- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » Research Paper – Structure, Examples and Writing Guide

Research Paper – Structure, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Research Paper
Definition:
Research Paper is a written document that presents the author’s original research, analysis, and interpretation of a specific topic or issue.
It is typically based on Empirical Evidence, and may involve qualitative or quantitative research methods, or a combination of both. The purpose of a research paper is to contribute new knowledge or insights to a particular field of study, and to demonstrate the author’s understanding of the existing literature and theories related to the topic.
Structure of Research Paper
The structure of a research paper typically follows a standard format, consisting of several sections that convey specific information about the research study. The following is a detailed explanation of the structure of a research paper:
The title page contains the title of the paper, the name(s) of the author(s), and the affiliation(s) of the author(s). It also includes the date of submission and possibly, the name of the journal or conference where the paper is to be published.
The abstract is a brief summary of the research paper, typically ranging from 100 to 250 words. It should include the research question, the methods used, the key findings, and the implications of the results. The abstract should be written in a concise and clear manner to allow readers to quickly grasp the essence of the research.
Introduction
The introduction section of a research paper provides background information about the research problem, the research question, and the research objectives. It also outlines the significance of the research, the research gap that it aims to fill, and the approach taken to address the research question. Finally, the introduction section ends with a clear statement of the research hypothesis or research question.
Literature Review
The literature review section of a research paper provides an overview of the existing literature on the topic of study. It includes a critical analysis and synthesis of the literature, highlighting the key concepts, themes, and debates. The literature review should also demonstrate the research gap and how the current study seeks to address it.
The methods section of a research paper describes the research design, the sample selection, the data collection and analysis procedures, and the statistical methods used to analyze the data. This section should provide sufficient detail for other researchers to replicate the study.
The results section presents the findings of the research, using tables, graphs, and figures to illustrate the data. The findings should be presented in a clear and concise manner, with reference to the research question and hypothesis.
The discussion section of a research paper interprets the findings and discusses their implications for the research question, the literature review, and the field of study. It should also address the limitations of the study and suggest future research directions.
The conclusion section summarizes the main findings of the study, restates the research question and hypothesis, and provides a final reflection on the significance of the research.
The references section provides a list of all the sources cited in the paper, following a specific citation style such as APA, MLA or Chicago.
How to Write Research Paper
You can write Research Paper by the following guide:
- Choose a Topic: The first step is to select a topic that interests you and is relevant to your field of study. Brainstorm ideas and narrow down to a research question that is specific and researchable.
- Conduct a Literature Review: The literature review helps you identify the gap in the existing research and provides a basis for your research question. It also helps you to develop a theoretical framework and research hypothesis.
- Develop a Thesis Statement : The thesis statement is the main argument of your research paper. It should be clear, concise and specific to your research question.
- Plan your Research: Develop a research plan that outlines the methods, data sources, and data analysis procedures. This will help you to collect and analyze data effectively.
- Collect and Analyze Data: Collect data using various methods such as surveys, interviews, observations, or experiments. Analyze data using statistical tools or other qualitative methods.
- Organize your Paper : Organize your paper into sections such as Introduction, Literature Review, Methods, Results, Discussion, and Conclusion. Ensure that each section is coherent and follows a logical flow.
- Write your Paper : Start by writing the introduction, followed by the literature review, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion. Ensure that your writing is clear, concise, and follows the required formatting and citation styles.
- Edit and Proofread your Paper: Review your paper for grammar and spelling errors, and ensure that it is well-structured and easy to read. Ask someone else to review your paper to get feedback and suggestions for improvement.
- Cite your Sources: Ensure that you properly cite all sources used in your research paper. This is essential for giving credit to the original authors and avoiding plagiarism.
Research Paper Example
Note : The below example research paper is for illustrative purposes only and is not an actual research paper. Actual research papers may have different structures, contents, and formats depending on the field of study, research question, data collection and analysis methods, and other factors. Students should always consult with their professors or supervisors for specific guidelines and expectations for their research papers.
Research Paper Example sample for Students:
Title: The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health among Young Adults
Abstract: This study aims to investigate the impact of social media use on the mental health of young adults. A literature review was conducted to examine the existing research on the topic. A survey was then administered to 200 university students to collect data on their social media use, mental health status, and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. The results showed that social media use is positively associated with depression, anxiety, and stress. The study also found that social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO (Fear of Missing Out) are significant predictors of mental health problems among young adults.
Introduction: Social media has become an integral part of modern life, particularly among young adults. While social media has many benefits, including increased communication and social connectivity, it has also been associated with negative outcomes, such as addiction, cyberbullying, and mental health problems. This study aims to investigate the impact of social media use on the mental health of young adults.
Literature Review: The literature review highlights the existing research on the impact of social media use on mental health. The review shows that social media use is associated with depression, anxiety, stress, and other mental health problems. The review also identifies the factors that contribute to the negative impact of social media, including social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO.
Methods : A survey was administered to 200 university students to collect data on their social media use, mental health status, and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. The survey included questions on social media use, mental health status (measured using the DASS-21), and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics and regression analysis.
Results : The results showed that social media use is positively associated with depression, anxiety, and stress. The study also found that social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO are significant predictors of mental health problems among young adults.
Discussion : The study’s findings suggest that social media use has a negative impact on the mental health of young adults. The study highlights the need for interventions that address the factors contributing to the negative impact of social media, such as social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO.
Conclusion : In conclusion, social media use has a significant impact on the mental health of young adults. The study’s findings underscore the need for interventions that promote healthy social media use and address the negative outcomes associated with social media use. Future research can explore the effectiveness of interventions aimed at reducing the negative impact of social media on mental health. Additionally, longitudinal studies can investigate the long-term effects of social media use on mental health.
Limitations : The study has some limitations, including the use of self-report measures and a cross-sectional design. The use of self-report measures may result in biased responses, and a cross-sectional design limits the ability to establish causality.
Implications: The study’s findings have implications for mental health professionals, educators, and policymakers. Mental health professionals can use the findings to develop interventions that address the negative impact of social media use on mental health. Educators can incorporate social media literacy into their curriculum to promote healthy social media use among young adults. Policymakers can use the findings to develop policies that protect young adults from the negative outcomes associated with social media use.
References :
- Twenge, J. M., & Campbell, W. K. (2019). Associations between screen time and lower psychological well-being among children and adolescents: Evidence from a population-based study. Preventive medicine reports, 15, 100918.
- Primack, B. A., Shensa, A., Escobar-Viera, C. G., Barrett, E. L., Sidani, J. E., Colditz, J. B., … & James, A. E. (2017). Use of multiple social media platforms and symptoms of depression and anxiety: A nationally-representative study among US young adults. Computers in Human Behavior, 69, 1-9.
- Van der Meer, T. G., & Verhoeven, J. W. (2017). Social media and its impact on academic performance of students. Journal of Information Technology Education: Research, 16, 383-398.
Appendix : The survey used in this study is provided below.
Social Media and Mental Health Survey
- How often do you use social media per day?
- Less than 30 minutes
- 30 minutes to 1 hour
- 1 to 2 hours
- 2 to 4 hours
- More than 4 hours
- Which social media platforms do you use?
- Others (Please specify)
- How often do you experience the following on social media?
- Social comparison (comparing yourself to others)
- Cyberbullying
- Fear of Missing Out (FOMO)
- Have you ever experienced any of the following mental health problems in the past month?
- Do you think social media use has a positive or negative impact on your mental health?
- Very positive
- Somewhat positive
- Somewhat negative
- Very negative
- In your opinion, which factors contribute to the negative impact of social media on mental health?
- Social comparison
- In your opinion, what interventions could be effective in reducing the negative impact of social media on mental health?
- Education on healthy social media use
- Counseling for mental health problems caused by social media
- Social media detox programs
- Regulation of social media use
Thank you for your participation!
Applications of Research Paper
Research papers have several applications in various fields, including:
- Advancing knowledge: Research papers contribute to the advancement of knowledge by generating new insights, theories, and findings that can inform future research and practice. They help to answer important questions, clarify existing knowledge, and identify areas that require further investigation.
- Informing policy: Research papers can inform policy decisions by providing evidence-based recommendations for policymakers. They can help to identify gaps in current policies, evaluate the effectiveness of interventions, and inform the development of new policies and regulations.
- Improving practice: Research papers can improve practice by providing evidence-based guidance for professionals in various fields, including medicine, education, business, and psychology. They can inform the development of best practices, guidelines, and standards of care that can improve outcomes for individuals and organizations.
- Educating students : Research papers are often used as teaching tools in universities and colleges to educate students about research methods, data analysis, and academic writing. They help students to develop critical thinking skills, research skills, and communication skills that are essential for success in many careers.
- Fostering collaboration: Research papers can foster collaboration among researchers, practitioners, and policymakers by providing a platform for sharing knowledge and ideas. They can facilitate interdisciplinary collaborations and partnerships that can lead to innovative solutions to complex problems.
When to Write Research Paper
Research papers are typically written when a person has completed a research project or when they have conducted a study and have obtained data or findings that they want to share with the academic or professional community. Research papers are usually written in academic settings, such as universities, but they can also be written in professional settings, such as research organizations, government agencies, or private companies.
Here are some common situations where a person might need to write a research paper:
- For academic purposes: Students in universities and colleges are often required to write research papers as part of their coursework, particularly in the social sciences, natural sciences, and humanities. Writing research papers helps students to develop research skills, critical thinking skills, and academic writing skills.
- For publication: Researchers often write research papers to publish their findings in academic journals or to present their work at academic conferences. Publishing research papers is an important way to disseminate research findings to the academic community and to establish oneself as an expert in a particular field.
- To inform policy or practice : Researchers may write research papers to inform policy decisions or to improve practice in various fields. Research findings can be used to inform the development of policies, guidelines, and best practices that can improve outcomes for individuals and organizations.
- To share new insights or ideas: Researchers may write research papers to share new insights or ideas with the academic or professional community. They may present new theories, propose new research methods, or challenge existing paradigms in their field.
Purpose of Research Paper
The purpose of a research paper is to present the results of a study or investigation in a clear, concise, and structured manner. Research papers are written to communicate new knowledge, ideas, or findings to a specific audience, such as researchers, scholars, practitioners, or policymakers. The primary purposes of a research paper are:
- To contribute to the body of knowledge : Research papers aim to add new knowledge or insights to a particular field or discipline. They do this by reporting the results of empirical studies, reviewing and synthesizing existing literature, proposing new theories, or providing new perspectives on a topic.
- To inform or persuade: Research papers are written to inform or persuade the reader about a particular issue, topic, or phenomenon. They present evidence and arguments to support their claims and seek to persuade the reader of the validity of their findings or recommendations.
- To advance the field: Research papers seek to advance the field or discipline by identifying gaps in knowledge, proposing new research questions or approaches, or challenging existing assumptions or paradigms. They aim to contribute to ongoing debates and discussions within a field and to stimulate further research and inquiry.
- To demonstrate research skills: Research papers demonstrate the author’s research skills, including their ability to design and conduct a study, collect and analyze data, and interpret and communicate findings. They also demonstrate the author’s ability to critically evaluate existing literature, synthesize information from multiple sources, and write in a clear and structured manner.
Characteristics of Research Paper
Research papers have several characteristics that distinguish them from other forms of academic or professional writing. Here are some common characteristics of research papers:
- Evidence-based: Research papers are based on empirical evidence, which is collected through rigorous research methods such as experiments, surveys, observations, or interviews. They rely on objective data and facts to support their claims and conclusions.
- Structured and organized: Research papers have a clear and logical structure, with sections such as introduction, literature review, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion. They are organized in a way that helps the reader to follow the argument and understand the findings.
- Formal and objective: Research papers are written in a formal and objective tone, with an emphasis on clarity, precision, and accuracy. They avoid subjective language or personal opinions and instead rely on objective data and analysis to support their arguments.
- Citations and references: Research papers include citations and references to acknowledge the sources of information and ideas used in the paper. They use a specific citation style, such as APA, MLA, or Chicago, to ensure consistency and accuracy.
- Peer-reviewed: Research papers are often peer-reviewed, which means they are evaluated by other experts in the field before they are published. Peer-review ensures that the research is of high quality, meets ethical standards, and contributes to the advancement of knowledge in the field.
- Objective and unbiased: Research papers strive to be objective and unbiased in their presentation of the findings. They avoid personal biases or preconceptions and instead rely on the data and analysis to draw conclusions.
Advantages of Research Paper
Research papers have many advantages, both for the individual researcher and for the broader academic and professional community. Here are some advantages of research papers:
- Contribution to knowledge: Research papers contribute to the body of knowledge in a particular field or discipline. They add new information, insights, and perspectives to existing literature and help advance the understanding of a particular phenomenon or issue.
- Opportunity for intellectual growth: Research papers provide an opportunity for intellectual growth for the researcher. They require critical thinking, problem-solving, and creativity, which can help develop the researcher’s skills and knowledge.
- Career advancement: Research papers can help advance the researcher’s career by demonstrating their expertise and contributions to the field. They can also lead to new research opportunities, collaborations, and funding.
- Academic recognition: Research papers can lead to academic recognition in the form of awards, grants, or invitations to speak at conferences or events. They can also contribute to the researcher’s reputation and standing in the field.
- Impact on policy and practice: Research papers can have a significant impact on policy and practice. They can inform policy decisions, guide practice, and lead to changes in laws, regulations, or procedures.
- Advancement of society: Research papers can contribute to the advancement of society by addressing important issues, identifying solutions to problems, and promoting social justice and equality.
Limitations of Research Paper
Research papers also have some limitations that should be considered when interpreting their findings or implications. Here are some common limitations of research papers:
- Limited generalizability: Research findings may not be generalizable to other populations, settings, or contexts. Studies often use specific samples or conditions that may not reflect the broader population or real-world situations.
- Potential for bias : Research papers may be biased due to factors such as sample selection, measurement errors, or researcher biases. It is important to evaluate the quality of the research design and methods used to ensure that the findings are valid and reliable.
- Ethical concerns: Research papers may raise ethical concerns, such as the use of vulnerable populations or invasive procedures. Researchers must adhere to ethical guidelines and obtain informed consent from participants to ensure that the research is conducted in a responsible and respectful manner.
- Limitations of methodology: Research papers may be limited by the methodology used to collect and analyze data. For example, certain research methods may not capture the complexity or nuance of a particular phenomenon, or may not be appropriate for certain research questions.
- Publication bias: Research papers may be subject to publication bias, where positive or significant findings are more likely to be published than negative or non-significant findings. This can skew the overall findings of a particular area of research.
- Time and resource constraints: Research papers may be limited by time and resource constraints, which can affect the quality and scope of the research. Researchers may not have access to certain data or resources, or may be unable to conduct long-term studies due to practical limitations.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

How to Cite Research Paper – All Formats and...

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Paper Format – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Structure of a Research Paper: Tips to Improve Your Manuscript
You’ve spent months or years conducting your academic research. Now it’s time to write your journal article. For some, this can become a daunting task because writing is not their forte. It might become difficult to even start writing. However, once you organize your thoughts and begin writing them down, the overall task will become easier.
We provide some helpful tips for you here.
Organize Your Thoughts
Perhaps one of the most important tasks before you even begin to write is to get organized. By this point, your data is compiled and analyzed. You most likely also have many pages of “notes”. These must also be organized. Fortunately, this is much easier to do than in the past with hand-written notes. Presuming that these tasks are completed, what’s next?
Related: Ready with your title and looking forward to manuscript submission ? Check these journal selection guidelines now!
When suggesting that you organize your thoughts, we mean to take a look at what you have compiled. Ask yourself what you are trying to convey to the reader. What is the most important message from your research? How will your results affect others? Is more research necessary?
Write your answers down and keep them where you can see them while writing. This will help you focus on your goals.
Aim for Clarity
Your paper should be presented as clearly as possible. You want your readers to understand your research. You also do not want them to stop reading because the text is too technical.
Keep in mind that your published research will be available in academic journals all over the world. This means that people of different languages will read it. Moreover, even with scientists, this could present a language barrier. According to a recent article , always remember the following points as you write:
- Clarity : Cleary define terms; avoid nonrelevant information.
- Simplicity : Keep sentence structure simple and direct.
- Accuracy : Represent all data and illustrations accurately.
For example, consider the following sentence:
“Chemical x had an effect on metabolism.”
This is an ambiguous statement. It does not tell the reader much. State the results instead:
“Chemical x increased fat metabolism by 20 percent.”
All scientific research also provide significance of findings, usually presented as defined “P” values. Be sure to explain these findings using descriptive terms. For example, rather than using the words “ significant effect ,” use a more descriptive term, such as “ significant increase .”
For more tips, please also see “Tips and Techniques for Scientific Writing”. In addition, it is very important to have your paper edited by a native English speaking professional editor. There are many editing services available for academic manuscripts and publication support services.
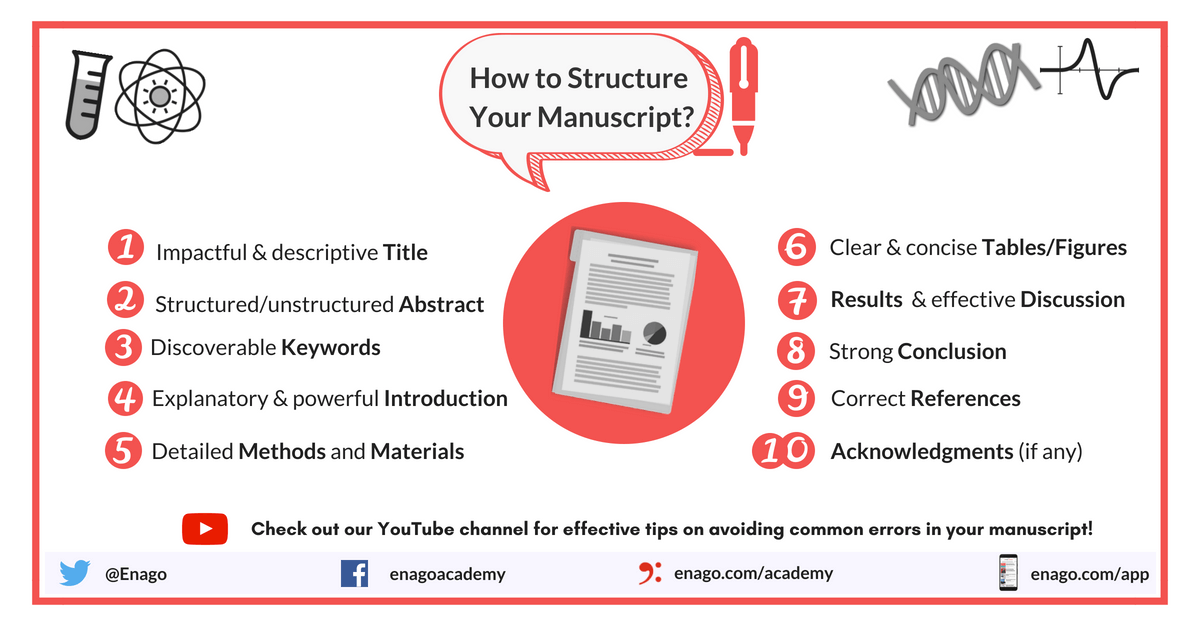
Research Paper Structure
With the above in mind, you can now focus on structure. Scientific papers are organized into specific sections and each has a goal. We have listed them here.
- Your title is the most important part of your paper. It draws the reader in and tells them what you are presenting. Moreover, if you think about the titles of papers that you might browse in a day and which papers you actually read, you’ll agree.
- The title should be clear and interesting otherwise the reader will not continue reading.
- Authors’ names and affiliations are on the title page.
- The abstract is a summary of your research. It is nearly as important as the title because the reader will be able to quickly read through it.
- Most journals, the abstract can become divided into very short sections to guide the reader through the summaries.
- Keep the sentences short and focused.
- Avoid acronyms and citations.
- Include background information on the subject and your objectives here.
- Describe the materials used and include the names and locations of the manufacturers.
- For any animal studies, include where you obtained the animals and a statement of humane treatment.
- Clearly and succinctly explain your methods so that it can be duplicated.
- Criteria for inclusion and exclusion in the study and statistical analyses should be included.
- Discuss your findings here.
- Be careful to not make definitive statements .
- Your results suggest that something is or is not true.
- This is true even when your results prove your hypothesis.
- Discuss what your results mean in this section.
- Discuss any study limitations. Suggest additional studies.
- Acknowledge all contributors.
- All citations in the text must have a corresponding reference.
- Check your author guidelines for format protocols.
- In most cases, your tables and figures appear at the end of your paper or in a separate file.
- The titles (legends) usually become listed after the reference section.
- Be sure that you define each acronym and abbreviation in each table and figure.
Helpful Rules
In their article entitled, “Ten simple rules for structuring papers,” in PLOS Computational Biology , authors Mensh and Kording provided 10 helpful tips as follows:
- Focus on a central contribution.
- Write for those who do not know your work.
- Use the “context-content-conclusion” approach.
- Avoid superfluous information and use parallel structures.
- Summarize your research in the abstract.
- Explain the importance of your research in the introduction.
- Explain your results in a logical sequence and support them with figures and tables.
- Discuss any data gaps and limitations.
- Allocate your time for the most important sections.
- Get feedback from colleagues.
Some of these rules have been briefly discussed above; however, the study done by the authors does provide detailed explanations on all of them.
Helpful Sites
Visit the following links for more helpful information:
- “ Some writing tips for scientific papers ”
- “ How to Structure Your Dissertation ”
- “ Conciseness in Academic Writing: How to Prune Sentences ”
- “ How to Optimize Sentence Length in Academic Writing ”
So, do you follow any additional tips when structuring your research paper ? Share them with us in the comments below!
Thanks for sharing this post. Great information provided. I really appreciate your writing. I like the way you put across your ideas.
Enago, is a good sources of academics presentation and interpretation tools in research writing
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Reporting Research
Beyond Spellcheck: How copyediting guarantees error-free submission
Submitting a manuscript is a complex and often an emotional experience for researchers. Whether it’s…
- Old Webinars
- Webinar Mobile App
How to Find the Right Journal and Fix Your Manuscript Before Submission
Selection of right journal Meets journal standards Plagiarism free manuscripts Rated from reviewer's POV

- Manuscripts & Grants
Research Aims and Objectives: The dynamic duo for successful research
Picture yourself on a road trip without a destination in mind — driving aimlessly, not…

How Academic Editors Can Enhance the Quality of Your Manuscript
Avoiding desk rejection Detecting language errors Conveying your ideas clearly Following technical requirements
Effective Data Presentation for Submission in Top-tier Journals
Importance of presenting research data effectively How to create tables and figures How to avoid…
Top 4 Guidelines for Health and Clinical Research Report
Top 10 Questions for a Complete Literature Review

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

What should universities' stance be on AI tools in research and academic writing?
- Search Menu
- Advance articles
- Editor's Choice
- Supplements
- French Abstracts
- Portuguese Abstracts
- Spanish Abstracts
- Author Guidelines
- Submission Site
- Open Access
- About International Journal for Quality in Health Care
- About the International Society for Quality in Health Care
- Editorial Board
- Advertising and Corporate Services
- Journals Career Network
- Self-Archiving Policy
- Dispatch Dates
- Contact ISQua
- Journals on Oxford Academic
- Books on Oxford Academic

Article Contents
Primacy of the research question, structure of the paper, writing a research article: advice to beginners.
- Article contents
- Figures & tables
- Supplementary Data
Thomas V. Perneger, Patricia M. Hudelson, Writing a research article: advice to beginners, International Journal for Quality in Health Care , Volume 16, Issue 3, June 2004, Pages 191–192, https://doi.org/10.1093/intqhc/mzh053
- Permissions Icon Permissions
Writing research papers does not come naturally to most of us. The typical research paper is a highly codified rhetorical form [ 1 , 2 ]. Knowledge of the rules—some explicit, others implied—goes a long way toward writing a paper that will get accepted in a peer-reviewed journal.
A good research paper addresses a specific research question. The research question—or study objective or main research hypothesis—is the central organizing principle of the paper. Whatever relates to the research question belongs in the paper; the rest doesn’t. This is perhaps obvious when the paper reports on a well planned research project. However, in applied domains such as quality improvement, some papers are written based on projects that were undertaken for operational reasons, and not with the primary aim of producing new knowledge. In such cases, authors should define the main research question a posteriori and design the paper around it.
Generally, only one main research question should be addressed in a paper (secondary but related questions are allowed). If a project allows you to explore several distinct research questions, write several papers. For instance, if you measured the impact of obtaining written consent on patient satisfaction at a specialized clinic using a newly developed questionnaire, you may want to write one paper on the questionnaire development and validation, and another on the impact of the intervention. The idea is not to split results into ‘least publishable units’, a practice that is rightly decried, but rather into ‘optimally publishable units’.
What is a good research question? The key attributes are: (i) specificity; (ii) originality or novelty; and (iii) general relevance to a broad scientific community. The research question should be precise and not merely identify a general area of inquiry. It can often (but not always) be expressed in terms of a possible association between X and Y in a population Z, for example ‘we examined whether providing patients about to be discharged from the hospital with written information about their medications would improve their compliance with the treatment 1 month later’. A study does not necessarily have to break completely new ground, but it should extend previous knowledge in a useful way, or alternatively refute existing knowledge. Finally, the question should be of interest to others who work in the same scientific area. The latter requirement is more challenging for those who work in applied science than for basic scientists. While it may safely be assumed that the human genome is the same worldwide, whether the results of a local quality improvement project have wider relevance requires careful consideration and argument.
Once the research question is clearly defined, writing the paper becomes considerably easier. The paper will ask the question, then answer it. The key to successful scientific writing is getting the structure of the paper right. The basic structure of a typical research paper is the sequence of Introduction, Methods, Results, and Discussion (sometimes abbreviated as IMRAD). Each section addresses a different objective. The authors state: (i) the problem they intend to address—in other terms, the research question—in the Introduction; (ii) what they did to answer the question in the Methods section; (iii) what they observed in the Results section; and (iv) what they think the results mean in the Discussion.
In turn, each basic section addresses several topics, and may be divided into subsections (Table 1 ). In the Introduction, the authors should explain the rationale and background to the study. What is the research question, and why is it important to ask it? While it is neither necessary nor desirable to provide a full-blown review of the literature as a prelude to the study, it is helpful to situate the study within some larger field of enquiry. The research question should always be spelled out, and not merely left for the reader to guess.
Typical structure of a research paper
The Methods section should provide the readers with sufficient detail about the study methods to be able to reproduce the study if so desired. Thus, this section should be specific, concrete, technical, and fairly detailed. The study setting, the sampling strategy used, instruments, data collection methods, and analysis strategies should be described. In the case of qualitative research studies, it is also useful to tell the reader which research tradition the study utilizes and to link the choice of methodological strategies with the research goals [ 3 ].
The Results section is typically fairly straightforward and factual. All results that relate to the research question should be given in detail, including simple counts and percentages. Resist the temptation to demonstrate analytic ability and the richness of the dataset by providing numerous tables of non-essential results.
The Discussion section allows the most freedom. This is why the Discussion is the most difficult to write, and is often the weakest part of a paper. Structured Discussion sections have been proposed by some journal editors [ 4 ]. While strict adherence to such rules may not be necessary, following a plan such as that proposed in Table 1 may help the novice writer stay on track.
References should be used wisely. Key assertions should be referenced, as well as the methods and instruments used. However, unless the paper is a comprehensive review of a topic, there is no need to be exhaustive. Also, references to unpublished work, to documents in the grey literature (technical reports), or to any source that the reader will have difficulty finding or understanding should be avoided.
Having the structure of the paper in place is a good start. However, there are many details that have to be attended to while writing. An obvious recommendation is to read, and follow, the instructions to authors published by the journal (typically found on the journal’s website). Another concerns non-native writers of English: do have a native speaker edit the manuscript. A paper usually goes through several drafts before it is submitted. When revising a paper, it is useful to keep an eye out for the most common mistakes (Table 2 ). If you avoid all those, your paper should be in good shape.
Common mistakes seen in manuscripts submitted to this journal
Huth EJ . How to Write and Publish Papers in the Medical Sciences , 2nd edition. Baltimore, MD: Williams & Wilkins, 1990 .
Browner WS . Publishing and Presenting Clinical Research . Baltimore, MD: Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins, 1999 .
Devers KJ , Frankel RM. Getting qualitative research published. Educ Health 2001 ; 14 : 109 –117.
Docherty M , Smith R. The case for structuring the discussion of scientific papers. Br Med J 1999 ; 318 : 1224 –1225.
Email alerts
Citing articles via.
- Recommend to your Library
Affiliations
- Online ISSN 1464-3677
- Print ISSN 1353-4505
- Copyright © 2024 International Society for Quality in Health Care and Oxford University Press
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Institutional account management
- Rights and permissions
- Get help with access
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.
- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers

Research Paper Structure: A Comprehensive Guide

Table of Contents
Writing a research paper is a daunting task, but understanding its structure can make the process more manageable and lead to a well-organized, coherent paper. This article provides a step-by-step approach to crafting a research paper, ensuring your work is not only informative but also structured for maximum impact.
Introduction
In any form of written communication, content structure plays a vital role in facilitating understanding. A well-structured research paper provides a framework that guides readers through the content, ensuring they grasp the main points efficiently. Without a clear structure, readers may become lost or confused, leading to a loss of interest and a failure to comprehend the intended message.
When it comes to research papers, structure is particularly important due to the complexity of the subject matter. Research papers often involve presenting and analyzing large amounts of data, theories, and arguments. Without a well-defined structure, readers may struggle to navigate through this information overload, resulting in a fragmented understanding of the topic.
How Structure Enhances Clarity and Coherence
A well-structured research paper not only helps readers follow the flow of ideas but also enhances the clarity and coherence of the content. By organizing information into sections, paragraphs, and sentences, researchers can present their thoughts logically and systematically. This logical organization allows readers to easily connect ideas, resulting in a more coherent and engaging reading experience.
One way in which structure enhances clarity is by providing a clear roadmap for readers to follow. By dividing the research paper into sections and subsections, researchers can guide readers through the different aspects of the topic. This allows readers to anticipate the flow of information and mentally prepare themselves for the upcoming content.
In addition, a well-structured research paper ensures that each paragraph serves a specific purpose and contributes to the overall argument or analysis. By clearly defining the main idea of each paragraph and providing supporting evidence or examples, researchers can avoid confusion and ensure that their points are effectively communicated.
Moreover, a structured research paper helps researchers maintain a consistent focus throughout their writing. By organizing their thoughts and ideas, researchers can ensure that they stay on track and avoid going off on tangents. This not only improves the clarity of the paper but also helps maintain the reader's interest and engagement.
Components of a Research Paper Structure
Title and abstract: the initial impression.
The title and abstract are the first elements readers encounter when accessing a research paper. The title should be concise, informative, and capture the essence of the study. For example, a title like "Exploring the Impact of Climate Change on Biodiversity in Tropical Rainforests" immediately conveys the subject matter and scope of the research. The abstract, on the other hand, provides a brief overview of the research problem, methodology, and findings, enticing readers to delve further into the paper. In a well-crafted abstract, researchers may highlight key results or implications of the study, giving readers a glimpse into the value of the research.
Introduction: Setting the Stage
The introduction serves as an invitation for readers to engage with the research paper. It should provide background information on the topic, highlight the research problem, and present the research question or thesis statement. By establishing the context and relevance of the study, the introduction piques readers' interest and prepares them for the content to follow. For instance, in a study on the impact of social media on mental health, the introduction may discuss the rise of social media platforms and the growing concerns about its effects on individuals' well-being. This contextual information helps readers understand the significance of the research and why it is worth exploring further.
Furthermore, the introduction may also outline the objectives of the study, stating what the researchers aim to achieve through their research. This helps readers understand the purpose and scope of the study, setting clear expectations for what they can expect to learn from the paper.
Literature Review: Building the Foundation
The literature review is a critical component of a research paper, as it demonstrates the researcher's understanding of existing knowledge and provides a foundation for the study. It involves reviewing and analyzing relevant scholarly articles, books, and other sources to identify gaps in research and establish the need for the current study. In a comprehensive literature review, researchers may summarize key findings from previous studies, identify areas of disagreement or controversy, and highlight the limitations of existing research.
Moreover, the literature review may also discuss theoretical frameworks or conceptual models that have been used in previous studies. By examining these frameworks, researchers can identify the theoretical underpinnings of their study and explain how their research fits within the broader academic discourse. This not only adds depth to the research paper but also helps readers understand the theoretical context in which the study is situated.
Methodology: Detailing the Process
The research design, data collection methods, and analysis techniques used in the study are described in the methodology section. It should be presented clearly and concisely, allowing readers to understand how the research was conducted and evaluated. A well-described methodology ensures the study's reliability and allows other researchers to replicate or build upon the findings.
Within the methodology section, researchers may provide a detailed description of the study population or sample, explaining how participants were selected and why they were chosen. This helps readers understand the generalizability of the findings and the extent to which they can be applied to a broader population.
In addition, researchers may also discuss any ethical considerations that were taken into account during the study. This could include obtaining informed consent from participants, ensuring confidentiality and anonymity, and following ethical guidelines set by relevant professional organizations. By addressing these ethical concerns, researchers demonstrate their commitment to conducting research in an ethical and responsible manner.
Results: Presenting the Findings
The results section represents the study findings. Researchers should organize their results in a logical manner, using tables, graphs, and descriptive statistics to support their conclusions. The results should be presented objectively, without interpretation or analysis. For instance, for a study on the effectiveness of a new drug in treating a specific medical condition, researchers may present the percentage of patients who experienced positive outcomes, along with any statistical significance associated with the results.
In addition to presenting the main findings, researchers may also include supplementary data or sub-analyses that provide further insights into the research question. This could include subgroup analyses, sensitivity analyses, or additional statistical tests that help explore the robustness of the findings.
Discussion: Interpreting the Results
In the discussion section, researchers analyze and interpret the results in light of the research question or thesis statement. This is an opportunity to explore the implications of the findings, compare them with existing literature, and offer insights into the broader significance of the study. The discussion should be supported by evidence and it is advised to avoid speculation.
Researchers may also discuss the limitations of their study, acknowledging any potential biases or confounding factors that may have influenced the results. By openly addressing these limitations, researchers demonstrate their commitment to transparency and scientific rigor.
Conclusion: Wrapping It Up
The conclusion provides a concise summary of the research paper, restating the main findings and their implications. It should also reflect on the significance of the study and suggest potential avenues for future research. A well-written conclusion leaves a lasting impression on readers, highlighting the importance of the research and its potential impact. By summarizing the key takeaways from the study, researchers ensure that readers walk away with a clear understanding of the research's contribution to the field.
Tips for Organizing Your Research Paper
Starting with a strong thesis statement.
A strong and clear thesis statement serves as the backbone of your research paper. It provides focus and direction, guiding the organization of ideas and arguments throughout the paper. Take the time to craft a well-defined thesis statement that encapsulates the core message of your research.
Creating an Outline: The Blueprint of Your Paper
An outline acts as a blueprint for your research paper, ensuring a logical flow of ideas and preventing disorganization. Divide your paper into sections and subsections, noting the main points and supporting arguments for each. This will help you maintain coherence and clarity throughout the writing process.
Balancing Depth and Breadth in Your Paper
When organizing your research paper, strike a balance between delving deeply into specific points and providing a broader overview. While depth is important for thorough analysis, too much detail can overwhelm readers. Consider your target audience and their level of familiarity with the topic to determine the appropriate level of depth and breadth for your paper.
By understanding the importance of research paper structure and implementing effective organizational strategies, researchers can ensure their work is accessible, engaging, and influential. A well-structured research paper not only communicates ideas clearly but also enhances the overall impact of the study. With careful planning and attention to detail, researchers can master the art of structuring their research papers, making them a valuable contribution to their field of study.
You might also like

Cybersecurity in Higher Education: Safeguarding Students and Faculty Data

How To Write An Argumentative Essay

Beyond Google Scholar: Why SciSpace is the best alternative
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Research Essays: Overview
The further you go in college, the more research you will do, and the more research essays you will write. Being able to collect and synthesize research into our own writing are among the most important skills we learn in college. Finding and using research sources are skills that you will use throughout your professional and personal lives. For this reason, it’s important that you learn early in college to successfully compose an academic research essay.
Composing a complex and thoroughly researched essay provides opportunities for you to develop your critical thinking skills. No research essay can be successful without careful consideration of how evidence fits together into a cohesive whole. Writing an effective research essay also enhances our credibility as writers and communicators. Once you’re able to connect the research dots in order to make logical points about some larger significance, then you are better equipped to understand the world around you as well as help others understand the world around them, too.
Academic research essays are formal essays that engage with complex questions, research, and issues. When you write a research essay, you will go beyond just talking about a topic and transition to making informed claims about a topic. Readers expect that an academic research essays will have a clear focus, address a significant issue, include insightful research evidence, and explore the implications of the issue being addressed.
Before you begin writing a research essay, however, you need to conduct some research. The below chapters will help you better understand and navigate the research process:
- Starting Your Research Process
- Search Strategies
- Evaluating Information
- The Ethics of Information
Key Features
A singular focus and clear perspective.
Many writers enter college believing that broad, generalized topics are easier to research and write about: this could not be farther from the truth. Choosing a broad topic gives you, as well as your reader, no clear direction. You will find yourself aimlessly sifting through thousands of search results, struggling to pull disparate sources together into a logically organized essay. These challenges can be avoided by deciding on a singular focus and clear perspective early in the process.
Developing a Singular Focus and Clear Perspective
Imagine you are interested in animal conservation. That’s a good start, but far too broad of a topic for a research essay. From this initial interest, you might:
- Identify a specific type of animal. Let’s go with lions.
- Identify a specific type of lion. Let’s choose African lions.
At this point, you have a singular focus: African lions. But you’re not done. African lions is still too broad for a research topic. You need a clear perspective. From here, you might:
- Identify a serious threat to the lions. Let’s go with illegal hunting.
- Develop a perspective on the illegal hunting of African lions. Let’s try the impact of illegal hunting on African lion populations.
Now you would have a topic with singular focus and clear perspective that is researchable and will be much easier to organize into an effective essay.
As you develop your own research essay topic, use the above walkthrough to help develop a singular focus and clear perspective.
Formal Writing Style
While some of the writing you do in college will be more informal, such as personal essays or online discussions, academic research essays require us to adopt a formal writing style as we engage with complex questions, research, and issues. If you write your research essay the way you write text messages or how you chat with your friends, your readers will find your essay to be much less credible. In order to be taken seriously, you want your writing to come off as professional and authoritative rather than casual and underdeveloped.
Informative Tone and Objective Stance
While you will write argumentatively at various times throughout your college career, your purpose when writing an academic research essay is typically to inform, and this means that your stance should be objective. Since your goal is to inform, you will need to make clear claims about why readers need to know this information. As you write a research essay, you may provide new information on a known subject, provide historical context, clear up misconceptions, introduce the audience to something unknown, or develop a profile of a person, place, or object. Even though you should remain objective, research essays are usually written for a specific audience and purpose, so it’s your job to define the purpose and decide what kinds of information your audience needs and how best to present that information.
Credible Evidence That Suits Your Purpose
Without taking the necessary time to seek out and collect credible evidence about your topic, your research essay is unlikely to successfully inform readers. Academic research essays should rely almost exclusively on evidence in each section and paragraph, and the credibility and relevance of that evidence should be made clear to your reader. It’s your job to find not just any evidence related to your topic, but the evidence that suits your purpose for your audience. Your evidence, the information you use to support your main points, will most likely include a mix of sources from the college’s library collection as well as credible materials from the internet. Also keep in mind that you will, and should, find many more sources during your research process than you ultimately use in your essay. The first sources we find are rarely the best sources to use. It’s your job to identify which sources are are most suited for your topic and purpose.

A Logical Structure
Research essays need to be logically organized with a clear structure that creates connections between the different parts of your essay. When organizing a research essay, you will need to make careful rhetorical choices about the order in which you introduce ideas, define key terms, provide background information, and address key issues for your audience. Readers expect that research essays will guide them through the information logically, and your structure will be how you ensure that readers understand how topics and subtopics relate to your main focus.
As we write research essays, it’s vital that we use a detailed citation process in order to demonstrate to our readers where our supporting evidence comes from and why it’s credible. This process will involve citations at the end of your essay, but also, and just as importantly, in-text citations throughout your essay. Using in-text citations and signal phrases is necessary to successfully guide readers through the information you have collected in your essay. Without in-text citations, readers are completely lost as to where the information came from, why it’s credible, and how it connects to the main topic.
Drafting Checklists
These questions should help guide you through the stages of drafting your research essay.
- How will you develop a singular focus and clear perspective on your topic?
- What are some subtopics or related ideas you might need to learn more about during your research?
- In other words, who do you want to share this information with? And why should they care about your research?
- Are there key terms or concepts you will need to define or describe?
- Where should try to find this evidence?
- Why should your audience care about this evidence?
- Why those sources and not others?
- How will you use those sources in your essay?
- What subtopics might you cover throughout your essay?
- How might your start your essay?
- How might you end your essay?
Writing and Revising
- Does your title or intro paragraph effectively establish your focus and perspective?
- Have you clearly made connections between your topic and subtopics?
- Have you presented your research in the best way to guide readers through the information?
- Does your conclusion offer readers intriguing final takeaways to consider?
- Would your readers be confused at any point?
- Would readers find your tone and style to be professional and authoritative? Or too casual and informal?
- Have you avoided using any slang or other informal language that would detract from your credibility?
- Have you written your essay from an objective stance that avoids using personal opinions or arguing a position?
- Have you created correct works cited entries for all your sources?
- Have you used signal phrases and in-text citations to integrate sources into your essay?
- Would readers question the credibility or relevance of any of your sources?
Sources Used to Create this Chapter
Parts of this chapter were remixed from:
- First-Year Composition: Writing as Inquiry and Argumentation , by Jackie Hoermann-Elliott and Kathy Quesenbury, which was published under a CC-BY 4.0 license.
Starting the Journey: An Intro to College Writing Copyright © by Leonard Owens III; Tim Bishop; and Scott Ortolano is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- U.S. Locations
- UMGC Europe
- Learn Online
- Find Answers
- 855-655-8682
- Current Students
Online Guide to Writing and Research
The research process, explore more of umgc.
- Online Guide to Writing
Structuring the Research Paper
Formal research structure.
These are the primary purposes for formal research:
enter the discourse, or conversation, of other writers and scholars in your field
learn how others in your field use primary and secondary resources
find and understand raw data and information

For the formal academic research assignment, consider an organizational pattern typically used for primary academic research. The pattern includes the following: introduction, methods, results, discussion, and conclusions/recommendations.
Usually, research papers flow from the general to the specific and back to the general in their organization. The introduction uses a general-to-specific movement in its organization, establishing the thesis and setting the context for the conversation. The methods and results sections are more detailed and specific, providing support for the generalizations made in the introduction. The discussion section moves toward an increasingly more general discussion of the subject, leading to the conclusions and recommendations, which then generalize the conversation again.
Sections of a Formal Structure
The introduction section.
Many students will find that writing a structured introduction gets them started and gives them the focus needed to significantly improve their entire paper.
Introductions usually have three parts:
presentation of the problem statement, the topic, or the research inquiry
purpose and focus of your paper
summary or overview of the writer’s position or arguments
In the first part of the introduction—the presentation of the problem or the research inquiry—state the problem or express it so that the question is implied. Then, sketch the background on the problem and review the literature on it to give your readers a context that shows them how your research inquiry fits into the conversation currently ongoing in your subject area.
In the second part of the introduction, state your purpose and focus. Here, you may even present your actual thesis. Sometimes your purpose statement can take the place of the thesis by letting your reader know your intentions.
The third part of the introduction, the summary or overview of the paper, briefly leads readers through the discussion, forecasting the main ideas and giving readers a blueprint for the paper.
The following example provides a blueprint for a well-organized introduction.
Example of an Introduction
Entrepreneurial Marketing: The Critical Difference
In an article in the Harvard Business Review, John A. Welsh and Jerry F. White remind us that “a small business is not a little big business.” An entrepreneur is not a multinational conglomerate but a profit-seeking individual. To survive, he must have a different outlook and must apply different principles to his endeavors than does the president of a large or even medium-sized corporation. Not only does the scale of small and big businesses differ, but small businesses also suffer from what the Harvard Business Review article calls “resource poverty.” This is a problem and opportunity that requires an entirely different approach to marketing. Where large ad budgets are not necessary or feasible, where expensive ad production squanders limited capital, where every marketing dollar must do the work of two dollars, if not five dollars or even ten, where a person’s company, capital, and material well-being are all on the line—that is, where guerrilla marketing can save the day and secure the bottom line (Levinson, 1984, p. 9).
By reviewing the introductions to research articles in the discipline in which you are writing your research paper, you can get an idea of what is considered the norm for that discipline. Study several of these before you begin your paper so that you know what may be expected. If you are unsure of the kind of introduction your paper needs, ask your professor for more information. The introduction is normally written in present tense.
THE METHODS SECTION
The methods section of your research paper should describe in detail what methodology and special materials if any, you used to think through or perform your research. You should include any materials you used or designed for yourself, such as questionnaires or interview questions, to generate data or information for your research paper. You want to include any methodologies that are specific to your particular field of study, such as lab procedures for a lab experiment or data-gathering instruments for field research. The methods section is usually written in the past tense.
THE RESULTS SECTION
How you present the results of your research depends on what kind of research you did, your subject matter, and your readers’ expectations.
Quantitative information —data that can be measured—can be presented systematically and economically in tables, charts, and graphs. Quantitative information includes quantities and comparisons of sets of data.
Qualitative information , which includes brief descriptions, explanations, or instructions, can also be presented in prose tables. This kind of descriptive or explanatory information, however, is often presented in essay-like prose or even lists.
There are specific conventions for creating tables, charts, and graphs and organizing the information they contain. In general, you should use them only when you are sure they will enlighten your readers rather than confuse them. In the accompanying explanation and discussion, always refer to the graphic by number and explain specifically what you are referring to; you can also provide a caption for the graphic. The rule of thumb for presenting a graphic is first to introduce it by name, show it, and then interpret it. The results section is usually written in the past tense.
THE DISCUSSION SECTION
Your discussion section should generalize what you have learned from your research. One way to generalize is to explain the consequences or meaning of your results and then make your points that support and refer back to the statements you made in your introduction. Your discussion should be organized so that it relates directly to your thesis. You want to avoid introducing new ideas here or discussing tangential issues not directly related to the exploration and discovery of your thesis. The discussion section, along with the introduction, is usually written in the present tense.
THE CONCLUSIONS AND RECOMMENDATIONS SECTION
Your conclusion ties your research to your thesis, binding together all the main ideas in your thinking and writing. By presenting the logical outcome of your research and thinking, your conclusion answers your research inquiry for your reader. Your conclusions should relate directly to the ideas presented in your introduction section and should not present any new ideas.
You may be asked to present your recommendations separately in your research assignment. If so, you will want to add some elements to your conclusion section. For example, you may be asked to recommend a course of action, make a prediction, propose a solution to a problem, offer a judgment, or speculate on the implications and consequences of your ideas. The conclusions and recommendations section is usually written in the present tense.
Key Takeaways
- For the formal academic research assignment, consider an organizational pattern typically used for primary academic research.
- The pattern includes the following: introduction, methods, results, discussion, and conclusions/recommendations.
Mailing Address: 3501 University Blvd. East, Adelphi, MD 20783 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License . © 2022 UMGC. All links to external sites were verified at the time of publication. UMGC is not responsible for the validity or integrity of information located at external sites.
Table of Contents: Online Guide to Writing
Chapter 1: College Writing
How Does College Writing Differ from Workplace Writing?
What Is College Writing?
Why So Much Emphasis on Writing?
Chapter 2: The Writing Process
Doing Exploratory Research
Getting from Notes to Your Draft
Introduction
Prewriting - Techniques to Get Started - Mining Your Intuition
Prewriting: Targeting Your Audience
Prewriting: Techniques to Get Started
Prewriting: Understanding Your Assignment
Rewriting: Being Your Own Critic
Rewriting: Creating a Revision Strategy
Rewriting: Getting Feedback
Rewriting: The Final Draft
Techniques to Get Started - Outlining
Techniques to Get Started - Using Systematic Techniques
Thesis Statement and Controlling Idea
Writing: Getting from Notes to Your Draft - Freewriting
Writing: Getting from Notes to Your Draft - Summarizing Your Ideas
Writing: Outlining What You Will Write
Chapter 3: Thinking Strategies
A Word About Style, Voice, and Tone
A Word About Style, Voice, and Tone: Style Through Vocabulary and Diction
Critical Strategies and Writing
Critical Strategies and Writing: Analysis
Critical Strategies and Writing: Evaluation
Critical Strategies and Writing: Persuasion
Critical Strategies and Writing: Synthesis
Developing a Paper Using Strategies
Kinds of Assignments You Will Write
Patterns for Presenting Information
Patterns for Presenting Information: Critiques
Patterns for Presenting Information: Discussing Raw Data
Patterns for Presenting Information: General-to-Specific Pattern
Patterns for Presenting Information: Problem-Cause-Solution Pattern
Patterns for Presenting Information: Specific-to-General Pattern
Patterns for Presenting Information: Summaries and Abstracts
Supporting with Research and Examples
Writing Essay Examinations
Writing Essay Examinations: Make Your Answer Relevant and Complete
Writing Essay Examinations: Organize Thinking Before Writing
Writing Essay Examinations: Read and Understand the Question
Chapter 4: The Research Process
Planning and Writing a Research Paper
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Ask a Research Question
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Cite Sources
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Collect Evidence
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Decide Your Point of View, or Role, for Your Research
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Draw Conclusions
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Find a Topic and Get an Overview
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Manage Your Resources
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Outline
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Survey the Literature
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Work Your Sources into Your Research Writing
Research Resources: Where Are Research Resources Found? - Human Resources
Research Resources: What Are Research Resources?
Research Resources: Where Are Research Resources Found?
Research Resources: Where Are Research Resources Found? - Electronic Resources
Research Resources: Where Are Research Resources Found? - Print Resources
Structuring the Research Paper: Formal Research Structure
Structuring the Research Paper: Informal Research Structure
The Nature of Research
The Research Assignment: How Should Research Sources Be Evaluated?
The Research Assignment: When Is Research Needed?
The Research Assignment: Why Perform Research?
Chapter 5: Academic Integrity
Academic Integrity
Giving Credit to Sources
Giving Credit to Sources: Copyright Laws
Giving Credit to Sources: Documentation
Giving Credit to Sources: Style Guides
Integrating Sources
Practicing Academic Integrity
Practicing Academic Integrity: Keeping Accurate Records
Practicing Academic Integrity: Managing Source Material
Practicing Academic Integrity: Managing Source Material - Paraphrasing Your Source
Practicing Academic Integrity: Managing Source Material - Quoting Your Source
Practicing Academic Integrity: Managing Source Material - Summarizing Your Sources
Types of Documentation
Types of Documentation: Bibliographies and Source Lists
Types of Documentation: Citing World Wide Web Sources
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations - APA Style
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations - CSE/CBE Style
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations - Chicago Style
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations - MLA Style
Types of Documentation: Note Citations
Chapter 6: Using Library Resources
Finding Library Resources
Chapter 7: Assessing Your Writing
How Is Writing Graded?
How Is Writing Graded?: A General Assessment Tool
The Draft Stage
The Draft Stage: The First Draft
The Draft Stage: The Revision Process and the Final Draft
The Draft Stage: Using Feedback
The Research Stage
Using Assessment to Improve Your Writing
Chapter 8: Other Frequently Assigned Papers
Reviews and Reaction Papers: Article and Book Reviews
Reviews and Reaction Papers: Reaction Papers
Writing Arguments
Writing Arguments: Adapting the Argument Structure
Writing Arguments: Purposes of Argument
Writing Arguments: References to Consult for Writing Arguments
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Anticipate Active Opposition
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Determine Your Organization
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Develop Your Argument
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Introduce Your Argument
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - State Your Thesis or Proposition
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Write Your Conclusion
Writing Arguments: Types of Argument
Appendix A: Books to Help Improve Your Writing
Dictionaries
General Style Manuals
Researching on the Internet
Special Style Manuals
Writing Handbooks
Appendix B: Collaborative Writing and Peer Reviewing
Collaborative Writing: Assignments to Accompany the Group Project
Collaborative Writing: Informal Progress Report
Collaborative Writing: Issues to Resolve
Collaborative Writing: Methodology
Collaborative Writing: Peer Evaluation
Collaborative Writing: Tasks of Collaborative Writing Group Members
Collaborative Writing: Writing Plan
General Introduction
Peer Reviewing
Appendix C: Developing an Improvement Plan
Working with Your Instructor’s Comments and Grades
Appendix D: Writing Plan and Project Schedule
Devising a Writing Project Plan and Schedule
Reviewing Your Plan with Others
By using our website you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more about how we use cookies by reading our Privacy Policy .
- Search This Site All UCSD Sites Faculty/Staff Search Term
- Contact & Directions
- Climate Statement
- Cognitive Behavioral Neuroscience
- Cognitive Psychology
- Developmental Psychology
- Social Psychology
- Adjunct Faculty
- Non-Senate Instructors
- Researchers
- Psychology Grads
- Affiliated Grads
- New and Prospective Students
- Honors Program
- Experiential Learning
- Programs & Events
- Psi Chi / Psychology Club
- Prospective PhD Students
- Current PhD Students
- Area Brown Bags
- Colloquium Series
- Anderson Distinguished Lecture Series
- Speaker Videos
- Undergraduate Program
- Academic and Writing Resources
Writing Research Papers
- Research Paper Structure
Whether you are writing a B.S. Degree Research Paper or completing a research report for a Psychology course, it is highly likely that you will need to organize your research paper in accordance with American Psychological Association (APA) guidelines. Here we discuss the structure of research papers according to APA style.
Major Sections of a Research Paper in APA Style
A complete research paper in APA style that is reporting on experimental research will typically contain a Title page, Abstract, Introduction, Methods, Results, Discussion, and References sections. 1 Many will also contain Figures and Tables and some will have an Appendix or Appendices. These sections are detailed as follows (for a more in-depth guide, please refer to " How to Write a Research Paper in APA Style ”, a comprehensive guide developed by Prof. Emma Geller). 2
What is this paper called and who wrote it? – the first page of the paper; this includes the name of the paper, a “running head”, authors, and institutional affiliation of the authors. The institutional affiliation is usually listed in an Author Note that is placed towards the bottom of the title page. In some cases, the Author Note also contains an acknowledgment of any funding support and of any individuals that assisted with the research project.
One-paragraph summary of the entire study – typically no more than 250 words in length (and in many cases it is well shorter than that), the Abstract provides an overview of the study.
Introduction
What is the topic and why is it worth studying? – the first major section of text in the paper, the Introduction commonly describes the topic under investigation, summarizes or discusses relevant prior research (for related details, please see the Writing Literature Reviews section of this website), identifies unresolved issues that the current research will address, and provides an overview of the research that is to be described in greater detail in the sections to follow.
What did you do? – a section which details how the research was performed. It typically features a description of the participants/subjects that were involved, the study design, the materials that were used, and the study procedure. If there were multiple experiments, then each experiment may require a separate Methods section. A rule of thumb is that the Methods section should be sufficiently detailed for another researcher to duplicate your research.
What did you find? – a section which describes the data that was collected and the results of any statistical tests that were performed. It may also be prefaced by a description of the analysis procedure that was used. If there were multiple experiments, then each experiment may require a separate Results section.
What is the significance of your results? – the final major section of text in the paper. The Discussion commonly features a summary of the results that were obtained in the study, describes how those results address the topic under investigation and/or the issues that the research was designed to address, and may expand upon the implications of those findings. Limitations and directions for future research are also commonly addressed.
List of articles and any books cited – an alphabetized list of the sources that are cited in the paper (by last name of the first author of each source). Each reference should follow specific APA guidelines regarding author names, dates, article titles, journal titles, journal volume numbers, page numbers, book publishers, publisher locations, websites, and so on (for more information, please see the Citing References in APA Style page of this website).
Tables and Figures
Graphs and data (optional in some cases) – depending on the type of research being performed, there may be Tables and/or Figures (however, in some cases, there may be neither). In APA style, each Table and each Figure is placed on a separate page and all Tables and Figures are included after the References. Tables are included first, followed by Figures. However, for some journals and undergraduate research papers (such as the B.S. Research Paper or Honors Thesis), Tables and Figures may be embedded in the text (depending on the instructor’s or editor’s policies; for more details, see "Deviations from APA Style" below).
Supplementary information (optional) – in some cases, additional information that is not critical to understanding the research paper, such as a list of experiment stimuli, details of a secondary analysis, or programming code, is provided. This is often placed in an Appendix.
Variations of Research Papers in APA Style
Although the major sections described above are common to most research papers written in APA style, there are variations on that pattern. These variations include:
- Literature reviews – when a paper is reviewing prior published research and not presenting new empirical research itself (such as in a review article, and particularly a qualitative review), then the authors may forgo any Methods and Results sections. Instead, there is a different structure such as an Introduction section followed by sections for each of the different aspects of the body of research being reviewed, and then perhaps a Discussion section.
- Multi-experiment papers – when there are multiple experiments, it is common to follow the Introduction with an Experiment 1 section, itself containing Methods, Results, and Discussion subsections. Then there is an Experiment 2 section with a similar structure, an Experiment 3 section with a similar structure, and so on until all experiments are covered. Towards the end of the paper there is a General Discussion section followed by References. Additionally, in multi-experiment papers, it is common for the Results and Discussion subsections for individual experiments to be combined into single “Results and Discussion” sections.
Departures from APA Style
In some cases, official APA style might not be followed (however, be sure to check with your editor, instructor, or other sources before deviating from standards of the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association). Such deviations may include:
- Placement of Tables and Figures – in some cases, to make reading through the paper easier, Tables and/or Figures are embedded in the text (for example, having a bar graph placed in the relevant Results section). The embedding of Tables and/or Figures in the text is one of the most common deviations from APA style (and is commonly allowed in B.S. Degree Research Papers and Honors Theses; however you should check with your instructor, supervisor, or editor first).
- Incomplete research – sometimes a B.S. Degree Research Paper in this department is written about research that is currently being planned or is in progress. In those circumstances, sometimes only an Introduction and Methods section, followed by References, is included (that is, in cases where the research itself has not formally begun). In other cases, preliminary results are presented and noted as such in the Results section (such as in cases where the study is underway but not complete), and the Discussion section includes caveats about the in-progress nature of the research. Again, you should check with your instructor, supervisor, or editor first.
- Class assignments – in some classes in this department, an assignment must be written in APA style but is not exactly a traditional research paper (for instance, a student asked to write about an article that they read, and to write that report in APA style). In that case, the structure of the paper might approximate the typical sections of a research paper in APA style, but not entirely. You should check with your instructor for further guidelines.
Workshops and Downloadable Resources
- For in-person discussion of the process of writing research papers, please consider attending this department’s “Writing Research Papers” workshop (for dates and times, please check the undergraduate workshops calendar).
Downloadable Resources
- How to Write APA Style Research Papers (a comprehensive guide) [ PDF ]
- Tips for Writing APA Style Research Papers (a brief summary) [ PDF ]
- Example APA Style Research Paper (for B.S. Degree – empirical research) [ PDF ]
- Example APA Style Research Paper (for B.S. Degree – literature review) [ PDF ]
Further Resources
How-To Videos
- Writing Research Paper Videos
APA Journal Article Reporting Guidelines
- Appelbaum, M., Cooper, H., Kline, R. B., Mayo-Wilson, E., Nezu, A. M., & Rao, S. M. (2018). Journal article reporting standards for quantitative research in psychology: The APA Publications and Communications Board task force report . American Psychologist , 73 (1), 3.
- Levitt, H. M., Bamberg, M., Creswell, J. W., Frost, D. M., Josselson, R., & Suárez-Orozco, C. (2018). Journal article reporting standards for qualitative primary, qualitative meta-analytic, and mixed methods research in psychology: The APA Publications and Communications Board task force report . American Psychologist , 73 (1), 26.
External Resources
- Formatting APA Style Papers in Microsoft Word
- How to Write an APA Style Research Paper from Hamilton University
- WikiHow Guide to Writing APA Research Papers
- Sample APA Formatted Paper with Comments
- Sample APA Formatted Paper
- Tips for Writing a Paper in APA Style
1 VandenBos, G. R. (Ed). (2010). Publication manual of the American Psychological Association (6th ed.) (pp. 41-60). Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
2 geller, e. (2018). how to write an apa-style research report . [instructional materials]. , prepared by s. c. pan for ucsd psychology.
Back to top
- Formatting Research Papers
- Using Databases and Finding References
- What Types of References Are Appropriate?
- Evaluating References and Taking Notes
- Citing References
- Writing a Literature Review
- Writing Process and Revising
- Improving Scientific Writing
- Academic Integrity and Avoiding Plagiarism
- Writing Research Papers Videos
- If you are writing in a new discipline, you should always make sure to ask about conventions and expectations for introductions, just as you would for any other aspect of the essay. For example, while it may be acceptable to write a two-paragraph (or longer) introduction for your papers in some courses, instructors in other disciplines, such as those in some Government courses, may expect a shorter introduction that includes a preview of the argument that will follow.
- In some disciplines (Government, Economics, and others), it’s common to offer an overview in the introduction of what points you will make in your essay. In other disciplines, you will not be expected to provide this overview in your introduction.
- Avoid writing a very general opening sentence. While it may be true that “Since the dawn of time, people have been telling love stories,” it won’t help you explain what’s interesting about your topic.
- Avoid writing a “funnel” introduction in which you begin with a very broad statement about a topic and move to a narrow statement about that topic. Broad generalizations about a topic will not add to your readers’ understanding of your specific essay topic.
- Avoid beginning with a dictionary definition of a term or concept you will be writing about. If the concept is complicated or unfamiliar to your readers, you will need to define it in detail later in your essay. If it’s not complicated, you can assume your readers already know the definition.
- Avoid offering too much detail in your introduction that a reader could better understand later in the paper.
- picture_as_pdf Introductions
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Write a Research Essay
Last Updated: January 12, 2023 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Michelle Golden, PhD . Michelle Golden is an English teacher in Athens, Georgia. She received her MA in Language Arts Teacher Education in 2008 and received her PhD in English from Georgia State University in 2015. There are 11 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 383,568 times.
Research essays are extremely common assignments in high school, college, and graduate school, and are not unheard of in middle school. If you are a student, chances are you will sooner or later be faced with the task of researching a topic and writing a paper about it. Knowing how to efficiently and successfully do simple research, synthesize information, and clearly present it in essay form will save you many hours and a lot of frustration.
Researching a Topic

- Be sure to stay within the guidelines you are given by your teacher or professor. For example, if you are free to choose a topic but the general theme must fall under human biology, do not write your essay on plant photosynthesis.
- Stick with topics that are not overly complicated, especially if the subject is not something you plan to continue studying. There's no need to make things harder on yourself!

- Specialty books; these can be found at your local public or school library. A book published on your topic is a great resource and will likely be one of your most reliable options for finding quality information. They also contain lists of references where you can look for more information.
- Academic journals; these are periodicals devoted to scholarly research on a specific field of study. Articles in academic journals are written by experts in that field and scrutinized by other professionals to ensure their accuracy. These are great options if you need to find detailed, sophisticated information on your topic; avoid these if you are only writing a general overview.
- Online encyclopedias; the most reliable information on the internet can be found in online encyclopedias like Encyclopedia.com and Britannica.com. While online wikis can be very helpful, they sometimes contain unverified information that you should probably not rely upon as your primary resources.
- Expert interviews; if possible, interview an expert in the subject of your research. Experts can be professionals working in the field you are studying, professors with advanced degrees in the subject of interest, etc.

- Organize your notes by sub-topic to keep them orderly and so you can easily find references when you are writing.
- If you are using books or physical copies of magazines or journals, use sticky tabs to mark pages or paragraphs where you found useful information. You might even want to number these tabs to correspond with numbers on your note sheet for easy reference.
- By keeping your notes brief and simple, you can make them easier to understand and reference while writing. Don't make your notes so long and detailed that they essentially copy what's already written in your sources, as this won't be helpful to you.

- Sometimes the objective of your research will be obvious to you before you even begin researching the topic; other times, you may have to do a bit of reading before you can determine the direction you want your essay to take.
- If you have an objective in mind from the start, you can incorporate this into online searches about your topic in order to find the most relevant resources. For example, if your objective is to outline the environmental hazards of hydraulic fracturing practices, search for that exact phrase rather than just "hydraulic fracturing."

- Avoid asking your teacher to give you a topic. Unless your topic was assigned to you in the first place, part of the assignment is for you to choose a topic relevant to the broader theme of the class or unit. By asking your teacher to do this for you, you risk admitting laziness or incompetence.
- If you have a few topics in mind but are not sure how to develop objectives for some of them, your teacher can help with this. Plan to discuss your options with your teacher and come to a decision yourself rather than having him or her choose the topic for you from several options.
Organizing your Essay

- Consider what background information is necessary to contextualize your research topic. What questions might the reader have right out of the gate? How do you want the reader to think about the topic? Answering these kinds of questions can help you figure out how to set up your argument.
- Match your paper sections to the objective(s) of your writing. For example, if you are trying to present two sides of a debate, create a section for each and then divide them up according to the aspects of each argument you want to address.

- An outline can be as detailed or general as you want, so long as it helps you figure out how to construct the essay. Some people like to include a few sentences under each heading in their outline to create a sort of "mini-essay" before they begin writing. Others find that a simple ordered list of topics is sufficient. Do whatever works best for you.
- If you have time, write your outline a day or two before you start writing and come back to it several times. This will give you an opportunity to think about how the pieces of your essay will best fit together. Rearrange things in your outline as many times as you want until you have a structure you are happy with.

- Style guides tell you exactly how to quote passages, cite references, construct works cited sections, etc. If you are assigned a specific format, you must take care to adhere to guidelines for text formatting and citations.
- Some computer programs (such as EndNote) allow you to construct a library of resources which you can then set to a specific format type; then you can automatically insert in-text citations from your library and populate a references section at the end of the document. This is an easy way to make sure your citations match your assigned style format.

- You may wish to start by simply assigning yourself a certain number of pages per day. Divide the number of pages you are required to write by the number of days you have to finish the essay; this is the number of pages (minimum) that you must complete each day in order to pace yourself evenly.
- If possible, leave a buffer of at least one day between finishing your paper and the due date. This will allow you to review your finished product and edit it for errors. This will also help in case something comes up that slows your writing progress.
Writing your Essay

- Keep your introduction relatively short. For most papers, one or two paragraphs will suffice. For really long essays, you may need to expand this.
- Don't assume your reader already knows the basics of the topic unless it truly is a matter of common knowledge. For example, you probably don't need to explain in your introduction what biology is, but you should define less general terms such as "eukaryote" or "polypeptide chain."

- You may need to include a special section at the beginning of the essay body for background information on your topic. Alternatively, you can consider moving this to the introductory section, but only if your essay is short and only minimal background discussion is needed.
- This is the part of your paper where organization and structure are most important. Arrange sections within the body so that they flow logically and the reader is introduced to ideas and sub-topics before they are discussed further.
- Depending upon the length and detail of your paper, the end of the body might contain a discussion of findings. This kind of section serves to wrap up your main findings but does not explicitly state your conclusions (which should come in the final section of the essay).
- Avoid repetition in the essay body. Keep your writing concise, yet with sufficient detail to address your objective(s) or research question(s).

- Always use quotation marks when using exact quotes from another source. If someone already said or wrote the words you are using, you must quote them this way! Place your in-text citation at the end of the quote.
- To include someone else's ideas in your essay without directly quoting them, you can restate the information in your own words; this is called paraphrasing. Although this does not require quotation marks, it should still be accompanied by an in-text citation.

- Except for very long essays, keep your conclusion short and to the point. You should aim for one or two paragraphs, if possible.
- Conclusions should directly correspond to research discussed in the essay body. In other words, make sure your conclusions logically connect to the rest of your essay and provide explanations when necessary.
- If your topic is complex and involves lots of details, you should consider including a brief summary of the main points of your research in your conclusion.

- Making changes to the discussion and conclusion sections instead of the introduction often requires a less extensive rewrite. Doing this also prevents you from removing anything from the beginning of your essay that could accidentally make subsequent portions of your writing seem out of place.
- It is okay to revise your thesis once you've finished the first draft of your essay! People's views often change once they've done research on a topic. Just make sure you don't end up straying too far from your assigned topic if you do this.
- You don't necessarily need to wait until you've finished your entire draft to do this step. In fact, it is a good idea to revisit your thesis regularly as you write. This can save you a lot of time in the end by helping you keep your essay content on track.

- Computer software such as EndNote is available for making citation organization as easy and quick as possible. You can create a reference library and link it to your document, adding in-text citations as you write; the program creates a formatted works cited section at the end of your document.
- Be aware of the formatting requirements of your chosen style guide for works cited sections and in-text citations. Reference library programs like EndNote have hundreds of pre-loaded formats to choose from.

- Create a catchy title. Waiting until you have finished your essay before choosing a title ensures that it will closely match the content of your essay. Research papers don't always take on the shape we expect them to, and it's easier to match your title to your essay than vice-versa.
- Read through your paper to identify and rework sentences or paragraphs that are confusing or unclear. Each section of your paper should have a clear focus and purpose; if any of yours seem not to meet these expectations, either rewrite or discard them.
- Review your works cited section (at the end of your essay) to ensure that it conforms to the standards of your chosen or assigned style format. You should at least make sure that the style is consistent throughout this section.
- Run a spell checker on your entire document to catch any spelling or grammar mistakes you may not have noticed during your read-through. All modern word processing programs include this function.

- Note that revising your draft is not the same as proofreading it. Revisions are done to make sure the content and substantive ideas are solid; editing is done to check for spelling and grammar errors. Revisions are arguably a more important part of writing a good paper.
- You may want to have a friend, classmate, or family member read your first draft and give you feedback. This can be immensely helpful when trying to decide how to improve upon your first version of the essay.
- Except in extreme cases, avoid a complete rewrite of your first draft. This will most likely be counterproductive and will waste a lot of time. Your first draft is probably already pretty good -- it likely just needs some tweaking before it is ready to submit.
Community Q&A
- Avoid use of the word "I" in research essay writing, even when conveying your personal opinion about a subject. This makes your writing sound biased and narrow in scope. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- Even if there is a minimum number of paragraphs, always do 3 or 4 more paragraphs more than needed, so you can always get a good grade. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

- Never plagiarize the work of others! Passing off others' writing as your own can land you in a lot of trouble and is usually grounds for failing an assignment or class. Thanks Helpful 12 Not Helpful 1
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/common_writing_assignments/research_papers/choosing_a_topic.html
- ↑ https://libguides.mit.edu/select-topic
- ↑ https://www.indeed.com/career-advice/career-development/research-objectives
- ↑ https://www.hunter.cuny.edu/rwc/handouts/the-writing-process-1/organization/Organizing-an-Essay
- ↑ https://www.lynchburg.edu/academics/writing-center/wilmer-writing-center-online-writing-lab/the-writing-process/organizing-your-paper/
- ↑ https://www.mla.org/MLA-Style
- ↑ http://www.apastyle.org/
- ↑ https://writing.wisc.edu/Handbook/PlanResearchPaper.html
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/apa6_style/apa_formatting_and_style_guide/in_text_citations_the_basics.html
- ↑ https://opentextbc.ca/writingforsuccess/chapter/chapter-12-peer-review-and-final-revisions/
- ↑ https://openoregon.pressbooks.pub/wrd/back-matter/creating-a-works-cited-page/
About This Article

The best way to write a research essay is to find sources, like specialty books, academic journals, and online encyclopedias, about your topic. Take notes as you research, and make sure you note which page and book you got your notes from. Create an outline for the paper that details your argument, various sections, and primary points for each section. Then, write an introduction, build the body of the essay, and state your conclusion. Cite your sources along the way, and follow the assigned format, like APA or MLA, if applicable. To learn more from our co-author with an English Ph.D. about how to choose a thesis statement for your research paper, keep reading! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Nov 18, 2018
Did this article help you?
Jun 11, 2017
Christina Wonodi
Oct 12, 2016
Caroline Scott
Jan 28, 2017
Fhatuwani Musinyali
Mar 14, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Level up your tech skills and stay ahead of the curve
Library Instruction
Structure of typical research article.
The basic structure of a typical research paper includes Introduction, Methods, Results, and Discussion. Each section addresses a different objective.
- the problem they intend to address -- in other words, the research question -- in the Introduction ;
- what they did to answer the question in Methodology ;
- what they observed in Results ; and
- what they think the results mean in Discussion .
A substantial study will sometimes include a literature review section which discusses previous works on the topic. The basic structure is outlined below:
- Author and author's professional affiliation is identified
- Introduction
- Literature review section (a discussion about what other scholars have written on the topic)
- Methodology section (methods of data gathering are explained)
- Discussion section
- Conclusions
- Reference list with citations (sources of information used in the article)
Thanks for helping us improve csumb.edu. Spot a broken link, typo, or didn't find something where you expected to? Let us know. We'll use your feedback to improve this page, and the site overall.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Elements of a Research Essay
Stephanie Ojeda Ponce
This section is an overview of the elements or parts of a research essay. Scholarly essays are long. There are several different styles of research essays and each have their own structure. For the argument-driven research essay, these are the main elements:
- Purpose or research question
- Your claim or thesis.
- One or more reasons for your thesis.
- Evidence for each reason.
- Others’ objections, counterarguments, or alternative solutions.
- Your acknowledgment of others’ objections, counterarguments, or alternative solutions.
- Your response to others’ objections, counterarguments, or alternative solutions.
The Purpose or Goal
Sometimes your professor will give you the research question, but probably more often you will need to develop your own research topic. Even though you are likely writing an essay for an assignment or as part of a class, you are also developing your own purpose for the research and writing. This part of the essay may not be written down, but it can be helpful to keep in mind a purpose or overall question. That question might even be something you answer through your research, but don’t have
Examples: Purpose and Goal for Research Essays
- How do at least some animals’ bones help control their weight?
- Did the death of his beloved daughter have any effect on the writings of Mark Twain?
Your Claim or Thesis
You write the claim or thesis–it doesn’t come directly from a source. Instead, it is the conclusion you come to in answer to your question after you’ve read/listened to/viewed some sources. So it is a statement, not a question or a hypothesis that you plan to prove or disprove with your research.
After you’ve read/listened to/viewed more sources, you may need to change your thesis. That happens all the time–not because you did anything wrong but because you learned more.
Examples: Claims (or Theses) for Hypothetical Essays or Term Papers
- Bone cells monitor whether more or less weight is pressing down on the skeleton and send biochemical signals to appetite centers in their brains to turn appetite down or up, accordingly.
- Mark Twain wrote more urgently and with less humor during the four years immediately after the death of his daughter.
One or More Reasons
You write what you believe makes your claim or thesis (the answer to your research question) true. That’s your reason or reasons. Each reason is a summary statement of evidence you found in your research. The kinds of evidence considered convincing varies by discipline, so you will be looking at different sources, depending on your discipline. How many reasons you need depends on how complex your thesis and subject matter are, what you found in your sources, and how long your essay or research paper must be. It’s always a good idea to write your reasons in a way that is easy for your audience to understand and be persuaded by.
Examples: Reasons in Hypothetical Essays or Term Papers
- Animals (including humans) have a biological tendency to regain any weight that they lose and lose any weight that they gain, seemingly in an effort to maintain whatever weight they have sustained for some time. Skeletons are logical places where any gains or losses could be noted, and recent studies seem to show that osteocytes (a kind of bone cell) are involved in whether appetites go up or down after weight gain or loss.
- My content analysis and a comparison of publication rates four years before and after Mark Twain’s daughter died indicate that his writing was more urgent and less humorous for four years after. It is reasonable to conclude that her death caused that change.
Evidence for Each Reason
You write this also. This is the evidence you summarized earlier as each reason your thesis is true. You will be directly quoting, paraphrasing, and summarizing your sources to make the case that your answer to your research question is correct, or at least reasonable.
Examples: Evidence for Reasons in Hypothetical Essays or Term Papers
- Report the results of studies about osteocyctes’ possible effect on weight grain or loss.
- Report the results of your comparison of writing content and publication rate before and after Twain’s daughter’s death.
Others’ Objections, Counterarguments, or Alternative Solutions
Do any of your sources not agree with your thesis? You’ll have to bring those up in your research paper. In addition, put yourself in your readers’ shoes. What might they not find logical in your argument? In other words, which reason(s) and corresponding evidence might they find lacking? Did you find clues to what these could be in your sources? Or maybe you can imagine them thinking some aspect of what you think is evidence doesn’t make sense.
Examples: Objections, Counterarguments, or Alternative Solutions in Hypothetical Essays or Term Papers
- Imagine that some readers might think: The hormone leptin is released by fat cells when they are added to animals’ bodies so it is leptin that tells appetite centers to turn down when weight is gained.
- Imagine that some readers might think: Computerized content analysis tools are sort of blunt instruments and shouldn’t be used to do precise work like this.
Your Acknowledgement of Others’ Objections, Counterarguments, or Alternative Solutions
So what will you write to bring up each of those objections, counterarguments, and alternative solutions? Some examples:
- I can imagine skeptics wanting to point out…
- Perhaps some readers would say…
- I think those who come from XYZ would differ with me…
It all depends on what objections, counterarguments, and alternative solutions your audience or your imagination come up with.
Examples: Acknowledgement of Others’ Objections, Counterarguments, or Alternative Solutions in Hypothetical Essays or Term Papers:
- Some readers may point out that the hormone leptin, which is released by fat cells, signals appetite centers to lower the appetite when weight is gained.
- Readers may think that a computerized content analysis tool cannot do justice to the subtleties of text.
Response to Others’ Objections, Counterarguments, or Alternative Solutions
You must write your response to each objection, counterargument, or alternative solution brought up or that you’ve thought of. (You’re likely to have found clues for what to say in your sources.) The reason you have to include this is that you can’t very easily convince your audience until you show them how your claim stacks up against the opinions and reasoning of other people who don’t at the moment agree with you.
Examples: Response to Others’ Objections, Counterarguments, or Alternative Solutions in Hypothetical Essays or Term Papers:
- But leptin must not be the entire system, since many animals do keep on the new weight.
- Unlike other content tools, the XYZ Content Analysis Measure is able to take into account an author’s tone.
Adaptations
This page has been adapted from Where you Get the Components from Choosing & Using Sources: A Guide to Academic Research Copyright © 2015 by Teaching & Learning, Ohio State University Libraries. CC BY 4.0 DEED .
Reading and Writing Research for Undergraduates Copyright © 2023 by Stephanie Ojeda Ponce is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Structure of a Research Paper

Structure of a Research Paper: IMRaD Format
I. The Title Page
- Title: Tells the reader what to expect in the paper.
- Author(s): Most papers are written by one or two primary authors. The remaining authors have reviewed the work and/or aided in study design or data analysis (International Committee of Medical Editors, 1997). Check the Instructions to Authors for the target journal for specifics about authorship.
- Keywords [according to the journal]
- Corresponding Author: Full name and affiliation for the primary contact author for persons who have questions about the research.
- Financial & Equipment Support [if needed]: Specific information about organizations, agencies, or companies that supported the research.
- Conflicts of Interest [if needed]: List and explain any conflicts of interest.
II. Abstract: “Structured abstract” has become the standard for research papers (introduction, objective, methods, results and conclusions), while reviews, case reports and other articles have non-structured abstracts. The abstract should be a summary/synopsis of the paper.
III. Introduction: The “why did you do the study”; setting the scene or laying the foundation or background for the paper.
IV. Methods: The “how did you do the study.” Describe the --
- Context and setting of the study
- Specify the study design
- Population (patients, etc. if applicable)
- Sampling strategy
- Intervention (if applicable)
- Identify the main study variables
- Data collection instruments and procedures
- Outline analysis methods
V. Results: The “what did you find” --
- Report on data collection and/or recruitment
- Participants (demographic, clinical condition, etc.)
- Present key findings with respect to the central research question
- Secondary findings (secondary outcomes, subgroup analyses, etc.)
VI. Discussion: Place for interpreting the results
- Main findings of the study
- Discuss the main results with reference to previous research
- Policy and practice implications of the results
- Strengths and limitations of the study
VII. Conclusions: [occasionally optional or not required]. Do not reiterate the data or discussion. Can state hunches, inferences or speculations. Offer perspectives for future work.
VIII. Acknowledgements: Names people who contributed to the work, but did not contribute sufficiently to earn authorship. You must have permission from any individuals mentioned in the acknowledgements sections.
IX. References: Complete citations for any articles or other materials referenced in the text of the article.
- IMRD Cheatsheet (Carnegie Mellon) pdf.
- Adewasi, D. (2021 June 14). What Is IMRaD? IMRaD Format in Simple Terms! . Scientific-editing.info.
- Nair, P.K.R., Nair, V.D. (2014). Organization of a Research Paper: The IMRAD Format. In: Scientific Writing and Communication in Agriculture and Natural Resources. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-03101-9_2
- Sollaci, L. B., & Pereira, M. G. (2004). The introduction, methods, results, and discussion (IMRAD) structure: a fifty-year survey. Journal of the Medical Library Association : JMLA , 92 (3), 364–367.
- Cuschieri, S., Grech, V., & Savona-Ventura, C. (2019). WASP (Write a Scientific Paper): Structuring a scientific paper. Early human development , 128 , 114–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2018.09.011
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Research Roundup: How the Pandemic Changed Management
- Mark C. Bolino,
- Jacob M. Whitney,
- Sarah E. Henry

Lessons from 69 articles published in top management and applied psychology journals.
Researchers recently reviewed 69 articles focused on the management implications of the Covid-19 pandemic that were published between March 2020 and July 2023 in top journals in management and applied psychology. The review highlights the numerous ways in which employees, teams, leaders, organizations, and societies were impacted and offers lessons for managing through future pandemics or other events of mass disruption.
The recent pandemic disrupted life as we know it, including for employees and organizations around the world. To understand such changes, we recently reviewed 69 articles focused on the management implications of the Covid-19 pandemic. These papers were published between March 2020 and July 2023 in top journals in management and applied psychology.
- Mark C. Bolino is the David L. Boren Professor and the Michael F. Price Chair in International Business at the University of Oklahoma’s Price College of Business. His research focuses on understanding how an organization can inspire its employees to go the extra mile without compromising their personal well-being.
- JW Jacob M. Whitney is a doctoral candidate in management at the University of Oklahoma’s Price College of Business and an incoming assistant professor at Kennesaw State University. His research interests include leadership, teams, and organizational citizenship behavior.
- SH Sarah E. Henry is a doctoral candidate in management at the University of Oklahoma’s Price College of Business and an incoming assistant professor at the University of South Florida. Her research interests include organizational citizenship behaviors, workplace interpersonal dynamics, and international management.
Partner Center

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Definition: Research Paper is a written document that presents the author's original research, analysis, and interpretation of a specific topic or issue. It is typically based on Empirical Evidence, and may involve qualitative or quantitative research methods, or a combination of both. The purpose of a research paper is to contribute new ...
Develop a thesis statement. Create a research paper outline. Write a first draft of the research paper. Write the introduction. Write a compelling body of text. Write the conclusion. The second draft. The revision process. Research paper checklist.
The Structure of an Academic Paper www.communicate.gse.harvard.edu Academic papers are like hourglasses. The paper opens at its widest point; the introduction makes broad connections to the reader's interests, hoping they will be persuaded to follow along, then gradually narrows to a tight, focused, thesis statement.
The basic structure of an essay always consists of an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. But for many students, the most difficult part of structuring an essay is deciding how to organize information within the body. This article provides useful templates and tips to help you outline your essay, make decisions about your structure, and ...
Use the "context-content-conclusion" approach. Avoid superfluous information and use parallel structures. Summarize your research in the abstract. Explain the importance of your research in the introduction. Explain your results in a logical sequence and support them with figures and tables.
Writing research papers does not come naturally to most of us. The typical research paper is a highly codified rhetorical form [1,2]. Knowledge of the rule ... The basic structure of a typical research paper is the sequence of Introduction, Methods, Results, and Discussion (sometimes abbreviated as IMRAD). Each section addresses a different ...
Table of contents. Step 1: Introduce your topic. Step 2: Describe the background. Step 3: Establish your research problem. Step 4: Specify your objective (s) Step 5: Map out your paper. Research paper introduction examples. Frequently asked questions about the research paper introduction.
A well-structured research paper not only helps readers follow the flow of ideas but also enhances the clarity and coherence of the content. By organizing information into sections, paragraphs, and sentences, researchers can present their thoughts logically and systematically. This logical organization allows readers to easily connect ideas ...
A Logical Structure. Research essays need to be logically organized with a clear structure that creates connections between the different parts of your essay. When organizing a research essay, you will need to make careful rhetorical choices about the order in which you introduce ideas, define key terms, provide background information, and ...
Formal Research Structure. These are the primary purposes for formal research: enter the discourse, or conversation, of other writers and scholars in your field. learn how others in your field use primary and secondary resources. find and understand raw data and information. For the formal academic research assignment, consider an ...
A complete research paper in APA style that is reporting on experimental research will typically contain a Title page, Abstract, Introduction, Methods, Results, Discussion, and References sections. 1 Many will also contain Figures and Tables and some will have an Appendix or Appendices. These sections are detailed as follows (for a more in ...
In general, your introductions should contain the following elements: When you're writing an essay, it's helpful to think about what your reader needs to know in order to follow your argument. Your introduction should include enough information so that readers can understand the context for your thesis. For example, if you are analyzing ...
Download Article. 1. Break up your essay into sub-topics. You will probably need to address several distinct aspects of your research topic in your essay. This is an important tactic for producing a well-organized research essay because it avoids 'stream of consciousness' writing, which typically lacks order.
Structure of Typical Research Article. The basic structure of a typical research paper includes Introduction, Methods, Results, and Discussion. Each section addresses a different objective. the problem they intend to address -- in other words, the research question -- in the Introduction; what they think the results mean in Discussion.
words, your goal is to find the "best structure" for your argument. Treat the outline as if it were a puzzle that you are trying to put together. In a puzzle, each piece has only one appropriate place. The same should be true of your paper. If it's easy to shift around your ideas - if paragraph five and paragraph nine could be switched around and
Example: BODY PARAGRAPH 1. First point. Sub-point. Sub-point of sub-point 1. Essentially the same as the alphanumeric outline, but with the text written in full sentences rather than short points. Example: First body paragraph of the research paper. First point of evidence to support the main argument.
Elements of a Research Essay Stephanie Ojeda Ponce. This section is an overview of the elements or parts of a research essay. Scholarly essays are long. There are several different styles of research essays and each have their own structure. For the argument-driven research essay, these are the main elements: Purpose or research question
Abstract: "Structured abstract" has become the standard for research papers (introduction, objective, methods, results and conclusions), while reviews, case reports and other articles have non-structured abstracts. The abstract should be a summary/synopsis of the paper. III. Introduction: The "why did you do the study"; setting the ...
Table of contents. Step 1: Identify the paragraph's purpose. Step 2: Show why the paragraph is relevant. Step 3: Give evidence. Step 4: Explain or interpret the evidence. Step 5: Conclude the paragraph. Step 6: Read through the whole paragraph. When to start a new paragraph.
Join us to learn the foundations of academic writing for a research paper. During the workshop, you will: Learn how to build an effective argument; Understand the differences between a topic sentence and a thesis statement; Gain experience in composing an outline and using transitions; Analyze a five-paragraph essay for organization and ...
The structure of an essay is divided into an introduction that presents your topic and thesis statement, a body containing your in-depth analysis and arguments, and a conclusion wrapping up your ideas. The structure of the body is flexible, but you should always spend some time thinking about how you can organize your essay to best serve your ...
These papers were published between March 2020 and July 2023 in top journals in management and applied psychology. ... His research interests include leadership, teams, and organizational ...
Table of contents. Step 1: Hook your reader. Step 2: Give background information. Step 3: Present your thesis statement. Step 4: Map your essay's structure. Step 5: Check and revise. More examples of essay introductions. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about the essay introduction.