wall Street Journal, D10.
- U.S. Department of Education, National Center for Education Statistics. (2010). Digest of education statistics, 2009 (NCES 2010-013).
- Zimbalist, A. (1999). Unpaid professionals: Commercialism and conflict in big-time college sports. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.

Share this:
Share this article, choose your platform.
What are your chances of acceptance?
Calculate for all schools, your chance of acceptance.
Your chancing factors
Extracurriculars.
Should College Athletes Be Paid? Pros and Cons
Do you know how to improve your profile for college applications.
See how your profile ranks among thousands of other students using CollegeVine. Calculate your chances at your dream schools and learn what areas you need to improve right now — it only takes 3 minutes and it's 100% free.
Show me what areas I need to improve
What’s Covered:
History of the debate: should college athletes be paid, why college athletes should be paid.
- Why College Athletes Shouldn’t Be Paid
- Where To Get Your Essay Edited For Free
College athletics provide big benefits for many schools: they increase their profile, generate millions of dollars in revenue, and have led to one of the most contentious questions in sports— should college athletes be paid? Like other difficult questions, there are good arguments on both sides of the issue of paying college athletes.
Historically, the debates over paying college athletes have only led to more questions, which is why it’s raged on for more than a century. Perhaps the earliest group to examine the quandary was Andrew Carnegie’s Foundation for the Advancement of Teaching, which produced a mammoth study in 1929 of amateur athletes and the profits they generate for their universities. You don’t have to get past the preface to find questions that feel at home in today’s world:
- “What relation has this astonishing athletic display to the work of an intelligence agency like a university?”
- “How do students, devoted to study, find either the time or the money to stage so costly a performance?”
Many of the questions asked way back in 1929 continue to resurface today, and many of them have eventually ended up seeking answers in court. The first case of note came in the 1950s, when the widow of Fort Lewis football player Ray Dennison took the college all the way to the Colorado Supreme Court in an effort to collect a death benefit after he was killed playing football. She lost the case, but future generations would have more success and have slowly whittled away at arguments against paying athletes.
The most noticeable victory for athletes occurred in 2019, when California Governor, Gavin Newsom, signed legislation effectively allowing college athletes in the state to earn compensation for the use of their likeness, sign endorsement deals, and hire agents to represent them.
The court fights between college athletes and the NCAA continue today—while not exactly about payment, a case regarding whether or not schools can offer athletes tens of thousands of dollars in education benefits such as computers, graduate scholarships, tutoring, study abroad, and internships was heard by the U.S. Supreme Court in March 2021. A decision is expected in June 2021.
There are a number of great reasons to pay college athletes, many of which will not only improve the lives of student-athletes, but also improve the product on the field and in the arena.
College Athletes Deserve to Get Paid
In 2019, the NCAA reported $18.9 billion in total athletics revenue. This money is used to finance a variety of paid positions that support athletics at colleges and universities, including administrators, directors, coaches, and staff, along with other employment less directly tied to sports, such as those in marketing and media. The only people not receiving a paycheck are the stars of the show: the athletes.
A testament to the disparate allocation of funds generated by college sports, of the $18.9 billion in athletics revenue in 2019, $3.6 billion went toward financial aid for student-athletes, and $3.7 billion was used for coaches’ compensation. A February 2020 USA Today article found that the average total pay for Football Bowl Subdivision (FBS) college football head coaches in 2020-21 was $2.7 million. The highest-paid college football coach—the University of Alabama’s Nick Saban—earns $9.3 million a year and is the highest-paid public employee in the country. He is not alone, college coaches dominate the list of public employees with the largest salaries.
If there’s money to provide college coaches with lavish seven-figure salaries (especially at public institutions), why shouldn’t there be funds to pay college athletes?
Vital Support for Athletes
A 2011 study published by the National College Players Association (NCPA) found that an overwhelming number of students on full athletics scholarships live below the federal poverty line—85% of athletes who live on campus and 86% athletes who live off-campus. “Full scholarship” itself is a misnomer; the same study found that the average annual scholarship for FBS athletes on “full” scholarships was actually $3,222. Find out more information about athletic scholarships .
Paying student-athletes would help eliminate the need for these student-athletes to take out loans, burden their families for monetary support, or add employment to their already busy schedules. The NCAA limits in-season practice time to 20 hours a week, but a 2008 NCAA report shows that in-season student-athletes commonly spent upward of 30 and 40 hours a week engaged in “athletic activities.”
Encouraged to Stay in College Longer
A report produced by the NCPA and Drexel University estimated the average annual fair market value of big-time college football and men’s basketball players between 2011 and 2015 was $137,357 and $289,031, respectively, and concluded that football players only receive about 17% of their fair market value, while men’s basketball players receive approximately 8% of theirs.
If colleges paid athletes even close to their worth, they would provide an incentive for the athletes to stay in college and earn degrees, rather than leaving college for a paycheck. This would also help keep top talents playing for college teams, improve the level of competition, and potentially lead to even higher revenue. On a side note, this would incentivize athletes to complete their degree, making them more employable after the end of their athletic career.
Limit Corruption
Just because there are rules prohibiting the compensation of college athletes doesn’t mean it doesn’t happen, and over the years there have been numerous scandals. For example, in 2009, six ex-University of Toledo players were indicted in a point-shaving scheme , and in 2010, Reggie Bush returned his Heisman Trophy after allegations that he was given hundreds of thousands of dollars from sports agents while he played for USC.
Paying college athletes will likely not totally eliminate corruption from college sports, but putting athletes in a less-precarious financial position would be a good step toward avoiding external influence, especially when you consider some of the players involved in the University of Toledo point-shaving scandal were paid as little as $500.
It’s a Job (and a Dangerous One)
As mentioned before, college athletes can put in upward of 40 hours a week practicing, training, and competing—being a “student-athlete” is a challenge when you’re devoting full-time hours to athletics. A New York Times study found a 0.20-point difference in average GPA between recruited male athletes and non-athletes. The difference is less pronounced among females, with non-athletes averaging a 3.24 GPA and recruited women athletes at 3.18.
It’s not just the time commitment that playing college athletics puts on student-athletes, it’s the risk to their health. A 2009-2010 CDC report found that more than 210,000 injuries are sustained by NCAA student-athletes each year. Full athletic scholarships are only guaranteed a year at a time, meaning student-athletes are one catastrophic injury away from potentially losing their scholarship. That is to say nothing of the lasting effects of an injury, like head traumas , which made up 7.4% of all injuries in college football players between 2004 and 2009.

Discover your chances at hundreds of schools
Our free chancing engine takes into account your history, background, test scores, and extracurricular activities to show you your real chances of admission—and how to improve them.
Why College Athletes Should Not Be Paid
There are a lot of great reasons why college athletes should be paid, but there are also some compelling reasons why college athletes should not be paid—and why not paying athletes is actually good for both the institutions and athletes.
Compensation Conundrum
One of the most common reasons cited against paying college players is compensation. Will all college athletes get compensated equally? For example, will the star quarterback receive the same amount as the backup catcher on the softball team? A 2014 CNBC article estimated that Andrew Wiggins, a University of Kansas forward (and soon-to-be first-overall draft pick), had a fair market value of around $1.6 million.
Similarly, will compensation take into account talent? Will the All-American point guard get the same amount as the captain of the swim team? In all likelihood, paying college athletes will benefit big-time, revenue-generating sports and hurt less popular sports.
Eliminate Competitive Balance
According to the NCAA , in 2019, the 65 Power Five schools exceeded revenue by $7 million, while all other Division I colleges had a $23 million deficit between expenses and revenue. If college athletes were to get paid, then large, well-funded schools such as those of the Power Five would be best positioned to acquire top talent and gain a competitive advantage.
From a student’s point of view, paying college athletes will alter their college experience. No longer would fit, college, university reputation, and values factor into their college decisions—rather, choices would be made simply based on who was offering the most money.
Professionalism vs. the Classroom
There’s a feeling that paying college athletes sends the wrong message and incentivizes them to focus on athletics instead of academics, when the reality is that very few college athletes will go on to play sports professionally. Just 1.6% of college football players will take an NFL field. NCAA men’s basketball players have even slimmer odds of playing in a major professional league ( 1.2% ), while the chances of a professional career are particularly grim for women basketball players, at a mere 0.8% .
Although the odds of a college athlete turning pro are low, the probability of them earning a degree is high, thanks in part to the academic support athletes are given. According to data released by the NCAA, 90% of Division I athletes enrolled in 2013 earned a degree within six years.
It Will End Less-Popular, Unprofitable Sports
If colleges and universities pay their athletes, there is a fear that resources will only go to popular, revenue-generating sports. Programs like football and men’s basketball would likely benefit greatly, but smaller, unprofitable sports such as gymnastics, swimming and diving, tennis, track and field, volleyball, and wrestling could find themselves at best cash-strapped and, at the worst, cut altogether.
It’s just not less-popular sports that paying athletes could threaten—women’s programs could also find themselves in the crosshairs of budget-conscious administrators. Keep in mind, it was just in March 2021 that the NCAA made national news for its unequal treatment of the men’s and women’s NCAA basketball tournaments.
Financial Irresponsibility
Former ESPN, and current FOX Sports, personality Colin Cowherd made news in 2014 when he voiced a popular argument against paying college athletes: financial irresponsibility. In Cowherd’s words:
“I don’t think paying all college athletes is great… Not every college is loaded, and most 19-year-olds [are] gonna spend it—and let’s be honest, they’re gonna spend it on weed and kicks! And spare me the ‘they’re being extorted’ thing. Listen, 90 percent of these college guys are gonna spend it on tats, weed, kicks, Xboxes, beer and swag. They are, get over it!”
A look at the professional ranks bolsters Cowherd’s argument about athletes’ frivolous spending. According to CNBC , 60% of NBA players go broke within five years of departing the league and 78% of former NFL players experience financial distress two years after retirement.
Writing an Essay on This? Where to Get Your Essay Edited for Free
Writing an essay on whether college athletes should or shouldn’t be paid? CollegeVine can help! Our peer review tool allows you to receive feedback and learn the strengths and weaknesses of your essay for free.
Looking for more debate, speech, or essay topics? Check out these other CollegeVine articles for ideas:
- 52 Argumentative Essays Ideas that are Actually Interesting
- 52 Persuasive Speech Topics That Are Actually Engaging
- 60 Debate Topics for High Schoolers

Related CollegeVine Blog Posts
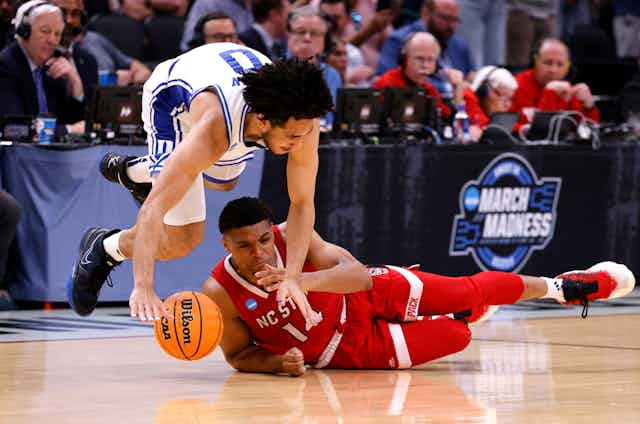


College athletes still are not allowed to be paid by universities − here’s why
Instructional Associate Professor, Sport Management, University of Florida
Disclosure statement
Cyntrice Thomas does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organisation that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.
University of Florida provides funding as a founding partner of The Conversation US.
View all partners
Ever since July 1, 2021, student-athletes have been able to pursue endorsement deals . But when it comes to getting paid by the universities for which they play, the students have been shut down. Here, Cyntrice Thomas, a professor of sport management at the University of Florida, answers questions about the hurdles that stand in the way of college athletes being compensated for their athleticism.
What stands in the way of paying college sports players?
NCAA rules are the main obstacle.
Not long after it was formed in 1906 , the NCAA prohibited schools from compensating student-athletes for their athletic ability. In 1948, the NCAA adopted the Sanity Code , which also prohibited athletic scholarships for students who couldn’t demonstrate financial need or economic hardship.
The organization began to allow athletic scholarships in 1956 without regard to financial need. But that was limited to tuition, room and board, and books.
Over time the NCAA has made more allowances, such as funding for medical insurance and by creating the Student Assistance Fund. The fund is meant to “ cover unforeseen expenses ” related to attending college .
Are the rules being challenged?
In 2009, Ed O'Bannon , a former UCLA basketball player, sued the NCAA over its rules that limited the amount in scholarships that schools could offer as well as the compensation for student-athletes with regard to the use of their image in video games. O'Bannon was successful in showing that the NCAA’s rules were unlawful, and the court allowed for schools to offer scholarships up to the cost of attendance .
Most recently, in 2021, the Supreme Court ruled in NCAA v. Alston that colleges must be allowed to compensate students for education-related expenses up to $5,980 annually. The Supreme Court found that the NCAA rules against this were a violation of antitrust law. The purpose of antitrust law is to protect and promote competition in the marketplace to keep prices competitive for consumers.
NCAA rules negatively affected competition because schools could offer only up to the cost of attendance in scholarships – not additional incentives that may attract student-athletes.
Currently, several lawsuits – including Johnson v. NCAA , Carter v. NCAA and House v. NCAA – have plaintiffs using different legal arguments to challenge NCAA rules that limit their access to compensation. In Carter v. NCAA, the plaintiffs claim the limitations on compensation are unlawful and that they are entitled to a share of the million-dollar television contracts of the conferences and NCAA.
Why are ‘name, image and likeness’ deals not enough?
States have passed laws that require student-athletes to be compensated by third parties for the use of their name, image and likeness . These laws directly contradict past NCAA rules that made this type of compensation an explicit NCAA violation because they threaten the notion of amateurism.
However, these laws do not apply to schools and universities. The laws apply only to third parties such as corporations like Gatorade or sport manufacturers like Nike, and that’s where these laws arguably fall short. Schools can continue to make millions of dollars from intercollegiate athletics without having to share that with student-athletes.
Schools and universities, however, can continue to use student-athletes’ names and images to promote their sports and do not have to compensate them. This is because NCAA rules prohibit schools from compensating student-athletes for their publicity or fame related to athletic ability.
Barbara Osborne , a sports scholar at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, argues that through scholarships, student-athletes do receive compensation. However, when recognizing that Division I schools, especially those in a Power Five conference, generate billions of dollars in revenue , other scholars, such as Mark Nagel and Richard Southall , argue that a scholarship is insufficient and that “profit-athletes,” as he refers to them, deserve the fair market value of their labor.
Instead of paying their athletes, schools pour the revenue they make back into the athletic departments and use it to fund salaries, operating costs, facilities and other expenses. This can include funding other sports that do not generate revenue.
Who has the power to change things?
The NCAA, for one. However, the NCAA sees change as the end of amateurism . In fact, at its most recent convention in January, the organization restated its hopes of regaining some of its power to regulate intercollegiate athletics . Specifically, it plans to do this by seeking legal protection from the continuous threat of lawsuits. The organization is also lobbying Congress to declare that student-athletes are not employees .
Another possibility is for schools and universities, specifically those in the Power Five conferences, to simply leave the NCAA . They could then create their own governing body with rules that allow for schools to pay student-athletes, which would allow them to get the best recruits and make more money.
A third possibility is the federal government. Because of the number of legal challenges to the NCAA rules brought by current and former student-athletes, the NCAA has tried to lobby Congress. The organization spent over $750,000 lobbying Congress to create limitations on athlete pay . They also sought to get Congress to pass laws that limit name, image and likeness deals and give the organization an exemption from antitrust laws .
There is reluctance from members of Congress , however, to support an exemption for the NCAA. Some congressional members have actually advocated for more protections for student-athletes. For example, several senators have been working on a bipartisan bill that would include protections for student-athletes with regard to medical care and agent certification.
- Higher education
- Advertising
- Compensation
- Broadcasting
- US higher education
- National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA)
- College athletics
- college football
- College basketball
- Higher ed attainment
- Broadcast TV

Project Officer, Student Volunteer Program

Audience Development Coordinator (fixed-term maternity cover)

Lecturer (Hindi-Urdu)

Director, Defence and Security

Opportunities with the new CIEHF

Should College Athletes Be Paid? Essay Examples & Guide
- 👍 Advantages
- 👎 Disadvantages
- 💡 Essay Topics
- 📑 Outlining Your Paper
- 💸 Essay Example #1
- 🙅 Essay Example #2
🔗 References
There are a lot of benefits of doing sports in college, for everyone except the athletes themselves. Surely, your sports achievements can get you recognition and respect. But the issue here is not being paid at all.
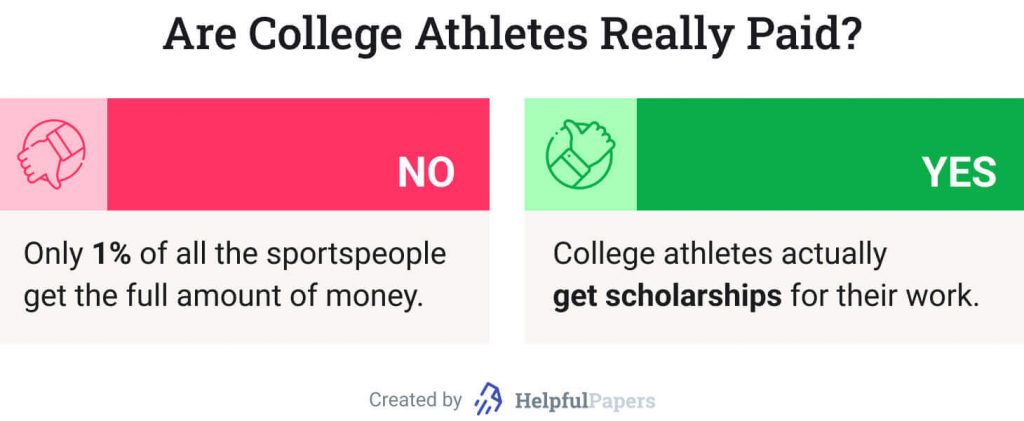
You see, sport is arduous labor. And any labor, according to common sense, must be rewarded with a salary. On the other hand, doing sports for the sake of sports can also be justified. There is no clear answer for “Should college athletes be paid?”. Writing an essay, though, can help you find it.
⚖️ Should College Athletes Be Paid: Pros and Cons
This matter is very recent. Therefore, there is a lot of space for discussion here. Some may say that athletes are paid. They actually get scholarships for their work.
Others may argue that only 1% of all the sportspeople get the full amount of money. Both statements are true, and the correct answer doesn’t really exist. To help you form your own opinion on the topic, here are some pros and cons:
- It would be fair to pay sportspeople for their hard work.
- The sport takes a lot of time from studies, and it must be compensated.
- The health risk is very high, and the reward for it is a must.
- The sport would become an excellent alternative for a work-study job.
- Many athletes’ families require monetary support, which athlete payments can give.
- A lot more people would be attracted to doing sports.
- The athletes already enjoy enough compensations.
- The amount of actual future sports pros is depressing.
- It can undermine the overall studying experience.
- Most of the sports programs cannot afford salaries.
- It would create room for inequity.
- Mixing studying and sports would become even more difficult due to increased demand.
- The concept of playing for the love of sports would cease to exist.
We will look into them deeper in the next section.
👍 Paying College Athletes: Advantages
- It is simply fair to pay athletes for their endeavors. A single sportsperson can generate millions of dollars for their college. It would be only fair if the stars themselves got at least some of this money.
- It is a great way to compensate for taking away from studies. Sport is a time-consuming activity. And time is a valuable thing when you are a student. Let’s not forget that college athletes also need time to study. Or at least compensation for the time they put into the sport.
- The money would at least partially make up for possible injuries. While health is priceless, risking it must be rewarded properly. And that’s exactly what college athletes do. They put their well-being on the line for their universities. Unfortunately, universities don’t seem to give the favor back.
- It would be a great way to substitute work. An average athlete puts 40 hours a week into doing sports for his college. You can easily compare this amount of time to a generic work-study job. The only difference is the latter brings you money, and the former does not.
- It’s a great way to motivate athletes to continue their sports careers. After graduation, the majority of college athletes will stop playing for their team. They are far more likely to simply find a job and get a steady income. Paying them would make a choice between sports and career not that obvious.
- It would support a lot of students’ families. While college sportspeople bath in success, their families often suffer financially. Sustaining a starting athlete can be really costly at times. That’s where a salary would be a saving grace for struggling families.
- It is a great motivation for more students to pursue a sports career. The possibility of making money will attract more people into playing for a sports team. And that brings a better chance to find young talent.
👎 Paying College Athletes: Disadvantages
- The athletes already have their compensations. The coach’s advice, the medical treatment, the strength training. All of these cost money. But the athletes don’t have to pay a single cent for these and many other services. They are provided for free as compensation already.
- Not a lot of athletes will actually become professionals. Out of all college athletes, a mere 2% go pro as a result. Most of them see doing sports as a way to receive education and nothing more.
- It can harm other colleges’ programs. Since the salary would come from the college budget, there would be inevitable cutbacks. As a result, every student in the institution suffers.
- There are not many sports that make a profit. More often than not, sport doesn’t bring a lot of money. Exceptions are basketball and football. Should football players make more money than, for example, swimmers? Here’s where the next issue occurs.
- Possible inequity. You see, if some students participate in a sport that has no profit, then why pay them? As a result of such logic, whole college teams will cease to exist.
- Possible study problems. With the appearance of salaries, the expectations from the players will rise. Attending training sessions and games will become a definite must. No skips would be allowed. In this case, ping-ponging your priorities from sports to studies is much more difficult.
- The love for the game would go away. College students play sports mostly because they want to do what they love. Paying them might destroy the compassion for doing sport. The amateur leagues will be filled with players who are in it for the money and nothing else.
💡 Should College Athletes Be Paid Essay Topics
- Balancing college sports and academic mission .
- Payments to collegiate athletes .
- Top college athletes are worth six figures.
- Title IX in the female sports development .
- Kids and sports: Lack of professional sports guides .
- College athletes do not deserve the degrees they’re studying for.
- Steroid abuse in the world of sports .
- Shortage of officials at the high school sports level .
- College sports should be made professional.
- Steroid use effects on professional young athletes .
- Is it justified for college athletes to be paid ?
- College sports should not require missing classes.
- Professional athletes allowed to use steroids.
- Paying college athletes: Reinforcing privilege or promoting growth ?
- If colleges pay college athletes, it would increase the disparity between small and bigger college teams.
- School athletes and drug tests.
- Arguments for adequate remuneration for college athletes .
- The NCAA definition of college athletes as amateurs is outdated.
- Sports-related problems and conflicts.
- African American studies. Negro baseball league.
- The moral side: “A gentlemen never competes for money” (Walter Camp).
- Running injuries, workout and controversies.
- Should college athletes be paid ?
- Ed O’Bannon’s lawsuit: Using athletes’ images in video games.
- Does youth sports play a part in character formation?
- Children participation in sports .
- Where does college sports money go?
- Sports analysis: steroids and HGH in sports.
- Steroid usage in professional sports.
- College athletes work as marketers for their college, as their success in sports improves admission rates.
- Physical activity and sports team participation.
- Using performance-enhancing drugs and in the world of sport .
- Research handbook of employment relations in sport .
- Successfully luring college athletes .
- College athletes should be paid .
Haven’t found anything inspiring in the list above? Try using our topic-generating tool !
📑 Should College Athletes Be Paid Essay Outline
Before writing your work, the first thing you want to do is outline. An argumentative-style essay would be perfect for writing on our topic.
We will go with a generic 5-paragraph format :
- Hook. A flashy sentence or two to evoke interest in your work. A joke or a shocking fact, for example.
- Background information. General info that the reader needs to know before going deeper into the essay.
- Thesis statement. It is a sentence that reflects the main idea of the further text. It leaves room for debate and briefly showcases the arguments you will discuss further.
- Body. The body is the biggest part of your work. In our case, it will be three paragraphs long. Each paragraph names and explains the argument you want to make.
- Conclusion. The end of your essay. Nothing new should be added. Just restate your thesis, summarize the points you made in the body, and be done with it.
💸 Why College Athletes Should Be Paid Essay Example
In 2017 National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) made over $1.04 billion in revenue. None of the college athletes have seen any part of this sum. A survey made the same year showed 60% of the sportspeople to be satisfied with the scholarship-only payments. The situation, however, has drastically changed over the years. The same 60% now agree that college athletes need monetary compensation. While college athletes' payments are a controversial topic, their hard work and health must be fairly compensated no matter what, and a salary seems to be the best way for it.
It is no surprise that doing sports consumes a solid number of things. Time is one of them. An average college student puts in their sports activities 35 hours a week. It can be compared to having a generic work-study job. The only difference is the job brings you money as any hard labor should. However, in the case of college sport, it seems to profit anyone but the athletes themselves. While the NCAA executives make six-figure salaries, the players, the actual stars of the competition, have the status of the unpaid workforce.
Another thing consumed by sports activities is health. In 2017 over 60% of all Division I players were reported to suffer a major injury. Although, this phenomenal danger to athletes' well-being seems to go unnoticed as well. The only "compensation" provided to people who risk their soundness for the sake of university is education itself. Usually, the health risk is considered a reason for a salary raise. Unfortunately, in our case, there is nothing to give a raise to.
Putting yourself to the fullest in any activity must be rewarded. And the sportspeople truly give it their best. Time, passion, health, everything is given. And for now, everything they give is given for nothing.
🙅 College Athletes Should Not Be Paid Essay Example
There are hundreds of sports college athletes do. Only two of them bring the college profit. The issue of paying the students involved with the college sports activities has been around for a while. Some are satisfied with their scholarship and the possibility to get an education. Others, however, demand more tangible rewards for their achievements. While payments may seem justified, the fact that the athletes already receive enough compensation for their work via scholarship and education is often overlooked.
National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) reports more than $3.6 billion in athletic scholarships to be provided annually to more than 180,000 student-athletes. A simple calculation shows $20.000 a year for each athlete. This sum is more than enough to cover the average cost of an academic year of $17,797.
Furthermore, most college athletic programs make barely enough money to sustain themselves, not to mention paying salaries. The only two kinds of sport that make enough profit to afford salaries are football and basketball. Others, sadly, do not. And this fact creates a significant equity problem. Do we pay all players equally? And if not, who do we pay more? All these questions remain unanswered.
While it seems just, creating salaries brings more problems than solves. The extent of the compensation necessary is, of course, negotiable. But all efforts made by college athletes are compensated in some way. That is a fact.
We hope that this info helped you with your assignment. Make sure to let us know what part you’ve found the most useful in the comments. And also, check out our title page maker . And good luck with your studies!
- 16 college athletes already getting paid under new NCAA rule
- Should College Athletes Be Paid? | BestColleges
- Should College Athletes Be Paid? Reasons Why or Why Not
- All college athletes in California can now get paid – KTVU
- Pay for Play: Should College Athletes Be Compensated?
Research Paper Analysis: How to Analyze a Research Article + Example
Film analysis: example, format, and outline + topics & prompts.
Home — Essay Samples — Life — Paying College Athletes — Paying College Athletes: Arguments for Fair Compensation
Paying College Athletes: Arguments for Fair Compensation
- Categories: College Tuition Paying College Athletes Student Athletes
About this sample

Words: 772 |
Published: Mar 18, 2021
Words: 772 | Pages: 2 | 4 min read

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Prof. Kifaru
Verified writer
- Expert in: Education Life

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
5 pages / 2125 words
2 pages / 711 words
3 pages / 1316 words
1 pages / 507 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Paying College Athletes
The question of whether coaches and players should receive equal compensation in the realm of professional sports is a topic that has sparked intense debate. The Should Coaches and Players Make the Same Amount of Money Essay [...]
In the past five to ten years, there has been a controversial question going around: should students who play a sport get paid as a reward of being a College Athlete? The answer is no. Student athletes should not get paid [...]
Should college athletes be paid? This essay argues that student athletes at universities around the country should not only obtain a percentage of income made off their athletic performance but also pursue business deals and [...]
The discussion whether the college athletes should be paid has been re-hashed several times. There are those who advocates in favor and many against the idea of paying athlete who plays sports for their colleges. Many reasons [...]
Imagine dedicating 20 hours a week to playing a sport in college while having to balance your schedule with school work with no financial gain. In high school, I played three sports and often found myself struggling to excel in [...]
On common on average only 1/3 of college athletes are given a scholarship and a majority are half as much as a full scholarships as stated by the National Collegiate Athletic Association. From that 1/3 about two percent make it [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
Persuasive Essay on College Athletes Should Be Paid
Student-athletes sacrifice a lot of time and effort to be where they are. During the week, these athletes will participate in very challenging practices and games while also having to perform well in school. All the responsibilities of a student-athlete, in addition to maintaining a life outside of school, is a full-time task. In division-one schools the big question is, do these athletes deserve to be paid?
College level athletes always have very loaded schedules. Every day, these athletes have a lot of different tasks to complete. Some of these tasks include, workouts, practices, games, homework, social lives, and some even have jobs. The duties of a student-athlete can be overwhelming and saying that they work hard is an understatement. Surely, all this hard work must be paying off for the athletes, right?
Unfortunately for the athletes, they aren’t allowed to be paid for their involvement in any school’s athletic programs. A lot of people have a problem with this because the athletes produce so much revenue for the NCAA, but they get none of it. The NCAA governs intercollegiate athletics, and they make a lot of money doing it. For example, in the 2010-2011 fiscal year, the president of the NCAA, Mark Emmert, said that the projected total revenue for said year was 757 million dollars. Of that amount, 452.2 million dollars was distributed to division-one schools (Johnson).
Because of the restriction on paying student-athletes, some of these players that don’t have very big scholarships may have to try to find jobs, which just adds to their busy week. If the athletes were compensated through their programs, it would eliminate the need for them to get jobs. In turn, they would be able to focus more on their sports and classes. Also, there would be more job openings for the students who have more available schedules than student-athletes. This is especially good news for normal students because majority of them don’t have big scholarships either.
Speaking of scholarships, every year the 30 biggest universities in the country generate over 100 million dollars each. However, most of the universities spend more money than they make, on scholarships and expenses related to their programs. Even though these colleges make so much money, they spend even more. Paying the athletes would mean other, smaller, athletic programs will eventually get cut to keep the programs that generate money alive (Mcdavis).
Sponsorships are another way that players could be paid without the school’s revenue being affected. Star athletes who have their name out there are likely to be known by some of the top sports brands. The issue is that the players aren’t allowed to receive any revenue from their involvement with the school. If a player is caught accepting money from their involvement with the school, they can have their scholarship revoked and even get expelled from the school. So, with sponsorships not being a realistic option, athletes will want to work hard for scholarships instead.
If the payment of athletes was allowed, competition among athletes for scholarships and sponsorships will increase. Increased competition often leads to an increase in the usage of performance enhancing drugs (PEDs). This competition would all be taking place at the high school level in this scenario. Now, you’re looking at high school age athletes taking hormones at a critical point in their life, all for a shot at playing at a division-one school. A dangerous epidemic among teens could develop if we begin paying division-one athletes, but that’s not all.
Still assuming that student-athletes are allowed to be paid, most colleges wouldn’t be able to keep up with the big ones that make hundreds of millions of dollars. Star athletes would go to the big schools because they’ll make the most money there. After a while of this process, super teams would form from the big schools, generating more and more income from viewership and sponsorships. The big universities will just continue recruiting star players because they have the power to do so, and the cycle repeats. Small universities would eventually be drowned out and the big guys will be running the show (Mcdavis).
Enlarging the pool of money available for scholarships to athletes, would decrease the pool of money available for scholarships to normal students. In terms of fairness, that decision does not make sense. Normal students need money just as much as student-athletes, if not worse. If one college offers a bigger scholarship than another, the student will likely go to that school, disregarding other variables.
The NCAA makes a ton of money from fans watching athletics, and so do the universities. However, while players are the main source of the revenue, the expenses to cover all the universities’ programs and scholarships make it unfavorable to pay athletes. Paying division-one athletes would indirectly end up promoting a dangerous amount of competition for young athletes. It would also hurt many other universities, causing them to close an enormous number of athletic programs in the long run. Said universities are likely to lose a chunk of their student body as well. There are more reasons to restrict athletes getting paid than not. It would be unfair, unsafe, and a flat-out bad idea.
Works Cited
Johnson, Dennis A., and John Acquaviva. "Point/counterpoint: paying college athletes." The Sport Journal, vol. 15, no. 1, annual 2012. Gale Academic OneFile, link.gale.com/apps/doc/A322563607/AONE?u=anke52316&sid=oclc&xid=e3899b0c. Accessed 4 Oct. 2021.
Mcdavis, Cody J. “Don't Pay College Athletes.” The New York Times, 26 Feb. 2019, p. A23(L). Gale Academic OneFile, https://link.gale.com/apps/doc/A575860557/AONE?u=anke52316&sid=bookmark-AONE&xid=630b749c. Accessed 4 Oct. 2021.
Related Samples
- Personal Essay Example: Freshman Year Goals
- Narrative Essay Example: My Trip to The Grand Canyon in Arizona
- Personal Essay Sample: Larry Bird is My Hero
- Comparative Essay Sample: My Thanksgiving Traditions and Other People’s Traditions
- Argumentative Essay on The Importance Of Summer Break
- Losing Weight Personal Essay Example
- The Importance Of Financial Literacy
- The Pros And Cons Of Later School Start Times
- The Education System Should Be Changed Argumentative Essay
- Narrative Essay Sample: My Story of Dedication
Didn't find the perfect sample?

You can order a custom paper by our expert writers
Paying College Athletes: Pros and Cons Essay
Human capital can be defined as a collection of knowledge, habits, and personal creativity that are important in performing labor with the goal of producing an economic value. From an economic perspective, human capital is associated with the ability of a state or an organization to improve performance outcomes significantly.
It is important to differentiate human capital from monetary capital, which does not grow for a long period. In fact, even its short-term growth trends are not always linear. Over the years, there has been a debate about whether students participating in college sports activities should be paid. This paper seeks to develop an argument to support the idea of rewarding college athletes with money on a regular basis.
Ross Eisenbrey states that the utilization of the unpaid labor of students on internships has been on the increase over the past ten years. He contends that if an individual works for any firm or person for financial gains, then he or she should be paid for his or her services. This is irrespective of whether individuals are students or graduates. Colbert claims that students who participate in athletic competitions on behalf of their colleges should be paid.
Based on the human capital model, the scope of athletics in colleges represents a positive contribution to human development and well-being. The model has six domains that should be considered before one can decide whether college athletes should be paid.
These are physical capital, emotional capital, individual capital, social capital, intellectual capital, and financial capital. For the purpose of the argument in this paper, financial capital is given a priority. It refers to gains with regard to earning power, productivity, and work attainment.
Some athletes come from low-income families. Thus, they can hardly sustain themselves. When they engage in college sports events, they cannot find time to look for jobs that would provide them with a regular source of income. It is evident that a significant amount of the funds generated from athletics is used to support other games, such as basketball and football. However, if students participating in athletics would be paid by institutions of learning, then they would focus on studying and developing their careers in sports.
In an era where the internet is playing a great role in broadcasting athletics events at colleges, it is no doubt that the institutions of learning are making huge profits, some of which can be used to reward the participating students financially.
Some college students qualify for scholarship grants that cater for expenses, such as travel and food. However, it is important to note that not all expenses are covered by the grants, implying that student athletes would hardly meet the demand of catering for their needs because most of their time is spent in sports exercises and practices.
It is notable that some team members engage in abuses, such as illegally taking cash from boosters. This can be avoided by remunerating them. Athletes may sustain injuries that might negatively impact them in the long-term. Although colleges might cater for their medical bills in the short-term, they might not cater for their health care for a long period. If student athletes would be paid, then they would cater for the long-term expenses in relation to treating injuries.
That notwithstanding, paying the students would lead to high levels of inequality in colleges due to the fact that some would feel that their efforts in other activities are not being appreciated. In addition, paying athletes in colleges is not supported by the law. Thus, a move to pay them could be challenged in a court of law, which could lead to huge financial implications.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2020, March 25). Paying College Athletes: Pros and Cons. https://ivypanda.com/essays/paying-college-athletes-pros-and-cons/
"Paying College Athletes: Pros and Cons." IvyPanda , 25 Mar. 2020, ivypanda.com/essays/paying-college-athletes-pros-and-cons/.
IvyPanda . (2020) 'Paying College Athletes: Pros and Cons'. 25 March.
IvyPanda . 2020. "Paying College Athletes: Pros and Cons." March 25, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/paying-college-athletes-pros-and-cons/.
1. IvyPanda . "Paying College Athletes: Pros and Cons." March 25, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/paying-college-athletes-pros-and-cons/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Paying College Athletes: Pros and Cons." March 25, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/paying-college-athletes-pros-and-cons/.
- College Athletics: Should College Athletes Be Paid?
- Risk Management in Athletics
- Athletic Trainers as Professionals in Inclusion and Diversity in Sport
- The Purpose of College Athletics
- College Athletics for Mental and Physical Health
- Intercollegiate Athletics Commercialization
- Trends in the External Environment That Affect Athletics Paper
- The Merits and Demerits of Paying Student-Athletes for Participating In College Sports
- Sports Demands and Stress Management in Athletics
- College Athletes Have a Right to Be Paid
- Revision of sport issues
- Juwan Howard's Power Play
- Student-Athletes and Socialization
- Coaching Philosophy
- Athletic Administration and Coaching: Statement of the Problem
Why Should College Athletes Be Paid, Essay Sample
One of the most pressing issues in college sports is the debate over whether or not college athletes should be paid. This topic has gained significant attention in recent years, with many arguing that it is only fair for college athletes to receive compensation for their hard work, dedication, and revenue-generating contributions. This free essay sample from Edusson will explore the various reasons why college athletes should be paid and will provide a comprehensive analysis of the issue.
Time Commitment and Workload
College athletes put in a tremendous amount of time and effort into their sport, often at the expense of their studies and personal life. As a student-athlete, I know firsthand the dedication it takes to balance academics and sports. We have rigorous practice schedules, intense training sessions, and games that require travel, leaving little time for anything else. Many athletes have to miss classes or sacrifice study time to attend competitions or travel with their teams. The workload of a college athlete can be overwhelming and can negatively impact their academic performance and mental health. Some may argue that athletes receive scholarships and other benefits, but these do not fully compensate for the amount of time and effort they put into their sport. Paying college athletes would help to alleviate some of the financial burden that many student-athletes face, while also compensating them for their time and workload.
Financial Struggles
As a student, I believe that college athletes should be paid for their hard work and dedication to their sports. One of the main reasons for this is the financial struggles that many college athletes face. These athletes come from low-income families and often struggle to make ends meet while attending college. They are unable to work part-time jobs to earn extra income due to the rigorous demands of their sport. This creates a challenging situation where they are unable to support themselves or their families financially. Paying college athletes would provide much-needed financial support and alleviate some of their financial struggles. This would allow them to focus on their studies and athletics without the added stress of financial instability. It would also give them the opportunity to contribute financially to their families, which many of them are unable to do currently. In short, paying college athletes would help alleviate the financial burdens they face and provide a fair compensation for their hard work and dedication to their sport.
Health and Safety Risks
As college athletes compete at a high level, they put their bodies on the line and are exposed to various health and safety risks. These athletes often play through injuries, which can exacerbate the severity of the injury, resulting in long-term physical damage. Therefore, it’s essential to consider the health and safety risks associated with college sports. Paying college athletes would acknowledge the risks that they take and provide a safety net if they get hurt. Furthermore, college athletes who are injured may not have access to the same level of healthcare as professional athletes. Paying them would help ensure they have the proper medical care and resources to recover from injuries. Moreover, paying college athletes could also incentivize schools to prioritize athlete safety and ensure that their health is a top priority. Overall, providing financial compensation to college athletes for the risks they take and the injuries they sustain is not only fair but also necessary for their wellbeing.
Revenue Generation
One of the main arguments in favor of paying college athletes is that they deserve to be compensated for their role in generating revenue for their universities and the National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA). When fans attend a college sports event or purchase team merchandise, they are supporting the team and the entire athletic program. The athletes who are responsible for the success of these programs, however, do not receive any monetary compensation for their efforts. It is unfair that the NCAA and universities benefit from the work of college athletes without providing them with fair compensation. It is also worth noting that college sports have become a commercial enterprise, with the NCAA and universities treating them as such. Many top college sports programs generate millions of dollars in revenue every year, and the athletes who contribute to this success are essential to the financial health of their respective programs. However, athletes often struggle to make ends meet due to the demands of their sport, and they don’t have the time or resources to work part-time jobs to earn extra income.
Fairness and Equity
As college athletes put in countless hours of hard work and dedication to their respective sports, it’s only fair to compensate them for their efforts. However, one aspect that often goes unnoticed is the lack of rights and privileges that college athletes are subjected to, especially when it comes to earning money from their name, image, and likeness.
It is unfortunate that college athletes are the only ones on campus who are not allowed to monetize their skills and talents. This is in stark contrast to everyone else on campus, including musicians, artists, and actors, who can earn money from their talents while attending college. This discrepancy can cause a sense of injustice among college athletes who are forced to watch others monetize their talents while they are restricted from doing so.
In recent years, the issue of fairness and equity has gained considerable attention, and rightfully so. Paying college athletes would go a long way in promoting fairness and equity among all students. It would ensure that athletes have the same rights and opportunities as other students, allowing them to monetize their skills and talents just like everyone else. Additionally, paying college athletes would help eliminate the economic disparities that exist on campuses, especially among low-income athletes who may not have the financial support they need to sustain themselves.
Furthermore, paying college athletes would promote gender equality. Female athletes have historically been paid less than male athletes, even at the professional level. This inequality also extends to college sports, where female athletes often receive less funding and attention than their male counterparts. By paying college athletes, regardless of gender, colleges and universities would help bridge this gap and promote equality among all athletes.
In this table, we will outline some of the main reasons why college athletes should be paid.
Related posts:
- College Research Paper Example
- Freedom of Speech Argumentative Essay
- Exploring My Motivations for Pursuing a Supervisory Role
- The Importance of Women’s Choice: Exploring the Reasons Why Abortion Should Be Legal Essay
Improve your writing with our guides

Youth Culture Essay Prompt and Discussion

Reasons Why Minimum Wage Should Be Raised Essay: Benefits for Workers, Society, and The Economy

Why Marijuana Should Not Be Legal: Potential Risks and Drawbacks
Get 15% off your first order with edusson.
Connect with a professional writer within minutes by placing your first order. No matter the subject, difficulty, academic level or document type, our writers have the skills to complete it.
100% privacy. No spam ever.

An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Front Sports Act Living

Stress in Academic and Athletic Performance in Collegiate Athletes: A Narrative Review of Sources and Monitoring Strategies
Marcel lopes dos santos.
1 School of Kinesiology, Applied Health and Recreation, Oklahoma State University, Stillwater, OK, United States
Melissa Uftring
Cody a. stahl, robert g. lockie.
2 Department of Kinesiology, California State University, Fullerton, CA, United States
Brent Alvar
3 Department of Kinesiology, Point Loma Nazarene University, San Diego, CA, United States
J. Bryan Mann
4 Department of Kinesiology and Sport Sciences, University of Miami, Miami, FL, United States
J. Jay Dawes
College students are required to manage a variety of stressors related to academic, social, and financial commitments. In addition to the burdens facing most college students, collegiate athletes must devote a substantial amount of time to improving their sporting abilities. The strength and conditioning professional sees the athlete on nearly a daily basis and is able to recognize the changes in performance and behavior an athlete may exhibit as a result of these stressors. As such, the strength and conditioning professional may serve an integral role in the monitoring of these stressors and may be able to alter training programs to improve both performance and wellness. The purpose of this paper is to discuss stressors experienced by collegiate athletes, developing an early detection system through monitoring techniques that identify the detrimental effects of stress, and discuss appropriate stress management strategies for this population.
Introduction
The college years are a period of time when young adults experience a significant amount of change and a variety of novel challenges. Academic performance, social demands, adjusting to life away from home, and financial challenges are just a few of the burdens college students must confront (Humphrey et al., 2000 ; Paule and Gilson, 2010 ; Aquilina, 2013 ). In addition to these stressors, collegiate athletes are required to spend a substantial amount of time participating in activities related to their sport, such as attending practices and training sessions, team meetings, travel, and competitions (Humphrey et al., 2000 ; López de Subijana et al., 2015 ; Davis et al., 2019 ; Hyatt and Kavazis, 2019 ). These commitments, in addition to the normal stress associated with college life, may increase a collegiate-athlete's risk of experiencing both physical and mental issues (Li et al., 2017 ; Moreland et al., 2018 ) that may affect their overall health and wellness. For these reasons, it is essential that coaches understand the types of stressors collegiate athletes face in order to help them manage the potentially deleterious effects stress may have on athletic and academic performance.
Strength and conditioning coaches are allied health care professionals whose primary job is to enhance fitness of individuals for the purpose of improving athletic performance (Massey et al., 2002 , 2004 , 2009 ). As such, many universities and colleges hire strength and conditioning coaches as part of their athletic staff to help athletes maximize their physical potential (Massey et al., 2002 , 2004 , 2009 ). Strength and conditioning coaches strive to increase athletic performance by the systematic application of physical stress to the body via resistance training, and other forms of exercise, to yield a positive adaptation response (Massey et al., 2002 , 2004 , 2009 ). For this reason, they need to understand and to learn how to manage athletes' stress. Additionally, based on the cumulative nature of stress, it is important that both mental and emotional stressors are also considered in programming. It is imperative that strength and conditioning coaches are aware of the multitude of stressors collegiate athletes encounter, in order to incorporate illness and injury risk management education into their training programs (Radcliffe et al., 2015 ; Ivarsson et al., 2017 ).
Based on the large number of contact hours strength and conditioning coaches spend with their athletes, they are in an optimal position to assist athletes with developing effective coping strategies to manage stress. By doing so, strength and conditioning coaches may be able to help reach the overarching goal of improving the health, wellness, fitness, and performance of the athletes they coach. The purpose of this review article is to provide the strength and conditioning professional with a foundational understanding of the types of stressors collegiate athletes may experience, and how these stressors may impact mental health and athletic performance. Suggestions for assisting athletes with developing effective coping strategies to reduce potential physiological and psychological impacts of stress will also be provided.
Stress and the Stress Response
In its most simplistic definition, stress can be described as a state of physical and psychological activation in response to external demands that exceed one's ability to cope and requires a person to adapt or change behavior. As such, both cognitive or environmental events that trigger stress are called stressors (Statler and DuBois, 2016 ). Stressors can be acute or chronic based on the duration of activation. Acute stressors may be defined as a stressful situation that occurs suddenly and results in physiological arousal (e.g., increase in hormonal levels, blood flow, cardiac output, blood sugar levels, pupil and airway dilation, etc.) (Selye, 1976 ). Once the situation is normalized, a cascade of hormonal reactions occurs to help the body return to a resting state (i.e., homeostasis). However, when acute stressors become chronic in nature, they may increase an individual's risk of developing anxiety, depression, or metabolic disorders (Selye, 1976 ). Moreover, the literature has shown that cumulative stress is correlated with an increased susceptibility to illness and injury (Szivak and Kraemer, 2015 ; Mann et al., 2016 ; Hamlin et al., 2019 ). The impact of stress is individualistic and subjective by nature (Williams and Andersen, 1998 ; Ivarsson et al., 2017 ). Additionally, the manner in which athletes respond to a situational or environmental stressor is often determined by their individual perception of the event (Gould and Udry, 1994 ; Williams and Andersen, 1998 ; Ivarsson et al., 2017 ). In this regard, the athlete's perception can either be positive (eustress) or negative (distress). Even though they both cause physiological arousal, eustress also generates positive mental energy whereas distress generates anxiety (Statler and DuBois, 2016 ). Therefore, it is essential that an athlete has the tools and ability to cope with these stressors in order to have the capacity to manage both acute and chronic stress. As such, it is important to understand the types of stressors collegiate athletes are confronted with and how these stressors impact an athlete's performance, both athletically and academically.
Literature Search/Data Collection
The articles included in this review were identified via online databases PubMed, MEDLINE, and ISI Web of Knowledge from October 15th 2019 through January 15th 2020. The search strategy combined the keywords “academic stress,” “athletic stress,” “stress,” “stressor,” “college athletes,” “student athletes,” “collegiate athletes,” “injury,” “training,” “monitoring.” Duplicated articles were then removed. After reading the titles and abstracts, all articles that met the inclusion criteria were considered eligible for inclusion in the review. Subsequently, all eligible articles were read in their entirety and were either included or removed from the present review.
Inclusion Criteria
The studies included met all the following criteria: (i) published in English-language journals; (ii) targeted college athletes; (iii) publication was either an original research paper or a literature review; (iv) allowed the extraction of data for analysis.
Data Analysis
Relevant data regarding participant characteristics (i.e., gender, academic status, sports) and study characteristics were extracted. Articles were analyzed and divided into two separate sections based on their specific topics: Academic Stress and Athletic Stress. Then, strategies for monitoring and workload management are discussed in the final section.
Academic Stress
Fundamentally, collegiate athletes have two major roles they must balance as part of their commitment to a university: being a college student and an athlete. Academic performance is a significant source of stress for most college students (Aquilina, 2013 ; López de Subijana et al., 2015 ; de Brandt et al., 2018 ; Davis et al., 2019 ). This stress may be further compounded among collegiate athletes based on their need to be successful in the classroom, while simultaneously excelling in their respective sport (Aquilina, 2013 ; López de Subijana et al., 2015 ; Huml et al., 2016 ; Hamlin et al., 2019 ). Davis et al. ( 2019 ) conducted surveys on 173 elite junior alpine skiers and reported significant moderate to strong correlations between perceived stress and several variables including depressed mood ( r = 0.591), sleep disturbance ( r = 0.459), fatigue ( r = 0.457), performance demands ( r = 0.523), and goals and development ( r = 0.544). Academic requirements were the highest scoring source of stress of all variables and was most strongly correlated with perceived stress ( r = 0.467). Interestingly, it was not academic rigor that was viewed by the athletes as the largest source of direct stress; rather, the athletes surveyed reported time management as being their biggest challenge related to academic performance (Davis et al., 2019 ). This further corroborates the findings of Hamlin et al. ( 2019 ). The investigators reported that during periods of the academic year in which levels of perceived academic stress were at their highest, students had trouble managing sport practices and studying. These stressors were also associated with a decrease in energy levels and overall sleep quality. These factors may significantly increase the collegiate athlete's susceptibility to illness and injury (Hamlin et al., 2019 ). For this reason, coaches should be aware of and sensitive to the stressors athletes experience as part of the cyclical nature of the academic year and attempt to help athletes find solutions to balancing athletic and academic demands.
According to Aquilina ( 2013 ), collegiate athletes tend to be more committed to sports development and may view their academic career as a contingency plan to their athletic career, rather than a source of personal development. As a result, collegiate athletes often, but certainly not always, prioritize athletic participation over their academic responsibilities (Miller and Kerr, 2002 ; Cosh and Tully, 2014 , 2015 ). Nonetheless, scholarships are usually predicated on both athletic and academic performance. For instance, the National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) requires collegiate athletes to achieve and maintain a certain grade point average (GPA). Furthermore, they are also often required to also uphold a certain GPA to maintain an athletic scholarship. The pressure to maintain both high levels of academic and athletic performance may increase the likelihood of triggering mental health issues (i.e., anxiety and depression) (Li et al., 2017 ; Moreland et al., 2018 ).
Mental health issues are a significant concern among college students. There has been an increased emphasis placed on the mental health of collegiate athletes in recent years (Petrie et al., 2014 ; Li et al., 2017 , 2019 ; Reardon et al., 2019 ). Based on the 2019 National College Health Assessment survey from the American College Health Association (ACHA) consisting of 67,972 participants, 27.8% of college students reported anxiety, and 20.2% reported experiencing depression which negatively affected their academic performance (American College Health Association American College Health Association-National College Health Assessment II, 2019 ). Approximately 65.7% (50.7% males and 71.8% females) reported feeling overwhelming anxiety in the past 12 months, and 45.1% (37.1% males and 47.6% females) reported feeling so depressed that it was difficult for them to function. However, only 24.3% (13% males and 28.4% females) reported being diagnosed and treated by a professional in the past 12 months. Collegiate athletes are not immune to these types of issues. According to information presented by the NCAA, many certified athletic trainers anecdotally state that anxiety is an issue affecting the collegiate-athlete population (NCAA, 2014 ). However, despite the fact that collegiate athletes are exposed to numerous stressors, they are less likely to seek help at a university counseling center than non-athletes (NCAA, 2014 ), which could be related to stigmas that surround mental health services (NCAA, 2014 ; Kaier et al., 2015 ; Egan, 2019 ). This not only has significant implications related to their psychological well-being, but also their physiological health, and consequently their performance. For instance, in a study by Li et al. ( 2017 ) it was found that NCAA Division I athletes who reported preseason anxiety symptoms had a 2.3 times greater injury incidence rate compared to athletes who did not report. This same study discovered that male athletes who reported preseason anxiety and depression had a 2.1 times greater injury incidence, compared to male athletes who did not report symptoms of anxiety and depression. (Lavallée and Flint, 1996 ) also reported a correlation between anxiety and both injury frequency and severity among college football players ( r = 0.43 and r = 0.44, respectively). In their study, athletes reporting high tension/anxiety had a higher rate of injury. It has been suggested that the occurrence of stress and anxiety may cause physiological responses, such as an increase in muscle tension, physical fatigue, and a decrease in neurocognitive and perception processes that can lead to physical injuries (Ivarsson et al., 2017 ). For this reason, it is reasonable to consider that academic stressors may potentiate effects of stress and result in injury and illness in collegiate athletes.
Periods of more intense academic stress increase the susceptibility to illness or injury (Mann et al., 2016 ; Hamlin et al., 2019 ; Li et al., 2019 ). For example, Hamlin et al. ( 2019 ) investigated levels of perceived stress, training loads, injury, and illness incidence in 182 collegiate athletes for the period of one academic year. The highest levels of stress and incidence of illness arise during the examination weeks occurring within the competitive season. In addition, the authors also reported the odds ratio, which is the occurrence of the outcome of interest (i.e., injury), based off the given exposure to the variables of interest (i.e., perceived mood, sleep duration, increased academic stress, and energy levels). Based on a logistic regression, they found that each of the four variables (i.e., mood, energy, sleep duration, and academic stress) was related to the collegiate athletes' likelihood to incur injuries. In summary, decreased levels of perceived mood (odds ratio of 0.89, 0.85–0.0.94 CI) and sleep duration (odds ratio of 0.94, 0.91–0.97 CI), and increased academic stress (odds ratio of 0.91, 0.88–0.94 CI) and energy levels (odds ratio of 1.07, 1.01–1.14 CI), were able to predict injury in these athletes. This corroborates Mann et al. ( 2016 ) who found NCAA Division I football athletes at a Bowl Championship Subdivision university were more likely to become ill or injured during an academically stressful period (i.e., midterm exams or other common test weeks) than during a non-testing week (odds ratio of 1.78 for high academic stress). The athletes were also less likely to get injured during training camp (odds ratio of 3.65 for training camp). Freshmen collegiate athletes may be especially more susceptible to mental health issues than older students. Their transition includes not only the academic environment with its requirements and expectations, but also the adaptation to working with a new coach and teammates. In this regard, Yang et al. ( 2007 ) found an increase in the likelihood of depression that freshmen athletes experienced, as these freshmen were 3.27 times more likely to experience depression than their older teammates. While some stressors are recurrent and inherent in academic life (e.g., attending classes, homework, etc.), others are more situational (e.g., exams, midterms, projects) and may be anticipated by the strength and conditioning coach.
Athletic Stress
The domain of athletics can expose collegiate athletes to additional stressors that are specific to their cohort (e.g., sport-specific, team vs. individual sport) (Aquilina, 2013 ). Time spent training (e.g., physical conditioning and sports practice), competition schedules (e.g., travel time, missing class), dealing with injuries (e.g., physical therapy/rehabilitation, etc.), sport-specific social support (e.g., teammates, coaches) and playing status (e.g., starting, non-starter, being benched, etc.) are just a few of the additional challenges collegiate athletes must confront relative to their dual role of being a student and an athlete (Maloney and McCormick, 1993 ; Scott et al., 2008 ; Etzel, 2009 ; Fogaca, 2019 ). Collegiate athletes who view the demands of stressors from academics and sports as a positive challenge (i.e., an individual's self-confidence or belief in oneself to accomplish the task outweighs any anxiety or emotional worry that is felt) may potentially increase learning capacity and competency (NCAA, 2014 ). However, when these demands are perceived as exceeding the athlete's capacity, this stress can be detrimental to the student's mental and physical health as well as to sport performance (Ivarsson et al., 2017 ; Li et al., 2017 ).
As previously stated, time management has been shown to be a challenge to collegiate athletes. The NCAA rules state that collegiate athletes may only engage in required athletic activities for 4 h per day and 20 h/week during in-season and 8 h/week during off-season throughout the academic year. Although these rules have been clearly outlined, the most recent NCAA GOALS (2016) study reported alarming numbers regarding time commitment to athletic-related activities. Data from over 21,000 collegiate athletes from 600 schools across Divisions I, II, and III were included in this study. Although a breakdown of time commitments was not provided, collegiate athletes reported dedicating up to 34 h per week to athletics (e.g., practices, weight training, meetings with coaches, tactical training, competitions, etc.), in addition to spending between 38.5 and 40 h per week working on academic-related tasks. This report also showed a notable trend related to athletes spending an increase of ~2 more athletics-related hours per week compared to the 2010 GOALS study, along with a decrease of 2 h of personal time (from 19.5 h per week in 2010 to 17.1 in 2015). Furthermore, ~66% of Division I and II and 50% of Division III athletes reported spending as much or more time in their practices during the off-season as during the competitive season (DTHOMAS, 2013 ). These numbers show how important it is for collegiate athletes to develop time management skills to be successful in both academics and athletics. Overall, most collegiate athletes have expressed a need to find time to enjoy their college experience outside of athletic obligations (Paule and Gilson, 2010 ). Despite that, because of the increasing demand for excellence in academics and athletics, collegiate athletes' free time with family and friends is often scarce (Paule and Gilson, 2010 ). Consequently, trainers, coaches, and teammates will likely be the primary source of their weekly social interactivity.
Social interactions within their sport have also been found to relate to factors that may impact an athlete's perceived stress. Interactions with coaches and trainers can be effective or deleterious to an athlete. Effective coaching includes a coaching style that allows for a boost of the athlete's motivation, self-esteem, and efficacy in addition to mitigating the effects of anxiety. On the other hand, poor coaching (i.e., the opposite of effective coaching) can have detrimental psychological effects on an athlete (Gearity and Murray, 2011 ). In a closer examination of the concept of poor coaching practices, Gearity and Murray ( 2011 ) interviewed athletes about their experiences of receiving poor coaching. Following analysis of the interviews, the authors identified the main themes of the “coach being uncaring and unfair,” “practicing poor teaching inhibiting athlete's mental skills,” and “athlete coping.” They stated that inhibition of an athlete's mental skills and coping are associated with the psychological well-being of an athlete. Also, poor coaching may result in mental skills inhibition, distraction, insecurity, and ultimately team division (Gearity and Murray, 2011 ). This combination of factors may compound the negative impacts of stress in athletes and might be especially important for in injured athletes.
Injured athletes have previously been reported to have elevated stress as a result of heightened worry about returning to pre-competition status (Crossman, 1997 ), isolation from teammates if the injury is over a long period of time (Podlog and Eklund, 2007 ) and/or reduced mood or depressive symptoms (Daly et al., 1995 ). In addition, athletes who experience prolonged negative thoughts may be more likely to have decreased rehabilitation attendance or adherence, worse functional outcomes from rehabilitation (e.g., on measures of proprioception, muscular endurance, and agility), and worse post-injury performance (Brewer, 2012 ).
Monitoring Considerations
In addition to poor coaching, insufficient workload management can hinder an athlete's ability to recover and adapt to training, leading to fatigue accumulation (Gabbett et al., 2017 ). Excessive fatigue can impair decision-making ability, coordination and neuromuscular control, and ultimately result in overtraining and injury (Soligard et al., 2016 ). For instance, central fatigue was found to be a direct contributor to anterior cruciate ligament injuries in soccer players (Mclean and Samorezov, 2009 ). Introducing monitoring tools may serve as a means to reduce the detrimental effects of stress in collegiate athletes. Recent research on relationships between athlete workloads, injury, and performance has highlighted the benefits of athlete monitoring (Drew and Finch, 2016 ; Jaspers et al., 2017 ).
Athlete monitoring is often assessed with the measuring and management of workload associated with a combination of sport-related and non-sport-related stressors (Soligard et al., 2016 ). An effective workload management program should aim to detect excessive fatigue, identify its causes, and constantly adapt rest, recovery, training, and competition loads respectively (Soligard et al., 2016 ). The workload for each athlete is based off their current levels of physical and psychological fatigue, wellness, fitness, health, and recovery (Soligard et al., 2016 ). Accumulation of situational or physical stressors will likely result in day-to-day fluctuations in the ability to move external loads and strength train effectively (Fry and Kraemer, 1997 ). Periods of increased academic stress may cause increased levels of fatigue, which can be identified by using these monitoring tools, thereby assisting the coaches with modulating the workload during these specific periods. Coaches who plan to incorporate monitoring and management strategies must have a clear understanding of what they want to achieve from athlete monitoring (Gabbett et al., 2017 ; Thornton et al., 2019 ).
Monitoring External Loads
External load refers to the physical work (e.g., number of sprints, weight lifted, distance traveled, etc.) completed by the athlete during competition, training, and activities of daily living (Soligard et al., 2016 ). This type of load is independent of the athlete's individual characteristics (Wallace et al., 2009 ). Monitoring external loading can aid in the designing of training programs which mimic the external load demands of an athlete's sport, guide rehabilitation programs, and aid in the detection of spikes in external load that may increase the risk of injury (Clubb and McGuigan, 2018 ).
The means of quantifying external load can involve metrics as simple as pitch counts in baseball and softball (Fleisig and Andrews, 2012 ; Shanley et al., 2012 ) or quantifying lifting session training loads (e.g., sum value of weight lifted during an exercise x number of repetitions × the number of sets). Neuromuscular function testing is another more common way of analyzing external load. This is typically done using such measures such as the counter movement jump, squat jump, or drop jump. A force platform can be used to measure a myriad of outcomes (e.g., peak power, ground contact time, time to take-off, reactive strength index, and jump height), or simply measure jump height in a more traditional manner. Jumping protocols, such as the countermovement jump, have been adopted to examine the recovery of neuromuscular function after athletic competition with significant decreases for up to 72 h commonly reported (Andersson et al., 2008 ; Magalhães et al., 2010 ; Twist and Highton, 2013 ). (Gathercole et al., 2015 ) found reductions in 18 different neuromuscular variables in collegiate athletes following a fatiguing protocol. The variables of eccentric duration, concentric duration, total duration, time to peak force/power, and flight time:contraction time ratio, derived from a countermovement jump were deemed suitable for detecting neuromuscular fatigue with the rise in the use of technology for monitoring, certain sports have adopted specific software that can aid in the monitoring of stress. For example, power output can be measured using devices such as SRM™ or PowerTap™ in cycling (Jobson et al., 2009 ). This data can be analyzed to provide information such as average power or normalized power. The power output can then be converted into a Training Stress Score™ via commercially available software (Marino, 2011 ). More sophisticated measures of external load may involve the use of wearable technology devices such as Global Positioning System (GPS) devices, accelerometers, magnetometer, and gyroscope inertial sensors (Akenhead and Nassis, 2016 ). These devices can quantify external load in several ways, such as duration of movement, total distance covered, speed of movement, acceleration, and decelerations, as well as sport specific movement such as number and height of jumps, number of tackles, or breakaways, etc. (Akenhead and Nassis, 2016 ). The expansion of marketing of wearable devices has been substantial; however, there are questions of validity and reliability related to external load tracking limitations related to proprietary metrics, as well as the overall cost that should be considered when considering the adoption of such devices (Aughey et al., 2016 ; Torres-Ronda and Schelling, 2017 ).
Monitoring Internal Loads
While external load may provide information about an athlete's performance capacity and work completed, it does not provide clear evidence of how athletes are coping with and adapting to the external load (Halson, 2014 ). This type of information comes from the monitoring of internal loads. The term internal load refers to the individual physiological and psychological response to the external stress or load imposed (Wallace et al., 2009 ). Internal load is influenced by a number of factors such as daily life stressors, the environment around the athlete, and coping ability (Soligard et al., 2016 ). Indirect measures, such as the use of heart rate (HR) monitoring, and subjective measurements, such as perceived effort (i.e., ratings of perceived exertion), are examples of internal load monitoring. Using subjective measurement systems is a simple and practical method when dealing with large numbers of athletes (Saw et al., 2016 ; Nässi et al., 2017 ). Subjective reporting of training load (Rating of Perceived Exertion—RPE) (Coyne et al., 2018 ), Session Rating of Perceived Exertion—sRPE) (Coyne et al., 2018 ), perceived stress and recovery (Recovery Stress Questionnaire for Athletes—RESTQ-S), and psychological mood states (Profile of Mood States—POMS) have all been found to be a reliable indicator of training load (Robson-Ansley et al., 2009 ; Saw et al., 2016 ) and only take a few moments to complete. In addition, subjective measures can be more responsive to tracking changes or training responses in athletes than objective measures (Saw et al., 2016 ).
Heart rate (HR) monitoring is a common intrinsic measure of how the body is responding to stress. With training, the reduction of resting HR is typically a clear indication of the heart becoming more efficient and not having to beat as frequently. Alternately, increases of resting HR over time with a continuation of training may be an indicator of too much stress. Improper nutrition, such as regular or ongoing suboptimal intakes of vitamins or minerals, may result in increased ventilation and/or increased heart rate (Lukaski, 2004 ). It has been suggested that the additional stress may lead to parasympathetic hyperactivity, leading to an increase in resting HR (Statler and DuBois, 2016 ). This largely stems from research examining the sensitivity of various HR derived metrics, such as resting HR, HR variability (HRV), and HR recovery (HRR) to fluctuations in training load (Borresen and Ian Lambert, 2009 ). HRR in athlete monitoring is the rate of HR decline after the cessation of exercise. A common measure of HHR is the use of a 2 min step test followed by a 60 s HR measurement. The combination of the exercise (stress) on the cardiovascular system and then its subsequent return toward baseline has been used as an indicator of autonomic function and training status in athletes (Daanen et al., 2012 ). In collegiate athletes it was found that hydration status impacted HRR following moderate to hard straining sessions (Ayotte and Corcoran, 2018 ). Athletes who followed a prescription hydration plan performed better in the standing long jump, tracked objects faster, and showed faster HRR vs. athletes who followed their normal self-selected hydration plan (Ayotte and Corcoran, 2018 ). To date, HR monitoring and the various derivatives have mainly been successful in detecting changes in training load and performance in endurance athletes (Borresen and Ian Lambert, 2009 ; Lamberts et al., 2009 ; Thorpe et al., 2017 ). Although heart rate monitoring can provide additional physiological insight for aerobic sessions or events, it thus far has not been found to be an accurate measurement for quantifying internal load during many explosive, short duration anaerobic activities (Bosquet et al., 2008 ).
A multitude of studies have reported the reliability and validity of using RPE and sRPE across a range of training modalities (Foster, 1998 ; Impellizzeri et al., 2004 ; Sweet et al., 2004 ). This measure can be used to create a number of metrics such as session load (sRPE × duration in minutes), daily load (sum of all session loads for that day), weekly training load (sum of all daily training loads for entire week), monotony (standard deviation of weekly training load), and strain (daily or weekly training load × monotony) (Foster, 1998 ). Qualitative questionnaires that monitor stress and fatigue have been well-established as tools to use with athletes (see Table 1 for examples of commonly used questionnaires in research). Using short daily wellness questionnaires may allow coaches to generate a wellness score which then can be adjusted based off of the stress the athlete may be feeling to meet the daily load target (Foster, 1998 ; Robson-Ansley et al., 2009 ). However, strength and conditioning coaches need to be mindful that these questionnaires may require sports psychologist or other licensed professional to examine and provide the results. An alternative that may be better suited for strength and conditioning professionals to use could be to incorporate some of the themes of those questionnaires into programing.
Overview of common tool/measures used by researchers to monitor training load.
A Multifaceted Approach
Dissociation between external and internal load units may be indicative of the state of fatigue of an athlete. Utilizing a monitoring system in which the athlete is able to make adjustments to their training loads in accordance with how they are feeling in that moment can be a useful tool for assisting the athlete in managing stress. Auto-regulation is a method of programming that allows for adjustments based on the results of one or more readiness tests. When implemented properly, auto regulation enables the coach or athlete to optimize training based on the athlete's given readiness for training on a particular day, thereby aiming to avoid potential overtraining (Kraemer and Fleck, 2018 ). Several studies have found that using movement velocity to designate resistance training intensities can result in significant improvements in maximal strength and athletic performance (Pareja-Blanco et al., 2014 , 2017 ; Mann et al., 2015 ). Velocity based training allows the coach and athlete to view real time feedback for the given lifts, thereby allowing them to observe how the athlete is performing in that moment. If the athlete is failing to meet the prescribed velocity or the velocity drops greater than a predetermined amount between sets, then this should signal the coach to investigate. If there is a higher than normal amount of stress on that athlete for the day, that could be a potential reason. This type of combination style program of using a quantitative or objective measurement (s) and a subjective measure of wellness (qualitative questionnaire) has recently been reported to be an effective tool in monitoring individuals apart of a team (Starling et al., 2019 ). The subjective measure in this study was the readiness to train questionnaire (RTT-Q) and the objective measures were the HRR 6min test (specifically the HRR 60s = recorded as decrease in HR in the 60 s after termination of the test) to assess autonomic function and the standing long jump (SLJ) to measure neuromuscular function. The findings found that, based on the absolute typical error of measurement, the HRR 60s and SLJ could detect medium and large changes in fatigue and readiness. The test took roughly 8 min for the entire team, which included a group consisting of 24 college-age athletes. There are many other combinations of monitoring variables and strategies that coaches and athletes may utilize.
Data Analysis – How to Utilize the Measures
Regardless of what type of monitoring tool a coach or athlete may incorporate, it is essential to understand how to analyze this data. There are excellent resources available which discuss this topic in great detail (Gabbett et al., 2017 ; Clubb and McGuigan, 2018 ; Thornton et al., 2019 ). This section will highlight two main conclusions from these sources and briefly describe two of the main statistical practices and concepts discussed. The use of z-scores or modified z-scores has been proposed as a method of detecting meaningful change in athlete data (Clubb and McGuigan, 2018 ; Thornton et al., 2019 ). For different monitoring tools listed in Table 1 , the following formula would be an example of how to assess changes: (Athlete daily score—Baseline score)/Standard deviation of baseline. The baseline would likely be based off an appropriate period such as the scores across 2 weeks during the preseason.
In sports and sports science, the use of a magnitude-based inference (MBI) has been suggested as more appropriate and easier to understand when examining meaningful changes in athletic data, than null-hypothesis significance testing (NHST) (Buchheit, 2014 ). Additional methods to assess meaningful change that are similar to MBI are using standard deviation, typical error, effect sizes, smallest worthwhile change (SWC), and coefficient of variation (Thornton et al., 2019 ). It should be noted that all of these methods have faced criticism from sources such as statisticians. It is important to understand that the testing methods, measurements, and analysis should be based on the resources and intended goals from use, which will differ from every group and individual. Once identified, it is up to the practitioner to keep this system the same, in order to collect data that can then be examined to understand meaningful information for each setting (Thornton et al., 2019 ).
Managing and Coping Strategies
Once the collegiate-athlete has been able to identify the need to balance their stress levels, the athlete may then need to seek out options for managing their stress. Coaches are be able to assist them by sharing information on health and wellness resources available for the students, both on and off campus. Another way a coach can potentially support their athletes is by establishing an open-door policy, wherein the team members feel comfortable approaching a member of the strength and conditioning staff in order to seek out resources for coping with challenges related to stress.
There are some basic skills that strength and conditioning coaches can teach (while staying within their scope of practice). Coaches can introduce their athletes to basic lifestyle concepts, such as practicing deep breathing techniques, positive self-talk, and developing healthy sleep habits (i.e., turning off their mobile devices 1 h before bed and aiming for 8 h of sleep each night, etc.). A survey of strength and conditioning practitioners by Radcliffe et al. ( 2015 ) found that strategies used by practitioners included a mix of cognitive and behavioral strategies, which was used as justification for recommending practitioners find opportunities to guide professional development toward awareness strategies. Practitioners reported using a wide variety of psychological skills and strategies, which following survey analysis, highlighted a significant emphasis on strategies that may influence athlete self-confidence and goal setting. Themes identified by Radcliffe et al. ( 2015 ) included confidence building, arousal management, and skill acquisition. Additionally, similar lower level themes that are connected (i.e., goal setting, increasing, or decreasing arousal intensities, self-talk, mental imagery) are all discussed in the 4th edition of the NSCA Essentials of Strength and Conditioning book (Haff et al., 2016 ). When the interventions aiming to improve mental health expand from basic concepts to mental training beyond a coach's scope, it would be pertinent for the coach to refer the collegiate-athlete to a sport psychology or other mental health consultant (Fogaca, 2019 ). Moreover, strength and conditioning coaches may find themselves in a position to become key players in facilitating management strategies for collegiate athletes, thereby guiding the athlete in their quest to learn how to best manage the mental and physical energy levels required in the quest for overall optimal performance (Statler and DuBois, 2016 ).
Conclusion and Future Directions
This review article has summarized some of the ways that strength and conditioning professionals may be able to gain a better understanding of the types of stressors encountered by collegiate athletes, the impact these stressors may have on athletic performance, and suggestions for assisting athletes with developing effective coping strategies to reduce the potential negative physiological and psychological impacts of stress. It has been suggested that strategies learned in the context of training may have a carry-over effect into other areas such as competition. More education is needed in order for strength and conditioning professionals to gain a greater understanding of how to support their athletes with stress-management techniques and resources. Some ways to disseminate further education on stress-management tools for coaches to share with their athletes may include professional development events, such as conferences and clinics.
Author Contributions
All of the authors have contributed to the development of the manuscript both in writing and conceptual development.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The handling editor declared a past collaboration with one of the authors RL.
- Akenhead R., Nassis G. P. (2016). Training load and player monitoring in high-level football: current practice and perceptions . Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 11 , 587–593. 10.1123/ijspp.2015-0331 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- American College Health Association and American College Health Association-National College Health Assessment II (2019). Reference Group Executive Summary Spring 2019 . Silver Spring, MD: American College Health Association. [ Google Scholar ]
- Andersson H., Raastad T., Nilsson J., Paulsen G., Garthe I., Kadi F. (2008). Neuromuscular fatigue and recovery in Elite female soccer: effects of active recovery . Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 40 , 372–380. 10.1249/mss.0b013e31815b8497 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Aquilina D. (2013). A study of the relationship between elite athletes' educational development and sporting performance . Int. J. Hist. Sport 30 , 374–392. 10.1080/09523367.2013.765723 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Aughey R. J. (2011). Applications of GPS technologies to field sports . Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 6 , 295–310. 10.1123/ijspp.6.3.295 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Aughey R. J., Elias G. P., Esmaeili A., Lazarus B., Stewart A. M. (2016). Does the recent internal load and strain on players affect match outcome in elite Australian football? J. Sci. Med. Sport. 19 , 182–186. 10.1016/j.jsams.2015.02.005 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ayotte D., Corcoran M. P. (2018). Individualized hydration plans improve performance outcomes for collegiate athletes engaging in in-season training . J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 15 :27. 10.1186/s12970-018-0230-2 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Borresen J., Ian Lambert M. (2009). The quantification of training load, the training response and the effect on performance . Sports Med. 39 , 779–795. 10.2165/11317780-000000000-00000 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bosquet L., Merkari S., Arvisais D., Aubert A. E. (2008). Is heart rate a convenient tool to monitor over-reaching? a systematic review of the literature. Br. J. Sports Med. 42 , 709–714. 10.1136/bjsm.2007.042200 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Brewer B. W. (2012). Psychology of sport injury rehabilitation, in Handbook of Sport Psychology , eds G. Tenenbaum, and R. C. Eklund (Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons, Inc; ), 404–424. 10.1002/9781118270011.ch18 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Buchheit M. (2014). Monitoring training status with HR measures: do all roads lead to Rome? Front. Physiol. 5 :73. 10.3389/fphys.2014.00073 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Clubb J., McGuigan M. (2018). Developing cost-effective, evidence-based load monitoring systems in strength and conditioning practice . Strength Cond. J. 40 , 75–81. 10.1519/SSC.0000000000000396 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cosh S., Tully P. J. (2014). All I have to do is pass: a discursive analysis of student athletes' talk about prioritising sport to the detriment of education to overcome stressors encountered in combining elite sport and tertiary education . Psychol. Sport Exerc. 15 , 180–189. 10.1016/j.psychsport.2013.10.015 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cosh S., Tully P. J. (2015). Stressors, coping, and support mechanisms for student athletes combining elite sport and tertiary education: implications for practice . Sport Psychol. 29 , 120–133. 10.1123/tsp.2014-0102 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Coyne J., Haff G., Coutts A., Newton R., Nimphius S. (2018). The current state of subjective training load monitoring—a practical perspective and call to action . Sports Med. 4 :58. 10.1186/s40798-018-0172-x [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Crossman J. (1997). Psychological rehabilitation from sports injuries . Sports Med. 23 , 333–339. 10.2165/00007256-199723050-00005 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Daanen H. A. M., Lamberts R. P., Kallen V. L., Jin A., van Meeteren N. L. U. (2012). A systematic review on heart-rate recovery to monitor changes in training status in athletes . Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 7 , 251–260. 10.1123/ijspp.7.3.251 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Daly J. M., Brewer B. W., van Raalte J. L., Petitpas A. J., Sklar J. H. (1995). Cognitive appraisal, emotional adjustment, and adherence to rehabilitation following knee surgery . J. Sport Rehabil. 4 , 23–30. 10.1123/jsr.4.1.23 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Davis P., Halvarsson A., Lundström W., Lundqvist C. (2019). Alpine ski coaches' and athletes' perceptions of factors influencing adaptation to stress in the classroom and on the slopes . Front. Psychol. 10 :1641. 10.3389/fpsyg.2019.01641 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- de Brandt K., Wylleman P., Torregrossa M., Schipper-van Veldhoven N., Minelli D., Defruyt S., et al. (2018). Exploring the factor structure of the dual career competency questionnaire for Athletes in European pupil- and student-athletes . J. Sport. Exercise. Psy. 1–18. 10.1080/1612197X.2018.1511619 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Drew M. K., Finch C. F. (2016). The relationship between training load and injury, illness and soreness: a systematic and literature review . Sports Med. 46 , 861–883. 10.1007/s40279-015-0459-8 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- DTHOMAS (2013). NCAA GOALS Study. NCAA.Org - The Official Site of the NCAA . Available online at: http://www.ncaa.org/about/resources/research/ncaa-goals-study (accessed October 5, 2019).
- Egan K. P. (2019). Supporting mental health and well-being among student-athletes . Clin. Sports Med. 38 , 537–544. 10.1016/j.csm.2019.05.003 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Etzel E. F. ed. (2009). Counseling and Psychological Services for College Student-Athletes . Morgantown, WV: Fitness Information Technology. [ Google Scholar ]
- Fleisig G. S., Andrews J. R. (2012). Prevention of elbow injuries in youth baseball pitchers . Sports Health 4 , 419–424. 10.1177/1941738112454828 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Fogaca J. L. (2019). Combining mental health and performance interventions: coping and social support for student-athletes . J. Appl. Sport Psychol. 1–16. 10.1080/10413200.2019.1648326 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Foster C. (1998). Monitoring training in athletes with reference to overtraining syndrome . Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 30 , 1164–1168. 10.1097/00005768-199807000-00023 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Fry A. C., Kraemer W. J. (1997). Resistance exercise overtraining and overreaching: neuroendocrine responses . Sports Med. 23 , 106–129. 10.2165/00007256-199723020-00004 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gabbett T. J., Nassis G. P., Oetter E., Pretorius J., Johnston N., Medina D., et al.. (2017). The athlete monitoring cycle: a practical guide to interpreting and applying training monitoring data . Br. J. Sports Med. 51 , 1451–1452. 10.1136/bjsports-2016-097298 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gathercole R. J., Sporer B. C., Stellingwerff T., Sleivert G. G. (2015). Comparison of the capacity of different jump and sprint field tests to detect neuromuscular fatigue . J. Strength Cond. Res. 29 , 2522–2531. 10.1519/JSC.0000000000000912 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gearity B. T., Murray M. A. (2011). Athletes' experiences of the psychological effects of poor coaching . Psychol. Sport Exerc. 12 , 213–221. 10.1016/j.psychsport.2010.11.004 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gould D., Udry E. (1994). Psychological skills for enhancing performance: arousal regulation strategies . Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 26 , 478–485. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Haff G., Triplett N. T., National Strength Conditioning Association (U.S.) eds. (2016). Essentials of Strength Training and Conditioning . 4th Edn Champaign, IL: Human Kinetics. [ Google Scholar ]
- Halson S. L. (2014). Monitoring training load to understand fatigue in athletes . Sports Med. 44 , 139–147. 10.1007/s40279-014-0253-z [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hamlin M. J., Wilkes D., Elliot C. A., Lizamore C. A., Kathiravel Y. (2019). Monitoring training loads and perceived stress in young elite university athletes . Front. Physiol. 10 :34. 10.3389/fphys.2019.00034 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hopkins W. G. (1991). Quantification of training in competitive sports: methods and applications . Sports Med. 12 , 161–183. 10.2165/00007256-199112030-00003 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Huml M. R., Hambrick M. E., Hums M. A. (2016). Coaches' perceptions of the reduction of athletic commitment for division II student-athletes: development and validation of a measure of athletic/academic balance . J. Intercoll. Sport 9 , 303–325. 10.1123/jis.2015-0055 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Humphrey J. H., Yow D. A., Bowden W. W. (2000). Stress in College Athletics: Causes, Consequences, Coping . New York, NY: Haworth Half-Court Press. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hyatt H. W., Kavazis A. N. (2019). Body composition and perceived stress through a calendar year in NCAA I female volleyball players . Int. J. Exerc. Sci. 12 , 433–443. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Impellizzeri F. M., Rampinini E., Coutts A. J., Sassi A., Marcora S. M. (2004). Use of RPE-based training load in Soccer . Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 36 , 1042–1047. 10.1249/01.MSS.0000128199.23901.2F [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ivarsson A., Johnson U., Andersen M. B., Tranaeus U., Stenling A., Lindwall M. (2017). Psychosocial factors and sport injuries: meta-analyses for prediction and prevention . Sports Med. 47 , 353–365. 10.1007/s40279-016-0578-x [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Jaspers A., Brink M. S., Probst S. G. M., Frencken W. G. P., Helsen W. F. (2017). Relationships between training load indicators and training outcomes in professional Soccer . Sports Med. 47 , 533–544. 10.1007/s40279-016-0591-0 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Jobson S. A., Passfield L., Atkinson G., Barton G., Scarf P. (2009). The analysis and utilization of cycling training data . Sports Med. 39 , 833–844. 10.2165/11317840-000000000-00000 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kaier E., Cromer L. D., Johnson M. D., Strunk K., Davis J. L. (2015). Perceptions of mental illness stigma: comparisons of athletes to nonathlete peers . J. Coll. Stud. Dev. 56 , 735–739. 10.1353/csd.2015.0079 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kallus W., Kellmann M. (2016). The Recovery-Stress . Questionnaires: User Manual . Frankfurt: Pearson Assessment & Information GmbH. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kenttä G., Hassmén P. (1998). Overtraining and recovery: a conceptual model . Sports Med. 26 , 1–16. 10.2165/00007256-199826010-00001 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kraemer W. J., Fleck S. J. (2018). Optimizing Strength Training: Designing Nonlinear Periodization Workouts . Champaign: Human Kinetics; Available online at: https://public.ebookcentral.proquest.com/choice/publicfullrecord.aspx?p=5730619 (accessed January 30, 2020). [ Google Scholar ]
- Lamberts R. P., Swart J., Capostagno B., Noakes T. D., Lambert M. I. (2009). Heart rate recovery as a guide to monitor fatigue and predict changes in performance parameters: heart rate recovery to monitor of performance . Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 20 , 449–457. 10.1111/j.1600-0838.2009.00977.x [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lavallée L., Flint F. (1996). The relationship of stress, competitive anxiety, mood state, and social support to athletic injury . J. Athl. Train. 31 , 296–299. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Li C., Ivarsson A., Lam L. T., Sun J. (2019). Basic psychological needs satisfaction and frustration, stress, and sports injury among university athletes: a four-wave prospective survey . Front. Psychol. 10 :665. 10.3389/fpsyg.2019.00665 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Li H., Moreland J. J., Peek-Asa C., Yang J. (2017). Preseason anxiety and depressive symptoms and prospective injury risk in collegiate athletes . Am. J. Sports Med. 45 , 2148–2155. 10.1177/0363546517702847 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- López de Subijana C., Barriopedro M., Conde E. (2015). Supporting dual career in Spain: Elite athletes' barriers to study . Psychol. Sport Exerc. 21 , 57–64. 10.1016/j.psychsport.2015.04.012 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lukaski H. C. (2004). Vitamin and mineral status: effects on physical performance . Nutrition 20 , 632–644. 10.1016/j.nut.2004.04.001 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Magalhães J., Rebelo A., Oliveira E., Silva J. R., Marques F., Ascensão A. (2010). Impact of loughborough intermittent shuttle test versus soccer match on physiological, biochemical and neuromuscular parameters . Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 108 , 39–48. 10.1007/s00421-009-1161-z [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Maloney M. T., McCormick R. E. (1993). An examination of the role that intercollegiate athletic participation plays in academic achievement: athletes' feats in the classroom . J. Hum. Resour. 28 :555 10.2307/146160 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mann J. B., Bryant K. R., Johnstone B., Ivey P. A., Sayers S. P. (2016). Effect of physical and academic stress on illness and injury in division 1 college football players . J. Strength Cond. Res. 30 , 20–25. 10.1519/JSC.0000000000001055 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mann J. B., Ivey P. A., Sayers S. P. (2015). Velocity-based training in football . Strength Cond. J. 37 , 52–57. 10.1519/SSC.0000000000000177 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Marino F. E. (ed.). (2011). Regulation of Fatigue in Exercise . Hauppauge, NY: Nova Science Publishers. [ Google Scholar ]
- Martin D. T., Andersen M. B. (2000). Heart rate-perceived exertion relationship during training and taper . J. Sports Med. Phys. Fitness 40 , 201–208. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Massey C. D., Maneval M. W., Phillips J., Vincent J., White G., Zoeller B. (2002). An analysis of teaching and coaching behaviors of elite strength and conditioning coaches . J. Strength Cond. Res. 16 , 456–460. 10.1519/00124278-200208000-00019 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Massey C. D., Schwind J. J., Andrews D. C., Maneval M. W. (2009). An analysis of the job of strength and conditioning coach for football at the division II Level . J. Strength Cond. Res. 23 , 2493–2499. 10.1519/JSC.0b013e3181bbe9b6 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Massey C. D., Vincent J., Maneval M. (2004). Job analysis of college division I-A football strength and conditioning coaches . J. Strength Cond. Res. 18 , 19–25. 10.1519/1533-4287(2004)018<0019:jaocdi>2.0.co;2 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mclean S. G., Samorezov J. E. (2009). Fatigue-induced ACL injury risk stems from a degradation in central control . Med. Sci. Sport Exerc. 41 , 1662–1673. 10.1249/MSS.0b013e31819ca07b [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Miller P. S., Kerr G. (2002). The athletic, academic and social experiences of intercollegiate student athletes . J. Sport Behav. 25 , 346–367. [ Google Scholar ]
- Moreland J. J., Coxe K. A., Yang J. (2018). Collegiate athletes' mental health services utilization: A systematic review of conceptualizations, operationalizations, facilitators, and barriers . J. Sport Health Sci. 7 , 58–69. 10.1016/j.jshs.2017.04.009 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Morgan W. P., Brown D. R., Raglin J. S., O'Connor P. J., Ellickson K. A. (1987). Psychological monitoring of overtraining and staleness . Br. J. Sports Med. 21 , 107–114. 10.1136/bjsm.21.3.107 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Morton R. H., Fitz-Clarke J. R., Banister E. W. (1990). Modeling human performance in running . J. Appl. Physiol. 69 , 1171–1177. 10.1152/jappl.1990.69.3.1171 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Nässi A., Ferrauti A., Meyer T., Pfeiffer M., Kellmann M. (2017). Psychological tools used for monitoring training responses of athletes . Perform. Enhanc. Health 5 , 125–133. 10.1016/j.peh.2017.05.001 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- NCAA (2014). Mind Body and Sport: Understanding and Supporting Student-Athlete Mental Wellness. Independent Publisher . Available online at: https://books.google.com/books?id=JA-5rQEACAAJ (accessed October 01, 2019).
- Pareja-Blanco F., Rodríguez-Rosell D., Sánchez-Medina L., Gorostiaga E., González-Badillo J. (2014). Effect of movement velocity during resistance training on neuromuscular performance . Int. J. Sports Med. 35 , 916–924. 10.1055/s-0033-1363985 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pareja-Blanco F., Rodríguez-Rosell D., Sánchez-Medina L., Sanchis-Moysi J., Dorado C., Mora-Custodio R., et al.. (2017). Effects of velocity loss during resistance training on athletic performance, strength gains and muscle adaptations . Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 27 , 724–735. 10.1111/sms.12678 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Paule A. L., Gilson T. A. (2010). Current collegiate experiences of big-time, non-revenue, NCAA athletes . J. Intercoll. Sport 3 , 333–347. 10.1123/jis.3.2.333 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Petrie T. A., Deiters J., Harmison R. J. (2014). Mental toughness, social support, and athletic identity: Moderators of the life stress–injury relationship in collegiate football players . Sport Exerc. Perform. Psychol. 3 , 13–27. 10.1037/a0032698 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Plews D. J., Laursen P. B., Stanley J., Kilding A. E., Buchheit M. (2013). Training adaptation and heart rate variability in elite endurance athletes: opening the door to effective monitoring . Sports Med. 43 , 773–781. 10.1007/s40279-013-0071-8 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Podlog L., Eklund R. C. (2007). Professional coaches' perspectives on the return to sport following serious injury . J. Appl. Sport Psychol. 19 , 207–225. 10.1080/10413200701188951 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pyne D. B., Martin D. T. (2011). Fatigue – insights from individual and team sports. in Regulation of Fatigue in Exercise , ed F. E. Marino, (New York, NY: Nova Publishers; ), 177–186. [ Google Scholar ]
- Radcliffe J. N., Comfort P., Fawcett T. (2015). Psychological strategies included by strength and conditioning coaches in applied strength and conditioning: J. Strength . Cond. Res. 29 , 2641–2654. 10.1519/JSC.0000000000000919 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Reardon C. L., Hainline B., Aron C. M., Baron D., Baum A. L., Bindra A., et al.. (2019). Mental health in elite athletes: international olympic committee consensus statement 2019 . Br. J. Sports Med. 53 , 667–699. 10.1136/bjsports-2019-100715 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Robson-Ansley P. J., Gleeson M., Ansley L. (2009). Fatigue management in the preparation of Olympic athletes . J. Sports Sci. 27 , 1409–1420. 10.1080/02640410802702186 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rushall B. S. (1990). A tool for measuring stress tolerance in elite athletes . J. Appl. Sport Psychol. 2 , 51–66. 10.1080/10413209008406420 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Saw A. E., Main L. C., Gastin P. B. (2016). Monitoring the athlete training response: subjective self-reported measures trump commonly used objective measures: a systematic review . Br. J. Sports Med. 50 :281. 10.1136/bjsports-2015-094758 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Scott B. M., Paskus T. S., Miranda M., Petr T. A., McArdle J. J. (2008). In-season vs. out-of-season academic performance of college student-athletes . J. Intercoll. Sport 1 , 202–226. 10.1123/jis.1.2.202 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Selye H. (ed.). (1976). The Stress of Life . New York, NY : McGraw-Hill. [ Google Scholar ]
- Shanley E., Michener L., Ellenbecker T., Rauh M. (2012). Shoulder range of motion, pitch count, and injuries among interscholastic female softball pitchers: a descriptive study . Int. J. Sports Phys. Ther. 7 , 548–557. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Soligard T., Schwellnus M., Alonso J.-M., Bahr R., Clarsen B., Dijkstra H. P., et al.. (2016). How much is too much? (Part 1) International Olympic Committee consensus statement on load in sport and risk of injury . Br. J. Sports Med. 50 , 1030–1041. 10.1136/bjsports-2016-096581 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Starling L. T., Nellemann S., Parkes A., Lambert M. I. (2019). The Fatigue and Fitness Test for Teams (FFITT): a practical option for monitoring athletes in a team as individuals . Eur. J. Sport Sci . 20 , 1–9. 10.1080/17461391.2019.1612951 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Statler T., DuBois A. (2016). Psychology of athletic preparation and performance, in Essentials of Strength Training and Conditioning , eds. G. Haff, and N. T. Triplett (Champaign, IL: Human Kinetics; ), 155–172. [ Google Scholar ]
- Sweet T. W., Foster C., McGuigan M. R., Brice G. (2004). Quantitation of resistance training using the session rating of perceived exertion method . J. Strength Cond. Res. 18 :796. 10.1519/14153.1 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Szivak T. K., Kraemer W. J. (2015). Physiological readiness and resilience: pillars of military preparedness . J. Strength Cond. Res. 29 , S34–S39. 10.1519/JSC.0000000000001073 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Taylor K.-L., Chapman D., Cronin J., Newton M., Gill N. (2012). Fatigue monitoring in high performance sport: a survey of current trends . J. Aust. Strength Cond. 20 , 12–23. [ Google Scholar ]
- Thornton H. R., Delaney J. A., Duthie G. M., Dascombe B. J. (2019). Developing athlete monitoring systems in team sports: data analysis and visualization . Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 14 , 698–705. 10.1123/ijspp.2018-0169 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Thorpe R. T., Atkinson G., Drust B., Gregson W. (2017). Monitoring fatigue status in elite team-sport athletes: implications for practice . Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perfrom. 12 , S2-27-S2–34. 10.1123/ijspp.2016-0434 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Torres-Ronda L., Schelling X. (2017). Critical process for the implementation of technology in sport organizations . Strength Cond. J. 39 , 54–59. 10.1519/SSC.0000000000000339 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Twist C., Highton J. (2013). Monitoring fatigue and recovery in rugby league players . Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 8 , 467–474. 10.1123/ijspp.8.5.467 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wallace L. K., Slattery K. M., Coutts A. J. (2009). The ecological validity and application of the session-rpe method for quantifying training loads in swimming . J. Strength Cond. Res. 23 , 33–38. 10.1519/JSC.0b013e3181874512 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Williams J. M., Andersen M. B. (1998). Psychosocial antecedents of sport injury: review and critique of the stress and injury model . J. Appl. Sport Psychol. 10 , 5–25. 10.1080/10413209808406375 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Yang J., Peek-Asa C., Corlette J. D., Cheng G., Foster D. T., Albright J. (2007). Prevalence of and risk factors associated with symptoms of depression in competitive collegiate student athletes . Clin. J. Sport Med. 17 , 481–487. 10.1097/JSM.0b013e31815aed6b [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
Should College Athletes be Paid?
March 31, 2024

Okay, I won’t hide the ball: my answer to the question, “Should college athletes be paid?” is a resounding, “Yes.” But before I go through the reasons why (and some countervailing streams of thought as well), I think it’s important to place the question in the larger context of money in college sports. Why? Because there just so happens to be a ton of money in college sports. On Saturdays during football season, hundreds of thousands of fans across the nation flock to iconic stadiums —the Big House, Death Valley, the Swamp—and pay premium ticket prices to watch their favorite teams go at it.
Millions more tune in to the games from home, and the NCAA conferences take advantage of the sport’s popularity to the tune of billions of dollars. In 2022, the Big Ten, for example, inked a seven-year media rights agreement with Fox, CBS, and NBC worth upwards of $7 billion.
The coaches are very much in on the action, too. College football coaches, especially those who strategize from the sidelines of premiere football schools, boast yearly salaries that are truly jaw-dropping. In the last year before his retirement, Alabama’s Nick Saban made $11.41 million. The same year, Clemson’s Dabo Swinney pocketed $10.88 million, and Georgia’s Kirby Smart took home $10.71 million. Sure, those are some of the best football programs in the country. But still: more than a hundred Division I coaches earn over $1 million. The top 25 college football coaches earn an average of $5.2 million per year. The top 25 college basketba l l coaches earn an average of $3.2 million per year.
Should College Athletes be Paid (Continued)
Every year, the NCAA rakes in about a billion dollars from March Madness alone. In 2019, Connecticut senator Chris Murphy released a report titled “Madness, Inc.”, which took aim at what the report termed the “college sports industrial complex.” The report cites Department of Education data which showed that college sports programs brought in a whopping $14 billion in revenue in 2018 alone. In terms of revenue, college sports beat out every professional sports league in the world, except the NFL.
And here’s the kicker: college athletes—the product that millions of Americans pay to watch compete—aren’t compensated for their on-the-field performance. That’s because the NCAA’s long-enshrined policy of amateurism states that student-athletes are students first—thus “amateurs”—and are therefore not eligible for compensation. The good news? In 2021, the NCAA implemented an interim policy. This allows student-athletes to make money from their name, image, and likeness. The so-called NIL rule permits students to engage in money-making “NIL activities,” like selling autographs and memorabilia, making paid appearances, and going into business with brands. The new NIL policy is a step in the right direction, but it doesn’t address the root of the problem. In 2022, only 17% of student-athletes at Division I schools participated in NIL activities. The median compensation (note: not the average, which can be distorted by particularly high-earners) was $65 per NIL activity.
America seems to have come to a consensus on the question of should college athletes be paid. According to a recent poll , 67% of Americans believe that college athletes should be compensated for their performance. Not just for their name, image, and likeness.
Should college athletes be paid?
Now let’s confront the question head on: should college athletes be paid? I’ve already gone on record with an unequivocal, “yes.” But to preserve a sense of fairness, I’ll go through some of the arguments on the opposite side of the issue, and in so doing hopefully provide a sound justification for my answer.
Should college athletes be paid? No, they’re already paid in the form of scholarships
Should college athletes be paid? No, some say, because college athletes already receive full scholarships, which is tantamount to payment. Unfortunately, this argument doesn’t pass the sniff test. Every year, Division I and II colleges dole out about $2.9 billion in scholarships to some 150,000 student-athletes. That sounds great until you realize that the average yearly scholarship is just about $18,000; that’s far from sufficient to cover tuition at most private schools or out-of-state tuition at state schools. Overall, only 1% of student-athletes receive a “full ride” scholarship. Under a little scrutiny, then, the argument that college athletes receive compensation in the form of scholarships falls apart.
So college athletes aren’t paid via scholarships. Sure, that’s a fact, but not an argument as to why college athletes should be paid. Well, here’s the argument: given the money and exposure that athletes generate for their schools, any just system would require they be compensated for the value they add. A phenomenon known as the Flutie Effect describes how a college football team’s success leads to an increase in applications. When college football teams go from “mediocre to great,” applications increase by as much as 18%. And better performance on the gridiron results in more donations to the school. Donations go up significantly when football squads post better records.
To put it concisely: athletes bring significant value to their schools in the form of exposure and monetary donations, and scholarships do not amount to an adequate form of compensation. Therefore, college athletes deserve to be paid.
But it would be too complicated to figure out salaries!
The “it’s just too difficult!” argument is a common retort to the question of should college athletes be paid. It’s also a fixture in American political discourse. Should the U.S., say, move towards single-payer healthcare? Of course not—it’d be too difficult to implement!
Here, the “it’s-too-difficult” argument suggests that determining which college athletes would get compensated, and how much they’d get compensated, would be a complicated and messy undertaking. Therefore, it’d be better simply not to pay college athletes.
But appealing to the apparent intractability of a problem is no reason not to address it. The fact that it might be difficult to correct an iniquity is no justification for not trying to correct it at all.
Professional sports leagues are far from shining models of equity and fairness. UFC fighters—who aren’t unionized, by the way— are only paid about 20% of overall revenue , whereas unionized leagues like the NBA, MLB, and NFL share roughly 50% of their revenue with players. There are issues of gender equity across leagues, too. The average WNBA base salary is $120,600 ; the average NBA base salary is $5.4 million. However, there are plenty of professional sports leagues that have managed to figure out how to fairly compensate their athletes, from superstars to bench players. When one considers this fact, the “it’s too complicated” argument falls apart, too.
Where would the money come from?
Another oft-heard argument that answers, “no,” to the question of should college athletes be paid goes like this: because so few college athletics programs are cash-flow positive, schools would have to make cuts to minor sports programs to come up with the money to pay athletes who compete in premiere sports, like football and basketball. This line of reasoning assumes that paying marquee college athletes would preclude the possibility of paying athletes who compete in more minor or niche sports. But that assumption is not warranted.
As I noted previously, professional sports leagues—from the NFL to independent league baseball to professional jai alai —have figured out how to compensate players with different levels of skill and star power. There’s no reason to think the NCAA couldn’t do it as well.
The way resources are allocated reflects an institution’s values. At least one highly-paid college football coach has gone on record as saying he’d happily take less money if it meant his players would be paid .
Paying athletes would take away from the love of the game
In doing research for this article, I confronted this argument or one of its variations quite a lot. It goes like this: college athletics should compete not for financial gain but for a nebulous “love of the game.” Paying college athletes would tarnish the otherwise pure and idealistic realm of college sports.
But we’ve already established that college sports are a big business. The NCAA, conferences, schools, and coaches all benefit from that business. Why should the athletes be the only ones who have to work with no pay, just to fulfill some romanticized and unrealistic idea of college sports?
Plus, participating in college sports amounts to a full-time job. Although NCAA policy states that athletes may only dedicate 20 hours per week to sports-related activity, studies have shown that Division I athletes spend an average of 35 hours per week on sports activities. A lawsuit filed by two UNC football players alleged that the NCAA skirted around its own policies and deprived players of a meaningful education.
Those who answer “no” to the question of should college athletes be paid are therefore confronted with a dilemma. If student-athletes should only be competing for the “love of the game,” why does their participation in college sports look a lot like a full-time job? And if their participation in college sports looks like a full-time job, why are they not compensated accordingly?
Should college athletes be paid? – a few more thoughts
Participation in college sports takes up a large chunk of a student-athlete’s time, study time included. Right now, student-athletes are getting the worst of both worlds. They’re not compensated for their positions as athletes (nor are the vast majority of them getting those coveted “free ride” educations), and their participation in sports precludes them from fully dedicating themselves to their studies. Student-athletes make a major sacrifice to participate in sports. Further, this sacrifice that brings immense value to their schools and the NCAA. Student athletes ought to be compensated for that sacrifice.
Speaking of sacrifices, college athletes are at constant risk of injury. A serious on-the-field injury could result in an athlete losing his or her scholarship and the opportunity to play professionally. But let’s put aside the potential financial ramifications of an injury. A 2017 study examined the deceased bodies of former American football players. The findings were shocking: 91% of college football players had the degenerative brain disease CTE. If schools want their athletes to risk their mental and physical well-being, they should pay them according to that risk.
Let’s end with some straight up common sense—athletes need money just like everyone else. Participating in a college sport and keeping up with academic demands makes it virtually impossible for a student-athlete to earn extra money working a part-time job. Paying student-athletes would act as a corrective to this untenable situation.
Should College Athletes be Paid – Additional Resources
We hope you have found our article on whether college athletes should be paid to be insightful. We also want to recommend checking out the following resources:
- D1 vs. D2 vs D3 College Athletics – What is the Difference?
- Best and Loudest College Football Stadiums
- Who Has the Most College Football Championships
- All-Time Women’s College Basketball Scoring
- D1 Colleges in Texas

Dane Gebauer
Dane Gebauer is a writer and teacher living in Miami, FL. He received his MFA in fiction from Columbia University, and his writing has appeared in Complex Magazine and Sinking City Review .
- 2-Year Colleges
- Application Strategies
- Best Colleges by Major
- Best Colleges by State
- Big Picture
- Career & Personality Assessment
- College Essay
- College Search/Knowledge
- College Success
- Costs & Financial Aid
- Dental School Admissions
- Extracurricular Activities
- Graduate School Admissions
- High School Success
- High Schools
- Law School Admissions
- Medical School Admissions
- Navigating the Admissions Process
- Online Learning
- Private High School Spotlight
- Summer Program Spotlight
- Summer Programs
- Test Prep Provider Spotlight

“Innovative and invaluable…use this book as your college lifeline.”
— Lynn O'Shaughnessy
Nationally Recognized College Expert
College Planning in Your Inbox
Join our information-packed monthly newsletter.
I am a... Student Student Parent Counselor Educator Other First Name Last Name Email Address Zip Code Area of Interest Business Computer Science Engineering Fine/Performing Arts Humanities Mathematics STEM Pre-Med Psychology Social Studies/Sciences Submit
College athletes can now get paid, but it's not easy. NFL prospect Braden Fiske shares the biggest do's and don'ts.
- Braden Fiske is a defensive tackle for Florida State projected to be drafted by the NFL.
- He shares his experience trying to make the most of his name, likeness, and image.
- He advises students to network and learn to say no to offers.
Until recently, the National Collegiate Athletic Association barred student athletes from being compensated despite the billions of dollars their efforts were earning for their universities.
That changed on July 1, 2021, when the US Supreme Court ruled that students could be paid through the use of their name, image, and likeness.
Students still cannot be paid by universities, but they can sign deals that allow them to participate in one-off marketing campaigns in exchange for free products, gift cards, or cash payouts. College athletes can also receive money by autographing signs, creating or sharing branded content, making guest appearances, and being a spokesperson for a company or brand.
We're now seeing college athletes from several sports score so-called NIL deals ranging from five to seven figures. For example, the son of LeBron James, Bronny James , is the highest-paid student athlete with an NIL valuation of $4.9 million, according to On3, a college sports news and data company.
But receiving NIL money is not easy and not every college athlete will score a big payout — or any payout in some cases.
To learn more about making the most of the NIL opportunity, Business Insider sat down with Braden Fiske, a defensive lineman at Florida State University who is projected to make millions if he is drafted to the NFL in April, according to news articles and reports.
He has signed several NIL deals since joining the Florida State Seminoles in 2023, and other deals are in the works. He shared what he has learned and what he would have done differently so younger athletes can learn from his experience. He advises college athletes to maintain a steady social media presence, build a team of advisors, invest the earnings wisely, and learn to say no.
This is an as-told-to essay based on a conversation with Fiske that has been edited for length and clarity.
My life-changing deal
I grew up playing football and decided to go to Western Michigan University for the start of my football career. The school was not a major football school, so I transferred to Florida State University for a better opportunity to make it to the NFL . It was a challenging transition, the culture was completely different, I was away from my family and I dealt with shoulder injury when I arrived. But looking back it ended up being one of the best decisions of my life because I signed my first NIL deal through The Battle End, a website that raises money for Florida State University football players.
That 6-figure NIL deal changed my life. I remember a time when I was down to my last $20 and had to decide if I was going to spend it on gas or food . The money I received gave me a peace of mind I did not have previously. It also allowed me to give back to the community by attending guest appearances as well as charity events.
I'm 24 and making the most of the NIL opportunity has been a learning experience, so, I came up with a few tips to help younger athletes get started.
Use social media
I think the biggest thing for guys and gals looking for NIL deals is to start building your brand. Get yourself out there even if it's an uncomfortable situation to post, which it was for me.
Social media is the one thing I didn't really take advantage of early on in my career. I am not really into that type of stuff so it was new ground for me. But my marketer, Nicole, explained how important it is because if you have nothing posted on your Instagram , what are brands supposed to work with? If you don't have a face on your page, how are they going to put your face on their brand?
Building my brand is something I've really started to pick up on this past year. And now I am starting to see the long-term benefits. You start building with a bigger following and once it starts to build, the more attention you get, the more brands want to come work with you.
Build a team
Because I signed my NIL deal through the collective, I did not need to hire an NIL expert to help me with the contract. But some guys definitely have NIL agents to help guide them through that process.
But if you want branding deals, you have to build a team to guide you. Currently, I have a team around me: I have my marketer and agent Nicole Kotler, publicist Daniel Flores, financial advisor Didier Occident, and NFL agent Joshua Grady. I mean, it's a lot of work to find these opportunities, so you need somebody in your corner that's reliable and ready to work. The PR and the marketing side of things is hard work. There's going to be a lot of nos, but once they get that one, yes, any door can open.
Learn to say no
I would say, just stay true to yourself. I know some of these big brands or these big people can kind of try to sway or persuade you in different directions and tell you what you need to do. But I mean, for one, do your own research . Know what your worth is. Don't let somebody put a dollar amount on your head because, at the end of the day, you know what your worth is and you've got to have the ability to say no.
I think for me, early on — even sometimes now — I can admit to it that I'm a people pleaser and it's hard to say no sometimes. But it's only two letters, man! A hundred percent stay true to yourself. Don't let anybody try to sway you.
Invest and spend wisely
A lot of guy's first instinct is to spend, go be the big baller, to go take care of family more than they're financially able to. But next thing they know, they're out of money or tax time comes and they don't have any money to pay back.
I definitely think there needs to be more financial literacy taught to student athletes, especially when they are receiving large amounts of money. It doesn't matter how much you make, even if you're only getting five grand. Whatever it may be, $5,000 or $500,000, you still need to have an understanding of how to manage your money and work with your money and give yourself a plan. That's the biggest thing guys don't have is a plan.
In my case, I used a lot of my NIL money for investments. I put much of that money into a brokerage account in the stock market to set myself up for retirement.
Definitely early on I made a few mistakes. I saw the dollar sign and hit the mall up to go shopping. I love buying shoes, that's one red flag about me. But other than that, I was actually pretty smart with it all and kept my head on straight. It did help that I was already 24 when I got my NIL not 18. If I was 18, I probably would be broke by now.
Get out and meet people
There's so much opportunity in the world, especially when you talk about name, image, and likeness on a deeper level than just making money. The hands I've gotten to shake, the amount of business cards I've gotten to take and just the relationships I made are the biggest takeaways from it all. NIL can open so many doors for people more than just building your pockets up.
The more people you get to meet, the more opportunities are going to arise and doors are going to open. So that's definitely for me, the biggest takeaway is just what people can you meet?
I know whenever I walk into a room, I will introduce myself and start building those relationships right away because you never know how important they will be later in life. You never know who's going to be in a position to help you that they're not in yet.
- Main content
Should College Athletes Be Paid? Essay Example, with Outline
Published by gudwriter on November 23, 2017 November 23, 2017
Here is an essay example on whether college athletes should be paid or not. We explore the pros and cons and conclude that college students have a right to be paid.
Elevate Your Writing with Our Free Writing Tools!
Did you know that we provide a free essay and speech generator, plagiarism checker, summarizer, paraphraser, and other writing tools for free?
If you find yourself struggling to complete your essay, don’t panic. We can help you complete your paper before the deadline through our homework help history . We help all students across the world excel in their academics.
Should College Athletes Be Paid Essay Outline
Introduction.
Thesis: College students should be paid given the nature and organization of college athletics.
Reasons Why College Athletes Should Be Paid
Paragraph 1:
Since college athletics programs are geared towards turning a profit at the end in terms of the revenue generated during the programs, it would only be fair to pay the athletes involved.
- Some of the revenues should be passed to the people who actually cause the fans to come to the pitch, the players.
- The NCCA should consider passing regulations that control the compensation made to coaches so that they do not get paid salaries that are unnecessarily high.
Paragraph 2:
Paying college athletes would also limit or even end corruption from such external influences as agents and boosters.
- Bribing players kills the spirit of whatever game they are involved because they would be playing to the tune of the bribe they receive.
- If they cannot get well compensated by their respective parent institutions, a player would be easily lured into corruption.
Paragraph 3:
Student athletes are subjected to huge workloads that only make it fair that they get paid.
- They are required to regularly attend physical therapy, weight trainings, team meetings, film sessions, and practice for the various sports they take part in.
- They are still required to attend all classes without fail and always post good grades
Reasons Why College Athletes Should Not Be Paid
Paragraph 4:
Paying college athletes would remove their competitive nature and the passion they have for the games they participate in.
- It would culminate into a situation where the only motive the athletes have for playing is money and not the sportsman drive of winning games and trophies.
- The hunger and passion usually shown in college sports would be traded for “lackadaisical plays and half-ass efforts that we sometime see from pros.”
Paragraph 5:
Paying college athletes would also lead to the erosion of the connection between athlete students and college values.
- College sports would be effectively reduced to a market where students who are yet to join college and are talented in sports are won over by the highest bidding institution.
- A student would join a college not for its values in academics and social values but because it offers the best compensation perks in sports.
Intercollegiate athletic competitions continue to grow and gain more prominence in the US. The NCAA and the institutions of higher learning involved continue to make high profits from college athletic programs. College athletes deserve being paid because without them, college sports would not be existent.
Crucial question to explore; describe how you have taken advantage of a significant educational opportunity .
Essay on “Should College Athletes Be Paid?”
College athletics is a prominent phenomenon in the United States of America and is controlled and regulated by the National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA). The Association is non-profit and is in charge of organizing the athletic programs of many higher learning institutions including universities and colleges. From the programs, the Association reaps significant revenues which it distributes to the institutions involved in spite of it being a non-profit organization. Noteworthy, the participants in the athletic programs from which the revenues are accrued are college students. This scenario has led to the emergence of the question of whether or not college students deserve being paid for their participation. This paper argues that college athletes should be paid given the nature and organization of college athletics.
Since college athletics programs are geared towards turning a profit at the end in terms of the revenue generated during the programs, it would only be fair to pay the athletes involved. “A report by CNN’s Chris Isidore in March 2015 named the Louisville Cardinals as the NCAA’s most profitable college basketball team for the 2013-14 season…” (Benjamin, 2017). Additionally, the programs have attracted huge coaching salaries which continue rising, with a basketball coach getting as high as $7.1 million in salaries. So, would it not be prudent to pass some of these revenues to the people who actually cause the fans to come to the pitch, the players? The NCCA should consider passing regulations that control the compensation made to coaches so that they do not get paid salaries that are unnecessarily high. This would allow for some part of the revenue to be channeled to compensating the players and give more meaning to collegiate athletics.
Paying college athletes would also limit or even end corruption from such external influences as agents and boosters. “Over the years we have seen and heard scandals involving players taking money and even point-shaving” (Lemmons, 2017). Bribing players kills the spirit of whatever game they are involved in because they would be playing to the tune of the bribe they would have received. But again, if they cannot get well compensated by their respective parent institutions, a player would be easily lured into corruption. It should be noted that since it is some sort of business, an institution would do all within its reach to enable its college sports team(s) win matches and even trophies, including bribing players of opponent teams. The most effective way of curbing this practice is to entitle every player to a substantial compensation amount for their services to college athletics teams.
Perhaps you maybe interested in understanding some of the mistakes to avoid when crafting an MBA essay .
Further, student athletes are subjected to huge workloads that only make it fair that they get paid. They are required to regularly attend physical therapy, weight trainings, team meetings, film sessions, and practice for the various sports they take part in. On top of all that, they are still required to attend all classes without fail and always post good grades (Thacker, 2017). Is this not too much to ask for from somebody who gets nothing in terms of monetary compensation? Take a situation whereby an athlete gets out of practice at about 7 pm and has got a sit-in paper to take the following day. He or she is expected to study just as hard as every other student in spite of being understandably tired from the practice. It beats logic how a student in such a tight situation is expected to get all their work successfully done. It becomes even less sensible when it is considered that these students still have a social life to make time for (Thacker, 2017). Being paid for this hectic schedule may give them the motivation they need to keep going each day despite the toll the schedule takes on them.
Paying college athletes would remove their competitive nature and the passion they have for the games they participate in. It would culminate into a situation where the only motive the athletes have for playing is money and not the sportsman drive of winning games and trophies. As noted by Lemmons (2017), the hunger and passion usually shown in college sports would be traded for “lackadaisical plays and half-ass efforts that we sometime see from pros.” College sports would morph into full blown business ventures whereby the athletes are like employees and the colleges the employers. Participation in a sport would become more important for students than the actual contribution their participation makes to the sport. Moreover, students would want to take part not in sports in which they are richly talented but in sports that can guarantee better payment.
Paying college athletes would also lead to the erosion of the connection between athlete students and college values. “If a high-school football prodigy reported that he chose Michigan not for its academic quality, tradition, or beautiful campus but because it outbid all other suitors, a connection to the university’s values would be lost” (Yankah, 2015). College sports would be effectively reduced to a market where students who are yet to join college and are talented in sports are won over by the highest bidding institution. The implication is that a student would join a college not for its values in academics and social values but because it offers the best compensation perks in sports. It is clear here that the connection would purely be pegged on sports and payment. This will also turn colleges from grounds of molding future professionals to sports ventures.
Intercollegiate athletic competitions continue to grow and gain more prominence in the US. The NCAA and the institutions of higher learning involved continue to make high profits from college athletic programs. There are even coaches whose salaries for offering their services to college sports teams run into millions of dollars. Yet, those who work so hard so that this revenue can be realized are sidelined when it comes to payment. College athletes deserve being paid because without them, college sports would not be existent. It is thus less logical to continue engaging them while they do not enjoy the proceeds from their work.
Benjamin, J. (2017). “ Is it time to start paying college athletes? Tubby Smith and Gary Williams weigh in” . Forbes . Retrieved 21 November 2017, from https://www.forbes.com/sites/joshbenjamin/2017/04/04/is-it-time-to-start-paying-college-athletes/#72b48b3af71f
Lemmons, M. (2017). “ College athletes getting paid? Here are some pros and cons” . HuffPost . Retrieved 21 November 2017, from https://www.huffingtonpost.com/entry/college-athletes-getting-paid-here-are-some-pros-cons_us_58cfcee0e4b07112b6472f9a
Thacker, D. (2017). Amateurism vs. capitalism: a practical approach to paying college athletes. Seattle Journal for Social Justice , 16(1), 183-216.
Yankah, E. (2015). “ Why N.C.A.A. athletes shouldn’t be paid” . The New Yorker . Retrieved 21 November 2017, from https://www.newyorker.com/news/sporting-scene/why-ncaa-athletes-shouldnt-be-paid

Special offer! Get 20% discount on your first order. Promo code: SAVE20
Related Posts
Free essays and research papers, artificial intelligence argumentative essay – with outline.
Artificial Intelligence Argumentative Essay Outline In recent years, Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become one of the rapidly developing fields and as its capabilities continue to expand, its potential impact on society has become a topic Read more…
Synthesis Essay Example – With Outline
The goal of a synthesis paper is to show that you can handle in-depth research, dissect complex ideas, and present the arguments. Most college or university students have a hard time writing a synthesis essay, Read more…

Examples of Spatial Order – With Outline
A spatial order is an organizational style that helps in the presentation of ideas or things as is in their locations. Most students struggle to understand the meaning of spatial order in writing and have Read more…

IMAGES
COMMENTS
The argumentative essay is one of the most frequently assigned types of essays in both high school and college writing-based courses. Instructors often ask students to write argumentative essays over topics that have "real-world relevance." The question, "Should college athletes be paid?" is one of these real-world relevant topics that can make a great essay subject!
Abstract. After fifty years of Title IX, the gap in participation rates between men and women in college athletics has closed significantly. In 1982, women comprised only 28% of all NCAA college athletes. In 2020, they made up 44%. Despite the progress in participation rates, a substantial gap in resources allocated to men's and women's ...
Intercollegiate sports have long been a part of what makes college appealing. Consequently, athletics programs bring in a lot of money for some colleges. In 2021, the largest college sports organization in the United States, the National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA), generated $18.9 billion in revenue. However, college athletes have...
This study uses new data from the National Sports. and Society Survey ( N = 3,993) to assess recent public opinions about allowing college athletes. to be paid more than it costs them to go to ...
spend on their sport in-season, which are 20 hours per week and 8 hours per week out-of-season. The NCAA has strict guidelines on what activities in a sport they consider countable versus. hours that are not countable, and these hours contribute to the maximum amount of hours. athletes can spend on athletics.
The Case for Paying College Athletes ... John J. Siegfried is a Visiting Research Fellow, School of Economics, University of Adelaide, Adelaide, Australia ; Secretary-Treasurer Emeritus, American Economic ... See historian Taylor Branch's essay in the October 2011 issue of The Atlantic ("The Shame of College Sports"), the documentary DVD ...
College athletes are currently permitted to receive "cost of attendance" stipends (up to approximately $6,000), unlimited education-related benefits, and awards. A 2023 survey found that 67% ...
Based on a workload of 1000 hours per year and an average scholarship value, economist Richard Sheehan (16) calculated the basic hourly wage of a college basketball player at $6.82 and a football player at $7.69. Coaches' hourly wages, on the other hand, ranged from $250-$647 per hour (depending on salary).
College Athletes Deserve to Get Paid. In 2019, the NCAA reported $18.9 billion in total athletics revenue. This money is used to finance a variety of paid positions that support athletics at colleges and universities, including administrators, directors, coaches, and staff, along with other employment less directly tied to sports, such as those ...
Published: April 5, 2024 3:41pm EDT. Ever since July 1, 2021, student-athletes have been able to pursue endorsement deals. But when it comes to getting paid by the universities for which they play ...
Pro 3 College athletes are often valued at more than $1 million, but they (and their families) frequently live below the poverty line. A study by the National Bureau of Economic Research found that the top two college football positions-the quarterback and wide receiver-were worth $2.4 million and $1.3 million per year respectively, while starting men's basketball players in the Power ...
The same 60% now agree that college athletes need monetary compensation. While college athletes' payments are a controversial topic, their hard work and health must be fairly compensated no matter what, and a salary seems to be the best way for it. It is no surprise that doing sports consumes a solid number of things.
In this essay, we will delve into the arguments for and against paying college athletes and explore the potential implications of such a change. Say no to plagiarism. Get a tailor-made essay on
Thus, college athletes should not be paid because they receive their wages in the form of scholarships, college sport cannot be compared with the commercialized professional sports industry, and there is no effective system to provide athletes with salaries according to their efforts and performance. The supporters of the idea to provide ...
Here are three most compelling arguments to support the idea of paying for playing: The time commitment and sacrifices made by athletes. College athletes dedicate countless hours to their sport, often sacrificing their personal lives and academic pursuits. They endure grueling training sessions, travel extensively for competitions, and face ...
One of the good reasons why college athletes should be paid is that it provides athletes to get good exposure. Every Saturday there are a bunch of college football games, top performers get rewarded with awards, for example the player of the week, and that goes for all sports. Exposure is a big thing in sports but some also agree it should be ...
Said universities are likely to lose a chunk of their student body as well. There are more reasons to restrict athletes getting paid than not. It would be unfair, unsafe, and a flat-out bad idea. Works Cited. Johnson, Dennis A., and John Acquaviva. "Point/counterpoint: paying college athletes." The Sport Journal, vol. 15, no. 1, annual 2012.
The model has six domains that should be considered before one can decide whether college athletes should be paid. These are physical capital, emotional capital, individual capital, social capital, intellectual capital, and financial capital. For the purpose of the argument in this paper, financial capital is given a priority.
One of the main arguments in favor of paying college athletes is that they deserve to be compensated for their role in generating revenue for their universities and the National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA). When fans attend a college sports event or purchase team merchandise, they are supporting the team and the entire athletic program.
Overall, most collegiate athletes have expressed a need to find time to enjoy their college experience outside of athletic obligations (Paule and Gilson, 2010). Despite that, because of the increasing demand for excellence in academics and athletics, collegiate athletes' free time with family and friends is often scarce (Paule and Gilson, 2010 ).
Overall, only 1% of student-athletes receive a "full ride" scholarship. Under a little scrutiny, then, the argument that college athletes receive compensation in the form of scholarships falls apart. So college athletes aren't paid via scholarships. Sure, that's a fact, but not an argument as to why college athletes should be paid.
Paying college athletes will increase the competitiveness of various sports programs. Tiered payments given to professional players in sports like basketball motivate them to perform better. The hard work from professional athletes boosts their total wages from sponsorship deals and media events (Steckler, 2015).
The Issue Of Payment For College Athletes. Paying College Athletes ; Student Athletes ; The purpose of this paper is to provide a detailed paper on both sides of the hot topic about college athletes being paid.
For example, the son of LeBron James, Bronny James, is the highest-paid student athlete with an NIL valuation of $4.9 million, according to On3, a college sports news and data company.
Imagine working for countless hours, six days a week, then making multiple performance just so someone else can be paid millions. That is the life of a college athletes. College athletes should be paid and here's why. They are working their butts off so that their team can have a good record and to draw more attention and fans to their arena ...
Paying college athletes would also lead to the erosion of the connection between athlete students and college values. "If a high-school football prodigy reported that he chose Michigan not for its academic quality, tradition, or beautiful campus but because it outbid all other suitors, a connection to the university's values would be lost ...